Multi-wavelength observations of H.E.S.S. AGN
|
|
|
- April Walters
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 83, 162 c SAIt 2012 Memorie della Multi-wavelength observations of H.E.S.S. AGN M. Tluczykont 1 for the H.E.S.S. Collaboration 2 1 Institut für Experimentalphysik, Universität Hamburg, Luruper Chaussee 149, 22761, Hamburg, Germany martin.tluczykont@physik.uni-hamburg.de Abstract. Multi-frequency observations are a powerful tool of astrophysical investigation. Not only is data in each wavelength band providing different clues to the objects nature, but taken simultaneously, these data can reveal the mechanisms at work in astrophysical objects. In the past years, joint multi-frequency observations with the H.E.S.S. telescopes in the very high energy (VHE, E>0 GeV) band and several other experiments in the radio, optical, X-ray, and high energy (HE, E>0 MeV) bands have lead to intriguing results that will ultimately help answering the open questions of the location of the very high energy emission, details of the acceleration mechanism, and the role of the central black hole. Key words. Galaxies: active Gamma rays: observations X-rays: galaxies 1. Introduction Very high energy (VHE, E>0 GeV) gammaray astronomy is the domain of Earth-bound air-shower experiments. The direction, energy and particle type (gamma-hadron separation) can be reconstructed via the measurement of air-shower particles, or by Cherenkov photons emitted by them. Imaging air Cherenkov telescopes (IACTs) make an image of the shower in Cherenkov light. In the last decade, the IACT technique has made the step from the pioneering era, dominated by experiments such as Whipple, HEGRA, CAT, or CANGAROO, to the now ongoing first physics era, with H.E.S.S. (Aharonian et al. 2006a), MAGIC (Albert et al. 2008), and VERITAS (Acciari et al. 2008). As compared to the non-imaging technique, advantages of IACTs are their good angular Send offprint requests to: M. Tluczykont resolution (< 0.1 ), a relative energy resolution around 15 %, a low energy threshold (E > 0 GeV for a 0 m 2 mirror dish) and a very good sensitivity to point-like sources. Today, Crab Nebula like sources can be detected in the VHE regime in 30 s (5 σ significance level). As compared to the previous generation of IACTs, a significant leap forward has been achieved. Not only has the number of known Galactic and extragalactic VHE sources sharply increased, see e.g. Giebels et al. (20) for an overview, or Raue (2011) for recent H.E.S.S. results. The quality of the measurements also improved to the point of resolving lightcurves down to the minute timescale, spectra extending from 0 GeV to beyond TeV, and sensitivities allowing to detect VHE emission from quiescent AGN (see below). The H.E.S.S. experiment is an array of four IACTs located in Namibia in the Khomas
2 Tluczykont: H.E.S.S. AGN 163 highlands, for observations of Galactic and extragalactic sources in the energy range from 0 GeV to several TeV. AGN are an ideal target for multifrequency observations. Their spectral energy distribution (SED) reaches from radio waves via optical, X-rays, to very-high-energies. In the widely-accepted unified model of AGN (e.g. Rees 1984; Urry & Padovani 1995), the central engine of these objects consists of a thin accretion disk of gas, accreting onto a super-massive central black hole (up to 9 M ), and surrounded by a dust torus. In radio-loud AGN, i.e. objects with a radio to B-band flux ratio F 5GHz /F B >, two relativistic plasma outflows (jets) presumably perpendicular to the plane of the accretion disk have been observed. AGN are known to be VHE γ-ray emitters since the detection of Mrk 421 above 300 GeV by the Whipple group (Punch et al. 1992). Almost all AGN that were detected in the VHE regime belong to the class of BL Lac objects, i.e. AGN having their jet pointing at a small angle to the line of sight. VHE gamma-rays were also detected from two radio galaxies, M 87 (see below), and Cen A (Aharonian et al. (2009c), also see Rieger (2011), these proceedings), the starburst galaxy NGC 253 (Acero et al. 2009) and the FSRQs 3C279 (Aleksić et al. 2011a) and PKS (Aleksić et al. 2011b). The characteristic two-peak SED of AGN can be explained by synchrotron emission of relativistic electrons, and an inverse Compton (IC) peak, resulting from scattering of electrons off a seed-photon population, see e.g. Sikora & Madejski (2001) and references therein. Alternatively, hadronic radiation models explain the emission via the interactions of relativistic protons with matter (Pohl & Schlickeiser 2000), ambient photons (Mannheim 1993) or magnetic field (Aharonian 2000), or photons and magnetic field (Mücke & Protheroe 2001). The observed VHE emission shows high variability ranging from short bursts on a minute time-scale, to long-term activity of the order of months. Studies of the variability of BL Lac type objects can contribute to the understanding of their intrinsic acceleration mechanisms (e.g. Krawczynski et al. 2001; Aharonian et al. 2002). VHE gamma-rays can be absorbed via e + e pair production with the photons of the extragalactic background light (EBL). Observations of distant objects in the VHE band therfore provide an indirect measurement of the SED of the EBL, see e.g. Stecker et al. (1992); Primack et al. (1999) and references therein. Open questions of VHE emission in AGN persist: - where in the jet does gamma-ray emission occur? While it is believed that the VHE emission must be beamed and thus originate somewhere along the jet axis, the exact location is still unknown. - What is the source of the soft seed photons for the inverse Compton effect? Seed photon fields can originate in different regions, such as the accretion disk, different parts of the jet, the broad line region, the dusty torus, and synchrotron photons. The latter are favoured, considering the practically feature-less spectra in the optical and ultra-violet, and for the sake of gamma-ray transparency (local radiation fields must be low enough to avoid intrinsic absorption by pair production). - Finally, what is the role of the central black hole in powering the jet? The transfer of binding energy of accreting gas to the jet as well as spin-energy extraction via the Blandford-Znajek mechanism (Blandford & Znajek 1977) are discussed. 2. Multi-frequency observations 2.1. Overview A number of AGN were observed by H.E.S.S. since the start of operation in Some sources were observed in the frame of organized multi-frequency campaings, or regular monitoring campaigns, while others were triggered by high-state observations reported by other instruments. Table 1 gives an overview of H.E.S.S. observations of AGN for which simultaneous multi-frequency data was taken.
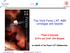
3 164 Tluczykont: H.E.S.S. AGN Table 1. Summary of published simultaneous multi-wavelength data sets of H.E.S.S. AGN. Object Years MWL arxiv:astro-ph/ or reference PKS ,-06,-08 RXTE, ROTSEIII, NRT, v1, Bronberg opt. RXTE, v1, Chandra, Swift, ATOM v1 H RXTE, ROTSEIII, NRT v1, XMM, ATOM, NRT v2 PKS XMM-Newton, RXTE v2 1ES ,2005 XMM-Newton, RXTE, optical v2 Mrk RXTE v1 1ES Swift v1 PG /2006 VLT (SINFONI) v2 RGB J RXTE, Swift, ATOM v2 PKS Swift v2 M Chandra, VLBA Aharonian et al. (2006d) Acciari et al. (2009) AP Librae 20 Swift, RXTE, Fermi Fortin et al. (2011) HESS J Fermi, NRT v Energy [ev] [erg/cm s]) log(ν Fν Archival radio data Archival optical data Archival BeppoSAX data NRT radio data ROTSE RXTE H.E.S.S. SSC model + EBL SSC model log(ν [Hz]) Fig. 1. Historically, this SED of H from 2004 was the first SED comprising simultaneous radio, optical, X-ray and VHE observations. Simultaneous data are shown as filled symbols. All other (archival) data are shown as open symbols. Radio emission arises from regions further out in the jet. A single-zone SSC model taking absorption into account is shown as a solid line (dashed line without absorption).
4 Tluczykont: H.E.S.S. AGN H and 1ES The high frequency peaked BL Lac object (HBL) H (z = 0.165) was first identified at optical frequencies by Schwartz et al. (1989). Its first detection in the X- ray band was done by satellite experiment UHURU (Forman et al. 1978). Later observations with BeppoSAX established it as an extreme synchrotron blazar (Costamante et al. 2001). H was discovered in the VHE gamma-ray regime by H.E.S.S. after observations in 2004 (Aharonian et al. 2006b). Simultaneous observations were carried out with RXTE in X-rays on 11th of November 2004, with the Nançay decimetric radio telescope (NRT) between June and October 2004 and with ROTSE in the optical, covering the whole 2004 H.E.S.S. observation campaign. With these data for the first time, an SED comprising simultaneous radio, optical, X-ray and VHE measurements could be made. The resulting broad-band SED from this observation campaign (Figure 1) can be well described by a single-zone synchrotron self Compton (SSC) model, using a reasonable set of parameters. A later multi-frequency campaign (HESS Collaboration et al. 20) with H.E.S.S., NRT, ATOM, and XMM-Newton, yielded similar results. The object still showed little variability (factor 2) and was in a historically low X-ray-level. A similar case of a broad-band SED compatible with a single-zone SSC model is given by multi-frequency observations of the extreme synchrotron blazar 1ES (Aharonian et al. 2007b). Due to their comparatively large redshift, the results obtained from H and 1ES (z = 0.186) lead to strong constraints on the density of the EBL (Aharonian et al. 2006c) PKS The high frequency peaked BL Lac object PKS (z = 0.117) is one of the best studied blazars in the southern hemisphere. After first being detected in the X- ray band (Cooke et al. 1978; Griffiths et al. 1979; Schwartz et al. 1979), it was detected in the VHE regime by the University of Durham Mark 6 Telescope in 1996 and 1997 (Chadwick et al. 1999). H.E.S.S. could confirm these findings in early observations before the completion of the experiment in 2002 and 2003 (Aharonian et al. 2005a). In a subsequent multi-frequency campaign in 2003 (Aharonian et al. 2005b), the object was observed in a hisorically low flux level in X-rays. Furthermore, the weak variability in the VHE H.E.S.S. data (smaller than factor 2.5) and the notable fact that PKS was detectable within each observation night by H.E.S.S. indicated that the object was observed in a quiescent flux state. Simultaneous multi-frequency observations in 2008 (Aharonian et al. 2009b, H.E.S.S., Fermi, RXTE, and ATOM) yielded a clear optical/vhe correlation and evidence for a correlation of the X-ray flux with the spectral index in the high energy regime (Fermi data, E>0 MeV). A behaviour that is difficult to explain in the framework of SSC models. The most notable events concerning this source, however, did happen in two exceptionally bright VHE outbursts in 2006 (Aharonian et al. 2007a, 2009a). In the first observation night covered by H.E.S.S., variability could be detected at the minute time-scale (3 min bins). Assuming a size of the emission region of the order of the Schwarzschild radius, causality requires a Doppler factor of more than 0 in order to accomodate the observed fast variability. As shown by Degrange et al. (2008), the data show log-normal flux variability in the VHE regime (also seen in Mrk 421, Tluczykont et al. 20). Such a variability pattern is indicative of a multiplicative process, implying a connection of the VHE emission to accretion disk activity (see Giebels & Degrange 2009, and references therein). Furthermore, a log-normal flux behaviour is incompatible with an additive process such as a multi-zone IC emission scenario. As opposed to the first observation night, the second H.E.S.S. observation night (Aharonian et al. 2009a) was also covered by observations by Chandra (and partly by RXTE and Swift) in X-rays, and the Bronberg optical observatory. A clear VHE/X-ray correlation was found, without significant timelags between both frequency bands. The main variability structure and sub-structures
5 166 Tluczykont: H.E.S.S. AGN of the VHE lightcurves are matched in X- rays. However, rapid sub-flares observed in the VHE band are not found in the Chandra data. Huge differences in the variability amplitudes of /2/1.15 were observed between the VHE/X-ray/optical bands. The ratio of VHE (inverse Compton) to X-ray (synchrotron) flux was at a maximum of 8 during the decaying phase of the flare, and reached a minimum at the end of the observation night. Such a high and rapidly varying Compton dominance was never observed before. Spectral analysis of the H.E.S.S. data show a curved spectrum with a stronger curvature at high flux states, indicating that the observed curvature is at least partly intrinsic. Overall, the spectral index shows a harder-when-brighter relationship in the VHE regime. While such a dependency is also seen in the simultaneous Chandra data, the partly sampled X-ray flare starting after the H.E.S.S. exposure shows a softer-when-brighter relation. Remarkably, the gamma-ray flux traces the variations of the X-ray flux much stronger than quadratically (Figure 2). Instead, a cubic relation is found. As discussed in Aharonian et al. (2009a), such a super-quadratic relationship is challenging common scenarios of VHE emission in blazars M 87 The giant radio galaxy M 87 (z = ) is located at the center of the Virgo cluster of galaxies, and hosts a central black hole of (3.2 ± 0.9) 9 M. As opposed to blazars, the jet of M 87 is orientated at an angle of 30 relative to the line of sight. The possibility of multi-frequency observations with radio instruments that are able to resolve substructures of its jet make M 87 a very interesting object for studying the location of the VHE emission. After first indications for a VHE signal in HEGRA data (Aharonian et al. 2003), H.E.S.S. observations between 2003 and 2006 could establish M 87 as the first VHE emitting radio galaxy (Aharonian et al. 2006d). The spectrum seen by H.E.S.S. is well described by a pure powerlaw. The hardness (spectral index 2.22 ± 0.15 in 2005) of the observed spec- Fig. 2. Correlation between X-ray and VHE flux during 3 different states of the second exceptional flare (MJD53946): maximum (black), decaying phase (blue), and broad sub-flare (green). Mostly, a cubic relationship between the VHE and X-ray bands is observed. trum extending beyond TeV and the lack of any absorption feature due to pair production imply a low central infra-red (IR) luminosity at 0.1 ev ( µm), as could be expected in the case of an advection-dominated accretion disk. It also excludes significant contributions of the IR radiation fields as external seed photon population. While the position of the VHE excess rules out the radio lobes as potential site for the gamma-ray production, the resolution of the H.E.S.S. Cherenkov telescopes does not allow to resolve structures smaller than the large scale lobe structure of M 87. However, the unexpectedly fast variability observed in H.E.S.S. data from 2005 allowed to strongly constrain the size of the emission region. Several potential sites and mechanisms for VHE gamma-ray production could thus be excluded: the elliptical host galaxy, dark matter, the kpc-scale jet, and the brightest knot (knot A) in the jet (see Aharonian et al. 2006d, for discussion). Remarkably, simultaneous observations carried out with the Chandra satellite showed that the highest VHE flux state observed by H.E.S.S. coincided with a maximum X-ray flux from the HST-1 hotspot.
6 Tluczykont: H.E.S.S. AGN 167 Fig. 3. Light curves for M 87 ( ) (from Acciari et al. 2009). (A) nightly VHE gamma-ray fluxes (E>0.35 TeV). (B) Chandra X-ray data (2 to kev) of the nucleus and the knot HST-1 (Harris et al. 2009). (C) Flux densities from the 43-GHz VLBA observations of the nucleus, the peak flux, and the flux integrated along the jet. For details, see (Acciari et al. 2009).
7 168 Tluczykont: H.E.S.S. AGN In order to bypass the poor angular resolution of IACTs, a multi-frequency campaign was carried out with participation of VERITAS, MAGIC, and H.E.S.S., together with the Very Long Baseline Array (VLBA) at 43 GHz with a resolution of mas, and Chandra in the X-ray band (Acciari et al. 2009). As opposed to the previous findings by H.E.S.S., the VHE maximum observed by all IACTs in 2008 occured during a minimum of X-ray activity from HST-1 (see Figure 3). Instead, the VLBA data shows that the VHE flare occurs during a rise of activity in the nucleus. These findings are an indication for the VHE emission to be taking place in the jet collimation region (see Acciari et al. 2009). Recent data on M 87 show an even more intriguing multi-frequency picture (see e.g. Raue 2011). 3. Summary In the past decade, observations with H.E.S.S. and other instruments in other wavelength bands have produced pieces of the puzzles of VHE emission from AGN (See open questions, Introduction, page 162). A log-normal flux pattern (multiplicative process) found in the VHE data of PKS (and in combined data on Mrk 421) might hint at a connection of the VHE emission to accretion disk activity, and are contradictory to an additive multi-zone IC scenario. During the second exceptional flare of PKS observed by H.E.S.S., a cubic relationship was found between the X-ray flux and the VHE flux, challenging common models of IC emission. The unprecedentedly fast variability (minute time-scale) seen from this source strongly constrains the size of the VHE emission region. A comparatively fast variability of the order of days was also found in H.E.S.S. data on the radio galaxy M 87, ruling out several hypotheses for the location of the VHE emission region. In a VHE/X-ray/radio multifrequency campaign, evidence was found for a connection of the VHE emission from M 87 to the jet collimation region. 4. Discussion SERGIO COLAFRANCESCO: It seems that the radio high-resolution observations are crucial for the location of the VHE emission. Do you also have radio polarization observations to better identify the radio blob responsible for the VHE emission? MARTIN TLUCZYKONT: We don t have results from polarization measurements yet. P.S.: during the session, the answer referred to results instead of existence of data. Data exist and analysis is in progress. JIM BEALL: Can you comment on the size scale where the VHE / radio emission occurs? MARTIN TLUCZYKONT: From causality arguments alone, the fast variability observed from M 87 implies an absolute size of the emission region of the order of 3 Schwarzschild radii of the central black hole (3 15 cm). The absolute position of the VHE emission can be derived to be within the jet collimation region, considering the simultaneity of the VHE flare with the radio emission from the nucleus in Acknowledgements. The support of the Namibian authorities and of the University of Namibia in facilitating the construction and operation of H.E.S.S. is gratefully acknowledged, as is the support by the German Ministry for Education and Research (BMBF), the Max Planck Society, the French Ministry for Research, the CNRS-IN2P3 and the Astroparticle Interdisciplinary Programme of the CNRS, the U.K. Science and Technology Facilities Council (STFC), the IPNP of the Charles University, the Polish Ministry of Science and Higher Education, the South African Department of Science and Technology and National Research Foundation, and by the University of Namibia. We appreciate the excellent work of the technical support staff in Berlin, Durham, Hamburg, Heidelberg, Palaiseau, Paris, Saclay, and in Namibia in the construction and operation of the equipment. The author thanks the organizers for their kind invitation to this inspiring workshop. References Acciari, V. A., et al. 2009, Sci., 325, 444 Acciari, V. A., et al. 2008, ApJ, 679, 1427 Acero, F., et al. 2009, Sci., 326, 80
8 Tluczykont: H.E.S.S. AGN 169 Aharonian, F., et al. 2003, A&A, 403, L1 Aharonian, F., et al. 2009a, A&A, 502, 749 Aharonian, F., et al. 2009b, ApJ, 696, L150 Aharonian, F., et al. 2009c, ApJ, 695, L40 Aharonian, F., et al. 2005a, A&A, 430, 865 Aharonian, F.,, et al. 2007a, ApJ, 664, L71 Aharonian, F., et al. 2006a, A&A, 457, 899 Aharonian, F., et al. 2006b, A&A, 455, 461 Aharonian, F., et al. 2006c, Nature, 440, 18 Aharonian, F.,, et al. 2005b, A&A, 442, 895 Aharonian, F.,, et al. 2007b, A&A, 470, 475 Aharonian, F., et al. 2006d, Sci., 314, 1424 Aharonian, F. A. 2000, New Astronomy, 5, 377 Aharonian, F. A., et al. 2002, A&A, 393, 89 Albert, J., et al. 2008, ApJ, 674, 37 Aleksić, J., et al. 2011a, A&A, 530, A4+ Aleksić, J., et al. 2011b, ApJ, 730, L8+ Blandford, R. D. & Znajek, R. L. 1977, MNRAS, 179, 433 Chadwick, P. M., et al. 1999, ApJ, 513, 161 Cooke, B. A., Lawrence, A., & Perola, G. C. 1978, MNRAS, 182, 661 Costamante, L., et al. 2001, å, 371, 512 Degrange, B., Superina, G., Giebels, B., & Volpe, F. 2008, in Blazar Variability across the Electromagnetic Spectrum Forman, W., et al. 1978, ApJSupplement, 38, 357 Fortin, P. et al. 2011, to appear in PoS(Texas 2011), Heidelberg, Germany Giebels, B., Aharonian, F., & Sol, H. 20, ArXiv e-prints Giebels, B. & Degrange, B. 2009, A&A, 503, 797 Griffiths, R. E., Briel, U., Chaisson, L., & Tapia, S. 1979, ApJ, 234, 8 Harris, R., et al. 2009, New Journal of Physics, 11, HESS Collaboration, Abramowski, A.,, et al. 20, A&A, 516, A56+ Krawczynski, H., et al. 2001, ApJ, 559, 187 Mannheim, K. 1993, A&A, 269, 67 Mücke, A. & Protheroe, R. J. 2001, Astroparticle Physics, 15, 121 Pohl, M. & Schlickeiser, R. 2000, A&A, 354, 395 Primack, J., Bullock, J., Summerville, R., & MacMinn, D. 1999, Astroparticle Physics, 11, 93 Punch, M., et al. 1992, Nature, 358, 477 Raue, M. 2011, to appear in Beamed and Unbeamed Gamma-rays from Galaxies, Muoino, Finnland Rees, M. J. 1984, ARA&A, 22, 471 Rieger, F. 2011, in Multifrequency Behaviour of High Energy Cosmic Sources, F. Giovannelli & L. Sabau-Graziati (eds.), Mem. SAIt. Vol. 83 n. 1 (in press). Schwartz, D., et al. 1989, in Lecture Notes in Physics, edited by L. Maraschi, Maccacaro, T. and Ulrich, H. (Springer Berlin), Vol. 334, p. 211 Schwartz, D. A., et al. 1979, ApJ, 229, L53 Sikora, M. & Madejski, G. 2001, AIP CONF.PROC., 558, 275 Stecker, F. W., de Jager, O. C., & Salamon, M. H. 1992, ApJ, 390, L49 Tluczykont, M., et al. 20, A&A, 524, A48+ Urry, C. M. & Padovani, P. 1995, PASP, 7, 803
Observations of Active Galactic Nuclei at very high energies with H.E.S.S.
 Observations of Active Galactic Nuclei at very high energies with H.E.S.S. Robert Wagner for the H.E.S.S. Collaboration http://www.mpi-hd.mpg.de/hess/ @hesstelescopes 1 H.E.S.S. High Energy Stereoscopic
Observations of Active Galactic Nuclei at very high energies with H.E.S.S. Robert Wagner for the H.E.S.S. Collaboration http://www.mpi-hd.mpg.de/hess/ @hesstelescopes 1 H.E.S.S. High Energy Stereoscopic
Gamma-ray observations of blazars with the Whipple 10 m telescope
 Gamma-ray observations of blazars with the Whipple 1 m telescope, presented on behalf of the VERITAS collaboration. E-mail: edward.collins.hughes@gmail.com This paper presents a status update of the current
Gamma-ray observations of blazars with the Whipple 1 m telescope, presented on behalf of the VERITAS collaboration. E-mail: edward.collins.hughes@gmail.com This paper presents a status update of the current
OBSERVATIONS OF VERY HIGH ENERGY GAMMA RAYS FROM M87 BY VERITAS
 OBSERVATIONS OF VERY HIGH ENERGY GAMMA RAYS FROM M87 BY VERITAS 1 Tülün Ergin (U. of Massachusetts Amherst, MA) on behalf of the VERITAS Collaboration (http://veritas.sao.arizona.edu) APOD, 2004 December
OBSERVATIONS OF VERY HIGH ENERGY GAMMA RAYS FROM M87 BY VERITAS 1 Tülün Ergin (U. of Massachusetts Amherst, MA) on behalf of the VERITAS Collaboration (http://veritas.sao.arizona.edu) APOD, 2004 December
Very High Energy gamma-ray radiogalaxies and blazars
 Very High Energy gamma-ray radiogalaxies and blazars Hélène Sol Paris Observatory, CNRS JD6, The connection between radio properties and High-Energy emission in AGNs Outline The sample of AGN currently
Very High Energy gamma-ray radiogalaxies and blazars Hélène Sol Paris Observatory, CNRS JD6, The connection between radio properties and High-Energy emission in AGNs Outline The sample of AGN currently
A Galaxy in VHE Gamma-rays: Observations of the Galactic Plane with the H.E.S.S. array
 : Observations of the Galactic Plane with the H.E.S.S. array Max-Planck-Institut für Kernphysik, Heidelberg, Germany E-mail: daniel.parsons@mpi-hd.mpg.de P. Bordas Max-Planck-Institut für Kernphysik, Heidelberg,
: Observations of the Galactic Plane with the H.E.S.S. array Max-Planck-Institut für Kernphysik, Heidelberg, Germany E-mail: daniel.parsons@mpi-hd.mpg.de P. Bordas Max-Planck-Institut für Kernphysik, Heidelberg,
Status of the MAGIC telescopes
 SNOWPAC 2010 Status of the MAGIC telescopes Pierre Colin for the MAGIC collaboration Max-Planck-Institut für physik (Munich) Status of the MAGIC telescopes MAGIC-1 MAGIC-2 Outline: Recent results of the
SNOWPAC 2010 Status of the MAGIC telescopes Pierre Colin for the MAGIC collaboration Max-Planck-Institut für physik (Munich) Status of the MAGIC telescopes MAGIC-1 MAGIC-2 Outline: Recent results of the
Scientific Highlights from AGN Observations with the MAGIC Telescope
 Scientific Highlights from AGN Observations with the MAGIC Telescope Robert Marcus WAGNER Max-Planck-Institut für Physik, München on behalf of the MAGIC COLLABORATION MAGIC Major Atmospheric Gamma-ray
Scientific Highlights from AGN Observations with the MAGIC Telescope Robert Marcus WAGNER Max-Planck-Institut für Physik, München on behalf of the MAGIC COLLABORATION MAGIC Major Atmospheric Gamma-ray
The 2006 Giant Flare in PKS and Unidentified TeV Sources. Justin Finke Naval Research Laboratory 5 June 2008
 The 2006 Giant Flare in PKS 2155-304 and Unidentified TeV Sources Justin Finke Naval Research Laboratory 5 June 2008 Outline Part I: The SSC Model Part II: The giant flare in PKS 2155-304 Part III: Blazars
The 2006 Giant Flare in PKS 2155-304 and Unidentified TeV Sources Justin Finke Naval Research Laboratory 5 June 2008 Outline Part I: The SSC Model Part II: The giant flare in PKS 2155-304 Part III: Blazars
Constraints on Extragalactic Background Light from Cherenkov telescopes: status and perspectives for the next 5 years
 Constraints on Extragalactic Background Light from Cherenkov telescopes: status and perspectives for the next 5 years Daniel Mazin 1 and Martin Raue 2 1: IFAE, Barcelona 2: MPIK, Heidelberg This research
Constraints on Extragalactic Background Light from Cherenkov telescopes: status and perspectives for the next 5 years Daniel Mazin 1 and Martin Raue 2 1: IFAE, Barcelona 2: MPIK, Heidelberg This research
AGILE and Blazars: the Unexpected, the Unprecedented, and the Uncut
 AGILE and Blazars: the Unexpected, the Unprecedented, and the Uncut Rome, AGILE γ-ray Symposium 2017.12.12 Stefano Vercellone (INAF-OAB) 1 Rationale A review of the whole set of AGILE results on extra-galactic
AGILE and Blazars: the Unexpected, the Unprecedented, and the Uncut Rome, AGILE γ-ray Symposium 2017.12.12 Stefano Vercellone (INAF-OAB) 1 Rationale A review of the whole set of AGILE results on extra-galactic
Multi-Wavelength Observations of PG
 Multi-Wavelength Observations of PG 1553+113 Daniela Dorner abc, Anita Reimer d, Olaf Reimer d, Luigi Costamante d and Greg Madejski de a Universität Würzburg, b Integral Science Data Centre, c ETH Zürich,
Multi-Wavelength Observations of PG 1553+113 Daniela Dorner abc, Anita Reimer d, Olaf Reimer d, Luigi Costamante d and Greg Madejski de a Universität Würzburg, b Integral Science Data Centre, c ETH Zürich,
10 Years. of TeV Extragalactic Science. with VERITAS. Amy Furniss California State University East Bay
 55 555 56 565 57 55 555 56 565 57 55 555 56 565 57 572 574 576 578 57 5712 5714 5716 572 574 576 578 57 5712 5714 5716 5712 5713 5714 5715 5716 5712 5713 5714 5715 5716 5712 5713 5714 5715 5716 5712 5713
55 555 56 565 57 55 555 56 565 57 55 555 56 565 57 572 574 576 578 57 5712 5714 5716 572 574 576 578 57 5712 5714 5716 5712 5713 5714 5715 5716 5712 5713 5714 5715 5716 5712 5713 5714 5715 5716 5712 5713
TeV γ-ray observations with VERITAS and the prospects of the TeV/radio connection
 TeV γ-ray observations with VERITAS and the prospects of the TeV/radio connection Matthias Beilicke for the VERITAS collaboration Washington University in St.Louis, Physics Department and McDonnell Center
TeV γ-ray observations with VERITAS and the prospects of the TeV/radio connection Matthias Beilicke for the VERITAS collaboration Washington University in St.Louis, Physics Department and McDonnell Center
Extreme high-energy variability of Markarian 421
 Extreme high-energy variability of Markarian 421 Mrk 421 an extreme blazar Previous observations outstanding science issues 2001 Observations by VERITAS/Whipple 10 m 2001 Light Curve Energy spectrum is
Extreme high-energy variability of Markarian 421 Mrk 421 an extreme blazar Previous observations outstanding science issues 2001 Observations by VERITAS/Whipple 10 m 2001 Light Curve Energy spectrum is
The blazar Mrk 421: a short multifrequency review
 Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 83, 122 c SAIt 2012 Memorie della The blazar Mrk 421: a short multifrequency review I. Donnarumma on behalf of the AGILE Team INAF IASF Roma, Via Fosso del Cavaliere 100, I-00133 Roma,
Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 83, 122 c SAIt 2012 Memorie della The blazar Mrk 421: a short multifrequency review I. Donnarumma on behalf of the AGILE Team INAF IASF Roma, Via Fosso del Cavaliere 100, I-00133 Roma,
Determining the TeV Gamma-Ray Emission Region in the Relativistic Jet of M87 using TeV and Radio Monitoring
 Determining the TeV Gamma-Ray Emission Region in the Relativistic Jet of M87 using TeV and Radio Monitoring R. M. Wagner Max-Planck-Institut für Physik, München and Excellence Cluster Origin and Structure
Determining the TeV Gamma-Ray Emission Region in the Relativistic Jet of M87 using TeV and Radio Monitoring R. M. Wagner Max-Planck-Institut für Physik, München and Excellence Cluster Origin and Structure
List of publications
 List of publications Jean-Philippe LENAIN September 16, 2009 Articles published in refereed scientific journals 1. The VERITAS collaboration, the VLBA 43 GHz M 87 monitoring team, the H.E.S.S. collaboration
List of publications Jean-Philippe LENAIN September 16, 2009 Articles published in refereed scientific journals 1. The VERITAS collaboration, the VLBA 43 GHz M 87 monitoring team, the H.E.S.S. collaboration
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 7 Nov 2016
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 7 Nov 2016 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 7 Nov 2016](/thumbs/92/110544227.jpg) The Complex VHE And Multiwavelength Flaring Activity Of The FSRQ PKS 1510-089 In May 2015 arxiv:1611.02098v1 [astro-ph.he] 7 Nov 2016 M. Zacharias 1,2,a), M. Böttcher 2, N. Chakraborty 3, G. Cologna 1,
The Complex VHE And Multiwavelength Flaring Activity Of The FSRQ PKS 1510-089 In May 2015 arxiv:1611.02098v1 [astro-ph.he] 7 Nov 2016 M. Zacharias 1,2,a), M. Böttcher 2, N. Chakraborty 3, G. Cologna 1,
Variability of Extragalactic VHE γ-ray Emitters
 Variability of Extragalactic VHE γ-ray Emitters Wystan Benbow Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics APS April 2011 Meeting, Anaheim, CA Very High Energy (VHE) γ-ray Astronomy VHE: ~100 GeV to ~100
Variability of Extragalactic VHE γ-ray Emitters Wystan Benbow Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics APS April 2011 Meeting, Anaheim, CA Very High Energy (VHE) γ-ray Astronomy VHE: ~100 GeV to ~100
Status of TeV AGN Studies
 Status of TeV AGN Studies Wystan Benbow Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics AGN Physics in the CTA Era Workshop, Toulouse, France, May 16, 2011 The Extragalactic VHE Gamma-ray Sky May 1, 2011:
Status of TeV AGN Studies Wystan Benbow Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics AGN Physics in the CTA Era Workshop, Toulouse, France, May 16, 2011 The Extragalactic VHE Gamma-ray Sky May 1, 2011:
The connection between millimeter and gamma-ray emission in AGNs
 The connection between millimeter and gamma-ray emission in AGNs Marcello Giroletti INAF Istituto di Radioastronomia Secondo Workshop sull'astronomia millimetrica e submillimetrica in Italia Bologna, 2-3
The connection between millimeter and gamma-ray emission in AGNs Marcello Giroletti INAF Istituto di Radioastronomia Secondo Workshop sull'astronomia millimetrica e submillimetrica in Italia Bologna, 2-3
Recent Results from VERITAS
 Recent Results from VERITAS Physics Department, McGill University, Montreal, Canada E-mail: hanna@physics.mcgill.ca VERITAS (Very Energetic Radiation Imaging Telescope Array System) is an array of four
Recent Results from VERITAS Physics Department, McGill University, Montreal, Canada E-mail: hanna@physics.mcgill.ca VERITAS (Very Energetic Radiation Imaging Telescope Array System) is an array of four
Modelling the Variability of Blazar Jets
 Modelling the Variability of Blazar Jets A Selfconsistent SSC Model Matthias Weidinger Institut für Theoretische Physik und Astrophysik, Universität Würzburg GRK Tage: 24. Juli 2009 M. Weidinger (Uni Wü)
Modelling the Variability of Blazar Jets A Selfconsistent SSC Model Matthias Weidinger Institut für Theoretische Physik und Astrophysik, Universität Würzburg GRK Tage: 24. Juli 2009 M. Weidinger (Uni Wü)
TeV Observations of Extragalactic Sources
 TeV Observations of Extragalactic Sources Henric Krawczynski (Washington University in St. Louis), Oct. 2, 2009 Plan of Talk: Status of Experiments Key-Results: Radio Galaxies Blazars Starburst Galaxies
TeV Observations of Extragalactic Sources Henric Krawczynski (Washington University in St. Louis), Oct. 2, 2009 Plan of Talk: Status of Experiments Key-Results: Radio Galaxies Blazars Starburst Galaxies
Investigating the jet structure and its link with the location of the high-energy emitting region in radio-loud AGN
 Investigating the jet structure and its link with the location of the high-energy emitting region in radio-loud AGN Filippo D Ammando (INAF-IRA and DIFA Bologna) Monica Orienti (INAF-IRA) Marcello Giroletti
Investigating the jet structure and its link with the location of the high-energy emitting region in radio-loud AGN Filippo D Ammando (INAF-IRA and DIFA Bologna) Monica Orienti (INAF-IRA) Marcello Giroletti
Diversity of Multi-wavelength Behavior of Relativistic Jet in 3C 279 Discovered During the Fermi Era
 Diversity of Multi-wavelength Behavior of Relativistic Jet in 3C 279 Discovered During the Fermi Era Rapid Variability of Blazar 3C 279 during Flaring States in 2013-2014 with Joint Fermi-LAT, NuSTAR,
Diversity of Multi-wavelength Behavior of Relativistic Jet in 3C 279 Discovered During the Fermi Era Rapid Variability of Blazar 3C 279 during Flaring States in 2013-2014 with Joint Fermi-LAT, NuSTAR,
Lecture 10: TeV Blazars and EBL
 40th Saas-Fee Course: Astrophysics at Very High Energies Lecture 10: TeV Blazars and EBL F.A. Aharonian, DIAS (Dublin) & MPIK (Heidelberg) Les Diablerets, March 15-20, 2010 Blazars - sub-class of AGN dominated
40th Saas-Fee Course: Astrophysics at Very High Energies Lecture 10: TeV Blazars and EBL F.A. Aharonian, DIAS (Dublin) & MPIK (Heidelberg) Les Diablerets, March 15-20, 2010 Blazars - sub-class of AGN dominated
A Theoretical Model to Explain TeV Gamma-ray and X-ray Correlation in Blazars
 A Theoretical Model to Explain TeV Gamma-ray and X-ray Correlation in Blazars Nissim Fraija In collaboration with: Magda Gonzalez Instituto de Astronomia - UNAM TAUP 2015, XIV International Conference
A Theoretical Model to Explain TeV Gamma-ray and X-ray Correlation in Blazars Nissim Fraija In collaboration with: Magda Gonzalez Instituto de Astronomia - UNAM TAUP 2015, XIV International Conference
SIMILARITY AND DIVERSITY OF BLACK HOLE SYSTEMS View from the Very High Energies
 SIMILARITY AND DIVERSITY OF BLACK HOLE SYSTEMS View from the Very High Energies 1 Symp. 324, 12-16 September, 2016 Classical view Spinning black hole Accretion disk Collimated jets of particles 2 Looking
SIMILARITY AND DIVERSITY OF BLACK HOLE SYSTEMS View from the Very High Energies 1 Symp. 324, 12-16 September, 2016 Classical view Spinning black hole Accretion disk Collimated jets of particles 2 Looking
Highlights from the VERITAS AGN Observation Program
 Highlights from the VERITAS AGN Observation Program W. Benbow 1,a) and the VERITAS Collaboration 2 1 Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, 60 Garden St, Cambridge, MA, 02180, USA 2 http://veritas.sao.arizona.edu/
Highlights from the VERITAS AGN Observation Program W. Benbow 1,a) and the VERITAS Collaboration 2 1 Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, 60 Garden St, Cambridge, MA, 02180, USA 2 http://veritas.sao.arizona.edu/
Relativistic jets in AGNs
 Mem. S.A.It. Suppl. Vol. 5, 211 c SAIt 2004 Memorie della Supplementi Relativistic jets in AGNs Fabrizio Tavecchio INAF Oss. Astron. di Brera, via Brera 28, 20121 Milano, Italy e-mail: fabrizio@brera.mi.astro.it
Mem. S.A.It. Suppl. Vol. 5, 211 c SAIt 2004 Memorie della Supplementi Relativistic jets in AGNs Fabrizio Tavecchio INAF Oss. Astron. di Brera, via Brera 28, 20121 Milano, Italy e-mail: fabrizio@brera.mi.astro.it
Very High Energy monitoring of the radio galaxy M87 with MAGIC during a low emission state between 2012 and 2015
 Very High Energy monitoring of the radio galaxy M87 with MAGIC during a low emission state between 2012 and 2015 ICRR, U-Tokyo and Max-Planck-Institute for Physics, Munich and P. Bangale, M. Manganaro,
Very High Energy monitoring of the radio galaxy M87 with MAGIC during a low emission state between 2012 and 2015 ICRR, U-Tokyo and Max-Planck-Institute for Physics, Munich and P. Bangale, M. Manganaro,
Diagnostics of Leptonic vs. Hadronic Emission Models for Blazars Prospects for H.E.S.S.-II and CTA Markus Böttcher North-West University
 Diagnostics of Leptonic vs. Hadronic Emission Models for Blazars Prospects for H.E.S.S.-II and CTA Markus Böttcher North-West University Potchefstroom South Africa Q e (g,t) Injection, acceleration of
Diagnostics of Leptonic vs. Hadronic Emission Models for Blazars Prospects for H.E.S.S.-II and CTA Markus Böttcher North-West University Potchefstroom South Africa Q e (g,t) Injection, acceleration of
The Extragalactic Gamma-Ray View of AGILE and Fermi
 INAF, Osservatorio Astronomico di Capodimonte 22 February 2012 The Extragalactic Gamma-Ray View of AGILE and Fermi Elena Pian INAF, Trieste Astronomical Observatory & Scuola Normale Superiore di Pisa UNIFIED
INAF, Osservatorio Astronomico di Capodimonte 22 February 2012 The Extragalactic Gamma-Ray View of AGILE and Fermi Elena Pian INAF, Trieste Astronomical Observatory & Scuola Normale Superiore di Pisa UNIFIED
VHE emission from radio galaxies
 VHE emission from radio galaxies Martin Hardcastle The future of gamma-ray astronomy and the CTA Leicester, October 2010 Outline Recap: radio galaxy physics Inverse-Compton emission Locations of high-energy
VHE emission from radio galaxies Martin Hardcastle The future of gamma-ray astronomy and the CTA Leicester, October 2010 Outline Recap: radio galaxy physics Inverse-Compton emission Locations of high-energy
Origin of X-rays in blazars
 Origin of X-rays in blazars Greg Madejski, Stanford / KIPAC With much of the work presented here done by Amy Furniss, Masaaki Hayashida, Krzysztof Nalewajko, Marek Sikora, Jim Chiang, David Paneque, Mislav
Origin of X-rays in blazars Greg Madejski, Stanford / KIPAC With much of the work presented here done by Amy Furniss, Masaaki Hayashida, Krzysztof Nalewajko, Marek Sikora, Jim Chiang, David Paneque, Mislav
Studies on the VHE γ-ray/x-ray correlation in high-synchrotron peak BL Lacs
 Studies on the VHE γ-ray/x-ray correlation in high-synchrotron peak BL Lacs Magda Gonzalez Instituto de Astronomía, UNAM, México Nissim Fraija 1, Barbara Patricelli 2, José Andrés García 3 & Simone Dichiara
Studies on the VHE γ-ray/x-ray correlation in high-synchrotron peak BL Lacs Magda Gonzalez Instituto de Astronomía, UNAM, México Nissim Fraija 1, Barbara Patricelli 2, José Andrés García 3 & Simone Dichiara
Flaring Active Galactic Nuclei: the view from Fermi-LAT
 Flaring Active Galactic Nuclei: the view from Fermi-LAT INAF-IASF IASF Palermo On behalf of the Fermi-LAT Collaboration and many multi-wavelength collaborators SciNeGHE 2010 1 The EGRET Era AGN dominate
Flaring Active Galactic Nuclei: the view from Fermi-LAT INAF-IASF IASF Palermo On behalf of the Fermi-LAT Collaboration and many multi-wavelength collaborators SciNeGHE 2010 1 The EGRET Era AGN dominate
Extreme blazars and the VHE connection
 Extreme blazars and the VHE connection Berrie Giebels - LLR Ecole Polytechnique Very High Energy (VHE) emission above 100 GeV has been confirmed from 6 extragalactic sources (Blazars) by multiple observatories.
Extreme blazars and the VHE connection Berrie Giebels - LLR Ecole Polytechnique Very High Energy (VHE) emission above 100 GeV has been confirmed from 6 extragalactic sources (Blazars) by multiple observatories.
PoS(SWIFT 10)142. The Swift-XRT observations of HBL Source 1ES
 The Swift-XRT observations of HBL Source 1ES 199+ ab, Patrizia Romano b, Stefano Vercellone b, Sergo Kapanadze a, Grigol Kharshiladze c a E. Kharadze Abastumani Astrophysical Observatory, Ilia State University,
The Swift-XRT observations of HBL Source 1ES 199+ ab, Patrizia Romano b, Stefano Vercellone b, Sergo Kapanadze a, Grigol Kharshiladze c a E. Kharadze Abastumani Astrophysical Observatory, Ilia State University,
High-z Blazar SEDs Clues to Evolution in the Early Universe. Hongjun An Roger Romani on behalf of the Fermi-LAT Collaboration
 High-z Blazar SEDs Clues to Evolution in the Early Universe Hongjun An Roger Romani on behalf of the Fermi-LAT Collaboration Outline Blazars Blazar emission and spectral energy distribution (SED) models
High-z Blazar SEDs Clues to Evolution in the Early Universe Hongjun An Roger Romani on behalf of the Fermi-LAT Collaboration Outline Blazars Blazar emission and spectral energy distribution (SED) models
GLAST and beyond GLAST: TeV Astrophysics
 GLAST and beyond GLAST: TeV Astrophysics Outline: Greg Madejski Assistant Director for Scientific Programs, SLAC / Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Cosmology Recent excitement of GLAST and plans for
GLAST and beyond GLAST: TeV Astrophysics Outline: Greg Madejski Assistant Director for Scientific Programs, SLAC / Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Cosmology Recent excitement of GLAST and plans for
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.he] 19 Jul 2013
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.he] 19 Jul 2013 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.he] 19 Jul 2013](/thumbs/73/68734128.jpg) CHARTING THE TEV MILKY WAY: H.E.S.S. GALACTIC PLANE SURVEY MAPS, CATALOG AND SOURCE POPULATIONS arxiv:1307.4868v2 [astro-ph.he] 19 Jul 2013 S. CARRIGAN 1, F. BRUN 1, R.C.G. CHAVES 2,1, C. DEIL 1, H. GAST
CHARTING THE TEV MILKY WAY: H.E.S.S. GALACTIC PLANE SURVEY MAPS, CATALOG AND SOURCE POPULATIONS arxiv:1307.4868v2 [astro-ph.he] 19 Jul 2013 S. CARRIGAN 1, F. BRUN 1, R.C.G. CHAVES 2,1, C. DEIL 1, H. GAST
Extragalactic Science with the CTA. A. Zech, LUTH
 Extragalactic Science with the CTA A. Zech, LUTH "extragalactic" KSPs Active Galaxies Transients Galaxy Clusters blazars, radio-galaxies, other AGN EBL, IGMF fundamental physics GRBs galactic transients
Extragalactic Science with the CTA A. Zech, LUTH "extragalactic" KSPs Active Galaxies Transients Galaxy Clusters blazars, radio-galaxies, other AGN EBL, IGMF fundamental physics GRBs galactic transients
Long term multi-wavelength variability studies of the blazar PKS
 52nd Rencontres de Moriond 2017 Very High Energy Phenomena in the Universe Long term multi-wavelength variability studies of the blazar PKS 2155-304 Jill Chevalier D. Sanchez, P. Serpico, J-P. Lenain,
52nd Rencontres de Moriond 2017 Very High Energy Phenomena in the Universe Long term multi-wavelength variability studies of the blazar PKS 2155-304 Jill Chevalier D. Sanchez, P. Serpico, J-P. Lenain,
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 28 Aug 2015
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 28 Aug 2015 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 28 Aug 2015](/thumbs/77/76508307.jpg) arxiv:1508.07358v1 [astro-ph.he] 28 Aug 2015 for the VERITAS Collaboration University of Minnesota E-mail: shahin@astro.umn.edu HESS J1943+213 is a very-high-energy (VHE; >0 GeV) gamma-ray point source
arxiv:1508.07358v1 [astro-ph.he] 28 Aug 2015 for the VERITAS Collaboration University of Minnesota E-mail: shahin@astro.umn.edu HESS J1943+213 is a very-high-energy (VHE; >0 GeV) gamma-ray point source
Recent Observations of Supernova Remnants
 1 Recent Observations of Supernova Remnants with VERITAS Tülün Ergin (U. of Massachusetts Amherst, MA) on behalf of the VERITAS Collaboration (http://veritas.sao.arizona.edu) 2 Contents Supernova Remnants
1 Recent Observations of Supernova Remnants with VERITAS Tülün Ergin (U. of Massachusetts Amherst, MA) on behalf of the VERITAS Collaboration (http://veritas.sao.arizona.edu) 2 Contents Supernova Remnants
Multiwaveband Observations of the TeV Blazar PKS with HESS, Fermi, RXTE and Swift
 Multiwaveband Observations of the TeV Blazar PKS 2155-304 with HESS, Fermi, RXTE and Swift David Sanchez on behalf of the Fermi LAT and H.E.S.S. collaborations. LLR 21 janvier 2009 D.Sanchez Multiwaveband
Multiwaveband Observations of the TeV Blazar PKS 2155-304 with HESS, Fermi, RXTE and Swift David Sanchez on behalf of the Fermi LAT and H.E.S.S. collaborations. LLR 21 janvier 2009 D.Sanchez Multiwaveband
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 9 Sep 2015
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 9 Sep 2015 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 9 Sep 2015](/thumbs/72/66461281.jpg) Observations of the Crab Nebula with H.E.S.S. Phase II arxiv:1509.090v1 [astro-ph.he] 9 Sep 015 a, D. Berge b, C. van Eldik c, J.-P. Lenain d, V. Marandon e, T. Murach f, M. de Naurois a, R.D. Parsons
Observations of the Crab Nebula with H.E.S.S. Phase II arxiv:1509.090v1 [astro-ph.he] 9 Sep 015 a, D. Berge b, C. van Eldik c, J.-P. Lenain d, V. Marandon e, T. Murach f, M. de Naurois a, R.D. Parsons
MWL. A Brief Advertisement Before Your Regularly Scheduled Program
 MWL A Brief Advertisement Before Your Regularly Scheduled Program PKS 1441+25 PKS 1441+25 z=0.939! VHE detection over more than a single day! PKS 1441+25 37.7% polarization! PKS 1441+25 Continues optical
MWL A Brief Advertisement Before Your Regularly Scheduled Program PKS 1441+25 PKS 1441+25 z=0.939! VHE detection over more than a single day! PKS 1441+25 37.7% polarization! PKS 1441+25 Continues optical
Gamma-ray Observations of Blazars with VERITAS and Fermi
 Gamma-ray Observations of Blazars with VERITAS and Fermi University College Dublin E-mail: annacannon1984@gmail.com VERITAS (the Very Energetic Radiation Imaging Telescope Array System) is an array of
Gamma-ray Observations of Blazars with VERITAS and Fermi University College Dublin E-mail: annacannon1984@gmail.com VERITAS (the Very Energetic Radiation Imaging Telescope Array System) is an array of
PoS(11th EVN Symposium)022
 The connection between radio and Very High Energy in Active Galactic Nuclei: perspectives with CTA, the Cherenkov Telescope Array 1 Observatoire de Paris, CNRS, LUTH Place J. Janssen, 92195 Meudon, France
The connection between radio and Very High Energy in Active Galactic Nuclei: perspectives with CTA, the Cherenkov Telescope Array 1 Observatoire de Paris, CNRS, LUTH Place J. Janssen, 92195 Meudon, France
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 27 Jun 2002
 Blazars Astroph. with BeppoSAX and other Observatories 1 The BeppoSAX view of extreme BL Lacs L. COSTAMANTE 1, G. GHISELLINI 1, A. CELOTTI 2, A. WOLTER 1 1 Osservatorio Astronomico di Brera, Milano, Italy
Blazars Astroph. with BeppoSAX and other Observatories 1 The BeppoSAX view of extreme BL Lacs L. COSTAMANTE 1, G. GHISELLINI 1, A. CELOTTI 2, A. WOLTER 1 1 Osservatorio Astronomico di Brera, Milano, Italy
Introduction to AGN. General Characteristics History Components of AGN The AGN Zoo
 Introduction to AGN General Characteristics History Components of AGN The AGN Zoo 1 AGN What are they? Active galactic nucleus compact object in the gravitational center of a galaxy that shows evidence
Introduction to AGN General Characteristics History Components of AGN The AGN Zoo 1 AGN What are they? Active galactic nucleus compact object in the gravitational center of a galaxy that shows evidence
Active Galactic Nuclei in the MeV-GeV band (first results from Fermi)
 Active Galactic Nuclei in the MeV-GeV band (first results from Fermi) Gino Tosti University & INFN Perugia On behalf of the Fermi-LAT Collaboration 1 Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN) EGRET showed that AGN
Active Galactic Nuclei in the MeV-GeV band (first results from Fermi) Gino Tosti University & INFN Perugia On behalf of the Fermi-LAT Collaboration 1 Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN) EGRET showed that AGN
Gamma-ray emitting narrow-line Seyfert 1 galaxies and their place in the AGN zoo
 Gamma-ray emitting narrow-line Seyfert 1 galaxies and their place in the AGN zoo Filippo D Ammando (DIFA and INAF-IRA Bologna) Monica Orienti, Justin Finke, Marcello Giroletti, Josefin Larsson on behalf
Gamma-ray emitting narrow-line Seyfert 1 galaxies and their place in the AGN zoo Filippo D Ammando (DIFA and INAF-IRA Bologna) Monica Orienti, Justin Finke, Marcello Giroletti, Josefin Larsson on behalf
Non-Blazar Gamma-ray Active Galactic Nuclei seen by Fermi-LAT. C.C. Teddy Cheung Naval Research Lab/NRC on behalf of the Fermi-LAT Collaboration
 Non-Blazar Gamma-ray Active Galactic Nuclei seen by Fermi-LAT C.C. Teddy Cheung Naval Research Lab/NRC on behalf of the Fermi-LAT Collaboration 1 st LAT AGN Catalog (1LAC) Summary FmJ 2010 Entire 1LAC:
Non-Blazar Gamma-ray Active Galactic Nuclei seen by Fermi-LAT C.C. Teddy Cheung Naval Research Lab/NRC on behalf of the Fermi-LAT Collaboration 1 st LAT AGN Catalog (1LAC) Summary FmJ 2010 Entire 1LAC:
Pulsar Wind Nebulae as seen by Fermi-Large Area Telescope
 Pulsar Wind Nebulae as seen by Fermi-Large Area Telescope Marie-Hélène Grondin Centre d'etudes Nucléaires de Bordeaux- Gradignan SNR/PWN Workshop Montpellier, 2010 June 1 th M.-H. Grondin, SNR/PWN Wokshop,
Pulsar Wind Nebulae as seen by Fermi-Large Area Telescope Marie-Hélène Grondin Centre d'etudes Nucléaires de Bordeaux- Gradignan SNR/PWN Workshop Montpellier, 2010 June 1 th M.-H. Grondin, SNR/PWN Wokshop,
H.E.S.S. High Energy Stereoscopic System
 H.E.S.S. High Energy Stereoscopic System MPI Kernphysik, Heidelberg Humboldt Univ. Berlin Ruhr-Univ. Bochum Univ. Hamburg Landessternwarte Heidelberg Univ. Kiel Ecole Polytechnique, Palaiseau College de
H.E.S.S. High Energy Stereoscopic System MPI Kernphysik, Heidelberg Humboldt Univ. Berlin Ruhr-Univ. Bochum Univ. Hamburg Landessternwarte Heidelberg Univ. Kiel Ecole Polytechnique, Palaiseau College de
Gamma-ray Astrophysics
 Gamma-ray Astrophysics AGN Pulsar SNR GRB Radio Galaxy The very high energy -ray sky NEPPSR 25 Aug. 2004 Many thanks to Rene Ong at UCLA Guy Blaylock U. of Massachusetts Why gamma rays? Extragalactic Background
Gamma-ray Astrophysics AGN Pulsar SNR GRB Radio Galaxy The very high energy -ray sky NEPPSR 25 Aug. 2004 Many thanks to Rene Ong at UCLA Guy Blaylock U. of Massachusetts Why gamma rays? Extragalactic Background
TeV Future: APS White Paper
 TeV Future: APS White Paper APS commissioned a white paper on the "Status and Future of very high energy gamma ray astronomy. For preliminary information, see http://cherenkov.physics.iastate.edu/wp Working
TeV Future: APS White Paper APS commissioned a white paper on the "Status and Future of very high energy gamma ray astronomy. For preliminary information, see http://cherenkov.physics.iastate.edu/wp Working
Energy-dependent variability in blazars SSC simulations
 Energy-dependent variability in blazars SSC simulations David Sanchez Laboratoire Leprince-Ringuet, CNRS/IN2P3, Ecole Polytechnique, 91128 Palaiseau, France E-mail: dsanchez@llr.in2p3.fr Berrie Giebels
Energy-dependent variability in blazars SSC simulations David Sanchez Laboratoire Leprince-Ringuet, CNRS/IN2P3, Ecole Polytechnique, 91128 Palaiseau, France E-mail: dsanchez@llr.in2p3.fr Berrie Giebels
VERITAS detection of VHE emission from the optically bright quasar OJ 287
 VERITAS detection of VHE emission from the optically bright quasar OJ 287 S. Zola & NASA/JPL S. O Brien For The VERITAS Collaboration Outline 1. OJ 287 2. Historical Observations and Monitoring Programs
VERITAS detection of VHE emission from the optically bright quasar OJ 287 S. Zola & NASA/JPL S. O Brien For The VERITAS Collaboration Outline 1. OJ 287 2. Historical Observations and Monitoring Programs
Very High-Energy Gamma- Ray Astrophysics
 Very High-Energy Gamma- Ray Astrophysics David A. Williams Santa Cruz Institute for Particle Physics UC Santa Cruz Quarknet July 12, 2013 Detecting High Energy Gamma Rays High Sensitivity HESS, MAGIC,
Very High-Energy Gamma- Ray Astrophysics David A. Williams Santa Cruz Institute for Particle Physics UC Santa Cruz Quarknet July 12, 2013 Detecting High Energy Gamma Rays High Sensitivity HESS, MAGIC,
Can blazar flares be triggered by the VHE gamma-rays from the surrounding of a supermassive black hole?
 Can blazar flares be triggered by the VHE gamma-rays from the surrounding of a supermassive black hole? Department of Astrophysics, University of Lodz, Lodz, Poland E-mail: p.banasinski@uni.lodz.pl Wlodek
Can blazar flares be triggered by the VHE gamma-rays from the surrounding of a supermassive black hole? Department of Astrophysics, University of Lodz, Lodz, Poland E-mail: p.banasinski@uni.lodz.pl Wlodek
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 17 Sep 2015
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 17 Sep 2015 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 17 Sep 2015](/thumbs/80/81271477.jpg) arxiv:159.6322v1 [astro-ph.im] 17 Sep 215 Max-Planck-Institut für Kernphysik, P.O. Box 398, D 6929, Heidelberg, Germany E-mail: daniel.parsons@mpi-hd.mpg.de M. Gajdus Institut für Physik, Humboldt-Universität
arxiv:159.6322v1 [astro-ph.im] 17 Sep 215 Max-Planck-Institut für Kernphysik, P.O. Box 398, D 6929, Heidelberg, Germany E-mail: daniel.parsons@mpi-hd.mpg.de M. Gajdus Institut für Physik, Humboldt-Universität
Two exceptional γ-ray flares of PKS and their implications on blazar and fundamental physics
 Two exceptional γ-ray flares of PKS 2155-304 and their implications on blazar and fundamental physics Rolf Bühler MPIK Heidelberg KIPAC Tea Talk SLAC 9th December 2008 H.E.S.S. Telescopes Located in Namibia
Two exceptional γ-ray flares of PKS 2155-304 and their implications on blazar and fundamental physics Rolf Bühler MPIK Heidelberg KIPAC Tea Talk SLAC 9th December 2008 H.E.S.S. Telescopes Located in Namibia
Multi-wavelength Astronomy
 astronomy Multi-wavelength Astronomy Content What do we measure Multi-wavelength approach Data Data Mining Virtual Observatory Hands on session Larmor's formula Maxwell's equations imply that all classical
astronomy Multi-wavelength Astronomy Content What do we measure Multi-wavelength approach Data Data Mining Virtual Observatory Hands on session Larmor's formula Maxwell's equations imply that all classical
H.E.S.S. Unidentified Gamma-ray Sources in a Pulsar Wind Nebula Scenario And HESS J
 H.E.S.S. Unidentified Gamma-ray Sources in a Pulsar Wind Nebula Scenario And HESS J1303-631 Matthew Dalton Humboldt University at Berlin For the H.E.S.S. Collaboration TeV Particle Astrophysics, Paris.
H.E.S.S. Unidentified Gamma-ray Sources in a Pulsar Wind Nebula Scenario And HESS J1303-631 Matthew Dalton Humboldt University at Berlin For the H.E.S.S. Collaboration TeV Particle Astrophysics, Paris.
PoS(Extremesky 2011)036
 Univ. Complutense of Madrid E-mail: marcos@gae.ucm.es The MAGIC (Major Atmospheric Gamma-ray Imaging Cherenkov) telescopes were designed to reach the lowest possible energy threshold using the ground-based
Univ. Complutense of Madrid E-mail: marcos@gae.ucm.es The MAGIC (Major Atmospheric Gamma-ray Imaging Cherenkov) telescopes were designed to reach the lowest possible energy threshold using the ground-based
Cosmology and fundamental physics with extragalactic TeV γ-rays?
 Cosmology and fundamental physics with extragalactic TeV γ-rays? Matthias Lorentz PhD with Pierre Brun at Irfu/SPP DDays 7-8 July 2016 Introduction : my PhD topic What we can learn from TeV photons propagating
Cosmology and fundamental physics with extragalactic TeV γ-rays? Matthias Lorentz PhD with Pierre Brun at Irfu/SPP DDays 7-8 July 2016 Introduction : my PhD topic What we can learn from TeV photons propagating
Cosmological Evolution of Blazars
 Cosmological Evolution of Blazars Chuck Dermer Naval Research Laboratory The impact of high energy astrophysics experiments on cosmological physics Kavli Institute for Cosmological Physics University of
Cosmological Evolution of Blazars Chuck Dermer Naval Research Laboratory The impact of high energy astrophysics experiments on cosmological physics Kavli Institute for Cosmological Physics University of
Gamma-ray Astrophysics with VERITAS: Exploring the violent Universe
 Gamma-ray Astrophysics with VERITAS: Exploring the violent Universe K. Ragan McGill University Soup & Science 11-Jan-2008 Soup & Science Jan. '08 1 How do we know about the Universe? Historically, all
Gamma-ray Astrophysics with VERITAS: Exploring the violent Universe K. Ragan McGill University Soup & Science 11-Jan-2008 Soup & Science Jan. '08 1 How do we know about the Universe? Historically, all
Blazars as the Astrophysical Counterparts of the IceCube Neutrinos
 Blazars as the Astrophysical Counterparts of the IceCube Neutrinos Maria Petropoulou Department of Physics & Astronomy, Purdue University, West Lafayette, USA Einstein Fellows Symposium Harvard-Smithsonian
Blazars as the Astrophysical Counterparts of the IceCube Neutrinos Maria Petropoulou Department of Physics & Astronomy, Purdue University, West Lafayette, USA Einstein Fellows Symposium Harvard-Smithsonian
Observations of Markarian 421 with VERITAS
 Observations of Markarian 421 with VERITAS Kerianna Butler A senior capstone project submitted to the faculty of Brigham Young University in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Bachelor
Observations of Markarian 421 with VERITAS Kerianna Butler A senior capstone project submitted to the faculty of Brigham Young University in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Bachelor
Monitoring of Blazars for variability from MIRO. Kiran S Baliyan Physical Research Laboratory, Ahmedabad, India
 Monitoring of Blazars for variability from MIRO Kiran S Baliyan Physical Research Laboratory, Ahmedabad, India Black-holes, Jets and Outflows, Kathmandu, Nepal, October 14, 2013 Enigmatic AGNs AGNs- Huge
Monitoring of Blazars for variability from MIRO Kiran S Baliyan Physical Research Laboratory, Ahmedabad, India Black-holes, Jets and Outflows, Kathmandu, Nepal, October 14, 2013 Enigmatic AGNs AGNs- Huge
The third Fermi LAT AGN catalogue and beyond
 The third Fermi LAT AGN catalogue and beyond Filippo D Ammando (DIFA and INAF-IRA Bologna) on behalf of the Fermi LAT Collaboration dammando@ira.inaf.it 1 Different classes of AGN Quasars Radio-quiet or
The third Fermi LAT AGN catalogue and beyond Filippo D Ammando (DIFA and INAF-IRA Bologna) on behalf of the Fermi LAT Collaboration dammando@ira.inaf.it 1 Different classes of AGN Quasars Radio-quiet or
arxiv:astro-ph/ v3 13 Nov 2006
 A Simple Analytic Treatment of the Intergalactic Absorption Effect in Blazar Gamma-Ray Spectra F.W. Stecker arxiv:astro-ph/0608110v3 13 Nov 2006 NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center stecker@milkyway.gsfc.nasa.gov
A Simple Analytic Treatment of the Intergalactic Absorption Effect in Blazar Gamma-Ray Spectra F.W. Stecker arxiv:astro-ph/0608110v3 13 Nov 2006 NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center stecker@milkyway.gsfc.nasa.gov
On the scientific motivation for a wide field-of-view TeV gamma-ray observatory in the Southern Hemisphere
 On the scientific motivation for a wide field-of-view TeV gamma-ray observatory in the Southern Hemisphere for the HAWC collaboration E-mail: miguel@psu.edu Observations of high energy gamma rays are an
On the scientific motivation for a wide field-of-view TeV gamma-ray observatory in the Southern Hemisphere for the HAWC collaboration E-mail: miguel@psu.edu Observations of high energy gamma rays are an
Recent highlights from VERITAS
 Recent highlights from VERITAS K. Ragan McGill University RICAP 2011, Rome, 26-May-2011 K. Ragan VERITAS RICAP '11 1 Outline Very high-energy (VHE) gamma-ray astrophysics Ground-based observations with
Recent highlights from VERITAS K. Ragan McGill University RICAP 2011, Rome, 26-May-2011 K. Ragan VERITAS RICAP '11 1 Outline Very high-energy (VHE) gamma-ray astrophysics Ground-based observations with
Active Galactic Nuclei
 Active Galactic Nuclei Optical spectra, distance, line width Varieties of AGN and unified scheme Variability and lifetime Black hole mass and growth Geometry: disk, BLR, NLR Reverberation mapping Jets
Active Galactic Nuclei Optical spectra, distance, line width Varieties of AGN and unified scheme Variability and lifetime Black hole mass and growth Geometry: disk, BLR, NLR Reverberation mapping Jets
TEV GAMMA RAY ASTRONOMY WITH VERITAS
 1 TEV GAMMA RAY ASTRONOMY WITH VERITAS Tülün Ergin (U. of Massachusetts Amherst, MA) on behalf of the VERITAS Collaboration 2 Contents The VERITAS Experiment Results and the Performance Galactic Sources
1 TEV GAMMA RAY ASTRONOMY WITH VERITAS Tülün Ergin (U. of Massachusetts Amherst, MA) on behalf of the VERITAS Collaboration 2 Contents The VERITAS Experiment Results and the Performance Galactic Sources
Observation of the Southern High Energy Peaked BL Lac Object PKS with CANGAROO-II Telescope
 The Universe Viewed in Gamma-Rays 1 Observation of the Southern High Energy Peaked BL Lac Object PKS 2155 34 with CANGAROO-II Telescope Tomokazu NAKASE and Kyoshi NISHIJIMA Department of Physics, Tokai
The Universe Viewed in Gamma-Rays 1 Observation of the Southern High Energy Peaked BL Lac Object PKS 2155 34 with CANGAROO-II Telescope Tomokazu NAKASE and Kyoshi NISHIJIMA Department of Physics, Tokai
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 14 Jun 1999
 Current Status of VHE Astronomy Gus Sinnis Los Alamos National Laboratory arxiv:astro-ph/9906242v1 14 Jun 1999 Very-high-energy astronomy studies the Universe at energies between 30 GeV and 100 TeV. The
Current Status of VHE Astronomy Gus Sinnis Los Alamos National Laboratory arxiv:astro-ph/9906242v1 14 Jun 1999 Very-high-energy astronomy studies the Universe at energies between 30 GeV and 100 TeV. The
VERITAS Observations of Starburst Galaxies. The Discovery of VHE Gamma Rays from a Starburst Galaxy
 VERITAS Observations of Starburst Galaxies The Discovery of VHE Gamma Rays from a Starburst Galaxy Wystan Benbow for the VERITAS Collaboration 1 Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics 1 see R.A. Ong
VERITAS Observations of Starburst Galaxies The Discovery of VHE Gamma Rays from a Starburst Galaxy Wystan Benbow for the VERITAS Collaboration 1 Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics 1 see R.A. Ong
X-ray and Gamma-ray Study of TeV Blazars with RXTE, XMM-Newton, and the Whipple 10 m Telescope
 X-ray and Gamma-ray Study of TeV Blazars with RXTE, XMM-Newton, and the Whipple m Telescope Jeffrey Grube November 21, 2007 Submitted in accordance with the requirements for the degree for Doctor in Philosophy.
X-ray and Gamma-ray Study of TeV Blazars with RXTE, XMM-Newton, and the Whipple m Telescope Jeffrey Grube November 21, 2007 Submitted in accordance with the requirements for the degree for Doctor in Philosophy.
RXTE Observations of PKS during the November 1997 Gamma-Ray Outburst
 RXTE Observations of PKS 2155-304 during the November 1997 Gamma-Ray Outburst W. Thomas Vestrand a and P. Sreekumar b a Space Science Center, University of New Hampshire, Durham, NH 03824 arxiv:astro-ph/9901404v1
RXTE Observations of PKS 2155-304 during the November 1997 Gamma-Ray Outburst W. Thomas Vestrand a and P. Sreekumar b a Space Science Center, University of New Hampshire, Durham, NH 03824 arxiv:astro-ph/9901404v1
Cherenkov Telescope Array ELINA LINDFORS, TUORLA OBSERVATORY ON BEHALF OF CTA CONSORTIUM, TAUP
 Cherenkov Telescope Array A SENSITIVE PROBE OF EXTREME UNIVERSE ELINA LINDFORS, TUORLA OBSERVATORY ON BEHALF OF CTA CONSORTIUM, TAUP 2015 1 The CTA Observatory SST ( 4m) LST ( 23m) MST ( 12m) South North
Cherenkov Telescope Array A SENSITIVE PROBE OF EXTREME UNIVERSE ELINA LINDFORS, TUORLA OBSERVATORY ON BEHALF OF CTA CONSORTIUM, TAUP 2015 1 The CTA Observatory SST ( 4m) LST ( 23m) MST ( 12m) South North
Radio and X-rays from GRS Close correlations of the third kind
 Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 82, 41 c SAIt 211 Memorie della Radio and -rays from GRS 1915+15 - Close correlations of the third kind Ralph Spencer 1 and Anthony Rushton 1,2,3 1 Jodrell Bank Centre for Astrophysics
Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 82, 41 c SAIt 211 Memorie della Radio and -rays from GRS 1915+15 - Close correlations of the third kind Ralph Spencer 1 and Anthony Rushton 1,2,3 1 Jodrell Bank Centre for Astrophysics
Galactic sources in GeV/TeV Astronomy and the new HESS Results
 Galactic sources in GeV/TeV Astronomy and the new HESS Results Martin Tluczykont for the HESS Collaboration LLR Ecole Polytechnique Joint Symposium on GeV-TeV Astrophysics in the GLAST Era Stanford, September
Galactic sources in GeV/TeV Astronomy and the new HESS Results Martin Tluczykont for the HESS Collaboration LLR Ecole Polytechnique Joint Symposium on GeV-TeV Astrophysics in the GLAST Era Stanford, September
Galaxies with Active Nuclei. Active Galactic Nuclei Seyfert Galaxies Radio Galaxies Quasars Supermassive Black Holes
 Galaxies with Active Nuclei Active Galactic Nuclei Seyfert Galaxies Radio Galaxies Quasars Supermassive Black Holes Active Galactic Nuclei About 20 25% of galaxies do not fit well into Hubble categories
Galaxies with Active Nuclei Active Galactic Nuclei Seyfert Galaxies Radio Galaxies Quasars Supermassive Black Holes Active Galactic Nuclei About 20 25% of galaxies do not fit well into Hubble categories
Diffuse Gamma-Ray Emission
 Diffuse Gamma-Ray Emission Debbijoy Bhattacharya Manipal Centre for Natural Sciences (MCNS) Manipal University 5 Sept 2014 Observational Gamma-Ray Astronomy Atmospheric Window 00 11 00 11 Figure: Atmospheric
Diffuse Gamma-Ray Emission Debbijoy Bhattacharya Manipal Centre for Natural Sciences (MCNS) Manipal University 5 Sept 2014 Observational Gamma-Ray Astronomy Atmospheric Window 00 11 00 11 Figure: Atmospheric
Very high energy gamma-emission of Perseus Cluster
 Very high energy gamma-emission of Perseus Cluster V.G. SINITSYNA, V.Y. SINITSYNA P. N. Lebedev Physical Institute, Leninsky prospect 53, Moscow, 119991 Russia VERY-HIGH ENERGY GAMMA-RAY ASTRONOMY of GALACTIC
Very high energy gamma-emission of Perseus Cluster V.G. SINITSYNA, V.Y. SINITSYNA P. N. Lebedev Physical Institute, Leninsky prospect 53, Moscow, 119991 Russia VERY-HIGH ENERGY GAMMA-RAY ASTRONOMY of GALACTIC
Cosmic Ray Electrons and GC Observations with H.E.S.S.
 Cosmic Ray Electrons and GC Observations with H.E.S.S. Christopher van Eldik (for the H.E.S.S. Collaboration) MPI für Kernphysik, Heidelberg, Germany TeVPA '09, SLAC, July 2009 The Centre of the Milky
Cosmic Ray Electrons and GC Observations with H.E.S.S. Christopher van Eldik (for the H.E.S.S. Collaboration) MPI für Kernphysik, Heidelberg, Germany TeVPA '09, SLAC, July 2009 The Centre of the Milky
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 7 Dec 1998
 PKS 2155 304 a source of VHE γ-rays P.M. Chadwick, K. Lyons, T.J.L. McComb, S.McQueen, K.J. Orford, J.L. Osborne, S.M. Rayner, S.E. Shaw, K.E. Turver 1, G.J. Wieczorek arxiv:astro-ph/9812122v1 7 Dec 1998
PKS 2155 304 a source of VHE γ-rays P.M. Chadwick, K. Lyons, T.J.L. McComb, S.McQueen, K.J. Orford, J.L. Osborne, S.M. Rayner, S.E. Shaw, K.E. Turver 1, G.J. Wieczorek arxiv:astro-ph/9812122v1 7 Dec 1998
Constraints on cosmic-ray origin from gamma-ray observations of supernova remnants
 Constraints on cosmic-ray origin from gamma-ray observations of supernova remnants Marianne Lemoine-Goumard (CENBG, Université Bordeaux, CNRS-IN2P3, France) On behalf of the Fermi-LAT and HESS Collaborations
Constraints on cosmic-ray origin from gamma-ray observations of supernova remnants Marianne Lemoine-Goumard (CENBG, Université Bordeaux, CNRS-IN2P3, France) On behalf of the Fermi-LAT and HESS Collaborations
Cosmological Background Radiation and Extragalactic Gamma-ray Opacity
 Cosmological Background Radiation and Extragalactic Gamma-ray Opacity Rudy Gilmore SISSA TeV Particle Astrophysics July 21, 2010 Collaborators: Joel Primack - UCSC Rachel Somerville - STScI (Baltimore)
Cosmological Background Radiation and Extragalactic Gamma-ray Opacity Rudy Gilmore SISSA TeV Particle Astrophysics July 21, 2010 Collaborators: Joel Primack - UCSC Rachel Somerville - STScI (Baltimore)
A Unified Model for AGN. Ryan Yamada Astro 671 March 27, 2006
 A Unified Model for AGN Ryan Yamada Astro 671 March 27, 2006 Overview Introduction to AGN Evidence for unified model Structure Radiative transfer models for dusty torus Active Galactic Nuclei Emission-line
A Unified Model for AGN Ryan Yamada Astro 671 March 27, 2006 Overview Introduction to AGN Evidence for unified model Structure Radiative transfer models for dusty torus Active Galactic Nuclei Emission-line
AGILE and multi-wavelength campaigns on blazars!
 14 th AGILE Workshop AGILE and multi-wavelength campaigns on blazars S. Vercellone (INAF/IASF Palermo) on behalf of the AGILE AGN WG S. Vercellone INAF/IASF Palermo 14 th AGILE Workshop Rome, June 20-21
14 th AGILE Workshop AGILE and multi-wavelength campaigns on blazars S. Vercellone (INAF/IASF Palermo) on behalf of the AGILE AGN WG S. Vercellone INAF/IASF Palermo 14 th AGILE Workshop Rome, June 20-21
Fermi Source Analyses and Identifying VERITAS Candidates
 Fermi Source Analyses and Identifying VERITAS Candidates 1 1 1. University of California, Berkeley 2 Overview Introduction VERITAS Fermi Analysis Likelihood Doppler Factor Estimation Motivations Blazars
Fermi Source Analyses and Identifying VERITAS Candidates 1 1 1. University of California, Berkeley 2 Overview Introduction VERITAS Fermi Analysis Likelihood Doppler Factor Estimation Motivations Blazars
