Comets and the Sinusoidal Poten1al
|
|
|
- Rosa Stanley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Comets and the Sinusoidal Poten1al by David F. Bartlett Brian Marsden One of the most influential comet investigators of the 20 th century 1
2 Matese & Whitmire s Expected Modula9on in Galac9c La9tude
3 Matese & Whitmire s Surprising Modula9on in Gal. Long. (1996)
4 Do Comets Get a Nudge from the Galaxy? Science Volume 274; 8 November 1996
5 Sinusoidal Poten9al with a Graviton having an imaginary mass m= ev Modified Gravitational Potential Here λ 0 is a universal wavelength. For r = 1AU, cos(k 0 r) differs from 1 by only 1 part in 10-14, making it too small a difference to have been detected in the motion of the planets. If k 0 r > 1, then the sinusoidal potential provides both a gravitational force and a tidal force which fall off as 1/r. The slow fall off in r can explain 5 the flat rotation curves of stars in disk galaxies.
6 Sinusoidal Poten9al Cont. Top View of Dust and Stars in the thin disk 6
7 Hill Sphere for Sun and Galaxy is 1 Light Year GR Correction falls off as 1/R Sun-sinsusoidal increases as R 2 Galactic radial tides increases as R 3
8 Milky Way: Periods at Solar Circle Conven9onal Sinusoidal Poisson s Eq. Helmholtz s Eq. Orbital 240 Myears 240 Myears Radial 170 Myears 10 Myears Z 62 Myears 200 Myears Info: C.W. Allen Astrophysical Quan33es, 3 rd Edi3on. 8
9 The New Comets Point A Minimum semi-major axis for which the galactic tidal force exceeds the solar force at some point in the rapid (8MYear) epicyclic oscillation of the sun in groove of the alternating galactic potential. R 1/2 - Resonance of 1 solar galactic epicyclic oscillation with two periods of the comet about the sun. (Kepler s law assumed for the orbit of the comet about the sun.)
10 Use Compressive Radial Tide to Remove Max from Orbit To GALACTIC CENTER 45 =ANGINPLNX F F
11 Defini9on of ANGINPLNX To GALACTIC CENTER ANGLINPLNX
12 Far Oort Comets Quality 1A Only Favored Galactic Longitudes for Radial Tide shown in red Perehelion North of Plane of the Galactic Disk shown in red Longitude, l Sine of gal latitude
13 Far Oort Cloud. Quality 1A only Angle in Plane for Compressive Tide (red) Angle in Plane for Expansive Tide (blue) ANGLEINPLN X ANGLEINPLN Y ANGLEINPLN Z
14 Far Oort Cloud. Distribution in Ecliptic Longitude & Latitude Ecliptic longitude Sine of Ecliptic latitude
15 Trans-Jovian Comets (q>5 AU) Favored Galactic Longitudes for Radial Tide Perehelion North of Plane of the Galactic Disk
16 Trans-Jovian Comets Angle in Plane for Compressive Tide Angle in Plane for Expansive Tide
17 Trans-Jovians. Distribution in Ecliptic Longitude & Sine of Latitude
18 Any Way You Slice It, Radial Tides Beat Z Tides Direc9on Cosines Between the Galac9c X,Y & Z Axes and the direc9on to the commetary perihelion are l, m, n. Marsden and others have Computed orbits for 499 Comets. All of these enter this tabula9on. Tabula9on is broken into 13 separate averages.
19 Trans Jovian Comets (q>5 AU) Quality <l^2> <m^2> <n^2> Number All Recall that max H is removed from cometary orbit when direc9on of 9dal force is in plane of cometary orbit and is at 45 degrees to aphelion direc9on Q.
20 Unbound Comets (1/a < 0) Quality <l^2> <m^2> <n^2> Number 1A B A B
21 Far Oort Comets (0<1/a < AU^ 1) Quality <l^2> <m^2> <n^2> Number 1A B A B
22 Near Oort Comets ( <1/a <0.002 AU^ 1) Quality <l^2> <m^2> <n^2> Number 1A B A B
23 Contours of Sinusoidal Potential Ф(r,z) out to Sun s Position (r = 20 λ) 22 mass rings with mass falling off as r Exp[-r/7λ]. In the plot the black color is a potential minimum and z/λ white color is a potential maximum. Note: As viewed from the z direction there is no clean view through material. (ie it is hard to observe the ring structure) r/λ
24 Contours of Sinusoidal Potential Ф(r,z) near Galactic Center 22 mass rings placed in median plane with mass falling off as r Exp[-r/7λ]. In the plot the black color is a potential minimum and white color is a potential maximum. z/λ r/λ
25 Butler Burton s HI layer of Milky Way Butler Burton has stated that the central wiggles are real (private communication). He also notes in the plot he assumed a distance from the sun to the galactic center of R 0 =10kpc. The step structure is equal to R 0 /20 25
26 Dames Contours of CO in the Milky Way CO is an observable substitute for the H2 needed for star formation. There are two dense bands of contours in this plot from Tom Dame et al (1987). These bands are approximately +/- λ/4 and are probably related to stall points in the z-motion of matter in the extreme disk. 26
27 Thanks to John Cumalat
28 HST Picture of NGC 7742 (A Thin SEYFERT) Spiral arms and oblique viewing angles usually suppress evidence of circular structure in external galaxies. Here the disk is thin enough and active enough for such structure to be evident. (The radius of the outer ring is about 2λ.) NGC 7742 is a face-on unbarred spiral galaxy in the constellation Pegasus. The galaxy is unusual in that it contains a ring but no bar.[4] Typically, bars are needed to produce a ring structure. The bars' gravitational forces move gas to the ends of the bars, where it forms into the rings seen in many barred spiral galaxies. In this galaxy, however, no bar is present, so this mechanism cannot be used to explain the formation of the ring. O. K. Sil'chenko and A. V. Moiseev proposed that the ring was formed partly as the result of a merger event in which a smaller gas-rich dwarf galaxy collided with NGC As evidence for this, they point to the unusually bright central region, the presence of highly-inclined central gas disk, and the presence of gas that is counterrotating (or rotating in the opposite 28 direction) with respect to the stars.
29
Epicycles the short form.
 Homework Set 3 Due Sept 9 CO 4.15 just part (a). (see CO pg. 908) CO 4.1 CO 4.36 (a),(b) CO 5.14 (assume that Sun currently has its max. u velocity.) CO 5.16 (Keplerian orbit = orbit around a point mass)
Homework Set 3 Due Sept 9 CO 4.15 just part (a). (see CO pg. 908) CO 4.1 CO 4.36 (a),(b) CO 5.14 (assume that Sun currently has its max. u velocity.) CO 5.16 (Keplerian orbit = orbit around a point mass)
Gravity: Motivation An initial theory describing the nature of the gravitational force by Newton is a product of the resolution of the
 Gravity: Motivation An initial theory describing the nature of the gravitational force by Newton is a product of the resolution of the Geocentric-Heliocentric debate (Brahe s data and Kepler s analysis)
Gravity: Motivation An initial theory describing the nature of the gravitational force by Newton is a product of the resolution of the Geocentric-Heliocentric debate (Brahe s data and Kepler s analysis)
LESSON 1. Solar System
 Astronomy Notes LESSON 1 Solar System 11.1 Structure of the Solar System axis of rotation period of rotation period of revolution ellipse astronomical unit What is the solar system? 11.1 Structure of the
Astronomy Notes LESSON 1 Solar System 11.1 Structure of the Solar System axis of rotation period of rotation period of revolution ellipse astronomical unit What is the solar system? 11.1 Structure of the
What is the solar system?
 Notes Astronomy What is the solar system? 11.1 Structure of the Solar System Our solar system includes planets and dwarf planets, their moons, a star called the Sun, asteroids and comets. Planets, dwarf
Notes Astronomy What is the solar system? 11.1 Structure of the Solar System Our solar system includes planets and dwarf planets, their moons, a star called the Sun, asteroids and comets. Planets, dwarf
Ay 1 Lecture 2. Starting the Exploration
 Ay 1 Lecture 2 Starting the Exploration 2.1 Distances and Scales Some Commonly Used Units Distance: Astronomical unit: the distance from the Earth to the Sun, 1 au = 1.496 10 13 cm ~ 1.5 10 13 cm Light
Ay 1 Lecture 2 Starting the Exploration 2.1 Distances and Scales Some Commonly Used Units Distance: Astronomical unit: the distance from the Earth to the Sun, 1 au = 1.496 10 13 cm ~ 1.5 10 13 cm Light
Stellar Dynamics and Structure of Galaxies
 Stellar Dynamics and Structure of Galaxies Gerry Gilmore H47 email: gil@ast.cam.ac.uk Lectures: Monday 12:10-13:00 Wednesday 11:15-12:05 Friday 12:10-13:00 Books: Binney & Tremaine Galactic Dynamics Princeton
Stellar Dynamics and Structure of Galaxies Gerry Gilmore H47 email: gil@ast.cam.ac.uk Lectures: Monday 12:10-13:00 Wednesday 11:15-12:05 Friday 12:10-13:00 Books: Binney & Tremaine Galactic Dynamics Princeton
Galaxies and Cosmology
 4/28/17 The Discovery of Galaxies Up to the 1920 s, astronomers were not sure exactly how far away galaxies were, and thus didn t know how big they are! Spiral Nebulae could be assumed to be inside our
4/28/17 The Discovery of Galaxies Up to the 1920 s, astronomers were not sure exactly how far away galaxies were, and thus didn t know how big they are! Spiral Nebulae could be assumed to be inside our
The Galaxy. (The Milky Way Galaxy)
 The Galaxy (The Milky Way Galaxy) Which is a picture of the Milky Way? A A is what we see from Earth inside the Milky Way while B is what the Milky Way might look like if we were far away looking back
The Galaxy (The Milky Way Galaxy) Which is a picture of the Milky Way? A A is what we see from Earth inside the Milky Way while B is what the Milky Way might look like if we were far away looking back
Chapter 19 Galaxies. Hubble Ultra Deep Field: Each dot is a galaxy of stars. More distant, further into the past. halo
 Chapter 19 Galaxies Hubble Ultra Deep Field: Each dot is a galaxy of stars. More distant, further into the past halo disk bulge Barred Spiral Galaxy: Has a bar of stars across the bulge Spiral Galaxy 1
Chapter 19 Galaxies Hubble Ultra Deep Field: Each dot is a galaxy of stars. More distant, further into the past halo disk bulge Barred Spiral Galaxy: Has a bar of stars across the bulge Spiral Galaxy 1
1 The Solar System. 1.1 a journey into our galaxy
 1 The Solar System Though Pluto, and the far-flung depths of the Solar System, is the focus of this book, it is essential that Pluto is placed in the context of the planetary system that it inhabits our
1 The Solar System Though Pluto, and the far-flung depths of the Solar System, is the focus of this book, it is essential that Pluto is placed in the context of the planetary system that it inhabits our
Stellar Populations in the Galaxy
 Stellar Populations in the Galaxy Stars are fish in the sea of the galaxy, and like fish they often travel in schools. Star clusters are relatively small groupings, the true schools are stellar populations.
Stellar Populations in the Galaxy Stars are fish in the sea of the galaxy, and like fish they often travel in schools. Star clusters are relatively small groupings, the true schools are stellar populations.
Chapter 15 Galaxies and the Foundation of Modern Cosmology
 15.1 Islands of stars Chapter 15 Galaxies and the Foundation of Modern Cosmology Cosmology: study of galaxies What are they 3 major types of galaxies? Spiral galaxies: like the milky way, look like flat,
15.1 Islands of stars Chapter 15 Galaxies and the Foundation of Modern Cosmology Cosmology: study of galaxies What are they 3 major types of galaxies? Spiral galaxies: like the milky way, look like flat,
Earth in the Universe Unit Notes
 Earth in the Universe Unit Notes The Universe - everything everywhere, 15-20 billion years old Inside the universe there are billions of Galaxies Inside each Galaxy there are billions of Solar Systems
Earth in the Universe Unit Notes The Universe - everything everywhere, 15-20 billion years old Inside the universe there are billions of Galaxies Inside each Galaxy there are billions of Solar Systems
Lecture 25 The Milky Way Galaxy November 29, 2017
 Lecture 25 The Milky Way Galaxy November 29, 2017 1 2 Size of the Universe The Milky Way galaxy is very much larger than the solar system Powers of Ten interactive applet 3 Galaxies Large collections of
Lecture 25 The Milky Way Galaxy November 29, 2017 1 2 Size of the Universe The Milky Way galaxy is very much larger than the solar system Powers of Ten interactive applet 3 Galaxies Large collections of
The motions of stars in the Galaxy
 The motions of stars in the Galaxy The stars in the Galaxy define various components, that do not only differ in their spatial distribution but also in their kinematics. The dominant motion of stars (and
The motions of stars in the Galaxy The stars in the Galaxy define various components, that do not only differ in their spatial distribution but also in their kinematics. The dominant motion of stars (and
Astronomy A BEGINNER S GUIDE TO THE UNIVERSE EIGHTH EDITION
 Astronomy A BEGINNER S GUIDE TO THE UNIVERSE EIGHTH EDITION CHAPTER 14 The Milky Way Galaxy Lecture Presentation 14.0 the Milky Way galaxy How do we know the Milky Way exists? We can see it even though
Astronomy A BEGINNER S GUIDE TO THE UNIVERSE EIGHTH EDITION CHAPTER 14 The Milky Way Galaxy Lecture Presentation 14.0 the Milky Way galaxy How do we know the Milky Way exists? We can see it even though
Unit 1: The Earth in the Universe
 Unit 1: The Earth in the Universe 1. The Universe 1.1. First ideas about the Universe 1.2. Components and origin 1.3. Sizes and distances 2. The Solar System 3. The planet Earth 3.1. Movements of the Earth
Unit 1: The Earth in the Universe 1. The Universe 1.1. First ideas about the Universe 1.2. Components and origin 1.3. Sizes and distances 2. The Solar System 3. The planet Earth 3.1. Movements of the Earth
Galaxies & Introduction to Cosmology
 Galaxies & Introduction to Cosmology Other Galaxies: How many are there? Hubble Deep Field Project 100 hour exposures over 10 days Covered an area of the sky about 1/100 the size of the full moon Probably
Galaxies & Introduction to Cosmology Other Galaxies: How many are there? Hubble Deep Field Project 100 hour exposures over 10 days Covered an area of the sky about 1/100 the size of the full moon Probably
Chapter 14 The Milky Way Galaxy
 Chapter 14 The Milky Way Galaxy Spiral Galaxy M81 - similar to our Milky Way Galaxy Our Parent Galaxy A galaxy is a giant collection of stellar and interstellar matter held together by gravity Billions
Chapter 14 The Milky Way Galaxy Spiral Galaxy M81 - similar to our Milky Way Galaxy Our Parent Galaxy A galaxy is a giant collection of stellar and interstellar matter held together by gravity Billions
Galaxies. Lecture Topics. Lecture 23. Discovering Galaxies. Galaxy properties. Local Group. History Cepheid variable stars. Classifying galaxies
 Galaxies Lecture 23 APOD: NGC 3628 (The Hamburger Galaxy) 1 Lecture Topics Discovering Galaxies History Cepheid variable stars Galaxy properties Classifying galaxies Local Group 2 23-1 Discovering Galaxies
Galaxies Lecture 23 APOD: NGC 3628 (The Hamburger Galaxy) 1 Lecture Topics Discovering Galaxies History Cepheid variable stars Galaxy properties Classifying galaxies Local Group 2 23-1 Discovering Galaxies
Kozai-Lidov oscillations
 Kozai-Lidov oscillations Kozai (1962 - asteroids); Lidov (1962 - artificial satellites) arise most simply in restricted three-body problem (two massive bodies on a Kepler orbit + a test particle) e.g.,
Kozai-Lidov oscillations Kozai (1962 - asteroids); Lidov (1962 - artificial satellites) arise most simply in restricted three-body problem (two massive bodies on a Kepler orbit + a test particle) e.g.,
The Gravitational Microlensing Planet Search Technique from Space
 The Gravitational Microlensing Planet Search Technique from Space David Bennett & Sun Hong Rhie (University of Notre Dame) Abstract: Gravitational microlensing is the only known extra-solar planet search
The Gravitational Microlensing Planet Search Technique from Space David Bennett & Sun Hong Rhie (University of Notre Dame) Abstract: Gravitational microlensing is the only known extra-solar planet search
2004 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Addison-Wesley
 By tracing their orbits and using our understanding of gravity, we can conclude that the object these stars are orbiting (shown here as a 5- pointed star) must have a mass over 2.5 million times greater
By tracing their orbits and using our understanding of gravity, we can conclude that the object these stars are orbiting (shown here as a 5- pointed star) must have a mass over 2.5 million times greater
TEK 8 Test Review. 15. Galaxies are best described as -
 TEK 8 Test Review 1. List the three subatomic particles and give each of their masses. 2. Describe and draw an illustration (Bohr Model) of the most common element in the Universe. 3. Describe and draw
TEK 8 Test Review 1. List the three subatomic particles and give each of their masses. 2. Describe and draw an illustration (Bohr Model) of the most common element in the Universe. 3. Describe and draw
Name Period Date Earth and Space Science. Solar System Review
 Name Period Date Earth and Space Science Solar System Review 1. is the spinning a planetary object on its axis. 2. is the backward motion of planets. 3. The is a unit less number between 0 and 1 that describes
Name Period Date Earth and Space Science Solar System Review 1. is the spinning a planetary object on its axis. 2. is the backward motion of planets. 3. The is a unit less number between 0 and 1 that describes
Astronomy 241: Review Questions #2 Distributed: November 7, 2013
 Astronomy 241: Review Questions #2 Distributed: November 7, 2013 Review the questions below, and be prepared to discuss them in class. For each question, list (a) the general topic, and (b) the key laws
Astronomy 241: Review Questions #2 Distributed: November 7, 2013 Review the questions below, and be prepared to discuss them in class. For each question, list (a) the general topic, and (b) the key laws
Peculiar (Interacting) Galaxies
 Peculiar (Interacting) Galaxies Not all galaxies fall on the Hubble sequence: many are peculiar! In 1966, Arp created an Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies based on pictures from the Palomar Sky Survey. In 1982,
Peculiar (Interacting) Galaxies Not all galaxies fall on the Hubble sequence: many are peculiar! In 1966, Arp created an Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies based on pictures from the Palomar Sky Survey. In 1982,
Laboratory: Milky Way
 Department of Physics and Geology Laboratory: Milky Way Astronomy 1402 Equipment Needed Quantity Equipment Needed Quantity Milky Way galaxy Model 1 Ruler 1 1.1 Our Milky Way Part 1: Background Milky Way
Department of Physics and Geology Laboratory: Milky Way Astronomy 1402 Equipment Needed Quantity Equipment Needed Quantity Milky Way galaxy Model 1 Ruler 1 1.1 Our Milky Way Part 1: Background Milky Way
Astronomy, PART 2. Vocabulary. A. Universe - Our Milky Way Galaxy is one of of galaxies in an expanding universe.
 Astronomy, PART 2 Vocabulary Aphelion Asteroid Astronomical Unit Comet Constellation Crater Eccentricity Eclipse Equinox Geocentric model Gravitation Heliocentric model Inertia Jovian Perihelion Revolution
Astronomy, PART 2 Vocabulary Aphelion Asteroid Astronomical Unit Comet Constellation Crater Eccentricity Eclipse Equinox Geocentric model Gravitation Heliocentric model Inertia Jovian Perihelion Revolution
Chapter 15 The Milky Way Galaxy. The Milky Way
 Chapter 15 The Milky Way Galaxy The Milky Way Almost everything we see in the night sky belongs to the Milky Way We see most of the Milky Way as a faint band of light across the sky From the outside, our
Chapter 15 The Milky Way Galaxy The Milky Way Almost everything we see in the night sky belongs to the Milky Way We see most of the Milky Way as a faint band of light across the sky From the outside, our
Star systems like our Milky Way. Galaxies
 Galaxies Star systems like our Milky Way Galaxies Contain a few thousand to tens of billions of stars,as well as varying amounts of gas and dust Large variety of shapes and sizes Gas and Dust in
Galaxies Star systems like our Milky Way Galaxies Contain a few thousand to tens of billions of stars,as well as varying amounts of gas and dust Large variety of shapes and sizes Gas and Dust in
AST101IN Final Exam. 1.) Arrange the objects below from smallest to largest. (3 points)
 Name: Possibly useful formulae: AST101IN Final Exam F g = Gm 1 m 2 /r 2 p 2 =a 3 F=ma E=mc 2 1.) Arrange the objects below from smallest to largest. (3 points) The sun The Earth The universe The Milky
Name: Possibly useful formulae: AST101IN Final Exam F g = Gm 1 m 2 /r 2 p 2 =a 3 F=ma E=mc 2 1.) Arrange the objects below from smallest to largest. (3 points) The sun The Earth The universe The Milky
ASTR 200 : Lecture 22 Structure of our Galaxy
 ASTR 200 : Lecture 22 Structure of our Galaxy 1 The 'Milky Way' is known to all cultures on Earth (perhaps, unfortunately, except for recent city-bound dwellers) 2 Fish Eye Lens of visible hemisphere (but
ASTR 200 : Lecture 22 Structure of our Galaxy 1 The 'Milky Way' is known to all cultures on Earth (perhaps, unfortunately, except for recent city-bound dwellers) 2 Fish Eye Lens of visible hemisphere (but
The Milky Way Galaxy (ch. 23)
 The Milky Way Galaxy (ch. 23) [Exceptions: We won t discuss sec. 23.7 (Galactic Center) much in class, but read it there will probably be a question or a few on it. In following lecture outline, numbers
The Milky Way Galaxy (ch. 23) [Exceptions: We won t discuss sec. 23.7 (Galactic Center) much in class, but read it there will probably be a question or a few on it. In following lecture outline, numbers
Stars, Galaxies & the Universe Lecture Outline
 Stars, Galaxies & the Universe Lecture Outline A galaxy is a collection of 100 billion stars! Our Milky Way Galaxy (1)Components - HII regions, Dust Nebulae, Atomic Gas (2) Shape & Size (3) Rotation of
Stars, Galaxies & the Universe Lecture Outline A galaxy is a collection of 100 billion stars! Our Milky Way Galaxy (1)Components - HII regions, Dust Nebulae, Atomic Gas (2) Shape & Size (3) Rotation of
What is Earth Science?
 What is Earth Science? A.EARTH SCIENCE: the study of Earth and its history B. Earth science is divided into 4 main branches: 1. Geology: study of the lithosphere 2. Oceanography: study of oceans 3. Meteorology:
What is Earth Science? A.EARTH SCIENCE: the study of Earth and its history B. Earth science is divided into 4 main branches: 1. Geology: study of the lithosphere 2. Oceanography: study of oceans 3. Meteorology:
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Chapter 4 - Group Homework Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Density is defined as A) mass times weight. B) mass per unit volume.
Chapter 4 - Group Homework Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Density is defined as A) mass times weight. B) mass per unit volume.
ASTRON 449: Stellar (Galactic) Dynamics. Fall 2014
 ASTRON 449: Stellar (Galactic) Dynamics Fall 2014 In this course, we will cover the basic phenomenology of galaxies (including dark matter halos, stars clusters, nuclear black holes) theoretical tools
ASTRON 449: Stellar (Galactic) Dynamics Fall 2014 In this course, we will cover the basic phenomenology of galaxies (including dark matter halos, stars clusters, nuclear black holes) theoretical tools
Astronomy 114. Lecture 29: Internal Properties of Galaxies. Martin D. Weinberg. UMass/Astronomy Department
 Astronomy 114 Lecture 29: Internal Properties of Galaxies Martin D. Weinberg weinberg@astro.umass.edu UMass/Astronomy Department A114: Lecture 29 20 Apr 2007 Read: Ch. 26 Astronomy 114 1/16 Announcements
Astronomy 114 Lecture 29: Internal Properties of Galaxies Martin D. Weinberg weinberg@astro.umass.edu UMass/Astronomy Department A114: Lecture 29 20 Apr 2007 Read: Ch. 26 Astronomy 114 1/16 Announcements
distribution of mass! The rotation curve of the Galaxy ! Stellar relaxation time! Virial theorem! Differential rotation of the stars in the disk
 Today in Astronomy 142:! The local standard of rest the Milky Way, continued! Rotation curves and the! Stellar relaxation time! Virial theorem! Differential rotation of the stars in the disk distribution
Today in Astronomy 142:! The local standard of rest the Milky Way, continued! Rotation curves and the! Stellar relaxation time! Virial theorem! Differential rotation of the stars in the disk distribution
Milky Way s Substance Loop
 Milky Way s Substance Loop Wei-Xiong Huang May 6, 2015 Abstract: Milky Way center exists a star of super huge mass, its called milky way "nuclear-star". Its rotation and gravitation led milky way all substances
Milky Way s Substance Loop Wei-Xiong Huang May 6, 2015 Abstract: Milky Way center exists a star of super huge mass, its called milky way "nuclear-star". Its rotation and gravitation led milky way all substances
EARTH SCIENCE UNIT 9 -NOTES ASTRONOMY
 EARTH SCIENCE UNIT 9 -NOTES ASTRONOMY UNIT 9- ASTRONOMY 2 THE SOLAR SYSTEM I. The Solar System:. a. Celestial Body:. i. Examples:. b. MAIN COMPONENTS/MEMBERS OF THE SOLAR SYSTEM: i. 1. Planets are objects
EARTH SCIENCE UNIT 9 -NOTES ASTRONOMY UNIT 9- ASTRONOMY 2 THE SOLAR SYSTEM I. The Solar System:. a. Celestial Body:. i. Examples:. b. MAIN COMPONENTS/MEMBERS OF THE SOLAR SYSTEM: i. 1. Planets are objects
Earth Science, 13e Tarbuck & Lutgens
 Earth Science, 13e Tarbuck & Lutgens Origins of Modern Astronomy Earth Science, 13e Chapter 21 Stanley C. Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Early history of astronomy Ancient Greeks Used philosophical
Earth Science, 13e Tarbuck & Lutgens Origins of Modern Astronomy Earth Science, 13e Chapter 21 Stanley C. Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Early history of astronomy Ancient Greeks Used philosophical
What Objects Are Part of the Solar System?
 What Objects Are Part of the Solar System? Lesson 1 Quiz Josleen divided some of the planets into two main groups. The table below shows how she grouped them. Paul created a poster showing the solar system.
What Objects Are Part of the Solar System? Lesson 1 Quiz Josleen divided some of the planets into two main groups. The table below shows how she grouped them. Paul created a poster showing the solar system.
Astronomy 1140 Quiz 4 Review
 Astronomy 1140 Quiz 4 Review Anil Pradhan November 16, 2017 I Jupiter 1. How do Jupiter s mass, size, day and year compare to Earth s? Mass: 318 Earth masses (or about 1/1000th the mass of the Sun). Radius:
Astronomy 1140 Quiz 4 Review Anil Pradhan November 16, 2017 I Jupiter 1. How do Jupiter s mass, size, day and year compare to Earth s? Mass: 318 Earth masses (or about 1/1000th the mass of the Sun). Radius:
GALAXY SPIRAL ARMS, DISK DISTURBANCES AND STATISTICS
 GALAXY SPIRAL ARMS, DISK DISTURBANCES AND STATISTICS Part I: NGC3081 to build background for NGC4622. Co-authors for Parts I and II: G. Byrd (Univ. of Alabama, Tuscaloosa), T. Freeman (Bevill State Comm.
GALAXY SPIRAL ARMS, DISK DISTURBANCES AND STATISTICS Part I: NGC3081 to build background for NGC4622. Co-authors for Parts I and II: G. Byrd (Univ. of Alabama, Tuscaloosa), T. Freeman (Bevill State Comm.
Galaxies: The Nature of Galaxies
 Galaxies: The Nature of Galaxies The Milky Way The Milky Way is visible to the unaided eye at most place on Earth Galileo in 1610 used his telescope to resolve the faint band into numerous stars In the
Galaxies: The Nature of Galaxies The Milky Way The Milky Way is visible to the unaided eye at most place on Earth Galileo in 1610 used his telescope to resolve the faint band into numerous stars In the
Coriolis Effect - the apparent curved paths of projectiles, winds, and ocean currents
 Regents Earth Science Unit 5: Astronomy Models of the Universe Earliest models of the universe were based on the idea that the Sun, Moon, and planets all orbit the Earth models needed to explain how the
Regents Earth Science Unit 5: Astronomy Models of the Universe Earliest models of the universe were based on the idea that the Sun, Moon, and planets all orbit the Earth models needed to explain how the
The Milky Way Part 3 Stellar kinematics. Physics of Galaxies 2011 part 8
 The Milky Way Part 3 Stellar kinematics Physics of Galaxies 2011 part 8 1 Stellar motions in the MW disk Let s continue with the rotation of the Galaxy, this time from the point of view of the stars First,
The Milky Way Part 3 Stellar kinematics Physics of Galaxies 2011 part 8 1 Stellar motions in the MW disk Let s continue with the rotation of the Galaxy, this time from the point of view of the stars First,
The Milky Way. Finding the Center. Milky Way Composite Photo. Finding the Center. Milky Way : A band of and a. Milky Way
 The Milky Way Milky Way : A band of and a The band of light we see is really 100 billion stars Milky Way probably looks like Andromeda. Milky Way Composite Photo Milky Way Before the 1920 s, astronomers
The Milky Way Milky Way : A band of and a The band of light we see is really 100 billion stars Milky Way probably looks like Andromeda. Milky Way Composite Photo Milky Way Before the 1920 s, astronomers
The Milky Way Part 2 Stellar kinematics. Physics of Galaxies 2012 part 7
 The Milky Way Part 2 Stellar kinematics Physics of Galaxies 2012 part 7 1 Stellar motions in the MW disk Let s look at the rotation of the Galactic disk First, we need to introduce the concept of the Local
The Milky Way Part 2 Stellar kinematics Physics of Galaxies 2012 part 7 1 Stellar motions in the MW disk Let s look at the rotation of the Galactic disk First, we need to introduce the concept of the Local
Galaxies: enormous collections of gases, dust and stars held together by gravity Our galaxy is called the milky way
 Celestial bodies are all of the natural objects in space ex. stars moons, planets, comets etc. Star: celestial body of hot gas that gives off light and heat the closest star to earth is the sun Planet:
Celestial bodies are all of the natural objects in space ex. stars moons, planets, comets etc. Star: celestial body of hot gas that gives off light and heat the closest star to earth is the sun Planet:
Topic 10: Earth in Space Workbook Chapters 10 and 11
 Topic 10: Earth in Space Workbook Chapters 10 and 11 We can imagine all the celestial objects seen from Earth the sun, stars, the Milky way, and planets as being positioned on a celestial sphere. Earth
Topic 10: Earth in Space Workbook Chapters 10 and 11 We can imagine all the celestial objects seen from Earth the sun, stars, the Milky way, and planets as being positioned on a celestial sphere. Earth
THE CHEMICAL EVOLUTION OF THE MILKY WAY DISK
 THE CHEMICAL EVOLUTION OF THE MILKY WAY DISK 1. The simple picture of disk evolution: independent ring evolution, successes and failures 2. The dynamical picture: stars (and gas) moving around 3. A model
THE CHEMICAL EVOLUTION OF THE MILKY WAY DISK 1. The simple picture of disk evolution: independent ring evolution, successes and failures 2. The dynamical picture: stars (and gas) moving around 3. A model
The Milky Way - Chapter 23
 The Milky Way - Chapter 23 The Milky Way Galaxy A galaxy: huge collection of stars (10 7-10 13 ) and interstellar matter (gas & dust). Held together by gravity. Much bigger than any star cluster we have
The Milky Way - Chapter 23 The Milky Way Galaxy A galaxy: huge collection of stars (10 7-10 13 ) and interstellar matter (gas & dust). Held together by gravity. Much bigger than any star cluster we have
The Cosmological Redshift. Cepheid Variables. Hubble s Diagram
 SOME NEGATIVE EFFECTS OF THE EXPANSION OF THE UNIVERSE. Lecture 22 Hubble s Law and the Large Scale Structure of the Universe PRS: According to modern ideas and observations, what can be said about the
SOME NEGATIVE EFFECTS OF THE EXPANSION OF THE UNIVERSE. Lecture 22 Hubble s Law and the Large Scale Structure of the Universe PRS: According to modern ideas and observations, what can be said about the
Match the words in the left hand column to the appropriate blank in the sentences in the right hand column. Use each word only once.
 Chapter 15 Homework Due: 11:59pm on Sunday, November 13, 2016 To understand how points are awarded, read the Grading Policy for this assignment. Question 1 Match the words in the left hand column to the
Chapter 15 Homework Due: 11:59pm on Sunday, November 13, 2016 To understand how points are awarded, read the Grading Policy for this assignment. Question 1 Match the words in the left hand column to the
Chapter 23 The Milky Way Galaxy Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 23 The Milky Way Galaxy The Milky Way is our own galaxy viewed from the inside. It is a vast collection of more than 200 billion stars, planets, nebulae, clusters, dust and gas. Our own sun and
Chapter 23 The Milky Way Galaxy The Milky Way is our own galaxy viewed from the inside. It is a vast collection of more than 200 billion stars, planets, nebulae, clusters, dust and gas. Our own sun and
... Explain how an orbiting planet causes a Doppler shift in the spectrum of a star
 Q1.In 1999 a planet was discovered orbiting a star in the constellation of Pegasus. (a) State one reason why it is difficult to make a direct observation of this planet..... (1) The initial discovery of
Q1.In 1999 a planet was discovered orbiting a star in the constellation of Pegasus. (a) State one reason why it is difficult to make a direct observation of this planet..... (1) The initial discovery of
PROBLEM SET #1. Galactic Structure 37 pts total. due Tuesday, 2/19/2019
 PROBLEM SET #1 Galactic Structure 37 pts total due Tuesday, 2/19/2019 1. Stellar cluster problem [26 pts] The following refers to a star cluster observed on Aug 15, 2010 at about 4am UT. The cluster is
PROBLEM SET #1 Galactic Structure 37 pts total due Tuesday, 2/19/2019 1. Stellar cluster problem [26 pts] The following refers to a star cluster observed on Aug 15, 2010 at about 4am UT. The cluster is
The Milky Way & Galaxies
 The Milky Way & Galaxies The Milky Way Appears as a milky band of light across the sky A small telescope reveals that it is composed of many stars (Galileo again!) Our knowledge of the Milky Way comes
The Milky Way & Galaxies The Milky Way Appears as a milky band of light across the sky A small telescope reveals that it is composed of many stars (Galileo again!) Our knowledge of the Milky Way comes
Astronomy: Division C Science Olympiad, Round 1 Tryout Test
 Astronomy: Division C Science Olympiad, Round 1 Tryout Test Student Name : Student Number : DIRECTIONS 1. Write the answers that you want graded legibly on the answer sheet, along with your name and student
Astronomy: Division C Science Olympiad, Round 1 Tryout Test Student Name : Student Number : DIRECTIONS 1. Write the answers that you want graded legibly on the answer sheet, along with your name and student
Large Scale Structure
 Large Scale Structure Measuring Distance in Universe-- a ladder of steps, building from nearby Redshift distance Redshift = z = (λ observed - λ rest )/ λ rest Every part of a distant spectrum has same
Large Scale Structure Measuring Distance in Universe-- a ladder of steps, building from nearby Redshift distance Redshift = z = (λ observed - λ rest )/ λ rest Every part of a distant spectrum has same
The Milky Way, Hubble Law, the expansion of the Universe and Dark Matter Chapter 14 and 15 The Milky Way Galaxy and the two Magellanic Clouds.
 The Milky Way, Hubble Law, the expansion of the Universe and Dark Matter Chapter 14 and 15 The Milky Way Galaxy and the two Magellanic Clouds. Image taken from the European Southern Observatory in Chile
The Milky Way, Hubble Law, the expansion of the Universe and Dark Matter Chapter 14 and 15 The Milky Way Galaxy and the two Magellanic Clouds. Image taken from the European Southern Observatory in Chile
Chapter 17. Galaxies. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Chapter 17 Galaxies Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Galaxies Beyond the Milky Way are billions of other galaxies Some galaxies are spiral like
Chapter 17 Galaxies Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Galaxies Beyond the Milky Way are billions of other galaxies Some galaxies are spiral like
British Olympiad in Astronomy and Astrophysics
 British Olympiad in Astronomy and Astrophysics Name School Competition Paper Total Mark/50 24 th April 2015 Time Allowed: One hour Attempt as many questions as you can. Write your answers on this question
British Olympiad in Astronomy and Astrophysics Name School Competition Paper Total Mark/50 24 th April 2015 Time Allowed: One hour Attempt as many questions as you can. Write your answers on this question
Thom et al. (2008), ApJ
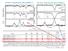 Star S674 along the same LOS as Complex C Star S441 along the same LOS as Complex C Thom et al. (2008), ApJ Distances to HVCs From spectroscopy of high Galactic latitude stars at small angular separations
Star S674 along the same LOS as Complex C Star S441 along the same LOS as Complex C Thom et al. (2008), ApJ Distances to HVCs From spectroscopy of high Galactic latitude stars at small angular separations
Mapping Document. GCSE (9-1) Astronomy. Pearson Edexcel Level 1/Level 2 GCSE (9-1) in Astronomy (1AS0)
 Mapping Document GCSE (9-1) Astronomy Pearson Edexcel Level 1/Level 2 GCSE (9-1) in Astronomy (1AS0) GCSE (9-1) Astronomy Mapping document This document is designed to help you compare the existing 2011
Mapping Document GCSE (9-1) Astronomy Pearson Edexcel Level 1/Level 2 GCSE (9-1) in Astronomy (1AS0) GCSE (9-1) Astronomy Mapping document This document is designed to help you compare the existing 2011
Examination, course FY2450 Astrophysics Wednesday 23 rd May, 2012 Time:
 Page 1 of 18 The Norwegian University of Science and Technology Department of Physics Contact person Name: Robert Hibbins Tel: 93551, mobile: 94 82 08 34 Examination, course FY2450 Astrophysics Wednesday
Page 1 of 18 The Norwegian University of Science and Technology Department of Physics Contact person Name: Robert Hibbins Tel: 93551, mobile: 94 82 08 34 Examination, course FY2450 Astrophysics Wednesday
Our Galaxy. We are located in the disk of our galaxy and this is why the disk appears as a band of stars across the sky.
 Our Galaxy Our Galaxy We are located in the disk of our galaxy and this is why the disk appears as a band of stars across the sky. Early attempts to locate our solar system produced erroneous results.
Our Galaxy Our Galaxy We are located in the disk of our galaxy and this is why the disk appears as a band of stars across the sky. Early attempts to locate our solar system produced erroneous results.
Big Galaxies Are Rare! Cepheid Distance Measurement. Clusters of Galaxies. The Nature of Galaxies
 Big Galaxies Are Rare! Potato Chip Rule: More small things than large things Big, bright spirals are easy to see, but least common Dwarf ellipticals & irregulars are most common Faint, hard to see Mostly
Big Galaxies Are Rare! Potato Chip Rule: More small things than large things Big, bright spirals are easy to see, but least common Dwarf ellipticals & irregulars are most common Faint, hard to see Mostly
Lecture 20: Planet formation II. Clues from Exoplanets
 Lecture 20: Planet formation II. Clues from Exoplanets 1 Outline Definition of a planet Properties of exoplanets Formation models for exoplanets gravitational instability model core accretion scenario
Lecture 20: Planet formation II. Clues from Exoplanets 1 Outline Definition of a planet Properties of exoplanets Formation models for exoplanets gravitational instability model core accretion scenario
It is about 100,000 ly across, 2,000 ly thick, and our solar system is located 26,000 ly away from the center of the galaxy.
 The Galaxies The Milky Way Galaxy Is a spiral galaxy in which our solar system is located. The center of the galaxy lies in the Sagittarius Constellation. It is about 100,000 ly across, 2,000 ly thick,
The Galaxies The Milky Way Galaxy Is a spiral galaxy in which our solar system is located. The center of the galaxy lies in the Sagittarius Constellation. It is about 100,000 ly across, 2,000 ly thick,
Lecture 16 Dwarf Planets and Comets January 8a, 2014
 1 Lecture 16 Dwarf Planets and Comets January 8a, 2014 2 Pluto -- Basic Information Discovered by Clyde Tombaugh in 1930 Period: P orb = 248 years Distance: a = 39.5 AU 3 moons (Charon, Nix, Hydra) Demoted
1 Lecture 16 Dwarf Planets and Comets January 8a, 2014 2 Pluto -- Basic Information Discovered by Clyde Tombaugh in 1930 Period: P orb = 248 years Distance: a = 39.5 AU 3 moons (Charon, Nix, Hydra) Demoted
Cosmology Vocabulary
 Cosmology Vocabulary Vocabulary Words Terrestrial Planets The Sun Gravity Galaxy Lightyear Axis Comets Kuiper Belt Oort Cloud Meteors AU Nebula Solar System Cosmology Universe Coalescence Jovian Planets
Cosmology Vocabulary Vocabulary Words Terrestrial Planets The Sun Gravity Galaxy Lightyear Axis Comets Kuiper Belt Oort Cloud Meteors AU Nebula Solar System Cosmology Universe Coalescence Jovian Planets
1star 1 star 9 8 planets 63 (major) moons asteroids, comets, meteoroids
 The Solar System 1star 1 star 9 8 planets 63 (major) moons asteroids, comets, meteoroids The distances to planets are known from Kepler s Laws (once calibrated with radar ranging to Venus) How are planet
The Solar System 1star 1 star 9 8 planets 63 (major) moons asteroids, comets, meteoroids The distances to planets are known from Kepler s Laws (once calibrated with radar ranging to Venus) How are planet
OUR SOLAR SYSTEM. James Martin. Facebook.com/groups/AstroLSSC Twitter.com/AstroLSSC
 OUR SOLAR SYSTEM James Martin Facebook.com/groups/AstroLSSC Twitter.com/AstroLSSC It s time for the human race to enter the solar system. -Dan Quayle Structure of the Solar System Our Solar System contains
OUR SOLAR SYSTEM James Martin Facebook.com/groups/AstroLSSC Twitter.com/AstroLSSC It s time for the human race to enter the solar system. -Dan Quayle Structure of the Solar System Our Solar System contains
The Classification of Galaxies
 Admin. 11/9/17 1. Class website http://www.astro.ufl.edu/~jt/teaching/ast1002/ 2. Optional Discussion sections: Tue. ~11.30am (period 5), Bryant 3; Thur. ~12.30pm (end of period 5 and period 6), start
Admin. 11/9/17 1. Class website http://www.astro.ufl.edu/~jt/teaching/ast1002/ 2. Optional Discussion sections: Tue. ~11.30am (period 5), Bryant 3; Thur. ~12.30pm (end of period 5 and period 6), start
lightyears observable universe astronomical unit po- laris perihelion Milky Way
 1 Chapter 1 Astronomical distances are so large we typically measure distances in lightyears: the distance light can travel in one year, or 9.46 10 12 km or 9, 600, 000, 000, 000 km. Looking into the sky
1 Chapter 1 Astronomical distances are so large we typically measure distances in lightyears: the distance light can travel in one year, or 9.46 10 12 km or 9, 600, 000, 000, 000 km. Looking into the sky
FCAT Review Space Science
 FCAT Review Space Science The Law of Universal Gravitation The law of universal gravitation states that ALL matter in the universe attracts each other. Gravity is greatly impacted by both mass and distance
FCAT Review Space Science The Law of Universal Gravitation The law of universal gravitation states that ALL matter in the universe attracts each other. Gravity is greatly impacted by both mass and distance
4/18/17. Our Schedule. Revisit Quasar 3C273. Dark Matter in the Universe. ASTR 1040: Stars & Galaxies
 ASTR 1040: Stars & Galaxies HST Abell 2218 Prof. Juri Toomre TAs: Piyush Agrawal, Connor Bice Lecture 25 Tues 18 Apr 2017 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre Our Schedule Observatory Night #8 + #9 (proj
ASTR 1040: Stars & Galaxies HST Abell 2218 Prof. Juri Toomre TAs: Piyush Agrawal, Connor Bice Lecture 25 Tues 18 Apr 2017 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre Our Schedule Observatory Night #8 + #9 (proj
Part 1. Estimates of the Sun s motion in the Milky Way Galaxy
 Homework 6: The Milky Way Astro 201 Prof. Bechtold Due: Thursday, October 21, 2010 This homework is patterned after lab assignments from the University of Michigan, and University of Washington Astronomy
Homework 6: The Milky Way Astro 201 Prof. Bechtold Due: Thursday, October 21, 2010 This homework is patterned after lab assignments from the University of Michigan, and University of Washington Astronomy
Gravitational Potential Energy. The Gravitational Field. Grav. Potential Energy Work. Grav. Potential Energy Work
 The Gravitational Field Exists at every point in space The gravitational force experienced by a test particle placed at that point divided by the mass of the test particle magnitude of the freefall acceleration
The Gravitational Field Exists at every point in space The gravitational force experienced by a test particle placed at that point divided by the mass of the test particle magnitude of the freefall acceleration
Star Formation and U/HLXs in the Cartwheel Galaxy Paper & Pencil Version
 Star Formation and U/HLXs in the Cartwheel Galaxy Paper & Pencil Version Introduction: The Cartwheel Galaxy Multi-Wavelength Composite The Cartwheel Galaxy is part of a group of galaxies ~five hundred
Star Formation and U/HLXs in the Cartwheel Galaxy Paper & Pencil Version Introduction: The Cartwheel Galaxy Multi-Wavelength Composite The Cartwheel Galaxy is part of a group of galaxies ~five hundred
The Milky Way Galaxy. Some thoughts. How big is it? What does it look like? How did it end up this way? What is it made up of?
 Some thoughts The Milky Way Galaxy How big is it? What does it look like? How did it end up this way? What is it made up of? Does it change 2 3 4 5 This is not a constant zoom The Milky Way Almost everything
Some thoughts The Milky Way Galaxy How big is it? What does it look like? How did it end up this way? What is it made up of? Does it change 2 3 4 5 This is not a constant zoom The Milky Way Almost everything
Earth Science, 11e. Origin of Modern Astronomy Chapter 21. Early history of astronomy. Early history of astronomy. Early history of astronomy
 2006 Pearson Prentice Hall Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 21 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
2006 Pearson Prentice Hall Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 21 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
There are three basic types of galaxies:
 Galaxies There are three basic types of galaxies: Spirals Ellipticals Irregulars To make a long story short, elliptical galaxies are galaxies that have used up all their gas forming stars, or they have
Galaxies There are three basic types of galaxies: Spirals Ellipticals Irregulars To make a long story short, elliptical galaxies are galaxies that have used up all their gas forming stars, or they have
The Milky Way Galaxy
 1/5/011 The Milky Way Galaxy Distribution of Globular Clusters around a Point in Sagittarius About 00 globular clusters are distributed in random directions around the center of our galaxy. 1 1/5/011 Structure
1/5/011 The Milky Way Galaxy Distribution of Globular Clusters around a Point in Sagittarius About 00 globular clusters are distributed in random directions around the center of our galaxy. 1 1/5/011 Structure
1UNIT. The Universe. What do you remember? Key language. Content objectives
 1UNIT The Universe What do you remember? What are the points of light in this photo? What is the difference between a star and a planet? a moon and a comet? Content objectives In this unit, you will Learn
1UNIT The Universe What do you remember? What are the points of light in this photo? What is the difference between a star and a planet? a moon and a comet? Content objectives In this unit, you will Learn
The History of the Solar System. From cloud to Sun, planets, and smaller bodies
 The History of the Solar System From cloud to Sun, planets, and smaller bodies The Birth of a Star Twenty years ago, we knew of only one star with planets the Sun and our understanding of the birth of
The History of the Solar System From cloud to Sun, planets, and smaller bodies The Birth of a Star Twenty years ago, we knew of only one star with planets the Sun and our understanding of the birth of
AST1100 Lecture Notes
 AST1100 Lecture Notes 4 Stellar orbits and dark matter 1 Using Kepler s laws for stars orbiting the center of a galaxy We will now use Kepler s laws of gravitation on much larger scales. We will study
AST1100 Lecture Notes 4 Stellar orbits and dark matter 1 Using Kepler s laws for stars orbiting the center of a galaxy We will now use Kepler s laws of gravitation on much larger scales. We will study
2.1 Patterns in the Night Sky
 2.1 Patterns in the Night Sky Our goals for learning: What are constellations? How do we locate objects in the sky? Why do stars rise and set? Why don t we see the same constellations throughout the year?
2.1 Patterns in the Night Sky Our goals for learning: What are constellations? How do we locate objects in the sky? Why do stars rise and set? Why don t we see the same constellations throughout the year?
Astronomy 111 Exam Review Problems (Real exam will be Tuesday Oct 25, 2016)
 Astronomy 111 Exam Review Problems (Real exam will be Tuesday Oct 25, 2016) Actual Exam rules: you may consult only one page of formulas and constants and a calculator while taking this test. You may not
Astronomy 111 Exam Review Problems (Real exam will be Tuesday Oct 25, 2016) Actual Exam rules: you may consult only one page of formulas and constants and a calculator while taking this test. You may not
Lecture 23: Jupiter. Solar System. Jupiter s Orbit. The semi-major axis of Jupiter s orbit is a = 5.2 AU
 Lecture 23: Jupiter Solar System Jupiter s Orbit The semi-major axis of Jupiter s orbit is a = 5.2 AU Jupiter Sun a Kepler s third law relates the semi-major axis to the orbital period 1 Jupiter s Orbit
Lecture 23: Jupiter Solar System Jupiter s Orbit The semi-major axis of Jupiter s orbit is a = 5.2 AU Jupiter Sun a Kepler s third law relates the semi-major axis to the orbital period 1 Jupiter s Orbit
Ch. 25 In-Class Notes: Beyond Our Solar System
 Ch. 25 In-Class Notes: Beyond Our Solar System ES2a. The solar system is located in an outer edge of the disc-shaped Milky Way galaxy, which spans 100,000 light years. ES2b. Galaxies are made of billions
Ch. 25 In-Class Notes: Beyond Our Solar System ES2a. The solar system is located in an outer edge of the disc-shaped Milky Way galaxy, which spans 100,000 light years. ES2b. Galaxies are made of billions
Spiral Structure. m ( Ω Ω gp ) = n κ. Closed orbits in non-inertial frames can explain the spiral pattern
 Spiral Structure In the mid-1960s Lin and Shu proposed that the spiral structure is caused by long-lived quasistatic density waves The density would be higher by about 10% to 20% Stars, dust and gas clouds
Spiral Structure In the mid-1960s Lin and Shu proposed that the spiral structure is caused by long-lived quasistatic density waves The density would be higher by about 10% to 20% Stars, dust and gas clouds
Normal Galaxies ASTR 2120 Sarazin
 Normal Galaxies ASTR 2120 Sarazin Test #2 Monday, April 8, 11-11:50 am ASTR 265 (classroom) Bring pencils, paper, calculator You may not consult the text, your notes, or any other materials or any person
Normal Galaxies ASTR 2120 Sarazin Test #2 Monday, April 8, 11-11:50 am ASTR 265 (classroom) Bring pencils, paper, calculator You may not consult the text, your notes, or any other materials or any person
The Milky Way - 2 ASTR 2110 Sarazin. Center of the Milky Way
 The Milky Way - 2 ASTR 2110 Sarazin Center of the Milky Way Final Exam Tuesday, December 12, 9:00 am noon Ruffner G006 (classroom) You may not consult the text, your notes, or any other materials or any
The Milky Way - 2 ASTR 2110 Sarazin Center of the Milky Way Final Exam Tuesday, December 12, 9:00 am noon Ruffner G006 (classroom) You may not consult the text, your notes, or any other materials or any
9. Formation of the Solar System
 9. Formation of the Solar System The evolution of the world may be compared to a display of fireworks that has just ended: some few red wisps, ashes, and smoke. Standing on a cool cinder, we see the slow
9. Formation of the Solar System The evolution of the world may be compared to a display of fireworks that has just ended: some few red wisps, ashes, and smoke. Standing on a cool cinder, we see the slow
Kinematics of the Solar Neighborhood
 Chapter 15 Kinematics of the Solar Neighborhood Unlike an elliptical galaxy, the Milky Way rotates with a speed much larger than the random velocities of typical stars. Our position inside the disk of
Chapter 15 Kinematics of the Solar Neighborhood Unlike an elliptical galaxy, the Milky Way rotates with a speed much larger than the random velocities of typical stars. Our position inside the disk of
