FLOWCAPT: A NEWACOUSTIC SENSOR TO MEASURE SNOWDRIFTAND WIND VELOCITY FOR AVALANCHE FORECASTING
|
|
|
- Brice Martin
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 FLOWCAPT: A NEWACOUSTC SENSOR TO MEASURE SNOWDRFTAND WND VELOCTY FOR AVALANCHE FORECASTNG Chritin 1 V. Bolognesi 2 R. Gubler 3 H. ABSTRACT : Wind can create even greater unstable accumulations of snow in mountainous areas than heavy snowfalls. But knowing wind conditions is not sufficient to predict these accumulations because their formations also depend on the snow quality of the snowpack surface upwind of the release zone. Consequently assessment of snowdrift is required to improve avalanche forecasting. n accordance with this assumption a new acoustic sensor was developed. The sensor includes a mechanical part designed to form a closed acoustic enclosure. The acoustic enclosure contains a microphone connected to an electrical amplifying and filtering device. Because the output information delivered by the instrument is proportional to the wind velocity and to the flux of solid particles (ice grains) drifted by the wind the instrument is called an anemo-driftometer. Prototypes of the instrument were first tested in a wind-tunnel and then at an experimental site in the Alps. Then an operational version called FlowCapt was developed and connected to an automatic weather station at 2700 m in the Aminona ski resort (SWitzerland). During the winter snowdrift is recorded on the test site along with other meteorological parameters and avalanche activity to provide extensive on-site calibration and testing of the sensor. The experiment demonstrates that the instrument is a useful component of the avalanche forecasting chain. KEYWORDS: Snow drifting snow engineering avalanche forecasting acoustics jet roof. 1. A NEW SNOWDRFT SENSOR TO MPROVE AVALANCHE FORECASTNG To improve the reliability of local avalanche warning systems parameters directly related to avalanche danger or slab stability have to be measured close to and within the potential avalanche release zones that endanger the area to be protected. Because wind can create even greater unstable accumulations of snow in mountainous areas than heavy snowfalls snowdrift is a very predictive parameter. Wind speed measurements are not sufficient to predict these accumulations which also depend on the ::~ snow quality of the snowpack surface all around measurement stations. Knowing snowdrift by direct measurements is subsequently of high importance for avalanche forecasting. At present time snowdrift can be measured by ski patrol men (Fig. 1) with the so-called Driftometer (Bolognesi et a. 1995). This simple instrument makes possible quantitative snowdrift assessments but it requires the presence of a human observer on the sites. f manual measurements are not possible snowdrift would have to be estimated from other parameters with significantly lower reliability. Fig. 1 : The Driftometer catches blown snow particles into a collector through a tube by the combined effects offilter and pressure fall. Weighting the collector directly gives a snowdrift index. The new FlowCapt acoustic sensor gives the possibility of a continuous and automatic recording of the snowdrift (_kg.m- 2.s- 1 ). nstalled upwind of the release zone FlowCapt provides additional information on the snow accumulation AV Engineering - Noise Vibration Control & Acoustic Systems - PSElA EPFL - CH-1015 Lausanne (Switzerland) - Phone + 41 (0) Fax + 41 (0) chritin@iav.epfl.ch. 2 GESTER SA - Major Hazards - 35 avenue Ritz Case Poslale CH-1950 SON 2 NORD (Switzerland) - Phone + 41 (0) Fax + 41 (0) bolo@gester.ch. 3 ALPUG _ Automatic weather stations - Richtstattweg 2 CH-7270 Davos Platz (SWitzerland) - Phone & Fax + 41 (0) alpug@csi.com. 197
2 process within the release zone deformability of the forming slab and erodibility of the snow surface. Because it was shown that snowdrift data increases the reliability of avalanche predictions (Bolognesi 1996) this information is used by the decision support system NivoLog to establish local avalanche predictions (cf. 5). 3. PROTOTYPNG DRFTOMETER OF THE ANEMO Theoretical and experimental campaigns have been carried-out at the Swiss Federal nstitute for Technology (EPFL) to develop FlowCapt prototypes (fig. 3). 2. PRNCPLE OF THE FLOWCAPT ANEMO DRFTOMETER The FlowCapt anemo-driftometer determines both wind velocity and snow particles flux. The detection principle is based on mechanicalacoustical coupling. The sensor is composed of closed pipes containing electro-acoustic transducers and a powering filtering and amplifying unit. When the sensor is placed into a snow particles flux the particles shock the sensor pipes inducing acoustical pressure (fig. 2 left). The pressure is picked-up by the transducers. The electrical outputs are filtered and time-averaged in given frequency ranges to provide a signal proportional to particles flux Q (kg.m 2.s 1). The formal relation between the measured acoustic pressure and the snow particles flux Q requires the determination of the mechanical-acoustical coupling equations for the sensor according to suitable hypothesis about particle impacts. The wind velocity is determined on a similar principle : the wind interacts with the body of the sensor and induces acoustic pressure into air enclosures (fig. 2 right). Suitable sensitivity can be obtained optimising the body shape and structure to the expected wind velocities. Fig. 3 : Top left - Prototypes tested in wind tunnel at LASEN-EPFL. The acoustic response of cylindrical and spherical forms excited by wind were characterised in the mls range (from Th. Castelle). Top right - Calibration with controlled particles flux on test-bench at LEMA-EPFL (from Th. Melly). Bottom - Prototype tested at Anzere ski resort (2400 my. Comparison of acoustic records to manual Driftometer indexes (from Th. Melly V. Chritin). Results obtained from the validation experiments carried-out with a reference snowdrift measuring device and a reference anemometer show good accordance. (fig. 4 5). Fig. 2 : Left - Saltation ice particles shocking a pipe. (from V. Chritin). Right - Visualisation of a turbulent flux around a cylindrical obstacle. (from H. Werle ONERA). Because snowdrift happens during windy periods it is necessary that the sensor strongly discriminates wind from snowdrift. This property can be obtained by an appropriate design of the mechanical-acoustical coupling. With no mobile components and full protected transducers (inside closed cavities) the FlowCapt is very suitable for stringent topographical and climatic environments. M.. manue'le _tghn 2 o+-=---l ! l-- -_~ SO.OO Fig. 4 : Comparison of snowdrift measured by the FlowCapt prototype and the Driftometer. 198
3 \ ~ 12 \! 10 '~ Fig 5 : Wind velocity measurements (mls vs time in s) in wind tunnel. (a) calibrated MiniAirS anemometerresponse (b) FlowCapt prototype response. On the basis of the obtained results the industrial development of the FlowCapt began. A particular attention was paid on the calibration and reliability to ensure precise quantitative snowdrift information. The sensitivity of the sensor to wind velocity was calibrated in a wind-tunnel by comparison with reference anemometers. To calibrate snowdrift no suitable reference instrument exists. Thus it is necessary to define a specific method to find the calibration param~~~rs under various conditions (fig. 6) : (1) sensitivity measurements in bench tests with controlled particles flux (2) continuous meteorological and snowdrift measurements for two winters on a test site (3) comparison of the FlowCapt response to Driftometer indexes during storms. station is located at an altitude of 2700m on a south facing slope of Mt. Bonvin. Values are recorded every minute (time constant =1s). Snowdrift is integrated from ground to 1m height and between 1m and 1.2 m (fig. 7). C Q 8 :> r-rl ọ.. ~o ~c:; ~o ~;; ~8 ~~ '" Average wnd Speed Snowdrift 1 < h < 1.2 m Snowdrift 0 <h < 1 m ~~ " 'il \ ll. '~~ "~' Lt '.-1 r't.. f' «) <0 «) «> ( :l C ~ 600 Ẹ. 400 := l! S 200 Date Fig. 7 : Wind and snowdrift recorded at Aminona ski resort between January 24th and 26th The upper sensor additionally measures wind speed. The station (fig. 8) is equipped with a set of sensors and a number of features that allow for a significant improvement of the assessment of the actual local avalanche danger: snow surface temperature measured by a special infrared radiation thermometer surface reflected short wave radiation ground temperature wind air temperature and humidity allow for a direct onsite indexing of the formation of weak layers one of the key parameters for the formation of dry slab avalanches (cloudiness near surface energy flux balance dendricity and sphericity (Brun et ai 1992) grain size of surface layer formation of surface rime surface melt). Fig. 6 : Left - Bench test. Centre - Test site with an automatic weather station. Right - Manual driftometer measurementplace (from V. Chritin). 4. OPERATONAL USE n December 1997 FlowCapt has been installed on a standard automatic remote station (Gubler 1996) at Aminona ski resort (Switzerland). The Fig 8 : Swiss Standard Remote Snow Station with additional sensors. The snow profiler measures the snow stratigraphy at an index point within the release zone settlement snow accumulation fracture height and penetration! damming of meltwater as well as 199
4 refreezing. The indication of damming of meltwater at a certain depth within the snow cover at a time resolution of about 30' improves the short term forecasting of wet slabs and surface slides. A specially prepared low priced TOR sensor attached to the ground surface indicates the arrival of meltwater at the snow ground interface an important parameter for the assessment of the danger from full depth avalanches. n the near future this sensor will possibly also provide additional information on the state of the base layer. A geophone attached to the system indicates avalanche activity and checks remote control of explosives for artificial avalanche releases. A reliable sensor for a direct measurement if initial fracturing as a precursor for slab avalanche formation is still missing but is currently under development. 5. COMBNATON WTH JET ROOF Protecting the FlowCapt with a jet roof is crucial for many applications where the optimal placement of the sensor regarding to snow drift is close to a ridge within the flow path of drifting snow. At these locations often large cornices may form. n such cases snow accumulation on the sensor is significantly reduced by placing the instrument below a jet roof. accumulations in the vicinity of the sensor. A combined structure has been developed and is currently being installed on a site in the Swiss Alps. 6. NTERFACNG POSSBLTES The FlowCapt system is battery powered and includes all necessary electronics to be externally powered by a solar panel or other AC or DC current sources. Total power consumption including the CR500 logger is 40mW. nterfacing to other systems or base stations include radio and GSM transmission SOl serial protocol and analog output signals. These features make the sensor extremely useful for remote installations. As snowdrift quantities is a parameter of high importance to analyse the avalanche release probabilities the current work consists in interfacing FlowCapt with the NivoLog avalanche forecasting support system (Bolognesi 1998). This link between hardware and software is a first step towards an automatic prediction system. Fig. 9 Jet roof placed on a ridge crest to protect an optical snow drift gauge from snow accumulations (Gubler SF/SAR 1982). The jet roof locally increases wind and drifting speed and therefore avoids permanent snow Fig 10 : NivoLog Graph software module displays simple graphics from FlowCapt data in order to show quickly snowdrift trends. 200
5 Automatic weather Station Observatioo FlowCapt..!. J-. NivoLog Observe inform On-site: automatic measurements Fig 11 : The FlowCapt snowdrift sensor and the NivoLog forecasting support systems can be interfaced to an automatic weather station to constitute an automatic prediction chain. 7. CONCLUSON FlowCapt an acoustic sensor is the first automatic anemo-driftometer. t can be connected to weather automatic stations located in stringent environments to provide quantitative snowdrift measurements which are significant data to predict avalanches. Thus FlowCapt is an essential component of the automatic avalanche forecasting chain : sensor - automatic weather station - decision support system. ACKNOWLEDGEMENT Ch. Wuilloud (Service des Forets et du Paysage du Canton du Valais) J.-C. Amos and F. Meyer (Tel-Arninona SA) A. Dussex (SAREM Anzere). REFERENCES Schmidt R A. et a Comparison of snow drifting measurements at an alpine ridge crest Cold Regions Science and Technology Vol. 9 pp Brun E. David P. Sudul M. Brunot G A numerical model to simulate snow-cover stratigraphy for operational avalanche forecasting. J. G/aciol. 38(128) Castelle Th Transport de neige par e vent en montagne : approche experimentale du site du col du lac blanc PhD Thesis 1303 Genie civil EPFL. Bolognesi R Daultier J.-M Naaim F. Ousset F Une evaluation quantitative du snowdrift pour la prevision locale des avalanches ANENA Revue n 0 69 march 95. Gubler H An integrated system for artificial avalanche control proc. ANENA Chamonix Symposium pp Bolognesi R 1996 The Driftometer Proc. of The nt. Snow and Science Workshop Banff. Gubler H Remote Avalanche Warning- Alarm- and Control Systems Fundamentals Applications and Experience. Proc. of the nt. Snow Science Workshop Banff Bolognesi R 1998 Prevention des avalanches : e systeme NivoLog ANENA Revuen?1. Chritin V. Bolognesi R Gubler H Acoustic sensor to measure snowdrift and wind velocity for avalanche forecasting proceedings ofng 2S h anniversary conference in press. 201
Remote Avalanche Warning-, Alarm- and Control Systems, Fundamentals, Applications and Experience
 Remote Avalanche Warning-, Alarm- and Control Systems, Fundamentals, Applications and Experience Hansueli Gubler AlpuG GmbH CH 7270 Davos Platz, Switzerland Phone/Fax ++41(0)81 416 10 19, Email alpug@alpug.ch
Remote Avalanche Warning-, Alarm- and Control Systems, Fundamentals, Applications and Experience Hansueli Gubler AlpuG GmbH CH 7270 Davos Platz, Switzerland Phone/Fax ++41(0)81 416 10 19, Email alpug@alpug.ch
I predict some avalanches today because I read in my database that many avalanches occurred during a past similar day...
 Acoustic Detection System for Operational Avalanche Forecasting v. Chritin 1, M. Rossj1 and R. Bolognesi 2 1EPFL, De-Lema, CH-1 015 Lausanne 2SFISAR, Weissfluhjoch, CH-7260 Davos Key Words.: Avalanche
Acoustic Detection System for Operational Avalanche Forecasting v. Chritin 1, M. Rossj1 and R. Bolognesi 2 1EPFL, De-Lema, CH-1 015 Lausanne 2SFISAR, Weissfluhjoch, CH-7260 Davos Key Words.: Avalanche
Use of the models Safran-Crocus-Mepra in operational avalanche forecasting
 Use of the models Safran-Crocus-Mepra in operational avalanche forecasting Coléou C *, Giraud G, Danielou Y, Dumas J-L, Gendre C, Pougatch E CEN, Météo France, Grenoble, France. ABSTRACT: Avalanche forecast
Use of the models Safran-Crocus-Mepra in operational avalanche forecasting Coléou C *, Giraud G, Danielou Y, Dumas J-L, Gendre C, Pougatch E CEN, Météo France, Grenoble, France. ABSTRACT: Avalanche forecast
SLOPE SCALE AVALANCHE FORECASTING IN THE ARCTIC (SVALBARD)
 SLOPE SCALE AVALANCHE FORECASTING IN THE ARCTIC (SVALBARD) Alexander Prokop 1,2 *, Holt Hancock 2, Martin Praz 3, and Elisabeth Jahn 1 1 Snow Scan Research, Engineering, Education GmbH, Vienna, Austria
SLOPE SCALE AVALANCHE FORECASTING IN THE ARCTIC (SVALBARD) Alexander Prokop 1,2 *, Holt Hancock 2, Martin Praz 3, and Elisabeth Jahn 1 1 Snow Scan Research, Engineering, Education GmbH, Vienna, Austria
SNOW TRANSPORT RATE: FIELD MEASUREMENTS AT SHORT TIME SCALES. F.-X. Cierco*, F. Naaim-Bouvet and H. Bellot Cemagref ETNA, Grenoble, France
 SNOW TRANSPORT RATE: FIELD MEASUREMENTS AT SHORT TIME SCALES F.-X. Cierco*, F. Naaim-Bouvet and H. Bellot Cemagref ETNA, Grenoble, France ABSTRACT: So as to study snowdrift at short time scales on an experimental
SNOW TRANSPORT RATE: FIELD MEASUREMENTS AT SHORT TIME SCALES F.-X. Cierco*, F. Naaim-Bouvet and H. Bellot Cemagref ETNA, Grenoble, France ABSTRACT: So as to study snowdrift at short time scales on an experimental
MODELING AND VALIDATION OF SNOW REDISTRIBUTION BY WIND.
 MODELING AND VALIDATION OF SNOW REDISTRIBUTION BY WIND. G. Guyomarc'h, Y. Durand and L. Mérindol Centre d'études de la Neige Météo-France CNRM, Grenoble, FRANCE ABSTRACT : As part of the effort of the
MODELING AND VALIDATION OF SNOW REDISTRIBUTION BY WIND. G. Guyomarc'h, Y. Durand and L. Mérindol Centre d'études de la Neige Météo-France CNRM, Grenoble, FRANCE ABSTRACT : As part of the effort of the
PREDICTING SNOW COVER STABILITY WITH THE SNOW COVER MODEL SNOWPACK
 PREDICTING SNOW COVER STABILITY WITH THE SNOW COVER MODEL SNOWPACK Sascha Bellaire*, Jürg Schweizer, Charles Fierz, Michael Lehning and Christine Pielmeier WSL, Swiss Federal Institute for Snow and Avalanche
PREDICTING SNOW COVER STABILITY WITH THE SNOW COVER MODEL SNOWPACK Sascha Bellaire*, Jürg Schweizer, Charles Fierz, Michael Lehning and Christine Pielmeier WSL, Swiss Federal Institute for Snow and Avalanche
MONITORING SNOWPACK TEMPERATURE GRADIENT USING AUTOMATIC SNOW DEPTH SENSOR
 MONITORING SNOWPACK TEMPERATURE GRADIENT USING AUTOMATIC SNOW DEPTH SENSOR Örn Ingólfsson* POLS Engineering, IS-400 Ísafjörður, ICELAND Harpa Grímsdóttir, Magni Hreinn Jónsson Icelandic Meteorological
MONITORING SNOWPACK TEMPERATURE GRADIENT USING AUTOMATIC SNOW DEPTH SENSOR Örn Ingólfsson* POLS Engineering, IS-400 Ísafjörður, ICELAND Harpa Grímsdóttir, Magni Hreinn Jónsson Icelandic Meteorological
Snow drift: acoustic sensors for avalanche warning and research
 Snow drift: acoustic sensors for avalanche warning and research M. Lehning, F. Naaim, M. Naaim, B. Brabec, J. Doorschot, Y. Durand, G. Guyomarc H, J.-L. Michaux, M. Zimmerli To cite this version: M. Lehning,
Snow drift: acoustic sensors for avalanche warning and research M. Lehning, F. Naaim, M. Naaim, B. Brabec, J. Doorschot, Y. Durand, G. Guyomarc H, J.-L. Michaux, M. Zimmerli To cite this version: M. Lehning,
Observatoire des Sciences de l Univers de Grenoble
 Involvment of the SOERE CRYOBS-CLIM (CRYosphere, an OBServatory of the CLIMate IR OZCAR) in snow and ice related hazards prevention in an Alpine context Delphine Six (Univ. Grenoble Alpes / IGE) Florence
Involvment of the SOERE CRYOBS-CLIM (CRYosphere, an OBServatory of the CLIMate IR OZCAR) in snow and ice related hazards prevention in an Alpine context Delphine Six (Univ. Grenoble Alpes / IGE) Florence
A METHOD FOR THE FORECASTING OF WIND IN MOUNTAINOUS REGIONS.
 A METHOD FOR THE FORECASTING OF WIND IN MOUNTAINOUS REGIONS. Gilbert Guyomarc'h\ Laurent Merindol 1 and Haraldur Olafsson 2 1 Meteo-France Centre d'etudes de la Neige Grenoble - FRANCE 2 Icelandic Meteorological
A METHOD FOR THE FORECASTING OF WIND IN MOUNTAINOUS REGIONS. Gilbert Guyomarc'h\ Laurent Merindol 1 and Haraldur Olafsson 2 1 Meteo-France Centre d'etudes de la Neige Grenoble - FRANCE 2 Icelandic Meteorological
Snow Disaster Forecasting System on Roads. Suyoshi, Maeyama, Nagaoka, Japan
 SIRWEC 26 25 th -27 th Snow Disaster Forecasting System on Roads K. Nishimura 1, H. Hirashima 1, K. Kosugi 1, T. Kobayashi 1, T. Sato 1, A. Sato 1 and M. Lehning 2 1 Nagaoka Institute of Snow and Ice Studies,
SIRWEC 26 25 th -27 th Snow Disaster Forecasting System on Roads K. Nishimura 1, H. Hirashima 1, K. Kosugi 1, T. Kobayashi 1, T. Sato 1, A. Sato 1 and M. Lehning 2 1 Nagaoka Institute of Snow and Ice Studies,
Proceedings, International Snow Science Workshop, Banff, 2014
 CHANGE IN SNOW PARTICLES SHAPE DURING BLOWING SNOW EVENT : EFFECTS ON THE SUSPENSION LAYER Florence Naaim-Bouvet 1,2 *, Vincent Vionnet 3, Hervé Bellot 1,2, Mohamed Naaim 1,2 and Gilbert Guyomarc h 3 1
CHANGE IN SNOW PARTICLES SHAPE DURING BLOWING SNOW EVENT : EFFECTS ON THE SUSPENSION LAYER Florence Naaim-Bouvet 1,2 *, Vincent Vionnet 3, Hervé Bellot 1,2, Mohamed Naaim 1,2 and Gilbert Guyomarc h 3 1
Proceedings, 2012 International Snow Science Workshop, Anchorage, Alaska
 POSITIONING OF AVALANCHE PROTECTION MEASURES USING SNOW DEPTH MAPPING VIA TERRESTRIAL LASER SCANNING Alexander Prokop* and Christina M. Delaney² Institute of Mountain Risk Engineering, Department of Civil
POSITIONING OF AVALANCHE PROTECTION MEASURES USING SNOW DEPTH MAPPING VIA TERRESTRIAL LASER SCANNING Alexander Prokop* and Christina M. Delaney² Institute of Mountain Risk Engineering, Department of Civil
Automatic Monitoring of Snow Depth
 Automatic Monitoring of Snow Depth Claude Labine Campbell Scientific Canada (Corp.), 11564 149 Street, dmonton, Alberta, T5M 1W7. Tel:(403) 454-2505, Fax: (403) 454-2655 mail: campsci@freenet.edmonton.ab.ca
Automatic Monitoring of Snow Depth Claude Labine Campbell Scientific Canada (Corp.), 11564 149 Street, dmonton, Alberta, T5M 1W7. Tel:(403) 454-2505, Fax: (403) 454-2655 mail: campsci@freenet.edmonton.ab.ca
Road weather forecast for different customer systems in Switzerland
 Proceedings of the 10th SIRWEC Conference. 22-24 March 2000. Davos. Switzerland 10 Road weather forecast for different customer systems in Switzerland Foreword André-Charles Letestu and Urs Keller Swiss
Proceedings of the 10th SIRWEC Conference. 22-24 March 2000. Davos. Switzerland 10 Road weather forecast for different customer systems in Switzerland Foreword André-Charles Letestu and Urs Keller Swiss
Swiss Avalanche-Dynamics Procedures for Dense Flow Avalanches
 Swiss Avalanche-Dynamics Procedures for Dense Flow Avalanches H. Gubler 1 Swiss Avalanche-Dynamics Procedures for Dense Flow Avalanches H.Gubler AlpuG Richtstattweg2 CH-7270 Davos Platz, Switzerland Introduction
Swiss Avalanche-Dynamics Procedures for Dense Flow Avalanches H. Gubler 1 Swiss Avalanche-Dynamics Procedures for Dense Flow Avalanches H.Gubler AlpuG Richtstattweg2 CH-7270 Davos Platz, Switzerland Introduction
SLAB AVALANCHES AND NEW SNOW. Alain Duclos
 SLAB AVALANCHES AND NEW SNOW Alain Duclos ABSTRACT : A three-year study based on observations carried out both on the field and inside the laboratory has enabled us to describe accurately 22 slab avalanches
SLAB AVALANCHES AND NEW SNOW Alain Duclos ABSTRACT : A three-year study based on observations carried out both on the field and inside the laboratory has enabled us to describe accurately 22 slab avalanches
An operational supporting tool for assessing wet-snow avalanche danger
 An operational supporting tool for assessing wet-snow avalanche danger Christoph Mitterer*, Frank Techel, Charles Fierz and Jürg Schweizer WSL Institute for Snow and Avalanche Research SLF, Davos, Switzerland
An operational supporting tool for assessing wet-snow avalanche danger Christoph Mitterer*, Frank Techel, Charles Fierz and Jürg Schweizer WSL Institute for Snow and Avalanche Research SLF, Davos, Switzerland
Proceedings, International Snow Science Workshop, Breckenridge, Colorado, 2016
 COUPLING OPERATIONAL SNOWCOVER SIMULATIONS WITH AVALANCHE DYNAMICS CALCU- LATIONS TO ASSESS AVALANCHE DANGER IN HIGH ALTITUDE MINING OPERATIONS Vera Valero, César 1 *, Wever, Nander 2 and Bartelt, Perry
COUPLING OPERATIONAL SNOWCOVER SIMULATIONS WITH AVALANCHE DYNAMICS CALCU- LATIONS TO ASSESS AVALANCHE DANGER IN HIGH ALTITUDE MINING OPERATIONS Vera Valero, César 1 *, Wever, Nander 2 and Bartelt, Perry
Proceedings, International Snow Science Workshop, Banff, 2014
 EVALUATING THE POTENTIAL OF USING SNOWPACK AND ALPINE3D SIMULATIONS IN THREE CANADIAN MOUNTAIN CLIMATES Côté K., Madore, J-B. and Langlois, A. Université de Sherbrooke, Sherbrooke, QC, Canada ABSTRACT:
EVALUATING THE POTENTIAL OF USING SNOWPACK AND ALPINE3D SIMULATIONS IN THREE CANADIAN MOUNTAIN CLIMATES Côté K., Madore, J-B. and Langlois, A. Université de Sherbrooke, Sherbrooke, QC, Canada ABSTRACT:
Development of Snow Avalanche Forecasting System in Japan
 Disaster Mitigation of Debris Flows, Slope Failures and Landslides 267 Development of Snow Avalanche Forecasting System in Japan Kouichi Nishimura, 1) Hiroyuki Hirashima, 1) Satoru Yamaguchi, 1) Kenji
Disaster Mitigation of Debris Flows, Slope Failures and Landslides 267 Development of Snow Avalanche Forecasting System in Japan Kouichi Nishimura, 1) Hiroyuki Hirashima, 1) Satoru Yamaguchi, 1) Kenji
Applications. Remote Weather Station with Telephone Communications. Tripod Tower Weather Station with 4-20 ma Outputs
 Tripod Tower Weather Station with 4-20 ma Outputs Remote Weather Station with Telephone Communications NEMA-4X Enclosure with Two Translator Boards and Analog Barometer Typical Analog Output Evaporation
Tripod Tower Weather Station with 4-20 ma Outputs Remote Weather Station with Telephone Communications NEMA-4X Enclosure with Two Translator Boards and Analog Barometer Typical Analog Output Evaporation
Proceedings, International Snow Science Workshop, Banff, 2014
 SIMULATION OF THE ALPINE SNOWPACK USING METEOROLOGICAL FIELDS FROM A NON- HYDROSTATIC WEATHER FORECAST MODEL V. Vionnet 1, I. Etchevers 1, L. Auger 2, A. Colomb 3, L. Pfitzner 3, M. Lafaysse 1 and S. Morin
SIMULATION OF THE ALPINE SNOWPACK USING METEOROLOGICAL FIELDS FROM A NON- HYDROSTATIC WEATHER FORECAST MODEL V. Vionnet 1, I. Etchevers 1, L. Auger 2, A. Colomb 3, L. Pfitzner 3, M. Lafaysse 1 and S. Morin
2010 International Snow Science Workshop
 mavalanche SMART AVALANCHE FORECASTING WITH SMARTPHONES Christoph Suter *, Stephan Harvey and Lukas Dürr WSL Institute for Snow and Avalanche Research SLF, Davos, Switzerland ABSTRACT: The common information
mavalanche SMART AVALANCHE FORECASTING WITH SMARTPHONES Christoph Suter *, Stephan Harvey and Lukas Dürr WSL Institute for Snow and Avalanche Research SLF, Davos, Switzerland ABSTRACT: The common information
Lac Blanc Pass : a natural wind-tunnel for studying drifting snow at 2700ma.s.l
 Lac Blanc Pass : a natural wind-tunnel for studying drifting snow at 2700ma.s.l Florence Naaim-Bouvet 1, Gilbert Guyomarc h 2, Hervé Bellot 1, Yves Durand 2, Mohamed Naaim 1, Vincent Vionnet 2, Christophe
Lac Blanc Pass : a natural wind-tunnel for studying drifting snow at 2700ma.s.l Florence Naaim-Bouvet 1, Gilbert Guyomarc h 2, Hervé Bellot 1, Yves Durand 2, Mohamed Naaim 1, Vincent Vionnet 2, Christophe
Back analysis of drifting snow measurements over an instrumented mountainous site
 Back analysis of drifting snow measurements over an instrumented mountainous site F. Naaim Bouvet, H. Bellot, M. Naaim To cite this version: F. Naaim Bouvet, H. Bellot, M. Naaim. Back analysis of drifting
Back analysis of drifting snow measurements over an instrumented mountainous site F. Naaim Bouvet, H. Bellot, M. Naaim To cite this version: F. Naaim Bouvet, H. Bellot, M. Naaim. Back analysis of drifting
Proceedings, International Snow Science Workshop, Breckenridge, Colorado, 2016
 CHARACTERISTICS OF AVALANCHE RELEASE AND AN APPROACH OF AVALANCHE FORECAST- ING SYSTEM USING SNOWPACK MODEL IN THE TIANSHAN MOUNTAINS, CHINA Osamu ABE 1*, Lanhai LI 2, Lei BAI 2, Jiansheng HAO 2, Hiroyuki
CHARACTERISTICS OF AVALANCHE RELEASE AND AN APPROACH OF AVALANCHE FORECAST- ING SYSTEM USING SNOWPACK MODEL IN THE TIANSHAN MOUNTAINS, CHINA Osamu ABE 1*, Lanhai LI 2, Lei BAI 2, Jiansheng HAO 2, Hiroyuki
INTERPRAEVENT 2008 Conference Proceedings, Vol. 2
 INTERPRAEVENT 2008 Conference Proceedings, Vol. 2 IMPROVING AVALANCHE FORECASTS BY EXTRACTING BOUNDARY CONDITIONS FROM MEASURED WIND DATA AND LOCAL WEATHER MODELS FOR SNOW DRIFT SIMULATION IN ALPINE AREAS
INTERPRAEVENT 2008 Conference Proceedings, Vol. 2 IMPROVING AVALANCHE FORECASTS BY EXTRACTING BOUNDARY CONDITIONS FROM MEASURED WIND DATA AND LOCAL WEATHER MODELS FOR SNOW DRIFT SIMULATION IN ALPINE AREAS
W. Douglas Wewer 1,2 *, Michael J. Jenkins 1
 A PRACTITIONER S PERSPECTIVE: PROVIDING TIMELY AND RELEVANT MOUNTAIN WEATHER INFORMATION TO AVALANCHE WORKERS AT SNOWBASIN, A SUN VALLEY RESORT AND THE FOREST SERVICE UTAH AVALANCHE CENTER W. Douglas Wewer
A PRACTITIONER S PERSPECTIVE: PROVIDING TIMELY AND RELEVANT MOUNTAIN WEATHER INFORMATION TO AVALANCHE WORKERS AT SNOWBASIN, A SUN VALLEY RESORT AND THE FOREST SERVICE UTAH AVALANCHE CENTER W. Douglas Wewer
 Canton du Valais, Service des forêts et du paysage (SFP), section des dangers naturels Kanton Graubünden, Amt für Wald Graubünden, Naturgefahren Regione Valle d Aosta, Dipartimento Difesa del Suolo e Risorse
Canton du Valais, Service des forêts et du paysage (SFP), section des dangers naturels Kanton Graubünden, Amt für Wald Graubünden, Naturgefahren Regione Valle d Aosta, Dipartimento Difesa del Suolo e Risorse
- SNOW - DEPOSITION, WIND TRANSPORT, METAMORPHISM
 ESS 431 PRINCIPLES OF GLACIOLOGY ESS 505 THE CRYOSPHERE - SNOW - DEPOSITION, WIND TRANSPORT, METAMORPHISM OCTOBER 10, 2016 Ed Waddington edw@uw.edu Homework Skating and the phase diagram See web page Sources
ESS 431 PRINCIPLES OF GLACIOLOGY ESS 505 THE CRYOSPHERE - SNOW - DEPOSITION, WIND TRANSPORT, METAMORPHISM OCTOBER 10, 2016 Ed Waddington edw@uw.edu Homework Skating and the phase diagram See web page Sources
Website Phone Mobile OVERVIEW Davis Vantage Pro2 Weather Station
 OVERVIEW If you're looking for a superior weather station, the Davis Vantage Pro2 Weather Station is as good as they come! Vantage Pro2 offers the professional weather observer and the serious weather
OVERVIEW If you're looking for a superior weather station, the Davis Vantage Pro2 Weather Station is as good as they come! Vantage Pro2 offers the professional weather observer and the serious weather
ESTIMATION OF NEW SNOW DENSITY USING 42 SEASONS OF METEOROLOGICAL DATA FROM JACKSON HOLE MOUNTAIN RESORT, WYOMING. Inversion Labs, Wilson, WY, USA 2
 ESTIMATION OF NEW SNOW DENSITY USING 42 SEASONS OF METEOROLOGICAL DATA FROM JACKSON HOLE MOUNTAIN RESORT, WYOMING Patrick J. Wright 1 *, Bob Comey 2,3, Chris McCollister 2,3, and Mike Rheam 2,3 1 Inversion
ESTIMATION OF NEW SNOW DENSITY USING 42 SEASONS OF METEOROLOGICAL DATA FROM JACKSON HOLE MOUNTAIN RESORT, WYOMING Patrick J. Wright 1 *, Bob Comey 2,3, Chris McCollister 2,3, and Mike Rheam 2,3 1 Inversion
AUTOMATIC MEASUREMENT OF ICING ON THE WEST OF THE CZECH REPUBLIC
 AUTOMATIC MEASUREMENT OF ICING ON THE WEST OF THE CZECH REPUBLIC J. Chum, J. Vojta, J. Hošek Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Boční II / 1401, Praha 4, Czech republic 1 INTRODUCTION We report our experience
AUTOMATIC MEASUREMENT OF ICING ON THE WEST OF THE CZECH REPUBLIC J. Chum, J. Vojta, J. Hošek Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Boční II / 1401, Praha 4, Czech republic 1 INTRODUCTION We report our experience
SIRWEC th International Road Weather Conference
 SIRWEC 2018 19th International Road Weather Conference Test methods for sensors of road weather stations Horst Badelt Sandra Eimermacher Federal Highway Research Institute Germany Content - test field
SIRWEC 2018 19th International Road Weather Conference Test methods for sensors of road weather stations Horst Badelt Sandra Eimermacher Federal Highway Research Institute Germany Content - test field
Cartographic analysis of avalanche hazard maps A comparison of relevant cartographic factors for the visualization of the avalanche bulletin
 Cartographic analysis of avalanche hazard maps A comparison of relevant cartographic factors for the visualization of the avalanche bulletin Markus Eckerstorfer, Karel Kriz University of Vienna, Department
Cartographic analysis of avalanche hazard maps A comparison of relevant cartographic factors for the visualization of the avalanche bulletin Markus Eckerstorfer, Karel Kriz University of Vienna, Department
Proceedings, International Snow Science Workshop, Banff, 2014
 DERIVING SNOW STABILITY INFORMATION FROM SIMULATED SNOW COVER STRATIGRAPHY Fabiano Monti 1,2, Jürg Schweizer 1 and Johan Gaume 1 1 WSL Institute for Snow and Avalanche Research SLF, Davos, Switzerland
DERIVING SNOW STABILITY INFORMATION FROM SIMULATED SNOW COVER STRATIGRAPHY Fabiano Monti 1,2, Jürg Schweizer 1 and Johan Gaume 1 1 WSL Institute for Snow and Avalanche Research SLF, Davos, Switzerland
Proceedings, International Snow Science Workshop, Banff, 2014
 CHANGES IN DESIGN STANDARDS AND REGIONAL CHARACTERISTICS OF AVALANCHE SUPPORTING STRUCTURES IN JAPAN Yusuke Harada 1 *, Hiroki Matsushita and Masaru Matsuzawa 1 1 Civil Engineering Research Institute for
CHANGES IN DESIGN STANDARDS AND REGIONAL CHARACTERISTICS OF AVALANCHE SUPPORTING STRUCTURES IN JAPAN Yusuke Harada 1 *, Hiroki Matsushita and Masaru Matsuzawa 1 1 Civil Engineering Research Institute for
HOUR-TO-HOUR SNOWMELT RATES AND LYSIMETER OUTFLOW DURING AN ENTIRE ABLATION PERIOD
 Snow Cover and Glacier Variations (Proceedings of the Baltimore Symposium, Maryland, May 1989) 19 IAHS Publ. no. 183, 1989. HOUR-TO-HOUR SNOWMELT RATES AND LYSIMETER OUTFLOW DURING AN ENTIRE ABLATION PERIOD
Snow Cover and Glacier Variations (Proceedings of the Baltimore Symposium, Maryland, May 1989) 19 IAHS Publ. no. 183, 1989. HOUR-TO-HOUR SNOWMELT RATES AND LYSIMETER OUTFLOW DURING AN ENTIRE ABLATION PERIOD
Whistler Mountain is located at about 50 0 North latitude by 123 0
 - 24 - WHISTLER MOUNTAIN AVALANCHE CONTROL PROGRAMME C. Stethem and J. Hetherington Introduction Whistler Mountain is located at about 50 0 North latitude by 123 0 longitude, in the Pacific Coast Range
- 24 - WHISTLER MOUNTAIN AVALANCHE CONTROL PROGRAMME C. Stethem and J. Hetherington Introduction Whistler Mountain is located at about 50 0 North latitude by 123 0 longitude, in the Pacific Coast Range
In-situ observations and snowdrift modeling on alpine topography.
 In-situ observations and snowdrift modeling on alpine topography. G. Guyomarc'h*, Y. Durand and L. Merindol Meteo-France, Centre d'etudes de la Neige (Snow Study Centre). Abstract: Recently, the Snow Study
In-situ observations and snowdrift modeling on alpine topography. G. Guyomarc'h*, Y. Durand and L. Merindol Meteo-France, Centre d'etudes de la Neige (Snow Study Centre). Abstract: Recently, the Snow Study
AVALANCHE HAZARD EVALUATION IN HELICOPTER SKIING. Hans Gmoser Canadian Mountain Holidays, Banff, Alberta. Introduction
 90 AVALANCHE HAZARD EVALUATION IN HELICOPTER SKIING Hans Gmoser Canadian Mountain Holidays, Banff, Alberta Introduction I delivered a paper at the previous Avalanche Workshop-in 1976 comparing the avalanche
90 AVALANCHE HAZARD EVALUATION IN HELICOPTER SKIING Hans Gmoser Canadian Mountain Holidays, Banff, Alberta Introduction I delivered a paper at the previous Avalanche Workshop-in 1976 comparing the avalanche
Snow and glacier change modelling in the French Alps
 International Network for Alpine Research Catchment Hydrology Inaugural Workshop Barrier Lake Field Station, Kananaskis Country, Alberta, Canada 22-24 October 2015 Snow and glacier change modelling in
International Network for Alpine Research Catchment Hydrology Inaugural Workshop Barrier Lake Field Station, Kananaskis Country, Alberta, Canada 22-24 October 2015 Snow and glacier change modelling in
Proceedings, International Snow Science Workshop, Innsbruck, Austria, 2018
 RELEASE OF AVALANCHES ON PERSISTENT WEAK LAYERS IN RELATION TO LOADING EVENTS IN COLORADO, USA Jason Konigsberg 1, Spencer Logan 1, and Ethan Greene 1 1 Colorado Avalanche Information Center, Boulder,
RELEASE OF AVALANCHES ON PERSISTENT WEAK LAYERS IN RELATION TO LOADING EVENTS IN COLORADO, USA Jason Konigsberg 1, Spencer Logan 1, and Ethan Greene 1 1 Colorado Avalanche Information Center, Boulder,
Canton du Valais, Service des forêts et du paysage (SFP), section des dangers naturels Kanton Graubünden, Amt für Wald Graubünden, Naturgefahren
 Canton du Valais, Service des forêts et du paysage (SFP), section des dangers naturels Kanton Graubünden, Amt für Wald Graubünden, Naturgefahren Regione Valle d Aosta, Dipartimento Difesa del Suolo e Risorse
Canton du Valais, Service des forêts et du paysage (SFP), section des dangers naturels Kanton Graubünden, Amt für Wald Graubünden, Naturgefahren Regione Valle d Aosta, Dipartimento Difesa del Suolo e Risorse
Product Description. 1 of 6
 Product Description The 6250 Vantage Vue Wireless Weather Station provides accurate, reliable weather monitoring in a self-contained, easy-to-install system. Designed to provide the weather data you need
Product Description The 6250 Vantage Vue Wireless Weather Station provides accurate, reliable weather monitoring in a self-contained, easy-to-install system. Designed to provide the weather data you need
Forecasting and modelling ice layer formation on the snowpack due to freezing precipitation in the Pyrenees
 Forecasting and modelling ice layer formation on the snowpack due to freezing precipitation in the Pyrenees L. Quéno 1, V. Vionnet 1, F. Cabot 2, D. Vrécourt 2, I. Dombrowski-Etchevers 3 1 Météo-France
Forecasting and modelling ice layer formation on the snowpack due to freezing precipitation in the Pyrenees L. Quéno 1, V. Vionnet 1, F. Cabot 2, D. Vrécourt 2, I. Dombrowski-Etchevers 3 1 Météo-France
TRIP SCHEDULE TRIP NOTE
 1 TRIP SCHEDULE 1) 17 Mar. 2003: Tsukuba--Narita--Ulaanbaatar (OM502) 2) 18 Mar. 2003: Ulaanbaatar--Baganuur--Mongonmorit Forest Site 3) 18 to 23 Mar. 2003: Mongonmorit Forest Site Installing sensors for
1 TRIP SCHEDULE 1) 17 Mar. 2003: Tsukuba--Narita--Ulaanbaatar (OM502) 2) 18 Mar. 2003: Ulaanbaatar--Baganuur--Mongonmorit Forest Site 3) 18 to 23 Mar. 2003: Mongonmorit Forest Site Installing sensors for
GLACIOLOGY LAB SNOW Introduction Equipment
 GLACIOLOGY LAB SNOW Introduction The objective of this lab is to achieve a working knowledge of the snowpack. This includes descriptions and genetic analysis of features that can be observed on the surface
GLACIOLOGY LAB SNOW Introduction The objective of this lab is to achieve a working knowledge of the snowpack. This includes descriptions and genetic analysis of features that can be observed on the surface
Rooster Comb Ridge Cornice Incident
 Rooster Comb Ridge Cornice Incident April 3, 2011 Date/time: Sunday, April 3, 2011 / ~12:45pm PDT Submitted by: Patty Morrison Stevens Pass Winter Resort Snow Safety; Mark Moore NWAC Place: High point
Rooster Comb Ridge Cornice Incident April 3, 2011 Date/time: Sunday, April 3, 2011 / ~12:45pm PDT Submitted by: Patty Morrison Stevens Pass Winter Resort Snow Safety; Mark Moore NWAC Place: High point
A new lidar for water vapor and temperature measurements in the Atmospheric Boundary Layer
 A new lidar for water vapor and temperature measurements in the Atmospheric Boundary Layer M. Froidevaux 1, I. Serikov 2, S. Burgos 3, P. Ristori 1, V. Simeonov 1, H. Van den Bergh 1, and M.B. Parlange
A new lidar for water vapor and temperature measurements in the Atmospheric Boundary Layer M. Froidevaux 1, I. Serikov 2, S. Burgos 3, P. Ristori 1, V. Simeonov 1, H. Van den Bergh 1, and M.B. Parlange
Name of research institute or organization: Federal Office of Meteorology and Climatology MeteoSwiss
 Name of research institute or organization: Federal Office of Meteorology and Climatology MeteoSwiss Title of project: The weather in 2016 Report by: Stephan Bader, Climate Division MeteoSwiss English
Name of research institute or organization: Federal Office of Meteorology and Climatology MeteoSwiss Title of project: The weather in 2016 Report by: Stephan Bader, Climate Division MeteoSwiss English
Weather Stations. Evaluation copy. 9. Post live weather data on the school s web site for students, faculty and community.
 Weather Stations Computer P6 Collecting and analyzing weather data can be an important part of your Earth Science curriculum. It might even be an ongoing part of your entire course. A variety of activities
Weather Stations Computer P6 Collecting and analyzing weather data can be an important part of your Earth Science curriculum. It might even be an ongoing part of your entire course. A variety of activities
LOG_aLevel. Tsunami Warning System
 LOG_aLevel Tsunami Warning System General Acoustics e.k. Am Kiel-Kanal 1 24106 Kiel Germany Phone: +49 431 5 80 81 80 www.generalacoustics.com Info@generalacoustics.com LOG_aLevel Tsunami Warning System
LOG_aLevel Tsunami Warning System General Acoustics e.k. Am Kiel-Kanal 1 24106 Kiel Germany Phone: +49 431 5 80 81 80 www.generalacoustics.com Info@generalacoustics.com LOG_aLevel Tsunami Warning System
R. S. Rosso, D. Howlett, S. Calhoun
 SNOWPACK TEMPERATURE AND DECREASES IN TENSILE STRENGTH R. S. Rosso, D. Howlett, S. Calhoun Alta Ski Lifts Co, Alta, Utah ABSTRACT. In an effort to understand post-control and other natural avalanches that
SNOWPACK TEMPERATURE AND DECREASES IN TENSILE STRENGTH R. S. Rosso, D. Howlett, S. Calhoun Alta Ski Lifts Co, Alta, Utah ABSTRACT. In an effort to understand post-control and other natural avalanches that
Wind Resource Assessment Practical Guidance for Developing A Successful Wind Project
 December 11, 2012 Wind Resource Assessment Practical Guidance for Developing A Successful Wind Project Michael C Brower, PhD Chief Technical Officer Presented at: What We Do AWS Truepower partners with
December 11, 2012 Wind Resource Assessment Practical Guidance for Developing A Successful Wind Project Michael C Brower, PhD Chief Technical Officer Presented at: What We Do AWS Truepower partners with
Fact Sheet on Snow Hydrology Products in GIN. SWE Maps
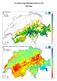 Fact Sheet on Snow Hydrology Products in GIN SWE Maps Description The snow water equivalent maps (SWE maps) present an estimation of the distribution of snow water resources in Switzerland. The maps have
Fact Sheet on Snow Hydrology Products in GIN SWE Maps Description The snow water equivalent maps (SWE maps) present an estimation of the distribution of snow water resources in Switzerland. The maps have
NUMERICAL SNOW DRIFT MODELING IN COMPLEX ALPINE TERRAIN AND COMPARISON WITH FIELD MEASUREMENTS
 NUMERICAL SNOW DRIFT MODELING IN COMPLEX ALPINE TERRAIN AND COMPARISON WITH FIELD MEASUREMENTS Peter Gauer* ABSTRACT: Blowing and drifting snow influences human activities in various ways. For example,
NUMERICAL SNOW DRIFT MODELING IN COMPLEX ALPINE TERRAIN AND COMPARISON WITH FIELD MEASUREMENTS Peter Gauer* ABSTRACT: Blowing and drifting snow influences human activities in various ways. For example,
The WOLF system: forecasting wet-snow loads on power lines in Italy
 Chongqing, China May 8-13, 2011 The WOLF system: forecasting wet-snow loads on power lines in Italy M. Lacavalla, P. Bonelli, G. Mariani, P. Marcacci, G. Stella Research on the Energy Systems - RSE S.p.A.
Chongqing, China May 8-13, 2011 The WOLF system: forecasting wet-snow loads on power lines in Italy M. Lacavalla, P. Bonelli, G. Mariani, P. Marcacci, G. Stella Research on the Energy Systems - RSE S.p.A.
Regional stability evaluation with modelled snow cover data
 Regional stability evaluation with modelled snow cover data Michael Schirmer *, Jürg Schweizer, Michael Lehning WSL Institute for Snow and Avalanche Research SLF, Davos, Switzerland ABSTRACT: Stability
Regional stability evaluation with modelled snow cover data Michael Schirmer *, Jürg Schweizer, Michael Lehning WSL Institute for Snow and Avalanche Research SLF, Davos, Switzerland ABSTRACT: Stability
Active Glacier Protection in Austria - An adaptation strategy for glacier skiing resorts
 in Austria - An adaptation strategy for glacier skiing resorts Presented by Marc Olefs Ice and Climate Group, Institute of Meteorology And Geophysics (IMGI), University of Innsbruck Centre for Natural
in Austria - An adaptation strategy for glacier skiing resorts Presented by Marc Olefs Ice and Climate Group, Institute of Meteorology And Geophysics (IMGI), University of Innsbruck Centre for Natural
Glide avalanche response to an extreme rain-on-snow event, Snoqualmie Pass, Washington, USA 2 METHODS
 Glide avalanche response to an extreme rain-on-snow event, Snoqualmie Pass, Washington, USA John Stimberis 1 * and Charles M. Rubin 2 1 Washington State Department of Transportation, Snoqualmie Pass, WA,
Glide avalanche response to an extreme rain-on-snow event, Snoqualmie Pass, Washington, USA John Stimberis 1 * and Charles M. Rubin 2 1 Washington State Department of Transportation, Snoqualmie Pass, WA,
Windcube TM Pulsed lidar wind profiler Overview of more than 2 years of field experience J.P.Cariou, R. Parmentier, M. Boquet, L.
 Windcube TM Pulsed lidar wind profiler Overview of more than 2 years of field experience J.P.Cariou, R. Parmentier, M. Boquet, L.Sauvage 15 th Coherent Laser Radar Conference Toulouse, France 25/06/2009
Windcube TM Pulsed lidar wind profiler Overview of more than 2 years of field experience J.P.Cariou, R. Parmentier, M. Boquet, L.Sauvage 15 th Coherent Laser Radar Conference Toulouse, France 25/06/2009
A TEST OF THE PRECIPITATION AMOUNT AND INTENSITY MEASUREMENTS WITH THE OTT PLUVIO
 A TEST OF THE PRECIPITATION AMOUNT AND INTENSITY MEASUREMENTS WITH THE OTT PLUVIO Wiel M.F. Wauben, Instrumental Department, Royal Netherlands Meteorological Institute (KNMI) P.O. Box 201, 3730 AE De Bilt,
A TEST OF THE PRECIPITATION AMOUNT AND INTENSITY MEASUREMENTS WITH THE OTT PLUVIO Wiel M.F. Wauben, Instrumental Department, Royal Netherlands Meteorological Institute (KNMI) P.O. Box 201, 3730 AE De Bilt,
OASIS WIRELESS WEATHER STATION
 User Manual 3910-B Royal Avenue, Simi Valley, Ca 93063 805-527-4498 RMIS Part No. 500760 TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION General Description 3 General Precautions 3 INSTALLATION Base Preparation 6 Tower
User Manual 3910-B Royal Avenue, Simi Valley, Ca 93063 805-527-4498 RMIS Part No. 500760 TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION General Description 3 General Precautions 3 INSTALLATION Base Preparation 6 Tower
Proceedings, International Snow Science Workshop, Banff, 2014
 IMPROVEMENT OF SNOW GRAIN SIMULATIONS FROM THE MULTI-LAYERED THERMODYNAMIC SNOW MODEL SNOWPACK: IMPLICATIONS TO AVALANCHE RISK ASSESSMENT Jean-Benoit Madore, Kevin Coté and Alexandre Langlois Université
IMPROVEMENT OF SNOW GRAIN SIMULATIONS FROM THE MULTI-LAYERED THERMODYNAMIC SNOW MODEL SNOWPACK: IMPLICATIONS TO AVALANCHE RISK ASSESSMENT Jean-Benoit Madore, Kevin Coté and Alexandre Langlois Université
NIVEXC: an electronic snow-pole for real-time monitoring of avalanche starting zones
 NIVEXC: an electronic snow-pole for real-time monitoring of avalanche starting zones Massimiliano Barbolini 1, *,Matteo Baudone 2, Francesco Ferro 1, Laura Ricchetti 2, Francesco Stefanini 1 1 FLOW-ING
NIVEXC: an electronic snow-pole for real-time monitoring of avalanche starting zones Massimiliano Barbolini 1, *,Matteo Baudone 2, Francesco Ferro 1, Laura Ricchetti 2, Francesco Stefanini 1 1 FLOW-ING
WIND AND MOUNTAIN CLIMATOLOGY IN SEVERE ENVIRONMENTS UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS CLIMATOLOGICAL RESEARCH IN THE WHITE MOUNTAINS, NH SELECTED
 WIND AND MOUNTAIN CLIMATOLOGY IN SEVERE ENVIRONMENTS UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS CLIMATOLOGICAL RESEARCH IN THE WHITE MOUNTAINS, NH 1972-73 SELECTED DATA AND SLIDES THE UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS PROJECT
WIND AND MOUNTAIN CLIMATOLOGY IN SEVERE ENVIRONMENTS UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS CLIMATOLOGICAL RESEARCH IN THE WHITE MOUNTAINS, NH 1972-73 SELECTED DATA AND SLIDES THE UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS PROJECT
Chapter 5: Weather. Only Section 1: What is Weather?
 Chapter 5: Weather Only Section 1: What is Weather? Find the definitions of: Meteorology, meteorologist, weather, climate Not in book? Use the dictionaries **Meteorology - Meteorology is the study of the
Chapter 5: Weather Only Section 1: What is Weather? Find the definitions of: Meteorology, meteorologist, weather, climate Not in book? Use the dictionaries **Meteorology - Meteorology is the study of the
Proceedings, International Snow Science Workshop, Breckenridge, Colorado, 2016
 COMBINING SNOWPACK MODELS AND OBSERVATIONS FOR BETTER AVALANCHE DANGER ASSESSMENTS Fabiano Monti 1,2 *, Christoph Mitterer 1, Walter Steinkogler 1, Mathias Bavay 3, Andrea Pozzi 2 2 1 ALPsolut, Livigno,
COMBINING SNOWPACK MODELS AND OBSERVATIONS FOR BETTER AVALANCHE DANGER ASSESSMENTS Fabiano Monti 1,2 *, Christoph Mitterer 1, Walter Steinkogler 1, Mathias Bavay 3, Andrea Pozzi 2 2 1 ALPsolut, Livigno,
Road weather forecasts and MDSS in Slovakia
 ID: 0030 Road weather forecasts and MDSS in Slovakia M. Benko Slovak Hydrometeorological Institute (SHMI), Jeséniova 17, 83315 Bratislava, Slovakia Corresponding author s E-mail: martin.benko@shmu.sk ABSTRACT
ID: 0030 Road weather forecasts and MDSS in Slovakia M. Benko Slovak Hydrometeorological Institute (SHMI), Jeséniova 17, 83315 Bratislava, Slovakia Corresponding author s E-mail: martin.benko@shmu.sk ABSTRACT
Lufft MARWIS-UMB Mobil Advanced Road Weather Information Sensor
 Lufft MARWIS-UMB Mobil Advanced Road Weather Information Sensor sion for precision passion pour la précision pasión por la precisión passione per la precisione a passion www.lufft.com/wondermadeingermany
Lufft MARWIS-UMB Mobil Advanced Road Weather Information Sensor sion for precision passion pour la précision pasión por la precisión passione per la precisione a passion www.lufft.com/wondermadeingermany
HyMet Company. Streamflow and Energy Generation Forecasting Model Columbia River Basin
 HyMet Company Streamflow and Energy Generation Forecasting Model Columbia River Basin HyMet Inc. Courthouse Square 19001 Vashon Hwy SW Suite 201 Vashon Island, WA 98070 Phone: 206-463-1610 Columbia River
HyMet Company Streamflow and Energy Generation Forecasting Model Columbia River Basin HyMet Inc. Courthouse Square 19001 Vashon Hwy SW Suite 201 Vashon Island, WA 98070 Phone: 206-463-1610 Columbia River
Complete Weather Intelligence for Public Safety from DTN
 Complete Weather Intelligence for Public Safety from DTN September 2017 White Paper www.dtn.com / 1.800.610.0777 From flooding to tornados to severe winter storms, the threats to public safety from weather-related
Complete Weather Intelligence for Public Safety from DTN September 2017 White Paper www.dtn.com / 1.800.610.0777 From flooding to tornados to severe winter storms, the threats to public safety from weather-related
SNOW CLIMATOLOGY OF THE EASTERN SIERRA NEVADA. Susan Burak, graduate student Hydrologic Sciences University of Nevada, Reno
 SNOW CLIMATOLOGY OF THE EASTERN SIERRA NEVADA Susan Burak, graduate student Hydrologic Sciences University of Nevada, Reno David Walker, graduate student Department of Geography/154 University of Nevada
SNOW CLIMATOLOGY OF THE EASTERN SIERRA NEVADA Susan Burak, graduate student Hydrologic Sciences University of Nevada, Reno David Walker, graduate student Department of Geography/154 University of Nevada
Road Weather: The Science Behind What You Know
 The Weather Road Weather: The Science Behind What You Know Jon Tarleton Global Roads Marketing Manager Meteorologist Jon.tarleton@vaisala.com Page 2 / date / name / Internal use / Vaisala Weather and Our
The Weather Road Weather: The Science Behind What You Know Jon Tarleton Global Roads Marketing Manager Meteorologist Jon.tarleton@vaisala.com Page 2 / date / name / Internal use / Vaisala Weather and Our
1 A 3 C 2 B 4 D. 5. During which month does the minimum duration of insolation occur in New York State? 1 February 3 September 2 July 4 December
 INSOLATION REVIEW 1. The map below shows isolines of average daily insolation received in calories per square centimeter per minute at the Earth s surface. If identical solar collectors are placed at the
INSOLATION REVIEW 1. The map below shows isolines of average daily insolation received in calories per square centimeter per minute at the Earth s surface. If identical solar collectors are placed at the
Lufft MARWIS-UMB Mobile Advanced Road Weather Information Sensor
 Lufft MARWIS-UMB Mobile Advanced Road Weather Information Sensor a passion for precision passion pour la précision pasión por la precisión passione per la precisione a www.lufft.com/wondermadeingermany
Lufft MARWIS-UMB Mobile Advanced Road Weather Information Sensor a passion for precision passion pour la précision pasión por la precisión passione per la precisione a www.lufft.com/wondermadeingermany
WEATHER STATION FOR SOLAR FARM MONITORING
 WEATHER STATION FOR SOLAR FARM MONITORING SOLAR FARM MONITORING SYSTEM: Measures global, horizontal, & background irradiance. Measures wind speed, wind direction, ambient temperature, and relative humidity.
WEATHER STATION FOR SOLAR FARM MONITORING SOLAR FARM MONITORING SYSTEM: Measures global, horizontal, & background irradiance. Measures wind speed, wind direction, ambient temperature, and relative humidity.
Observing Weather: Making the Invisible Visible. Dr. Michael J. Passow
 Observing Weather: Making the Invisible Visible Dr. Michael J. Passow What Is Weather? Weather refers to the conditions of the atmosphere at a certain place and time. Weather differs from Climate, which
Observing Weather: Making the Invisible Visible Dr. Michael J. Passow What Is Weather? Weather refers to the conditions of the atmosphere at a certain place and time. Weather differs from Climate, which
Comparison of a snowpack on a slope and flat land by focusing on the effect of water infiltration
 Comparison of a snowpack on a slope and flat land by focusing on the effect of water infiltration Shinji Ikeda 1*, Takafumi Katsushima 2, Yasuhiko Ito 1, Hiroki Matsushita 3, Yukari Takeuchi 4, Kazuya
Comparison of a snowpack on a slope and flat land by focusing on the effect of water infiltration Shinji Ikeda 1*, Takafumi Katsushima 2, Yasuhiko Ito 1, Hiroki Matsushita 3, Yukari Takeuchi 4, Kazuya
UNIT 1. WEATHER AND CLIMATE. PRIMARY 4/ Social Science Pedro Antonio López Hernández
 UNIT 1. WEATHER AND CLIMATE PRIMARY 4/ Social Science Pedro Antonio López Hernández LAYERS OF THE ATMOSPHERE The atmosphere is a mixture of gases that surround Earth and separate it from the rest of the
UNIT 1. WEATHER AND CLIMATE PRIMARY 4/ Social Science Pedro Antonio López Hernández LAYERS OF THE ATMOSPHERE The atmosphere is a mixture of gases that surround Earth and separate it from the rest of the
The Meteorological Observatory from Neumayer Gert König-Langlo, Bernd Loose Alfred-Wegener-Institut, Bremerhaven, Germany
 The Meteorological Observatory from Neumayer Gert König-Langlo, Bernd Loose Alfred-Wegener-Institut, Bremerhaven, Germany History of Neumayer In March 1981, the Georg von Neumayer Station (70 37 S, 8 22
The Meteorological Observatory from Neumayer Gert König-Langlo, Bernd Loose Alfred-Wegener-Institut, Bremerhaven, Germany History of Neumayer In March 1981, the Georg von Neumayer Station (70 37 S, 8 22
Proceedings, International Snow Science Workshop, Banff, 2014
 EVALUATING THE LOCAL AVALANCHE DANGER IN TROMSØ, NORTHERN NORWAY USING FIELD MONITORING, FIELD INVESTIGATIONS AND THE SURFEX/ISBA-CROCUS SNOWPACK MODEL. Markus Eckerstorfer 1 *, Dagrun Vikhamar-Schuler
EVALUATING THE LOCAL AVALANCHE DANGER IN TROMSØ, NORTHERN NORWAY USING FIELD MONITORING, FIELD INVESTIGATIONS AND THE SURFEX/ISBA-CROCUS SNOWPACK MODEL. Markus Eckerstorfer 1 *, Dagrun Vikhamar-Schuler
Getting through the winter safely
 CARTE BLANCHE PROJECTS Getting through the winter safely The Canton of Lucerne s Road Inspection Office looks after the operation and maintenance of the canton s roads and streets, and has joint responsibility
CARTE BLANCHE PROJECTS Getting through the winter safely The Canton of Lucerne s Road Inspection Office looks after the operation and maintenance of the canton s roads and streets, and has joint responsibility
How to detect snow fall occurence during blowing snow event?
 How to detect snow fall occurence during blowing snow event? Florence Naaim-Bouvet, Hervé Bellot, Kouichi Nishimura, Christophe Genthon, Cyril Palerme, Gilbert Guyomarc H To cite this version: Florence
How to detect snow fall occurence during blowing snow event? Florence Naaim-Bouvet, Hervé Bellot, Kouichi Nishimura, Christophe Genthon, Cyril Palerme, Gilbert Guyomarc H To cite this version: Florence
GIS Techniques for Avalanche Path Mapping and Snow Science Observations. By Douglas D. Scott AVALANCHE MAPPING/IDEA INTEGRATION
 GIS Techniques for Avalanche Path Mapping and Snow Science Observations GIS Techniques for Avalanche Path Mapping and Snow Science Observations. By Douglas D. Scott AVALANCHE MAPPING/IDEA INTEGRATION For
GIS Techniques for Avalanche Path Mapping and Snow Science Observations GIS Techniques for Avalanche Path Mapping and Snow Science Observations. By Douglas D. Scott AVALANCHE MAPPING/IDEA INTEGRATION For
Interview with Dr. Jaya Singh. 1. How critical is weather monitoring in a solar power plant and what are all the parameters to be monitored?
 Interview with Dr. Jaya Singh Dr. Jaya Singh is an entrepreneur and scientist with experience in a range of industries including biotech, environmental sciences, and agriculture. She currently drives strategy
Interview with Dr. Jaya Singh Dr. Jaya Singh is an entrepreneur and scientist with experience in a range of industries including biotech, environmental sciences, and agriculture. She currently drives strategy
Innovative Sustainable Technology
 Innovative Sustainable Technology DIG is committed to practices that contribute to irrigation and energy efficiency, creating healthy living conditions while maintaining environmentally sound operating
Innovative Sustainable Technology DIG is committed to practices that contribute to irrigation and energy efficiency, creating healthy living conditions while maintaining environmentally sound operating
Abstract. 1 Introduction. 2 Experimental Setup. 2.1 Data Set
 ERAD - THE SEVENTH EUROPEAN CONFERENCE ON RADAR IN METEOROLOGY AND HYDROLOGY Comparison of the seasonal small-scale spatial variability in alpine snowfall and snow accumulation D. E. Scipión,, R. Mott,
ERAD - THE SEVENTH EUROPEAN CONFERENCE ON RADAR IN METEOROLOGY AND HYDROLOGY Comparison of the seasonal small-scale spatial variability in alpine snowfall and snow accumulation D. E. Scipión,, R. Mott,
HoloOptics 1 February 2011
 Wind power in cold regions To De Ice or Not To De Ice Wind power in cold regions benefits from high winds, high air density due to low temperature and often spaciously populated areas [1][2]. The main
Wind power in cold regions To De Ice or Not To De Ice Wind power in cold regions benefits from high winds, high air density due to low temperature and often spaciously populated areas [1][2]. The main
AVALANCHE FORECASTER EXCHANGE PROGRAM U.S. SWITZERLAND
 AVALANCHE FORECASTER EXCHANGE PROGRAM U.S. SWITZERLAND Matt Hill* Mount Shasta Avalanche Center, USDA Forest Service, Mt. Shasta City, CA, U.S.A. Thomas Wiesinger Swiss Federal Institute for Snow and Avalanche
AVALANCHE FORECASTER EXCHANGE PROGRAM U.S. SWITZERLAND Matt Hill* Mount Shasta Avalanche Center, USDA Forest Service, Mt. Shasta City, CA, U.S.A. Thomas Wiesinger Swiss Federal Institute for Snow and Avalanche
SNOW CREEP MOVEMENT IN THE SAN JUAN MOUNTAIN SNOWPACK RED MOUNTAIN PASS
 SOW CREEP MOVEMET I THE SA JUA MOUTAI SOWPACK RED MOUTAI PASS Walter Walker Coordinator of Outdoor Pursuits Fort Lewis College Durango, Colorado 8131 Phone (33) 247-7293, Fax (33) 259-1n4 r [ J ABSTRACT
SOW CREEP MOVEMET I THE SA JUA MOUTAI SOWPACK RED MOUTAI PASS Walter Walker Coordinator of Outdoor Pursuits Fort Lewis College Durango, Colorado 8131 Phone (33) 247-7293, Fax (33) 259-1n4 r [ J ABSTRACT
University Centre in Svalbard AT 301 Infrastructure in a changing climate 10. September 2009 Physics of Snow drift
 University Centre in Svalbard AT 301 Infrastructure in a changing climate 10. September 2009 Personal report by Christian Katlein 2 Introduction This personal report for the graduate course AT 301 Infrastructure
University Centre in Svalbard AT 301 Infrastructure in a changing climate 10. September 2009 Personal report by Christian Katlein 2 Introduction This personal report for the graduate course AT 301 Infrastructure
The avalanche climate of Glacier National Park, B.C., Canada during
 The avalanche climate of Glacier National Park, B.C., Canada during 1965-2011 Sascha Bellaire 1,2*, Bruce Jamieson 1, Grant Statham 3 1 Institute of Meteorology and Geophysics, University of Innsbruck,
The avalanche climate of Glacier National Park, B.C., Canada during 1965-2011 Sascha Bellaire 1,2*, Bruce Jamieson 1, Grant Statham 3 1 Institute of Meteorology and Geophysics, University of Innsbruck,
Quality assurance for sensors at the Deutscher Wetterdienst (DWD)
 Quality assurance for sensors at the Deutscher Wetterdienst (DWD) Quality assurance / maintenance / calibration Holger Dörschel, Dr Tilman Holfelder WMO International Conference on Automatic Weather Stations
Quality assurance for sensors at the Deutscher Wetterdienst (DWD) Quality assurance / maintenance / calibration Holger Dörschel, Dr Tilman Holfelder WMO International Conference on Automatic Weather Stations
Special edition paper
 Development of a Method for Estimation of Volume of Snowmelt from Snowpack Asako Tokari* Hiroyuki Morishima* To secure safe train operation against slope failure in the snowmelt period, we are performing
Development of a Method for Estimation of Volume of Snowmelt from Snowpack Asako Tokari* Hiroyuki Morishima* To secure safe train operation against slope failure in the snowmelt period, we are performing
REINHARDT Weather Stations with Microprocessor
 REINHARDT Weather Stations with Microprocessor MWS 88 MWS 10 MWS 3 MWS 55 zz Precise measurements at the physical limits zz High long-time stability und high quality materials zz Big internal data logger
REINHARDT Weather Stations with Microprocessor MWS 88 MWS 10 MWS 3 MWS 55 zz Precise measurements at the physical limits zz High long-time stability und high quality materials zz Big internal data logger
The role of snowpack in producing floods under heavy rainfall
 Hydrology, Water Resources and Ecology in Headwaters (Proceedings of the HcadWater'98 Conference held at Itféran/Merano, Italy, April 1998). IAHS Publ. no. 248, 1998. QQ y The role of snowpack in producing
Hydrology, Water Resources and Ecology in Headwaters (Proceedings of the HcadWater'98 Conference held at Itféran/Merano, Italy, April 1998). IAHS Publ. no. 248, 1998. QQ y The role of snowpack in producing
