A 2-d modeling approach for studying the formation, maintenance, and decay of Tropical Tropopause Layer (TTL) cirrus associated with Deep Convection
|
|
|
- Marjory Rose
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A 2-d modeling approach for studying the formation, maintenance, and decay of Tropical Tropopause Layer (TTL) cirrus associated with Deep Convection Presenting: Daniel R. Henz Masters Student Atmospheric, Oceanic, and Space Sciences Department University of Wisconsin Madison 07/28/2009
2 OUTLINE: Introduction Recent Studies of the TTL UW-NMS Microphysics Preliminary Results Merging observational data sets Future Work References Questions/Discussion
3 INTRODUCTION Cirrus located in the Tropical Transition Layer (TTL) have become a focal point much of research over the last decade. Understanding their role and contribution to the overall water vapor concentration in the stratosphere has drawn significant interest. Recent studies have been conducted to study the ice nucleation processes and role of aerosols during deep convective events as well comparing model simulations with in situ observational data sets. Simulations in this study will utilize a new microphysical scheme that has been created called AMPS, which predicts multiple distributions of CCN and IN, liquid and ice mass spectral. The ice scheme called SHIPS is unique in that ice particle properties (such as size, particle density, and crystal habitats) are explicitly predicted in a CRM (Hashino and Tripoli, 2007, 2008). A new radiative transfer model to handle ice particles with arbitrary density and shape was developed for AMPS. Strong tool that effectively enables the explicit modeling of the TTL cloud microphysics and dynamical processes.
4 What is the TTL? The Tropical Tropopause Layer (TTL) is the layer between the level of zero net radiative heating which is found typically around 15 km (Gettelman et al., 2004) and the cold point tropopause at 17 to 18 km. The TTL layer represents the layer between approx. 14 to 18km alt. through which tropospheric air enters the stratosphere. It is characterized by high vertical gradients in water concentration and a local minimum in temperature (Garrett et al., 2006). This layer is characterized by slow ascent and forms the source region for the stratospheric Brewer- Dobson circulation (Immler et al., 2008).
5 TTL Cirrus Formation Two general classes of tropical cirrus 1.) Formation related to detrainment of particles and water vapor from deep convection (Pfister et al., 2001). 2.) In-situ formation: TTL cirrus formation related to vertical propagating Kelvin and gravity waves (Boehm and Verlinde, 2000) while Pfister et al. (2001) argued that they could form through synoptic scale ascent along isentropic surfaces. Formation of Cirrus by direct injection from convective systems into the TTL most likely moistens the air by evaporation of the particles (Nielsen et al. 2007) In situ formation of Cirrus in slowly ascending air will most always lead to dehydration (Jensen and Pfister, 2004; Immler et al. 2007)
6 IMPORTANCE? Cirrus play a role in the maintenance of the water vapor distribution in the Tropics. In the vertical region bounded by the detrainment layer of deep convection and the stratosphere, tropical cirrus help regulate the water vapor concentrations entering the lower stratosphere in the Tropics (Jensen et al., 1996; Hartmann 2002: Dessler and Sherwood 2000; etc.) Up to 20% of the global Tropics are regularly covered by extensive cirrus systems (Liou, 1986). These cloud layers can reduce the solar radiation reaching the earth s surface due to reflection. These cloud layers also can absorb a portion of the upwelling IR radiation emitted by the surface and lower atmosphere and emit IR at a lower temperature (Mace et al., 2005) Net effect can be to reduce OLR and thus heating of the atmosphere
7 RECENT STUDIES Recent Campaigns Related to the study of the TTL Cirrus Regional Study of Tropical Anvils and Cirrus Layers - Florida Area Cirrus Experiment (CRYSTAL- FACE), 2002, Jul, Key West, FL Tropical Warm Pool - International Cloud Experiment (TWP-ICE), 2006, Jan-Feb, Australia Costa Rica Aura Validation Experiment (CR-AVE) 2006,Jan-Feb, San Jose, Costa Rica Tropical Composition, Cloud and Climate Coupling (TC4), 2007, Jul-Aug, Costa Rica, Panama These campaigns are crucial for the gathering of observational data in the TTL and validating remote sensed space borne observations
8 UW-NMS The University of Wisconsin Non-Hydrostatic Modeling System is a non-hydrostatic cloud resolving research model used to investigate processes at a large range of scales, from hemispheric to micro-. Key Features: Scalability in all directions (x,y,z), Two-way interactive grid nesting, Long and short wave radiation parameterization, and recently added the Advanced Microphysics Prediction System (AMPS) Spectral Aerosol Prediction System (SAPS) Spectral Liquid Prediction System (SLIPS) Spectral Habit Ice Prediction System (SHIPS)
9 Advanced Microphysics Prediction System (AMPS) - liquid, ice, aerosol Spectral Habit Ice Prediction System (SHIPS) Hashino and Tripoli (2007 and 2008) PPVs Integrated based on local conditions and history of particles Each bin has different properties of ice particles. The properties change in time and space. No use of categorization! Bin model Bulk micro. par.
10 Convective Case #1 Rigorous Convective Updraft (developing stage) Overshooting top
11 Convective Case #2 Typical Convective tower (mature stage) Developed convective anvil
12 Predicted particle type and crystal habit for KWAJEX CPI observation during CR-AVE for subvisible cirrus (Lawson et al., 2008) Type Habit
13 UTILIZING DIFFERENT OBSERVATIONS We will be comparing the ice nucleation and aerosol properties simulated at the tropopause by NMS/AMPS model to the CloudSat and Calipso observations during the TC4 campaign as well as the in situ and remote sensed ER 2, WB 57, and DC 8 aircraft observations. Information: layer optical thickness, number concentration, Vertical distribution particle size and aerosols, etc. Recognition of the limitations associated with the data sets
14 ONGOING WORK Full simulation of the TTL using the NMS- AMPS system and TC4 observational data High-resolution simulation of local cloud processes for case study dates to determine cirrus cloud development, maintenance, and dissipation dynamics. Aerosol studies to determine the role of sulfates on ice crystals in the TTL Validation of high-resolution simulations through collected data.
15 REFERENCES Boehm, M. T., and J. Verlinde (2000), Stratospheric influence on upper tropospheric tropical cirrus, Geophys. Res. Lett., 27, Garrrett, T.J., Dean-Day, J., Liu, C., Barnett, B., Mace, et al., 2008: Convective formation of pileus cloud near the tropopause, Atmos. Chem. Phys., 6, Gettelman, A., P. M. de F. Forster, M. Fujiwara, Q. Fu, H. Vömel, L. K. Gohar, C. Johanson, and M. Ammerman (2004a), Radiation balance of the tropical tropopause layer, J. Geophys. Res., 109, D Hartmann, D. L., J. R. Holton, and Q. Fu (2001), The heat balance of the tropical tropopause, cirrus, and stratospheric dehydration, Geophys. Res. Lett., 28, Hashino, T., and G. Tripoli, 2007: The spectral Ice Habit Prediction System (SHIPS). Part I: Model description and simulation of vapor deposition process. J. Atmos. Sci., 64, Immler, F., Treffeisen, R., Engelbart, D., Krüger,K., and Schrems, O., 2008:Cirrus, contrails and ice supersaturated regions in high pressure systems at northern mid latitudes, Atmos. Chem. Phys. 8, Jensen, E. J., O. B. Toon, H. B. Selkirk, J. D. Spinhirne, and M. R. Schoeberl,1996b: On the formation and persistence of subvisible cirrus clouds near the tropical tropopause, J. Geophys. Res., 101, 21,361 21,375. Lawson, R. P., Pilson B., Baker, B., Mo Q., Jensen, E., Pfister, L., and Pui, P., 2008: Aircraft measurements of microphysical properties of subvisible cirrus in the tropical tropopause layer. Atmos. Chem. Phys., 8, Liou, K.-N, 1986: Influence of cirrus clouds on weather and climate processes: A global perspective, Mon. Weather Rev., 114, Mace, G.G., Deng, M., Soden, B., Zipser, E., 2005: Association of Tropical Cirrus in the 10-15km Layer with Deep Convective Sources: An observational etc., J. Atmos. Sci., 63, Pfister, L., et al. (2001), Aircraft observations of thin cirrus clouds near the tropical tropopause, J. Geophys. Res., 106(D9), Sherwood, S. A., and Dessler, A. E., 2000, On the control of stratospheric humidity, Geophys. Res. Lett., 27, Tripoli, G.J., 1992: A nonhydrostatic mesoscale model designed to simulate scale interaction. Mon. Wea. Rev., 120,
16 QUESTIONS? Contact Info: Daniel Henz Phone: (608) Address: 1225 W Dayton St Madison, WI 53706
Mid High Latitude Cirrus Precipitation Processes. Jon Sauer, Dan Crocker, Yanice Benitez
 Mid High Latitude Cirrus Precipitation Processes Jon Sauer, Dan Crocker, Yanice Benitez Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, University of California, San Diego, CA 92093, USA *To whom correspondence
Mid High Latitude Cirrus Precipitation Processes Jon Sauer, Dan Crocker, Yanice Benitez Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, University of California, San Diego, CA 92093, USA *To whom correspondence
Water Vapor in the Stratospheric Overworld
 Water Vapor in the Stratospheric Overworld Jonathon S. Wright Tsinghua University Center for Earth System Science March 12, 2012 Overview 1 What is the stratospheric overworld? 2 The importance of stratospheric
Water Vapor in the Stratospheric Overworld Jonathon S. Wright Tsinghua University Center for Earth System Science March 12, 2012 Overview 1 What is the stratospheric overworld? 2 The importance of stratospheric
Climate Dynamics (PCC 587): Feedbacks & Clouds
 Climate Dynamics (PCC 587): Feedbacks & Clouds DARGAN M. W. FRIERSON UNIVERSITY OF WASHINGTON, DEPARTMENT OF ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES DAY 6: 10-14-13 Feedbacks Climate forcings change global temperatures directly
Climate Dynamics (PCC 587): Feedbacks & Clouds DARGAN M. W. FRIERSON UNIVERSITY OF WASHINGTON, DEPARTMENT OF ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES DAY 6: 10-14-13 Feedbacks Climate forcings change global temperatures directly
Climate Modeling Issues at GFDL on the Eve of AR5
 Climate Modeling Issues at GFDL on the Eve of AR5 Leo Donner, Chris Golaz, Yi Ming, Andrew Wittenberg, Bill Stern, Ming Zhao, Paul Ginoux, Jeff Ploshay, S.J. Lin, Charles Seman CPPA PI Meeting, 29 September
Climate Modeling Issues at GFDL on the Eve of AR5 Leo Donner, Chris Golaz, Yi Ming, Andrew Wittenberg, Bill Stern, Ming Zhao, Paul Ginoux, Jeff Ploshay, S.J. Lin, Charles Seman CPPA PI Meeting, 29 September
Ubiquitous Influence of Waves on Tropical High Cirrus Cloud
 1 Ubiquitous Influence of Waves on Tropical High Cirrus Cloud 2 3 4 Ji-Eun Kim, 1,2* M. Joan Alexander, 3 T. Paul Bui, 4 Jonathan M. Dean-Day, 5 R. Paul Lawson, 6 Sarah Woods, 6 Dennis Hlavka, 7 Leonhard
1 Ubiquitous Influence of Waves on Tropical High Cirrus Cloud 2 3 4 Ji-Eun Kim, 1,2* M. Joan Alexander, 3 T. Paul Bui, 4 Jonathan M. Dean-Day, 5 R. Paul Lawson, 6 Sarah Woods, 6 Dennis Hlavka, 7 Leonhard
Role of atmospheric aerosol concentration on deep convective precipitation: Cloud-resolving model simulations
 Role of atmospheric aerosol concentration on deep convective precipitation: Cloud-resolving model simulations Wei-Kuo Tao,1 Xiaowen Li,1,2 Alexander Khain,3 Toshihisa Matsui,1,2 Stephen Lang,4 and Joanne
Role of atmospheric aerosol concentration on deep convective precipitation: Cloud-resolving model simulations Wei-Kuo Tao,1 Xiaowen Li,1,2 Alexander Khain,3 Toshihisa Matsui,1,2 Stephen Lang,4 and Joanne
Clouds and water vapor in the Northern Hemisphere summertime stratosphere
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 114,, doi:10.1029/2009jd012075, 2009 Clouds and water vapor in the Northern Hemisphere summertime stratosphere A. E. Dessler 1 Received 16 March 2009; revised 18 August
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 114,, doi:10.1029/2009jd012075, 2009 Clouds and water vapor in the Northern Hemisphere summertime stratosphere A. E. Dessler 1 Received 16 March 2009; revised 18 August
Instantaneous cloud overlap statistics in the tropical area revealed by ICESat/GLAS data
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33, L15804, doi:10.1029/2005gl024350, 2006 Instantaneous cloud overlap statistics in the tropical area revealed by ICESat/GLAS data Likun Wang 1,2 and Andrew E. Dessler
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33, L15804, doi:10.1029/2005gl024350, 2006 Instantaneous cloud overlap statistics in the tropical area revealed by ICESat/GLAS data Likun Wang 1,2 and Andrew E. Dessler
1. INTRODUCTION. investigating the differences in actual cloud microphysics.
 MICROPHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF DEVELOPING VERSUS NON-DEVELOPING CLOUD CLUSTERS DURING TROPICAL CYCLOGENESIS 4B.5 Nathan D. Johnson,* William C. Conant, and Elizabeth A. Ritchie Department of Atmospheric Sciences,
MICROPHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF DEVELOPING VERSUS NON-DEVELOPING CLOUD CLUSTERS DURING TROPICAL CYCLOGENESIS 4B.5 Nathan D. Johnson,* William C. Conant, and Elizabeth A. Ritchie Department of Atmospheric Sciences,
Distribution of water vapour. in the atmosphere
 in the atmosphere Bernard Legras Laboratoire de Météorologie Dynamique Institut Pierre Simon Laplace ENS /CNRS/UPMC, Paris, France 1 http://www.lmd.ens.fr/legras The origin of water 2 There is plenty of
in the atmosphere Bernard Legras Laboratoire de Météorologie Dynamique Institut Pierre Simon Laplace ENS /CNRS/UPMC, Paris, France 1 http://www.lmd.ens.fr/legras The origin of water 2 There is plenty of
Leo Donner GFDL/NOAA, Princeton University. EGU, Vienna, 18 April 2016
 Cloud Dynamical Controls on Climate Forcing by Aerosol-Cloud Interactions: New Insights from Observations, High- Resolution Models, and Parameterizations Leo Donner GFDL/NOAA, Princeton University EGU,
Cloud Dynamical Controls on Climate Forcing by Aerosol-Cloud Interactions: New Insights from Observations, High- Resolution Models, and Parameterizations Leo Donner GFDL/NOAA, Princeton University EGU,
CLIMATE AND CLIMATE CHANGE MIDTERM EXAM ATM S 211 FEB 9TH 2012 V1
 CLIMATE AND CLIMATE CHANGE MIDTERM EXAM ATM S 211 FEB 9TH 2012 V1 Name: Student ID: Please answer the following questions on your Scantron Multiple Choice [1 point each] (1) The gases that contribute to
CLIMATE AND CLIMATE CHANGE MIDTERM EXAM ATM S 211 FEB 9TH 2012 V1 Name: Student ID: Please answer the following questions on your Scantron Multiple Choice [1 point each] (1) The gases that contribute to
8.2 Numerical Study of Relationships between Convective Vertical Velocity, Radar Reflectivity Profiles, and Passive Microwave Brightness Temperatures
 8.2 Numerical Study of Relationships between Convective Vertical Velocity, Radar Reflectivity Profiles, and Passive Microwave Brightness Temperatures Yaping Li, Edward J. Zipser, Steven K. Krueger, and
8.2 Numerical Study of Relationships between Convective Vertical Velocity, Radar Reflectivity Profiles, and Passive Microwave Brightness Temperatures Yaping Li, Edward J. Zipser, Steven K. Krueger, and
Stratospheric sulfate geoengineering has limited efficacy and increases tropospheric burdens
 Stratospheric sulfate geoengineering has limited efficacy and increases tropospheric burdens Jason English PhD Candidate Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics, and Department of Atmospheric and
Stratospheric sulfate geoengineering has limited efficacy and increases tropospheric burdens Jason English PhD Candidate Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics, and Department of Atmospheric and
THIN CLOUD LENGTH SCALES USING CALIPSO AND CLOUDSAT DATA. A Thesis JEREMY EDWARD SOLBRIG
 THIN CLOUD LENGTH SCALES USING CALIPSO AND CLOUDSAT DATA A Thesis by JEREMY EDWARD SOLBRIG Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment of the requirements
THIN CLOUD LENGTH SCALES USING CALIPSO AND CLOUDSAT DATA A Thesis by JEREMY EDWARD SOLBRIG Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment of the requirements
Climate Dynamics (PCC 587): Clouds and Feedbacks
 Climate Dynamics (PCC 587): Clouds and Feedbacks D A R G A N M. W. F R I E R S O N U N I V E R S I T Y O F W A S H I N G T O N, D E P A R T M E N T O F A T M O S P H E R I C S C I E N C E S D A Y 7 : 1
Climate Dynamics (PCC 587): Clouds and Feedbacks D A R G A N M. W. F R I E R S O N U N I V E R S I T Y O F W A S H I N G T O N, D E P A R T M E N T O F A T M O S P H E R I C S C I E N C E S D A Y 7 : 1
Is there a stratospheric fountain?
 Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss., 7, 8933 890, 07 www.atmos-chem-phys-discuss.net/7/8933/07/ Author(s) 07. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics Discussions
Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss., 7, 8933 890, 07 www.atmos-chem-phys-discuss.net/7/8933/07/ Author(s) 07. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics Discussions
P1.61 Impact of the mass-accomodation coefficient on cirrus
 P1.61 Impact of the mass-accomodation coefficient on cirrus Robert W. Carver and Jerry Y. Harrington Department of Meteorology, Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA 1. Introduction Recent
P1.61 Impact of the mass-accomodation coefficient on cirrus Robert W. Carver and Jerry Y. Harrington Department of Meteorology, Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA 1. Introduction Recent
Analysis of Cloud-Radiation Interactions Using ARM Observations and a Single-Column Model
 Analysis of Cloud-Radiation Interactions Using ARM Observations and a Single-Column Model S. F. Iacobellis, R. C. J. Somerville, D. E. Lane, and J. Berque Scripps Institution of Oceanography University
Analysis of Cloud-Radiation Interactions Using ARM Observations and a Single-Column Model S. F. Iacobellis, R. C. J. Somerville, D. E. Lane, and J. Berque Scripps Institution of Oceanography University
Stratospheric sulfate geoengineering has limited efficacy and increases tropospheric sulfate burdens
 Stratospheric sulfate geoengineering has limited efficacy and increases tropospheric sulfate burdens Jason English PhD Candidate Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics, and Department of Atmospheric
Stratospheric sulfate geoengineering has limited efficacy and increases tropospheric sulfate burdens Jason English PhD Candidate Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics, and Department of Atmospheric
A model of HDO in the tropical tropopause layer
 Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics A model of HDO in the tropical tropopause layer A. E. Dessler 1 and S. C. Sherwood 1 Earth Systems Science Interdisciplinary Center, University of Maryland, College Park,
Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics A model of HDO in the tropical tropopause layer A. E. Dessler 1 and S. C. Sherwood 1 Earth Systems Science Interdisciplinary Center, University of Maryland, College Park,
OBSERVING CIRRUS FORMATION AND DECAY WITH METEOSAT
 OBSERVING CIRRUS FORMATION AND DECAY WITH METEOSAT Hermann Mannstein, Kaspar Graf, Stephan Kox, Bernhard Mayer and Ulrich Schumann Institut für Physik der Atmosphäre, Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt,
OBSERVING CIRRUS FORMATION AND DECAY WITH METEOSAT Hermann Mannstein, Kaspar Graf, Stephan Kox, Bernhard Mayer and Ulrich Schumann Institut für Physik der Atmosphäre, Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt,
x = x a +(K T S e -1 K+S a -1 ) -1 K T S e -1 *[R-F(x)+K*(x-x a )]
![x = x a +(K T S e -1 K+S a -1 ) -1 K T S e -1 *[R-F(x)+K*(x-x a )] x = x a +(K T S e -1 K+S a -1 ) -1 K T S e -1 *[R-F(x)+K*(x-x a )]](/thumbs/86/93497200.jpg) P2.7 RETRIEVALS OF ATMOSPHERIC THERMODYNAMIC STRUCTURE FROM UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN SCANNING-HIGH-RESOLUTION INTERFEROMETER SOUNDER (S-HIS) UPWELLING RADIANCE OBSERVATIONS USING A BAYESIAN MAXIMUM A POSTERIORI
P2.7 RETRIEVALS OF ATMOSPHERIC THERMODYNAMIC STRUCTURE FROM UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN SCANNING-HIGH-RESOLUTION INTERFEROMETER SOUNDER (S-HIS) UPWELLING RADIANCE OBSERVATIONS USING A BAYESIAN MAXIMUM A POSTERIORI
A FROZEN DROP PRECIPITATION MECHANISM OVER AN OPEN OCEAN AND ITS EFFECT ON RAIN, CLOUD PATTERN, AND HEATING
 A FROZEN DROP PRECIPITATION MECHANISM OVER AN OPEN OCEAN AND ITS EFFECT ON RAIN, CLOUD PATTERN, AND HEATING 13.6 Tsutomu Takahashi* University of Hawaii, Honolulu, Hawaii Kazunori Shimura JFE Techno-Research
A FROZEN DROP PRECIPITATION MECHANISM OVER AN OPEN OCEAN AND ITS EFFECT ON RAIN, CLOUD PATTERN, AND HEATING 13.6 Tsutomu Takahashi* University of Hawaii, Honolulu, Hawaii Kazunori Shimura JFE Techno-Research
CloudSat adding new insight into tropical penetrating convection
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L19819, doi:10.1029/2008gl035330, 2008 CloudSat adding new insight into tropical penetrating convection Zhengzhao Luo, 1 Guangyuan Y.
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L19819, doi:10.1029/2008gl035330, 2008 CloudSat adding new insight into tropical penetrating convection Zhengzhao Luo, 1 Guangyuan Y.
Remote sensing of ice clouds
 Remote sensing of ice clouds Carlos Jimenez LERMA, Observatoire de Paris, France GDR microondes, Paris, 09/09/2008 Outline : ice clouds and the climate system : VIS-NIR, IR, mm/sub-mm, active 3. Observing
Remote sensing of ice clouds Carlos Jimenez LERMA, Observatoire de Paris, France GDR microondes, Paris, 09/09/2008 Outline : ice clouds and the climate system : VIS-NIR, IR, mm/sub-mm, active 3. Observing
Thermodynamics of Atmospheres and Oceans
 Thermodynamics of Atmospheres and Oceans Judith A. Curry and Peter J. Webster PROGRAM IN ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF AEROSPACE ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF COLORADO BOULDER, COLORADO USA
Thermodynamics of Atmospheres and Oceans Judith A. Curry and Peter J. Webster PROGRAM IN ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF AEROSPACE ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF COLORADO BOULDER, COLORADO USA
A more detailed and quantitative consideration of organized convection: Part I Cold pool dynamics and the formation of squall lines
 A more detailed and quantitative consideration of organized convection: Part I Cold pool dynamics and the formation of squall lines Note: Lecture notes presented here based on course Daily Weather Laboratory
A more detailed and quantitative consideration of organized convection: Part I Cold pool dynamics and the formation of squall lines Note: Lecture notes presented here based on course Daily Weather Laboratory
Evidence that Nitric Acid Increases Relative Humidity in Low-Temperature Cirrus
 Supporting Online Material for: Evidence that Nitric Acid Increases Relative Humidity in Low-Temperature Cirrus Clouds R. S. Gao, P. J. Popp, D. W. Fahey, T. P. Marcy, R. L. Herman, E. M. Weinstock, D.
Supporting Online Material for: Evidence that Nitric Acid Increases Relative Humidity in Low-Temperature Cirrus Clouds R. S. Gao, P. J. Popp, D. W. Fahey, T. P. Marcy, R. L. Herman, E. M. Weinstock, D.
Radiative Control of Deep Tropical Convection
 Radiative Control of Deep Tropical Convection Dennis L. Hartmann with collaboration of Mark Zelinka and Bryce Harrop Department of Atmospheric Sciences University of Washington Outline Review Tropical
Radiative Control of Deep Tropical Convection Dennis L. Hartmann with collaboration of Mark Zelinka and Bryce Harrop Department of Atmospheric Sciences University of Washington Outline Review Tropical
Testing the Fixed Anvil Temperature Hypothesis in a Cloud-Resolving Model
 15 MAY 2007 K U A N G A N D H A R T M A N N 2051 Testing the Fixed Anvil Temperature Hypothesis in a Cloud-Resolving Model ZHIMING KUANG Department of Earth and Planetary Sciences, and Division of Engineering
15 MAY 2007 K U A N G A N D H A R T M A N N 2051 Testing the Fixed Anvil Temperature Hypothesis in a Cloud-Resolving Model ZHIMING KUANG Department of Earth and Planetary Sciences, and Division of Engineering
Formation of large ( 100 µm) ice crystals near the tropical tropopause
 Atmos. Chem. Phys., 8, 1621 1633, 2008 Author(s) 2008. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics Formation of large ( µm) ice crystals near the tropical
Atmos. Chem. Phys., 8, 1621 1633, 2008 Author(s) 2008. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics Formation of large ( µm) ice crystals near the tropical
Climate impacts of ice nucleation
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 117,, doi:10.1029/2012jd017950, 2012 Climate impacts of ice nucleation A. Gettelman, 1,2 X. Liu, 3 D. Barahona, 4,5 U. Lohmann, 2 and C. Chen 1 Received 16 April 2012;
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 117,, doi:10.1029/2012jd017950, 2012 Climate impacts of ice nucleation A. Gettelman, 1,2 X. Liu, 3 D. Barahona, 4,5 U. Lohmann, 2 and C. Chen 1 Received 16 April 2012;
Sensitivity of Thin Cirrus Clouds in the Tropical Tropopause Layer to Ice Crystal Shape and Radiative Absorption
 Sensitivity of Thin Cirrus Clouds in the Tropical Tropopause Layer to Ice Crystal Shape and Radiative Absorption R. D. Russotto, 1 T. P. Ackerman, 1,2 D. R. Durran 1 1 Department of Atmospheric Sciences,
Sensitivity of Thin Cirrus Clouds in the Tropical Tropopause Layer to Ice Crystal Shape and Radiative Absorption R. D. Russotto, 1 T. P. Ackerman, 1,2 D. R. Durran 1 1 Department of Atmospheric Sciences,
The role of cloud heating within the atmosphere on the high cloud amount and top-of-atmosphere cloud radiative effect
 JAMES, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:./, The role of cloud heating within the atmosphere on the high cloud amount and top-of-atmosphere cloud radiative effect Bryce E. Harrop, Dennis L. Hartmann, Key Points. ACRE
JAMES, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:./, The role of cloud heating within the atmosphere on the high cloud amount and top-of-atmosphere cloud radiative effect Bryce E. Harrop, Dennis L. Hartmann, Key Points. ACRE
Impact of the 2002 stratospheric warming in the southern hemisphere on the tropical cirrus clouds and convective activity
 The Third International SOWER meeting,, Lake Shikotsu,, July 18-20, 2006 1 Impact of the 2002 stratospheric warming in the southern hemisphere on the tropical cirrus clouds and convective activity Eguchi,
The Third International SOWER meeting,, Lake Shikotsu,, July 18-20, 2006 1 Impact of the 2002 stratospheric warming in the southern hemisphere on the tropical cirrus clouds and convective activity Eguchi,
Prediction of cirrus clouds in GCMs
 Prediction of cirrus clouds in GCMs Bernd Kärcher, Ulrike Burkhardt, Klaus Gierens, and Johannes Hendricks DLR Institut für Physik der Atmosphäre Oberpfaffenhofen, 82234 Wessling, Germany bernd.kaercher@dlr.de
Prediction of cirrus clouds in GCMs Bernd Kärcher, Ulrike Burkhardt, Klaus Gierens, and Johannes Hendricks DLR Institut für Physik der Atmosphäre Oberpfaffenhofen, 82234 Wessling, Germany bernd.kaercher@dlr.de
Clouds on Mars Cloud Classification
 Lecture Ch. 8 Cloud Classification Descriptive approach to clouds Drop Growth and Precipitation Processes Microphysical characterization of clouds Complex (i.e. Real) Clouds Examples Curry and Webster,
Lecture Ch. 8 Cloud Classification Descriptive approach to clouds Drop Growth and Precipitation Processes Microphysical characterization of clouds Complex (i.e. Real) Clouds Examples Curry and Webster,
Some Issues in Isentropic Coordinate Modelling and Modelling the Tropopause
 Some Issues in Isentropic Coordinate Modelling and Modelling the Tropopause 1. Introduction J Thuburn Department of Meteorology, University of Reading, Reading, United Kingdom j.thuburn@reading.ac.uk The
Some Issues in Isentropic Coordinate Modelling and Modelling the Tropopause 1. Introduction J Thuburn Department of Meteorology, University of Reading, Reading, United Kingdom j.thuburn@reading.ac.uk The
TTL & H 2 O Brewer-Dobson Circulation (~years) Waves. Waves T T TEMPERATURE. Tropical Tropopause Layer (TTL) Equator. Stratosphere Ozone Layer QBO
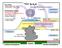 H 2 O in Strato. - Radiative Balance (IR cooling) - Source of HOx Ozone Layer H 2 O Distribution in Strato. - Dehydration/cold trap in TTL (microphysics of cirrus clouds matter!) - Brewer-Dobson Circ.
H 2 O in Strato. - Radiative Balance (IR cooling) - Source of HOx Ozone Layer H 2 O Distribution in Strato. - Dehydration/cold trap in TTL (microphysics of cirrus clouds matter!) - Brewer-Dobson Circ.
A more mechanistic view of ECS. Graeme Stephens
 A more mechanistic view of ECS Graeme Stephens ECS strongly correlates with UTH Su et al., 2014 And low cloud feedbacks strongly correlate to UTH changes. This merely underscores the fact (to me) that
A more mechanistic view of ECS Graeme Stephens ECS strongly correlates with UTH Su et al., 2014 And low cloud feedbacks strongly correlate to UTH changes. This merely underscores the fact (to me) that
Diagnosis of Relative Humidity Changes in a Warmer Climate Using Tracers of Last Saturation
 Diagnosis of Relative Humidity Changes in a Warmer Climate Using Tracers of Last Saturation 8 March, 2011 Jonathon Wright Department of Applied Mathematics & Theoretical Physics University of Cambridge
Diagnosis of Relative Humidity Changes in a Warmer Climate Using Tracers of Last Saturation 8 March, 2011 Jonathon Wright Department of Applied Mathematics & Theoretical Physics University of Cambridge
Recent anthropogenic increases in SO2 from Asia have minimal impact on stratospheric aerosol
 !1 Recent anthropogenic increases in SO2 from Asia have minimal impact on stratospheric aerosol Ryan R. Neely III (NCAR/ASP), O. Brian Toon, Susan Solomon, Karen H. Rosenlof, John S Daniel, J. English,
!1 Recent anthropogenic increases in SO2 from Asia have minimal impact on stratospheric aerosol Ryan R. Neely III (NCAR/ASP), O. Brian Toon, Susan Solomon, Karen H. Rosenlof, John S Daniel, J. English,
Testing the Fixed Anvil Temperature hypothesis in a cloudresolving
 Testing the Fixed Anvil Temperature hypothesis in a cloudresolving model Zhiming Kuang Department of Earth and Planetary Sciences and Division of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Harvard University Dennis
Testing the Fixed Anvil Temperature hypothesis in a cloudresolving model Zhiming Kuang Department of Earth and Planetary Sciences and Division of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Harvard University Dennis
Researcher. Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences. University of Wisconsin-Madison W. Dayton Street, Madison, WI 53706
 Researcher Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences University of Wisconsin-Madison 1225 W. Dayton Street, Madison, WI 53706 http://www.aos.wisc.edu/~meteor75 rowe1@wisc.edu PUBLICATIONS Rowe, S.
Researcher Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences University of Wisconsin-Madison 1225 W. Dayton Street, Madison, WI 53706 http://www.aos.wisc.edu/~meteor75 rowe1@wisc.edu PUBLICATIONS Rowe, S.
CRM and LES approaches for simulating tropical deep convection: successes and challenges
 ECMWF workshop on shedding light on the greyzone, Reading, UK, 13-16 Nov 2017 CRM and LES approaches for simulating tropical deep convection: successes and challenges Jean-Pierre CHABOUREAU Laboratoire
ECMWF workshop on shedding light on the greyzone, Reading, UK, 13-16 Nov 2017 CRM and LES approaches for simulating tropical deep convection: successes and challenges Jean-Pierre CHABOUREAU Laboratoire
MEASUREMENTS IN LOW LATITUDE HIGH ALTITUDE CIRRUS
 MEASUREMENTS IN LOW LATITUDE HIGH ALTITUDE CIRRUS 1. INTRODUCTION Andrew J. Heymsfield, Carl Schmitt and Aaron Bansemer National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado According to the ISCCP
MEASUREMENTS IN LOW LATITUDE HIGH ALTITUDE CIRRUS 1. INTRODUCTION Andrew J. Heymsfield, Carl Schmitt and Aaron Bansemer National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado According to the ISCCP
Crux of AGW s Flawed Science (Wrong water-vapor feedback and missing ocean influence)
 1 Crux of AGW s Flawed Science (Wrong water-vapor feedback and missing ocean influence) William M. Gray Professor Emeritus Colorado State University There are many flaws in the global climate models. But
1 Crux of AGW s Flawed Science (Wrong water-vapor feedback and missing ocean influence) William M. Gray Professor Emeritus Colorado State University There are many flaws in the global climate models. But
Large-Eddy Simulations of Tropical Convective Systems, the Boundary Layer, and Upper Ocean Coupling
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Large-Eddy Simulations of Tropical Convective Systems, the Boundary Layer, and Upper Ocean Coupling Eric D. Skyllingstad
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Large-Eddy Simulations of Tropical Convective Systems, the Boundary Layer, and Upper Ocean Coupling Eric D. Skyllingstad
Aerosol Effects on Water and Ice Clouds
 Aerosol Effects on Water and Ice Clouds Ulrike Lohmann Department of Physics and Atmospheric Science, Dalhousie University, Halifax, N. S., Canada Contributions from Johann Feichter, Johannes Hendricks,
Aerosol Effects on Water and Ice Clouds Ulrike Lohmann Department of Physics and Atmospheric Science, Dalhousie University, Halifax, N. S., Canada Contributions from Johann Feichter, Johannes Hendricks,
Tropical Convection and the Energy Balance at the Top of the Atmosphere
 4495 Tropical Convection and the Energy Balance at the Top of the Atmosphere DENNIS L. HARTMANN, LESLIE A. MOY, AND QIANG FU Department of Atmospheric Sciences, University of Washington, Seattle, Washington
4495 Tropical Convection and the Energy Balance at the Top of the Atmosphere DENNIS L. HARTMANN, LESLIE A. MOY, AND QIANG FU Department of Atmospheric Sciences, University of Washington, Seattle, Washington
9 Condensation. Learning Goals. After studying this chapter, students should be able to:
 9 Condensation Learning Goals After studying this chapter, students should be able to: 1. explain the microphysical processes that operate in clouds to influence the formation and growth of cloud droplets
9 Condensation Learning Goals After studying this chapter, students should be able to: 1. explain the microphysical processes that operate in clouds to influence the formation and growth of cloud droplets
Parametrizing Cloud Cover in Large-scale Models
 Parametrizing Cloud Cover in Large-scale Models Stephen A. Klein Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory Ming Zhao Princeton University Robert Pincus Earth System Research Laboratory November 14, 006 European
Parametrizing Cloud Cover in Large-scale Models Stephen A. Klein Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory Ming Zhao Princeton University Robert Pincus Earth System Research Laboratory November 14, 006 European
Influence of condensate evaporation on water vapor and its stable isotopes in a GCM
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L12804, doi:10.1029/2009gl038091, 2009 Influence of condensate evaporation on water vapor and its stable isotopes in a GCM Jonathon S.
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L12804, doi:10.1029/2009gl038091, 2009 Influence of condensate evaporation on water vapor and its stable isotopes in a GCM Jonathon S.
Object-based approaches for exploring high-resolution simulations
 GEWEX Convection-Permitting Climate Modeling Meeting, Boulder, Colorado, 6-8 Sept 2016 Object-based approaches for exploring high-resolution simulations Jean-Pierre CHABOUREAU Laboratoire d Aérologie,
GEWEX Convection-Permitting Climate Modeling Meeting, Boulder, Colorado, 6-8 Sept 2016 Object-based approaches for exploring high-resolution simulations Jean-Pierre CHABOUREAU Laboratoire d Aérologie,
Influence of convection on the water isotopic composition of the tropical tropopause layer and tropical stratosphere
 See discussions, stats, and author profiles for this publication at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/251438067 Influence of convection on the water isotopic composition of the tropical tropopause
See discussions, stats, and author profiles for this publication at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/251438067 Influence of convection on the water isotopic composition of the tropical tropopause
Chapter 8 cont. Clouds and Storms. Spring 2018
 Chapter 8 cont. Clouds and Storms Spring 2018 Clouds and Storms Clouds cover ~ 50% of earth at any time. Clouds are linked to a number of condensation processes. Cloud morphology, cloud types, associated
Chapter 8 cont. Clouds and Storms Spring 2018 Clouds and Storms Clouds cover ~ 50% of earth at any time. Clouds are linked to a number of condensation processes. Cloud morphology, cloud types, associated
Cloud properties & bulk microphysical properties of semi-transparent cirrus from AIRS & IASI
 Cloud properties & bulk microphysical properties of semi-transparent cirrus from AIRS & Claudia Stubenrauch A. Feofilov, R. Armante, A. Guignard* ABC(t) ARA team Laboratoire de Météorologie Dynamique /
Cloud properties & bulk microphysical properties of semi-transparent cirrus from AIRS & Claudia Stubenrauch A. Feofilov, R. Armante, A. Guignard* ABC(t) ARA team Laboratoire de Météorologie Dynamique /
Evaluation and Improvement of Clouds Simulated by the Global Nonhydrostatic Model NICAM and Satellite Data
 Evaluation and Improvement of Clouds Simulated by the Global Nonhydrostatic Model NICAM and Satellite Data NICAM: dx=3.5 km simulations EarthCARE satellite mission (2016?) Joint Simulator for Satellite
Evaluation and Improvement of Clouds Simulated by the Global Nonhydrostatic Model NICAM and Satellite Data NICAM: dx=3.5 km simulations EarthCARE satellite mission (2016?) Joint Simulator for Satellite
Isotopic Fractionations in the TTL in cloud-resolving simulations of an idealized tropical circulation
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:.29/, Isotopic Fractionations in the TTL in cloud-resolving simulations of an idealized tropical circulation Peter N. Blossey, 1 Zhiming Kuang, 2 and
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:.29/, Isotopic Fractionations in the TTL in cloud-resolving simulations of an idealized tropical circulation Peter N. Blossey, 1 Zhiming Kuang, 2 and
ATMOS 5140 Lecture 1 Chapter 1
 ATMOS 5140 Lecture 1 Chapter 1 Atmospheric Radiation Relevance for Weather and Climate Solar Radiation Thermal Infrared Radiation Global Heat Engine Components of the Earth s Energy Budget Relevance for
ATMOS 5140 Lecture 1 Chapter 1 Atmospheric Radiation Relevance for Weather and Climate Solar Radiation Thermal Infrared Radiation Global Heat Engine Components of the Earth s Energy Budget Relevance for
Torben Königk Rossby Centre/ SMHI
 Fundamentals of Climate Modelling Torben Königk Rossby Centre/ SMHI Outline Introduction Why do we need models? Basic processes Radiation Atmospheric/Oceanic circulation Model basics Resolution Parameterizations
Fundamentals of Climate Modelling Torben Königk Rossby Centre/ SMHI Outline Introduction Why do we need models? Basic processes Radiation Atmospheric/Oceanic circulation Model basics Resolution Parameterizations
Impact of Solar and Sulfate Geoengineering on Surface Ozone
 Impact of Solar and Sulfate Geoengineering on Surface Ozone Lili Xia 1, Peer J. Nowack 2, Simone Tilmes 3 and Alan Robock 1 1 Department of Environmental Sciences, Rutgers University, New Brunswick, NJ
Impact of Solar and Sulfate Geoengineering on Surface Ozone Lili Xia 1, Peer J. Nowack 2, Simone Tilmes 3 and Alan Robock 1 1 Department of Environmental Sciences, Rutgers University, New Brunswick, NJ
Tropical cirrus and water vapor: an effective Earth infrared iris feedback?
 Atmos. Chem. Phys.,, 31 3, www.atmos-chem-phys.org/acp//31/ Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics Tropical cirrus and water vapor: an effective Earth infrared iris feedback? Q. Fu, M. Baker, and D. L. Hartmann
Atmos. Chem. Phys.,, 31 3, www.atmos-chem-phys.org/acp//31/ Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics Tropical cirrus and water vapor: an effective Earth infrared iris feedback? Q. Fu, M. Baker, and D. L. Hartmann
A Possible Role for Immersion Freezing in Mixed-phase Stratus Clouds. Gijs de Boer T. Hashino, G.J. Tripoli, and E.W. Eloranta
 A Possible Role for Immersion Freezing in Mixed-phase Stratus Clouds Gijs de Boer T. Hashino, G.J. Tripoli, and E.W. Eloranta Introduction EUREKA BARROW HSRL/MMCR combination - Barrow (8/04-11/04) M-PACE
A Possible Role for Immersion Freezing in Mixed-phase Stratus Clouds Gijs de Boer T. Hashino, G.J. Tripoli, and E.W. Eloranta Introduction EUREKA BARROW HSRL/MMCR combination - Barrow (8/04-11/04) M-PACE
Observed and Simulated Upper-Tropospheric Water Vapor Feedback
 3282 J O U R N A L O F C L I M A T E VOLUME 21 Observed and Simulated Upper-Tropospheric Water Vapor Feedback A. GETTELMAN National Center for Atmospheric Research,* Boulder, Colorado Q. FU University
3282 J O U R N A L O F C L I M A T E VOLUME 21 Observed and Simulated Upper-Tropospheric Water Vapor Feedback A. GETTELMAN National Center for Atmospheric Research,* Boulder, Colorado Q. FU University
Modeling Challenges At High Latitudes. Judith Curry Georgia Institute of Technology
 Modeling Challenges At High Latitudes Judith Curry Georgia Institute of Technology Physical Process Parameterizations Radiative transfer Surface turbulent fluxes Cloudy boundary layer Cloud microphysics
Modeling Challenges At High Latitudes Judith Curry Georgia Institute of Technology Physical Process Parameterizations Radiative transfer Surface turbulent fluxes Cloudy boundary layer Cloud microphysics
On the Satellite Determination of Multilayered Multiphase Cloud Properties. Science Systems and Applications, Inc., Hampton, Virginia 2
 JP1.10 On the Satellite Determination of Multilayered Multiphase Cloud Properties Fu-Lung Chang 1 *, Patrick Minnis 2, Sunny Sun-Mack 1, Louis Nguyen 1, Yan Chen 2 1 Science Systems and Applications, Inc.,
JP1.10 On the Satellite Determination of Multilayered Multiphase Cloud Properties Fu-Lung Chang 1 *, Patrick Minnis 2, Sunny Sun-Mack 1, Louis Nguyen 1, Yan Chen 2 1 Science Systems and Applications, Inc.,
5. General Circulation Models
 5. General Circulation Models I. 3-D Climate Models (General Circulation Models) To include the full three-dimensional aspect of climate, including the calculation of the dynamical transports, requires
5. General Circulation Models I. 3-D Climate Models (General Circulation Models) To include the full three-dimensional aspect of climate, including the calculation of the dynamical transports, requires
Chapter 8 cont. Clouds and Storms
 Chapter 8 cont. Clouds and Storms Spring 2007 Clouds and Storms Clouds cover ~ 50% of earth at any time. Clouds are linked to a number of condensation processes. Cloud morphology, cloud types, associated
Chapter 8 cont. Clouds and Storms Spring 2007 Clouds and Storms Clouds cover ~ 50% of earth at any time. Clouds are linked to a number of condensation processes. Cloud morphology, cloud types, associated
Implications of Sulfate Aerosols on Clouds, Precipitation and Hydrological Cycle
 Implications of Sulfate Aerosols on Clouds, Precipitation and Hydrological Cycle Source: Sulfate aerosols are produced by chemical reactions in the atmosphere from gaseous precursors (with the exception
Implications of Sulfate Aerosols on Clouds, Precipitation and Hydrological Cycle Source: Sulfate aerosols are produced by chemical reactions in the atmosphere from gaseous precursors (with the exception
The dependence of contrail formation on the weather pattern and altitude in the North Atlantic
 The dependence of contrail formation on the weather pattern and altitude in the North Atlantic AB C DE F E A A DC EC A A E A E A A A A E E AD A DE A D DEADEA A A EA E A A EA A D A E A D C A C A C A A A
The dependence of contrail formation on the weather pattern and altitude in the North Atlantic AB C DE F E A A DC EC A A E A E A A A A E E AD A DE A D DEADEA A A EA E A A EA A D A E A D C A C A C A A A
NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE. On the Occurrence of Hollow Bullet Rosette and Column-Shaped Ice Crystals in Midlatitude Cirrus
 4514 J O U R N A L O F T H E A T M O S P H E R I C S C I E N C E S VOLUME 64 NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE On the Occurrence of Hollow Bullet Rosette and Column-Shaped Ice Crystals in Midlatitude Cirrus C.
4514 J O U R N A L O F T H E A T M O S P H E R I C S C I E N C E S VOLUME 64 NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE On the Occurrence of Hollow Bullet Rosette and Column-Shaped Ice Crystals in Midlatitude Cirrus C.
Estimating the influence of summertime deep convection over the Tibetan Plateau on water vapor transport into the tropical lower stratosphere
 Estimating the influence of summertime deep convection over the Tibetan Plateau on water vapor transport into the tropical lower stratosphere Jonathon S. Wright Tsinghua University Center for Earth System
Estimating the influence of summertime deep convection over the Tibetan Plateau on water vapor transport into the tropical lower stratosphere Jonathon S. Wright Tsinghua University Center for Earth System
9D.3 THE INFLUENCE OF VERTICAL WIND SHEAR ON DEEP CONVECTION IN THE TROPICS
 9D.3 THE INFLUENCE OF VERTICAL WIND SHEAR ON DEEP CONVECTION IN THE TROPICS Ulrike Wissmeier, Robert Goler University of Munich, Germany 1 Introduction One does not associate severe storms with the tropics
9D.3 THE INFLUENCE OF VERTICAL WIND SHEAR ON DEEP CONVECTION IN THE TROPICS Ulrike Wissmeier, Robert Goler University of Munich, Germany 1 Introduction One does not associate severe storms with the tropics
Meteorological Satellite Image Interpretations, Part III. Acknowledgement: Dr. S. Kidder at Colorado State Univ.
 Meteorological Satellite Image Interpretations, Part III Acknowledgement: Dr. S. Kidder at Colorado State Univ. Dates EAS417 Topics Jan 30 Introduction & Matlab tutorial Feb 1 Satellite orbits & navigation
Meteorological Satellite Image Interpretations, Part III Acknowledgement: Dr. S. Kidder at Colorado State Univ. Dates EAS417 Topics Jan 30 Introduction & Matlab tutorial Feb 1 Satellite orbits & navigation
Name Class Date STUDY GUIDE FOR CONTENT MASTERY
 Atmosphere SECTION 11.1 Atmospheric Basics In your textbook, read about the composition of the atmosphere. Circle the letter of the choice that best completes the statement. 1. Most of Earth s atmosphere
Atmosphere SECTION 11.1 Atmospheric Basics In your textbook, read about the composition of the atmosphere. Circle the letter of the choice that best completes the statement. 1. Most of Earth s atmosphere
Large-Eddy Simulations of Tropical Convective Systems, the Boundary Layer, and Upper Ocean Coupling
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Large-Eddy Simulations of Tropical Convective Systems, the Boundary Layer, and Upper Ocean Coupling Eric D. Skyllingstad
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Large-Eddy Simulations of Tropical Convective Systems, the Boundary Layer, and Upper Ocean Coupling Eric D. Skyllingstad
WACCM: The High-Top Model
 WACCM: The High-Top Model WACCM top Michael Mills CAM top WACCM Liaison mmills@ucar.edu (303) 497-1425 http://bb.cgd.ucar.edu/ 40 km Ozone Layer Jarvis, Bridging the Atmospheric Divide, Science, 293, 2218,
WACCM: The High-Top Model WACCM top Michael Mills CAM top WACCM Liaison mmills@ucar.edu (303) 497-1425 http://bb.cgd.ucar.edu/ 40 km Ozone Layer Jarvis, Bridging the Atmospheric Divide, Science, 293, 2218,
The Structure and Motion of the Atmosphere OCEA 101
 The Structure and Motion of the Atmosphere OCEA 101 Why should you care? - the atmosphere is the primary driving force for the ocean circulation. - the atmosphere controls geographical variations in ocean
The Structure and Motion of the Atmosphere OCEA 101 Why should you care? - the atmosphere is the primary driving force for the ocean circulation. - the atmosphere controls geographical variations in ocean
Czech Hydrometeorological Institute, Na Šabatce 17, CZ Praha 4, Czech Republic. 3
 MOISTURE DETECTION ABOVE CONVECTIVE STORMS UTILIZING THE METHOD OF BRIGHTNESS TEMPERATURE DIFFERENCES BETWEEN WATER VAPOR AND IR WINDOW BANDS, BASED ON 2008 MSG RAPID SCAN SERVICE DATA Jindřich Šťástka1,2,
MOISTURE DETECTION ABOVE CONVECTIVE STORMS UTILIZING THE METHOD OF BRIGHTNESS TEMPERATURE DIFFERENCES BETWEEN WATER VAPOR AND IR WINDOW BANDS, BASED ON 2008 MSG RAPID SCAN SERVICE DATA Jindřich Šťástka1,2,
The Atmosphere. Topic 3: Global Cycles and Physical Systems. Topic 3: Global Cycles and Physical Systems. Topic 3: Global Cycles and Physical Systems
 The Atmosphere 1 How big is the atmosphere? Why is it cold in Geneva? Why do mountaineers need oxygen on Everest? 2 A relatively thin layer of gas over the Earths surface Earth s radius ~ 6400km Atmospheric
The Atmosphere 1 How big is the atmosphere? Why is it cold in Geneva? Why do mountaineers need oxygen on Everest? 2 A relatively thin layer of gas over the Earths surface Earth s radius ~ 6400km Atmospheric
Parameterization for Atmospheric Radiation: Some New Perspectives
 Parameterization for Atmospheric Radiation: Some New Perspectives Kuo-Nan Liou Joint Institute for Regional Earth System Science and Engineering (JIFRESSE) and Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences Department
Parameterization for Atmospheric Radiation: Some New Perspectives Kuo-Nan Liou Joint Institute for Regional Earth System Science and Engineering (JIFRESSE) and Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences Department
Upper Tropospheric Cloud Systems. what can be achieved? A GEWEX Perspective
 Upper Tropospheric Cloud Systems from Satellite Observations: what can be achieved? A GEWEX Perspective Global Energy & Water EXchanges Claudia Stubenrauch, Graeme Stephens IPSL LMD, Paris, France, NASA
Upper Tropospheric Cloud Systems from Satellite Observations: what can be achieved? A GEWEX Perspective Global Energy & Water EXchanges Claudia Stubenrauch, Graeme Stephens IPSL LMD, Paris, France, NASA
Characteristics of cirrus clouds from ICESat/GLAS observations
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L09810, doi:10.1029/2007gl029529, 2007 Characteristics of cirrus clouds from ICESat/GLAS observations Nawo Eguchi, 1 Tatsuya Yokota, 1 and Gen Inoue 2 Received 30
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L09810, doi:10.1029/2007gl029529, 2007 Characteristics of cirrus clouds from ICESat/GLAS observations Nawo Eguchi, 1 Tatsuya Yokota, 1 and Gen Inoue 2 Received 30
Some remarks on climate modeling
 Some remarks on climate modeling A. Gettelman & J. J. Hack National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado USA Selected overheads by Doug Nychka Outline Hierarchy of atmospheric modeling strategies
Some remarks on climate modeling A. Gettelman & J. J. Hack National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado USA Selected overheads by Doug Nychka Outline Hierarchy of atmospheric modeling strategies
Introduction. Effect of aerosols on precipitation: - challenging problem - no agreement between the results (quantitative and qualitative)
 Introduction Atmospheric aerosols affect the cloud mycrophysical structure & formation (observations, numerical studies) An increase of the aerosol particles: - increases CCN concentrations - decreases
Introduction Atmospheric aerosols affect the cloud mycrophysical structure & formation (observations, numerical studies) An increase of the aerosol particles: - increases CCN concentrations - decreases
CONVECTIVE CLOUD MICROPHYSICS IN A HIGH-RESOLUTION NWP MODEL
 CONVECTIVE CLOUD MICROPHYSICS IN A HIGH-RESOLUTION NWP MODEL J. Trentmann 1, A. Seifert 2, H. Wernli 1 1 Institute for Atmospheric Physics, Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz, Germany 2 German Weather
CONVECTIVE CLOUD MICROPHYSICS IN A HIGH-RESOLUTION NWP MODEL J. Trentmann 1, A. Seifert 2, H. Wernli 1 1 Institute for Atmospheric Physics, Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz, Germany 2 German Weather
SENSITIVITY OF SPACE-BASED PRECIPITATION MEASUREMENTS
 SENSITIVITY OF SPACE-BASED PRECIPITATION MEASUREMENTS JP7.2 TO CHANGES IN MESOSCALE FEATURES Joseph Hoch *, Gregory J. Tripoli, Mark Kulie University of Wisconsin, Madison, Wisconsin 1. INTRODUCTION The
SENSITIVITY OF SPACE-BASED PRECIPITATION MEASUREMENTS JP7.2 TO CHANGES IN MESOSCALE FEATURES Joseph Hoch *, Gregory J. Tripoli, Mark Kulie University of Wisconsin, Madison, Wisconsin 1. INTRODUCTION The
The water vapour channels of SEVIRI (Meteosat). An introduction
 The water vapour channels of SEVIRI (Meteosat). An introduction jose.prieto@eumetsat.int Cachoeira P. July 2006 Formats 1.5 1 Objectives 2 Describe the characteristics of WV channels on board of SEVIRI
The water vapour channels of SEVIRI (Meteosat). An introduction jose.prieto@eumetsat.int Cachoeira P. July 2006 Formats 1.5 1 Objectives 2 Describe the characteristics of WV channels on board of SEVIRI
An Introduction to Coupled Models of the Atmosphere Ocean System
 An Introduction to Coupled Models of the Atmosphere Ocean System Jonathon S. Wright jswright@tsinghua.edu.cn Atmosphere Ocean Coupling 1. Important to climate on a wide range of time scales Diurnal to
An Introduction to Coupled Models of the Atmosphere Ocean System Jonathon S. Wright jswright@tsinghua.edu.cn Atmosphere Ocean Coupling 1. Important to climate on a wide range of time scales Diurnal to
Tropopause Cirrus Variation by Equatorial Kelvin Waves
 Tropopause Cirrus Variation by Equatorial Kelvin Waves Masatomo Fujiwara Hokkaido University SOWER Meeting, 19 July 2006 Outline Kelvin waves in the TTL (10 min) Cirrus in the TTL (5 min) Results from
Tropopause Cirrus Variation by Equatorial Kelvin Waves Masatomo Fujiwara Hokkaido University SOWER Meeting, 19 July 2006 Outline Kelvin waves in the TTL (10 min) Cirrus in the TTL (5 min) Results from
Unprecedented evidence for deep convection hydrating the tropical stratosphere
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L10810, doi:10.1029/2008gl033641, 2008 Unprecedented evidence for deep convection hydrating the tropical stratosphere T. Corti, 1 B. P. Luo, 1 M. de Reus, 2 D. Brunner,
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L10810, doi:10.1029/2008gl033641, 2008 Unprecedented evidence for deep convection hydrating the tropical stratosphere T. Corti, 1 B. P. Luo, 1 M. de Reus, 2 D. Brunner,
p = ρrt p = ρr d = T( q v ) dp dz = ρg
 Chapter 1: Properties of the Atmosphere What are the major chemical components of the atmosphere? Atmospheric Layers and their major characteristics: Troposphere, Stratosphere Mesosphere, Thermosphere
Chapter 1: Properties of the Atmosphere What are the major chemical components of the atmosphere? Atmospheric Layers and their major characteristics: Troposphere, Stratosphere Mesosphere, Thermosphere
P7.14 Cloud optical depth from UW-NMS and GEOS-DAS and comparisons with MODIS and ISCCP satellite observations
 P7.14 Cloud optical depth from UW-NMS and GEOS-DAS and comparisons with MODIS and ISCCP satellite observations Hongyu Liu 1*, Robert B. Pierce 2, James H. Crawford 2, Peter Norris 3,4, Chieko Kittaka 5,
P7.14 Cloud optical depth from UW-NMS and GEOS-DAS and comparisons with MODIS and ISCCP satellite observations Hongyu Liu 1*, Robert B. Pierce 2, James H. Crawford 2, Peter Norris 3,4, Chieko Kittaka 5,
ECMWF Workshop on "Parametrization of clouds and precipitation across model resolutions
 ECMWF Workshop on "Parametrization of clouds and precipitation across model resolutions Themes: 1. Parametrization of microphysics 2. Representing sub-grid cloud variability 3. Constraining cloud and precipitation
ECMWF Workshop on "Parametrization of clouds and precipitation across model resolutions Themes: 1. Parametrization of microphysics 2. Representing sub-grid cloud variability 3. Constraining cloud and precipitation
Importance of clouds. climate. ocean. radiation. life. hydrological cycle. latent heat + loading. clouds & precip + aerosols.
 Importance of clouds climate life ocean radiation hydrological cycle clouds & precip + aerosols latent heat + loading dynamics electricity aqueous chemistry Ulrike Lohmann (IACETH) Physics and Dynamics
Importance of clouds climate life ocean radiation hydrological cycle clouds & precip + aerosols latent heat + loading dynamics electricity aqueous chemistry Ulrike Lohmann (IACETH) Physics and Dynamics
Physical and Optical Properties of the Stratospheric Aerosol Layer
 Physical and Optical Properties of the Stratospheric Aerosol Layer Patrick Hamill Department of Physics and Astronomy San Jose State University San Jose, California Justification for this Talk Much debate
Physical and Optical Properties of the Stratospheric Aerosol Layer Patrick Hamill Department of Physics and Astronomy San Jose State University San Jose, California Justification for this Talk Much debate
Global Cloud Climatologies from satellite-based InfraRed Sounders (TOVS, AIRS, IASI) +
 Global Cloud Climatologies from satellite-based InfraRed Sounders (TOVS, AIRS, IASI) + AIRS-CALIPSO-CloudSat Synergy Claudia Stubenrauch * until 2010 S. Cros*, A. Guignard, N. Lamquin*, R. Armante, A.
Global Cloud Climatologies from satellite-based InfraRed Sounders (TOVS, AIRS, IASI) + AIRS-CALIPSO-CloudSat Synergy Claudia Stubenrauch * until 2010 S. Cros*, A. Guignard, N. Lamquin*, R. Armante, A.
Parametrizing cloud and precipitation in today s NWP and climate models. Richard Forbes
 Parametrizing cloud and precipitation in today s NWP and climate models Richard Forbes (ECMWF) with thanks to Peter Bechtold and Martin Köhler RMetS National Meeting on Clouds and Precipitation, 16 Nov
Parametrizing cloud and precipitation in today s NWP and climate models Richard Forbes (ECMWF) with thanks to Peter Bechtold and Martin Köhler RMetS National Meeting on Clouds and Precipitation, 16 Nov
