Managing Call Centers with Many Strategic Agents
|
|
|
- Lee Golden
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Managing Call Centers with Many Strategic Agents Rouba Ibrahim, Kenan Arifoglu Management Science and Innovation, UCL YEQT Workshop - Eindhoven November 2014
2 Work Schedule Flexibility 86SwofwthewqBestwCompanieswtowWorkwForqwofferw employeeswsomewtypewofwflexiblewschedule. -3Fortune, Swofwemployerswallowedwsomewworkerswtow periodicallywchangewtheirwstartingwandwquittingwtimes.w -3National3Study3of3Employers3(USA), InwthewUS,wallwfederalwemployeeswnowwhavewthew rightwtowrequestwmorewflexiblewworkwoptions.ww -ywhiteyhouseymemoyissuedyonyjuney23,y2014.y InwthewUK,wthewrightwtowrequestwflexiblewworkingw hourswiswnowwextendedwtowallwworkers.ww -yflexibleyworkingylawyissuedyonyjulyy1,y2014.y
3 Flexitime at Hydro-Québec Flexitime schedule: 30% of call center agents have flexible work hours Must be there during core periods (2 periods of 2 hours each) Are otherwise free to choose their time schedules Don t need to inform their managers ahead of time Must be there for a total of 70 hours per 2 weeks
4 Flexitime at Hydro-Québec Flexitime schedule: 30% of call center agents have flexible work hours Must be there during core periods (2 periods of 2 hours each) Are otherwise free to choose their time schedules Don t need to inform their managers ahead of time Must be there for a total of 70 hours per 2 weeks Major headaches for Hydro-Québec s call center managers!
5 Research Questions What is the impact of strategic agent behavior on the system? What are optimal operational decisions with strategic agents? Can we align the objectives of the system manager and the agents?
6 Related Literature Staffing and routing in many-server systems Queueing games Strategic servers in queues Gopalakrishnan, R., Dorouli, S., Ward, A. and A. Weirman Routing and staffing when servers are strategic. Gurvich, I., Lariviere, M. and A. Moreno-Garcia Staffing service systems when capacity has a mind of its own.
7 Staffing Decisions with Non-Strategic Agents
8 Non-Strategic Agents Queueing Framework µ µ θ θ λ A Period A λ B Period B Poisson arrival processes with rates λ A, λ B No overlap between periods A and B I.I.D. exponential service times with rate µ = 1 I.I.D. exponential abandonment times with rate θ
9 Non-Strategic Agents System Manager s Problem with Non-Strategic Agents Staffing Costs c: Fixed compensation r: Variable compensation rate t A, t B : Total compensations t A = c + r λa n A and t B = c + r λb n B. Customer-Related Costs p: Abandonment penalty cost ($ per customer who abandons) h: Delay cost ($ per customer per minute wait)
10 Non-Strategic Agents Fluid Approximation to the System Manager s Problem For t = A, B: n t : Number of servers in period t q t : Queue length in period t η t : Total abandonment rate in period t η t = (λ t n t ) + and q t = η t θ. The system manager determines optimal staffing levels n A and n B : ( min {n A n A 0,n B 0 + c + r λ A n A ( p + h θ ) ( + n B c + r λ B n B ) (λ A n A ) + + ) ( p + h θ ) (λ B n B ) + } Bassamboo and Randhawa (2010).
11 Non-Strategic Agents Fluid-Based Prescriptions with Non-Strategic Agents Recall: c = staffing cost; p = abandonment cost; h = delay cost. Optimal Staffing Levels (i) if c p + h/θ, then n A = λ A and n B = λ B, (ii) if c > p + h/θ, then n A = n B = 0. In (i), both A and B are critically loaded. In this case, n A α = na + n B = λ A λ A + λ B and ρ A = ρ B = 1, where ρ t = λ t /n t.
12 Strategic Agents Staffing Decisions with Strategic Agents
13 Strategic Agents Strategic Agent Behavior µ µ θ θ λ A Period A λ B Period B Agents have individual valuations for working in either period Strategic agents select working period of their choice
14 Strategic Agents A Two-Stage Sequential Game Sequence of events Stage 1: System manager selects total staffing level n Stage 2: Agents in pool of size n select working period An equilibrium arises in the system. We determine this equilibrium by using backward induction.
15 Strategic Agents Second Stage: Agent s Problem
16 Strategic Agents Individual Agent Preferences n: Total number of agents in the system (given) n A, n B : To be determined by the agents Independent and heterogeneous agents v A, v B : agent valuations v A (n A ) = c + r λa n A and v B (n B ) = c + (r + X ) λb n B, where X is a random variable (cdf F, ccdf F ). Agent selects period A if, and only if, v A (n A ) v B (n B ).
17 Strategic Agents Subgame Perfect Nash Equilibrium Let α e be the equilibrium proportion of agents who select A. Existence and Uniqueness of Equilibrium We show that there exists a unique equilibrium threshold, t e, such that α e = P(X t e ) = F (t e ). We also show that t e is the unique solution of: r λ A F (t e ) λ B F (t e ) r te = 0.
18 Strategic Agents Impact of Strategic Agent Behavior Recall that we have at optimum in the non-strategic case: α = λ A /(λ A + λ B ) is the optimal proportion of agents who are in A ρ A = ρ B = 1 Comparison with the Non-Strategic Case We show that, for any value of n, the following hold: (i) F (0) = α α e = α (ii) F (0) < α α e < α (iii) F (0) > α α e > α where F (0) = P(X 0).
19 Strategic Agents Explanation: Case (i) Suppose that the staffing levels in periods A and B are as follows: Period A Period B n A = λ A Then, let agents select their periods. n B = λ B The proportion of agents who choose period A is: ( P(v B v A ) = P c + (r + X ) λ B c + r λ ) A = P(X 0) = F (0). n B n A So, for the above to be an equilibrium state, we need to have: F (0) = In this case, α e = F (0) = α. λ A λ A + λ B = α.
20 Strategic Agents Case (ii): System Imbalance Now, what happens if F (0) < α? Period A Period B n A < λ A n B > λ B The proportion of agents who choose period A is: ( P(v B v A ) = P c + (r + X ) λ B c + r λ ) A = P(X 0) = F (0) < α. n B n A In this case, some agents in A will now select B instead. So, our initial state cannot be an equilibrium, and we have: F (0) < α e < α. In this case, period A becomes overloaded and period B underloaded.
21 Strategic Agents First Stage: System Manager s Problem
22 Strategic Agents Fluid Approximation with Strategic Agents In this stage, assume that α e is given. The system manager determines the optimal total staffing level n: ( min {nα e n 0 + c + r λ A nα ( e p + h θ ) ( + n(1 α e ) ) (λ A nα e ) + + ) λ B c + r n(1 α e ) ( p + h ) } (λ B n(1 α e )) + θ
23 Strategic Agents Fluid-Based Prescriptions: Asymptotically Optimal Regimes It is never optimal to have: Both A and B underloaded Both A and B overloaded So, have at least one period critically loaded. A overloaded B critically loaded A critically loaded B underloaded A underloaded B critically loaded A critically loaded B overloaded 0 c/(p+h/θ) α * 1 c/(p+h/θ) 1 α e
24 Strategic Agents Cost Impact of Strategic Agents Percent cost increase α * 10 0 c = 0.5, p = 0.7, h = 1, and µ = θ = 1 λ A = 150 and λ B = 250 X uniform on (x l, x u ) Vary r, x l, and x u to vary α e α e
25 System Controls
26 A Coordinating Compensation Scheme Let r A = r + β A and r B = r + β B be the variable compensation rates for periods A and B. Unequal Compensation Rates We show that the compensation scheme with β A = (1 α )F 1 (α ) and β B = α F 1 (α ), is a budget-neutral compensation scheme for which α e (r A, r B ) = α. The system manager can control the system by increasing compensation in the period which is busier at equilibrium.
27 Conclusions We proposed a model for strategic agents We quantified the impact of strategic agent behavior We derived optimal staffing levels with strategic agents We developed a compensation scheme that makes agents behave in line with the system manager s objective
28 Extensions We also considered the following extensions: Social welfare Different agent valuation models Routing Decisions What if the system manager doesn t honor or only partially honors agents choices? General abandonment Heterogeneous service rates
29 Thank You!
Making Delay Announcements
 Making Delay Announcements Performance Impact and Predicting Queueing Delays Ward Whitt With Mor Armony, Rouba Ibrahim and Nahum Shimkin March 7, 2012 Last Class 1 The Overloaded G/GI/s + GI Fluid Queue
Making Delay Announcements Performance Impact and Predicting Queueing Delays Ward Whitt With Mor Armony, Rouba Ibrahim and Nahum Shimkin March 7, 2012 Last Class 1 The Overloaded G/GI/s + GI Fluid Queue
Stochastic Networks and Parameter Uncertainty
 Stochastic Networks and Parameter Uncertainty Assaf Zeevi Graduate School of Business Columbia University Stochastic Processing Networks Conference, August 2009 based on joint work with Mike Harrison Achal
Stochastic Networks and Parameter Uncertainty Assaf Zeevi Graduate School of Business Columbia University Stochastic Processing Networks Conference, August 2009 based on joint work with Mike Harrison Achal
Dynamic Control of Parallel-Server Systems
 Dynamic Control of Parallel-Server Systems Jim Dai Georgia Institute of Technology Tolga Tezcan University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign May 13, 2009 Jim Dai (Georgia Tech) Many-Server Asymptotic Optimality
Dynamic Control of Parallel-Server Systems Jim Dai Georgia Institute of Technology Tolga Tezcan University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign May 13, 2009 Jim Dai (Georgia Tech) Many-Server Asymptotic Optimality
A STAFFING ALGORITHM FOR CALL CENTERS WITH SKILL-BASED ROUTING: SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
 A STAFFING ALGORITHM FOR CALL CENTERS WITH SKILL-BASED ROUTING: SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL by Rodney B. Wallace IBM and The George Washington University rodney.wallace@us.ibm.com Ward Whitt Columbia University
A STAFFING ALGORITHM FOR CALL CENTERS WITH SKILL-BASED ROUTING: SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL by Rodney B. Wallace IBM and The George Washington University rodney.wallace@us.ibm.com Ward Whitt Columbia University
The Performance Impact of Delay Announcements
 The Performance Impact of Delay Announcements Taking Account of Customer Response IEOR 4615, Service Engineering, Professor Whitt Supplement to Lecture 21, April 21, 2015 Review: The Purpose of Delay Announcements
The Performance Impact of Delay Announcements Taking Account of Customer Response IEOR 4615, Service Engineering, Professor Whitt Supplement to Lecture 21, April 21, 2015 Review: The Purpose of Delay Announcements
Delay Announcements. Predicting Queueing Delays for Delay Announcements. IEOR 4615, Service Engineering, Professor Whitt. Lecture 21, April 21, 2015
 Delay Announcements Predicting Queueing Delays for Delay Announcements IEOR 4615, Service Engineering, Professor Whitt Lecture 21, April 21, 2015 OUTLINE Delay Announcements: Why, What and When? [Slide
Delay Announcements Predicting Queueing Delays for Delay Announcements IEOR 4615, Service Engineering, Professor Whitt Lecture 21, April 21, 2015 OUTLINE Delay Announcements: Why, What and When? [Slide
Online Supplement to Delay-Based Service Differentiation with Many Servers and Time-Varying Arrival Rates
 Online Supplement to Delay-Based Service Differentiation with Many Servers and Time-Varying Arrival Rates Xu Sun and Ward Whitt Department of Industrial Engineering and Operations Research, Columbia University
Online Supplement to Delay-Based Service Differentiation with Many Servers and Time-Varying Arrival Rates Xu Sun and Ward Whitt Department of Industrial Engineering and Operations Research, Columbia University
Dynamic Call Center Routing Policies Using Call Waiting and Agent Idle Times Online Supplement
 Submitted to imanufacturing & Service Operations Management manuscript MSOM-11-370.R3 Dynamic Call Center Routing Policies Using Call Waiting and Agent Idle Times Online Supplement (Authors names blinded
Submitted to imanufacturing & Service Operations Management manuscript MSOM-11-370.R3 Dynamic Call Center Routing Policies Using Call Waiting and Agent Idle Times Online Supplement (Authors names blinded
Dynamic Call Center Routing Policies Using Call Waiting and Agent Idle Times Online Supplement
 Dynamic Call Center Routing Policies Using Call Waiting and Agent Idle Times Online Supplement Wyean Chan DIRO, Université de Montréal, C.P. 6128, Succ. Centre-Ville, Montréal (Québec), H3C 3J7, CANADA,
Dynamic Call Center Routing Policies Using Call Waiting and Agent Idle Times Online Supplement Wyean Chan DIRO, Université de Montréal, C.P. 6128, Succ. Centre-Ville, Montréal (Québec), H3C 3J7, CANADA,
Lecture 9: Deterministic Fluid Models and Many-Server Heavy-Traffic Limits. IEOR 4615: Service Engineering Professor Whitt February 19, 2015
 Lecture 9: Deterministic Fluid Models and Many-Server Heavy-Traffic Limits IEOR 4615: Service Engineering Professor Whitt February 19, 2015 Outline Deterministic Fluid Models Directly From Data: Cumulative
Lecture 9: Deterministic Fluid Models and Many-Server Heavy-Traffic Limits IEOR 4615: Service Engineering Professor Whitt February 19, 2015 Outline Deterministic Fluid Models Directly From Data: Cumulative
DELAY PREDICTORS FOR CUSTOMER SERVICE SYSTEMS WITH TIME-VARYING PARAMETERS. Rouba Ibrahim Ward Whitt
 Proceedings of the 21 Winter Simulation Conference B. Johansson, S. Jain, J. Montoya-Torres, J. Hugan, and E. Yücesan, eds. DELAY PREDICTORS FOR CUSTOMER SERVICE SYSTEMS WITH TIME-VARYING PARAMETERS Rouba
Proceedings of the 21 Winter Simulation Conference B. Johansson, S. Jain, J. Montoya-Torres, J. Hugan, and E. Yücesan, eds. DELAY PREDICTORS FOR CUSTOMER SERVICE SYSTEMS WITH TIME-VARYING PARAMETERS Rouba
Erlang-C = M/M/N. agents. queue ACD. arrivals. busy ACD. queue. abandonment BACK FRONT. lost calls. arrivals. lost calls
 Erlang-C = M/M/N agents arrivals ACD queue Erlang-A lost calls FRONT BACK arrivals busy ACD queue abandonment lost calls Erlang-C = M/M/N agents arrivals ACD queue Rough Performance Analysis
Erlang-C = M/M/N agents arrivals ACD queue Erlang-A lost calls FRONT BACK arrivals busy ACD queue abandonment lost calls Erlang-C = M/M/N agents arrivals ACD queue Rough Performance Analysis
Operations Research II, IEOR161 University of California, Berkeley Spring 2007 Final Exam. Name: Student ID:
 Operations Research II, IEOR161 University of California, Berkeley Spring 2007 Final Exam 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 7 questions. 1. [5+5] Let X and Y be independent exponential random variables where X has
Operations Research II, IEOR161 University of California, Berkeley Spring 2007 Final Exam 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 7 questions. 1. [5+5] Let X and Y be independent exponential random variables where X has
We consider how two networked large-scale service systems that normally operate separately, such as call
 MANAGEMENT SCIENCE Vol. 55, No. 8, August 2009, pp. 1353 1367 issn 0025-1909 eissn 1526-5501 09 5508 1353 informs doi 10.1287/mnsc.1090.1025 2009 INFORMS Responding to Unexpected Overloads in Large-Scale
MANAGEMENT SCIENCE Vol. 55, No. 8, August 2009, pp. 1353 1367 issn 0025-1909 eissn 1526-5501 09 5508 1353 informs doi 10.1287/mnsc.1090.1025 2009 INFORMS Responding to Unexpected Overloads in Large-Scale
Electronic Companion Fluid Models for Overloaded Multi-Class Many-Server Queueing Systems with FCFS Routing
 Submitted to Management Science manuscript MS-251-27 Electronic Companion Fluid Models for Overloaded Multi-Class Many-Server Queueing Systems with FCFS Routing Rishi Talreja, Ward Whitt Department of
Submitted to Management Science manuscript MS-251-27 Electronic Companion Fluid Models for Overloaded Multi-Class Many-Server Queueing Systems with FCFS Routing Rishi Talreja, Ward Whitt Department of
Proactive Care with Degrading Class Types
 Proactive Care with Degrading Class Types Yue Hu (DRO, Columbia Business School) Joint work with Prof. Carri Chan (DRO, Columbia Business School) and Prof. Jing Dong (DRO, Columbia Business School) Motivation
Proactive Care with Degrading Class Types Yue Hu (DRO, Columbia Business School) Joint work with Prof. Carri Chan (DRO, Columbia Business School) and Prof. Jing Dong (DRO, Columbia Business School) Motivation
Wait-Time Predictors for Customer Service Systems with Time-Varying Demand and Capacity
 OPERATIONS RESEARCH Vol. 59, No. 5, September October 211, pp. 116 1118 issn 3-364X eissn 1526-5463 11 595 116 http://dx.doi.org/1.1287/opre.111.974 211 INFORMS Wait-Time Predictors for Customer Service
OPERATIONS RESEARCH Vol. 59, No. 5, September October 211, pp. 116 1118 issn 3-364X eissn 1526-5463 11 595 116 http://dx.doi.org/1.1287/opre.111.974 211 INFORMS Wait-Time Predictors for Customer Service
Proactive customer service: operational benefits and economic frictions
 Proactive customer service: operational benefits and economic frictions Kraig Delana Nicos Savva Tolga Tezcan London Business School, Regent s Park, London NW1 4SA, UK kdelana@london.edu nsavva@london.edu
Proactive customer service: operational benefits and economic frictions Kraig Delana Nicos Savva Tolga Tezcan London Business School, Regent s Park, London NW1 4SA, UK kdelana@london.edu nsavva@london.edu
λ λ λ In-class problems
 In-class problems 1. Customers arrive at a single-service facility at a Poisson rate of 40 per hour. When two or fewer customers are present, a single attendant operates the facility, and the service time
In-class problems 1. Customers arrive at a single-service facility at a Poisson rate of 40 per hour. When two or fewer customers are present, a single attendant operates the facility, and the service time
Queueing Theory II. Summary. ! M/M/1 Output process. ! Networks of Queue! Method of Stages. ! General Distributions
 Queueing Theory II Summary! M/M/1 Output process! Networks of Queue! Method of Stages " Erlang Distribution " Hyperexponential Distribution! General Distributions " Embedded Markov Chains M/M/1 Output
Queueing Theory II Summary! M/M/1 Output process! Networks of Queue! Method of Stages " Erlang Distribution " Hyperexponential Distribution! General Distributions " Embedded Markov Chains M/M/1 Output
Managing Queueing Systems Where Capacity Is Random. and Customers Are Impatient. Rouba Ibrahim. August 6, 2017
 Managing Queueing Systems Where Capacity Is Random and Customers Are Impatient Rouba Ibrahim UCL School of Management, 1 Canada Square, London E14 5AB, U.K. rouba.ibrahim@ucl.ac.uk August 6, 2017 Abstract.
Managing Queueing Systems Where Capacity Is Random and Customers Are Impatient Rouba Ibrahim UCL School of Management, 1 Canada Square, London E14 5AB, U.K. rouba.ibrahim@ucl.ac.uk August 6, 2017 Abstract.
Design heuristic for parallel many server systems under FCFS-ALIS Adan, I.J.B.F.; Boon, M.A.A.; Weiss, G.
 Design heuristic for parallel many server systems under FCFS-ALIS Adan, I.J.B.F.; Boon, M.A.A.; Weiss, G. Published in: arxiv Published: 04/03/2016 Document Version Accepted manuscript including changes
Design heuristic for parallel many server systems under FCFS-ALIS Adan, I.J.B.F.; Boon, M.A.A.; Weiss, G. Published in: arxiv Published: 04/03/2016 Document Version Accepted manuscript including changes
Exercises Stochastic Performance Modelling. Hamilton Institute, Summer 2010
 Exercises Stochastic Performance Modelling Hamilton Institute, Summer Instruction Exercise Let X be a non-negative random variable with E[X ]
Exercises Stochastic Performance Modelling Hamilton Institute, Summer Instruction Exercise Let X be a non-negative random variable with E[X ]
Design and evaluation of overloaded service systems with skill based routing, under FCFS policies
 Design and evaluation of overloaded service systems with skill based routing, under FCFS policies Ivo Adan Marko Boon Gideon Weiss April 2, 2013 Abstract We study an overloaded service system with servers
Design and evaluation of overloaded service systems with skill based routing, under FCFS policies Ivo Adan Marko Boon Gideon Weiss April 2, 2013 Abstract We study an overloaded service system with servers
REAL-TIME DELAY ESTIMATION BASED ON DELAY HISTORY SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
 REAL-TIME DELAY ESTIMATION BASED ON DELAY HISTORY SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL by Rouba Ibrahim and Ward Whitt IEOR Department Columbia University {rei2101, ww2040}@columbia.edu Abstract Motivated by interest
REAL-TIME DELAY ESTIMATION BASED ON DELAY HISTORY SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL by Rouba Ibrahim and Ward Whitt IEOR Department Columbia University {rei2101, ww2040}@columbia.edu Abstract Motivated by interest
Solutions to COMP9334 Week 8 Sample Problems
 Solutions to COMP9334 Week 8 Sample Problems Problem 1: Customers arrive at a grocery store s checkout counter according to a Poisson process with rate 1 per minute. Each customer carries a number of items
Solutions to COMP9334 Week 8 Sample Problems Problem 1: Customers arrive at a grocery store s checkout counter according to a Poisson process with rate 1 per minute. Each customer carries a number of items
ec1 e-companion to Liu and Whitt: Stabilizing Performance
 ec1 This page is intentionally blank. Proper e-companion title page, with INFORMS branding and exact metadata of the main paper, will be produced by the INFORMS office when the issue is being assembled.
ec1 This page is intentionally blank. Proper e-companion title page, with INFORMS branding and exact metadata of the main paper, will be produced by the INFORMS office when the issue is being assembled.
Routing and Staffing in Large-Scale Service Systems: The Case of Homogeneous Impatient Customers and Heterogeneous Servers
 OPERATIONS RESEARCH Vol. 59, No. 1, January February 2011, pp. 50 65 issn 0030-364X eissn 1526-5463 11 5901 0050 informs doi 10.1287/opre.1100.0878 2011 INFORMS Routing and Staffing in Large-Scale Service
OPERATIONS RESEARCH Vol. 59, No. 1, January February 2011, pp. 50 65 issn 0030-364X eissn 1526-5463 11 5901 0050 informs doi 10.1287/opre.1100.0878 2011 INFORMS Routing and Staffing in Large-Scale Service
Routing and Staffing in Large-Scale Service Systems: The Case of Homogeneous Impatient Customers and Heterogeneous Servers 1
 Routing and Staffing in Large-Scale Service Systems: The Case of Homogeneous Impatient Customers and Heterogeneous Servers 1 Mor Armony 2 Avishai Mandelbaum 3 June 25, 2008 Abstract Motivated by call centers,
Routing and Staffing in Large-Scale Service Systems: The Case of Homogeneous Impatient Customers and Heterogeneous Servers 1 Mor Armony 2 Avishai Mandelbaum 3 June 25, 2008 Abstract Motivated by call centers,
The shortest queue problem
 The shortest queue problem Ivo Adan March 19, 2002 1/40 queue 1 join the shortest queue queue 2 Where: Poisson arrivals with rate Exponential service times with mean 1/ 2/40 queue 1 queue 2 randomly assign
The shortest queue problem Ivo Adan March 19, 2002 1/40 queue 1 join the shortest queue queue 2 Where: Poisson arrivals with rate Exponential service times with mean 1/ 2/40 queue 1 queue 2 randomly assign
SOLUTIONS IEOR 3106: Second Midterm Exam, Chapters 5-6, November 8, 2012
 SOLUTIONS IEOR 3106: Second Midterm Exam, Chapters 5-6, November 8, 2012 This exam is closed book. YOU NEED TO SHOW YOUR WORK. Honor Code: Students are expected to behave honorably, following the accepted
SOLUTIONS IEOR 3106: Second Midterm Exam, Chapters 5-6, November 8, 2012 This exam is closed book. YOU NEED TO SHOW YOUR WORK. Honor Code: Students are expected to behave honorably, following the accepted
REAL-TIME DELAY ESTIMATION BASED ON DELAY HISTORY IN MANY-SERVER SERVICE SYSTEMS WITH TIME-VARYING ARRIVALS
 REAL-TIME DELAY ESTIMATION BASED ON DELAY HISTORY IN MANY-SERVER SERVICE SYSTEMS WITH TIME-VARYING ARRIVALS by Rouba Ibrahim and Ward Whitt IEOR Department Columbia University 500 West 120th Street 313
REAL-TIME DELAY ESTIMATION BASED ON DELAY HISTORY IN MANY-SERVER SERVICE SYSTEMS WITH TIME-VARYING ARRIVALS by Rouba Ibrahim and Ward Whitt IEOR Department Columbia University 500 West 120th Street 313
Blind Fair Routing in Large-Scale Service Systems with Heterogeneous Customers and Servers
 Blind Fair Routing in Large-Scale Service Systems with Heterogeneous Customers and Servers Mor Armony Amy R. Ward 2 October 6, 2 Abstract In a call center, arriving customers must be routed to available
Blind Fair Routing in Large-Scale Service Systems with Heterogeneous Customers and Servers Mor Armony Amy R. Ward 2 October 6, 2 Abstract In a call center, arriving customers must be routed to available
Blind Fair Routing in Large-Scale Service Systems with Heterogeneous Customers and Servers
 OPERATIONS RESEARCH Vol. 6, No., January February 23, pp. 228 243 ISSN 3-364X (print) ISSN 526-5463 (online) http://dx.doi.org/.287/opre.2.29 23 INFORMS Blind Fair Routing in Large-Scale Service Systems
OPERATIONS RESEARCH Vol. 6, No., January February 23, pp. 228 243 ISSN 3-364X (print) ISSN 526-5463 (online) http://dx.doi.org/.287/opre.2.29 23 INFORMS Blind Fair Routing in Large-Scale Service Systems
6 Solving Queueing Models
 6 Solving Queueing Models 6.1 Introduction In this note we look at the solution of systems of queues, starting with simple isolated queues. The benefits of using predefined, easily classified queues will
6 Solving Queueing Models 6.1 Introduction In this note we look at the solution of systems of queues, starting with simple isolated queues. The benefits of using predefined, easily classified queues will
arxiv: v1 [math.oc] 10 Jan 2019
![arxiv: v1 [math.oc] 10 Jan 2019 arxiv: v1 [math.oc] 10 Jan 2019](/thumbs/93/112693503.jpg) Revenue maximization with access and information pricing schemes in a partially-observable queueing game Tesnim Naceur and Yezekael Hayel LIA/CERI University of Avignon France E-mail: {tesnimnaceuryezekaelhayel}@univ-avignonfr
Revenue maximization with access and information pricing schemes in a partially-observable queueing game Tesnim Naceur and Yezekael Hayel LIA/CERI University of Avignon France E-mail: {tesnimnaceuryezekaelhayel}@univ-avignonfr
Stabilizing Customer Abandonment in Many-Server Queues with Time-Varying Arrivals
 OPERATIONS RESEARCH Vol. 6, No. 6, November December 212, pp. 1551 1564 ISSN 3-364X (print) ISSN 1526-5463 (online) http://dx.doi.org/1.1287/opre.112.114 212 INFORMS Stabilizing Customer Abandonment in
OPERATIONS RESEARCH Vol. 6, No. 6, November December 212, pp. 1551 1564 ISSN 3-364X (print) ISSN 1526-5463 (online) http://dx.doi.org/1.1287/opre.112.114 212 INFORMS Stabilizing Customer Abandonment in
One billion+ terminals in voice network alone
 Traffic Engineering Traffic Engineering One billion+ terminals in voice networ alone Plus data, video, fax, finance, etc. Imagine all users want service simultaneously its not even nearly possible (despite
Traffic Engineering Traffic Engineering One billion+ terminals in voice networ alone Plus data, video, fax, finance, etc. Imagine all users want service simultaneously its not even nearly possible (despite
Design, staffing and control of large service systems: The case of a single customer class and multiple server types. April 2, 2004 DRAFT.
 Design, staffing and control of large service systems: The case of a single customer class and multiple server types. Mor Armony 1 Avishai Mandelbaum 2 April 2, 2004 DRAFT Abstract Motivated by modern
Design, staffing and control of large service systems: The case of a single customer class and multiple server types. Mor Armony 1 Avishai Mandelbaum 2 April 2, 2004 DRAFT Abstract Motivated by modern
COMP9334: Capacity Planning of Computer Systems and Networks
 COMP9334: Capacity Planning of Computer Systems and Networks Week 2: Operational analysis Lecturer: Prof. Sanjay Jha NETWORKS RESEARCH GROUP, CSE, UNSW Operational analysis Operational: Collect performance
COMP9334: Capacity Planning of Computer Systems and Networks Week 2: Operational analysis Lecturer: Prof. Sanjay Jha NETWORKS RESEARCH GROUP, CSE, UNSW Operational analysis Operational: Collect performance
Congestion Equilibrium for Differentiated Service Classes Richard T. B. Ma
 Congestion Equilibrium for Differentiated Service Classes Richard T. B. Ma School of Computing National University of Singapore Allerton Conference 2011 Outline Characterize Congestion Equilibrium Modeling
Congestion Equilibrium for Differentiated Service Classes Richard T. B. Ma School of Computing National University of Singapore Allerton Conference 2011 Outline Characterize Congestion Equilibrium Modeling
Non Markovian Queues (contd.)
 MODULE 7: RENEWAL PROCESSES 29 Lecture 5 Non Markovian Queues (contd) For the case where the service time is constant, V ar(b) = 0, then the P-K formula for M/D/ queue reduces to L s = ρ + ρ 2 2( ρ) where
MODULE 7: RENEWAL PROCESSES 29 Lecture 5 Non Markovian Queues (contd) For the case where the service time is constant, V ar(b) = 0, then the P-K formula for M/D/ queue reduces to L s = ρ + ρ 2 2( ρ) where
What You Should Know About Queueing Models To Set Staffing Requirements in Service Systems
 What You Should Know About Queueing Models To Set Staffing Requirements in Service Systems by Ward Whitt Department of Industrial Engineering and Operations Research Columbia University 304 S. W. Mudd
What You Should Know About Queueing Models To Set Staffing Requirements in Service Systems by Ward Whitt Department of Industrial Engineering and Operations Research Columbia University 304 S. W. Mudd
CS 798: Homework Assignment 3 (Queueing Theory)
 1.0 Little s law Assigned: October 6, 009 Patients arriving to the emergency room at the Grand River Hospital have a mean waiting time of three hours. It has been found that, averaged over the period of
1.0 Little s law Assigned: October 6, 009 Patients arriving to the emergency room at the Grand River Hospital have a mean waiting time of three hours. It has been found that, averaged over the period of
A Fluid Approximation for Service Systems Responding to Unexpected Overloads
 OPERATIONS RESEARCH Vol. 59, No. 5, September October 2011, pp. 1159 1170 issn 0030-364X eissn 1526-5463 11 5905 1159 http://dx.doi.org/10.1287/opre.1110.0985 2011 INFORMS A Fluid Approximation for Service
OPERATIONS RESEARCH Vol. 59, No. 5, September October 2011, pp. 1159 1170 issn 0030-364X eissn 1526-5463 11 5905 1159 http://dx.doi.org/10.1287/opre.1110.0985 2011 INFORMS A Fluid Approximation for Service
Wait-Time Predictors for Customer Service Systems With Time-Varying Demand and Capacity
 Submitted to Operations Research manuscript (Please, provide the mansucript number!) Wait-Time Predictors for Customer Service Systems With Time-Varying Demand and Capacity Rouba Ibrahim, Ward Whitt Department
Submitted to Operations Research manuscript (Please, provide the mansucript number!) Wait-Time Predictors for Customer Service Systems With Time-Varying Demand and Capacity Rouba Ibrahim, Ward Whitt Department
A Fluid Approximation for Service Systems Responding to Unexpected Overloads
 Submitted to Operations Research manuscript 28-9-55.R2, Longer Online Version 6/28/1 A Fluid Approximation for Service Systems Responding to Unexpected Overloads Ohad Perry Centrum Wiskunde & Informatica
Submitted to Operations Research manuscript 28-9-55.R2, Longer Online Version 6/28/1 A Fluid Approximation for Service Systems Responding to Unexpected Overloads Ohad Perry Centrum Wiskunde & Informatica
Since D has an exponential distribution, E[D] = 0.09 years. Since {A(t) : t 0} is a Poisson process with rate λ = 10, 000, A(0.
![Since D has an exponential distribution, E[D] = 0.09 years. Since {A(t) : t 0} is a Poisson process with rate λ = 10, 000, A(0. Since D has an exponential distribution, E[D] = 0.09 years. Since {A(t) : t 0} is a Poisson process with rate λ = 10, 000, A(0.](/thumbs/95/124116804.jpg) IEOR 46: Introduction to Operations Research: Stochastic Models Chapters 5-6 in Ross, Thursday, April, 4:5-5:35pm SOLUTIONS to Second Midterm Exam, Spring 9, Open Book: but only the Ross textbook, the
IEOR 46: Introduction to Operations Research: Stochastic Models Chapters 5-6 in Ross, Thursday, April, 4:5-5:35pm SOLUTIONS to Second Midterm Exam, Spring 9, Open Book: but only the Ross textbook, the
Dynamic Atomic Congestion Games with Seasonal Flows
 Dynamic Atomic Congestion Games with Seasonal Flows Marc Schröder Marco Scarsini, Tristan Tomala Maastricht University Department of Quantitative Economics Scarsini, Schröder, Tomala Dynamic Atomic Congestion
Dynamic Atomic Congestion Games with Seasonal Flows Marc Schröder Marco Scarsini, Tristan Tomala Maastricht University Department of Quantitative Economics Scarsini, Schröder, Tomala Dynamic Atomic Congestion
Motivated by models of tenant assignment in public housing, we study approximating deterministic fluid
 MANAGEMENT SCIENCE Vol. 54, No. 8, August 2008, pp. 1513 1527 issn 0025-1909 eissn 1526-5501 08 5408 1513 informs doi 10.1287/mnsc.1080.0868 2008 INFORMS Fluid Models for Overloaded Multiclass Many-Server
MANAGEMENT SCIENCE Vol. 54, No. 8, August 2008, pp. 1513 1527 issn 0025-1909 eissn 1526-5501 08 5408 1513 informs doi 10.1287/mnsc.1080.0868 2008 INFORMS Fluid Models for Overloaded Multiclass Many-Server
Queueing Review. Christos Alexopoulos and Dave Goldsman 10/6/16. (mostly from BCNN) Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA, USA
 1 / 24 Queueing Review (mostly from BCNN) Christos Alexopoulos and Dave Goldsman Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA, USA 10/6/16 2 / 24 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Queueing Notation 3 Transient
1 / 24 Queueing Review (mostly from BCNN) Christos Alexopoulos and Dave Goldsman Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA, USA 10/6/16 2 / 24 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Queueing Notation 3 Transient
BRAVO for QED Queues
 1 BRAVO for QED Queues Yoni Nazarathy, The University of Queensland Joint work with Daryl J. Daley, The University of Melbourne, Johan van Leeuwaarden, EURANDOM, Eindhoven University of Technology. Applied
1 BRAVO for QED Queues Yoni Nazarathy, The University of Queensland Joint work with Daryl J. Daley, The University of Melbourne, Johan van Leeuwaarden, EURANDOM, Eindhoven University of Technology. Applied
Overflow Networks: Approximations and Implications to Call-Center Outsourcing
 Overflow Networks: Approximations and Implications to Call-Center Outsourcing Itai Gurvich (Northwestern University) Joint work with Ohad Perry (CWI) Call Centers with Overflow λ 1 λ 2 Source of complexity:
Overflow Networks: Approximations and Implications to Call-Center Outsourcing Itai Gurvich (Northwestern University) Joint work with Ohad Perry (CWI) Call Centers with Overflow λ 1 λ 2 Source of complexity:
On the Partitioning of Servers in Queueing Systems during Rush Hour
 On the Partitioning of Servers in Queueing Systems during Rush Hour This paper is motivated by two phenomena observed in many queueing systems in practice. The first is the partitioning of server capacity
On the Partitioning of Servers in Queueing Systems during Rush Hour This paper is motivated by two phenomena observed in many queueing systems in practice. The first is the partitioning of server capacity
We study a capacity sizing problem in a service system that is modeled as a single-class queue with multiple
 MANAGEMENT SCIENCE Vol. 56, No. 1, October 21, pp. 1668 1686 issn 25-199 eissn 1526-551 1 561 1668 informs doi 1.1287/mnsc.11.123 21 INFORMS Capacity Sizing Under Parameter Uncertainty: Safety Staffing
MANAGEMENT SCIENCE Vol. 56, No. 1, October 21, pp. 1668 1686 issn 25-199 eissn 1526-551 1 561 1668 informs doi 1.1287/mnsc.11.123 21 INFORMS Capacity Sizing Under Parameter Uncertainty: Safety Staffing
Figure 10.1: Recording when the event E occurs
 10 Poisson Processes Let T R be an interval. A family of random variables {X(t) ; t T} is called a continuous time stochastic process. We often consider T = [0, 1] and T = [0, ). As X(t) is a random variable
10 Poisson Processes Let T R be an interval. A family of random variables {X(t) ; t T} is called a continuous time stochastic process. We often consider T = [0, 1] and T = [0, ). As X(t) is a random variable
Session-Based Queueing Systems
 Session-Based Queueing Systems Modelling, Simulation, and Approximation Jeroen Horters Supervisor VU: Sandjai Bhulai Executive Summary Companies often offer services that require multiple steps on the
Session-Based Queueing Systems Modelling, Simulation, and Approximation Jeroen Horters Supervisor VU: Sandjai Bhulai Executive Summary Companies often offer services that require multiple steps on the
Sandwich shop : a queuing net work with finite disposable resources queue and infinite resources queue
 Sandwich shop : a queuing net work with finite disposable resources queue and infinite resources queue Final project for ISYE 680: Queuing systems and Applications Hongtan Sun May 5, 05 Introduction As
Sandwich shop : a queuing net work with finite disposable resources queue and infinite resources queue Final project for ISYE 680: Queuing systems and Applications Hongtan Sun May 5, 05 Introduction As
STRATEGIC EQUILIBRIUM VS. GLOBAL OPTIMUM FOR A PAIR OF COMPETING SERVERS
 R u t c o r Research R e p o r t STRATEGIC EQUILIBRIUM VS. GLOBAL OPTIMUM FOR A PAIR OF COMPETING SERVERS Benjamin Avi-Itzhak a Uriel G. Rothblum c Boaz Golany b RRR 33-2005, October, 2005 RUTCOR Rutgers
R u t c o r Research R e p o r t STRATEGIC EQUILIBRIUM VS. GLOBAL OPTIMUM FOR A PAIR OF COMPETING SERVERS Benjamin Avi-Itzhak a Uriel G. Rothblum c Boaz Golany b RRR 33-2005, October, 2005 RUTCOR Rutgers
Link Models for Packet Switching
 Link Models for Packet Switching To begin our study of the performance of communications networks, we will study a model of a single link in a message switched network. The important feature of this model
Link Models for Packet Switching To begin our study of the performance of communications networks, we will study a model of a single link in a message switched network. The important feature of this model
Stabilizing Customer Abandonment in Many-Server Queues with Time-Varying Arrivals
 Submitted to Operations Research manuscript OPRE-29-6-259; OPRE-211-12-597.R1 Stabilizing Customer Abandonment in Many-Server Queues with -Varying Arrivals Yunan Liu Department of Industrial Engineering,
Submitted to Operations Research manuscript OPRE-29-6-259; OPRE-211-12-597.R1 Stabilizing Customer Abandonment in Many-Server Queues with -Varying Arrivals Yunan Liu Department of Industrial Engineering,
STABILIZING PERFORMANCE IN NETWORKS OF QUEUES WITH TIME-VARYING ARRIVAL RATES
 Probability in the Engineering and Informational Sciences, 28, 24, 49 449. doi:.7/s2699648484 STABILIZING PERFORMANCE IN NETWORKS OF QUEUES WITH TIME-VARYING ARRIVAL RATES YUNAN LIU AND WARD WHITT Department
Probability in the Engineering and Informational Sciences, 28, 24, 49 449. doi:.7/s2699648484 STABILIZING PERFORMANCE IN NETWORKS OF QUEUES WITH TIME-VARYING ARRIVAL RATES YUNAN LIU AND WARD WHITT Department
Economy of Scale in Multiserver Service Systems: A Retrospective. Ward Whitt. IEOR Department. Columbia University
 Economy of Scale in Multiserver Service Systems: A Retrospective Ward Whitt IEOR Department Columbia University Ancient Relics A. K. Erlang (1924) On the rational determination of the number of circuits.
Economy of Scale in Multiserver Service Systems: A Retrospective Ward Whitt IEOR Department Columbia University Ancient Relics A. K. Erlang (1924) On the rational determination of the number of circuits.
Scheduling I. Today. Next Time. ! Introduction to scheduling! Classical algorithms. ! Advanced topics on scheduling
 Scheduling I Today! Introduction to scheduling! Classical algorithms Next Time! Advanced topics on scheduling Scheduling out there! You are the manager of a supermarket (ok, things don t always turn out
Scheduling I Today! Introduction to scheduling! Classical algorithms Next Time! Advanced topics on scheduling Scheduling out there! You are the manager of a supermarket (ok, things don t always turn out
Nitzan Carmeli. MSc Advisors: Prof. Haya Kaspi, Prof. Avishai Mandelbaum Empirical Support: Dr. Galit Yom-Tov
 Nitzan Carmeli MSc Advisors: Prof. Haya Kaspi, Prof. Avishai Mandelbaum Empirical Support: Dr. Galit Yom-Tov Industrial Engineering and Management Technion 23.06.2014 1 Introduction o Interactive Voice
Nitzan Carmeli MSc Advisors: Prof. Haya Kaspi, Prof. Avishai Mandelbaum Empirical Support: Dr. Galit Yom-Tov Industrial Engineering and Management Technion 23.06.2014 1 Introduction o Interactive Voice
Advanced Computer Networks Lecture 3. Models of Queuing
 Advanced Computer Networks Lecture 3. Models of Queuing Husheng Li Min Kao Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University of Tennessee, Knoxville Spring, 2016 1/13 Terminology of
Advanced Computer Networks Lecture 3. Models of Queuing Husheng Li Min Kao Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University of Tennessee, Knoxville Spring, 2016 1/13 Terminology of
Class 11 Non-Parametric Models of a Service System; GI/GI/1, GI/GI/n: Exact & Approximate Analysis.
 Service Engineering Class 11 Non-Parametric Models of a Service System; GI/GI/1, GI/GI/n: Exact & Approximate Analysis. G/G/1 Queue: Virtual Waiting Time (Unfinished Work). GI/GI/1: Lindley s Equations
Service Engineering Class 11 Non-Parametric Models of a Service System; GI/GI/1, GI/GI/n: Exact & Approximate Analysis. G/G/1 Queue: Virtual Waiting Time (Unfinished Work). GI/GI/1: Lindley s Equations
Queueing Review. Christos Alexopoulos and Dave Goldsman 10/25/17. (mostly from BCNN) Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA, USA
 1 / 26 Queueing Review (mostly from BCNN) Christos Alexopoulos and Dave Goldsman Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA, USA 10/25/17 2 / 26 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Queueing Notation 3 Transient
1 / 26 Queueing Review (mostly from BCNN) Christos Alexopoulos and Dave Goldsman Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA, USA 10/25/17 2 / 26 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Queueing Notation 3 Transient
CPSC 531: System Modeling and Simulation. Carey Williamson Department of Computer Science University of Calgary Fall 2017
 CPSC 531: System Modeling and Simulation Carey Williamson Department of Computer Science University of Calgary Fall 2017 Quote of the Day A person with one watch knows what time it is. A person with two
CPSC 531: System Modeling and Simulation Carey Williamson Department of Computer Science University of Calgary Fall 2017 Quote of the Day A person with one watch knows what time it is. A person with two
The Social Value of Credible Public Information
 The Social Value of Credible Public Information Ercan Karadas NYU September, 2017 Introduction Model Analysis MOTIVATION This paper is motivated by the paper Social Value of Public Information, Morris
The Social Value of Credible Public Information Ercan Karadas NYU September, 2017 Introduction Model Analysis MOTIVATION This paper is motivated by the paper Social Value of Public Information, Morris
Classical Queueing Models.
 Sergey Zeltyn January 2005 STAT 99. Service Engineering. The Wharton School. University of Pennsylvania. Based on: Classical Queueing Models. Mandelbaum A. Service Engineering course, Technion. http://iew3.technion.ac.il/serveng2005w
Sergey Zeltyn January 2005 STAT 99. Service Engineering. The Wharton School. University of Pennsylvania. Based on: Classical Queueing Models. Mandelbaum A. Service Engineering course, Technion. http://iew3.technion.ac.il/serveng2005w
Wars of Attrition with Budget Constraints
 Wars of Attrition with Budget Constraints Gagan Ghosh Bingchao Huangfu Heng Liu October 19, 2017 (PRELIMINARY AND INCOMPLETE: COMMENTS WELCOME) Abstract We study wars of attrition between two bidders who
Wars of Attrition with Budget Constraints Gagan Ghosh Bingchao Huangfu Heng Liu October 19, 2017 (PRELIMINARY AND INCOMPLETE: COMMENTS WELCOME) Abstract We study wars of attrition between two bidders who
Lecture 9: Dynamics in Load Balancing
 Computational Game Theory Spring Semester, 2003/4 Lecture 9: Dynamics in Load Balancing Lecturer: Yishay Mansour Scribe: Anat Axelrod, Eran Werner 9.1 Lecture Overview In this lecture we consider dynamics
Computational Game Theory Spring Semester, 2003/4 Lecture 9: Dynamics in Load Balancing Lecturer: Yishay Mansour Scribe: Anat Axelrod, Eran Werner 9.1 Lecture Overview In this lecture we consider dynamics
Data analysis and stochastic modeling
 Data analysis and stochastic modeling Lecture 7 An introduction to queueing theory Guillaume Gravier guillaume.gravier@irisa.fr with a lot of help from Paul Jensen s course http://www.me.utexas.edu/ jensen/ormm/instruction/powerpoint/or_models_09/14_queuing.ppt
Data analysis and stochastic modeling Lecture 7 An introduction to queueing theory Guillaume Gravier guillaume.gravier@irisa.fr with a lot of help from Paul Jensen s course http://www.me.utexas.edu/ jensen/ormm/instruction/powerpoint/or_models_09/14_queuing.ppt
16:330:543 Communication Networks I Midterm Exam November 7, 2005
 l l l l l l l l 1 3 np n = ρ 1 ρ = λ µ λ. n= T = E[N] = 1 λ µ λ = 1 µ 1. 16:33:543 Communication Networks I Midterm Exam November 7, 5 You have 16 minutes to complete this four problem exam. If you know
l l l l l l l l 1 3 np n = ρ 1 ρ = λ µ λ. n= T = E[N] = 1 λ µ λ = 1 µ 1. 16:33:543 Communication Networks I Midterm Exam November 7, 5 You have 16 minutes to complete this four problem exam. If you know
ISyE 6644 Fall 2014 Test #2 Solutions (revised 11/7/16)
 1 NAME ISyE 6644 Fall 2014 Test #2 Solutions (revised 11/7/16) This test is 85 minutes. You are allowed two cheat sheets. Good luck! 1. Some short answer questions to get things going. (a) Consider the
1 NAME ISyE 6644 Fall 2014 Test #2 Solutions (revised 11/7/16) This test is 85 minutes. You are allowed two cheat sheets. Good luck! 1. Some short answer questions to get things going. (a) Consider the
Service-Level Differentiation in Many-Server Service Systems Via Queue-Ratio Routing
 Submitted to Operations Research manuscript (Please, provide the mansucript number!) Service-Level Differentiation in Many-Server Service Systems Via Queue-Ratio Routing Itay Gurvich Kellogg School of
Submitted to Operations Research manuscript (Please, provide the mansucript number!) Service-Level Differentiation in Many-Server Service Systems Via Queue-Ratio Routing Itay Gurvich Kellogg School of
Allocating Resources, in the Future
 Allocating Resources, in the Future Sid Banerjee School of ORIE May 3, 2018 Simons Workshop on Mathematical and Computational Challenges in Real-Time Decision Making online resource allocation: basic model......
Allocating Resources, in the Future Sid Banerjee School of ORIE May 3, 2018 Simons Workshop on Mathematical and Computational Challenges in Real-Time Decision Making online resource allocation: basic model......
Queueing Systems: Lecture 3. Amedeo R. Odoni October 18, Announcements
 Queueing Systems: Lecture 3 Amedeo R. Odoni October 18, 006 Announcements PS #3 due tomorrow by 3 PM Office hours Odoni: Wed, 10/18, :30-4:30; next week: Tue, 10/4 Quiz #1: October 5, open book, in class;
Queueing Systems: Lecture 3 Amedeo R. Odoni October 18, 006 Announcements PS #3 due tomorrow by 3 PM Office hours Odoni: Wed, 10/18, :30-4:30; next week: Tue, 10/4 Quiz #1: October 5, open book, in class;
Equilibrium solutions in the observable M/M/1 queue with overtaking
 TEL-AVIV UNIVERSITY RAYMOND AND BEVERLY SACKLER FACULTY OF EXACT SCIENCES SCHOOL OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES, DEPARTMENT OF STATISTICS AND OPERATION RESEARCH Equilibrium solutions in the observable M/M/ queue
TEL-AVIV UNIVERSITY RAYMOND AND BEVERLY SACKLER FACULTY OF EXACT SCIENCES SCHOOL OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES, DEPARTMENT OF STATISTICS AND OPERATION RESEARCH Equilibrium solutions in the observable M/M/ queue
FCFS Infinite Bipartite Matching with Applications
 FF Infinite Bipartite Matching with Applications Workshop on ongestion Games, IM, NU ingapore December 2015 Gideon Weiss University of Haifa urvey of work since 2007, with Ed Kaplan, Rene aldentey, Ivo
FF Infinite Bipartite Matching with Applications Workshop on ongestion Games, IM, NU ingapore December 2015 Gideon Weiss University of Haifa urvey of work since 2007, with Ed Kaplan, Rene aldentey, Ivo
Staffing Call-Centers With Uncertain Demand Forecasts: A Chance-Constrained Optimization Approach
 Staffing Call-Centers With Uncertain Demand Forecasts: A Chance-Constrained Optimization Approach Itai Gurvich James Luedtke Tolga Tezcan May 25, 2009 Abstract We consider the problem of staffing large-scale
Staffing Call-Centers With Uncertain Demand Forecasts: A Chance-Constrained Optimization Approach Itai Gurvich James Luedtke Tolga Tezcan May 25, 2009 Abstract We consider the problem of staffing large-scale
A multi-class fluid model for a contact center with skill-based routing
 Int. J. Electron. Commun. (AEÜ) ( ) www.elsevier.de/aeue A multi-class fluid model for a contact center with skill-based routing Ward Whitt Department of Industrial Engineering and Operations Research,
Int. J. Electron. Commun. (AEÜ) ( ) www.elsevier.de/aeue A multi-class fluid model for a contact center with skill-based routing Ward Whitt Department of Industrial Engineering and Operations Research,
Solutions to Homework Discrete Stochastic Processes MIT, Spring 2011
 Exercise 6.5: Solutions to Homework 0 6.262 Discrete Stochastic Processes MIT, Spring 20 Consider the Markov process illustrated below. The transitions are labelled by the rate q ij at which those transitions
Exercise 6.5: Solutions to Homework 0 6.262 Discrete Stochastic Processes MIT, Spring 20 Consider the Markov process illustrated below. The transitions are labelled by the rate q ij at which those transitions
Computer Systems Modelling
 Computer Systems Modelling Computer Laboratory Computer Science Tripos, Part II Lent Term 2010/11 R. J. Gibbens Problem sheet William Gates Building 15 JJ Thomson Avenue Cambridge CB3 0FD http://www.cl.cam.ac.uk/
Computer Systems Modelling Computer Laboratory Computer Science Tripos, Part II Lent Term 2010/11 R. J. Gibbens Problem sheet William Gates Building 15 JJ Thomson Avenue Cambridge CB3 0FD http://www.cl.cam.ac.uk/
Routing and Staffing when Servers are Strategic
 Routing and Staffing when Servers are Strategic Ragavendran Gopalakrishnan Department of Electrical, Computer, and Energy Engineering, University of Colorado at Boulder, Boulder, CO 80309, raga@colorado.edu
Routing and Staffing when Servers are Strategic Ragavendran Gopalakrishnan Department of Electrical, Computer, and Energy Engineering, University of Colorado at Boulder, Boulder, CO 80309, raga@colorado.edu
We consider a call center model with m input flows and r pools of agents; the m-vector of instantaneous
 MANUFACTURING & SERVICE OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT Vol. 7, No. 1, Winter 2005, pp. 20 36 issn 1523-4614 eissn 1526-5498 05 0701 0020 informs doi 10.1287/msom.1040.0052 2005 INFORMS A Method for Staffing Large
MANUFACTURING & SERVICE OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT Vol. 7, No. 1, Winter 2005, pp. 20 36 issn 1523-4614 eissn 1526-5498 05 0701 0020 informs doi 10.1287/msom.1040.0052 2005 INFORMS A Method for Staffing Large
Basics of Game Theory
 Basics of Game Theory Giacomo Bacci and Luca Sanguinetti Department of Information Engineering University of Pisa, Pisa, Italy {giacomo.bacci,luca.sanguinetti}@iet.unipi.it April - May, 2010 G. Bacci and
Basics of Game Theory Giacomo Bacci and Luca Sanguinetti Department of Information Engineering University of Pisa, Pisa, Italy {giacomo.bacci,luca.sanguinetti}@iet.unipi.it April - May, 2010 G. Bacci and
LIMITS FOR QUEUES AS THE WAITING ROOM GROWS. Bell Communications Research AT&T Bell Laboratories Red Bank, NJ Murray Hill, NJ 07974
 LIMITS FOR QUEUES AS THE WAITING ROOM GROWS by Daniel P. Heyman Ward Whitt Bell Communications Research AT&T Bell Laboratories Red Bank, NJ 07701 Murray Hill, NJ 07974 May 11, 1988 ABSTRACT We study the
LIMITS FOR QUEUES AS THE WAITING ROOM GROWS by Daniel P. Heyman Ward Whitt Bell Communications Research AT&T Bell Laboratories Red Bank, NJ 07701 Murray Hill, NJ 07974 May 11, 1988 ABSTRACT We study the
Homework 1 - SOLUTION
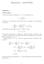 Homework - SOLUTION Problem M/M/ Queue ) Use the fact above to express π k, k > 0, as a function of π 0. π k = ( ) k λ π 0 µ 2) Using λ < µ and the fact that all π k s sum to, compute π 0 (as a function
Homework - SOLUTION Problem M/M/ Queue ) Use the fact above to express π k, k > 0, as a function of π 0. π k = ( ) k λ π 0 µ 2) Using λ < µ and the fact that all π k s sum to, compute π 0 (as a function
Random Walk on a Graph
 IOR 67: Stochastic Models I Second Midterm xam, hapters 3 & 4, November 2, 200 SOLUTIONS Justify your answers; show your work.. Random Walk on a raph (25 points) Random Walk on a raph 2 5 F B 3 3 2 Figure
IOR 67: Stochastic Models I Second Midterm xam, hapters 3 & 4, November 2, 200 SOLUTIONS Justify your answers; show your work.. Random Walk on a raph (25 points) Random Walk on a raph 2 5 F B 3 3 2 Figure
Time-dependent Performance Approximation of Truck Handling Operations at an Air Cargo Terminal
 Time-dependent Performance Approximation of Truck Handling Operations at an Air Cargo Terminal Gregor Selinka, Axel Franz, Raik Stolletz Chair of Production Management, Business School, University of Mannheim,
Time-dependent Performance Approximation of Truck Handling Operations at an Air Cargo Terminal Gregor Selinka, Axel Franz, Raik Stolletz Chair of Production Management, Business School, University of Mannheim,
The M/M/n+G Queue: Summary of Performance Measures
 The M/M/n+G Queue: Summary of Performance Measures Avishai Mandelbaum and Sergey Zeltyn Faculty of Industrial Engineering & Management Technion Haifa 32 ISRAEL emails: avim@tx.technion.ac.il zeltyn@ie.technion.ac.il
The M/M/n+G Queue: Summary of Performance Measures Avishai Mandelbaum and Sergey Zeltyn Faculty of Industrial Engineering & Management Technion Haifa 32 ISRAEL emails: avim@tx.technion.ac.il zeltyn@ie.technion.ac.il
NATCOR: Stochastic Modelling
 NATCOR: Stochastic Modelling Queueing Theory II Chris Kirkbride Management Science 2017 Overview of Today s Sessions I Introduction to Queueing Modelling II Multiclass Queueing Models III Queueing Control
NATCOR: Stochastic Modelling Queueing Theory II Chris Kirkbride Management Science 2017 Overview of Today s Sessions I Introduction to Queueing Modelling II Multiclass Queueing Models III Queueing Control
IEOR 6711: Stochastic Models I, Fall 2003, Professor Whitt. Solutions to Final Exam: Thursday, December 18.
 IEOR 6711: Stochastic Models I, Fall 23, Professor Whitt Solutions to Final Exam: Thursday, December 18. Below are six questions with several parts. Do as much as you can. Show your work. 1. Two-Pump Gas
IEOR 6711: Stochastic Models I, Fall 23, Professor Whitt Solutions to Final Exam: Thursday, December 18. Below are six questions with several parts. Do as much as you can. Show your work. 1. Two-Pump Gas
NANYANG TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY SEMESTER I EXAMINATION MH4702/MAS446/MTH437 Probabilistic Methods in OR
 NANYANG TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY SEMESTER I EXAMINATION 2013-201 MH702/MAS6/MTH37 Probabilistic Methods in OR December 2013 TIME ALLOWED: 2 HOURS INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES 1. This examination paper contains
NANYANG TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY SEMESTER I EXAMINATION 2013-201 MH702/MAS6/MTH37 Probabilistic Methods in OR December 2013 TIME ALLOWED: 2 HOURS INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES 1. This examination paper contains
BIRTH DEATH PROCESSES AND QUEUEING SYSTEMS
 BIRTH DEATH PROCESSES AND QUEUEING SYSTEMS Andrea Bobbio Anno Accademico 999-2000 Queueing Systems 2 Notation for Queueing Systems /λ mean time between arrivals S = /µ ρ = λ/µ N mean service time traffic
BIRTH DEATH PROCESSES AND QUEUEING SYSTEMS Andrea Bobbio Anno Accademico 999-2000 Queueing Systems 2 Notation for Queueing Systems /λ mean time between arrivals S = /µ ρ = λ/µ N mean service time traffic
Dynamic Call Center Routing Policies Using Call Waiting and Agent Idle Times
 MANUFACTURING & SERVICE OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT Vol. 00, No. 0, Xxxxx 0000, pp. 000 000 issn 1523-4614 eissn 1526-5498 00 0000 0001 INFORMS doi 10.1287/xxxx.0000.0000 c 0000 INFORMS Dynamic Call Center Routing
MANUFACTURING & SERVICE OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT Vol. 00, No. 0, Xxxxx 0000, pp. 000 000 issn 1523-4614 eissn 1526-5498 00 0000 0001 INFORMS doi 10.1287/xxxx.0000.0000 c 0000 INFORMS Dynamic Call Center Routing
NICTA Short Course. Network Analysis. Vijay Sivaraman. Day 1 Queueing Systems and Markov Chains. Network Analysis, 2008s2 1-1
 NICTA Short Course Network Analysis Vijay Sivaraman Day 1 Queueing Systems and Markov Chains Network Analysis, 2008s2 1-1 Outline Why a short course on mathematical analysis? Limited current course offering
NICTA Short Course Network Analysis Vijay Sivaraman Day 1 Queueing Systems and Markov Chains Network Analysis, 2008s2 1-1 Outline Why a short course on mathematical analysis? Limited current course offering
Strategic Dynamic Jockeying Between Two Parallel Queues
 Strategic Dynamic Jockeying Between Two Parallel Queues Amin Dehghanian 1 and Jeffrey P. Kharoufeh 2 Department of Industrial Engineering University of Pittsburgh 1048 Benedum Hall 3700 O Hara Street Pittsburgh,
Strategic Dynamic Jockeying Between Two Parallel Queues Amin Dehghanian 1 and Jeffrey P. Kharoufeh 2 Department of Industrial Engineering University of Pittsburgh 1048 Benedum Hall 3700 O Hara Street Pittsburgh,
