IMPLEMENTATION OF A QUASI-OPTICAL FREE-SPACE S-PARAMETERS MEASUREMENT SYSTEM
|
|
|
- Pierce Jacob Willis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
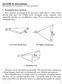
1 IMPLEMENTATION OF A QUASI-OPTICAL FREE-SPACE S-PARAMETERS MEASUREMENT SYSTEM B. Maffei, S. Legg, M. Robinson, F. Ozturk, M. W. Ng, P. Schemmel and G. Pisano. JBCA, School of Physics and Astronomy, The University of Manchester, UK ABSTRACT A quasi-optical (QO) free-space test bench, based on two dual reflector Compact Test Range (CTR) systems, has been developed to characterise the RF properties of materials and QO components used in mm-wave astronomical instrumentation. While this facility has been designed to operate for several spectral bandwidths, in the first instance measurements have been performed in the W-band (75-11 GHz). We present the modelled and performance of the test bench and the procedure for calibrating and measuring samples under test. First results of the field across a 1 cm quiet zone indicate a maximum intensity variation of -4.5 db and a maximum phase variation of 7. Measurements of the cross-polarisation indicate higher levels than were predicted. A free-space calibration method has been developed based on the use of 3 calibration standards (Thru-Reflect-Line). Initial measurements of the reflectivity and transmittance for a range of materials have been performed, allowing the deduction of the refractive index. 1. INTRODUCTION Measuring the Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) polarisation is a powerful tool for testing cosmological models. Several present and future projects aiming at measuring this polarisation are based on the use of cold detectors coupled to microwave waveguide components and quasi-optical (QO) components. Some of them will contain interference filters, dewar windows and lenses for instance. The signal from the B-mode CMB polarisation is predicted to be extremely faint. Therefore these instruments require highly sensitive detectors and receiver components with well-known and characterised systematic effects that they will inevitably introduce in the signal. A test set-up has been constructed to accurately test the RF and optical properties of quasi-optical components that are being developed, and to study their systematic effects. Components such as interference filters, half-wave plates and polarisers are all under study. This test bench will also allow the RF characterisation of materials from which these quasi-optical components are constructed. For instance, the accurate modelling and performance prediction of the QO components that are being developed are highly sensitive to the refractive index of the material being used. For the same material, the refractive index could vary from one supplier to another. In order to retrieve the most accurate performance, these measurements must be performed in a collimated beam, to disentangle systematic effects that might arise from an oblique incidence on the sample under test. Moreover, since the QO components will be used in instruments dedicated to the study of the CMB, it is vital that they are tested within a zone with low aberrations and a low cross-polarisation [1] and where the electro-magnetic field is well controlled and known (referred as the Quiet Zone). The CMB is best studied in the frequency domain comprised between 4 to 3 GHz. While this range could be covered in principle, our test set-up has been optimised for W-band to be used with our Vector Network Analyser in order to reach a typical maximum cross-polarisation of -4 db [2]. 2. SYSTEM DESIGN AND MANUFACTURE The optical design of the test set-up coupled to a Vector Network Analyser (Rohde & Schwarz ZVNA-4) is detailed in a previous article [1]. It is based on two dual reflector Compact Test Ranges (CTR), each comprising a parabolic and a hyperbolic mirror (Fig. 1). Each CTR has a VNA converter head located at its focus acting both as a receiver and emitter. For these tests, the converters are operating in the W-band (75 11 GHz). However the corrugated horns that have been used on the converter waveguide outputs only transmit above 82 GHz. The combination of the converter, horn and CTR is creating a collimated beam where the EM field is pseudo-planar where the samples under test can be located. This cylindrical Quiet Zone (QZ) region has
2 low intensity and phase variations. The beam is then refocused on the horn aperture of the second VNA converter located at the focus of the second CTR. The mirrors have serrated edges in order to minimise the phase and amplitude variations across the QZ [1]. system, the feed horn is located in a fixed position. The reflectors (Main parabolic and Secondary hyperbolic) are positioned geometrically according to the CTR design parameters, with the feed horn acting as the point of origin. Each mirror is then roughly adjusted in order to maximise the signal between the emitter and the receiver. The CTR systems are then aligned independently to each other. A reflector is inserted in the QZ region and the Return Loss (RL) is optimised to be as close as possible to db (S parameter maximised close to 1) for each CTR individually by adjusting the position and tilt of the sub-reflector and the tilt of the main-reflector. Each component is repositioned in an iterative fashion until the optimum RL is reached. The beam of each CTR is then investigated to ensure that it is at normal incidence to the QZ by scanning the phase across the reference plane using a 3D scanning system [3]. For these measurements the field probe consists of a circular to rectangular waveguide transition matched to free space and surrounded by absorber to eliminate reflections as shown in Fig. 2. Any misalignment would introduce a phase gradient over the scanned region. Adjusting the tilt of the main reflector accordingly can counteract this gradient. To achieve the optimal alignment the whole process is repeated iteratively, optimising the RL and correcting the phase gradient each time until no further improvement can be achieved. Figure 1. Test set-up. Each Compact Test Range (CTR) consists of a corrugated feed horn (Feed), a hyperbolic Sub-Reflector (SR) of size 17 cm and a parabolic MainReflector (MR) of 2 cm aperture, creating a central cylindrical Quiet Zone (QZ) region of 1 cm diameter, extending axially 5 cm towards each MR. Samples under test (SUT) are placed within this QZ, positioned such that the centre of the SUT lies coplanar to a reference plane, which is defined to be halfway between the two main reflectors. A Sample Holder (SH) secures an 11 cm diameter SUT and absorbs unwanted radiation from outside the QZ using a piece of RF absorber. The sample holder has been connected to a 3axis positioning stage to allow accurate positioning. 3. ALIGNMENT Each component has several degrees of freedom, making the alignment procedure difficult. To reduce the number of alignment parameters associated with the Figure 2. Image of the system configured to enable measurements of the QZ field in 3-dimensions using a circular to rectangular waveguide transition as the field probe.
3 Once each CTR is aligned, both are assembled together and the signal between the two converters maximised. When the free-space S-parameter system is in place, a loss of less than 1dB between the two VNA converters is observed. 4. CALIBRATION precise amount when taking the Thru standard, therefore one CTR has been mounted on a micrometre controlled sliding platform. The TRL method is performed using the following procedure [5] (see Fig. 3): 1) Starting with the set-up initially in the Thru position, the Reflect standard is taken by placing a reflector of thickness W between the two CTRs, with one of the reflector faces aligned collinear to the reference plane, then moving CTR 1 back by a corresponding distance W. 2) The Line standard is obtained by removing the calibration reflector whilst keeping the separation distance between the two CTRs unchanged. The line length must satisfy: 1º < k W < 17º over the spectral band, where k = 2π / λ and λ is the free-space wavelength. The restriction is to ensure that any phase ambiguity is avoided. 3) The Thru standard is taken by moving CTR 1 back to its initial position. 5. SYSTEM VERIFICATION 5.1 Simulation and measurement procedure Initial position Figure 3. TRL calibration method of the set-up adapted from [5]. The initial position of the set-up is shown as the Thru standard, where the reference plane lies halfway between the two CTRs. The Reflect standard is taken by placing a calibration reflector of thickness W between the CTRs and moving CTR 1 back by a corresponding distance W. The Line standard is taken by removing the calibration reflector whilst keeping the separation distance between the two CTRs unchanged. The Thru standard is taken by moving CTR 1 back to its original position. The set-up needs to be calibrated to remove systematic errors caused by transmission losses in the CTR components and the cables of the VNA. A wellestablished calibration method known as Thru-Reflect- Line [4] (TRL) is appropriate for this free-space set-up. This method requires the propagation distance between the two feed horns to be increased by a pre-determined The free-space measurement system is modelled in GRASP [6]. Physical Optics (PO) calculations are conducted to simulate the properties of the RF field produced in the QZ. Further to simulation work conducted previously [1], the far field radiation pattern of the corrugated feed horn is inputted as the radiation source instead of a simple linearly polarised Gaussian beam. The intensity and phase of the field produced by the CTR system in the QZ region is sampled along the x- axis (as defined in Fig. 2) using the 3D scanning system described in section 3. In order to verify the performance of the system both GRASP simulations and the data are presented in the following two sections. 5.2 Intensity and phase measurements As demonstrated in Fig. 4, the beam intensity observed across the QZ agrees well with the simulation over a 7.5 cm radius with increasing deviations from the model at larger radii. However, upon closer inspection over a 5 cm radius, deviations from the simulation in excess of.5 db are observed. Over this 5 cm radius QZ, the
4 intensities observed have a range of 4.5 db; 1 db larger than predicted using the GRASP model. The general phase evolution over a 1 cm diameter QZ matches that of the model, however larger oscillations are observed over the plateau region as shown in Fig. 5. Deviations from the model are typically less than 5 and the maximum phase variation over this 1 cm QZ is 7. Further agreement with the model is likely to be hindered by component inefficiencies such as in the VNA cables and imperfections on the reflector surfaces Figure 4. Comparison of the field intensities across the QZ and the intensities using a circular to rectangular waveguide transition as a field probe. Data has been normalised using the maximum intensity of the model as the definition for the zero point. Top: comparison over a 3 cm diameter QZ. Bottom: comparison over a 1 cm diameter QZ. 5.3 Cross-polarisation measurements It is predicted that the maximum cross-polarisation produced by the CTR system is in a diagonal cut through the QZ orientated at an angle of φ=45 to the test bench. In order to measure the field in this cut along the x-axis of the laboratory system, an additional waveguide was used, which rotated the beam pattern through an angle of 45. The field could then be using the 3D scanning system. Phase (deg) Figure 5. Comparison of the phase of the QZ field predicted by the GRASP simulation with the phase in the laboratory system over a 2 cm diameter QZ Figure 6. Measurements of the co-polarised intensity and cross-polarisation of the QZ field over a 3 cm diameter scan compared with the model prediction. Data is normalised so that the maximum intensity of the co-polarised field in the model is at zero. Fig. 6 shows that the diagonal co-polarised intensity exhibits larger deviations from the model when compared with Fig. 4 (φ= ), particularly at radii greater
5 than 5 cm. The cross-polarisation is also significantly higher than predicted across the entire 3 cm diameter scan zone. Most noticeable is the lack of a dip near zero. It is expected that this high crosspolarisation can be in part attributed to the field probe used for data collection and part to the manufacture error of the corrugated horn. Z (cm) Z (cm) Figure 7: Top: Beam evolution predicted from the GRASP model. Bottom: Evolution of the beam from the CTR system using a circular to rectangular waveguide transition as a field probe. 5.4 Beam evolution db In order to further test the alignment of this measurement system, further field scans were conducted at increasing distances from the main-reflector along the z-axis. Fig. 7 illustrates how the QZ beam evolves along the z-axis. Both model simulations and the laboratory measurements are shown. The field db exhibits ripples associated with the performances of the feed pattern and diffraction effects [1]. Artefacts in the outer beam region are also observed due to reflections from the edge of the sub- reflector. 6. COMPONENT CHARACTERISATION 6.1 RF properties of materials A useful parameter when describing a dielectric is its permittivity (or refractive index). The knowledge of a material's refractive index is important as it describes how the material will interact with an external electric field and will be crucial to model the RF properties of the QO components that we are developing. When a SUT is placed in the set-up, the resulting S-parameter, corresponding to reflections, has a series of troughs at specific frequencies due to destructive interference within the sample, as shown in Fig Frequency (GHz) Figure 8. Illustration of the pattern in reflected power due to destructive interference within a 2.8 mm thick sample of Ultra-High-Molecular-Weight- Polyethylene (UHMWPE). The position of the troughs is given by Eq. 1.!!!!! =! (1) where α is an unknown integer corresponding to the number of half-wavelengths in the sample, λ is the free-space wavelength, n is the refractive index of the sample and d is the sample thickness. Using an initial guess for the refractive index that is close to its true value, the integer, α, can be found for the first trough in
6 the series. For each consecutive trough the value of α simply increases by 1. Samples of 8.3mm thick Ultra-High-Molecular-Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE) and 2.8 mm thick Polypropylene (PP) were both characterised using an initial guess for the refractive index of 1.5. The results are shown in Table 1 and 2 respectively. The two main sources of error are identified to be due to inhomogeneities in the sample thickness and sample positioning errors during the characterisation process. The later error can be determined by repeating the procedure multiple times to determine a statistical error. For each result only the most dominant error has been quoted, and this varied between individual measurements. Table 1. Measurements of the refractive index of Ultra- High-Molecular-Weight Polyethylene. Frequency (GHz) Refractive index ± ± ±.7 Table 2. Measurements of the refractive index of Polypropylene. Frequency (GHz) Refractive index ±.1 7. CONCLUSION order to limit the standing waves created by reflections of the SUTs, which can impact their RF performance. The use of the time domain gating function of the VNA can limit their effects. Another solution would be to perform an average across the spectral bandwidth. REFERENCES [1] F. Ozturk, B. Maffei, and M.W. Ng, A quasioptical free-space s-parameters measurement system for material characterization in W and Ka bands, Proceedings of the 33rd ESA Antenna Workshop on Challenges for Space Antenna Systems, ser. ESA Special Publication, 211 [2] B. Maffei, et. al., Effects of quasi-optical components on feed-horn co- and cross-polarisation radiation patterns, Proc. of SPIE, Vol. 72, 722H- 1, 28 [3] P. Schemmel et al, A near field 3D scanner for millimeter wavelegths, these proceedings [4] G. F. Engen and C. A. Hoer, Thru-reflect-line: An improved technique for calibrating the dual six port automatic network analyzer, IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech., vol. MTT-27, no. 12, pp , Dec [5] D. Bourreau, A. Péden, and S. L. Maguer, A Quasi- Optical Free-Space Measurement Setup Without Time- Domain Gating for Material Characterization in the W- Band, IEEE Transactions on instrumentation and measurement, vol. 55, no. 6, December 26 [6] GRASP available online at the web address: In this paper, the alignment techniques and TRL calibration for the CTR system operating in the W-band have been discussed. In addition, the QZ field has been and it has been compared against a model created in GRASP. The field characteristics exhibit a maximum intensity variation of 4.5 db and maximum phase variation of 7 over a 1 cm diameter QZ. Measurements of the cross-polarisation indicate higher levels than were predicted however further work needs to be done in this area in terms of limiting the effects of the field probe on these measurements. First measurements of materials have also been conducted in the system. The refractive index of UHMWPE and PP was extracted from the s-parameters to be 1.517±.1 at 95.5 GHz and 1.56±.1 at 18 GHz respectively. Improvements of this system need to be performed in
Revisiting the ALMA Band 1 Optics Design P. Zorzi 1, D. Henke 2, S. Claude 2, P. Mena 1, L. Bronfman 3, and J. May 3
 Revisiting the ALMA Band 1 Optics Design P. Zorzi 1, D. Henke 2, S. Claude 2, P. Mena 1, L. Bronfman 3, and J. May 3 1 Department of Electrical Engineering, Universidad de Chile, Santiago, Chile 2 NRC
Revisiting the ALMA Band 1 Optics Design P. Zorzi 1, D. Henke 2, S. Claude 2, P. Mena 1, L. Bronfman 3, and J. May 3 1 Department of Electrical Engineering, Universidad de Chile, Santiago, Chile 2 NRC
Quasi-Optical Design and Analysis (MBI) Créidhe O Sullivan, J.Anthony Murphy, Marcin Gradziel, Neil Trappe, Tully Peacocke & graduate students
 Quasi-Optical Design and Analysis (MBI) Créidhe O Sullivan, J.Anthony Murphy, Marcin Gradziel, Neil Trappe, Tully Peacocke & graduate students Outline Corrugated Horns Analysis Techniques MBI/MODAL 2 Analysis
Quasi-Optical Design and Analysis (MBI) Créidhe O Sullivan, J.Anthony Murphy, Marcin Gradziel, Neil Trappe, Tully Peacocke & graduate students Outline Corrugated Horns Analysis Techniques MBI/MODAL 2 Analysis
Final Design and Testing of the 94 GHz Quasi-Optical-Feed for the EarthCARE S Cloud Profiling Radar
 Final Design and Testing of the 94 GHz Quasi-Optical-Feed for the EarthCARE S Cloud Profiling Radar J. Hartmann #, Chr. Hartwanger #, R. Wylde +, C. Cappellin*, H. Horie x # Astrium GmbH - Satellites,
Final Design and Testing of the 94 GHz Quasi-Optical-Feed for the EarthCARE S Cloud Profiling Radar J. Hartmann #, Chr. Hartwanger #, R. Wylde +, C. Cappellin*, H. Horie x # Astrium GmbH - Satellites,
THE RELATIVE permittivity is an important electrical
 2022 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INSTRUMENTATION AND MEASUREMENT, VOL. 55, NO. 6, DECEMBER 2006 A Quasi-Optical Free-Space Measurement Setup Without Time-Domain Gating for Material Characterization in the W -Band
2022 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INSTRUMENTATION AND MEASUREMENT, VOL. 55, NO. 6, DECEMBER 2006 A Quasi-Optical Free-Space Measurement Setup Without Time-Domain Gating for Material Characterization in the W -Band
feed. The fundamental principle of the matched feed depends on the field matching
 CHAPTER-2 MATCHED FEED FOR OFFSET REFLECTOR ANTENNA The primary objective of this chapter is to discuss the basic concept of matched feed. The fundamental principle of the matched feed depends on the field
CHAPTER-2 MATCHED FEED FOR OFFSET REFLECTOR ANTENNA The primary objective of this chapter is to discuss the basic concept of matched feed. The fundamental principle of the matched feed depends on the field
Measuring Complex Permittivity, Permeability, or Sheet Impedance of Materials at Microwave Frequencies with a Free-Space Focused Beam
 1. Scope Measuring Complex Permittivity, Permeability, or Sheet Impedance of Materials at Microwave Frequencies with a Free-Space Focused Beam 1.1 This test method covers a procedure for determining relative
1. Scope Measuring Complex Permittivity, Permeability, or Sheet Impedance of Materials at Microwave Frequencies with a Free-Space Focused Beam 1.1 This test method covers a procedure for determining relative
STATISTICS OF MULTIPLE EXTRANEOUS SIGNALS ON A COMPACT RANGE
 STATISTICS OF MULTIPLE EXTRANEOUS SIGNALS ON A COMPACT RANGE by John R. Jones and Esko A. Jaska Microwave and Antenna Technology Development Laboratory Georgia Tech Research Institute Georgia Institute
STATISTICS OF MULTIPLE EXTRANEOUS SIGNALS ON A COMPACT RANGE by John R. Jones and Esko A. Jaska Microwave and Antenna Technology Development Laboratory Georgia Tech Research Institute Georgia Institute
Astronomy 203 practice final examination
 Astronomy 203 practice final examination Fall 1999 If this were a real, in-class examination, you would be reminded here of the exam rules, which are as follows: You may consult only one page of formulas
Astronomy 203 practice final examination Fall 1999 If this were a real, in-class examination, you would be reminded here of the exam rules, which are as follows: You may consult only one page of formulas
Measuring Complex Permittivity, Permeability, or Sheet Impedance of Materials at Microwave Frequencies with a Free-Space Spot Probe System
 1. Scope Measuring Complex Permittivity, Permeability, or Sheet Impedance of Materials at Microwave Frequencies with a Free-Space Spot Probe System 1.1 This test method covers a procedure for determining
1. Scope Measuring Complex Permittivity, Permeability, or Sheet Impedance of Materials at Microwave Frequencies with a Free-Space Spot Probe System 1.1 This test method covers a procedure for determining
Atmospheric Lidar The Atmospheric Lidar (ATLID) is a high-spectral resolution lidar and will be the first of its type to be flown in space.
 www.esa.int EarthCARE mission instruments ESA s EarthCARE satellite payload comprises four instruments: the Atmospheric Lidar, the Cloud Profiling Radar, the Multi-Spectral Imager and the Broad-Band Radiometer.
www.esa.int EarthCARE mission instruments ESA s EarthCARE satellite payload comprises four instruments: the Atmospheric Lidar, the Cloud Profiling Radar, the Multi-Spectral Imager and the Broad-Band Radiometer.
CROSS-POLARISATION AND ASTIGMATISM IN MATCHING GROOVES. James W. Lamb. Abstract. Introduction
 159 CROSS-POLARISATION AND ASTIGMATISM IN MATCHING GROOVES James W. Lamb IRAM, 300 rue de la Piscine F-38406 St-Martin d'hères France Abstract Circular grooves are frequently cut in dielectric lenses and
159 CROSS-POLARISATION AND ASTIGMATISM IN MATCHING GROOVES James W. Lamb IRAM, 300 rue de la Piscine F-38406 St-Martin d'hères France Abstract Circular grooves are frequently cut in dielectric lenses and
Design and cold test of an S-band waveguide dual circular polarizer
 Radiation Detection Technology and Methods (017) 1:6 https://doi.org/10.1007/s41605-017-008-9 ORIGINAL PAPER Design and cold test of an S-band waveguide dual circular polarizer Jie Lei 1, Xiang He 1 Guo-Xi
Radiation Detection Technology and Methods (017) 1:6 https://doi.org/10.1007/s41605-017-008-9 ORIGINAL PAPER Design and cold test of an S-band waveguide dual circular polarizer Jie Lei 1, Xiang He 1 Guo-Xi
CHARACTERIZATION OF MAGNETICALLY LOADED MICROWAVE ABSORBERS
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research B, Vol. 33, 277 289, 2011 CHARACTERIZATION OF MAGNETICALLY LOADED MICROWAVE ABSORBERS I. Zivkovic * and A. Murk Institute of Applied Physics, University of Bern Siedlerstrasse
Progress In Electromagnetics Research B, Vol. 33, 277 289, 2011 CHARACTERIZATION OF MAGNETICALLY LOADED MICROWAVE ABSORBERS I. Zivkovic * and A. Murk Institute of Applied Physics, University of Bern Siedlerstrasse
Villa Galileo Firenze, 12 ottobre 2017 Antenna Pattern Measurement: Theory and Techniques
 Villa Galileo Firenze, 12 ottobre 2017 Antenna Pattern Measurement: Theory and Techniques F. D Agostino, M. Migliozzi University of Salerno, Italy ANTENNAE REGIONS The REACTIVE NEAR-FIELD REGION is the
Villa Galileo Firenze, 12 ottobre 2017 Antenna Pattern Measurement: Theory and Techniques F. D Agostino, M. Migliozzi University of Salerno, Italy ANTENNAE REGIONS The REACTIVE NEAR-FIELD REGION is the
! #! % && ( ) ) +++,. # /0 % 1 /21/ 3 && & 44&, &&7 4/ 00
 ! #! % && ( ) ) +++,. # /0 % 1 /21/ 3 &&4 2 05 6. 4& 44&, &&7 4/ 00 8 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ANTENNAS AND PROPAGATION, VOL. 56, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2008 345 Moment Method Analysis of an Archimedean Spiral Printed
! #! % && ( ) ) +++,. # /0 % 1 /21/ 3 &&4 2 05 6. 4& 44&, &&7 4/ 00 8 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ANTENNAS AND PROPAGATION, VOL. 56, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2008 345 Moment Method Analysis of an Archimedean Spiral Printed
In-Flight Retrieval of Reflector Anomalies for the Planck Space Telescope
 Presented at The 4 th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EuCAP 2010), Barcelona, Spain, 12-16 April 2010. In-Flight Retrieval of Reflector Anomalies for the Planck Space Telescope Frank Jensen*,
Presented at The 4 th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EuCAP 2010), Barcelona, Spain, 12-16 April 2010. In-Flight Retrieval of Reflector Anomalies for the Planck Space Telescope Frank Jensen*,
Multiphysics Simulation of Polymer-Based Filters for Sub-Millimetre Space Optics
 Multiphysics Simulation of Polymer-Based Filters for Sub-Millimetre Space Optics N. Baccichet 1, G. Savini 1 1 Department of Physics and Astronomy, University College London, London, UK Sponsored by: EU
Multiphysics Simulation of Polymer-Based Filters for Sub-Millimetre Space Optics N. Baccichet 1, G. Savini 1 1 Department of Physics and Astronomy, University College London, London, UK Sponsored by: EU
Part I. The Quad-Ridged Flared Horn
 9 Part I The Quad-Ridged Flared Horn 10 Chapter 2 Key Requirements of Radio Telescope Feeds Almost all of today s radio telescopes operating above 0.5 GHz use reflector antennas consisting of one or more
9 Part I The Quad-Ridged Flared Horn 10 Chapter 2 Key Requirements of Radio Telescope Feeds Almost all of today s radio telescopes operating above 0.5 GHz use reflector antennas consisting of one or more
Radio Observation of Milky Way at MHz. Amateur Radio Astronomy Observation of the Milky Way at MHz from the Northern Hemisphere
 Amateur Radio Astronomy Observation of the Milky Way at 1453.5MHz from the Northern Hemisphere Dr David Morgan February 2011 Introduction The measurements reported here were made in March and April 2007
Amateur Radio Astronomy Observation of the Milky Way at 1453.5MHz from the Northern Hemisphere Dr David Morgan February 2011 Introduction The measurements reported here were made in March and April 2007
J.-C. Zhang, Y.-Z. Yin, and J.-P. Ma National Laboratory of Antennas and Microwave Technology Xidian University Xi an, Shaanxi , P. R.
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 6, 55 60, 2009 MULTIFUNCTIONAL MEANDER LINE POLARIZER J.-C. Zhang, Y.-Z. Yin, and J.-P. Ma National Laboratory of Antennas and Microwave Technology Xidian
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 6, 55 60, 2009 MULTIFUNCTIONAL MEANDER LINE POLARIZER J.-C. Zhang, Y.-Z. Yin, and J.-P. Ma National Laboratory of Antennas and Microwave Technology Xidian
Creation of a gradient index structure inside foam material - Microwave application for a lens antenna at 60 GHz
 Creation of a gradient index structure inside foam material - Microwave application for a lens antenna at 60 GHz Jonathan Bor, Olivier Lafond, Mohamed Himdi To cite this version: Jonathan Bor, Olivier
Creation of a gradient index structure inside foam material - Microwave application for a lens antenna at 60 GHz Jonathan Bor, Olivier Lafond, Mohamed Himdi To cite this version: Jonathan Bor, Olivier
LECTURE 18: Horn Antennas (Rectangular horn antennas. Circular apertures.) Equation Section 18
 LCTUR 18: Horn Antennas (Rectangular horn antennas. Circular apertures.) quation Section 18 1 Rectangular horn antennas Horn antennas are popular in the microwave band (above 1 GHz). Horns provide high
LCTUR 18: Horn Antennas (Rectangular horn antennas. Circular apertures.) quation Section 18 1 Rectangular horn antennas Horn antennas are popular in the microwave band (above 1 GHz). Horns provide high
Ultra-narrow-band tunable laserline notch filter
 Appl Phys B (2009) 95: 597 601 DOI 10.1007/s00340-009-3447-6 Ultra-narrow-band tunable laserline notch filter C. Moser F. Havermeyer Received: 5 December 2008 / Revised version: 2 February 2009 / Published
Appl Phys B (2009) 95: 597 601 DOI 10.1007/s00340-009-3447-6 Ultra-narrow-band tunable laserline notch filter C. Moser F. Havermeyer Received: 5 December 2008 / Revised version: 2 February 2009 / Published
Design and Characterization of a Dual-Band Metamaterial Absorber Based on Destructive Interferences
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 47, 95, 24 Design and Characterization of a Dual-Band Metamaterial Absorber Based on Destructive Interferences Saeid Jamilan, *, Mohammad N. Azarmanesh, and
Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 47, 95, 24 Design and Characterization of a Dual-Band Metamaterial Absorber Based on Destructive Interferences Saeid Jamilan, *, Mohammad N. Azarmanesh, and
Author(s) Tamayama, Y; Nakanishi, T; Sugiyama. Citation PHYSICAL REVIEW B (2006), 73(19)
 Observation of Brewster's effect fo Titleelectromagnetic waves in metamateri theory Author(s) Tamayama, Y; Nakanishi, T; Sugiyama Citation PHYSICAL REVIEW B (2006), 73(19) Issue Date 2006-05 URL http://hdl.handle.net/2433/39884
Observation of Brewster's effect fo Titleelectromagnetic waves in metamateri theory Author(s) Tamayama, Y; Nakanishi, T; Sugiyama Citation PHYSICAL REVIEW B (2006), 73(19) Issue Date 2006-05 URL http://hdl.handle.net/2433/39884
Large Scale Polarization Explorer
 Science goal and performance (Univ. Roma La Sapienza) for the LSPE collaboration Page 1 LSPE is a balloon payload aimed at: Measure large scale CMB polarization and temperature anisotropies Explore large
Science goal and performance (Univ. Roma La Sapienza) for the LSPE collaboration Page 1 LSPE is a balloon payload aimed at: Measure large scale CMB polarization and temperature anisotropies Explore large
Gradient-index metamaterials and spoof surface plasmonic waveguide
 Gradient-index metamaterials and spoof surface plasmonic waveguide Hui Feng Ma State Key Laboratory of Millimeter Waves Southeast University, Nanjing 210096, China City University of Hong Kong, 11 October
Gradient-index metamaterials and spoof surface plasmonic waveguide Hui Feng Ma State Key Laboratory of Millimeter Waves Southeast University, Nanjing 210096, China City University of Hong Kong, 11 October
POLARISATION DEPENDENT SCATTERING FROM THE SERRATIONS OF COMPACT RANGES 1
 Paper presented at Antenna Measurement Techniques Association 29 th Annual Symposium (AMTA 2007), St. Louis, MO, USA, 4-9 November 2007, Proceedings pp. 150-155 (Session 5). POLARISATION DEPENDENT SCATTERING
Paper presented at Antenna Measurement Techniques Association 29 th Annual Symposium (AMTA 2007), St. Louis, MO, USA, 4-9 November 2007, Proceedings pp. 150-155 (Session 5). POLARISATION DEPENDENT SCATTERING
Current Antenna Research at NIST
 Current Antenna Research at NIST Perry Wilson Electromagnetics Division National Institute of Standards and Technology B O U L D E R, C O L O R A D O 1 NIST Organizational Structure B O U L D E R, C O
Current Antenna Research at NIST Perry Wilson Electromagnetics Division National Institute of Standards and Technology B O U L D E R, C O L O R A D O 1 NIST Organizational Structure B O U L D E R, C O
A Novel Design of Photonic Crystal Lens Based on Negative Refractive Index
 PIERS ONLINE, VOL. 4, NO. 2, 2008 296 A Novel Design of Photonic Crystal Lens Based on Negative Refractive Index S. Haxha 1 and F. AbdelMalek 2 1 Photonics Group, Department of Electronics, University
PIERS ONLINE, VOL. 4, NO. 2, 2008 296 A Novel Design of Photonic Crystal Lens Based on Negative Refractive Index S. Haxha 1 and F. AbdelMalek 2 1 Photonics Group, Department of Electronics, University
Application of Electromagnetic Waves in Damage Detection of Concrete Structures
 Application of Electromagnetic Waves in Damage Detection of Concrete Structures Maria Q. Feng a, Franco De Flaviis b, Yoo Jin Kim a, and Rudy Diaz c a Dept. of Civil and Environmental Engineering, University
Application of Electromagnetic Waves in Damage Detection of Concrete Structures Maria Q. Feng a, Franco De Flaviis b, Yoo Jin Kim a, and Rudy Diaz c a Dept. of Civil and Environmental Engineering, University
Radio Astronomy with a Satellite Dish
 Radio Astronomy with a Satellite Dish Michael Gaylard Hartebeesthoek Radio Astronomy Observatory September 13, 2012 1 Theory 1.1 Radio Waves Radio waves are electromagnetic waves having wavelengths greater
Radio Astronomy with a Satellite Dish Michael Gaylard Hartebeesthoek Radio Astronomy Observatory September 13, 2012 1 Theory 1.1 Radio Waves Radio waves are electromagnetic waves having wavelengths greater
Laser Optics-II. ME 677: Laser Material Processing Instructor: Ramesh Singh 1
 Laser Optics-II 1 Outline Absorption Modes Irradiance Reflectivity/Absorption Absorption coefficient will vary with the same effects as the reflectivity For opaque materials: reflectivity = 1 - absorptivity
Laser Optics-II 1 Outline Absorption Modes Irradiance Reflectivity/Absorption Absorption coefficient will vary with the same effects as the reflectivity For opaque materials: reflectivity = 1 - absorptivity
Modeling the quasi-optical performance of CMB astronomical interferometers
 Modeling the quasi-optical performance of CMB astronomical interferometers Gareth S. Curran* a, Marcin L. Gradziel b, Créidhe O Sullivan b, J. Anthony Murphy b, Andrei Korotkov c, Siddharth Malu d, Peter
Modeling the quasi-optical performance of CMB astronomical interferometers Gareth S. Curran* a, Marcin L. Gradziel b, Créidhe O Sullivan b, J. Anthony Murphy b, Andrei Korotkov c, Siddharth Malu d, Peter
Antenna measurements
 Course on Microwave Measurements Antenna measurements Prof. Luca Perregrini Dept. of Electrical, Computer and Biomedical Engineering University of Pavia e-mail: luca.perregrini@unipv.it web: microwave.unipv.it
Course on Microwave Measurements Antenna measurements Prof. Luca Perregrini Dept. of Electrical, Computer and Biomedical Engineering University of Pavia e-mail: luca.perregrini@unipv.it web: microwave.unipv.it
Supplementary Materials for
 wwwsciencemagorg/cgi/content/full/scienceaaa3035/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Spatially structured photons that travel in free space slower than the speed of light Daniel Giovannini, Jacquiline Romero,
wwwsciencemagorg/cgi/content/full/scienceaaa3035/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Spatially structured photons that travel in free space slower than the speed of light Daniel Giovannini, Jacquiline Romero,
TM-Radiation From an Obliquely Flanged Parallel-Plate Waveguide
 1534 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ANTENNAS AND PROPAGATION, VOL. 50, NO. 11, NOVEMBER 2002 TM-Radiation From an Obliquely Flanged Parallel-Plate Waveguide Jae Yong Kwon, Member, IEEE, Jae Wook Lee, Associate Member,
1534 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ANTENNAS AND PROPAGATION, VOL. 50, NO. 11, NOVEMBER 2002 TM-Radiation From an Obliquely Flanged Parallel-Plate Waveguide Jae Yong Kwon, Member, IEEE, Jae Wook Lee, Associate Member,
FEASIBILITY STUDY FOR THE FOCALISATION OF THE NEW 40m RADIOTELESCOPE OF CENTRO ASTRONÓMICO DE YEBES
 Thirteenth international Symposium on Space Terahertz Technology, Harvard University, March 2002. FEASIBILITY STUDY FOR THE FOCALISATION OF THE NEW 40m RADIOTELESCOPE OF CENTRO ASTRONÓMICO DE YEBES E.
Thirteenth international Symposium on Space Terahertz Technology, Harvard University, March 2002. FEASIBILITY STUDY FOR THE FOCALISATION OF THE NEW 40m RADIOTELESCOPE OF CENTRO ASTRONÓMICO DE YEBES E.
Electromagnetic Implosion Using a Lens
 Sensor and Simulation Notes Note 516 July 2006 Electromagnetic Implosion Using a Lens Carl E. Baum University of New Mexico Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Albuquerque New Mexico 87131
Sensor and Simulation Notes Note 516 July 2006 Electromagnetic Implosion Using a Lens Carl E. Baum University of New Mexico Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Albuquerque New Mexico 87131
RF properties. of the Planck telescope. Designed by ALCATEL. CASE No. 1. Per Heighwood Nielsen
 TICRA engineering consultants communications systems and antennas RF properties of the Planck telescope Designed by ALCATEL CASE No. 1 November, 1999 S-801-04 Author: Per Heighwood Nielsen TICRA KRON PRINSENS
TICRA engineering consultants communications systems and antennas RF properties of the Planck telescope Designed by ALCATEL CASE No. 1 November, 1999 S-801-04 Author: Per Heighwood Nielsen TICRA KRON PRINSENS
Polarization of Light and Birefringence of Materials
 Polarization of Light and Birefringence of Materials Ajit Balagopal (Team Members Karunanand Ogirala, Hui Shen) ECE 614- PHOTONIC INFORMATION PROCESSING LABORATORY Abstract-- In this project, we study
Polarization of Light and Birefringence of Materials Ajit Balagopal (Team Members Karunanand Ogirala, Hui Shen) ECE 614- PHOTONIC INFORMATION PROCESSING LABORATORY Abstract-- In this project, we study
Characterising Properties and Loss in High Powered Metamaterials
 Characterising Properties and Loss in High Powered Metamaterials Aimée Hopper PhD Student Supervisor: R. Seviour International Institute for Accelerator Applications University of Huddersfield (UK) Email:
Characterising Properties and Loss in High Powered Metamaterials Aimée Hopper PhD Student Supervisor: R. Seviour International Institute for Accelerator Applications University of Huddersfield (UK) Email:
Lab #13: Polarization
 Lab #13: Polarization Introduction In this experiment we will investigate various properties associated with polarized light. We will study both its generation and application. Real world applications
Lab #13: Polarization Introduction In this experiment we will investigate various properties associated with polarized light. We will study both its generation and application. Real world applications
P5 Revision Questions
 P5 Revision Questions Part 2 Question 1 How can microwaves be used to communicate? Answer 1 Sent from transmitter, received and amplified by satellite in space, re-transmitted back to earth and picked
P5 Revision Questions Part 2 Question 1 How can microwaves be used to communicate? Answer 1 Sent from transmitter, received and amplified by satellite in space, re-transmitted back to earth and picked
LECTURE 11 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES & POLARIZATION. Instructor: Kazumi Tolich
 LECTURE 11 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES & POLARIZATION Instructor: Kazumi Tolich Lecture 11 2 25.5 Electromagnetic waves Induced fields Properties of electromagnetic waves Polarization Energy of electromagnetic
LECTURE 11 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES & POLARIZATION Instructor: Kazumi Tolich Lecture 11 2 25.5 Electromagnetic waves Induced fields Properties of electromagnetic waves Polarization Energy of electromagnetic
Millimetre Wave Reflectarray Antenna Unit Cell Measurements
 Millimetre Wave Reflectarray Antenna Unit Cell Measurements G. Ahmad*, T. W. C. Brown*, C. I. Underwood*, T. H. Loh * University of Surrey, UK, g.ahmad@surrey.ac.uk, National Physical Laboratory (NPL),UK
Millimetre Wave Reflectarray Antenna Unit Cell Measurements G. Ahmad*, T. W. C. Brown*, C. I. Underwood*, T. H. Loh * University of Surrey, UK, g.ahmad@surrey.ac.uk, National Physical Laboratory (NPL),UK
Quasi-optical beam waveguide analysis using frame based Gaussian beam expansion
 Thirteenth international Symposium on Space Terahertz Technology, Harvard University, March 2002. Quasi-optical beam waveguide analysis using frame based Gaussian beam expansion Torsten Bondw and Stig
Thirteenth international Symposium on Space Terahertz Technology, Harvard University, March 2002. Quasi-optical beam waveguide analysis using frame based Gaussian beam expansion Torsten Bondw and Stig
Polarimetry. Dave McConnell, CASS Radio Astronomy School, Narrabri 30 September kpc. 8.5 GHz B-vectors Perley & Carilli (1996)
 VLA @ 8.5 GHz B-vectors Perley & Carilli (1996) 10 kpc Polarimetry Dave McConnell, CASS Radio Astronomy School, Narrabri 30 September 2010 1 Electro-magnetic waves are polarized E H S = c/4π (E H) S E/M
VLA @ 8.5 GHz B-vectors Perley & Carilli (1996) 10 kpc Polarimetry Dave McConnell, CASS Radio Astronomy School, Narrabri 30 September 2010 1 Electro-magnetic waves are polarized E H S = c/4π (E H) S E/M
POLARIZATION OF LIGHT
 POLARIZATION OF LIGHT OVERALL GOALS The Polarization of Light lab strongly emphasizes connecting mathematical formalism with measurable results. It is not your job to understand every aspect of the theory,
POLARIZATION OF LIGHT OVERALL GOALS The Polarization of Light lab strongly emphasizes connecting mathematical formalism with measurable results. It is not your job to understand every aspect of the theory,
Technique for the electric and magnetic parameter measurement of powdered materials
 Computational Methods and Experimental Measurements XIV 41 Technique for the electric and magnetic parameter measurement of powdered materials R. Kubacki,. Nowosielski & R. Przesmycki Faculty of Electronics,
Computational Methods and Experimental Measurements XIV 41 Technique for the electric and magnetic parameter measurement of powdered materials R. Kubacki,. Nowosielski & R. Przesmycki Faculty of Electronics,
PHY410 Optics Exam #3
 PHY410 Optics Exam #3 NAME: 1 2 Multiple Choice Section - 5 pts each 1. A continuous He-Ne laser beam (632.8 nm) is chopped, using a spinning aperture, into 500 nanosecond pulses. Compute the resultant
PHY410 Optics Exam #3 NAME: 1 2 Multiple Choice Section - 5 pts each 1. A continuous He-Ne laser beam (632.8 nm) is chopped, using a spinning aperture, into 500 nanosecond pulses. Compute the resultant
Vector diffraction theory of refraction of light by a spherical surface
 S. Guha and G. D. Gillen Vol. 4, No. 1/January 007/J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 1 Vector diffraction theory of refraction of light by a spherical surface Shekhar Guha and Glen D. Gillen* Materials and Manufacturing
S. Guha and G. D. Gillen Vol. 4, No. 1/January 007/J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 1 Vector diffraction theory of refraction of light by a spherical surface Shekhar Guha and Glen D. Gillen* Materials and Manufacturing
USAGE OF NUMERICAL METHODS FOR ELECTROMAGNETIC SHIELDS OPTIMIZATION
 October 4-6, 2007 - Chiinu, Rep.Moldova USAGE OF NUMERICAL METHODS FOR ELECTROMAGNETIC SHIELDS OPTIMIZATION Ionu- P. NICA, Valeriu Gh. DAVID, /tefan URSACHE Gh. Asachi Technical University Iai, Faculty
October 4-6, 2007 - Chiinu, Rep.Moldova USAGE OF NUMERICAL METHODS FOR ELECTROMAGNETIC SHIELDS OPTIMIZATION Ionu- P. NICA, Valeriu Gh. DAVID, /tefan URSACHE Gh. Asachi Technical University Iai, Faculty
Constitutive parameter extraction and experimental validation of single and double negative metamaterials Y. Hollander 1 R.
 Published in IET Microwaves, Antennas & Propagation Received on 20th January 2010 Revised on 27th May 2010 ISSN 1751-8725 Constitutive parameter extraction and experimental validation of single and double
Published in IET Microwaves, Antennas & Propagation Received on 20th January 2010 Revised on 27th May 2010 ISSN 1751-8725 Constitutive parameter extraction and experimental validation of single and double
Beam Scan Properties of Nonparabolic Reflectors. P.J. N a p ie r National Radio Astronomy Observatory, Socorro, New Mexico 87801
 NLSRT Memo No.. / / ' /ft Beam Scan Properties of Nonparabolic Reflectors P.J. N a p ie r National Radio Astronomy Observatory, Socorro, New Mexico 87801 Abstract. Nonparabolic reflector systems such as
NLSRT Memo No.. / / ' /ft Beam Scan Properties of Nonparabolic Reflectors P.J. N a p ie r National Radio Astronomy Observatory, Socorro, New Mexico 87801 Abstract. Nonparabolic reflector systems such as
6 th International Conference on Electromagnetic Wave Interaction with Water and Moist Substances
 6 th International Conference on Electromagnetic Wave Interaction with Water and Moist Substances Papers, Posters and Exhibits Conference Proceedings + CD-ROM Editor: Klaus Kupfer Co-Editors: Christof
6 th International Conference on Electromagnetic Wave Interaction with Water and Moist Substances Papers, Posters and Exhibits Conference Proceedings + CD-ROM Editor: Klaus Kupfer Co-Editors: Christof
Courtesy of ESS and TheRGA web pages part of a series of application and theory notes for public use which are provided free of charge by ESS.
 ESS The RGA freenotes Theory page 1 of 14 RGA Theory Notes Courtesy of ESS and TheRGA web pages part of a series of application and theory notes for public use which are provided free of charge by ESS.
ESS The RGA freenotes Theory page 1 of 14 RGA Theory Notes Courtesy of ESS and TheRGA web pages part of a series of application and theory notes for public use which are provided free of charge by ESS.
A REVISED PROPOSAL FOR A FEED SYSTEM FOR THE VLBA ANTENNA P. J. NAPIER 1/11/82 INTRODUCTION
 A REVISED PROPOSAL FOR A FEED SYSTEM FOR THE VLBA ANTENNA P. J. NAPIER 1/11/82 INTRODUCTION In a previous report a concept for a feed system for the VLBA antenna was presented. Further study of the problem
A REVISED PROPOSAL FOR A FEED SYSTEM FOR THE VLBA ANTENNA P. J. NAPIER 1/11/82 INTRODUCTION In a previous report a concept for a feed system for the VLBA antenna was presented. Further study of the problem
Displaced-Axis-Ellipse Reflector Antenna for Spacecraft Communications
 Displaced-Axis-Ellipse Reflector Antenna for Spacecraft Communications Aluizio Prata, Jr., Fernando J. S. Moreira, and Luis R. Amaro Abstract This work discusses the electrical characteristics of axially-symmetric
Displaced-Axis-Ellipse Reflector Antenna for Spacecraft Communications Aluizio Prata, Jr., Fernando J. S. Moreira, and Luis R. Amaro Abstract This work discusses the electrical characteristics of axially-symmetric
PROOF-OF-CONCEPT DEMONSTRATION OF A MILLIMETRE WAVE IMAGING SOUNDER FOR GEOSTATIONARY EARTH ORBIT
 PROOF-OF-CONCEPT DEMONSTRATION OF A MILLIMETRE WAVE IMAGING SOUNDER FOR GEOSTATIONARY EARTH ORBIT Anders Carlström 1, Jacob Christensen 1, Anders Emrich 2, Johan Embretsén 2, Karl-Erik Kempe 2, and Peter
PROOF-OF-CONCEPT DEMONSTRATION OF A MILLIMETRE WAVE IMAGING SOUNDER FOR GEOSTATIONARY EARTH ORBIT Anders Carlström 1, Jacob Christensen 1, Anders Emrich 2, Johan Embretsén 2, Karl-Erik Kempe 2, and Peter
One-Dimensional Numerical Solution of the Maxwell-Minkowski Equations
 Tamkang Journal of Science and Engineering, Vol. 12, No. 2, pp. 161168 (2009) 161 One-Dimensional Numerical Solution of the Maxwell-Minkowski Equations Mingtsu Ho 1 and Yao-Han Chen 2 1 Department of Electronic
Tamkang Journal of Science and Engineering, Vol. 12, No. 2, pp. 161168 (2009) 161 One-Dimensional Numerical Solution of the Maxwell-Minkowski Equations Mingtsu Ho 1 and Yao-Han Chen 2 1 Department of Electronic
Manipulation of circular polarised electromagnetic waves by artificial periodic structures (Invited Paper)
 Manipulation of circular polarised electromagnetic waves b artificial periodic structures (Invited Paper) Zelenchuk, D., & Fusco, V. (215). Manipulation of circular polarised electromagnetic waves b artificial
Manipulation of circular polarised electromagnetic waves b artificial periodic structures (Invited Paper) Zelenchuk, D., & Fusco, V. (215). Manipulation of circular polarised electromagnetic waves b artificial
Shielding Effectiveness of Modern Energy Saving Windows
 Shielding Effectiveness of Modern Energy Saving Windows Žilvinas Kancleris, Head of Microwave laboratory zilvinas.kancleris@ftmc.lt Shielding effectiveness of modern... Before starting my talk I would
Shielding Effectiveness of Modern Energy Saving Windows Žilvinas Kancleris, Head of Microwave laboratory zilvinas.kancleris@ftmc.lt Shielding effectiveness of modern... Before starting my talk I would
BLUE-PRINT II XII Physics
 BLUE-PRINT II XII Physics S.No. UNIT VSA SA I SA II LA Total (1 Mark) (2 Marks) (3Marks) (5 Marks) 1. Electrostatics 1(1) 4(2) 3(1) - 8(4) 2. Current Electricity - 2(1) - 5(1) 7(2) 3. Magnetic Effect of
BLUE-PRINT II XII Physics S.No. UNIT VSA SA I SA II LA Total (1 Mark) (2 Marks) (3Marks) (5 Marks) 1. Electrostatics 1(1) 4(2) 3(1) - 8(4) 2. Current Electricity - 2(1) - 5(1) 7(2) 3. Magnetic Effect of
Lecture 36 Date:
 Lecture 36 Date: 5.04.04 Reflection of Plane Wave at Oblique Incidence (Snells Law, Brewster s Angle, Parallel Polarization, Perpendicular Polarization etc.) Introduction to RF/Microwave Introduction One
Lecture 36 Date: 5.04.04 Reflection of Plane Wave at Oblique Incidence (Snells Law, Brewster s Angle, Parallel Polarization, Perpendicular Polarization etc.) Introduction to RF/Microwave Introduction One
Design of an off set optics with high polarization purity and large Focal plane Area for CMB polarization observations
 Designofanoff setopticswith highpolarizationpurityandlargefocal planearea forcmbpolarizationobservations P.Bolli %,E.Carretti *,A.Navarrini % % OsservatorioAstronomicodiCagliari INAF Loc.PoggiodeiPini,Strada54
Designofanoff setopticswith highpolarizationpurityandlargefocal planearea forcmbpolarizationobservations P.Bolli %,E.Carretti *,A.Navarrini % % OsservatorioAstronomicodiCagliari INAF Loc.PoggiodeiPini,Strada54
ZONE PLATE LENS ANTENNAS FOR MILLIMETER AND SUBMILLIMETER WAVELENGTHS
 Third International Symposium on Space Terahertz Technology Page 345 ZONE PLATE LENS ANTENNAS FOR MILLIMETER AND SUBMILLIMETER WAVELENGTHS Paul F. Goldsmith Five College Radio Astronomy Observatory Department
Third International Symposium on Space Terahertz Technology Page 345 ZONE PLATE LENS ANTENNAS FOR MILLIMETER AND SUBMILLIMETER WAVELENGTHS Paul F. Goldsmith Five College Radio Astronomy Observatory Department
High Directivity Horn Antenna of Metamaterial in Terahertz Xiangjin Quan, Shiquan Zhang, Hui Li
 International Power, Electronics and Materials Engineering Conference (IPEMEC 215) High Directivity Horn Antenna of Metamaterial in Terahertz Xiangjin Quan, Shiquan Zhang, Hui Li Engineering University
International Power, Electronics and Materials Engineering Conference (IPEMEC 215) High Directivity Horn Antenna of Metamaterial in Terahertz Xiangjin Quan, Shiquan Zhang, Hui Li Engineering University
Correcting Polarization Distortion in a Compact Range Feed
 Correcting Polarization Distortion in a Compact Range Feed Brett T. alkenhorst, David Tammen NSI-MI Technologies Suwanee, GA 324 bwalkenhorst@nsi-mi.com dtammen@nsi-mi.com Abstract A high quality antenna
Correcting Polarization Distortion in a Compact Range Feed Brett T. alkenhorst, David Tammen NSI-MI Technologies Suwanee, GA 324 bwalkenhorst@nsi-mi.com dtammen@nsi-mi.com Abstract A high quality antenna
Investigation of Coherent Emission from the NSLS VUV Ring
 SPIE Accelerator Based Infrared Sources and Spectroscopic Applications Proc. 3775, 88 94 (1999) Investigation of Coherent Emission from the NSLS VUV Ring G.L. Carr, R.P.S.M. Lobo, J.D. LaVeigne, D.H. Reitze,
SPIE Accelerator Based Infrared Sources and Spectroscopic Applications Proc. 3775, 88 94 (1999) Investigation of Coherent Emission from the NSLS VUV Ring G.L. Carr, R.P.S.M. Lobo, J.D. LaVeigne, D.H. Reitze,
Transmission-Reflection Method to Estimate Permittivity of Polymer
 Transmission-Reflection Method to Estimate Permittivity of Polymer Chanchal Yadav Department of Physics & Electronics, Rajdhani College, University of Delhi, Delhi, India Abstract In transmission-reflection
Transmission-Reflection Method to Estimate Permittivity of Polymer Chanchal Yadav Department of Physics & Electronics, Rajdhani College, University of Delhi, Delhi, India Abstract In transmission-reflection
An Introduction to ASKAP Bringing Radio Interferometers Into the Multi-pixel Era
 An Introduction to ASKAP Bringing Radio Interferometers Into the Multi-pixel Era Aidan Hotan and Lisa Harvey-Smith 3 rd October 2014 CSIRO ASTRONOMY AND SPACE SCIENCE Introducing ASKAP The Australian SKA
An Introduction to ASKAP Bringing Radio Interferometers Into the Multi-pixel Era Aidan Hotan and Lisa Harvey-Smith 3 rd October 2014 CSIRO ASTRONOMY AND SPACE SCIENCE Introducing ASKAP The Australian SKA
A beam of coherent monochromatic light from a distant galaxy is used in an optics experiment on Earth.
 Waves_P2 [152 marks] A beam of coherent monochromatic light from a distant galaxy is used in an optics experiment on Earth. The beam is incident normally on a double slit. The distance between the slits
Waves_P2 [152 marks] A beam of coherent monochromatic light from a distant galaxy is used in an optics experiment on Earth. The beam is incident normally on a double slit. The distance between the slits
8. The Michelson Interferometer
 M 8. The Michelson Interferometer 8.1 Introduction Interference patterns from superposed coherent waves may be used for precise determination of wavelength or, if the wavelength is known, time-of-flight,
M 8. The Michelson Interferometer 8.1 Introduction Interference patterns from superposed coherent waves may be used for precise determination of wavelength or, if the wavelength is known, time-of-flight,
OPSE FINAL EXAM Fall 2016 YOU MUST SHOW YOUR WORK. ANSWERS THAT ARE NOT JUSTIFIED WILL BE GIVEN ZERO CREDIT.
 CLOSED BOOK. Equation Sheet is provided. YOU MUST SHOW YOUR WORK. ANSWERS THAT ARE NOT JUSTIFIED WILL BE GIVEN ZERO CREDIT. ALL NUMERICAL ANSERS MUST HAVE UNITS INDICATED. (Except dimensionless units like
CLOSED BOOK. Equation Sheet is provided. YOU MUST SHOW YOUR WORK. ANSWERS THAT ARE NOT JUSTIFIED WILL BE GIVEN ZERO CREDIT. ALL NUMERICAL ANSERS MUST HAVE UNITS INDICATED. (Except dimensionless units like
Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering. ECE426F Optical Engineering. Final Exam. Dec. 17, 2003.
 Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE426F Optical Engineering Final Exam Dec. 17, 2003 Exam Type: D (Close-book + one 2-sided aid sheet + a non-programmable calculator)
Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE426F Optical Engineering Final Exam Dec. 17, 2003 Exam Type: D (Close-book + one 2-sided aid sheet + a non-programmable calculator)
A Highly Tunable Sub-Wavelength Chiral Structure for Circular Polarizer
 A Highly Tunable Sub-Wavelength Chiral Structure for Circular Polarizer Menglin. L. N. Chen 1, Li Jun Jiang 1, Wei E. I. Sha 1 and Tatsuo Itoh 2 1 Dept. Of EEE, The University Of Hong Kong 2 EE Dept.,
A Highly Tunable Sub-Wavelength Chiral Structure for Circular Polarizer Menglin. L. N. Chen 1, Li Jun Jiang 1, Wei E. I. Sha 1 and Tatsuo Itoh 2 1 Dept. Of EEE, The University Of Hong Kong 2 EE Dept.,
The Einstein Polarization Interferometer for Cosmology (EPIC)
 The Einstein Polarization Interferometer for Cosmology (EPIC) Greg Tucker Brown University for the EPIC collaboration 25 October 2006 BPol Satellite Workshop 1 EPIC Mission Concept Study Team Brown University
The Einstein Polarization Interferometer for Cosmology (EPIC) Greg Tucker Brown University for the EPIC collaboration 25 October 2006 BPol Satellite Workshop 1 EPIC Mission Concept Study Team Brown University
x Contents Segmented Mirror Telescopes Metal and Lightweight Mirrors Mirror Polishing
 Contents 1 Fundamentals of Optical Telescopes... 1 1.1 A Brief History of Optical Telescopes.................... 1 1.2 General Astronomical Requirements..................... 6 1.2.1 Angular Resolution.............................
Contents 1 Fundamentals of Optical Telescopes... 1 1.1 A Brief History of Optical Telescopes.................... 1 1.2 General Astronomical Requirements..................... 6 1.2.1 Angular Resolution.............................
Spectroscopic Measurements of Optical Elements For Submillimeter Receivers
 5- Abstract Spectroscopic Measurements of Optical Elements For Submillimeter Receivers J. Kawamura, S. Paine, and D. C. Papa Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics 60 Garden Street Cambridge, Massachusetts
5- Abstract Spectroscopic Measurements of Optical Elements For Submillimeter Receivers J. Kawamura, S. Paine, and D. C. Papa Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics 60 Garden Street Cambridge, Massachusetts
RESONANT BEHAVIOR MEASUREMENTS AND TWO- DIMENSIONAL IMAGING OF SMALL CONDUCTING SPHERES IN CATR
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 10, 25 35, 2009 RESONANT BEHAVIOR MEASUREMENTS AND TWO- DIMENSIONAL IMAGING OF SMALL CONDUCTING SPHERES IN CATR S. H. Quan and Q. H. Liu Beijing University
Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 10, 25 35, 2009 RESONANT BEHAVIOR MEASUREMENTS AND TWO- DIMENSIONAL IMAGING OF SMALL CONDUCTING SPHERES IN CATR S. H. Quan and Q. H. Liu Beijing University
Full Wave Analysis of RF Signal Attenuation in a Lossy Rough Surface Cave Using a High Order Time Domain Vector Finite Element Method
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Symposium 2006, Cambridge, USA, March 26-29 425 Full Wave Analysis of RF Signal Attenuation in a Lossy Rough Surface Cave Using a High Order Time Domain Vector Finite
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Symposium 2006, Cambridge, USA, March 26-29 425 Full Wave Analysis of RF Signal Attenuation in a Lossy Rough Surface Cave Using a High Order Time Domain Vector Finite
Experiment O-2. The Michelson Interferometer
 Experiment O-2 The Michelson Interferometer The Michelson interferometer is one of the best known and historically important interferometers. It is a very accurate length-measuring device and has been
Experiment O-2 The Michelson Interferometer The Michelson interferometer is one of the best known and historically important interferometers. It is a very accurate length-measuring device and has been
Dr. Linlin Ge The University of New South Wales
 GMAT 9600 Principles of Remote Sensing Week2 Electromagnetic Radiation: Definition & Physics Dr. Linlin Ge www.gmat.unsw.edu.au/linlinge Basic radiation quantities Outline Wave and quantum properties Polarization
GMAT 9600 Principles of Remote Sensing Week2 Electromagnetic Radiation: Definition & Physics Dr. Linlin Ge www.gmat.unsw.edu.au/linlinge Basic radiation quantities Outline Wave and quantum properties Polarization
The Principles of Astronomical Telescope Design
 The Principles of Astronomical Telescope Design Jingquan Cheng National Radio Astronomy Observatory Charlottesville, Virginia,.USA " 4y Springer Fundamentals of Optical Telescopes 1 1.1 A Brief History
The Principles of Astronomical Telescope Design Jingquan Cheng National Radio Astronomy Observatory Charlottesville, Virginia,.USA " 4y Springer Fundamentals of Optical Telescopes 1 1.1 A Brief History
Effective testing for wafer reject minimization by terahertz analysis and sub-surface imaging
 Effective testing for wafer reject minimization by terahertz analysis and sub-surface imaging Anis Rahman and Aunik K. Rahman Applied Research & Photonics 470 Friendship Road, Suite 10 Harrisburg, PA 17111,
Effective testing for wafer reject minimization by terahertz analysis and sub-surface imaging Anis Rahman and Aunik K. Rahman Applied Research & Photonics 470 Friendship Road, Suite 10 Harrisburg, PA 17111,
Quasi-Optical Filters
 Quasi-Optical Filters Peter Ade Cardiff School of Physics and Astronomy, Cardiff University, Queens Buildings, The Parade, Cardiff, CF24 3AA Peter.Ade@astro.cf.ac.uk Abstract: We describe the current state-of-art
Quasi-Optical Filters Peter Ade Cardiff School of Physics and Astronomy, Cardiff University, Queens Buildings, The Parade, Cardiff, CF24 3AA Peter.Ade@astro.cf.ac.uk Abstract: We describe the current state-of-art
Design of a Multi-Mode Interference Crossing Structure for Three Periodic Dielectric Waveguides
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 75, 47 52, 2018 Design of a Multi-Mode Interference Crossing Structure for Three Periodic Dielectric Waveguides Haibin Chen 1, Zhongjiao He 2,andWeiWang
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 75, 47 52, 2018 Design of a Multi-Mode Interference Crossing Structure for Three Periodic Dielectric Waveguides Haibin Chen 1, Zhongjiao He 2,andWeiWang
Short course: 101 level introductory course to provide a foundation for everyone coming to the workshop to understand the field.
 Designing future CMB experiments: how this will work Short course: 101 level introductory course to provide a foundation for everyone coming to the workshop to understand the field. Study visions and goals
Designing future CMB experiments: how this will work Short course: 101 level introductory course to provide a foundation for everyone coming to the workshop to understand the field. Study visions and goals
Simulations of an etched spiral axial attenuation scheme for an on-axis reflecting telescope
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Simulations of an etched spiral axial attenuation scheme for an on-axis reflecting telescope To cite this article: Aaron Spector and Guido Mueller
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Simulations of an etched spiral axial attenuation scheme for an on-axis reflecting telescope To cite this article: Aaron Spector and Guido Mueller
The Effect of Cooling Systems on HTS Microstrip Antennas
 PIERS ONLINE, VOL. 4, NO. 2, 28 176 The Effect of Cooling Systems on HTS Microstrip Antennas S. F. Liu 1 and S. D. Liu 2 1 Xidian University, Xi an 7171, China 2 Xi an Institute of Space Radio Technology,
PIERS ONLINE, VOL. 4, NO. 2, 28 176 The Effect of Cooling Systems on HTS Microstrip Antennas S. F. Liu 1 and S. D. Liu 2 1 Xidian University, Xi an 7171, China 2 Xi an Institute of Space Radio Technology,
To determine the wavelengths of light emitted by a mercury vapour lamp by using a diffraction grating.
 12. Diffraction grating OBJECT To determine the wavelengths of light emitted by a mercury vapour lamp by using a diffraction grating. INTRODUCTION: Consider a light beam transmitted through an aperture
12. Diffraction grating OBJECT To determine the wavelengths of light emitted by a mercury vapour lamp by using a diffraction grating. INTRODUCTION: Consider a light beam transmitted through an aperture
Asymmetrical features of mass spectral peaks produced by quadrupole mass filters
 RAPID COMMUNICATIONS IN MASS SPECTROMETRY Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2003; 17: 1051 1055 Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/rcm.1017 Asymmetrical features
RAPID COMMUNICATIONS IN MASS SPECTROMETRY Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2003; 17: 1051 1055 Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/rcm.1017 Asymmetrical features
LECTURE 11 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES & POLARIZATION. Instructor: Kazumi Tolich
 LECTURE 11 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES & POLARIZATION Instructor: Kazumi Tolich Lecture 11 2 25.5 Electromagnetic waves Induced fields Properties of electromagnetic waves Polarization Energy of electromagnetic
LECTURE 11 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES & POLARIZATION Instructor: Kazumi Tolich Lecture 11 2 25.5 Electromagnetic waves Induced fields Properties of electromagnetic waves Polarization Energy of electromagnetic
DOUBLE-SLOT ANTENNAS ON EXTENDED HEMISPHERICAL DIELECTRIC LENSES
 Page 382 Third International Symposium on Space Terahertz Technology The material presented below is intended as a review only. A full length paper has been submitted for publication in IEEE/MTT (May 1992).
Page 382 Third International Symposium on Space Terahertz Technology The material presented below is intended as a review only. A full length paper has been submitted for publication in IEEE/MTT (May 1992).
APPLICATION OF NON-BIASED FERRITES
 IMS-004 Workshop WMH APPLICATION OF NON-BIASED FERRITES FOR THE SUPPRESSION OF EMI FROM RF TO MM WAVES Karén Kocharyan RENAISSANCE Electronics Corporation 1 Lancaster County Rd., Harvard, MA 01451 kkocharyan@rec-usa.com
IMS-004 Workshop WMH APPLICATION OF NON-BIASED FERRITES FOR THE SUPPRESSION OF EMI FROM RF TO MM WAVES Karén Kocharyan RENAISSANCE Electronics Corporation 1 Lancaster County Rd., Harvard, MA 01451 kkocharyan@rec-usa.com
The Co-Conical Field Generation System A 40 GHz Antenna Test Cell
 A 40 GHz Antenna Test Cell David R. Novotny and Robert T. Johnk RF Technology Division 325 Broadway Boulder, Colorado 80303-3328 http://www.boulder.nist.gov/div813/rffields/emc_emi/co_con.html An Effort
A 40 GHz Antenna Test Cell David R. Novotny and Robert T. Johnk RF Technology Division 325 Broadway Boulder, Colorado 80303-3328 http://www.boulder.nist.gov/div813/rffields/emc_emi/co_con.html An Effort
Mandatory Assignment 2013 INF-GEO4310
 Mandatory Assignment 2013 INF-GEO4310 Deadline for submission: 12-Nov-2013 e-mail the answers in one pdf file to vikashp@ifi.uio.no Part I: Multiple choice questions Multiple choice geometrical optics
Mandatory Assignment 2013 INF-GEO4310 Deadline for submission: 12-Nov-2013 e-mail the answers in one pdf file to vikashp@ifi.uio.no Part I: Multiple choice questions Multiple choice geometrical optics
CHAPTER 2. COULOMB S LAW AND ELECTRONIC FIELD INTENSITY. 2.3 Field Due to a Continuous Volume Charge Distribution
 CONTENTS CHAPTER 1. VECTOR ANALYSIS 1. Scalars and Vectors 2. Vector Algebra 3. The Cartesian Coordinate System 4. Vector Cartesian Coordinate System 5. The Vector Field 6. The Dot Product 7. The Cross
CONTENTS CHAPTER 1. VECTOR ANALYSIS 1. Scalars and Vectors 2. Vector Algebra 3. The Cartesian Coordinate System 4. Vector Cartesian Coordinate System 5. The Vector Field 6. The Dot Product 7. The Cross
Unstable optical resonators. Laser Physics course SK3410 Aleksandrs Marinins KTH ICT OFO
 Unstable optical resonators Laser Physics course SK3410 Aleksandrs Marinins KTH ICT OFO Outline Types of resonators Geometrical description Mode analysis Experimental results Other designs of unstable
Unstable optical resonators Laser Physics course SK3410 Aleksandrs Marinins KTH ICT OFO Outline Types of resonators Geometrical description Mode analysis Experimental results Other designs of unstable
