BIFILAR SUNDIAL. by Fer J. de Vries
|
|
|
- Rose Higgins
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 BIFILAR SUNDIAL by Fer J. de Vries Introduction Hugo Michnik of Germany invented the bifilar sundial in its horizontal form in His idea was the first really new sundial type since centuries. Instead of a pole style or other single gnomon, two crossing wires are used. One wire runs north-south, the other east-west. They are parallel to the dial plate but have differing heights. At a certain height ratio, all hour lines come out equally spaced, fifteen degrees apart, like on an equatorial sundial. The sundial is read where the shadows of the wires cross. A procedure for this simplest form is described here. Example of a bifilar sundial. From: Die Sonnenuhr, René R.J. Rohr A bifilar sundial could also be called a two-wire dial or a cross-wire dial, but instead of wires, the edges of planes could be used. For a long time after its invention, not much was published about the bifilar sundial. About 1980 however, this dial began to attract interest again, and it was developed further. One example, the use of curved wires, is shown below. 1
2 Bifilar sundial with curved east-west "wire" in Appingedam Basic procedure, part 1 This page describes the basics of a bifilar sundial. The description is limited to the horizontal implementation as first described by Hugo Michnik in The hour lines Draw the necessary hour lines as if on an equatorial sundial. All hour lines are fifteen degrees apart. Of course, half-hour lines could be drawn every 7.5 degrees, of even quarters of an hour, or minutes. All this is easily done with compass and ruler, and no special constructions of calculations are needed. 2
3 Hour lines spaced at 15º intervals The wires The north-south wire should be over the north-south line (which is also the substyle) at a height g1 that may be chosen freely. The height of the east-west wire should then be g2 = g1. SIN(latitude). If, for example, g1 = 20 mm and the sundial is intended for a latitude of 50 degrees, then g2 = 20. SIN(50) = mm. But where should the east-west wire be? It should be over a point that is on the north-south line, a distance y = g1. COS(latitude) from centre C. In our example, this would be y = 20. COS(50) = mm. Position of the wires 3
4 Placing numerals, and the final result In the Northern Hemisphere, the hour numbers run clockwise, in the Southern Hemisphere anti-clockwise. If the hour lines and numerals are on a plate that can rotate about C, then any correction (for longitude or Equation of Time) may be applied by such rotation. This is a great advantage of any sundial with equiangular hour lines. The final result for a horizontal bifilar sundial on the Southern Hemisphere Universal horizontal bifilar sundial Draw twenty-four hour lines, all spaced fifteen degrees. (Not shown in the figure) Place a wire over the north-south line, at height g1. Place a similar wire over the east-west line through C, but make the supports rotatable about the east-west line. Adjust the angle between the supports and the horizontal plane to the desired latitude. This will automatically place the east-west wire at a height g2 = g1. SIN(latitude) and distance y = g1. COS(latitude) from the hour line centre C. Swinging the wire northward produces a sundial for the Northern Hemisphere; swinging it southward produces one for the Southern Hemisphere. 4
5 Universal bifilar sundial Other lines Many other lines may be applied to a bifilar sundial, but that is outside the scope of this basic article. These lines are subject of a more extensive procedure. See basic procedure, part 2. Remarks The bifilar sundial is not suitable for low latitudes. As shown by the universal instrument, the east-west wire will be almost in the dial plane, and the dial would have no practical use. Likewise, the bifilar dial is not attractive for use on either Pole. Both wires will be at the same height, and might just as well be replaced with a single gnomon. basic procedure part 2 The bifilar sundial on an arbitrary plane Here is a worked example for a bifilar sundial with equiangular hour lines on an arbitrary plane. The starting data for this dial are: Latitude: 50 degrees (northern latitude) Inclination of the plane: 100 degrees (a wall leaning forward 10 degrees) Declination of the plane: 25 degrees (a plane facing 25 degrees westerly of south) We calculate some sundial constants for the plane as if we were planning to build an ordinary sundial. 5
6 Style height, v = Hour angle of the substyle, ts = (= 2 hours 24 minutes) Angle between substyle and y-axis, b = These values can be calculated with the computer program ZW2000, downloadable from ZW2000 will also draw the bifilar sundials discussed here. Location of the substyle on the pole style sundial These constants tell us that the dial face corresponds to a horizontal plane in a southern latitude of degrees and a longitude of degrees westerly of ours (translation rule). The hour lines run anti-clockwise (the style height is negative). The pattern for apparent solar time on this dial is pictured above. Of particular interest are the location of the substyle and the value for the style height. Instead of a pole style, we place a gnomon of height g perpendicularly to the sundial, at a distance of g / tan( style height ) from the hour line centre. In our example we choose g = 20 mm, making this distance 20 / tan(44.97) = mm. The top of the gnomon is an indicator on the now imaginary pole style, and the sundial will function as before. Now, we place two wires in the same height equal to g = 20 mm, through the gnomon top and parallel to the dial face. We remove the gnomon. One wire should be over the substyle, the other at right angles to it. The wires intersect and the sundial will function as before, but it is still not the wanted bifilar dial. 6
7 Still the same sundial Transformation Now we lower the wire which is at right angles to the substyle, to a height of g2 = g1. SIN( style height ). This value is 20. SIN(44.97) = mm. At any point in time, the shadow of the unchanged wire at g1 will be in the same place, but that of the lowered wire g2 will now have moved by a factor equal to SIN( style height ) = SIN(44.97) = This will compress the sundial pattern in the direction of the substyle by that factor. A photo copier could do this. After this procedure, the sundial will look like the figure below. The hour lines need to be extended somewhat. 7
8 Transformation by a factor in the indicated direction Hour lines are now equiangular. Other sundial lines The transformation just applied to the apparent solar time hour lines is equally applicable to all other sorts of lines on a sundial. Here is the starting sundial again, expanded with three date lines, an equation of time curve around the XII-hour line and the horizon. You could add various other lines if you wish. The indicator on the (imaginary) pole style is once more replaced by a gnomon of height g = 20 mm, and that, in turn, by two wires at equal heights g = 20 mm. 8
9 The starting sundial We lower the wire at right angles to the substyle again by the factor SIN( style height ) = SIN(44.97) = , which compresses the pattern by that factor. This creates the desired bifilar sundial with equiangular hour lines. Notice that after this procedure, the horizon line is no longer horizontal. 9
10 Transformed into bifilar sundial with equiangular hour lines Summary To construct a bifilar sundial, use an ordinary sundial, with all the desired lines, as a basis. Through the point where the indicator for all these lines would be, place a wire in the direction of the substyle and let its height = g1. At right angles, place a wire of height g2 = g1. SIN( style height ). Compress the entire sundial pattern in the direction of the substyle with the factor SIN( style height ). This will create the bifilar sundial with hour lines for local suntime all spaced fifteen degrees. As you can see, there are no difficult equations and calculations at all, as long as you know how to construct the starting sundial. Remarks There are many more degrees of freedom in the construction of bifilar sundials. The height factor for the second wire may be different. Depending on value, the pattern is either compressed (0 < factor < 1) or enlarged (factor > 1). But the hour lines will not be equiangular anymore. 10
11 The wires do not need to be parallel to the dial face, nor do they have to be at right angles to each other. They do not have to be over the substyle, and they may even be curved. However, all this would be outside the scope of these pages, which mean to present only the basics from English translation: Ruud Hooijenga 11
ZW2000 and Your Sundial
 1 The Sundial Primer created by At this point I assume that you have downloaded and set up ZW2000 on your computer. If not please read Getting Started with ZW2000. Initiate the program ZW2000. Figure 1
1 The Sundial Primer created by At this point I assume that you have downloaded and set up ZW2000 on your computer. If not please read Getting Started with ZW2000. Initiate the program ZW2000. Figure 1
ZW2000 and Your Vertical Sundial Carl Sabanski
 1 The Sundial Primer created by At this point I assume that you have downloaded and set up ZW2000 on your computer and have also read the overview document. If not please read Getting Started with ZW2000
1 The Sundial Primer created by At this point I assume that you have downloaded and set up ZW2000 on your computer and have also read the overview document. If not please read Getting Started with ZW2000
A UNIFORM METHOD TO COMPUTE FLAT SUNDIALS
 A UNIFORM METHOD TO COMPUTE FLAT SUNDIALS usable all over the world by fer j. de vries, netherlands example of sundials on a dodecahedron date: january 1997, revised october 2002 Last Modified 02/05/2004
A UNIFORM METHOD TO COMPUTE FLAT SUNDIALS usable all over the world by fer j. de vries, netherlands example of sundials on a dodecahedron date: january 1997, revised october 2002 Last Modified 02/05/2004
Polar Sundial. Cut carefully on this line. Cut on this line.
 1 The Sundial Primer - "Dialling Guides" The purpose of the "Dialling Guides" is to provide an easy method for laying out the hour lines for a number of polar sundials located at any latitude in either
1 The Sundial Primer - "Dialling Guides" The purpose of the "Dialling Guides" is to provide an easy method for laying out the hour lines for a number of polar sundials located at any latitude in either
CA1 2.11: Designing an Equatorial Sundial Activity
 Purpose: To design an equatorial sundial and learn about motions of the sun and earth that have a bearing on its design. Materials: poster board, length of stiff wire or dowel rod, tape, protractor, ruler,
Purpose: To design an equatorial sundial and learn about motions of the sun and earth that have a bearing on its design. Materials: poster board, length of stiff wire or dowel rod, tape, protractor, ruler,
The Sundial Primer - "Dialling Guides" Double Gnomon Polar Sundial
 1 Double Polar Sundial he purpose of the "Dialling Guides" is to provide an easy method for laying out the hour lines for a number of double gnomon polar sundials located at any latitude in either the
1 Double Polar Sundial he purpose of the "Dialling Guides" is to provide an easy method for laying out the hour lines for a number of double gnomon polar sundials located at any latitude in either the
Horizontal/Vertical/Inclining Sundial
 1 The Sundial Primer created by At this point I assume that you have downloaded and set up SONNE on your computer and have also read the overview document. If not please read Getting Started with SONNE
1 The Sundial Primer created by At this point I assume that you have downloaded and set up SONNE on your computer and have also read the overview document. If not please read Getting Started with SONNE
Making a Sundial. Build a sundial and discover how time can be measured. Space Awareness, Leiden Observatory. iau.org/astroedu
 Making a Sundial Build a sundial and discover how time can be measured. Space Awareness, Leiden Observatory Age 6-10 Supervised Unsupervised Core skills Asking questions, Developing and using models, Analysing
Making a Sundial Build a sundial and discover how time can be measured. Space Awareness, Leiden Observatory Age 6-10 Supervised Unsupervised Core skills Asking questions, Developing and using models, Analysing
Compendium* A Mean Time Sundial by Hendrik Hollander
 Volume 3 Number ISSN 074-397 (printed) ISSN 074-8059 (digital) June 006 The Journal of the North American Sundial Society Compendium* A Mean Time Sundial by Hendrik Hollander Time and reflection change
Volume 3 Number ISSN 074-397 (printed) ISSN 074-8059 (digital) June 006 The Journal of the North American Sundial Society Compendium* A Mean Time Sundial by Hendrik Hollander Time and reflection change
Sec 1.1 CC Geometry History of Trigonometry Name:
 Sec. CC Geometry History of Trigonometry Name: The word trigonometry is of Greek origin and literally translates to Triangle Measurements. Some of the earliest trigonometric ratios recorded date back to
Sec. CC Geometry History of Trigonometry Name: The word trigonometry is of Greek origin and literally translates to Triangle Measurements. Some of the earliest trigonometric ratios recorded date back to
rises in the east High Noon sets in the west, 9:00 a.m. 12:00 p.m. 3:30 p.m. flagpole meter stick
 . Sec 3.5 Right Triangle Trigonometry Solving with Trigonometry The word trigonometry is of Greek origin and literally translates to Triangle Measurements. Some of the earliest trigonometric ratios recorded
. Sec 3.5 Right Triangle Trigonometry Solving with Trigonometry The word trigonometry is of Greek origin and literally translates to Triangle Measurements. Some of the earliest trigonometric ratios recorded
 June 15, 2006 July 19, 2009 A south facing vertical declining sundial by a barn in, Silver City, NM Using a trigon and empirical methods, and a gnomon whose sub-style was vertical True N Magnetic N Silver
June 15, 2006 July 19, 2009 A south facing vertical declining sundial by a barn in, Silver City, NM Using a trigon and empirical methods, and a gnomon whose sub-style was vertical True N Magnetic N Silver
Module 2: Mapping Topic 2 Content: Determining Latitude and Longitude Notes
 Introduction In order to more easily locate points on a globe or map, cartographers designed a system of imaginary vertical lines (also called parallels) and horizontal lines (also called meridians) that
Introduction In order to more easily locate points on a globe or map, cartographers designed a system of imaginary vertical lines (also called parallels) and horizontal lines (also called meridians) that
Fundamentals of Satellite technology
 Fundamentals of Satellite technology Prepared by A.Kaviyarasu Assistant Professor Department of Aerospace Engineering Madras Institute Of Technology Chromepet, Chennai Orbital Plane All of the planets,
Fundamentals of Satellite technology Prepared by A.Kaviyarasu Assistant Professor Department of Aerospace Engineering Madras Institute Of Technology Chromepet, Chennai Orbital Plane All of the planets,
Calibration of a Horizontal Sundial
 Calibration of a Horizontal Sundial Barbara Rovšek Citation: The Physics Teacher 48, 397 (2010); doi: 10.1119/1.3479720 View online: http://dx.doi.org/10.1119/1.3479720 View Table of Contents: http://scitation.aip.org/content/aapt/journal/tpt/48/6?ver=pdfcov
Calibration of a Horizontal Sundial Barbara Rovšek Citation: The Physics Teacher 48, 397 (2010); doi: 10.1119/1.3479720 View online: http://dx.doi.org/10.1119/1.3479720 View Table of Contents: http://scitation.aip.org/content/aapt/journal/tpt/48/6?ver=pdfcov
Latitude and Longitude Pre Test
 Name Date Latitude and Longitude Pre Test Multiple Choice Directions: For questions, 1 10 circle the answer that letter that best answers the question. Each question is worth 1 point each. 1. To locate
Name Date Latitude and Longitude Pre Test Multiple Choice Directions: For questions, 1 10 circle the answer that letter that best answers the question. Each question is worth 1 point each. 1. To locate
ILLUSTRATING SHADOWS TABLE OF CONTENTS
 ILLUSTRATING SHADOWS TABLE OF CONTENTS 316 pages Introduction Chapter Page Introduction and "A Quick Hands On Project" Part One 1 10 The approximate evolution of the dial 2 13 How the earth does its thing
ILLUSTRATING SHADOWS TABLE OF CONTENTS 316 pages Introduction Chapter Page Introduction and "A Quick Hands On Project" Part One 1 10 The approximate evolution of the dial 2 13 How the earth does its thing
CUTTING Shadows SOME CUTOUT DIALS FOR YOUR AMUSEMENT. ALL YOU NEED ARE SOME SCISSORS, AND YOUR LATITUDE, AND LONGITUDE.
 CUTTING Shadows SOME CUTOUT DIALS FOR YOUR AMUSEMENT. ALL YOU NEED ARE SOME SCISSORS, AND YOUR LATITUDE, AND LONGITUDE. Simon Wheaton-Smith December 2009 CUTOUTS FOR PAPER SUN DIALS armillary (also equatorial
CUTTING Shadows SOME CUTOUT DIALS FOR YOUR AMUSEMENT. ALL YOU NEED ARE SOME SCISSORS, AND YOUR LATITUDE, AND LONGITUDE. Simon Wheaton-Smith December 2009 CUTOUTS FOR PAPER SUN DIALS armillary (also equatorial
The Sun -D ial of the I.H.B. Le cadran solaire du B.H.I.
 The Sun -D ial of the I.H.B. Le cadran solaire du B.H.I. The new building erected by the Princely Government on the Quai de Plaisance of the Port of Monaco, and set apart for the use of the International
The Sun -D ial of the I.H.B. Le cadran solaire du B.H.I. The new building erected by the Princely Government on the Quai de Plaisance of the Port of Monaco, and set apart for the use of the International
ANALEMMAS. on the gnomon and on the dial plate. Declining Shadows (Declining-Shadows.pdf ) for declination curve insights and methods.
 ANALEMMAS on the gnomon and on the dial plate armillary dials equatorial dials horizontal and vertical dials also and vertical decliners and polar and meridian please read: NOTE: using these: also see:
ANALEMMAS on the gnomon and on the dial plate armillary dials equatorial dials horizontal and vertical dials also and vertical decliners and polar and meridian please read: NOTE: using these: also see:
Solar Schoolhouse Human Sundial Building a Sundial with the Online Calculator
 Solar Schoolhouse Solar Schoolhouse Human Sundial Building a Sundial with the Online Calculator Overview Analemmatic sundials are sundials which have a movable gnomon (the gnomon is the part that casts
Solar Schoolhouse Solar Schoolhouse Human Sundial Building a Sundial with the Online Calculator Overview Analemmatic sundials are sundials which have a movable gnomon (the gnomon is the part that casts
Compass Basics. Quick Map Basics Review For Compass Use
 Compass Basics Quick Map Basics Review For Compass Use A topographic map tells you where things are and how to get to them, whether you're hiking, biking, hunting, fishing, or just interested in the world
Compass Basics Quick Map Basics Review For Compass Use A topographic map tells you where things are and how to get to them, whether you're hiking, biking, hunting, fishing, or just interested in the world
Look at the date line of today and look at the shadow of the correct side of the cone. Read the mean time on the date line.
 MEANTIME SUNDIAL WITH A CONE GNOMON Amsterdam, the Netherlands, 6 June 006 By Hendrik Hollander Basic principles of the mean time sundial with a cone gnomon On the sundial plane the hour lines and date
MEANTIME SUNDIAL WITH A CONE GNOMON Amsterdam, the Netherlands, 6 June 006 By Hendrik Hollander Basic principles of the mean time sundial with a cone gnomon On the sundial plane the hour lines and date
For most observers on Earth, the sun rises in the eastern
 632 CHAPTER 25: EARTH, SUN, AND SEASONS WHAT IS THE SUN S APPARENT PATH ACROSS THE SKY? For most observers on Earth, the sun rises in the eastern part of the sky. The sun reaches its greatest angular altitude
632 CHAPTER 25: EARTH, SUN, AND SEASONS WHAT IS THE SUN S APPARENT PATH ACROSS THE SKY? For most observers on Earth, the sun rises in the eastern part of the sky. The sun reaches its greatest angular altitude
Naples: A Disguised Analemmatic Dial
 aples: A Disguised Analemmatic Dial A Gnomonic xplanation by Frank H. King The ew Dial nearing completion In the autumn of 200 a novel analemmatic sundial was laid out in aples. The hour points are arranged
aples: A Disguised Analemmatic Dial A Gnomonic xplanation by Frank H. King The ew Dial nearing completion In the autumn of 200 a novel analemmatic sundial was laid out in aples. The hour points are arranged
Unit 2 Math II - History of Trigonometry
 TSK # Unit Math II - History of Trigonometry The word trigonometry is of Greek origin and literally translates to Triangle Measurements. Some of the earliest trigonometric ratios recorded date back to
TSK # Unit Math II - History of Trigonometry The word trigonometry is of Greek origin and literally translates to Triangle Measurements. Some of the earliest trigonometric ratios recorded date back to
East Anglian Trophy 2016 As Time Goes By
 East Anglian Trophy 2016 As Time Goes By This year the theme is sundials. Until I started setting this year s competition I knew very little about them, but there are quite a few interesting facts. As
East Anglian Trophy 2016 As Time Goes By This year the theme is sundials. Until I started setting this year s competition I knew very little about them, but there are quite a few interesting facts. As
Lab: Constructing a Sundial PRACTICAL PHYSICS
 Name Date Period Lab: Constructing a Sundial PRACTICAL PHYSICS Background: As the earth turns on its axis, the sun appears to move across our sky. The shadows cast by the sun move in a clockwise (hence
Name Date Period Lab: Constructing a Sundial PRACTICAL PHYSICS Background: As the earth turns on its axis, the sun appears to move across our sky. The shadows cast by the sun move in a clockwise (hence
A Universal Sundial Ruler for Shadow-Following Clocks
 A Universal Sundial Ruler for Shadow-Following Clocks by Heinz Sigmund (Heidelberg, Germany) Preliminary Remarks My interest in the combination of sundials and mechanical clocks was confirmed by a fine
A Universal Sundial Ruler for Shadow-Following Clocks by Heinz Sigmund (Heidelberg, Germany) Preliminary Remarks My interest in the combination of sundials and mechanical clocks was confirmed by a fine
The Measurement of Time
 CHAPTER TWO The Measurement of Time Solar Time In antiquity the time of day was measured by the direction of a shadow cast in sunlight. This resulted in the development of a wide variety of sophisticated
CHAPTER TWO The Measurement of Time Solar Time In antiquity the time of day was measured by the direction of a shadow cast in sunlight. This resulted in the development of a wide variety of sophisticated
Sundials and the Celestial Sphere. Katie Hausknecht
 Sundials and the Celestial Sphere Katie Hausknecht What is a sundial? A sundial is a device that uses the shadow cast by the sun to indicate what time of day it is, often by hours. The Celestial Sphere
Sundials and the Celestial Sphere Katie Hausknecht What is a sundial? A sundial is a device that uses the shadow cast by the sun to indicate what time of day it is, often by hours. The Celestial Sphere
Latitude and Longitude. Begin
 Latitude and Longitude Begin The Earth is divided in two halves, the top half is called the northern hemisphere, and the bottom half is called the southern hemisphere. The dividing line between the two
Latitude and Longitude Begin The Earth is divided in two halves, the top half is called the northern hemisphere, and the bottom half is called the southern hemisphere. The dividing line between the two
learning outcomes end product a small sundial indoors a large sundial outdoors
 The sundial Use the Sun time 55 minutes, spread across two days learning outcomes To: know that you can tell the time using a sundial tell the time using the Sun discover that long ago it was much more
The sundial Use the Sun time 55 minutes, spread across two days learning outcomes To: know that you can tell the time using a sundial tell the time using the Sun discover that long ago it was much more
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. In this sundial, in Melbourne, Australia, the gnomon is the triangular blade. The style is its inclined edge.
 1 of 28 1/5/2017 9:25 AM From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia A sundial is a device that tells the time of day by the apparent position of the Sun in the sky. In the narrowest sense of the word it consists
1 of 28 1/5/2017 9:25 AM From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia A sundial is a device that tells the time of day by the apparent position of the Sun in the sky. In the narrowest sense of the word it consists
REVISION: MAPWORK 18 SEPTEMBER 2014
 REVISION: MAPWORK 18 SEPTEMBER 2014 Lesson Description In this lesson we revise: Various mapwork calculations Summary Relative Position Bearing is the angular (angle) distance between two points True Bearing
REVISION: MAPWORK 18 SEPTEMBER 2014 Lesson Description In this lesson we revise: Various mapwork calculations Summary Relative Position Bearing is the angular (angle) distance between two points True Bearing
USING YOUR FIELD GUIDE AND STAR CHARTS PRELAB
 USING YOUR FIELD GUIDE AND STAR CHARTS PRELAB 1. Explain the main differences between using a star wheel and a star chart to find things in the night sky. 2. Explain the terms Hour Angle, Meridian and
USING YOUR FIELD GUIDE AND STAR CHARTS PRELAB 1. Explain the main differences between using a star wheel and a star chart to find things in the night sky. 2. Explain the terms Hour Angle, Meridian and
Oberth: Energy vs. Momentum
 1 2 The Oberth Effect 3 Oberth: Energy vs. Momentum 4 The Celestial Sphere From our perspective on Earth the stars appear embedded on a distant 2-dimensional surface the Celestial Sphere. 5 The Celestial
1 2 The Oberth Effect 3 Oberth: Energy vs. Momentum 4 The Celestial Sphere From our perspective on Earth the stars appear embedded on a distant 2-dimensional surface the Celestial Sphere. 5 The Celestial
Meridian Circle through Zenith, North Celestial Pole, Zenith Direction Straight Up from Observer. South Celestial Pole
 Chapter 3 How Earth and Sky Work- Effects of Latitude In chapters 3 and 4we will learn why our view of the heavens depends on our position on the Earth, the time of day, and the day of the year. We will
Chapter 3 How Earth and Sky Work- Effects of Latitude In chapters 3 and 4we will learn why our view of the heavens depends on our position on the Earth, the time of day, and the day of the year. We will
MATHEMATICAL INSTRUMENTATION IN FOURTEENTH-CENTURY EGYPT AND SYRIA
 MATHEMATICAL INSTRUMENTATION IN FOURTEENTH-CENTURY EGYPT AND SYRIA The Illustrated Treatise of JVajm al-din al-misn BY FRANQOIS CHARETTE BRILL LEIDEN BOSTON 2003 Parti 1. Introduction 3 1.1 Learning and
MATHEMATICAL INSTRUMENTATION IN FOURTEENTH-CENTURY EGYPT AND SYRIA The Illustrated Treatise of JVajm al-din al-misn BY FRANQOIS CHARETTE BRILL LEIDEN BOSTON 2003 Parti 1. Introduction 3 1.1 Learning and
Direction: the reference system
 Adapted from Liebenberg and Vlok 2000, The interpretation of maps, aerial photographs and satellite images. Direction: the reference system Direction provides us with one way of answering "Where?" questions.
Adapted from Liebenberg and Vlok 2000, The interpretation of maps, aerial photographs and satellite images. Direction: the reference system Direction provides us with one way of answering "Where?" questions.
NAVIGATION THEORY QUESTIONS Basics of Navigation
 NAVIGATION THEORY QUESTIONS Basics of Navigation Q610065 look at it The angle between the plane of the ecliptic and the plane of equator is approx? 23.5 degrees In which two months of the year is the difference
NAVIGATION THEORY QUESTIONS Basics of Navigation Q610065 look at it The angle between the plane of the ecliptic and the plane of equator is approx? 23.5 degrees In which two months of the year is the difference
HOW TO TRAVEL ON EARTH WITHOUT GETTING LOST
 HOW TO TRAVEL ON EARTH WITHOUT GETTING LOST Using a globe to learn how a position on Earth can be described. Rui Dilão, Instituto Superior Técnico Curriculum topic latitude, longitude, coordinate system
HOW TO TRAVEL ON EARTH WITHOUT GETTING LOST Using a globe to learn how a position on Earth can be described. Rui Dilão, Instituto Superior Técnico Curriculum topic latitude, longitude, coordinate system
Energy Efficiency, Acoustics & Daylighting in building Prof. B. Bhattacharjee Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi
 Energy Efficiency, Acoustics & Daylighting in building Prof. B. Bhattacharjee Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture - 05 Introduction & Environmental Factors (contd.)
Energy Efficiency, Acoustics & Daylighting in building Prof. B. Bhattacharjee Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture - 05 Introduction & Environmental Factors (contd.)
Introduction To Modern Astronomy I: Solar System
 ASTR 111 003 Fall 2007 Lecture 02 Sep. 10, 2007 Introduction To Modern Astronomy I: Solar System Introducing Astronomy (chap. 1-6) Planets and Moons (chap. 7-15) Chap. 16: Our Sun Chap. 28: Search for
ASTR 111 003 Fall 2007 Lecture 02 Sep. 10, 2007 Introduction To Modern Astronomy I: Solar System Introducing Astronomy (chap. 1-6) Planets and Moons (chap. 7-15) Chap. 16: Our Sun Chap. 28: Search for
announcements 4/29/08
 Solar Geometry ARCH 331/431 Spring 2008 Lecture 9 announcements 4/29/08 Firm of the Month Presentation: SRG Architects Wednesday May 30, 12:30, ARCH 042 Assignment 4: Shading Model Studies Available Thursday;
Solar Geometry ARCH 331/431 Spring 2008 Lecture 9 announcements 4/29/08 Firm of the Month Presentation: SRG Architects Wednesday May 30, 12:30, ARCH 042 Assignment 4: Shading Model Studies Available Thursday;
L9 Solar Geometry 4/29/08
 Solar Geometry ARCH 331/431 Spring 2008 Lecture 9 announcements 4/29/08 Firm of the Month Presentation: SRG Architects Wednesday May 30, 12:30, ARCH 042 Assignment 4: Shading Model Studies Available Thursday;
Solar Geometry ARCH 331/431 Spring 2008 Lecture 9 announcements 4/29/08 Firm of the Month Presentation: SRG Architects Wednesday May 30, 12:30, ARCH 042 Assignment 4: Shading Model Studies Available Thursday;
ME 476 Solar Energy UNIT THREE SOLAR RADIATION
 ME 476 Solar Energy UNIT THREE SOLAR RADIATION Unit Outline 2 What is the sun? Radiation from the sun Factors affecting solar radiation Atmospheric effects Solar radiation intensity Air mass Seasonal variations
ME 476 Solar Energy UNIT THREE SOLAR RADIATION Unit Outline 2 What is the sun? Radiation from the sun Factors affecting solar radiation Atmospheric effects Solar radiation intensity Air mass Seasonal variations
CALCULATING THE NATAL CHART LESSON 4
 CALCULATING THE NATAL CHART THE TABLES OF HOUSES LESSON 4 At this stage, if you haven't done so already, it is a good idea to invest in a calculator. It does not have to be a complicated one. You will
CALCULATING THE NATAL CHART THE TABLES OF HOUSES LESSON 4 At this stage, if you haven't done so already, it is a good idea to invest in a calculator. It does not have to be a complicated one. You will
SOLAR ENERGY: THAT S HOT Grades 4-6
 NJCCCS: 5.1, 5.2, 5.4 SOLAR ENERGY: THAT S HOT Grades 4-6 Field Trip Overview: This program illuminates the various ways in which our nearest star affects life on Earth. Students will learn about the apparent
NJCCCS: 5.1, 5.2, 5.4 SOLAR ENERGY: THAT S HOT Grades 4-6 Field Trip Overview: This program illuminates the various ways in which our nearest star affects life on Earth. Students will learn about the apparent
+ 35º 53ʹ 16ʺ 84º 09ʹ 35ʺ
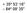 + 35º 53ʹ 16ʺ 84º 09ʹ 35ʺ 35º 53ʹ 16ʺ N 84º 09ʹ 35ʺ W (the precise location of Farragut High School!) Spherical Coordinates Mapping a Sphere The student will be able to: HW: 1 Utilize and convert SI units
+ 35º 53ʹ 16ʺ 84º 09ʹ 35ʺ 35º 53ʹ 16ʺ N 84º 09ʹ 35ʺ W (the precise location of Farragut High School!) Spherical Coordinates Mapping a Sphere The student will be able to: HW: 1 Utilize and convert SI units
How to design a vertical sundial by means of the Orologi Solari program
 How to design a vertical sundial by means of the Orologi Solari program It is not that difficult to design and to build a vertical sundial: everyone could experiment. For sundial design the following parameters
How to design a vertical sundial by means of the Orologi Solari program It is not that difficult to design and to build a vertical sundial: everyone could experiment. For sundial design the following parameters
Elementary. Angles and directions
 Elementary Surveying Angles and directions Prepared by: Andre Paul C. Ampong 3 Vertical angles Vertical angles are referenced to: The horizon by plus or minus The zenith The nadir Zenith and nadir are
Elementary Surveying Angles and directions Prepared by: Andre Paul C. Ampong 3 Vertical angles Vertical angles are referenced to: The horizon by plus or minus The zenith The nadir Zenith and nadir are
Transforming from Geographic to Celestial Coordinates
 Transforming from Geographic to Celestial Coordinates Michael McEllin 1 Introduction The simplest astronomical observation of all is that the stars appear to move around the Earth (which, of course is
Transforming from Geographic to Celestial Coordinates Michael McEllin 1 Introduction The simplest astronomical observation of all is that the stars appear to move around the Earth (which, of course is
CHAPTER II THE COORDINATES SYSTEM AND FORMULARIES
 CHAPTER II THE COORDINATES SYSTEM AND FORMULARIES www.loxodrome.org/ Introduction to Celestial Navigation/Chapter II THE CO-ORDINATES SYSTEMS AND FORMULARIES In previous section we had a purely geometrical
CHAPTER II THE COORDINATES SYSTEM AND FORMULARIES www.loxodrome.org/ Introduction to Celestial Navigation/Chapter II THE CO-ORDINATES SYSTEMS AND FORMULARIES In previous section we had a purely geometrical
Solar Schoolhouse Human Sundial. Building a Sundial with the Online Calculator
 Sol Schoolho use ar Solar Schoolhouse Human Sundial Project Description Analemmatic sundials are sundials which have a movable gnomon (the gnomon is the part that casts the shadow). Humans are common gnomons
Sol Schoolho use ar Solar Schoolhouse Human Sundial Project Description Analemmatic sundials are sundials which have a movable gnomon (the gnomon is the part that casts the shadow). Humans are common gnomons
Thursday 13 June 2013 Morning
 Thursday 13 June 2013 Morning A2 GCE MATHEMATICS (MEI) 4754/01B Applications of Advanced Mathematics (C4) Paper B: Comprehension INSERT * 4 7 1 5 7 1 0 6 1 3 * INFORMATION FOR CANDIDATES This Insert contains
Thursday 13 June 2013 Morning A2 GCE MATHEMATICS (MEI) 4754/01B Applications of Advanced Mathematics (C4) Paper B: Comprehension INSERT * 4 7 1 5 7 1 0 6 1 3 * INFORMATION FOR CANDIDATES This Insert contains
Astronomy 291. Professor Bradley M. Peterson
 Astronomy 291 Professor Bradley M. Peterson The Sky As a first step, we need to understand the appearance of the sky. Important points (to be explained): The relative positions of stars remain the same
Astronomy 291 Professor Bradley M. Peterson The Sky As a first step, we need to understand the appearance of the sky. Important points (to be explained): The relative positions of stars remain the same
THE PLANISPHERIC ASTROLABE
 THE PLANISPHERIC ASTROLABE Feb 4, 2006 A half Dinar note from Iraq with an astrolabe portrayal Of old, the astrolabe was used for various astronomical and astrological calculations, In particular, it could
THE PLANISPHERIC ASTROLABE Feb 4, 2006 A half Dinar note from Iraq with an astrolabe portrayal Of old, the astrolabe was used for various astronomical and astrological calculations, In particular, it could
Map Projections. Chapter 4 MAP PROJECTION
 Map Projections Chapter 4 Map Projections What is map projection? Why are map projections drawn? What are the different types of projections? Which projection is most suitably used for which area? In this
Map Projections Chapter 4 Map Projections What is map projection? Why are map projections drawn? What are the different types of projections? Which projection is most suitably used for which area? In this
Earth & Space Science, Interpreting Data DURATION Preparation: 5 minutes Activity: 40 minutes (total over one day)
 Objectives In this activity students will: 1. Observe how the position of the sun in the sky changes during the course of the day 2. Discover the cardinal directions by tracking the motion of the sun Materials
Objectives In this activity students will: 1. Observe how the position of the sun in the sky changes during the course of the day 2. Discover the cardinal directions by tracking the motion of the sun Materials
The Earth and its representation
 GEOGRAPHY UNIT 1 The Earth and its representation THE SOLAR SYSTEM AND THE EARTH THE SOLAR SYSTEM The solar system is a planetary system. Is a group of astronomical objects who surround a star, in this
GEOGRAPHY UNIT 1 The Earth and its representation THE SOLAR SYSTEM AND THE EARTH THE SOLAR SYSTEM The solar system is a planetary system. Is a group of astronomical objects who surround a star, in this
PHOENIX ARIZONA. Various sundials. This space left blank intentionally. Latitude: 33.5 Longitude: Legal: 105 Magnetic Var/Decl:
 PHOENIX ARIZONA Latitude: 33.5 Longitude: 112.1 Legal: 105 Magnetic Var/Decl: City Country, State, City Hemi- Latitude Long Mag Time Long id sphere +n -s +w -e dec/var ref corr PHX USA AZ Phoenix N +ve
PHOENIX ARIZONA Latitude: 33.5 Longitude: 112.1 Legal: 105 Magnetic Var/Decl: City Country, State, City Hemi- Latitude Long Mag Time Long id sphere +n -s +w -e dec/var ref corr PHX USA AZ Phoenix N +ve
The Transfer of Heat
 The Transfer of Heat Outcomes: S2-4-03 Explain effects of heat transfer within the atmosphere and hydrosphere on the development and movement of wind and ocean currents. Coriolis Effect In our ecology
The Transfer of Heat Outcomes: S2-4-03 Explain effects of heat transfer within the atmosphere and hydrosphere on the development and movement of wind and ocean currents. Coriolis Effect In our ecology
Maps and Globes. By Kennedy s Korner
 Maps and Globes By Kennedy s Korner Map Key or Symbols Maps use symbols to show places and things on Earth. Symbols are drawings that stand for something real. A map key tells you what each symbol stands
Maps and Globes By Kennedy s Korner Map Key or Symbols Maps use symbols to show places and things on Earth. Symbols are drawings that stand for something real. A map key tells you what each symbol stands
Geostationary Satellites and Astrophotography
 Geostationary Satellites and Astrophotography By Clay S. Turner 11/14/08 Introduction When I first started doing astrophotography last January, it was only natural to take pictures of some of Orion s deep
Geostationary Satellites and Astrophotography By Clay S. Turner 11/14/08 Introduction When I first started doing astrophotography last January, it was only natural to take pictures of some of Orion s deep
Scaling the Universe via a Transit of Venus
 Scaling the Universe via a Transit of Venus On 3 June 1769 Captain Cook observed the Transit of Venus in Tahiti. The intention was to use the observations to obtain an accurate estimate of the distance
Scaling the Universe via a Transit of Venus On 3 June 1769 Captain Cook observed the Transit of Venus in Tahiti. The intention was to use the observations to obtain an accurate estimate of the distance
Section 2. Locating Astronomical Objects in the Night Sky What Do You See? What Do You See? Think About It. Investigate.
 Section 2 Locating Astronomical Objects in the Night Sky Section 2 Locating Astronomical Objects in the Night Sky What Do You See? What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Construct
Section 2 Locating Astronomical Objects in the Night Sky Section 2 Locating Astronomical Objects in the Night Sky What Do You See? What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Construct
What is a map? A Map is a two or three-dimensional model or representation of the Earth s surface. 2-Dimensional map
 What is a map? A Map is a two or three-dimensional model or representation of the Earth s surface. 2-Dimensional map What is a Map Projection? Planar Projection Projection A Projection is a mathematical
What is a map? A Map is a two or three-dimensional model or representation of the Earth s surface. 2-Dimensional map What is a Map Projection? Planar Projection Projection A Projection is a mathematical
Electromagnetism 2. D. the charge moves at right angles to the lines of the magnetic field. (1)
 ame: Date: Electromagnetism 2 1. A magnetic force acts on an electric charge in a magnetic field when A. the charge is not moving. B. the charge moves in the direction of the magnetic field. C. the charge
ame: Date: Electromagnetism 2 1. A magnetic force acts on an electric charge in a magnetic field when A. the charge is not moving. B. the charge moves in the direction of the magnetic field. C. the charge
LONGITUDE AND LATITUDE. Semi great circles joining the true or geographic poles of the earth (true meridians).
 MERIDIANS OF LONGITUDE LONGITUDE AND LATITUDE Semi great circles joining the true or geographic poles of the earth (true meridians). They are measured from 0 to 180 degrees East and West of the PRIME MERIDIAN,
MERIDIANS OF LONGITUDE LONGITUDE AND LATITUDE Semi great circles joining the true or geographic poles of the earth (true meridians). They are measured from 0 to 180 degrees East and West of the PRIME MERIDIAN,
Latitude and Longitude
 Latitude and Longitude Finding Your Location on a Sphere Coordinate Systems n When you are locating a point on a flat surface you can use Cartesian coordinates of x and y. n The point 2, 3 is plotted on
Latitude and Longitude Finding Your Location on a Sphere Coordinate Systems n When you are locating a point on a flat surface you can use Cartesian coordinates of x and y. n The point 2, 3 is plotted on
Unit 1: Geography and Social Studies Skills
 Unit 1: Geography and Social Studies Skills Standard(s) of Learning: WHI.1 The student will improve skills in historical research and geographical analysis by a) Identifying, analyzing, and interpreting
Unit 1: Geography and Social Studies Skills Standard(s) of Learning: WHI.1 The student will improve skills in historical research and geographical analysis by a) Identifying, analyzing, and interpreting
CHAPTER EXIT CHAPTER. Models of Earth. 3.1 Modeling the Planet. 3.2 Mapmaking and Technology. 3.3 Topographic Maps CHAPTER OUTLINE
 EXIT CHAPTER.1 Modeling the Planet.2 Mapmaking and Technology. Topographic Maps CHAPTER OUTLINE CHAPTER.1 Modeling the Planet A flat of Earth is a convenient tool, but it can distort the shape, distance,
EXIT CHAPTER.1 Modeling the Planet.2 Mapmaking and Technology. Topographic Maps CHAPTER OUTLINE CHAPTER.1 Modeling the Planet A flat of Earth is a convenient tool, but it can distort the shape, distance,
Contents [1] CIELO - Celestial times...[3] Measuring time by the Sun...[3] Time zones...[4]
![Contents [1] CIELO - Celestial times...[3] Measuring time by the Sun...[3] Time zones...[4] Contents [1] CIELO - Celestial times...[3] Measuring time by the Sun...[3] Time zones...[4]](/thumbs/77/75592191.jpg) CIELO MANUAL Contents CIELO - Celestial times....................[3] Measuring time by the Sun..............[3] Time zones..........................[4] Adjusting the sundial and reading the time.....[5]
CIELO MANUAL Contents CIELO - Celestial times....................[3] Measuring time by the Sun..............[3] Time zones..........................[4] Adjusting the sundial and reading the time.....[5]
A SECOND DIY GARDEN HELIOCHRONOMETER
 A SECOND DIY GARDEN HELIOCHRONOMETER BRIAN HUGGETT U ntil the summer of 2016, I knew very little about sundials. In fact, dare I confess, I had never heard of the British Sundial Society. I thought, however,
A SECOND DIY GARDEN HELIOCHRONOMETER BRIAN HUGGETT U ntil the summer of 2016, I knew very little about sundials. In fact, dare I confess, I had never heard of the British Sundial Society. I thought, however,
Please Visit us at:
 IMPORTANT QUESTIONS WITH ANSWERS Q # 1. Differentiate among scalars and vectors. Scalars Vectors (i) The physical quantities that are completely (i) The physical quantities that are completely described
IMPORTANT QUESTIONS WITH ANSWERS Q # 1. Differentiate among scalars and vectors. Scalars Vectors (i) The physical quantities that are completely (i) The physical quantities that are completely described
Local Horizon and Sundials
 Rosa M. Ros International Astronomical Union, Technical University of Catalonia (Barcelona, Spain) Summary The study of the horizon is crucial to facilitate the students' first observations in an educational
Rosa M. Ros International Astronomical Union, Technical University of Catalonia (Barcelona, Spain) Summary The study of the horizon is crucial to facilitate the students' first observations in an educational
b. Assuming that the sundial is set up correctly, explain this observation.
 Astronomy 100 Name(s): Exercise 3: Seasons in the sun The following exercise illustrates some basic ideas about time, and how our position in the solar system uniquely configures the measurement of time.
Astronomy 100 Name(s): Exercise 3: Seasons in the sun The following exercise illustrates some basic ideas about time, and how our position in the solar system uniquely configures the measurement of time.
Local Horizon and Sundials
 Rosa M. Ros International Astronomical Union, Technical University of Catalonia (Barcelona, Spain) Summary The study of the horizon is crucial to facilitate the students' first observations in an educational
Rosa M. Ros International Astronomical Union, Technical University of Catalonia (Barcelona, Spain) Summary The study of the horizon is crucial to facilitate the students' first observations in an educational
6/17. Universe from Smallest to Largest:
 6/17 Universe from Smallest to Largest: 1. Quarks and Leptons fundamental building blocks of the universe size about 0 (?) importance: quarks combine together to form neutrons and protons. One of the leptons
6/17 Universe from Smallest to Largest: 1. Quarks and Leptons fundamental building blocks of the universe size about 0 (?) importance: quarks combine together to form neutrons and protons. One of the leptons
Time, coordinates and how the Sun and Moon move in the sky
 Time, coordinates and how the Sun and Moon move in the sky Using the colors and magnitudes of quasars drawn from the SDSS Catalog Archive Server to distinguish quasars from stars using the light they emit
Time, coordinates and how the Sun and Moon move in the sky Using the colors and magnitudes of quasars drawn from the SDSS Catalog Archive Server to distinguish quasars from stars using the light they emit
Geography Class 6 Chapters 3 and
 CHAPTER 3 MOTIONS OF THE EARTH The Earth is always travelling in Space. That makes each person on Earth, a Space Traveller. No one feels the movement of the Earth because humans are too tiny when compared
CHAPTER 3 MOTIONS OF THE EARTH The Earth is always travelling in Space. That makes each person on Earth, a Space Traveller. No one feels the movement of the Earth because humans are too tiny when compared
2010 Teacher Created Resources, Inc.
 Editor Sara Connolly Illustrators Kevin McCarthy Mark Mason Cover Artist Brenda DiAntonis Editor in Chief Ina Massler Levin, M.A. Creative Director Karen J. Goldfluss, M.S. Ed. Art Coordinator Renée Christine
Editor Sara Connolly Illustrators Kevin McCarthy Mark Mason Cover Artist Brenda DiAntonis Editor in Chief Ina Massler Levin, M.A. Creative Director Karen J. Goldfluss, M.S. Ed. Art Coordinator Renée Christine
LOCATING CELESTIAL OBJECTS: COORDINATES AND TIME. a. understand the basic concepts needed for any astronomical coordinate system.
 UNIT 2 UNIT 2 LOCATING CELESTIAL OBJECTS: COORDINATES AND TIME Goals After mastery of this unit, you should: a. understand the basic concepts needed for any astronomical coordinate system. b. understand
UNIT 2 UNIT 2 LOCATING CELESTIAL OBJECTS: COORDINATES AND TIME Goals After mastery of this unit, you should: a. understand the basic concepts needed for any astronomical coordinate system. b. understand
Complete the following: a. Lines of latitude are parallel to the equator. Name:
 Name: Date: Social Studies Introduction: Basic Geography Period: Latitude Latitude is defined as a measurement of distance in degrees north and south of the equator. The word latitude is derived from the
Name: Date: Social Studies Introduction: Basic Geography Period: Latitude Latitude is defined as a measurement of distance in degrees north and south of the equator. The word latitude is derived from the
Calculation of a symmetric Gnomon that approximately corrects the Equation of Time. Werner Riegler,
 Calculation of a symmetric Gnomon that approximately corrects the Equation of Time, 30.3. 2009 1 The Gnomon of a sundial can be shaped such that the Equation of Time is automatically corrected and the
Calculation of a symmetric Gnomon that approximately corrects the Equation of Time, 30.3. 2009 1 The Gnomon of a sundial can be shaped such that the Equation of Time is automatically corrected and the
THE EARTH AND ITS REPRESENTATION
 UNIT 7 THE EARTH AND ITS REPRESENTATION TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 THE EARTH AND THE SOLAR SYSTEM... 2 2 THE EARTH S MOVEMENTS... 2 2.1 Rotation.... 2 2.2 The revolution of the Earth: seasons of the year....
UNIT 7 THE EARTH AND ITS REPRESENTATION TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 THE EARTH AND THE SOLAR SYSTEM... 2 2 THE EARTH S MOVEMENTS... 2 2.1 Rotation.... 2 2.2 The revolution of the Earth: seasons of the year....
Latitude and Longitude. Finding your location throughout the world!
 Latitude and Longitude Finding your location throughout the world! What is Latitude? Latitude is defined as a measurement of distance in degrees north and south of the equator The word latitude is derived
Latitude and Longitude Finding your location throughout the world! What is Latitude? Latitude is defined as a measurement of distance in degrees north and south of the equator The word latitude is derived
How to measure the wall declination by means of the Orologi Solari program
 How to measure the wall declination by means of the Orologi Solari program An important point in the design of a sundial is the measurement of the declination of the wall. Orologi Solari can help to perform
How to measure the wall declination by means of the Orologi Solari program An important point in the design of a sundial is the measurement of the declination of the wall. Orologi Solari can help to perform
2. Modern: A constellation is a region in the sky. Every object in the sky, whether we can see it or not, is part of a constellation.
 6/14 10. Star Cluster size about 10 14 to 10 17 m importance: where stars are born composed of stars. 11. Galaxy size about 10 21 m importance: provide a stable environment for stars. Composed of stars.
6/14 10. Star Cluster size about 10 14 to 10 17 m importance: where stars are born composed of stars. 11. Galaxy size about 10 21 m importance: provide a stable environment for stars. Composed of stars.
5 - Seasons. Figure 1 shows two pictures of the Sun taken six months apart with the same camera, at the same time of the day, from the same location.
 ASTR 110L 5 - Seasons Purpose: To plot the distance of the Earth from the Sun over one year and to use the celestial sphere to understand the cause of the seasons. What do you think? Write answers to questions
ASTR 110L 5 - Seasons Purpose: To plot the distance of the Earth from the Sun over one year and to use the celestial sphere to understand the cause of the seasons. What do you think? Write answers to questions
Chapter 1 Test on Geography Skills
 Name Score Chapter 1 Test on Geography Skills Part 1 Matching (14 pts.) Match each term in Column B with its correct definition in Column A by clearly writing the number in the blank space provided. Two
Name Score Chapter 1 Test on Geography Skills Part 1 Matching (14 pts.) Match each term in Column B with its correct definition in Column A by clearly writing the number in the blank space provided. Two
A Review of Coordinates
 A Review of Coordinates Latitude and Longitude On Earth, one way to describe a location is with a coordinate system which is fixed to the Earth's surface. The system is oriented by the spin axis of the
A Review of Coordinates Latitude and Longitude On Earth, one way to describe a location is with a coordinate system which is fixed to the Earth's surface. The system is oriented by the spin axis of the
Standard Indicator That s the Latitude! Students will use latitude and longitude to locate places in Indiana and other parts of the world.
 Standard Indicator 4.3.1 That s the Latitude! Purpose Students will use latitude and longitude to locate places in Indiana and other parts of the world. Materials For the teacher: graph paper, globe showing
Standard Indicator 4.3.1 That s the Latitude! Purpose Students will use latitude and longitude to locate places in Indiana and other parts of the world. Materials For the teacher: graph paper, globe showing
MAPPING THE EARTH HOW DO YOU FIND A LOCATION ON THE EARTH?
 MAPPING THE EARTH HOW DO YOU FIND A LOCATION ON THE EARTH? UNIT TOPICS TOPIC 1: LATITUDE & LONGITUDE TOPIC 2: FIELD MAPS TOPIC 3: TOPOGRAPHIC MAPS TOPIC 4: NYS LANDSCAPES TOPIC 1: LATITUDE & LONGITUDE
MAPPING THE EARTH HOW DO YOU FIND A LOCATION ON THE EARTH? UNIT TOPICS TOPIC 1: LATITUDE & LONGITUDE TOPIC 2: FIELD MAPS TOPIC 3: TOPOGRAPHIC MAPS TOPIC 4: NYS LANDSCAPES TOPIC 1: LATITUDE & LONGITUDE
Mapping Earth s Surface Chapter 2 Section 3
 Mapping Earth s Surface Chapter 2 Section 3 Day 1 Objective I will understand maps can be used to find locations on Earth and to represent information about features on Earth s Surface I will understand
Mapping Earth s Surface Chapter 2 Section 3 Day 1 Objective I will understand maps can be used to find locations on Earth and to represent information about features on Earth s Surface I will understand
APPENDIX A GLOSSARY. Appendix A.1
 APPENDIX A GLOSSARY Appendix A.1 Appendix A.2 Back Bearing A back bearing is measured from the object to your position. It is the exact opposite of a direct bearing. Base Line An imaginary line on the
APPENDIX A GLOSSARY Appendix A.1 Appendix A.2 Back Bearing A back bearing is measured from the object to your position. It is the exact opposite of a direct bearing. Base Line An imaginary line on the
Sundials With Punctiform Hour Lines Gianni Ferrari (Modena, Italy)
 Sundials With Punctiform our Lines Gianni Ferrari (Modena, Italy) Part 1 General Description Introduction Let us consider the line drawn in the sky by the points occupied by the Suns center at a given
Sundials With Punctiform our Lines Gianni Ferrari (Modena, Italy) Part 1 General Description Introduction Let us consider the line drawn in the sky by the points occupied by the Suns center at a given
UNIT 6 CELESTIAL SPHERE AND EQUINOCTIAL SYSTEM OF COORDINATES
 UNIT 6 CELESTIAL SPHERE AND EQUINOCTIAL SYSTEM OF COORDINATES Structure 6.1 Introduction Objectives 6.2 References 6.3 Apparent Annual Motion of the Sun and the Concept of the Ecliptic and the Obliquity
UNIT 6 CELESTIAL SPHERE AND EQUINOCTIAL SYSTEM OF COORDINATES Structure 6.1 Introduction Objectives 6.2 References 6.3 Apparent Annual Motion of the Sun and the Concept of the Ecliptic and the Obliquity
Downloaded from
 Geo Globe : Latitudes and Longitudes 1.Suppose the time at 30 east is 2 p.m. then what is the time at Greenwich? (A) 2 p.m. (B) 12 p.m. (C) 1 p.m. (D) Cannot find 2.What does the term 'Grid' mean
Geo Globe : Latitudes and Longitudes 1.Suppose the time at 30 east is 2 p.m. then what is the time at Greenwich? (A) 2 p.m. (B) 12 p.m. (C) 1 p.m. (D) Cannot find 2.What does the term 'Grid' mean
