Quasi-optical beam waveguide analysis using frame based Gaussian beam expansion
|
|
|
- Roxanne Cunningham
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Thirteenth international Symposium on Space Terahertz Technology, Harvard University, March Quasi-optical beam waveguide analysis using frame based Gaussian beam expansion Torsten Bondw and Stig Busk Sorensen Ticra, Laederstraede 34, DK-1201, Copenhagen Abstract A frame based Gaussian beam expansion method which can be used for analysis of quasi-optical beam waveguides is presented. The method is tested for the scattered field of an ellipsoid at 321 GHz and 3.21 THz. Keywords: Quasi-optics, Beam waveguide, THz, Gaussian beams, PO, frames. Introduction For reflector antennas and mirrors with diameters less than 250 wavelengths Physical Optics (P0) is a fast and accurate calculation method for determining the scattered fields. In optics where the diameter of the mirrors are much larger than a thousand wavelengths ray tracing methods as Geometrical Optics (GO) are efficient ways of determining the scattered fields. However, at Quasi-optical frequencies the mirrors are typically in the order of a thousand wavelengths in diameter and in this range neither PO nor GO methods suffice. The computational time for PO increases with the frequency to the fourth power and GO methods become inaccurate or impractical. A fast analysis method useful for this wavelength range is the Gaussian beam analysis method. Imbriale et. al. [1] expand the field in a beam waveguide in Gauss-Laguerre beams, which are used to propagate the field from a reflector A to a reflector B. On the reflector B the currents are calculated by the PO approximation. The scattered field of the reflector B is found by making a new expansion in Gauss-Lagucrre modes on an output plane in front of the reflector B. This involves the calculation of orthogonality integrals with respect to the reflected field which is unknown at this stage. By use of the reciprocity theorem the orthogonality integrals can be transformed to surface integrals on the reflector B that only involve the known surface cuffents. The method is fast, but it has the major disadvantage that the Gauss-LagueiTe expansion is only accurate in the paraxial region so that diffractions from the reflector are not accurately described. Parini et. al. [2] use a frame based expansion [41 consisting of fundamental Gaussian beam modes that are shifted and rotated in space. Reflector scattering is computed by GO and GTD using Gaussian beam diffraction techniques. This gives the scattered field on an output plane where a new frame expansion is made. In contrast to [I] the method is also able to compute non-paraxial fields since only the fundamental Gaussian beam modes are used in the expansion. The major drawback is the use of GO and GTD for computation of the scattered field which involves ray-tracing and may be inaccurate if the surface or rim has a complicated shape (e.g. a rectangular rim). In this paper a method is presented which combines the features of [I] and [2] avoiding the major disadvantages of the two methods. The frame based expansion that consists of the fundamental Gaussian modes that are shifted and rotated in space is used to describe the field, and the reciprocity theorem is used instead of the GO+GTD analysis. The method has been implemented in a computer program for analysis of a sequence of two 3D reflectors. If a sufficiently large number of expansion functions is included the accuracy of the new method is comparable 1 Correspondence: tb q 'ticra.com.web: 271
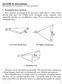
2 to PO also outside the main beam but the computation time may then be longer than for PO. However, close to the main beam a good accuracy can be obtained with a small number of expansion functions and with a considerable saving of computation time in comparison to PO. Especially for computing the near -field at THz frequencies the method proves to be much faster than PO. Frame based expansion In [3]a uniform _D aperture field is expanded in fundamental Gaussian beam modes that are shifted and rotated over the aperture plane. This method can be generalized to an arbitrary aperture distribution in 3D and will be used in the next section for an ellipsoidal reflector antenna. The mathematics of this method is described in and involves the concept of windowed Fourier transforms and frame based expansion. In 2D the expansion functions on the aperture plane are defined by: g1 (t) = 1 / t e ( 1 ) This corresponds to Gaussian beams linearly shifted and rotated in space. it, Trt are integers that define the translation and the rotation of a gaussian beam, respectively and p go are characteristic constants that define the form of the function. An arbitrary aperture field f (t) can then be expanded in the series: 1(0 = grirrt (1) (2) ran where oc c = < /Inn > ( t ) f (t)dt. (3), The function g yn, is the dual function to g m, in this paper called the frame function. It can be computed from g m, as described in Pt In this way an arbitrary aperture field is expanded in Gaussian fundamental beams which can be propagated to the next reflector in the beam wave-guide. Computation of the reflected field A mathematical surface S is considered which provides an aperture plane and encloses the reflector currents J 1, see Figure I. 1:7 1 H i are generated by the currents J i and the fields E, and 11 2 are Maxwellian fields propagating in a region with no sources. The fields E2 and H, propagate in the opposite direction of E Assuming that S is an infinite plane orthogonal to the z-axis at z = 0 the reciprocity theorem reduces to fs x ) cis (4) 272
3 2 ft Figure I: Illustration of the use of the reciprocity theorem and frame functions. By a suitable choice of E2 and fr, the left hand side of (4) reduces to the integral in (3) such that the expansion coefficients e m, can be computed from the right hand side of (4). The currents 1 are the known PO currents on the reflector. Hence, a method is constructed which uses the known PO currents on the reflector to compute a set of frame coefficients defined on an output plane by means of the reciprocity theorem. Once the coefficients are known the field value at any distance can be reconstructed as a sum of frame functions on the output plane weighted with the frame coefficients. Results for a 3D ellipsoidal reflector To evaluate the speed and accuracy of the frame based expansion method a comparison to PO at different frequencies and in different output planes is made. A beam waveguide is considered which is operated at two frequencies 321 GHz and 3.21 THz. A coordinate system origin is placed at the reflection point of the ellipsoid where the centre ray combining the two focal points has a 90' reflection angle (see Fig. 2). In this coordinate system the two focal points are located in 63.5 rnm along the negative 37-direction and at mm along the positive 2-direction. The projection of the rim of the ellipsoid onto the plane orthogonal to the output direction along the z-axis, is a circle with diameter D=46.5 mm. The product po * go must be < 27:- to ensure a stable expansion [A. We have chosen p qo = with go = 1.5 (see ( I )) because it gives a simple frame function similar to the Gaussian fundamental function, but other values of po and go can also be used (and may prove to be more efficient - this will not be discussed in this paper). The equations (1), (2), (3) must take into account the actual geometry of the system. Therefore, a scaling variable x = L t is introduced, where L = f a) 0 -\/- and wo is the waist radius of the output beam. By this choice of scaling the width of the expansion frame functions matches the width of the output Gaussian beam in the waist. At the waist plane for 321 GHz, L mm and for 3.21 THz. L =0.245 mm. The input Gaussian 273
4 Ellipsoid Plane A Near-field Plane B. Waist 40. Focal point.- i Focal point Next reflector VGaussian feed Figure 2: Geometry of the beam waveguide system. beam has wo = 2.12 mm at 321 GHz and wo = mm at 3.21 THz. The Gaussian feed is radiating from 60 mm and 63.5 mm along the negative x-axis at 321 GHz and at 3.21 THz, respectively 1. The beam is then scattered by the ellipsoid and the field is evaluated in three planes A, B and C (see Figure 2) A. The near-field plane of the reflector in a distance of 40 mm along the z-axis. The field is evaluated from x = 25 nun to x = 25 mni which is approx. the size of the projected diameter (D 46.5 mm). B. The plane located in the waist of the reflector which is placed at a distance of 88.7 mm for 321 GHz and in a distance of mm for 3.21 THz along the z-axis. This is also the plane used to calculate the frame coefficients. The main lobe and approx. 4-5 side lobes are plotted for both frequencies along the x-axis. C. The plane orthogonal to the ray along the z-axis at the reflection point of the next reflector in the beam waveguide at a distance of 240 mm along the z-axis. The field is evaluated from x 40 mm to x = 40 mm which is the size of the projected diameter of the next reflector (D 80 mm). The speed of the frame method can be compared to the speed of the PO method by comparing the number of PO current elements to the number of frame coefficients. A total of 3969 frame coefficients is used in the frame based expansion. In the expansion the n-number of the frame coefficients denotes the translation of the Gaussian beam and the Iv-number the rotation of the Gaussian beam (see (1) and Figure 1). Therefore, the n-number must be chosen such that the Gaussian beams cover the field to be expanded. Furthermore, the m-number determines the degree of rotation of the Gaussian beams. By increasing or decreasing this number the area in which the radiated field is converged increases or diminishes. I At THz the Gaussian beam is radiating from the focal point 274
5 GHz h7-20 dbi Waist plane Ô 10 1Tffl ci Bi Next reflector plane H Frame field PO reference field :30 ininium PO field Figure 3: Near field at Plane A, waist field at plane B and field at the next reflector at plane C for 321 GHz and 3.21 THz (see Fig. 2 for set-up). Three types of fields are plotted: the frame field, a converged PO reference field and a PO field where the minimum number of PO points that ensures field convergence 45 db below peak is used. The normalization of the curves is such that power flux in db per unit area can be calculated by adding 20 log, 0 k. Only one PO curve is shown in Plane B, as the minimum PO solution and the reference PO curve overlap in this field region. Near field plane Waist plane Next reflector plane PO 321 GHz PO 121 THz Frame 321 GHz Frame 3.21 THz Figure 4: Table of the number of PO current elements for the minimum PO solution and the number of frame functions at 321 GHz and 3.21 THz that is used to obtain the results presented in Figure 1 275
6 In Figure 3 the results of the tests are shown and table 4 contains the number of PO current elements and the number of frame functions at 321 GHz and 3.21 THz that are used to obtain the results presented in Figure 3. Two types of PO solutions are shown: The reference PO solution where a sufficiently large Dumber of PO points is used to obtain field convergence over the whole output plane area and the minimum PO solution where the number of points are just sufficient for convergence down to -45 db below the peak value. The results show that a constant number of frame coefficient can be used for both frequencies on all output planes. In all cases the frame results are converged down to approx. 45dB below peak value. This stable results should be compared to PO where the necessary number of current elements is both frequency and position dependent. Especially in the near field at the high frequency a very high number of PO points must be used to make the field converge down to 45 db. PO is, however. a fast method for computing the field in the waist of the beam waveguide, where the field is in phase. For the plane of the next reflector PO is very fast at low frequencies but becomes slow at high frequencies. Conclusion As a beam waveguide analysis tool at THz frequencies a frame based Gaussian beam method using a combination of two different techniques [, 2] has been presented. The method is frequency independent and only the number of the Gaussian beam functions determines the computational time. The accuracy of the method increases with trt, and n and can reach PO accuracy. However, for high rn, and ni numbers the method can no longer compete with PO in speed. Also for simple field calculations where the field is in phase on the output plane, PO is a faster method. For computing the near field the method proves to be very successful at THz frequencies, where PO is very time consuming when the near-field plane is close to the scattering object. The method also has the advantage, that the fundamental Gaussian beam modes used in the expansion method are not limited to the paraxial region and a general reflector shape and rim can be handled in a beam waveguide system. We believe that the frame based Gaussian beam method with the right tuning (eg. choice of the grid parameters po, go) can work as an intermediate accurate and stable alternative to the accurate, but in some cases slow method of PO and the fast and more unstable method of GO+GTD. References [1] Recent Trends in the Analysis of Ouasioptical systems, W. A. lmbriale and D.J. Hoppe, Paper from "Davos Proceedings 2000", Switzerland william.a.imbriale@jpi.nasa.gov [2] Diffracted Gaussian beam analysis of quasi -optical multi-afiector systems, C. Rieckmann, M. R. Rayner and C. Parini, Paper from "Davos Proceedings 2000", Switzerland m.r.rayner@elec.qmw.ac.uk [3] Alternative to Gabor 's representation of plane aperture radiation, D. Lugara and C. Letrou, Electronics letter 26th novemeber 1998 Vol. 34 No. 24 [4] The wavelet Transform, Time-Frequency Localization and Signal Analvis, I. Daubechies, IEEE Transactions on Information Theory,m vol. 36, no. 5, september
Part I. The Quad-Ridged Flared Horn
 9 Part I The Quad-Ridged Flared Horn 10 Chapter 2 Key Requirements of Radio Telescope Feeds Almost all of today s radio telescopes operating above 0.5 GHz use reflector antennas consisting of one or more
9 Part I The Quad-Ridged Flared Horn 10 Chapter 2 Key Requirements of Radio Telescope Feeds Almost all of today s radio telescopes operating above 0.5 GHz use reflector antennas consisting of one or more
POLARISATION DEPENDENT SCATTERING FROM THE SERRATIONS OF COMPACT RANGES 1
 Paper presented at Antenna Measurement Techniques Association 29 th Annual Symposium (AMTA 2007), St. Louis, MO, USA, 4-9 November 2007, Proceedings pp. 150-155 (Session 5). POLARISATION DEPENDENT SCATTERING
Paper presented at Antenna Measurement Techniques Association 29 th Annual Symposium (AMTA 2007), St. Louis, MO, USA, 4-9 November 2007, Proceedings pp. 150-155 (Session 5). POLARISATION DEPENDENT SCATTERING
COMBINING GTD WITH MOM IN ANALYSING THE SCATTERING FROM THE LICEF ANTENNAS ON THE SMOS SATELLITE
 Paper presented at European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EuCAP 2006), Nice, France, November 6-10, 2006, 5 pages. COMBINING GTD WITH MOM IN ANALYSING THE SCATTERING FROM THE LICEF ANTENNAS ON
Paper presented at European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EuCAP 2006), Nice, France, November 6-10, 2006, 5 pages. COMBINING GTD WITH MOM IN ANALYSING THE SCATTERING FROM THE LICEF ANTENNAS ON
Final Design and Testing of the 94 GHz Quasi-Optical-Feed for the EarthCARE S Cloud Profiling Radar
 Final Design and Testing of the 94 GHz Quasi-Optical-Feed for the EarthCARE S Cloud Profiling Radar J. Hartmann #, Chr. Hartwanger #, R. Wylde +, C. Cappellin*, H. Horie x # Astrium GmbH - Satellites,
Final Design and Testing of the 94 GHz Quasi-Optical-Feed for the EarthCARE S Cloud Profiling Radar J. Hartmann #, Chr. Hartwanger #, R. Wylde +, C. Cappellin*, H. Horie x # Astrium GmbH - Satellites,
Quasi-Optical Design and Analysis (MBI) Créidhe O Sullivan, J.Anthony Murphy, Marcin Gradziel, Neil Trappe, Tully Peacocke & graduate students
 Quasi-Optical Design and Analysis (MBI) Créidhe O Sullivan, J.Anthony Murphy, Marcin Gradziel, Neil Trappe, Tully Peacocke & graduate students Outline Corrugated Horns Analysis Techniques MBI/MODAL 2 Analysis
Quasi-Optical Design and Analysis (MBI) Créidhe O Sullivan, J.Anthony Murphy, Marcin Gradziel, Neil Trappe, Tully Peacocke & graduate students Outline Corrugated Horns Analysis Techniques MBI/MODAL 2 Analysis
In-Flight Retrieval of Reflector Anomalies for the Planck Space Telescope
 Presented at The 4 th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EuCAP 2010), Barcelona, Spain, 12-16 April 2010. In-Flight Retrieval of Reflector Anomalies for the Planck Space Telescope Frank Jensen*,
Presented at The 4 th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EuCAP 2010), Barcelona, Spain, 12-16 April 2010. In-Flight Retrieval of Reflector Anomalies for the Planck Space Telescope Frank Jensen*,
FEASIBILITY STUDY FOR THE FOCALISATION OF THE NEW 40m RADIOTELESCOPE OF CENTRO ASTRONÓMICO DE YEBES
 Thirteenth international Symposium on Space Terahertz Technology, Harvard University, March 2002. FEASIBILITY STUDY FOR THE FOCALISATION OF THE NEW 40m RADIOTELESCOPE OF CENTRO ASTRONÓMICO DE YEBES E.
Thirteenth international Symposium on Space Terahertz Technology, Harvard University, March 2002. FEASIBILITY STUDY FOR THE FOCALISATION OF THE NEW 40m RADIOTELESCOPE OF CENTRO ASTRONÓMICO DE YEBES E.
feed. The fundamental principle of the matched feed depends on the field matching
 CHAPTER-2 MATCHED FEED FOR OFFSET REFLECTOR ANTENNA The primary objective of this chapter is to discuss the basic concept of matched feed. The fundamental principle of the matched feed depends on the field
CHAPTER-2 MATCHED FEED FOR OFFSET REFLECTOR ANTENNA The primary objective of this chapter is to discuss the basic concept of matched feed. The fundamental principle of the matched feed depends on the field
RF properties. of the Planck telescope. Designed by ALCATEL. CASE No. 1. Per Heighwood Nielsen
 TICRA engineering consultants communications systems and antennas RF properties of the Planck telescope Designed by ALCATEL CASE No. 1 November, 1999 S-801-04 Author: Per Heighwood Nielsen TICRA KRON PRINSENS
TICRA engineering consultants communications systems and antennas RF properties of the Planck telescope Designed by ALCATEL CASE No. 1 November, 1999 S-801-04 Author: Per Heighwood Nielsen TICRA KRON PRINSENS
DOUBLE-SLOT ANTENNAS ON EXTENDED HEMISPHERICAL DIELECTRIC LENSES
 Page 382 Third International Symposium on Space Terahertz Technology The material presented below is intended as a review only. A full length paper has been submitted for publication in IEEE/MTT (May 1992).
Page 382 Third International Symposium on Space Terahertz Technology The material presented below is intended as a review only. A full length paper has been submitted for publication in IEEE/MTT (May 1992).
Electromagnetic Implosion Using a Lens
 Sensor and Simulation Notes Note 516 July 2006 Electromagnetic Implosion Using a Lens Carl E. Baum University of New Mexico Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Albuquerque New Mexico 87131
Sensor and Simulation Notes Note 516 July 2006 Electromagnetic Implosion Using a Lens Carl E. Baum University of New Mexico Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Albuquerque New Mexico 87131
Design of an off set optics with high polarization purity and large Focal plane Area for CMB polarization observations
 Designofanoff setopticswith highpolarizationpurityandlargefocal planearea forcmbpolarizationobservations P.Bolli %,E.Carretti *,A.Navarrini % % OsservatorioAstronomicodiCagliari INAF Loc.PoggiodeiPini,Strada54
Designofanoff setopticswith highpolarizationpurityandlargefocal planearea forcmbpolarizationobservations P.Bolli %,E.Carretti *,A.Navarrini % % OsservatorioAstronomicodiCagliari INAF Loc.PoggiodeiPini,Strada54
Beam Scan Properties of Nonparabolic Reflectors. P.J. N a p ie r National Radio Astronomy Observatory, Socorro, New Mexico 87801
 NLSRT Memo No.. / / ' /ft Beam Scan Properties of Nonparabolic Reflectors P.J. N a p ie r National Radio Astronomy Observatory, Socorro, New Mexico 87801 Abstract. Nonparabolic reflector systems such as
NLSRT Memo No.. / / ' /ft Beam Scan Properties of Nonparabolic Reflectors P.J. N a p ie r National Radio Astronomy Observatory, Socorro, New Mexico 87801 Abstract. Nonparabolic reflector systems such as
A REVISED PROPOSAL FOR A FEED SYSTEM FOR THE VLBA ANTENNA P. J. NAPIER 1/11/82 INTRODUCTION
 A REVISED PROPOSAL FOR A FEED SYSTEM FOR THE VLBA ANTENNA P. J. NAPIER 1/11/82 INTRODUCTION In a previous report a concept for a feed system for the VLBA antenna was presented. Further study of the problem
A REVISED PROPOSAL FOR A FEED SYSTEM FOR THE VLBA ANTENNA P. J. NAPIER 1/11/82 INTRODUCTION In a previous report a concept for a feed system for the VLBA antenna was presented. Further study of the problem
IMPLEMENTATION OF A QUASI-OPTICAL FREE-SPACE S-PARAMETERS MEASUREMENT SYSTEM
 IMPLEMENTATION OF A QUASI-OPTICAL FREE-SPACE S-PARAMETERS MEASUREMENT SYSTEM B. Maffei, S. Legg, M. Robinson, F. Ozturk, M. W. Ng, P. Schemmel and G. Pisano. JBCA, School of Physics and Astronomy, The
IMPLEMENTATION OF A QUASI-OPTICAL FREE-SPACE S-PARAMETERS MEASUREMENT SYSTEM B. Maffei, S. Legg, M. Robinson, F. Ozturk, M. W. Ng, P. Schemmel and G. Pisano. JBCA, School of Physics and Astronomy, The
Electromagnetic Theory for Microwaves and Optoelectronics
 Keqian Zhang Dejie Li Electromagnetic Theory for Microwaves and Optoelectronics Second Edition With 280 Figures and 13 Tables 4u Springer Basic Electromagnetic Theory 1 1.1 Maxwell's Equations 1 1.1.1
Keqian Zhang Dejie Li Electromagnetic Theory for Microwaves and Optoelectronics Second Edition With 280 Figures and 13 Tables 4u Springer Basic Electromagnetic Theory 1 1.1 Maxwell's Equations 1 1.1.1
Offset Spheroidal Mirrors for Gaussian Beam Optics in ZEMAX
 Offset Spheroidal Mirrors for Gaussian Beam Optics in ZEMAX Antony A. Stark and Urs Graf Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory, University of Cologne aas@cfa.harvard.edu 1 October 2013 This memorandum
Offset Spheroidal Mirrors for Gaussian Beam Optics in ZEMAX Antony A. Stark and Urs Graf Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory, University of Cologne aas@cfa.harvard.edu 1 October 2013 This memorandum
Prolate Spheroidal Scatterer for Spherical TEM Waves
 Sensor and Simulation Notes Note 508 January 2006 Prolate Spheroidal Scatterer for Spherical TEM Waves Carl E. Baum University of New Mexico Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Albuquerque
Sensor and Simulation Notes Note 508 January 2006 Prolate Spheroidal Scatterer for Spherical TEM Waves Carl E. Baum University of New Mexico Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Albuquerque
Vectors Coordinate frames 2D implicit curves 2D parametric curves. Graphics 2008/2009, period 1. Lecture 2: vectors, curves, and surfaces
 Graphics 2008/2009, period 1 Lecture 2 Vectors, curves, and surfaces Computer graphics example: Pixar (source: http://www.pixar.com) Computer graphics example: Pixar (source: http://www.pixar.com) Computer
Graphics 2008/2009, period 1 Lecture 2 Vectors, curves, and surfaces Computer graphics example: Pixar (source: http://www.pixar.com) Computer graphics example: Pixar (source: http://www.pixar.com) Computer
Heating Beam Pattern Optical Design CO2 Laser Thermal Compensation Bench
 LASER INTERFEROMETER GRAVITATIONAL WAVE OBSERVATORY LIGO Laboratory / LIGO Scientific Collaboration LIGO 4//4 Heating Beam Pattern Optical Design CO Laser Thermal Compensation Bench Michael Smith, David
LASER INTERFEROMETER GRAVITATIONAL WAVE OBSERVATORY LIGO Laboratory / LIGO Scientific Collaboration LIGO 4//4 Heating Beam Pattern Optical Design CO Laser Thermal Compensation Bench Michael Smith, David
Uncertainty Principle Applied to Focused Fields and the Angular Spectrum Representation
 Uncertainty Principle Applied to Focused Fields and the Angular Spectrum Representation Manuel Guizar, Chris Todd Abstract There are several forms by which the transverse spot size and angular spread of
Uncertainty Principle Applied to Focused Fields and the Angular Spectrum Representation Manuel Guizar, Chris Todd Abstract There are several forms by which the transverse spot size and angular spread of
GEOMETRICAL OPTICS Practical 1. Part II. OPTICAL SYSTEMS
 GEOMETRICAL OPTICS Practical 1. Part II. OPTICAL SYSTEMS 1 Introduction Optical systems can consist of a one element (a one lens or a mirror, a magnifying glass), two or three lenses (an eyepiece, theatrical
GEOMETRICAL OPTICS Practical 1. Part II. OPTICAL SYSTEMS 1 Introduction Optical systems can consist of a one element (a one lens or a mirror, a magnifying glass), two or three lenses (an eyepiece, theatrical
ANALYSIS OF THE OPTICAL DESIGN FOR THE SAFIR TELESCOPE
 ANALYSIS OF THE OPTICAL DESIGN FOR THE SAFIR TELESCOPE Paul Goldsmith, Behrouz Khayatian, Matt Bradford, Mark Dragovan, Daniel Hoppe, William Imbriale, Roger Lee, Chris Paine, Dick Turner, and Harold Yorke
ANALYSIS OF THE OPTICAL DESIGN FOR THE SAFIR TELESCOPE Paul Goldsmith, Behrouz Khayatian, Matt Bradford, Mark Dragovan, Daniel Hoppe, William Imbriale, Roger Lee, Chris Paine, Dick Turner, and Harold Yorke
TM-Radiation From an Obliquely Flanged Parallel-Plate Waveguide
 1534 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ANTENNAS AND PROPAGATION, VOL. 50, NO. 11, NOVEMBER 2002 TM-Radiation From an Obliquely Flanged Parallel-Plate Waveguide Jae Yong Kwon, Member, IEEE, Jae Wook Lee, Associate Member,
1534 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ANTENNAS AND PROPAGATION, VOL. 50, NO. 11, NOVEMBER 2002 TM-Radiation From an Obliquely Flanged Parallel-Plate Waveguide Jae Yong Kwon, Member, IEEE, Jae Wook Lee, Associate Member,
Efficient sorting of orbital angular momentum states of light
 CHAPTER 6 Efficient sorting of orbital angular momentum states of light We present a method to efficiently sort orbital angular momentum (OAM) states of light using two static optical elements. The optical
CHAPTER 6 Efficient sorting of orbital angular momentum states of light We present a method to efficiently sort orbital angular momentum (OAM) states of light using two static optical elements. The optical
Gaussian Beam Analysis of Relay Optics for the SEQUOIA Focal Plane Array
 15th International Symposium on Space Terahert Technology Gaussian Beam Analysis of Relay Optics for the SEQUOIA Focal Plane Array Gopal Narayananl Department of Astronomy, University of Massachusetts,
15th International Symposium on Space Terahert Technology Gaussian Beam Analysis of Relay Optics for the SEQUOIA Focal Plane Array Gopal Narayananl Department of Astronomy, University of Massachusetts,
Step index planar waveguide
 N. Dubreuil S. Lebrun Exam without document Pocket calculator permitted Duration of the exam: 2 hours The exam takes the form of a multiple choice test. Annexes are given at the end of the text. **********************************************************************************
N. Dubreuil S. Lebrun Exam without document Pocket calculator permitted Duration of the exam: 2 hours The exam takes the form of a multiple choice test. Annexes are given at the end of the text. **********************************************************************************
A Survey of Computational High Frequency Wave Propagation I
 A Survey of Computational High Frequency Wave Propagation I Bjorn Engquist University of Texas at Austin CSCAMM Workshop on High Frequency Wave Propagation, University of Maryland, September 19-22, 2005
A Survey of Computational High Frequency Wave Propagation I Bjorn Engquist University of Texas at Austin CSCAMM Workshop on High Frequency Wave Propagation, University of Maryland, September 19-22, 2005
Supplementary Materials for
 wwwsciencemagorg/cgi/content/full/scienceaaa3035/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Spatially structured photons that travel in free space slower than the speed of light Daniel Giovannini, Jacquiline Romero,
wwwsciencemagorg/cgi/content/full/scienceaaa3035/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Spatially structured photons that travel in free space slower than the speed of light Daniel Giovannini, Jacquiline Romero,
Electromagnetic Theory for Microwaves and Optoelectronics
 Keqian Zhang Dejie Li Electromagnetic Theory for Microwaves and Optoelectronics Translated by authors With 259 Figures Springer Contents 1 Basic Electromagnetic Theory 1 1.1 Maxwell's Equations 1 1.1.1
Keqian Zhang Dejie Li Electromagnetic Theory for Microwaves and Optoelectronics Translated by authors With 259 Figures Springer Contents 1 Basic Electromagnetic Theory 1 1.1 Maxwell's Equations 1 1.1.1
Probing the orbital angular momentum of light with a multipoint interferometer
 CHAPTER 2 Probing the orbital angular momentum of light with a multipoint interferometer We present an efficient method for probing the orbital angular momentum of optical vortices of arbitrary sizes.
CHAPTER 2 Probing the orbital angular momentum of light with a multipoint interferometer We present an efficient method for probing the orbital angular momentum of optical vortices of arbitrary sizes.
One-Dimensional Numerical Solution of the Maxwell-Minkowski Equations
 Tamkang Journal of Science and Engineering, Vol. 12, No. 2, pp. 161168 (2009) 161 One-Dimensional Numerical Solution of the Maxwell-Minkowski Equations Mingtsu Ho 1 and Yao-Han Chen 2 1 Department of Electronic
Tamkang Journal of Science and Engineering, Vol. 12, No. 2, pp. 161168 (2009) 161 One-Dimensional Numerical Solution of the Maxwell-Minkowski Equations Mingtsu Ho 1 and Yao-Han Chen 2 1 Department of Electronic
Is the speed of light in free-space always c? Miles Padgett FRS Kelvin Chair of Natural Philosophy
 Is the speed of light in free-space always c? Miles Padgett FRS Kelvin Chair of Natural Philosophy 1 What s the speed of light in free space? Always? The team www.physics.gla.ac.uk/optics Jacqui Romero
Is the speed of light in free-space always c? Miles Padgett FRS Kelvin Chair of Natural Philosophy 1 What s the speed of light in free space? Always? The team www.physics.gla.ac.uk/optics Jacqui Romero
3.1 The Plane Mirror Resonator 3.2 The Spherical Mirror Resonator 3.3 Gaussian modes and resonance frequencies 3.4 The Unstable Resonator
 Quantum Electronics Laser Physics Chapter 3 The Optical Resonator 3.1 The Plane Mirror Resonator 3. The Spherical Mirror Resonator 3.3 Gaussian modes and resonance frequencies 3.4 The Unstable Resonator
Quantum Electronics Laser Physics Chapter 3 The Optical Resonator 3.1 The Plane Mirror Resonator 3. The Spherical Mirror Resonator 3.3 Gaussian modes and resonance frequencies 3.4 The Unstable Resonator
Massimiliano Casaletti * and Stefano Maci Department of Information Engineering, University of Siena, Via Roma 56, Siena 53100, Italy
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 28, 245 257, 213 APERTURE BEAM EXPANSION BY USING A SPECTRAL 2D-GPOF METHOD Massimiliano Casaletti * and Stefano Maci Department of Information Engineering,
Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 28, 245 257, 213 APERTURE BEAM EXPANSION BY USING A SPECTRAL 2D-GPOF METHOD Massimiliano Casaletti * and Stefano Maci Department of Information Engineering,
Revisiting the ALMA Band 1 Optics Design P. Zorzi 1, D. Henke 2, S. Claude 2, P. Mena 1, L. Bronfman 3, and J. May 3
 Revisiting the ALMA Band 1 Optics Design P. Zorzi 1, D. Henke 2, S. Claude 2, P. Mena 1, L. Bronfman 3, and J. May 3 1 Department of Electrical Engineering, Universidad de Chile, Santiago, Chile 2 NRC
Revisiting the ALMA Band 1 Optics Design P. Zorzi 1, D. Henke 2, S. Claude 2, P. Mena 1, L. Bronfman 3, and J. May 3 1 Department of Electrical Engineering, Universidad de Chile, Santiago, Chile 2 NRC
Optics for Engineers Chapter 9
 Optics for Engineers Chapter 9 Charles A. DiMarzio Northeastern University Nov. 202 Gaussian Beams Applications Many Laser Beams Minimum Uncertainty Simple Equations Good Approximation Extensible (e.g.
Optics for Engineers Chapter 9 Charles A. DiMarzio Northeastern University Nov. 202 Gaussian Beams Applications Many Laser Beams Minimum Uncertainty Simple Equations Good Approximation Extensible (e.g.
SPHERICAL NEAR-FIELD ANTENNA MEASUREMENTS
 SPHERICAL NEAR-FIELD ANTENNA MEASUREMENTS Edited by J.E.Hansen Peter Peregrinus Ltd. on behalf of the Institution of Electrical Engineers Contents Contributing authors listed Preface v xiii 1 Introduction
SPHERICAL NEAR-FIELD ANTENNA MEASUREMENTS Edited by J.E.Hansen Peter Peregrinus Ltd. on behalf of the Institution of Electrical Engineers Contents Contributing authors listed Preface v xiii 1 Introduction
Lecture 19 Optical MEMS (1)
 EEL6935 Advanced MEMS (Spring 5) Instructor: Dr. Huikai Xie Lecture 19 Optical MEMS (1) Agenda: Optics Review EEL6935 Advanced MEMS 5 H. Xie 3/8/5 1 Optics Review Nature of Light Reflection and Refraction
EEL6935 Advanced MEMS (Spring 5) Instructor: Dr. Huikai Xie Lecture 19 Optical MEMS (1) Agenda: Optics Review EEL6935 Advanced MEMS 5 H. Xie 3/8/5 1 Optics Review Nature of Light Reflection and Refraction
Chapter 1. Ray Optics
 Chapter 1. Ray Optics Postulates of Ray Optics n c v A ds B Reflection and Refraction Fermat s Principle: Law of Reflection Fermat s principle: Light rays will travel from point A to point B in a medium
Chapter 1. Ray Optics Postulates of Ray Optics n c v A ds B Reflection and Refraction Fermat s Principle: Law of Reflection Fermat s principle: Light rays will travel from point A to point B in a medium
PART 1 Introduction to Theory of Solids
 Elsevier UK Job code: MIOC Ch01-I044647 9-3-2007 3:03p.m. Page:1 Trim:165 240MM TS: Integra, India PART 1 Introduction to Theory of Solids Elsevier UK Job code: MIOC Ch01-I044647 9-3-2007 3:03p.m. Page:2
Elsevier UK Job code: MIOC Ch01-I044647 9-3-2007 3:03p.m. Page:1 Trim:165 240MM TS: Integra, India PART 1 Introduction to Theory of Solids Elsevier UK Job code: MIOC Ch01-I044647 9-3-2007 3:03p.m. Page:2
Gaussian Beam Mode Analysis of Imaging Arrays
 Gaussian Beam Mode Analysis of Imaging Arrays J.A. Murphy, St. Patrick's College, Maynooth, Co.Kildare, Ireland & Stafford Withington, Cavendish Laboratory, Cambridge CB3 OHE, UK Abstract In this paper
Gaussian Beam Mode Analysis of Imaging Arrays J.A. Murphy, St. Patrick's College, Maynooth, Co.Kildare, Ireland & Stafford Withington, Cavendish Laboratory, Cambridge CB3 OHE, UK Abstract In this paper
Course Secretary: Christine Berber O3.095, phone x-6351,
 IMPRS: Ultrafast Source Technologies Franz X. Kärtner (Umit Demirbas) & Thorsten Uphues, Bldg. 99, O3.097 & Room 6/3 Email & phone: franz.kaertner@cfel.de, 040 8998 6350 thorsten.uphues@cfel.de, 040 8998
IMPRS: Ultrafast Source Technologies Franz X. Kärtner (Umit Demirbas) & Thorsten Uphues, Bldg. 99, O3.097 & Room 6/3 Email & phone: franz.kaertner@cfel.de, 040 8998 6350 thorsten.uphues@cfel.de, 040 8998
Optics for Engineers Chapter 9
 Optics for Engineers Chapter 9 Charles A. DiMarzio Northeastern University Mar. 204 Gaussian Beams Applications Many Laser Beams Minimum Uncertainty Simple Equations Good Approximation Extensible (e.g.
Optics for Engineers Chapter 9 Charles A. DiMarzio Northeastern University Mar. 204 Gaussian Beams Applications Many Laser Beams Minimum Uncertainty Simple Equations Good Approximation Extensible (e.g.
all dimensions are mm the minus means meniscus lens f 2
 TEM Gauss-beam described with ray-optics. F.A. van Goor, University of Twente, Enschede The Netherlands. fred@uttnqe.utwente.nl December 8, 994 as significantly modified by C. Nelson - 26 Example of an
TEM Gauss-beam described with ray-optics. F.A. van Goor, University of Twente, Enschede The Netherlands. fred@uttnqe.utwente.nl December 8, 994 as significantly modified by C. Nelson - 26 Example of an
Phys 531 Lecture 27 6 December 2005
 Phys 531 Lecture 27 6 December 2005 Final Review Last time: introduction to quantum field theory Like QM, but field is quantum variable rather than x, p for particle Understand photons, noise, weird quantum
Phys 531 Lecture 27 6 December 2005 Final Review Last time: introduction to quantum field theory Like QM, but field is quantum variable rather than x, p for particle Understand photons, noise, weird quantum
Displaced-Axis-Ellipse Reflector Antenna for Spacecraft Communications
 Displaced-Axis-Ellipse Reflector Antenna for Spacecraft Communications Aluizio Prata, Jr., Fernando J. S. Moreira, and Luis R. Amaro Abstract This work discusses the electrical characteristics of axially-symmetric
Displaced-Axis-Ellipse Reflector Antenna for Spacecraft Communications Aluizio Prata, Jr., Fernando J. S. Moreira, and Luis R. Amaro Abstract This work discusses the electrical characteristics of axially-symmetric
21. Propagation of Gaussian beams
 1. Propagation of Gaussian beams How to propagate a Gaussian beam Rayleigh range and confocal parameter Transmission through a circular aperture Focusing a Gaussian beam Depth of field Gaussian beams and
1. Propagation of Gaussian beams How to propagate a Gaussian beam Rayleigh range and confocal parameter Transmission through a circular aperture Focusing a Gaussian beam Depth of field Gaussian beams and
Gradient-index metamaterials and spoof surface plasmonic waveguide
 Gradient-index metamaterials and spoof surface plasmonic waveguide Hui Feng Ma State Key Laboratory of Millimeter Waves Southeast University, Nanjing 210096, China City University of Hong Kong, 11 October
Gradient-index metamaterials and spoof surface plasmonic waveguide Hui Feng Ma State Key Laboratory of Millimeter Waves Southeast University, Nanjing 210096, China City University of Hong Kong, 11 October
PROCEEDINGS OF SPIE. Scaling rules for the design of a narrow-band grating filter at the focus of a free-space beam
 PROCEEDINGS OF SPIE SPIEDigitalLibrary.org/conference-proceedings-of-spie Scaling rules for the design of a narrow-band grating filter at the focus of a free-space beam Eanuel Bonnet, Alain Cachard, Alexandre
PROCEEDINGS OF SPIE SPIEDigitalLibrary.org/conference-proceedings-of-spie Scaling rules for the design of a narrow-band grating filter at the focus of a free-space beam Eanuel Bonnet, Alain Cachard, Alexandre
OPTI510R: Photonics. Khanh Kieu College of Optical Sciences, University of Arizona Meinel building R.626
 OPTI510R: Photonics Khanh Kieu College of Optical Sciences, University of Arizona kkieu@optics.arizona.edu Meinel building R.626 Announcements Homework #4 is assigned, due March 25 th Start discussion
OPTI510R: Photonics Khanh Kieu College of Optical Sciences, University of Arizona kkieu@optics.arizona.edu Meinel building R.626 Announcements Homework #4 is assigned, due March 25 th Start discussion
Vector diffraction theory of refraction of light by a spherical surface
 S. Guha and G. D. Gillen Vol. 4, No. 1/January 007/J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 1 Vector diffraction theory of refraction of light by a spherical surface Shekhar Guha and Glen D. Gillen* Materials and Manufacturing
S. Guha and G. D. Gillen Vol. 4, No. 1/January 007/J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 1 Vector diffraction theory of refraction of light by a spherical surface Shekhar Guha and Glen D. Gillen* Materials and Manufacturing
Intro Vectors 2D implicit curves 2D parametric curves. Graphics 2012/2013, 4th quarter. Lecture 2: vectors, curves, and surfaces
 Lecture 2, curves, and surfaces Organizational remarks Tutorials: TA sessions for tutorial 1 start today Tutorial 2 will go online after lecture 3 Practicals: Make sure to find a team partner very soon
Lecture 2, curves, and surfaces Organizational remarks Tutorials: TA sessions for tutorial 1 start today Tutorial 2 will go online after lecture 3 Practicals: Make sure to find a team partner very soon
So far, we have considered three basic classes of antennas electrically small, resonant
 Unit 5 Aperture Antennas So far, we have considered three basic classes of antennas electrically small, resonant (narrowband) and broadband (the travelling wave antenna). There are amny other types of
Unit 5 Aperture Antennas So far, we have considered three basic classes of antennas electrically small, resonant (narrowband) and broadband (the travelling wave antenna). There are amny other types of
There and back again A short trip to Fourier Space. Janet Vonck 23 April 2014
 There and back again A short trip to Fourier Space Janet Vonck 23 April 2014 Where can I find a Fourier Transform? Fourier Transforms are ubiquitous in structural biology: X-ray diffraction Spectroscopy
There and back again A short trip to Fourier Space Janet Vonck 23 April 2014 Where can I find a Fourier Transform? Fourier Transforms are ubiquitous in structural biology: X-ray diffraction Spectroscopy
IMPRS: Ultrafast Source Technologies
 IMPRS: Ultrafast Source Technologies Fran X. Kärtner & Thorsten Uphues, Bldg. 99, O3.097 & Room 6/3 Email & phone: fran.kaertner@cfel.de, 040 8998 6350 Thorsten.Uphues@cfel.de, 040 8998 706 Lectures: Tuesday
IMPRS: Ultrafast Source Technologies Fran X. Kärtner & Thorsten Uphues, Bldg. 99, O3.097 & Room 6/3 Email & phone: fran.kaertner@cfel.de, 040 8998 6350 Thorsten.Uphues@cfel.de, 040 8998 706 Lectures: Tuesday
MODERN OPTICS. P47 Optics: Unit 9
 MODERN OPTICS P47 Optics: Unit 9 Course Outline Unit 1: Electromagnetic Waves Unit 2: Interaction with Matter Unit 3: Geometric Optics Unit 4: Superposition of Waves Unit 5: Polarization Unit 6: Interference
MODERN OPTICS P47 Optics: Unit 9 Course Outline Unit 1: Electromagnetic Waves Unit 2: Interaction with Matter Unit 3: Geometric Optics Unit 4: Superposition of Waves Unit 5: Polarization Unit 6: Interference
High Directivity Horn Antenna of Metamaterial in Terahertz Xiangjin Quan, Shiquan Zhang, Hui Li
 International Power, Electronics and Materials Engineering Conference (IPEMEC 215) High Directivity Horn Antenna of Metamaterial in Terahertz Xiangjin Quan, Shiquan Zhang, Hui Li Engineering University
International Power, Electronics and Materials Engineering Conference (IPEMEC 215) High Directivity Horn Antenna of Metamaterial in Terahertz Xiangjin Quan, Shiquan Zhang, Hui Li Engineering University
RESONANT BEHAVIOR MEASUREMENTS AND TWO- DIMENSIONAL IMAGING OF SMALL CONDUCTING SPHERES IN CATR
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 10, 25 35, 2009 RESONANT BEHAVIOR MEASUREMENTS AND TWO- DIMENSIONAL IMAGING OF SMALL CONDUCTING SPHERES IN CATR S. H. Quan and Q. H. Liu Beijing University
Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 10, 25 35, 2009 RESONANT BEHAVIOR MEASUREMENTS AND TWO- DIMENSIONAL IMAGING OF SMALL CONDUCTING SPHERES IN CATR S. H. Quan and Q. H. Liu Beijing University
METIS- ESA Solar Orbiter Mission: internal straylight analysis
 METIS- ESA Solar Orbiter Mission: internal straylight analysis E. Verroi, V. Da Deppo, G. Naletto, S. Fineschi, E. Antonucci University of Padova (Italy) CNR-Institute for Photonics and Nanotechnologies
METIS- ESA Solar Orbiter Mission: internal straylight analysis E. Verroi, V. Da Deppo, G. Naletto, S. Fineschi, E. Antonucci University of Padova (Italy) CNR-Institute for Photonics and Nanotechnologies
CHAPTER 4 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES IN CYLINDRICAL SYSTEMS
 CHAPTER 4 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES IN CYLINDRICAL SYSTEMS The vector Helmholtz equations satisfied by the phasor) electric and magnetic fields are where. In low-loss media and for a high frequency, i.e.,
CHAPTER 4 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES IN CYLINDRICAL SYSTEMS The vector Helmholtz equations satisfied by the phasor) electric and magnetic fields are where. In low-loss media and for a high frequency, i.e.,
LECTURE 18: Horn Antennas (Rectangular horn antennas. Circular apertures.) Equation Section 18
 LCTUR 18: Horn Antennas (Rectangular horn antennas. Circular apertures.) quation Section 18 1 Rectangular horn antennas Horn antennas are popular in the microwave band (above 1 GHz). Horns provide high
LCTUR 18: Horn Antennas (Rectangular horn antennas. Circular apertures.) quation Section 18 1 Rectangular horn antennas Horn antennas are popular in the microwave band (above 1 GHz). Horns provide high
LASCAD Tutorial No. 4: Dynamic analysis of multimode competition and Q-Switched operation
 LASCAD Tutorial No. 4: Dynamic analysis of multimode competition and Q-Switched operation Revised: January 17, 2014 Copyright 2014 LAS-CAD GmbH Table of Contents 1 Table of Contents 1 Introduction...
LASCAD Tutorial No. 4: Dynamic analysis of multimode competition and Q-Switched operation Revised: January 17, 2014 Copyright 2014 LAS-CAD GmbH Table of Contents 1 Table of Contents 1 Introduction...
Intro Vectors 2D implicit curves 2D parametric curves. Graphics 2011/2012, 4th quarter. Lecture 2: vectors, curves, and surfaces
 Lecture 2, curves, and surfaces Organizational remarks Tutorials: Tutorial 1 will be online later today TA sessions for questions start next week Practicals: Exams: Make sure to find a team partner very
Lecture 2, curves, and surfaces Organizational remarks Tutorials: Tutorial 1 will be online later today TA sessions for questions start next week Practicals: Exams: Make sure to find a team partner very
M2 TP. Low-Energy Electron Diffraction (LEED)
 M2 TP Low-Energy Electron Diffraction (LEED) Guide for report preparation I. Introduction: Elastic scattering or diffraction of electrons is the standard technique in surface science for obtaining structural
M2 TP Low-Energy Electron Diffraction (LEED) Guide for report preparation I. Introduction: Elastic scattering or diffraction of electrons is the standard technique in surface science for obtaining structural
Simulation of a linear Fresnel solar collector concentrator
 *Corresponding author: acoliv@fe.up.pt Simulation of a linear Fresnel solar collector concentrator... Jorge Facão and Armando C. Oliveira * Faculty of Engineering, University of Porto-New Energy Tec. Unit,
*Corresponding author: acoliv@fe.up.pt Simulation of a linear Fresnel solar collector concentrator... Jorge Facão and Armando C. Oliveira * Faculty of Engineering, University of Porto-New Energy Tec. Unit,
Astronomy 203 practice final examination
 Astronomy 203 practice final examination Fall 1999 If this were a real, in-class examination, you would be reminded here of the exam rules, which are as follows: You may consult only one page of formulas
Astronomy 203 practice final examination Fall 1999 If this were a real, in-class examination, you would be reminded here of the exam rules, which are as follows: You may consult only one page of formulas
Propagation dynamics of abruptly autofocusing Airy beams with optical vortices
 Propagation dynamics of abruptly autofocusing Airy beams with optical vortices Yunfeng Jiang, 1 Kaikai Huang, 1,2 and Xuanhui Lu 1, * 1 Institute of Optics, Department of Physics, Zhejiang University,
Propagation dynamics of abruptly autofocusing Airy beams with optical vortices Yunfeng Jiang, 1 Kaikai Huang, 1,2 and Xuanhui Lu 1, * 1 Institute of Optics, Department of Physics, Zhejiang University,
Geometric Optics. Scott Freese. Physics 262
 Geometric Optics Scott Freese Physics 262 10 April 2008 Abstract The primary goal for this experiment was to learn the basic physics of the concept of geometric optics. The specific concepts to be focused
Geometric Optics Scott Freese Physics 262 10 April 2008 Abstract The primary goal for this experiment was to learn the basic physics of the concept of geometric optics. The specific concepts to be focused
Radio Astronomy An Introduction
 Radio Astronomy An Introduction Felix James Jay Lockman NRAO Green Bank, WV References Thompson, Moran & Swenson Kraus (1966) Christiansen & Hogbom (1969) Condon & Ransom (nrao.edu) Single Dish School
Radio Astronomy An Introduction Felix James Jay Lockman NRAO Green Bank, WV References Thompson, Moran & Swenson Kraus (1966) Christiansen & Hogbom (1969) Condon & Ransom (nrao.edu) Single Dish School
USAGE OF NUMERICAL METHODS FOR ELECTROMAGNETIC SHIELDS OPTIMIZATION
 October 4-6, 2007 - Chiinu, Rep.Moldova USAGE OF NUMERICAL METHODS FOR ELECTROMAGNETIC SHIELDS OPTIMIZATION Ionu- P. NICA, Valeriu Gh. DAVID, /tefan URSACHE Gh. Asachi Technical University Iai, Faculty
October 4-6, 2007 - Chiinu, Rep.Moldova USAGE OF NUMERICAL METHODS FOR ELECTROMAGNETIC SHIELDS OPTIMIZATION Ionu- P. NICA, Valeriu Gh. DAVID, /tefan URSACHE Gh. Asachi Technical University Iai, Faculty
Measurements of the DL0SHF 8 GHz Antenna
 Measurements of the DL0SHF 8 GHz Antenna Joachim Köppen, DF3GJ Inst.Theoret.Physik u.astrophysik, Univ. Kiel September 2015 Pointing Correction Position errors had already been determined on a few days
Measurements of the DL0SHF 8 GHz Antenna Joachim Köppen, DF3GJ Inst.Theoret.Physik u.astrophysik, Univ. Kiel September 2015 Pointing Correction Position errors had already been determined on a few days
A Survey of Computational High Frequency Wave Propagation II. Olof Runborg NADA, KTH
 A Survey of Computational High Frequency Wave Propagation II Olof Runborg NADA, KTH High Frequency Wave Propagation CSCAMM, September 19-22, 2005 Numerical methods Direct methods Wave equation (time domain)
A Survey of Computational High Frequency Wave Propagation II Olof Runborg NADA, KTH High Frequency Wave Propagation CSCAMM, September 19-22, 2005 Numerical methods Direct methods Wave equation (time domain)
Physics I : Oscillations and Waves Prof. S. Bharadwaj Department of Physics and Meteorology Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Physics I : Oscillations and Waves Prof. S. Bharadwaj Department of Physics and Meteorology Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 21 Diffraction-II Good morning. In the last class, we had
Physics I : Oscillations and Waves Prof. S. Bharadwaj Department of Physics and Meteorology Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 21 Diffraction-II Good morning. In the last class, we had
A family of closed form expressions for the scalar field of strongly focused
 Scalar field of non-paraxial Gaussian beams Z. Ulanowski and I. K. Ludlow Department of Physical Sciences University of Hertfordshire Hatfield Herts AL1 9AB UK. A family of closed form expressions for
Scalar field of non-paraxial Gaussian beams Z. Ulanowski and I. K. Ludlow Department of Physical Sciences University of Hertfordshire Hatfield Herts AL1 9AB UK. A family of closed form expressions for
5 RCS Management of Edge Diffracted Waves
 5 RCS Management of Edge Diffracted Waves 5.1 Introduction Radar absorbing materials (RAM s) applied as a coating on the surface of an object, partially transform the energy of an incident radar beam into
5 RCS Management of Edge Diffracted Waves 5.1 Introduction Radar absorbing materials (RAM s) applied as a coating on the surface of an object, partially transform the energy of an incident radar beam into
PHYSICS 253 SAMPLE FINAL EXAM. Student Number. The last two pages of the exam have some equations and some physical constants.
 PHYSICS 253 SAMPLE FINAL EXAM Name Student Number CHECK ONE: Instructor 1 10:00 Instructor 2 1:00 Note that problems 1-19 are worth 2 points each, while problem 20 is worth 15 points and problems 21 and
PHYSICS 253 SAMPLE FINAL EXAM Name Student Number CHECK ONE: Instructor 1 10:00 Instructor 2 1:00 Note that problems 1-19 are worth 2 points each, while problem 20 is worth 15 points and problems 21 and
Villa Galileo Firenze, 12 ottobre 2017 Antenna Pattern Measurement: Theory and Techniques
 Villa Galileo Firenze, 12 ottobre 2017 Antenna Pattern Measurement: Theory and Techniques F. D Agostino, M. Migliozzi University of Salerno, Italy ANTENNAE REGIONS The REACTIVE NEAR-FIELD REGION is the
Villa Galileo Firenze, 12 ottobre 2017 Antenna Pattern Measurement: Theory and Techniques F. D Agostino, M. Migliozzi University of Salerno, Italy ANTENNAE REGIONS The REACTIVE NEAR-FIELD REGION is the
RAY TRAJECTORIES, BINOMIAL OF A NEW TYPE, AND THE BINARY SYSTEM
 Alexander Yurkin A.M. Prokhorov General Physics Institute of the Russian Academy of Sciences e-mail: yurkin@fpl.gpi.ru RAY TRAJECTORIES, BINOMIAL OF A NEW TYPE, AND THE BINARY SYSTEM Abstract The paper
Alexander Yurkin A.M. Prokhorov General Physics Institute of the Russian Academy of Sciences e-mail: yurkin@fpl.gpi.ru RAY TRAJECTORIES, BINOMIAL OF A NEW TYPE, AND THE BINARY SYSTEM Abstract The paper
In this method, one defines
 1 Feautrier s Method for Radiative Transfer This project is to use Feautrier s method to solve the Gray Atmosphere problem for a plane-parallel atmosphere Although we have developed alternate techniques
1 Feautrier s Method for Radiative Transfer This project is to use Feautrier s method to solve the Gray Atmosphere problem for a plane-parallel atmosphere Although we have developed alternate techniques
12 주 /15 주 작은구멍이나장애물을만나면넘어가거나돌아간다. 원거리에돌이 ( 프라운호퍼에돌이 ) 에돌이 ( 회절 )- 불확정성의원리 근거리에돌이 ( 프레스넬에돌이 )
 12 주 /15 주 작은구멍이나장애물을만나면넘어가거나돌아간다. 원거리에돌이 ( 프라운호퍼에돌이 ) 에돌이 ( 회절 )- 불확정성의원리 근거리에돌이 ( 프레스넬에돌이 ) 2014-12-17 1 현대물리 : 광학 5 장 Diffraction 목포해양대학교기관공학부 김상훈 2014-12-17 2 2014-12-17 3 2014-12-17 4 2014-12-17 5
12 주 /15 주 작은구멍이나장애물을만나면넘어가거나돌아간다. 원거리에돌이 ( 프라운호퍼에돌이 ) 에돌이 ( 회절 )- 불확정성의원리 근거리에돌이 ( 프레스넬에돌이 ) 2014-12-17 1 현대물리 : 광학 5 장 Diffraction 목포해양대학교기관공학부 김상훈 2014-12-17 2 2014-12-17 3 2014-12-17 4 2014-12-17 5
STATISTICS OF MULTIPLE EXTRANEOUS SIGNALS ON A COMPACT RANGE
 STATISTICS OF MULTIPLE EXTRANEOUS SIGNALS ON A COMPACT RANGE by John R. Jones and Esko A. Jaska Microwave and Antenna Technology Development Laboratory Georgia Tech Research Institute Georgia Institute
STATISTICS OF MULTIPLE EXTRANEOUS SIGNALS ON A COMPACT RANGE by John R. Jones and Esko A. Jaska Microwave and Antenna Technology Development Laboratory Georgia Tech Research Institute Georgia Institute
ITD Double-Edge Diffraction for Complex Source Beam Illumination
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ANTENNAS AND PROPAGATION 1 ITD Double-Edge Diffraction for Complex Source Beam Illumination Alberto Toccafondi, Senior Member, IEEE, Stefano Mihai Canta, Member, IEEE Danilo Erricolo,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ANTENNAS AND PROPAGATION 1 ITD Double-Edge Diffraction for Complex Source Beam Illumination Alberto Toccafondi, Senior Member, IEEE, Stefano Mihai Canta, Member, IEEE Danilo Erricolo,
Semi-analytical Fourier transform and its application to physical-optics modelling
 SPIE Optical System Design 2018, Paper 10694-24 Semi-analytical Fourier transform and its application to physical-optics modelling Zongzhao Wang 1,2, Site Zhang 1,3, Olga Baladron-Zorito 1,2 and Frank
SPIE Optical System Design 2018, Paper 10694-24 Semi-analytical Fourier transform and its application to physical-optics modelling Zongzhao Wang 1,2, Site Zhang 1,3, Olga Baladron-Zorito 1,2 and Frank
Arbitrary Patterning Techniques for Anisotropic Surfaces, and Line Waves
 Arbitrary Patterning Techniques for Anisotropic Surfaces, and Line Waves Dan Sievenpiper, Jiyeon Lee, and Dia a Bisharat January 11, 2016 1 Outline Arbitrary Anisotropic Surface Patterning Surface wave
Arbitrary Patterning Techniques for Anisotropic Surfaces, and Line Waves Dan Sievenpiper, Jiyeon Lee, and Dia a Bisharat January 11, 2016 1 Outline Arbitrary Anisotropic Surface Patterning Surface wave
for Image Restoration
 An Eddy Current Transducer Model for Image Restoration Bennett R. Groshong Griff L. Bilbro Wesley E. Snyder Center for Communications and Signal Processing Department Electrical and Computer Engineering
An Eddy Current Transducer Model for Image Restoration Bennett R. Groshong Griff L. Bilbro Wesley E. Snyder Center for Communications and Signal Processing Department Electrical and Computer Engineering
ROINN NA FISICE Department of Physics
 ROINN NA FISICE Department of 1.1 Astrophysics Telescopes Profs Gabuzda & Callanan 1.2 Astrophysics Faraday Rotation Prof. Gabuzda 1.3 Laser Spectroscopy Cavity Enhanced Absorption Spectroscopy Prof. Ruth
ROINN NA FISICE Department of 1.1 Astrophysics Telescopes Profs Gabuzda & Callanan 1.2 Astrophysics Faraday Rotation Prof. Gabuzda 1.3 Laser Spectroscopy Cavity Enhanced Absorption Spectroscopy Prof. Ruth
1 ESO's Compact Laser Guide Star Unit Ottobeuren, Germany Beam optics!
 1 ESO's Compact Laser Guide Star Unit Ottobeuren, Germany www.eso.org Introduction Characteristics Beam optics! ABCD matrices 2 Background! A paraxial wave has wavefronts whose normals are paraxial rays.!!
1 ESO's Compact Laser Guide Star Unit Ottobeuren, Germany www.eso.org Introduction Characteristics Beam optics! ABCD matrices 2 Background! A paraxial wave has wavefronts whose normals are paraxial rays.!!
2. Diffraction as a means to determine crystal structure
 2. Diffraction as a means to determine crystal structure Recall de Broglie matter waves: He atoms: [E (ev)] 1/2 = 0.14 / (Å) E 1Å = 0.0196 ev Neutrons: [E (ev)] 1/2 = 0.28 / (Å) E 1Å = 0.0784 ev Electrons:
2. Diffraction as a means to determine crystal structure Recall de Broglie matter waves: He atoms: [E (ev)] 1/2 = 0.14 / (Å) E 1Å = 0.0196 ev Neutrons: [E (ev)] 1/2 = 0.28 / (Å) E 1Å = 0.0784 ev Electrons:
Huygens principle-based wavefront tracing in non-uniform media
 Presented at the 2015 Sherwood Fusion Theory Conference March 16-18, 2015, Courant Institute at New York University, NY, USA Huygens principle-based wavefront tracing in non-uniform media A. Zhao, P.-D.
Presented at the 2015 Sherwood Fusion Theory Conference March 16-18, 2015, Courant Institute at New York University, NY, USA Huygens principle-based wavefront tracing in non-uniform media A. Zhao, P.-D.
Focal shift in vector beams
 Focal shift in vector beams Pamela L. Greene The Institute of Optics, University of Rochester, Rochester, New York 1467-186 pgreene@optics.rochester.edu Dennis G. Hall The Institute of Optics and The Rochester
Focal shift in vector beams Pamela L. Greene The Institute of Optics, University of Rochester, Rochester, New York 1467-186 pgreene@optics.rochester.edu Dennis G. Hall The Institute of Optics and The Rochester
Digital Image Processing
 Digital Image Processing, 2nd ed. Digital Image Processing Chapter 7 Wavelets and Multiresolution Processing Dr. Kai Shuang Department of Electronic Engineering China University of Petroleum shuangkai@cup.edu.cn
Digital Image Processing, 2nd ed. Digital Image Processing Chapter 7 Wavelets and Multiresolution Processing Dr. Kai Shuang Department of Electronic Engineering China University of Petroleum shuangkai@cup.edu.cn
IMPACT OF FINITE GROUND PLANE EDGE DIFFRA- CTIONS ON RADIATION PATTERNS OF APERTURE ANTENNAS
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research B, Vol. 55, 1 21, 2013 IMPACT OF FINITE GROUND PLANE EDGE DIFFRA- CTIONS ON RADIATION PATTERNS OF APERTURE ANTENNAS Nafati A. Aboserwal, Constantine A. Balanis *,
Progress In Electromagnetics Research B, Vol. 55, 1 21, 2013 IMPACT OF FINITE GROUND PLANE EDGE DIFFRA- CTIONS ON RADIATION PATTERNS OF APERTURE ANTENNAS Nafati A. Aboserwal, Constantine A. Balanis *,
PRINCIPLES OF PHYSICAL OPTICS
 PRINCIPLES OF PHYSICAL OPTICS C. A. Bennett University of North Carolina At Asheville WILEY- INTERSCIENCE A JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC., PUBLICATION CONTENTS Preface 1 The Physics of Waves 1 1.1 Introduction
PRINCIPLES OF PHYSICAL OPTICS C. A. Bennett University of North Carolina At Asheville WILEY- INTERSCIENCE A JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC., PUBLICATION CONTENTS Preface 1 The Physics of Waves 1 1.1 Introduction
Handout 7 Reciprocal Space
 Handout 7 Reciprocal Space Useful concepts for the analysis of diffraction data http://homepages.utoledo.edu/clind/ Concepts versus reality Reflection from lattice planes is just a concept that helps us
Handout 7 Reciprocal Space Useful concepts for the analysis of diffraction data http://homepages.utoledo.edu/clind/ Concepts versus reality Reflection from lattice planes is just a concept that helps us
Addition of a Lens Before the Second Focus of a Prolate-Spheroidal IRA
 Sensor and Simulation Notes Note 512 April 2006 Addition of a Lens Before the Second Focus of a Prolate-Spheroidal IRA Carl E. Baum University of New Mexico Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
Sensor and Simulation Notes Note 512 April 2006 Addition of a Lens Before the Second Focus of a Prolate-Spheroidal IRA Carl E. Baum University of New Mexico Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
2. Diffraction as a means to determine crystal structure
 Page 1 of 22 2. Diffraction as a means to determine crystal structure Recall de Broglie matter waves: 2 p h E = where p = 2m λ h 1 E = ( ) 2m λ hc E = hυ = ( photons) λ ( matter wave) He atoms: [E (ev)]
Page 1 of 22 2. Diffraction as a means to determine crystal structure Recall de Broglie matter waves: 2 p h E = where p = 2m λ h 1 E = ( ) 2m λ hc E = hυ = ( photons) λ ( matter wave) He atoms: [E (ev)]
Interference, Diffraction and Fourier Theory. ATI 2014 Lecture 02! Keller and Kenworthy
 Interference, Diffraction and Fourier Theory ATI 2014 Lecture 02! Keller and Kenworthy The three major branches of optics Geometrical Optics Light travels as straight rays Physical Optics Light can be
Interference, Diffraction and Fourier Theory ATI 2014 Lecture 02! Keller and Kenworthy The three major branches of optics Geometrical Optics Light travels as straight rays Physical Optics Light can be
The Fractional Fourier Transform with Applications in Optics and Signal Processing
 * The Fractional Fourier Transform with Applications in Optics and Signal Processing Haldun M. Ozaktas Bilkent University, Ankara, Turkey Zeev Zalevsky Tel Aviv University, Tel Aviv, Israel M. Alper Kutay
* The Fractional Fourier Transform with Applications in Optics and Signal Processing Haldun M. Ozaktas Bilkent University, Ankara, Turkey Zeev Zalevsky Tel Aviv University, Tel Aviv, Israel M. Alper Kutay
Unstable optical resonators. Laser Physics course SK3410 Aleksandrs Marinins KTH ICT OFO
 Unstable optical resonators Laser Physics course SK3410 Aleksandrs Marinins KTH ICT OFO Outline Types of resonators Geometrical description Mode analysis Experimental results Other designs of unstable
Unstable optical resonators Laser Physics course SK3410 Aleksandrs Marinins KTH ICT OFO Outline Types of resonators Geometrical description Mode analysis Experimental results Other designs of unstable
