Department of Physics and Astronomy 2 nd Year Laboratory. L2 Light Scattering
|
|
|
- Ross Osborne
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 nd ear laborator script L Light Scattering Department o Phsics and Astronom nd Year Laborator L Light Scattering Scientiic aims and objectives To determine the densit o nano-spheres o polstrene suspended in the tubes o water b their Raleigh scattering cross section. To determine the validit o the hpothesis that the scattering mechanism is Raleigh and not geometric or Mie. Learning Outcomes To determine the origin o sstematic errors To determine the validit o using web based literature to ind values or material properties. To know that there are dierent regimes or light scattering depending on the size o an object Apparatus Four light scattering stations with dierent laser wavelengths o 473 ± 5 nm o 635 ± 5 nm o 660 ± 5 nm o 780 ± 15 nm Each station is comprised o o Laser o Moving light detector, ampliier and meter o Ruler Saet instructions This eperiment uses low power class IIIb laser beams, one o which is invisible. Never look directl into the beam, Take care not to allow shin objects jeweller, watches etc to relect the beam at ee level. Be particularl careul with the invisible laser. χ Ecel sotware September 010 V.1 Page 1
2 nd ear laborator script L Light Scattering Task 1 - Pre-session questions You are required to complete the questions ound at the back o the script beore starting our laborator work. These questions will prepare ou or the eperiment b teaching ou about dierent scattering mechanisms. Task The eperiment The objective is to determine the number densit o polstrene spheres suspended in tubes o water b measuring the change in intensit o scattered light rom laser beams o varing wavelength. The dependence o scattering attenuation on laser wavelength should ollow that o Raleigh scattering since the polstrene sphere size 11 nm is less than the wavelength o light. However, ou should check this hpothesis in an attempt to eclude other possible scattering mechanisms such as Mie scattering or geometric scattering. The attenuation o laser light in the tube has contributions rom the absorption o water itsel α and rom the scattering rom the polstrene spheres Nσ. You should account or both in our attempts to validate the Raleigh equation and quanti the densit o spheres in the tubes. This eperiment is particularl prone to sstematic errors. For eample, misalignment o the laser such that the beam is not travelling down the centre o the tube, or misalignment o the detector such that it becomes urther awa rom the tube as the distance rom the laser source increases. You should make some measurements and calculations to numericall quanti these kinds o contributions to the error in the eperiment and determine whether the are signiicant or not. These assessments o sstematic errors should be combined with repeat measurements to determine random error contribution. χ should be used when itting straight lines to our data. Task 3 Reporting You should report a number densit o the polstrene spheres and a proportion o the volume o the tubes that is taken up b the spheres. You should assess whether the hpothesis that Raleigh scattering is the dominant mechanism is correct based on our eperimental evidence. You should also spend time considering both sstematic and random errors that could occur in the eperiment and report our indings. September 010 V.1 Page
3 nd ear laborator script L Light Scattering Appendi o supporting inormation Contents 1. Scattering o light. Mie, Raleigh and geometric scattering 3. Measurement procedure 4. Absorption coeicient o water 5. Straight line itting using χ 6. Compound errors 7. Sstematic errors 1. Scattering o light I a light beam passes through a medium in which there are suspended spheres with a reractive inde that is dierent rom that o the medium, the beam is attenuated because some o the light is scattered out o the original beam direction. This is obvious in ogg weather and when sunlight passes through a dust atmosphere. Scattering o light is important in astronom, where light rom stars is oten viewed through interstellar dust clouds, and also in the optical ibre telecommunications industr, where light scatters rom impurities and inhomogeneities in the ibre. The scattering is convenientl described in terms o the scattering cross-section σ o the sphere concerned; this is the eective area which the sphere eliminates rom the beam. I we consider a beam o intensit I and area A propagating through a suspension o spheres with N spheres per unit volume, each o which has a scattering cross-section σ. The decrease in intensit di on passing through a distance d is given b: di total area o scatterers - raction o beam intercepted A1 I area o beam Thereore: Nvolume o liquid σ N Ad σ Nσd A A A I ln I Nσ I I ep Nσ l n 0 or 0. A3 The light intensit will also deca as a consequence o absorption b the water molecules. This is characterised b the absorption coeicient α. The attenuation processes act independentl o each other and so their separate contributions can be added together. The variation o the intensit with is thereore given b: I I ep[ Nσ α ] A4 0 Together with eperimental data or the deca o the intensit o light, equation A4 can be used to determine Nσ α or the dierent wavelengths o laser b itting a straight line to a ln I vs plot. September 010 V.1 Page 3
4 nd ear laborator script L Light Scattering. Mie, Raleigh and geometric scattering The scattering o electromagnetic radiation b spherical particles can be analsed rigorousl b solving Mawell s equations or the sstem. Such an analsis is normall done with the aid o computers and can accuratel predict man scattering phenomena. Gustav Mie was the irst scientist to attempt these calculations and hence the generic terminolog or scattering where the light has comparable wavelength to the size o the sphere is know as Mie scattering. Although the Mie scattering approach is valid or spheres o an size, there are two limiting cases that ield simple analtical epressions or σ. Raleigh Scattering applies when a << λ, where a is the radius o the sphere and λ is the wavelength o light. The scattering cross-section or Raleigh scattering is where n n n π a σ 4 3λ 6 n n 1. n 1 is the reractive inde o the sphere and n that o the medium. A5 Geometric Scattering applies when a >> λ. The sphere simpl blanks out the light rom its geometrical shadow and σ πa. In this eperiment we hpothesise that scattering should ollow the Raleigh equation A5 since the polstrene sphere diameter o 11 nm is signiicantl smaller that o the shortest laser wavelength. Using our eperimental results ou should discuss the validit o this hpothesis. One approach is to plot our eperimentall determined values or σ against 1/λ 4 and assess the linearit o the plot. Raleigh scattering should eild a perectl straight line. The reractive inde o water varies rom at 400 nm to at 800 nm The reractive inde o polstrene varies rom at 400 nm to at 800 nm 3. Measurement procedure For each set o apparatus, the relative intensit o the beam as a unction o distance along the tube should be measured. Since the measurements o scattered intensit as a unction o distance need to be made with minimal background light, it is a requirement that the lid on the bo be closed. Thereore the number o turns made b the screw thread needs to be calibrated against distance beore measurements can proceed. A second requirement is to setup the detector so it measures the intensit o the scattered light with the greatest dnamic range, to give the greatest sensitivit to the measurements. You should set the gain controls o the photodiode ampliier to achieve this condition. Finall ou will need to zero the photodetector ampliier so that ou are onl measuring the scattered light rom the laser as it passes through the tube, and not stra light rom the room lights or windows. This can be done b blocking the laser with a piece o black card or similar, closing the lid, and then setting the ampliier controls so that the signal reads zero. Do not zero the detector b turning the laser September 010 V.1 Page 4
5 nd ear laborator script L Light Scattering o since lasers need a considerable length o time to settle to a stable emission power. 4. Absorption coeicient o water Water is highl transparent in the visible part o the spectrum since there are no resonant electronic or vibrational transitions. However a small background absorption is present and has been characterised and documented man times. Data or the absorption coeicient o pure water taken rom an online resource has been plotted below. You should consider the validit o the use o this data in our eperiment, and using this data, or other data that ou can ind, determine values and associated errors or the absorption coeicients required at the dierent laser wavelengths. 5. Straight line itting using χ The χ ecel spreadsheet has been developed to enable ou to perorm a χ it to our data that takes into account our error bars. In general the error bars should be larger than our error bars and hence dominant. I this is not the case rearrange our data appropriatel. I our data are not epected to be represented b a straight line e.g. b an eponential unction o then tr to transorm our values appropriatel. Then ollow these instructions. 1. Cop and paste our, and σ values into Columns C, D and E respectivel, starting at Row 17. Remember to use Paste Special i our values are derived rom ormulae.. Enter the number 1 in Column B or ever Row in which ou have data. September 010 V.1 Page 5
6 nd ear laborator script L Light Scattering September 010 V.1 Page 6 3. Read o the values or the gradient and uncertaint and intercept and uncertaint rom cells B5, C5, B6 and C6. 4. The goodness o it how accuratel our straight line model actuall represents the data can be estimated rom the χ value Cell B8 divided b the number o data given in Cell B9. For a good it the χ /n value should be approimatel 1.0. A value signiicantl less than this shows ou have iddled our data, or over-estimated the uncertainties on our points! A value signiicantl greater than 1.0 shows that the data are not well-represented b the model think about wh this might be. 5. Don t orget to plot the itted line using mc in our graph as a line alongside our data-points with error bars. Do not use Add Trendline. I everthing has worked correctl, χ /n ~ 1.0, and errors are Gaussian, then approimatel 68% o the points should lie on the itted line within their error bars. 6. Compound errors Absolute error Proportional error n n n 1 n / 4 7. Sstematic errors See and reerences therein.
7 nd ear laborator script L Light Scattering Pre-lab multiple choice questions Mie scattering can onl be calculated numericall or a speciic sstem o scattering particles. Using an online numerical calculator ound at ou can investigate Mie scattering, and see how the scattering direction and cross section depends on particle size. Using the sotware ind out which is the most likel particle size or the angular scattering patterns below. You can assume polstrene spheres as in the eperiment. Q1 A: 0.05 µm B: 0.1 µm C: 0.5 µm D:.0 µm Q A: 0.05 µm B: 0.1 µm C: 0.5 µm D:.0 µm Q3 A: 0.05 µm B: 0.1 µm C: 0.5 µm D:.0 µm September 010 V.1 Page 7
Part I: Thin Converging Lens
 Laboratory 1 PHY431 Fall 011 Part I: Thin Converging Lens This eperiment is a classic eercise in geometric optics. The goal is to measure the radius o curvature and ocal length o a single converging lens
Laboratory 1 PHY431 Fall 011 Part I: Thin Converging Lens This eperiment is a classic eercise in geometric optics. The goal is to measure the radius o curvature and ocal length o a single converging lens
Comments on Problems. 3.1 This problem offers some practice in deriving utility functions from indifference curve specifications.
 CHAPTER 3 PREFERENCES AND UTILITY These problems provide some practice in eamining utilit unctions b looking at indierence curve maps and at a ew unctional orms. The primar ocus is on illustrating the
CHAPTER 3 PREFERENCES AND UTILITY These problems provide some practice in eamining utilit unctions b looking at indierence curve maps and at a ew unctional orms. The primar ocus is on illustrating the
Math-3 Lesson 1-4. Review: Cube, Cube Root, and Exponential Functions
 Math- Lesson -4 Review: Cube, Cube Root, and Eponential Functions Quiz - Graph (no calculator):. y. y ( ) 4. y What is a power? vocabulary Power: An epression ormed by repeated Multiplication o the same
Math- Lesson -4 Review: Cube, Cube Root, and Eponential Functions Quiz - Graph (no calculator):. y. y ( ) 4. y What is a power? vocabulary Power: An epression ormed by repeated Multiplication o the same
. This is the Basic Chain Rule. x dt y dt z dt Chain Rule in this context.
 Math 18.0A Gradients, Chain Rule, Implicit Dierentiation, igher Order Derivatives These notes ocus on our things: (a) the application o gradients to ind normal vectors to curves suraces; (b) the generaliation
Math 18.0A Gradients, Chain Rule, Implicit Dierentiation, igher Order Derivatives These notes ocus on our things: (a) the application o gradients to ind normal vectors to curves suraces; (b) the generaliation
9.1 The Square Root Function
 Section 9.1 The Square Root Function 869 9.1 The Square Root Function In this section we turn our attention to the square root unction, the unction deined b the equation () =. (1) We begin the section
Section 9.1 The Square Root Function 869 9.1 The Square Root Function In this section we turn our attention to the square root unction, the unction deined b the equation () =. (1) We begin the section
Measurements & Error Analysis
 It is better to be roughl right than precisel wrong. Alan Greenspan The Uncertaint o Measurements Some numerical statements are eact: Mar has 3 brothers, and + 4. However, all measurements have some degree
It is better to be roughl right than precisel wrong. Alan Greenspan The Uncertaint o Measurements Some numerical statements are eact: Mar has 3 brothers, and + 4. However, all measurements have some degree
AP Calculus AB Summer Assignment
 AP Calculus AB Summer Assignment As Advanced placement students, our irst assignment or the 07-08 school ear is to come to class the ver irst da in top mathematical orm. Calculus is a world o change. While
AP Calculus AB Summer Assignment As Advanced placement students, our irst assignment or the 07-08 school ear is to come to class the ver irst da in top mathematical orm. Calculus is a world o change. While
Physics Lab 1 - Measurements
 Phsics 203 - Lab 1 - Measurements Introduction An phsical science requires measurement. This lab will involve making several measurements of the fundamental units of length, mass, and time. There is no
Phsics 203 - Lab 1 - Measurements Introduction An phsical science requires measurement. This lab will involve making several measurements of the fundamental units of length, mass, and time. There is no
8.4 Inverse Functions
 Section 8. Inverse Functions 803 8. Inverse Functions As we saw in the last section, in order to solve application problems involving eponential unctions, we will need to be able to solve eponential equations
Section 8. Inverse Functions 803 8. Inverse Functions As we saw in the last section, in order to solve application problems involving eponential unctions, we will need to be able to solve eponential equations
Curve Sketching. The process of curve sketching can be performed in the following steps:
 Curve Sketching So ar you have learned how to ind st and nd derivatives o unctions and use these derivatives to determine where a unction is:. Increasing/decreasing. Relative extrema 3. Concavity 4. Points
Curve Sketching So ar you have learned how to ind st and nd derivatives o unctions and use these derivatives to determine where a unction is:. Increasing/decreasing. Relative extrema 3. Concavity 4. Points
APPENDIX 1 ERROR ESTIMATION
 1 APPENDIX 1 ERROR ESTIMATION Measurements are always subject to some uncertainties no matter how modern and expensive equipment is used or how careully the measurements are perormed These uncertainties
1 APPENDIX 1 ERROR ESTIMATION Measurements are always subject to some uncertainties no matter how modern and expensive equipment is used or how careully the measurements are perormed These uncertainties
RATIONAL FUNCTIONS. Finding Asymptotes..347 The Domain Finding Intercepts Graphing Rational Functions
 RATIONAL FUNCTIONS Finding Asymptotes..347 The Domain....350 Finding Intercepts.....35 Graphing Rational Functions... 35 345 Objectives The ollowing is a list o objectives or this section o the workbook.
RATIONAL FUNCTIONS Finding Asymptotes..347 The Domain....350 Finding Intercepts.....35 Graphing Rational Functions... 35 345 Objectives The ollowing is a list o objectives or this section o the workbook.
Objectives. By the time the student is finished with this section of the workbook, he/she should be able
 FUNCTIONS Quadratic Functions......8 Absolute Value Functions.....48 Translations o Functions..57 Radical Functions...61 Eponential Functions...7 Logarithmic Functions......8 Cubic Functions......91 Piece-Wise
FUNCTIONS Quadratic Functions......8 Absolute Value Functions.....48 Translations o Functions..57 Radical Functions...61 Eponential Functions...7 Logarithmic Functions......8 Cubic Functions......91 Piece-Wise
Methods for Advanced Mathematics (C3) Coursework Numerical Methods
 Woodhouse College 0 Page Introduction... 3 Terminolog... 3 Activit... 4 Wh use numerical methods?... Change of sign... Activit... 6 Interval Bisection... 7 Decimal Search... 8 Coursework Requirements on
Woodhouse College 0 Page Introduction... 3 Terminolog... 3 Activit... 4 Wh use numerical methods?... Change of sign... Activit... 6 Interval Bisection... 7 Decimal Search... 8 Coursework Requirements on
Regular Physics - Notes Ch. 1
 Regular Phsics - Notes Ch. 1 What is Phsics? the stud of matter and energ and their relationships; the stud of the basic phsical laws of nature which are often stated in simple mathematical equations.
Regular Phsics - Notes Ch. 1 What is Phsics? the stud of matter and energ and their relationships; the stud of the basic phsical laws of nature which are often stated in simple mathematical equations.
Quadratic Functions. The graph of the function shifts right 3. The graph of the function shifts left 3.
 Quadratic Functions The translation o a unction is simpl the shiting o a unction. In this section, or the most part, we will be graphing various unctions b means o shiting the parent unction. We will go
Quadratic Functions The translation o a unction is simpl the shiting o a unction. In this section, or the most part, we will be graphing various unctions b means o shiting the parent unction. We will go
Lecture Outline. Basics of Spatial Filtering Smoothing Spatial Filters. Sharpening Spatial Filters
 1 Lecture Outline Basics o Spatial Filtering Smoothing Spatial Filters Averaging ilters Order-Statistics ilters Sharpening Spatial Filters Laplacian ilters High-boost ilters Gradient Masks Combining Spatial
1 Lecture Outline Basics o Spatial Filtering Smoothing Spatial Filters Averaging ilters Order-Statistics ilters Sharpening Spatial Filters Laplacian ilters High-boost ilters Gradient Masks Combining Spatial
nm nm
 The Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom You have seen how Bohr s model of the atom eplains the emission spectrum of hdrogen. The emission spectra of other atoms, however, posed a problem. A mercur atom,
The Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom You have seen how Bohr s model of the atom eplains the emission spectrum of hdrogen. The emission spectra of other atoms, however, posed a problem. A mercur atom,
Experimental Uncertainty Review. Abstract. References. Measurement Uncertainties and Uncertainty Propagation
 Experimental Uncertaint Review Abstract This is intended as a brief summar of the basic elements of uncertaint analsis, and a hand reference for laborator use. It provides some elementar "rules-of-thumb"
Experimental Uncertaint Review Abstract This is intended as a brief summar of the basic elements of uncertaint analsis, and a hand reference for laborator use. It provides some elementar "rules-of-thumb"
New Functions from Old Functions
 .3 New Functions rom Old Functions In this section we start with the basic unctions we discussed in Section. and obtain new unctions b shiting, stretching, and relecting their graphs. We also show how
.3 New Functions rom Old Functions In this section we start with the basic unctions we discussed in Section. and obtain new unctions b shiting, stretching, and relecting their graphs. We also show how
Basic properties of limits
 Roberto s Notes on Dierential Calculus Chapter : Limits and continuity Section Basic properties o its What you need to know already: The basic concepts, notation and terminology related to its. What you
Roberto s Notes on Dierential Calculus Chapter : Limits and continuity Section Basic properties o its What you need to know already: The basic concepts, notation and terminology related to its. What you
3. Several Random Variables
 . Several Random Variables. Two Random Variables. Conditional Probabilit--Revisited. Statistical Independence.4 Correlation between Random Variables. Densit unction o the Sum o Two Random Variables. Probabilit
. Several Random Variables. Two Random Variables. Conditional Probabilit--Revisited. Statistical Independence.4 Correlation between Random Variables. Densit unction o the Sum o Two Random Variables. Probabilit
Functions. Essential Question What are some of the characteristics of the graph of a logarithmic function?
 5. Logarithms and Logarithmic Functions Essential Question What are some o the characteristics o the graph o a logarithmic unction? Ever eponential unction o the orm () = b, where b is a positive real
5. Logarithms and Logarithmic Functions Essential Question What are some o the characteristics o the graph o a logarithmic unction? Ever eponential unction o the orm () = b, where b is a positive real
Increasing and Decreasing Functions and the First Derivative Test. Increasing and Decreasing Functions. Video
 SECTION and Decreasing Functions and the First Derivative Test 79 Section and Decreasing Functions and the First Derivative Test Determine intervals on which a unction is increasing or decreasing Appl
SECTION and Decreasing Functions and the First Derivative Test 79 Section and Decreasing Functions and the First Derivative Test Determine intervals on which a unction is increasing or decreasing Appl
Time Series Analysis for Quality Improvement: a Soft Computing Approach
 ESANN'4 proceedings - European Smposium on Artiicial Neural Networks Bruges (Belgium), 8-3 April 4, d-side publi., ISBN -9337-4-8, pp. 19-114 ime Series Analsis or Qualit Improvement: a Sot Computing Approach
ESANN'4 proceedings - European Smposium on Artiicial Neural Networks Bruges (Belgium), 8-3 April 4, d-side publi., ISBN -9337-4-8, pp. 19-114 ime Series Analsis or Qualit Improvement: a Sot Computing Approach
Tangent Line Approximations
 60_009.qd //0 :8 PM Page SECTION.9 Dierentials Section.9 EXPLORATION Tangent Line Approimation Use a graphing utilit to graph. In the same viewing window, graph the tangent line to the graph o at the point,.
60_009.qd //0 :8 PM Page SECTION.9 Dierentials Section.9 EXPLORATION Tangent Line Approimation Use a graphing utilit to graph. In the same viewing window, graph the tangent line to the graph o at the point,.
Relating axial motion of optical elements to focal shift
 Relating aial motion o optical elements to ocal shit Katie Schwertz and J. H. Burge College o Optical Sciences, University o Arizona, Tucson AZ 857, USA katie.schwertz@gmail.com ABSTRACT In this paper,
Relating aial motion o optical elements to ocal shit Katie Schwertz and J. H. Burge College o Optical Sciences, University o Arizona, Tucson AZ 857, USA katie.schwertz@gmail.com ABSTRACT In this paper,
Section 1.2 Domain and Range
 Section 1. Domain and Range 1 Section 1. Domain and Range One o our main goals in mathematics is to model the real world with mathematical unctions. In doing so, it is important to keep in mind the limitations
Section 1. Domain and Range 1 Section 1. Domain and Range One o our main goals in mathematics is to model the real world with mathematical unctions. In doing so, it is important to keep in mind the limitations
Relating axial motion of optical elements to focal shift
 Relating aial motion o optical elements to ocal shit Katie Schwertz and J. H. Burge College o Optical Sciences, University o Arizona, Tucson AZ 857, USA katie.schwertz@gmail.com ABSTRACT In this paper,
Relating aial motion o optical elements to ocal shit Katie Schwertz and J. H. Burge College o Optical Sciences, University o Arizona, Tucson AZ 857, USA katie.schwertz@gmail.com ABSTRACT In this paper,
3.2 LOGARITHMIC FUNCTIONS AND THEIR GRAPHS
 Section. Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs 7. LOGARITHMIC FUNCTIONS AND THEIR GRAPHS Ariel Skelle/Corbis What ou should learn Recognize and evaluate logarithmic functions with base a. Graph logarithmic
Section. Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs 7. LOGARITHMIC FUNCTIONS AND THEIR GRAPHS Ariel Skelle/Corbis What ou should learn Recognize and evaluate logarithmic functions with base a. Graph logarithmic
( x) f = where P and Q are polynomials.
 9.8 Graphing Rational Functions Lets begin with a deinition. Deinition: Rational Function A rational unction is a unction o the orm ( ) ( ) ( ) P where P and Q are polynomials. Q An eample o a simple rational
9.8 Graphing Rational Functions Lets begin with a deinition. Deinition: Rational Function A rational unction is a unction o the orm ( ) ( ) ( ) P where P and Q are polynomials. Q An eample o a simple rational
Algebra II Foundations
 Algebra II Foundations Non Linear Functions Student Journal Problems of the Da First Semester Page 35 Problem Set 35 CHALLENGE Tr the following problem, and eplain how ou determined our answer. If it takes
Algebra II Foundations Non Linear Functions Student Journal Problems of the Da First Semester Page 35 Problem Set 35 CHALLENGE Tr the following problem, and eplain how ou determined our answer. If it takes
HYDROGEN SPECTRUM = 2
 MP6 OBJECT 3 HYDROGEN SPECTRUM MP6. The object o this experiment is to observe some o the lines in the emission spectrum o hydrogen, and to compare their experimentally determined wavelengths with those
MP6 OBJECT 3 HYDROGEN SPECTRUM MP6. The object o this experiment is to observe some o the lines in the emission spectrum o hydrogen, and to compare their experimentally determined wavelengths with those
Chemistry 141 Laboratory Lab Lecture Notes for Kinetics Lab Dr Abrash
 Q: What is Kinetics? Chemistr 141 Laborator Lab Lecture Notes for Kinetics Lab Dr Abrash Kinetics is the stud of rates of reaction, i.e., the stud of the factors that control how quickl a reaction occurs.
Q: What is Kinetics? Chemistr 141 Laborator Lab Lecture Notes for Kinetics Lab Dr Abrash Kinetics is the stud of rates of reaction, i.e., the stud of the factors that control how quickl a reaction occurs.
Unit 12 Study Notes 1 Systems of Equations
 You should learn to: Unit Stud Notes Sstems of Equations. Solve sstems of equations b substitution.. Solve sstems of equations b graphing (calculator). 3. Solve sstems of equations b elimination. 4. Solve
You should learn to: Unit Stud Notes Sstems of Equations. Solve sstems of equations b substitution.. Solve sstems of equations b graphing (calculator). 3. Solve sstems of equations b elimination. 4. Solve
Differential Equations
 LOCUS Dierential Equations CONCEPT NOTES 0. Motiation 0. Soling Dierential Equations LOCUS Dierential Equations Section - MOTIVATION A dierential equation can simpl be said to be an equation inoling deriaties
LOCUS Dierential Equations CONCEPT NOTES 0. Motiation 0. Soling Dierential Equations LOCUS Dierential Equations Section - MOTIVATION A dierential equation can simpl be said to be an equation inoling deriaties
Syllabus Objective: 2.9 The student will sketch the graph of a polynomial, radical, or rational function.
 Precalculus Notes: Unit Polynomial Functions Syllabus Objective:.9 The student will sketch the graph o a polynomial, radical, or rational unction. Polynomial Function: a unction that can be written in
Precalculus Notes: Unit Polynomial Functions Syllabus Objective:.9 The student will sketch the graph o a polynomial, radical, or rational unction. Polynomial Function: a unction that can be written in
Lab on Taylor Polynomials. This Lab is accompanied by an Answer Sheet that you are to complete and turn in to your instructor.
 Lab on Taylor Polynomials This Lab is accompanied by an Answer Sheet that you are to complete and turn in to your instructor. In this Lab we will approimate complicated unctions by simple unctions. The
Lab on Taylor Polynomials This Lab is accompanied by an Answer Sheet that you are to complete and turn in to your instructor. In this Lab we will approimate complicated unctions by simple unctions. The
Chapter 4 Imaging. Lecture 21. d (110) Chem 793, Fall 2011, L. Ma
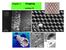 Chapter 4 Imaging Lecture 21 d (110) Imaging Imaging in the TEM Diraction Contrast in TEM Image HRTEM (High Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy) Imaging or phase contrast imaging STEM imaging a
Chapter 4 Imaging Lecture 21 d (110) Imaging Imaging in the TEM Diraction Contrast in TEM Image HRTEM (High Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy) Imaging or phase contrast imaging STEM imaging a
MODULE 6 LECTURE NOTES 1 REVIEW OF PROBABILITY THEORY. Most water resources decision problems face the risk of uncertainty mainly because of the
 MODULE 6 LECTURE NOTES REVIEW OF PROBABILITY THEORY INTRODUCTION Most water resources decision problems ace the risk o uncertainty mainly because o the randomness o the variables that inluence the perormance
MODULE 6 LECTURE NOTES REVIEW OF PROBABILITY THEORY INTRODUCTION Most water resources decision problems ace the risk o uncertainty mainly because o the randomness o the variables that inluence the perormance
1036: Probability & Statistics
 1036: Probabilit & Statistics Lecture 4 Mathematical pectation Prob. & Stat. Lecture04 - mathematical epectation cwliu@twins.ee.nctu.edu.tw 4-1 Mean o a Random Variable Let be a random variable with probabilit
1036: Probabilit & Statistics Lecture 4 Mathematical pectation Prob. & Stat. Lecture04 - mathematical epectation cwliu@twins.ee.nctu.edu.tw 4-1 Mean o a Random Variable Let be a random variable with probabilit
STRAND: GRAPHS Unit 5 Growth and Decay
 CMM Subject Support Strand: GRAPHS Unit 5 Growth and Deca: Tet STRAND: GRAPHS Unit 5 Growth and Deca TEXT Contents Section 5. Modelling Population 5. Models of Growth and Deca 5. Carbon Dating 5.4 Rate
CMM Subject Support Strand: GRAPHS Unit 5 Growth and Deca: Tet STRAND: GRAPHS Unit 5 Growth and Deca TEXT Contents Section 5. Modelling Population 5. Models of Growth and Deca 5. Carbon Dating 5.4 Rate
NCERT-XII / Unit- 09 Ray Optics
 REFLECTION OF LIGHT The laws o relection are.. (i) The incident ray, relected ray and the normal to the relecting surace at the point o incidence lie in the same plane (ii) The angle o relection (i.e.,
REFLECTION OF LIGHT The laws o relection are.. (i) The incident ray, relected ray and the normal to the relecting surace at the point o incidence lie in the same plane (ii) The angle o relection (i.e.,
Inverse of a Function
 . Inverse o a Function Essential Question How can ou sketch the graph o the inverse o a unction? Graphing Functions and Their Inverses CONSTRUCTING VIABLE ARGUMENTS To be proicient in math, ou need to
. Inverse o a Function Essential Question How can ou sketch the graph o the inverse o a unction? Graphing Functions and Their Inverses CONSTRUCTING VIABLE ARGUMENTS To be proicient in math, ou need to
CHAPTER-III CONVECTION IN A POROUS MEDIUM WITH EFFECT OF MAGNETIC FIELD, VARIABLE FLUID PROPERTIES AND VARYING WALL TEMPERATURE
 CHAPER-III CONVECION IN A POROUS MEDIUM WIH EFFEC OF MAGNEIC FIELD, VARIABLE FLUID PROPERIES AND VARYING WALL EMPERAURE 3.1. INRODUCION Heat transer studies in porous media ind applications in several
CHAPER-III CONVECION IN A POROUS MEDIUM WIH EFFEC OF MAGNEIC FIELD, VARIABLE FLUID PROPERIES AND VARYING WALL EMPERAURE 3.1. INRODUCION Heat transer studies in porous media ind applications in several
SHADOW AND BACKGROUND ORIENTED SCHLIEREN INVESTIGATION OF SHOCK WAVES IN GAS-DISCHARGE MEDIUM
 SHADOW AND BACKGROUND ORIENTED SCHLIEREN INVESTIGATION OF SHOCK WAVES IN GAS-DISCHARGE MEDIUM J. JIN 1, I.V. MURSENKOVA 1,c, N. N. SYSOEV 1 and I.A. ZNAMENSKAYA 1 1 Department of Phsics, Lomonosov Moscow
SHADOW AND BACKGROUND ORIENTED SCHLIEREN INVESTIGATION OF SHOCK WAVES IN GAS-DISCHARGE MEDIUM J. JIN 1, I.V. MURSENKOVA 1,c, N. N. SYSOEV 1 and I.A. ZNAMENSKAYA 1 1 Department of Phsics, Lomonosov Moscow
Chem 406 Biophysical Chemistry Lecture 1 Transport Processes, Sedimentation & Diffusion
 Chem 406 Biophysical Chemistry Lecture 1 Transport Processes, Sedimentation & Diusion I. Introduction A. There are a group o biophysical techniques that are based on transport processes. 1. Transport processes
Chem 406 Biophysical Chemistry Lecture 1 Transport Processes, Sedimentation & Diusion I. Introduction A. There are a group o biophysical techniques that are based on transport processes. 1. Transport processes
Determination of Young s modulus of glass by Cornu s apparatus
 Determination of Young s modulus of glass b Cornu s apparatus Objective To determine Young s modulus and Poisson s ratio of a glass plate using Cornu s method. Theoretical Background Young s modulus, also
Determination of Young s modulus of glass b Cornu s apparatus Objective To determine Young s modulus and Poisson s ratio of a glass plate using Cornu s method. Theoretical Background Young s modulus, also
6.4 graphs OF logarithmic FUnCTIOnS
 SECTION 6. graphs of logarithmic functions 9 9 learning ObjeCTIveS In this section, ou will: Identif the domain of a logarithmic function. Graph logarithmic functions. 6. graphs OF logarithmic FUnCTIOnS
SECTION 6. graphs of logarithmic functions 9 9 learning ObjeCTIveS In this section, ou will: Identif the domain of a logarithmic function. Graph logarithmic functions. 6. graphs OF logarithmic FUnCTIOnS
Lab #13: Polarization
 Lab #13: Polarization Introduction In this experiment we will investigate various properties associated with polarized light. We will study both its generation and application. Real world applications
Lab #13: Polarization Introduction In this experiment we will investigate various properties associated with polarized light. We will study both its generation and application. Real world applications
Math Review and Lessons in Calculus
 Math Review and Lessons in Calculus Agenda Rules o Eponents Functions Inverses Limits Calculus Rules o Eponents 0 Zero Eponent Rule a * b ab Product Rule * 3 5 a / b a-b Quotient Rule 5 / 3 -a / a Negative
Math Review and Lessons in Calculus Agenda Rules o Eponents Functions Inverses Limits Calculus Rules o Eponents 0 Zero Eponent Rule a * b ab Product Rule * 3 5 a / b a-b Quotient Rule 5 / 3 -a / a Negative
( 3x. Chapter Review. Review Key Vocabulary. Review Examples and Exercises 6.1 Properties of Square Roots (pp )
 6 Chapter Review Review Ke Vocabular closed, p. 266 nth root, p. 278 eponential function, p. 286 eponential growth, p. 296 eponential growth function, p. 296 compound interest, p. 297 Vocabular Help eponential
6 Chapter Review Review Ke Vocabular closed, p. 266 nth root, p. 278 eponential function, p. 286 eponential growth, p. 296 eponential growth function, p. 296 compound interest, p. 297 Vocabular Help eponential
1.7 Inverse Functions
 71_0107.qd 1/7/0 10: AM Page 17 Section 1.7 Inverse Functions 17 1.7 Inverse Functions Inverse Functions Recall from Section 1. that a function can be represented b a set of ordered pairs. For instance,
71_0107.qd 1/7/0 10: AM Page 17 Section 1.7 Inverse Functions 17 1.7 Inverse Functions Inverse Functions Recall from Section 1. that a function can be represented b a set of ordered pairs. For instance,
y,z the subscript y, z indicating that the variables y and z are kept constant. The second partial differential with respect to x is written x 2 y,z
 8 Partial dierentials I a unction depends on more than one variable, its rate o change with respect to one o the variables can be determined keeping the others ied The dierential is then a partial dierential
8 Partial dierentials I a unction depends on more than one variable, its rate o change with respect to one o the variables can be determined keeping the others ied The dierential is then a partial dierential
Mathematical Preliminaries. Developed for the Members of Azera Global By: Joseph D. Fournier B.Sc.E.E., M.Sc.E.E.
 Mathematical Preliminaries Developed or the Members o Azera Global B: Joseph D. Fournier B.Sc.E.E., M.Sc.E.E. Outline Chapter One, Sets: Slides: 3-27 Chapter Two, Introduction to unctions: Slides: 28-36
Mathematical Preliminaries Developed or the Members o Azera Global B: Joseph D. Fournier B.Sc.E.E., M.Sc.E.E. Outline Chapter One, Sets: Slides: 3-27 Chapter Two, Introduction to unctions: Slides: 28-36
Physical Measurement
 Order of Magnitude Estimations: estimations to the nearest power of ten The ranges of magnitude that occur in the universe: Sizes: 10-15 m to 10 +25 m (subnuclear particles to etent of the visible universe).
Order of Magnitude Estimations: estimations to the nearest power of ten The ranges of magnitude that occur in the universe: Sizes: 10-15 m to 10 +25 m (subnuclear particles to etent of the visible universe).
Ala-Arg-Pro-Tyr-Asn-Phe-Cpa-Leu-NH 2
 Applied Spectroscop Ala-Arg-Pro-Tr-Asn-Phe-Cpa-Leu-NH 2 Cpa Ala Pro Guillermo Mona What is Spectroscop? Without going into latin or greek, spectroscop is the stud of the interactions between light and
Applied Spectroscop Ala-Arg-Pro-Tr-Asn-Phe-Cpa-Leu-NH 2 Cpa Ala Pro Guillermo Mona What is Spectroscop? Without going into latin or greek, spectroscop is the stud of the interactions between light and
between electron energy levels. Using the spectrum of electron energy (1) and the law of energy-momentum conservation for photon absorption:
 ENERGY MEASUREMENT O RELATIVISTIC ELECTRON BEAMS USING RESONANCE ABSORPTION O LASER LIGHT BY ELECTRONS IN A MAGNETIC IELD R.A. Melikian Yerevan Physics Institute, Yerevan ABSTRACT The possibility o a precise
ENERGY MEASUREMENT O RELATIVISTIC ELECTRON BEAMS USING RESONANCE ABSORPTION O LASER LIGHT BY ELECTRONS IN A MAGNETIC IELD R.A. Melikian Yerevan Physics Institute, Yerevan ABSTRACT The possibility o a precise
This is only a list of questions use a separate sheet to work out the problems. 1. (1.2 and 1.4) Use the given graph to answer each question.
 Mth Calculus Practice Eam Questions NOTE: These questions should not be taken as a complete list o possible problems. The are merel intended to be eamples o the diicult level o the regular eam questions.
Mth Calculus Practice Eam Questions NOTE: These questions should not be taken as a complete list o possible problems. The are merel intended to be eamples o the diicult level o the regular eam questions.
9.3 Graphing Functions by Plotting Points, The Domain and Range of Functions
 9. Graphing Functions by Plotting Points, The Domain and Range o Functions Now that we have a basic idea o what unctions are and how to deal with them, we would like to start talking about the graph o
9. Graphing Functions by Plotting Points, The Domain and Range o Functions Now that we have a basic idea o what unctions are and how to deal with them, we would like to start talking about the graph o
Filtration. Praktikum Mechanical Engineering. Spring semester ML F16 Tel.:
 Praktikum Mechanical Engineering Spring semester 2018 Filtration Supervisor: Davide Stucchi ML F16 stucchid@ptl.mavt.ethz.ch Tel.: 044 632 25 05 1 1 Table o Contents 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS... 2 2 INTRODUCTION...
Praktikum Mechanical Engineering Spring semester 2018 Filtration Supervisor: Davide Stucchi ML F16 stucchid@ptl.mavt.ethz.ch Tel.: 044 632 25 05 1 1 Table o Contents 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS... 2 2 INTRODUCTION...
Symmetry Arguments and the Role They Play in Using Gauss Law
 Smmetr Arguments and the Role The la in Using Gauss Law K. M. Westerberg (9/2005) Smmetr plas a ver important role in science in general, and phsics in particular. Arguments based on smmetr can often simplif
Smmetr Arguments and the Role The la in Using Gauss Law K. M. Westerberg (9/2005) Smmetr plas a ver important role in science in general, and phsics in particular. Arguments based on smmetr can often simplif
Explore 1 Graphing and Analyzing f(x) = e x. The following table represents the function ƒ (x) = (1 + 1 x) x for several values of x.
 1_ 8 6 8 Locker LESSON 13. The Base e Teas Math Standards The student is epected to: A.5.A Determine the effects on the ke attributes of the graphs of ƒ () = b and ƒ () = log b () where b is, 1, and e
1_ 8 6 8 Locker LESSON 13. The Base e Teas Math Standards The student is epected to: A.5.A Determine the effects on the ke attributes of the graphs of ƒ () = b and ƒ () = log b () where b is, 1, and e
The Scattering of Light by Small Particles. Advanced Laboratory, Physics 407 University of Wisconsin Madison, Wisconsin 53706
 (4/28/09) The Scattering of Light by Small Particles Advanced Laboratory, Physics 407 University of Wisconsin Madison, Wisconsin 53706 Abstract In this experiment we study the scattering of light from
(4/28/09) The Scattering of Light by Small Particles Advanced Laboratory, Physics 407 University of Wisconsin Madison, Wisconsin 53706 Abstract In this experiment we study the scattering of light from
3. Several Random Variables
 . Several Random Variables. To Random Variables. Conditional Probabilit--Revisited. Statistical Independence.4 Correlation beteen Random Variables Standardied (or ero mean normalied) random variables.5
. Several Random Variables. To Random Variables. Conditional Probabilit--Revisited. Statistical Independence.4 Correlation beteen Random Variables Standardied (or ero mean normalied) random variables.5
DIGITAL CORRELATION OF FIRST ORDER SPACE TIME IN A FLUCTUATING MEDIUM
 DIGITAL CORRELATION OF FIRST ORDER SPACE TIME IN A FLUCTUATING MEDIUM Budi Santoso Center For Partnership in Nuclear Technolog, National Nuclear Energ Agenc (BATAN) Puspiptek, Serpong ABSTRACT DIGITAL
DIGITAL CORRELATION OF FIRST ORDER SPACE TIME IN A FLUCTUATING MEDIUM Budi Santoso Center For Partnership in Nuclear Technolog, National Nuclear Energ Agenc (BATAN) Puspiptek, Serpong ABSTRACT DIGITAL
Chapter 3: Image Enhancement in the. Office room : 841
 Chapter 3: Image Enhancement in the Spatial Domain Lecturer: Jianbing Shen Email : shenjianbing@bit.edu.cn Oice room : 841 http://cs.bit.edu.cn/shenjianbing cn/shenjianbing Principle Objective o Enhancement
Chapter 3: Image Enhancement in the Spatial Domain Lecturer: Jianbing Shen Email : shenjianbing@bit.edu.cn Oice room : 841 http://cs.bit.edu.cn/shenjianbing cn/shenjianbing Principle Objective o Enhancement
Delay Analysis of Spatio-Temporal Channel Access for Cognitive Networks
 Dela Analsis o Spatio-Temporal Channel Access or Cognitive Networks Chia-han Lee chiahan@citi.sinica.edu.tw Research Center or IT Innovation Academia Sinica Taipei, Taiwan Martin Haenggi mhaenggi@nd.edu
Dela Analsis o Spatio-Temporal Channel Access or Cognitive Networks Chia-han Lee chiahan@citi.sinica.edu.tw Research Center or IT Innovation Academia Sinica Taipei, Taiwan Martin Haenggi mhaenggi@nd.edu
Saturday X-tra X-Sheet: 8. Inverses and Functions
 Saturda X-tra X-Sheet: 8 Inverses and Functions Ke Concepts In this session we will ocus on summarising what ou need to know about: How to ind an inverse. How to sketch the inverse o a graph. How to restrict
Saturda X-tra X-Sheet: 8 Inverses and Functions Ke Concepts In this session we will ocus on summarising what ou need to know about: How to ind an inverse. How to sketch the inverse o a graph. How to restrict
1. Radium has a half-life of 1600 years. How much radium will be left from a 1000-gram sample after 1600 years?
 The Radioactive Deca Eperiment ACTIVITY 7 Learning Targets: Given a verbal description of a function, make a table and a graph of the function. Graph a function and identif and interpret ke features of
The Radioactive Deca Eperiment ACTIVITY 7 Learning Targets: Given a verbal description of a function, make a table and a graph of the function. Graph a function and identif and interpret ke features of
Introduction Direct Variation Rates of Change Scatter Plots. Introduction. EXAMPLE 1 A Mathematical Model
 APPENDIX B Mathematical Modeling B1 Appendi B Mathematical Modeling B.1 Modeling Data with Linear Functions Introduction Direct Variation Rates of Change Scatter Plots Introduction The primar objective
APPENDIX B Mathematical Modeling B1 Appendi B Mathematical Modeling B.1 Modeling Data with Linear Functions Introduction Direct Variation Rates of Change Scatter Plots Introduction The primar objective
FUNDAMENTALS OF REMOTE SENSING FOR RISKS ASSESSMENT. 1. Introduction
 FUNDAMENTALS OF REMOTE SENSING FOR RISKS ASSESSMENT FRANÇOIS BECKER International Space University and University Louis Pasteur, Strasbourg, France; E-mail: becker@isu.isunet.edu Abstract. Remote sensing
FUNDAMENTALS OF REMOTE SENSING FOR RISKS ASSESSMENT FRANÇOIS BECKER International Space University and University Louis Pasteur, Strasbourg, France; E-mail: becker@isu.isunet.edu Abstract. Remote sensing
is on the graph of y = f 1 (x).
 Objective 2 Inverse Functions Illustrate the idea of inverse functions. f() = 2 + f() = Two one-to-one functions are inverses of each other if (f g)() = of g, and (g f)() = for all in the domain of f.
Objective 2 Inverse Functions Illustrate the idea of inverse functions. f() = 2 + f() = Two one-to-one functions are inverses of each other if (f g)() = of g, and (g f)() = for all in the domain of f.
Chapter 4: Functions of Two Variables
 Chapter 4 Functions o Two Variables Applied Calculus 39 Chapter 4: Functions o Two Variables PreCalculus Idea -- Topographical Maps I ou ve ever hiked, ou have probabl seen a topographical map. Here is
Chapter 4 Functions o Two Variables Applied Calculus 39 Chapter 4: Functions o Two Variables PreCalculus Idea -- Topographical Maps I ou ve ever hiked, ou have probabl seen a topographical map. Here is
Speed (km/h) How can you determine the inverse of a function?
 .7 Inverse of a Function Engineers have been able to determine the relationship between the speed of a car and its stopping distance. A tpical function describing this relationship is D.v, where D is the
.7 Inverse of a Function Engineers have been able to determine the relationship between the speed of a car and its stopping distance. A tpical function describing this relationship is D.v, where D is the
Volume light transport
 Volume light transport Steve Marschner Cornell Universit CS 6630 Spring 2012, 1 6 March So far we have alwas assumed that, other than surfaces, there is nothing that impedes the flow of light. This means
Volume light transport Steve Marschner Cornell Universit CS 6630 Spring 2012, 1 6 March So far we have alwas assumed that, other than surfaces, there is nothing that impedes the flow of light. This means
Chapter 3. Theory of measurement
 Chapter. Introduction An energetic He + -ion beam is incident on thermal sodium atoms. Figure. shows the configuration in which the interaction one is determined b the crossing of the laser-, sodium- and
Chapter. Introduction An energetic He + -ion beam is incident on thermal sodium atoms. Figure. shows the configuration in which the interaction one is determined b the crossing of the laser-, sodium- and
Warm-up Adding Like Terms Simplify each expression and write a general rule for adding like terms. Start with teams Pong bit.
 Chapter 8: Eponents and Eponential Functions Section 8.1: Appl Eponents Properties Involving Products Name: Warm-up Adding Like Terms Simplif each epression and write a general rule for adding like terms.
Chapter 8: Eponents and Eponential Functions Section 8.1: Appl Eponents Properties Involving Products Name: Warm-up Adding Like Terms Simplif each epression and write a general rule for adding like terms.
TFY4102 Exam Fall 2015
 FY40 Eam Fall 05 Short answer (4 points each) ) Bernoulli's equation relating luid low and pressure is based on a) conservation o momentum b) conservation o energy c) conservation o mass along the low
FY40 Eam Fall 05 Short answer (4 points each) ) Bernoulli's equation relating luid low and pressure is based on a) conservation o momentum b) conservation o energy c) conservation o mass along the low
Systems of Linear Equations: Solving by Graphing
 8.1 Sstems of Linear Equations: Solving b Graphing 8.1 OBJECTIVE 1. Find the solution(s) for a set of linear equations b graphing NOTE There is no other ordered pair that satisfies both equations. From
8.1 Sstems of Linear Equations: Solving b Graphing 8.1 OBJECTIVE 1. Find the solution(s) for a set of linear equations b graphing NOTE There is no other ordered pair that satisfies both equations. From
is on the graph of y = f 1 (x).
 Objective 2 Inverse Functions Illustrate the idea of inverse functions. f() = 2 + f() = Two one-to-one functions are inverses of each other if (f g)() = of g, and (g f)() = for all in the domain of f.
Objective 2 Inverse Functions Illustrate the idea of inverse functions. f() = 2 + f() = Two one-to-one functions are inverses of each other if (f g)() = of g, and (g f)() = for all in the domain of f.
Module B4 Relations and functions. ModuleB4. Relations and functions
 Module B Relations and unctions ModuleB Relations and unctions B Table o Contents Introduction..... What are relations and unctions?...... Domain and range o relations and unctions....8.. Function notation.....
Module B Relations and unctions ModuleB Relations and unctions B Table o Contents Introduction..... What are relations and unctions?...... Domain and range o relations and unctions....8.. Function notation.....
PHSY133 Lab 5 Atomic Spectra
 Instructional Goals: PHSY133 Lab 5 Goal: Investigate the wavelengths of light produced b atoms. Background Reading: Background reading for this lab can be found in our class notes and Chapter 5 of our
Instructional Goals: PHSY133 Lab 5 Goal: Investigate the wavelengths of light produced b atoms. Background Reading: Background reading for this lab can be found in our class notes and Chapter 5 of our
Experimental and numerical analyses of FRC slabs on grade
 Eperimental and numerical analses o FRC slabs on grade B. Belletti & R. Cerioni Department o Civil and Environmental Engineering and Architecture, Universit o Parma, Ital A. Meda Department o Civil Engineering,
Eperimental and numerical analses o FRC slabs on grade B. Belletti & R. Cerioni Department o Civil and Environmental Engineering and Architecture, Universit o Parma, Ital A. Meda Department o Civil Engineering,
SECTION 8-7 De Moivre s Theorem. De Moivre s Theorem, n a Natural Number nth-roots of z
 8-7 De Moivre s Theorem 635 B eactl; compute the modulus and argument for part C to two decimal places. 9. (A) 3 i (B) 1 i (C) 5 6i 10. (A) 1 i 3 (B) 3i (C) 7 4i 11. (A) i 3 (B) 3 i (C) 8 5i 12. (A) 3
8-7 De Moivre s Theorem 635 B eactl; compute the modulus and argument for part C to two decimal places. 9. (A) 3 i (B) 1 i (C) 5 6i 10. (A) 1 i 3 (B) 3i (C) 7 4i 11. (A) i 3 (B) 3 i (C) 8 5i 12. (A) 3
Exam 3 Practice Questions Psych , Fall 9
 Vocabular Eam 3 Practice Questions Psch 3101-100, Fall 9 Rather than choosing some practice terms at random, I suggest ou go through all the terms in the vocabular lists. The real eam will ask for definitions
Vocabular Eam 3 Practice Questions Psch 3101-100, Fall 9 Rather than choosing some practice terms at random, I suggest ou go through all the terms in the vocabular lists. The real eam will ask for definitions
Graphs. 1. Graph paper 2. Ruler
 Graphs Objective The purpose of this activity is to learn and develop some of the necessary techniques to graphically analyze data and extract relevant relationships between independent and dependent phenomena,
Graphs Objective The purpose of this activity is to learn and develop some of the necessary techniques to graphically analyze data and extract relevant relationships between independent and dependent phenomena,
X-ray Diffraction. Interaction of Waves Reciprocal Lattice and Diffraction X-ray Scattering by Atoms The Integrated Intensity
 X-ray Diraction Interaction o Waves Reciprocal Lattice and Diraction X-ray Scattering by Atoms The Integrated Intensity Basic Principles o Interaction o Waves Periodic waves characteristic: Frequency :
X-ray Diraction Interaction o Waves Reciprocal Lattice and Diraction X-ray Scattering by Atoms The Integrated Intensity Basic Principles o Interaction o Waves Periodic waves characteristic: Frequency :
AP CALCULUS. Summer Assignment. Name:
 AP CALCULUS Summer Assignment Name: 08/09 North Point High School AP Calculus AB Summer Assignment 08 Congratulations on making it to AP Calculus! In order to complete the curriculum before the AP Eam
AP CALCULUS Summer Assignment Name: 08/09 North Point High School AP Calculus AB Summer Assignment 08 Congratulations on making it to AP Calculus! In order to complete the curriculum before the AP Eam
Mathematical Notation Math Calculus & Analytic Geometry III
 Mathematical Notation Math 221 - alculus & Analytic Geometry III Use Word or WordPerect to recreate the ollowing documents. Each article is worth 10 points and should be emailed to the instructor at james@richland.edu.
Mathematical Notation Math 221 - alculus & Analytic Geometry III Use Word or WordPerect to recreate the ollowing documents. Each article is worth 10 points and should be emailed to the instructor at james@richland.edu.
7Exponential and. Logarithmic Functions
 7Eponential and Logarithmic Functions A band of green light occasionall appears above the rising or setting sun. This phenomenon is known as a green flash because it lasts for a ver brief period of time.
7Eponential and Logarithmic Functions A band of green light occasionall appears above the rising or setting sun. This phenomenon is known as a green flash because it lasts for a ver brief period of time.
We would now like to turn our attention to a specific family of functions, the one to one functions.
 9.6 Inverse Functions We would now like to turn our attention to a speciic amily o unctions, the one to one unctions. Deinition: One to One unction ( a) (b A unction is called - i, or any a and b in the
9.6 Inverse Functions We would now like to turn our attention to a speciic amily o unctions, the one to one unctions. Deinition: One to One unction ( a) (b A unction is called - i, or any a and b in the
Molecular and Condensed Matter Physics Laboratory (PHYS 4580) Photovoltaic Materials and Device Physics Laboratory (PHYS 6/7280)
 Molecular and Condensed Matter Phsics Laborator (PHYS 4580) Photovoltaic Materials and Device Phsics Laborator (PHYS 6/780) Instructors: Prof. Rand Ellingson, Prof. Mike Heben Teaching Assistant: TBD Course
Molecular and Condensed Matter Phsics Laborator (PHYS 4580) Photovoltaic Materials and Device Phsics Laborator (PHYS 6/780) Instructors: Prof. Rand Ellingson, Prof. Mike Heben Teaching Assistant: TBD Course
CHAPTER 10 EXPERIMENTAL ESTIMATION OF DYNAMIC PARAMETERS OF BEARINGS
 CHAPTE 10 EXPEIMENTAL ESTIMATION OF DYNAMIC PAAMETES OF BEAINGS One o the important actors governing the vibration characteristics o rotating machiner is the eective dnamic stiness o the supports as seen
CHAPTE 10 EXPEIMENTAL ESTIMATION OF DYNAMIC PAAMETES OF BEAINGS One o the important actors governing the vibration characteristics o rotating machiner is the eective dnamic stiness o the supports as seen
A NOVEL METHOD OF INTERPOLATION AND EXTRAPOLATION OF FUNCTIONS BY A LINEAR INITIAL VALUE PROBLEM
 A OVEL METHOD OF ITERPOLATIO AD EXTRAPOLATIO OF FUCTIOS BY A LIEAR IITIAL VALUE PROBLEM Michael Shatalov Sensor Science and Technolog o CSIR Manuacturing and Materials, P.O.Bo 395, Pretoria, CSIR and Department
A OVEL METHOD OF ITERPOLATIO AD EXTRAPOLATIO OF FUCTIOS BY A LIEAR IITIAL VALUE PROBLEM Michael Shatalov Sensor Science and Technolog o CSIR Manuacturing and Materials, P.O.Bo 395, Pretoria, CSIR and Department
Phys 172 Exam 1, 2010 fall, Purdue University
 Phs 17 Eam 1, 010 all, Purdue Universit What to bring: 1. Your student ID we will check it!. Calculator: an calculator as long as it does not have internet/phone connection 3. Pencils Eam will take place
Phs 17 Eam 1, 010 all, Purdue Universit What to bring: 1. Your student ID we will check it!. Calculator: an calculator as long as it does not have internet/phone connection 3. Pencils Eam will take place
Calculus of Several Variables (TEN A), (TEN 1)
 Famil name: First name: I number: KTH Campus Haninge EXAMINATION Jan 6 Time: 8.5-.5 Calculus o Several Variables TEN A TEN Course: Transorm Methods and Calculus o Several Variables 6H79 Ten Ten A Lecturer
Famil name: First name: I number: KTH Campus Haninge EXAMINATION Jan 6 Time: 8.5-.5 Calculus o Several Variables TEN A TEN Course: Transorm Methods and Calculus o Several Variables 6H79 Ten Ten A Lecturer
5A Exponential functions
 Chapter 5 5 Eponential and logarithmic functions bjectives To graph eponential and logarithmic functions and transformations of these functions. To introduce Euler s number e. To revise the inde and logarithm
Chapter 5 5 Eponential and logarithmic functions bjectives To graph eponential and logarithmic functions and transformations of these functions. To introduce Euler s number e. To revise the inde and logarithm
Physics/Science Unit P1: Universal Physics
 Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Physics/Science Unit P1: Universal Physics Wednesday 9 November 2011 Morning Time: 1 hour You must have: Calculator, ruler Candidate
Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Physics/Science Unit P1: Universal Physics Wednesday 9 November 2011 Morning Time: 1 hour You must have: Calculator, ruler Candidate
So far you have worked with linear equations in intercept form, y a bx. y x. x 1 b
 LESSON. PLANNING LESSON OUTLINE One da: 0 min Eample 0 min Investigation min Sharing min Closing 0 min Eercises MATERIALS Calculator Note A Sketchpad demonstration Point- Slope Form, optional LESSON. Success
LESSON. PLANNING LESSON OUTLINE One da: 0 min Eample 0 min Investigation min Sharing min Closing 0 min Eercises MATERIALS Calculator Note A Sketchpad demonstration Point- Slope Form, optional LESSON. Success
