Pre-Construction Progress of Giant Steerable Science Mirror for TMT
|
|
|
- Laura Blair
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Pre-Construction Progress of Giant Steerable Science Mirror for TMT Yang Fei *1, Zhao Hongchao 1, An Qichang 1, Guo Peng 1,Jiang Haibo 1, Han Linchu 1, Virginia Ford 2, Glen Cole 2, Byron Smith 3, Marvin Campbell 4 1.Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Changchun , China 2. Thirty Meter Telescope International Organization, Pasadena, CA, USA 3. XDoubleDout LLC, Flagstaff, AZ, USA 4. MF Campbell Consulting, Garland, TX, USA ABSTRACT The Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics (CIOMP) team is developing the Giant Steerable Science Mirror (GSSM) for Thirty Meter Telescope (TMT) which will enter the preliminary design phase in The GSSM is the tertiary mirror of TMT and consists of the world s largest flat telescope mirror (approximately 3.4m X 2.4 m X 100mm thick) having an elliptical perimeter positioned with an extremely smooth tracking and pointing mechanism in a gravity-varying environment. In order to prepare for developing this unique mirror system, CIOMP has been developing a 1/4 scale, functionally accurate version of the GSSM prototype during the pre-construction phase of GSSM. The prototype will incorporate the same optomechanical system and servo control system as the GSSM. The size of the prototype mirror is 898.5mm 634mm 12.5mm with an elliptical perimeter. The mirror will be supported axially by an 18 point whiffletree and laterally with a 12 point whiffletree. The main objective of the preconstruction phase includes requirement validation and risk reduction for GSSM and to increase confidence that the challenge of developing the GSSM can be met. The precision mechanism system and the optical mirror polishing and testing have made good progress. CIOMP has completed polishing the mirror, the prototype mechanism is nearly assembled, some testing has been performed, and additional testing is being planned and prepared. A dummy mirror is being integrated into the cell assembly prototype to verify the design, analysis and interface and will be used when testing the prototype positioner tilt and rotation motions. The prototype positioner tilt and rotator structures have been assembled and tested to measure each subsystem s jitter and dynamic motion. The mirror prototype has been polished and tested to verify the polishing specification requirement and the mirror manufacturing process. The complete assembly, integration and verification of the prototype will be soon finished. Final testing will verify the prototype requirements including mounted mirror surface figure accuracy in 5 different orientations; rotation and tilt motion calibration and pointing precision; motion jitter; and internally generated vibrations. CIOMP has scheduled to complete the prototype by the end of July CIOMP will get the sufficient test results during the pre-construction phase to prepare to enter the preliminary design for GSSM. Keywords: Giant Steerable Science Mirror, Prototype of GSSM, TMT, Large Aperture Telescope 1. INTRODUCTION TMT (Thirty Meter Telescope) will be one of the largest ground-based telescopes including E-ELT (Europe Extremely Large Telescope) and GMT (Giant Magellan Telescope). All three telescopes will have 30 meter class apertures-larger than any existing optical telescopes in the world so far. Each large telescope has unique features. In the case of TMT, the * yangf@ciomp.ac.cn Ground-based and Airborne Telescopes VI, edited by Helen J. Hall, Roberto Gilmozzi, Heather K. Marshall, Proc. of SPIE Vol. 9906, 99064M 2016 SPIE CCC code: X/16/$18 doi: / Proc. of SPIE Vol M-1
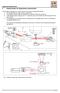
2 tertiary mirror has the function of relaying the optical beam from secondary mirror to science instruments that are located on Nasmyth platforms that rotate in azimuth with the telescope, but do not tilt in elevation with it. This architecture places stability and precision requirements on the GSSM that are unprecedented considering the large geometrical size of the nearly 4 meter class optic. The tertiary mirror of TMT is called GSSM (Giant Steerable Science Mirror) because this architecture enables many science advantages such as rapid switching between instruments to allow observing transient phenomenon quickly and by multiple instruments. The GSSM is mounted on a support tower that protrudes through the central hole of primary mirror. Figure 1 shows the GSSM location in the TMT. Figure 2 shows the scheme of GSSM. Instruments Secondary Mirror (M2) Tertiary Mirror (GSSM) Primary Mirror (M1) Instruments Figure 1. The location of GSSM in TMT Proc. of SPIE Vol M-2
3 MIRROR SUPPORT STRUCTURE CELL MIRROR ORIGIN (CENTER OF TILT AND ROTATION) TILT CRADLE MIRROR ORIGIN MIRROR BAFFLE M3 CELL ASSEMBLY M3 POSITIONER ASSEMBLY INTERFACE TO TELESCOPE REPEATABLE INTERFACE HARDWARE ROTATION GIMBAL POSITIONER BASE CABLE WRAP Figure 2. Scheme and configuration of GSSM 2. DESIGN OF GIANT STEERABLE SCIENCE MIRROR PROTOTYPE 2.1Design of Prototype Cell Assembly (CAP) Many support methods were investigated for the Cell Assembly (M3CA) of the GSSM [2]. The active support system was employed at first, in which 60 axial actuators supported the tertiary mirror. But it is difficult to decouple GSSM active optics system and M1 s. In the end, the active support system was abandoned. Then an 18-point whiffletree system was developed to support the mirror axially, with a 12-point whiffletree system acting as the lateral support. The mirror cell assembly concept design was approved in May 2013, and the concept will be verified in the GSSMP system. Detail design (Figure 3) of the GSSMP CAP was completed in Figure 3.The Detailed Design of M3CAP 2.2 Design of Prototype Positioner Assembly (PAP) The Positioner Assembly (M3PA) is the subsystem of the GSSM which rotates and tilts them3 Cell Assembly to point the telescope beam towards any selected instrument on either Nasmyth Platform during observing [1][7]. This subassembly is responsible for all rigid body motion of the M3 Cell Assembly (M3CA). TheM3PA also rotates and tilts the M3CA to enable servicing and maintenance functions on the Telescope. M3PAP is a prototype model of the M3PA. It has the same Proc. of SPIE Vol M-3
4 function as the M3PA. There are two subassemblies in the PAP including of a Rotator and a Tilt Assembly. The Rotator axis is a challenging subassembly [6]. The angle between the Rotator axis and the gravity varies from 0 to 90. Then the working conditions require that the Rotator axis supports the axial load, lateral load and the tilting moment. This is a challenge to the designer. Three drive solutions were investigated for Rotator drive system. They were direct drive, gear transmission and frictional roller transmission. We chose the direct drive for the M3PAP. The final design of the Rotator structure is illustrated in Figure 4. Figure 4.Cross section view of M3PAP Rotator Due to the volume requirement of GSSM to stay within the obscuration shadow of the M2, the Tilt Assembly needs a compact design [3]. In addition, the angle between the Tilt axis and the gravity varies from 0 to 90. Thus the Tilt axis must withstand the combination load. There are four key components in Tilt Assembly. They are a turntable, a set of axes, a cradle, and the interface with the M3CAP. The turntable is a plate welded structure, while the cradle is a welded truss. The tilt axes are hollow forgings with inner diameters large enough for to contain direct drive motor systems. The Tilt Assembly design details are illustrated in Figure 5. Figure 5. Cross section of the tilt structure Static analysis and modal analysis were carried out to evaluate M3PAP performance. The structure has been constructed in ANSYS (figure 6). And the other non-structure components are represented by mass-points. Proc. of SPIE Vol M-4
5 F_F71.1> Figure 6. FE Model and 3-D model Table.1 Modal analysis results 1Yi1`:1] Modal frequency Hz Modal shape Modal frequency Hz Modal shape Sway in x direction Cradle bending and yoke bending Rotate about z direction Too complex Sway in y direction Cradle rotates about x axis Two arms bend in opposite Too complex direction along x axis Complex modal shape combined by tilt and sway in y direction Cradle deformation After 4 months fabrication, all the parts were received. Assembly phase started at the beginning of PROGRESS OF GSSMP 3.1 CAP progress As shown in figure 7, axial pads were glued onto the dummy-mirror in April A laser tracker was used to assist the process. The location error was controlled to less than 0.1 mm. Figure 7. Axial pads in place Proc. of SPIE Vol M-5
6 Figure 8. Axial whiffletree installed Then the designers installed the axial whiffletree structure onto the mirror cell. Using the advantage of the mobile coordinate measuring machine, the accuracy of the 18 axial support points was within 1mm as shown in figure 8. The final assembly of the axial whiffletree mirror support on the Cell structure is shown in Figure Mirror Prototype progress The mirror prototype was polished to meet a of SlopeRMS less than 1 µradian on the polishing support structure. The result of the mirror surface accuracy measured with an on-site subaperture Fizeau interferometer and using sub-aperture stitching technology is shown in figure 9. - Figure 9. Phasemap of M3MP after polish (low order error removed) In addition, to measure low order polished mirror error, a scanning pentaprism assembly was developed and used to measure focus and astigmatism of the resulting mirror surface. A photograph of the scanning pentaprism equipment is shown in Figure 10. The mirror easily met its low order requirement. Proc. of SPIE Vol M-6
7 Figure 10. Scanning pentaprism equipment for M3MP 3.3 PAP progress The wobble of the Rotator has been measured to be 1.6 arcseconds after removing the first order component that the TMT telescope is able to filter out. The measure curves can be found in figure 11. TIP /ARCSEC WOBBLE OF THE ROTATOR AXIS ANGLE /DEG raw data The first order component removed Figure 11. Rotator axis wobble measurement and result Proc. of SPIE Vol M-7
8 TIP /arcsec WOBBLE OF TITL AXIS ANGLE /deg the first order component removed Raw data Figure 12. Wobble measurement of Tilt axis and results A same process was used on the tilt axis. Fortunately, both of the two axes performances meet requirements. The testing data can be found in figure 12. In order to ensure the performance of GSSMP, some dynamic tests about the key components have been done. Take the cradle as an example. An impact test was carried out with the cradle suspended. The response can be found in figure 13. The test result is consistent with the FEA. And the first modal frequency is about 78 Hz. P,,,A X =Ink)...P.i D Ord 53 OS in Name -'Mode 3:76.031HL0A7A -.Mode 2:1106S0H ? = Mode 3: Hi. 1, Mode 4: H; 013'n if Ht Stable N `=11,11=9:=2:1==1===========n111111V.yW%I LMS test.lat, Figure 13. Impact test of the Cradle The yoke was supported on an isolating foam pad and measured. An accelerometer was bonded tothe yoke to show the characteristics motion of the yoke. The test result is consistent with the FEA. And the first modal frequency is about 241 Hz. Proc. of SPIE Vol M-8
9 foam acclerom ëiër oa Figure 14. Impact test of the Yoke The assembled Tilt Assembly is shown in figure 15. There are two tilt axis spindles, a cradle which contains the two spindles that integrate the whole assembly. Due to the mass imbalance of the mirror cell assembly, lead counterweights are installed on the two cradle arms to balance the tilt axis. Figure 15.Tilt axis has been completed 4TESTING PLANNING 4.1 Mirror surface figure test The polished mirror surface figure has been measured in the face up configuration resting on a specially designed test support that duplicates the configuration of the Cell Assembly axial support. In order to determine the influence of the Cell Assembly support on the mirror surface, testing will be performed with the mirror mounted to the Cell Assembly Proc. of SPIE Vol M-9
10 in 5 gravity orientations. The same interferometer set-up that was used to measure the face up configuration will be used to measure the mounted mirror surface. A horizontally oriented 24 ZYGO interferometer will be used for the other four orientations which are horizontal. A test fixture to hold and align the mounted mirror has been designed. This fixture is still being fabricated; but a CAD model is shown in Figure 16. It can translate the CAP in two directions and can tip/tilt the CAP to collimate with the 24 ZYGO interferometer. The weight of the CAP is counterbalanced, so there equipment has locks for safety while the CAP is installed or removed. Also, there will be mark along the guide to monitor the location of the CAP. Figure 16. The sketch of the testing fixture I-x Figure 17.Arrangement of sub-aperture for optical testing and the location of the mark (dark spot) 4.2 Calibration and motion test Pointing precision of the CAP will be measured using a Laser Tracker [4][5]. Spherically Mounted Retroreflectors (SMRs) will be mounted to a dummy mirror mounted on the Cell Assembly which reflect the laser beam back to its source from any direction. Mounting hardware for the SMRs are shown in figure 18. The repeatability accuracy of this facility has been measured to be is less than 10 µm in the lab with controlled temperature of Proc. of SPIE Vol M-10
11 Figure 18. The interface of the laser tracker During the calibration testing, the GSSMP will be located on a flat testing base, then raised and located on a tilted testing base to understand the influence of gravity. The interface between the GSSMP and the testing base consists of a kinematic arrangement of ball-cone, ball-groove and ball-plane, as shown in Figure 19. As the GSSMP is lowered by crane onto the interface, two guide rods are used to help turn around about the interface 1,the interface2 will be firmly attached then, as shown on the right side. The last interface to be fastened will be interface 3. Interfacel Balll-Cone Interface2 Ba112-Grove Interfacel Ballt -Cone Interface2 Ba112-Grove Interface3 Ba113-Plane Interface3 Ba113-Plane Figure 19. The Kinemics Interface (left) and the Assemble of the Interface(right) In order to calibrate the motion, laser tracker measurements of the actual mirror position will be made at 1 degree increments that step through the rotation and tilt ranges of motion. The resulting data will be used to create look-up tables that calibrate actual position to encoder readings. After calibration is performed, then the required motions will be measured using calibrated encoder readings to measure velocity, step size and settling time, and jitter. 4.3 Vibration testing Modal testing The test objective is to validate the FEA results and revise the CAD model according to the following procedure, 1. The dummy mirror will be used in this test 2. The accelerometers will be located as follows: Proc. of SPIE Vol M-11
12 - 4 on the dummy mirror - 3 on the CAP - 2 on the Yoke - 1 on the rotation table - 3 at the interface to the mount fixture There are two kinds of accelerometers. One has only one axis, and the other can measure acceleration in three directions. There are screw holes in the dummy mirror for the location of the accelerometers. I. AO. screw hole fole acclerometers Figure 20. The allocation of the accelerometer for the GSSMP 1 D O F 3 DOF 13.% `. Z-DOF =DOF Z- OF14 Figure 21. The types and orders of accelerometers on the GSSMP 3. The set-up for the hammer test is the GSSMP mounted to an isolation stand. The sensor cables are attached to the GSSMP with soft plastic foam to prevent parasitic vibrations. 4. The next step is to impact the GSSMP with hammer using the following sequence: a) Impact close to the accelerometer at point 1. b) Remove the accelerometer. c) Impact at point 1. Proc. of SPIE Vol M-12
13 d) Every impact will be repeated for five times to constrain the noise. e) Attach the accelerometer at point For points 2~14, repeat the steps described in After the hammer testing, the excitation will be applied to the GSSMP mounted on the isolation stand using an exciter. The excitation points are chosen as 13, 14 and For the excitation testing, the wave plot chosen is the fast sin sweep Internal vibration testing The internal vibration requirement is that the force transmitted from the drive systems of the GSSMP to the tower shall be less than = The GSSMP will be mounted to an isolation base for the test. The following equations calculate the accuracy required for the measurement and the parameters of the test set-up. In order to make the measurement, measurements must have accuracy that is less than = 0.1 Converting, = m where thegssmp is 0.7 ton.the accuracy of the accelerometers must beless than the following: = 0.1 = The system stiffness is then used to estimate the displacement amount. = the system is 0.7 ton, the frequency is 30/2=15Hz, the stiffness =.the accuracy of the displacement metrology facility is =. / = 16 Figure 22 shows a schematic of the test set-up. The mass, stiffness and damping parameters for subsystems 1and 2 are and The internal force between 1 and 2 is. With Laplace transform F(s), = ( ) + ( ) = + + ( ) ( ) + and are the displacements of the mass 1 and mass 2, with Laplace transforms ( ) ( ) The transfer function of the two subsystems are ( ) ( ) Proc. of SPIE Vol M-13
14 mz System under test cl T2 (S) Tila i Laplace transform of the force can be expressed as Figure 22. Schematic of the internal vibration test F(s) = ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) The relationship of F(s)and Laplace transform of the accelerometer ( ) can be expressed as if, then : F(s) ( ) = 1 ( ) ( ) ( ) + 1 ( ) F(s) ( ) = 1 1 ( ) + 1 ( ) The transfer function can be determined by the frequency response function and the frequency response function can be reached by the modal testing or FEA model. 4. CONCLUSION Pre-construction of Giant Steerable Science Mirror for TMT is currently under the way to complete final testing by the end of July To date, the design goals of the prototype and gains from optical manufacturing and mechanical structure assembly are being met. REFERENCES 1. DENG Yong-ting, LI Hong-wen, WANG Jian-li. Overview of AC servo control system for the large telescope[j]. Chinese Optics, 2015,8(6): Yang F, Zhao H, Guo P, et al. Pre-construction of giant steerable science mirror for TMT[C]//SPIE Optical Engineering+ Applications. International Society for Optics and Photonics, 2015: 95730T-95730T Zhao H, Zhang J, Yang F, et al. Study of tilt axis bearing arrangement for M3S of TMT project[c]//7th International Proc. of SPIE Vol M-14
15 Symposium on Advanced Optical Manufacturing and Testing Technologies (AOMATT 2014). International Society for Optics and Photonics, 2014: 92800M-92800M An Q C, Yang F, Guo P, et al. Power spectral density specification and analysis of system optical jitter[c]//international Symposium on Optoelectronic Technology and Application International Society for Optics and Photonics, 2014: Yang F, An Q C, Wang F G, et al. Analysis of power spectral density as a performance metric for TMT M3[C]//7th International Symposium on Advanced Optical Manufacturing and Testing Technologies (AOMATT 2014). International Society for Optics and Photonics, 2014: 92820C-92820C Su Y, Zhang J, Yang F, et al. Structure performance analysis for TMT tertiary mirror system[c]//7th International Symposium on Advanced Optical Manufacturing and Testing Technologies (AOMATT 2014). International Society for Optics and Photonics, 2014: 92800L-92800L Deng Y, Li H, Yang F, et al. Integrated modeling and dynamics simulation for the TMT-M3 control system[c]//7th International Symposium on Advanced Optical Manufacturing and Testing Technologies (AOMATT 2014). International Society for Optics and Photonics, 2014: 92800J-92800J-7. Proc. of SPIE Vol M-15
Development of surface metrology for the Giant Magellan Telescope primary mirror
 Development of surface metrology for the Giant Magellan Telescope primary mirror J. H. Burge a,b, W. Davison a, H. M. Martin a, C. Zhao b a Steward Observatory, University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ 85721,
Development of surface metrology for the Giant Magellan Telescope primary mirror J. H. Burge a,b, W. Davison a, H. M. Martin a, C. Zhao b a Steward Observatory, University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ 85721,
OWL: Further steps in designing the telescope mechanical structure and in assessing its performance
 OWL: Further steps in designing the telescope mechanical structure and in assessing its performance Enzo Brunetto, Franz Koch, Marco Quattri European Southern Observatory ABSTRACT The baseline concept
OWL: Further steps in designing the telescope mechanical structure and in assessing its performance Enzo Brunetto, Franz Koch, Marco Quattri European Southern Observatory ABSTRACT The baseline concept
E-ELT Overview. Alistair McPherson Programme Manager
 E-ELT Overview Alistair McPherson Programme Manager Science drivers Planets in other stellar systems Imaging and spectroscopy The quest for Earth-like exo-planets Stellar populations In galaxies inaccessible
E-ELT Overview Alistair McPherson Programme Manager Science drivers Planets in other stellar systems Imaging and spectroscopy The quest for Earth-like exo-planets Stellar populations In galaxies inaccessible
Tomelleri S.r.l. Copyright 2007 ADVANCED SYSTEMS
 Tomelleri S.r.l. Copyright 2007 ADVANCED SYSTEMS s.r.l.started its activities back in 1984, developing projects (feasibility studies and designs) in astronomy and other sectors (such as machine tools,
Tomelleri S.r.l. Copyright 2007 ADVANCED SYSTEMS s.r.l.started its activities back in 1984, developing projects (feasibility studies and designs) in astronomy and other sectors (such as machine tools,
Use of computer generated holograms for alignment of complex null correctors
 Use of computer generated holograms for alignment of complex null correctors Rene Zehnder, James H. Burge and Chunyu Zhao College of Optical Sciences, the University of Arizona 1630 E. University Blvd,
Use of computer generated holograms for alignment of complex null correctors Rene Zehnder, James H. Burge and Chunyu Zhao College of Optical Sciences, the University of Arizona 1630 E. University Blvd,
APPENDIX 4.4.A STRAWMAN STRUCTURAL DESIGN OF A 30-M GSMT
 APPENDIX 4.4.A STRAWMAN STRUCTURAL DESIGN OF A 30-M GSMT Report prepared for the New Initiatives Office by Simpson Gumpertz & Heger Inc., January 2001. Strawman Structural Design of a 30-m Giant Segmented
APPENDIX 4.4.A STRAWMAN STRUCTURAL DESIGN OF A 30-M GSMT Report prepared for the New Initiatives Office by Simpson Gumpertz & Heger Inc., January 2001. Strawman Structural Design of a 30-m Giant Segmented
TMT Metrology study for M2 and M3
 Consultants for Optical Metrology Tucson, Arizona 1 Introduction... 2 2 Requirements for optical test hardware... 3 3 Subaperture interferometry with stitching software... 4 3.1 Fizeau interferometry...
Consultants for Optical Metrology Tucson, Arizona 1 Introduction... 2 2 Requirements for optical test hardware... 3 3 Subaperture interferometry with stitching software... 4 3.1 Fizeau interferometry...
1 Naval Research Laboratory Remote Sensing Division, Code Aberdeen Ave SE Kirtland AFB, NM 87117
 Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer (CFRP) Telescope Program at the Naval Research Laboratory Sergio R. Restaino 1, Ty Martinez 1, Jonathan R. Andrews 1, Christopher C. Wilcox 1, S. Teare 2, Robert Romeo 3,
Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer (CFRP) Telescope Program at the Naval Research Laboratory Sergio R. Restaino 1, Ty Martinez 1, Jonathan R. Andrews 1, Christopher C. Wilcox 1, S. Teare 2, Robert Romeo 3,
Telescope Project Development Seminar
 Telescope Project Development Seminar Session 4: Telescope Performance Matt Johns 4/19/2017 U. Tokyo 4/9/2017 Telescope Project Development 1 Session Outline GMT imaging Image Size Atmospheric dispersion
Telescope Project Development Seminar Session 4: Telescope Performance Matt Johns 4/19/2017 U. Tokyo 4/9/2017 Telescope Project Development 1 Session Outline GMT imaging Image Size Atmospheric dispersion
Opto-Mechanical I/F for ANSYS
 Opto-Mechanical I/F for ANSYS Victor Genberg, Gregory Michels, Keith Doyle Sigmadyne, Inc. Abstract Thermal and structural output from ANSYS is not in a form useful for optical analysis software. Temperatures,
Opto-Mechanical I/F for ANSYS Victor Genberg, Gregory Michels, Keith Doyle Sigmadyne, Inc. Abstract Thermal and structural output from ANSYS is not in a form useful for optical analysis software. Temperatures,
Figure measurement of a large optical flat with a Fizeau interferometer and stitching technique
 Figure measurement of a large optical flat with a Fizeau interferometer and stitching technique Chunyu Zhao a, Robert A. Sprowl a, Michael Bray b, James H. Burge a a College of Optical Sciences, the University
Figure measurement of a large optical flat with a Fizeau interferometer and stitching technique Chunyu Zhao a, Robert A. Sprowl a, Michael Bray b, James H. Burge a a College of Optical Sciences, the University
Selection Calculations For Linear & Rotary Actuators
 H-8 For Electric Linear Slides and Electric Cylinders First determine your series, then select your product. Select the actuator that you will use based on the following flow charts: Selection Procedure
H-8 For Electric Linear Slides and Electric Cylinders First determine your series, then select your product. Select the actuator that you will use based on the following flow charts: Selection Procedure
Chapter 5: Random Vibration. ANSYS Mechanical. Dynamics. 5-1 July ANSYS, Inc. Proprietary 2009 ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 5: Random Vibration ANSYS Mechanical Dynamics 5-1 July 2009 Analysis Random Vibration Analysis Topics covered: Definition and purpose Overview of Workbench capabilities Procedure 5-2 July 2009
Chapter 5: Random Vibration ANSYS Mechanical Dynamics 5-1 July 2009 Analysis Random Vibration Analysis Topics covered: Definition and purpose Overview of Workbench capabilities Procedure 5-2 July 2009
Fine Alignment of the ATF Damping Ring
 Fine Alignment of the ATF Damping Ring M. Takano, S. Araki (a), Y. Funahashi (a), H. Hayano (a), T. Matsui (b), J. Urakawa (a) Toho University 2 2 1 Miyama, Funabashi, Chiba 275, Japan (a) KEK, High Energy
Fine Alignment of the ATF Damping Ring M. Takano, S. Araki (a), Y. Funahashi (a), H. Hayano (a), T. Matsui (b), J. Urakawa (a) Toho University 2 2 1 Miyama, Funabashi, Chiba 275, Japan (a) KEK, High Energy
Hard and Soft X-ray Mirror System Design Status
 Hard and Soft X-ray Mirror System Design Status From FEL Gas Attenuator & Diagnostics HOMS/SOMS Mirror System To Experiment Stations This work performed under the auspices of the U.S. Department of Energy
Hard and Soft X-ray Mirror System Design Status From FEL Gas Attenuator & Diagnostics HOMS/SOMS Mirror System To Experiment Stations This work performed under the auspices of the U.S. Department of Energy
A PRELIMINARY ALIGNMENT PLAN FOR RIA AT MSU
 IWAA2004, CERN, Geneva, 4-7 October 2004 A PRELIMINARY ALIGNMENT PLAN FOR RIA AT MSU D. P. Sanderson, NSCL-MSU, 1 Cyclotron Lab, East Lansing, MI 48824, USA 1. INTRODUCTION The Rare Isotope Accelerator
IWAA2004, CERN, Geneva, 4-7 October 2004 A PRELIMINARY ALIGNMENT PLAN FOR RIA AT MSU D. P. Sanderson, NSCL-MSU, 1 Cyclotron Lab, East Lansing, MI 48824, USA 1. INTRODUCTION The Rare Isotope Accelerator
Telescope Project Development Seminar
 Telescope Project Development Seminar Session 5a: Science Instruments & Adaptive Optics Session 5b: Lessons Learned & Discussion Matt Johns 4/27/2017 U. Tokyo 4/27/2017 Telescope Project Development 1
Telescope Project Development Seminar Session 5a: Science Instruments & Adaptive Optics Session 5b: Lessons Learned & Discussion Matt Johns 4/27/2017 U. Tokyo 4/27/2017 Telescope Project Development 1
Control of the Keck and CELT Telescopes. Douglas G. MacMartin Control & Dynamical Systems California Institute of Technology
 Control of the Keck and CELT Telescopes Douglas G. MacMartin Control & Dynamical Systems California Institute of Technology Telescope Control Problems Light from star Primary mirror active control system
Control of the Keck and CELT Telescopes Douglas G. MacMartin Control & Dynamical Systems California Institute of Technology Telescope Control Problems Light from star Primary mirror active control system
PICTURE sounding rocket telescope
 PICTURE sounding rocket telescope D. Content, S. Antonille, D. Rabin, T. Wallace NASA GSFC 1 Overview of talk Two {ambitious} sounding rocket concepts sharing a telescope OTA overview PM development program
PICTURE sounding rocket telescope D. Content, S. Antonille, D. Rabin, T. Wallace NASA GSFC 1 Overview of talk Two {ambitious} sounding rocket concepts sharing a telescope OTA overview PM development program
Physics 476LW Advanced Physics Laboratory Michelson Interferometer
 Physics 476LW Advanced Physics Laboratory Michelson Interferometer Introduction An optical interferometer is an instrument which splits a beam of light into two beams, each beam follows a different path
Physics 476LW Advanced Physics Laboratory Michelson Interferometer Introduction An optical interferometer is an instrument which splits a beam of light into two beams, each beam follows a different path
VACUUM SUPPORT FOR A LARGE INTERFEROMETRIC REFERENCE SURFACE
 VACUUM SUPPORT FOR A LARGE INTERFEROMETRIC REFERENCE SURFACE Masaki Hosoda, Robert E. Parks, and James H. Burge College of Optical Sciences University of Arizona Tucson, Arizona 85721 OVERVIEW This paper
VACUUM SUPPORT FOR A LARGE INTERFEROMETRIC REFERENCE SURFACE Masaki Hosoda, Robert E. Parks, and James H. Burge College of Optical Sciences University of Arizona Tucson, Arizona 85721 OVERVIEW This paper
Daily Alignment Procedure with 2 AO Wave Front Sensors
 Daily Alignment Procedure with 2 AO Wave Front Sensors First Version Judit Sturmann Talk Outline AO at CHARA design scheme Before sky alignment Keeping the alignment during the night Lab and Telescope
Daily Alignment Procedure with 2 AO Wave Front Sensors First Version Judit Sturmann Talk Outline AO at CHARA design scheme Before sky alignment Keeping the alignment during the night Lab and Telescope
EUCLID M2 MIRROR MECHANISM
 EUCLID M2 MIRROR MECHANISM Aiala Artiagoitia (1), Carlos Compostizo (1), Laura Rivera (1) (1) SENER, Av. Zugazarte 56, 48930 Las Arenas (Bizkaia) Spain, Email: aiala.artiagoitia@sener.es ABSTRACT Euclid
EUCLID M2 MIRROR MECHANISM Aiala Artiagoitia (1), Carlos Compostizo (1), Laura Rivera (1) (1) SENER, Av. Zugazarte 56, 48930 Las Arenas (Bizkaia) Spain, Email: aiala.artiagoitia@sener.es ABSTRACT Euclid
Optical metrology for very large convex aspheres
 Optical metrology for very large convex aspheres J. H. Burge, P. Su, and C. Zhao College of Optical Sciences, University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ 85721, USA ABSTRACT Telescopes with very large diameter or
Optical metrology for very large convex aspheres J. H. Burge, P. Su, and C. Zhao College of Optical Sciences, University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ 85721, USA ABSTRACT Telescopes with very large diameter or
David Chaney Space Symposium Radius of Curvature Actuation for the James Webb Space Telescope
 2018 Space Symposium Radius of Curvature Actuation for the James Webb Space Telescope David Chaney Optical Engineering Staff Consultant Ball Aerospace 4/2/18 1 JWST Overview James Webb Space Telescope
2018 Space Symposium Radius of Curvature Actuation for the James Webb Space Telescope David Chaney Optical Engineering Staff Consultant Ball Aerospace 4/2/18 1 JWST Overview James Webb Space Telescope
THE LOSMANDY G-11 MOUNT
 Checking the parts THE LOSMANDY G-11 MOUNT Depending on which accessories you ordered, your G-11 mount was shipped in four or more boxes. The contents of each box are as follows: Equatorial Mount Adjustable
Checking the parts THE LOSMANDY G-11 MOUNT Depending on which accessories you ordered, your G-11 mount was shipped in four or more boxes. The contents of each box are as follows: Equatorial Mount Adjustable
GP-B Telescope Determine Metering Tube Length P0364 Rev -
 Stanford University W.W. Hansen Experimental Physics Laboratory Gravity Probe B Relativity Mission Stanford, California 94305-4085 GP-B Telescope Determine Metering Tube Length P0364 Rev - March 11, 1998
Stanford University W.W. Hansen Experimental Physics Laboratory Gravity Probe B Relativity Mission Stanford, California 94305-4085 GP-B Telescope Determine Metering Tube Length P0364 Rev - March 11, 1998
Product Description. Further highlights. Outstanding features. 4 Bosch Rexroth Corporation Miniature Linear Modules R310A 2418 (2009.
 4 Bosch Rexroth orporation Miniature Linear Modules R310A 2418 (2009.05) Product Description Outstanding features Rexroth Miniature Linear Modules are precise, ready-to-install linear motion systems that
4 Bosch Rexroth orporation Miniature Linear Modules R310A 2418 (2009.05) Product Description Outstanding features Rexroth Miniature Linear Modules are precise, ready-to-install linear motion systems that
Optical Interface for MSC.Nastran
 Optical Interface for MSC.Nastran Victor Genberg, Keith Doyle, Gregory Michels Sigmadyne, Inc., 803 West Ave, Rochester, NY 14611 genberg@sigmadyne.com Abstract Thermal and structural output from MSC.Nastran
Optical Interface for MSC.Nastran Victor Genberg, Keith Doyle, Gregory Michels Sigmadyne, Inc., 803 West Ave, Rochester, NY 14611 genberg@sigmadyne.com Abstract Thermal and structural output from MSC.Nastran
Position calibration of cryogenic dark matter detectors
 Abstract Position calibration of cryogenic dark matter detectors Aliya Merali University of Florida REU Participant, Summer 2010 Advisor: Dr. Tarek Saab Preparations for a position calibration of cryogenic
Abstract Position calibration of cryogenic dark matter detectors Aliya Merali University of Florida REU Participant, Summer 2010 Advisor: Dr. Tarek Saab Preparations for a position calibration of cryogenic
ARCUATE ARM PROFILOMETRY - TRACEABLE METROLOGY FOR LARGE MIRRORS
 ARCUATE ARM PROFILOMETRY - TRACEABLE METROLOGY FOR LARGE MIRRORS Andrew Lewis and Simon Oldfield National Physical Laboratory Hampton Road Teddington, Middlesex, TW11 0LW, UK P: +44 20 8943 6124, F: +44
ARCUATE ARM PROFILOMETRY - TRACEABLE METROLOGY FOR LARGE MIRRORS Andrew Lewis and Simon Oldfield National Physical Laboratory Hampton Road Teddington, Middlesex, TW11 0LW, UK P: +44 20 8943 6124, F: +44
Compact, lightweight, and athermalized mirror and mount for use on JWST's NIRCam instrument
 Compact, lightweight, and athermalized mirror and mount for use on JWST's NIRCam instrument Derek Edinger, Paul Mammini*, Liz Osborne Lockheed Martin Advanced Technology Center, 3251 Hanover St., Palo
Compact, lightweight, and athermalized mirror and mount for use on JWST's NIRCam instrument Derek Edinger, Paul Mammini*, Liz Osborne Lockheed Martin Advanced Technology Center, 3251 Hanover St., Palo
Special edition paper
 Development of New Aseismatic Structure Using Escalators Kazunori Sasaki* Atsushi Hayashi* Hajime Yoshida** Toru Masuda* Aseismatic reinforcement work is often carried out in parallel with improvement
Development of New Aseismatic Structure Using Escalators Kazunori Sasaki* Atsushi Hayashi* Hajime Yoshida** Toru Masuda* Aseismatic reinforcement work is often carried out in parallel with improvement
Analysis of shock force measurements for the model based dynamic calibration
 8 th Worshop on Analysis of Dynamic Measurements May 5-6, 4 Turin Analysis of shoc force measurements for the model based dynamic calibration Michael Kobusch, Sascha Eichstädt, Leonard Klaus, and Thomas
8 th Worshop on Analysis of Dynamic Measurements May 5-6, 4 Turin Analysis of shoc force measurements for the model based dynamic calibration Michael Kobusch, Sascha Eichstädt, Leonard Klaus, and Thomas
NR ROTARY RING TABLE: FLEXIBLE IN EVERY RESPECT
 NR FREELY PROGRAMMABLE ROTARY TABLES NR ROTARY RING TABLE All NR rings allow customer-specific drive motors to be connected NR ROTARY RING TABLE: FLEXIBLE IN EVERY RESPECT WHEN IT S GOT TO BE EXACT We
NR FREELY PROGRAMMABLE ROTARY TABLES NR ROTARY RING TABLE All NR rings allow customer-specific drive motors to be connected NR ROTARY RING TABLE: FLEXIBLE IN EVERY RESPECT WHEN IT S GOT TO BE EXACT We
New concept of a 3D-probing system for micro-components
 Research Collection Journal Article New concept of a 3D-probing system for micro-components Author(s): Liebrich, Thomas; Kanpp, W. Publication Date: 2010 Permanent Link: https://doi.org/10.3929/ethz-a-006071031
Research Collection Journal Article New concept of a 3D-probing system for micro-components Author(s): Liebrich, Thomas; Kanpp, W. Publication Date: 2010 Permanent Link: https://doi.org/10.3929/ethz-a-006071031
Thermal-optical property of fore optical system in space hyper spectral imager
 3 6 2010 12 Chinese Journal of Optics and Applied Optics Vol. 3 No. 6 Dec. 2010 1674-2915( 2010) 06-0572-08 Thermal-optical property of fore optical system in space hyper spectral imager ZHANG Yi-cha 1,
3 6 2010 12 Chinese Journal of Optics and Applied Optics Vol. 3 No. 6 Dec. 2010 1674-2915( 2010) 06-0572-08 Thermal-optical property of fore optical system in space hyper spectral imager ZHANG Yi-cha 1,
SOFIA Telescope Manufacturing - Lessons Learned
 SOFIA Telescope Manufacturing - Lessons Learned Hans J. Kaercher, Senior Telescope Engineer MT Mechatronics GmbH, Mainz, Germany hans.kaercher@mt-mechatronics.de 1 Experience with Telescopes at Exposed
SOFIA Telescope Manufacturing - Lessons Learned Hans J. Kaercher, Senior Telescope Engineer MT Mechatronics GmbH, Mainz, Germany hans.kaercher@mt-mechatronics.de 1 Experience with Telescopes at Exposed
Development of the Screw-driven Motors by Stacked Piezoelectric Actuators
 Proceedings of the 4th IIAE International Conference on Industrial Application Engineering 2016 Development of the Screw-driven Motors by Stacked Piezoelectric Actuators Shine-Tzong Ho a,*, Hao-Wei Chen
Proceedings of the 4th IIAE International Conference on Industrial Application Engineering 2016 Development of the Screw-driven Motors by Stacked Piezoelectric Actuators Shine-Tzong Ho a,*, Hao-Wei Chen
x Contents Segmented Mirror Telescopes Metal and Lightweight Mirrors Mirror Polishing
 Contents 1 Fundamentals of Optical Telescopes... 1 1.1 A Brief History of Optical Telescopes.................... 1 1.2 General Astronomical Requirements..................... 6 1.2.1 Angular Resolution.............................
Contents 1 Fundamentals of Optical Telescopes... 1 1.1 A Brief History of Optical Telescopes.................... 1 1.2 General Astronomical Requirements..................... 6 1.2.1 Angular Resolution.............................
Lattice Cell/Girder Assembly
 SPEAR3 Magnets Jack Tanabe, Nanyang Li, Ann Trautwein, Domenico Dell Orco, Dave Ernst, Zach Wolf (SLAC Magnet Measurements), Catherine L Coq (SLAC Alignment), Jeff Corbett, Bob Hettel (SPEAR3 Physics)
SPEAR3 Magnets Jack Tanabe, Nanyang Li, Ann Trautwein, Domenico Dell Orco, Dave Ernst, Zach Wolf (SLAC Magnet Measurements), Catherine L Coq (SLAC Alignment), Jeff Corbett, Bob Hettel (SPEAR3 Physics)
Experimental and Numerical Modal Analysis of a Compressor Mounting Bracket
 IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 2278-1684,p-ISSN: 2320-334X, Volume 14, Issue 1 Ver. VI (Jan. - Feb. 2017), PP 01-07 www.iosrjournals.org Experimental and Numerical
IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 2278-1684,p-ISSN: 2320-334X, Volume 14, Issue 1 Ver. VI (Jan. - Feb. 2017), PP 01-07 www.iosrjournals.org Experimental and Numerical
CHARA Meeting 2017 Pasadena, California
 MORE AUTOMATION Laszlo Sturmann M7 ACTUATORS LAB. LASER ALIGNMENT TELESCOPE OPTICAL ALIGNMENT NEW ACTUATORS REMOTELY ACTUATED M7 MOUNT MOTIVATION THE PRECISION OF THE COUDE ALIGNMENT WAS NOT SUFFICIENT
MORE AUTOMATION Laszlo Sturmann M7 ACTUATORS LAB. LASER ALIGNMENT TELESCOPE OPTICAL ALIGNMENT NEW ACTUATORS REMOTELY ACTUATED M7 MOUNT MOTIVATION THE PRECISION OF THE COUDE ALIGNMENT WAS NOT SUFFICIENT
The Secret Behind the Nobeyama 45-m Radio Telescope s Excellent
 The Secret Behind the Nobeyama 45-m Radio Telescope s Excellent Even now over 30 years after its completion in 1982, the 45 m diameter radio telescope at NAOJ s Nobeyama Radio Observatory boasts world
The Secret Behind the Nobeyama 45-m Radio Telescope s Excellent Even now over 30 years after its completion in 1982, the 45 m diameter radio telescope at NAOJ s Nobeyama Radio Observatory boasts world
Laser on-line Thickness Measurement Technology Based on Judgment and Wavelet De-noising
 Sensors & Transducers, Vol. 168, Issue 4, April 214, pp. 137-141 Sensors & Transducers 214 by IFSA Publishing, S. L. http://www.sensorsportal.com Laser on-line Thickness Measurement Technology Based on
Sensors & Transducers, Vol. 168, Issue 4, April 214, pp. 137-141 Sensors & Transducers 214 by IFSA Publishing, S. L. http://www.sensorsportal.com Laser on-line Thickness Measurement Technology Based on
OPTICAL FIBRES IN ASTRONOMY (OP-006) Course Overview
 OPTICAL FIBRES IN ASTRONOMY (OP-006) Course Overview The course, based on practical experience and containing several examples of real instruments, is focused on the application of optical fibres in Astronomy.
OPTICAL FIBRES IN ASTRONOMY (OP-006) Course Overview The course, based on practical experience and containing several examples of real instruments, is focused on the application of optical fibres in Astronomy.
FOUR-POINT CONTACT SLEWING RINGS - without gear [ O ]
![FOUR-POINT CONTACT SLEWING RINGS - without gear [ O ] FOUR-POINT CONTACT SLEWING RINGS - without gear [ O ]](/thumbs/96/126795264.jpg) FOUR-POINT CONTACT SLEWING RINGS - without gear [ O ] Number of the Loading Boundary Dimensions Static Ax.Basic Load Rating Designation Weight Abutment Dimensions Curve d D T C oa G J 1 J 2 N 1 N 2 n 1
FOUR-POINT CONTACT SLEWING RINGS - without gear [ O ] Number of the Loading Boundary Dimensions Static Ax.Basic Load Rating Designation Weight Abutment Dimensions Curve d D T C oa G J 1 J 2 N 1 N 2 n 1
Table of Contents. iii
 Table of Contents Foreword..................................................... xv Preface...................................................... xvii Acknowledgements.............................................
Table of Contents Foreword..................................................... xv Preface...................................................... xvii Acknowledgements.............................................
Atmospheric dispersion correction for the Subaru AO system
 Atmospheric dispersion correction for the Subaru AO system Sebastian Egner a, Yuji Ikeda b, Makoto Watanabe c,y.hayano a,t.golota a, M. Hattori a,m.ito a,y.minowa a,s.oya a,y.saito a,h.takami a,m.iye d
Atmospheric dispersion correction for the Subaru AO system Sebastian Egner a, Yuji Ikeda b, Makoto Watanabe c,y.hayano a,t.golota a, M. Hattori a,m.ito a,y.minowa a,s.oya a,y.saito a,h.takami a,m.iye d
Adaptive Cable-mesh Reflector for the FAST
 Vol.44 Suppl. ACTA ASTRONOMICA SINICA Feb., 2003 Adaptive Cable-mesh Reflector for the FAST Rendong Nan 1, Gexue Ren 2, Wenbai Zhu 1 & Yingjie Lu 2 (1 National Astronomical Observatories, Chinese Academy
Vol.44 Suppl. ACTA ASTRONOMICA SINICA Feb., 2003 Adaptive Cable-mesh Reflector for the FAST Rendong Nan 1, Gexue Ren 2, Wenbai Zhu 1 & Yingjie Lu 2 (1 National Astronomical Observatories, Chinese Academy
SKF actuators available for quick delivery. Selection guide
 SKF actuators available for quick delivery Selection guide A wide range of SKF actuators available for quick delivery Industrial actuator 24 Volt DC Load range 1 000 to 4 000 N Speed range 5 to 52 mm/s
SKF actuators available for quick delivery Selection guide A wide range of SKF actuators available for quick delivery Industrial actuator 24 Volt DC Load range 1 000 to 4 000 N Speed range 5 to 52 mm/s
DEVELOPMENT OF DROP WEIGHT IMPACT TEST MACHINE
 CHAPTER-8 DEVELOPMENT OF DROP WEIGHT IMPACT TEST MACHINE 8.1 Introduction The behavior of materials is different when they are subjected to dynamic loading [9]. The testing of materials under dynamic conditions
CHAPTER-8 DEVELOPMENT OF DROP WEIGHT IMPACT TEST MACHINE 8.1 Introduction The behavior of materials is different when they are subjected to dynamic loading [9]. The testing of materials under dynamic conditions
The University of California Ten-Meter Telescope Project
 The University of California Ten-Meter Telescope Project JERRY NELSON Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory and Astronomy Department University of California Berkeley, California 94720 INTRODUCTION In recent years
The University of California Ten-Meter Telescope Project JERRY NELSON Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory and Astronomy Department University of California Berkeley, California 94720 INTRODUCTION In recent years
Research on the synchronous vibration of the non-integral. mechanism under the vibration environment
 International Journal of Research in Engineering and Science (IJRES) ISSN (Online): 3-9364 ISSN (Print): 3-9356 Volume 3 Issue ǁ December. 5 ǁ PP.-6 Research on the synchronous vibration of the non-integral
International Journal of Research in Engineering and Science (IJRES) ISSN (Online): 3-9364 ISSN (Print): 3-9356 Volume 3 Issue ǁ December. 5 ǁ PP.-6 Research on the synchronous vibration of the non-integral
Announcements. Equilibrium of a Rigid Body
 Announcements Equilibrium of a Rigid Body Today s Objectives Identify support reactions Draw a free body diagram Class Activities Applications Support reactions Free body diagrams Examples Engr221 Chapter
Announcements Equilibrium of a Rigid Body Today s Objectives Identify support reactions Draw a free body diagram Class Activities Applications Support reactions Free body diagrams Examples Engr221 Chapter
Expected Performance From WIYN Tip-Tilt Imaging
 Expected Performance From WIYN Tip-Tilt Imaging C. F. Claver 3 September 1997 Overview Image motion studies done at WIYN show that a significant improvement to delivered image quality can be obtained from
Expected Performance From WIYN Tip-Tilt Imaging C. F. Claver 3 September 1997 Overview Image motion studies done at WIYN show that a significant improvement to delivered image quality can be obtained from
The LAT Electronics consists of five distinct box assemblies as follows:
 I. SYNOPSIS The preliminary stress analyses for the DAQ Electronics assemblies have been performed per the conditions specified in the Environmental Specification LAT-SS-00778. The analysis considered
I. SYNOPSIS The preliminary stress analyses for the DAQ Electronics assemblies have been performed per the conditions specified in the Environmental Specification LAT-SS-00778. The analysis considered
Fatigue Crack Analysis on the Bracket of Sanding Nozzle of CRH5 EMU Bogie
 Journal of Applied Mathematics and Physics, 2015, 3, 577-583 Published Online May 2015 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/jamp http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/jamp.2015.35071 Fatigue Crack Analysis on the
Journal of Applied Mathematics and Physics, 2015, 3, 577-583 Published Online May 2015 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/jamp http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/jamp.2015.35071 Fatigue Crack Analysis on the
Overview of Thirty Meter Telescope Project
 Overview of Thirty Meter Telescope Project L. Stepp November 16, 2010 TMT.TEL.PRE.10.016.REL02 1 Outline Introduction to TMT TMT site selection TMT partners Summary of TMT design TMT requirements for segments
Overview of Thirty Meter Telescope Project L. Stepp November 16, 2010 TMT.TEL.PRE.10.016.REL02 1 Outline Introduction to TMT TMT site selection TMT partners Summary of TMT design TMT requirements for segments
Force/Torque measuring facility for friction coefficient and multicomponent
 DOI 10.516/sensor013/A1. Force/Torque measuring facility for friction coefficient and multicomponent sensors S. Baumgarten 1, D. Röske 1, H. Kahmann 1, D. Mauersberger 1 and R. Kumme 1 1 Physikalisch-Technische
DOI 10.516/sensor013/A1. Force/Torque measuring facility for friction coefficient and multicomponent sensors S. Baumgarten 1, D. Röske 1, H. Kahmann 1, D. Mauersberger 1 and R. Kumme 1 1 Physikalisch-Technische
THE NEW 1.1 MN m TORQUE STANDARD MACHINE OF THE PTB BRAUNSCHWEIG/GERMANY
 THE NEW 1.1 MN m TORQUE STANDARD MACHINE OF THE PTB BRAUNSCHWEIG/GERMANY D. Peschel 1, D. Mauersberger 1, D. Schwind 2, U. Kolwinski 2 1 Solid mechanics department, PTB, Germany 2 Gassmann Theiss Messtechnik
THE NEW 1.1 MN m TORQUE STANDARD MACHINE OF THE PTB BRAUNSCHWEIG/GERMANY D. Peschel 1, D. Mauersberger 1, D. Schwind 2, U. Kolwinski 2 1 Solid mechanics department, PTB, Germany 2 Gassmann Theiss Messtechnik
Interferometer for Squareness measurement
 F Interferometer for Squareness measurement The deviation of squareness of two machine axes can be measured as follows: 1. The straightness of a machine axis is measured. 2. The Angular reflector stops
F Interferometer for Squareness measurement The deviation of squareness of two machine axes can be measured as follows: 1. The straightness of a machine axis is measured. 2. The Angular reflector stops
Large FOV Mobile E-O Telescope for Searching and Tracking Low-earth Orbit Micro-satellites and Space Debris
 Large FOV Mobile E-O Telescope for Searching and Tracking Low-earth Orbit Micro-satellites and Space Debris WANG Jian-li, ZHAO Jin-yu, ZHANG Shi-xue Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics,
Large FOV Mobile E-O Telescope for Searching and Tracking Low-earth Orbit Micro-satellites and Space Debris WANG Jian-li, ZHAO Jin-yu, ZHANG Shi-xue Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics,
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS. Prepared by Engr. John Paul Timola
 MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Prepared by Engr. John Paul Timola Mechanics of materials branch of mechanics that studies the internal effects of stress and strain in a solid body. stress is associated with the
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Prepared by Engr. John Paul Timola Mechanics of materials branch of mechanics that studies the internal effects of stress and strain in a solid body. stress is associated with the
The MMT f/5 secondary support system: design, implementation, and performance
 The MMT f/5 secondary support system: design, implementation, and performance S. Callahan *a, B. Cuerden b, D. Fabricant c, B. Martin b a MMT Observatory, University of Arizona, 933 N. Cherry Ave., Tucson,
The MMT f/5 secondary support system: design, implementation, and performance S. Callahan *a, B. Cuerden b, D. Fabricant c, B. Martin b a MMT Observatory, University of Arizona, 933 N. Cherry Ave., Tucson,
Facts Underlying the High Performance of the 188-cm Reflector Telescope
 Facts Underlying the High Performance of the 188-cm Reflector Telescope Okayama Astrophysical Observatory s 188-cm Reflector Telescope is the largest optical-infrared telescope in Japan. When introduced
Facts Underlying the High Performance of the 188-cm Reflector Telescope Okayama Astrophysical Observatory s 188-cm Reflector Telescope is the largest optical-infrared telescope in Japan. When introduced
Design and performance of Hall probe measurement system in CSNS
 Radiat Detect Technol Methods (2017) 1:18 https://doi.org/10.1007/s41605-017-0017-z ORIGINAL PAPER Design and performance of Hall probe measurement system in CSNS Xi Wu 1,2 Wen Kang 1,2 Wan Chen 1,2 Chang-dong
Radiat Detect Technol Methods (2017) 1:18 https://doi.org/10.1007/s41605-017-0017-z ORIGINAL PAPER Design and performance of Hall probe measurement system in CSNS Xi Wu 1,2 Wen Kang 1,2 Wan Chen 1,2 Chang-dong
Facts underlying the ultrahigh accuracy of the Subaru Telescope
 Facts underlying the ultrahigh accuracy of the Subaru Telescope The Subaru Telescope is a large-scale optical/infrared telescope located near the summit of Maunakea (4200 m elevation) on Hawai`i Island,
Facts underlying the ultrahigh accuracy of the Subaru Telescope The Subaru Telescope is a large-scale optical/infrared telescope located near the summit of Maunakea (4200 m elevation) on Hawai`i Island,
HERSCHEL/UVCI ALIGNMENT PLAN
 DIPARTIMENTO DI ASTRONOMIA E SCIENZA DELLO SPAZIO HERSCHEL/UVCI ALIGNMENT PLAN M. Romoli (a), G. Corti (a), F. Landini (a) (a) Dipartimento di Astronomia e Scienza dello Spazio, Università di Firenze (Italy)
DIPARTIMENTO DI ASTRONOMIA E SCIENZA DELLO SPAZIO HERSCHEL/UVCI ALIGNMENT PLAN M. Romoli (a), G. Corti (a), F. Landini (a) (a) Dipartimento di Astronomia e Scienza dello Spazio, Università di Firenze (Italy)
Linear guide drives. Synchronous shafts The use of synchronous shafts enables several linear axes to be operated with one drive.
 Linear guide drives Drive concept The linear guides are driven via the hollow shaft in the drive head. The drive head is used to directly install a motor or alternatively (in connection with a center shaft)
Linear guide drives Drive concept The linear guides are driven via the hollow shaft in the drive head. The drive head is used to directly install a motor or alternatively (in connection with a center shaft)
The Principles of Astronomical Telescope Design
 The Principles of Astronomical Telescope Design Jingquan Cheng National Radio Astronomy Observatory Charlottesville, Virginia,.USA " 4y Springer Fundamentals of Optical Telescopes 1 1.1 A Brief History
The Principles of Astronomical Telescope Design Jingquan Cheng National Radio Astronomy Observatory Charlottesville, Virginia,.USA " 4y Springer Fundamentals of Optical Telescopes 1 1.1 A Brief History
Construction of a Vibrating Structure for Demonstration of Vibration Measurement
 Paper ID #9316 Construction of a Vibrating Structure for Demonstration of Vibration Measurement and FFT Analysis Prof. Aaron Alexander, Oklahoma State University Aaron Alexander is an Assistant Professor
Paper ID #9316 Construction of a Vibrating Structure for Demonstration of Vibration Measurement and FFT Analysis Prof. Aaron Alexander, Oklahoma State University Aaron Alexander is an Assistant Professor
Gemini 8m Telescope Design Requirements Document
 GEMINI 8-M Telescopes Project SPE-TE-G0002 Revision 1 Gemini 8m Telescope Design Requirements Document Telescope Structure, Building, and Enclosure Group 19 November 1992 GEMINI PROJECT OFFICE 950 N. Cherry
GEMINI 8-M Telescopes Project SPE-TE-G0002 Revision 1 Gemini 8m Telescope Design Requirements Document Telescope Structure, Building, and Enclosure Group 19 November 1992 GEMINI PROJECT OFFICE 950 N. Cherry
A Portable Optical DSPI System for Residual Stresses Measurement by Hole Drilling Using the Integral Method in Terms of Displacement
 A Portable Optical DSPI System for Residual Stresses Measurement by Hole Drilling Using the Integral Method in Terms of Displacement Armando Albertazzi G. Jr. 1, a*, Matias Viotti 1, b, Celso Veiga 1,c
A Portable Optical DSPI System for Residual Stresses Measurement by Hole Drilling Using the Integral Method in Terms of Displacement Armando Albertazzi G. Jr. 1, a*, Matias Viotti 1, b, Celso Veiga 1,c
TE 75R RESEARCH RUBBER FRICTION TEST MACHINE
 TE 75R RESEARCH RUBBER FRICTION TEST MACHINE Background: The Research Rubber Friction Test Machine offers the ability to investigate fully the frictional behaviour of rubbery materials both in dry and
TE 75R RESEARCH RUBBER FRICTION TEST MACHINE Background: The Research Rubber Friction Test Machine offers the ability to investigate fully the frictional behaviour of rubbery materials both in dry and
Experimental test of static and dynamic characteristics of tilting-pad thrust bearings
 Special Issue Article Experimental test of static and dynamic characteristics of tilting-pad thrust bearings Advances in Mechanical Engineering 2015, Vol. 7(7) 1 8 Ó The Author(s) 2015 DOI: 10.1177/1687814015593878
Special Issue Article Experimental test of static and dynamic characteristics of tilting-pad thrust bearings Advances in Mechanical Engineering 2015, Vol. 7(7) 1 8 Ó The Author(s) 2015 DOI: 10.1177/1687814015593878
Moog CSA, 2581 Leghorn St., Mountain View, CA, USA ABSTRACT 1. INTRODUCTION
 Testing and Status of the LSST Hexapods and Rotator Ryan Sneed* b, Douglas R Neill a, Brendan Caldwell b, Bryan Walter b Harini Sundararaman a, Mike Warner a a Large Synoptic Survey Telescope, 950 N Cherry
Testing and Status of the LSST Hexapods and Rotator Ryan Sneed* b, Douglas R Neill a, Brendan Caldwell b, Bryan Walter b Harini Sundararaman a, Mike Warner a a Large Synoptic Survey Telescope, 950 N Cherry
Adaptive Optics for the Giant Magellan Telescope. Marcos van Dam Flat Wavefronts, Christchurch, New Zealand
 Adaptive Optics for the Giant Magellan Telescope Marcos van Dam Flat Wavefronts, Christchurch, New Zealand How big is your telescope? 15-cm refractor at Townsend Observatory. Talk outline Introduction
Adaptive Optics for the Giant Magellan Telescope Marcos van Dam Flat Wavefronts, Christchurch, New Zealand How big is your telescope? 15-cm refractor at Townsend Observatory. Talk outline Introduction
Integrating MD Nastran with Optical Performance Analysis
 Integrating MD Nastran with Optical Performance Analysis Victor Genberg, Gregory Michels Sigmadyne, Inc., 803 West Ave, Rochester, NY 14611 genberg@sigmadyne.com Abstract The development of products in
Integrating MD Nastran with Optical Performance Analysis Victor Genberg, Gregory Michels Sigmadyne, Inc., 803 West Ave, Rochester, NY 14611 genberg@sigmadyne.com Abstract The development of products in
VERIFICATION OF TAPPING MACHINES. Håkan Andersson
 VERIFICATION OF TAPPING MACHINES Håkan Andersson SP Swedish National Testing and Research Institute Acoustics Laboratory Box 57, SE-51 15 Borås, Sweden hakan.andersson@sp.se ABSTRACT Six tapping machines
VERIFICATION OF TAPPING MACHINES Håkan Andersson SP Swedish National Testing and Research Institute Acoustics Laboratory Box 57, SE-51 15 Borås, Sweden hakan.andersson@sp.se ABSTRACT Six tapping machines
Active optics challenges of a thirty meter segmented mirror telescope
 Active optics challenges of a thirty meter segmented mirror telescope George Z. Angeli 1, Robert Upton 1, Anna Segurson 1, Brent Ellerbroek 1 1 New Initiatives Office, AURA Inc. ABSTRACT Ground-based telescopes
Active optics challenges of a thirty meter segmented mirror telescope George Z. Angeli 1, Robert Upton 1, Anna Segurson 1, Brent Ellerbroek 1 1 New Initiatives Office, AURA Inc. ABSTRACT Ground-based telescopes
Experimental Modal Analysis of a Flat Plate Subjected To Vibration
 American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) 2016 American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) e-issn: 2320-0847 p-issn : 2320-0936 Volume-5, Issue-6, pp-30-37 www.ajer.org Research Paper Open Access
American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) 2016 American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) e-issn: 2320-0847 p-issn : 2320-0936 Volume-5, Issue-6, pp-30-37 www.ajer.org Research Paper Open Access
GP-B Telescope Determine Reticle Plate Pattern Position P0445 Rev -
 SUGP-B P0445 Rev - Stanford University W.W. Hansen Experimental Physics Laboratory Gravity Probe B Relativity Mission Stanford, California 94305-4085 GP-B Telescope Determine Reticle Plate Pattern Position
SUGP-B P0445 Rev - Stanford University W.W. Hansen Experimental Physics Laboratory Gravity Probe B Relativity Mission Stanford, California 94305-4085 GP-B Telescope Determine Reticle Plate Pattern Position
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 10 Oct 2016
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 10 Oct 2016 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 10 Oct 2016](/thumbs/87/97095243.jpg) Building Medium Size Telescope Structures for the Cherenkov Telescope Array arxiv:1610.02913v1 [astro-ph.im] 10 Oct 2016 A. Schulz 1,a), M. Garczarczyk 1, L. Oakes 2, S. Schlenstedt 1, U. Schwanke 2 and
Building Medium Size Telescope Structures for the Cherenkov Telescope Array arxiv:1610.02913v1 [astro-ph.im] 10 Oct 2016 A. Schulz 1,a), M. Garczarczyk 1, L. Oakes 2, S. Schlenstedt 1, U. Schwanke 2 and
University of California Santa Cruz, CA, USA Contents
 University of California Santa Cruz, CA, 95064 USA jnelson@ucolick.org Contents 1. Introduction 1.1. Organization 1.2. Site Selection 1.3. Schedule 1.4. Cost 2. Telescope Overview 3. Key Features of TMT
University of California Santa Cruz, CA, 95064 USA jnelson@ucolick.org Contents 1. Introduction 1.1. Organization 1.2. Site Selection 1.3. Schedule 1.4. Cost 2. Telescope Overview 3. Key Features of TMT
the foundation of any business starts here
 the foundation of any business starts here TABLE OF CONTENT The Company... 3 Electric Motors... 4 Gearboxes... 5 Automation Products... 6 Electric Components... 9 Pneumatics... 12 Hydraulics... 13 Handling
the foundation of any business starts here TABLE OF CONTENT The Company... 3 Electric Motors... 4 Gearboxes... 5 Automation Products... 6 Electric Components... 9 Pneumatics... 12 Hydraulics... 13 Handling
An experimental indoor phasing system based on active optics using dispersed Hartmann sensing technology in the visible waveband
 Research in Astron. Astrophys. 2011 Vol. 11 No. 9, 1111 1122 http://www.raa-journal.org http://www.iop.org/journals/raa Research in Astronomy and Astrophysics An experimental indoor phasing system based
Research in Astron. Astrophys. 2011 Vol. 11 No. 9, 1111 1122 http://www.raa-journal.org http://www.iop.org/journals/raa Research in Astronomy and Astrophysics An experimental indoor phasing system based
PFIS Camera and Collimator CDR Conceptual Design Report. March 5, 2003 J. Alan Schier
 PFIS Camera and Collimator CDR Conceptual Design Report March 5, 2003 J. Alan Schier Contents I. Summary of Design Features II. Summary of Quantitative Results Mounting Tolerances Element Stresses Optical
PFIS Camera and Collimator CDR Conceptual Design Report March 5, 2003 J. Alan Schier Contents I. Summary of Design Features II. Summary of Quantitative Results Mounting Tolerances Element Stresses Optical
Element size effect on the analysis of heavy-duty machine cross-rail Jianhua Wang1,Jianke Chen1,a,Tieneng Guo1 Bin Song 2, Dongliang Guo3
 4th International Conference on Machinery, Materials and Computing Technology (ICMMCT 2016) Element size effect on the analysis of heavy-duty machine cross-rail Jianhua Wang1,Jianke Chen1,a,Tieneng Guo1
4th International Conference on Machinery, Materials and Computing Technology (ICMMCT 2016) Element size effect on the analysis of heavy-duty machine cross-rail Jianhua Wang1,Jianke Chen1,a,Tieneng Guo1
MMT CONVERSION. Technical Report #31 SECONDARY MIRRORS SUPPORT. M2/F15 and M2/F9 HEXAPOD DESIGN. W. Gallieni, R. Pozzi
 Doc.No. : D00001 Steward Observatory Technical Report #31 SECONDARY MIRRORS SUPPORT M2/F15 and M2/F9 HEXAPOD DESIGN W. Gallieni, R. Pozzi 1 Applicable Documents 1.1 Optical scheme and secondary hub position
Doc.No. : D00001 Steward Observatory Technical Report #31 SECONDARY MIRRORS SUPPORT M2/F15 and M2/F9 HEXAPOD DESIGN W. Gallieni, R. Pozzi 1 Applicable Documents 1.1 Optical scheme and secondary hub position
Ultra-Lightweight Telescope Mount
 PUBLICATIONS OF THE ASTRONOMICAL SOCIETY OF THE PACIFIC, 121:266 271, 2009 March 2009. The Astronomical Society of the Pacific. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. Ultra-Lightweight Telescope Mount
PUBLICATIONS OF THE ASTRONOMICAL SOCIETY OF THE PACIFIC, 121:266 271, 2009 March 2009. The Astronomical Society of the Pacific. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. Ultra-Lightweight Telescope Mount
Development of a probe traversing system for an open test section wind tunnel
 Development of a probe traversing system for an open test section wind tunnel Gépészet 2012 Conference 24 th of May, 2012 Section Energy 2. Árpád Varga Mechanical Engineering Modelling MSc, Contractual
Development of a probe traversing system for an open test section wind tunnel Gépészet 2012 Conference 24 th of May, 2012 Section Energy 2. Árpád Varga Mechanical Engineering Modelling MSc, Contractual
Appendix 2: Disassembling and Assembling the Telescopes and the Celestron Equatorial Mounts
 Appendix 2: Disassembling and Assembling the Telescopes and the Celestron Equatorial Mounts Disassembling (classroom) 1. The mount must be locked with the telescope situated horizontally. Note the telescope
Appendix 2: Disassembling and Assembling the Telescopes and the Celestron Equatorial Mounts Disassembling (classroom) 1. The mount must be locked with the telescope situated horizontally. Note the telescope
Development of Measuring System for the Non-Repetitive Run-Out(NRRO) of Ball Bearing
 Journal of Engineering Mechanics and Machinery (207) Vol. 2, Num. Clausius Scientific Press, Canada Development of Measuring System for the Non-Repetitive Run-Out(NRRO) of Ball Bearing Y. Chen,a,*, G.F.
Journal of Engineering Mechanics and Machinery (207) Vol. 2, Num. Clausius Scientific Press, Canada Development of Measuring System for the Non-Repetitive Run-Out(NRRO) of Ball Bearing Y. Chen,a,*, G.F.
How to improve the high-frequency capabilities of the SRT
 Mem. S.A.It. Suppl. Vol. 10, 136 c SAIt 2006 Memorie della Supplementi How to improve the high-frequency capabilities of the SRT T. Pisanu 1, F. Buffa 2, M. Morsiani 3, M. Natalini 1, C. Pernechele 2,
Mem. S.A.It. Suppl. Vol. 10, 136 c SAIt 2006 Memorie della Supplementi How to improve the high-frequency capabilities of the SRT T. Pisanu 1, F. Buffa 2, M. Morsiani 3, M. Natalini 1, C. Pernechele 2,
Automatic Level Maintenance Manual SAL-XX W/ AIR DAMPENED COMPENSATOR
 Automatic Level Maintenance Manual SAL-XX W/ AIR DAMPENED COMPENSATOR CST/Berger 2001 SAL 20/24/28/32 PAGE 1 REV. C 071803 Automatic Level Maintenance Manual User Calibration and Testing... 3 Circular
Automatic Level Maintenance Manual SAL-XX W/ AIR DAMPENED COMPENSATOR CST/Berger 2001 SAL 20/24/28/32 PAGE 1 REV. C 071803 Automatic Level Maintenance Manual User Calibration and Testing... 3 Circular
Constrained Rectilinear Motion Dynamics Laboratory, Spring 2008
 Constrained Rectilinear Motion Dynamics Laboratory, Spring 2008 Pulley systems are commonly used (in cranes, for example) to gain a mechanical advantage, allowing heavy loads to be lifted by smaller forces
Constrained Rectilinear Motion Dynamics Laboratory, Spring 2008 Pulley systems are commonly used (in cranes, for example) to gain a mechanical advantage, allowing heavy loads to be lifted by smaller forces
D : SOLID MECHANICS. Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. Q.1 Find the force (in kn) in the member BH of the truss shown.
 D : SOLID MECHANICS Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. Q.1 Find the force (in kn) in the member BH of the truss shown. Q.2 Consider the forces of magnitude F acting on the sides of the regular hexagon having
D : SOLID MECHANICS Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. Q.1 Find the force (in kn) in the member BH of the truss shown. Q.2 Consider the forces of magnitude F acting on the sides of the regular hexagon having
DEVELOPMENT OF A BAR-SHAPED ULTRASONIC MOTOR FOR MULTI-DEGREES OF FREEDOM MOTION
 DEVELOPMENT OF A BAR-SHAPED ULTRASONIC MOTOR FOR MULTI-DEGREES OF FREEDOM MOTION Kenjiro Takemura KEIO University, Yokohama, Kanagawa, JAPAN, m982468@msr.st.keio.ac.jp Nobuyuki Kojima Canon Inc., Ohta-ku,
DEVELOPMENT OF A BAR-SHAPED ULTRASONIC MOTOR FOR MULTI-DEGREES OF FREEDOM MOTION Kenjiro Takemura KEIO University, Yokohama, Kanagawa, JAPAN, m982468@msr.st.keio.ac.jp Nobuyuki Kojima Canon Inc., Ohta-ku,
Force and Motion 20 N. Force: Net Force on 2 kg mass = N. Net Force on 3 kg mass = = N. Motion: Mass Accel. of 2 kg mass = = kg m/s 2.
 Force and Motion Team In previous labs, you used a motion sensor to measure the position, velocity, and acceleration of moving objects. You were not concerned about the mechanism that caused the object
Force and Motion Team In previous labs, you used a motion sensor to measure the position, velocity, and acceleration of moving objects. You were not concerned about the mechanism that caused the object
