A Universal Sundial Ruler for Shadow-Following Clocks
|
|
|
- Francis Jackson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A Universal Sundial Ruler for Shadow-Following Clocks by Heinz Sigmund (Heidelberg, Germany) Preliminary Remarks My interest in the combination of sundials and mechanical clocks was confirmed by a fine handcrafted work by David Buschmann dating from 1660, which I admired on a visit to the Deutsches Museum in Munich, Germany. From there I developed some geometrical possibilities, taking into consideration especially the elliptical distortion of the equatorial circle for horizontal and vertical sundials. Then, several years later, after having studied the history of gnomonic schemas and rulers for designing flat sundials, once more I was fascinated, thinking that there must be other simple possibilities to combine sundials with modern timekeepers. and mathematicians, which led to a large variety of graphical layouts. I would like to mention only some well-known authors, such as Dürer, Benedetti, Clavius, Foster, Serle, Leybourn and Ozanam. To describe all these interesting geometrically similar solutions goes beyond the scope of this article. It would be like bringing brass to gold to do so, because we have plenty of well-researched and detailed information on this subject in excellent articles published during the last 20 years, most of them in The Compendium and especially by Fred Sawyer. A Simple Sundial Ruler For the geometrical construction, we refer to the wellknown fundamental diagram, which Albrecht Dürer published in During the last centuries, schemas or dialing scales have been described by many famous astronomers Figure 1 shows that the radius of the circles for different geographical latitudes depends on the basic Figure 1. Fundamental diagram according to Albrecht Dürer. 264 May June 2017 NAWCC Watch & Clock Bulletin
2 Figure 2. Equatorial dial. triangle (upper right-hand side) which represents the needed planes for drawing flat sundials. The diagonal line marks the direction of the inclined gnomon positioned toward geographical North/South. Figure 2 explains the design in detail for a geographical latitude of 50 (Horizontal Sundial) or 40 (Vertical Sundial). We now have two centers: Point B for the Equatorial Dial, and Point D for Horizontal and Vertical Dials. The hour lines starting from B include 15 for each hour and may simply be drawn by a compass (that means: division of the circumference of the circle in 24 equal parts) or by using a protractor. The meeting points of the two hour line systems form the Equinoctial Line. To complete the design, the missing hour lines must be added symmetrically on the right side. It is important to put the numbers in the right order: for the horizontal dial they go from right to left (i.e., clockwise) and for the vertical dial from left to right. Figure 3 shows the three parts of our sundial ruler. (Print and cut them out to make your own instrument.) The shown latitude scale (blue ground) has been obtained by continuing the procedure (Figure 2) for different latitudes. In our example the geographical distances are drawn mostly for every 2nd degree, starting at a position on the Pole (90 ) for the Figure 3. Parts of the ruler. NAWCC Watch & Clock Bulletin May June
3 horizontal dial and at the Equator for the vertical dial and ending (for practical reasons) at 18 or 72. Both scales turn to infinity! The other two scales mark the distance of the hour points from the center (A = Noon). To finish the instrument, the two hour rulers have to be fixed at the points C1 and C2, so that they may be turned around these centers. If we lay them on the larger ruler, we have a short and easily transportable instrument (Photo 1c). As a designing tool, the two yellow arms must be stretched so that they form an exact right angle (Photo 1b). Instead of using it for layouts (especially for large sundials), we can use the backside directly as a universal sundial. Therefore, we only add (in the middle of the blue ruler) a runner, where you can move a gnomon (e.g., in the form of a wooden stylus), which has to be inclined corresponding to the geographical latitude (Photo 1a). Then the complete instrument should be oriented exactly to the geographical South Pole as a horizontal dial and on a wall facing direct south as a vertical dial. The shadow cast by the inclined gnomon then marks (on the central line) True Local Time (TLT) for the chosen geographical Latitude. Remarks: The scales also may be calculated by the following formulas (see Figure 2): AD = R/sin ø (for the distance AD of the gnomon s center) L = R tan t (for the distance L from noon on the equinoctial line) Clockwork as Shadow Follower Remember that the equatorial dial has equidistant hour lines (see Figure 2); we can then install a 24-hour clock in the center (B). So if it is hand-driven by a clock s movement, it can now follow the shadow cast by an inclined gnomon fixed in the center D. If we wish the hand to touch the equinoctial line exactly as the meeting line of the two faces, the clock`s hand should be changed to the suitable length. We have solved this problem in different ways and describe these for each presented model (Photos 2-4). The dial in Photo 3/Figure 5 has been constructed as a vertical dial consisting of two parts in black and white. The upper half representing the sundial is translucent, so that the shadow cast by a gnomon outside can be seen from behind, looking from north to south. The other part has a 12-hour clock movement modified by cogs to 24-hours indication because of Photo 1a. Ruler as universal sundial. 266 May June 2017 NAWCC Watch & Clock Bulletin
4 the required direction of turning (i.e., counterclockwise). To use this dial, it has to be turned in so that the (white) hand and the (dark) shadow line cross themselves over the equinoctial line. Photo 1b, above. Ruler as drawing instrument. Photo 1c, left. Folded ruler. In Photo 2/Figure 4 the different hours have been marked by the colors of the spectrum and the vertical sundial (upper side) is posed partially over the face of the 24-hour clock; thus, we avoid the above-mentioned problem. In this model, we added two other hands (for minutes and seconds) for better accuracy. It would also be possible to adjust the dial for legal time by superimposing a turnable disk on the 24-hour clock. The two described models show that the equinoctial line as boundary between the dial faces is only reached by the hour line of 8 a.m. or 4 p.m., because of the quickly increasing values of the tangents. The disadvantage of this geometrical layout is well known and has been described by Sawyer in Horizontal Layouts. To avoid this inconvenience, I refer to the other method proposed there also. Figure 6 demonstrates the procedure: The hour lines before 9 a.m. and after 3 p.m. are drawn from new centers, which can be obtained by extending the six hour lines horizontally from the center for the chosen geographical latitude, until they cross the diagonal line (i.e., the prolonged hour line for 3 p.m./9 a.m. on the equatorial dial). NAWCC Watch & Clock Bulletin May June
5 Photo 2, above. Colored vertical dial. Photo 3, left. Translucent vertical dial. 268 May June 2017 NAWCC Watch & Clock Bulletin
6 Now we must deal with three centers for our clock movement and two other tangential lines forming right angles to the equinoctial line. In Photo 4b we give the solution to this problem: a 12-hour clockwork modified to a 24-hour indication (by a supplementary cog) is joined by a chain to the two other centers. Because our dial (Photo 4a) is conceived for a horizontal plane, we must observe that the gnomon s shadow is moving clockwise (in the northern hemisphere) so the three hands (all driven by the same clock movement) must turn counterclockwise. Figure 6 also shows that the shadow cast by the gnomon can sometimes touch the end of two hands on their tangential lines. As we mentioned above, the hour hand cannot always touch exactly the equinoctial line, so we propose a kind of limitation mechanism (Figure 7) bringing the hand`s point in the suitable position by pushing the point or the end of the hand that, however, is still turning around its center. Our last combination of sundials with clocks can be regarded as a vertical Shadow Simulation Dial indicating (without sunshine) the position of the shadow by a clock s hour hand (Photo 5a). There also may be an added inclined gnomon, allowing then to orient the face of the dial toward south, when its shadow falls straight on the black hour hand of the clock (Photo 5c). The inside mechanism for this simulation is shown in Photo 5b: first, there are three hands in the form of gliders/runners of which two are fixed in their centers, where they can be turned around. One of them (on the button) is driven by the movement of a 24-hour clock; the other sticks in the center of a vertical sundial. Its runner/glider is joined to the hour hand on the face outside and also to the clockwork runner taking it with himself while gliding it in the equinoctial line. I refer the reader to Sigmund s Combinations of Vertical and Horizontal Sundials with Mechanical Clocks. In this context, here is a convenient method to determine the declination of a vertical wall from direct south by one of the described Sun s shadow Followers. The procedure is as follows: Choose one of the vertical dials (I recommend the dial from Photo 2), and adjust the clock movement Figure 4. Vertical dial (spectral colors). Figure 5. Black-and-white face for a vertical dial. exactly to True Local Time, considering the geographical longitude distance to the corresponding time meridian and respecting also the amount of the equation of time for the day. Then turn the instrument until sundial and clock show the same time and are then also positioned to direct south (as described above). Immediately measure (by a simple protractor) the declination of the wall from south. NAWCC Watch & Clock Bulletin May June
7 Figure 6. Face of the Sun s shadow Follower. 270 May June 2017 NAWCC Watch & Clock Bulletin
8 Photo 4a. Horizontal dial with shadow Follower clock. Bibliography Gunella, Alessandro. The Pons Asinorum of Clavius (1586). The Compendium Vol. 10, No. 2 (June 2003): Rohr, Rene R. J. Sundials: History, Theory and Practice. New York, NY: Dover Publications, Sawyer, Fred. Horizontal Layouts 1-4. The Compendium Vol. 19, No. 1 (March 2012): Towards a General Theory of Dialing Scales, The Compendium No. 4 (pp ) Sigmund, Heinz. Azimut-und Höhenanzeigen auf ebenen Sonnenuhren. Jahresschrift der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Chronometrie No. 46 (2007) Bestimmung der Nord-Süd-Richtung durch Entwurf einer deklinierenden Vertikalsonnenuhr. Jahresschrift der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Chronometrie No. 48 (2009). Photo 4b. Mechanism (backside). NAWCC Watch & Clock Bulletin May June
9 Photo 5a, above. Shadow simulation dial. Photo 5b, left. Mechanism (backside). 272 May June 2017 NAWCC Watch & Clock Bulletin
10 Photo 5c, above. Shadow simulation dial with inclined gnomon. Figure 7, left. Limitation for the hour hand. NAWCC Watch & Clock Bulletin May June
11 Combinations of Vertical and Horizontal Sundials With Mechanical Clocks. The Compendium Vol. 12, No.3 (September 2005). Orientierung und Navigation mit [Sonnen-] Uhren. Jahresschrift der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Chronometrie No. 49 (2010). Verbindung von Vertikal- und Horizontalsonnenuhren mit Räderuhren. Jahresschrift der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Chronometrie No. 43 (2004). Zeichengeräte zur Markierung von Zeitpunkten auf ebenen Sonnenuhren. Jahresschrift der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Chronometri No. 44 (2005). Sonderegger, Helmut. A Universal Sundial presented by Johannes Gaupp. The Compendium Vol. 20, No. 2 (June 2013) Syndram, Dirk. Wissenschaftliche Instrumente und Sonnenuhren. Callwey: München, Editor s Note: The original version of this article was published in the December 2016 issue of The Compendum (Vol. 23, No. 4), the journal of the North American Sundial Society. It is reprinted here with permission. The Linnaeus Flower Dial By Stephen Luecking A garden dial offers a dialist, who is also an avid gardener, the opportunity to integrate the dial with another form of timekeeping proffered by Carl Linnaeus ( ), the founder of biologic taxonomy. Linnaeus noted that certain species of flowers regularly bloom during specific periods of daylight hours. A garden, he surmised, could comprise a series of beds arranged according to the hours of a clock face. The gardener could simply plant those flowers coming into bloom in the bed corresponding to the prescribed hour on the clock. Substitute the face of a sundial for that of the clock and, as the day progresses, the flowers will bloom in step with the movement of the gnomon s shadow. Editor s Note: The original version of this article was published in the December 2015 issue of The Compendum (Vol. 22, No. 4), the journal of the North American Sundial Society. It is reprinted here with permission. 274 May June 2017 NAWCC Watch & Clock Bulletin
Compendium* A Mean Time Sundial by Hendrik Hollander
 Volume 3 Number ISSN 074-397 (printed) ISSN 074-8059 (digital) June 006 The Journal of the North American Sundial Society Compendium* A Mean Time Sundial by Hendrik Hollander Time and reflection change
Volume 3 Number ISSN 074-397 (printed) ISSN 074-8059 (digital) June 006 The Journal of the North American Sundial Society Compendium* A Mean Time Sundial by Hendrik Hollander Time and reflection change
Polar Sundial. Cut carefully on this line. Cut on this line.
 1 The Sundial Primer - "Dialling Guides" The purpose of the "Dialling Guides" is to provide an easy method for laying out the hour lines for a number of polar sundials located at any latitude in either
1 The Sundial Primer - "Dialling Guides" The purpose of the "Dialling Guides" is to provide an easy method for laying out the hour lines for a number of polar sundials located at any latitude in either
The Sundial Primer - "Dialling Guides" Double Gnomon Polar Sundial
 1 Double Polar Sundial he purpose of the "Dialling Guides" is to provide an easy method for laying out the hour lines for a number of double gnomon polar sundials located at any latitude in either the
1 Double Polar Sundial he purpose of the "Dialling Guides" is to provide an easy method for laying out the hour lines for a number of double gnomon polar sundials located at any latitude in either the
Calibration of a Horizontal Sundial
 Calibration of a Horizontal Sundial Barbara Rovšek Citation: The Physics Teacher 48, 397 (2010); doi: 10.1119/1.3479720 View online: http://dx.doi.org/10.1119/1.3479720 View Table of Contents: http://scitation.aip.org/content/aapt/journal/tpt/48/6?ver=pdfcov
Calibration of a Horizontal Sundial Barbara Rovšek Citation: The Physics Teacher 48, 397 (2010); doi: 10.1119/1.3479720 View online: http://dx.doi.org/10.1119/1.3479720 View Table of Contents: http://scitation.aip.org/content/aapt/journal/tpt/48/6?ver=pdfcov
BIFILAR SUNDIAL. by Fer J. de Vries
 BIFILAR SUNDIAL by Fer J. de Vries Introduction Hugo Michnik of Germany invented the bifilar sundial in its horizontal form in 1923. His idea was the first really new sundial type since centuries. Instead
BIFILAR SUNDIAL by Fer J. de Vries Introduction Hugo Michnik of Germany invented the bifilar sundial in its horizontal form in 1923. His idea was the first really new sundial type since centuries. Instead
CA1 2.11: Designing an Equatorial Sundial Activity
 Purpose: To design an equatorial sundial and learn about motions of the sun and earth that have a bearing on its design. Materials: poster board, length of stiff wire or dowel rod, tape, protractor, ruler,
Purpose: To design an equatorial sundial and learn about motions of the sun and earth that have a bearing on its design. Materials: poster board, length of stiff wire or dowel rod, tape, protractor, ruler,
Sec 1.1 CC Geometry History of Trigonometry Name:
 Sec. CC Geometry History of Trigonometry Name: The word trigonometry is of Greek origin and literally translates to Triangle Measurements. Some of the earliest trigonometric ratios recorded date back to
Sec. CC Geometry History of Trigonometry Name: The word trigonometry is of Greek origin and literally translates to Triangle Measurements. Some of the earliest trigonometric ratios recorded date back to
ILLUSTRATING SHADOWS TABLE OF CONTENTS
 ILLUSTRATING SHADOWS TABLE OF CONTENTS 316 pages Introduction Chapter Page Introduction and "A Quick Hands On Project" Part One 1 10 The approximate evolution of the dial 2 13 How the earth does its thing
ILLUSTRATING SHADOWS TABLE OF CONTENTS 316 pages Introduction Chapter Page Introduction and "A Quick Hands On Project" Part One 1 10 The approximate evolution of the dial 2 13 How the earth does its thing
rises in the east High Noon sets in the west, 9:00 a.m. 12:00 p.m. 3:30 p.m. flagpole meter stick
 . Sec 3.5 Right Triangle Trigonometry Solving with Trigonometry The word trigonometry is of Greek origin and literally translates to Triangle Measurements. Some of the earliest trigonometric ratios recorded
. Sec 3.5 Right Triangle Trigonometry Solving with Trigonometry The word trigonometry is of Greek origin and literally translates to Triangle Measurements. Some of the earliest trigonometric ratios recorded
ZW2000 and Your Sundial
 1 The Sundial Primer created by At this point I assume that you have downloaded and set up ZW2000 on your computer. If not please read Getting Started with ZW2000. Initiate the program ZW2000. Figure 1
1 The Sundial Primer created by At this point I assume that you have downloaded and set up ZW2000 on your computer. If not please read Getting Started with ZW2000. Initiate the program ZW2000. Figure 1
 June 15, 2006 July 19, 2009 A south facing vertical declining sundial by a barn in, Silver City, NM Using a trigon and empirical methods, and a gnomon whose sub-style was vertical True N Magnetic N Silver
June 15, 2006 July 19, 2009 A south facing vertical declining sundial by a barn in, Silver City, NM Using a trigon and empirical methods, and a gnomon whose sub-style was vertical True N Magnetic N Silver
Gnomon (a thin, round stick at least a foot long and capable of being put into the ground or stood up vertically)
 Name: Partner(s): Lab #3 Celestial Navigation Due 7/2 Objectives In this lab you will take measurements of the sun s motion around noon and the north star s position in the sky. You will use this data
Name: Partner(s): Lab #3 Celestial Navigation Due 7/2 Objectives In this lab you will take measurements of the sun s motion around noon and the north star s position in the sky. You will use this data
Lab: Constructing a Sundial PRACTICAL PHYSICS
 Name Date Period Lab: Constructing a Sundial PRACTICAL PHYSICS Background: As the earth turns on its axis, the sun appears to move across our sky. The shadows cast by the sun move in a clockwise (hence
Name Date Period Lab: Constructing a Sundial PRACTICAL PHYSICS Background: As the earth turns on its axis, the sun appears to move across our sky. The shadows cast by the sun move in a clockwise (hence
Energy Efficiency, Acoustics & Daylighting in building Prof. B. Bhattacharjee Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi
 Energy Efficiency, Acoustics & Daylighting in building Prof. B. Bhattacharjee Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture - 05 Introduction & Environmental Factors (contd.)
Energy Efficiency, Acoustics & Daylighting in building Prof. B. Bhattacharjee Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture - 05 Introduction & Environmental Factors (contd.)
For most observers on Earth, the sun rises in the eastern
 632 CHAPTER 25: EARTH, SUN, AND SEASONS WHAT IS THE SUN S APPARENT PATH ACROSS THE SKY? For most observers on Earth, the sun rises in the eastern part of the sky. The sun reaches its greatest angular altitude
632 CHAPTER 25: EARTH, SUN, AND SEASONS WHAT IS THE SUN S APPARENT PATH ACROSS THE SKY? For most observers on Earth, the sun rises in the eastern part of the sky. The sun reaches its greatest angular altitude
Earth & Space Science, Interpreting Data DURATION Preparation: 5 minutes Activity: 40 minutes (total over one day)
 Objectives In this activity students will: 1. Observe how the position of the sun in the sky changes during the course of the day 2. Discover the cardinal directions by tracking the motion of the sun Materials
Objectives In this activity students will: 1. Observe how the position of the sun in the sky changes during the course of the day 2. Discover the cardinal directions by tracking the motion of the sun Materials
Solar Schoolhouse Human Sundial Building a Sundial with the Online Calculator
 Solar Schoolhouse Solar Schoolhouse Human Sundial Building a Sundial with the Online Calculator Overview Analemmatic sundials are sundials which have a movable gnomon (the gnomon is the part that casts
Solar Schoolhouse Solar Schoolhouse Human Sundial Building a Sundial with the Online Calculator Overview Analemmatic sundials are sundials which have a movable gnomon (the gnomon is the part that casts
The Earth is a Rotating Sphere
 The Earth is a Rotating Sphere The Shape of the Earth Earth s Rotation ( and relative movement of the Sun and Moon) The Geographic Grid Map Projections Global Time The Earth s Revolution around the Sun
The Earth is a Rotating Sphere The Shape of the Earth Earth s Rotation ( and relative movement of the Sun and Moon) The Geographic Grid Map Projections Global Time The Earth s Revolution around the Sun
Nodal Sundial Teacher s Notes
 Ancient people noticed that shadows thrown by the Sun moved in regular and predictable ways. They used this to make sundials. Almost noon at midsummer The nodal sundial measures 12 solar hours of different
Ancient people noticed that shadows thrown by the Sun moved in regular and predictable ways. They used this to make sundials. Almost noon at midsummer The nodal sundial measures 12 solar hours of different
A UNIFORM METHOD TO COMPUTE FLAT SUNDIALS
 A UNIFORM METHOD TO COMPUTE FLAT SUNDIALS usable all over the world by fer j. de vries, netherlands example of sundials on a dodecahedron date: january 1997, revised october 2002 Last Modified 02/05/2004
A UNIFORM METHOD TO COMPUTE FLAT SUNDIALS usable all over the world by fer j. de vries, netherlands example of sundials on a dodecahedron date: january 1997, revised october 2002 Last Modified 02/05/2004
Horizontal/Vertical/Inclining Sundial
 1 The Sundial Primer created by At this point I assume that you have downloaded and set up SONNE on your computer and have also read the overview document. If not please read Getting Started with SONNE
1 The Sundial Primer created by At this point I assume that you have downloaded and set up SONNE on your computer and have also read the overview document. If not please read Getting Started with SONNE
The Sun -D ial of the I.H.B. Le cadran solaire du B.H.I.
 The Sun -D ial of the I.H.B. Le cadran solaire du B.H.I. The new building erected by the Princely Government on the Quai de Plaisance of the Port of Monaco, and set apart for the use of the International
The Sun -D ial of the I.H.B. Le cadran solaire du B.H.I. The new building erected by the Princely Government on the Quai de Plaisance of the Port of Monaco, and set apart for the use of the International
ZW2000 and Your Vertical Sundial Carl Sabanski
 1 The Sundial Primer created by At this point I assume that you have downloaded and set up ZW2000 on your computer and have also read the overview document. If not please read Getting Started with ZW2000
1 The Sundial Primer created by At this point I assume that you have downloaded and set up ZW2000 on your computer and have also read the overview document. If not please read Getting Started with ZW2000
Fundamentals of Satellite technology
 Fundamentals of Satellite technology Prepared by A.Kaviyarasu Assistant Professor Department of Aerospace Engineering Madras Institute Of Technology Chromepet, Chennai Orbital Plane All of the planets,
Fundamentals of Satellite technology Prepared by A.Kaviyarasu Assistant Professor Department of Aerospace Engineering Madras Institute Of Technology Chromepet, Chennai Orbital Plane All of the planets,
World Time-Day Calculator Lab
 Background: Time zones around the Earth are bounded by imaginary lines called lines of longitude, or meridians. On a globe or map of the world, they are the lines that are perpendicular to the equator.
Background: Time zones around the Earth are bounded by imaginary lines called lines of longitude, or meridians. On a globe or map of the world, they are the lines that are perpendicular to the equator.
PHAS 1511: Foundations of Astronomy
 PHAS 1511: Foundations of Astronomy Dr Roger Wesson Research interests: deaths of stars. Planetary nebulae, novae and supernovae. Astronomy: some maths You can see that distances in astronomy are huge.
PHAS 1511: Foundations of Astronomy Dr Roger Wesson Research interests: deaths of stars. Planetary nebulae, novae and supernovae. Astronomy: some maths You can see that distances in astronomy are huge.
WHERE ARE YOU? LOCATING BY THE SUN
 WHERE ARE YOU? LOCATING BY THE SUN Sakari Ekko EAAE Summer School Working Group (Finland) Abstract In this workshop, we first find our location on the globe by the Sun and Polaris, the Pole Star. After
WHERE ARE YOU? LOCATING BY THE SUN Sakari Ekko EAAE Summer School Working Group (Finland) Abstract In this workshop, we first find our location on the globe by the Sun and Polaris, the Pole Star. After
Published with permission by Fred Sawyer (c) Fred Sawyer
 Published with permission by Fred Sawyer (c) Fred Sawyer Elliptical Sundials: General & Craticular Fred Sawyer (Manchester CT) The analemmatic dial, that indicates time by the azimuth of a vertical stile
Published with permission by Fred Sawyer (c) Fred Sawyer Elliptical Sundials: General & Craticular Fred Sawyer (Manchester CT) The analemmatic dial, that indicates time by the azimuth of a vertical stile
Chapter 3 Models of the Earth. 3.1 Finding Locations on the Earth. 3.1 Objectives
 Chapter 3 Models of the Earth 3.1 Finding Locations on the Earth 3.1 Objectives Explain latitude and longitude. How can latitude and longitude be used to find locations on Earth? How can a magnetic compass
Chapter 3 Models of the Earth 3.1 Finding Locations on the Earth 3.1 Objectives Explain latitude and longitude. How can latitude and longitude be used to find locations on Earth? How can a magnetic compass
1.4j interpret simple shadow stick data to determine local noon and observer s longitude
 1.4j interpret simple shadow stick data to determine local noon and observer s longitude There are many opportunities for making observations of shadows cast with a vertical stick and the Sun. Observations
1.4j interpret simple shadow stick data to determine local noon and observer s longitude There are many opportunities for making observations of shadows cast with a vertical stick and the Sun. Observations
Look at the date line of today and look at the shadow of the correct side of the cone. Read the mean time on the date line.
 MEANTIME SUNDIAL WITH A CONE GNOMON Amsterdam, the Netherlands, 6 June 006 By Hendrik Hollander Basic principles of the mean time sundial with a cone gnomon On the sundial plane the hour lines and date
MEANTIME SUNDIAL WITH A CONE GNOMON Amsterdam, the Netherlands, 6 June 006 By Hendrik Hollander Basic principles of the mean time sundial with a cone gnomon On the sundial plane the hour lines and date
The Measurement of Time
 CHAPTER TWO The Measurement of Time Solar Time In antiquity the time of day was measured by the direction of a shadow cast in sunlight. This resulted in the development of a wide variety of sophisticated
CHAPTER TWO The Measurement of Time Solar Time In antiquity the time of day was measured by the direction of a shadow cast in sunlight. This resulted in the development of a wide variety of sophisticated
ANALEMMAS. on the gnomon and on the dial plate. Declining Shadows (Declining-Shadows.pdf ) for declination curve insights and methods.
 ANALEMMAS on the gnomon and on the dial plate armillary dials equatorial dials horizontal and vertical dials also and vertical decliners and polar and meridian please read: NOTE: using these: also see:
ANALEMMAS on the gnomon and on the dial plate armillary dials equatorial dials horizontal and vertical dials also and vertical decliners and polar and meridian please read: NOTE: using these: also see:
5 - Seasons. Figure 1 shows two pictures of the Sun taken six months apart with the same camera, at the same time of the day, from the same location.
 ASTR 110L 5 - Seasons Purpose: To plot the distance of the Earth from the Sun over one year and to use the celestial sphere to understand the cause of the seasons. What do you think? Write answers to questions
ASTR 110L 5 - Seasons Purpose: To plot the distance of the Earth from the Sun over one year and to use the celestial sphere to understand the cause of the seasons. What do you think? Write answers to questions
Making a Sundial. Build a sundial and discover how time can be measured. Space Awareness, Leiden Observatory. iau.org/astroedu
 Making a Sundial Build a sundial and discover how time can be measured. Space Awareness, Leiden Observatory Age 6-10 Supervised Unsupervised Core skills Asking questions, Developing and using models, Analysing
Making a Sundial Build a sundial and discover how time can be measured. Space Awareness, Leiden Observatory Age 6-10 Supervised Unsupervised Core skills Asking questions, Developing and using models, Analysing
THE EARTH AND ITS REPRESENTATION
 UNIT 7 THE EARTH AND ITS REPRESENTATION TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 THE EARTH AND THE SOLAR SYSTEM... 2 2 THE EARTH S MOVEMENTS... 2 2.1 Rotation.... 2 2.2 The revolution of the Earth: seasons of the year....
UNIT 7 THE EARTH AND ITS REPRESENTATION TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 THE EARTH AND THE SOLAR SYSTEM... 2 2 THE EARTH S MOVEMENTS... 2 2.1 Rotation.... 2 2.2 The revolution of the Earth: seasons of the year....
Unit 2 Math II - History of Trigonometry
 TSK # Unit Math II - History of Trigonometry The word trigonometry is of Greek origin and literally translates to Triangle Measurements. Some of the earliest trigonometric ratios recorded date back to
TSK # Unit Math II - History of Trigonometry The word trigonometry is of Greek origin and literally translates to Triangle Measurements. Some of the earliest trigonometric ratios recorded date back to
Vigyan Pratibha Learning Unit (Student version) Shadows
 Shadows Take a look around and you will notice that all things form shadows. You must have played in the ground on a bright sunny day and seen that shadow formed by your body runs around with you. Have
Shadows Take a look around and you will notice that all things form shadows. You must have played in the ground on a bright sunny day and seen that shadow formed by your body runs around with you. Have
SOLAR ENERGY: THAT S HOT Grades 4-6
 NJCCCS: 5.1, 5.2, 5.4 SOLAR ENERGY: THAT S HOT Grades 4-6 Field Trip Overview: This program illuminates the various ways in which our nearest star affects life on Earth. Students will learn about the apparent
NJCCCS: 5.1, 5.2, 5.4 SOLAR ENERGY: THAT S HOT Grades 4-6 Field Trip Overview: This program illuminates the various ways in which our nearest star affects life on Earth. Students will learn about the apparent
3. The Sun s Position
 3. The Sun s Position In order to understand how to collect energy from the sun, one must first be able to predict the location of the sun relative to the collection device. In this chapter we develop
3. The Sun s Position In order to understand how to collect energy from the sun, one must first be able to predict the location of the sun relative to the collection device. In this chapter we develop
Vigyan Pratibha Learning Unit (Teacher version) Shadows
 Shadows Take a look around and you will notice that all things form shadows. You must have played in the ground on a bright sunny day and seen that shadow formed by your body runs around with you. Have
Shadows Take a look around and you will notice that all things form shadows. You must have played in the ground on a bright sunny day and seen that shadow formed by your body runs around with you. Have
CUTTING Shadows SOME CUTOUT DIALS FOR YOUR AMUSEMENT. ALL YOU NEED ARE SOME SCISSORS, AND YOUR LATITUDE, AND LONGITUDE.
 CUTTING Shadows SOME CUTOUT DIALS FOR YOUR AMUSEMENT. ALL YOU NEED ARE SOME SCISSORS, AND YOUR LATITUDE, AND LONGITUDE. Simon Wheaton-Smith December 2009 CUTOUTS FOR PAPER SUN DIALS armillary (also equatorial
CUTTING Shadows SOME CUTOUT DIALS FOR YOUR AMUSEMENT. ALL YOU NEED ARE SOME SCISSORS, AND YOUR LATITUDE, AND LONGITUDE. Simon Wheaton-Smith December 2009 CUTOUTS FOR PAPER SUN DIALS armillary (also equatorial
Map Projections. Chapter 4 MAP PROJECTION
 Map Projections Chapter 4 Map Projections What is map projection? Why are map projections drawn? What are the different types of projections? Which projection is most suitably used for which area? In this
Map Projections Chapter 4 Map Projections What is map projection? Why are map projections drawn? What are the different types of projections? Which projection is most suitably used for which area? In this
THE PLANISPHERIC ASTROLABE
 THE PLANISPHERIC ASTROLABE Feb 4, 2006 A half Dinar note from Iraq with an astrolabe portrayal Of old, the astrolabe was used for various astronomical and astrological calculations, In particular, it could
THE PLANISPHERIC ASTROLABE Feb 4, 2006 A half Dinar note from Iraq with an astrolabe portrayal Of old, the astrolabe was used for various astronomical and astrological calculations, In particular, it could
Motions of the Sun Model Exploration
 Name Date Bell Motions of the Sun Model Exploration 1. Go to the University of Nebraska-Lincoln Motions of the Sun Simulator: http://astro.unl.edu/naap/motion3/animations/sunmotions.swf 2. This is what
Name Date Bell Motions of the Sun Model Exploration 1. Go to the University of Nebraska-Lincoln Motions of the Sun Simulator: http://astro.unl.edu/naap/motion3/animations/sunmotions.swf 2. This is what
3 N. Follow these instructions carefully to construct a simplified Analemmic Sundial (a vertical gnomon sundial).
 Use your own shadow to tell time. 5 4 3 2 12 11 10 9 8 7 Follow these instructions carefully to construct a simplified Analemmic undial (a vertical gnomon sundial). 1 ach sun dial team should have at least
Use your own shadow to tell time. 5 4 3 2 12 11 10 9 8 7 Follow these instructions carefully to construct a simplified Analemmic undial (a vertical gnomon sundial). 1 ach sun dial team should have at least
UNIT 6 CELESTIAL SPHERE AND EQUINOCTIAL SYSTEM OF COORDINATES
 UNIT 6 CELESTIAL SPHERE AND EQUINOCTIAL SYSTEM OF COORDINATES Structure 6.1 Introduction Objectives 6.2 References 6.3 Apparent Annual Motion of the Sun and the Concept of the Ecliptic and the Obliquity
UNIT 6 CELESTIAL SPHERE AND EQUINOCTIAL SYSTEM OF COORDINATES Structure 6.1 Introduction Objectives 6.2 References 6.3 Apparent Annual Motion of the Sun and the Concept of the Ecliptic and the Obliquity
Solar Schoolhouse Human Sundial. Building a Sundial with the Online Calculator
 Sol Schoolho use ar Solar Schoolhouse Human Sundial Project Description Analemmatic sundials are sundials which have a movable gnomon (the gnomon is the part that casts the shadow). Humans are common gnomons
Sol Schoolho use ar Solar Schoolhouse Human Sundial Project Description Analemmatic sundials are sundials which have a movable gnomon (the gnomon is the part that casts the shadow). Humans are common gnomons
CHARTING THE HEAVENS USING A VIRTUAL PLANETARIUM
 Name Partner(s) Section Date CHARTING THE HEAVENS USING A VIRTUAL PLANETARIUM You have had the opportunity to look at two different tools to display the night sky, the celestial sphere and the star chart.
Name Partner(s) Section Date CHARTING THE HEAVENS USING A VIRTUAL PLANETARIUM You have had the opportunity to look at two different tools to display the night sky, the celestial sphere and the star chart.
Time, coordinates and how the Sun and Moon move in the sky
 Time, coordinates and how the Sun and Moon move in the sky Using the colors and magnitudes of quasars drawn from the SDSS Catalog Archive Server to distinguish quasars from stars using the light they emit
Time, coordinates and how the Sun and Moon move in the sky Using the colors and magnitudes of quasars drawn from the SDSS Catalog Archive Server to distinguish quasars from stars using the light they emit
Earth Motions Packet 14
 Earth Motions Packet 14 Your Name Group Members Score Minutes Standard 4 Key Idea 1 Performance Indicator 1.1 Explain complex phenomena, such as tides, variations in day length, solar insolation, apparent
Earth Motions Packet 14 Your Name Group Members Score Minutes Standard 4 Key Idea 1 Performance Indicator 1.1 Explain complex phenomena, such as tides, variations in day length, solar insolation, apparent
Eratosthenes Project
 Eratosthenes Project This is an introduction to Teacher's Guide: it first recounts the observations made by Eratosthenes, his hypotheses and conclusions, followed by an overview of the way these can be
Eratosthenes Project This is an introduction to Teacher's Guide: it first recounts the observations made by Eratosthenes, his hypotheses and conclusions, followed by an overview of the way these can be
Sundials With Punctiform Hour Lines Gianni Ferrari (Modena, Italy)
 Sundials With Punctiform our Lines Gianni Ferrari (Modena, Italy) Part 1 General Description Introduction Let us consider the line drawn in the sky by the points occupied by the Suns center at a given
Sundials With Punctiform our Lines Gianni Ferrari (Modena, Italy) Part 1 General Description Introduction Let us consider the line drawn in the sky by the points occupied by the Suns center at a given
Kids Garden Teacher s Guide: Grade 3
 Kids Garden Teacher s Guide: Grade 3 California Content Standards Grade 2 Science: 2a, 6a, 6c, 6d, 6e What s Going On? The Kids Garden gives children the opportunity to explore the natural community of
Kids Garden Teacher s Guide: Grade 3 California Content Standards Grade 2 Science: 2a, 6a, 6c, 6d, 6e What s Going On? The Kids Garden gives children the opportunity to explore the natural community of
A SECOND DIY GARDEN HELIOCHRONOMETER
 A SECOND DIY GARDEN HELIOCHRONOMETER BRIAN HUGGETT U ntil the summer of 2016, I knew very little about sundials. In fact, dare I confess, I had never heard of the British Sundial Society. I thought, however,
A SECOND DIY GARDEN HELIOCHRONOMETER BRIAN HUGGETT U ntil the summer of 2016, I knew very little about sundials. In fact, dare I confess, I had never heard of the British Sundial Society. I thought, however,
Map projections. Rüdiger Gens
 Rüdiger Gens 2 Outline! Relevant terms! Why map projections?! Map projection categories " Projection surfaces " Features preserved from distortions! Map projection examples! Right choice Relevant terms!
Rüdiger Gens 2 Outline! Relevant terms! Why map projections?! Map projection categories " Projection surfaces " Features preserved from distortions! Map projection examples! Right choice Relevant terms!
3. a. In the figure below, indicate the direction of the Sun with an arrow.
 Astronomy 100, Fall 2005 Name(s): Exercise 2: Seasons in the sun The following exercise illustrates some basic ideas about time, and how our position in the solar system uniquely configures the measurement
Astronomy 100, Fall 2005 Name(s): Exercise 2: Seasons in the sun The following exercise illustrates some basic ideas about time, and how our position in the solar system uniquely configures the measurement
Astronomy 101 Lab: Seasons
 Name: Astronomy 101 Lab: Seasons Pre-Lab Assignment: In class, we've talked about the cause of the seasons. In this lab, you will use globes to study the relative positions of Earth and the Sun during
Name: Astronomy 101 Lab: Seasons Pre-Lab Assignment: In class, we've talked about the cause of the seasons. In this lab, you will use globes to study the relative positions of Earth and the Sun during
The time they chose was the Vernal Equinox of March 20, 2000, at 7:30 AM Greenwich Mean Time (GMT). Right Ascension Offset
 Star Coordinates and the Celestial Dome Astronomers have mapped out the sky in the shape of a spherical dome the Celestial Sphere, where earth is just a tiny spec at the center of the dome. The celestial
Star Coordinates and the Celestial Dome Astronomers have mapped out the sky in the shape of a spherical dome the Celestial Sphere, where earth is just a tiny spec at the center of the dome. The celestial
3 - Celestial Sphere
 3 - Celestial Sphere Purpose: To construct and use a celestial sphere to show the motion of the Sun and stars in the sky. There are six questions, Q1 Q6, to answer on a separate piece of paper. Due: in
3 - Celestial Sphere Purpose: To construct and use a celestial sphere to show the motion of the Sun and stars in the sky. There are six questions, Q1 Q6, to answer on a separate piece of paper. Due: in
b. Assuming that the sundial is set up correctly, explain this observation.
 Astronomy 100 Name(s): Exercise 3: Seasons in the sun The following exercise illustrates some basic ideas about time, and how our position in the solar system uniquely configures the measurement of time.
Astronomy 100 Name(s): Exercise 3: Seasons in the sun The following exercise illustrates some basic ideas about time, and how our position in the solar system uniquely configures the measurement of time.
5 - Seasons. Figure 1 shows two pictures of the Sun taken six months apart with the same camera, at the same time of the day, from the same location.
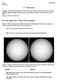 Name: Partner(s): 5 - Seasons ASTR110L Purpose: To measure the distance of the Earth from the Sun over one year and to use the celestial sphere to understand the cause of the seasons. Answer all questions
Name: Partner(s): 5 - Seasons ASTR110L Purpose: To measure the distance of the Earth from the Sun over one year and to use the celestial sphere to understand the cause of the seasons. Answer all questions
The Sun-Earth-Moon System
 chapter 311 section 1 Earth The Sun-Earth-Moon System Before You Read What do you already know about Earth s shape, its size, and how it moves? Write what you know on the lines below. What You ll Learn
chapter 311 section 1 Earth The Sun-Earth-Moon System Before You Read What do you already know about Earth s shape, its size, and how it moves? Write what you know on the lines below. What You ll Learn
Transforming from Geographic to Celestial Coordinates
 Transforming from Geographic to Celestial Coordinates Michael McEllin 1 Introduction The simplest astronomical observation of all is that the stars appear to move around the Earth (which, of course is
Transforming from Geographic to Celestial Coordinates Michael McEllin 1 Introduction The simplest astronomical observation of all is that the stars appear to move around the Earth (which, of course is
learning outcomes end product a small sundial indoors a large sundial outdoors
 The sundial Use the Sun time 55 minutes, spread across two days learning outcomes To: know that you can tell the time using a sundial tell the time using the Sun discover that long ago it was much more
The sundial Use the Sun time 55 minutes, spread across two days learning outcomes To: know that you can tell the time using a sundial tell the time using the Sun discover that long ago it was much more
GLOBE : LATITUDES AND LONGITUDES
 2 Figure 2.1 : Globe Let s Do Take a big round potato or a ball. Pierce a knitting needle through it. The needle resembles the axis shown in a globe. You can now move the potato or the ball around this
2 Figure 2.1 : Globe Let s Do Take a big round potato or a ball. Pierce a knitting needle through it. The needle resembles the axis shown in a globe. You can now move the potato or the ball around this
wikihow to Find True North Without a Compass
 wikihow to Find True North Without a Compass wikihow.com /Find-True-North-Without-a-Compass Which way is north? Whether you're lost in the woods or you're trying to install a sundial in your yard, you're
wikihow to Find True North Without a Compass wikihow.com /Find-True-North-Without-a-Compass Which way is north? Whether you're lost in the woods or you're trying to install a sundial in your yard, you're
The Sphere of the Earth Activities
 The Sphere of the Earth Activities December 20, 2012 Daniel Ramos MMACA (Museu de Matemàtiques de Catalunya) These activities are designed to be done with the materials, posters and software of the exhibit
The Sphere of the Earth Activities December 20, 2012 Daniel Ramos MMACA (Museu de Matemàtiques de Catalunya) These activities are designed to be done with the materials, posters and software of the exhibit
Telling Time By: Sophia James Education, LLC
 Telling Time By: Sophia James Education, LLC The world is fascinated by how time goes by fast or how we never have enough time in a day. For ages the concept of time have fascinated people. For thousand
Telling Time By: Sophia James Education, LLC The world is fascinated by how time goes by fast or how we never have enough time in a day. For ages the concept of time have fascinated people. For thousand
01) The Sun s rays strike the surface of the Earth at 90 degrees at the on December 22.
 Package Title: Testbank Course Title: Introducing Physical Geography 6e Chapter Number: 01 Question Type: Multiple Choice 01) The Sun s rays strike the surface of the Earth at 90 degrees at the on December
Package Title: Testbank Course Title: Introducing Physical Geography 6e Chapter Number: 01 Question Type: Multiple Choice 01) The Sun s rays strike the surface of the Earth at 90 degrees at the on December
announcements 4/29/08
 Solar Geometry ARCH 331/431 Spring 2008 Lecture 9 announcements 4/29/08 Firm of the Month Presentation: SRG Architects Wednesday May 30, 12:30, ARCH 042 Assignment 4: Shading Model Studies Available Thursday;
Solar Geometry ARCH 331/431 Spring 2008 Lecture 9 announcements 4/29/08 Firm of the Month Presentation: SRG Architects Wednesday May 30, 12:30, ARCH 042 Assignment 4: Shading Model Studies Available Thursday;
L9 Solar Geometry 4/29/08
 Solar Geometry ARCH 331/431 Spring 2008 Lecture 9 announcements 4/29/08 Firm of the Month Presentation: SRG Architects Wednesday May 30, 12:30, ARCH 042 Assignment 4: Shading Model Studies Available Thursday;
Solar Geometry ARCH 331/431 Spring 2008 Lecture 9 announcements 4/29/08 Firm of the Month Presentation: SRG Architects Wednesday May 30, 12:30, ARCH 042 Assignment 4: Shading Model Studies Available Thursday;
Eratosthenes method of measuring the Earth
 Eratosthenes method of measuring the Earth Credit for the first determination of the size of the Earth goes to the Greek polymath Eratosthenes, who lived from around 276 BC to 195 BC. Born in the Greek
Eratosthenes method of measuring the Earth Credit for the first determination of the size of the Earth goes to the Greek polymath Eratosthenes, who lived from around 276 BC to 195 BC. Born in the Greek
Discovering the Universe for Yourself (Chapter 2) Years, Seasons, and Months: The Motions of Sun, Earth, and Moon
 Discovering the Universe for Yourself (Chapter 2) Years, Seasons, and Months: The Motions of Sun, Earth, and Moon Based on Chapter 2 This material will be useful for understanding Chapters 3 and 4 on The
Discovering the Universe for Yourself (Chapter 2) Years, Seasons, and Months: The Motions of Sun, Earth, and Moon Based on Chapter 2 This material will be useful for understanding Chapters 3 and 4 on The
Weather Study. DesigN details. and Observation Features. B uilt features
 B uilt features Weather Study and Observation Features Observing weather helps to connect students to their surroundings and is an excellent way to build fun and learning into the curriculum. Providing
B uilt features Weather Study and Observation Features Observing weather helps to connect students to their surroundings and is an excellent way to build fun and learning into the curriculum. Providing
East Anglian Trophy 2016 As Time Goes By
 East Anglian Trophy 2016 As Time Goes By This year the theme is sundials. Until I started setting this year s competition I knew very little about them, but there are quite a few interesting facts. As
East Anglian Trophy 2016 As Time Goes By This year the theme is sundials. Until I started setting this year s competition I knew very little about them, but there are quite a few interesting facts. As
THE SUN. LENGTH: Course of the semester
 ASTR 1030 Astronomy Lab 139 The Sun THE SUN SYNOPSIS: This exercise involves making measurements of the Sun every week throughout the semester, and then analyzing your results at semester s end. You ll
ASTR 1030 Astronomy Lab 139 The Sun THE SUN SYNOPSIS: This exercise involves making measurements of the Sun every week throughout the semester, and then analyzing your results at semester s end. You ll
FRIOT'S EXPLANATION OF THE TIP OF THE EARTH'S CONTRIBUTION TO THE EQUATION OF TIME
 FRIOT'S EXPLANATION OF THE TIP OF THE EARTH'S CONTRIBUTION TO THE EQUATION OF TIME For this explanation it has been assumed that the reader is knowledgeable of certain facts and scientific understandings.
FRIOT'S EXPLANATION OF THE TIP OF THE EARTH'S CONTRIBUTION TO THE EQUATION OF TIME For this explanation it has been assumed that the reader is knowledgeable of certain facts and scientific understandings.
The Earth and its representation
 GEOGRAPHY UNIT 1 The Earth and its representation THE SOLAR SYSTEM AND THE EARTH THE SOLAR SYSTEM The solar system is a planetary system. Is a group of astronomical objects who surround a star, in this
GEOGRAPHY UNIT 1 The Earth and its representation THE SOLAR SYSTEM AND THE EARTH THE SOLAR SYSTEM The solar system is a planetary system. Is a group of astronomical objects who surround a star, in this
CHAPTER 2 Strand 1: Structure and Motion within the Solar System
 CHAPTER 2 Strand 1: Structure and Motion within the Solar System Chapter Outline 2.1 EARTH, MOON, AND SUN SYSTEM (6.1.1) 2.2 GRAVITY AND INERTIA (6.1.2) 2.3 SCALE OF SOLAR SYSTEM (6.1.3) 2.4 REFERENCES
CHAPTER 2 Strand 1: Structure and Motion within the Solar System Chapter Outline 2.1 EARTH, MOON, AND SUN SYSTEM (6.1.1) 2.2 GRAVITY AND INERTIA (6.1.2) 2.3 SCALE OF SOLAR SYSTEM (6.1.3) 2.4 REFERENCES
ME 476 Solar Energy UNIT THREE SOLAR RADIATION
 ME 476 Solar Energy UNIT THREE SOLAR RADIATION Unit Outline 2 What is the sun? Radiation from the sun Factors affecting solar radiation Atmospheric effects Solar radiation intensity Air mass Seasonal variations
ME 476 Solar Energy UNIT THREE SOLAR RADIATION Unit Outline 2 What is the sun? Radiation from the sun Factors affecting solar radiation Atmospheric effects Solar radiation intensity Air mass Seasonal variations
R.L. Kellogg, Ph.D. North American Sundial Society June 2013
 R.L. Kellogg, Ph.D. North American Sundial Society June 2013 1 Analemmatic Sundials The Human Sundial The Analemmatic Sundial or Human Sundial was first described by M. de Vaulezard in 1640 in a Treatise
R.L. Kellogg, Ph.D. North American Sundial Society June 2013 1 Analemmatic Sundials The Human Sundial The Analemmatic Sundial or Human Sundial was first described by M. de Vaulezard in 1640 in a Treatise
OBSERVING PROJECT PARTNER ELECTION
 ASTRONOMY 25 NOON SUN PROJECT P. P. 1 Name(s) Section Day/Time Fill in either Part 1 or Part 2. OBSERVING PROJECT PARTNER ELECTION Part I. SOLO OBSERVER I will do the observing project by myself. I will
ASTRONOMY 25 NOON SUN PROJECT P. P. 1 Name(s) Section Day/Time Fill in either Part 1 or Part 2. OBSERVING PROJECT PARTNER ELECTION Part I. SOLO OBSERVER I will do the observing project by myself. I will
It is obviously illogical. What
 Illogical: What Else Would You Call It? by Dr. Clayton Boyer (CA) Author s Note: The beautiful mechanisms shown in this article were all imaginatively crafted through the artistry of Forrest Burnett. The
Illogical: What Else Would You Call It? by Dr. Clayton Boyer (CA) Author s Note: The beautiful mechanisms shown in this article were all imaginatively crafted through the artistry of Forrest Burnett. The
Gnomon Sundial Teacher s Notes
 GNOMON (shadow maker) Angle of latitude in blue Time read at point of shadow Arab philosophers of 9 th and 10 th centuries were amongst the first advanced scientists and mathematicians in Europe. They
GNOMON (shadow maker) Angle of latitude in blue Time read at point of shadow Arab philosophers of 9 th and 10 th centuries were amongst the first advanced scientists and mathematicians in Europe. They
What is a map? A Map is a two or three-dimensional model or representation of the Earth s surface. 2-Dimensional map
 What is a map? A Map is a two or three-dimensional model or representation of the Earth s surface. 2-Dimensional map What is a Map Projection? Planar Projection Projection A Projection is a mathematical
What is a map? A Map is a two or three-dimensional model or representation of the Earth s surface. 2-Dimensional map What is a Map Projection? Planar Projection Projection A Projection is a mathematical
MOTIONS OF THE EARTH. Figure 3.1 : Inclination of the Earth s axis and the orbital plane. Figure 3.2 : Day and Night on the Earth due to rotation
 3 Let s Do Take a ball to represent the earth and a lighted candle to represent the sun. Mark a point on the ball to represent a town X. Place the ball in such a way that the town X is in darkness. Now
3 Let s Do Take a ball to represent the earth and a lighted candle to represent the sun. Mark a point on the ball to represent a town X. Place the ball in such a way that the town X is in darkness. Now
Georeferencing. datum. projection. scale. The next few lectures will introduce you to these elements. on the Earth, you ll need to understand how
 Georeferencing GOAL: To assign a location to all the features represented in our geographic information data In order to do so, we need to make use of the following elements: ellipsoid/geoid To determine
Georeferencing GOAL: To assign a location to all the features represented in our geographic information data In order to do so, we need to make use of the following elements: ellipsoid/geoid To determine
Page 1. Name:
 Name: 1) What is the primary reason New York State is warmer in July than in February? A) The altitude of the noon Sun is greater in February. B) The insolation in New York is greater in July. C) The Earth
Name: 1) What is the primary reason New York State is warmer in July than in February? A) The altitude of the noon Sun is greater in February. B) The insolation in New York is greater in July. C) The Earth
THE DESIGN OF THE NEW SUN-REFLECTION-DIAL IN HEILIGENKREUZ/AUSTRIA
 THE DESIGN OF THE NEW SUN-REFLECTION-DIAL IN HEILIGENKREUZ/AUSTRIA Hellmuth Stachel 1 Abstract A few years ago, the author was involved in the design of a sundial in connection with a big mosaic-work on
THE DESIGN OF THE NEW SUN-REFLECTION-DIAL IN HEILIGENKREUZ/AUSTRIA Hellmuth Stachel 1 Abstract A few years ago, the author was involved in the design of a sundial in connection with a big mosaic-work on
Introduction To Modern Astronomy I: Solar System
 ASTR 111 003 Fall 2007 Lecture 02 Sep. 10, 2007 Introduction To Modern Astronomy I: Solar System Introducing Astronomy (chap. 1-6) Planets and Moons (chap. 7-15) Chap. 16: Our Sun Chap. 28: Search for
ASTR 111 003 Fall 2007 Lecture 02 Sep. 10, 2007 Introduction To Modern Astronomy I: Solar System Introducing Astronomy (chap. 1-6) Planets and Moons (chap. 7-15) Chap. 16: Our Sun Chap. 28: Search for
Why does Earth rotate and what s the evidence? (besides watching it from space ships or satellites) Week 18 January 5, 2015
 Why does Earth rotate and what s the evidence? (besides watching it from space ships or satellites) Week 18 January 5, 2015 The sun determines our solar time everywhere on earth as Earth rotates. Can you
Why does Earth rotate and what s the evidence? (besides watching it from space ships or satellites) Week 18 January 5, 2015 The sun determines our solar time everywhere on earth as Earth rotates. Can you
CELESTIAL COORDINATES
 ASTR 1030 Astronomy Lab 27 Celestial Coordinates CELESTIAL COORDINATES GEOGRAPHIC COORDINATES The Earth's geographic coordinate system is familiar to everyone - the north and south poles are defined by
ASTR 1030 Astronomy Lab 27 Celestial Coordinates CELESTIAL COORDINATES GEOGRAPHIC COORDINATES The Earth's geographic coordinate system is familiar to everyone - the north and south poles are defined by
Section 2. Locating Astronomical Objects in the Night Sky What Do You See? What Do You See? Think About It. Investigate.
 Section 2 Locating Astronomical Objects in the Night Sky Section 2 Locating Astronomical Objects in the Night Sky What Do You See? What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Construct
Section 2 Locating Astronomical Objects in the Night Sky Section 2 Locating Astronomical Objects in the Night Sky What Do You See? What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Construct
Celestial Sphere & Solar Motion Lab (Norton s Star Atlas pages 1-4)
 Name: Date: Celestial Sphere & Solar Motion Lab (Norton s Star Atlas pages 1-4) Italicized topics below will be covered only at the instructor s discretion. 1.0 Purpose: To understand a) the celestial
Name: Date: Celestial Sphere & Solar Motion Lab (Norton s Star Atlas pages 1-4) Italicized topics below will be covered only at the instructor s discretion. 1.0 Purpose: To understand a) the celestial
The Analemmas of Vitruvius and Ptolemy
 The Analemmas of Vitruvius and Ptolemy 2007 Ron Doerfler Dead Reckonings: Lost Art in the Mathematical Sciences http://www.myreckonings.com/wordpress November 29, 2007 Have you ever had to calculate the
The Analemmas of Vitruvius and Ptolemy 2007 Ron Doerfler Dead Reckonings: Lost Art in the Mathematical Sciences http://www.myreckonings.com/wordpress November 29, 2007 Have you ever had to calculate the
Sundials and the Celestial Sphere. Katie Hausknecht
 Sundials and the Celestial Sphere Katie Hausknecht What is a sundial? A sundial is a device that uses the shadow cast by the sun to indicate what time of day it is, often by hours. The Celestial Sphere
Sundials and the Celestial Sphere Katie Hausknecht What is a sundial? A sundial is a device that uses the shadow cast by the sun to indicate what time of day it is, often by hours. The Celestial Sphere
THE LONGWOOD GARDENS ANALEMMATIC SUNDIAL
 (Preprint) AAS 11-682 THE LONGWOOD GARDENS ANALEMMATIC SUNDIAL P. Kenneth Seidelmann * The analemmatic sundial at Longwood Gardens was originally built in 1939, based on the design of a sundial at the
(Preprint) AAS 11-682 THE LONGWOOD GARDENS ANALEMMATIC SUNDIAL P. Kenneth Seidelmann * The analemmatic sundial at Longwood Gardens was originally built in 1939, based on the design of a sundial at the
CALCULATING THE NATAL CHART LESSON 4
 CALCULATING THE NATAL CHART THE TABLES OF HOUSES LESSON 4 At this stage, if you haven't done so already, it is a good idea to invest in a calculator. It does not have to be a complicated one. You will
CALCULATING THE NATAL CHART THE TABLES OF HOUSES LESSON 4 At this stage, if you haven't done so already, it is a good idea to invest in a calculator. It does not have to be a complicated one. You will
extracted from the book ILLUSTRATING TIME S SHADOW The book ILLUSTRATING TIME S SHADOW is available using PayPal on the web site CUBIC Shadows
 CUBIC Shadows How to make a CUBIC sun dial for the common latitudes of the planet earth. The cube dial pictured above is latitude specific. This book shows how to use one set of dial plates for any latitude.
CUBIC Shadows How to make a CUBIC sun dial for the common latitudes of the planet earth. The cube dial pictured above is latitude specific. This book shows how to use one set of dial plates for any latitude.
