History of the Universe Unit Tracking Sheet
|
|
|
- Candice Mathews
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Name Period Mrs. Coates Earth Science History of the Universe Unit Tracking Sheet Learning Target Question Example Date Target was Taught in Class The Big Bang Theory explains how the universe formed The Doppler Effect is evidence of an expanding universe The Big Bang created the first two elements Hydrogen and Helium How did the Big Bang start? When a galaxy is traveling away from the Earth what is happening to the light waves? Over 99% of the atoms in our Universe are The Big Bang left behind an echo of energy Fusion inside stars created the elements on the Periodic Table How does Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation support the Big Bang theory? Where did all of the iron, oxygen, gold, and other elements on Earth come from? My Progress 4 (90-100%) Pre-Test The Big Bang Theory Doppler Effect H and He Background Radiation Stellar Fusion Post Test 3 (80-89%) 2 (70-79%) 1 (0-69%) 1
2 AH-HA! Why do scientists accept the Big Bang Theory? 2
3 Science Starter Sheet Date Question Answer 3
4 Science Starter Sheet Date Question Answer 4
5 History of the Universe Timeline Activity Part 1 Put these Universe events in the order that you believe they occurred (from the first event to the last event) The first flowers appeared on Earth The first galaxies were formed The first stars in the Universe were formed The first dinosaurs appeared on Earth The formation of our Moon The Big Bang The formation of our Sun The first bacteria appeared on Earth The formation of Earth s oceans The first protons and neutrons were formed The first humans appeared on Earth The formation of our Earth The first atoms were formed Part 2 Now that you know the correct order of Universe events, estimate how long ago each event happened. (HINT: Scientists believe the Universe is nearly 14 billion years old). Estimate Event How Many Years Ago? Event How Many Years Ago? Part 3 Use the Register Tape provided by your teacher to map out the event dates that you predicted in part 2. Mark one end of the tape 14 billion years ago and the other end Present Day. Every 3 inches is equal to 1 billion years. 14 Present Day 5
6 Part 4 After seeing the correct answers to Part 3, explain how close your answers were to the correct answers (which events did you most closely map): Part 5 Write down the correct time line of events below: Correct Answers Event How Long Ago? Event How Long Ago? Analysis: 1. Why do you believe it is difficult for some people to understand how old the Universe is? 2. Name two new things that you learned today: 6
7 1. What is everything made out of? Birth of the Universe Video Notes 2. Where does all matter come from? 3. What size was the universe at the very beginning? 4. Name the American astronomer who first came up with the idea that the universe was once tiny? 5. Describe what was happening to the baby universe in the first seconds of its life. 6. What was the baby universe made out of? 7. What were the first atomic nuclei to be formed once the universe cooled off enough? Why were they not atoms yet? 8. What enabled light to come through the universe? 9. What does that flash of light tell us about the universe now? 10. What other evidence do we have of the big bang? 11. Why are stars important for you and I to exist? 7
8 12. What kind of information does the picture of the cosmic background radiation give scientists? 13. How do stars form? 14. What is going on inside stars? 15. In what year was the Hubble Space telescope launched into space? 16. What is the importance of the Hubble space telescope? 17. How are heavy elements made inside stars? 18. What has to happen for heavier elements than iron to form? 19. Describe the death of a star. 20. Explain the importance of supernova explosions. 21. How did our Earth form? 8
9 H i s t o r y o f t h e U n i v e r s e N o t e s How was the Universe Created? What is a Theory? Events that formed the Universe THE - superfast expansion The universe is a hot soup of,, and other particles. Quarks clump into and neutrons 3 minutes after the big bang, the universe enough for the first to form. The First atoms were (H) and (He) Matter separates into. Gas and dusts accumulate as a. Nebula to form a spinning disk pulls gases to the center of the disk Gas at the center of the disk becomes hot and dense enough for to begin Then and form Moving Galaxies Most galaxies are from Earth Only a couple are moving us The away a galaxy is the it is moving. The universe is! The Big Bang Theory If all galaxies are moving away from each other, then they must have been at some point. All the matter in the universe came together at. Then billion years ago the universe formed in an enormous. How do we know the Universe is expanding? The Effect The change in the of a wave caused by the relative between the source of the wave and the observer. 9
10 Waves = the distance from the top of one crest to the top of the next one The of a wave is equal to the number of waves that pass a particular point in one second. Doppler Effect in Water Draw and describe what you see. Stationary Bug Bug Moving Doppler Effect in Sound What happens to sound when it is in motion? Describe or Draw it. LIGHT Light is an wave. The is a continuous range of waves extending from radio waves to gamma rays. The Doppler Effect also occurs for. When a light source approaches, there is an increase in ; when it moves away, there is a decrease if frequency. An increase in frequency is called a. A decrease in frequency is called a Because most galaxies show a in the color of their light, this is evidence that they are moving from one another. So is evidence that our universe is! 10
11 S p e c t r u m L a b S h e e t Use a spectroscope or diffraction grating film to observe the different sources of light. Color the spectral lines that you see for each source. Hydrogen Gas Helium Gas Neon Gas Traditional Light Bulb Florescent Light Bulb Electronic Device Analysis: 1. Why do traditional light bulbs and florescent light bulbs have different spectral lines? 2. What happens when you look through TWO spectroscopes or TWO pieces of film? 3. Why do you believe each atom has different spectral lines? 4. How could a spectroscope inform an astronomer of what elements are in a star? 11
12 W h a t i s t h e B i g B a n g? Recall how previously you learned that using the Doppler Effect will help determine if a red shift or a blue shift is occurring with respect to stars. This activity is designed to help you see how the red shift provides the opportunity to model the big bang Theory as it relates to the red shift. Procedure: 1. Blow up the balloon until it is about 10 centimeters in diameter. o Do not tie the end. o Have a partner mark six dots scattered around the surface of the balloon. o Label one of dot as "MW," to represent the Milky Way Galaxy. o The other dots represent other galaxies throughout the universe. 2. Without letting any air out of the balloon, blow more air into the balloon until the diameter is approximately 5 cm larger. o Observe the change in the location of the dots relative to each other. 3. Repeat the process, this time blowing up the balloon so that it is 5 cm larger in diameter. 4. Now blow up the balloon so that it is almost as full as it can go. DO NOT POP IT. Repeat your observations. Analysis: 1. If you were standing at the point labeled "MW," what kind of shift would you expect to see in the spectra of the dots representing other galaxies? 2. Why are color shifts important in understanding what is happening to the universe? 3. Imagine that you didn't see the balloon start expanding; but you then witnessed the balloon continue to expand, what could you infer about the size of the balloon before you began watching? 4. How does the expansion of the balloon relate to the expansion of the universe? Hubble's explanation of the expanding universe When Hubble noticed all of the red shifts compared to the very few blue shifts, he realized that the universe is expanding. Just as you did during the balloon analysis, scientists can now point to what the universe must have looked like in the past if we are currently watching it expand. Remember our loaf of raisin bread. If you walked into the kitchen and observed that the bread had been rising, what could you say about what the loaf looked like 15 or 20 minutes ago? The same thing happens with the universe. As we watch the universe get larger, we can say that at some point in time, the matter and energy that forms the universe must have been much closer together. What could have sent all of that material flying outward into space? Only an explosion beyond anything we have ever seen could have done that. This explosion is known as the big bang, and is generally referred to as the beginning of the universe. At a certain time in the past, all matter and energy was found in one spot. Over 13 billion years ago, the big bang sent that matter and energy outward, and the universe began. If the universe is truly expanding, then that means that at some point in time, all of the matter must have been together, just as in the balloon analysis. 12
13 G r a p h i n g R e d s h i f t For the last century, Astronomers have gathered information about bright objects in our sky. Below you will find information about 16 celestial objects. The objects are labeled as M objects (M stands for Messier, an Astronomer from the 18 th century), or NGC objects (NGC stands for New General Catalog, which is a worldwide complied list of objects in our night sky). Object M60, which is 55 million light-years away (Mly), is traveling at 1,117 km/s. Object M82 is 11.5 Mly away, traveling 203 km/s. Object NGC 5010 is 140 Mly away, traveling 2975 km/s. The object named NGC 5078, which is 94 Mly away, is traveling 2168 km/s. M101, just 21 Mly away, is traveling 241 km/s. NGC 5490 is a whopping 218 Mly from Earth, and it is traveling 4,928 km/s. Object M64 is 24 Mly from our planet, traveling 408 km/s, while object NGC 5101 is 89 Mly away, traveling at 1,868 km/s. M51, 23 Mly away, is moving at a speed of 463 km/s. NGC 5091 is 150 Mly away from Earth, traveling at 3,420 km/s. An object called M105 is 32 Mly away, traveling at 911 km/s, and just a little farther is object M95, 33 Mly away, and it is moving at 778 km/s. M74 is closer than those last two, at just 30 Mly away. Its speed is 657 km/s. M84 is twice as far, 60 Mly away! Its speed is 1,060 km/s! Object M49 is 56 Mly away, traveling at 997 km/s. And M66 is 36 Mly away, traveling at 727 km/s. Organize the data above into a table: Object Speed (km/s) Distance (Mly) M60 1,
14 Now make a scatter plot graph with each celestial object below. Don t forget to label the objects on the graph as well as the x and y axis. (HINTS: speed will be on the x-axis and distance will be on the y-axis; label the x-axis in increments of 200 up to 5000, and the y-axis in increments of 10 up to 250) Analysis Questions: 1. Which object is farthest from Earth? 2. Which object is closest to Earth? 3. Which object has the fastest speed? 4. Which object has the slowest speed? 5. Finish the following sentence: The farther away an object is from Earth, the 14
15 6. Match each of the following objects to a wavelength below. Remember, the farther an object is from the Earth, the longer the wavelength of light that is emitted. Objects: M105 NGC 5091 M101 NGC 5010 A. B. C. D. 7. If astronomers found a galaxy that was 90 Mly away, traveling at 100 km/s, would that information fit the pattern on your graph? Explain your answer with a full sentence. 8. There are many galaxies and other celestial objects in our sky that are listed as having negative speeds (like -230 km/s, or -1,056 km/s). What do you think this means? Why? 15
16 C o l o r i n g R e d a n d B l u e S h i f t A. Color the DASHED spectroscopy lines. B. Use the spectrum key to name the element OR the ELEMENTS. C. Identify whether the star has red shift or blue shift (which way did the lines move?) Star 1: UV Violet Blue Green Yel. Org. Red Infrared (Units = Angstroms) Which element? What shift? Star 2: UV Violet Blue Green Yello w Oran ge Red Infrared (Units = Angstroms) Which element? What shift? Star 3: UV Violet Blue Green Yel. Org. Red Infrared (Units = Angstroms) Which element? What shift? 16
17 Now each star will have MORE THAN ONE element within it! Star 4: UV Violet Blue Green Yel. Org. Red Infrared (Units = Angstroms) Which 2 Elements? What shift? Star 5: UV Violet Blue Green Yel. Orag. Red Infrared (Units = Angstroms) Which 2 Elements? What shift? Star 6: UV Violet Blue Green Yel. Org. Red Infrared (Units = Angstroms) Which 2 Elements? What shift? 17
18 Star Life Cycle 18
19 Star Life Cycle Extra Notes: 19
20 lready discussed star cycle and fusion, this will be necessary before students begin the worksheet. 20
21 P e r i o d i c T a b l e a n d H e a v y E l e m e n t s I. Shade in the following elements on your periodic table with a different color for each group Light elements produced in Big Bang Heavier elements formed by nuclear fusion. Heaviest elements form in supernova Hydrogen (H) Iron (Fe) Tin (Sn) Helium (He) Nitrogen (N) Nickel (Ni) Lithium (Li) Silicon (Si) Lead (Pb) Magnesium (Mg) Zinc (Zn) Sulfur (S) II. For each of the following elements identify whether it most likely originated from the big bang, nuclear fusion in stars, or through supernovas 1. Gold (Au): 4. Carbon (C): 7. Oxygen (O): 2. Sodium (Na): 5. Helium (He): 8. Lead (Pb): 3. Hydrogen (H): 6. Uranium (U): 9. Xenon (Xe): Name the element shown by the following drawings: Now draw a picture of an Oxygen atom:
o Terms to know o Big Bang Theory o Doppler Effect o Redshift o Universe
 Standard 1: Students will understand the scientific evidence that supports theories that explain how the universe and the solar system developed. They will compare Earth to other objects in the solar system.
Standard 1: Students will understand the scientific evidence that supports theories that explain how the universe and the solar system developed. They will compare Earth to other objects in the solar system.
CHAPTER 28 STARS AND GALAXIES
 CHAPTER 28 STARS AND GALAXIES 28.1 A CLOSER LOOK AT LIGHT Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation, which is energy that travels in waves. Waves of energy travel at 300,000 km/sec (speed of light Ex:
CHAPTER 28 STARS AND GALAXIES 28.1 A CLOSER LOOK AT LIGHT Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation, which is energy that travels in waves. Waves of energy travel at 300,000 km/sec (speed of light Ex:
Week 2: Isotopes and Stellar Fusion. Part 1: Isotopes Part 2: Nucleosynthesis in Stars
 Week 2: Isotopes and Stellar Fusion Part 1: Isotopes Part 2: Nucleosynthesis in Stars Part 1: Isotopes Part 1: Isotopes After this lesson I can define isotopes. determine the number of protons & neutrons
Week 2: Isotopes and Stellar Fusion Part 1: Isotopes Part 2: Nucleosynthesis in Stars Part 1: Isotopes Part 1: Isotopes After this lesson I can define isotopes. determine the number of protons & neutrons
Figure 19.19: HST photo called Hubble Deep Field.
 19.3 Galaxies and the Universe Early civilizations thought that Earth was the center of the universe. In the sixteenth century, we became aware that Earth is a small planet orbiting a medium-sized star.
19.3 Galaxies and the Universe Early civilizations thought that Earth was the center of the universe. In the sixteenth century, we became aware that Earth is a small planet orbiting a medium-sized star.
Big Bang Theory PowerPoint
 Big Bang Theory PowerPoint Name: # Period: 1 2 3 4 5 6 Recombination Photon Epoch Big Bang Nucleosynthesis Hadron Epoch Hadron Epoch Quark Epoch The Primordial Era Electroweak Epoch Inflationary Epoch
Big Bang Theory PowerPoint Name: # Period: 1 2 3 4 5 6 Recombination Photon Epoch Big Bang Nucleosynthesis Hadron Epoch Hadron Epoch Quark Epoch The Primordial Era Electroweak Epoch Inflationary Epoch
Study Guide Chapter 2
 Section: Stars Pages 32-38 Study Guide Chapter 2 Circle the letter of the best answer for each question. 1. What do scientists study to learn about stars? a. gravity c. space b. starlight d. colors COLOR
Section: Stars Pages 32-38 Study Guide Chapter 2 Circle the letter of the best answer for each question. 1. What do scientists study to learn about stars? a. gravity c. space b. starlight d. colors COLOR
The Universe. Unit 3 covers the following framework standards: ES 8 and 12. Content was adapted the following:
 Unit 3 The Universe Chapter 4 ~ The Formation of the Universe o Section 1 ~ The Scale of the Universe o Section 2 ~ The Formation of the Universe o Section 3 ~ The Future of the Universe Chapter 5 ~ Galaxies
Unit 3 The Universe Chapter 4 ~ The Formation of the Universe o Section 1 ~ The Scale of the Universe o Section 2 ~ The Formation of the Universe o Section 3 ~ The Future of the Universe Chapter 5 ~ Galaxies
SOLAR SYSTEM, STABILITY OF ORBITAL MOTIONS, SATELLITES
 SOLAR SYSTEM, STABILITY OF ORBITAL MOTIONS, SATELLITES Q1. The figure below shows what scientists over 1000 years ago thought the solar system was like. Give one way that the historical model of the solar
SOLAR SYSTEM, STABILITY OF ORBITAL MOTIONS, SATELLITES Q1. The figure below shows what scientists over 1000 years ago thought the solar system was like. Give one way that the historical model of the solar
Solar System Unit Tracking Sheet
 Name Period Mrs. Coates Earth Science Solar System Unit Tracking Sheet Learning Target The Solar System is 4.6 billion years old Question Example How is the age of the solar system estimated by scientists?
Name Period Mrs. Coates Earth Science Solar System Unit Tracking Sheet Learning Target The Solar System is 4.6 billion years old Question Example How is the age of the solar system estimated by scientists?
Galaxies and the Universe
 Standard 7.3.1: Recognize and describe that the Sun is a medium-sized star located near the edge of a diskshaped galaxy of stars and that the universe contains many billions of galaxies and each galaxy
Standard 7.3.1: Recognize and describe that the Sun is a medium-sized star located near the edge of a diskshaped galaxy of stars and that the universe contains many billions of galaxies and each galaxy
Big Bang Theory How the Universe was Formed
 Big Bang Theory How the Universe was Formed Objectives Explain the Big Bang Theory. Give evidence to support the Big Bang Theory. Dispel misconceptions about the Big Bang Theory. Explain problems with
Big Bang Theory How the Universe was Formed Objectives Explain the Big Bang Theory. Give evidence to support the Big Bang Theory. Dispel misconceptions about the Big Bang Theory. Explain problems with
The Formation of the Solar System
 Earth and the Solar System The Formation of the Solar System Write a number beside each picture to rank each from the oldest (1) to the youngest (4). The universe includes everything that exists: all matter,
Earth and the Solar System The Formation of the Solar System Write a number beside each picture to rank each from the oldest (1) to the youngest (4). The universe includes everything that exists: all matter,
THE UNIVERSE CHAPTER 20
 THE UNIVERSE CHAPTER 20 THE UNIVERSE UNIVERSE everything physical in and Includes all space, matter, and energy that has existed, now exists, and will exist in the future. How did our universe form, how
THE UNIVERSE CHAPTER 20 THE UNIVERSE UNIVERSE everything physical in and Includes all space, matter, and energy that has existed, now exists, and will exist in the future. How did our universe form, how
The Universe and Light
 The Big Bang The big bang theory states that at one time, the entire universe was confined to a dense, hot, supermassive ball. Then, about 13.7 billion years ago, a violent explosion occurred, hurling
The Big Bang The big bang theory states that at one time, the entire universe was confined to a dense, hot, supermassive ball. Then, about 13.7 billion years ago, a violent explosion occurred, hurling
Light. Transverse electromagnetic wave, or electromagnetic radiation. Includes radio waves, microwaves, infra-red, visible, UV, X-rays, and gamma rays
 Light Transverse electromagnetic wave, or electromagnetic radiation Includes radio waves, microwaves, infra-red, visible, UV, X-rays, and gamma rays The type of light is determined purely by wavelength.
Light Transverse electromagnetic wave, or electromagnetic radiation Includes radio waves, microwaves, infra-red, visible, UV, X-rays, and gamma rays The type of light is determined purely by wavelength.
LESSON 1. Solar System
 Astronomy Notes LESSON 1 Solar System 11.1 Structure of the Solar System axis of rotation period of rotation period of revolution ellipse astronomical unit What is the solar system? 11.1 Structure of the
Astronomy Notes LESSON 1 Solar System 11.1 Structure of the Solar System axis of rotation period of rotation period of revolution ellipse astronomical unit What is the solar system? 11.1 Structure of the
What is the solar system?
 Notes Astronomy What is the solar system? 11.1 Structure of the Solar System Our solar system includes planets and dwarf planets, their moons, a star called the Sun, asteroids and comets. Planets, dwarf
Notes Astronomy What is the solar system? 11.1 Structure of the Solar System Our solar system includes planets and dwarf planets, their moons, a star called the Sun, asteroids and comets. Planets, dwarf
Test Name: 09.LCW.0352.SCIENCE.GR Q1.S.THEUNIVERSE-SOLARSYSTEMHONORS Test ID: Date: 09/21/2017
 Test Name: 09.LCW.0352.SCIENCE.GR7.2017.Q1.S.THEUNIVERSE-SOLARSYSTEMHONORS Test ID: 243920 Date: 09/21/2017 Section 1.1 - According to the Doppler Effect, what happens to the wavelength of light as galaxies
Test Name: 09.LCW.0352.SCIENCE.GR7.2017.Q1.S.THEUNIVERSE-SOLARSYSTEMHONORS Test ID: 243920 Date: 09/21/2017 Section 1.1 - According to the Doppler Effect, what happens to the wavelength of light as galaxies
Introduction to Astronomy
 Introduction to Astronomy Have you ever wondered what is out there in space besides Earth? As you see the stars and moon, many questions come up with the universe, possibility of living on another planet
Introduction to Astronomy Have you ever wondered what is out there in space besides Earth? As you see the stars and moon, many questions come up with the universe, possibility of living on another planet
Stars and Galaxies 1
 Stars and Galaxies 1 Characteristics of Stars 2 Star - body of gases that gives off great amounts of radiant energy as light and heat 3 Most stars look white but are actually different colors Antares -
Stars and Galaxies 1 Characteristics of Stars 2 Star - body of gases that gives off great amounts of radiant energy as light and heat 3 Most stars look white but are actually different colors Antares -
Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation
 Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the passage below and on your knowledge of Earth Science. Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation In the 1920s, Edwin Hubble's discovery of a pattern in the red
Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the passage below and on your knowledge of Earth Science. Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation In the 1920s, Edwin Hubble's discovery of a pattern in the red
The Big Bang Theory. Rachel Fludd and Matthijs Hoekstra
 The Big Bang Theory Rachel Fludd and Matthijs Hoekstra Theories from Before the Big Bang came from a black hole from another universe? our universe is part of a multiverse? just random particles? The Big
The Big Bang Theory Rachel Fludd and Matthijs Hoekstra Theories from Before the Big Bang came from a black hole from another universe? our universe is part of a multiverse? just random particles? The Big
How Old is the Universe? How Do We Know It s So Old?
 How Old is the Universe? Until recently, astronomers estimated that the Big Bang occurred between 12 and 14 billion years ago. To put this in perspective, our own Solar System is thought to be 4.5 billion
How Old is the Universe? Until recently, astronomers estimated that the Big Bang occurred between 12 and 14 billion years ago. To put this in perspective, our own Solar System is thought to be 4.5 billion
Abundance of Elements. Relative abundance of elements in the Solar System
 Abundance of Elements Relative abundance of elements in the Solar System What is the origin of elements in the universe? Three elements formed in the first minutes after the big bang (hydrogen, helium
Abundance of Elements Relative abundance of elements in the Solar System What is the origin of elements in the universe? Three elements formed in the first minutes after the big bang (hydrogen, helium
How Did the Universe Begin?
 How Did the Universe Begin? As we will discuss in this lecture, it looks like the Universe started about 14 billion years ago and has been expanding (space stretching) ever since. The model of what happened
How Did the Universe Begin? As we will discuss in this lecture, it looks like the Universe started about 14 billion years ago and has been expanding (space stretching) ever since. The model of what happened
Formation of the Universe. What evidence supports current scientific theory?
 Formation of the Universe What evidence supports current scientific theory? Cosmology Cosmology is the study of the Nature, Structure, Origin, And fate of the universe. How did it all begin? Astronomers
Formation of the Universe What evidence supports current scientific theory? Cosmology Cosmology is the study of the Nature, Structure, Origin, And fate of the universe. How did it all begin? Astronomers
Name: P8 SPACE PHYSICS. Class: Question Practice. Date: 140 minutes. Time: 140 marks. Marks: GCSE PHYSICS ONLY. Comments:
 P8 SPACE PHYSICS Question Practice Name: Class: Date: Time: 40 minutes Marks: 40 marks Comments: GCSE PHYSICS ONLY Page of 52 In 929, the astronomer Edwin Hubble observed that the light from galaxies moving
P8 SPACE PHYSICS Question Practice Name: Class: Date: Time: 40 minutes Marks: 40 marks Comments: GCSE PHYSICS ONLY Page of 52 In 929, the astronomer Edwin Hubble observed that the light from galaxies moving
Formation of the Universe & What is in Space? The Big Bang Theory and components of the Universe
 Formation of the Universe & What is in Space? The Big Bang Theory and components of the Universe The Big Bang Theory The Big Bang Theory The Big Bang Theory is the most widely accepted scientific explanation
Formation of the Universe & What is in Space? The Big Bang Theory and components of the Universe The Big Bang Theory The Big Bang Theory The Big Bang Theory is the most widely accepted scientific explanation
TA Final Review. Class Announcements. Objectives Today. Compare True and Apparent brightness. Finding Distances with Cepheids
 Class Announcements Vocab Quiz 4 deadline is Saturday Midterm 4 has started, ends Monday Lab was in the Planetarium. You still need to do the 2 questions Check PS100 webpage, make sure your clicker is
Class Announcements Vocab Quiz 4 deadline is Saturday Midterm 4 has started, ends Monday Lab was in the Planetarium. You still need to do the 2 questions Check PS100 webpage, make sure your clicker is
Electromagnetic Waves
 Big Bang Theory OUTLINE First 25 minutes of the video Notes on waves, Doppler effect, and red/blue shift Mini lab on spectrums and how they are used to understand red and blue shift Mini lab on the expanding
Big Bang Theory OUTLINE First 25 minutes of the video Notes on waves, Doppler effect, and red/blue shift Mini lab on spectrums and how they are used to understand red and blue shift Mini lab on the expanding
Chapter 28 Stars and Their Characteristics
 Chapter 28 Stars and Their Characteristics Origin of the Universe Big Bang Theory about 10-20 bya all matter in the universe existed in a hot dense state about the size of an atom (tiny). That matter sort
Chapter 28 Stars and Their Characteristics Origin of the Universe Big Bang Theory about 10-20 bya all matter in the universe existed in a hot dense state about the size of an atom (tiny). That matter sort
Name: Space Questions. Class: Date: Time: Marks: Comment s:
 Space 2 33 Questions Name: Class: Date: Time: Marks: Comment s: Q. Read the passage. In the SolarSystem, the inner planets, such as the Earth, contain elements which are eavierthan the elements hydrogen
Space 2 33 Questions Name: Class: Date: Time: Marks: Comment s: Q. Read the passage. In the SolarSystem, the inner planets, such as the Earth, contain elements which are eavierthan the elements hydrogen
Chapter 5. Periodic Law.
 Chapter 5 Periodic Law http://www.sciencedump.com/content/new-periodic-table-song Chapter 5.1 History of the Periodic Table 5.1 Objectives Explain the roles of Mendeleev and Moseley in the development
Chapter 5 Periodic Law http://www.sciencedump.com/content/new-periodic-table-song Chapter 5.1 History of the Periodic Table 5.1 Objectives Explain the roles of Mendeleev and Moseley in the development
Spectrographs: instrument to separate white light into the bands of color.
 (BIG BANG PACKET 2) Name: Period: wavelength and lowest frequencies Broadcast waves and microwaves Infrared Rays Wavelength shorter than radio waves The invisible you feel Visible Light You can see The
(BIG BANG PACKET 2) Name: Period: wavelength and lowest frequencies Broadcast waves and microwaves Infrared Rays Wavelength shorter than radio waves The invisible you feel Visible Light You can see The
3. It became unstable and exploded 2. This point was. Timeline of Events 4. This outward expansion
 NOTES BB.notebook The Universe started as a single point of highly concentrated matter 3. It became unstable and exploded 2. This point was extremely dense Density: the amount of mass contained in a certain
NOTES BB.notebook The Universe started as a single point of highly concentrated matter 3. It became unstable and exploded 2. This point was extremely dense Density: the amount of mass contained in a certain
The Universe. But first, let s talk about light! 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 The Universe But first, let s talk about light! Light is fast! The study of light All forms of radiation travel at 300,000,000 meters (186,000 miles) per second Since objects in space are so far away,
The Universe But first, let s talk about light! Light is fast! The study of light All forms of radiation travel at 300,000,000 meters (186,000 miles) per second Since objects in space are so far away,
The Contents of the Universe (or/ what do we mean by dark matter and dark energy?)
 The Contents of the Universe (or/ what do we mean by dark matter and dark energy?) Unseen Influences Dark Matter: An undetected form of mass that emits little or no light but whose existence we infer from
The Contents of the Universe (or/ what do we mean by dark matter and dark energy?) Unseen Influences Dark Matter: An undetected form of mass that emits little or no light but whose existence we infer from
The Universe and Galaxies
 The Universe and Galaxies 16.1 http://dingo.care-mail.com/cards/flash/5409/galaxy.swf Universe The sum of all matter and energy that exists, that has ever existed, and that will ever exist. We will focus
The Universe and Galaxies 16.1 http://dingo.care-mail.com/cards/flash/5409/galaxy.swf Universe The sum of all matter and energy that exists, that has ever existed, and that will ever exist. We will focus
8/30/2010. Classifying Stars. Classifying Stars. Classifying Stars
 Classifying Stars In the early 1900s, Ejnar Hertzsprung and Henry Russell made some important observations. They noticed that, in general, stars with higher temperatures also have brighter absolute magnitudes.
Classifying Stars In the early 1900s, Ejnar Hertzsprung and Henry Russell made some important observations. They noticed that, in general, stars with higher temperatures also have brighter absolute magnitudes.
Expanding Universe. 1) Hubble s Law 2) Expanding Universe 3) Fate of the Universe. Final Exam will be held in Ruby Diamond Auditorium
 Expanding Universe November 20, 2002 1) Hubble s Law 2) Expanding Universe 3) Fate of the Universe Final Exam will be held in Ruby Diamond Auditorium NOTE THIS!!! not UPL Dec. 11, 2002 10am-noon Review
Expanding Universe November 20, 2002 1) Hubble s Law 2) Expanding Universe 3) Fate of the Universe Final Exam will be held in Ruby Diamond Auditorium NOTE THIS!!! not UPL Dec. 11, 2002 10am-noon Review
GraspIT Questions AQA GCSE Physics Space physics
 A. Solar system: stability of orbital motions; satellites (physics only) 1. Put these astronomical objects in order of size from largest to smallest. (3) Fill in the boxes in the correct order. the Moon
A. Solar system: stability of orbital motions; satellites (physics only) 1. Put these astronomical objects in order of size from largest to smallest. (3) Fill in the boxes in the correct order. the Moon
Fingerprinting the Stars Lab
 Name: Block: Fingerprinting the Stars Lab Background: Every element produces a unique fingerprint of spectral lines. By identifying the spectral features in stellar spectra, we can determine the composition
Name: Block: Fingerprinting the Stars Lab Background: Every element produces a unique fingerprint of spectral lines. By identifying the spectral features in stellar spectra, we can determine the composition
Cosmology. What is Cosmology?
 Cosmology What is Cosmology? The study of the structure and evolution of the entire universe The idea is to form picture of the entire Universe: origin, size, and future We will make assumptions that what
Cosmology What is Cosmology? The study of the structure and evolution of the entire universe The idea is to form picture of the entire Universe: origin, size, and future We will make assumptions that what
Spectroscopy Lesson Outline
 Spectroscopy Lesson Outline Syllabus References 9.7.3.1 Spectroscopy is a vital tool for astronomers and provides a wealth of information Pre-video Activity: Spectroscopy Worksheet Resources Video: Spectra
Spectroscopy Lesson Outline Syllabus References 9.7.3.1 Spectroscopy is a vital tool for astronomers and provides a wealth of information Pre-video Activity: Spectroscopy Worksheet Resources Video: Spectra
Cosmology, Galaxies, and Stars OUR VISIBLE UNIVERSE
 Cosmology, Galaxies, and Stars OUR VISIBLE UNIVERSE Cosmology Cosmology is the study of the universe; its nature, origin and evolution. General Relativity is the mathematical basis of cosmology from which
Cosmology, Galaxies, and Stars OUR VISIBLE UNIVERSE Cosmology Cosmology is the study of the universe; its nature, origin and evolution. General Relativity is the mathematical basis of cosmology from which
Wallace Hall Academy
 Wallace Hall Academy CfE Higher Physics Unit 1 - Universe Notes Name 1 Newton and Gravity Newton s Thought Experiment Satellite s orbit as an Application of Projectiles Isaac Newton, as well as giving
Wallace Hall Academy CfE Higher Physics Unit 1 - Universe Notes Name 1 Newton and Gravity Newton s Thought Experiment Satellite s orbit as an Application of Projectiles Isaac Newton, as well as giving
Name Date Period. 10. convection zone 11. radiation zone 12. core
 240 points CHAPTER 29 STARS SECTION 29.1 The Sun (40 points this page) In your textbook, read about the properties of the Sun and the Sun s atmosphere. Use each of the terms below just once to complete
240 points CHAPTER 29 STARS SECTION 29.1 The Sun (40 points this page) In your textbook, read about the properties of the Sun and the Sun s atmosphere. Use each of the terms below just once to complete
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 33 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 33 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 33 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
What is Astronomy? 1. The study of. A. EM spectrum includes waves of all different that travel through space, NOT just visible light
 Name Period NOTE OUTLINE: Ch 30-31 Stars & Universe Objectives 1. Describe electromagnetic radiation (EM). This means I can: A. Describe how the EM is organized and which forms of EM waves are the most
Name Period NOTE OUTLINE: Ch 30-31 Stars & Universe Objectives 1. Describe electromagnetic radiation (EM). This means I can: A. Describe how the EM is organized and which forms of EM waves are the most
Astronomy. Study of objects in space such as the Sun, stars, planets, comets, gas, & galaxies. *Also, the Earth s place in the universe.
 Astronomy Study of objects in space such as the Sun, stars, planets, comets, gas, & galaxies. *Also, the Earth s place in the universe. Universe = everything that exists Disclaimer: Astrology is NOT science!!!
Astronomy Study of objects in space such as the Sun, stars, planets, comets, gas, & galaxies. *Also, the Earth s place in the universe. Universe = everything that exists Disclaimer: Astrology is NOT science!!!
5) Which stage lasts the longest? a) viii b) I c) iv d) iii e) vi
 1) Which of the following statements about globular clusters is false? a) Globular cluster stars are very metal- poor relative to the Sun. b) Globular cluster stars are more than 12 billion years old.
1) Which of the following statements about globular clusters is false? a) Globular cluster stars are very metal- poor relative to the Sun. b) Globular cluster stars are more than 12 billion years old.
Introduction to exploding stars and pulsars
 Introduction to exploding stars and pulsars Harsha Blumer Department of Physics & Astronomy West Virginia University Winnipeg, Canada About me WV, USA Kerala, India Carl Sagan (1934-1996) Neil degrasse
Introduction to exploding stars and pulsars Harsha Blumer Department of Physics & Astronomy West Virginia University Winnipeg, Canada About me WV, USA Kerala, India Carl Sagan (1934-1996) Neil degrasse
The Earth in the Universe
 The Earth in the Universe (OCR) Evidence for the age of the Earth Scientists once thought that the Earth was only 6000 years old. Rocks have provided lots of evidence for the world being older. 1) Erosion
The Earth in the Universe (OCR) Evidence for the age of the Earth Scientists once thought that the Earth was only 6000 years old. Rocks have provided lots of evidence for the world being older. 1) Erosion
According to the currents models of stellar life cycle, our sun will eventually become a. Chapter 34: Cosmology. Cosmology: How the Universe Works
 Chapter 34: Cosmology According to the currents models of stellar life cycle, our sun will eventually become a a) Cloud of hydrogen gas b) Protostar c) Neutron star d) Black hole e) White dwarf id you
Chapter 34: Cosmology According to the currents models of stellar life cycle, our sun will eventually become a a) Cloud of hydrogen gas b) Protostar c) Neutron star d) Black hole e) White dwarf id you
Stars & Galaxies. Chapter 27 Modern Earth Science
 Stars & Galaxies Chapter 27 Modern Earth Science Chapter 27, Section 1 27.1 Characteristics of Stars How do astronomers determine the composition and surface temperature of a star? Composition & Temperature
Stars & Galaxies Chapter 27 Modern Earth Science Chapter 27, Section 1 27.1 Characteristics of Stars How do astronomers determine the composition and surface temperature of a star? Composition & Temperature
Stars & Galaxies. Chapter 27, Section 1. Composition & Temperature. Chapter 27 Modern Earth Science Characteristics of Stars
 Stars & Galaxies Chapter 27 Modern Earth Science Chapter 27, Section 1 27.1 Characteristics of Stars Composition & Temperature Scientists use the following tools to study stars Telescope Observation Spectral
Stars & Galaxies Chapter 27 Modern Earth Science Chapter 27, Section 1 27.1 Characteristics of Stars Composition & Temperature Scientists use the following tools to study stars Telescope Observation Spectral
chapter 31 Stars and Galaxies
 chapter 31 Stars and Galaxies Day 1:Technology and the Big Bang Studying the Stars A. Telescopes - Electromagnetic radiation emitted by stars and other objects include light, radio, and X-ray Space telescopes
chapter 31 Stars and Galaxies Day 1:Technology and the Big Bang Studying the Stars A. Telescopes - Electromagnetic radiation emitted by stars and other objects include light, radio, and X-ray Space telescopes
How do we measure properties of a star? Today. Some Clicker Questions - #1. Some Clicker Questions - #1
 Today Announcements: HW#8 due Friday 4/9 at 8:00 am. The size of the Universe (It s expanding!) The Big Bang Video on the Big Bang NOTE: I will take several questions on exam 3 and the final from the videos
Today Announcements: HW#8 due Friday 4/9 at 8:00 am. The size of the Universe (It s expanding!) The Big Bang Video on the Big Bang NOTE: I will take several questions on exam 3 and the final from the videos
Earth s Formation Unit [Astronomy] Student Success Sheets (SSS)
![Earth s Formation Unit [Astronomy] Student Success Sheets (SSS) Earth s Formation Unit [Astronomy] Student Success Sheets (SSS)](/thumbs/77/76655554.jpg) Page1 Earth s Formation Unit [Astronomy] Student Success Sheets (SSS) HS-ESSI-1; HS-ESS1-2; HS-ESS1-3; HS-ESSI-4 NGSS Civic Memorial High School - Earth Science A Concept # What we will be learning Mandatory
Page1 Earth s Formation Unit [Astronomy] Student Success Sheets (SSS) HS-ESSI-1; HS-ESS1-2; HS-ESS1-3; HS-ESSI-4 NGSS Civic Memorial High School - Earth Science A Concept # What we will be learning Mandatory
Big Bang Theory. How did this theory develop, and what is the evidence for it?
 Big Bang Theory Big Bang Theory Big bang theory suggests that the universe began from a single point about 13.82 billion years ago. What existed before this event is completely unknown to science, but
Big Bang Theory Big Bang Theory Big bang theory suggests that the universe began from a single point about 13.82 billion years ago. What existed before this event is completely unknown to science, but
Modern Astronomy Review #1
 Modern Astronomy Review #1 1. The red-shift of light from distant galaxies provides evidence that the universe is (1) shrinking, only (3) shrinking and expanding in a cyclic pattern (2) expanding, only
Modern Astronomy Review #1 1. The red-shift of light from distant galaxies provides evidence that the universe is (1) shrinking, only (3) shrinking and expanding in a cyclic pattern (2) expanding, only
Astronomy 104: Second Exam
 Astronomy 104: Second Exam Stephen Lepp October 29, 2014 Each question is worth 2 points. Write your name on this exam and on the scantron. Short Answer A The Sun is powered by converting hydrogen to what?
Astronomy 104: Second Exam Stephen Lepp October 29, 2014 Each question is worth 2 points. Write your name on this exam and on the scantron. Short Answer A The Sun is powered by converting hydrogen to what?
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE
 Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 25 Beyond Our Solar System 25.1 Properties of Stars Characteristics of Stars A constellation is an apparent group of stars originally named for mythical
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 25 Beyond Our Solar System 25.1 Properties of Stars Characteristics of Stars A constellation is an apparent group of stars originally named for mythical
What is a star? A body of gases that gives off tremendous amounts of energy in the form of light & heat. What star is closest to the earth?
 Stars What is a star? A body of gases that gives off tremendous amounts of energy in the form of light & heat. What star is closest to the earth? Answer: The SUN It s about 150,000,000 km from earth =
Stars What is a star? A body of gases that gives off tremendous amounts of energy in the form of light & heat. What star is closest to the earth? Answer: The SUN It s about 150,000,000 km from earth =
The Big Bang Theory was first proposed in the late 1920 s. This singularity was incredibly dense and hot.
 The Big Bang Theory was first proposed in the late 1920 s. It states that there was an infinitely small, infinitely dense point that contained everything that is the universe. This singularity was incredibly
The Big Bang Theory was first proposed in the late 1920 s. It states that there was an infinitely small, infinitely dense point that contained everything that is the universe. This singularity was incredibly
Universe Celestial Object Galaxy Solar System
 ASTRONOMY Universe- Includes all known matter (everything). Celestial Object Any object outside or above Earth s atmosphere. Galaxy- A large group (billions) of stars (held together by gravity). Our galaxy
ASTRONOMY Universe- Includes all known matter (everything). Celestial Object Any object outside or above Earth s atmosphere. Galaxy- A large group (billions) of stars (held together by gravity). Our galaxy
v = H o d Hubble s Law: Distant galaxies move away fastest Velocity (v) is proportional to Distance (d):
 Hubble s Law: Distant galaxies move away fastest Velocity (v) is proportional to Distance (d): v = H o d The Hubble Constant was measured after decades of observation: H 0 = 70 km/s/mpc Velocity (km/s)
Hubble s Law: Distant galaxies move away fastest Velocity (v) is proportional to Distance (d): v = H o d The Hubble Constant was measured after decades of observation: H 0 = 70 km/s/mpc Velocity (km/s)
Stars and Galaxies. Evolution of Stars
 chapter 13 3 Stars and Galaxies section 3 Evolution of Stars Before You Read What makes one star different from another? Do you think the Sun is the same as other stars? Write your ideas on the lines below.
chapter 13 3 Stars and Galaxies section 3 Evolution of Stars Before You Read What makes one star different from another? Do you think the Sun is the same as other stars? Write your ideas on the lines below.
Sit in your appropriate seat quietly Have all necessary materials out All back packs on the floor All cell phones on silent and away in backpacks All
 Sit in your appropriate seat quietly Have all necessary materials out All back packs on the floor All cell phones on silent and away in backpacks All IPods off and headphones out of your ears Hats off
Sit in your appropriate seat quietly Have all necessary materials out All back packs on the floor All cell phones on silent and away in backpacks All IPods off and headphones out of your ears Hats off
Hubble s Law. Our goals for learning. What is Hubble s Law? How do distance measurements tell us the age of the universe?
 Hubble s Law Our goals for learning What is Hubble s Law? How do distance measurements tell us the age of the universe? How does the universe s expansion affect our distance measurements? We measure speeds
Hubble s Law Our goals for learning What is Hubble s Law? How do distance measurements tell us the age of the universe? How does the universe s expansion affect our distance measurements? We measure speeds
the evidence that the size of the observable Universe is changing;
 Q1. Describe, in as much detail as you can: the evidence that the size of the observable Universe is changing; the evidence that, billions of years ago, all the matter in the Universe was tightly packed
Q1. Describe, in as much detail as you can: the evidence that the size of the observable Universe is changing; the evidence that, billions of years ago, all the matter in the Universe was tightly packed
the evidence that the size of the observable Universe is changing;
 Q. Describe, in as much detail as you can: the evidence that the size of the observable Universe is changing; the evidence that, billions of years ago, all the matter in the Universe was tightly packed
Q. Describe, in as much detail as you can: the evidence that the size of the observable Universe is changing; the evidence that, billions of years ago, all the matter in the Universe was tightly packed
Chapter 2 - The Big Bang
 stretched out and appear more red. When an object is moving toward an observer, the object is moving in the same direction the light is being emitted from, and the wavelengths of light become squished
stretched out and appear more red. When an object is moving toward an observer, the object is moving in the same direction the light is being emitted from, and the wavelengths of light become squished
How to Build a Habitable Planet Summary. Chapter 1 The Setting
 How to Build a Habitable Planet Summary Chapter 1 The Setting The universe as we know it began about 15 billion years ago with an explosion that is called the big bang. There is no record of any prior
How to Build a Habitable Planet Summary Chapter 1 The Setting The universe as we know it began about 15 billion years ago with an explosion that is called the big bang. There is no record of any prior
CST Prep- 8 th Grade Astronomy
 CST Prep- 8 th Grade Astronomy Chapter 15 (Part 1) 1. The theory of how the universe was created is called the 2. Which equation states that matter and energy are interchangeable? 3. All matter in the
CST Prep- 8 th Grade Astronomy Chapter 15 (Part 1) 1. The theory of how the universe was created is called the 2. Which equation states that matter and energy are interchangeable? 3. All matter in the
ANSWER KEY. Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe. Telescopes Guided Reading and Study. Characteristics of Stars Guided Reading and Study
 Stars, Galaxies, a the Universe Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe Telescopes Use Target Reading Skills Check student definitions for accuracy. 1. Electromagneticradiationisenergythatcan travel through
Stars, Galaxies, a the Universe Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe Telescopes Use Target Reading Skills Check student definitions for accuracy. 1. Electromagneticradiationisenergythatcan travel through
Chapter 17 Cosmology
 Chapter 17 Cosmology Over one thousand galaxies visible The Universe on the Largest Scales No evidence of structure on a scale larger than 200 Mpc On very large scales, the universe appears to be: Homogenous
Chapter 17 Cosmology Over one thousand galaxies visible The Universe on the Largest Scales No evidence of structure on a scale larger than 200 Mpc On very large scales, the universe appears to be: Homogenous
Observing the Night Sky. Observing the Night Sky. Observing the Night Sky. Observing the Night Sky. Observing the Night Sky. Chapter 29 THE UNIVERSE
 Hewitt/Lyons/Suchocki/Yeh Conceptual Integrated Science Constellations are groups of stars named over antiquity. A familiar constellation is Ursa Major, the Great Bear. Chapter 29 THE UNIVERSE The monthly
Hewitt/Lyons/Suchocki/Yeh Conceptual Integrated Science Constellations are groups of stars named over antiquity. A familiar constellation is Ursa Major, the Great Bear. Chapter 29 THE UNIVERSE The monthly
- Both reactions sacrifice. - This in a nuclear reaction is called the. and is the energy in the reaction
 Unit 2: Origins I. Time Begins a. The b. The universe begins as the size of a single atom c. The universe began as a i. All matter and space were created from a single point of pure energy in an instant
Unit 2: Origins I. Time Begins a. The b. The universe begins as the size of a single atom c. The universe began as a i. All matter and space were created from a single point of pure energy in an instant
1 A Solar System Is Born
 CHAPTER 16 1 A Solar System Is Born SECTION Our Solar System California Science Standards 8.2.g, 8.4.b, 8.4.c, 8.4.d BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions:
CHAPTER 16 1 A Solar System Is Born SECTION Our Solar System California Science Standards 8.2.g, 8.4.b, 8.4.c, 8.4.d BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions:
Understanding the Universe S TA R T ING WITH EARTH A ND B E YO ND
 Unit Overview: Understanding the Universe S TA R T ING WITH EARTH A ND B E YO ND Our solar system examining size and scale in space 6.11B UNDERSTAND THAT GRAVITY IS THE FORCE THAT GOVERNS MOTION IN OUR
Unit Overview: Understanding the Universe S TA R T ING WITH EARTH A ND B E YO ND Our solar system examining size and scale in space 6.11B UNDERSTAND THAT GRAVITY IS THE FORCE THAT GOVERNS MOTION IN OUR
Q1. Describe, in as much detail as you can, the life history of a star like our Sun
 Q1. Describe, in as much detail as you can, the life history of a star like our Sun..................................... (Total 6 marks) Q2. The energy radiated by a main sequence star like the Sun is
Q1. Describe, in as much detail as you can, the life history of a star like our Sun..................................... (Total 6 marks) Q2. The energy radiated by a main sequence star like the Sun is
Stars. The composition of the star It s temperature It s lifespan
 Stars Stars A star is a ball of different elements in the form of gases The elements and gases give off electromagnetic radiation (from nuclear fusion) in the form of light Scientists study the light coming
Stars Stars A star is a ball of different elements in the form of gases The elements and gases give off electromagnetic radiation (from nuclear fusion) in the form of light Scientists study the light coming
NSCI 314 LIFE IN THE COSMOS
 NSCI 314 LIFE IN THE COSMOS 2 BASIC ASTRONOMY, AND STARS AND THEIR EVOLUTION Dr. Karen Kolehmainen Department of Physics CSUSB COURSE WEBPAGE: http://physics.csusb.edu/~karen MOTIONS IN THE SOLAR SYSTEM
NSCI 314 LIFE IN THE COSMOS 2 BASIC ASTRONOMY, AND STARS AND THEIR EVOLUTION Dr. Karen Kolehmainen Department of Physics CSUSB COURSE WEBPAGE: http://physics.csusb.edu/~karen MOTIONS IN THE SOLAR SYSTEM
[11] SD4.1 The student demonstrates an understanding of the theories regarding the origin and evolution of the
![[11] SD4.1 The student demonstrates an understanding of the theories regarding the origin and evolution of the [11] SD4.1 The student demonstrates an understanding of the theories regarding the origin and evolution of the](/thumbs/83/88208135.jpg) A STAR IS BORN Overview: Students will research the four stages of the life cycle of a star then further research the ramifications of the stage of the sun on Earth. Objectives: The student will: research,
A STAR IS BORN Overview: Students will research the four stages of the life cycle of a star then further research the ramifications of the stage of the sun on Earth. Objectives: The student will: research,
WHAT WE KNOW. Scientists observe that every object in the universe is moving away from each other. Objects furthest away are moving the fastest. So..
 ASTRONOMY THE BIG BANG THEORY WHAT WE KNOW Scientists observe that every object in the universe is moving away from each other. Objects furthest away are moving the fastest. So.. WHAT DOES THIS MEAN? If
ASTRONOMY THE BIG BANG THEORY WHAT WE KNOW Scientists observe that every object in the universe is moving away from each other. Objects furthest away are moving the fastest. So.. WHAT DOES THIS MEAN? If
Directed Reading A. Section: The Life Cycle of Stars TYPES OF STARS THE LIFE CYCLE OF SUNLIKE STARS A TOOL FOR STUDYING STARS.
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: The Life Cycle of Stars TYPES OF STARS (pp. 444 449) 1. Besides by mass, size, brightness, color, temperature, and composition, how are stars classified? a.
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: The Life Cycle of Stars TYPES OF STARS (pp. 444 449) 1. Besides by mass, size, brightness, color, temperature, and composition, how are stars classified? a.
A supernova is the explosion of a star. It is the largest explosion that takes place in space.
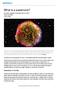 What is a supernova? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 03.28.17 Word Count 974 Level 1110L TOP: A vivid view of a supernova remnant captured by NASA's Spitzer and Chandra space observatories and the
What is a supernova? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 03.28.17 Word Count 974 Level 1110L TOP: A vivid view of a supernova remnant captured by NASA's Spitzer and Chandra space observatories and the
Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe
 Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe Chapter Test A Multiple Choice Write the letter of the correct answer on the line at the left. 1. What is a giant ball of hot gases that undergo nuclear fusion? a. a planet
Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe Chapter Test A Multiple Choice Write the letter of the correct answer on the line at the left. 1. What is a giant ball of hot gases that undergo nuclear fusion? a. a planet
The Expanding Universe
 Cosmology Expanding Universe History of the Universe Cosmic Background Radiation The Cosmological Principle Cosmology and General Relativity Dark Matter and Dark Energy Primitive Cosmology If the universe
Cosmology Expanding Universe History of the Universe Cosmic Background Radiation The Cosmological Principle Cosmology and General Relativity Dark Matter and Dark Energy Primitive Cosmology If the universe
Name: Space Questions Questions. Class: Date: Time: Marks: Comment s:
 Space Questions 35 Questions Name: Class: Date: Time: Marks: Comment s: Q. The figure below shows what scientists over 000 years ago thought the solar system was like. Give one way that the historical
Space Questions 35 Questions Name: Class: Date: Time: Marks: Comment s: Q. The figure below shows what scientists over 000 years ago thought the solar system was like. Give one way that the historical
Protostars on the HR Diagram. Lifetimes of Stars. Lifetimes of Stars: Example. Pressure-Temperature Thermostat. Hydrostatic Equilibrium
 Protostars on the HR Diagram Once a protostar is hot enough to start, it can blow away the surrounding gas Then it is visible: crosses the on the HR diagram The more the cloud, the it will form stars Lifetimes
Protostars on the HR Diagram Once a protostar is hot enough to start, it can blow away the surrounding gas Then it is visible: crosses the on the HR diagram The more the cloud, the it will form stars Lifetimes
3. c 4. a 5. f 6. b 7. e. 1. Stars are bright and hot. 2. Distances between stars are measured in light-years. 3. The sun is a yellow star.
 Stars, Galaxies, Use Target Reading Skills Check student definitions for accuracy. 1. Electromagnetic radiation is energy that can travel through space in the form of waves. 2. visible light 3. wavelength
Stars, Galaxies, Use Target Reading Skills Check student definitions for accuracy. 1. Electromagnetic radiation is energy that can travel through space in the form of waves. 2. visible light 3. wavelength
ASTRONOMY 1 FINAL EXAM 1 Name
 ASTRONOMY 1 FINAL EXAM 1 Name Multiple Choice (2 pts each) 1. Sullivan Star is an F spectral class star that is part of a binary star system. It has a MS lifetime of 5 billion years. Its life will eventually
ASTRONOMY 1 FINAL EXAM 1 Name Multiple Choice (2 pts each) 1. Sullivan Star is an F spectral class star that is part of a binary star system. It has a MS lifetime of 5 billion years. Its life will eventually
Module 3: Astronomy The Universe Topic 1 Content: Cosmology Presentation Notes
 Pretend that you have been given the opportunity to travel through time to explore cosmology. Cosmology is the study of how the universe formed and what will happen to it. Watch through your viewport as
Pretend that you have been given the opportunity to travel through time to explore cosmology. Cosmology is the study of how the universe formed and what will happen to it. Watch through your viewport as
Using the spectrometer
 MATERIALS LIST Investigation 13.1 Stars and Spectroscopy 4 Spectrometer (also known as a spectroscope) 4 Colored pencils 4 Incandescent light source ChAPTER 13 The Universe How can we use a spectrometer
MATERIALS LIST Investigation 13.1 Stars and Spectroscopy 4 Spectrometer (also known as a spectroscope) 4 Colored pencils 4 Incandescent light source ChAPTER 13 The Universe How can we use a spectrometer
Beyond Our Solar System Chapter 24
 Beyond Our Solar System Chapter 24 PROPERTIES OF STARS Distance Measuring a star's distance can be very difficult Stellar parallax Used for measuring distance to a star Apparent shift in a star's position
Beyond Our Solar System Chapter 24 PROPERTIES OF STARS Distance Measuring a star's distance can be very difficult Stellar parallax Used for measuring distance to a star Apparent shift in a star's position
Earth in the Universe Unit Notes
 Earth in the Universe Unit Notes The Universe - everything everywhere, 15-20 billion years old Inside the universe there are billions of Galaxies Inside each Galaxy there are billions of Solar Systems
Earth in the Universe Unit Notes The Universe - everything everywhere, 15-20 billion years old Inside the universe there are billions of Galaxies Inside each Galaxy there are billions of Solar Systems
Grade 8 - Science Interim Assessment Third Grading Period. 1. Four cubes are placed into water.
 Name Date ID 1. Four cubes are placed into water. Grade 8 - Science Interim Assessment Third Grading Period What property determines whether they will float or sink? number of electrons in the outer shell
Name Date ID 1. Four cubes are placed into water. Grade 8 - Science Interim Assessment Third Grading Period What property determines whether they will float or sink? number of electrons in the outer shell
The Stars. Chapter 14
 The Stars Chapter 14 Great Idea: The Sun and other stars use nuclear fusion reactions to convert mass into energy. Eventually, when a star s nuclear fuel is depleted, the star must burn out. Chapter Outline
The Stars Chapter 14 Great Idea: The Sun and other stars use nuclear fusion reactions to convert mass into energy. Eventually, when a star s nuclear fuel is depleted, the star must burn out. Chapter Outline
