LI ABUNDANCES IN PTPS RED CLUMP GIANTS
|
|
|
- Gladys Cain
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Dig Sites of Stellar Archeology: Giant Stars in the Milky Way Ege Uni. J. of Faculty of Sci., Special Issue, 2014, LI ABUNDANCES IN PTPS RED CLUMP GIANTS Monika Adamów 1, *, Andrzej Niedzielski 1, Grzegorz Nowak 1, Beata Deka 1, Michalina Górecka 1, Aleksander Wolszczan 2,3 1 Centre for Astronomy, Faculty of Physics, Astronomy and Informatics, Nicolaus Copernicus University, Grudziadzka 5, Torun, Poland 2 Department of Astronomy and Astrophysics, Pennsylvania State University, 525 Davey Laboratory, University Park, PA 16802, USA 3 Center for Exoplanets and Habitable Worlds, Pennsylvania State University, 525 Davey Laboratory, University Park, PA 16802, USA Abstract: Lithium is a very intriguing element. While built into the stars it may be easily destroyed at temperatures of only 2.5 mln K, which makes it a very sensitive indicator of processes in stellar interiors, i.e. stellar age. Hence, investigation of lithium abundances requires understanding of various mechanisms occurring during stellar evolution. We therefore pay much attention to lithium within the ongoing PennState - Toruń Planet Search (PTPS) with the Hobby Eberly-Telescope. Here we present preliminary results of spectral analysis focused on Li and alpha-element abundances for 348 most evolved PTPS giants. Keywords: stars: abundances; late-type stars; planetary systems. 1. INTRODUCTION According to both observations and stellar evolution theory Lithium is destroyed during stellar evolution on the Red Giant Branch (RGB), initially due to the so-called first dredge-up and later on due to slow extra mixing mechanism. Nevertheless, some giants reveal high surface lithium enhancement. This phenomenon is usually explained with some internal lithium production process, supported by fast, non-standard mixing or alternatively by accretion of Li-rich material from a supernova remnants, or from a Lirich companion - brown dwarf or planet. More extensive description of those processes may be found in e.g. [1]. The PennState - Toruń Planet Search (PTPS) program is a long term, ongoing project dedicated to search for planets around evolved stars with the radial velocity technique using the Hobby-Eberly Telescope. The ultimate goal of PTPS is analysis of evolution of planetary systems. Within PTPS in parallel to a planet search we * Corresponding Author: Tel: +48 (56) Monika.Adamow@astri.uni.torun.pl 19
2 also perform a detailed in-depth spectral analysis of all observed stars with the aim to better constrain their evolutionary status. Details of our survey (observing strategy, motivation, and data analysis) have been presented in detail elsewhere [2]. The richness of the PTPS sample in stars at various stages of stellar evolution allows for discussion of lithium abundance evolution in relation to evolutionary status of stars. As we have data from a precise radial velocity survey we may discuss lithium abundances in the context of stellar binarity or hosting low-mass companions. Here we present preliminary results of the A(Li) investigation of red giants from PTPS sample. 2. OBSERVATIONS AND DATA ANALYSIS 2.1. Sample The total PTPS sample that we have been monitoring since early 2004 is composed of field solar- and intermediate-mass stars at various stages of stellar evolution. Here we discuss a subsample of 348 stars, selected to be presumably RGC stars. They constitute the so-called RGC subsample of the PTPS and fall in the clump giant region of the HR-diagram, which contains stars of various masses over a range of evolutionary stages. Detailed description of this sample and selection criteria can be found in paper [3] Observations PTPS is conducted with the 9.2 m Hobby-Eberly Telescope (HET) [4], operated in the queue-scheduled mode [5] and equipped with the High Resolution Spectrograph (HRS, [6]). For PTPS the HRS is used in its R= resolving power mode with a I 2 gas cell. The spectra consist of 46 echelle orders recorded on the blue CCD chip ( nm) and 24 orders on the red one ( nm). The signal-to-noise ratio was typically better than per resolution element at 590 nm. The blue spectra are used for precise radial velocity determinations with the gas cell. For detailed spectroscopic analysis both red' spectrum, unaffected by the I 2 lines and blue template (obtained with no gas cell inserted into the optical path) are used. 20
3 In the Li abundance analysis only one order of the red spectra containing the 7 Li 670,8 nm line was used. Since the HET/HRS flat-field spectra are occasionally contaminated with a spectral feature near the 7 Li line, which (depending on the actual RV of a star) may mimic the Li line and influence the abundance analysis, all flat field spectra were checked and those affected by this feature were omitted to avoid the contamination Data analysis Spectral analysis was performed with Spectroscopy Made Easy package (SME) [7]. SME assumes LTE and plane-parallel geometry, but ignores magnetic field, molecular lines and mass loss. Spectrum synthesis is based on Kurucz s models of stellar atmospheres [8]. In SME analysis the observed spectrum is considered as a model constraint. As an input SME requires a set of lines from Vienna Atomic Line Database (VALD) [9] identified in the spectrum, stellar data (including radial velocity) and the instrumental profile. Although SME requires the metallicity ratio [M/H] rather than [Fe/H], we used [Fe/H] determined in [3] as the closest approximation to metallicity. We used SME in the nm ranges and fitted the 7 Li line at nm as well as several lines of Al, Ti, Si and Ca, rotation velocity and macroturbulent velocity together. In the first attempt only template spectra (with no I 2 gas cell inserted) were used for the analysis. However, I 2 molecular absorption affects the spectrum up to 660 nm only, so it does not influence 7 Li line region. Hence, in the final analysis it was also possible to use the red spectra obtained with the gas-cell inserted, which allowed for A(Li) uncertainty estimates (rms). We analyzed 4750 spectra in total - from 2 to about 100 spectra per star depending of its status in PTPS, 14 for one object on average. 3. RESULTS The collection of lithium abundances in combination with an existing PTPS database of radial velocities is in position to give a new insight into possible lithium enhancement mechanisms for giants. Fig. 1 presents the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram for stars from the PTPS giant sample. We have identified 17 Li-rich stars, defined here as those with A(Li)>1.3. Not all of them may be considered as Li-overabundant as their evolutionary status is not 21
4 certain. It cannot be excluded that some of such stars are objects undergoing first dredge up. However, we have found also two objects with A(Li) exceeding the so-called Figure 1. The HR diagram for the PTPS giant-star sample. Lithium abundances are color-coded (vertical bar on the right). meteoritic value of A(Li)=3.3 [10], therefore they definitely have undergone some lithium production process. One of the most intriguing stars in this sample is BD [11]. It is the first case of an exceptionally Li-overabundant giant (A(Li)=2.2) that is very likely accompanied by a giant planet. BD b travels in a highly eccentric orbit. One possible interpretation of this detection is that a migration episode in the original system left behind a close-in planet, which has subsequently merged with the star, and a more distant, surviving planet in an eccentric orbit. Hence enhanced lithium abundance might be a consequence of a recent planet engulfment episode by the parent star. 22
5 BD is not the only Li-rich star exhibiting changes in radial velocities that might be interpreted as presence of stellar or low mass companion (planets or brown dwarfs). Among 17 red giant stars with enhanced Li abundance only a few do not show significant variations in radial velocities, which makes them single, non-active stars within the precision maintained within PTPS. Ten stars in the Li-rich giants sample are being monitored as probable planet hosts and the other six objects are binaries. In addition to RV measurements, we have determined basic atmospheric parameters (effective temperature, surface gravity, microturbulent velocity, chemical composition), luminosities, masses, radii [3] and rotational velocities for all stars in the sample. Therefore the data collected within PTPS represent also a great tool for verifying connection of lithium abundance with stellar parameters. We have found that stars with easily detectable Li lines tend to be slightly more massive when compared to the rest of the sample. Li-rich stars reveal also faster rotational velocities, however not all of them might be classified as fast rotators. A more detailed study of PTPS giants will be presented elsewhere [12]. ACKNOWLEDGMENT We thank Dr. Nikolai Piskunov and Dr. Jeff Valenti for making SME available for us. We thank the HET resident astronomers and telescope operators for obtaining the PTPS spectra..a., G.N., B.D., M.G. and A.N. were supported in part by the Polish Ministry of Science and Higher Education grant N N and by the Polish National Science Centre grant no. UMO-2012/07/B/ST9/ M.A. is also supported by the Polish National Science Centre grant no. UMO-2012/05/N/ST9/ A.W. was supported by the NASA grant NNX09AB36G. The HET is a joint project of the University of Texas at Austin, the Pennsylvania State University, Stanford University, Ludwig-Maximilians- Universität München, and Georg-August- Universität Göttingen. The HET is named in honor of its principal benefactors, William P. Hobby and Robert E. Eberly. The Center for Exoplanets and Habitable Worlds is supported by the Pennsylvania State University, the Eberly College of Science, and the Pennsylvania Space Grant Consortium. 23
6 REFERENCES [1] J. K. Carlberg, K. Cunha, V. V. Smith and S.R. Majewski, Observable signatures of planet accretion in red giants. I. Rapid rotation and light element replenishment, Astroph. J., vol. 757, p. 109, [2] A. Niedzielski A. and Wolszczan, The PennState/Toruń Center for Astronomy search for planets around evolved stars, in Astronomical Society of the Pacific Conference Series, vol. 398, Extreme Solar Systems, ed. D. Fischer, F. A. Rasio, S. E. Thorsett, and A. Wolszczan, p. 71, [3] P. Zieliński, A. Niedzielski, A. Wolszczan, M. Adamów and G. Nowak, The Penn State- Toruń Centre for Astronomy Planet Search stars. I. Spectroscopic analysis of 348 red giants, Astron. and Astroph., vol. 547, p. 91, [4] L. W. Ramsey, M. T. Adams, T. G. Barnes et al., Early performance and present status of the Hobby-Eberly Telescope, in Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers (SPIE) Conference Series, Vol. 3352, ed. L. M. Stepp, pp , [5] M. Shetrone, M. E. Cornell, J.R. Fowler, et al., The year review of queue scheduling of the Hobby-Eberly Telescope, Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac., vol. 119, p. 556, [6] R. G. Tull, High-resolution fiber-coupled spectrograph of the Hobby-Eberly Telescope, in Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers (SPIE), Conference Series, vol. 3355, ed. S. D Odorico, pp , [7] J. A. Valenti and N. Piskunov, Spectroscopy Made Easy: A new tool for fitting observations with synthetic spectra, Astroph. and Space Sci., vol. 118, p. 595, [8] R. Kurucz, ATLAS9 Stellar Atmosphere Programs and 2 km/s grid. Kurucz CD-ROM No. 13. Cambridge, Mass.: Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory, p. 13, [9] F. Kupka, N. Piskunov, T. A. Ryabchikova H. C. Stempels and W. W. Weiss, VALD-2: Progress of the Vienna Atomic Line Data Base, Astroph. and Space Sci., vol. 138, p. 119, [10] M. Asplund, N. Grevesse, A. J. Sauval and P. Scott, The chemical composition of the Sun, Ann. Rev. of Astron. and Astroph., vol. 47, p. 481, [11] M. Adamów, A. Niedzielski, E. Villaver, G. Nowak, G. and A. Wolszczan, BD Li overabundant giant star with a planet: A case of recent engulfment?, Astroph. J. Let., vol. 754, L15, [12] M. Adamów et al. 2013, PhD Thesis, Nicolaus Copernicus Univerity, Toruń - unpublished. 24
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 26 Oct 2015
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 26 Oct 2015 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 26 Oct 2015](/thumbs/81/83990357.jpg) Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. aa c ESO 2018 July 3, 2018 Masses and luminosities for 342 stars from the PennState-Toruń Centre for Astronomy Planet Search (Research Note) M. Adamczyk, B. Deka-Szymankiewicz,
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. aa c ESO 2018 July 3, 2018 Masses and luminosities for 342 stars from the PennState-Toruń Centre for Astronomy Planet Search (Research Note) M. Adamczyk, B. Deka-Szymankiewicz,
Low- mass companions to Bright Giants.
 Low- mass companions to Bright Giants. Andrzej Niedzielski Alex Wolszczan, Grzegorz Nowak, Monika Adamów, Beata Deka, Michalina Górecka, Kacper Kowalik 1 Planets around other stars. 1992 Wolszczan & Frail
Low- mass companions to Bright Giants. Andrzej Niedzielski Alex Wolszczan, Grzegorz Nowak, Monika Adamów, Beata Deka, Michalina Górecka, Kacper Kowalik 1 Planets around other stars. 1992 Wolszczan & Frail
Red giants with brown dwarfs companions
 Red giants with brown dwarfs companions Andrzej Niedzielski Toruń Center for Astronomy, Nicolaus Copernicus University in Toruń, Poland Planets around evolved stars 1992 Wolszczan & Frail - first planet
Red giants with brown dwarfs companions Andrzej Niedzielski Toruń Center for Astronomy, Nicolaus Copernicus University in Toruń, Poland Planets around evolved stars 1992 Wolszczan & Frail - first planet
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 21 Jun 2012
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 21 Jun 2012 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 21 Jun 2012](/thumbs/88/114932289.jpg) BD+48 740 Li overabundant giant star with a planet. A case of recent engulfment? M. Adamów 1, A. Niedzielski 1, E. Villaver 2, G. Nowak 1, A. Wolszczan 3,4 arxiv:1206.4938v1 [astro-ph.sr] 21 Jun 2012 ABSTRACT
BD+48 740 Li overabundant giant star with a planet. A case of recent engulfment? M. Adamów 1, A. Niedzielski 1, E. Villaver 2, G. Nowak 1, A. Wolszczan 3,4 arxiv:1206.4938v1 [astro-ph.sr] 21 Jun 2012 ABSTRACT
WHAT DO RADIAL VELOCITY MEASUREMENTS TELL ABOUT RV TAURI STARS?
 Dig Sites of Stellar Archeology: Giant Stars in the Milky Way Ege Uni. J. of Faculty of Sci., Special Issue, 2014, 113-120 WHAT DO RADIAL VELOCITY MEASUREMENTS TELL ABOUT RV TAURI STARS? Timur Şahin 1*,
Dig Sites of Stellar Archeology: Giant Stars in the Milky Way Ege Uni. J. of Faculty of Sci., Special Issue, 2014, 113-120 WHAT DO RADIAL VELOCITY MEASUREMENTS TELL ABOUT RV TAURI STARS? Timur Şahin 1*,
Astronomy. Astrophysics. The Penn State Toruń Centre for Astronomy Planet Search stars, II. Lithium abundance analysis of the red giant clump sample
 A&A 569, A55 (2014) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361/201423400 c ESO 2014 Astronomy & Astrophysics The Penn State Toruń Centre for Astronomy Planet Search stars, II. Lithium abundance analysis of the red giant clump
A&A 569, A55 (2014) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361/201423400 c ESO 2014 Astronomy & Astrophysics The Penn State Toruń Centre for Astronomy Planet Search stars, II. Lithium abundance analysis of the red giant clump
High resolution spectroscopy of two metal-poor red giants: HD and HD
 High resolution spectroscopy of two metal-poor red giants: HD 3078 and HD 1873 Faculty of Physics and Mathematics, University of Latvia, Raiņa bulv. 19, Riga, LV-1586, Latvia E-mail: arturs_ lv@inbox.lv
High resolution spectroscopy of two metal-poor red giants: HD 3078 and HD 1873 Faculty of Physics and Mathematics, University of Latvia, Raiņa bulv. 19, Riga, LV-1586, Latvia E-mail: arturs_ lv@inbox.lv
CHEMICAL ABUNDANCE ANALYSIS OF RC CANDIDATE STAR HD (46 LMi) : PRELIMINARY RESULTS
 Dig Sites of Stellar Archeology: Giant Stars in the Milky Way Ege Uni. J. of Faculty of Sci., Special Issue, 2014, 145-150 CHEMICAL ABUNDANCE ANALYSIS OF RC CANDIDATE STAR HD 94264 (46 LMi) : PRELIMINARY
Dig Sites of Stellar Archeology: Giant Stars in the Milky Way Ege Uni. J. of Faculty of Sci., Special Issue, 2014, 145-150 CHEMICAL ABUNDANCE ANALYSIS OF RC CANDIDATE STAR HD 94264 (46 LMi) : PRELIMINARY
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature10389 Observations The Kepler satellite gathered 30 days of uninterrupted data for HD 187547 (KIC 7548479) between October 19 and November 18, 2009, corresponding to Kepler s observing
doi:10.1038/nature10389 Observations The Kepler satellite gathered 30 days of uninterrupted data for HD 187547 (KIC 7548479) between October 19 and November 18, 2009, corresponding to Kepler s observing
Exoplanet Host Stars
 Exoplanet Host Stars The Hertzsprung-Russel (HR)Diagram The Hertzsprung-Russel (HR)Diagram Standard Doppler Surveys The Hertzsprung-Russel (HR)Diagram Direct Imaging detections Standard Doppler Surveys
Exoplanet Host Stars The Hertzsprung-Russel (HR)Diagram The Hertzsprung-Russel (HR)Diagram Standard Doppler Surveys The Hertzsprung-Russel (HR)Diagram Direct Imaging detections Standard Doppler Surveys
Metallicities of M Dwarf Planet Hosts from Spectral Synthesis
 Metallicities of M Dwarf Planet Hosts from Spectral Synthesis Jacob L. Bean Dept. of Astronomy, University of Texas, 1 University Station, C1402, Austin, TX 78712 bean@astro.as.utexas.edu arxiv:astro-ph/0611060v1
Metallicities of M Dwarf Planet Hosts from Spectral Synthesis Jacob L. Bean Dept. of Astronomy, University of Texas, 1 University Station, C1402, Austin, TX 78712 bean@astro.as.utexas.edu arxiv:astro-ph/0611060v1
DWARFS IN THE LOCAL REGION
 The Astronomical Journal, 131:3069 3092, 2006 June # 2006. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. A DWARFS IN THE LOCAL REGION R. Earle Luck 1 and Ulrike Heiter 2 Received
The Astronomical Journal, 131:3069 3092, 2006 June # 2006. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. A DWARFS IN THE LOCAL REGION R. Earle Luck 1 and Ulrike Heiter 2 Received
Chemical Abundance Analysis of the Symbiotic Red Giants
 Chemical Abundance Analysis of the Symbiotic Red Giants Cezary Ga lan 1, Joanna Miko lajewska 1, and Kenneth H. Hinkle 2 1 N. Copernicus Astronomical Center, Bartycka 18, PL-00-716 Warsaw, Poland 2 National
Chemical Abundance Analysis of the Symbiotic Red Giants Cezary Ga lan 1, Joanna Miko lajewska 1, and Kenneth H. Hinkle 2 1 N. Copernicus Astronomical Center, Bartycka 18, PL-00-716 Warsaw, Poland 2 National
DETERMINATION OF STELLAR ROTATION WITH GAIA AND EFFECTS OF SPECTRAL MISMATCH. A. Gomboc 1,2, D. Katz 3
 537 DETERMINATION OF STELLAR ROTATION WITH GAIA AND EFFECTS OF SPECTRAL MISMATCH A. Gomboc,2, D. Katz 3 University in Ljubljana, Jadranska 9, 00 Ljubljana, Slovenia 2 ARI, Liverpool John Moores University,
537 DETERMINATION OF STELLAR ROTATION WITH GAIA AND EFFECTS OF SPECTRAL MISMATCH A. Gomboc,2, D. Katz 3 University in Ljubljana, Jadranska 9, 00 Ljubljana, Slovenia 2 ARI, Liverpool John Moores University,
Characterizing Stars
 Characterizing Stars 1 Guiding Questions 1. How far away are the stars? 2. What evidence do astronomers have that the Sun is a typical star? 3. What is meant by a first-magnitude or second magnitude star?
Characterizing Stars 1 Guiding Questions 1. How far away are the stars? 2. What evidence do astronomers have that the Sun is a typical star? 3. What is meant by a first-magnitude or second magnitude star?
Characterizing Stars. Guiding Questions. Parallax. Careful measurements of the parallaxes of stars reveal their distances
 Guiding Questions Characterizing Stars 1. How far away are the stars? 2. What evidence do astronomers have that the Sun is a typical star? 3. What is meant by a first-magnitude or second magnitude star?
Guiding Questions Characterizing Stars 1. How far away are the stars? 2. What evidence do astronomers have that the Sun is a typical star? 3. What is meant by a first-magnitude or second magnitude star?
THE OBSERVATION AND ANALYSIS OF STELLAR PHOTOSPHERES
 THE OBSERVATION AND ANALYSIS OF STELLAR PHOTOSPHERES DAVID F. GRAY University of Western Ontario, London, Ontario, Canada CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Preface to the first edition Preface to the
THE OBSERVATION AND ANALYSIS OF STELLAR PHOTOSPHERES DAVID F. GRAY University of Western Ontario, London, Ontario, Canada CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Preface to the first edition Preface to the
Lithium abundances and metallicities: trends from metal-poor and AGB/RGB stars
 Mem. S.A.It. Suppl. Vol. 22, 103 c SAIt 2012 Memorie della Supplementi Lithium abundances and metallicities: trends from metal-poor and AGB/RGB stars W. J. Maciel and R. D. D. Costa Astronomy Department
Mem. S.A.It. Suppl. Vol. 22, 103 c SAIt 2012 Memorie della Supplementi Lithium abundances and metallicities: trends from metal-poor and AGB/RGB stars W. J. Maciel and R. D. D. Costa Astronomy Department
Stars and their properties: (Chapters 11 and 12)
 Stars and their properties: (Chapters 11 and 12) To classify stars we determine the following properties for stars: 1. Distance : Needed to determine how much energy stars produce and radiate away by using
Stars and their properties: (Chapters 11 and 12) To classify stars we determine the following properties for stars: 1. Distance : Needed to determine how much energy stars produce and radiate away by using
Characterization of the exoplanet host stars. Exoplanets Properties of the host stars. Characterization of the exoplanet host stars
 Characterization of the exoplanet host stars Exoplanets Properties of the host stars Properties of the host stars of exoplanets are derived from a combination of astrometric, photometric, and spectroscopic
Characterization of the exoplanet host stars Exoplanets Properties of the host stars Properties of the host stars of exoplanets are derived from a combination of astrometric, photometric, and spectroscopic
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 9 Jan 2018
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 9 Jan 2018 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 9 Jan 2018](/thumbs/93/112706990.jpg) Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. PTPS dwarfs fin c ESO 218 January 1, 218 arxiv:181.2899v1 [astro-ph.sr] 9 Jan 218 The Penn State - Toruń Centre for Astronomy Planet Search stars IV. Dwarfs and
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. PTPS dwarfs fin c ESO 218 January 1, 218 arxiv:181.2899v1 [astro-ph.sr] 9 Jan 218 The Penn State - Toruń Centre for Astronomy Planet Search stars IV. Dwarfs and
Detailed chemical abundances of M-dwarf planet hosts from APOGEE observations
 Detailed chemical abundances of M-dwarf planet hosts from APOGEE observations Diogo Souto Observatório Nacional - ON/MCTI + Katia Cunha Anibal Verne Smith C. Allende Prieto Garcia Hernandez Olga Zamora
Detailed chemical abundances of M-dwarf planet hosts from APOGEE observations Diogo Souto Observatório Nacional - ON/MCTI + Katia Cunha Anibal Verne Smith C. Allende Prieto Garcia Hernandez Olga Zamora
Tests of MATISSE on large spectral datasets from the ESO Archive
 Tests of MATISSE on large spectral datasets from the ESO Archive Preparing MATISSE for the ESA Gaia Mission C.C. Worley, P. de Laverny, A. Recio-Blanco, V. Hill, Y. Vernisse, C. Ordenovic and A. Bijaoui
Tests of MATISSE on large spectral datasets from the ESO Archive Preparing MATISSE for the ESA Gaia Mission C.C. Worley, P. de Laverny, A. Recio-Blanco, V. Hill, Y. Vernisse, C. Ordenovic and A. Bijaoui
On the relation between stars and their planets
 On the relation between stars and their planets Nuno C. Santos Centro de Astrofísica, Universidade do Porto Instituto de Astrofísica e Ciências do Espaço Why we stellar parameters are important in exoplanets
On the relation between stars and their planets Nuno C. Santos Centro de Astrofísica, Universidade do Porto Instituto de Astrofísica e Ciências do Espaço Why we stellar parameters are important in exoplanets
Importance of the study of extrasolar planets. Exoplanets Introduction. Importance of the study of extrasolar planets
 Importance of the study of extrasolar planets Exoplanets Introduction Planets and Astrobiology (2017-2018) G. Vladilo Technological and scientific spin-offs Exoplanet observations are driving huge technological
Importance of the study of extrasolar planets Exoplanets Introduction Planets and Astrobiology (2017-2018) G. Vladilo Technological and scientific spin-offs Exoplanet observations are driving huge technological
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ep] 24 Mar 2016
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ep] 24 Mar 2016 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ep] 24 Mar 2016](/thumbs/80/81438443.jpg) Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. 28417_ap c ESO 2018 June 11, 2018 Letter to the Editor Tracking Advanced Planetary Systems (TAPAS) with HARPS-N. IV. TYC 3667-1280-1 - the most massive red giant
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. 28417_ap c ESO 2018 June 11, 2018 Letter to the Editor Tracking Advanced Planetary Systems (TAPAS) with HARPS-N. IV. TYC 3667-1280-1 - the most massive red giant
Star-planet connection:
 : The role of stellar metallicity Centro de Astrofísica da Universidade do Porto Instituto de Astrofísica e Ciências do Espaço 18 September 2014 Porto, Portugal 1 Planet formation and metallicity Giant
: The role of stellar metallicity Centro de Astrofísica da Universidade do Porto Instituto de Astrofísica e Ciências do Espaço 18 September 2014 Porto, Portugal 1 Planet formation and metallicity Giant
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ep] 13 Jul 2015
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ep] 13 Jul 2015 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ep] 13 Jul 2015](/thumbs/72/66497348.jpg) Draft version July 14, 2015 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 5/2/11 THE METALLICITIES OF STARS WITH AND WITHOUT TRANSITING PLANETS Lars A. Buchhave 1,2 David W. Latham 1 Draft version
Draft version July 14, 2015 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 5/2/11 THE METALLICITIES OF STARS WITH AND WITHOUT TRANSITING PLANETS Lars A. Buchhave 1,2 David W. Latham 1 Draft version
Classical Methods for Determining Stellar Masses, Temperatures, and Radii
 Classical Methods for Determining Stellar Masses, Temperatures, and Radii Willie Torres Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics 2010 Sagan Exoplanet Summer Workshop 1 Outline Basic properties of stars
Classical Methods for Determining Stellar Masses, Temperatures, and Radii Willie Torres Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics 2010 Sagan Exoplanet Summer Workshop 1 Outline Basic properties of stars
Astr 5465 Feb. 6, 2018 Today s Topics
 Astr 5465 Feb. 6, 2018 Today s Topics Stars: Binary Stars Determination of Stellar Properties via Binary Stars Classification of Binary Stars Visual Binaries Both stars visible Only one star visible Spectroscopic
Astr 5465 Feb. 6, 2018 Today s Topics Stars: Binary Stars Determination of Stellar Properties via Binary Stars Classification of Binary Stars Visual Binaries Both stars visible Only one star visible Spectroscopic
Science Olympiad Astronomy C Division Event National Exam
 Science Olympiad Astronomy C Division Event National Exam University of Nebraska-Lincoln May 15-16, 2015 Team Number: Team Name: Instructions: 1) Please turn in all materials at the end of the event. 2)
Science Olympiad Astronomy C Division Event National Exam University of Nebraska-Lincoln May 15-16, 2015 Team Number: Team Name: Instructions: 1) Please turn in all materials at the end of the event. 2)
Heavy meteal rules. Vardan Adibekyan Institute of Astrophysics and Space Sciences. The star-planet connection. 1 June 2015 NAOJ, Tokyo
 The star-planet connection Institute of Astrophysics and Space Sciences 1 June 2015 NAOJ, Tokyo 1 Introduction to exoplanets Diversity of exoplanets Planet formation theories 2 Planet formation and metallicity
The star-planet connection Institute of Astrophysics and Space Sciences 1 June 2015 NAOJ, Tokyo 1 Introduction to exoplanets Diversity of exoplanets Planet formation theories 2 Planet formation and metallicity
CHEMICAL ABUNDANCES OF WEAK T TAURI STARS
 CHEMICAL ABUNDANCES OF WEAK T TAURI STARS Gustavo de Araujo Rojas Universidade de São Paulo Instituto de Astronomia, Geofísica e Ciências Atmosféricas rojas@astro.iag.usp.br Jane Gregorio-Hetem Universidade
CHEMICAL ABUNDANCES OF WEAK T TAURI STARS Gustavo de Araujo Rojas Universidade de São Paulo Instituto de Astronomia, Geofísica e Ciências Atmosféricas rojas@astro.iag.usp.br Jane Gregorio-Hetem Universidade
Surface abundances of light elements for a large sample of early B-type stars IV. The magnesium abundance in 52 stars a test of metallicity
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 358, 193 201 (2005) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2005.08795.x Surface abundances of light elements for a large sample of early B-type stars IV. The magnesium abundance in 52 stars
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 358, 193 201 (2005) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2005.08795.x Surface abundances of light elements for a large sample of early B-type stars IV. The magnesium abundance in 52 stars
Differential abundances in the HAT-P-4 binary system
 Differential abundances in the HAT-P-4 binary system Carlos Saffe 1,4, Emiliano Jofré 2,4, Eder Martioli 3 Matías Flores 1,4, Romina Petrucci 2,4 & Marcelo Jaque 1,4 (1) Instituto de Ciencias Astronómicas,
Differential abundances in the HAT-P-4 binary system Carlos Saffe 1,4, Emiliano Jofré 2,4, Eder Martioli 3 Matías Flores 1,4, Romina Petrucci 2,4 & Marcelo Jaque 1,4 (1) Instituto de Ciencias Astronómicas,
The Composition of the Old, Metal-Rich Open Cluster, NGC 6791
 The Composition of the Old, Metal-Rich Open Cluster, NGC 6791 Liz Jensen --- Smith College, REU at IFA, University of Hawaii 2006 Mentor: Ann M. Boesgaard --- Institute for Astronomy, University of Hawaii
The Composition of the Old, Metal-Rich Open Cluster, NGC 6791 Liz Jensen --- Smith College, REU at IFA, University of Hawaii 2006 Mentor: Ann M. Boesgaard --- Institute for Astronomy, University of Hawaii
The Hertzsprung Russell Diagram. The Main Sequence
 The Hertzsprung Russell Diagram H R diagram plots stellar luminosity against surface temperature Luminosity ranges 10-4 10 4 L. Temperature ranges by a factor of 10 increases to the left spectral sequence
The Hertzsprung Russell Diagram H R diagram plots stellar luminosity against surface temperature Luminosity ranges 10-4 10 4 L. Temperature ranges by a factor of 10 increases to the left spectral sequence
Young Solar-like Systems
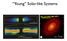 Young Solar-like Systems FIG.2. Panels(a),(b),and(c)show 2.9,1.3,and 0.87 mm ALMA continuum images of other panels, as well as an inset with an enlarged view of the inner 300 mas centered on the (f) show
Young Solar-like Systems FIG.2. Panels(a),(b),and(c)show 2.9,1.3,and 0.87 mm ALMA continuum images of other panels, as well as an inset with an enlarged view of the inner 300 mas centered on the (f) show
Chapter 10 Measuring the Stars
 Chapter 10 Measuring the Stars Some of the topics included in this chapter Stellar parallax Distance to the stars Stellar motion Luminosity and apparent brightness of stars The magnitude scale Stellar
Chapter 10 Measuring the Stars Some of the topics included in this chapter Stellar parallax Distance to the stars Stellar motion Luminosity and apparent brightness of stars The magnitude scale Stellar
Chemical abundances in solar analogs Ricardo López Valdivia
 Chemical abundances in solar analogs Ricardo López Valdivia Dr. Miguel Chávez Dr. Emanuele Bertone Objetive Make a detailed analysis of chemical abundances in G0-G3 main sequence stars (solar analogs)
Chemical abundances in solar analogs Ricardo López Valdivia Dr. Miguel Chávez Dr. Emanuele Bertone Objetive Make a detailed analysis of chemical abundances in G0-G3 main sequence stars (solar analogs)
PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF PLANET-HOSTING STARS AND OPTIMIZATION OF THE EXTRASOLAR PLANET SEARCHES
 Proc. VI Serbian-Bulgarian Astronomical Conference, Belgrade 7-11 May 2008, Eds. M. S. Dimitrijevi, M. Tsvetkov, L.. Popovi, V. Golev Publ. Astr. Soc. "Rudjer Boškovi ", No. 9, 2009, 381-386 PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Proc. VI Serbian-Bulgarian Astronomical Conference, Belgrade 7-11 May 2008, Eds. M. S. Dimitrijevi, M. Tsvetkov, L.. Popovi, V. Golev Publ. Astr. Soc. "Rudjer Boškovi ", No. 9, 2009, 381-386 PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS
TrES Exoplanets and False Positives: Finding the Needle in the Haystack
 Transiting Extrasolar Planets Workshop ASP Conference Series, Vol. 366, 2007 C. Afonso, D. Weldrake and Th. Henning TrES Exoplanets and False Positives: Finding the Needle in the Haystack F. T. O Donovan
Transiting Extrasolar Planets Workshop ASP Conference Series, Vol. 366, 2007 C. Afonso, D. Weldrake and Th. Henning TrES Exoplanets and False Positives: Finding the Needle in the Haystack F. T. O Donovan
II. Results from Transiting Planets. 1. Global Properties 2. The Rossiter-McClaughlin Effect
 II. Results from Transiting Planets 1. Global Properties 2. The Rossiter-McClaughlin Effect Planet Radius Most transiting planets tend to be inflated. Approximately 68% of all transiting planets have radii
II. Results from Transiting Planets 1. Global Properties 2. The Rossiter-McClaughlin Effect Planet Radius Most transiting planets tend to be inflated. Approximately 68% of all transiting planets have radii
Exoplanets Atmospheres. Characterization of planetary atmospheres. Photometry of planetary atmospheres from direct imaging
 Photometry of planetary atmospheres from direct imaging Exoplanets Atmospheres Planets and Astrobiology (2016-2017) G. Vladilo Example: planetary system detected with direct imaging HR 8799 b, c, d (Marois
Photometry of planetary atmospheres from direct imaging Exoplanets Atmospheres Planets and Astrobiology (2016-2017) G. Vladilo Example: planetary system detected with direct imaging HR 8799 b, c, d (Marois
SISD Training Lectures in Spectroscopy
 SISD Training Lectures in Spectroscopy Anatomy of a Spectrum Visual Spectrum of the Sun Blue Spectrum of the Sun Morphological Features in Spectra λ 2 Line Flux = Fλ dλ λ1 (Units: erg s -1 cm -2 ) Continuum
SISD Training Lectures in Spectroscopy Anatomy of a Spectrum Visual Spectrum of the Sun Blue Spectrum of the Sun Morphological Features in Spectra λ 2 Line Flux = Fλ dλ λ1 (Units: erg s -1 cm -2 ) Continuum
Measuring Radial & Tangential Velocity. Radial velocity measurement. Tangential velocity measurement. Measure the star s Doppler shift
 17. The Nature of the Stars Parallax reveals stellar distance Stellar distance reveals luminosity Luminosity reveals total energy production The stellar magnitude scale Surface temperature determines stellar
17. The Nature of the Stars Parallax reveals stellar distance Stellar distance reveals luminosity Luminosity reveals total energy production The stellar magnitude scale Surface temperature determines stellar
SpectroWeb: An Interactive Graphical Database of Digital Stellar Spectral Atlases
 : An Interactive Graphical Database of Digital Stellar Spectral Atlases arxiv:0707.3722v1 [astro-ph] 25 Jul 2007. A. LOBEL 1 1 Royal Observatory of Belgium, Ringlaan 3, Brussels, B-1180, Belgium ABSTRACT
: An Interactive Graphical Database of Digital Stellar Spectral Atlases arxiv:0707.3722v1 [astro-ph] 25 Jul 2007. A. LOBEL 1 1 Royal Observatory of Belgium, Ringlaan 3, Brussels, B-1180, Belgium ABSTRACT
Extrasolar Planets. Methods of detection Characterization Theoretical ideas Future prospects
 Extrasolar Planets Methods of detection Characterization Theoretical ideas Future prospects Methods of detection Methods of detection Methods of detection Pulsar timing Planetary motion around pulsar
Extrasolar Planets Methods of detection Characterization Theoretical ideas Future prospects Methods of detection Methods of detection Methods of detection Pulsar timing Planetary motion around pulsar
International Olympiad on Astronomy and Astrophysics (IOAA)
 Syllabus of International Olympiad on Astronomy and Astrophysics (IOAA) General Notes 1. Extensive contents in basic astronomical concepts are required in theoretical and practical problems. 2. Basic concepts
Syllabus of International Olympiad on Astronomy and Astrophysics (IOAA) General Notes 1. Extensive contents in basic astronomical concepts are required in theoretical and practical problems. 2. Basic concepts
Determination of [α/fe] and its Application to SEGUE F/G Stars. Young Sun Lee
![Determination of [α/fe] and its Application to SEGUE F/G Stars. Young Sun Lee Determination of [α/fe] and its Application to SEGUE F/G Stars. Young Sun Lee](/thumbs/83/87302303.jpg) Determination of [α/fe] and its Application to SEGUE F/G Stars Young Sun Lee Research Group Meeting on June 16, 2010 Outline Introduction Why [α/fe]? Determination of [α/fe] Validation of estimate of [α/fe]
Determination of [α/fe] and its Application to SEGUE F/G Stars Young Sun Lee Research Group Meeting on June 16, 2010 Outline Introduction Why [α/fe]? Determination of [α/fe] Validation of estimate of [α/fe]
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 22 Oct 2007
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 22 Oct 2007 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 22 Oct 2007](/thumbs/94/120774244.jpg) arxiv:0710.4134v1 [astro-ph] 22 Oct 2007 Radial velocities of giant stars: an investigation of line profile variations. S Hekker 1, I A G Snellen 1, C Aerts 2,3, A Quirrenbach 4, S Reffert 4 and D S Mitchell
arxiv:0710.4134v1 [astro-ph] 22 Oct 2007 Radial velocities of giant stars: an investigation of line profile variations. S Hekker 1, I A G Snellen 1, C Aerts 2,3, A Quirrenbach 4, S Reffert 4 and D S Mitchell
Introduction The Role of Astronomy p. 3 Astronomical Objects of Research p. 4 The Scale of the Universe p. 7 Spherical Astronomy Spherical
 Introduction The Role of Astronomy p. 3 Astronomical Objects of Research p. 4 The Scale of the Universe p. 7 Spherical Astronomy Spherical Trigonometry p. 9 The Earth p. 12 The Celestial Sphere p. 14 The
Introduction The Role of Astronomy p. 3 Astronomical Objects of Research p. 4 The Scale of the Universe p. 7 Spherical Astronomy Spherical Trigonometry p. 9 The Earth p. 12 The Celestial Sphere p. 14 The
Origin of Li Anomaly in K giants. Planet engulfment scenario plays role? Bharat Kumar Yerra. Lunch Talk, 22nd October 2014
 : Planet engulfment scenario plays role? Stellar Abundances & Galactic Evolution Group NAOC, Beijing Lunch Talk, 22nd October 2014 Collaborators: Dr. B. Eswar Reddy (IIAP, Bangalore, India) Dr. David L.
: Planet engulfment scenario plays role? Stellar Abundances & Galactic Evolution Group NAOC, Beijing Lunch Talk, 22nd October 2014 Collaborators: Dr. B. Eswar Reddy (IIAP, Bangalore, India) Dr. David L.
Astronomy 1143 Final Exam Review Answers
 Astronomy 1143 Final Exam Review Answers Prof. Pradhan April 24, 2015 What is Science? 1. Explain the difference between astronomy and astrology. 2. What number is the metric system based around? What
Astronomy 1143 Final Exam Review Answers Prof. Pradhan April 24, 2015 What is Science? 1. Explain the difference between astronomy and astrology. 2. What number is the metric system based around? What
The Hertzprung-Russell Diagram. The Hertzprung-Russell Diagram. Question
 Key Concepts: Lecture 21: Measuring the properties of stars (cont.) The Hertzsprung-Russell (HR) Diagram (L versus T) The Hertzprung-Russell Diagram The Stefan-Boltzmann Law: flux emitted by a black body
Key Concepts: Lecture 21: Measuring the properties of stars (cont.) The Hertzsprung-Russell (HR) Diagram (L versus T) The Hertzprung-Russell Diagram The Stefan-Boltzmann Law: flux emitted by a black body
Chapter 8: The Family of Stars
 Chapter 8: The Family of Stars Motivation We already know how to determine a star s surface temperature chemical composition surface density In this chapter, we will learn how we can determine its distance
Chapter 8: The Family of Stars Motivation We already know how to determine a star s surface temperature chemical composition surface density In this chapter, we will learn how we can determine its distance
Lecture 20: Planet formation II. Clues from Exoplanets
 Lecture 20: Planet formation II. Clues from Exoplanets 1 Outline Definition of a planet Properties of exoplanets Formation models for exoplanets gravitational instability model core accretion scenario
Lecture 20: Planet formation II. Clues from Exoplanets 1 Outline Definition of a planet Properties of exoplanets Formation models for exoplanets gravitational instability model core accretion scenario
Components of Galaxies Stars What Properties of Stars are Important for Understanding Galaxies?
 Components of Galaxies Stars What Properties of Stars are Important for Understanding Galaxies? Temperature Determines the λ range over which the radiation is emitted Chemical Composition metallicities
Components of Galaxies Stars What Properties of Stars are Important for Understanding Galaxies? Temperature Determines the λ range over which the radiation is emitted Chemical Composition metallicities
ASTRONOMY CURRICULUM Unit 1: Introduction to Astronomy
 Chariho Regional School District - Science Curriculum September, 2016 ASTRONOMY CURRICULUM Unit 1: Introduction to Astronomy OVERVIEW Summary Students will be introduced to the overarching concept of astronomy.
Chariho Regional School District - Science Curriculum September, 2016 ASTRONOMY CURRICULUM Unit 1: Introduction to Astronomy OVERVIEW Summary Students will be introduced to the overarching concept of astronomy.
Introduction to nucleosynthesis in asymptotic giant branch stars
 Introduction to nucleosynthesis in asymptotic giant branch stars Amanda Karakas 1 and John Lattanzio 2 1) Research School of Astronomy & Astrophysics Mt. Stromlo Observatory 2) School of Mathematical Sciences,
Introduction to nucleosynthesis in asymptotic giant branch stars Amanda Karakas 1 and John Lattanzio 2 1) Research School of Astronomy & Astrophysics Mt. Stromlo Observatory 2) School of Mathematical Sciences,
Measuring Radial Velocities of Low Mass Eclipsing Binaries
 Measuring Radial Velocities of Low Mass Eclipsing Binaries Rebecca Rattray, Leslie Hebb, Keivan G. Stassun College of Arts and Science, Vanderbilt University Due to the complex nature of the spectra of
Measuring Radial Velocities of Low Mass Eclipsing Binaries Rebecca Rattray, Leslie Hebb, Keivan G. Stassun College of Arts and Science, Vanderbilt University Due to the complex nature of the spectra of
Tracking Advanced Planetary Systems with HARPS-N (TAPAS). I. A multiple planetary system around the red giant star TYC
 Tracking Advanced Planetary Systems with HARPS-N (TAPAS). I. A multiple planetary system around the red giant star TYC 1422-614-1. A. Niedzielski 1, E. Villaver 2, A. Wolszczan 3,4, M. Adamów 1, K. Kowalik
Tracking Advanced Planetary Systems with HARPS-N (TAPAS). I. A multiple planetary system around the red giant star TYC 1422-614-1. A. Niedzielski 1, E. Villaver 2, A. Wolszczan 3,4, M. Adamów 1, K. Kowalik
Fusion in first few minutes after Big Bang form lightest elements
 Fusion in first few minutes after Big Bang form lightest elements Stars build the rest of the elements up to Iron (Fe) through fusion The rest of the elements beyond Iron (Fe) are produced in the dying
Fusion in first few minutes after Big Bang form lightest elements Stars build the rest of the elements up to Iron (Fe) through fusion The rest of the elements beyond Iron (Fe) are produced in the dying
HD Transits HST/STIS First Transiting Exo-Planet. Exoplanet Discovery Methods. Paper Due Tue, Feb 23. (4) Transits. Transits.
 Paper Due Tue, Feb 23 Exoplanet Discovery Methods (1) Direct imaging (2) Astrometry position (3) Radial velocity velocity Seager & Mallen-Ornelas 2003 ApJ 585, 1038. "A Unique Solution of Planet and Star
Paper Due Tue, Feb 23 Exoplanet Discovery Methods (1) Direct imaging (2) Astrometry position (3) Radial velocity velocity Seager & Mallen-Ornelas 2003 ApJ 585, 1038. "A Unique Solution of Planet and Star
From the first stars to planets
 High precision stellar spectroscopy: From the first stars to planets Jorge Meléndez Departamento de Astronomia, IAG, Universidade de São Paulo My group: SAMPA Stellar Atmospheres, Planets & Abundances
High precision stellar spectroscopy: From the first stars to planets Jorge Meléndez Departamento de Astronomia, IAG, Universidade de São Paulo My group: SAMPA Stellar Atmospheres, Planets & Abundances
A list of data for the broadening of metallic lines by neutral hydrogen collisions
 ASTRONOMY & ASTROPHYSICS MARCH II 2000, PAGE 467 SUPPLEMENT SERIES Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 142, 467 473 (2000) A list of data for the broadening of metallic lines by neutral hydrogen collisions
ASTRONOMY & ASTROPHYSICS MARCH II 2000, PAGE 467 SUPPLEMENT SERIES Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 142, 467 473 (2000) A list of data for the broadening of metallic lines by neutral hydrogen collisions
What can we learn by evolving the host star? Eva Villaver Universidad Autónoma de Madrid
 What can we learn by evolving the host star? Eva Villaver Universidad Autónoma de Madrid WD POLUTION PLANET STIRRING A LEFT OVER DEBRIS DISK ROTATION 1-3 % FAST RGB ROTATORS PLANET STAR CHEMISTRY LITHIUM
What can we learn by evolving the host star? Eva Villaver Universidad Autónoma de Madrid WD POLUTION PLANET STIRRING A LEFT OVER DEBRIS DISK ROTATION 1-3 % FAST RGB ROTATORS PLANET STAR CHEMISTRY LITHIUM
Actuality of Exoplanets Search. François Bouchy OHP - IAP
 Actuality of Exoplanets Search François Bouchy OHP - IAP How detect extrasolar planets? Two main difficulties : 1 A tiny angular separation 0.75 arcsec Sun Jupiter at 4 light years 4 Sun Jupiter at 100
Actuality of Exoplanets Search François Bouchy OHP - IAP How detect extrasolar planets? Two main difficulties : 1 A tiny angular separation 0.75 arcsec Sun Jupiter at 4 light years 4 Sun Jupiter at 100
MARVELS: Revealing the Formation and Dynamical Evolution of Giant Planet Systems
 MARVELS: Revealing the Formation and Dynamical Evolution of Giant Planet Systems White Paper for the Astro2010 PSF Science Frontier Panel Submitted by the SDSS-III Collaboration Contact Information: Jian
MARVELS: Revealing the Formation and Dynamical Evolution of Giant Planet Systems White Paper for the Astro2010 PSF Science Frontier Panel Submitted by the SDSS-III Collaboration Contact Information: Jian
Substellar-mass companions to the K-dwarf BD and the K-giants HD and BD
 Substellar-mass companions to the K-dwarf BD +14 4559 and the K-giants HD 240210 and BD +20 2457 A. Niedzielski 1, G. Nowak 1, M. Adamów 1, A. Wolszczan 2,3 ABSTRACT We present the discovery of substellar-mass
Substellar-mass companions to the K-dwarf BD +14 4559 and the K-giants HD 240210 and BD +20 2457 A. Niedzielski 1, G. Nowak 1, M. Adamów 1, A. Wolszczan 2,3 ABSTRACT We present the discovery of substellar-mass
Data from: The Extrasolar Planet Encyclopaedia.
 Data from: The Extrasolar Planet Encyclopaedia http://exoplanet.eu/ 2009->10 Status of Exoplanet Searches Direct Detection: 5->9 planets detected Sensitive to large planets in large orbits around faint
Data from: The Extrasolar Planet Encyclopaedia http://exoplanet.eu/ 2009->10 Status of Exoplanet Searches Direct Detection: 5->9 planets detected Sensitive to large planets in large orbits around faint
Detecting Earth-Sized Planets with Laser Frequency Combs
 Detecting Earth-Sized Planets with Laser Frequency Combs Hayley Finley Department of Physics, Drexel University, 3141 Chestnut Street, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania 19104 Abstract Detection of Earth-mass
Detecting Earth-Sized Planets with Laser Frequency Combs Hayley Finley Department of Physics, Drexel University, 3141 Chestnut Street, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania 19104 Abstract Detection of Earth-mass
Lecture 12: Extrasolar planets. Astronomy 111 Monday October 9, 2017
 Lecture 12: Extrasolar planets Astronomy 111 Monday October 9, 2017 Reminders Star party Thursday night! Homework #6 due Monday The search for extrasolar planets The nature of life on earth and the quest
Lecture 12: Extrasolar planets Astronomy 111 Monday October 9, 2017 Reminders Star party Thursday night! Homework #6 due Monday The search for extrasolar planets The nature of life on earth and the quest
Stellar Astronomy Sample Questions for Exam 3
 Stellar Astronomy Sample Questions for Exam 3 Chapter 7 1. A protostar is formed by a) the rapid expansion of gas from an exploding star. b) the gravitational collapse of a rotating interstellar cloud.
Stellar Astronomy Sample Questions for Exam 3 Chapter 7 1. A protostar is formed by a) the rapid expansion of gas from an exploding star. b) the gravitational collapse of a rotating interstellar cloud.
Oxygen in red giants from near-infrared OH lines: 3D effects and first results from. Puerto de la Cruz, May 14, 2012! Carlos Allende Prieto!
 Oxygen in red giants from near-infrared OH lines: 3D effects and first results from Puerto de la Cruz, May 14, 2012! Carlos Allende Prieto! Overview! 1. APOGEE: status and prospects! 2. A first look at
Oxygen in red giants from near-infrared OH lines: 3D effects and first results from Puerto de la Cruz, May 14, 2012! Carlos Allende Prieto! Overview! 1. APOGEE: status and prospects! 2. A first look at
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 The View from Earth Lesson 2 The Sun and Other Stars Lesson 3 Evolution of Stars Lesson 4 Galaxies and the Universe
 Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 The View from Earth Lesson 2 The Sun and Other Stars Lesson 3 Evolution of Stars Lesson 4 Galaxies and the Universe Chapter Wrap-Up What makes up the universe and how does
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 The View from Earth Lesson 2 The Sun and Other Stars Lesson 3 Evolution of Stars Lesson 4 Galaxies and the Universe Chapter Wrap-Up What makes up the universe and how does
OGLE-TR-56. Guillermo Torres, Maciej Konacki, Dimitar D. Sasselov and Saurabh Jha INTRODUCTION
 OGLE-TR-56 Guillermo Torres, Maciej Konacki, Dimitar D. Sasselov and Saurabh Jha Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Caltech, Department of Geological and Planetary Sciences University of California
OGLE-TR-56 Guillermo Torres, Maciej Konacki, Dimitar D. Sasselov and Saurabh Jha Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Caltech, Department of Geological and Planetary Sciences University of California
RV- method: disturbing oscilla8ons Example: F- star Procyon
 Star spots RV- method: disturbing oscilla8ons Example: F- star Procyon In- class ac8vity (1) 1) You are working with the HARPS instrument and you want to unambiguously detect Jupiter-twins around nearby
Star spots RV- method: disturbing oscilla8ons Example: F- star Procyon In- class ac8vity (1) 1) You are working with the HARPS instrument and you want to unambiguously detect Jupiter-twins around nearby
Astronomical Study: A Multi-Perspective Approach
 Astronomical Study: A Multi-Perspective Approach Overview of Stars Motion Distances Physical Properties Spectral Properties Magnitudes Luminosity class Spectral trends Binary stars and getting masses Stellar
Astronomical Study: A Multi-Perspective Approach Overview of Stars Motion Distances Physical Properties Spectral Properties Magnitudes Luminosity class Spectral trends Binary stars and getting masses Stellar
Lecture 16 The Measuring the Stars 3/26/2018
 Lecture 16 The Measuring the Stars 3/26/2018 Test 2 Results D C B A Questions that I thought were unfair: 13, 18, 25, 76, 77, 80 Curved from 85 to 79 Measuring stars How far away are they? How bright are
Lecture 16 The Measuring the Stars 3/26/2018 Test 2 Results D C B A Questions that I thought were unfair: 13, 18, 25, 76, 77, 80 Curved from 85 to 79 Measuring stars How far away are they? How bright are
2019 Astronomy Team Selection Test
 2019 Astronomy Team Selection Test Acton-Boxborough Regional High School Written by Antonio Frigo Do not flip over this page until instructed. Instructions You will have 45 minutes to complete this exam.
2019 Astronomy Team Selection Test Acton-Boxborough Regional High School Written by Antonio Frigo Do not flip over this page until instructed. Instructions You will have 45 minutes to complete this exam.
Fundamental Astronomy
 H. Karttunen P. Kroger H. Oja M.Poutanen K.J. Donner (Eds.) Fundamental Astronomy Fifth Edition With 449 Illustrations Including 34 Colour Plates and 75 Exercises with Solutions < J Springer VII 1. Introduction
H. Karttunen P. Kroger H. Oja M.Poutanen K.J. Donner (Eds.) Fundamental Astronomy Fifth Edition With 449 Illustrations Including 34 Colour Plates and 75 Exercises with Solutions < J Springer VII 1. Introduction
JINA Observations, Now and in the Near Future
 JINA Observations, Now and in the Near Future Timothy C. Beers Department of Physics & Astronomy Michigan State University & JINA: Joint Institute for Nuclear Astrophysics Examples SDSS-I, II, and III
JINA Observations, Now and in the Near Future Timothy C. Beers Department of Physics & Astronomy Michigan State University & JINA: Joint Institute for Nuclear Astrophysics Examples SDSS-I, II, and III
A Survey of Stellar Families Multiplicity of Solar-type Stars
 A Survey of Stellar Families Multiplicity of Solar-type Stars Advisor: Dr. Hal McAlister GSU Committee members: Dr. Doug Gies GSU Deepak Raghavan Ph.D. Dissertation Talk March 17, 2009 Dr. Todd Henry GSU
A Survey of Stellar Families Multiplicity of Solar-type Stars Advisor: Dr. Hal McAlister GSU Committee members: Dr. Doug Gies GSU Deepak Raghavan Ph.D. Dissertation Talk March 17, 2009 Dr. Todd Henry GSU
Other planetary systems
 Exoplanets are faint! Other planetary systems Planets are seen only by reflected light at optical wavelengths At the distance of another star the faint light of a planet is lost in the glare of the star
Exoplanets are faint! Other planetary systems Planets are seen only by reflected light at optical wavelengths At the distance of another star the faint light of a planet is lost in the glare of the star
Planet-like Companion to a Brown Dwarf
 National Aeronautics and Space Administration Planet-like Companion to a Brown Dwarf Taken from: Hubble 2010: Science Year in Review Produced by NASA Goddard Space Flight Center and the Space Telescope
National Aeronautics and Space Administration Planet-like Companion to a Brown Dwarf Taken from: Hubble 2010: Science Year in Review Produced by NASA Goddard Space Flight Center and the Space Telescope
High-resolution Spectroscopy of CARMENCITA objects. Patrick Schöfer
 High-resolution Spectroscopy of CARMENCITA objects Patrick Schöfer 2015-10-22 Overview Motivation Aims of the analysis and data sample Prelude I: Data reduction Prelude II: Target identification Analysis
High-resolution Spectroscopy of CARMENCITA objects Patrick Schöfer 2015-10-22 Overview Motivation Aims of the analysis and data sample Prelude I: Data reduction Prelude II: Target identification Analysis
HR Diagram, Star Clusters, and Stellar Evolution
 Ay 1 Lecture 9 M7 ESO HR Diagram, Star Clusters, and Stellar Evolution 9.1 The HR Diagram Stellar Spectral Types Temperature L T Y The Hertzsprung-Russel (HR) Diagram It is a plot of stellar luminosity
Ay 1 Lecture 9 M7 ESO HR Diagram, Star Clusters, and Stellar Evolution 9.1 The HR Diagram Stellar Spectral Types Temperature L T Y The Hertzsprung-Russel (HR) Diagram It is a plot of stellar luminosity
Habitability Outside the Solar System. A discussion of Bennett & Shostak Chapter 11 HNRS 228 Dr. H. Geller
 Habitability Outside the Solar System A discussion of Bennett & Shostak Chapter 11 HNRS 228 Dr. H. Geller 1 Chapter Overview Distant Suns (11.1) Life cycle of stars and their habitability zones Extrasolar
Habitability Outside the Solar System A discussion of Bennett & Shostak Chapter 11 HNRS 228 Dr. H. Geller 1 Chapter Overview Distant Suns (11.1) Life cycle of stars and their habitability zones Extrasolar
Searching For Planets Like Earth around stars like the Sun
 Searching For Planets Like Earth around stars like the Sun Derek Buzasi FGCU Roadmap Who am I and how did I get here? Motivation for my research What makes a star like the Sun? How do we find planets?
Searching For Planets Like Earth around stars like the Sun Derek Buzasi FGCU Roadmap Who am I and how did I get here? Motivation for my research What makes a star like the Sun? How do we find planets?
Combing the Brown Dwarf Desert with APOGEE
 Combing the Brown Dwarf Desert with APOGEE NICHOLAS TROUP UNIVERSITY OF VIRGINIA SESAPS 2016 Brown Dwarfs (BDs) Missing link between low mass stars and gas giant planets. Lack the mass to ignite Hydrogen
Combing the Brown Dwarf Desert with APOGEE NICHOLAS TROUP UNIVERSITY OF VIRGINIA SESAPS 2016 Brown Dwarfs (BDs) Missing link between low mass stars and gas giant planets. Lack the mass to ignite Hydrogen
Outline. c.f. Zhao et al. 2006, ChJA&A, 6, 265. Stellar Abundance and Galactic Chemical Evolution through LAMOST Spectroscopic Survey
 KIAA-CambridgeJoint Workshop on Near-Field Cosmology and Galactic Archeology ZHAO Gang National Astronomical Observatories, Chinese Academy of Sciences Dec 1-5, 2008 Beijing Outline LAMOST stellar spectroscopic
KIAA-CambridgeJoint Workshop on Near-Field Cosmology and Galactic Archeology ZHAO Gang National Astronomical Observatories, Chinese Academy of Sciences Dec 1-5, 2008 Beijing Outline LAMOST stellar spectroscopic
Signatures of Peculiar Supernova Nucleosynthesis in Extremely α-enhanced Metal-poor Stars
 Signatures of Peculiar Supernova Nucleosynthesis in Extremely α-enhanced Metal-poor Stars Hye-Eun Jang 1, Sung-Chul Yoon 1, Young Sun Lee 2, Ho-Gyu Lee 3, Wonseok Kang 4 and Sang-Gak Lee 1 1 Seoul National
Signatures of Peculiar Supernova Nucleosynthesis in Extremely α-enhanced Metal-poor Stars Hye-Eun Jang 1, Sung-Chul Yoon 1, Young Sun Lee 2, Ho-Gyu Lee 3, Wonseok Kang 4 and Sang-Gak Lee 1 1 Seoul National
Measuring Radial & Tangential Velocity. Radial velocity measurement. Tangential velocity measurement. Measure the star s Doppler shift
 17. The Nature of the Stars Parallax reveals stellar distance Stellar distance reveals luminosity Luminosity reveals total energy production The stellar magnitude scale Surface temperature determines stellar
17. The Nature of the Stars Parallax reveals stellar distance Stellar distance reveals luminosity Luminosity reveals total energy production The stellar magnitude scale Surface temperature determines stellar
The stability of planets in the Alpha Centauri system
 The stability of planets in the Alpha Centauri system Paul A. Wiegert 1, Matt Holman 2 1 Department of Astronomy, University of Toronto, Toronto, Canada 2 Canadian Institute for Theoretical Astrophysics,
The stability of planets in the Alpha Centauri system Paul A. Wiegert 1, Matt Holman 2 1 Department of Astronomy, University of Toronto, Toronto, Canada 2 Canadian Institute for Theoretical Astrophysics,
Neutron-capture element abundances in the globular clusters: 47 Tuc, NGC 6388, NGC 362 & ω Cen
 Neutron-capture element abundances in the globular clusters: 47 Tuc, NGC 6388, NGC 362 & ω Cen C. C. Worley Université de Nice Sophia Antipolis, CNRS (UMR 6202), Observatoire de la Côte d Azur, Cassiopée,
Neutron-capture element abundances in the globular clusters: 47 Tuc, NGC 6388, NGC 362 & ω Cen C. C. Worley Université de Nice Sophia Antipolis, CNRS (UMR 6202), Observatoire de la Côte d Azur, Cassiopée,
Project RISARD. - the story so far. Marcin P. Gawroński (Toruń Centre for Astronomy)
 Project RISARD - the story so far credit : wiki Marcin P. Gawroński (Toruń Centre for Astronomy) in collaboration with K. Goźdzewski, K. Katarzyński, G. Rycyk (TCfA) Overview RISARD motivation and current
Project RISARD - the story so far credit : wiki Marcin P. Gawroński (Toruń Centre for Astronomy) in collaboration with K. Goźdzewski, K. Katarzyński, G. Rycyk (TCfA) Overview RISARD motivation and current
PENNSYLVANIA SCIENCE OLYMPIAD STATE FINALS 2012 ASTRONOMY C DIVISION EXAM APRIL 27, 2012
 PENNSYLVANIA SCIENCE OLYMPIAD STATE FINALS 2012 ASTRONOMY C DIVISION EXAM APRIL 27, 2012 TEAM NUMBER SCHOOL NAME INSTRUCTIONS: 1. Turn in all exam materials at the end of this event. Missing exam materials
PENNSYLVANIA SCIENCE OLYMPIAD STATE FINALS 2012 ASTRONOMY C DIVISION EXAM APRIL 27, 2012 TEAM NUMBER SCHOOL NAME INSTRUCTIONS: 1. Turn in all exam materials at the end of this event. Missing exam materials
Parallax: Measuring the distance to Stars
 Measuring the Stars Parallax: Measuring the distance to Stars Use Earth s orbit as baseline Parallactic angle = 1/2 angular shift Distance from the Sun required for a star to have a parallactic angle of
Measuring the Stars Parallax: Measuring the distance to Stars Use Earth s orbit as baseline Parallactic angle = 1/2 angular shift Distance from the Sun required for a star to have a parallactic angle of
