An adapted coarse space for Balancing domain decomposition method to solve nonlinear elastodynamic problems
|
|
|
- Jeffrey Stokes
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A adapted coarse space for Balacig domai decompositio method to solve oliear elastodyamic problems Mikaël Barboteu Uiversity of Perpiga, 52 aveue Paul-Alduy, Perpiga, Frace This work is devoted to preset a scalable domai decompositio method to solve oliear elastodyamic problems. Large o liear elastodyamic problems represet a appropriate applicatio field for substructurig methods which are efficiet o parallel computer with the proviso of usig specific precoditioer techiques well adapted to the mechaical modelig. Accordig to this reaso, we develop a adapted Balacig domai decompositio method [Ma93, LeT94] appropriated to solve this kid of systems. By usig the theoretical framework of Schwarz additive decompositio method [LeT94, LMV98] ad by usig argumets developed i [ABLV00], we propose a two level Neuma-Neuma precoditioer based o the costructio of a coarse space of "lower eergy" modes adapted to fiite deformatios problems with dyamic process. I sectio 1, oliear elastodyamic problems ad domai decompositio frameworks are recalled. The sectio 2 is devoted to preset the defiitio of a adapted coarse space by usig Schwarz additive formulatio. The costructio of the two level Neuma-Neuma precoditioer is detailled i sectio 3. I last sectio 4, we test the efficiecy of this updated Balacig domai decompositio method o umerical solutios of a academic o liear dyamic problem. 1 Noliear elastodyamic problems ad domai decompositio frameworks Dyamic deformable body systems i large deformatios are govered by o liear time depedet equatios. A typical o liear elastodyamic problem defied i a referece cofiguratio ca take the followig variatioal form, { Fid u L 2 (]0; T[; U 0 ) such that for each t ]0; T[, Ω ρü(t).v + Ω Π(t) : v Ω f(t).v g(t).v = 0, v U (1) gω 0
2 2 Mikaël Barboteu where ρ deotes the mass desity; Π is the first Piola-Kirchoff tesor; f ad g are the exteral force desities. A dot superscript idicates the time derivative. The set U 0 = {v H 1 (Ω) dim ;v = 0 o 0 Ω} represets the space of kiematically admissible displacemet fields. The problem (1) ca be solved by a eergy coservative time itegratio scheme [Go00] which is appropriate due to his log term time itegratio accuracy ad stability. I the followig, we cosider a collectio of discrete times (t p ) p=1..p which defie a partitio of the time iterval [0; T] = P p=1 [t p; t p+1 ] with t p+1 = t p + t ad t = T P. By usig a secod order time itegratio scheme (adapted midpoit scheme) [Go00], the weak form (1) itegrated betwee the times t p ad t p+1 gives the followig system, { Fid up+1 U 0 such that 1 t Ω ρ( u p+1 u p ).v + Ω Π algo : v Ω f p+ 1.v 2 g gω p+ 1.v = 0, 2 (2) where p+ 1 2 = 1 2 ( p + p+1 ) ad p deotes the approximatio of (t p ). The eergy coservative scheme (2) used i this work, is characterized by the tesor Π algo proposed by Gozalez [Go00]. After a fully discretizatio step (time ad space), we deduce the o liear systems defied by 1 t M( u p+1 u p ) + G algo (u p+1,u p ) q p+ 1 = 0 (3) 2 where M comes from the discretizatio of the iertia term 1 t Ω ρ( u p+1 u p ).v ad G algo is due to the discretizatio of the hyperelastic part Ω Π algo : v ad q p+ 1 comes from the discretizatio of the exteral forces 2 Ω f.v + gω g.v. The o liear system (3) ca be solved by a iterative liearizatio scheme idexed by i which leads to the solutio of liear systems: Ka i,p+1 u i,p+1 = 1 t M( u i,p+1 u p ) G algo (u i,p+1,u p ) + q p+ 1 (4) 2 with Ka i,p+1 = 2 t 2Ma + K i,p+1 ad u i,p+1 = u i+1,p+1 u i,p+1 where Ma = up+1 M represets the mass matrix ad Ka i,p+1 = up+1 G algo the hyperelastic taget matrix. We ca isist o the fact that the matrix Ka i,p+1 of system (4) is o symmetric; the o symmetry comes from the form of tesor Π algo (see [Go00]). The liear systems (4) ca be solved by a domai decompositio method [LeT94] which has to be adapted to the o symmetry but also to the presece of iertia terms. Before givig the adaptatios to o liear dyamic problems (sectios 2 ad 3), we preset briefly ow the pricipal features of the Balacig domai decompositio method [Ma93, LeT94]. We choose to adopt a primal Schur complemet method writte with displacemet variables. The basic idea i ooverlappig domai decompositio methods is to split the domai Ω of study ito N small ooverlappig subdomais Ω
3 A adapted coarse space for Balacig domai decompositio method 3 ad iterfaces Γ ( = 1, N). The Schur complemet method cosist the i reducig the global system to a iterface problem by a block Gaussia elimiatio of iteral degrees of freedom. The iterface problem ca take the followig variatioal form: ū V / < S i,p+1 ū, v >=< f i,p+1, v > v V = tr(v ) Γ, (5) where V is the discrete set defied from the space U 0 ad Γ = N =1 Γ. The matrices S i,p+1 = N =1 R S i,p+1 (R ) t deote the global Schur complemet matrices defied o Γ; (R ) t is the restrictio operator which goes from Γ to Γ. The local Schur complemet matrices S i,p+1 are defied o Γ by S i,p+1 = Ka i,p+1 (B i,p+1) t ( Ka i,p+1) 1 B i,p+1. (6) To do that, we( have cosidered the ) subdomai stiffess matrix formulated Ka by Ka i,p+1 = i,p+1 B i,p+1 (B i,p+1 )t Ka. The blocks Ka i,p+1 ad Ka i,p+1 correspod respectively to the iteral ad iterface degrees of freedom. The i,p+1 matrix B i,p+1 represets the cotributio coectig Γ to Ω. The iterface problem (5) ca be solved by a GMRES method (o symmetric cases) with the multilevel Neuma-Neuma precoditioer [LeT94, ABLV00]. This iterative techique eeds to form the matrix vector products S p ad M 1 r by solvig idepedet auxiliary Dirichlet ad Neuma problems o the local subdomais ad a global coarse problem defied o a space of sigular (rigid body) motios. The adaptatio of the Balacig Method to solve liear systems issued from o liear elastodyamic problems [Bar05] ca be realized by usig the theoritical frameworks of Schwarz additive decompositio method with itroductio of a adapted coarse space. 2 Schwarz additive formulatio: towards a defiitio of a adapted coarse space The two-level Neuma-Neuma precoditioer may be iterpreted as a stadard additive Schwarz algorithm [LeT94]. This method cosists i decomposig the iterface space V ito a coarse ad a fie compoet: V G ad V f. The coarse space V G = N =1 D Z (D is a give partitio of uity defied o the iterface, N =1 D R = Id V ) ca be defied by addig local lower eergy compoets ad the fie space V f is defied by duality as follows: V f = N =1 D V f where V f = { v f V, < SR v,r z >= 0, z Z }. (7) The key poit is the costructio of the local spaces Z of rigid motios. This costructio must, if that is ecessary, regularize local Neuma problems
4 4 Mikaël Barboteu but more especially set the costats or the lower eergy modes (like rigid body motios) to zero i the solutio of local Neuma problems. For more details o the presetatio of the Schwarz additive method, we ca refer to [LeT94, LMV98] for symmetric cases ad [ABLV00] for o symmetric cases. With fiite deformatios ad dyamic problems, some lower eergy modes caot be detected i the factorizatio step of the local taget matrices of Neuma problems [Bar05]. These drawbacks come from the fiite deformatios modelig but also from the regularizig cotributio of the mass matrix. Moreover, we also eed to improve the cotiuity betwee subdomais by takig ito accout specific modes (like corers modes...). So we have to itroduce a specific costructio of these lower eergy modes. I the followig, we preset i detail the costructio of the coarse space V G for o liear dyamic problems. The orthogoality relatio used i (7) characterizig the space V f permits to obtai iformatios i order to defie the local coarse space Z. Ideed the expasio of this orthogoality relatio by usig S i,p+1 = N =1 R S i,p+1 (R ) t ivolves oly terms issued from the subdomais eighbourig to the th ad oe term from the th itself, eigh() l=1 < v, (R ) t R l (S l i,p+1 )t (R l ) t R z > } {{ } (8i) + < v, (S i,p+1 )t z > }{{} (8ii) = 0 (8) The relatio (8) ca be verified by imposig the terms (8i) ad (8ii) to zero. Let us see ow what the use of these relatios imply: - use of the term (8ii): this term may be elimiated by imposig that the kerel of (S i,p+1 )t is icluded i the local coarse space Z, (Ker(S i,p+1 )t Z ). Such a choice leads to the same simplificatio tha those obtaied with the kerel of S for the more commo symmetric case [LeT94]. For o symmetric cases, this choice leads to the itroductio of Dual Rigid Modes (DRM) defied through the kerel of (S i,p+1 )t (see [ABLV00] for more precisios). I a pratical poit of view ad accordig to the form S i,p+1 give i (6), the dual rigid modes (oted by vgα ) defied o Ω ca be calculated through the local matrices (Ka i,p+1 )t by the solutio of this followig Neuma systems: v Gα V / (Ka i,p+1 )t v Gα = 0, α = 1, bdrm. (9) where bdrm represets the total umber of dual rigid modes of subdomais Ω. Oe ca easily prove that the modes v Gα Ker(Ka i,p+1 )t are coectig to the elemets z Ker(S i,p+1 )t by the relatio z = v Gα (where v Gα represets the cotributio of v Gα o Γ ). - cotributio of the term (8i): a simple maer to cacel the term (8i) is to fix all the terms of the sum to zero; the elemets z of Z could the be caracterized by the solutio of (R ) t R l (S l i,p+1 )t (R l ) t R z = 0. That makes it possible to esure the cotiuity of the coarse space elemets through the iterface Γ of Ω by cosiderig the cotributios relatig to corers, edges
5 A adapted coarse space for Balacig domai decompositio method 5 ad faces of the eighbourig subdomais Ω l. Ideed, the elemets z ca be foud respectively by these followig relatios : z l Z l / (S l i,p+1 )t z l = 0 l = 1, eigh() (10) z Z / (R l ) t R z = z l l = 1, eigh() (11) The use of the (8ii) ad (10) permits to calculte the dual rigid modes of the subdomais Ω ad his eighbours Ω l ; furthermore the relatio (11) represets the cotiuity costrait of dual modes through the iterface (corers, edges ad faces) betwee Ω ad Ω l. This last poit makes it possible to coect this approach with the Balacig Domai Decompositio Method with Costraits [MD03]; the eforcemet of these kid of costrait leads to expesive computatioal cost. A iexpesive way, ispired by [LMV98] ad [MD03] would be to impose oly the cotiuity o the corers of subdomais Ω. That ca be doe by the computatio of the bdcm Dual Corer Modes (DCM) of subdomais Ω by eforcig a same arbitrary Dirichlet boudary value o the corer iterface degrees of freedom for all cocered subdomais Ω ad Ω l (where bdcm is the total umber of DCM). I coclusio, the coarse space Z ca be geerated by cosiderig the bdrm dual rigid modes defied by solutios of the systems (12) ad particulary by the bdcm dual corer modes give by the systems (13) (see the ext sectio 3 for more details o the computatio of these modes). 3 Adaptatio of the 2-level Neuma-Neuma precoditioer Accordig to the defiitio of the coarse space itroduced i sectio 2, we propose a adapted costructio of the two level Neuma-Neuma precoditioer based o the followig steps: 1. Prelimiary step : We idetify the local iteral degrees of freedom {Prα; α = 1, bdrm } which cacel all bdrm rigid motios of subdomai Ω. This detectio ca be realized durig the factorizatio of the stiffess matrix (K e ) comig from the liear elastostatic system associated to the o liear elastodyamic problem (3). Notice that we ca also make arbitrary this detectio. 2. For each Newto iteratio i of each time step p a) We costruct the local regularized matrices Ka i,p+1 by usig the degrees of freedom {Prα} detected i step (1). These matrices ca be writte by usig the cotributios accordig to iteral ad iterface degrees of freedom; the oly the iteral cotributio Ka i,p+1 of the matrix Ka i,p+1 is regularized by usig the matrix Q α : Ka i,p+1 = Ka i,p+1 + Q α where ( Q α ) jk = { BV if j = k = Prα 0 else
6 6 Mikaël Barboteu where BV is a arbitrary big value (like for example). This regularizatio is ot ecessary for dyamic problems due to the cotributio of the iertia terms Ma which esures the matrices Ka t 2 i,p+1 2 to be o sigular. O the other had, we eed to costruct the regularized matrices Ka i,p+1 i order to impose the boudary coditios o the corers degrees of freedom oted by {Pc γ; γ = 1, bdcm }: Ka i,p+1 = Ka i,p+1 + Q γ where ( Q γ ) jk = { BV if j = k = Pc γ 0 else b) We compute the dual rigid modes {vgα ; α = 1, bdrm } by solvig the (regularized) local Neuma problems set o the space V of subdomai displacemets fuctios, ( Ka i,p+1 B i,p+1 (B i,p+1 )t Ka i,p+1 ) ) ( v Gα = v Gα ( e α0 ) ; α = 1, bdrm (12) where the j th compoet ( e α ) j of the vector e α is equal to the arbitrary big value BV if j = Prα ad to the value zero if ot. c) We compute the dual corer modes {vgγ ; γ = 1, bdcm } by solvig local Neuma problems i which the cotiuity of modes o corers ca be realized by eforcig the same arbitrary Dirichlet boudary value (1 for example) o the corers iterface degrees of freedom {Pc γ; γ = 1, bdcm } for all cocered subdomais Ω : ( ) Ka i,p+1 B ) i,p+1 ( v Gα )t Ka v i,p+1 Gα (B i,p+1 = ( 0 ē γ ) ; γ = 1, bdcm (13) where the j th compoet (ē γ) j of the vector ē γ is equal to the arbitrary big value BV if j = Pc γ ad to the value zero if ot. 3. We defie the local coarse space by: Z = vect ( { v Gα; α = 1, bdrm }, { v Gγ; γ = 1, bdcm } ). With this costructio of lower eergy modes, the two-level Neuma-Neuma precoditioer is classically defied for each time step p ad each Newto iteratio i by M 1 i,p+1 = P G + N (I P G )D i,p+1( S i,p+1) 1 (D i,p+1) t (I P G ) t, (14) =1 where ( S i,p+1 ) 1 is the regularized Schur iverse matrix ad P G deotes the orthogoal S-projectio of V o V G.
7 A adapted coarse space for Balacig domai decompositio method 7 4 A oliear dyamic problem: the catilever beam I this sectio, we illustrate umerically the previous adaptatios i the case of the solutio of a 2-dimesioal o liear elastodyamic problem. The applicatio relates to the dyamic evolutio of a catilever beam i plae displacemets. To do that, we cosider a elastic beam clamped o oe of hyperelastic beam g subdomais corers domai decompositio iterfaces Fig. 1. Deformed sequece of a catilever beam. Fig. 2. Substructuratio of the beam i 40 subdomais. its tips ad a exteral time idepedet loadig g o the opposite tip. The compressible material respose cosidered is govered by a Ogde costitutive law. The mesh ad its deformed cofiguratios durig the time are preseted i figure 1. From this umerical experimet, we aalyse the scalability of the iterface solver (GMRES) with some versios of the two-level Neuma-Neuma precoditioers. The cosidered precoditioers are : - the o symmetric Neuma-Neuma precoditioer give i [ABLV00] (curve ) without o liear dyamic adaptatios, - the o symmetric Neuma-Neuma precoditioer give i [Bar05] (curve ) preseted i sectio 3 but without dual corer modes (step (c)), - the improved o symmetric Neuma-Neuma precoditioer itroduced i sectio 3 (curve ) with all the features (steps (a), (b) ad (c)). The figure 3 gives the evolutio of average umber of GMRES iteratios (per Newto iteratios) for a beam decomposed i 2, 5, 10, 20, 40, 80 ad 160 subdomais (see figure 2 for a decompositio i 40 subdomais). We observe that the umber of iteratios obtaied with the 2-level Neuma-Neuma precoditioer without adaptatios (curve ) grows up with respect to the umber of subdomais. So the iterface solver with this precoditioer loses its classical scalability. We ca remark that the precoditioer (curve ) give i [Bar05] (without corers modes) permits to strogly decrease the solver iteratios but the depedece with respect to the umber of subdomais is already preset. O the other had, the improved Neuma-Neuma precoditioer
8 8 Mikaël Barboteu iteratios of iterface solver catilever beam umber of subdomais N.-N. precoditioer without adaptatios N.-N. precoditioer give i [Bar05] (without corer modes) improved N.-N. precoditioer (preseted i sectio 3) umber of subdomais N.-N. precoditioers Fig. 3. Numerical scalability with Neuma-Neuma (N.-N.) precoditioers. (curve ) leads to recover the umerical scalability properties i.e. the idepedece of the solver iteratios with respect to the umber of subdomais. Furthermore, the performaces of this precoditioer are pratically the same as the oes obtaied to solve liear elastostatic problems. Ideed, the average umber of iteratios is equal to 7 for a decompositio i 160 subdomais (see table i figure 3) ad if we cosider the associated liear elastostatic problem the umber of iteratios is equal to 6. I order to validate these performaces, we must test this precoditioer o other less academic simulatios. Refereces [ABLV00] Alart, P., Barboteu, M., Le Tallec, P., Vidrascu, M.: Additive Schwarz method for osymmetric problems: applicatio to frictioal multicotact problems. Domai decompositio methods i sciece ad egieerig (Lyo, 2000), Theory Eg. Appl. Comput. Methods, Iterat. Ceter Numer. Methods Eg. (CIMNE), Barceloa, 3-13, (2002) [Bar05] Barboteu, M.: Costructio du précoditioeur Neuma-Neuma de décompositio de domaie de iveau 2 pour les problèmes élastodyamiques e grades déformatios. C. R. Acad. Sci., 340 (I), (2005) [Go00] Gozalez, O.: Exact eergy ad mometum coservig algorithms for geeral models i o liear elasticity. Comput. Meth. Appl. Mech. Egrg., 190, (2000) [LeT94] Le Tallec, P.: Domai decompositio methods i computatioal mechaics. Comput. Mech. Adv., 1, (1994) [LMV98] Le Tallec, P., Madel, J., Vidrascu, M.: A Neuma-Neuma domai decompositio algorithm for solvig plate ad shell problems SIAM J. Numer. Aal., 35, (1998). [Ma93] Madel, J.: Balacig domai decompositio. Comm. Numer. Methods Egrg., 9, (1993) [MD03] Madel, J., Dohrma, C. R.: Covergece of a Balacig Domai Decompositio by Costraits ad Eergy Miimizatio, Numer. Li. Alg. Appl., 10, (2003)
Research Article A New Second-Order Iteration Method for Solving Nonlinear Equations
 Abstract ad Applied Aalysis Volume 2013, Article ID 487062, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/487062 Research Article A New Secod-Order Iteratio Method for Solvig Noliear Equatios Shi Mi Kag, 1 Arif
Abstract ad Applied Aalysis Volume 2013, Article ID 487062, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/487062 Research Article A New Secod-Order Iteratio Method for Solvig Noliear Equatios Shi Mi Kag, 1 Arif
Numerical Solution of the Two Point Boundary Value Problems By Using Wavelet Bases of Hermite Cubic Spline Wavelets
 Australia Joural of Basic ad Applied Scieces, 5(): 98-5, ISSN 99-878 Numerical Solutio of the Two Poit Boudary Value Problems By Usig Wavelet Bases of Hermite Cubic Splie Wavelets Mehdi Yousefi, Hesam-Aldie
Australia Joural of Basic ad Applied Scieces, 5(): 98-5, ISSN 99-878 Numerical Solutio of the Two Poit Boudary Value Problems By Usig Wavelet Bases of Hermite Cubic Splie Wavelets Mehdi Yousefi, Hesam-Aldie
Algebra of Least Squares
 October 19, 2018 Algebra of Least Squares Geometry of Least Squares Recall that out data is like a table [Y X] where Y collects observatios o the depedet variable Y ad X collects observatios o the k-dimesioal
October 19, 2018 Algebra of Least Squares Geometry of Least Squares Recall that out data is like a table [Y X] where Y collects observatios o the depedet variable Y ad X collects observatios o the k-dimesioal
TMA4205 Numerical Linear Algebra. The Poisson problem in R 2 : diagonalization methods
 TMA4205 Numerical Liear Algebra The Poisso problem i R 2 : diagoalizatio methods September 3, 2007 c Eiar M Røquist Departmet of Mathematical Scieces NTNU, N-749 Trodheim, Norway All rights reserved A
TMA4205 Numerical Liear Algebra The Poisso problem i R 2 : diagoalizatio methods September 3, 2007 c Eiar M Røquist Departmet of Mathematical Scieces NTNU, N-749 Trodheim, Norway All rights reserved A
A collocation method for singular integral equations with cosecant kernel via Semi-trigonometric interpolation
 Iteratioal Joural of Mathematics Research. ISSN 0976-5840 Volume 9 Number 1 (017) pp. 45-51 Iteratioal Research Publicatio House http://www.irphouse.com A collocatio method for sigular itegral equatios
Iteratioal Joural of Mathematics Research. ISSN 0976-5840 Volume 9 Number 1 (017) pp. 45-51 Iteratioal Research Publicatio House http://www.irphouse.com A collocatio method for sigular itegral equatios
DECOMPOSITION METHOD FOR SOLVING A SYSTEM OF THIRD-ORDER BOUNDARY VALUE PROBLEMS. Park Road, Islamabad, Pakistan
 Mathematical ad Computatioal Applicatios, Vol. 9, No. 3, pp. 30-40, 04 DECOMPOSITION METHOD FOR SOLVING A SYSTEM OF THIRD-ORDER BOUNDARY VALUE PROBLEMS Muhammad Aslam Noor, Khalida Iayat Noor ad Asif Waheed
Mathematical ad Computatioal Applicatios, Vol. 9, No. 3, pp. 30-40, 04 DECOMPOSITION METHOD FOR SOLVING A SYSTEM OF THIRD-ORDER BOUNDARY VALUE PROBLEMS Muhammad Aslam Noor, Khalida Iayat Noor ad Asif Waheed
METHOD OF FUNDAMENTAL SOLUTIONS FOR HELMHOLTZ EIGENVALUE PROBLEMS IN ELLIPTICAL DOMAINS
 Please cite this article as: Staisław Kula, Method of fudametal solutios for Helmholtz eigevalue problems i elliptical domais, Scietific Research of the Istitute of Mathematics ad Computer Sciece, 009,
Please cite this article as: Staisław Kula, Method of fudametal solutios for Helmholtz eigevalue problems i elliptical domais, Scietific Research of the Istitute of Mathematics ad Computer Sciece, 009,
ON WELLPOSEDNESS QUADRATIC FUNCTION MINIMIZATION PROBLEM ON INTERSECTION OF TWO ELLIPSOIDS * M. JA]IMOVI], I. KRNI] 1.
![ON WELLPOSEDNESS QUADRATIC FUNCTION MINIMIZATION PROBLEM ON INTERSECTION OF TWO ELLIPSOIDS * M. JA]IMOVI], I. KRNI] 1. ON WELLPOSEDNESS QUADRATIC FUNCTION MINIMIZATION PROBLEM ON INTERSECTION OF TWO ELLIPSOIDS * M. JA]IMOVI], I. KRNI] 1.](/thumbs/94/121685725.jpg) Yugoslav Joural of Operatios Research 1 (00), Number 1, 49-60 ON WELLPOSEDNESS QUADRATIC FUNCTION MINIMIZATION PROBLEM ON INTERSECTION OF TWO ELLIPSOIDS M. JA]IMOVI], I. KRNI] Departmet of Mathematics
Yugoslav Joural of Operatios Research 1 (00), Number 1, 49-60 ON WELLPOSEDNESS QUADRATIC FUNCTION MINIMIZATION PROBLEM ON INTERSECTION OF TWO ELLIPSOIDS M. JA]IMOVI], I. KRNI] Departmet of Mathematics
PAijpam.eu ON TENSOR PRODUCT DECOMPOSITION
 Iteratioal Joural of Pure ad Applied Mathematics Volume 103 No 3 2015, 537-545 ISSN: 1311-8080 (prited versio); ISSN: 1314-3395 (o-lie versio) url: http://wwwijpameu doi: http://dxdoiorg/1012732/ijpamv103i314
Iteratioal Joural of Pure ad Applied Mathematics Volume 103 No 3 2015, 537-545 ISSN: 1311-8080 (prited versio); ISSN: 1314-3395 (o-lie versio) url: http://wwwijpameu doi: http://dxdoiorg/1012732/ijpamv103i314
Optimization Methods MIT 2.098/6.255/ Final exam
 Optimizatio Methods MIT 2.098/6.255/15.093 Fial exam Date Give: December 19th, 2006 P1. [30 pts] Classify the followig statemets as true or false. All aswers must be well-justified, either through a short
Optimizatio Methods MIT 2.098/6.255/15.093 Fial exam Date Give: December 19th, 2006 P1. [30 pts] Classify the followig statemets as true or false. All aswers must be well-justified, either through a short
Analysis of composites with multiple rigid-line reinforcements by the BEM
 Aalysis of composites with multiple rigid-lie reiforcemets by the BEM Piotr Fedeliski* Departmet of Stregth of Materials ad Computatioal Mechaics, Silesia Uiversity of Techology ul. Koarskiego 18A, 44-100
Aalysis of composites with multiple rigid-lie reiforcemets by the BEM Piotr Fedeliski* Departmet of Stregth of Materials ad Computatioal Mechaics, Silesia Uiversity of Techology ul. Koarskiego 18A, 44-100
A new formulation of internal forces for non-linear hypoelastic constitutive models verifying conservation laws
 A ew formulatio of iteral forces for o-liear hypoelastic costitutive models verifyig coservatio laws Ludovic NOELS 1, Lauret STAINIER 1, Jea-Philippe PONTHOT 1 ad Jérôme BONINI. 1 LTAS-Milieux Cotius et
A ew formulatio of iteral forces for o-liear hypoelastic costitutive models verifyig coservatio laws Ludovic NOELS 1, Lauret STAINIER 1, Jea-Philippe PONTHOT 1 ad Jérôme BONINI. 1 LTAS-Milieux Cotius et
Streamfunction-Vorticity Formulation
 Streamfuctio-Vorticity Formulatio A. Salih Departmet of Aerospace Egieerig Idia Istitute of Space Sciece ad Techology, Thiruvaathapuram March 2013 The streamfuctio-vorticity formulatio was amog the first
Streamfuctio-Vorticity Formulatio A. Salih Departmet of Aerospace Egieerig Idia Istitute of Space Sciece ad Techology, Thiruvaathapuram March 2013 The streamfuctio-vorticity formulatio was amog the first
On Strongly Consistent Finite Dierence Approximations
 D.Michels et al. (KAUST,JINR,SSU) Strogly Cosistet Approximatios 17 April 2018 1 / 25 O Strogly Cosistet Fiite Dierece Approximatios Domiik Michels 1, Vladimir Gerdt 2, Dmitry Lyakhov 1, ad Yuri Blikov
D.Michels et al. (KAUST,JINR,SSU) Strogly Cosistet Approximatios 17 April 2018 1 / 25 O Strogly Cosistet Fiite Dierece Approximatios Domiik Michels 1, Vladimir Gerdt 2, Dmitry Lyakhov 1, ad Yuri Blikov
Journal of Computational Physics 149, (1999) Article ID jcph , available online at
 Joural of Computatioal Physics 149, 418 422 (1999) Article ID jcph.1998.6131, available olie at http://www.idealibrary.com o NOTE Defiig Wave Amplitude i Characteristic Boudary Coditios Key Words: Euler
Joural of Computatioal Physics 149, 418 422 (1999) Article ID jcph.1998.6131, available olie at http://www.idealibrary.com o NOTE Defiig Wave Amplitude i Characteristic Boudary Coditios Key Words: Euler
Singular Continuous Measures by Michael Pejic 5/14/10
 Sigular Cotiuous Measures by Michael Peic 5/4/0 Prelimiaries Give a set X, a σ-algebra o X is a collectio of subsets of X that cotais X ad ad is closed uder complemetatio ad coutable uios hece, coutable
Sigular Cotiuous Measures by Michael Peic 5/4/0 Prelimiaries Give a set X, a σ-algebra o X is a collectio of subsets of X that cotais X ad ad is closed uder complemetatio ad coutable uios hece, coutable
CHAPTER 10 INFINITE SEQUENCES AND SERIES
 CHAPTER 10 INFINITE SEQUENCES AND SERIES 10.1 Sequeces 10.2 Ifiite Series 10.3 The Itegral Tests 10.4 Compariso Tests 10.5 The Ratio ad Root Tests 10.6 Alteratig Series: Absolute ad Coditioal Covergece
CHAPTER 10 INFINITE SEQUENCES AND SERIES 10.1 Sequeces 10.2 Ifiite Series 10.3 The Itegral Tests 10.4 Compariso Tests 10.5 The Ratio ad Root Tests 10.6 Alteratig Series: Absolute ad Coditioal Covergece
Similarity Solutions to Unsteady Pseudoplastic. Flow Near a Moving Wall
 Iteratioal Mathematical Forum, Vol. 9, 04, o. 3, 465-475 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/0.988/imf.04.48 Similarity Solutios to Usteady Pseudoplastic Flow Near a Movig Wall W. Robi Egieerig
Iteratioal Mathematical Forum, Vol. 9, 04, o. 3, 465-475 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/0.988/imf.04.48 Similarity Solutios to Usteady Pseudoplastic Flow Near a Movig Wall W. Robi Egieerig
A brief introduction to linear algebra
 CHAPTER 6 A brief itroductio to liear algebra 1. Vector spaces ad liear maps I what follows, fix K 2{Q, R, C}. More geerally, K ca be ay field. 1.1. Vector spaces. Motivated by our ituitio of addig ad
CHAPTER 6 A brief itroductio to liear algebra 1. Vector spaces ad liear maps I what follows, fix K 2{Q, R, C}. More geerally, K ca be ay field. 1.1. Vector spaces. Motivated by our ituitio of addig ad
Numerical Methods in Fourier Series Applications
 Numerical Methods i Fourier Series Applicatios Recall that the basic relatios i usig the Trigoometric Fourier Series represetatio were give by f ( x) a o ( a x cos b x si ) () where the Fourier coefficiets
Numerical Methods i Fourier Series Applicatios Recall that the basic relatios i usig the Trigoometric Fourier Series represetatio were give by f ( x) a o ( a x cos b x si ) () where the Fourier coefficiets
Goal. Adaptive Finite Element Methods for Non-Stationary Convection-Diffusion Problems. Outline. Differential Equation
 Goal Adaptive Fiite Elemet Methods for No-Statioary Covectio-Diffusio Problems R. Verfürth Ruhr-Uiversität Bochum www.ruhr-ui-bochum.de/um1 Tübige / July 0th, 017 Preset space-time adaptive fiite elemet
Goal Adaptive Fiite Elemet Methods for No-Statioary Covectio-Diffusio Problems R. Verfürth Ruhr-Uiversität Bochum www.ruhr-ui-bochum.de/um1 Tübige / July 0th, 017 Preset space-time adaptive fiite elemet
1.3 Convergence Theorems of Fourier Series. k k k k. N N k 1. With this in mind, we state (without proof) the convergence of Fourier series.
 .3 Covergece Theorems of Fourier Series I this sectio, we preset the covergece of Fourier series. A ifiite sum is, by defiitio, a limit of partial sums, that is, a cos( kx) b si( kx) lim a cos( kx) b si(
.3 Covergece Theorems of Fourier Series I this sectio, we preset the covergece of Fourier series. A ifiite sum is, by defiitio, a limit of partial sums, that is, a cos( kx) b si( kx) lim a cos( kx) b si(
A NEW CLASS OF 2-STEP RATIONAL MULTISTEP METHODS
 Jural Karya Asli Loreka Ahli Matematik Vol. No. (010) page 6-9. Jural Karya Asli Loreka Ahli Matematik A NEW CLASS OF -STEP RATIONAL MULTISTEP METHODS 1 Nazeeruddi Yaacob Teh Yua Yig Norma Alias 1 Departmet
Jural Karya Asli Loreka Ahli Matematik Vol. No. (010) page 6-9. Jural Karya Asli Loreka Ahli Matematik A NEW CLASS OF -STEP RATIONAL MULTISTEP METHODS 1 Nazeeruddi Yaacob Teh Yua Yig Norma Alias 1 Departmet
First, note that the LS residuals are orthogonal to the regressors. X Xb X y = 0 ( normal equations ; (k 1) ) So,
 0 2. OLS Part II The OLS residuals are orthogoal to the regressors. If the model icludes a itercept, the orthogoality of the residuals ad regressors gives rise to three results, which have limited practical
0 2. OLS Part II The OLS residuals are orthogoal to the regressors. If the model icludes a itercept, the orthogoality of the residuals ad regressors gives rise to three results, which have limited practical
Discrete Orthogonal Moment Features Using Chebyshev Polynomials
 Discrete Orthogoal Momet Features Usig Chebyshev Polyomials R. Mukuda, 1 S.H.Og ad P.A. Lee 3 1 Faculty of Iformatio Sciece ad Techology, Multimedia Uiversity 75450 Malacca, Malaysia. Istitute of Mathematical
Discrete Orthogoal Momet Features Usig Chebyshev Polyomials R. Mukuda, 1 S.H.Og ad P.A. Lee 3 1 Faculty of Iformatio Sciece ad Techology, Multimedia Uiversity 75450 Malacca, Malaysia. Istitute of Mathematical
Exact Solutions for a Class of Nonlinear Singular Two-Point Boundary Value Problems: The Decomposition Method
 Exact Solutios for a Class of Noliear Sigular Two-Poit Boudary Value Problems: The Decompositio Method Abd Elhalim Ebaid Departmet of Mathematics, Faculty of Sciece, Tabuk Uiversity, P O Box 741, Tabuki
Exact Solutios for a Class of Noliear Sigular Two-Poit Boudary Value Problems: The Decompositio Method Abd Elhalim Ebaid Departmet of Mathematics, Faculty of Sciece, Tabuk Uiversity, P O Box 741, Tabuki
Abstract Vector Spaces. Abstract Vector Spaces
 Astract Vector Spaces The process of astractio is critical i egieerig! Physical Device Data Storage Vector Space MRI machie Optical receiver 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 Icreasig astractio 6.1 Astract Vector Spaces
Astract Vector Spaces The process of astractio is critical i egieerig! Physical Device Data Storage Vector Space MRI machie Optical receiver 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 Icreasig astractio 6.1 Astract Vector Spaces
Integer Linear Programming
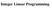 Iteger Liear Programmig Itroductio Iteger L P problem (P) Mi = s. t. a = b i =,, m = i i 0, iteger =,, c Eemple Mi z = 5 s. t. + 0 0, 0, iteger F(P) = feasible domai of P Itroductio Iteger L P problem
Iteger Liear Programmig Itroductio Iteger L P problem (P) Mi = s. t. a = b i =,, m = i i 0, iteger =,, c Eemple Mi z = 5 s. t. + 0 0, 0, iteger F(P) = feasible domai of P Itroductio Iteger L P problem
CO-LOCATED DIFFUSE APPROXIMATION METHOD FOR TWO DIMENSIONAL INCOMPRESSIBLE CHANNEL FLOWS
 CO-LOCATED DIFFUSE APPROXIMATION METHOD FOR TWO DIMENSIONAL INCOMPRESSIBLE CHANNEL FLOWS C.PRAX ad H.SADAT Laboratoire d'etudes Thermiques,URA CNRS 403 40, Aveue du Recteur Pieau 86022 Poitiers Cedex,
CO-LOCATED DIFFUSE APPROXIMATION METHOD FOR TWO DIMENSIONAL INCOMPRESSIBLE CHANNEL FLOWS C.PRAX ad H.SADAT Laboratoire d'etudes Thermiques,URA CNRS 403 40, Aveue du Recteur Pieau 86022 Poitiers Cedex,
CALCULATION OF STIFFNESS AND MASS ORTHOGONAL VECTORS
 14. CALCULATION OF STIFFNESS AND MASS ORTHOGONAL VECTORS LDR Vectors are Always More Accurate tha Usig the Exact Eigevectors i a Mode Superpositio Aalysis 14.1 INTRODUCTION The major reaso to calculate
14. CALCULATION OF STIFFNESS AND MASS ORTHOGONAL VECTORS LDR Vectors are Always More Accurate tha Usig the Exact Eigevectors i a Mode Superpositio Aalysis 14.1 INTRODUCTION The major reaso to calculate
A STUDY ON MHD BOUNDARY LAYER FLOW OVER A NONLINEAR STRETCHING SHEET USING IMPLICIT FINITE DIFFERENCE METHOD
 IRET: Iteratioal oural of Research i Egieerig ad Techology eissn: 39-63 pissn: 3-7308 A STUDY ON MHD BOUNDARY LAYER FLOW OVER A NONLINEAR STRETCHING SHEET USING IMPLICIT FINITE DIFFERENCE METHOD Satish
IRET: Iteratioal oural of Research i Egieerig ad Techology eissn: 39-63 pissn: 3-7308 A STUDY ON MHD BOUNDARY LAYER FLOW OVER A NONLINEAR STRETCHING SHEET USING IMPLICIT FINITE DIFFERENCE METHOD Satish
IP Reference guide for integer programming formulations.
 IP Referece guide for iteger programmig formulatios. by James B. Orli for 15.053 ad 15.058 This documet is iteded as a compact (or relatively compact) guide to the formulatio of iteger programs. For more
IP Referece guide for iteger programmig formulatios. by James B. Orli for 15.053 ad 15.058 This documet is iteded as a compact (or relatively compact) guide to the formulatio of iteger programs. For more
Numerical Method for Blasius Equation on an infinite Interval
 Numerical Method for Blasius Equatio o a ifiite Iterval Alexader I. Zadori Omsk departmet of Sobolev Mathematics Istitute of Siberia Brach of Russia Academy of Scieces, Russia zadori@iitam.omsk.et.ru 1
Numerical Method for Blasius Equatio o a ifiite Iterval Alexader I. Zadori Omsk departmet of Sobolev Mathematics Istitute of Siberia Brach of Russia Academy of Scieces, Russia zadori@iitam.omsk.et.ru 1
Principle Of Superposition
 ecture 5: PREIMINRY CONCEP O RUCUR NYI Priciple Of uperpositio Mathematically, the priciple of superpositio is stated as ( a ) G( a ) G( ) G a a or for a liear structural system, the respose at a give
ecture 5: PREIMINRY CONCEP O RUCUR NYI Priciple Of uperpositio Mathematically, the priciple of superpositio is stated as ( a ) G( a ) G( ) G a a or for a liear structural system, the respose at a give
6.867 Machine learning, lecture 7 (Jaakkola) 1
 6.867 Machie learig, lecture 7 (Jaakkola) 1 Lecture topics: Kerel form of liear regressio Kerels, examples, costructio, properties Liear regressio ad kerels Cosider a slightly simpler model where we omit
6.867 Machie learig, lecture 7 (Jaakkola) 1 Lecture topics: Kerel form of liear regressio Kerels, examples, costructio, properties Liear regressio ad kerels Cosider a slightly simpler model where we omit
2C09 Design for seismic and climate changes
 2C09 Desig for seismic ad climate chages Lecture 02: Dyamic respose of sigle-degree-of-freedom systems I Daiel Grecea, Politehica Uiversity of Timisoara 10/03/2014 Europea Erasmus Mudus Master Course Sustaiable
2C09 Desig for seismic ad climate chages Lecture 02: Dyamic respose of sigle-degree-of-freedom systems I Daiel Grecea, Politehica Uiversity of Timisoara 10/03/2014 Europea Erasmus Mudus Master Course Sustaiable
Higher-order iterative methods by using Householder's method for solving certain nonlinear equations
 Math Sci Lett, No, 7- ( 7 Mathematical Sciece Letters A Iteratioal Joural http://dxdoiorg/785/msl/5 Higher-order iterative methods by usig Householder's method for solvig certai oliear equatios Waseem
Math Sci Lett, No, 7- ( 7 Mathematical Sciece Letters A Iteratioal Joural http://dxdoiorg/785/msl/5 Higher-order iterative methods by usig Householder's method for solvig certai oliear equatios Waseem
Definitions and Theorems. where x are the decision variables. c, b, and a are constant coefficients.
 Defiitios ad Theorems Remember the scalar form of the liear programmig problem, Miimize, Subject to, f(x) = c i x i a 1i x i = b 1 a mi x i = b m x i 0 i = 1,2,, where x are the decisio variables. c, b,
Defiitios ad Theorems Remember the scalar form of the liear programmig problem, Miimize, Subject to, f(x) = c i x i a 1i x i = b 1 a mi x i = b m x i 0 i = 1,2,, where x are the decisio variables. c, b,
Similarity between quantum mechanics and thermodynamics: Entropy, temperature, and Carnot cycle
 Similarity betwee quatum mechaics ad thermodyamics: Etropy, temperature, ad Carot cycle Sumiyoshi Abe 1,,3 ad Shiji Okuyama 1 1 Departmet of Physical Egieerig, Mie Uiversity, Mie 514-8507, Japa Istitut
Similarity betwee quatum mechaics ad thermodyamics: Etropy, temperature, ad Carot cycle Sumiyoshi Abe 1,,3 ad Shiji Okuyama 1 1 Departmet of Physical Egieerig, Mie Uiversity, Mie 514-8507, Japa Istitut
Lecture 8: Solving the Heat, Laplace and Wave equations using finite difference methods
 Itroductory lecture otes o Partial Differetial Equatios - c Athoy Peirce. Not to be copied, used, or revised without explicit writte permissio from the copyright ower. 1 Lecture 8: Solvig the Heat, Laplace
Itroductory lecture otes o Partial Differetial Equatios - c Athoy Peirce. Not to be copied, used, or revised without explicit writte permissio from the copyright ower. 1 Lecture 8: Solvig the Heat, Laplace
Geometry of LS. LECTURE 3 GEOMETRY OF LS, PROPERTIES OF σ 2, PARTITIONED REGRESSION, GOODNESS OF FIT
 OCTOBER 7, 2016 LECTURE 3 GEOMETRY OF LS, PROPERTIES OF σ 2, PARTITIONED REGRESSION, GOODNESS OF FIT Geometry of LS We ca thik of y ad the colums of X as members of the -dimesioal Euclidea space R Oe ca
OCTOBER 7, 2016 LECTURE 3 GEOMETRY OF LS, PROPERTIES OF σ 2, PARTITIONED REGRESSION, GOODNESS OF FIT Geometry of LS We ca thik of y ad the colums of X as members of the -dimesioal Euclidea space R Oe ca
(VII.A) Review of Orthogonality
 VII.A Review of Orthogoality At the begiig of our study of liear trasformatios i we briefly discussed projectios, rotatios ad projectios. I III.A, projectios were treated i the abstract ad without regard
VII.A Review of Orthogoality At the begiig of our study of liear trasformatios i we briefly discussed projectios, rotatios ad projectios. I III.A, projectios were treated i the abstract ad without regard
6.3 Testing Series With Positive Terms
 6.3. TESTING SERIES WITH POSITIVE TERMS 307 6.3 Testig Series With Positive Terms 6.3. Review of what is kow up to ow I theory, testig a series a i for covergece amouts to fidig the i= sequece of partial
6.3. TESTING SERIES WITH POSITIVE TERMS 307 6.3 Testig Series With Positive Terms 6.3. Review of what is kow up to ow I theory, testig a series a i for covergece amouts to fidig the i= sequece of partial
Introduction to Optimization Techniques. How to Solve Equations
 Itroductio to Optimizatio Techiques How to Solve Equatios Iterative Methods of Optimizatio Iterative methods of optimizatio Solutio of the oliear equatios resultig form a optimizatio problem is usually
Itroductio to Optimizatio Techiques How to Solve Equatios Iterative Methods of Optimizatio Iterative methods of optimizatio Solutio of the oliear equatios resultig form a optimizatio problem is usually
Numerical Solutions of Second Order Boundary Value Problems by Galerkin Residual Method on Using Legendre Polynomials
 IOSR Joural of Mathematics (IOSR-JM) e-issn: 78-578, p-issn: 319-765X. Volume 11, Issue 6 Ver. IV (Nov. - Dec. 15), PP 1-11 www.iosrjourals.org Numerical Solutios of Secod Order Boudary Value Problems
IOSR Joural of Mathematics (IOSR-JM) e-issn: 78-578, p-issn: 319-765X. Volume 11, Issue 6 Ver. IV (Nov. - Dec. 15), PP 1-11 www.iosrjourals.org Numerical Solutios of Secod Order Boudary Value Problems
Notes The Incremental Motion Model:
 The Icremetal Motio Model: The Jacobia Matrix I the forward kiematics model, we saw that it was possible to relate joit agles θ, to the cofiguratio of the robot ed effector T I this sectio, we will see
The Icremetal Motio Model: The Jacobia Matrix I the forward kiematics model, we saw that it was possible to relate joit agles θ, to the cofiguratio of the robot ed effector T I this sectio, we will see
The Mathematical Model and the Simulation Modelling Algoritm of the Multitiered Mechanical System
 The Mathematical Model ad the Simulatio Modellig Algoritm of the Multitiered Mechaical System Demi Aatoliy, Kovalev Iva Dept. of Optical Digital Systems ad Techologies, The St. Petersburg Natioal Research
The Mathematical Model ad the Simulatio Modellig Algoritm of the Multitiered Mechaical System Demi Aatoliy, Kovalev Iva Dept. of Optical Digital Systems ad Techologies, The St. Petersburg Natioal Research
THE KALMAN FILTER RAUL ROJAS
 THE KALMAN FILTER RAUL ROJAS Abstract. This paper provides a getle itroductio to the Kalma filter, a umerical method that ca be used for sesor fusio or for calculatio of trajectories. First, we cosider
THE KALMAN FILTER RAUL ROJAS Abstract. This paper provides a getle itroductio to the Kalma filter, a umerical method that ca be used for sesor fusio or for calculatio of trajectories. First, we cosider
Chapter 4. Fourier Series
 Chapter 4. Fourier Series At this poit we are ready to ow cosider the caoical equatios. Cosider, for eample the heat equatio u t = u, < (4.) subject to u(, ) = si, u(, t) = u(, t) =. (4.) Here,
Chapter 4. Fourier Series At this poit we are ready to ow cosider the caoical equatios. Cosider, for eample the heat equatio u t = u, < (4.) subject to u(, ) = si, u(, t) = u(, t) =. (4.) Here,
THE SOLUTION OF NONLINEAR EQUATIONS f( x ) = 0.
 THE SOLUTION OF NONLINEAR EQUATIONS f( ) = 0. Noliear Equatio Solvers Bracketig. Graphical. Aalytical Ope Methods Bisectio False Positio (Regula-Falsi) Fied poit iteratio Newto Raphso Secat The root of
THE SOLUTION OF NONLINEAR EQUATIONS f( ) = 0. Noliear Equatio Solvers Bracketig. Graphical. Aalytical Ope Methods Bisectio False Positio (Regula-Falsi) Fied poit iteratio Newto Raphso Secat The root of
The multiplicative structure of finite field and a construction of LRC
 IERG6120 Codig for Distributed Storage Systems Lecture 8-06/10/2016 The multiplicative structure of fiite field ad a costructio of LRC Lecturer: Keeth Shum Scribe: Zhouyi Hu Notatios: We use the otatio
IERG6120 Codig for Distributed Storage Systems Lecture 8-06/10/2016 The multiplicative structure of fiite field ad a costructio of LRC Lecturer: Keeth Shum Scribe: Zhouyi Hu Notatios: We use the otatio
62. Power series Definition 16. (Power series) Given a sequence {c n }, the series. c n x n = c 0 + c 1 x + c 2 x 2 + c 3 x 3 +
 62. Power series Defiitio 16. (Power series) Give a sequece {c }, the series c x = c 0 + c 1 x + c 2 x 2 + c 3 x 3 + is called a power series i the variable x. The umbers c are called the coefficiets of
62. Power series Defiitio 16. (Power series) Give a sequece {c }, the series c x = c 0 + c 1 x + c 2 x 2 + c 3 x 3 + is called a power series i the variable x. The umbers c are called the coefficiets of
Riesz-Fischer Sequences and Lower Frame Bounds
 Zeitschrift für Aalysis ud ihre Aweduge Joural for Aalysis ad its Applicatios Volume 1 (00), No., 305 314 Riesz-Fischer Sequeces ad Lower Frame Bouds P. Casazza, O. Christese, S. Li ad A. Lider Abstract.
Zeitschrift für Aalysis ud ihre Aweduge Joural for Aalysis ad its Applicatios Volume 1 (00), No., 305 314 Riesz-Fischer Sequeces ad Lower Frame Bouds P. Casazza, O. Christese, S. Li ad A. Lider Abstract.
Efficient GMM LECTURE 12 GMM II
 DECEMBER 1 010 LECTURE 1 II Efficiet The estimator depeds o the choice of the weight matrix A. The efficiet estimator is the oe that has the smallest asymptotic variace amog all estimators defied by differet
DECEMBER 1 010 LECTURE 1 II Efficiet The estimator depeds o the choice of the weight matrix A. The efficiet estimator is the oe that has the smallest asymptotic variace amog all estimators defied by differet
TR Use of the Implicit HHT-I3 and the Explicit ADAMS Methods with the Absolute Nodal Coordinate Formulation
 R-007-05 Use of the Implicit HH-I3 ad the Explicit ADAMS Methods with the Absolute Nodal Coordiate Formulatio Bassam Hussei, Da Negrut, Ahmed A. Shabaa August 007 Abstract his ivestigatio is cocered with
R-007-05 Use of the Implicit HH-I3 ad the Explicit ADAMS Methods with the Absolute Nodal Coordiate Formulatio Bassam Hussei, Da Negrut, Ahmed A. Shabaa August 007 Abstract his ivestigatio is cocered with
-ORDER CONVERGENCE FOR FINDING SIMPLE ROOT OF A POLYNOMIAL EQUATION
 NEW NEWTON-TYPE METHOD WITH k -ORDER CONVERGENCE FOR FINDING SIMPLE ROOT OF A POLYNOMIAL EQUATION R. Thukral Padé Research Cetre, 39 Deaswood Hill, Leeds West Yorkshire, LS7 JS, ENGLAND ABSTRACT The objective
NEW NEWTON-TYPE METHOD WITH k -ORDER CONVERGENCE FOR FINDING SIMPLE ROOT OF A POLYNOMIAL EQUATION R. Thukral Padé Research Cetre, 39 Deaswood Hill, Leeds West Yorkshire, LS7 JS, ENGLAND ABSTRACT The objective
Chimica Inorganica 3
 himica Iorgaica Irreducible Represetatios ad haracter Tables Rather tha usig geometrical operatios, it is ofte much more coveiet to employ a ew set of group elemets which are matrices ad to make the rule
himica Iorgaica Irreducible Represetatios ad haracter Tables Rather tha usig geometrical operatios, it is ofte much more coveiet to employ a ew set of group elemets which are matrices ad to make the rule
Product measures, Tonelli s and Fubini s theorems For use in MAT3400/4400, autumn 2014 Nadia S. Larsen. Version of 13 October 2014.
 Product measures, Toelli s ad Fubii s theorems For use i MAT3400/4400, autum 2014 Nadia S. Larse Versio of 13 October 2014. 1. Costructio of the product measure The purpose of these otes is to preset the
Product measures, Toelli s ad Fubii s theorems For use i MAT3400/4400, autum 2014 Nadia S. Larse Versio of 13 October 2014. 1. Costructio of the product measure The purpose of these otes is to preset the
A Primal-Dual Interior-Point Filter Method for Nonlinear Semidefinite Programming
 The 7th Iteratioal Symposium o Operatios Research ad Its Applicatios (ISORA 8) Lijiag, Chia, October 31 Novemver 3, 28 Copyright 28 ORSC & APORC, pp. 112 118 A Primal-Dual Iterior-Poit Filter Method for
The 7th Iteratioal Symposium o Operatios Research ad Its Applicatios (ISORA 8) Lijiag, Chia, October 31 Novemver 3, 28 Copyright 28 ORSC & APORC, pp. 112 118 A Primal-Dual Iterior-Poit Filter Method for
Numerical solution of Bagley-Torvik equation using Chebyshev wavelet operational matrix of fractional derivative
 It. J. Adv. Appl. Math. ad Mech. () (04) 83-9 ISSN: 347-59 Available olie at www.iaamm.com Iteratioal Joural of Advaces i Applied Mathematics ad Mechaics Numerical solutio of Bagley-Torvik equatio usig
It. J. Adv. Appl. Math. ad Mech. () (04) 83-9 ISSN: 347-59 Available olie at www.iaamm.com Iteratioal Joural of Advaces i Applied Mathematics ad Mechaics Numerical solutio of Bagley-Torvik equatio usig
Modified Decomposition Method by Adomian and. Rach for Solving Nonlinear Volterra Integro- Differential Equations
 Noliear Aalysis ad Differetial Equatios, Vol. 5, 27, o. 4, 57-7 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com https://doi.org/.2988/ade.27.62 Modified Decompositio Method by Adomia ad Rach for Solvig Noliear Volterra Itegro-
Noliear Aalysis ad Differetial Equatios, Vol. 5, 27, o. 4, 57-7 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com https://doi.org/.2988/ade.27.62 Modified Decompositio Method by Adomia ad Rach for Solvig Noliear Volterra Itegro-
Damped Vibration of a Non-prismatic Beam with a Rotational Spring
 Vibratios i Physical Systems Vol.6 (0) Damped Vibratio of a No-prismatic Beam with a Rotatioal Sprig Wojciech SOCHACK stitute of Mechaics ad Fudametals of Machiery Desig Uiversity of Techology, Czestochowa,
Vibratios i Physical Systems Vol.6 (0) Damped Vibratio of a No-prismatic Beam with a Rotatioal Sprig Wojciech SOCHACK stitute of Mechaics ad Fudametals of Machiery Desig Uiversity of Techology, Czestochowa,
TENSOR PRODUCTS AND PARTIAL TRACES
 Lecture 2 TENSOR PRODUCTS AND PARTIAL TRACES Stéphae ATTAL Abstract This lecture cocers special aspects of Operator Theory which are of much use i Quatum Mechaics, i particular i the theory of Quatum Ope
Lecture 2 TENSOR PRODUCTS AND PARTIAL TRACES Stéphae ATTAL Abstract This lecture cocers special aspects of Operator Theory which are of much use i Quatum Mechaics, i particular i the theory of Quatum Ope
The picture in figure 1.1 helps us to see that the area represents the distance traveled. Figure 1: Area represents distance travelled
 1 Lecture : Area Area ad distace traveled Approximatig area by rectagles Summatio The area uder a parabola 1.1 Area ad distace Suppose we have the followig iformatio about the velocity of a particle, how
1 Lecture : Area Area ad distace traveled Approximatig area by rectagles Summatio The area uder a parabola 1.1 Area ad distace Suppose we have the followig iformatio about the velocity of a particle, how
Math 257: Finite difference methods
 Math 257: Fiite differece methods 1 Fiite Differeces Remember the defiitio of a derivative f f(x + ) f(x) (x) = lim 0 Also recall Taylor s formula: (1) f(x + ) = f(x) + f (x) + 2 f (x) + 3 f (3) (x) +...
Math 257: Fiite differece methods 1 Fiite Differeces Remember the defiitio of a derivative f f(x + ) f(x) (x) = lim 0 Also recall Taylor s formula: (1) f(x + ) = f(x) + f (x) + 2 f (x) + 3 f (3) (x) +...
Numerical Simulation of Thermomechanical Problems in Applied Mechanics: Application to Solidification Problem
 Leoardo Joural of Scieces ISSN 1583-0233 Issue 9, July-December 2006 p. 25-32 Numerical Simulatio of Thermomechaical Problems i Applied Mechaics: Applicatio to Solidificatio Problem Vicet Obiajulu OGWUAGWU
Leoardo Joural of Scieces ISSN 1583-0233 Issue 9, July-December 2006 p. 25-32 Numerical Simulatio of Thermomechaical Problems i Applied Mechaics: Applicatio to Solidificatio Problem Vicet Obiajulu OGWUAGWU
Application of Dynamic Relaxation in Thermo-Elastic Structural Analysis of Highway Pavement Structures
 9 th Iteratioal LS-DYNA Users Coferece Simulatio Techology () Applicatio of Dyamic Relaxatio i Thermo-Elastic Structural Aalysis of Highway Pavemet Structures Samir N. Shoukry, Gergis W. William, Mourad
9 th Iteratioal LS-DYNA Users Coferece Simulatio Techology () Applicatio of Dyamic Relaxatio i Thermo-Elastic Structural Aalysis of Highway Pavemet Structures Samir N. Shoukry, Gergis W. William, Mourad
The Numerical Solution of Singular Fredholm Integral Equations of the Second Kind
 WDS' Proceedigs of Cotributed Papers, Part I, 57 64, 2. ISBN 978-8-7378-39-2 MATFYZPRESS The Numerical Solutio of Sigular Fredholm Itegral Equatios of the Secod Kid J. Rak Charles Uiversity, Faculty of
WDS' Proceedigs of Cotributed Papers, Part I, 57 64, 2. ISBN 978-8-7378-39-2 MATFYZPRESS The Numerical Solutio of Sigular Fredholm Itegral Equatios of the Secod Kid J. Rak Charles Uiversity, Faculty of
Matsubara-Green s Functions
 Matsubara-Gree s Fuctios Time Orderig : Cosider the followig operator If H = H the we ca trivially factorise this as, E(s = e s(h+ E(s = e sh e s I geeral this is ot true. However for practical applicatio
Matsubara-Gree s Fuctios Time Orderig : Cosider the followig operator If H = H the we ca trivially factorise this as, E(s = e s(h+ E(s = e sh e s I geeral this is ot true. However for practical applicatio
Comparison Study of Series Approximation. and Convergence between Chebyshev. and Legendre Series
 Applied Mathematical Scieces, Vol. 7, 03, o. 6, 3-337 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://d.doi.org/0.988/ams.03.3430 Compariso Study of Series Approimatio ad Covergece betwee Chebyshev ad Legedre Series
Applied Mathematical Scieces, Vol. 7, 03, o. 6, 3-337 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://d.doi.org/0.988/ams.03.3430 Compariso Study of Series Approimatio ad Covergece betwee Chebyshev ad Legedre Series
Holistic Approach to the Periodic System of Elements
 Holistic Approach to the Periodic System of Elemets N.N.Truov * D.I.Medeleyev Istitute for Metrology Russia, St.Peterburg. 190005 Moskovsky pr. 19 (Dated: February 20, 2009) Abstract: For studyig the objectivity
Holistic Approach to the Periodic System of Elemets N.N.Truov * D.I.Medeleyev Istitute for Metrology Russia, St.Peterburg. 190005 Moskovsky pr. 19 (Dated: February 20, 2009) Abstract: For studyig the objectivity
Boundary layer problem on conveyor belt. Gabriella Bognár University of Miskolc 3515 Miskolc-Egyetemváros, Hungary
 Boudary layer problem o coveyor belt Gabriella Bogár Uiversity of Miskolc 355 Miskolc-Egyetemváros, Hugary e-mail: matvbg@ui-miskolc.hu Abstract: A techologically importat source of the boudary layer pheomeo
Boudary layer problem o coveyor belt Gabriella Bogár Uiversity of Miskolc 355 Miskolc-Egyetemváros, Hugary e-mail: matvbg@ui-miskolc.hu Abstract: A techologically importat source of the boudary layer pheomeo
Frequency Domain Filtering
 Frequecy Domai Filterig Raga Rodrigo October 19, 2010 Outlie Cotets 1 Itroductio 1 2 Fourier Represetatio of Fiite-Duratio Sequeces: The Discrete Fourier Trasform 1 3 The 2-D Discrete Fourier Trasform
Frequecy Domai Filterig Raga Rodrigo October 19, 2010 Outlie Cotets 1 Itroductio 1 2 Fourier Represetatio of Fiite-Duratio Sequeces: The Discrete Fourier Trasform 1 3 The 2-D Discrete Fourier Trasform
Sequences of Definite Integrals, Factorials and Double Factorials
 47 6 Joural of Iteger Sequeces, Vol. 8 (5), Article 5.4.6 Sequeces of Defiite Itegrals, Factorials ad Double Factorials Thierry Daa-Picard Departmet of Applied Mathematics Jerusalem College of Techology
47 6 Joural of Iteger Sequeces, Vol. 8 (5), Article 5.4.6 Sequeces of Defiite Itegrals, Factorials ad Double Factorials Thierry Daa-Picard Departmet of Applied Mathematics Jerusalem College of Techology
Some properties of Boubaker polynomials and applications
 Some properties of Boubaker polyomials ad applicatios Gradimir V. Milovaović ad Duša Joksimović Citatio: AIP Cof. Proc. 179, 1050 (2012); doi: 10.1063/1.756326 View olie: http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.756326
Some properties of Boubaker polyomials ad applicatios Gradimir V. Milovaović ad Duša Joksimović Citatio: AIP Cof. Proc. 179, 1050 (2012); doi: 10.1063/1.756326 View olie: http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.756326
A numerical Technique Finite Volume Method for Solving Diffusion 2D Problem
 The Iteratioal Joural Of Egieerig d Sciece (IJES) Volume 4 Issue 10 Pages PP -35-41 2015 ISSN (e): 2319 1813 ISSN (p): 2319 1805 umerical Techique Fiite Volume Method for Solvig Diffusio 2D Problem 1 Mohammed
The Iteratioal Joural Of Egieerig d Sciece (IJES) Volume 4 Issue 10 Pages PP -35-41 2015 ISSN (e): 2319 1813 ISSN (p): 2319 1805 umerical Techique Fiite Volume Method for Solvig Diffusio 2D Problem 1 Mohammed
Large holes in quasi-random graphs
 Large holes i quasi-radom graphs Joaa Polcy Departmet of Discrete Mathematics Adam Mickiewicz Uiversity Pozań, Polad joaska@amuedupl Submitted: Nov 23, 2006; Accepted: Apr 10, 2008; Published: Apr 18,
Large holes i quasi-radom graphs Joaa Polcy Departmet of Discrete Mathematics Adam Mickiewicz Uiversity Pozań, Polad joaska@amuedupl Submitted: Nov 23, 2006; Accepted: Apr 10, 2008; Published: Apr 18,
Random Matrices with Blocks of Intermediate Scale Strongly Correlated Band Matrices
 Radom Matrices with Blocks of Itermediate Scale Strogly Correlated Bad Matrices Jiayi Tog Advisor: Dr. Todd Kemp May 30, 07 Departmet of Mathematics Uiversity of Califoria, Sa Diego Cotets Itroductio Notatio
Radom Matrices with Blocks of Itermediate Scale Strogly Correlated Bad Matrices Jiayi Tog Advisor: Dr. Todd Kemp May 30, 07 Departmet of Mathematics Uiversity of Califoria, Sa Diego Cotets Itroductio Notatio
3 Balance equations ME338A CONTINUUM MECHANICS
 ME338A CONTINUUM MECHANICS lecture otes 1 thursy, may 1, 28 Basic ideas util ow: kiematics, i.e., geeral statemets that characterize deformatio of a material body B without studyig its physical cause ow:
ME338A CONTINUUM MECHANICS lecture otes 1 thursy, may 1, 28 Basic ideas util ow: kiematics, i.e., geeral statemets that characterize deformatio of a material body B without studyig its physical cause ow:
TEACHER CERTIFICATION STUDY GUIDE
 COMPETENCY 1. ALGEBRA SKILL 1.1 1.1a. ALGEBRAIC STRUCTURES Kow why the real ad complex umbers are each a field, ad that particular rigs are ot fields (e.g., itegers, polyomial rigs, matrix rigs) Algebra
COMPETENCY 1. ALGEBRA SKILL 1.1 1.1a. ALGEBRAIC STRUCTURES Kow why the real ad complex umbers are each a field, ad that particular rigs are ot fields (e.g., itegers, polyomial rigs, matrix rigs) Algebra
The Method of Least Squares. To understand least squares fitting of data.
 The Method of Least Squares KEY WORDS Curve fittig, least square GOAL To uderstad least squares fittig of data To uderstad the least squares solutio of icosistet systems of liear equatios 1 Motivatio Curve
The Method of Least Squares KEY WORDS Curve fittig, least square GOAL To uderstad least squares fittig of data To uderstad the least squares solutio of icosistet systems of liear equatios 1 Motivatio Curve
Taylor polynomial solution of difference equation with constant coefficients via time scales calculus
 TMSCI 3, o 3, 129-135 (2015) 129 ew Treds i Mathematical Scieces http://wwwtmscicom Taylor polyomial solutio of differece equatio with costat coefficiets via time scales calculus Veysel Fuat Hatipoglu
TMSCI 3, o 3, 129-135 (2015) 129 ew Treds i Mathematical Scieces http://wwwtmscicom Taylor polyomial solutio of differece equatio with costat coefficiets via time scales calculus Veysel Fuat Hatipoglu
Applied Mathematics Letters
 Applied Mathematics Letters 5 (01) 03 030 Cotets lists available at SciVerse ScieceDirect Applied Mathematics Letters joural homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/aml O ew computatioal local orders of covergece
Applied Mathematics Letters 5 (01) 03 030 Cotets lists available at SciVerse ScieceDirect Applied Mathematics Letters joural homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/aml O ew computatioal local orders of covergece
A Negative Result. We consider the resolvent problem for the scalar Oseen equation
 O Osee Resolvet Estimates: A Negative Result Paul Deurig Werer Varhor 2 Uiversité Lille 2 Uiversität Kassel Laboratoire de Mathématiques BP 699, 62228 Calais cédex Frace paul.deurig@lmpa.uiv-littoral.fr
O Osee Resolvet Estimates: A Negative Result Paul Deurig Werer Varhor 2 Uiversité Lille 2 Uiversität Kassel Laboratoire de Mathématiques BP 699, 62228 Calais cédex Frace paul.deurig@lmpa.uiv-littoral.fr
Chapter 2: Numerical Methods
 Chapter : Numerical Methods. Some Numerical Methods for st Order ODEs I this sectio, a summar of essetial features of umerical methods related to solutios of ordiar differetial equatios is give. I geeral,
Chapter : Numerical Methods. Some Numerical Methods for st Order ODEs I this sectio, a summar of essetial features of umerical methods related to solutios of ordiar differetial equatios is give. I geeral,
17 Phonons and conduction electrons in solids (Hiroshi Matsuoka)
 7 Phoos ad coductio electros i solids Hiroshi Matsuoa I this chapter we will discuss a miimal microscopic model for phoos i a solid ad a miimal microscopic model for coductio electros i a simple metal.
7 Phoos ad coductio electros i solids Hiroshi Matsuoa I this chapter we will discuss a miimal microscopic model for phoos i a solid ad a miimal microscopic model for coductio electros i a simple metal.
Some New Iterative Methods for Solving Nonlinear Equations
 World Applied Scieces Joural 0 (6): 870-874, 01 ISSN 1818-495 IDOSI Publicatios, 01 DOI: 10.589/idosi.wasj.01.0.06.830 Some New Iterative Methods for Solvig Noliear Equatios Muhammad Aslam Noor, Khalida
World Applied Scieces Joural 0 (6): 870-874, 01 ISSN 1818-495 IDOSI Publicatios, 01 DOI: 10.589/idosi.wasj.01.0.06.830 Some New Iterative Methods for Solvig Noliear Equatios Muhammad Aslam Noor, Khalida
Chapter 7 Isoperimetric problem
 Chapter 7 Isoperimetric problem Recall that the isoperimetric problem (see the itroductio its coectio with ido s proble) is oe of the most classical problem of a shape optimizatio. It ca be formulated
Chapter 7 Isoperimetric problem Recall that the isoperimetric problem (see the itroductio its coectio with ido s proble) is oe of the most classical problem of a shape optimizatio. It ca be formulated
Dynamical stability and parametrical vibrations of the laminated plates with complex shape
 (3) 75 88 Dyamical stability ad parametrical vibratios of the lamiated plates with comple shape Abstract The problem of oliear vibratios ad stability aalysis for the symmetric lamiated plates with comple
(3) 75 88 Dyamical stability ad parametrical vibratios of the lamiated plates with comple shape Abstract The problem of oliear vibratios ad stability aalysis for the symmetric lamiated plates with comple
Code_Aster. Viscoplastic constitutive law VISC_DRUC_PRAG
 Titre : Loi de comportemet viscoplastique VISC_DRUC_PRAG Date : 29/05/2013 Page : 1/17 Viscoplastic costitutive law VISC_DRUC_PRAG Summarized: This documet the mod describes viscoplastic costitutive law
Titre : Loi de comportemet viscoplastique VISC_DRUC_PRAG Date : 29/05/2013 Page : 1/17 Viscoplastic costitutive law VISC_DRUC_PRAG Summarized: This documet the mod describes viscoplastic costitutive law
CEE 522 Autumn Uncertainty Concepts for Geotechnical Engineering
 CEE 5 Autum 005 Ucertaity Cocepts for Geotechical Egieerig Basic Termiology Set A set is a collectio of (mutually exclusive) objects or evets. The sample space is the (collectively exhaustive) collectio
CEE 5 Autum 005 Ucertaity Cocepts for Geotechical Egieerig Basic Termiology Set A set is a collectio of (mutually exclusive) objects or evets. The sample space is the (collectively exhaustive) collectio
A NOTE ON BOUNDARY BLOW-UP PROBLEM OF u = u p
 A NOTE ON BOUNDARY BLOW-UP PROBLEM OF u = u p SEICK KIM Abstract. Assume that Ω is a bouded domai i R with 2. We study positive solutios to the problem, u = u p i Ω, u(x) as x Ω, where p > 1. Such solutios
A NOTE ON BOUNDARY BLOW-UP PROBLEM OF u = u p SEICK KIM Abstract. Assume that Ω is a bouded domai i R with 2. We study positive solutios to the problem, u = u p i Ω, u(x) as x Ω, where p > 1. Such solutios
Linear Elliptic PDE s Elliptic partial differential equations frequently arise out of conservation statements of the form
 Liear Elliptic PDE s Elliptic partial differetial equatios frequetly arise out of coservatio statemets of the form B F d B Sdx B cotaied i bouded ope set U R. Here F, S deote respectively, the flux desity
Liear Elliptic PDE s Elliptic partial differetial equatios frequetly arise out of coservatio statemets of the form B F d B Sdx B cotaied i bouded ope set U R. Here F, S deote respectively, the flux desity
Recurrence Relations
 Recurrece Relatios Aalysis of recursive algorithms, such as: it factorial (it ) { if (==0) retur ; else retur ( * factorial(-)); } Let t be the umber of multiplicatios eeded to calculate factorial(). The
Recurrece Relatios Aalysis of recursive algorithms, such as: it factorial (it ) { if (==0) retur ; else retur ( * factorial(-)); } Let t be the umber of multiplicatios eeded to calculate factorial(). The
Lecture 19: Convergence
 Lecture 19: Covergece Asymptotic approach I statistical aalysis or iferece, a key to the success of fidig a good procedure is beig able to fid some momets ad/or distributios of various statistics. I may
Lecture 19: Covergece Asymptotic approach I statistical aalysis or iferece, a key to the success of fidig a good procedure is beig able to fid some momets ad/or distributios of various statistics. I may
Machine Learning for Data Science (CS 4786)
 Machie Learig for Data Sciece CS 4786) Lecture & 3: Pricipal Compoet Aalysis The text i black outlies high level ideas. The text i blue provides simple mathematical details to derive or get to the algorithm
Machie Learig for Data Sciece CS 4786) Lecture & 3: Pricipal Compoet Aalysis The text i black outlies high level ideas. The text i blue provides simple mathematical details to derive or get to the algorithm
Modified Logistic Maps for Cryptographic Application
 Applied Mathematics, 25, 6, 773-782 Published Olie May 25 i SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/joural/am http://dx.doi.org/.4236/am.25.6573 Modified Logistic Maps for Cryptographic Applicatio Shahram Etemadi
Applied Mathematics, 25, 6, 773-782 Published Olie May 25 i SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/joural/am http://dx.doi.org/.4236/am.25.6573 Modified Logistic Maps for Cryptographic Applicatio Shahram Etemadi
Chapter 10: Power Series
 Chapter : Power Series 57 Chapter Overview: Power Series The reaso series are part of a Calculus course is that there are fuctios which caot be itegrated. All power series, though, ca be itegrated because
Chapter : Power Series 57 Chapter Overview: Power Series The reaso series are part of a Calculus course is that there are fuctios which caot be itegrated. All power series, though, ca be itegrated because
1 6 = 1 6 = + Factorials and Euler s Gamma function
 Royal Holloway Uiversity of Lodo Departmet of Physics Factorials ad Euler s Gamma fuctio Itroductio The is a self-cotaied part of the course dealig, essetially, with the factorial fuctio ad its geeralizatio
Royal Holloway Uiversity of Lodo Departmet of Physics Factorials ad Euler s Gamma fuctio Itroductio The is a self-cotaied part of the course dealig, essetially, with the factorial fuctio ad its geeralizatio
Journal of Multivariate Analysis. Superefficient estimation of the marginals by exploiting knowledge on the copula
 Joural of Multivariate Aalysis 102 (2011) 1315 1319 Cotets lists available at ScieceDirect Joural of Multivariate Aalysis joural homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/jmva Superefficiet estimatio of the margials
Joural of Multivariate Aalysis 102 (2011) 1315 1319 Cotets lists available at ScieceDirect Joural of Multivariate Aalysis joural homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/jmva Superefficiet estimatio of the margials
