Clouds and Rain Unit (3 pts)
|
|
|
- Lambert Atkinson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Name: Section: Clouds and Rain Unit (Topic 8A-2) page 1 Clouds and Rain Unit (3 pts) As air rises, it cools due to the reduction in atmospheric pressure Air mainly consists of oxygen molecules and nitrogen molecules. Remember that warm molecules move faster than cold molecules. This allows warm air molecules to push aside nearby molecules and spread out, which lowers their density and causes them to rise. Atmospheric pressure is caused by the weight of the air above. Thus, up in the mountains, air pressure is lower, because there is less atmosphere above you (less air pressing down on top of you). Therefore, as warm air rises higher into the atmosphere, it experiences lower pressure. Since the group of warm, rising air molecules are no longer being squeezed together as strongly by the air above, the group of warm, rising air molecules can now push outward (i.e., the warm air expands as it rises). However, in pushing outward against the neighboring cooler air molecules, they give their energy to the neighboring air, causing the warm, rising air to cool down. Experiment: Blow into your hand. First, keep your mouth opening small, then open wide as if yawning. In which case does the air feel warm? In which case does it feel cool? When the opening is small, the air is forced together, and quickly expands once outside your mouth. If the water molecules in the air cool down enough, they will begin to bond with one another. (The water molecules are no longer moving fast enough to fly apart when they get to close to one another and strong hydrogen bonds form between them.) Thus, rising air produces cloudy and rainy skies. As the rising air cools down more and more, it loses its water as rain. By the time the air reaches the location where air sinks, it is completely dry; dry air cannot produce clouds or rain. lower pressure low pressure high pressure Note: In most situations water vapor needs additional help from aerosols tiny solid particles like dust or drops of liquid in the air to condense: it is easier for water molecule to bond with big, slower-moving objects. The kind and size of aerosols available can have a big impact on whether clouds form and rain occurs and how much rain occurs. 1. As air rises, does it become warmer or cooler? water has fallen out as rain mountain 2. Does water vapor cool and condense into clouds and rain when air rises or when air sinks?
2 Clouds and Rain Unit (Topic 8A-2) page 2 Surface Air Pressure, Temperature, and Cloudy Skies and Clear Skies In the previous section, we saw that as air rises, it cools, causing Clear High Altitude Winds Skies the water vapor in the air to condense into clouds and rain (if enough is present). If we apply this idea to a convection cell, clouds and rain will be High Surface Winds more common above the warm Pressure spot. The sinking air at the cold spot will not have any water Cold vapor (it was lost at the warm Ocean spot, and in any case air warms as it sinks), so clear skies will be more common above the cold spot. Low Pressure Warm Beneath regions of warm, low-density, rising air, the pressure at the surface of the Earth is lower (fewer air molecules above), and beneath regions of cold, high-density, sinking air, the pressure at the surface of the Earth is higher (more air molecules above). Another way to think about this: if the air is rising going up it is not pressing down very hard, and if the air is sinking going down it is pressing down harder. Thus, lower air pressure at the surface is associated with cloudy and rainy skies, and high pressure is associated with clear skies. (Just listen to weather forecasters on the news!). Also, notice that the winds blow from the place with higher pressure at the surface to places with lower pressure at the surface. 3. Where are the cloudy and rainy skies, at the warm spot or at the cold spot? 4. Where are the clear skies, at the warm spot or at the cold spot? 5. Where is the surface air pressure higher, at the warm spot or at the cold spot? 6. When do we typically get more clouds and rain, when air pressure is higher or lower? 7. Does air move from the place with lower pressure at the surface to the place with higher pressure at the surface, or does air move from the place with higher pressure at the surface to the place with lower pressure at the surface? In other words, do winds blow towards the place with lower pressure or towards the place with higher pressure?
3 Clouds and Rain Unit (Topic 8A-2) page 3 The Global Rainfall Pattern Memorize the global rainfall pattern shown below, as well as the global wind pattern. If you know where surface winds come together and the air rises, then you know where it rains. Similarly, where surface winds move apart, air sinks, and the skies are clear. Remember that the dotted arrows show air rising and sinking air going towards or away from the surface of the Earth. As we saw in Unit 8A-1 in which we examined the global wind pattern, warm air rises at the Equator and cold air sinks at the Poles. Air moving away from the Poles and Equator turns under the influence of the Coriolis effect, so it cannot travel all the way from the Equator to the Poles or from the Poles to the Equator. As a result, air sinks at 30 o N and 30 o S where it is cooler than the Equator, and air rises at 60 o N and 60 o S where it is warmer than the Poles. (90 o N) North Pole 60 o N 30 o N Equator (0 o ) 30 o S 60 o S South Pole (90 o S) Clear Rainy Clear Rainy Clear Rainy Clear 8. At what latitudes does air rise? 9. At what latitudes does air sink? 10. At which latitudes are cloudy and rainy skies more common? 11. At which latitudes are clear skies more common?
4 Clouds and Rain Unit (Topic 8A-2) page 4 Weather, Climate, & Fronts Up till now, we have been discussing climate, not weather. Climate is the long-term average of weather conditions (what the weather is usually like). For example, Southern California has a warm, dry climate. This does not mean that it is always warm (we have our cooler days) or that it does not rain in Southern California; it means that our weather is warm most of the time and that rain is less common here than elsewhere. Another way to think about it: weather is what conditions are like a particular day, climate is what conditions are like over a season or a year. Your own experience of actual storms and rain may contradict something that I said before: warm, rising air leads to clouds and rain. Many of you will say: wait a minute, the weather is cold when it rains! Before: After: Warm Air Storms often form along what meteorologists call fronts, a place where 2 air masses meet. An air mass is a collection of air with similar properties (e.g., temperature, moisture), often determined by where it comes from. For Cold Air Warm Air Cold Air example, warm, moist air moves up into the United States from the Gulf of Mexico, while cool, dry air comes down from Canada. We also use the word front to describe the location where two opposing armies meet and are shooting at one another. As in the military, the frontlines typically are where the action is (clouds, rain, hail, snow, etc.) in the atmosphere. At the locations where air masses meet (the front), the cooler air pushes the warmer air up, sliding in underneath to replace it, or the warmer air can move up and over the cooler air. As the warmer air rises, it becomes cooler, and if the change in temperature is strong enough and the rising air contains enough moisture, the water vapor in the rising air will condense into rain. If the warmer, rising air does not contain water, there cannot be rain along the front. Thus, the weather is cooler when it rains, because cooler air is coming in and lifting up the warmer air. (Remember, the warmer air might not be very warm, it is just warmer than the cooler air on the other side of the front.) 12. When warm air pushes into cold air, which one rises up on top, the warm air or the cold air? 13. What happens to the temperature of the air as it rises? Does it get warmer or cooler?
5 Clouds and Rain Unit (Topic 8A-2) page 5 Distribution of Heat from the Sun In this section, you will learn why temperature changes with the seasons, why some parts of the world are warmer than others, and how the motion of the ocean and atmosphere keep the warm places from getting too hot and the cool places from getting too cold. The Equator is warmer than the Poles, because it receives more heat from the Sun. Sunlight shines directly down upon the Equator, but approaches the Poles at an angle. As a result, sunlight is spread out over a wider area at the Poles (It is less Spread Out concentrated, so these places are colder.) In addition, sunlight that comes in at an angle is more North Pole likely to get reflected back into space (the white snow and ice at the Poles help a lot too) rather Equator Sun than absorbed, and passes through more of the atmosphere Concentrated (which absorbs a little bit more light than normal). An experiment that you might try: Get a flashlight. Hold your hand flat with your fingers pointing towards the ceiling. Hold the flashlight horizontal and shine it on your hand. Now, tilt you palm upwards towards the ceiling. What happens to the circle of light on your hand? You can see how sunlight is spread out at the Poles because it strikes the surface at an angle. 14. Which receives more light from the Sun, the Equator or the Poles? 15. Why does the Equator receive more heat than the Poles?
6 Clouds and Rain Unit (Topic 8A-2) page 6 Heat Distribution and the Seasons These factors also help explain why some parts of the year are warmer than other parts of the year (in other words, why we have seasons). Notice how the Earth is tilted relative to the Sun; the Earth s North Pole always points towards a star we call Polaris (creative, huh?), also known as the North Star. So, as the Earth orbits (travels around) the Sun, its tilt never changes. (The Earth s tilt is called its declination.) During our summer, the northern hemisphere is tilted towards the Sun, so we get more sunlight and become warmer. (The warmest spot is north of the Equator.) On the other hand, the southern hemisphere is tilted away from the Sun, so it gets less sunlight and becomes cooler. It takes the Earth 1 year to travel all the way around the Sun, so in 6 months, the Earth will be on the other side of the Sun. The tilt does not change (it always points towards the north star, Polaris), so now the northern hemisphere is tilted away from the Sun. (The warmest spot is south of the Equator.) We get less sunlight during this part of the year, so it is our winter. Earth N. Pole N. Pole Equator Sun Equator S. Pole S. Pole Northern Hemisphere Summer Earth Sun Northern Hemisphere Winter Earth Actually, the Earth s tilt wobbles very slowly in a small circle over thousands of years due to the gravitational pulls of Jupiter and other planets on the Earth. 16. How long does it take the Earth orbit the Sun one time? 17. Does the Earth s tilt change as it orbits the Sun over year? 18. Why are there seasons? For example, why does summer become winter?
7 Clouds and Rain Unit (Topic 8A-2) page 7 Temperature Distribution and Heat Emission The temperature of a place is not merely a matter of how much heat it receives, because if an object only gains heat, then it continues to get hotter and hotter. Objects also lose heat by conducting it to the neighboring environment (for example, your hand if you touch a cold surface) or radiating it away as infrared light (invisible to us because our eyes cannot capture it, but we can feel its heat when we get close to a hot object). Irrespective of how the heat is lost, the basic rule of heat loss is: The hotter an object is, the more heat it gives off. As an object gives away heat, it cools down, and therefore it gives away less and less heat over time. Even frozen objects give off heat, and therefore get even colder! (They just get colder slower and slower.) Every moment of the day and night, the Earth gives away heat to the atmosphere (via conduction) and radiates the rest towards outer space as infrared light. Over 99% of the atmosphere is made of nitrogen and oxygen. Infrared light goes right through these gases. The remaining less than 1% of the atmosphere includes greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide and water vapor which absorb infrared light, trapping its heat in the atmosphere. The heat in the atmosphere is eventually radiated into space too, helped by the fact that warm air rises upward (transporting the heat through the greenhouse gases). The Earth does not run out of heat, because it gains more heat each day by absorbing visible light from the Sun. The Poles are colder than the Equator, so they give off less heat than the Equator, but they still radiate heat into space. Interestingly, observations from satellites show that the Poles give off more heat each day than they receive from the Sun. Similarly, the Equator radiates less heat into space then it receives from the Sun. If the Poles are sending away more heat than they receive, they should get colder, and if the Equator sends away less heat than it receives, it should get warmer. But, of course, they are not getting warmer or colder; their temperatures are stable (global warming issues aside). An object s temperature is stable (does not increase or decrease) if the amount of heat it receives is exactly equal to the amount it gives away (just like how your bank account won t go up or down if the deposits are exactly equal to the withdrawals). 19. Which emits ( gives away ) more heat, a hot object or a cold object? 20. True or false? Cold objects emit heat, but less heat than hot objects. 21. If an object gives away (emits) as much heat as it receives, what happens to its temperature? In other words, does its temperature increase, decrease, or stay the same?
8 Clouds and Rain Unit (Topic 8A-2) page What 2 gases is the atmosphere primarily made of? 23. Give 2 examples of greenhouse gases. 24. Do greenhouse gases warm or cool the atmosphere (and thus the Earth)? Temperature Distribution and the Motions of the Atmosphere and Ocean The temperatures of the Poles and Equator are not increasing or decreasing, because the ocean and atmosphere are moving ( transporting ) heat from the Equator towards the Poles (so the Equator has less to spend and the Poles more to spend ). In convection cells, the cool air moves away from the cold spot and towards the warm spot. The air then warms up at the warm spot, and rises (absorbs heat from the warm spot, cooling it down). Similarly, the cold spot cools the air above it. In other words, heat goes from the air to cold spot, warming the cold spot. Thus, the air moving in the convection cell is cooling down the warm spot (the Equator) and warming up the cool spot (the Poles). As we will see in the next lecture, the ocean does the same thing by moving warm water from the Equator towards the Poles and cool water from the Poles towards the Equator. The movement of water between the ocean and atmosphere also plays an important role in transporting heat from low latitudes (e.g., the Equator) towards high latitudes (e.g., the Poles). Warm ocean water evaporates under the clear skies of 30 o N/S (e.g., southern California), moving heat from the ocean into the atmosphere. (Remember: the hot, fastest-moving water molecules tend to be the ones that evaporate.) Some of the air moves towards the Poles in the winds called the westerlies (the convection cell between 30 o N/S and 60 o N/S). The air gives up its heat to the cooler ground beneath (e.g., Seattle), causing the water to condense into clouds and rain. Thus, the motion of the atmosphere keeps the Poles from becoming too cold and the Equator from becoming too hot. As the air moves, it carries the heat away from the hot places and moves cold air away from the cold places. The motion of the ocean the ocean currents performs a similar job, making the Earth a much more pleasant place to live. 25. Does the motion of the atmosphere warm or cool the Equator? 26. Does the motion of the atmosphere warm or cool the Poles?
Climate versus Weather
 Climate versus Weather What is climate? Climate is the average weather usually taken over a 30-year time period for a particular region and time period. Climate is not the same as weather, but rather,
Climate versus Weather What is climate? Climate is the average weather usually taken over a 30-year time period for a particular region and time period. Climate is not the same as weather, but rather,
Lesson Overview. Climate. Lesson Overview. 4.1 Climate
 Lesson Overview 4.1 THINK ABOUT IT When you think about climate, you might think of dramatic headlines: Hurricane Katrina floods New Orleans! or Drought parches the Southeast! But big storms and seasonal
Lesson Overview 4.1 THINK ABOUT IT When you think about climate, you might think of dramatic headlines: Hurricane Katrina floods New Orleans! or Drought parches the Southeast! But big storms and seasonal
The Transfer of Heat
 The Transfer of Heat Outcomes: S2-4-03 Explain effects of heat transfer within the atmosphere and hydrosphere on the development and movement of wind and ocean currents. Coriolis Effect In our ecology
The Transfer of Heat Outcomes: S2-4-03 Explain effects of heat transfer within the atmosphere and hydrosphere on the development and movement of wind and ocean currents. Coriolis Effect In our ecology
Weather and Climate. An Introduction
 Weather and Climate An Introduction Basic Plant Anatomy Leaves Absorbs sunlight to produce glucose for food Roots Supports the plant, absorbs water & minerals Flower Attracting pollinators to help with
Weather and Climate An Introduction Basic Plant Anatomy Leaves Absorbs sunlight to produce glucose for food Roots Supports the plant, absorbs water & minerals Flower Attracting pollinators to help with
Background: What is Weather?
 Weather Maps Background: What is Weather? Weather is the day-to-day state of the atmosphere. The interaction of three important factors result in weather systems: air temperature, air pressure, and the
Weather Maps Background: What is Weather? Weather is the day-to-day state of the atmosphere. The interaction of three important factors result in weather systems: air temperature, air pressure, and the
Science Chapter 13,14,15
 Science 1206 Chapter 13,14,15 1 Weather dynamics is the study of how the motion of water and air causes weather patterns. Energy from the Sun drives the motion of clouds, air, and water. Earth s tilt at
Science 1206 Chapter 13,14,15 1 Weather dynamics is the study of how the motion of water and air causes weather patterns. Energy from the Sun drives the motion of clouds, air, and water. Earth s tilt at
I T A T I O N H B I T B T V A O C J K M R S A T M O S P H E R E
 Word Search Directions: Below are definitions of vocabulary terms. Figure out each term and then find and circle it in the puzzle. Words may appear horizontally, vertically, or diagonally. K E M I S S
Word Search Directions: Below are definitions of vocabulary terms. Figure out each term and then find and circle it in the puzzle. Words may appear horizontally, vertically, or diagonally. K E M I S S
Planetary Atmospheres (Chapter 10)
 Planetary Atmospheres (Chapter 10) Based on Chapter 10 This material will be useful for understanding Chapters 11 and 13 on Jovian planet systems and Extrasolar planets Chapters 4, 5, and 8 on Momentum,
Planetary Atmospheres (Chapter 10) Based on Chapter 10 This material will be useful for understanding Chapters 11 and 13 on Jovian planet systems and Extrasolar planets Chapters 4, 5, and 8 on Momentum,
3 Weather and Climate
 CHAPTER 22 3 Weather and Climate SECTION The Atmosphere KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What are fronts? What are some types of severe weather? How is climate different
CHAPTER 22 3 Weather and Climate SECTION The Atmosphere KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What are fronts? What are some types of severe weather? How is climate different
Earth Science Chapter 16 and 17. Weather and Climate
 Earth Science Chapter 16 and 17 Weather and Climate Prediction Old way Groundhog Color of the sky Modern way satellites instruments computers Goal Weather Factors Studied by meteorologists Several factors
Earth Science Chapter 16 and 17 Weather and Climate Prediction Old way Groundhog Color of the sky Modern way satellites instruments computers Goal Weather Factors Studied by meteorologists Several factors
Space Atmospheric Gases. the two most common gases; found throughout all the layers a form of oxygen found in the stratosphere
 Earth s atmospheric layers Earth s atmosphere is the layer of gases that surrounds the planet and makes conditions on Earth suitable for living things. Layers Earth s atmosphere is divided into several
Earth s atmospheric layers Earth s atmosphere is the layer of gases that surrounds the planet and makes conditions on Earth suitable for living things. Layers Earth s atmosphere is divided into several
Science 1206 Chapter 1 - Inquiring about Weather
 Science 1206 Chapter 1 - Inquiring about Weather 1.1 - The Atmosphere: Energy Transfer and Properties (pp. 10-25) Weather and the Atmosphere weather the physical conditions of the atmosphere at a specific
Science 1206 Chapter 1 - Inquiring about Weather 1.1 - The Atmosphere: Energy Transfer and Properties (pp. 10-25) Weather and the Atmosphere weather the physical conditions of the atmosphere at a specific
Ocean s Influence on Weather and Climate
 Earth is often called the Blue Planet because so much of its surface (about 71%) is covered by water. Of all the water on Earth, about 96.5%, is held in the world s oceans. As you can imagine, these oceans
Earth is often called the Blue Planet because so much of its surface (about 71%) is covered by water. Of all the water on Earth, about 96.5%, is held in the world s oceans. As you can imagine, these oceans
Global Weather Trade Winds etc.notebook February 17, 2017
 Global Weather 1 north pole northern hemisphere equator southern hemisphere south pole 2 We have seasons because of the Earth's tilt The seasons are opposite in the northern and southern hemispheres winter
Global Weather 1 north pole northern hemisphere equator southern hemisphere south pole 2 We have seasons because of the Earth's tilt The seasons are opposite in the northern and southern hemispheres winter
1 What Is Climate? TAKE A LOOK 2. Explain Why do areas near the equator tend to have high temperatures?
 CHAPTER 17 1 What Is Climate? SECTION Climate BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is climate? What factors affect climate? How do climates differ
CHAPTER 17 1 What Is Climate? SECTION Climate BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is climate? What factors affect climate? How do climates differ
Name Period 4 th Six Weeks Notes 2013 Weather
 Name Period 4 th Six Weeks Notes 2013 Weather Radiation Convection Currents Winds Jet Streams Energy from the Sun reaches Earth as electromagnetic waves This energy fuels all life on Earth including the
Name Period 4 th Six Weeks Notes 2013 Weather Radiation Convection Currents Winds Jet Streams Energy from the Sun reaches Earth as electromagnetic waves This energy fuels all life on Earth including the
UNIT TEST PRACTICE TEST
 Page 1 of 1 Directions: Match the best answer to complete each question. Some words may be used more than once and some may not be used at all. e 1. The condition of Earth s atmosphere at a given time
Page 1 of 1 Directions: Match the best answer to complete each question. Some words may be used more than once and some may not be used at all. e 1. The condition of Earth s atmosphere at a given time
Global Wind Patterns
 Name: Earth Science: Date: Period: Global Wind Patterns 1. Which factor causes global wind patterns? a. changes in the distance between Earth and the Moon b. unequal heating of Earth s surface by the Sun
Name: Earth Science: Date: Period: Global Wind Patterns 1. Which factor causes global wind patterns? a. changes in the distance between Earth and the Moon b. unequal heating of Earth s surface by the Sun
Why is the air cooler at higher altitudes? Short answer lapse rate troposphere
 Why is the air cooler at higher altitudes? This vertical temperature trend is a consequence of 1) lower atmospheric pressure at higher altitude and 2) heating that takes place at the bottom of the troposphere
Why is the air cooler at higher altitudes? This vertical temperature trend is a consequence of 1) lower atmospheric pressure at higher altitude and 2) heating that takes place at the bottom of the troposphere
Climate Change Lecture Notes
 Climate Change Lecture Notes (Topic 12A) page 1 Climate Change Lecture Notes Learning Outcomes for the Climate Change Unit 1. Students can list observations which suggest that the world is warming, and
Climate Change Lecture Notes (Topic 12A) page 1 Climate Change Lecture Notes Learning Outcomes for the Climate Change Unit 1. Students can list observations which suggest that the world is warming, and
General Comments about the Atmospheres of Terrestrial Planets
 General Comments about the Atmospheres of Terrestrial Planets Mercury Very little atmosphere Contents: vaporized micrometeorites, solar wind Sky is black Venus Very thick (10% density of water), dense
General Comments about the Atmospheres of Terrestrial Planets Mercury Very little atmosphere Contents: vaporized micrometeorites, solar wind Sky is black Venus Very thick (10% density of water), dense
Thermal / Solar. When air is warmed it... Rises. Solar Energy. Evaporation. Condensation Forms Clouds
 Thermal / Solar Light from the Sun is transformed into what type of energy when it hits Earth's surface? Rises When air is warmed it... Solar Energy Water moves through the water cycle using what type
Thermal / Solar Light from the Sun is transformed into what type of energy when it hits Earth's surface? Rises When air is warmed it... Solar Energy Water moves through the water cycle using what type
Outline. Planetary Atmospheres. General Comments about the Atmospheres of Terrestrial Planets. General Comments, continued
 Outline Planetary Atmospheres Chapter 10 General comments about terrestrial planet atmospheres Atmospheric structure & the generic atmosphere Greenhouse effect Magnetosphere & the aurora Weather & climate
Outline Planetary Atmospheres Chapter 10 General comments about terrestrial planet atmospheres Atmospheric structure & the generic atmosphere Greenhouse effect Magnetosphere & the aurora Weather & climate
Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds
 Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds 10.1 Atmospheric Basics Our goals for learning: What is an atmosphere? How does the greenhouse effect warm a planet? Why do atmospheric
Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds 10.1 Atmospheric Basics Our goals for learning: What is an atmosphere? How does the greenhouse effect warm a planet? Why do atmospheric
Atmosphere, Weather & Climate Review for Unit Assessment (Can be taken on Study Island Due Mon., 11/26/12)
 Name Class Period Atmosphere, Weather & Climate Review for Unit Assessment (Can be taken on Study Island Due Mon., 11/26/12) 1. When hot and cold air meet, the hot air rises to the top. Which process causes
Name Class Period Atmosphere, Weather & Climate Review for Unit Assessment (Can be taken on Study Island Due Mon., 11/26/12) 1. When hot and cold air meet, the hot air rises to the top. Which process causes
2/22/ Atmospheric Characteristics
 17.1 Atmospheric Characteristics Atmosphere: the gaseous layer that surrounds the Earth I. In the past, gases came from volcanic eruptions A. Water vapor was a major component of outgassing B. Other gases
17.1 Atmospheric Characteristics Atmosphere: the gaseous layer that surrounds the Earth I. In the past, gases came from volcanic eruptions A. Water vapor was a major component of outgassing B. Other gases
Haines ACC science Midterm study guide
 Haines ACC science Midterm study guide Which state of matter is the most common state of matter visible in the universe? a. Solid b. Liquid c. Gas d. plasma Molecules flow freely and take the shape of
Haines ACC science Midterm study guide Which state of matter is the most common state of matter visible in the universe? a. Solid b. Liquid c. Gas d. plasma Molecules flow freely and take the shape of
What Is Air Temperature?
 2.2 Read What Is Air Temperature? In Learning Set 1, you used a thermometer to measure air temperature. But what exactly was the thermometer measuring? What is different about cold air and warm air that
2.2 Read What Is Air Temperature? In Learning Set 1, you used a thermometer to measure air temperature. But what exactly was the thermometer measuring? What is different about cold air and warm air that
Midterm Study Guide: Haines, Manzanares & Soto
 Midterm Study Guide: Haines, Manzanares & Soto 1. High level pushes air masses to new regions. (Wind) Easy 2. How is the atmosphere like a greenhouse? ( Greenhouse gasses trap heat like the walls of a
Midterm Study Guide: Haines, Manzanares & Soto 1. High level pushes air masses to new regions. (Wind) Easy 2. How is the atmosphere like a greenhouse? ( Greenhouse gasses trap heat like the walls of a
Directed Reading. Section: Solar Energy and the Atmosphere RADIATION. identical point on the next wave. waves
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Solar Energy and the Atmosphere 1. How is Earth s atmosphere heated? 2. Name the two primary sources of heat in the atmosphere. RADIATION In the space provided,
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Solar Energy and the Atmosphere 1. How is Earth s atmosphere heated? 2. Name the two primary sources of heat in the atmosphere. RADIATION In the space provided,
Weather Notes. Chapter 16, 17, & 18
 Weather Notes Chapter 16, 17, & 18 Weather Weather is the condition of the Earth s atmosphere at a particular place and time Weather It is the movement of energy through the atmosphere Energy comes from
Weather Notes Chapter 16, 17, & 18 Weather Weather is the condition of the Earth s atmosphere at a particular place and time Weather It is the movement of energy through the atmosphere Energy comes from
Chapter 15: Weather and Climate
 Chapter 15: Weather and Climate Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The short-term state of the atmosphere is called a. climate. c. water cycle.
Chapter 15: Weather and Climate Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The short-term state of the atmosphere is called a. climate. c. water cycle.
3 Severe Weather. Critical Thinking
 CHAPTER 2 3 Severe Weather SECTION Understanding Weather BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are some types of severe weather? How can you stay
CHAPTER 2 3 Severe Weather SECTION Understanding Weather BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are some types of severe weather? How can you stay
The Cosmic Perspective Planetary Atmospheres: Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds
 Chapter 10 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Planetary Atmospheres: Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds Planetary Atmospheres: Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds 10.1 Atmospheric Basics
Chapter 10 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Planetary Atmospheres: Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds Planetary Atmospheres: Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds 10.1 Atmospheric Basics
10.1 TEMPERATURE, THERMAL ENERGY AND HEAT Name: Date: Block: (Reference: pp of BC Science 10)
 10.1 TEMPERATURE, THERMAL ENERGY AND HEAT Name: Date: Block: (Reference: pp. 424-435 of BC Science 10) kinetic molecular theory: explains that matter is made up of tiny that are constantly. These atoms
10.1 TEMPERATURE, THERMAL ENERGY AND HEAT Name: Date: Block: (Reference: pp. 424-435 of BC Science 10) kinetic molecular theory: explains that matter is made up of tiny that are constantly. These atoms
Three things necessary for weather are Heat, Air, Moisture (HAM) Weather takes place in the Troposphere (The lower part of the atmosphere).
 Grade 5 SCIENCE WEATHER WATCH Name: STUDY NOTES Weather - The condition of the atmosphere with respect to heat/cold, wetness/dryness, clearness/ cloudiness for a period of time. Weather changes over time
Grade 5 SCIENCE WEATHER WATCH Name: STUDY NOTES Weather - The condition of the atmosphere with respect to heat/cold, wetness/dryness, clearness/ cloudiness for a period of time. Weather changes over time
Unit 3 Review Guide: Atmosphere
 Unit 3 Review Guide: Atmosphere Atmosphere: A thin layer of gases that forms a protective covering around the Earth. Photosynthesis: Process where plants take in carbon dioxide and release oxygen. Trace
Unit 3 Review Guide: Atmosphere Atmosphere: A thin layer of gases that forms a protective covering around the Earth. Photosynthesis: Process where plants take in carbon dioxide and release oxygen. Trace
Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds
 Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds What is an atmosphere? 10.1 Atmospheric Basics Our goals for learning:! What is an atmosphere?! How does the greenhouse effect warm
Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds What is an atmosphere? 10.1 Atmospheric Basics Our goals for learning:! What is an atmosphere?! How does the greenhouse effect warm
also known as barometric pressure; weight of the air above the surface of the earth; measured by a barometer air pressure, high
 Weather Vocabulary Vocabulary Term Meaning/Definition air mass * large bodies of air that have the similar properties throughout such as temperature, humidity, and air pressure; causes most of the weather
Weather Vocabulary Vocabulary Term Meaning/Definition air mass * large bodies of air that have the similar properties throughout such as temperature, humidity, and air pressure; causes most of the weather
Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres: Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds. What is an atmosphere? Earth s Atmosphere. Atmospheric Pressure
 Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres: Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds 10.1 Atmospheric Basics Our goals for learning What is an atmosphere? How does the greenhouse effect warm a planet? Why do atmospheric
Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres: Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds 10.1 Atmospheric Basics Our goals for learning What is an atmosphere? How does the greenhouse effect warm a planet? Why do atmospheric
Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres: Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds
 Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres: Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds 10.1 Atmospheric Basics Our goals for learning What is an atmosphere? How does the greenhouse effect warm a planet? Why do atmospheric
Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres: Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds 10.1 Atmospheric Basics Our goals for learning What is an atmosphere? How does the greenhouse effect warm a planet? Why do atmospheric
Meteorology Study Guide
 Name: Date: Meteorology Study Guide 1. Label the following steps in the water cycle diagram. Be sure to include arrows to show the flow of water through the cycle. - Transpiration - Precipitation -Evaporation
Name: Date: Meteorology Study Guide 1. Label the following steps in the water cycle diagram. Be sure to include arrows to show the flow of water through the cycle. - Transpiration - Precipitation -Evaporation
Earth s Atmosphere. Energy Transfer in the Atmosphere. 3. All the energy from the Sun reaches Earth s surface.
 CHAPTER 11 LESSON 2 Earth s Atmosphere Energy Transfer in the Atmosphere Key Concepts How does energy transfer from the Sun to Earth and to the atmosphere? How are air circulation patterns within the atmosphere
CHAPTER 11 LESSON 2 Earth s Atmosphere Energy Transfer in the Atmosphere Key Concepts How does energy transfer from the Sun to Earth and to the atmosphere? How are air circulation patterns within the atmosphere
1. CLIMATOLOGY: 2. ATMOSPHERIC CHEMISTRY:
 What is meteorology? A. METEOROLOGY: an atmospheric science that studies the day to day changes in the atmosphere 1. ATMOSPHERE: the blanket of gas that surrounds the surface of Earth; the air 2. WEATHER:
What is meteorology? A. METEOROLOGY: an atmospheric science that studies the day to day changes in the atmosphere 1. ATMOSPHERE: the blanket of gas that surrounds the surface of Earth; the air 2. WEATHER:
PHYSICAL SCIENCE SPRING FINAL REVIEW GUIDE
 PHYSICAL SCIENCE SPRING FINAL REVIEW GUIDE 1. Draw a diagram to show the position of the Earth (include axis) and sun during the N. Hemisphere: a. Winter b. Spring 2. What times of year do the Sun s rays
PHYSICAL SCIENCE SPRING FINAL REVIEW GUIDE 1. Draw a diagram to show the position of the Earth (include axis) and sun during the N. Hemisphere: a. Winter b. Spring 2. What times of year do the Sun s rays
The Atmosphere. Characteristics of the Atmosphere. Section 23.1 Objectives. Chapter 23. Chapter 23 Modern Earth Science. Section 1
 The Atmosphere Chapter 23 Modern Earth Science Characteristics of the Atmosphere Chapter 23 Section 1 Section 23.1 Objectives Describe the composition of Earth s atmosphere. Explain how two types of barometers
The Atmosphere Chapter 23 Modern Earth Science Characteristics of the Atmosphere Chapter 23 Section 1 Section 23.1 Objectives Describe the composition of Earth s atmosphere. Explain how two types of barometers
Table of Contents. Chapter: Atmosphere. Section 1: Earth's Atmosphere. Section 2: Energy Transfer in the Atmosphere. Section 3: Air Movement
 Table of Contents Chapter: Atmosphere Section 1: Earth's Atmosphere Section 2: Energy Transfer in the Atmosphere Section 3: Air Movement Table of Contents Chapter 4: Atmosphere Section 1: Earth's Atmosphere
Table of Contents Chapter: Atmosphere Section 1: Earth's Atmosphere Section 2: Energy Transfer in the Atmosphere Section 3: Air Movement Table of Contents Chapter 4: Atmosphere Section 1: Earth's Atmosphere
Natural Causes of Climate. 3B Day 2
 Natural Causes of Climate 3B Day 2 Critical Content 3B: Investigate how daily weather over time determines climate patterns in a given region 2C: Recall the difference between weather and climate Describe
Natural Causes of Climate 3B Day 2 Critical Content 3B: Investigate how daily weather over time determines climate patterns in a given region 2C: Recall the difference between weather and climate Describe
1 What Is Climate? TAKE A LOOK 2. Explain Why do areas near the equator tend to have high temperatures?
 CHAPTER 3 1 What Is Climate? SECTION Climate BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is climate? What factors affect climate? How do climates differ
CHAPTER 3 1 What Is Climate? SECTION Climate BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is climate? What factors affect climate? How do climates differ
2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres: Mars, Venus, Earth What is an atmosphere? An atmosphere is a (usually very thin) layer of gas that surrounds a world. How does the greenhouse effect warm a planet? No
Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres: Mars, Venus, Earth What is an atmosphere? An atmosphere is a (usually very thin) layer of gas that surrounds a world. How does the greenhouse effect warm a planet? No
The Atmosphere. All weather occurs here 99% of water vapor found here ~75 % of total mass of the atmosphere
 The Atmosphere Structure/Layers Contains 4 major layers See E.S.R.T pg 14 o Troposphere All weather occurs here 99% of water vapor found here ~75 % of total mass of the atmosphere o Stratosphere Contains
The Atmosphere Structure/Layers Contains 4 major layers See E.S.R.T pg 14 o Troposphere All weather occurs here 99% of water vapor found here ~75 % of total mass of the atmosphere o Stratosphere Contains
Weather. Describing Weather
 CHAPTER 13 Weather LESSON 1 Describing Weather What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the
CHAPTER 13 Weather LESSON 1 Describing Weather What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the
Air Masses, Fronts, Storm Systems, and the Jet Stream
 Air Masses, Fronts, Storm Systems, and the Jet Stream Air Masses When a large bubble of air remains over a specific area of Earth long enough to take on the temperature and humidity characteristics of
Air Masses, Fronts, Storm Systems, and the Jet Stream Air Masses When a large bubble of air remains over a specific area of Earth long enough to take on the temperature and humidity characteristics of
4-1 The Role of Climate
 4-1 The Role of Climate 1 of 26 What Is Climate? What Is Climate? Weather is the day-to-day condition of Earth's atmosphere at a particular time and place. Climate refers to the average year-after-year
4-1 The Role of Climate 1 of 26 What Is Climate? What Is Climate? Weather is the day-to-day condition of Earth's atmosphere at a particular time and place. Climate refers to the average year-after-year
4-1 The Role of Climate
 biology 1 of 26 2 of 26 What Is Climate? What Is Climate? Weather is the day-to-day condition of Earth's atmosphere at a particular time and place. Climate refers to the average year-after-year conditions
biology 1 of 26 2 of 26 What Is Climate? What Is Climate? Weather is the day-to-day condition of Earth's atmosphere at a particular time and place. Climate refers to the average year-after-year conditions
Atoms and molecules are in motion and have energy
 Atoms and molecules are in motion and have energy By now you know that substances are made of atoms and molecules. These atoms and molecules are always in motion and have attractions to each other. When
Atoms and molecules are in motion and have energy By now you know that substances are made of atoms and molecules. These atoms and molecules are always in motion and have attractions to each other. When
A Quick Look at the Atmosphere and Climate
 A Quick Look at the Atmosphere and Climate The thin, light blue line around the Earth is about all there is of the Atmosphere. Because of the confining pressure of the gas above, the bottommost part of
A Quick Look at the Atmosphere and Climate The thin, light blue line around the Earth is about all there is of the Atmosphere. Because of the confining pressure of the gas above, the bottommost part of
Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds. What is an atmosphere? Planetary Atmospheres
 Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds What is an atmosphere? Planetary Atmospheres Pressure Composition Greenhouse effect Atmospheric structure Color of the sky 1 Atmospheres
Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds What is an atmosphere? Planetary Atmospheres Pressure Composition Greenhouse effect Atmospheric structure Color of the sky 1 Atmospheres
1 What Is Climate? TAKE A LOOK 2. Explain Why do areas near the equator tend to have high temperatures?
 CHAPTER 17 1 What Is Climate? SECTION Climate BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is climate? What factors affect climate? How do climates differ
CHAPTER 17 1 What Is Climate? SECTION Climate BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is climate? What factors affect climate? How do climates differ
Water in the Atmosphere The Role of Water in Earth s Surface Processes. Hurricane Warning
 Hurricane Warning 1 Earth, the lue Planet. What makes Earth blue? It has to do with all of the water on Earth. There is water in more places than the vast oceans. Water is also in the atmosphere. High
Hurricane Warning 1 Earth, the lue Planet. What makes Earth blue? It has to do with all of the water on Earth. There is water in more places than the vast oceans. Water is also in the atmosphere. High
Table of Contents. Chapter: Atmosphere. Section 1: Earth's Atmosphere. Section 2: Energy Transfer in the Atmosphere. Section 3: Air Movement
 Table of Contents Chapter: Atmosphere Section 1: Earth's Atmosphere Section 2: Energy Transfer in the Atmosphere Section 3: Air Movement 1 Earth s Atmosphere Importance of the Atmosphere Earth's atmosphere
Table of Contents Chapter: Atmosphere Section 1: Earth's Atmosphere Section 2: Energy Transfer in the Atmosphere Section 3: Air Movement 1 Earth s Atmosphere Importance of the Atmosphere Earth's atmosphere
Weather. A. atmosphere is a layer of gases that wrap around the Earth like a blanket.
 Weather I. The air around us A. atmosphere is a layer of gases that wrap around the Earth like a blanket. II. Weather Temperature Humidity Air pressure Wind 1. contains the air we breathe, protects us
Weather I. The air around us A. atmosphere is a layer of gases that wrap around the Earth like a blanket. II. Weather Temperature Humidity Air pressure Wind 1. contains the air we breathe, protects us
Chapter 3 Packet. and causes seasons Earth tilted at 23.5 / 365 1/4 days = one year or revolution
 Name Chapter 3 Packet Sequence Section 1 Seasons and Weather : and causes seasons Earth tilted at 23.5 / 365 1/4 days = one year or revolution solstice - begins summer in N. hemisphere, longest day winter
Name Chapter 3 Packet Sequence Section 1 Seasons and Weather : and causes seasons Earth tilted at 23.5 / 365 1/4 days = one year or revolution solstice - begins summer in N. hemisphere, longest day winter
THE EARTH S CLIMATE SYSTEM
 THE EARTH S CLIMATE SYSTEM Earth s Climate System is driven by interactions between the parts of our biosphere So.what is the Biosphere? a relatively thin layer of Earth that has conditions suitable for
THE EARTH S CLIMATE SYSTEM Earth s Climate System is driven by interactions between the parts of our biosphere So.what is the Biosphere? a relatively thin layer of Earth that has conditions suitable for
Topic 1 The Atmosphere and Atmospheric Variables
 Name Notes: Topic 1 The Atmosphere Regents Earth Science Topic 1 The Atmosphere and Atmospheric Variables What is the atmosphere? Meteorology is the study of A. Structure of the Atmosphere: What two gases
Name Notes: Topic 1 The Atmosphere Regents Earth Science Topic 1 The Atmosphere and Atmospheric Variables What is the atmosphere? Meteorology is the study of A. Structure of the Atmosphere: What two gases
GEOGRAPHY EYA NOTES. Weather. atmosphere. Weather and climate
 GEOGRAPHY EYA NOTES Weather and climate Weather The condition of the atmosphere at a specific place over a relatively short period of time Climate The atmospheric conditions of a specific place over a
GEOGRAPHY EYA NOTES Weather and climate Weather The condition of the atmosphere at a specific place over a relatively short period of time Climate The atmospheric conditions of a specific place over a
Chapter 2. Heating Earth's Surface & Atmosphere
 Chapter 2 Heating Earth's Surface & Atmosphere Topics Earth-Sun Relationships Energy, Heat and Temperature Mechanisms of Heat Transfer What happens to Incoming Solar Radiation? Radiation Emitted by the
Chapter 2 Heating Earth's Surface & Atmosphere Topics Earth-Sun Relationships Energy, Heat and Temperature Mechanisms of Heat Transfer What happens to Incoming Solar Radiation? Radiation Emitted by the
The Atmosphere - Chapter Characteristics of the Atmosphere
 Section Objectives Describe the composition of Earth s atmosphere. Explain how two types of barometers work. Identify the layers of the atmosphere. Identify two effects of air pollution. The Atmosphere
Section Objectives Describe the composition of Earth s atmosphere. Explain how two types of barometers work. Identify the layers of the atmosphere. Identify two effects of air pollution. The Atmosphere
Website Lecture 3 The Physical Environment Part 1
 Website http://websites.rcc.edu/halama Lecture 3 The Physical Environment Part 1 1 Lectures 3 & 4 1. Biogeochemical Cycling 2. Solar Radiation 3. The Atmosphere 4. The Global Ocean 5. Weather and Climate
Website http://websites.rcc.edu/halama Lecture 3 The Physical Environment Part 1 1 Lectures 3 & 4 1. Biogeochemical Cycling 2. Solar Radiation 3. The Atmosphere 4. The Global Ocean 5. Weather and Climate
Climate vs. Weather. Weather: Short term state of the atmosphere. Climate: The average weather conditions in an area over a long period of time
 Weather and Climate Climate vs. Weather Weather: Short term state of the atmosphere. Temperature, humidity, cloud cover, precipitation, winds, visibility, air pressure, air pollution, etc Climate: The
Weather and Climate Climate vs. Weather Weather: Short term state of the atmosphere. Temperature, humidity, cloud cover, precipitation, winds, visibility, air pressure, air pollution, etc Climate: The
3) What is the difference between latitude and longitude and what is their affect on local and world weather and climate?
 www.discoveryeducation.com 1) Describe the difference between climate and weather citing an example of each. Describe how water (ocean, lake, river) has a local effect on weather and climate and provide
www.discoveryeducation.com 1) Describe the difference between climate and weather citing an example of each. Describe how water (ocean, lake, river) has a local effect on weather and climate and provide
Earth s Atmosphere About 10 km thick
 10.1 Atmospheric Basics Our goals for learning: What is an atmosphere? How does the greenhouse effect warm a planet? Why do atmospheric properties vary with altitude? Earth s Atmosphere About 10 km thick
10.1 Atmospheric Basics Our goals for learning: What is an atmosphere? How does the greenhouse effect warm a planet? Why do atmospheric properties vary with altitude? Earth s Atmosphere About 10 km thick
Standard 3: Students will understand the atmospheric processes that support life and cause weather and climate.
 Course: 9 th Grade Earth Systems Science Standard 3: Students will understand the atmospheric processes that support life and cause weather and climate. Instructions: In the space provided, write the letter
Course: 9 th Grade Earth Systems Science Standard 3: Students will understand the atmospheric processes that support life and cause weather and climate. Instructions: In the space provided, write the letter
The Atmosphere. Composition of the Atmosphere. Section 2
 The Atmosphere Earth is surrounded by a mixture of gases known as the Nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, and other gases are all parts of this mixture. Earth s atmosphere changes constantly as these gases
The Atmosphere Earth is surrounded by a mixture of gases known as the Nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, and other gases are all parts of this mixture. Earth s atmosphere changes constantly as these gases
Assessment Schedule 2017 Earth and Space Science: Demonstrate understanding of processes in the atmosphere system (91414)
 NCEA Level 3 Earth and Space Science (91414) 2017 page 1 of 6 Assessment Schedule 2017 Earth and Space Science: Demonstrate understanding of processes in the atmosphere system (91414) Evidence Statement
NCEA Level 3 Earth and Space Science (91414) 2017 page 1 of 6 Assessment Schedule 2017 Earth and Space Science: Demonstrate understanding of processes in the atmosphere system (91414) Evidence Statement
Name Period Date 8R MIDTERM REVIEW I. ASTRONOMY 1. Most stars are made mostly of. 2. The dark, cooler areas on the sun s surface are
 Name Period Date 8R MIDTERM REVIEW I. ASTRONOMY 1. Most stars are made mostly of 2. The dark, cooler areas on the sun s surface are 3. When hydrogen nuclei fuse they form 4. Einstein s equation is 5. The
Name Period Date 8R MIDTERM REVIEW I. ASTRONOMY 1. Most stars are made mostly of 2. The dark, cooler areas on the sun s surface are 3. When hydrogen nuclei fuse they form 4. Einstein s equation is 5. The
Seasons, Global Wind and Climate Study Guide
 Seasons, Global Wind and Climate Study Guide Seasons 1. Know what is responsible for the change in seasons on Earth. 2. Be able to determine seasons in the northern and southern hemispheres given the position
Seasons, Global Wind and Climate Study Guide Seasons 1. Know what is responsible for the change in seasons on Earth. 2. Be able to determine seasons in the northern and southern hemispheres given the position
Hurricanes. Where's the Really Bad Weather 1. What: Rotating wind/rain storm Winds from 75 to 200 mph As big as 600 miles wide
 Where's the Really Bad Weather 1 Hurricanes What: Rotating wind/rain storm Winds from 75 to 200 mph As big as 600 miles wide Where: Start over oceans, fizzle out over land Investigation 1 What is Weather?
Where's the Really Bad Weather 1 Hurricanes What: Rotating wind/rain storm Winds from 75 to 200 mph As big as 600 miles wide Where: Start over oceans, fizzle out over land Investigation 1 What is Weather?
IV. Atmospheric Science Section
 EAPS 100 Planet Earth Lecture Topics Brief Outlines IV. Atmospheric Science Section 1. Introduction, Composition and Structure of the Atmosphere Learning objectives: Understand the basic characteristics
EAPS 100 Planet Earth Lecture Topics Brief Outlines IV. Atmospheric Science Section 1. Introduction, Composition and Structure of the Atmosphere Learning objectives: Understand the basic characteristics
Meteorology. I. The Atmosphere - the thin envelope of gas that surrounds the earth.
 Meteorology I. The Atmosphere - the thin envelope of gas that surrounds the earth. A. Atmospheric Structure - the atmosphere is divided into five distinct layers that are based on their unique characteristics.
Meteorology I. The Atmosphere - the thin envelope of gas that surrounds the earth. A. Atmospheric Structure - the atmosphere is divided into five distinct layers that are based on their unique characteristics.
ATMOSPHERE PACKET CHAPTER 22 PAGES Section 1 page 546
 Name: Period: ATMOSPHERE PACKET CHAPTER 22 PAGES 546-564 Section 1 page 546 1. Identify five main components of the atmosphere 2. Explain the cause of atmospheric pressure. 3. Why is atmospheric pressure
Name: Period: ATMOSPHERE PACKET CHAPTER 22 PAGES 546-564 Section 1 page 546 1. Identify five main components of the atmosphere 2. Explain the cause of atmospheric pressure. 3. Why is atmospheric pressure
1 Our Dynamic Climate Guiding Question: What factors determine Earth s climate?
 LESSON 1 Our Dynamic Climate Guiding Question: What factors determine Earth s climate? Describe factors that affect how the sun warms Earth. Discuss the role of wind patterns in determining climate. Explain
LESSON 1 Our Dynamic Climate Guiding Question: What factors determine Earth s climate? Describe factors that affect how the sun warms Earth. Discuss the role of wind patterns in determining climate. Explain
Atmospheric Basics Atmospheric Composition
 Atmospheric Basics Atmospheric Composition Air is a combination of many gases, each with its own unique characteristics. About 99 percent of the atmosphere is composed of nitrogen and oxygen, with the
Atmospheric Basics Atmospheric Composition Air is a combination of many gases, each with its own unique characteristics. About 99 percent of the atmosphere is composed of nitrogen and oxygen, with the
4 Forecasting Weather
 CHAPTER 2 4 Forecasting Weather SECTION Understanding Weather BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What instruments are used to forecast weather? How
CHAPTER 2 4 Forecasting Weather SECTION Understanding Weather BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What instruments are used to forecast weather? How
4-1 The Role of Climate. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 4-1 The Role of Climate Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall What Is Climate? Weather is the day-to-day condition of Earth's atmosphere at a particular time and place. Climate refers to the average year-after-year
4-1 The Role of Climate Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall What Is Climate? Weather is the day-to-day condition of Earth's atmosphere at a particular time and place. Climate refers to the average year-after-year
Composition of the Atmosphere
 Introduction to Oceanography Lecture 15: Wind Atmospheric water vapor map, Sept. 13 Nov. 2, 2017. Data from http://www.ssec.wisc.edu/data/comp/wv/ Composition of the Atmosphere Dry Air: 78% Nitrogen, 21%
Introduction to Oceanography Lecture 15: Wind Atmospheric water vapor map, Sept. 13 Nov. 2, 2017. Data from http://www.ssec.wisc.edu/data/comp/wv/ Composition of the Atmosphere Dry Air: 78% Nitrogen, 21%
How Does the Sun s Energy Cause Rain?
 1.2 Investigate 3.3 Read How Does the Sun s Energy Cause Rain? In the water-cycle simulation, you observed water change from a liquid to a gas, and then back to a liquid falling to the bottom of the container.
1.2 Investigate 3.3 Read How Does the Sun s Energy Cause Rain? In the water-cycle simulation, you observed water change from a liquid to a gas, and then back to a liquid falling to the bottom of the container.
Composition of the Atmosphere
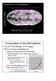 Introduction to Oceanography Lecture 15: Wind Atmospheric water vapor map, Sept. 13 Nov. 2, 2017. Data from http://www.ssec.wisc.edu/data/comp/wv/ Composition of the Atmosphere Dry Air: 78% Nitrogen, 21%
Introduction to Oceanography Lecture 15: Wind Atmospheric water vapor map, Sept. 13 Nov. 2, 2017. Data from http://www.ssec.wisc.edu/data/comp/wv/ Composition of the Atmosphere Dry Air: 78% Nitrogen, 21%
Overview Atmosphere. Meeting Individual Needs. Directed Reading for Content Mastery
 Directed Reading for Content Mastery Overview Atmosphere Directions: Complete the concept map using the terms in the list below. weather exosphere coldest air temperature ionosphere stratosphere 1. which
Directed Reading for Content Mastery Overview Atmosphere Directions: Complete the concept map using the terms in the list below. weather exosphere coldest air temperature ionosphere stratosphere 1. which
Unit 2 Meteorology Test **Please do not write on this test** 5. El Nino & La Nina 6. Photosynthesis 7. Coriolis Effect 8.
 Matching (2 points each) 1. weather 2. climate 3. Greenhouse Effect 4. Convection Unit 2 Meteorology Test **Please do not write on this test** 5. El Nino & La Nina 6. Photosynthesis 7. Coriolis Effect
Matching (2 points each) 1. weather 2. climate 3. Greenhouse Effect 4. Convection Unit 2 Meteorology Test **Please do not write on this test** 5. El Nino & La Nina 6. Photosynthesis 7. Coriolis Effect
Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres: Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds. What is an atmosphere? About 10 km thick
 Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres: Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds What is an atmosphere? Sources of Gas Losses of Gas Thermal Escape Earth s Atmosphere About 10 km thick Consists mostly of molecular
Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres: Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds What is an atmosphere? Sources of Gas Losses of Gas Thermal Escape Earth s Atmosphere About 10 km thick Consists mostly of molecular
Weather Review. Use this graph to answer the next questions. A B C D
 Weather Review 1. Which of the following lists elements of the weather? a. Radiation, Wind Speed, Precipitation b. Soil type, Plate type, Water type c. Temperature, Precipitation, Air Pressure d. Ocean
Weather Review 1. Which of the following lists elements of the weather? a. Radiation, Wind Speed, Precipitation b. Soil type, Plate type, Water type c. Temperature, Precipitation, Air Pressure d. Ocean
Our Planet Earth. I nteractions of Earth Systems
 CHAPTER 3 LESSON 2 Our Planet Earth I nteractions of Earth Systems Key Concepts How does the water cycle show interactions of Earth systems? How does weather show interactions of Earth systems? How does
CHAPTER 3 LESSON 2 Our Planet Earth I nteractions of Earth Systems Key Concepts How does the water cycle show interactions of Earth systems? How does weather show interactions of Earth systems? How does
1 Characteristics of the Atmosphere
 CHAPTER 1 1 Characteristics of the Atmosphere SECTION The Atmosphere BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is Earth s atmosphere made of? How do
CHAPTER 1 1 Characteristics of the Atmosphere SECTION The Atmosphere BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is Earth s atmosphere made of? How do
1/2/2016 WEATHER DEFINITION
 WEATHER DEFINITION Weather state or condition of the variables of the atmosphere at a given time Weather variables temperature, air pressure, wind, moisture, cloud cover, precipitation, storms Weather
WEATHER DEFINITION Weather state or condition of the variables of the atmosphere at a given time Weather variables temperature, air pressure, wind, moisture, cloud cover, precipitation, storms Weather
Weather Maps. The Sun s radiation produces weather on Earth.
 Sunny days give way to rainy days. Storms appear, then fade away. Howling winds become gentle breezes. At one o clock on an autumn afternoon, an outdoor thermometer reads 20 C. An hour later, the temperature
Sunny days give way to rainy days. Storms appear, then fade away. Howling winds become gentle breezes. At one o clock on an autumn afternoon, an outdoor thermometer reads 20 C. An hour later, the temperature
Weather is the state or condition of the atmosphere at a given location for a brief time period.
 Topic 8: WEATHER Workbook chapter 7 Weather is the state or condition of the atmosphere at a given location for a brief time period. Differences in how Earth s surfaces absorb and reradiate energy from
Topic 8: WEATHER Workbook chapter 7 Weather is the state or condition of the atmosphere at a given location for a brief time period. Differences in how Earth s surfaces absorb and reradiate energy from
Chapter 4 Lesson 1: Describing Earth s Atmosphere
 Chapter 4 Lesson 1: Describing Earth s Atmosphere Vocabulary Importance of Earth s Atmosphere The atmosphere is a thin layer of gases surrounding Earth. o Contains the oxygen and water needed for life.
Chapter 4 Lesson 1: Describing Earth s Atmosphere Vocabulary Importance of Earth s Atmosphere The atmosphere is a thin layer of gases surrounding Earth. o Contains the oxygen and water needed for life.
Weather and Climate. Weather the condition of the Earth s atmosphere at a particular time and place
 Weather and Climate Weather the condition of the Earth s atmosphere at a particular time and place Climate the average year-after-year conditions of temperature, precipitation, winds and clouds in an area
Weather and Climate Weather the condition of the Earth s atmosphere at a particular time and place Climate the average year-after-year conditions of temperature, precipitation, winds and clouds in an area
Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres: Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres: Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds 10.1 Atmospheric Basics Our goals for learning: What is an atmosphere? How does the greenhouse effect warm a planet? Why do atmospheric
Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres: Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds 10.1 Atmospheric Basics Our goals for learning: What is an atmosphere? How does the greenhouse effect warm a planet? Why do atmospheric
