Chapter 1 Magnetic Materials
|
|
|
- Mervin Montgomery
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 1 Magnetic Materials Figures cited with the notation [RCO] Fig. X.Y are fro O Handley, Robert C. Modern Magnetic Materials: Principles and Applications. New York: Wiley-Interscience, Courtesy of John Wiley and Sons, Inc. Used with perission. Spring ter, 2004 Magnetic Materials
2 Bob O Handley This course is about agnetic aterials Understanding properties Fro ultidisciplinary perspectives: Physics, Cheistry, Electrical Engineering, Materials Science Selecting aterials for applications Designing aterials / properties for applications Materials science ( phase diagras, bonding) Cheical physics (electronic structure) Engineering new cobinations of aterials Spring ter, 2004 Magnetic Materials
3 Malaysia University of Science and Technology Progra: M.U.S.T. MIT Technology Developent Progra (TDP) working with Malaysia & Motorola to create elite private teaching and research university near Kuala Lupur, Malaysia Short courses, seinars, curriculu & research developent Graduate-level instruction, research Prof. Ridha Berriche in Malaysia Proote MUST-industry-governent ties MUST progra is distinct fro, but siilar in spirit, to Singapore/MIT, Argentina, back to early 60s, IIT, Kanpur (late Noran Dahl, Course II) Spring ter, 2004 Magnetic Materials
4 Magnetic Materials Ground rules A. Text Modern Magnetic Materials Principles and Applications, R.C. O Handley (Wiley, 2000); (Discounted at B. Grades Test (id ter) 20% Hoe works 20% Written assignent 40% Oral presentation 20% 05/11/04, 05/13/04 C. Lab exercises, easureents, basic properties and ore Spring ter, 2004 Magnetic Materials
5 Magnetic Materials Approach in text is inductive, Socratic INPUT fro you. A. Observations explanations, principles B. Free energy, iniization Doains, M-H Ch. 1-9 C. Applications to soft, hard, nanocrystalline aterials, transport, surfaces, agnetic recording Ch Read handouts, text; what do you find effective, what do you need? Suggest other topics for possible coverage? Spring ter, 2004 Magnetic Materials
6 Where are Magnetic Materials Used? Volue usage Iages reoved due to copyright considerations. Transforers and coputer disk drive. Dollar value [RCO] Fig Spring ter, 2004 Magnetic Materials
7 OBSERVATIONS OF MAGNETISM Field about wire [RCO] Fig. 1.1 Apére Solenoid [RCO] Fig. 1.2 Faraday [RCO] Fig. 1.3 We will ake these concepts quantitative and apply to aterials... Spring ter, 2004 Magnetic Materials
8 CONSTUTIVE RELATIONS Electric Polarization p =qd d q p P = P = χ E D = ε 0 E + P = ε 0 (1 + e p vol. χ e = n p )E = ε 0 ε r E ε E P Magnetic Polarization p = µ = agnetic oent, µ µ M = = n µ νol. M = agnetic oent density, or agnetization. Spring ter, 2004 Magnetic Materials
9 THREE MAGNETIC FIELDS: M, H, B 2 fields M = χh, χ is diensionless in MKS; M, H have sae units. H is field intensity, M is agnetization, oent density 3 rd field B = µ 0 (H + M ) = µ 0 (1 + χ) H = µ 0 µ H MKS r [B = H + 4 πm = (1 + 4 πχ)h ] cgs MAGNETIC POTENTIAL ENERGY: θ B µ U = µ B u = M B MKS µ H M H cgs [RCO] Fig. 1.4 Spring ter, 2004 Magnetic Materials
10 THREE MAGNETIC FIELDS, M, H, B Field source: Coupled fields: Maxwell Equations E = ρ ε B = 0 E = B t B = µ 0 J + µ 0 ε E t Faraday Apère B field lines do not eanate fro a agnetic charge Integral Forulas for source equations ρ = charge / volue, integrate over volue: E(x x )d 3 x = 1 ρ(x x )d 3 x, B d 3 ε 0 E Gauss Theore Gauss Theore E nda = 1 ρ(x x )d 3 x ε 0 Electric field lines eanate fro positive charge x = 0 B nda = 0 But there is no agnetic onopole source of B! Spring ter, 2004 Magnetic Materials B
11 Integral fors for COUPLED Maxwell Equations B = agnetic flux per unit area, and J = current per unit area, so integrate over area ( E) da = B da B da = µ Ý 0 J 0 da + µ 0 DdA t Stokes Theore E dl V = φ t Faraday s Law of induction: V = N B A N = No. of turns t B = φ A [RCO] Fig. A1.2 Stokes Theore B dl = µ 0 I Apère s Law: This is how agnetic fields are generated by currents. More on this Spring ter, 2004 Magnetic Materials
12 QUANTITATIVE current-field relations (Right-hand rules) FIELD OUTSIDE CURRENT-CARRYING WIRE B dl = µ 0 I [RCO] Fig. 1.6 B = µ 0 I 2πR for closed circular path 2πRB = µ 0 I (In a agnetic ediu, B includes icroscopic and acroscopic currents) I H = 2πR M H (H includes only acroscopic currents) φ B = A what area? Spring ter, 2004 Magnetic Materials
13 Alternate derivation: Integrate differential for in cylindrical coordinates: B R 1 [rb θ (r)]= µ 0 J r r (rbθ ) = µ 0 Jr dr r 0 RB θ (R) = µ 0JR 2 + C, 2 I J = 2 πr I B = µ 0 2πR +C C = 0 because B vanishes at R = µ 0 I dl r Biot-Savart for ore useful: db = 3 4π r dl I r Spring ter, 2004 Magnetic Materials
14 Filed inside Solenoid ( B) da = B dl = µ 0 J da = µ 0 NI sense of is RH rule, [RCO] Fig. 1.8 B NI out dl + B in dl = µ 0 NI B i = µ, H i = NI 0 l l, = 0 REVIEW N / l = # turns / length ( B)d 2 x = µ 0 Jd 2 x B dl = µ 0 J Field about wire B = µ 0 NI 2πR NI B = µ 0 Field inside solenoid Spring ter, 2004 Magnetic Materials
15 More on p, M. ORIGIN OF MAGNETISM IN MATTER Let s approxiate a aterial as a stack of electron orbits: Assue orbits are coplanar (M is saturated) and B = µ (H + M ) = µ 0 M 0 H ext = 0 Cobine solenoid equations with constitutive relation N M = vol. µ [RCO] Fig. 1.9 µ = IA = e ω πr 2 = 2 e B = µ NI = µ N µ µ = IA 0 0 l v Atoic agnetic 2 πr 0 v = 2E oents due to current 2π π r0 orbits ( l 0) Al (E 1s for hydrogen is 13.6 ev) Spring ter, 2004 Magnetic Materials
16 Nuerical consistency: er 0 er 0 2π 2 2 λ µ = v = λ = 2πr 0 in the Bohr odel e µ = = A 2 2 This is the Bohr agneton, µ Β, agnetic oent of one electron spin. A agnetic aterial has n = # / vol of these, so B = µ = 1.16T Observe: Fe: µ = 2.2 µ Β Ni: µ = 0.6 µ Β Spring ter, 2004 Magnetic Materials
17 Review B dl = µ 0 I µ 0 I B = 2πR Faraday s Law of B induction: V = N t A N = No. of turns NI B i = µ, H i = 0 l NI l, N / l = # turns / length Spring ter, 2004 Magnetic Materials
18 Review B = µ 0 (H + M ) = µ 0 (1 + χ) H = µ 0 µ H r (In a agnetic ediu, B includes icroscopic and acroscopic currents) M H Magnetic Polarization p = µ = agnetic oent, µ µ M = = n µ νol. M = agnetic oent density, or agnetization. µ = IA e µ = = A 2 2 NI N µ Fe: Β s = 2.2 Τ B = µ 0 = µ 0 l Al Ni: Β s = 0.6 Τ Spring ter, 2004 Magnetic Materials
19 Types of Magnetic Materials Weak Magnetis Ferroagnetis [RCO] Fig.1.11 [RCO] Fig Spring ter, 2004 Magnetic Materials
20 Magnetic Doains [RCO] Fig [RCO] Fig Calculate doain structures fro free energy expressions for shape, crystallography and stress Spring ter, 2004 Magnetic Materials
21 Technical Magnetis [RCO] Fig.1.14 Flux density: B = µh = µ 0 (H + M ) Pereability: µ = B H Magnetic Field: H = NI l Spring ter, 2004 Magnetic Materials
22 Suary Pereability: µ = B H Ferroagnetis Magnetic Field: Flux density: H = NI l B = µh = µ 0 (H M ) In vacuu: B = µ 0 H (Tesla) N M = vol. µ In aterial: B = µ 0 (H + M) = µ 0 (1+ χ)h = µh Spring ter, 2004 Magnetic Materials
Electromagnetic Waves
 Electroagnetic Waves Physics 4 Maxwell s Equations Maxwell s equations suarize the relationships between electric and agnetic fields. A ajor consequence of these equations is that an accelerating charge
Electroagnetic Waves Physics 4 Maxwell s Equations Maxwell s equations suarize the relationships between electric and agnetic fields. A ajor consequence of these equations is that an accelerating charge
Important Formulae & Basic concepts. Unit 3: CHAPTER 4 - MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF CURRENT AND MAGNETISM CHAPTER 5 MAGNETISM AND MATTER
 Iportant Forulae & Basic concepts Unit 3: CHAPTER 4 - MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF CURRENT AND MAGNETISM CHAPTER 5 MAGNETISM AND MATTER S. No. Forula Description 1. Magnetic field induction at a point due to current
Iportant Forulae & Basic concepts Unit 3: CHAPTER 4 - MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF CURRENT AND MAGNETISM CHAPTER 5 MAGNETISM AND MATTER S. No. Forula Description 1. Magnetic field induction at a point due to current
72. (30.2) Interaction between two parallel current carrying wires.
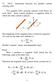 7. (3.) Interaction between two parallel current carrying wires. Two parallel wires carrying currents exert forces on each other. Each current produces a agnetic field in which the other current is placed.
7. (3.) Interaction between two parallel current carrying wires. Two parallel wires carrying currents exert forces on each other. Each current produces a agnetic field in which the other current is placed.
( ') ( ) 3. Magnetostatic Field Introduction
 3. Magnetostatic Field 3.. Introduction A agnetostatic field is a agnetic field produced by electric charge in peranent unifor oveent, i.e. in a peranent oveent with constant velocity. Any directed oveent
3. Magnetostatic Field 3.. Introduction A agnetostatic field is a agnetic field produced by electric charge in peranent unifor oveent, i.e. in a peranent oveent with constant velocity. Any directed oveent
Faraday's Law Warm Up
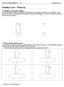 Faraday's Law-1 Faraday's Law War Up 1. Field lines of a peranent agnet For each peranent agnet in the diagra below draw several agnetic field lines (or a agnetic vector field if you prefer) corresponding
Faraday's Law-1 Faraday's Law War Up 1. Field lines of a peranent agnet For each peranent agnet in the diagra below draw several agnetic field lines (or a agnetic vector field if you prefer) corresponding
Louisiana State University Physics 2102, Exam 3 April 2nd, 2009.
 PRINT Your Name: Instructor: Louisiana State University Physics 2102, Exam 3 April 2nd, 2009. Please be sure to PRINT your name and class instructor above. The test consists of 4 questions (multiple choice),
PRINT Your Name: Instructor: Louisiana State University Physics 2102, Exam 3 April 2nd, 2009. Please be sure to PRINT your name and class instructor above. The test consists of 4 questions (multiple choice),
Magnetic Materials. The inductor Φ B = LI (Q = CV) = L I = N Φ. Power = VI = LI. Energy = Power dt = LIdI = 1 LI 2 = 1 NΦ B capacitor CV 2
 Magnetic Materials The inductor Φ B = LI (Q = CV) Φ B 1 B = L I E = (CGS) t t c t EdS = 1 ( BdS )= 1 Φ V EMF = N Φ B = L I t t c t B c t I V Φ B magnetic flux density V = L (recall I = C for the capacitor)
Magnetic Materials The inductor Φ B = LI (Q = CV) Φ B 1 B = L I E = (CGS) t t c t EdS = 1 ( BdS )= 1 Φ V EMF = N Φ B = L I t t c t B c t I V Φ B magnetic flux density V = L (recall I = C for the capacitor)
Dispersion. February 12, 2014
 Dispersion February 1, 014 In aterials, the dielectric constant and pereability are actually frequency dependent. This does not affect our results for single frequency odes, but when we have a superposition
Dispersion February 1, 014 In aterials, the dielectric constant and pereability are actually frequency dependent. This does not affect our results for single frequency odes, but when we have a superposition
Research and Experiments on Electromagnetic Field Induced by Two. Coaxial Solenoid Coils of Axially Mag-lev Driving Needle
 3rd International Conference on Mechatronics and Inforation Technology (ICMIT 16) Research and Experients on Electroagnetic Field Induced by Two Coaxial Solenoid Coils of Axially Mag-lev Driving Needle
3rd International Conference on Mechatronics and Inforation Technology (ICMIT 16) Research and Experients on Electroagnetic Field Induced by Two Coaxial Solenoid Coils of Axially Mag-lev Driving Needle
AP Physics C Electricity and Magnetism
 AP Physics C Electricity and Magnetism Course overview This is a calculus based course in physics. The course is the equivalent of an introductory engineering course in Physics. The main objective of the
AP Physics C Electricity and Magnetism Course overview This is a calculus based course in physics. The course is the equivalent of an introductory engineering course in Physics. The main objective of the
Stern-Gerlach Experiment
 Stern-Gerlach Experient HOE: The Physics of Bruce Harvey This is the experient that is said to prove that the electron has an intrinsic agnetic oent. Hydrogen like atos are projected in a bea through a
Stern-Gerlach Experient HOE: The Physics of Bruce Harvey This is the experient that is said to prove that the electron has an intrinsic agnetic oent. Hydrogen like atos are projected in a bea through a
Principles of Physics II
 Principles of Physics II J. M. Veal, Ph. D. version 18.05.4 Contents 1 Fluid Mechanics 3 1.1 Fluid pressure............................ 3 1. Buoyancy.............................. 3 1.3 Fluid flow..............................
Principles of Physics II J. M. Veal, Ph. D. version 18.05.4 Contents 1 Fluid Mechanics 3 1.1 Fluid pressure............................ 3 1. Buoyancy.............................. 3 1.3 Fluid flow..............................
Currents (1) Line charge λ (C/m) with velocity v : in time t, This constitutes a current I = λv (vector). Magnetic force on a segment of length dl is
 Magnetostatics 1. Currents 2. Relativistic origin of magnetic field 3. Biot-Savart law 4. Magnetic force between currents 5. Applications of Biot-Savart law 6. Ampere s law in differential form 7. Magnetic
Magnetostatics 1. Currents 2. Relativistic origin of magnetic field 3. Biot-Savart law 4. Magnetic force between currents 5. Applications of Biot-Savart law 6. Ampere s law in differential form 7. Magnetic
Magnetic Materials. 1. Magnetization 2. Potential and field of a magnetized object
 Magnetic Materials 1. Magnetization 2. Potential and field of a magnetized object 3. H-field 4. Susceptibility and permeability 5. Boundary conditions 6. Magnetic field energy and magnetic pressure 1 Magnetic
Magnetic Materials 1. Magnetization 2. Potential and field of a magnetized object 3. H-field 4. Susceptibility and permeability 5. Boundary conditions 6. Magnetic field energy and magnetic pressure 1 Magnetic
PAP342-Solid State Physics I Solution 09/10 Semester 2
 PAP342-Solid State Physics I Solution 09/10 Seester 2 Wang Shengtao May 10, 2010 Question 1. (a) A scheatic showing the position of the Feri level related to the (b) band edges can be found in [Kittel]
PAP342-Solid State Physics I Solution 09/10 Seester 2 Wang Shengtao May 10, 2010 Question 1. (a) A scheatic showing the position of the Feri level related to the (b) band edges can be found in [Kittel]
Physics 505 Fall 2005 Homework Assignment #7 Solutions
 Physics 505 Fall 005 Homework Assignment #7 Solutions Textbook problems: Ch. 4: 4.10 Ch. 5: 5.3, 5.6, 5.7 4.10 Two concentric conducting spheres of inner and outer radii a and b, respectively, carry charges
Physics 505 Fall 005 Homework Assignment #7 Solutions Textbook problems: Ch. 4: 4.10 Ch. 5: 5.3, 5.6, 5.7 4.10 Two concentric conducting spheres of inner and outer radii a and b, respectively, carry charges
Yell if you have any questions
 Class 36: Outline Hour 1: Concept Review / Overview PRS Questions Possible Exam Questions Hour : Sample Exam Yell if you have any questions P36-1 Before Starting All of your grades should now be posted
Class 36: Outline Hour 1: Concept Review / Overview PRS Questions Possible Exam Questions Hour : Sample Exam Yell if you have any questions P36-1 Before Starting All of your grades should now be posted
6.641 Electromagnetic Fields, Forces, and Motion
 MIT OpenCoureWare http://ocw.it.edu 6.64 Electroagnetic Field, Force, and Motion Spring 009 For inforation about citing thee aterial or our Ter of Ue, viit: http://ocw.it.edu/ter. 6.64 Electroagnetic Field,
MIT OpenCoureWare http://ocw.it.edu 6.64 Electroagnetic Field, Force, and Motion Spring 009 For inforation about citing thee aterial or our Ter of Ue, viit: http://ocw.it.edu/ter. 6.64 Electroagnetic Field,
Physics 202, Lecture 14
 Physics 202, Lecture 14 Today s Topics Sources of the Magnetic Field (Ch. 27) Review of Biot-Savart Law Ampere s Law Magnetism in Matter Magnetic Fields (Biot-Savart): Summary Current loop, distance on
Physics 202, Lecture 14 Today s Topics Sources of the Magnetic Field (Ch. 27) Review of Biot-Savart Law Ampere s Law Magnetism in Matter Magnetic Fields (Biot-Savart): Summary Current loop, distance on
Problem T1. Main sequence stars (11 points)
 Proble T1. Main sequence stars 11 points Part. Lifetie of Sun points i..7 pts Since the Sun behaves as a perfectly black body it s total radiation power can be expressed fro the Stefan- Boltzann law as
Proble T1. Main sequence stars 11 points Part. Lifetie of Sun points i..7 pts Since the Sun behaves as a perfectly black body it s total radiation power can be expressed fro the Stefan- Boltzann law as
Magnetic susceptibility measurements of transition metal containing compounds
 Magnetic susceptibility easureents of transition etal containing copounds Introduction: Measureents of agnetic properties have been used to characterize a wide range of systes fro oxygen, etallic alloys,
Magnetic susceptibility easureents of transition etal containing copounds Introduction: Measureents of agnetic properties have been used to characterize a wide range of systes fro oxygen, etallic alloys,
Preliminary Examination - Day 1 Thursday, August 10, 2017
 UNL - Department of Physics and Astronomy Preliminary Examination - Day Thursday, August, 7 This test covers the topics of Quantum Mechanics (Topic ) and Electrodynamics (Topic ). Each topic has 4 A questions
UNL - Department of Physics and Astronomy Preliminary Examination - Day Thursday, August, 7 This test covers the topics of Quantum Mechanics (Topic ) and Electrodynamics (Topic ). Each topic has 4 A questions
Dr. Naser Abu-Zaid; Lecture notes in electromagnetic theory 1; Referenced to Engineering electromagnetics by Hayt, 8 th edition 2012; Text Book
 Text Book Dr. Naser Abu-Zaid Page 1 9/4/2012 Course syllabus Electroagnetic 2 (63374) Seester Language Copulsory / Elective Prerequisites Course Contents Course Objectives Learning Outcoes and Copetences
Text Book Dr. Naser Abu-Zaid Page 1 9/4/2012 Course syllabus Electroagnetic 2 (63374) Seester Language Copulsory / Elective Prerequisites Course Contents Course Objectives Learning Outcoes and Copetences
Fundamental Constants
 Fundamental Constants Atomic Mass Unit u 1.660 540 2 10 10 27 kg 931.434 32 28 MeV c 2 Avogadro s number N A 6.022 136 7 36 10 23 (g mol) 1 Bohr magneton μ B 9.274 015 4(31) 10-24 J/T Bohr radius a 0 0.529
Fundamental Constants Atomic Mass Unit u 1.660 540 2 10 10 27 kg 931.434 32 28 MeV c 2 Avogadro s number N A 6.022 136 7 36 10 23 (g mol) 1 Bohr magneton μ B 9.274 015 4(31) 10-24 J/T Bohr radius a 0 0.529
VII. Magnetostatics. VII. Magnetostatics. 1. Discovery of Magnets. Thales of Miletos ( BC) (a) Loadstone: Magnetite. A.
 VII. Magnetostatics VII. Magnetostatics A. Magnetic Field Dr. Bill Pezzaglia B. Current is a source of Magnetic Field Updated 01Feb8 C. Electrodynaics A. Magnetic Field 1. Discovery of Magnets 4 1) Magnets
VII. Magnetostatics VII. Magnetostatics A. Magnetic Field Dr. Bill Pezzaglia B. Current is a source of Magnetic Field Updated 01Feb8 C. Electrodynaics A. Magnetic Field 1. Discovery of Magnets 4 1) Magnets
Effects of an Inhomogeneous Magnetic Field (E =0)
 Effects of an Inhoogeneous Magnetic Field (E =0 For soe purposes the otion of the guiding centers can be taken as a good approxiation of that of the particles. ut it ust be recognized that during the particle
Effects of an Inhoogeneous Magnetic Field (E =0 For soe purposes the otion of the guiding centers can be taken as a good approxiation of that of the particles. ut it ust be recognized that during the particle
Ch. 28: Sources of Magnetic Fields
 Ch. 28: Sources of Magnetic Fields Electric Currents Create Magnetic Fields A long, straight wire A current loop A solenoid Slide 24-14 Biot-Savart Law Current produces a magnetic field The Biot-Savart
Ch. 28: Sources of Magnetic Fields Electric Currents Create Magnetic Fields A long, straight wire A current loop A solenoid Slide 24-14 Biot-Savart Law Current produces a magnetic field The Biot-Savart
Physics 202, Lecture 14
 Physics 202, Lecture 14 Today s Topics Sources of the Magnetic Field (Ch 30) Review: The Biot-Savart Law The Ampere s Law Applications And Exercises of ampere s Law Straight line, Loop, Solenoid, Toroid
Physics 202, Lecture 14 Today s Topics Sources of the Magnetic Field (Ch 30) Review: The Biot-Savart Law The Ampere s Law Applications And Exercises of ampere s Law Straight line, Loop, Solenoid, Toroid
A NEW ELECTROSTATIC FIELD GEOMETRY. Jerry E. Bayles
 INTRODUCTION A NEW ELECTROSTATIC FIELD GEOMETRY by Jerry E Bayles The purpose of this paper is to present the electrostatic field in geoetrical ters siilar to that of the electrogravitational equation
INTRODUCTION A NEW ELECTROSTATIC FIELD GEOMETRY by Jerry E Bayles The purpose of this paper is to present the electrostatic field in geoetrical ters siilar to that of the electrogravitational equation
Physics 202, Lecture 14
 Physics 202, Lecture 14 Today s Topics Sources of the Magnetic Field (Ch. 30) Review: iot-savart Law, Ampere s Law Displacement Current: Ampere-Maxwell Law Magnetism in Matter Maxwell s Equations (prelude)
Physics 202, Lecture 14 Today s Topics Sources of the Magnetic Field (Ch. 30) Review: iot-savart Law, Ampere s Law Displacement Current: Ampere-Maxwell Law Magnetism in Matter Maxwell s Equations (prelude)
Physics Education Centre EXAMINATION. PHYS2016_Semester 2 Electromagnetism
 Venue Student Number Physics Education Centre EXAMINATION This paper is for ANU students. Examination Duration: Reading Time: 180 minutes 15 minutes Exam Conditions: Central Examination Students must return
Venue Student Number Physics Education Centre EXAMINATION This paper is for ANU students. Examination Duration: Reading Time: 180 minutes 15 minutes Exam Conditions: Central Examination Students must return
Chapter 28 Magnetic Fields Sources
 Chapter 28 Magnetic Fields Sources All known magnetic sources are due to magnetic dipoles and inherently macroscopic current sources or microscopic spins and magnetic moments Goals for Chapter 28 Study
Chapter 28 Magnetic Fields Sources All known magnetic sources are due to magnetic dipoles and inherently macroscopic current sources or microscopic spins and magnetic moments Goals for Chapter 28 Study
Moment of Inertia. Terminology. Definitions Moment of inertia of a body with mass, m, about the x axis: Transfer Theorem - 1. ( )dm. = y 2 + z 2.
 Terinology Moent of Inertia ME 202 Moent of inertia (MOI) = second ass oent Instead of ultiplying ass by distance to the first power (which gives the first ass oent), we ultiply it by distance to the second
Terinology Moent of Inertia ME 202 Moent of inertia (MOI) = second ass oent Instead of ultiplying ass by distance to the first power (which gives the first ass oent), we ultiply it by distance to the second
Ampere s Law. Outline. Objectives. BEE-Lecture Notes Anurag Srivastava 1
 Outline Introduce as an analogy to Gauss Law. Define. Applications of. Objectives Recognise to be analogous to Gauss Law. Recognise similar concepts: (1) draw an imaginary shape enclosing the current carrying
Outline Introduce as an analogy to Gauss Law. Define. Applications of. Objectives Recognise to be analogous to Gauss Law. Recognise similar concepts: (1) draw an imaginary shape enclosing the current carrying
Physics 8.02 Exam Two Mashup Spring 2003
 Physics 8.0 Exam Two Mashup Spring 003 Some (possibly useful) Relations: closedsurface da Q κ d = ε E A inside points from inside to outside b V = V V = E d s moving from a to b b a E d s = 0 V many point
Physics 8.0 Exam Two Mashup Spring 003 Some (possibly useful) Relations: closedsurface da Q κ d = ε E A inside points from inside to outside b V = V V = E d s moving from a to b b a E d s = 0 V many point
Physics 202, Lecture 13. Today s Topics. Magnetic Forces: Hall Effect (Ch. 27.8)
 Physics 202, Lecture 13 Today s Topics Magnetic Forces: Hall Effect (Ch. 27.8) Sources of the Magnetic Field (Ch. 28) B field of infinite wire Force between parallel wires Biot-Savart Law Examples: ring,
Physics 202, Lecture 13 Today s Topics Magnetic Forces: Hall Effect (Ch. 27.8) Sources of the Magnetic Field (Ch. 28) B field of infinite wire Force between parallel wires Biot-Savart Law Examples: ring,
Chapter 29 Solutions
 Chapter 29 Solutions 29.1 (a) up out of the page, since the charge is negative. (c) no deflection (d) into the page 29.2 At the equator, the Earth's agnetic field is horizontally north. Because an electron
Chapter 29 Solutions 29.1 (a) up out of the page, since the charge is negative. (c) no deflection (d) into the page 29.2 At the equator, the Earth's agnetic field is horizontally north. Because an electron
Electricity & Optics
 Physics 24100 Electricity & Optics Lecture 15 Chapter 27 sec. 3-5 Fall 2016 Semester Professor Koltick Magnetic Fields B = μ 0 4π I dl r r 2 = μ 0 4π I dl r r 3 B = μ 0 2I 4π R B = μ 0 2 IR 2 R 2 + z 2
Physics 24100 Electricity & Optics Lecture 15 Chapter 27 sec. 3-5 Fall 2016 Semester Professor Koltick Magnetic Fields B = μ 0 4π I dl r r 2 = μ 0 4π I dl r r 3 B = μ 0 2I 4π R B = μ 0 2 IR 2 R 2 + z 2
Chapter 28 Sources of Magnetic Field
 Chapter 28 Sources of Magnetic Field In this chapter we investigate the sources of magnetic field, in particular, the magnetic field produced by moving charges (i.e., currents), Ampere s Law is introduced
Chapter 28 Sources of Magnetic Field In this chapter we investigate the sources of magnetic field, in particular, the magnetic field produced by moving charges (i.e., currents), Ampere s Law is introduced
Electromagnetism Answers to Problem Set 9 Spring 2006
 Electromagnetism 70006 Answers to Problem et 9 pring 006. Jackson Prob. 5.: Reformulate the Biot-avart law in terms of the solid angle subtended at the point of observation by the current-carrying circuit.
Electromagnetism 70006 Answers to Problem et 9 pring 006. Jackson Prob. 5.: Reformulate the Biot-avart law in terms of the solid angle subtended at the point of observation by the current-carrying circuit.
MAKE SURE TA & TI STAMPS EVERY PAGE BEFORE YOU START
 Laboratory Section: Last Revised on Deceber 15, 2014 Partners Naes: Grade: EXPERIMENT 8 Electron Beas 0. Pre-Laboratory Work [2 pts] 1. Nae the 2 forces that are equated in order to derive the charge to
Laboratory Section: Last Revised on Deceber 15, 2014 Partners Naes: Grade: EXPERIMENT 8 Electron Beas 0. Pre-Laboratory Work [2 pts] 1. Nae the 2 forces that are equated in order to derive the charge to
Introduction to Robotics (CS223A) (Winter 2006/2007) Homework #5 solutions
 Introduction to Robotics (CS3A) Handout (Winter 6/7) Hoework #5 solutions. (a) Derive a forula that transfors an inertia tensor given in soe frae {C} into a new frae {A}. The frae {A} can differ fro frae
Introduction to Robotics (CS3A) Handout (Winter 6/7) Hoework #5 solutions. (a) Derive a forula that transfors an inertia tensor given in soe frae {C} into a new frae {A}. The frae {A} can differ fro frae
ELECTRO MAGNETIC FIELDS
 SET - 1 1. a) State and explain Gauss law in differential form and also list the limitations of Guess law. b) A square sheet defined by -2 x 2m, -2 y 2m lies in the = -2m plane. The charge density on the
SET - 1 1. a) State and explain Gauss law in differential form and also list the limitations of Guess law. b) A square sheet defined by -2 x 2m, -2 y 2m lies in the = -2m plane. The charge density on the
Yell if you have any questions
 Class 36: Outline Hour 1: Concept Review / Overview PRS Questions Possible Exam Questions Hour : Sample Exam Yell if you have any questions P36-1 efore Starting All of your grades should now be posted
Class 36: Outline Hour 1: Concept Review / Overview PRS Questions Possible Exam Questions Hour : Sample Exam Yell if you have any questions P36-1 efore Starting All of your grades should now be posted
Motion of Charges in Uniform E
 Motion of Charges in Unifor E and Fields Assue an ionized gas is acted upon by a unifor (but possibly tie-dependent) electric field E, and a unifor, steady agnetic field. These fields are assued to be
Motion of Charges in Unifor E and Fields Assue an ionized gas is acted upon by a unifor (but possibly tie-dependent) electric field E, and a unifor, steady agnetic field. These fields are assued to be
Lecture contents. Magnetic properties Diamagnetism Band paramagnetism Atomic paramagnetism. NNSE508 / NENG452 Lecture #14
 1 Lecture contents agnetic properties Diaagnetis and paraagnetis Atoic paraagnetis NNSE58 / NENG45 Lecture #14 agnetic units H /r V s 1 Wb T 1 T Wb T 1H A A Fro Treolet de Lacheisserie, 5 NNSE58 / NENG45
1 Lecture contents agnetic properties Diaagnetis and paraagnetis Atoic paraagnetis NNSE58 / NENG45 Lecture #14 agnetic units H /r V s 1 Wb T 1 T Wb T 1H A A Fro Treolet de Lacheisserie, 5 NNSE58 / NENG45
Handout 8: Sources of magnetic field. Magnetic field of moving charge
 1 Handout 8: Sources of magnetic field Magnetic field of moving charge Moving charge creates magnetic field around it. In Fig. 1, charge q is moving at constant velocity v. The magnetic field at point
1 Handout 8: Sources of magnetic field Magnetic field of moving charge Moving charge creates magnetic field around it. In Fig. 1, charge q is moving at constant velocity v. The magnetic field at point
Definition of Work, The basics
 Physics 07 Lecture 16 Lecture 16 Chapter 11 (Work) v Eploy conservative and non-conservative forces v Relate force to potential energy v Use the concept of power (i.e., energy per tie) Chapter 1 v Define
Physics 07 Lecture 16 Lecture 16 Chapter 11 (Work) v Eploy conservative and non-conservative forces v Relate force to potential energy v Use the concept of power (i.e., energy per tie) Chapter 1 v Define
Chapter 4: Hypothesis of Diffusion-Limited Growth
 Suary This section derives a useful equation to predict quantu dot size evolution under typical organoetallic synthesis conditions that are used to achieve narrow size distributions. Assuing diffusion-controlled
Suary This section derives a useful equation to predict quantu dot size evolution under typical organoetallic synthesis conditions that are used to achieve narrow size distributions. Assuing diffusion-controlled
Pearson Physics Level 30 Unit VI Forces and Fields: Chapter 12 Solutions
 Concept Check (top) Pearson Physics Level 30 Unit VI Forces and Fields: Chapter 12 Solutions Student Book page 583 Concept Check (botto) The north-seeking needle of a copass is attracted to what is called
Concept Check (top) Pearson Physics Level 30 Unit VI Forces and Fields: Chapter 12 Solutions Student Book page 583 Concept Check (botto) The north-seeking needle of a copass is attracted to what is called
In this chapter we will start the discussion on wave phenomena. We will study the following topics:
 Chapter 16 Waves I In this chapter we will start the discussion on wave phenoena. We will study the following topics: Types of waves Aplitude, phase, frequency, period, propagation speed of a wave Mechanical
Chapter 16 Waves I In this chapter we will start the discussion on wave phenoena. We will study the following topics: Types of waves Aplitude, phase, frequency, period, propagation speed of a wave Mechanical
(1) I have completed at least 50% of the reading and study-guide assignments associated with the lecture, as indicated on the course schedule.
 iclicker Quiz (1) I have completed at least 50% of the reading and study-guide assignments associated with the lecture, as indicated on the course schedule. a) True b) False Hint: pay attention to how
iclicker Quiz (1) I have completed at least 50% of the reading and study-guide assignments associated with the lecture, as indicated on the course schedule. a) True b) False Hint: pay attention to how
Exam 3 Solutions. 1. Which of the following statements is true about the LR circuit shown?
 PHY49 Spring 5 Prof. Darin Acosta Prof. Paul Avery April 4, 5 PHY49, Spring 5 Exa Solutions. Which of the following stateents is true about the LR circuit shown? It is (): () Just after the switch is closed
PHY49 Spring 5 Prof. Darin Acosta Prof. Paul Avery April 4, 5 PHY49, Spring 5 Exa Solutions. Which of the following stateents is true about the LR circuit shown? It is (): () Just after the switch is closed
Chapter 28 Sources of Magnetic Field
 Chapter 28 Sources of Magnetic Field In this chapter we investigate the sources of magnetic of magnetic field, in particular, the magnetic field produced by moving charges (i.e., currents). Ampere s Law
Chapter 28 Sources of Magnetic Field In this chapter we investigate the sources of magnetic of magnetic field, in particular, the magnetic field produced by moving charges (i.e., currents). Ampere s Law
Physics GRE: Electromagnetism. G. J. Loges 1. University of Rochester Dept. of Physics & Astronomy. xkcd.com/567/
 Physics GRE: Electromagnetism G. J. Loges University of Rochester Dept. of Physics & stronomy xkcd.com/567/ c Gregory Loges, 206 Contents Electrostatics 2 Magnetostatics 2 3 Method of Images 3 4 Lorentz
Physics GRE: Electromagnetism G. J. Loges University of Rochester Dept. of Physics & stronomy xkcd.com/567/ c Gregory Loges, 206 Contents Electrostatics 2 Magnetostatics 2 3 Method of Images 3 4 Lorentz
CHAPTER 4 TWO STANDARD SHORTCUTS USED TO TRANSFORM ELECTROMAGNETIC EQUATIONS 4.1 THE FREE-PARAMETER METHOD
 CHAPTER 4 TWO STANDARD SHORTCUTS USED TO TRANSFORM ELECTROMAGNETIC EQUATIONS The last several chapters have explained how the standard rules for changing units apply to electroagnetic physical quantities.
CHAPTER 4 TWO STANDARD SHORTCUTS USED TO TRANSFORM ELECTROMAGNETIC EQUATIONS The last several chapters have explained how the standard rules for changing units apply to electroagnetic physical quantities.
Electromagnetic Induction! March 11, 2014 Chapter 29 1
 Electromagnetic Induction! March 11, 2014 Chapter 29 1 Notes! Exam 4 next Tuesday Covers Chapters 27, 28, 29 in the book Magnetism, Magnetic Fields, Electromagnetic Induction Material from the week before
Electromagnetic Induction! March 11, 2014 Chapter 29 1 Notes! Exam 4 next Tuesday Covers Chapters 27, 28, 29 in the book Magnetism, Magnetic Fields, Electromagnetic Induction Material from the week before
8.1 Force Laws Hooke s Law
 8.1 Force Laws There are forces that don't change appreciably fro one instant to another, which we refer to as constant in tie, and forces that don't change appreciably fro one point to another, which
8.1 Force Laws There are forces that don't change appreciably fro one instant to another, which we refer to as constant in tie, and forces that don't change appreciably fro one point to another, which
Lecture 4: Charge in motor Dr. Anyuan Chen
 Lecture 4: Charge in motor Dr. Anyuan Chen Charges in motion (an electrical current) produce a magnetic field Magnetic field B generated by point charge q: B = μ 0 qv r 4π r 2 v r = v sin θ n n is a unit
Lecture 4: Charge in motor Dr. Anyuan Chen Charges in motion (an electrical current) produce a magnetic field Magnetic field B generated by point charge q: B = μ 0 qv r 4π r 2 v r = v sin θ n n is a unit
Causality and the Kramers Kronig relations
 Causality and the Kraers Kronig relations Causality describes the teporal relationship between cause and effect. A bell rings after you strike it, not before you strike it. This eans that the function
Causality and the Kraers Kronig relations Causality describes the teporal relationship between cause and effect. A bell rings after you strike it, not before you strike it. This eans that the function
Construction of the Electronic Angular Wave Functions and Probability Distributions of the Hydrogen Atom
 Construction of the Electronic Angular Wave Functions and Probability Distributions of the Hydrogen Ato Thoas S. Kuntzlean Mark Ellison John Tippin Departent of Cheistry Departent of Cheistry Departent
Construction of the Electronic Angular Wave Functions and Probability Distributions of the Hydrogen Ato Thoas S. Kuntzlean Mark Ellison John Tippin Departent of Cheistry Departent of Cheistry Departent
2.141 Modeling and Simulation of Dynamic Systems Assignment #2
 2.141 Modeling and Siulation of Dynaic Systes Assignent #2 Out: Wednesday Septeber 20, 2006 Due: Wednesday October 4, 2006 Proble 1 The sketch shows a highly siplified diagra of a dry-dock used in ship
2.141 Modeling and Siulation of Dynaic Systes Assignent #2 Out: Wednesday Septeber 20, 2006 Due: Wednesday October 4, 2006 Proble 1 The sketch shows a highly siplified diagra of a dry-dock used in ship
Model Fitting. CURM Background Material, Fall 2014 Dr. Doreen De Leon
 Model Fitting CURM Background Material, Fall 014 Dr. Doreen De Leon 1 Introduction Given a set of data points, we often want to fit a selected odel or type to the data (e.g., we suspect an exponential
Model Fitting CURM Background Material, Fall 014 Dr. Doreen De Leon 1 Introduction Given a set of data points, we often want to fit a selected odel or type to the data (e.g., we suspect an exponential
PY /005 Practice Test 1, 2004 Feb. 10
 PY 205-004/005 Practice Test 1, 2004 Feb. 10 Print nae Lab section I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this test. Sign ature: When you turn in the test (including forula page) you ust
PY 205-004/005 Practice Test 1, 2004 Feb. 10 Print nae Lab section I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this test. Sign ature: When you turn in the test (including forula page) you ust
Ch 30 - Sources of Magnetic Field
 Ch 30 - Sources of Magnetic Field Currents produce Magnetism? 1820, Hans Christian Oersted: moving charges produce a magnetic field. The direction of the field is determined using a RHR. Oersted (1820)
Ch 30 - Sources of Magnetic Field Currents produce Magnetism? 1820, Hans Christian Oersted: moving charges produce a magnetic field. The direction of the field is determined using a RHR. Oersted (1820)
Introduction to Discrete Optimization
 Prof. Friedrich Eisenbrand Martin Nieeier Due Date: March 9 9 Discussions: March 9 Introduction to Discrete Optiization Spring 9 s Exercise Consider a school district with I neighborhoods J schools and
Prof. Friedrich Eisenbrand Martin Nieeier Due Date: March 9 9 Discussions: March 9 Introduction to Discrete Optiization Spring 9 s Exercise Consider a school district with I neighborhoods J schools and
Lecture Frontier of complexity more is different Think of a spin - a multitude gives all sorts of magnetism due to interactions
 Lecture 1 Motivation for course The title of this course is condensed atter physics which includes solids and liquids (and occasionally gases). There are also interediate fors of atter, e.g., glasses,
Lecture 1 Motivation for course The title of this course is condensed atter physics which includes solids and liquids (and occasionally gases). There are also interediate fors of atter, e.g., glasses,
COS 424: Interacting with Data. Written Exercises
 COS 424: Interacting with Data Hoework #4 Spring 2007 Regression Due: Wednesday, April 18 Written Exercises See the course website for iportant inforation about collaboration and late policies, as well
COS 424: Interacting with Data Hoework #4 Spring 2007 Regression Due: Wednesday, April 18 Written Exercises See the course website for iportant inforation about collaboration and late policies, as well
PHY331 Magnetism. Lecture 1
 PHY331 Magnetism Lecture 1 Overview Course syllabus / general information Quick revision of basic concepts Magnetization and susceptibility Using susceptibility to define magnetic materials Diamagnetic
PHY331 Magnetism Lecture 1 Overview Course syllabus / general information Quick revision of basic concepts Magnetization and susceptibility Using susceptibility to define magnetic materials Diamagnetic
University of Illinois at Chicago Department of Physics
 University of Illinois at Chicago Department of Physics Electromagnetism Qualifying Examination January 4, 2017 9.00 am - 12.00 pm Full credit can be achieved from completely correct answers to 4 questions.
University of Illinois at Chicago Department of Physics Electromagnetism Qualifying Examination January 4, 2017 9.00 am - 12.00 pm Full credit can be achieved from completely correct answers to 4 questions.
Ferromagnetism. So that once magnetized the material will stay that way even in the absence of external current it is a permanent magnet.
 Ferroagnetis We now turn to the case where is not proportional to. We distinguish two cases: soft and hard ferroagnets. In a soft ferroagnet a graph of vs looks like If is now reduced, will retrace the
Ferroagnetis We now turn to the case where is not proportional to. We distinguish two cases: soft and hard ferroagnets. In a soft ferroagnet a graph of vs looks like If is now reduced, will retrace the
Name: Partner(s): Date: Angular Momentum
 Nae: Partner(s): Date: Angular Moentu 1. Purpose: In this lab, you will use the principle of conservation of angular oentu to easure the oent of inertia of various objects. Additionally, you develop a
Nae: Partner(s): Date: Angular Moentu 1. Purpose: In this lab, you will use the principle of conservation of angular oentu to easure the oent of inertia of various objects. Additionally, you develop a
Today in Physics 218: the Maxwell equations
 Today in Physics 218: the Maxwell equations Beyond magnetoquasistatics Displacement current, and Maxwell s repair of Ampère s Law The Maxwell equations Symmetry of the equations: magnetic monopoles? Rainbow
Today in Physics 218: the Maxwell equations Beyond magnetoquasistatics Displacement current, and Maxwell s repair of Ampère s Law The Maxwell equations Symmetry of the equations: magnetic monopoles? Rainbow
Chapter 27 Sources of Magnetic Field
 Chapter 27 Sources of Magnetic Field In this chapter we investigate the sources of magnetic of magnetic field, in particular, the magnetic field produced by moving charges (i.e., currents). Ampere s Law
Chapter 27 Sources of Magnetic Field In this chapter we investigate the sources of magnetic of magnetic field, in particular, the magnetic field produced by moving charges (i.e., currents). Ampere s Law
Where k = 1. The electric field produced by a point charge is given by
 Ch 21 review: 1. Electric charge: Electric charge is a property of a matter. There are two kinds of charges, positive and negative. Charges of the same sign repel each other. Charges of opposite sign attract.
Ch 21 review: 1. Electric charge: Electric charge is a property of a matter. There are two kinds of charges, positive and negative. Charges of the same sign repel each other. Charges of opposite sign attract.
Magnetism. March 10, 2014 Physics for Scientists & Engineers 2, Chapter 27 1
 Magnetism March 10, 2014 Physics for Scientists & Engineers 2, Chapter 27 1 Notes! Homework is due on We night! Exam 4 next Tuesday Covers Chapters 27, 28, 29 in the book Magnetism, Magnetic Fields, Electromagnetic
Magnetism March 10, 2014 Physics for Scientists & Engineers 2, Chapter 27 1 Notes! Homework is due on We night! Exam 4 next Tuesday Covers Chapters 27, 28, 29 in the book Magnetism, Magnetic Fields, Electromagnetic
THE UNIVERSITY OF SYDNEY FACULTY OF SCIENCE INTERMEDIATE PHYSICS PHYS 2912 PHYSICS 2B (ADVANCED) ALL QUESTIONS HAVE THE VALUE SHOWN
 CC0936 THE UNIVERSITY OF SYDNEY FACULTY OF SCIENCE INTERMEDIATE PHYSICS PHYS 91 PHYSICS B (ADVANCED SEMESTER, 015 TIME ALLOWED: 3 HOURS ALL QUESTIONS HAVE THE VALUE SHOWN INSTRUCTIONS: This paper consists
CC0936 THE UNIVERSITY OF SYDNEY FACULTY OF SCIENCE INTERMEDIATE PHYSICS PHYS 91 PHYSICS B (ADVANCED SEMESTER, 015 TIME ALLOWED: 3 HOURS ALL QUESTIONS HAVE THE VALUE SHOWN INSTRUCTIONS: This paper consists
Research on Power Output Characteristics of Magnetic Core in Energy Harvesting Devices
 Sensors & Transducers Vol. 74 Issue 7 July 04 pp. 53-59 Sensors & Transducers 04 by IFSA Publishing S. L. http://www.sensorsportal.co Research on Power Output Characteristics of Magnetic Core in Energy
Sensors & Transducers Vol. 74 Issue 7 July 04 pp. 53-59 Sensors & Transducers 04 by IFSA Publishing S. L. http://www.sensorsportal.co Research on Power Output Characteristics of Magnetic Core in Energy
Contents. Notes based on Fundamentals of Applied Electromagnetics (Ulaby et al) for ECE331, PSU.
 1 Contents 5 Magnetostatics 3 5.1 Magnetic forces and torques............... 4 5.1.1 Magnetic force on a current-carrying conductor 8 5.1.2 Magnetic torque on a current-carrying loop.. 16 5.2 Biot-Savart
1 Contents 5 Magnetostatics 3 5.1 Magnetic forces and torques............... 4 5.1.1 Magnetic force on a current-carrying conductor 8 5.1.2 Magnetic torque on a current-carrying loop.. 16 5.2 Biot-Savart
Fluids A. Joel Voldman* Massachusetts Institute of Technology *(with thanks to SDS)
 Cite as: Joel Voldan, course aterials for 6.777J / 2.372J Design and Fabrication of Microelectroechanical Devices, Spring 2007. MIT JV: 6.777J/2.372J Spring 2007, Lecture 14-1 Fluids A Joel Voldan* Massachusetts
Cite as: Joel Voldan, course aterials for 6.777J / 2.372J Design and Fabrication of Microelectroechanical Devices, Spring 2007. MIT JV: 6.777J/2.372J Spring 2007, Lecture 14-1 Fluids A Joel Voldan* Massachusetts
Physics Electricity and Magnetism Lecture 11 - Faraday s Law of Induction. Y&F Chapter 29, Sect. 1-5
 Physics 11 - lectricity and Magnetism Lecture 11 - Faraday s Law of Induction Y&F Chapter 9, Sect. 1-5 Magnetic Flux Motional MF: moving wire in a field Two Magnetic Induction xperiments Faraday s Law
Physics 11 - lectricity and Magnetism Lecture 11 - Faraday s Law of Induction Y&F Chapter 9, Sect. 1-5 Magnetic Flux Motional MF: moving wire in a field Two Magnetic Induction xperiments Faraday s Law
Electric vs Magnetic Comparison
 5. MAGNETOSTATICS Electric vs Magnetic Comparison J=σE Most dielectrics µ = µo excluding ferromagnetic materials Gauss s Law E field is conservative Gauss s law (integral) Conservative E field Electric
5. MAGNETOSTATICS Electric vs Magnetic Comparison J=σE Most dielectrics µ = µo excluding ferromagnetic materials Gauss s Law E field is conservative Gauss s law (integral) Conservative E field Electric
Faraday s Law. Underpinning of Much Technology
 Module 21: Faraday s Law 1 Faraday s Law Fourth (Final) Maxwell s Equation Underpinning of Much Technology 2 Demonstration: Falling Magnet 3 Magnet Falling Through a Ring Link to movie Falling magnet slows
Module 21: Faraday s Law 1 Faraday s Law Fourth (Final) Maxwell s Equation Underpinning of Much Technology 2 Demonstration: Falling Magnet 3 Magnet Falling Through a Ring Link to movie Falling magnet slows
ECE 3209 Electromagnetic Fields Final Exam Example. University of Virginia Solutions
 ECE 3209 Electromagnetic Fields Final Exam Example University of Virginia Solutions (print name above) This exam is closed book and closed notes. Please perform all work on the exam sheets in a neat and
ECE 3209 Electromagnetic Fields Final Exam Example University of Virginia Solutions (print name above) This exam is closed book and closed notes. Please perform all work on the exam sheets in a neat and
Chapter 31: Electromagnetic Induction and Faraday s Law All sections covered.
 About Exam 3 When and where (same as before) Monday Nov. 22 rd 5:30-7:00 pm Bascom 272: Sections 301, 302, 303, 304, 305, 311,322, 327, 329 Ingraham B10: Sections 306, 307, 312, 321, 323, 324, 325, 328,
About Exam 3 When and where (same as before) Monday Nov. 22 rd 5:30-7:00 pm Bascom 272: Sections 301, 302, 303, 304, 305, 311,322, 327, 329 Ingraham B10: Sections 306, 307, 312, 321, 323, 324, 325, 328,
All Excuses must be taken to 233 Loomis before 4:15, Monday, April 30.
 Miscellaneous Notes he end is near don t get behind. All Excuses ust be taken to 233 Loois before 4:15, Monday, April 30. he PHYS 213 final exa ties are * 8-10 AM, Monday, May 7 * 8-10 AM, uesday, May
Miscellaneous Notes he end is near don t get behind. All Excuses ust be taken to 233 Loois before 4:15, Monday, April 30. he PHYS 213 final exa ties are * 8-10 AM, Monday, May 7 * 8-10 AM, uesday, May
2. A crack which is oblique (Swedish sned ) with respect to the xy coordinate system is to be analysed. TMHL
 (Del I, teori; 1 p.) 1. In fracture echanics, the concept of energy release rate is iportant. Fro the fundaental energy balance of a case with possible crack growth, one usually derives the equation where
(Del I, teori; 1 p.) 1. In fracture echanics, the concept of energy release rate is iportant. Fro the fundaental energy balance of a case with possible crack growth, one usually derives the equation where
Magnetostatics and the vector potential
 Magnetostatics and the vector potential December 8, 2015 1 The divergence of the magnetic field Starting with the general form of the Biot-Savart law, B (x 0 ) we take the divergence of both sides with
Magnetostatics and the vector potential December 8, 2015 1 The divergence of the magnetic field Starting with the general form of the Biot-Savart law, B (x 0 ) we take the divergence of both sides with
B r Solved Problems Magnetic Field of a Straight Wire
 (4) Equate Iencwith d s to obtain I π r = NI NI = = ni = l π r 9. Solved Problems 9.. Magnetic Field of a Straight Wire Consider a straight wire of length L carrying a current I along the +x-direction,
(4) Equate Iencwith d s to obtain I π r = NI NI = = ni = l π r 9. Solved Problems 9.. Magnetic Field of a Straight Wire Consider a straight wire of length L carrying a current I along the +x-direction,
SUMMARY Phys 2523 (University Physics II) Compiled by Prof. Erickson. F e (r )=q E(r ) dq r 2 ˆr = k e E = V. V (r )=k e r = k q i. r i r.
 SUMMARY Phys 53 (University Physics II) Compiled by Prof. Erickson q 1 q Coulomb s Law: F 1 = k e r ˆr where k e = 1 4π =8.9875 10 9 N m /C, and =8.85 10 1 C /(N m )isthepermittivity of free space. Generally,
SUMMARY Phys 53 (University Physics II) Compiled by Prof. Erickson q 1 q Coulomb s Law: F 1 = k e r ˆr where k e = 1 4π =8.9875 10 9 N m /C, and =8.85 10 1 C /(N m )isthepermittivity of free space. Generally,
Physics 112. Study Notes for Exam II
 Chapter 20 Electric Forces and Fields Physics 112 Study Notes for Exam II 4. Electric Field Fields of + and point charges 5. Both fields and forces obey (vector) superposition Example 20.5; Figure 20.29
Chapter 20 Electric Forces and Fields Physics 112 Study Notes for Exam II 4. Electric Field Fields of + and point charges 5. Both fields and forces obey (vector) superposition Example 20.5; Figure 20.29
Magnetostatics III. P.Ravindran, PHY041: Electricity & Magnetism 1 January 2013: Magntostatics
 Magnetostatics III Magnetization All magnetic phenomena are due to motion of the electric charges present in that material. A piece of magnetic material on an atomic scale have tiny currents due to electrons
Magnetostatics III Magnetization All magnetic phenomena are due to motion of the electric charges present in that material. A piece of magnetic material on an atomic scale have tiny currents due to electrons
8.03 Lecture 12. Systems we have learned: Wave equation: (1) String with constant tension and mass per unit length ρ L T v p = ρ L
 8.03 Lecture 1 Systems we have learned: Wave equation: ψ = ψ v p x There are three different kinds of systems discussed in the lecture: (1) String with constant tension and mass per unit length ρ L T v
8.03 Lecture 1 Systems we have learned: Wave equation: ψ = ψ v p x There are three different kinds of systems discussed in the lecture: (1) String with constant tension and mass per unit length ρ L T v
Chapter 2 Basics of Electricity and Magnetism
 Chapter 2 Basics of Electricity and Magnetism My direct path to the special theory of relativity was mainly determined by the conviction that the electromotive force induced in a conductor moving in a
Chapter 2 Basics of Electricity and Magnetism My direct path to the special theory of relativity was mainly determined by the conviction that the electromotive force induced in a conductor moving in a
Order Recursion Introduction Order versus Time Updates Matrix Inversion by Partitioning Lemma Levinson Algorithm Interpretations Examples
 Order Recursion Introduction Order versus Tie Updates Matrix Inversion by Partitioning Lea Levinson Algorith Interpretations Exaples Introduction Rc d There are any ways to solve the noral equations Solutions
Order Recursion Introduction Order versus Tie Updates Matrix Inversion by Partitioning Lea Levinson Algorith Interpretations Exaples Introduction Rc d There are any ways to solve the noral equations Solutions
Preliminary Examination - Day 1 Thursday, May 10, 2018
 UNL - Department of Physics and Astronomy Preliminary Examination - Day Thursday, May, 28 This test covers the topics of Classical Mechanics (Topic ) and Electrodynamics (Topic 2). Each topic has 4 A questions
UNL - Department of Physics and Astronomy Preliminary Examination - Day Thursday, May, 28 This test covers the topics of Classical Mechanics (Topic ) and Electrodynamics (Topic 2). Each topic has 4 A questions
L2 IntroSurvey. EIEN20 Design of Electrical Machines, IEA, Today s goal. L2: Variety of electrical machines.
 L: Variety of electrical achines Machine construction: an overview Transforer is it achine too? Today s goal ntroduction to achine construction Constructional layouts and echanical arrangeents Supply &
L: Variety of electrical achines Machine construction: an overview Transforer is it achine too? Today s goal ntroduction to achine construction Constructional layouts and echanical arrangeents Supply &
AP Physics C Syllabus
 Course Overview AP Physics C Syllabus AP Physics C will meet for 90 minutes on block scheduling and for 45 minutes on regular scheduling. Class activities will include lecture, demonstration, problem solving
Course Overview AP Physics C Syllabus AP Physics C will meet for 90 minutes on block scheduling and for 45 minutes on regular scheduling. Class activities will include lecture, demonstration, problem solving
Exam 2 Fall 2014
 1 95.144 Exam 2 Fall 2014 Section instructor Section number Last/First name Last 3 Digits of Student ID Number: Show all work. Show all formulas used for each problem prior to substitution of numbers.
1 95.144 Exam 2 Fall 2014 Section instructor Section number Last/First name Last 3 Digits of Student ID Number: Show all work. Show all formulas used for each problem prior to substitution of numbers.
Hysteresis model for magnetic materials using the Jiles-Atherton model
 Hysteresis odel for agnetic aterials using the Jiles-Atherton odel Predrag Petrovic Technical faculty Svetog Save 65 32 Cacak, pegi@ei.yu Nebojsa itrovic Technical faculty Svetog Save 65 32 Cacak, itar@tfc.tfc.kg.ac.yu
Hysteresis odel for agnetic aterials using the Jiles-Atherton odel Predrag Petrovic Technical faculty Svetog Save 65 32 Cacak, pegi@ei.yu Nebojsa itrovic Technical faculty Svetog Save 65 32 Cacak, itar@tfc.tfc.kg.ac.yu
