CHANDRA X-RAY OBSERVATORY
|
|
|
- Iris Lane
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CHANDRA X-RAY OBSERVATORY The Chandra X-ray Observatory is the third in NASA's family of Great Observatories that includes the Hubble Space Telescope and the Compton Gamma Ray Observatory. NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center manages the Chandra program. TRW is the prime contractor for the spacecraft. Key subcontractors include Ball Aerospace & Technologies, Inc., Eastman Kodak Company, and Raytheon Optical Systems, Inc. The scientific instruments were built by teams from MIT, Pennsylvania State University, the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory, the Laboratory for Space Research in the Netherlands, and the Max Planck Institute in Germany. The Smithsonian's Chandra X-ray Center controls science and flight operations from Cambridge, MA. XTE J Press Kit Contents: I. NASA Press Release II. Press Guide to Science Contacts III. Fact Sheets & Biographies A. Fact Sheet 1. The Chandra X-Ray Observatory B. Biographies 1. John A. Tomsick 2. Philip Kaaret 3. Kimberly Weaver 4. Neil de Grasse Tyson IV. Still Images A. Collage of Chandra's Observations of XTE J B. Illustration of X-ray Binary System C. Close-up Image of Western Jet in XTE J D. Chandra Image of X-ray Jet PKS
2 PRESS GUIDE TO SCIENCE CONTACTS CXC Contact Megan Watzke, Chandra X-Ray Center Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory, Cambridge, MA Phone: Fax: Science Contacts Dr. John A. Tomsick University of California at San Diego Phone: Dr. Philip Kaaret Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Phone: Dr. Neil degrasse Tyson Hayden Planetarium, American Museum of Natural History Phone: /13 Dr. Kimberly Weaver Goddard Space Flight Center Phone: Dr. Stephane Corbel University of Paris VII & French Atomic Energy Commission (Saclay) Phone: corbel@discovery.saclay.cea.fr NASA Contacts Dolores Beasley, Public Affairs Officer NASA Headquarters, Washington D.C. Phone: dolores.beasley@hq.nasa.gov Steve Roy, Media Relations Office Marshall Space Flight Center, Huntsville, AL Phone: steve.roy@msfc.nasa.gov
3 THE CHANDRA X-RAY OBSERVATORY The Chandra X-Ray Observatory, launched on July 23, 1999, has taken its place with the Hubble Space Telescope and Compton Gamma Ray Observatory in NASA's fleet of Great Observatories. As the world's premier X-ray observatory, Chandra gives astronomers a powerful new tool to investigate the hot regions of the universe where black holes, exploding stars, and colliding galaxies hold sway. With its combination of four pairs of ultra smooth, high-resolution mirrors and efficient X-ray detectors, Chandra makes images at least thirty times sharper than any previous X-ray telescope. The High Resolution Camera, and the Advanced CCD Imaging Spectrometer record images electronically, and two transmission gratings enable scientists to make precise measurements of the energies of incoming X rays. The Chandra X-Ray Observatory Center The Chandra program, managed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, is an example of NASA's initiative to streamline the operations of its space science missions. The Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory's Chandra X-Ray Center (CXC), under the direction of Dr.Harvey Tananbaum, is located at the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics in Cambridge, Massachusetts. The CXC is responsible for planning the science observations based on proposals from the scientific community, processing data received from the observatory, and providing technical and scientific support to the scientists who use Chandra. The Center operates the observatory from its Operations & Control facility located at One Hampshire Street in Cambridge, Massachusetts. The CXC is a collaboration of personnel from the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory, the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), and the Chandra prime contractor, TRW. The Operations & Control Center (OCC) is staffed by the CXC, with the Flight Operations Team provided by TRW. The OCC has a glass-walled area outside the main control room where visitors and press can watch the Flight Operations Team and mission specialists as they communicate with the observatory and carry out the space flight operations. Commands for executing the observation plan are transmitted from the OCC to one of three ground stations (in Spain, Australia, or California) that make up NASA's Deep Space Network (DSN). The DSN relays the commands to the orbiting spacecraft. The spacecraft carries out the commands and points the telescope to the specified targets, and moves the science instruments to their appropriate positions. During routine operations, science data and monitoring data are sent from the spacecraft to the OCC, via the DSN, approximately every eight hours. Scientists and engineers use monitoring data to assess Chandra's condition. If the health or safety of the observatory appears to be in danger, the operating mode and the observation plans are modified. Data from Chandra observations are processed at the Chandra Center. Observatory calibration data are made public as soon as possible. The scientific data belonging to guest observers and guaranteed time observers can be held by them for one year to allow time for analysis and publication of scientific results. The data are then placed in the public archive.
4 Dr. John A. Tomsick Scientist, University of California at San Diego John Tomsick is a Scientist at the Center for Astrophysics and Space Sciences at UC San Diego. Tomsick received a Bachelor s degree in Physics from UCSD in 1993 and a Ph.D. in Physics from Columbia University in He has been conducting research at UCSD since receiving his Ph.D. Tomsick specializes in X-ray and optical observations of black holes and neutron stars and is interested in using these objects to test physical theories in extreme environments. Dr. Philip Kaaret Astrophysicist, Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory Philip Kaaret is an Astrophysicist at the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory and a member of the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics. Kaaret received a B.S. in Physics in 1984 from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, and a Ph.D. in experimental particle physics from Princeton University in He was subsequently on the faculty of the Physics Department at Columbia University in New York City before coming to SAO in Kaaret s main interest is understanding the intense gravitational fields surrounding black holes and neutron stars made luminous by accreting gas from a companion star. He conducts observations at X-ray, optical, and radio wavelengths of objects in our Milky Way galaxy and in nearby galaxies such as the Andromeda galaxy and the starburst galaxy M82. His current work concerns the highly luminous X-ray sources in nearby galaxies which have been interpreted as being intermediate mass black holes, jet ejection from black holes, and the study of black hole populations to probe the star formation history of galaxies.
5 Dr. Kimberly Weaver Astronomer, Laboratory for High Energy Astrophysics, NASA s Goddard Space Flight Center Dr. Kimberly Weaver is an astronomer with the Laboratory for High Energy Astrophysics at NASA s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD. She received her Ph.D. in Astronomy from the University of Maryland at College Park, MD, specializing in X-ray studies of active galactic nuclei. She also holds a position as adjunct assistant professor in the Department of Physics and Astronomy at the Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore, MD. Weaver has authored over 50 papers in scientific journals and has worked with data from almost every X-ray astronomy satellite flown in the last 20 years. Dr. Neil de Grasse Tyson Astrophysicist & Director, Hayden Planetarium Neil de Grasse Tyson is the first occupant of the Frederick P. Rose Directorship of the Hayden Planetarium and he is a Visiting Research Scientist in astrophysics at Princeton University, where he also teaches. Tyson earned his BA in Physics from Harvard and his Ph.D. in Astrophysics from Columbia University. His professional research interests include star formation, exploding stars, dwarf galaxies, and the structure of our Milky Way. Tyson obtains his data from telescopes in California, New Mexico, Arizona, and in the Andes Mountains of Chile. In addition to dozens of professional publications, Tyson has written, and continues to write, for the public. And since January 1995, has become a monthly essayist for Natural History magazine under the title Universe. Tyson s recent books include a memoir The Sky is Not the Limit: Adventures of an Urban Astrophysicist; the companion book to the opening of the new Rose Center for Earth and Space One Universe: At Home in the Cosmos (coauthored with Charles Liu and Robert Irion); and a playful Q&A book on the universe for all ages titled Just Visiting This Planet.
6 COLLAGE OF CHANDRA'S OBSERVATIONS OF XTE J Image Caption This series of images of XTE J shows the black hole (center), the approaching eastern jet, and the receding western jet (right). In four years, the jets have moved about two light years from the black hole, and the eastern jet has faded dramatically. Credit: NASA/CXC
7 ILLUSTRATION OF X-RAY BINARY SYSTEM Image Caption An artist s conception shows a double star system with a normal Sun-like star in orbit around a black hole. As gaseous matter is pulled from the normal star, it forms a disk around the black hole and is heated to temperatures of millions of degrees. Intense electromagnetic forces in the disk can expel jets of high-energy particles. Credit: CXC/M.Weiss
8 CLOSE-UP IMAGE OF WESTERN JET IN XTE J Image Caption In this Chandra image of XTE J , taken in June 2002, red represents the central black hole and blue shows the western jet emanating from it. The cometary shape of the western jet indicates that it is being slowed down by interstellar gas. Credit: NASA/CXC
9 CHANDRA IMAGE OF X-RAY JET PKS Image Caption The Chandra X-ray image of the quasar PKS , a highly luminous source of X-rays and visible light about 10 billion light years from Earth, shows an enormous X-ray jet that extends at least a million light years from the quasar. The inset box compares the relative size of the Milky Way with the jet. Furthermore, the system XTE J is just a fraction of the size and is found in one of the spiral arms of the Milky Way galaxy. Credit: NASA/CXC/A. Siemiginowska (CfA)/J. Bechtold (U. Arizona)
CHANDRA X-RAY OBSERVATORY
 CHANDRA X-RAY OBSERVATORY The Chandra X-ray Observatory is the third in NASA's family of Great Observatories that includes the Hubble Space Telescope and the Compton Gamma Ray Observatory. NASA's Marshall
CHANDRA X-RAY OBSERVATORY The Chandra X-ray Observatory is the third in NASA's family of Great Observatories that includes the Hubble Space Telescope and the Compton Gamma Ray Observatory. NASA's Marshall
TELESCOPES POWERFUL. Beyond the Book. FOCUS Book
 FOCUS Book POWERFUL TELESCOPES Why do we need telescopes in order to observe stars that are very far away? Why do stars look bright in the sky while most galaxies, which have billions of stars, are too
FOCUS Book POWERFUL TELESCOPES Why do we need telescopes in order to observe stars that are very far away? Why do stars look bright in the sky while most galaxies, which have billions of stars, are too
Riccardo Giacconi Papers,
 , 1955-2002 Finding aid prepared by Smithsonian Institution Archives Smithsonian Institution Archives Washington, D.C. Contact us at osiaref@si.edu Table of Contents Collection Overview... 1 Administrative
, 1955-2002 Finding aid prepared by Smithsonian Institution Archives Smithsonian Institution Archives Washington, D.C. Contact us at osiaref@si.edu Table of Contents Collection Overview... 1 Administrative
Planet-like Companion to a Brown Dwarf
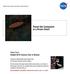 National Aeronautics and Space Administration Planet-like Companion to a Brown Dwarf Taken from: Hubble 2010: Science Year in Review Produced by NASA Goddard Space Flight Center and the Space Telescope
National Aeronautics and Space Administration Planet-like Companion to a Brown Dwarf Taken from: Hubble 2010: Science Year in Review Produced by NASA Goddard Space Flight Center and the Space Telescope
WILHELM. The X-Ray Universe. X-ray images of the Universe are strikingly different from the usual visible-light images. by WALLACE H.
 The X-Ray Universe by WALLACE H. TUCKER X-ray images of the Universe are strikingly different from the usual visible-light images. WILHELM ROENTGEN S INITIAL DISCOVERY of X-radiation in 1895 led immediately
The X-Ray Universe by WALLACE H. TUCKER X-ray images of the Universe are strikingly different from the usual visible-light images. WILHELM ROENTGEN S INITIAL DISCOVERY of X-radiation in 1895 led immediately
Produced by NASA Goddard Space Flight Center and the Space Telescope Science Institute.
 National Aeronautics and Space Administration Interacting Galaxies Taken from: Hubble 2008: Science Year in Review Produced by NASA Goddard Space Flight Center and the Space Telescope Science Institute.
National Aeronautics and Space Administration Interacting Galaxies Taken from: Hubble 2008: Science Year in Review Produced by NASA Goddard Space Flight Center and the Space Telescope Science Institute.
SMITHSONIAN ASTROPHYSICAL OBSERVATORY
 SMITHSONIAN ASTROPHYSICAL OBSERVATORY FEDERAL APPROPRIATIONS APPLICATION OF OPERATING RESOURCES GENERAL TRUST DONOR/SPONSOR DESIGNATED GOV T GRANTS & CONTRACTS FTE $000 FTE $000 FTE $000 FTE $000 FY 2002
SMITHSONIAN ASTROPHYSICAL OBSERVATORY FEDERAL APPROPRIATIONS APPLICATION OF OPERATING RESOURCES GENERAL TRUST DONOR/SPONSOR DESIGNATED GOV T GRANTS & CONTRACTS FTE $000 FTE $000 FTE $000 FTE $000 FY 2002
Figure 19.19: HST photo called Hubble Deep Field.
 19.3 Galaxies and the Universe Early civilizations thought that Earth was the center of the universe. In the sixteenth century, we became aware that Earth is a small planet orbiting a medium-sized star.
19.3 Galaxies and the Universe Early civilizations thought that Earth was the center of the universe. In the sixteenth century, we became aware that Earth is a small planet orbiting a medium-sized star.
Chapter 26. Objectives. Describe characteristics of the universe in terms of time, distance, and organization
 Objectives Describe characteristics of the universe in terms of time, distance, and organization Identify the visible and nonvisible parts of the electromagnetic spectrum Compare refracting telescopes
Objectives Describe characteristics of the universe in terms of time, distance, and organization Identify the visible and nonvisible parts of the electromagnetic spectrum Compare refracting telescopes
Part two of a year-long introduction to astrophysics:
 ASTR 3830 Astrophysics 2 - Galactic and Extragalactic Phil Armitage office: JILA tower A909 email: pja@jilau1.colorado.edu Spitzer Space telescope image of M81 Part two of a year-long introduction to astrophysics:
ASTR 3830 Astrophysics 2 - Galactic and Extragalactic Phil Armitage office: JILA tower A909 email: pja@jilau1.colorado.edu Spitzer Space telescope image of M81 Part two of a year-long introduction to astrophysics:
9.6. Other Components of the Universe. Star Clusters. Types of Galaxies
 Other Components of the Universe 9.6 The most common type of celestial object astronomers see in space is a star. Most stars appear to be gravitationally bound together into groups, and some groups are
Other Components of the Universe 9.6 The most common type of celestial object astronomers see in space is a star. Most stars appear to be gravitationally bound together into groups, and some groups are
Search for Baryonic Matter in Intergalactic Space
 National Aeronautics and Space Administration Search for Baryonic Matter in Intergalactic Space Taken from: Hubble 2008: Science Year in Review Produced by NASA Goddard Space Flight Center and the Space
National Aeronautics and Space Administration Search for Baryonic Matter in Intergalactic Space Taken from: Hubble 2008: Science Year in Review Produced by NASA Goddard Space Flight Center and the Space
Lecture Outlines. Chapter 24. Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outlines Chapter 24 Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 24 Galaxies Units of Chapter 24 24.1 Hubble s Galaxy Classification 24.2 The Distribution of Galaxies in Space 24.3 Hubble
Lecture Outlines Chapter 24 Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 24 Galaxies Units of Chapter 24 24.1 Hubble s Galaxy Classification 24.2 The Distribution of Galaxies in Space 24.3 Hubble
Star Formation and U/HLXs in the Cartwheel Galaxy Paper & Pencil Version
 Star Formation and U/HLXs in the Cartwheel Galaxy Paper & Pencil Version Introduction: The Cartwheel Galaxy Multi-Wavelength Composite The Cartwheel Galaxy is part of a group of galaxies ~five hundred
Star Formation and U/HLXs in the Cartwheel Galaxy Paper & Pencil Version Introduction: The Cartwheel Galaxy Multi-Wavelength Composite The Cartwheel Galaxy is part of a group of galaxies ~five hundred
Bright Quasar 3C 273 Thierry J-L Courvoisier. Encyclopedia of Astronomy & Astrophysics P. Murdin
 eaa.iop.org DOI: 10.1888/0333750888/2368 Bright Quasar 3C 273 Thierry J-L Courvoisier From Encyclopedia of Astronomy & Astrophysics P. Murdin IOP Publishing Ltd 2006 ISBN: 0333750888 Institute of Physics
eaa.iop.org DOI: 10.1888/0333750888/2368 Bright Quasar 3C 273 Thierry J-L Courvoisier From Encyclopedia of Astronomy & Astrophysics P. Murdin IOP Publishing Ltd 2006 ISBN: 0333750888 Institute of Physics
Dwarf Stars. Taken from: Hubble 2011: Science Year in Review. Produced by NASA Goddard Space Flight Center and the Space Telescope Science Institute.
 National Aeronautics and Space Administration Dwarf Stars National Aeronautics and Space Administration The full contents of this book include Hubble science articles, an overview of the telescope, and
National Aeronautics and Space Administration Dwarf Stars National Aeronautics and Space Administration The full contents of this book include Hubble science articles, an overview of the telescope, and
Chapter 15 2/19/2014. Lecture Outline Hubble s Galaxy Classification. Normal and Active Galaxies Hubble s Galaxy Classification
 Lecture Outline Chapter 15 Normal and Active Galaxies Spiral galaxies are classified according to the size of their central bulge. Chapter 15 Normal and Active Galaxies Type Sa has the largest central
Lecture Outline Chapter 15 Normal and Active Galaxies Spiral galaxies are classified according to the size of their central bulge. Chapter 15 Normal and Active Galaxies Type Sa has the largest central
A New Population of Active Galactic Nuclei
 National Aeronautics and Space Administration A New Population of Active Galactic Nuclei Amy J. Barger Taken from: Hubble 2006 Science Year in Review The full contents of this book include more Hubble
National Aeronautics and Space Administration A New Population of Active Galactic Nuclei Amy J. Barger Taken from: Hubble 2006 Science Year in Review The full contents of this book include more Hubble
Science Olympiad Astronomy C Division Event Golden Gate Invitational
 Science Olympiad Astronomy C Division Event Golden Gate Invitational University of California, Berkeley Berkeley, CA February 9, 2019 Team Number: Team Name: Instructions: 1) Please turn in all materials
Science Olympiad Astronomy C Division Event Golden Gate Invitational University of California, Berkeley Berkeley, CA February 9, 2019 Team Number: Team Name: Instructions: 1) Please turn in all materials
GAMMA RAYS. 1 P a g e
 GAMMA RAYS 1 P a g e 2 P a g e 3 P a g e Death Stars Do the most powerful blasts of energy in the universe threaten Earth? You don't want to be anywhere near a giant star when it dies. In just a few seconds,
GAMMA RAYS 1 P a g e 2 P a g e 3 P a g e Death Stars Do the most powerful blasts of energy in the universe threaten Earth? You don't want to be anywhere near a giant star when it dies. In just a few seconds,
A Cosmic Perspective. Scott Fisher, Ph.D. - Director of Undergraduate Studies - UO Department of Physics
 A Cosmic Perspective Scott Fisher, Ph.D. - Director of Undergraduate Studies - UO Department of Physics Presentation Overview Let s talk about 3 (or 4) important and relevant topics: Me You and your place
A Cosmic Perspective Scott Fisher, Ph.D. - Director of Undergraduate Studies - UO Department of Physics Presentation Overview Let s talk about 3 (or 4) important and relevant topics: Me You and your place
Active Galaxies and Galactic Structure Lecture 22 April 18th
 Active Galaxies and Galactic Structure Lecture 22 April 18th FINAL Wednesday 5/9/2018 6-8 pm 100 questions, with ~20-30% based on material covered since test 3. Do not miss the final! Extra Credit: Thursday
Active Galaxies and Galactic Structure Lecture 22 April 18th FINAL Wednesday 5/9/2018 6-8 pm 100 questions, with ~20-30% based on material covered since test 3. Do not miss the final! Extra Credit: Thursday
Galaxies. Beyond the Book. FOCUS Book. Make a model that helps demonstrate how the universe is expanding. Follow these steps:
 FOCUS Book Galaxies Make a model that helps demonstrate how the universe is expanding. Follow these steps: 1 Use markers to make dots on the outside of an uninflated balloon to represent galaxies full
FOCUS Book Galaxies Make a model that helps demonstrate how the universe is expanding. Follow these steps: 1 Use markers to make dots on the outside of an uninflated balloon to represent galaxies full
ANSWER KEY. Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe. Telescopes Guided Reading and Study. Characteristics of Stars Guided Reading and Study
 Stars, Galaxies, a the Universe Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe Telescopes Use Target Reading Skills Check student definitions for accuracy. 1. Electromagneticradiationisenergythatcan travel through
Stars, Galaxies, a the Universe Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe Telescopes Use Target Reading Skills Check student definitions for accuracy. 1. Electromagneticradiationisenergythatcan travel through
Relativistic Jets from the Black Hole in SS 433
 Relativistic Jets from the Black Hole in SS 433 Herman L. Marshall and Laura A. Lopez with Claude R. Canizares, Norbert S. Schulz, and Julie F. Kane MIT Center for Space Research using NASA s Chandra X-ray
Relativistic Jets from the Black Hole in SS 433 Herman L. Marshall and Laura A. Lopez with Claude R. Canizares, Norbert S. Schulz, and Julie F. Kane MIT Center for Space Research using NASA s Chandra X-ray
Chandra: Revolution through Resolution. Martin Elvis, Chandra X-ray Center
 Chandra: Revolution through Resolution Martin Elvis, Chandra X-ray Center The Chandra X-ray Observatory Launched 5 years ago revolutionized X-ray astronomy, and all of astronomy. What is X-ray Astronomy?
Chandra: Revolution through Resolution Martin Elvis, Chandra X-ray Center The Chandra X-ray Observatory Launched 5 years ago revolutionized X-ray astronomy, and all of astronomy. What is X-ray Astronomy?
AST 101 Intro to Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies
 AST 101 Intro to Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies Telescopes Mauna Kea Observatories, Big Island, HI Imaging with our Eyes pupil allows light to enter the eye lens focuses light to create an image retina detects
AST 101 Intro to Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies Telescopes Mauna Kea Observatories, Big Island, HI Imaging with our Eyes pupil allows light to enter the eye lens focuses light to create an image retina detects
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE
 Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 24 Studying the Sun 24.1 The Study of Light Electromagnetic Radiation Electromagnetic radiation includes gamma rays, X-rays, ultraviolet light, visible
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 24 Studying the Sun 24.1 The Study of Light Electromagnetic Radiation Electromagnetic radiation includes gamma rays, X-rays, ultraviolet light, visible
The Milky Way Galaxy
 The Milky Way Galaxy A. Expert - I have done a lot of reading in this area already. B. Above Average - I have learned some information about this topic. C. Moderate - I know a little about this topic.
The Milky Way Galaxy A. Expert - I have done a lot of reading in this area already. B. Above Average - I have learned some information about this topic. C. Moderate - I know a little about this topic.
Writing very large numbers
 19.1 Tools of Astronomers Frequently in the news we hear about discoveries that involve space. Since the 1970s, space probes have been sent to all of the planets in the solar system and we have seen them
19.1 Tools of Astronomers Frequently in the news we hear about discoveries that involve space. Since the 1970s, space probes have been sent to all of the planets in the solar system and we have seen them
Galaxy Collisions & the Origin of Starburst Galaxies & Quasars. February 24, 2003 Hayden Planetarium
 Galaxy Collisions & the Origin of Starburst Galaxies & Quasars February 24, 2003 Hayden Planetarium Normal massive galaxy types elliptical & spiral galaxies Spiral Bulge of old stars Large black hole Very
Galaxy Collisions & the Origin of Starburst Galaxies & Quasars February 24, 2003 Hayden Planetarium Normal massive galaxy types elliptical & spiral galaxies Spiral Bulge of old stars Large black hole Very
An x-ray image of teeth. Can you see the filling?
 X-Rays APA National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Science Mission Directorate. (2010). X-Rays. Retrieved December 12, 2012, from Mission:Science website: http://missionscience.nasa.gov /ems/11_xrays.html
X-Rays APA National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Science Mission Directorate. (2010). X-Rays. Retrieved December 12, 2012, from Mission:Science website: http://missionscience.nasa.gov /ems/11_xrays.html
The phenomenon of gravitational lenses
 The phenomenon of gravitational lenses The phenomenon of gravitational lenses If we look carefully at the image taken with the Hubble Space Telescope, of the Galaxy Cluster Abell 2218 in the constellation
The phenomenon of gravitational lenses The phenomenon of gravitational lenses If we look carefully at the image taken with the Hubble Space Telescope, of the Galaxy Cluster Abell 2218 in the constellation
The Moon s relationship with Earth The formation of the Moon The surface of the Moon Phases of the Moon Travelling to the Moon
 The Moon The Moon s relationship with Earth The Moon orbits the Earth every 27.3 days. The tides on Earth are caused mostly by the gravitational pull of the Moon and the Sun. The Moon's gravitational pull
The Moon The Moon s relationship with Earth The Moon orbits the Earth every 27.3 days. The tides on Earth are caused mostly by the gravitational pull of the Moon and the Sun. The Moon's gravitational pull
Educational Product Teachers Grades K-12 EG MSFC
 Educational Product Teachers Grades K-12 NASA Spacelink Optics: An Educators Guide With Activities In Science and Mathematics is available in electronic format through NASA Spacelink one of the Agency
Educational Product Teachers Grades K-12 NASA Spacelink Optics: An Educators Guide With Activities In Science and Mathematics is available in electronic format through NASA Spacelink one of the Agency
The Milky Way Galaxy is Heading for a Major Cosmic Collision
 The Milky Way Galaxy is Heading for a Major Cosmic Collision Roeland van der Marel (STScI) [based on work with a team of collaborators reported in the Astrophysical Journal July 2012] Hubble Science Briefing
The Milky Way Galaxy is Heading for a Major Cosmic Collision Roeland van der Marel (STScI) [based on work with a team of collaborators reported in the Astrophysical Journal July 2012] Hubble Science Briefing
Chapter 21 Galaxy Evolution. How do we observe the life histories of galaxies?
 Chapter 21 Galaxy Evolution How do we observe the life histories of galaxies? Deep observations show us very distant galaxies as they were much earlier in time (old light from young galaxies). 1 Observing
Chapter 21 Galaxy Evolution How do we observe the life histories of galaxies? Deep observations show us very distant galaxies as they were much earlier in time (old light from young galaxies). 1 Observing
Formation of the Universe & What is in Space? The Big Bang Theory and components of the Universe
 Formation of the Universe & What is in Space? The Big Bang Theory and components of the Universe The Big Bang Theory The Big Bang Theory The Big Bang Theory is the most widely accepted scientific explanation
Formation of the Universe & What is in Space? The Big Bang Theory and components of the Universe The Big Bang Theory The Big Bang Theory The Big Bang Theory is the most widely accepted scientific explanation
A High-energy Life. Professor Lynn Cominsky Department of Physics and Astronomy Sonoma State University
 A High-energy Life Professor Lynn Cominsky Department of Physics and Astronomy Sonoma State University My Mom and the Stars I first learned about the stars from my Mom She taught me the constellations
A High-energy Life Professor Lynn Cominsky Department of Physics and Astronomy Sonoma State University My Mom and the Stars I first learned about the stars from my Mom She taught me the constellations
X-ray Astronomy F R O M V - R O CKETS TO AT HENA MISSION. Thanassis Akylas
 X-ray Astronomy F R O M V - R O CKETS TO AT HENA MISSION Thanassis Akylas Telescopes & Light Gallileo turned his telescope into the sky 400 years ago He enhanced his natural vision or the so called natural
X-ray Astronomy F R O M V - R O CKETS TO AT HENA MISSION Thanassis Akylas Telescopes & Light Gallileo turned his telescope into the sky 400 years ago He enhanced his natural vision or the so called natural
ASTRONOMY. Chapter 27 ACTIVE GALAXIES, QUASARS, AND SUPERMASSIVE BLACK HOLES PowerPoint Image Slideshow
 ASTRONOMY Chapter 27 ACTIVE GALAXIES, QUASARS, AND SUPERMASSIVE BLACK HOLES PowerPoint Image Slideshow FIGURE 27.1 Hubble Ultra-Deep Field. The deepest picture of the sky in visible light (left) shows
ASTRONOMY Chapter 27 ACTIVE GALAXIES, QUASARS, AND SUPERMASSIVE BLACK HOLES PowerPoint Image Slideshow FIGURE 27.1 Hubble Ultra-Deep Field. The deepest picture of the sky in visible light (left) shows
Review of Lecture 15 3/17/10. Lecture 15: Dark Matter and the Cosmic Web (plus Gamma Ray Bursts) Prof. Tom Megeath
 Lecture 15: Dark Matter and the Cosmic Web (plus Gamma Ray Bursts) Prof. Tom Megeath A2020 Disk Component: stars of all ages, many gas clouds Review of Lecture 15 Spheroidal Component: bulge & halo, old
Lecture 15: Dark Matter and the Cosmic Web (plus Gamma Ray Bursts) Prof. Tom Megeath A2020 Disk Component: stars of all ages, many gas clouds Review of Lecture 15 Spheroidal Component: bulge & halo, old
ASTRONOMY (ASTR) 100 Level Courses. 200 Level Courses. 300 Level Courses
 Astronomy (ASTR) 1 ASTRONOMY (ASTR) 100 Level Courses ASTR 103: Astronomy. 3 credits. Introduction to origin of life, Earth, planets and sun, stars, galaxies, quasars, nature of space radiation, and general
Astronomy (ASTR) 1 ASTRONOMY (ASTR) 100 Level Courses ASTR 103: Astronomy. 3 credits. Introduction to origin of life, Earth, planets and sun, stars, galaxies, quasars, nature of space radiation, and general
Astronomy Universe: all of space and everything in it
 Astronomy Universe: all of space and everything in it Most (90%) of the universe is made up of: dark matter: stuff we think is there due to amount of mass we think is there but is not detected by the instruments
Astronomy Universe: all of space and everything in it Most (90%) of the universe is made up of: dark matter: stuff we think is there due to amount of mass we think is there but is not detected by the instruments
Bringing Real-time Astronomical Observations into the Classroom
 Bringing Real-time Astronomical Observations into the Classroom Prof. Lynn Cominsky Sonoma State University Department of Physics and Astronomy and NASA Education and Public Outreach Group Why do astronomical
Bringing Real-time Astronomical Observations into the Classroom Prof. Lynn Cominsky Sonoma State University Department of Physics and Astronomy and NASA Education and Public Outreach Group Why do astronomical
UNIT E: SPACE EXPLORATION
 UNIT E: SPACE EXPLORATION S C I E N C E 9 1 Science 9 Unit E Section 3.0 OPTICAL TELESCOPES, RADIO TELESCOPES, AND OTHER TECHNOLOGIES ADVANCE OUR UNDERSTANDING OF SPACE SECTI ON 3.0 Science 9 Unit E Section
UNIT E: SPACE EXPLORATION S C I E N C E 9 1 Science 9 Unit E Section 3.0 OPTICAL TELESCOPES, RADIO TELESCOPES, AND OTHER TECHNOLOGIES ADVANCE OUR UNDERSTANDING OF SPACE SECTI ON 3.0 Science 9 Unit E Section
Chapter 23 The Milky Way Galaxy Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 23 The Milky Way Galaxy The Milky Way is our own galaxy viewed from the inside. It is a vast collection of more than 200 billion stars, planets, nebulae, clusters, dust and gas. Our own sun and
Chapter 23 The Milky Way Galaxy The Milky Way is our own galaxy viewed from the inside. It is a vast collection of more than 200 billion stars, planets, nebulae, clusters, dust and gas. Our own sun and
Exploring the Depths of the Universe
 Exploring the Depths of the Universe Jennifer Lotz Hubble Science Briefing Jan. 16, 2014 Hubble is now observing galaxies 97% of the way back to the Big Bang, during the first 500 million years 2 Challenge:
Exploring the Depths of the Universe Jennifer Lotz Hubble Science Briefing Jan. 16, 2014 Hubble is now observing galaxies 97% of the way back to the Big Bang, during the first 500 million years 2 Challenge:
On to Telescopes. Imaging with our Eyes. Telescopes and cameras work much like our eyes. ASTR 1120 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies !
 ASTR 1120 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies On to Telescopes!AST CLASS Learning from light: temperature (from continuum spectrum) chemical composition (from spectral lines) velocity (from Doppler shift)
ASTR 1120 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies On to Telescopes!AST CLASS Learning from light: temperature (from continuum spectrum) chemical composition (from spectral lines) velocity (from Doppler shift)
Multiple-Mirror Telescope Interviews, 1989
 , 1989 by Smithsonian Institution Archives Smithsonian Institution Archives Washington, D.C. Contact us at osiaref@si.edu http://siarchives.si.edu Table of Contents Collection Overview... 1 Administrative
, 1989 by Smithsonian Institution Archives Smithsonian Institution Archives Washington, D.C. Contact us at osiaref@si.edu http://siarchives.si.edu Table of Contents Collection Overview... 1 Administrative
Galaxies & Introduction to Cosmology
 Galaxies & Introduction to Cosmology Other Galaxies: How many are there? Hubble Deep Field Project 100 hour exposures over 10 days Covered an area of the sky about 1/100 the size of the full moon Probably
Galaxies & Introduction to Cosmology Other Galaxies: How many are there? Hubble Deep Field Project 100 hour exposures over 10 days Covered an area of the sky about 1/100 the size of the full moon Probably
Chapter 0 Introduction X-RAY BINARIES
 X-RAY BINARIES 1 Structure of this course 0. Introduction 1. Compact stars: formation and observational appearance. Mass transfer in binaries 3. Observational properties of XRBs 4. Formation and evolution
X-RAY BINARIES 1 Structure of this course 0. Introduction 1. Compact stars: formation and observational appearance. Mass transfer in binaries 3. Observational properties of XRBs 4. Formation and evolution
Visions of the Universe. Four Centuries of Discovery. Future. Visions
 Visions of the Universe ~ Four Centuries of Discovery Future Visions Future Visions Table of Contents - Exhibit Overview... 3 Science Background... 4 Science Misconceptions... 6 Glossary... 8 Related Educational
Visions of the Universe ~ Four Centuries of Discovery Future Visions Future Visions Table of Contents - Exhibit Overview... 3 Science Background... 4 Science Misconceptions... 6 Glossary... 8 Related Educational
Star systems like our Milky Way. Galaxies
 Galaxies Star systems like our Milky Way Galaxies Contain a few thousand to tens of billions of stars,as well as varying amounts of gas and dust Large variety of shapes and sizes Gas and Dust in
Galaxies Star systems like our Milky Way Galaxies Contain a few thousand to tens of billions of stars,as well as varying amounts of gas and dust Large variety of shapes and sizes Gas and Dust in
National Aeronautics and Space Administration X-RAY THE SCIENCE OF. technology
 National Aeronautics and Space Administration X-RAY THE SCIENCE OF technology www.nasa.gov chandra.si.edu/tech BACKGROUND ON X-RAY TECHNOLOGY X-ray astronomy is a relatively new science. It was pioneered
National Aeronautics and Space Administration X-RAY THE SCIENCE OF technology www.nasa.gov chandra.si.edu/tech BACKGROUND ON X-RAY TECHNOLOGY X-ray astronomy is a relatively new science. It was pioneered
Physics HW Set 3 Spring 2015
 1) If the Sun were replaced by a one solar mass black hole 1) A) life here would be unchanged. B) we would still orbit it in a period of one year. C) all terrestrial planets would fall in immediately.
1) If the Sun were replaced by a one solar mass black hole 1) A) life here would be unchanged. B) we would still orbit it in a period of one year. C) all terrestrial planets would fall in immediately.
Editorial comment: research and teaching at UT
 Wednesday, March 23, 2017 Reading for Exam 3: Chapter 6, end of Section 6 (binary evolution), Section 6.7 (radioactive decay), Chapter 7 (SN 1987A), Background: Sections 3.1, 3.2, 3.3, 3.4, 3.5, 3.8, 3.10,
Wednesday, March 23, 2017 Reading for Exam 3: Chapter 6, end of Section 6 (binary evolution), Section 6.7 (radioactive decay), Chapter 7 (SN 1987A), Background: Sections 3.1, 3.2, 3.3, 3.4, 3.5, 3.8, 3.10,
GLAST. Exploring the Extreme Universe. Kennedy Space Center. The Gamma-ray Large Area Space Telescope
 GLAST Gamma-ray Large Area Space Telescope The Gamma-ray Large Area Space Telescope Exploring the Extreme Universe Kennedy Space Center Dave Thompson GLAST Deputy Project Scientist David.J.Thompson@nasa.gov
GLAST Gamma-ray Large Area Space Telescope The Gamma-ray Large Area Space Telescope Exploring the Extreme Universe Kennedy Space Center Dave Thompson GLAST Deputy Project Scientist David.J.Thompson@nasa.gov
NuSTAR s Extreme Universe. Prof. Lynn Cominsky NASA Education and Public Outreach Sonoma State University
 NuSTAR s Extreme Universe Prof. Lynn Cominsky NASA Education and Public Outreach Sonoma State University The NASA Education and Public Outreach Program at SSU We are a group of scientists and educators
NuSTAR s Extreme Universe Prof. Lynn Cominsky NASA Education and Public Outreach Sonoma State University The NASA Education and Public Outreach Program at SSU We are a group of scientists and educators
Chapter 19 Galaxies. Hubble Ultra Deep Field: Each dot is a galaxy of stars. More distant, further into the past. halo
 Chapter 19 Galaxies Hubble Ultra Deep Field: Each dot is a galaxy of stars. More distant, further into the past halo disk bulge Barred Spiral Galaxy: Has a bar of stars across the bulge Spiral Galaxy 1
Chapter 19 Galaxies Hubble Ultra Deep Field: Each dot is a galaxy of stars. More distant, further into the past halo disk bulge Barred Spiral Galaxy: Has a bar of stars across the bulge Spiral Galaxy 1
Assignment 9. Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Assignment 9 Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The astrophysicist who first calculated the highest mass that a dying star can
Assignment 9 Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The astrophysicist who first calculated the highest mass that a dying star can
The Imaging Chain for X-Ray Astronomy
 The Imaging Chain for X-Ray Astronomy Pop quiz (1): Which is the X-ray Image? B. A. Answer: B!!! (But You Knew That) Pop quiz (2): Which of These is the X-Ray Image? A. B. C. B. A. The dying star ( planetary
The Imaging Chain for X-Ray Astronomy Pop quiz (1): Which is the X-ray Image? B. A. Answer: B!!! (But You Knew That) Pop quiz (2): Which of These is the X-Ray Image? A. B. C. B. A. The dying star ( planetary
Collecting Light. In a dark-adapted eye, the iris is fully open and the pupil has a diameter of about 7 mm. pupil
 Telescopes Collecting Light The simplest means of observing the Universe is the eye. The human eye is sensitive to light with a wavelength of about 400 and 700 nanometers. In a dark-adapted eye, the iris
Telescopes Collecting Light The simplest means of observing the Universe is the eye. The human eye is sensitive to light with a wavelength of about 400 and 700 nanometers. In a dark-adapted eye, the iris
ASTR 1120 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies
 ASTR 1120 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies!AST CLASS Learning from light: temperature (from continuum spectrum) chemical composition (from spectral lines) velocity (from Doppler shift) "ODA# Detecting
ASTR 1120 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies!AST CLASS Learning from light: temperature (from continuum spectrum) chemical composition (from spectral lines) velocity (from Doppler shift) "ODA# Detecting
Telescopes 3 Feb. Purpose
 Telescopes 3 Feb Key parameters of telescopes Optical telescopes SOAR Telescope, MSU s window on the universe Radio telescopes Telescopes in space SOAR Telescope Cerro Pachon, Chile First Test is Thurs
Telescopes 3 Feb Key parameters of telescopes Optical telescopes SOAR Telescope, MSU s window on the universe Radio telescopes Telescopes in space SOAR Telescope Cerro Pachon, Chile First Test is Thurs
1. Using, scientists can use a few smaller telescopes to take images with the. 2. To double the resolving power of a telescope, you must.
 Chapter 5 Telescopes Multiple Choice Questions 1. Using, scientists can use a few smaller telescopes to take images with the same resolution as a much larger telescope. A. Satellite telescopes B. Charge-coupled
Chapter 5 Telescopes Multiple Choice Questions 1. Using, scientists can use a few smaller telescopes to take images with the same resolution as a much larger telescope. A. Satellite telescopes B. Charge-coupled
Astronomy 102: Stars and Galaxies Examination 3 Review Problems
 Astronomy 102: Stars and Galaxies Examination 3 Review Problems Multiple Choice Questions: The first eight questions are multiple choice. Except where explicitly noted, only one answer is correct for each
Astronomy 102: Stars and Galaxies Examination 3 Review Problems Multiple Choice Questions: The first eight questions are multiple choice. Except where explicitly noted, only one answer is correct for each
Today in Astronomy 102: prologue in outer space, continued
 Today in Astronomy 102: prologue in outer space, continued Visit 10 9 M, 10 13 M and 45 M black holes Image: mid infrared picture of Centaurus A, probably the nearest galaxy with a billionsolar-mass central
Today in Astronomy 102: prologue in outer space, continued Visit 10 9 M, 10 13 M and 45 M black holes Image: mid infrared picture of Centaurus A, probably the nearest galaxy with a billionsolar-mass central
Astronomy 102, Fall September 2009
 Today in Astronomy 102: prologue in outer space, continued Visit 10 9 M, 10 13 M and 45 M black holes Image: mid infrared picture of Centaurus A, probably the nearest galaxy with a billionsolar-mass central
Today in Astronomy 102: prologue in outer space, continued Visit 10 9 M, 10 13 M and 45 M black holes Image: mid infrared picture of Centaurus A, probably the nearest galaxy with a billionsolar-mass central
Galaxies. CESAR s Booklet
 What is a galaxy? Figure 1: A typical galaxy: our Milky Way (artist s impression). (Credit: NASA) A galaxy is a huge collection of stars and interstellar matter isolated in space and bound together by
What is a galaxy? Figure 1: A typical galaxy: our Milky Way (artist s impression). (Credit: NASA) A galaxy is a huge collection of stars and interstellar matter isolated in space and bound together by
Galaxies. Say Thanks to the Authors Click (No sign in required)
 Galaxies Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a customizable version of this book, as well as other interactive content, visit www.ck12.org CK-12
Galaxies Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a customizable version of this book, as well as other interactive content, visit www.ck12.org CK-12
Active Galaxies & Quasars
 Active Galaxies & Quasars Normal Galaxy Active Galaxy Galactic Nuclei Bright Active Galaxy NGC 5548 Galaxy Nucleus: Exact center of a galaxy and its immediate surroundings. If a spiral galaxy, it is the
Active Galaxies & Quasars Normal Galaxy Active Galaxy Galactic Nuclei Bright Active Galaxy NGC 5548 Galaxy Nucleus: Exact center of a galaxy and its immediate surroundings. If a spiral galaxy, it is the
What is the sun? The sun is a star at the center of our solar system.
 What is the sun? The sun is a star at the center of our solar system. Galileo Galilei (1564-1642) Galileo was one of the first Europeans to observe the sun. How did Galileo look at the sun? He lined up
What is the sun? The sun is a star at the center of our solar system. Galileo Galilei (1564-1642) Galileo was one of the first Europeans to observe the sun. How did Galileo look at the sun? He lined up
New Ideas from Astronomy and Cosmology. Martin Buoncristiani Session 5 4/21/2011
 New Ideas from Astronomy and Cosmology Martin Buoncristiani Session 5 Agenda Introduction Space, Time and Matter Early views of the cosmos Important Ideas from Classical Physics Two 20 th Century revolutions
New Ideas from Astronomy and Cosmology Martin Buoncristiani Session 5 Agenda Introduction Space, Time and Matter Early views of the cosmos Important Ideas from Classical Physics Two 20 th Century revolutions
Monday, October 14, 2013 Reading: Chapter 8. Astronomy in the news?
 Monday, October 14, 2013 Reading: Chapter 8 Astronomy in the news? Goal: To understand the nature and importance of SN 1987A for our understanding of massive star evolution and iron core collapse. 1 st
Monday, October 14, 2013 Reading: Chapter 8 Astronomy in the news? Goal: To understand the nature and importance of SN 1987A for our understanding of massive star evolution and iron core collapse. 1 st
Narrated by Whoopi Goldberg
 Narrated by Whoopi Goldberg Easily the most beautiful planetarium show I have ever seen. The New York Times OVERVIEW Featuring extraordinary images from ground- and space-based telescopes and stunning,
Narrated by Whoopi Goldberg Easily the most beautiful planetarium show I have ever seen. The New York Times OVERVIEW Featuring extraordinary images from ground- and space-based telescopes and stunning,
Galaxies. The majority of known galaxies fall into one of three major classes: spirals (78 %), ellipticals (18 %) and irregulars (4 %).
 Galaxies Collection of stars, gas and dust bound together by their common gravitational pull. Galaxies range from 10,000 to 200,000 light-years in size. 1781 Charles Messier 1923 Edwin Hubble The distribution
Galaxies Collection of stars, gas and dust bound together by their common gravitational pull. Galaxies range from 10,000 to 200,000 light-years in size. 1781 Charles Messier 1923 Edwin Hubble The distribution
PART 3 Galaxies. Gas, Stars and stellar motion in the Milky Way
 PART 3 Galaxies Gas, Stars and stellar motion in the Milky Way The Interstellar Medium The Sombrero Galaxy Space is far from empty! Clouds of cold gas Clouds of dust In a galaxy, gravity pulls the dust
PART 3 Galaxies Gas, Stars and stellar motion in the Milky Way The Interstellar Medium The Sombrero Galaxy Space is far from empty! Clouds of cold gas Clouds of dust In a galaxy, gravity pulls the dust
Results better than Quiz 5, back to normal Distribution not ready yet, sorry Correct up to 4 questions, due Monday, Apr. 26
 Brooks observing April 19-22: 9:00 PM to at least 10:15 PM Tonight is a go! April 26-29: 9:30 PM to at least 10:45 PM Regular Friday evening public observing after planetarium shows also an option Begins
Brooks observing April 19-22: 9:00 PM to at least 10:15 PM Tonight is a go! April 26-29: 9:30 PM to at least 10:45 PM Regular Friday evening public observing after planetarium shows also an option Begins
Sergio B. Dieterich Updated September, 2014 sdieterich at carnegiescience dot edu
 Sergio B. Dieterich Updated September, 2014 sdieterich at carnegiescience dot edu www.hlimit.org Education 2013 Ph. D. in Astronomy, Atlanta, Georgia, USA Dissertation: Characterization of the Stellar/Substellar
Sergio B. Dieterich Updated September, 2014 sdieterich at carnegiescience dot edu www.hlimit.org Education 2013 Ph. D. in Astronomy, Atlanta, Georgia, USA Dissertation: Characterization of the Stellar/Substellar
2019 Astronomy Team Selection Test
 2019 Astronomy Team Selection Test Acton-Boxborough Regional High School Written by Antonio Frigo Do not flip over this page until instructed. Instructions You will have 45 minutes to complete this exam.
2019 Astronomy Team Selection Test Acton-Boxborough Regional High School Written by Antonio Frigo Do not flip over this page until instructed. Instructions You will have 45 minutes to complete this exam.
Galaxies and Star Systems
 Chapter 5 Section 5.1 Galaxies and Star Systems Galaxies Terms: Galaxy Spiral Galaxy Elliptical Galaxy Irregular Galaxy Milky Way Galaxy Quasar Black Hole Types of Galaxies A galaxy is a huge group of
Chapter 5 Section 5.1 Galaxies and Star Systems Galaxies Terms: Galaxy Spiral Galaxy Elliptical Galaxy Irregular Galaxy Milky Way Galaxy Quasar Black Hole Types of Galaxies A galaxy is a huge group of
Earth s Atmosphere & Telescopes. Atmospheric Effects
 Earth s Atmosphere & Telescopes Whether light is absorbed by the atmosphere or not depends greatly on its wavelength. Earth s atmosphere can absorb certain wavelengths of light so much that astronomers
Earth s Atmosphere & Telescopes Whether light is absorbed by the atmosphere or not depends greatly on its wavelength. Earth s atmosphere can absorb certain wavelengths of light so much that astronomers
Galaxies Guiding Questions
 Galaxies Guiding Questions How did astronomers first discover other galaxies? How did astronomers first determine the distances to galaxies? Do all galaxies have spiral arms, like the Milky Way? How do
Galaxies Guiding Questions How did astronomers first discover other galaxies? How did astronomers first determine the distances to galaxies? Do all galaxies have spiral arms, like the Milky Way? How do
Light and Telescopes
 Light and Telescopes Astronomy 1 Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Spring F2015 Quotes & Cartoon of the Day We find them smaller and fainter, in constantly increasing numbers, and we know that we
Light and Telescopes Astronomy 1 Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Spring F2015 Quotes & Cartoon of the Day We find them smaller and fainter, in constantly increasing numbers, and we know that we
Today in Astronomy 102: the Galactic center
 Today in Astronomy 102: the Galactic center The center of the Milky Way Galaxy: compelling evidence for a 3.6- million-solar-mass black hole. Image: wide-angle photo and overlay key of the Sagittarius
Today in Astronomy 102: the Galactic center The center of the Milky Way Galaxy: compelling evidence for a 3.6- million-solar-mass black hole. Image: wide-angle photo and overlay key of the Sagittarius
Detailed Dark Matter Map
 National Aeronautics and Space Administration Detailed Dark Matter Map Taken from: Hubble 2010: Science Year in Review Produced by NASA Goddard Space Flight Center and the Space Telescope Science Institute.
National Aeronautics and Space Administration Detailed Dark Matter Map Taken from: Hubble 2010: Science Year in Review Produced by NASA Goddard Space Flight Center and the Space Telescope Science Institute.
What Channel Is That?
 TOPIC 5 What Channel Is That? Light isn t the only kind of radiation coming from the stars. In the late nineteenth century, scientists found out that light is just one form of electromagnetic radiation.
TOPIC 5 What Channel Is That? Light isn t the only kind of radiation coming from the stars. In the late nineteenth century, scientists found out that light is just one form of electromagnetic radiation.
LIGHT AND GRAVITY: Using multi-messenger astronomy to see the Cosmos
 LIGHT AND GRAVITY: Using multi-messenger astronomy to see the Cosmos Shane L. Larson Department of Physics Utah State University s.larson@usu.edu Gravity Seminar UW Milwaukee 11 May 2012 1 Storyline The
LIGHT AND GRAVITY: Using multi-messenger astronomy to see the Cosmos Shane L. Larson Department of Physics Utah State University s.larson@usu.edu Gravity Seminar UW Milwaukee 11 May 2012 1 Storyline The
Taken from: Hubble 2007: Science Year in Review. Produced by NASA Goddard Space Flight Center and Space Telescope Science Institute.
 National Aeronautics and Space Administration Coming Attractions Taken from: Produced by NASA Goddard Space Flight Center and Space Telescope Science Institute. The full contents of this book include more
National Aeronautics and Space Administration Coming Attractions Taken from: Produced by NASA Goddard Space Flight Center and Space Telescope Science Institute. The full contents of this book include more
Chapter 15 Galaxies and the Foundation of Modern Cosmology
 15.1 Islands of stars Chapter 15 Galaxies and the Foundation of Modern Cosmology Cosmology: study of galaxies What are they 3 major types of galaxies? Spiral galaxies: like the milky way, look like flat,
15.1 Islands of stars Chapter 15 Galaxies and the Foundation of Modern Cosmology Cosmology: study of galaxies What are they 3 major types of galaxies? Spiral galaxies: like the milky way, look like flat,
8/30/2010. Classifying Stars. Classifying Stars. Classifying Stars
 Classifying Stars In the early 1900s, Ejnar Hertzsprung and Henry Russell made some important observations. They noticed that, in general, stars with higher temperatures also have brighter absolute magnitudes.
Classifying Stars In the early 1900s, Ejnar Hertzsprung and Henry Russell made some important observations. They noticed that, in general, stars with higher temperatures also have brighter absolute magnitudes.
The Large Synoptic Survey Telescope
 The Large Synoptic Survey Telescope Philip A. Pinto Steward Observatory University of Arizona for the LSST Collaboration 17 May, 2006 NRAO, Socorro Large Synoptic Survey Telescope The need for a facility
The Large Synoptic Survey Telescope Philip A. Pinto Steward Observatory University of Arizona for the LSST Collaboration 17 May, 2006 NRAO, Socorro Large Synoptic Survey Telescope The need for a facility
TWO SMALL PIECES OF GLASS A Space Science Program for Grades 5-12
 Teacher Idea Kit TWO SMALL PIECES OF GLASS A Space Science Program for Grades 5-12 Presented by Funded in part by: Two Small Pieces of Glass Suggested for Grades 5-12 Objectives After visiting the planetarium
Teacher Idea Kit TWO SMALL PIECES OF GLASS A Space Science Program for Grades 5-12 Presented by Funded in part by: Two Small Pieces of Glass Suggested for Grades 5-12 Objectives After visiting the planetarium
Astronomy Summer Camps. Directed by Dr. Jian Ge Professor of Astronomy, University of Florida 1/15/2018
 Astronomy Summer Camps Directed by Dr. Jian Ge Professor of Astronomy, University of Florida 1/15/2018 Two astronomy summer camps will be offered during the summer of 2018. Both camps involve students
Astronomy Summer Camps Directed by Dr. Jian Ge Professor of Astronomy, University of Florida 1/15/2018 Two astronomy summer camps will be offered during the summer of 2018. Both camps involve students
QUASARS and ACTIVE GALAXIES. - a Detective Story
 QUASARS and ACTIVE GALAXIES - a Detective Story Twinkle, twinkle, quasi-star, Biggest puzzle from afar. How unlike the other ones, Brighter than a trillion Suns. Twinkle, twinkle, quasi-star, How I wonder
QUASARS and ACTIVE GALAXIES - a Detective Story Twinkle, twinkle, quasi-star, Biggest puzzle from afar. How unlike the other ones, Brighter than a trillion Suns. Twinkle, twinkle, quasi-star, How I wonder
Galaxies. With a touch of cosmology
 Galaxies With a touch of cosmology Types of Galaxies Spiral Elliptical Irregular Spiral Galaxies Spiral Galaxies Disk component where the spiral arms are Interstellar medium Star formation Spheroidal
Galaxies With a touch of cosmology Types of Galaxies Spiral Elliptical Irregular Spiral Galaxies Spiral Galaxies Disk component where the spiral arms are Interstellar medium Star formation Spheroidal
GRAVITATIONAL WAVES MOHAMMAD ISHTIAQ
 GRAVITATIONAL WAVES MOHAMMAD ISHTIAQ Introduction It all started with Einstein s theory of general relativity What is Einstein s theory of general relativity? Theory which predicted that objects cause
GRAVITATIONAL WAVES MOHAMMAD ISHTIAQ Introduction It all started with Einstein s theory of general relativity What is Einstein s theory of general relativity? Theory which predicted that objects cause
Other Galaxy Types. Active Galaxies. A diagram of an active galaxy, showing the primary components. Active Galaxies
 Other Galaxy Types Active Galaxies Active Galaxies Seyfert galaxies Radio galaxies Quasars Origin??? Different in appearance Produce huge amount of energy Similar mechanism a Galactic mass black hole at
Other Galaxy Types Active Galaxies Active Galaxies Seyfert galaxies Radio galaxies Quasars Origin??? Different in appearance Produce huge amount of energy Similar mechanism a Galactic mass black hole at
What Objects Are Part of the Solar System?
 What Objects Are Part of the Solar System? Lesson 1 Quiz Josleen divided some of the planets into two main groups. The table below shows how she grouped them. Paul created a poster showing the solar system.
What Objects Are Part of the Solar System? Lesson 1 Quiz Josleen divided some of the planets into two main groups. The table below shows how she grouped them. Paul created a poster showing the solar system.
