Space News: Insight Safely Lands on Mars
|
|
|
- Arlene Moody
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Space News: Insight Safely Lands on Mars Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport MarCO-A and -B (EVE and Wall-E) are also sending signals back!
2 Study Points What is a supercluster? How are galaxies distributed in the universe? What is Hubble Law? Can you apply it to stars? To galaxies in the Local Group? To more distant galaxies? How do astronomers calculate distances to galaxies? What does Hubble s Law tell us about the origin of the universe? When we see objects like stars or galaxies in pictures, are we seeing them as they look now or in the past? Why? Is the red shift caused by galaxies moving through space or by space-time expanding? Is the universe expanding, contracting or neither? How do we know? Is the universe cooling? Discuss the raisin bread model or balloon model to explain why we do not have to be at the center of the universe. What is the name of the theory of how the universe evolved? How old is our universe? How old is our solar system?
3 Review Hubble s Law Galaxies Collide Cluster of Galaxies The Local Group Superclusters Hubble s Law Red Shift of galaxies Big Bang model
4 Do galaxies collide? Galactic collision simulation od1evg&feature=related
5 NGC 2207 and IC 2163 colliding, 80 MLY away
6 Clusters of Galaxies Galaxy cluster mass ~160 trillion times the mass of the sun
7 The Local Group Group of galaxies including Milky Way
8 Virgo Supercluster Milky Way is part of the Virgo Supercluster Supercluster* Cluster of galaxy clusters
9 Neigboring Superclusters within 1 billion light years Every dot is a galaxy
10 Laniakea Supercluster Named & Discovered in 2014 Home to the Milky Way & 100,000 Galaxies
11 Laniakea Supercluster in yellow Superclusters: Virgo (MW) Hydra Centaurus Pavo-Indus More Info here: Picture:
12 Superclusters How are galaxies distributed? In great strings and voids* What does the distribution look like to you?
13 Superclusters How are galaxies distributed? In great strings and voids* What does the distribution look like to you? Edges of soap bubbles Holes of Swiss cheese
14 Superclusters Laniakea: Our home supercluster Watch Video by Nature, Sept. 3,
15 Doppler Effect What does the red shift or blue shift tell you?
16 Doppler Effect Red shift / blue shift tells you Direction of motion (away/toward) & speed Bigger shift means faster For all cases like galaxies, stars, cars For light and sound
17 FOR DISTANT GALAXIES ONLY (not stars or cars) we can use Hubble s Law Measure distance, D, to galaxies Recall: Type of star gives L, then B = kl/d 2 Measure red shift of those galaxies to get their speeds, v. Edwin Hubble 1929
18 Speed, v Distance, D Edwin Hubble, 1929 Graphed v vs. D
19 Hubble s Law V Straight Line!! speed * * * * * * * D Distance
20 Hubble s Law V speed Distant galaxies move faster.* * * * * * * * D Distance
21 V * * * Hubble s Law * * * v = HD * Distant galaxies move faster* D
22 Hubble s Law Implications? For distant galaxies, the speed gives you the distance!* V * * * * * * * v = H*D D H = Hubble s Constant (slope)
23 Hubble s Law *So, today, to measure distance to a galaxy Measure the Red Shift. That gives the speed. V * * * * * * * D Then use Hubble s Law ( v = H*D ) to get distance.* (Don t try this with stars or cars! Only for far-off galaxies.)*
24 Hubble s Law All galaxies (outside the Local Group) show a Red Shift.* Distant galaxies move faster* v = H*D V * * * * * * * D
25 Hubble s Law Implications? What does this mean? All galaxies Red Shifted* All galaxies moving away from us!* V * * * * * * * D Universe is expanding!* This expansion is from the expansion of spacetime.*
26 Hubble s Law But if universe is expanding, what was it like yesterday? Smaller!* V * * * * * * * D And billions of years ago?? Even smaller!
27 So at one point it must have been very small. Hence the name V * * * * * * * D BIG BANG
28 BIG BANG Bad Name (misnamed) Was not BIG Did not BANG V * * * * * * * More descriptive name Great Unfolding Or Big Stretch D
29 Big Bang Universe (space and time) springs into (tiny) existence about 14 billion years ago.
30 Big Bang Universe (space and time) springs into (tiny) existence about 14 billion years ago. Expanding ever since Science states that is the universe is expanding, and it is cooling as it expands. The universe started hot and has been cooling ever since. The expansion should be slowing down due to the force of gravity pulling everything inward.
31 Big Bang Universe (space and time) springs into (tiny) existence about 14 billion years ago. Expanding, cooling ever since Does this expansion ever run out of energy?
32 Big Bang Universe (space and time) springs into (tiny) existence about 14 billion years ago. Expanding, cooling ever since What is the rate of expansion now? Is the rate a) Slowing down b) Speeding up c) Not changing
33 Big Bang Universe (space and time) springs into (tiny) existence about 14 billion years ago. Expanding, cooling ever since What is the rate of expansion now? Is the rate a) Slowing down due to gravity Old Model b) Speeding up c) Not changing
34 Big Bang Universe (space and time) springs into (tiny) existence about 14 billion years ago. Expanding, cooling ever since What is the rate of expansion now? Is the rate a) Slowing down due to gravity Old Model b) Speeding up Current Model* c) Not changing
35 Big Bang Universe (space and time) springs into (tiny) existence about 14 billion years ago. Expanding, cooling ever since* (started hot) Expansion slowing due to gravity (first ~9 Byr) Expansion speeding up due to dark energy (last ~5 Byr & currently) Rate of expansion is speeding up!* The cause is named Dark Energy.* (more on dark energy in next lecture) Expansion Rate is about 14 (mi/sec)/million light years
36 Time (~14 billion Time years) (~14 billion years) Universe Expansion Acceleration Due to Dark Energy ~5 Byrs ~9 Byrs
37 After accounting for the universe expansion: Galaxies moving away from us are in red, those moving toward us in blue (Nature Video, based on Tully et al 2014)
38 Why do distant galaxies move faster? Remember that space-time itself is expanding! Galaxies are NOT moving much through space but space-time is expanding, dragging galaxies with it.
39 Why do distant galaxies move faster? Think of a rubber map and stretch it.
40 Why do distant galaxies move faster? Think of a rubber map and stretch it. Example: Triple size (3X) in one hour. A city 10 miles away will then be 30 miles away moved 20 mi/h A city 100 miles away will then be 300 miles away. moved 200 mi/h When the map stretches, more distant city moves faster. Similarly, as space-time expands, more distant galaxies move faster.
41 Universe Expansion Distant objects move faster Universe
42 Doesn t seeing a Red Shift of ALL galaxies imply that we are at the center of the universe? (all moving away?) NO! But why?
43 Raisin Bread Model Everything can appear to move away from you, no matter where you are located.*
44 Balloon Expanding Demo One piece of balloon sees all other pieces moving away That piece does not need to be at the center You can read more here about why we can t find the center of the universe.
45 Doesn t seeing a Red Shift of ALL galaxies imply that we are at the center of the universe? (all moving away?) NO! Expansion You see all other parts moving away You are not at center
46 I see a galaxy 10 BLY away
47 as it was 10 Byrs ago
48 when the universe was smaller
49 so I m looking back toward the center.
50 Yes and so are we looking out toward the center. so I m looking out toward the center.
51 We re all looking out toward the center
52 Center is here Center is here Center is here Center is here Center is here Center is here Center is here Center is here Center is here
53 An ant on a balloon has no way to know where the center is.* We can t find the center of the universe! And we don t think a center exists!* 09/07/31/the-size-of-the-universe-a-har/ CH27/CHAP27AT.HTM
54 Big Bang and the Evolution of the Universe
55 Big Bang and Evolution of the Universe* In the beginning??? What happened? How the universe evolved and changed after it started.* Rough timeline of events Evidence (next lecture)
56 Very Rough Cosmic Timeline Big Bang t > 0 Stuff Happens Now 14 billion years later H, He Milky Way First galaxies First stars Galaxies collide and grow Solar system and Earth First human s
57 Cosmic Calendar (From The Dragons of Eden 1977 & Cosmos TV Series - Carl Sagan) Jan Big Bang H and He, First stars, First galaxies Apr Feb Milky Way Galaxy May Milky Way Galaxy Mar Jun Jul Aug Sep Solar system, Earth Life on Earth Oct Oldest fossils Nov Dec First cells with nuclei
58 1 December O 2 Mars channels Worms Plankton 19 Fish Insects 22 Amphibians 23 Trees 24 Dinosaurs Mammals 27 Birds 28 Flowers 29 Primates 30 Hominids 31 Humans
59
60
61 December 31 11:59:37 p.m. Agriculture 11:59:45 p.m. The Wheel 11:59:56 p.m. Ptolemy astronomy 11:59:58 p.m. Mayan civilization; Byzantine empire 11:59:59 p.m. Renaissance; experimental method in science; the telescope Now Watch Video. Cosmos: a Space-Time Odyssey with Neil degrasse Tyson, Episode 1
62 About how old is our universe?*
63 About how old is our universe?* 14 billion years*
64 About how old is our Milky Way Galaxy?
65 About how old is our Milky Way Galaxy? 13 billion years
66 About how old is our solar system?*
67 About how old is our solar system?* 5 billion years* (same age as our Sun)*
68 Observations Remaining Sunset Part 2 Due Dec. 6 (10 points) Take 2 nd picture of sunset in same location (about 4pm) Astrophysics Lecture Dec. 18 (10 points) Report option remains Planetarium (Plan) Due Dec. 18 (10 points) Go to a planetarium show Star Gazing (SG) Due Dec. 18 (25 points) Expert/volunteer shows student stars & more OR Student writes a report Telescope (Tel) Due Dec. 18 (25 points) Look through a telescope Moon Craters (MC) Due Dec. 18 (10 points) (Moon has to be visible) Look at moon craters through a telescope or binoculars Binoculars are available to borrow
69 Next Tuesday, 11/27: Lab Test 1 for Tuesday class Thursday, 11/29: Big Bang part 1 & Lab Test 1 for Thurs class Tuesday, 12/4: Life in the Universe & pick up lab notebooks Thursday, 12/6: Test 3 (60 multiple choice questions) Based on last 8 lectures & 5 D2L quizzes 9-13 Some questions from D2L quizzes Bring pencil, no calculator needed Tuesday, 12/11: Review for Final Test & handback Test 3 optional Lab Test 2! Thursday, 12/13: No lecture & optional Lab Test 2 Tuesday, 12/18: Final Test (60 multiple choice questions) Based on all 22 lectures & 13 D2L quizzes (the whole semester) Many questions from D2L quizzes Bring pencil, & calculator if you have one (some in classroom for you) Remember lowest of 4 tests is dropped (Test 1, 2, 3, & Final). If you took 3 previous tests and are happy with your grade, then you don t have to take the Final Test. If you missed a previous test, you must take the Final Test. If you are trying to increase your grade, take the final to hopefully drop a different test. No Astronomy on 12/20.
70 Class Feedback One side: What did you like about astronomy class? Topic Method of teaching/class structure Turn over, Other side: What would you change or improve about astronomy class? Any other thoughts? Name is optional When finished, place in big envelope
o Terms to know o Big Bang Theory o Doppler Effect o Redshift o Universe
 Standard 1: Students will understand the scientific evidence that supports theories that explain how the universe and the solar system developed. They will compare Earth to other objects in the solar system.
Standard 1: Students will understand the scientific evidence that supports theories that explain how the universe and the solar system developed. They will compare Earth to other objects in the solar system.
The Universe. Unit 3 covers the following framework standards: ES 8 and 12. Content was adapted the following:
 Unit 3 The Universe Chapter 4 ~ The Formation of the Universe o Section 1 ~ The Scale of the Universe o Section 2 ~ The Formation of the Universe o Section 3 ~ The Future of the Universe Chapter 5 ~ Galaxies
Unit 3 The Universe Chapter 4 ~ The Formation of the Universe o Section 1 ~ The Scale of the Universe o Section 2 ~ The Formation of the Universe o Section 3 ~ The Future of the Universe Chapter 5 ~ Galaxies
Active Galaxies and Galactic Structure Lecture 22 April 18th
 Active Galaxies and Galactic Structure Lecture 22 April 18th FINAL Wednesday 5/9/2018 6-8 pm 100 questions, with ~20-30% based on material covered since test 3. Do not miss the final! Extra Credit: Thursday
Active Galaxies and Galactic Structure Lecture 22 April 18th FINAL Wednesday 5/9/2018 6-8 pm 100 questions, with ~20-30% based on material covered since test 3. Do not miss the final! Extra Credit: Thursday
Relative Sizes of Stars. Today Exam#3 Review. Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram. Blackbody Radiation
 Today Exam#3 Review Exam #3 is Thursday April 4th in this room, BPS 40; Extra credit is due 8:00 am Tuesday April 9 Final Exam is 3:00pm Monday April 8 in BPS 40 The exam is 40 multiple choice questions.
Today Exam#3 Review Exam #3 is Thursday April 4th in this room, BPS 40; Extra credit is due 8:00 am Tuesday April 9 Final Exam is 3:00pm Monday April 8 in BPS 40 The exam is 40 multiple choice questions.
Chapter 1 Our Place in the Universe
 Chapter 1 Our Place in the Universe 1.1 Our Modern View of the Universe Topics we will explore: What is our place in the universe? How did we come to be? How can we know what the universe was like in the
Chapter 1 Our Place in the Universe 1.1 Our Modern View of the Universe Topics we will explore: What is our place in the universe? How did we come to be? How can we know what the universe was like in the
How Did the Universe Begin?
 How Did the Universe Begin? As we will discuss in this lecture, it looks like the Universe started about 14 billion years ago and has been expanding (space stretching) ever since. The model of what happened
How Did the Universe Begin? As we will discuss in this lecture, it looks like the Universe started about 14 billion years ago and has been expanding (space stretching) ever since. The model of what happened
Today. Announcements. Big Bang theory cont d Introduction to black holes
 Today Announcements HW #8 due Friday (tomorrow) 8am Test #2 average was 31/40 not as bad as it first appeared (several answer sheets were put in the wrong pile) Big Bang theory cont d Introduction to black
Today Announcements HW #8 due Friday (tomorrow) 8am Test #2 average was 31/40 not as bad as it first appeared (several answer sheets were put in the wrong pile) Big Bang theory cont d Introduction to black
Outline. Astronomy: The Big Picture. Galaxies are the Fundamental Ecosystems of the Universe
 Outline Homework due on Friday 11:50 am Honor credit need to have those papers soon! Exam 2 Grades are posted. THE FINAL IS DECEMBER 15 th : 7-10pm! Style Galaxies are the Fundamental Ecosystems of the
Outline Homework due on Friday 11:50 am Honor credit need to have those papers soon! Exam 2 Grades are posted. THE FINAL IS DECEMBER 15 th : 7-10pm! Style Galaxies are the Fundamental Ecosystems of the
Astronomy 210 Final. Astronomy: The Big Picture. Outline
 Astronomy 210 Final This Class (Lecture 40): The Big Bang Next Class: The end HW #11 Due next Weds. Final is May 10 th. Review session: May 6 th or May 9 th? Designed to be 2 hours long 1 st half is just
Astronomy 210 Final This Class (Lecture 40): The Big Bang Next Class: The end HW #11 Due next Weds. Final is May 10 th. Review session: May 6 th or May 9 th? Designed to be 2 hours long 1 st half is just
Revision Guide for Chapter 12
 Revision Guide for Chapter 12 Contents Student s Checklist Revision Notes The speed of light... 4 Doppler effect... 4 Expansion of the Universe... 5 Microwave background radiation... 5 Galaxy... 6 Summary
Revision Guide for Chapter 12 Contents Student s Checklist Revision Notes The speed of light... 4 Doppler effect... 4 Expansion of the Universe... 5 Microwave background radiation... 5 Galaxy... 6 Summary
Origin, early history, and fate of the Universe Does the Universe have a beginning? An end? What physics processes caused the Universe to be what it
 Cosmology Origin, early history, and fate of the Universe Does the Universe have a beginning? An end? What physics processes caused the Universe to be what it is? Are other universes possible? Would they
Cosmology Origin, early history, and fate of the Universe Does the Universe have a beginning? An end? What physics processes caused the Universe to be what it is? Are other universes possible? Would they
Galaxies and the Universe
 Standard 7.3.1: Recognize and describe that the Sun is a medium-sized star located near the edge of a diskshaped galaxy of stars and that the universe contains many billions of galaxies and each galaxy
Standard 7.3.1: Recognize and describe that the Sun is a medium-sized star located near the edge of a diskshaped galaxy of stars and that the universe contains many billions of galaxies and each galaxy
Expanding Universe. 1) Hubble s Law 2) Expanding Universe 3) Fate of the Universe. Final Exam will be held in Ruby Diamond Auditorium
 Expanding Universe November 20, 2002 1) Hubble s Law 2) Expanding Universe 3) Fate of the Universe Final Exam will be held in Ruby Diamond Auditorium NOTE THIS!!! not UPL Dec. 11, 2002 10am-noon Review
Expanding Universe November 20, 2002 1) Hubble s Law 2) Expanding Universe 3) Fate of the Universe Final Exam will be held in Ruby Diamond Auditorium NOTE THIS!!! not UPL Dec. 11, 2002 10am-noon Review
Chapter 2 - The Big Bang
 stretched out and appear more red. When an object is moving toward an observer, the object is moving in the same direction the light is being emitted from, and the wavelengths of light become squished
stretched out and appear more red. When an object is moving toward an observer, the object is moving in the same direction the light is being emitted from, and the wavelengths of light become squished
Welcome Aboard!! CHANGE OF KOMATSU S OFFICE HOURS. Briefing Welcome to the Cosmic Tour: Some Guide Lines. Lecture 1 Our Place in the Universe
 CHANGE OF KOMATSU S OFFICE HOURS (Previous) Tuesdays & Thursdays 3:30 to 4:30 (New) Tuesdays 4:45 to 5:30 Thursdays 3:30 to 4:30 YOURNAME 31AUG Welcome Aboard!! AUSTIN AST 301 YOURNAME 31AUG 2.5 MILLION
CHANGE OF KOMATSU S OFFICE HOURS (Previous) Tuesdays & Thursdays 3:30 to 4:30 (New) Tuesdays 4:45 to 5:30 Thursdays 3:30 to 4:30 YOURNAME 31AUG Welcome Aboard!! AUSTIN AST 301 YOURNAME 31AUG 2.5 MILLION
Killer Skies. HW 10/Moon Report due today Exam 3, Dec 11 Last time: Galaxies Collide Today: Hubble s Law
 Killer Skies HW 10/Moon Report due today Exam 3, Dec 11 Last time: Galaxies Collide Today: Hubble s Law Music: The Universe is You Sophie Ellis-Bextor 1 Hour Exam 3 Hour Exam 3 Wed, Dec 11th, in class
Killer Skies HW 10/Moon Report due today Exam 3, Dec 11 Last time: Galaxies Collide Today: Hubble s Law Music: The Universe is You Sophie Ellis-Bextor 1 Hour Exam 3 Hour Exam 3 Wed, Dec 11th, in class
The Universe April 2, Lecture 2 1
 Beyond Our Comfort Zone Direct Experience: 10-5 to 10 5 meters Dust grain may have 0.01 mm = 10 micron diameter View from mountaintop may extend 100 km Experts may claim comfort with 10-7 to 10 7 m Optical
Beyond Our Comfort Zone Direct Experience: 10-5 to 10 5 meters Dust grain may have 0.01 mm = 10 micron diameter View from mountaintop may extend 100 km Experts may claim comfort with 10-7 to 10 7 m Optical
What is the solar system?
 Notes Astronomy What is the solar system? 11.1 Structure of the Solar System Our solar system includes planets and dwarf planets, their moons, a star called the Sun, asteroids and comets. Planets, dwarf
Notes Astronomy What is the solar system? 11.1 Structure of the Solar System Our solar system includes planets and dwarf planets, their moons, a star called the Sun, asteroids and comets. Planets, dwarf
How do we measure properties of a star? Today. Some Clicker Questions - #1. Some Clicker Questions - #1
 Today Announcements: HW#8 due Friday 4/9 at 8:00 am. The size of the Universe (It s expanding!) The Big Bang Video on the Big Bang NOTE: I will take several questions on exam 3 and the final from the videos
Today Announcements: HW#8 due Friday 4/9 at 8:00 am. The size of the Universe (It s expanding!) The Big Bang Video on the Big Bang NOTE: I will take several questions on exam 3 and the final from the videos
Dark Energy and Dark Matter
 Dark Energy and Dark Matter Attendance Quiz Are you here today? (a) yes (b) no Here! (c) The Dark Lord wants his ring back! Final Exam The final exam is Thursday, 6/8, from 11:30am to 1:30pm (2 hours),
Dark Energy and Dark Matter Attendance Quiz Are you here today? (a) yes (b) no Here! (c) The Dark Lord wants his ring back! Final Exam The final exam is Thursday, 6/8, from 11:30am to 1:30pm (2 hours),
Astronomy 150: Killer Skies Lecture 35, April 23
 Assignments: ICES available online Astronomy 150: Killer Skies Lecture 35, April 23 HW11 due next Friday: last homework! note: lowest HW score dropped but: HW11 material will be on Exam 3, so be sure to
Assignments: ICES available online Astronomy 150: Killer Skies Lecture 35, April 23 HW11 due next Friday: last homework! note: lowest HW score dropped but: HW11 material will be on Exam 3, so be sure to
ISP205-2 Visions of the Universe
 ISP205-2 Visions of the Universe The big questions Course details Example of how scientific discoveries are made Brief tour of the universe Reading for next class The Big Questions 1. Laws of physics.
ISP205-2 Visions of the Universe The big questions Course details Example of how scientific discoveries are made Brief tour of the universe Reading for next class The Big Questions 1. Laws of physics.
Today. life the university & everything. Reminders: Review Wed & Fri Eyes to the web Final Exam Tues May 3 Check in on accomodations
 life the university & everything Phys 2130 Day 41: Questions? The Universe Reminders: Review Wed & Fri Eyes to the web Final Exam Tues May 3 Check in on accomodations Today Today: - how big is the universe?
life the university & everything Phys 2130 Day 41: Questions? The Universe Reminders: Review Wed & Fri Eyes to the web Final Exam Tues May 3 Check in on accomodations Today Today: - how big is the universe?
Astronomy 122 Outline
 Astronomy 122 Outline This Class (Lecture 26): The Primeval Fireball Next Class: Dark Matter & Dark Energy ICES Form!!! HW10 due Friday Hubble s Law implications An expanding Universe! Run in movie in
Astronomy 122 Outline This Class (Lecture 26): The Primeval Fireball Next Class: Dark Matter & Dark Energy ICES Form!!! HW10 due Friday Hubble s Law implications An expanding Universe! Run in movie in
The Cosmic Microwave Background
 The Cosmic Microwave Background Class 22 Prof J. Kenney June 26, 2018 The Cosmic Microwave Background Class 22 Prof J. Kenney November 28, 2016 Cosmic star formation history inf 10 4 3 2 1 0 z Peak of
The Cosmic Microwave Background Class 22 Prof J. Kenney June 26, 2018 The Cosmic Microwave Background Class 22 Prof J. Kenney November 28, 2016 Cosmic star formation history inf 10 4 3 2 1 0 z Peak of
The Virgo Cluster. Distance today: 20 Mpc (million parsecs) Distance in 100 years: 20 Mpc Mpc. (Oh well) Look-back time to Virgo Cluster:
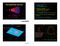 The Virgo Cluster Map by Jan Wisniewski Distance today: 20 Mpc (million parsecs) Distance in 100 years: 20 Mpc + 1 10-9 Mpc. (Oh well) Look-back time to Virgo Cluster: 1 parsec = 3.26 light-years Light
The Virgo Cluster Map by Jan Wisniewski Distance today: 20 Mpc (million parsecs) Distance in 100 years: 20 Mpc + 1 10-9 Mpc. (Oh well) Look-back time to Virgo Cluster: 1 parsec = 3.26 light-years Light
History of the Universe Unit Tracking Sheet
 Name Period Mrs. Coates Earth Science History of the Universe Unit Tracking Sheet Learning Target Question Example Date Target was Taught in Class The Big Bang Theory explains how the universe formed The
Name Period Mrs. Coates Earth Science History of the Universe Unit Tracking Sheet Learning Target Question Example Date Target was Taught in Class The Big Bang Theory explains how the universe formed The
The Age of the Universe If the entire age of the Universe were 1 calendar year, then 1 month would be equivalent to roughly 1 billion years
 Astro.101 Sept. 9, 2008 Announcements A few slots are still open in the class; see prof. to sign up Web-page computer has been down; o.k. now Turn in your student contract Don t forget to do the OWL tutorial
Astro.101 Sept. 9, 2008 Announcements A few slots are still open in the class; see prof. to sign up Web-page computer has been down; o.k. now Turn in your student contract Don t forget to do the OWL tutorial
Island Universes. Up to 1920 s, many thought that Milky Way encompassed entire universe.
 Island Universes Up to 1920 s, many thought that Milky Way encompassed entire universe. Observed three types of nebulas (clouds): - diffuse, spiral, elliptical - many were faint, indistinct - originally
Island Universes Up to 1920 s, many thought that Milky Way encompassed entire universe. Observed three types of nebulas (clouds): - diffuse, spiral, elliptical - many were faint, indistinct - originally
Galaxies. Beyond the Book. FOCUS Book. Make a model that helps demonstrate how the universe is expanding. Follow these steps:
 FOCUS Book Galaxies Make a model that helps demonstrate how the universe is expanding. Follow these steps: 1 Use markers to make dots on the outside of an uninflated balloon to represent galaxies full
FOCUS Book Galaxies Make a model that helps demonstrate how the universe is expanding. Follow these steps: 1 Use markers to make dots on the outside of an uninflated balloon to represent galaxies full
GraspIT Questions AQA GCSE Physics Space physics
 A. Solar system: stability of orbital motions; satellites (physics only) 1. Put these astronomical objects in order of size from largest to smallest. (3) Fill in the boxes in the correct order. the Moon
A. Solar system: stability of orbital motions; satellites (physics only) 1. Put these astronomical objects in order of size from largest to smallest. (3) Fill in the boxes in the correct order. the Moon
The expansion of the Universe, and the big bang
 The expansion of the Universe, and the big bang Q: What is Hubble s law? A. The larger the galaxy, the faster it is moving way from us. B. The farther away the galaxy, the faster it is moving away from
The expansion of the Universe, and the big bang Q: What is Hubble s law? A. The larger the galaxy, the faster it is moving way from us. B. The farther away the galaxy, the faster it is moving away from
April 11, Astronomy Notes Chapter 16.notebook. Types of Galaxies
 The Milky Way is just one of about 50 billion galaxies that are thought to exist. Just as stars can be classified using an H R diagram, galaxies can also be classified according to certain physical properties.
The Milky Way is just one of about 50 billion galaxies that are thought to exist. Just as stars can be classified using an H R diagram, galaxies can also be classified according to certain physical properties.
The Formation of the Solar System
 Earth and the Solar System The Formation of the Solar System Write a number beside each picture to rank each from the oldest (1) to the youngest (4). The universe includes everything that exists: all matter,
Earth and the Solar System The Formation of the Solar System Write a number beside each picture to rank each from the oldest (1) to the youngest (4). The universe includes everything that exists: all matter,
(Astronomy for Dummies) remark : apparently I spent more than 1 hr giving this lecture
 (Astronomy for Dummies) remark : apparently I spent more than 1 hr giving this lecture A.D. 125? Ptolemy s geocentric model Planets ( ) wander among stars ( ) For more info: http://aeea.nmns.edu.tw/aeea/contents_list/universe_concepts.html
(Astronomy for Dummies) remark : apparently I spent more than 1 hr giving this lecture A.D. 125? Ptolemy s geocentric model Planets ( ) wander among stars ( ) For more info: http://aeea.nmns.edu.tw/aeea/contents_list/universe_concepts.html
Exam #3. Final Exam. Exam 3 review. How do we measure properties of a star? A detailed outline of study topics is here:
 Exam #3 Exam #3 is Thursday 4/9 in this room You can bring page of notes (front and back) Bring your calculator and a # pencil Exam 3 covers material from 4/1 onward (only 8 lectures) Consequently, no
Exam #3 Exam #3 is Thursday 4/9 in this room You can bring page of notes (front and back) Bring your calculator and a # pencil Exam 3 covers material from 4/1 onward (only 8 lectures) Consequently, no
Big Bang, Black Holes, No Math
 ASTR/PHYS 109 Dr. David Toback Lecture 26 & 27 Early Times & Fate of the Universe Topic 1: Possibilities 1 Was due Today L27 Last day of Class Reading: (Unit 6) Pre-Lecture Reading Questions (PLRQ) Unit
ASTR/PHYS 109 Dr. David Toback Lecture 26 & 27 Early Times & Fate of the Universe Topic 1: Possibilities 1 Was due Today L27 Last day of Class Reading: (Unit 6) Pre-Lecture Reading Questions (PLRQ) Unit
Module 8: The Cosmos in Motion. UNC-TFA H.S. Astronomy Collaboration, Copyright 2011
 Objectives/Key Points Module 8: The Cosmos in Motion UNC-TFA H.S. Astronomy Collaboration, Copyright 2011 1. Differentiate between classical motions across space (peculiar velocities) and cosmological
Objectives/Key Points Module 8: The Cosmos in Motion UNC-TFA H.S. Astronomy Collaboration, Copyright 2011 1. Differentiate between classical motions across space (peculiar velocities) and cosmological
LESSON 1. Solar System
 Astronomy Notes LESSON 1 Solar System 11.1 Structure of the Solar System axis of rotation period of rotation period of revolution ellipse astronomical unit What is the solar system? 11.1 Structure of the
Astronomy Notes LESSON 1 Solar System 11.1 Structure of the Solar System axis of rotation period of rotation period of revolution ellipse astronomical unit What is the solar system? 11.1 Structure of the
Galaxies and Cosmology
 Galaxies and Cosmology Attendance Quiz Are you here today? (a) yes (b) no Here! (c) Cosmetology? Like hair and nails and makeup? Next Tuesday, 5/30: Dr. Jorge Moreno is unavailable, so class will be cancelled
Galaxies and Cosmology Attendance Quiz Are you here today? (a) yes (b) no Here! (c) Cosmetology? Like hair and nails and makeup? Next Tuesday, 5/30: Dr. Jorge Moreno is unavailable, so class will be cancelled
The Big Bang. Olber s Paradox. Hubble s Law. Why is the night sky dark? The Universe is expanding and We cannot see an infinite Universe
 The Big Bang Olber s Paradox Why is the night sky dark? The Universe is expanding and We cannot see an infinite Universe Hubble s Law v = H0 d v = recession velocity in km/sec d = distance in Mpc H 0 =
The Big Bang Olber s Paradox Why is the night sky dark? The Universe is expanding and We cannot see an infinite Universe Hubble s Law v = H0 d v = recession velocity in km/sec d = distance in Mpc H 0 =
Formation of the Universe. What evidence supports current scientific theory?
 Formation of the Universe What evidence supports current scientific theory? Cosmology Cosmology is the study of the Nature, Structure, Origin, And fate of the universe. How did it all begin? Astronomers
Formation of the Universe What evidence supports current scientific theory? Cosmology Cosmology is the study of the Nature, Structure, Origin, And fate of the universe. How did it all begin? Astronomers
Big Bang, Black Holes, No Math
 ASTR/PHYS 109 Dr. David Toback Lectures 21 and 22 1 Was Due Today L22 Reading: (BBBHNM Unit 3) Pre-Lecture Reading Questions (PLRQ) Unit 3: Let us know if you think you were misgraded Unit 3 Revision (if
ASTR/PHYS 109 Dr. David Toback Lectures 21 and 22 1 Was Due Today L22 Reading: (BBBHNM Unit 3) Pre-Lecture Reading Questions (PLRQ) Unit 3: Let us know if you think you were misgraded Unit 3 Revision (if
How Old is the Universe? How Do We Know It s So Old?
 How Old is the Universe? Until recently, astronomers estimated that the Big Bang occurred between 12 and 14 billion years ago. To put this in perspective, our own Solar System is thought to be 4.5 billion
How Old is the Universe? Until recently, astronomers estimated that the Big Bang occurred between 12 and 14 billion years ago. To put this in perspective, our own Solar System is thought to be 4.5 billion
The Expanding Universe
 Cosmology Expanding Universe History of the Universe Cosmic Background Radiation The Cosmological Principle Cosmology and General Relativity Dark Matter and Dark Energy Primitive Cosmology If the universe
Cosmology Expanding Universe History of the Universe Cosmic Background Radiation The Cosmological Principle Cosmology and General Relativity Dark Matter and Dark Energy Primitive Cosmology If the universe
Hubble Ultra Deep Space View
 Galaxies stars come in large groups (20-1000 billion stars) called Galaxies >2 trillion observable galaxies. Come in Shapes and Sizes depending on how they were formed Elliptical (football shape) Spirals
Galaxies stars come in large groups (20-1000 billion stars) called Galaxies >2 trillion observable galaxies. Come in Shapes and Sizes depending on how they were formed Elliptical (football shape) Spirals
3. It is expanding: the galaxies are moving apart, accelerating slightly The mystery of Dark Energy
 II. Cosmology: How the universe developed Outstanding features of the universe today: 1. It is big, and full of galaxies. 2. It has structure: the galaxies are clumped in filaments and sheets The structure
II. Cosmology: How the universe developed Outstanding features of the universe today: 1. It is big, and full of galaxies. 2. It has structure: the galaxies are clumped in filaments and sheets The structure
Doppler Effect. Sound moving TOWARDS. Sound moving AWAY 9/22/2017. Occurs when the source of sound waves moves towards or away
 Burkey- ESS QUIZ Thursday At the instant of the Big Bang, all the matter, energy, time, & space in the Universe was condensed into a single, tiny point. We call this Singularity. Doppler Effect Occurs
Burkey- ESS QUIZ Thursday At the instant of the Big Bang, all the matter, energy, time, & space in the Universe was condensed into a single, tiny point. We call this Singularity. Doppler Effect Occurs
11/9/2010. Stars, Galaxies & the Universe Announcements. Sky & Telescope s Week at a Glance. iphone App available now.
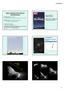 Stars, Galaxies & the Universe Announcements Reading Quiz #11 Wednesday Mix of questions from today s lecture & reading for Wed. on active galaxies HW#10 in ICON due Friday (11/12) by 5 pm - available
Stars, Galaxies & the Universe Announcements Reading Quiz #11 Wednesday Mix of questions from today s lecture & reading for Wed. on active galaxies HW#10 in ICON due Friday (11/12) by 5 pm - available
AST 301 Introduction to Astronomy
 AST 301 Introduction to Astronomy John Lacy RLM 16.332 471-1469 lacy@astro.as.utexas.edu Myoungwon Jeon RLM 16.216 471-0445 myjeon@astro.as.utexas.edu Bohua Li RLM 16.212 471-8443 bohuali@astro.as.utexas.edu
AST 301 Introduction to Astronomy John Lacy RLM 16.332 471-1469 lacy@astro.as.utexas.edu Myoungwon Jeon RLM 16.216 471-0445 myjeon@astro.as.utexas.edu Bohua Li RLM 16.212 471-8443 bohuali@astro.as.utexas.edu
The Modern Origins Story: From the Big Bang to Habitable Planets
 The Modern Origins Story: From the Big Bang to Habitable Planets Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley) The Solar System Age 4.5Gyrs 8 (9? 10? 12?) planets orbiting the sun all in roughly the same plane Lots of
The Modern Origins Story: From the Big Bang to Habitable Planets Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley) The Solar System Age 4.5Gyrs 8 (9? 10? 12?) planets orbiting the sun all in roughly the same plane Lots of
Normal Galaxies (Ch. 24) + Galaxies and Dark Matter (Ch. 25) Symbolically: E0.E7.. S0..Sa..Sb..Sc..Sd..Irr
 Normal Galaxies (Ch. 24) + Galaxies and Dark Matter (Ch. 25) Here we will cover topics in Ch. 24 up to 24.4, but then skip 24.4, 24.5 and proceed to 25.1, 25.2, 25.3. Then, if there is time remaining,
Normal Galaxies (Ch. 24) + Galaxies and Dark Matter (Ch. 25) Here we will cover topics in Ch. 24 up to 24.4, but then skip 24.4, 24.5 and proceed to 25.1, 25.2, 25.3. Then, if there is time remaining,
CH 14 MODERN COSMOLOGY The Study of Nature, origin and evolution of the universe Does the Universe have a center and an edge? What is the evidence
 CH 14 MODERN COSMOLOGY The Study of Nature, origin and evolution of the universe Does the Universe have a center and an edge? What is the evidence that the Universe began with a Big Bang? How has the Universe
CH 14 MODERN COSMOLOGY The Study of Nature, origin and evolution of the universe Does the Universe have a center and an edge? What is the evidence that the Universe began with a Big Bang? How has the Universe
Fire and Ice. The Fate of the Universe. Jon Thaler
 Fire and Ice The Fate of the Universe Jon Thaler Saturday Physics Honors Program Oct. 13, 2007 Some say the world will end in fire, Some say in ice. From what I've tasted of desire I hold with those who
Fire and Ice The Fate of the Universe Jon Thaler Saturday Physics Honors Program Oct. 13, 2007 Some say the world will end in fire, Some say in ice. From what I've tasted of desire I hold with those who
Beyond Our Solar System Chapter 24
 Beyond Our Solar System Chapter 24 PROPERTIES OF STARS Distance Measuring a star's distance can be very difficult Stellar parallax Used for measuring distance to a star Apparent shift in a star's position
Beyond Our Solar System Chapter 24 PROPERTIES OF STARS Distance Measuring a star's distance can be very difficult Stellar parallax Used for measuring distance to a star Apparent shift in a star's position
Observing the Night Sky. Observing the Night Sky. Observing the Night Sky. Observing the Night Sky. Observing the Night Sky. Chapter 29 THE UNIVERSE
 Hewitt/Lyons/Suchocki/Yeh Conceptual Integrated Science Constellations are groups of stars named over antiquity. A familiar constellation is Ursa Major, the Great Bear. Chapter 29 THE UNIVERSE The monthly
Hewitt/Lyons/Suchocki/Yeh Conceptual Integrated Science Constellations are groups of stars named over antiquity. A familiar constellation is Ursa Major, the Great Bear. Chapter 29 THE UNIVERSE The monthly
Start with known facts and reasonable guesses. More on order of magnitude Astronomy How many piano tuners are there in Boulder County?
 ASTR 101 Introduction to Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies Prof. Rosalba Perna TA: Cameron Clarke http://amalfi.astrosunysb.edu/rosalba/ast101/ast101.html MAKE SURE TO GO OVER THE SYLLABUS (if you haven t already
ASTR 101 Introduction to Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies Prof. Rosalba Perna TA: Cameron Clarke http://amalfi.astrosunysb.edu/rosalba/ast101/ast101.html MAKE SURE TO GO OVER THE SYLLABUS (if you haven t already
A Brief Guide to Our Cosmic Context
 A Brief Guide to Our Cosmic Context Todd Duncan (duncant@pdx.edu) PSU Center for Science Education last modified 11/21/08 There is a theory which states that if ever anyone discovers exactly what the Universe
A Brief Guide to Our Cosmic Context Todd Duncan (duncant@pdx.edu) PSU Center for Science Education last modified 11/21/08 There is a theory which states that if ever anyone discovers exactly what the Universe
ASTR 101 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies
 ASTR 101 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies ANNOUNCEMENTS MIDTERM III: Tuesday, Nov 24 th Midterm alternate day: Fri, Nov 20th, 11am, ESS 450 At LAST: In the very Beginning BIG BANG: beginning of Time
ASTR 101 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies ANNOUNCEMENTS MIDTERM III: Tuesday, Nov 24 th Midterm alternate day: Fri, Nov 20th, 11am, ESS 450 At LAST: In the very Beginning BIG BANG: beginning of Time
The Contents of the Universe (or/ what do we mean by dark matter and dark energy?)
 The Contents of the Universe (or/ what do we mean by dark matter and dark energy?) Unseen Influences Dark Matter: An undetected form of mass that emits little or no light but whose existence we infer from
The Contents of the Universe (or/ what do we mean by dark matter and dark energy?) Unseen Influences Dark Matter: An undetected form of mass that emits little or no light but whose existence we infer from
Astronomy 9 Concepts of the Cosmos
 Astronomy 9 Concepts of the Cosmos Monday/Wednesday, 1:30-2:45 pm, Cabot Auditorium LECTURE 2: I.Our Place in the Universe Lecture on Mon., Feb. 1 st Pre-course Test - REQUIRED! (if you want the attendance
Astronomy 9 Concepts of the Cosmos Monday/Wednesday, 1:30-2:45 pm, Cabot Auditorium LECTURE 2: I.Our Place in the Universe Lecture on Mon., Feb. 1 st Pre-course Test - REQUIRED! (if you want the attendance
Cosmology and the Evolution of the Universe. Implications of the Hubble Law: - Universe is changing (getting bigger!) - it is not static, unchanging
 Cosmology and the Evolution of the Edwin Hubble, 1929: -almost all galaxies have a redshift -moving away from us -exceptions in Local Group -with distance measurements - found a relationship greater distance
Cosmology and the Evolution of the Edwin Hubble, 1929: -almost all galaxies have a redshift -moving away from us -exceptions in Local Group -with distance measurements - found a relationship greater distance
Implications of the Hubble Law: - it is not static, unchanging - Universe had a beginning!! - could not have been expanding forever HUBBLE LAW:
 Cosmology and the Evolution of the Universe Edwin Hubble, 1929: -almost all galaxies have a redshift -moving away from us -greater distance greater redshift Implications of the Hubble Law: - Universe is
Cosmology and the Evolution of the Universe Edwin Hubble, 1929: -almost all galaxies have a redshift -moving away from us -greater distance greater redshift Implications of the Hubble Law: - Universe is
The Universe and Galaxies. Adapted from:
 The Universe and Galaxies Adapted from: http://www.west-jefferson.k12.oh.us/earthandspacescience.aspx Astronomy The study of objects and matter outside the Earth s atmosphere and of their physical and
The Universe and Galaxies Adapted from: http://www.west-jefferson.k12.oh.us/earthandspacescience.aspx Astronomy The study of objects and matter outside the Earth s atmosphere and of their physical and
Hubble s Law & Black Holes at a Galaxy s Center. Simplicio s questions about Hubble s Law
 Hubble s Law & Black Holes at a Galaxy s Center Questions about Hubble s Law Quasars, active galaxies, & black holes in centers of galaxies Astronomical Horizons Public Talks First Light for the Spartan
Hubble s Law & Black Holes at a Galaxy s Center Questions about Hubble s Law Quasars, active galaxies, & black holes in centers of galaxies Astronomical Horizons Public Talks First Light for the Spartan
Big Bang, Black Holes, No Math
 ASTR/PHYS 109 Dr. David Toback Lecture 5 1 Prep For Today (is now due) L5 Reading: No new reading Unit 2 reading assigned at the end of class Pre-Lecture Reading Questions: Unit 1: Grades have been posted
ASTR/PHYS 109 Dr. David Toback Lecture 5 1 Prep For Today (is now due) L5 Reading: No new reading Unit 2 reading assigned at the end of class Pre-Lecture Reading Questions: Unit 1: Grades have been posted
2011 Arizona State University Page 1 of 6
 AST 114 Spring 2017 NAME: HUBBLE EXPANSION What will you learn in this Lab? In this lab, you will reproduce the 20 th century discovery by Edwin Hubble that the Universe is expanding. You will determine
AST 114 Spring 2017 NAME: HUBBLE EXPANSION What will you learn in this Lab? In this lab, you will reproduce the 20 th century discovery by Edwin Hubble that the Universe is expanding. You will determine
Answers. The Universe. Year 10 Science Chapter 6
 Answers The Universe Year 10 Science Chapter 6 p133 1 The universe is considered to be the whole of all matter, energy, planets, solar systems, galaxies, and space. Many definitions of the universe also
Answers The Universe Year 10 Science Chapter 6 p133 1 The universe is considered to be the whole of all matter, energy, planets, solar systems, galaxies, and space. Many definitions of the universe also
Chapter 23 Lecture. The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition. Dark Matter, Dark Energy, and the Fate of the Universe Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 23 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Dark Matter, Dark Energy, and the Fate of the Universe Curvature of the Universe The Density Parameter of the Universe Ω 0 is defined as the ratio
Chapter 23 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Dark Matter, Dark Energy, and the Fate of the Universe Curvature of the Universe The Density Parameter of the Universe Ω 0 is defined as the ratio
Chapter 23: Dark Matter, Dark Energy & Future of the Universe. Galactic rotation curves
 Chapter 23: Dark Matter, Dark Energy & Future of the Universe Galactic rotation curves Orbital speed as a function of distance from the center: rotation_of_spiral_galaxy.htm Use Kepler s Third Law to get
Chapter 23: Dark Matter, Dark Energy & Future of the Universe Galactic rotation curves Orbital speed as a function of distance from the center: rotation_of_spiral_galaxy.htm Use Kepler s Third Law to get
Earth Science, 13e Tarbuck & Lutgens
 Earth Science, 13e Tarbuck & Lutgens Beyond Our Solar System Earth Science, 13e Chapter 24 Stanley C. Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Properties of stars Distance Distances to the stars are very
Earth Science, 13e Tarbuck & Lutgens Beyond Our Solar System Earth Science, 13e Chapter 24 Stanley C. Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Properties of stars Distance Distances to the stars are very
Galaxies & Introduction to Cosmology
 Galaxies & Introduction to Cosmology Other Galaxies: How many are there? Hubble Deep Field Project 100 hour exposures over 10 days Covered an area of the sky about 1/100 the size of the full moon Probably
Galaxies & Introduction to Cosmology Other Galaxies: How many are there? Hubble Deep Field Project 100 hour exposures over 10 days Covered an area of the sky about 1/100 the size of the full moon Probably
Lecture #24: Plan. Cosmology. Expansion of the Universe Olber s Paradox Birth of our Universe
 Lecture #24: Plan Cosmology Expansion of the Universe Olber s Paradox Birth of our Universe Reminder: Redshifts and the Expansion of the Universe Early 20 th century astronomers noted: Spectra from most
Lecture #24: Plan Cosmology Expansion of the Universe Olber s Paradox Birth of our Universe Reminder: Redshifts and the Expansion of the Universe Early 20 th century astronomers noted: Spectra from most
9/5/16. Astronomy 1001 Syllabus Sec 1 T,Th AM; Sec 2 T,TH PM. Astronomy 1001 First Assignments: Chapter 1: A Modern View of the Universe
 9/5/16 Astronomy 1001 Syllabus Sec 1 T,Th AM; Sec 2 T,TH PM Syllabus: http://www.astro.umn.edu/courses/1001/syllabi/ Lecture notes: http://www.astro.umn.edu/courses/1001/ lecnotes/ Exams: http://www.astro.umn.edu/courses/1001/
9/5/16 Astronomy 1001 Syllabus Sec 1 T,Th AM; Sec 2 T,TH PM Syllabus: http://www.astro.umn.edu/courses/1001/syllabi/ Lecture notes: http://www.astro.umn.edu/courses/1001/ lecnotes/ Exams: http://www.astro.umn.edu/courses/1001/
8/30/2010. Classifying Stars. Classifying Stars. Classifying Stars
 Classifying Stars In the early 1900s, Ejnar Hertzsprung and Henry Russell made some important observations. They noticed that, in general, stars with higher temperatures also have brighter absolute magnitudes.
Classifying Stars In the early 1900s, Ejnar Hertzsprung and Henry Russell made some important observations. They noticed that, in general, stars with higher temperatures also have brighter absolute magnitudes.
Astronomy 162, Week 10 Cosmology Patrick S. Osmer Spring, 2006
 Astronomy 162, Week 10 Cosmology Patrick S. Osmer Spring, 2006 Information Makeup quiz Wednesday, May 31, 5-6PM, Planetarium Review Session, Monday, June 5 6PM, Planetarium Cosmology Study of the universe
Astronomy 162, Week 10 Cosmology Patrick S. Osmer Spring, 2006 Information Makeup quiz Wednesday, May 31, 5-6PM, Planetarium Review Session, Monday, June 5 6PM, Planetarium Cosmology Study of the universe
Question 1. Question 2. Correct. Chapter 16 Homework. Part A
 Chapter 16 Homework Due: 11:59pm on Thursday, November 17, 2016 To understand how points are awarded, read the Grading Policy for this assignment. Question 1 Following are a number of distinguishing characteristics
Chapter 16 Homework Due: 11:59pm on Thursday, November 17, 2016 To understand how points are awarded, read the Grading Policy for this assignment. Question 1 Following are a number of distinguishing characteristics
Prelab 9: The Hubble Redshift Distance Relation
 Name: Section: Date: Prelab 9: The Hubble Redshift Distance Relation The Doppler Effect: When objects are moving, the frequency or pitch of waves can change. Think of the noise a car makes when you are
Name: Section: Date: Prelab 9: The Hubble Redshift Distance Relation The Doppler Effect: When objects are moving, the frequency or pitch of waves can change. Think of the noise a car makes when you are
Energy Source for Active Galactic Nuclei
 Quasars Quasars are small, extremely luminous, extremely distant galactic nuclei Bright radio sources Name comes from Quasi-Stellar Radio Source, as they appeared to be stars! Can have clouds of gas near
Quasars Quasars are small, extremely luminous, extremely distant galactic nuclei Bright radio sources Name comes from Quasi-Stellar Radio Source, as they appeared to be stars! Can have clouds of gas near
Who should take this course? How to succeed in this course. Course Information
 ASTR 1040 Accel Intro Astronomy 2: Stars & Galaxies Spring 2011 Prof. Juri Toomre TA: Nicholas Nelson TR 9:30am, Duane G-125 G + M recitations (E-126: 9am, 10am, noon) Lecture 1 12 Jan 2010 Detailed course
ASTR 1040 Accel Intro Astronomy 2: Stars & Galaxies Spring 2011 Prof. Juri Toomre TA: Nicholas Nelson TR 9:30am, Duane G-125 G + M recitations (E-126: 9am, 10am, noon) Lecture 1 12 Jan 2010 Detailed course
Hubble Ultra Deep Space View PHYS 162 2
 Galaxies stars come in large groups (20-200 billion stars) called Galaxies >2 trillion observable galaxies. Come in Shapes and Sizes depending on how they were formed Elliptical (football shape) Spirals
Galaxies stars come in large groups (20-200 billion stars) called Galaxies >2 trillion observable galaxies. Come in Shapes and Sizes depending on how they were formed Elliptical (football shape) Spirals
PHY323:Lecture 7 Dark Matter with Gravitational Lensing
 PHY323:Lecture 7 Dark Matter with Gravitational Lensing Strong Gravitational Lensing Theory of Gravitational Lensing Weak Gravitational Lensing Large Scale Structure Experimental Evidence for Dark Matter
PHY323:Lecture 7 Dark Matter with Gravitational Lensing Strong Gravitational Lensing Theory of Gravitational Lensing Weak Gravitational Lensing Large Scale Structure Experimental Evidence for Dark Matter
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS
 DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS TSOKOS OPTION E-6 GALAXIES Introductory Video: The Big Bang Theory Objectives Understand the Hubble classification scheme of galaxies and describe the
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS TSOKOS OPTION E-6 GALAXIES Introductory Video: The Big Bang Theory Objectives Understand the Hubble classification scheme of galaxies and describe the
Chapter 25 (and end of 24): Lecture Notes
 Chapter 25 (and end of 24): Lecture Notes In order to understand the Hubble Law and its implications both for estimating distances and for interpreting the evolution of the universe, you have to be comfortable
Chapter 25 (and end of 24): Lecture Notes In order to understand the Hubble Law and its implications both for estimating distances and for interpreting the evolution of the universe, you have to be comfortable
Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation
 Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the passage below and on your knowledge of Earth Science. Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation In the 1920s, Edwin Hubble's discovery of a pattern in the red
Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the passage below and on your knowledge of Earth Science. Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation In the 1920s, Edwin Hubble's discovery of a pattern in the red
Formation of the Universe & What is in Space? The Big Bang Theory and components of the Universe
 Formation of the Universe & What is in Space? The Big Bang Theory and components of the Universe The Big Bang Theory The Big Bang Theory The Big Bang Theory is the most widely accepted scientific explanation
Formation of the Universe & What is in Space? The Big Bang Theory and components of the Universe The Big Bang Theory The Big Bang Theory The Big Bang Theory is the most widely accepted scientific explanation
Chapter 26: Cosmology
 Chapter 26: Cosmology Cosmology means the study of the structure and evolution of the entire universe as a whole. First of all, we need to know whether the universe has changed with time, or if it has
Chapter 26: Cosmology Cosmology means the study of the structure and evolution of the entire universe as a whole. First of all, we need to know whether the universe has changed with time, or if it has
Figure 19.19: HST photo called Hubble Deep Field.
 19.3 Galaxies and the Universe Early civilizations thought that Earth was the center of the universe. In the sixteenth century, we became aware that Earth is a small planet orbiting a medium-sized star.
19.3 Galaxies and the Universe Early civilizations thought that Earth was the center of the universe. In the sixteenth century, we became aware that Earth is a small planet orbiting a medium-sized star.
Chapter 23 Lecture. The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition. Dark Matter, Dark Energy, and the Fate of the Universe Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 23 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Dark Matter, Dark Energy, and the Fate of the Universe Curvature of the Universe The Density Parameter of the Universe Ω 0 is defined as the ratio
Chapter 23 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Dark Matter, Dark Energy, and the Fate of the Universe Curvature of the Universe The Density Parameter of the Universe Ω 0 is defined as the ratio
The Universe and Light
 The Big Bang The big bang theory states that at one time, the entire universe was confined to a dense, hot, supermassive ball. Then, about 13.7 billion years ago, a violent explosion occurred, hurling
The Big Bang The big bang theory states that at one time, the entire universe was confined to a dense, hot, supermassive ball. Then, about 13.7 billion years ago, a violent explosion occurred, hurling
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 33 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 33 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 33 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
Astronomy. Study of objects in space such as the Sun, stars, planets, comets, gas, & galaxies. *Also, the Earth s place in the universe.
 Astronomy Study of objects in space such as the Sun, stars, planets, comets, gas, & galaxies. *Also, the Earth s place in the universe. Universe = everything that exists Disclaimer: Astrology is NOT science!!!
Astronomy Study of objects in space such as the Sun, stars, planets, comets, gas, & galaxies. *Also, the Earth s place in the universe. Universe = everything that exists Disclaimer: Astrology is NOT science!!!
The Dawn of Time - II. A Cosmos is Born
 The Dawn of Time - II. A Cosmos is Born Learning Objectives! Why does Olbers paradox show the Universe began?! How does Hubble s Law tell us the age of the Universe? If Hubble s Constant is large, is the
The Dawn of Time - II. A Cosmos is Born Learning Objectives! Why does Olbers paradox show the Universe began?! How does Hubble s Law tell us the age of the Universe? If Hubble s Constant is large, is the
The Beginning of the Universe 8/11/09. Astronomy 101
 The Beginning of the Universe 8/11/09 Astronomy 101 Astronomy Picture of the Day Astronomy 101 Outline for Today Astronomy Picture of the Day Return Lab 11 Astro News Q&A Session Dark Energy Cosmic Microwave
The Beginning of the Universe 8/11/09 Astronomy 101 Astronomy Picture of the Day Astronomy 101 Outline for Today Astronomy Picture of the Day Return Lab 11 Astro News Q&A Session Dark Energy Cosmic Microwave
AST 301 Introduction to Astronomy
 AST 301 Introduction to Astronomy John Lacy RLM 16.332 471-1469 lacy@astro.as.utexas.edu Myoungwon Jeon RLM 16.216 471-0445 myjeon@astro.as.utexas.edu Bohua Li RLM 16.212 471-8443 bohuali@astro.as.utexas.edu
AST 301 Introduction to Astronomy John Lacy RLM 16.332 471-1469 lacy@astro.as.utexas.edu Myoungwon Jeon RLM 16.216 471-0445 myjeon@astro.as.utexas.edu Bohua Li RLM 16.212 471-8443 bohuali@astro.as.utexas.edu
Understanding the Universe S TA R T ING WITH EARTH A ND B E YO ND
 Unit Overview: Understanding the Universe S TA R T ING WITH EARTH A ND B E YO ND Our solar system examining size and scale in space 6.11B UNDERSTAND THAT GRAVITY IS THE FORCE THAT GOVERNS MOTION IN OUR
Unit Overview: Understanding the Universe S TA R T ING WITH EARTH A ND B E YO ND Our solar system examining size and scale in space 6.11B UNDERSTAND THAT GRAVITY IS THE FORCE THAT GOVERNS MOTION IN OUR
GraspIT Questions AQA GCSE Physics Space physics
 A. Solar system: stability of orbital motions; satellites (physics only) 1. Put these astronomical objects in order of size from largest to smallest. (3) Fill in the boxes in the correct order. the Moon
A. Solar system: stability of orbital motions; satellites (physics only) 1. Put these astronomical objects in order of size from largest to smallest. (3) Fill in the boxes in the correct order. the Moon
Seating Chart for Final Exam (same as for midterms)
 Seating Chart for Final Exam (same as for midterms) Section 3, 10:20-11:10 SIT IN YOUR ASSIGNED ROW! (this seating chart is in the Study Guide on Angel) WHEN THE TESTS ARE HANDED OUT, TAKE ONLY THE TEST
Seating Chart for Final Exam (same as for midterms) Section 3, 10:20-11:10 SIT IN YOUR ASSIGNED ROW! (this seating chart is in the Study Guide on Angel) WHEN THE TESTS ARE HANDED OUT, TAKE ONLY THE TEST
Today in Astronomy 102: relativity and the Universe
 Today in Astronomy 102: relativity and the Universe General relativity and the Universe. Hubble: the Universe is observed to be homogeneous, isotropic, and expanding Redshift and distance: Hubble s Law
Today in Astronomy 102: relativity and the Universe General relativity and the Universe. Hubble: the Universe is observed to be homogeneous, isotropic, and expanding Redshift and distance: Hubble s Law
Grade 8 - Science Interim Assessment Third Grading Period. 1. Four cubes are placed into water.
 Name Date ID 1. Four cubes are placed into water. Grade 8 - Science Interim Assessment Third Grading Period What property determines whether they will float or sink? number of electrons in the outer shell
Name Date ID 1. Four cubes are placed into water. Grade 8 - Science Interim Assessment Third Grading Period What property determines whether they will float or sink? number of electrons in the outer shell
