Dark matter & Cosmology
|
|
|
- Alisha West
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Dark matter & Cosmology CL Jee et al 06 Françoise Combes Observatoire de Paris Thursday June 7, 2012
2 Evidences of dark matter Galaxy clusters, Virial /visible mass ~100 (Zwicky 1937) Coma cluster: galaxy velocity dispersion i Rotation curves for instance our Galaxy, The Milky Way R 0 Problem of DM, below a certain Acceleration R>Ro Ro 2
3 Galaxies with HI M83: optical HI: cartography of atomic hydrogen Wavelength 21cm HI in M83: a galaxy similar to the Milky Way 3
4 Gravitationnal shear, weak lensing Red: X-ray gas Blue: total matter Cosmos field Constraints on the Dark Matter, and Dark Energy Massey et al
5 Tully-Fisher relation Relation between maximum velocity and luminosity V corrected from inclination Much hless scatter in I or K-band (no extinction) Correlation with Vflat Better than Vmax Ursa cluster Verheijen
6 Tully-Fisher relation for gaseous galaxies works much hbetter in adding gas mass Relation M baryons with Rotational V M b ~ V 4 c McGaugh et al (2000) Baryonic Tully-Fisher 6
7 Baryonic Tully-Fisher relation f b baryon fraction= 17% CDM: Cold Dark Matter dark energy V 4 McGaugh
8 Where are the baryons? 6% in galaxies ; 3% in galaxy clusters as hot X-ray gas <18% in the Lyman-alpha forest (cosmic filaments) 5-10% in the WHIM (Warm-Hot Intergalactic Medium) K OVI lines 65% are not yet identified or localised! Most of them are not in galaxies 8
9 Fraction of baryons detected Fraction = Mb / (0.17 M500) M500 dynamical mass within R500 R500 radius where the density is 500 times the mean cosmic density Clusters Local dwarfs Galaxies Groups 9
10 Mass & Light Distribution Functions CDM: Too many bright and too many faint galaxies M/L = 80 Baugh 2006, Eke et al 2006, Jenkins et al 2001
11 Star Formation Feedback to fit faint end Gas is heated in dwarfs, but falls in heavier haloes worsen the bright end problem No AGN AGN feedback Requires AGN feedback at the bright end Somerville et al 2008
12 Problems of the standard -CDM model Prediction of cusps in galaxy center, which are in particular absent in dw-irr, dominated by dark matter Low angular momentum of baryons, and as a consequence formation of much htoo small galaxy disks Prediction of a large number of small halos, not observed The solution to all these problems could come from some baryonic physics (SF, feedback?), or lack of spatial resolution in simulations, or wrong nature of dark matter? 12
13 Dwarf Irr : DDO154 the prototype Carignan & Beaulieu 1989 No cusp Low surface brightness galaxies are dominated by dark matter Swaters et al
14 SIDM Self-interactive DM Size of cusps depends on the galaxy. Dwarfs rc ~10kpc SIDM cross section is fit to galaxies, then too big for clusters. Collisionless SIDM simulations Koda et al
15 Cusps and Warm DM (WDM) The density profile is universal: NFW, for HDM, WDM and CDM (Wang & White 2009) The universality is not due to mergers In monolithic collapse, same features Concentrations, cusps, shapes of haloes Spins of haloes, kinematics The only big difference is the power spectrum Can be fitted, to limit small scales Temperature at decoupling, could limit phase-space space densities, but r < -3 c /r Cores in galaxies r c /r 200 = 5% Villaescusa-Navarro, Dalal (2011) 15
16 Missing satellites Aquarius simulations of MW Steep versus flat cum mulative numbe er Springel et al Boylan-Kolchin et al
17 Abundance matching for satellites Stellar mass matching ass ellar ma ste Springel et al Boylan-Kolchin et al
18 Misfits of satellites 9-10 satellites with L v > 10 5 Lo MW M* f b M DM From hl halo abundance matching, the efficiency to form stars is derived, must peak at 20% of baryons in stars at M ~E12Mo (MW-type galaxies) 18
19 Problems of the WDM To account for dwarf galaxies cores, m ~0.1 kev But for large scales 1-10kev is required Dwarf galaxies have to be formed anyway, with a kpc scale cores. But the mwdm required for their core suppress the dwarf formation Maccio et al
20 Alternative theories of gravity («venture capital») Scalar-tensor theories Chameleon Einstein-Aether Theories Modifed Newtonian dynamics Tensor-Vector-Scalar Theories Bekenstein TeVeS Other theories, for dark energy, degravitation.. higher order derivatives f(r) Higher Dimensional Theories of Gravity Branes 20
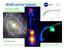
21 a = (a 0 a N ) 1/2 MOND =MOdified Newtonian Dynamics Modification at weak acceleration a N ~ 1/r 2 a ~ 1/r V 2 = cste a 2 ~V 4 /R 2 ~ GM/R 2 (TF) (Milgrom 1983) a N = a (x) N x = a/a 0 a 0 = m/s 2 or 1 Angstroms/s 2 x << 1 Mondian regime (x) x x>>1 Newtonian (x) 1 Covariant theory: TeVeS Account for lensing 21
22 Dynamic Mass / Visible Mass The ratio remarquably depends on acceleration, The only variable controling the gravity regime universally Radius Velocity Acceleration 22
23 Tully-Fisher relation g M2 = a 0 g N = a 0 GM/r 2 = V 4 /r 2 V 4 = a 0 GM LSB N1560 Rotation curves are fit for all types (dwarfs LSB, giant HSB) HSB N2903 gas stars gas stars 23
24 Pressure-supported systems From GC to galaxies and clusters Sanders & McGaugh
25 Multiple rotation curves.. All types, all masses, with the same parameter a0, universal for ~1000 curves Sanders & Verheijen 1998 dwarf N6946 : massive baryons only M33 25
26 Problems of MOND in galaxy clusters Inside galaxy clusters, there still exists some missing mass, which cannot be explained by MOND, since the cluster center is only moderately in the MOND regime (~0.5 a 0 ) Observations in X-rays: hot gas in hydrostatic equilibrium, and weak gravitational lenses (shear) MOND reduces by a factor 2 the missing mass It remains another component, which could be neutrinos. (plus baryons) The baryon fraction is not the universal one in clusters (so baryons could still exist in the standard CDM model) But if CDM does not exist, there is no limiting fraction 26
27 MOND & galaxy clusters According to baryon physics, cold gas could accumulate at the cluster centers Alternatively, neutrinos could represent 2x more mass than the baryons 27
28 The bullet cluster X-ray gas Proof of the existence of non-baryonic matter Total mass Accounted for in MOND + neutrinos (2eV, Angus et al 2006) 28
29 CDM simulation Collision velocity from the bow-shock = km/s (Mach 3) Hayashi & White 2006 Farrar & Rosen 2007 impossible to reconcile with CDM Milosavljevic et al 2007, Springel & Farrar 2007 CDM can only V < 3500 km/s MOND > 4500 km/s Relative velocities between halos 4 times higher in MOND Linares et al 2009 Collision by 16% over-estimated? 29 V_gas could be higher than V_CDM
30 Mahdavi et al 2007 Abell 520 z=0.201 Red= X-ray gas Contours= lensing Massive DM core Coinciding with X gas but devoid of galaxies Cosmic train wreck Opposite case! 30
31 Abell 520 merging clusters Contours=total mass Contours = X-ray gas How are the galaxies ejected from the CDM peak?? 31
32 Jee et al 2012 Dark core at 10 Contours of DM (weak lensing HST) on X-ray (red) A520: Dark core with X-ray B-band CFH (blue) Collisional dark matter? DM /m DM ~3.8cm 2 /g Real counter-example of the bullet where DM /m DM < 1 cm 2 /g 32
33 Constraints from galaxy dynamics and observations Are the stability, evolution & formation of galaxies stringent tests of the theory? --Galaxy interactions --Bars and their pattern speeds --Different dynamical friction 33
34 Influence of DM halo With DM halo Without DM (MOND) Tiret & Combes
35 Bar strength and pattern speed with and w/o DM DM With DM, the bar appears later, and can reform after the peanut weakening through h halo AM exchange, But b falls off b Tiret & Combes
36 Interactions of galaxies: the Antennae: MOND versus CDM Dynamical friction is much lower with MOND: mergers last much longer CDM MOND Also much longer time-scale for merging of dissipationless galaxies (Nipoti et al 2007) 36
37 Simulations of the Antennae 37
38 Dynamical friction Analytically, the dynamical friction is predicted stronger with MOND than in the equivalent Newtonian system with dark matter Ciotti & Binney 2004 (CB04), Nipoti et al 2008 However simulations show DF less efficient in galaxy interactions In CDM, a lot of particles acquire E and AM, and DF concept applicable In MOND, a small number of particles in the outer parts acquire big quantities (no analytical treatment) Nipoti et al 2007, Tiret & Combes
39 Merger induced starbursts degeneracy CDM: dynamical friction on DM particles very efficient mergers in one passage MOND: with the same angular momentum, merger will require many passages Starburst at each passage gewhen minimal approach Number of "merger/sb" can be explained both ways Di Matteo et al
40 Formation of Tidal Dwarf Galaxies Exchange of AM is within the disk: much easier with MOND to form TDG In DM, requires very extended DM distribution (Bournaud et al 03) 40
41 TDG in N5291 HI ring Head-on collision simulation Bournaud et al
42 Dynamics of the TDGs With MOND, Gentile et al 2007 All inclinations= 45, from simulations (Bournaud et al 07) dark H 2 42
43 MOND and the dark baryons Is MOND compatible ewith the eexistence e ceof dark gas in galaxies? What fraction provides the best fit to the rotation curves? Fit of ~50 rotation curves, c=m(dark)/mhi Tiret & Combes 08, Milgrom 07 43
44 Combination with MOND NGC 1560: fits with variation i of a 0 ~ 1/(gas/HI) / 44 V 4 = a 0 GM Tiret & Combes 2008
45 Dark matter in Ellipticals Planetary Nebulae: Romanowsky et al 2003 Dearth of dark matter??.. Visible matter (isotropic) isothermal (isotropic) 45
46 Anisotropy of velocities = 1 r, -, 0, 1 circular, isotropic and radial orbits When galaxy form by mergers, orbits in the outer parts are strongly gy radial, which could explain the low projected dispersion (Dekel et al 2005) Radius The observation of the velocity profile is somewhat degenerate and cannot lead to the dark matter content univocally 46
47 Young stars are in yellow contours Comparison with data for N821 (green), N3379(violet) N4494 (brown), N4697 (blue) 47
48 DM profile from satellites SDSS, 2500 deg 2, 3000 satellites Mb=-16, -18 (galaxies 14) Removal of interlopers v =120km/s at 20kpc and 60km/s at 350kpc (Prada et al 2003) Declines agree with ~r -3 of NFW (CDM profile) v within 100kpc varies as L 0.3, quite close to TF relation In average 2 satellites per galaxy, and 0.2 interlopers See also McKay et al (2002) ~L from 1225 SDSS satellites M 260 in agreement with lensing results But flat velocity dispersion recovered (as if ~r -2 ) 48
49 Satellites in SDSS Klypin & Prada 2009 Statistical satellites Only 1 or 0 for each galaxy 49
50 Test of the SDSS satellites Tiret et al t types of fcdm CDM1: NFW cusp CDM2: as required by rotation curves DV Km/s PN satellites Radius (kpc) 50
51 Tully Fisher Equivalent Asterisk: Lenses (Hoekstra et al 2002) ~L TF normal spirals (Verheijen 2001) 120kpc ~L kpc ~L 0.5 Prada et al (2003) 51
52 Large scale structure In comoving coordinates: r = a x, v = da/dt x + a u = 4 G (g M / ) g M =g N +C C = rot (h) critical acceleration (=a0) Previous approximations h=0 (Nusser 2002, Knebe & Gibson 2004) Newton and MOND accelerations are then parallel Start from a cosmological Newton+ CDM then find MOND produces as much clustering ( = cste) ~ a 2, instead of ~a for Newton+ CDM New code AMIGA, taking into account the curl (Llinares et al 2009) Initial conditions from CMBFAST, displacements ( Zeldovich approx) grid, 32h -1 Mpc, assuming Newtonian initial state For that critical acceleration varies with time = a 0 52
53 MOND cosmological simulations Starting z=50, dissipationless matter, 2 low models + CDM Easier to form large masses early Llinares et al 2009 z=2 CDM MOND1 MOND2 z=5 CDM MOND1 MOND2 53
54 Evolution with time Does the critical acceleration vary? a 0 ~ c H o, or also a 0 ~ c ( /3) 1/2 Possible to imagine variations, in either way (more or less MOND in the early universe) Open question, as is the evolution of H(t) () R(t) 54
55 MOND: fit of CMB data, WMAP Include massive neutrinos 1-2eV Fit with MOND (no-dm) of Acoustic peaks (Skordis et al 2006) : =78% =17% b =5% MOND b -- - : =95% b =5%.... : CDM Fit with CDM + 55
56 TeVeS: CMB and LSS Skordis 2009 Growth of structures due to the vector field Scalar field aceleration of expansion, DE 56
57 WMAP-5 + ACBAR The 3rd peak is not lower (damped) than the 2 nd peak There must exists something else: sterile neutrinos, or other terms in relativistic theory (BSTV) HDM Neutrinos 11ev ---- CDM Angus (2011) 57
58 Conclusion: Success and Problems of each model CDM: great success at large scale, but problems at galaxy scales WDM: does not solve the cusps, not enough small-scale l power MOND solves the problems of galaxies, but has to solve its own problem at group and cluster scales (neutrinos, baryons..) More tuned SN and AGN feedback, to solve CDM models Numerical simulations with improved physics, resolution Lorentz covariant theory, TeVeS (Bekenstein 2004) with a lot of varieties (GEA, BSTV, k-essence essence..) Different metric (BIMOND), still free parameters to explore 58 Other propositions? Modif of inertia?, non-local? Dipolar DM..
59 Acceleration parameter a ~ V f4 /M b Famaey & McGaugh
Galaxy constraints on Dark matter
 Galaxy constraints on Dark matter 25% 5% 70% CL 0152-1357. 1357 Jee et al 06 WMAP+Planck Françoise Combes Observatoire de Paris Thursday March 28, 2013 Evidences of dark matter Galaxy clusters, Virial
Galaxy constraints on Dark matter 25% 5% 70% CL 0152-1357. 1357 Jee et al 06 WMAP+Planck Françoise Combes Observatoire de Paris Thursday March 28, 2013 Evidences of dark matter Galaxy clusters, Virial
MOND and the Galaxies
 MOND and the Galaxies Françoise Combes Observatoire de Paris With Olivier Tiret Angus, Famaey, Gentile, Wu, Zhao Wednesday 1st July 2009 MOND =MOdified Newtonian Dynamics Modification at weak acceleration
MOND and the Galaxies Françoise Combes Observatoire de Paris With Olivier Tiret Angus, Famaey, Gentile, Wu, Zhao Wednesday 1st July 2009 MOND =MOdified Newtonian Dynamics Modification at weak acceleration
What are the best constraints on theories from galaxy dynamics?
 What are the best constraints on theories from galaxy dynamics? TDG in MOND DM MOND Françoise Combes Observatoire de Paris Tuesday 29 June 2010 O.Tiret Still most baryons are unidentified 6% in galaxies
What are the best constraints on theories from galaxy dynamics? TDG in MOND DM MOND Françoise Combes Observatoire de Paris Tuesday 29 June 2010 O.Tiret Still most baryons are unidentified 6% in galaxies
modified gravity? Chaire Galaxies et Cosmologie XENON1T Abel & Kaehler
 Dark matter or modified gravity? Chaire Galaxies et Cosmologie Françoise Combes 11 December, 2017 XENON1T Abel & Kaehler Why modified gravity? CDM models beautifully account for LSS, CMB, galaxy formation
Dark matter or modified gravity? Chaire Galaxies et Cosmologie Françoise Combes 11 December, 2017 XENON1T Abel & Kaehler Why modified gravity? CDM models beautifully account for LSS, CMB, galaxy formation
Everything in baryons?
 Everything in baryons? Benoit Famaey (ULB) Rencontres de Blois 2007 General Relativity -> Dark Matter R αβ - 1/2 R g αβ + Λg αβ = (8πG/c 4 ) T αβ very precisely tested on solar system scales (but Pioneer)
Everything in baryons? Benoit Famaey (ULB) Rencontres de Blois 2007 General Relativity -> Dark Matter R αβ - 1/2 R g αβ + Λg αβ = (8πG/c 4 ) T αβ very precisely tested on solar system scales (but Pioneer)
MOND and the Galaxies
 MOND and the Galaxies F. Combes a and O. Tiret b a Observatoire de Paris, LERMA, 61 Av de l Observatoire, F-75014 Paris, France b SISSA, via Beirut 4, I-34014 Trieste, Italy Abstract. We review galaxy
MOND and the Galaxies F. Combes a and O. Tiret b a Observatoire de Paris, LERMA, 61 Av de l Observatoire, F-75014 Paris, France b SISSA, via Beirut 4, I-34014 Trieste, Italy Abstract. We review galaxy
Dark Matter. 4/24: Homework 4 due 4/26: Exam ASTR 333/433. Today. Modified Gravity Theories MOND
 Dark Matter ASTR 333/433 Today Modified Gravity Theories MOND 4/24: Homework 4 due 4/26: Exam Not any theory will do - length scale based modifications can be immediately excluded as the discrepancy does
Dark Matter ASTR 333/433 Today Modified Gravity Theories MOND 4/24: Homework 4 due 4/26: Exam Not any theory will do - length scale based modifications can be immediately excluded as the discrepancy does
MOND + 11eV sterile neutrinos
 MOND + 11eV sterile neutrinos PPC10 - Day 2 13 -July-2010 th Garry Angus Caustic Group @ UTorino (INFN) In collaboration with Antonaldo Diaferio & Benoit Famaey Modified Newtonian Dynamics MOND new physical
MOND + 11eV sterile neutrinos PPC10 - Day 2 13 -July-2010 th Garry Angus Caustic Group @ UTorino (INFN) In collaboration with Antonaldo Diaferio & Benoit Famaey Modified Newtonian Dynamics MOND new physical
GMU, April 13, The Pros and Cons of Invisible Mass and Modified Gravity. Stacy McGaugh University of Maryland
 GMU, April 13, 2007 The Pros and Cons of Invisible Mass and Modified Gravity Stacy McGaugh University of Maryland What gets us into trouble is not what we don t know. It s what we know for sure that just
GMU, April 13, 2007 The Pros and Cons of Invisible Mass and Modified Gravity Stacy McGaugh University of Maryland What gets us into trouble is not what we don t know. It s what we know for sure that just
Modified Newtonian Dynamics (MOND) and the Bullet Cluster (1E )
 Modified Newtonian Dynamics (MOND) and the Bullet Cluster (1E 0657-558) Alan G. Aversa ABSTRACT Modified Newtonian Dynamics (MOND) is a theory that modifies Newton s force law to explain observations that
Modified Newtonian Dynamics (MOND) and the Bullet Cluster (1E 0657-558) Alan G. Aversa ABSTRACT Modified Newtonian Dynamics (MOND) is a theory that modifies Newton s force law to explain observations that
Dark matter and galaxy formation
 Dark matter and galaxy formation Galaxy rotation The virial theorem Galaxy masses via K3 Mass-to-light ratios Rotation curves Milky Way Nearby galaxies Dark matter Baryonic or non-baryonic A problem with
Dark matter and galaxy formation Galaxy rotation The virial theorem Galaxy masses via K3 Mass-to-light ratios Rotation curves Milky Way Nearby galaxies Dark matter Baryonic or non-baryonic A problem with
Rotation curves of spiral galaxies
 Rotation curves of spiral galaxies Rotation curves Mass discrepancy Circular velocity of spherical systems and disks Dark matter halos Inner and outer regions Tully-Fisher relation From datacubes to rotation
Rotation curves of spiral galaxies Rotation curves Mass discrepancy Circular velocity of spherical systems and disks Dark matter halos Inner and outer regions Tully-Fisher relation From datacubes to rotation
Dark Matter. Galaxy Counts Redshift Surveys Galaxy Rotation Curves Cluster Dynamics Gravitational Lenses ~ 0.3 Ω M Ω b.
 Dark Matter Galaxy Counts Redshift Surveys Galaxy Rotation Curves Cluster Dynamics Gravitational Lenses Ω M ~ 0.3 2 1 Ω b 0.04 3 Mass Density by Direct Counting Add up the mass of all the galaxies per
Dark Matter Galaxy Counts Redshift Surveys Galaxy Rotation Curves Cluster Dynamics Gravitational Lenses Ω M ~ 0.3 2 1 Ω b 0.04 3 Mass Density by Direct Counting Add up the mass of all the galaxies per
Small-scale problems of cosmology and how modified dynamics might address them
 Small-scale problems of cosmology and how modified dynamics might address them Marcel S. Pawlowski Email: marcel.pawlowski@case.edu Twitter: @8minutesold with support from the John Templeton Foundation
Small-scale problems of cosmology and how modified dynamics might address them Marcel S. Pawlowski Email: marcel.pawlowski@case.edu Twitter: @8minutesold with support from the John Templeton Foundation
MOND s Problem in Local Group
 MOND s Problem in Local Group Yan-Chi Shi 1 ABSTRACT I use the distances and motions of Local Group galaxies to test Modified Newtonian Dynamics (MOND). The old Local Group timing argument of Kahn & Woltjer,
MOND s Problem in Local Group Yan-Chi Shi 1 ABSTRACT I use the distances and motions of Local Group galaxies to test Modified Newtonian Dynamics (MOND). The old Local Group timing argument of Kahn & Woltjer,
Evidence for/constraints on dark matter in galaxies and clusters
 Nov 11, 2015 Evidence for/constraints on dark matter in galaxies and clusters HW#9 is due; please hand in your summaries; then you get to talk (I have slides of the different facilities/telescopes. HW#10
Nov 11, 2015 Evidence for/constraints on dark matter in galaxies and clusters HW#9 is due; please hand in your summaries; then you get to talk (I have slides of the different facilities/telescopes. HW#10
The Dark Matter Problem
 The Dark Matter Problem Dr. Yves Gaspar, Ph.D. ( University of Cambridge, UK) Università Cattolica del Sacro Cuore, Brescia Department of Mathematics and Physics. Implications of astronomical data. James
The Dark Matter Problem Dr. Yves Gaspar, Ph.D. ( University of Cambridge, UK) Università Cattolica del Sacro Cuore, Brescia Department of Mathematics and Physics. Implications of astronomical data. James
Modified Dark Matter: Does Dark Matter Know about the Cosmological Constant?
 Modified Dark Matter: Does Dark Matter Know about the Cosmological Constant? Douglas Edmonds Emory & Henry College (moving to Penn State, Hazleton) Collaborators Duncan Farrah Chiu Man Ho Djordje Minic
Modified Dark Matter: Does Dark Matter Know about the Cosmological Constant? Douglas Edmonds Emory & Henry College (moving to Penn State, Hazleton) Collaborators Duncan Farrah Chiu Man Ho Djordje Minic
The Current Status of Too Big To Fail problem! based on Warm Dark Matter cosmology
 The Current Status of Too Big To Fail problem! based on Warm Dark Matter cosmology 172th Astronomical Seminar Dec.3 2013 Chiba Lab.M2 Yusuke Komuro Key Word s Too Big To Fail TBTF Cold Dark Matter CDM
The Current Status of Too Big To Fail problem! based on Warm Dark Matter cosmology 172th Astronomical Seminar Dec.3 2013 Chiba Lab.M2 Yusuke Komuro Key Word s Too Big To Fail TBTF Cold Dark Matter CDM
Dark Matter Halos of Spiral Galaxies
 Dark Matter Halos of Spiral Galaxies Arunima Banerjee National Centre for Radio Astrophysics Tata Institute of Fundamental Research Pune, India email: arunima@ncra.tifr.res.in Web: http://www.ncra.tifr.res.in/~arunima
Dark Matter Halos of Spiral Galaxies Arunima Banerjee National Centre for Radio Astrophysics Tata Institute of Fundamental Research Pune, India email: arunima@ncra.tifr.res.in Web: http://www.ncra.tifr.res.in/~arunima
Dynamical friction, galaxy merging, and radial-orbit instability in MOND
 Dynamical friction, galaxy merging, and radial-orbit instability in MOND Carlo Nipoti Dipartimento di Astronomia Università di Bologna Strasbourg, 29 June 2010 Outline MOND and Equivalent Newtonian Systems
Dynamical friction, galaxy merging, and radial-orbit instability in MOND Carlo Nipoti Dipartimento di Astronomia Università di Bologna Strasbourg, 29 June 2010 Outline MOND and Equivalent Newtonian Systems
Observational Evidence for Dark Matter. Simona Murgia, SLAC-KIPAC
 Observational Evidence for Dark Matter Simona Murgia, SLAC-KIPAC XXXIX SLAC Summer Institute 28 July 2011 Outline Evidence for dark matter at very different scales Galaxies Clusters of galaxies Universe???
Observational Evidence for Dark Matter Simona Murgia, SLAC-KIPAC XXXIX SLAC Summer Institute 28 July 2011 Outline Evidence for dark matter at very different scales Galaxies Clusters of galaxies Universe???
ASTRON 449: Stellar (Galactic) Dynamics. Fall 2014
 ASTRON 449: Stellar (Galactic) Dynamics Fall 2014 In this course, we will cover the basic phenomenology of galaxies (including dark matter halos, stars clusters, nuclear black holes) theoretical tools
ASTRON 449: Stellar (Galactic) Dynamics Fall 2014 In this course, we will cover the basic phenomenology of galaxies (including dark matter halos, stars clusters, nuclear black holes) theoretical tools
Dark Matter: Observational Constraints
 Dark Matter: Observational Constraints Properties of Dark Matter: What is it? And what isn t it? Leo Blitz UC Berkeley Stanford July 31, 2007 How much is there? WMAP results Rotation curves of Galaxies
Dark Matter: Observational Constraints Properties of Dark Matter: What is it? And what isn t it? Leo Blitz UC Berkeley Stanford July 31, 2007 How much is there? WMAP results Rotation curves of Galaxies
MOdified Newtonian Dynamics an introductory review. Riccardo Scarpa European Southern Observatory
 MOdified Newtonian Dynamics an introductory review By Riccardo Scarpa European Southern Observatory Everything started in 1933 with the work by Zwicky on the Coma cluster of galaxies, but were galaxy rotation
MOdified Newtonian Dynamics an introductory review By Riccardo Scarpa European Southern Observatory Everything started in 1933 with the work by Zwicky on the Coma cluster of galaxies, but were galaxy rotation
Dark Matter in Galaxies
 Dark Matter in Galaxies Garry W. Angus VUB FWO 3rd COSPA Meeting Université de Liège Ellipticals. Old stars. Gas poor. Low star formation rate. Spiral (disk) galaxies. Often gas rich => star formation.
Dark Matter in Galaxies Garry W. Angus VUB FWO 3rd COSPA Meeting Université de Liège Ellipticals. Old stars. Gas poor. Low star formation rate. Spiral (disk) galaxies. Often gas rich => star formation.
The Formation and Evolution of Galaxy Clusters
 IAU Joint Discussion # 10 Sydney, July, 2003 The Formation and Evolution of Galaxy Clusters Simon D.M. White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics The WMAP of the whole CMB sky Bennett et al 2003 > 105
IAU Joint Discussion # 10 Sydney, July, 2003 The Formation and Evolution of Galaxy Clusters Simon D.M. White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics The WMAP of the whole CMB sky Bennett et al 2003 > 105
Current status of the ΛCDM structure formation model. Simon White Max Planck Institut für Astrophysik
 Current status of the ΛCDM structure formation model Simon White Max Planck Institut für Astrophysik The idea that DM might be a neutral, weakly interacting particle took off around 1980, following a measurement
Current status of the ΛCDM structure formation model Simon White Max Planck Institut für Astrophysik The idea that DM might be a neutral, weakly interacting particle took off around 1980, following a measurement
Some like it warm. Andrea V. Macciò
 Some like it warm Andrea V. Macciò MPIA - Heidelberg D. Aderhalden, A. Schneider, B. Moore (Zurich), F. Fontanot (HITS), A. Dutton, J. Herpich, G. Stinson (MPIA), X. Kang (PMO) CDM problems, hence WDM
Some like it warm Andrea V. Macciò MPIA - Heidelberg D. Aderhalden, A. Schneider, B. Moore (Zurich), F. Fontanot (HITS), A. Dutton, J. Herpich, G. Stinson (MPIA), X. Kang (PMO) CDM problems, hence WDM
Brief update (3 mins/2 slides) on astrophysics behind final project
 Nov 1, 2017 Brief update (3 mins/2 slides) on astrophysics behind final project Evidence for Dark Matter Next Wed: Prelim #2, similar to last one (30 mins). Review especially lecture slides, PEs and non-project
Nov 1, 2017 Brief update (3 mins/2 slides) on astrophysics behind final project Evidence for Dark Matter Next Wed: Prelim #2, similar to last one (30 mins). Review especially lecture slides, PEs and non-project
ROE, Edinburgh, 20 April Observational Constraints on the Acceleration Discrepancy Problem. Stacy McGaugh University of Maryland
 ROE, Edinburgh, 20 April 2006 Observational Constraints on the Acceleration Discrepancy Problem Stacy McGaugh University of Maryland What gets us into trouble is not what we don t know. It s what we know
ROE, Edinburgh, 20 April 2006 Observational Constraints on the Acceleration Discrepancy Problem Stacy McGaugh University of Maryland What gets us into trouble is not what we don t know. It s what we know
Solving small scale structure puzzles with. dissipative dark matter
 Solving small scale structure puzzles with. dissipative dark matter Robert Foot, COEPP, University of Melbourne Okinawa, March 2016 Dark matter: why we think it exists Dark matter issues on small scales
Solving small scale structure puzzles with. dissipative dark matter Robert Foot, COEPP, University of Melbourne Okinawa, March 2016 Dark matter: why we think it exists Dark matter issues on small scales
Dwarf Galaxies as Cosmological Probes
 Dwarf Galaxies as Cosmological Probes Julio F. Navarro The Ursa Minor dwarf spheroidal First Light First Light The Planck Satellite The Cosmological Paradigm The Clustering of Dark Matter The Millennium
Dwarf Galaxies as Cosmological Probes Julio F. Navarro The Ursa Minor dwarf spheroidal First Light First Light The Planck Satellite The Cosmological Paradigm The Clustering of Dark Matter The Millennium
Dark matter from cosmological probes
 PLANCK 2014 Ferrara Dark matter from cosmological probes Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Dark matter was discovered in the Coma Cluster by Zwicky (1933) Fritz Zwicky Abell 2218 Corbelli
PLANCK 2014 Ferrara Dark matter from cosmological probes Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Dark matter was discovered in the Coma Cluster by Zwicky (1933) Fritz Zwicky Abell 2218 Corbelli
Reionization. High-Redshift Galaxy UV Luminosity Function. Axion Dark Matter. Rosemary Wyse
 Reionization and the High-Redshift Galaxy UV Luminosity Function with Axion Dark Matter Rosemary Wyse Johns Hopkins University and University of Edinburgh Brandon Bozek, Doddy Marsh & Joe Silk Galaxy-scale
Reionization and the High-Redshift Galaxy UV Luminosity Function with Axion Dark Matter Rosemary Wyse Johns Hopkins University and University of Edinburgh Brandon Bozek, Doddy Marsh & Joe Silk Galaxy-scale
ASTR 610 Theory of Galaxy Formation Lecture 18: Disk Galaxies
 ASTR 610 Theory of Galaxy Formation Lecture 18: Disk Galaxies Frank van den Bosch Yale University, spring 2017 The Structure & Formation of Disk Galaxies In this lecture we discuss the structure and formation
ASTR 610 Theory of Galaxy Formation Lecture 18: Disk Galaxies Frank van den Bosch Yale University, spring 2017 The Structure & Formation of Disk Galaxies In this lecture we discuss the structure and formation
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 15 Jan 2015
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 15 Jan 2015 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 15 Jan 2015](/thumbs/94/122279818.jpg) Explaining the formation of bulges with MOND Françoise Combes arxiv:1501.03603v1 [astro-ph.ga] 15 Jan 2015 Abstract In the cold dark matter (CDM) paradigm, bulges easily form through galaxy mergers, either
Explaining the formation of bulges with MOND Françoise Combes arxiv:1501.03603v1 [astro-ph.ga] 15 Jan 2015 Abstract In the cold dark matter (CDM) paradigm, bulges easily form through galaxy mergers, either
Dark Matter & Dark Energy. Astronomy 1101
 Dark Matter & Dark Energy Astronomy 1101 Key Ideas: Dark Matter Matter we cannot see directly with light Detected only by its gravity (possible future direct detection in the lab) Most of the matter in
Dark Matter & Dark Energy Astronomy 1101 Key Ideas: Dark Matter Matter we cannot see directly with light Detected only by its gravity (possible future direct detection in the lab) Most of the matter in
Large-Scale Structure
 Large-Scale Structure Evidence for Dark Matter Dark Halos in Ellipticals Hot Gas in Ellipticals Clusters Hot Gas in Clusters Cluster Galaxy Velocities and Masses Large-Scale Distribution of Galaxies 1
Large-Scale Structure Evidence for Dark Matter Dark Halos in Ellipticals Hot Gas in Ellipticals Clusters Hot Gas in Clusters Cluster Galaxy Velocities and Masses Large-Scale Distribution of Galaxies 1
Tidal streams as gravitational experiments!
 Tidal streams as gravitational experiments! Benoit Famaey CNRS - Observatoire astronomique de Strasbourg MOND paradigm MDAR: McGaugh et al. 2016 Lelli et al. 2016 Famaey & McGaugh 2012 MOND paradigm Prediction:
Tidal streams as gravitational experiments! Benoit Famaey CNRS - Observatoire astronomique de Strasbourg MOND paradigm MDAR: McGaugh et al. 2016 Lelli et al. 2016 Famaey & McGaugh 2012 MOND paradigm Prediction:
Isotropy and Homogeneity
 Cosmic inventory Isotropy and Homogeneity On large scales the Universe is isotropic (looks the same in all directions) and homogeneity (the same average density at all locations. This is determined from
Cosmic inventory Isotropy and Homogeneity On large scales the Universe is isotropic (looks the same in all directions) and homogeneity (the same average density at all locations. This is determined from
The Dark Matter Problem
 The Dark Matter Problem matter : anything with equation of state w=0 more obvious contribution to matter: baryons (stars, planets, us!) and both Big Bang Nucleosynthesis and WMAP tell us that Ω baryons
The Dark Matter Problem matter : anything with equation of state w=0 more obvious contribution to matter: baryons (stars, planets, us!) and both Big Bang Nucleosynthesis and WMAP tell us that Ω baryons
The galaxy population in cold and warm dark matter cosmologies
 The galaxy population in cold and warm dark matter cosmologies Lan Wang National Astronomical Observatories, CAS Collaborators: Violeta Gonzalez-Perez, Lizhi Xie, Andrew Cooper, Carlos Frenk, Liang Gao,
The galaxy population in cold and warm dark matter cosmologies Lan Wang National Astronomical Observatories, CAS Collaborators: Violeta Gonzalez-Perez, Lizhi Xie, Andrew Cooper, Carlos Frenk, Liang Gao,
Angular Momentum Problems in Disk Formation
 Angular Momentum Problems in Disk Formation MPIA Theory Group Seminar, 07/03/2006 The Standard Picture Disks galaxies are systems in centrifugal equilibrium Structure of disks is governed by angular momentum
Angular Momentum Problems in Disk Formation MPIA Theory Group Seminar, 07/03/2006 The Standard Picture Disks galaxies are systems in centrifugal equilibrium Structure of disks is governed by angular momentum
AST1100 Lecture Notes
 AST1100 Lecture Notes 4 Stellar orbits and dark matter 1 Using Kepler s laws for stars orbiting the center of a galaxy We will now use Kepler s laws of gravitation on much larger scales. We will study
AST1100 Lecture Notes 4 Stellar orbits and dark matter 1 Using Kepler s laws for stars orbiting the center of a galaxy We will now use Kepler s laws of gravitation on much larger scales. We will study
Components of Galaxies: Dark Matter
 Components of Galaxies: Dark Matter Dark Matter: Any Form of matter whose existence is inferred solely through its gravitational effects. -B&T, pg 590 Nature of Major Component of Universe Galaxy Formation
Components of Galaxies: Dark Matter Dark Matter: Any Form of matter whose existence is inferred solely through its gravitational effects. -B&T, pg 590 Nature of Major Component of Universe Galaxy Formation
AST-1002 Section 0459 Review for Final Exam Please do not forget about doing the evaluation!
 AST-1002 Section 0459 Review for Final Exam Please do not forget about doing the evaluation! Bring pencil #2 with eraser No use of calculator or any electronic device during the exam We provide the scantrons
AST-1002 Section 0459 Review for Final Exam Please do not forget about doing the evaluation! Bring pencil #2 with eraser No use of calculator or any electronic device during the exam We provide the scantrons
Clusters: Observations
 Clusters: Observations Last time we talked about some of the context of clusters, and why observations of them have importance to cosmological issues. Some of the reasons why clusters are useful probes
Clusters: Observations Last time we talked about some of the context of clusters, and why observations of them have importance to cosmological issues. Some of the reasons why clusters are useful probes
Astronomy 730. Evolution
 Astronomy 730 Evolution Outline } Evolution } Formation of structure } Processes on the galaxy scale } Gravitational collapse, merging, and infall } SF, feedback and chemical enrichment } Environment }
Astronomy 730 Evolution Outline } Evolution } Formation of structure } Processes on the galaxy scale } Gravitational collapse, merging, and infall } SF, feedback and chemical enrichment } Environment }
OBSERVATIONAL EVIDENCE FOR DARK MATTER AND DARK ENERGY. Marco Roncadelli INFN Pavia (Italy)
 OBSERVATIONAL EVIDENCE FOR DARK MATTER AND DARK ENERGY Marco Roncadelli INFN Pavia (Italy) ABSTRACT Assuming KNOWN physical laws, I first discuss OBSERVATIONAL evidence for dark matter in galaxies and
OBSERVATIONAL EVIDENCE FOR DARK MATTER AND DARK ENERGY Marco Roncadelli INFN Pavia (Italy) ABSTRACT Assuming KNOWN physical laws, I first discuss OBSERVATIONAL evidence for dark matter in galaxies and
AS1001:Extra-Galactic Astronomy
 AS1001:Extra-Galactic Astronomy Lecture 5: Dark Matter Simon Driver Theatre B spd3@st-andrews.ac.uk http://www-star.st-and.ac.uk/~spd3 Stars and Gas in Galaxies Stars form from gas in galaxy In the high-density
AS1001:Extra-Galactic Astronomy Lecture 5: Dark Matter Simon Driver Theatre B spd3@st-andrews.ac.uk http://www-star.st-and.ac.uk/~spd3 Stars and Gas in Galaxies Stars form from gas in galaxy In the high-density
What do we need to know about galaxy formation?
 What do we need to know about galaxy formation? rachel somerville University of Michigan Hubble Science Legacy Workshop April 2002 what s next? test the CDM paradigm constrain the nature of the dark matter
What do we need to know about galaxy formation? rachel somerville University of Michigan Hubble Science Legacy Workshop April 2002 what s next? test the CDM paradigm constrain the nature of the dark matter
Dark Matter. Jaan Einasto Tartu Observatory and ICRANet 16 December Saturday, December 15, 12
 Dark Matter Jaan Einasto Tartu Observatory and ICRANet 16 December 2012 Local Dark Matter: invisible matter in the Galaxy in Solar vicinity Global Dark Matter: invisible matter surrounding galaxies Global
Dark Matter Jaan Einasto Tartu Observatory and ICRANet 16 December 2012 Local Dark Matter: invisible matter in the Galaxy in Solar vicinity Global Dark Matter: invisible matter surrounding galaxies Global
Cosmologists dedicate a great deal of effort to determine the density of matter in the universe. Type Ia supernovae observations are consistent with
 Notes for Cosmology course, fall 2005 Dark Matter Prelude Cosmologists dedicate a great deal of effort to determine the density of matter in the universe Type Ia supernovae observations are consistent
Notes for Cosmology course, fall 2005 Dark Matter Prelude Cosmologists dedicate a great deal of effort to determine the density of matter in the universe Type Ia supernovae observations are consistent
Astro-2: History of the Universe. Lecture 5; April
 Astro-2: History of the Universe Lecture 5; April 23 2013 Previously.. On Astro-2 Galaxies do not live in isolation but in larger structures, called groups, clusters, or superclusters This is called the
Astro-2: History of the Universe Lecture 5; April 23 2013 Previously.. On Astro-2 Galaxies do not live in isolation but in larger structures, called groups, clusters, or superclusters This is called the
Self-Interacting Dark Matter
 Self-Interacting Dark Matter James Bullock UC Irvine Garrison-Kimmel, Oñorbe et al. Act I Motivations Missing Satellites Problem (1999) Theory: N>>1000 Klypin et al. 1999; Moore et al. 1999; Kauffmann
Self-Interacting Dark Matter James Bullock UC Irvine Garrison-Kimmel, Oñorbe et al. Act I Motivations Missing Satellites Problem (1999) Theory: N>>1000 Klypin et al. 1999; Moore et al. 1999; Kauffmann
3 The lives of galaxies
 Discovering Astronomy : Galaxies and Cosmology 24 3 The lives of galaxies In this section, we look at how galaxies formed and evolved, and likewise how the large scale pattern of galaxies formed. But before
Discovering Astronomy : Galaxies and Cosmology 24 3 The lives of galaxies In this section, we look at how galaxies formed and evolved, and likewise how the large scale pattern of galaxies formed. But before
The dark matter crisis
 The dark matter crisis Ben Moore Department of Physics, Durham University, UK. arxiv:astro-ph/0103100 v2 8 Mar 2001 Abstract I explore several possible solutions to the missing satellites problem that
The dark matter crisis Ben Moore Department of Physics, Durham University, UK. arxiv:astro-ph/0103100 v2 8 Mar 2001 Abstract I explore several possible solutions to the missing satellites problem that
Peculiar (Interacting) Galaxies
 Peculiar (Interacting) Galaxies Not all galaxies fall on the Hubble sequence: many are peculiar! In 1966, Arp created an Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies based on pictures from the Palomar Sky Survey. In 1982,
Peculiar (Interacting) Galaxies Not all galaxies fall on the Hubble sequence: many are peculiar! In 1966, Arp created an Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies based on pictures from the Palomar Sky Survey. In 1982,
Strategies for Dark Matter Searches
 SMR.1761-1 SUMMER SCHOOL IN COSMOLOGY AND ASTROPARTICLE PHYSICS 10-21 July 2006 Strategies for dark matter detection B. SADOULET University of California Department of Physics 366 Le Conte Hall Berkeley,
SMR.1761-1 SUMMER SCHOOL IN COSMOLOGY AND ASTROPARTICLE PHYSICS 10-21 July 2006 Strategies for dark matter detection B. SADOULET University of California Department of Physics 366 Le Conte Hall Berkeley,
Astronomy 422. Lecture 15: Expansion and Large Scale Structure of the Universe
 Astronomy 422 Lecture 15: Expansion and Large Scale Structure of the Universe Key concepts: Hubble Flow Clusters and Large scale structure Gravitational Lensing Sunyaev-Zeldovich Effect Expansion and age
Astronomy 422 Lecture 15: Expansion and Large Scale Structure of the Universe Key concepts: Hubble Flow Clusters and Large scale structure Gravitational Lensing Sunyaev-Zeldovich Effect Expansion and age
Advanced Topics on Astrophysics: Lectures on dark matter
 Advanced Topics on Astrophysics: Lectures on dark matter Jesús Zavala Franco e-mail: jzavalaf@uwaterloo.ca UW, Department of Physics and Astronomy, office: PHY 208C, ext. 38400 Perimeter Institute for
Advanced Topics on Astrophysics: Lectures on dark matter Jesús Zavala Franco e-mail: jzavalaf@uwaterloo.ca UW, Department of Physics and Astronomy, office: PHY 208C, ext. 38400 Perimeter Institute for
Dark Matter in Disk Galaxies
 Chapter 14 Dark Matter in Disk Galaxies Rotation curves of disk galaxies rise steeply in their inner regions and then remain roughly flat out to the last point measured. To explain these observations within
Chapter 14 Dark Matter in Disk Galaxies Rotation curves of disk galaxies rise steeply in their inner regions and then remain roughly flat out to the last point measured. To explain these observations within
Dark Matter ASTR 2120 Sarazin. Bullet Cluster of Galaxies - Dark Matter Lab
 Dark Matter ASTR 2120 Sarazin Bullet Cluster of Galaxies - Dark Matter Lab Mergers: Test of Dark Matter vs. Modified Gravity Gas behind DM Galaxies DM = location of gravity Gas = location of most baryons
Dark Matter ASTR 2120 Sarazin Bullet Cluster of Galaxies - Dark Matter Lab Mergers: Test of Dark Matter vs. Modified Gravity Gas behind DM Galaxies DM = location of gravity Gas = location of most baryons
Detecting Dark Matter in the X-ray
 Detecting Dark Matter in the X-ray Kev Abazajian University of Maryland Quantum 2 Cosmos 3: Airlie Center, July 8, 2008 The CDM Ansatz Problems in Cold Dark Matter? Halo Substructure: satellite galaxies
Detecting Dark Matter in the X-ray Kev Abazajian University of Maryland Quantum 2 Cosmos 3: Airlie Center, July 8, 2008 The CDM Ansatz Problems in Cold Dark Matter? Halo Substructure: satellite galaxies
REINVENTING GRAVITY: Living Without Dark Matter
 REINVENTING GRAVITY: Living Without Dark Matter John Moffat Perimeter Institute for Theoretical Physics and Department of Physics University of Toronto and University of Waterloo Talk given at Astronomy
REINVENTING GRAVITY: Living Without Dark Matter John Moffat Perimeter Institute for Theoretical Physics and Department of Physics University of Toronto and University of Waterloo Talk given at Astronomy
First detection of dark matter How Much Dark Matter is There?
 Galaxies AS7007, 2012 Lecture 3: Dark matter in galaxies Outline I What is dark matter? How much dark matter is there? How do we know it exists? Dark matter candidates The Cold Dark Matter (CDM) model
Galaxies AS7007, 2012 Lecture 3: Dark matter in galaxies Outline I What is dark matter? How much dark matter is there? How do we know it exists? Dark matter candidates The Cold Dark Matter (CDM) model
Ay 127 Systematics of Galaxy Properties and Scaling Relations
 Ay 127 Systematics of Galaxy Properties and Scaling Relations Morphological Classification and Galaxy Types The first step in any empirical science: look for patterns and trends, then try to understand
Ay 127 Systematics of Galaxy Properties and Scaling Relations Morphological Classification and Galaxy Types The first step in any empirical science: look for patterns and trends, then try to understand
Galaxies Astro 530 Prof. Jeff Kenney
 Galaxies Astro 530 Prof. Jeff Kenney CLASS 7 February 5, 2018 Tully-Fisher Relation (finish) & Spiral Structure (start) 1 Tully-Fisher relation M B,i Tradi7onal Tully- Fisher rela7on: Good correla7on between
Galaxies Astro 530 Prof. Jeff Kenney CLASS 7 February 5, 2018 Tully-Fisher Relation (finish) & Spiral Structure (start) 1 Tully-Fisher relation M B,i Tradi7onal Tully- Fisher rela7on: Good correla7on between
Galaxy Formation! Lecture Seven: Galaxy Formation! Cosmic History. Big Bang! time! present! ...fluctuations to galaxies!
 Galaxy Formation Lecture Seven: Why is the universe populated by galaxies, rather than a uniform sea of stars? Galaxy Formation...fluctuations to galaxies Why are most stars in galaxies with luminosities
Galaxy Formation Lecture Seven: Why is the universe populated by galaxies, rather than a uniform sea of stars? Galaxy Formation...fluctuations to galaxies Why are most stars in galaxies with luminosities
Lecture 19: Clusters and Dark Matter
 GALAXIES 626 Lecture 19: Clusters and Dark Matter Fundamental plane Plots show edge-on views of the fundamental plane for observed elliptical galaxies in a galaxy cluster. Approximately:. 82 R e µs1. 24
GALAXIES 626 Lecture 19: Clusters and Dark Matter Fundamental plane Plots show edge-on views of the fundamental plane for observed elliptical galaxies in a galaxy cluster. Approximately:. 82 R e µs1. 24
Laws of Galactic Rotation. Stacy McGaugh Case Western Reserve University
 Laws of Galactic Rotation Stacy McGaugh Case Western Reserve University UGC 2885 Galaxies NGC 2403 Huge dynamic range in 10 kpc Gravitationally self-bound entities composed of stars, gas, dust, [& dark
Laws of Galactic Rotation Stacy McGaugh Case Western Reserve University UGC 2885 Galaxies NGC 2403 Huge dynamic range in 10 kpc Gravitationally self-bound entities composed of stars, gas, dust, [& dark
NMAGIC Made-to-Measure Modeling of Elliptical Galaxies NMAGIC - 2 M2M
 NMAGIC Made-to-Measure Modeling of Elliptical Galaxies Ortwin Gerhard, MPE, Garching gerhard@mpe.mpg.de I. Made-to-measure dynamical modeling with NMAGIC II Elliptical galaxy halo kinematics with planetary
NMAGIC Made-to-Measure Modeling of Elliptical Galaxies Ortwin Gerhard, MPE, Garching gerhard@mpe.mpg.de I. Made-to-measure dynamical modeling with NMAGIC II Elliptical galaxy halo kinematics with planetary
What are the Contents of the Universe? Taking an Inventory of the Baryonic and Dark Matter Content of the Universe
 What are the Contents of the Universe? Taking an Inventory of the Baryonic and Dark Matter Content of the Universe Layout of the Course Sept 4: Introduction / Overview / General Concepts Sept 11: No Class
What are the Contents of the Universe? Taking an Inventory of the Baryonic and Dark Matter Content of the Universe Layout of the Course Sept 4: Introduction / Overview / General Concepts Sept 11: No Class
Recent developments in the understanding of Dark Matter
 Liverpool Physics Teachers Conference 20th June 2013 Recent developments in the understanding of Dark Matter Phil James Liverpool John Moores University Astrophysics Research Institute OUTLINE OF TALK
Liverpool Physics Teachers Conference 20th June 2013 Recent developments in the understanding of Dark Matter Phil James Liverpool John Moores University Astrophysics Research Institute OUTLINE OF TALK
Visible Matter. References: Ryden, Introduction to Cosmology - Par. 8.1 Liddle, Introduction to Modern Cosmology - Par. 9.1
 COSMOLOGY PHYS 30392 DENSITY OF THE UNIVERSE Part I Giampaolo Pisano - Jodrell Bank Centre for Astrophysics The University of Manchester - March 2013 http://www.jb.man.ac.uk/~gp/ giampaolo.pisano@manchester.ac.uk
COSMOLOGY PHYS 30392 DENSITY OF THE UNIVERSE Part I Giampaolo Pisano - Jodrell Bank Centre for Astrophysics The University of Manchester - March 2013 http://www.jb.man.ac.uk/~gp/ giampaolo.pisano@manchester.ac.uk
Insights into galaxy formation from dwarf galaxies
 Potsdam, August 2014 Insights into galaxy formation from dwarf galaxies Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Planck CMB map: the IC's for structure formation Planck CMB map: the IC's for structure
Potsdam, August 2014 Insights into galaxy formation from dwarf galaxies Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Planck CMB map: the IC's for structure formation Planck CMB map: the IC's for structure
Gravitational Lensing of the Largest Scales
 What is dark matter? Good question. How do we answer it? Gravitational lensing! Gravitational lensing is fantastic Why Clusters of Galaxies Because they are cool!! Studying empirical properties of dark
What is dark matter? Good question. How do we answer it? Gravitational lensing! Gravitational lensing is fantastic Why Clusters of Galaxies Because they are cool!! Studying empirical properties of dark
Where are the missing baryons? Craig Hogan SLAC Summer Institute 2007
 Where are the missing baryons? Craig Hogan SLAC Summer Institute 2007 Reasons to care Concordance of many measures of baryon number (BBN, CMB,.) Evolution of our personal baryons (galaxies, stars, planets,
Where are the missing baryons? Craig Hogan SLAC Summer Institute 2007 Reasons to care Concordance of many measures of baryon number (BBN, CMB,.) Evolution of our personal baryons (galaxies, stars, planets,
Structure formation in the concordance cosmology
 Structure formation in the Universe, Chamonix, May 2007 Structure formation in the concordance cosmology Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics WMAP3 team WMAP3 team WMAP3 team WMAP3 team In
Structure formation in the Universe, Chamonix, May 2007 Structure formation in the concordance cosmology Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics WMAP3 team WMAP3 team WMAP3 team WMAP3 team In
Galaxy clusters. Dept. of Physics of Complex Systems April 6, 2018
 Galaxy clusters László Dobos Dept. of Physics of Complex Systems dobos@complex.elte.hu É 5.60 April 6, 2018 Satellite galaxies Large galaxies are surrounded by orbiting dwarfs approx. 14-16 satellites
Galaxy clusters László Dobos Dept. of Physics of Complex Systems dobos@complex.elte.hu É 5.60 April 6, 2018 Satellite galaxies Large galaxies are surrounded by orbiting dwarfs approx. 14-16 satellites
Secular Evolution of Galaxies
 Secular Evolution of Galaxies Outline:!Disk size evolution! Bar fraction vs mass & color! AM transfers, radial migrations! Bulges, thick disks Françoise Combes Durham, 19 July 2011 Two modes to assemble
Secular Evolution of Galaxies Outline:!Disk size evolution! Bar fraction vs mass & color! AM transfers, radial migrations! Bulges, thick disks Françoise Combes Durham, 19 July 2011 Two modes to assemble
4. Structure of Dark Matter halos. Hence the halo mass, virial radius, and virial velocity are related by
 13-4-12see http://www.strw.leidenuniv.nl/ franx/college/galaxies12 12-c04-1 13-4-12see http://www.strw.leidenuniv.nl/ franx/college/galaxies12 12-c04-2 4. Structure of Dark Matter halos Obviously, we cannot
13-4-12see http://www.strw.leidenuniv.nl/ franx/college/galaxies12 12-c04-1 13-4-12see http://www.strw.leidenuniv.nl/ franx/college/galaxies12 12-c04-2 4. Structure of Dark Matter halos Obviously, we cannot
Theorem : Proof... Pavel Kroupa. Pavel Kroupa: AIfA, University of Bonn
 Theorem : dsph = TDG = LCDM Proof... Pavel Kroupa 1 Two Zwicky Conjectures of fundamental importance : 1. Zwicky (1937) galaxies are about 500 times heavier in the Coma galaxy cluster than judged from
Theorem : dsph = TDG = LCDM Proof... Pavel Kroupa 1 Two Zwicky Conjectures of fundamental importance : 1. Zwicky (1937) galaxies are about 500 times heavier in the Coma galaxy cluster than judged from
Survey of Astrophysics A110
 Goals: Galaxies To determine the types and distributions of galaxies? How do we measure the mass of galaxies and what comprises this mass? How do we measure distances to galaxies and what does this tell
Goals: Galaxies To determine the types and distributions of galaxies? How do we measure the mass of galaxies and what comprises this mass? How do we measure distances to galaxies and what does this tell
Baryonic Masses from Rotation Curves. Stacy McGaugh University of Maryland
 Unveiling the Mass - Extracting and Interpreting Galaxy Masses, Kingston, Ontario, 19 June 2009 Baryonic Masses from Rotation Curves Stacy McGaugh University of Maryland Rotation curves tend to become
Unveiling the Mass - Extracting and Interpreting Galaxy Masses, Kingston, Ontario, 19 June 2009 Baryonic Masses from Rotation Curves Stacy McGaugh University of Maryland Rotation curves tend to become
80 2 Observational Cosmology L and the mean energy
 80 2 Observational Cosmology fluctuations, short-wavelength modes have amplitudes that are suppressed because these modes oscillated as acoustic waves during the radiation epoch whereas the amplitude of
80 2 Observational Cosmology fluctuations, short-wavelength modes have amplitudes that are suppressed because these modes oscillated as acoustic waves during the radiation epoch whereas the amplitude of
The cosmic distance scale
 The cosmic distance scale Distance information is often crucial to understand the physics of astrophysical objects. This requires knowing the basic properties of such an object, like its size, its environment,
The cosmic distance scale Distance information is often crucial to understand the physics of astrophysical objects. This requires knowing the basic properties of such an object, like its size, its environment,
The Early Universe John Peacock ESA Cosmic Vision Paris, Sept 2004
 The Early Universe John Peacock ESA Cosmic Vision Paris, Sept 2004 The history of modern cosmology 1917 Static via cosmological constant? (Einstein) 1917 Expansion (Slipher) 1952 Big Bang criticism (Hoyle)
The Early Universe John Peacock ESA Cosmic Vision Paris, Sept 2004 The history of modern cosmology 1917 Static via cosmological constant? (Einstein) 1917 Expansion (Slipher) 1952 Big Bang criticism (Hoyle)
3/6/12! Astro 358/Spring 2012! Galaxies and the Universe! Dark Matter in Spiral Galaxies. Dark Matter in Galaxies!
 3/6/12 Astro 358/Spring 2012 Galaxies and the Universe Dark Matter in Galaxies Figures + Tables for Lectures (Feb 16-Mar 6) Dark Matter in Spiral Galaxies Flat rotation curve of Milky Way at large radii
3/6/12 Astro 358/Spring 2012 Galaxies and the Universe Dark Matter in Galaxies Figures + Tables for Lectures (Feb 16-Mar 6) Dark Matter in Spiral Galaxies Flat rotation curve of Milky Way at large radii
Galaxies in dark matter halos: luminosity-velocity relation, abundance and baryon content
 Galaxies in dark matter halos: luminosity-velocity relation, abundance and baryon content arxiv:1005.1289 arxiv:1002.3660 S. Trujillo-Gomez (NMSU) in collaboration with: A. Klypin (NMSU), J. Primack (UCSC)
Galaxies in dark matter halos: luminosity-velocity relation, abundance and baryon content arxiv:1005.1289 arxiv:1002.3660 S. Trujillo-Gomez (NMSU) in collaboration with: A. Klypin (NMSU), J. Primack (UCSC)
A. Thermal radiation from a massive star cluster. B. Emission lines from hot gas C. 21 cm from hydrogen D. Synchrotron radiation from a black hole
 ASTR 1040 Accel Astro: Stars & Galaxies Prof. Juri Toomre TA: Nicholas Nelson Lecture 26 Thur 14 Apr 2011 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre toomre HST Abell 2218 Reading clicker what makes the light? What
ASTR 1040 Accel Astro: Stars & Galaxies Prof. Juri Toomre TA: Nicholas Nelson Lecture 26 Thur 14 Apr 2011 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre toomre HST Abell 2218 Reading clicker what makes the light? What
Galaxy Formation and Evolution
 Galaxy Formation and Evolution Houjun Mo Department of Astronomy, University of Massachusetts 710 North Pleasant Str., Amherst, MA 01003-9305, USA Frank van den Bosch Department of Physics & Astronomy,
Galaxy Formation and Evolution Houjun Mo Department of Astronomy, University of Massachusetts 710 North Pleasant Str., Amherst, MA 01003-9305, USA Frank van den Bosch Department of Physics & Astronomy,
Clusters of Galaxies
 Clusters of Galaxies Galaxies are not randomly strewn throughout space. Instead the majority belong to groups and clusters of galaxies. In these structures, galaxies are bound gravitationally and orbit
Clusters of Galaxies Galaxies are not randomly strewn throughout space. Instead the majority belong to groups and clusters of galaxies. In these structures, galaxies are bound gravitationally and orbit
Galaxy Formation: Overview
 Galaxy Formation: Overview Houjun Mo March 30, 2004 The basic picture Formation of dark matter halos. Gas cooling in dark matter halos Star formation in cold gas Evolution of the stellar populaion Metal
Galaxy Formation: Overview Houjun Mo March 30, 2004 The basic picture Formation of dark matter halos. Gas cooling in dark matter halos Star formation in cold gas Evolution of the stellar populaion Metal
WOLFGANG KLASSEN DARK MATTER
 1 WOLFGANG KLASSEN DARK MATTER "Hubble Maps the Cosmic Web of "Clumpy" Dark Matter in 3-D" (Press release). NASA. 7 January 2007. DARK MATTER 2 CONTENTS 1.Relating Mass and Light Tulley-Fisher relation
1 WOLFGANG KLASSEN DARK MATTER "Hubble Maps the Cosmic Web of "Clumpy" Dark Matter in 3-D" (Press release). NASA. 7 January 2007. DARK MATTER 2 CONTENTS 1.Relating Mass and Light Tulley-Fisher relation
Killing Dwarfs with Hot Pancakes. Frank C. van den Bosch (MPIA) with Houjun Mo, Xiaohu Yang & Neal Katz
 Killing Dwarfs with Hot Pancakes Frank C. van den Bosch (MPIA) with Houjun Mo, Xiaohu Yang & Neal Katz The Paradigm... SN feedback AGN feedback The halo mass function is much steeper than luminosity function
Killing Dwarfs with Hot Pancakes Frank C. van den Bosch (MPIA) with Houjun Mo, Xiaohu Yang & Neal Katz The Paradigm... SN feedback AGN feedback The halo mass function is much steeper than luminosity function
Numerical Cosmology & Galaxy Formation
 Numerical Cosmology & Galaxy Formation Lecture 13: Example simulations Isolated galaxies, mergers & zooms Benjamin Moster 1 Outline of the lecture course Lecture 1: Motivation & Historical Overview Lecture
Numerical Cosmology & Galaxy Formation Lecture 13: Example simulations Isolated galaxies, mergers & zooms Benjamin Moster 1 Outline of the lecture course Lecture 1: Motivation & Historical Overview Lecture
Firenze (JPO: 28/07/17) Small Scale Crisis for CDM: Fatal or a Baryon Physics Fix
 Firenze (JPO: 28/07/17) Small Scale Crisis for CDM: Fatal or a Baryon Physics Fix CBR Spectrum Planck and all-a Perfect Fit to the CDM Expectation Precise measurements of the CBR specify the cosmological
Firenze (JPO: 28/07/17) Small Scale Crisis for CDM: Fatal or a Baryon Physics Fix CBR Spectrum Planck and all-a Perfect Fit to the CDM Expectation Precise measurements of the CBR specify the cosmological
Modified Gravity (MOG) and Dark Matter: Can Dark Matter be Detected in the Present Universe?
 Modified Gravity (MOG) and Dark Matter: Can Dark Matter be Detected in the Present Universe? John Moffat Perimeter Institute, Waterloo, Ontario, Canada Talk given at the Miami 2014 topical conference on
Modified Gravity (MOG) and Dark Matter: Can Dark Matter be Detected in the Present Universe? John Moffat Perimeter Institute, Waterloo, Ontario, Canada Talk given at the Miami 2014 topical conference on
