Hourly Precipitation Estimation through Rain-Gauge and Radar: CombiPrecip
|
|
|
- Janis Mills
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
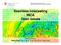
1 Federal Department of Home Affairs FDHA Federal Office of Meteorology and Climatology MeteoSwiss Documentation of MeteoSwiss Grid-Data Products Hourly Precipitation Estimation through Rain-Gauge and Radar: CombiPrecip Figure 1: Hourly precipitation total (mm) on 31 August 2017 between 16:00 and 17:00 UTC. The circles represent raingauge measurements of precipitation. Variable Precipitation for hour H (UTC), corresponding to rainfall accumulated in the interval from H-1 UTC to H UTC. Estimates are in millimeters (equivalent to liters per square meter). Application Hydrology and rainfall runoff modeling, civil protection, flash flood and debris flow warnings, intervention during flooding, flood prevention, hydropower management, verification of precipitation forecasts of numerical weather prediction models, environmental modeling, agriculture, tourism, and water resources modeling.
2 Overview CombiPrecip is a dataset of hourly precipitation fields, which are computed using a geostatistical combination of raingauge measurements and radar estimates. The CombiPrecip fields cover the entire area monitored by the Swiss radars. This extends typically to about km away from the Swiss border. The CombiPrecip fields are generated in real-time, with update time 10 minutes, and represent hourly sums (sum over a 60-minutes moving window). They are available since A real-time delivery is possible, about minutes after the nominal hour. Every week, a reprocessed CombiPrecip product becomes available, in which errors and limitations present in the real-time environment have been taken care of, for instance, rain-gauge values have been subject to an in-depth quality control. Data base CombiPrecip combines information from two sources: (a) hourly aggregations of rain-gauge precipitation measurements at the SwissMetNet (SMN) stations and (b) radar precipitation estimates from the radar composite precipitation product (Germann and Joss, 2004, Germann et al., 2006). The temporal resolution of the SMN rain gauges is 10 minutes, and there are currently over 250 automatic stations operating in real-time. The algorithm has the configurable capability to include in its computations rain-gauge measurements from additional networks (other than SMN). The radar estimates result from a series of processing steps and a composition of backscatter measurements made by five weather C-band radars located within Switzerland. The spatial resolution of the radar product is 1 km 2, while its temporal resolution is 5 min. Method The hourly precipitation fields are computed using geostatistical techniques, where precipitation is treated as a stochastic process (Creutin et al. 1988; Erdin 2009; Erdin and Frei 2012; Goovaerts 1997; Haberlandt 2007; Krajewski 1987; Schuurmans et al. 2007; Seo et al. 1990). Correlations that characterize the observed precipitation radar and rain-gauge measurements are computed modelled accordingly. The modeling technique currently employed by CombiPrecip extracts both spatial and temporal information from the observations and models them using co-kriging with external drift. This spatiotemporal approach provides enhanced stability in comparison to geostatistical techniques incorporating spatial data only. As a result, modeling failures are decreased and unrealistic outputs are avoided. This sophistication is justified since is practically attempted to carry out a complex statistical procedure in real-time without human-intervention. The details of the technique are discussed extensively in Sideris et al A relaxation towards the original radar raster for regions outside Switzerland has been introduced into the mechanism. This was motivated by the need for a smooth transition between the geostatistical precipitation estimates within the Swiss area, and the radar estimates far away from Switzerland, where no rain-gauge measurements are available. The effect is achieved through a combination of virtual rain gauges (radar precipitation estimates that pose as rain-gauge measurements) and follow-up filtering, and is described in Sideris et al Target users CombiPrecip is useful for a number of practical applications where high spatial and temporal resolution in precipitation estimates are of importance, e.g. civil protection, flash flood warnings, intervention during flooding. The archived dataset is also interesting for flood prevention, hydro-power management, agriculture, tourism, validation and research. Accuracy and interpretation The accuracy of the product depends significantly on the quality of the input i.e. the raingauge measurements and the radar estimates of precipitation. The rain-gauge data are intro-
3 duced into the mechanism as a primary variable, the value of which has to be respected within the extent of a variance used to describe errors and micro-variability effects while the radar raster is used as an external trend. The quality of radar precipitation estimates depends to a large extent on: (a) the distance from the radar, the so-called range degradation effect, and (b) the height above sea level of the lowest unshielded beams above the target region, the so-called radar visibility (including Earth s curvature, partial beam shielding by orography and the highly variable in space and time vertical reflectivity profile). The most reliable radar echoes are at short range (say between 3 and 60 km) and at an altitude where most or all hydrometeors are in liquid phase (hence, summer better than winter). A chain of procedures is followed to assure the high quality of radar data: automatic hardware calibration and monitoring, clutter removal, correction for radar visibility, VPR correction, and others. Rain-gauge measurements, are subject to an extensive quality control (Grüter et al. 2003) before they are used as input of CombiPrecip. This involves: (i) limit tests (comparison to physical and climatological limits), (ii) variability tests (tests of maximum and minimum acceptable variability during a specified time interval), (iii) inter-parameter consistency tests, and (iv) spatial consistency tests (between nearby stations). Moreover, CombiPrecip checks the rain-gauge measurements for outliers and occasionally excludes measurements that are highly suspicious (either too high or too low). The combination relies on modeling reasonably well the correlation structure of precipitation a process that takes place through the construction and modeling of a representative variogram. However, the modeled variogram becomes less accurate the smaller the number of wet rain gauges is which affects directly the quality of the outcome. A quality flag accompanies the CombiPrecip product. This flag combines the information of the quality flag of the radar composite product (which depends on how many of the five radars were operational at the time of the measurement) and the number of the available wet rain gauges. The lowest value of this flag is 0 and the highest is 9. Provided that the number of wet rain gauges is sufficiently large and the original radar coverage is satisfactory the combination map is considered to be reasonably accurate. Low values of the CombiPrecip quality flag do not signify necessarily that the product is wrong, but they aim at informing the client on the level of confidence he/she should have on this product. CombiPrecip is particularly adequate for observing widespread and long lasting precipitations events, whereas situations characterized by very small and isolated precipitations cells that might not be resolved by the ground based rain-gauge network, are to be evaluated with care. Tests over several individual cases different in nature, but also over extensive periods of time suggest that the overall bias of the cross-validated results produced by CombiPrecip, is very close to zero (Erdin 2011; Keller 2012; Willi et al. 2011). Moreover, there is a sizeable improvement on numerous other skill scores like the root-mean-squared-error (RMSE), the Hanssen-Kuipers discriminant (HK), and the scatter, but this improvement depends on factors like the weather situation (e.g. convective or not-convective situation), the season or the region in question. A multi-year validation based on cross-validation of hourly amounts of summer precipitation products evaluated in the same 68 sites during six two-year periods provides the following results regarding bias and scatter in db: Bias Product Radar-only +0..8± ± ± ± ± ±0.32 CombiPrecip +0.0± ± ± ± ± ±0.13
4 Scatter Product Radar-only 3.1± ± ± ± ± ±0.04 CombiPrecip 2.5± ± ± ± ± ±0.07 Finally, it has to be mentioned that the uncertainty of the rain-gauge-radar combination process drops with increasing distance from the rain-gauge locations. This situation does not affect significantly the interior of Switzerland since this is monitored sufficiently well by rain gauges, but it does affect the region outside the Swiss border. Understandably, in very large distances from the border the confidence of the combination estimation is no better than the confidence in the original radar product. For this reason, an algorithm complements the typical modeling-estimation geostatistical scheme, by relaxing in a continuous fashion the combination output towards the original radar map as distance from rain gauges increases. This solution provides conceptually the best possible precipitation map within and nearby Switzerland (combination), and far from Switzerland (radar). Related products Radar PRECIP: Original radar precipitation estimates. This product is continuously updated, is available in real-time at a resolution up to 2.5 minutes, ready to be distributed to the clients less than 60 seconds after nominal time. The PRECIP product results from a sequence of processing steps applied to the early-stage-processed radar data, aiming to produce the best quantitative precipitation estimation without using external measurements such as raingauge data in a short-time basis (e.g. hourly); the radar product incorporates only a broader, yearly-based, rain-gauge adjustment. The PRECIP product has a spatial resolution of 1 km (same as CombiPrecip) and is available for the period 2005-present. RhiresD; RhiresM; RhiresY: Spatial analyses from rain gauge data have been elaborated as daily, monthly or yearly time resolution, precipitation fields over Switzerland. Grid structures Regular 1-km grid in the Swiss coordinate system over the domain covered by the C-band Swiss weather radar network. Versions Current version: CombiPrecip 3.1 Previous versions: CombiPrecip 2.1 Update cycle References The update cycle has not yet been decided. Creutin J., G. Dekrieu and T. Lebel, 1988: Rain measurement by raingage-radar combination: a geostatistical approach, J. of Atmosph. and Ocean. Technology, 5(1), Erdin R., 2009: Combining rain gauge and radar measurements of a heavy precipitation event over Switzerland. Veroeffentlichungen der MeteoSchweiz, MeteoSwiss, 110 pp. Erdin R., 2011: Evaluation guidelines of CombiPrecip. Internal report, MeteoSwiss, 10pp. Erdin R, C. Frei and H.R. Künsch, 2012: Data transformation and uncertainty in geostatistical combination of radar and rain gauges. J. of Hydrometeorology 13, Keller D., 2012: Evaluation And comparison of radar-rain gauge combination methods, Veroeffentlichungen der MeteoSchweiz, MeteoSwiss, 68 pp. Gabella M., Speirs P., Hamann U., Germann U., and A. Berne, 2017: Measurement of Precipitation in the Alps Using Dual-Polarization C-Band Ground-Based Radars, the GPM Spaceborne Ku-Band Radar, and Rain Gauges, Remote Sensing, 9, 19 pages. doi: /rs Gabella M., Panziera L., Sideris I.V., Boscacci M., Clementi L., Sartori M., Germann U., 2015: Twelve-year of operational real-time precipitation estimation in the Alps: better performance of the radar-only and radar-gauge products in recent years, 11 th International Workshop on Precipitation in Urban Areas, 2018, Pontresina, Switzerland. Germann U. and J. Joss, 2004: Operational measurement of precipitation in mountainous terrain. Pp in Weather radar: Principles and advanced applications. Ed. P.Meischner. In series Physics of Earth and Space Environment, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Germany. Germann U., G. Galli, M. Boscacci and M. Bolliger, 2006: Radar precipitation measurement in a mountainous region Q. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc., 132(618), Goovaerts P., 1997: Geostatistics for Natural Resources Evaluation. Oxford University Press. Grüter E., Abbt M., Häberli C., Häller E., Küng U., Musa M., Konzelmann T., Dössegger R., 2003: Quality control tools for meteorological data in the MeteoSwiss data warehouse system, Internal report, MeteoSwiss, 11pp. Haberlandt U., 2007: Geostatistical interpolation of hourly precipitation. J. Hydrol. 332,
5 Krajewski, W.F., 1987: Cokriging radar-rainfall and rain gage data, J. of Geophysical Research, 92(D8), Schuurmans J.M., M.F.P. Bierkens, E.J. Pebesma, R.Uilenhoet, 2007: Automatic prediction of high-resolution daily rainfall fields for multiple extents: the potenial of operational radar. J. of Hydrometeorology 8, Seo, D., W.F. Krajewski and D.S. Bowles, 1990: Stochastic interpolation of rainfall data from rain gages and radar using cokriging. 1. Design of experiments, Water Resources Research, 26, Sideris I., M. Gabella, R. Erdin and U. Germann, 2014: Real-time radar-raingauge merging using spatiotemporal cokriging with external drift in the alpine terrain of Switzerland, Q. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc.140: DOI: /qj Sideris I., M. Gabella, M. Sassi and U. Germann, 2012: Real-time spatiotemporal merging of radar and raingauge precipitation measurements in Switzerland, 9 th International Workshop on Precipitation in Urban Areas, 2012, St.Moritz, Switzerland. Willi M., M. Gabella, U. Germann and C. Frei, 2011: CombiPrecip test cases. Internal report. MeteoSwiss.
Radar precipitation measurement in the Alps big improvements triggered by MAP
 Radar precipitation measurement in the Alps big improvements triggered by MAP Urs Germann, Gianmario Galli, Marco Boscacci MeteoSwiss, Locarno-Monti MeteoSwiss radar Monte Lema, 1625m Can we measure precipitation
Radar precipitation measurement in the Alps big improvements triggered by MAP Urs Germann, Gianmario Galli, Marco Boscacci MeteoSwiss, Locarno-Monti MeteoSwiss radar Monte Lema, 1625m Can we measure precipitation
Progress in Operational Quantitative Precipitation Estimation in the Czech Republic
 Progress in Operational Quantitative Precipitation Estimation in the Czech Republic Petr Novák 1 and Hana Kyznarová 1 1 Czech Hydrometeorological Institute,Na Sabatce 17, 143 06 Praha, Czech Republic (Dated:
Progress in Operational Quantitative Precipitation Estimation in the Czech Republic Petr Novák 1 and Hana Kyznarová 1 1 Czech Hydrometeorological Institute,Na Sabatce 17, 143 06 Praha, Czech Republic (Dated:
Early detection of thunderstorms using satellite, radar and
 Federal Department of Home of Home Affairs Affairs FDHA FDHA Federal Office of of Meteorology and and Climatology MeteoSwiss Early detection of thunderstorms using satellite, radar and Observing convection
Federal Department of Home of Home Affairs Affairs FDHA FDHA Federal Office of of Meteorology and and Climatology MeteoSwiss Early detection of thunderstorms using satellite, radar and Observing convection
REQUIREMENTS FOR WEATHER RADAR DATA. Review of the current and likely future hydrological requirements for Weather Radar data
 WORLD METEOROLOGICAL ORGANIZATION COMMISSION FOR BASIC SYSTEMS OPEN PROGRAMME AREA GROUP ON INTEGRATED OBSERVING SYSTEMS WORKSHOP ON RADAR DATA EXCHANGE EXETER, UK, 24-26 APRIL 2013 CBS/OPAG-IOS/WxR_EXCHANGE/2.3
WORLD METEOROLOGICAL ORGANIZATION COMMISSION FOR BASIC SYSTEMS OPEN PROGRAMME AREA GROUP ON INTEGRATED OBSERVING SYSTEMS WORKSHOP ON RADAR DATA EXCHANGE EXETER, UK, 24-26 APRIL 2013 CBS/OPAG-IOS/WxR_EXCHANGE/2.3
Improvement of quantitative precipitation estimates in Belgium
 Improvement of quantitative precipitation estimates in Belgium L. Delobbe, E. Goudenhoofdt, and B. Mohymont Royal Meteorological Institute of Belgium 1. Introduction In this paper we describe the recent
Improvement of quantitative precipitation estimates in Belgium L. Delobbe, E. Goudenhoofdt, and B. Mohymont Royal Meteorological Institute of Belgium 1. Introduction In this paper we describe the recent
ERAD Quantitative precipitation estimation in the Alps: where do we stand? Proceedings of ERAD (2004): 2 6 c Copernicus GmbH 2004
 Proceedings of ERAD (2004): 2 6 c Copernicus GmbH 2004 ERAD 2004 Quantitative precipitation estimation in the Alps: where do we stand? U. Germann 1, G. Galli 1, M. Boscacci 1, M. Bolliger 1, and M. Gabella
Proceedings of ERAD (2004): 2 6 c Copernicus GmbH 2004 ERAD 2004 Quantitative precipitation estimation in the Alps: where do we stand? U. Germann 1, G. Galli 1, M. Boscacci 1, M. Bolliger 1, and M. Gabella
Combining Satellite And Gauge Precipitation Data With Co-Kriging Method For Jakarta Region
 City University of New York (CUNY) CUNY Academic Works International Conference on Hydroinformatics 8-1-214 Combining Satellite And Gauge Precipitation Data With Co-Kriging Method For Jakarta Region Chi
City University of New York (CUNY) CUNY Academic Works International Conference on Hydroinformatics 8-1-214 Combining Satellite And Gauge Precipitation Data With Co-Kriging Method For Jakarta Region Chi
MeteoSwiss Spatial Climate Analyses: Documentation of Datasets for Users
 Federal Department of Home Affairs FDHA Federal Office of Meteorology and Climatology MeteoSwiss MeteoSwiss Spatial Climate Analyses: Documentation of Datasets for Users Figure 1: Distribution of the 48-hour
Federal Department of Home Affairs FDHA Federal Office of Meteorology and Climatology MeteoSwiss MeteoSwiss Spatial Climate Analyses: Documentation of Datasets for Users Figure 1: Distribution of the 48-hour
Real-time radar rain-gauge merging using spatio-temporal co-kriging with external drift in the alpine terrain of Switzerland
 Quarterly Journalof the Royal Meteorological Society Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 14: 197 1111, April 214 DOI:1.12/qj.2188 Real-time radar rain-gauge merging using spatio-temporal co-kriging with external drift
Quarterly Journalof the Royal Meteorological Society Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 14: 197 1111, April 214 DOI:1.12/qj.2188 Real-time radar rain-gauge merging using spatio-temporal co-kriging with external drift
A RADAR-BASED CLIMATOLOGY OF HIGH PRECIPITATION EVENTS IN THE EUROPEAN ALPS:
 2.6 A RADAR-BASED CLIMATOLOGY OF HIGH PRECIPITATION EVENTS IN THE EUROPEAN ALPS: 2000-2007 James V. Rudolph*, K. Friedrich, Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences, University of Colorado at Boulder,
2.6 A RADAR-BASED CLIMATOLOGY OF HIGH PRECIPITATION EVENTS IN THE EUROPEAN ALPS: 2000-2007 James V. Rudolph*, K. Friedrich, Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences, University of Colorado at Boulder,
The Australian Operational Daily Rain Gauge Analysis
 The Australian Operational Daily Rain Gauge Analysis Beth Ebert and Gary Weymouth Bureau of Meteorology Research Centre, Melbourne, Australia e.ebert@bom.gov.au Daily rainfall data and analysis procedure
The Australian Operational Daily Rain Gauge Analysis Beth Ebert and Gary Weymouth Bureau of Meteorology Research Centre, Melbourne, Australia e.ebert@bom.gov.au Daily rainfall data and analysis procedure
A Multiple-Point Statistics Approach to Generate Rainfall Maps at High Spatial-Temporal Resolution Merging Radar and Rain-Gauge Measurements
 A Multiple-Point Statistics Approach to Generate Rainfall Maps at High Spatial-Temporal Resolution Merging Radar and Rain-Gauge Measurements G. Ghiggi 1, G. Mariéthoz 2, A. Berne 1 1 Environmental Remote
A Multiple-Point Statistics Approach to Generate Rainfall Maps at High Spatial-Temporal Resolution Merging Radar and Rain-Gauge Measurements G. Ghiggi 1, G. Mariéthoz 2, A. Berne 1 1 Environmental Remote
Evaluation of radar-gauge merging methods for quantitative precipitation estimates
 Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci., 3, 95 3, 9 www.hydrol-earth-syst-sci.net/3/95/9/ Author(s) 9. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3. License. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences Evaluation
Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci., 3, 95 3, 9 www.hydrol-earth-syst-sci.net/3/95/9/ Author(s) 9. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3. License. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences Evaluation
Radars, Hydrology and Uncertainty
 Radars, Hydrology and Uncertainty Francesca Cecinati University of Bristol, Department of Civil Engineering francesca.cecinati@bristol.ac.uk Supervisor: Miguel A. Rico-Ramirez Research objectives Study
Radars, Hydrology and Uncertainty Francesca Cecinati University of Bristol, Department of Civil Engineering francesca.cecinati@bristol.ac.uk Supervisor: Miguel A. Rico-Ramirez Research objectives Study
Rainfall-runoff modelling using merged rainfall from radar and raingauge measurements
 Rainfall-runoff modelling using merged rainfall from radar and raingauge measurements Nergui Nanding, Miguel Angel Rico-Ramirez and Dawei Han Department of Civil Engineering, University of Bristol Queens
Rainfall-runoff modelling using merged rainfall from radar and raingauge measurements Nergui Nanding, Miguel Angel Rico-Ramirez and Dawei Han Department of Civil Engineering, University of Bristol Queens
The development of a Kriging based Gauge and Radar merged product for real-time rainfall accumulation estimation
 The development of a Kriging based Gauge and Radar merged product for real-time rainfall accumulation estimation Sharon Jewell and Katie Norman Met Office, FitzRoy Road, Exeter, UK (Dated: 16th July 2014)
The development of a Kriging based Gauge and Radar merged product for real-time rainfall accumulation estimation Sharon Jewell and Katie Norman Met Office, FitzRoy Road, Exeter, UK (Dated: 16th July 2014)
Application of Radar QPE. Jack McKee December 3, 2014
 Application of Radar QPE Jack McKee December 3, 2014 Topics Context Precipitation Estimation Techniques Study Methodology Preliminary Results Future Work Questions Introduction Accurate precipitation data
Application of Radar QPE Jack McKee December 3, 2014 Topics Context Precipitation Estimation Techniques Study Methodology Preliminary Results Future Work Questions Introduction Accurate precipitation data
A radar-based regional extreme rainfall analysis to derive the thresholds for a novel automatic alert system in Switzerland
 doi:10.5194/hess-20-2317-2016 Author(s) 2016. CC Attribution 3.0 License. A radar-based regional extreme rainfall analysis to derive the thresholds for a novel automatic alert system in Switzerland Luca
doi:10.5194/hess-20-2317-2016 Author(s) 2016. CC Attribution 3.0 License. A radar-based regional extreme rainfall analysis to derive the thresholds for a novel automatic alert system in Switzerland Luca
Gridding of precipitation and air temperature observations in Belgium. Michel Journée Royal Meteorological Institute of Belgium (RMI)
 Gridding of precipitation and air temperature observations in Belgium Michel Journée Royal Meteorological Institute of Belgium (RMI) Gridding of meteorological data A variety of hydrologic, ecological,
Gridding of precipitation and air temperature observations in Belgium Michel Journée Royal Meteorological Institute of Belgium (RMI) Gridding of meteorological data A variety of hydrologic, ecological,
Daily, Monthly and Yearly Norm Temperature ( ): TnormD8110, TnormM8110 and TnormY8110
 Federal Department of Home Affairs FDHA Federal Office of Meteorology and Climatology MeteoSwiss Documentation of MeteoSwiss Grid-Data Products Daily, Monthly and Yearly Norm Temperature (1981-2010): TnormD8110,
Federal Department of Home Affairs FDHA Federal Office of Meteorology and Climatology MeteoSwiss Documentation of MeteoSwiss Grid-Data Products Daily, Monthly and Yearly Norm Temperature (1981-2010): TnormD8110,
Seamless nowcasting. Open issues
 Federal Department of Home Affairs FDHA Federal Office of Meteorology and Climatology MeteoSwiss Seamless nowcasting INCA Open issues Pierre Eckert Matteo Buzzi, Marco Sassi, Guido della Bruna, Marco Gaia
Federal Department of Home Affairs FDHA Federal Office of Meteorology and Climatology MeteoSwiss Seamless nowcasting INCA Open issues Pierre Eckert Matteo Buzzi, Marco Sassi, Guido della Bruna, Marco Gaia
Evaluation and correction of uncertainty due to Gaussian approximation in radar rain gauge merging using kriging with external drift
 Evaluation and correction of uncertainty due to Gaussian approximation in radar rain gauge merging using kriging with external drift F. Cecinati* 1, O. Wani 2,3, M. A. Rico-Ramirez 1 1 University of Bristol,
Evaluation and correction of uncertainty due to Gaussian approximation in radar rain gauge merging using kriging with external drift F. Cecinati* 1, O. Wani 2,3, M. A. Rico-Ramirez 1 1 University of Bristol,
Adaptation for global application of calibration and downscaling methods of medium range ensemble weather forecasts
 Adaptation for global application of calibration and downscaling methods of medium range ensemble weather forecasts Nathalie Voisin Hydrology Group Seminar UW 11/18/2009 Objective Develop a medium range
Adaptation for global application of calibration and downscaling methods of medium range ensemble weather forecasts Nathalie Voisin Hydrology Group Seminar UW 11/18/2009 Objective Develop a medium range
EUMETSAT Hydrological SAF H05 product development at CNMCA
 EUMETSAT Conference 2013 Session 3 - Quantitative applications for nowcasting Poster Presentation EUMETSAT Hydrological SAF H05 product development at CNMCA Antonio Vocino, Valentina Scappiti, Daniele
EUMETSAT Conference 2013 Session 3 - Quantitative applications for nowcasting Poster Presentation EUMETSAT Hydrological SAF H05 product development at CNMCA Antonio Vocino, Valentina Scappiti, Daniele
Uncertainty in merged radar - rain gauge rainfall products
 Uncertainty in merged radar - rain gauge rainfall products Francesca Cecinati University of Bristol francesca.cecinati@bristol.ac.uk Supervisor: Miguel A. Rico-Ramirez This project has received funding
Uncertainty in merged radar - rain gauge rainfall products Francesca Cecinati University of Bristol francesca.cecinati@bristol.ac.uk Supervisor: Miguel A. Rico-Ramirez This project has received funding
118 RECONSTRUCTION OF RADAR RFLECTIVITY IN CLUTTER AREAS
 8 RECONSTRUCTION OF RADAR RFLECTIVITY IN CLUTTER AREAS Shinju Park, Marc Berenguer Centre de Recerca Aplicada en Hidrometeorologia, Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya (BarcelonaTech), Barcelona, Spain..
8 RECONSTRUCTION OF RADAR RFLECTIVITY IN CLUTTER AREAS Shinju Park, Marc Berenguer Centre de Recerca Aplicada en Hidrometeorologia, Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya (BarcelonaTech), Barcelona, Spain..
FLORA: FLood estimation and forecast in complex Orographic areas for Risk mitigation in the Alpine space
 Natural Risk Management in a changing climate: Experiences in Adaptation Strategies from some European Projekts Milano - December 14 th, 2011 FLORA: FLood estimation and forecast in complex Orographic
Natural Risk Management in a changing climate: Experiences in Adaptation Strategies from some European Projekts Milano - December 14 th, 2011 FLORA: FLood estimation and forecast in complex Orographic
Met Éireann Climatological Note No. 15 Long-term rainfall averages for Ireland,
 Met Éireann Climatological Note No. 15 Long-term rainfall averages for Ireland, 1981-2010 Séamus Walsh Glasnevin Hill, Dublin 9 2016 Disclaimer Although every effort has been made to ensure the accuracy
Met Éireann Climatological Note No. 15 Long-term rainfall averages for Ireland, 1981-2010 Séamus Walsh Glasnevin Hill, Dublin 9 2016 Disclaimer Although every effort has been made to ensure the accuracy
Application and verification of ECMWF products 2016
 Application and verification of ECMWF products 2016 Icelandic Meteorological Office (www.vedur.is) Bolli Pálmason and Guðrún Nína Petersen 1. Summary of major highlights Medium range weather forecasts
Application and verification of ECMWF products 2016 Icelandic Meteorological Office (www.vedur.is) Bolli Pálmason and Guðrún Nína Petersen 1. Summary of major highlights Medium range weather forecasts
Application of Probability Density Function - Optimal Interpolation in Hourly Gauge-Satellite Merged Precipitation Analysis over China
 Application of Probability Density Function - Optimal Interpolation in Hourly Gauge-Satellite Merged Precipitation Analysis over China Yan Shen, Yang Pan, Jingjing Yu National Meteorological Information
Application of Probability Density Function - Optimal Interpolation in Hourly Gauge-Satellite Merged Precipitation Analysis over China Yan Shen, Yang Pan, Jingjing Yu National Meteorological Information
Huw W. Lewis *, Dawn L. Harrison and Malcolm Kitchen Met Office, United Kingdom
 2.6 LOCAL VERTICAL PROFILE CORRECTIONS USING DATA FROM MULTIPLE SCAN ELEVATIONS Huw W. Lewis *, Dawn L. Harrison and Malcolm Kitchen Met Office, United Kingdom 1. INTRODUCTION The variation of reflectivity
2.6 LOCAL VERTICAL PROFILE CORRECTIONS USING DATA FROM MULTIPLE SCAN ELEVATIONS Huw W. Lewis *, Dawn L. Harrison and Malcolm Kitchen Met Office, United Kingdom 1. INTRODUCTION The variation of reflectivity
QPE and QPF in the Bureau of Meteorology
 QPE and QPF in the Bureau of Meteorology Current and future real-time rainfall products Carlos Velasco (BoM) Alan Seed (BoM) and Luigi Renzullo (CSIRO) OzEWEX 2016, 14-15 December 2016, Canberra Why do
QPE and QPF in the Bureau of Meteorology Current and future real-time rainfall products Carlos Velasco (BoM) Alan Seed (BoM) and Luigi Renzullo (CSIRO) OzEWEX 2016, 14-15 December 2016, Canberra Why do
Application and verification of ECMWF products 2010
 Application and verification of ECMWF products 2010 Icelandic Meteorological Office (www.vedur.is) Guðrún Nína Petersen 1. Summary of major highlights Medium range weather forecasts issued at IMO are mainly
Application and verification of ECMWF products 2010 Icelandic Meteorological Office (www.vedur.is) Guðrún Nína Petersen 1. Summary of major highlights Medium range weather forecasts issued at IMO are mainly
PLANNED UPGRADE OF NIWA S HIGH INTENSITY RAINFALL DESIGN SYSTEM (HIRDS)
 PLANNED UPGRADE OF NIWA S HIGH INTENSITY RAINFALL DESIGN SYSTEM (HIRDS) G.A. Horrell, C.P. Pearson National Institute of Water and Atmospheric Research (NIWA), Christchurch, New Zealand ABSTRACT Statistics
PLANNED UPGRADE OF NIWA S HIGH INTENSITY RAINFALL DESIGN SYSTEM (HIRDS) G.A. Horrell, C.P. Pearson National Institute of Water and Atmospheric Research (NIWA), Christchurch, New Zealand ABSTRACT Statistics
Abstract. 1 Introduction. 2 Experimental Setup. 2.1 Data Set
 ERAD - THE SEVENTH EUROPEAN CONFERENCE ON RADAR IN METEOROLOGY AND HYDROLOGY Comparison of the seasonal small-scale spatial variability in alpine snowfall and snow accumulation D. E. Scipión,, R. Mott,
ERAD - THE SEVENTH EUROPEAN CONFERENCE ON RADAR IN METEOROLOGY AND HYDROLOGY Comparison of the seasonal small-scale spatial variability in alpine snowfall and snow accumulation D. E. Scipión,, R. Mott,
Evaluation of the Version 7 TRMM Multi-Satellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA) 3B42 product over Greece
 15 th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology Rhodes, Greece, 31 August to 2 September 2017 Evaluation of the Version 7 TRMM Multi-Satellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA) 3B42
15 th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology Rhodes, Greece, 31 August to 2 September 2017 Evaluation of the Version 7 TRMM Multi-Satellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA) 3B42
Combining Rain Gauge and Radar Measurements of a Heavy Precipitation Event over Switzerland
 Veröffentlichung MeteoSchweiz Nr. 81 Combining Rain Gauge and Radar Measurements of a Heavy Precipitation Event over Switzerland Comparison of Geostatistical Methods and Investigation of Important Influencing
Veröffentlichung MeteoSchweiz Nr. 81 Combining Rain Gauge and Radar Measurements of a Heavy Precipitation Event over Switzerland Comparison of Geostatistical Methods and Investigation of Important Influencing
Simulation of heavy precipitation events with the COSMO model
 LM User Seminar, 6 March 2007, Langen Federal Department of Home Affairs FDHA Federal Office of Meteorology and Climatology MeteoSwiss Simulation of heavy precipitation events with the COSMO model Silke
LM User Seminar, 6 March 2007, Langen Federal Department of Home Affairs FDHA Federal Office of Meteorology and Climatology MeteoSwiss Simulation of heavy precipitation events with the COSMO model Silke
Hail nowcast exploiting radar and satellite observations
 Federal Department of Home Affairs FDHA Federal Office of Meteorology and Climatology MeteoSwiss Hail nowcast exploiting radar and satellite observations Ulrich Hamann, Elena Leonarduzzi, Kristopher Bedka,
Federal Department of Home Affairs FDHA Federal Office of Meteorology and Climatology MeteoSwiss Hail nowcast exploiting radar and satellite observations Ulrich Hamann, Elena Leonarduzzi, Kristopher Bedka,
and hydrological applications
 Overview of QPE/QPF techniques and hydrological applications Siriluk Chumchean Department of Civil Engineering Mahanakorn University of Technology Typhoon Committee Roving Seminar 2011, Malaysia (20-23
Overview of QPE/QPF techniques and hydrological applications Siriluk Chumchean Department of Civil Engineering Mahanakorn University of Technology Typhoon Committee Roving Seminar 2011, Malaysia (20-23
Characterizing the diurnal cycle of precipitation over complex Alpine orography using fourdimensional
 Characterizing the diurnal cycle of precipitation over complex Alpine orography using fourdimensional radar observations Pradeep V. Mandapaka 1, Urs Germann 1, Luca Panziera 1 1 MeteoSwiss, Locarno Monti,
Characterizing the diurnal cycle of precipitation over complex Alpine orography using fourdimensional radar observations Pradeep V. Mandapaka 1, Urs Germann 1, Luca Panziera 1 1 MeteoSwiss, Locarno Monti,
National Weather Service Flood Forecast Needs: Improved Rainfall Estimates
 National Weather Service Flood Forecast Needs: Improved Rainfall Estimates Weather Forecast Offices Cleveland and Northern Indiana Ohio River Forecast Center Presenter: Sarah Jamison, Service Hydrologist
National Weather Service Flood Forecast Needs: Improved Rainfall Estimates Weather Forecast Offices Cleveland and Northern Indiana Ohio River Forecast Center Presenter: Sarah Jamison, Service Hydrologist
Rainfall estimation in mountainous regions using X-band polarimetric weather radar
 Rainfall estimation in mountainous regions using X-band polarimetric weather radar Shakti P.C. 1,2, M. Maki 1,2, S. Shimizu 2, T. Maesaka 2, D.-S. Kim 2, D.-I. Lee 3 and H. Iida 4 1 Graduate School of
Rainfall estimation in mountainous regions using X-band polarimetric weather radar Shakti P.C. 1,2, M. Maki 1,2, S. Shimizu 2, T. Maesaka 2, D.-S. Kim 2, D.-I. Lee 3 and H. Iida 4 1 Graduate School of
an experiment to assess the hydrological value of a portable X-band radar
 ERAD 12 - THE SEVENTH EUROPEAN CONFERENCE ON RADAR IN METEOROLOGY AND HYDROLOGY RAINSCANNER@Barcelona: an experiment to assess the hydrological value of a portable X-band radar Marc Berenguer1, Shinju
ERAD 12 - THE SEVENTH EUROPEAN CONFERENCE ON RADAR IN METEOROLOGY AND HYDROLOGY RAINSCANNER@Barcelona: an experiment to assess the hydrological value of a portable X-band radar Marc Berenguer1, Shinju
AUTOMATIC ESTIMATION OF RAINFALL FIELDS FOR HYDROLOGICAL APPLICATIONS: BLENDING RADAR AND RAIN GAUGE DATA IN REAL TIME
 P13R.12 AUTOMATIC ESTIMATION OF RAINFALL FIELDS FOR HYDROLOGICAL APPLICATIONS: BLENDING RADAR AND RAIN GAUGE DATA IN REAL TIME Carlos Velasco-Forero 1,*, Daniel Sempere-Torres 1, Rafael Sánchez-Diezma
P13R.12 AUTOMATIC ESTIMATION OF RAINFALL FIELDS FOR HYDROLOGICAL APPLICATIONS: BLENDING RADAR AND RAIN GAUGE DATA IN REAL TIME Carlos Velasco-Forero 1,*, Daniel Sempere-Torres 1, Rafael Sánchez-Diezma
Establishing a high-resolution precipitation dataset for the Alps
 Federal Department of Home Affairs FDHA Federal Office of Meteorology and Climatology MeteoSwiss Establishing a high-resolution precipitation dataset for the Alps F. A. Isotta, C. Lukasczyk, and C. Frei
Federal Department of Home Affairs FDHA Federal Office of Meteorology and Climatology MeteoSwiss Establishing a high-resolution precipitation dataset for the Alps F. A. Isotta, C. Lukasczyk, and C. Frei
MeteoSwiss acceptance procedure for automatic weather stations
 MeteoSwiss acceptance procedure for automatic weather stations J. Fisler, M. Kube, E. Grueter and B. Calpini MeteoSwiss, Krähbühlstrasse 58, 8044 Zurich, Switzerland Phone:+41 44 256 9433, Email: joel.fisler@meteoswiss.ch
MeteoSwiss acceptance procedure for automatic weather stations J. Fisler, M. Kube, E. Grueter and B. Calpini MeteoSwiss, Krähbühlstrasse 58, 8044 Zurich, Switzerland Phone:+41 44 256 9433, Email: joel.fisler@meteoswiss.ch
Verification of precipitation and drought indices forecasts at subseasonal to seasonal time scales
 Federal Department of Home Affairs FDHA Federal Office of Meteorology and Climatology MeteoSwiss Verification of precipitation and drought indices forecasts at subseasonal to seasonal time scales Christoph
Federal Department of Home Affairs FDHA Federal Office of Meteorology and Climatology MeteoSwiss Verification of precipitation and drought indices forecasts at subseasonal to seasonal time scales Christoph
Study on the rainfall dependence structure using radar and rain gauge data
 International Workshop Advances in Statistical hydrology, May 23-25 2010, Taormina, Italy Study on the rainfall dependence structure using radar and rain gauge data V. Montesarchio, F. Russo, F. Napolitano
International Workshop Advances in Statistical hydrology, May 23-25 2010, Taormina, Italy Study on the rainfall dependence structure using radar and rain gauge data V. Montesarchio, F. Russo, F. Napolitano
Application and verification of ECMWF products 2009
 Application and verification of ECMWF products 2009 Icelandic Meteorological Office (www.vedur.is) Gu rún Nína Petersen 1. Summary of major highlights Medium range weather forecasts issued at IMO are mainly
Application and verification of ECMWF products 2009 Icelandic Meteorological Office (www.vedur.is) Gu rún Nína Petersen 1. Summary of major highlights Medium range weather forecasts issued at IMO are mainly
Merging Rain-Gauge and Radar Data
 Merging Rain-Gauge and Radar Data Dr Sharon Jewell, Obserations R&D, Met Office, FitzRoy Road, Exeter sharon.jewell@metoffice.gov.uk Outline 1. Introduction The Gauge and radar network Interpolation techniques
Merging Rain-Gauge and Radar Data Dr Sharon Jewell, Obserations R&D, Met Office, FitzRoy Road, Exeter sharon.jewell@metoffice.gov.uk Outline 1. Introduction The Gauge and radar network Interpolation techniques
Application and verification of ECMWF products 2015
 Application and verification of ECMWF products 2015 Instituto Português do Mar e da Atmosfera, I.P. 1. Summary of major highlights At Instituto Português do Mar e da Atmosfera (IPMA) ECMWF products are
Application and verification of ECMWF products 2015 Instituto Português do Mar e da Atmosfera, I.P. 1. Summary of major highlights At Instituto Português do Mar e da Atmosfera (IPMA) ECMWF products are
ERAD THE SIXTH EUROPEAN CONFERENCE ON RADAR IN METEOROLOGY AND HYDROLOGY
 Real-time adjustment of radar data for water management systems using a PDF technique: The City RainNet Project Chris. G. Collier 1, Rod Hawnt 2 and John Powell 2 1. National Centre for Atmospheric Science,
Real-time adjustment of radar data for water management systems using a PDF technique: The City RainNet Project Chris. G. Collier 1, Rod Hawnt 2 and John Powell 2 1. National Centre for Atmospheric Science,
Temperature grid dataset for climate monitoring based on homogeneous time series in Switzerland
 Federal Department of Home Affairs FDHA Federal Office of Meteorology and Climatology MeteoSwiss Temperature grid dataset for climate monitoring based on homogeneous time series in Switzerland F. A. Isotta,
Federal Department of Home Affairs FDHA Federal Office of Meteorology and Climatology MeteoSwiss Temperature grid dataset for climate monitoring based on homogeneous time series in Switzerland F. A. Isotta,
Verification of different wind gust parametrizations Overview of verification results at MeteoSwiss in the year 2012
 Federal Department of Home Affairs FDHA Federal Office of Meteorology and Climatology MeteoSwiss Verification of different wind gust parametrizations Overview of verification results at MeteoSwiss in the
Federal Department of Home Affairs FDHA Federal Office of Meteorology and Climatology MeteoSwiss Verification of different wind gust parametrizations Overview of verification results at MeteoSwiss in the
HEPS. #HEPEX Quebec 2016 UPGRADED METEOROLOGICAL FORCING FOR OPERATIONAL HYDROLOGICAL ENSEMBLE PREDICTIONS: CHALLENGES, RISKS AND CHANCES
 Zappa M, Andres N, Bogner K, Liechti K #HEPEX Quebec 2016 UPGRADED METEOROLOGICAL FORCING FOR OPERATIONAL HYDROLOGICAL ENSEMBLE PREDICTIONS: CHALLENGES, RISKS AND CHANCES HEPS Contact: massimiliano.zappa@wsl.ch
Zappa M, Andres N, Bogner K, Liechti K #HEPEX Quebec 2016 UPGRADED METEOROLOGICAL FORCING FOR OPERATIONAL HYDROLOGICAL ENSEMBLE PREDICTIONS: CHALLENGES, RISKS AND CHANCES HEPS Contact: massimiliano.zappa@wsl.ch
ERAD THE EIGHTH EUROPEAN CONFERENCE ON RADAR IN METEOROLOGY AND HYDROLOGY
 High-resolution X-band polarimetric radar Observations during the HyMeX 2012 Special Observation Period in North-East Italian Alpine Region: Evaluating hydrologic impacts Anagnostou M. N. 1*, Nikolopoulos
High-resolution X-band polarimetric radar Observations during the HyMeX 2012 Special Observation Period in North-East Italian Alpine Region: Evaluating hydrologic impacts Anagnostou M. N. 1*, Nikolopoulos
MAIN ATTRIBUTES OF THE PRECIPITATION PRODUCTS DEVELOPED BY THE HYDROLOGY SAF PROJECT RESULTS OF THE VALIDATION IN HUNGARY
 MAIN ATTRIBUTES OF THE PRECIPITATION PRODUCTS DEVELOPED BY THE HYDROLOGY SAF PROJECT RESULTS OF THE VALIDATION IN HUNGARY Eszter Lábó OMSZ-Hungarian Meteorological Service, Budapest, Hungary labo.e@met.hu
MAIN ATTRIBUTES OF THE PRECIPITATION PRODUCTS DEVELOPED BY THE HYDROLOGY SAF PROJECT RESULTS OF THE VALIDATION IN HUNGARY Eszter Lábó OMSZ-Hungarian Meteorological Service, Budapest, Hungary labo.e@met.hu
The Radar Quality Control and Quantitative Precipitation Estimation Intercomparison Project. RQQI (pronounced Rickey)
 The Radar Quality Control and Quantitative Precipitation Estimation Intercomparison Project RQQI (pronounced Rickey) Paul Joe and Alan Seed Environment Canada Centre for Australian Weather and Climate
The Radar Quality Control and Quantitative Precipitation Estimation Intercomparison Project RQQI (pronounced Rickey) Paul Joe and Alan Seed Environment Canada Centre for Australian Weather and Climate
2.14 NOWCASTING THUNDERSTORMS IN COMPLEX CASES USING RADAR DATA
 2.14 NOWCASTING THUNDERSTORMS IN COMPLEX CASES USING RADAR DATA Alessandro M. Hering* 1, Stéphane Sénési 2, Paolo Ambrosetti 1, and Isabelle Bernard-Bouissières 2 1 MeteoSwiss, ML, Locarno-Monti, Switzerland
2.14 NOWCASTING THUNDERSTORMS IN COMPLEX CASES USING RADAR DATA Alessandro M. Hering* 1, Stéphane Sénési 2, Paolo Ambrosetti 1, and Isabelle Bernard-Bouissières 2 1 MeteoSwiss, ML, Locarno-Monti, Switzerland
DETECTION AND FORECASTING - THE CZECH EXPERIENCE
 1 STORM RAINFALL DETECTION AND FORECASTING - THE CZECH EXPERIENCE J. Danhelka * Czech Hydrometeorological Institute, Prague, Czech Republic Abstract Contribution presents the state of the art of operational
1 STORM RAINFALL DETECTION AND FORECASTING - THE CZECH EXPERIENCE J. Danhelka * Czech Hydrometeorological Institute, Prague, Czech Republic Abstract Contribution presents the state of the art of operational
QualiMET 2.0. The new Quality Control System of Deutscher Wetterdienst
 QualiMET 2.0 The new Quality Control System of Deutscher Wetterdienst Reinhard Spengler Deutscher Wetterdienst Department Observing Networks and Data Quality Assurance of Meteorological Data Michendorfer
QualiMET 2.0 The new Quality Control System of Deutscher Wetterdienst Reinhard Spengler Deutscher Wetterdienst Department Observing Networks and Data Quality Assurance of Meteorological Data Michendorfer
Imke Durre * and Matthew J. Menne NOAA National Climatic Data Center, Asheville, North Carolina 2. METHODS
 9.7 RADAR-TO-GAUGE COMPARISON OF PRECIPITATION TOTALS: IMPLICATIONS FOR QUALITY CONTROL Imke Durre * and Matthew J. Menne NOAA National Climatic Data Center, Asheville, North Carolina 1. INTRODUCTION Comparisons
9.7 RADAR-TO-GAUGE COMPARISON OF PRECIPITATION TOTALS: IMPLICATIONS FOR QUALITY CONTROL Imke Durre * and Matthew J. Menne NOAA National Climatic Data Center, Asheville, North Carolina 1. INTRODUCTION Comparisons
ERAD Challenges for precipitation estimation in mountainous regions. Proceedings of ERAD (2002): c Copernicus GmbH 2002
 Proceedings of ERAD (2002): 250 254 c Copernicus GmbH 2002 ERAD 2002 Challenges for precipitation estimation in mountainous regions U. Gjertsen and J. I. Dahl Norwegian Meteorological Institute, Research
Proceedings of ERAD (2002): 250 254 c Copernicus GmbH 2002 ERAD 2002 Challenges for precipitation estimation in mountainous regions U. Gjertsen and J. I. Dahl Norwegian Meteorological Institute, Research
Model Output Statistics (MOS)
 Model Output Statistics (MOS) Numerical Weather Prediction (NWP) models calculate the future state of the atmosphere at certain points of time (forecasts). The calculation of these forecasts is based on
Model Output Statistics (MOS) Numerical Weather Prediction (NWP) models calculate the future state of the atmosphere at certain points of time (forecasts). The calculation of these forecasts is based on
Multi-Sensor Precipitation Reanalysis
 Multi-Sensor Precipitation Reanalysis Brian R. Nelson, Dongsoo Kim, and John J. Bates NOAA National Climatic Data Center, Asheville, North Carolina D.J. Seo NOAA NWS Office of Hydrologic Development, Silver
Multi-Sensor Precipitation Reanalysis Brian R. Nelson, Dongsoo Kim, and John J. Bates NOAA National Climatic Data Center, Asheville, North Carolina D.J. Seo NOAA NWS Office of Hydrologic Development, Silver
Archival precipitation data set for the Mississippi River Basin: Evaluation
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 32, L18403, doi:10.1029/2005gl023334, 2005 Archival precipitation data set for the Mississippi River Basin: Evaluation Brian R. Nelson, 1,2 Witold F. Krajewski, 1 James
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 32, L18403, doi:10.1029/2005gl023334, 2005 Archival precipitation data set for the Mississippi River Basin: Evaluation Brian R. Nelson, 1,2 Witold F. Krajewski, 1 James
Assessment of Ensemble Forecasts
 Assessment of Ensemble Forecasts S. L. Mullen Univ. of Arizona HEPEX Workshop, 7 March 2004 Talk Overview Ensemble Performance for Precipitation Global EPS and Mesoscale 12 km RSM Biases, Event Discrimination
Assessment of Ensemble Forecasts S. L. Mullen Univ. of Arizona HEPEX Workshop, 7 March 2004 Talk Overview Ensemble Performance for Precipitation Global EPS and Mesoscale 12 km RSM Biases, Event Discrimination
Improved radar QPE with temporal interpolation using an advection scheme
 Improved radar QPE with temporal interpolation using an advection scheme Alrun Jasper-Tönnies 1 and Markus Jessen 1 1 hydro & meteo GmbH & Co, KG, Breite Str. 6-8, 23552 Lübeck, Germany (Dated: 18 July
Improved radar QPE with temporal interpolation using an advection scheme Alrun Jasper-Tönnies 1 and Markus Jessen 1 1 hydro & meteo GmbH & Co, KG, Breite Str. 6-8, 23552 Lübeck, Germany (Dated: 18 July
Heavier summer downpours with climate change revealed by weather forecast resolution model
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE2258 Heavier summer downpours with climate change revealed by weather forecast resolution model Number of files = 1 File #1 filename: kendon14supp.pdf File
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE2258 Heavier summer downpours with climate change revealed by weather forecast resolution model Number of files = 1 File #1 filename: kendon14supp.pdf File
Regional climate modelling in the future. Ralf Döscher, SMHI, Sweden
 Regional climate modelling in the future Ralf Döscher, SMHI, Sweden The chain Global H E H E C ( m 3/s ) Regional downscaling 120 adam 3 C HAM 4 adam 3 C HAM 4 trl A2 A2 B2 B2 80 40 0 J F M A M J J A S
Regional climate modelling in the future Ralf Döscher, SMHI, Sweden The chain Global H E H E C ( m 3/s ) Regional downscaling 120 adam 3 C HAM 4 adam 3 C HAM 4 trl A2 A2 B2 B2 80 40 0 J F M A M J J A S
The Impact of Horizontal Resolution and Ensemble Size on Probabilistic Forecasts of Precipitation by the ECMWF EPS
 The Impact of Horizontal Resolution and Ensemble Size on Probabilistic Forecasts of Precipitation by the ECMWF EPS S. L. Mullen Univ. of Arizona R. Buizza ECMWF University of Wisconsin Predictability Workshop,
The Impact of Horizontal Resolution and Ensemble Size on Probabilistic Forecasts of Precipitation by the ECMWF EPS S. L. Mullen Univ. of Arizona R. Buizza ECMWF University of Wisconsin Predictability Workshop,
2.12 Inter-Comparison of Real-Time Rain Gage and Radar-Estimated Rainfall on a Monthly Basis for Midwestern United States Counties
 2.12 Inter-Comparison of Real-Time Rain and -Estimated Rainfall on a Monthly Basis for Midwestern United States Counties Nancy Westcott* and Kenneth E. Kunkel Illinois State Water Survey Champaign, Illinois
2.12 Inter-Comparison of Real-Time Rain and -Estimated Rainfall on a Monthly Basis for Midwestern United States Counties Nancy Westcott* and Kenneth E. Kunkel Illinois State Water Survey Champaign, Illinois
ABSTRACT 3 RADIAL VELOCITY ASSIMILATION IN BJRUC 3.1 ASSIMILATION STRATEGY OF RADIAL
 REAL-TIME RADAR RADIAL VELOCITY ASSIMILATION EXPERIMENTS IN A PRE-OPERATIONAL FRAMEWORK IN NORTH CHINA Min Chen 1 Ming-xuan Chen 1 Shui-yong Fan 1 Hong-li Wang 2 Jenny Sun 2 1 Institute of Urban Meteorology,
REAL-TIME RADAR RADIAL VELOCITY ASSIMILATION EXPERIMENTS IN A PRE-OPERATIONAL FRAMEWORK IN NORTH CHINA Min Chen 1 Ming-xuan Chen 1 Shui-yong Fan 1 Hong-li Wang 2 Jenny Sun 2 1 Institute of Urban Meteorology,
*Corresponding author address: Charles Barrere, Weather Decision Technologies, 1818 W Lindsey St, Norman, OK
 P13R.11 Hydrometeorological Decision Support System for the Lower Colorado River Authority *Charles A. Barrere, Jr. 1, Michael D. Eilts 1, and Beth Clarke 2 1 Weather Decision Technologies, Inc. Norman,
P13R.11 Hydrometeorological Decision Support System for the Lower Colorado River Authority *Charles A. Barrere, Jr. 1, Michael D. Eilts 1, and Beth Clarke 2 1 Weather Decision Technologies, Inc. Norman,
Application and verification of ECMWF products 2011
 Application and verification of ECMWF products 2011 Icelandic Meteorological Office (www.vedur.is) Guðrún Nína Petersen 1. Summary of major highlights Medium range weather forecasts issued at IMO are mainly
Application and verification of ECMWF products 2011 Icelandic Meteorological Office (www.vedur.is) Guðrún Nína Petersen 1. Summary of major highlights Medium range weather forecasts issued at IMO are mainly
120 ASSESMENT OF MULTISENSOR QUANTITATIVE PRECIPITATION ESTIMATION IN THE RUSSIAN RIVER BASIN
 120 ASSESMENT OF MULTISENSOR QUANTITATIVE PRECIPITATION ESTIMATION IN THE RUSSIAN RIVER BASIN 1 Delbert Willie *, 1 Haonan Chen, 1 V. Chandrasekar 2 Robert Cifelli, 3 Carroll Campbell 3 David Reynolds
120 ASSESMENT OF MULTISENSOR QUANTITATIVE PRECIPITATION ESTIMATION IN THE RUSSIAN RIVER BASIN 1 Delbert Willie *, 1 Haonan Chen, 1 V. Chandrasekar 2 Robert Cifelli, 3 Carroll Campbell 3 David Reynolds
Upscaled and fuzzy probabilistic forecasts: verification results
 4 Predictability and Ensemble Methods 124 Upscaled and fuzzy probabilistic forecasts: verification results Zied Ben Bouallègue Deutscher Wetterdienst (DWD), Frankfurter Str. 135, 63067 Offenbach, Germany
4 Predictability and Ensemble Methods 124 Upscaled and fuzzy probabilistic forecasts: verification results Zied Ben Bouallègue Deutscher Wetterdienst (DWD), Frankfurter Str. 135, 63067 Offenbach, Germany
RADAR RAINFALL ESTIMATION ASSESSMENT FOR HEAVY RAINFALL EVENTS
 RADAR RAINFALL ESTIMATION ASSESSMENT FOR HEAVY RAINFALL EVENTS Fabrizio Tonelli, Marco Borga 2, Mauro Tollardo 3 and Marta Pendesini 4 Department of Land and Agroforest Environments, AGRIPOLIS, University
RADAR RAINFALL ESTIMATION ASSESSMENT FOR HEAVY RAINFALL EVENTS Fabrizio Tonelli, Marco Borga 2, Mauro Tollardo 3 and Marta Pendesini 4 Department of Land and Agroforest Environments, AGRIPOLIS, University
Toward the new CH2018 climate scenarios for Switzerland
 Federal Department of Home Affairs FDHA Federal Office of Meteorology and Climatology MeteoSwiss Toward the new CH2018 climate scenarios for Switzerland Andreas Fischer, Abteilung Klima, MeteoSchweiz Elias
Federal Department of Home Affairs FDHA Federal Office of Meteorology and Climatology MeteoSwiss Toward the new CH2018 climate scenarios for Switzerland Andreas Fischer, Abteilung Klima, MeteoSchweiz Elias
APPENDIX 2 OVERVIEW OF THE GLOBAL PRECIPITATION MEASUREMENT (GPM) AND THE TROPICAL RAINFALL MEASURING MISSION (TRMM) 2-1
 APPENDIX 2 OVERVIEW OF THE GLOBAL PRECIPITATION MEASUREMENT (GPM) AND THE TROPICAL RAINFALL MEASURING MISSION (TRMM) 2-1 1. Introduction Precipitation is one of most important environmental parameters.
APPENDIX 2 OVERVIEW OF THE GLOBAL PRECIPITATION MEASUREMENT (GPM) AND THE TROPICAL RAINFALL MEASURING MISSION (TRMM) 2-1 1. Introduction Precipitation is one of most important environmental parameters.
Hailstorms evidence from smart-phone users:
 Hailstorms evidence from smart-phone users: Crowd-sourced hail size data over Switzerland Noti Pascal A. Martynov, A. Hering, and O. Martius Bern 21.04.2017 Motivation & Objectives > Is crowd-sourcing
Hailstorms evidence from smart-phone users: Crowd-sourced hail size data over Switzerland Noti Pascal A. Martynov, A. Hering, and O. Martius Bern 21.04.2017 Motivation & Objectives > Is crowd-sourcing
Representing radar rainfall uncertainty with ensembles based on a time-variant geostatistical error modelling approach
 Representing radar rainfall uncertainty with ensembles based on a time-variant geostatistical error modelling approach Bristol, 4 th March 2016 Francesca Cecinati Background M.Eng. Environmental and Water
Representing radar rainfall uncertainty with ensembles based on a time-variant geostatistical error modelling approach Bristol, 4 th March 2016 Francesca Cecinati Background M.Eng. Environmental and Water
An Overview of Operations at the West Gulf River Forecast Center Gregory Waller Service Coordination Hydrologist NWS - West Gulf River Forecast Center
 National Weather Service West Gulf River Forecast Center An Overview of Operations at the West Gulf River Forecast Center Gregory Waller Service Coordination Hydrologist NWS - West Gulf River Forecast
National Weather Service West Gulf River Forecast Center An Overview of Operations at the West Gulf River Forecast Center Gregory Waller Service Coordination Hydrologist NWS - West Gulf River Forecast
2009 Progress Report To The National Aeronautics and Space Administration NASA Energy and Water Cycle Study (NEWS) Program
 2009 Progress Report To The National Aeronautics and Space Administration NASA Energy and Water Cycle Study (NEWS) Program Proposal Title: Grant Number: PI: The Challenges of Utilizing Satellite Precipitation
2009 Progress Report To The National Aeronautics and Space Administration NASA Energy and Water Cycle Study (NEWS) Program Proposal Title: Grant Number: PI: The Challenges of Utilizing Satellite Precipitation
Enhancing Weather Information with Probability Forecasts. An Information Statement of the American Meteorological Society
 Enhancing Weather Information with Probability Forecasts An Information Statement of the American Meteorological Society (Adopted by AMS Council on 12 May 2008) Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 89 Summary This
Enhancing Weather Information with Probability Forecasts An Information Statement of the American Meteorological Society (Adopted by AMS Council on 12 May 2008) Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 89 Summary This
Comparison of Interpolation Methods for Precipitation Data in a mountainous Region (Upper Indus Basin-UIB)
 Comparison of Interpolation Methods for Precipitation Data in a mountainous Region (Upper Indus Basin-UIB) AsimJahangir Khan, Doctoral Candidate, Department of Geohydraulicsand Engineering Hydrology, University
Comparison of Interpolation Methods for Precipitation Data in a mountainous Region (Upper Indus Basin-UIB) AsimJahangir Khan, Doctoral Candidate, Department of Geohydraulicsand Engineering Hydrology, University
Measurements of a network of mobile radars during the experimental campaign of the HydroRad project
 ERAD 2012 - THE SEVENTH EUROPEAN CONFERENCE ON RADAR IN METEOROLOGY AND HYDROLOGY Measurements of a network of mobile radars during the experimental campaign of the HydroRad project Kalogiros J. 1, Anagnostou
ERAD 2012 - THE SEVENTH EUROPEAN CONFERENCE ON RADAR IN METEOROLOGY AND HYDROLOGY Measurements of a network of mobile radars during the experimental campaign of the HydroRad project Kalogiros J. 1, Anagnostou
Added Value of Convection Resolving Climate Simulations (CRCS)
 Added Value of Convection Resolving Climate Simulations (CRCS) Prein Andreas, Gobiet Andreas, Katrin Lisa Kapper, Martin Suklitsch, Nauman Khurshid Awan, Heimo Truhetz Wegener Center for Climate and Global
Added Value of Convection Resolving Climate Simulations (CRCS) Prein Andreas, Gobiet Andreas, Katrin Lisa Kapper, Martin Suklitsch, Nauman Khurshid Awan, Heimo Truhetz Wegener Center for Climate and Global
CLIMATE CHANGE ADAPTATION BY MEANS OF PUBLIC PRIVATE PARTNERSHIP TO ESTABLISH EARLY WARNING SYSTEM
 CLIMATE CHANGE ADAPTATION BY MEANS OF PUBLIC PRIVATE PARTNERSHIP TO ESTABLISH EARLY WARNING SYSTEM By: Dr Mamadou Lamine BAH, National Director Direction Nationale de la Meteorologie (DNM), Guinea President,
CLIMATE CHANGE ADAPTATION BY MEANS OF PUBLIC PRIVATE PARTNERSHIP TO ESTABLISH EARLY WARNING SYSTEM By: Dr Mamadou Lamine BAH, National Director Direction Nationale de la Meteorologie (DNM), Guinea President,
Precipitation verification. Thanks to CMC, CPTEC, DWD, ECMWF, JMA, MF, NCEP, NRL, RHMC, UKMO
 Precipitation verification Thanks to CMC, CPTEC, DWD, ECMWF, JMA, MF, NCEP, NRL, RHMC, UKMO Outline 1) Status of WGNE QPF intercomparisons 2) Overview of the use of recommended methods for the verification
Precipitation verification Thanks to CMC, CPTEC, DWD, ECMWF, JMA, MF, NCEP, NRL, RHMC, UKMO Outline 1) Status of WGNE QPF intercomparisons 2) Overview of the use of recommended methods for the verification
Application and verification of the ECMWF products Report 2007
 Application and verification of the ECMWF products Report 2007 National Meteorological Administration Romania 1. Summary of major highlights The medium range forecast activity within the National Meteorological
Application and verification of the ECMWF products Report 2007 National Meteorological Administration Romania 1. Summary of major highlights The medium range forecast activity within the National Meteorological
Analysis of radar and gauge rainfall during the warm season in Oklahoma
 Analysis of radar and gauge rainfall during the warm season in Oklahoma Bin Wang 1, Jian Zhang 2, Wenwu Xia 2, Kenneth Howard 3, and Xiaoyong Xu 2 1 Wuhan Institute of Heavy Rain, China Meteorological
Analysis of radar and gauge rainfall during the warm season in Oklahoma Bin Wang 1, Jian Zhang 2, Wenwu Xia 2, Kenneth Howard 3, and Xiaoyong Xu 2 1 Wuhan Institute of Heavy Rain, China Meteorological
At the start of the talk will be a trivia question. Be prepared to write your answer.
 Operational hydrometeorological forecasting activities of the Australian Bureau of Meteorology Thomas Pagano At the start of the talk will be a trivia question. Be prepared to write your answer. http://scottbridle.com/
Operational hydrometeorological forecasting activities of the Australian Bureau of Meteorology Thomas Pagano At the start of the talk will be a trivia question. Be prepared to write your answer. http://scottbridle.com/
University of Bristol - Explore Bristol Research
 Fadhel, S., Rico-Ramirez, M., & Han, D. (2017). Exploration of an adaptive merging scheme for optimal precipitation estimation over ungauged urban catchment. Journal of Hydroinformatics, 19(2), 225-237.
Fadhel, S., Rico-Ramirez, M., & Han, D. (2017). Exploration of an adaptive merging scheme for optimal precipitation estimation over ungauged urban catchment. Journal of Hydroinformatics, 19(2), 225-237.
Operational quantitative precipitation estimation using radar, gauge g and
 Operational quantitative precipitation estimation using radar, gauge g and satellite for hydrometeorological applications in Southern Brazil Leonardo Calvetti¹, Cesar Beneti¹, Diogo Stringari¹, i¹ Alex
Operational quantitative precipitation estimation using radar, gauge g and satellite for hydrometeorological applications in Southern Brazil Leonardo Calvetti¹, Cesar Beneti¹, Diogo Stringari¹, i¹ Alex
Some examples on the use of radar observations for the verification of NWP models in the Alpine region
 Proceedings of ERAD (2004): 509 515 c Copernicus GmbH 2004 ERAD 2004 Some examples on the use of radar observations for the verification of NWP models in the Alpine region M. Gabella, V. Calvia, and G.
Proceedings of ERAD (2004): 509 515 c Copernicus GmbH 2004 ERAD 2004 Some examples on the use of radar observations for the verification of NWP models in the Alpine region M. Gabella, V. Calvia, and G.
ERAD Comparing data from radar, rain gauges and a NWP model. Proceedings of ERAD (2002): c Copernicus GmbH 2002
 Proceedings of ERAD (2002): 422 427 c Copernicus GmbH 2002 ERAD 2002 Comparing data from radar, rain gauges and a NWP model M. Gabella 1, G. Galli 2, J. Joss 3, and G. Perona 1 1 Politecnico di Torino,
Proceedings of ERAD (2002): 422 427 c Copernicus GmbH 2002 ERAD 2002 Comparing data from radar, rain gauges and a NWP model M. Gabella 1, G. Galli 2, J. Joss 3, and G. Perona 1 1 Politecnico di Torino,
Regional Flash Flood Guidance and Early Warning System
 WMO Training for Trainers Workshop on Integrated approach to flash flood and flood risk management 24-28 October 2010 Kathmandu, Nepal Regional Flash Flood Guidance and Early Warning System Dr. W. E. Grabs
WMO Training for Trainers Workshop on Integrated approach to flash flood and flood risk management 24-28 October 2010 Kathmandu, Nepal Regional Flash Flood Guidance and Early Warning System Dr. W. E. Grabs
Combining Deterministic and Probabilistic Methods to Produce Gridded Climatologies
 Combining Deterministic and Probabilistic Methods to Produce Gridded Climatologies Michael Squires Alan McNab National Climatic Data Center (NCDC - NOAA) Asheville, NC Abstract There are nearly 8,000 sites
Combining Deterministic and Probabilistic Methods to Produce Gridded Climatologies Michael Squires Alan McNab National Climatic Data Center (NCDC - NOAA) Asheville, NC Abstract There are nearly 8,000 sites
