Physics Final Exam Formulas
|
|
|
- Todd Singleton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 INSTRUCTIONS: Write your NAME on the front of the blue exam booklet. The exam is closed book, and you may have only pens/pencils and a calculator. Show all of your work in the blue book. For problems II-VI, an answer alone is worth very little credit, even if it is correct so show how you get it. Small print: Do not assume ANYTHING is obvious if it s not clear, please ask. It s hard to write these questions, and we often forget things. Suggestions: Draw a diagram when possible, circle or box your final answers, and cross out parts which you do not want us to consider. Physics Final Exam Formulas Kinematics : Constant a x : x = x 0 + v 0,x t a xt 2 v x = v 0,x + a x t v 2 x = v2 0,x + 2a x(x x 0 ) 3D : v = d r = v xî + v yĵ + v zˆk = dx î + dy ĵ + dz ˆk at 2 + bt + c = 0 t = b ± b 2 4ac ; Newton : 2a a = d v = a xî +... = dv x î +... = d2 x 2 î +... F = Ftot = m a Work : W on object = Fon object d r U = W K = W U gravity = mg h Power = F v = τ ω = W/ t = dw/ F x, spring = kx U spring = 1 2 kx2 F centrip = mv2 r Conservation of Energy : K f + U f = K i + U i + W into system K lin = 1 2 mv2 F kinetic friction = µ k F normal F static friction µ s F normal p = m v J = p = pf p i Systems : M tot x c.m. = i m i x i p tot = M tot v c.m. v c.m. = d r c.m. U grav = M tot gy c.m. Rotation : α = const. ω = ω 0 + αt ω 2 = ω α(θ θ 0 ) θ = θ 0 + ω 0 t αt2 1 rev. = 2π rad τ = Iα vt = rω a t = rα a r = rω 2 I = i m i r 2 i K rot = 1 2 Iω2 L = r p = I ω τ = r F = r F sin φ = r F I parallel = I c.m. + Mh 2 F net = d P c.m. τ net = d L c.m. Elastic : v i + v f = V i + V f f = ω/2π f = 1/T F grav = GM 1M 2 r 2 U grav = GM 1M 2 r (U = 0 at r = ) G = Nm 2 /kg 2 Fluid Statics : p 2 = p 1 + ρg h Pascal : p 1 = p 2 F 1 A 1 = F 2 A 2 Archimedes : F b = ρ W gv displ Fluid Dynamics : Continuity : A 1 v 1 = A 2 v 2 Bernoulli : p 1 + ρgy ρv2 1 = p 2 + ρgy ρv2 2 d SHM : 2 x = ( ) k 2 m x ω = k/m = 2πf = 2π/T x = A cos(ωt + φ) Waves : y = A sin(kx ωt + φ) k = 2π/λ fλ = v = ω/k v = F/µ φ/2π = x/λ P ave E 2 A 2 Intensity : I = P ave /Area A sin α + A sin β = 2A cos [ 1 (α 2 β)] sin [ 1(α + β)] 2 Decibels : SL = 10 log I/I 0 I 0 = W/m 2 Doppler : f = f 0 v v±v s Shock : sin θ = v/v s Expansion : L = αl T V = 3αV T pv = Nk B T = nrt M = mn A P ave = 1 2 µvω2 A 2 K ave = 3k 2 BT K tot = 3nRT E 2 i = 1k 2 BT v rms = 3p/ρ = 3RT/M HeatConduction : dq = ka dt dx First Law : dq + dw = de int Q = mc T Q f = ml f Page 1 of 6
2 W = p dv pv γ = const W = 1 γ 1 (p fv f p i V i ) C V + R = C P γ = C P C V S = dq T S = nr ln V f V i + nc V ln T f T i ε = W Q in = Q H Q C Q H = 1 Q C Q H = 1 T C TH (engine) multiplicity : w = N! (N r)!r! S = k B ln w ln N! N ln N N γ = 1 1 v 2 /c 2 Length : L = L 0 /γ Time : t = γt 0 E tot = γmc 2 E rest = mc 2 p = mvγ Lorentz Transformations :( v = vˆx) t = γ(t vx/c 2 ) x = γ(x vt) y = y z = z Some Constants: Velocity Addition : v = v u x 1 vu x /c 2 E 2 = p 2 c 2 + m 2 c 4 Mass of the Earth kg Radius of Earth m Mass of the Sun kg Radius of Earth s Orbit m Density of Water 1000 kg/m 3 Boltzmann k B = J/K N A R 8.31 J/mol K L f ice 333 kj/kg L f steam 2256 kj/kg c water 4190 J/kg K 1 atm Pa Page 2 of 6
3 I. Multiple Choice Questions (4 points each) Please write the letter corresponding to your answer for each question in the grid you made on the first inside page of your blue book. No partial credit is given for these questions. 1. For the Carnot cycle shown in the S-T diagram below, the total heat that enters the system during one entire cycle is T (K) S (J/K) (a) 75J (b) 200J (c) 125J (d) 125J (e) 75J 2. Oxygen has a molar mass of 32 g/mol and nitrogen has a molar mass of 28 g/mol. The oxygen and nitrogen molecules in a room of uniform temperature have (a) equal average kinetic energies, but the oxygen molecules are faster. (b) equal average kinetic energies, but the nitrogen molecules are faster. (c) equal average kinetic energies and speeds. (d) equal average speeds, but the oxygen molecules have a higher average kinetic energy. (e) equal average speeds, but the nitrogen molecules have a higher average kinetic energy. 3. Water flows out of a huge tank through the plumbing shown in the diagram. At which point is the pressure the least? (a) A (b) B (c) C (d) D (e) All of the pressures are the same. A B C D Page 3 of 6
4 4. Five satellites orbit the earth in circular orbits, each with different orbit radius and mass, as shown. Which of these would require the most energy to escape from earth orbit? ½ m (a) R 2R m (b) 3R (e) 5R (c) 3m 4R (d) 2m ½ m 5. Astronauts heading towards Jupiter at a speed of 0.6c relative to the earth see a cosmic ray shower that contains protons moving toward them. From earth, the speed of the protons is measured to be 0.2c. The astronauts measure the speed of the protons to be (a) 0.8c (b) 0.71c (c) 0.95c (d) 0.69c (e) 0.45c 6. The transverse displacement for a standing wave on a string is given by: y(x,t) = (4.2m) sin[(0.20 m 1 )x] cos[(3.0 s 1 )t] Which of the following is NOT true? (a) When t = π/2 seconds, the string is flat. (b) The wavelength is 10π meters. (c) The maximum transverse velocity v y of a point on the string is 2.1 m/s. (d) The point at x = 5π meters is a node. (e) The period of the oscillation is 2π/3 seconds. Page 4 of 6
5 Problems (15 Points for each problem) II. An ideal fluid sits inside of a cylindrical container which is open to the atmosphere at the top. The fluid has volume V, mass M, and temperature T 0. Its specific heat is c F K/kg, and its coefficient of thermal expansion is α. Q Joules of heat are applied in a reversible manner to the fluid, which expands at constant (atmospheric) pressure. (a) Find the final temperature of the fluid. (b) How much work does the fluid do on the atmosphere during its expansion? (c) Find the change in entropy of the fluid. III. In a binary star system, two stars with masses M and 3M orbit each other in circular orbits about their center-of-mass. The distance between the centers of the two stars is D. Newton s gravitational constant is G. D CofM (a) Find the tangential velocity of the lighter star. (Hint: gravity provides the centripetal force.) (b) Find the period of the orbital motion. (c) A system like this emits gravity waves, which travel outward at the speed of light. This causes the orbit to shrink and the period to change with time, providing us with the best evidence yet that gravity waves exist, since we see this happening in nature. The rate of energy loss due to gravitational radiation is: de/ = (128G/5c 5 )ω n M m D p. Find the values of the exponents n, m, and p such that de/ has the correct units. Here, ω is the orbital frequency, M is the mass of a star, and D is the distance between the two stars. IV. In a nuclear reactor, 235 U (Uranium 235) splits (at rest) into two smaller identical nuclei, 116 Ag. The molar masses of the three elements involved are 235g, 115.9g, respectively. (a) If one mole of 235 U undergoes fission, how much energy is released? (Note: Momentum and energy must be conserved! What are the final kinetic energies of the decay products?) Reactors are cooled by water. The kinetic energy of the reactor products are absorbed by the cooling water, heating it up. Assume that the cooling water is at 100 C. (If you didn t get part (a) assume a value of 3 J.) (b) How many moles of steam can be generated from the fission energy? (c) If the space into which the steam can expand is 1 liter/mole, what is the steam pressure? Assume a constant temperature of 100 C. (d) At some point later in the cycle, the steam is condensed to liquid at 100 C by passing it through a heat exchanger that contains coils of cooler water. If the cooling water is pulled from a reservoir at a temperature of 22 C, how many moles of cooling water are required to condense one mole of steam if the exit temperature of the cooling water is 40 C? (i.e., each mole of cooling water is only heated from 22 C to 40 C.) Page 5 of 6
6 V. Following up on the reactor problem, let s consider what happens when the steam is used to drive a turbine. The steam flows along a pipe of cross sectional area 300 cm 2 with velocity 100m/s. The pressure in the steam is 100atm, and it is at a temperature of 200 C. (a) Find the density of the steam in kg/m 3. The molar mass of water is 18g. (b) Find the rate of mass flow in kg/sec past an arbitrary point in the pipe. The steam then expands across a turbine, making it spin to generate electricity. The cross-sectional area of the new pipe after the expansion is 600 cm 2. (c) Assume an adiabatic expansion; γ = 4/3 for steam. What is the final density of the steam? (d) What is the final velocity of the steam? (Hint: conserve mass in the flow.) VI. Astérix and Obélix, heroes of Gaul, have laid siege to the castle of their sworn enemy, Nastius Maximus. In order to get a better view of the castle, they devise a simple device to throw Obélix into the air. It is based on a massless vertical spring, spring constant k=2000 N/m, with a small massless platform on top. (a) Obélix, whose mass is M 0 = 300 kg, sits on top of the spring. How far is the spring compressed? (b) To fire the catapult, Astérix pushes Obélix down another 0.2 meters and releases him from rest. Obélix, scared out of his mind, holds on for dear life. What is the angular frequency of his resulting oscillation? (c) At what elapsed time after his release does he reach the equilibrium position of his oscillation? Page 6 of 6
Physics Exam 1 Formulas
 INSTRUCTIONS: Write your NAME on the front of the blue exam booklet. The exam is closed book, and you may have only pens/pencils and a calculator (no stored equations or programs and no graphing). Show
INSTRUCTIONS: Write your NAME on the front of the blue exam booklet. The exam is closed book, and you may have only pens/pencils and a calculator (no stored equations or programs and no graphing). Show
Physics Final Exam Formulas
 INSTRUCTIONS: Write your NAME on the front of the blue exam booklet. The exam is closed book, and you may have only pens/pencils and a calculator (no stored equations or programs and no graphing). Show
INSTRUCTIONS: Write your NAME on the front of the blue exam booklet. The exam is closed book, and you may have only pens/pencils and a calculator (no stored equations or programs and no graphing). Show
Dr. Gundersen Phy 206 Test 2 March 6, 2013
 Signature: Idnumber: Name: You must do all four questions. There are a total of 100 points. Each problem is worth 25 points and you have to do ALL problems. A formula sheet is provided on the LAST page
Signature: Idnumber: Name: You must do all four questions. There are a total of 100 points. Each problem is worth 25 points and you have to do ALL problems. A formula sheet is provided on the LAST page
PHY2053 General Physics I
 PHY2053 General Physics I Section 584771 Prof. Douglas H. Laurence Final Exam May 3, 2018 Name: 1 Instructions: This final exam is a take home exam. It will be posted online sometime around noon of the
PHY2053 General Physics I Section 584771 Prof. Douglas H. Laurence Final Exam May 3, 2018 Name: 1 Instructions: This final exam is a take home exam. It will be posted online sometime around noon of the
First major ( 043 ) a) 180 degrees b) 90 degrees c) 135 degrees d) 45 degrees e) 270 degrees
 First major ( 043 ) 1) The displacement of a string carrying a traveling sinusoidal wave is given by y(x,t) = y m sin( kx ωt ϕ ). At time t = 0 the point at x = 0 has a displacement of zero and is moving
First major ( 043 ) 1) The displacement of a string carrying a traveling sinusoidal wave is given by y(x,t) = y m sin( kx ωt ϕ ). At time t = 0 the point at x = 0 has a displacement of zero and is moving
Physics 2101, Final Exam, Form A
 Physics 2101, Final Exam, Form A December 11, 2007 Name: SOLUTIONS Section: (Circle one) 1 (Rupnik, MWF 7:40am) 2 (Rupnik, MWF 9:40am) 3 (González, MWF 2:40pm) 4 (Pearson, TTh 9:10am) 5 (Pearson, TTh 12:10pm)
Physics 2101, Final Exam, Form A December 11, 2007 Name: SOLUTIONS Section: (Circle one) 1 (Rupnik, MWF 7:40am) 2 (Rupnik, MWF 9:40am) 3 (González, MWF 2:40pm) 4 (Pearson, TTh 9:10am) 5 (Pearson, TTh 12:10pm)
PHYSICS 221, FALL 2010 FINAL EXAM MONDAY, DECEMBER 13, 2010
 PHYSICS 221, FALL 2010 FINAL EXAM MONDAY, DECEMBER 13, 2010 Name (printed): Nine-digit ID Number: Section Number: Recitation Instructor: INSTRUCTIONS: i. Put away all materials except for pens, pencils,
PHYSICS 221, FALL 2010 FINAL EXAM MONDAY, DECEMBER 13, 2010 Name (printed): Nine-digit ID Number: Section Number: Recitation Instructor: INSTRUCTIONS: i. Put away all materials except for pens, pencils,
kg C 10 C = J J = J kg C 20 C = J J = J J
 Seat: PHYS 1500 (Spring 2007) Exam #3, V1 Name: 5 pts 1. A pendulum is made with a length of string of negligible mass with a 0.25 kg mass at the end. A 2nd pendulum is identical except the mass is 0.50
Seat: PHYS 1500 (Spring 2007) Exam #3, V1 Name: 5 pts 1. A pendulum is made with a length of string of negligible mass with a 0.25 kg mass at the end. A 2nd pendulum is identical except the mass is 0.50
Momentum Circular Motion and Gravitation Rotational Motion Fluid Mechanics
 Momentum Circular Motion and Gravitation Rotational Motion Fluid Mechanics Momentum Momentum Collisions between objects can be evaluated using the laws of conservation of energy and of momentum. Momentum
Momentum Circular Motion and Gravitation Rotational Motion Fluid Mechanics Momentum Momentum Collisions between objects can be evaluated using the laws of conservation of energy and of momentum. Momentum
b) (6) What is the volume of the iron cube, in m 3?
 General Physics I Exam 4 - Chs. 10,11,12 - Fluids, Waves, Sound Nov. 14, 2012 Name Rec. Instr. Rec. Time For full credit, make your work clear to the grader. Show formulas used, essential steps, and results
General Physics I Exam 4 - Chs. 10,11,12 - Fluids, Waves, Sound Nov. 14, 2012 Name Rec. Instr. Rec. Time For full credit, make your work clear to the grader. Show formulas used, essential steps, and results
Harold s AP Physics Cheat Sheet 23 February Electricity / Magnetism
 Harold s AP Physics Cheat Sheet 23 February 206 Kinematics Position (m) (rad) Translation Horizontal: x = x 0 + v x0 t + 2 at2 Vertical: y = y 0 + v y0 t 2 gt2 x = x 0 + vt s = rθ x = v / Rotational Motion
Harold s AP Physics Cheat Sheet 23 February 206 Kinematics Position (m) (rad) Translation Horizontal: x = x 0 + v x0 t + 2 at2 Vertical: y = y 0 + v y0 t 2 gt2 x = x 0 + vt s = rθ x = v / Rotational Motion
b) (6) With 10.0 N applied to the smaller piston, what pressure force F 2 (in newtons) is produced on the larger piston?
 General Physics I Exam 4 - Chs. 10,11,12 - Fluids, Waves, Sound Nov. 17, 2010 Name Rec. Instr. Rec. Time For full credit, make your work clear to the grader. Show formulas used, essential steps, and results
General Physics I Exam 4 - Chs. 10,11,12 - Fluids, Waves, Sound Nov. 17, 2010 Name Rec. Instr. Rec. Time For full credit, make your work clear to the grader. Show formulas used, essential steps, and results
Physics Exam 3 Formulas
 Phyic 10411 Exam III November 20, 2009 INSTRUCTIONS: Write your NAME on the front of the blue exam booklet. The exam i cloed book, and you may have only pen/pencil and a calculator (no tored equation or
Phyic 10411 Exam III November 20, 2009 INSTRUCTIONS: Write your NAME on the front of the blue exam booklet. The exam i cloed book, and you may have only pen/pencil and a calculator (no tored equation or
Phys102 Term: 103 First Major- July 16, 2011
 Q1. A stretched string has a length of.00 m and a mass of 3.40 g. A transverse sinusoidal wave is travelling on this string, and is given by y (x, t) = 0.030 sin (0.75 x 16 t), where x and y are in meters,
Q1. A stretched string has a length of.00 m and a mass of 3.40 g. A transverse sinusoidal wave is travelling on this string, and is given by y (x, t) = 0.030 sin (0.75 x 16 t), where x and y are in meters,
Quiz 3 July 31, 2007 Chapters 16, 17, 18, 19, 20 Phys 631 Instructor R. A. Lindgren 9:00 am 12:00 am
 Quiz 3 July 31, 2007 Chapters 16, 17, 18, 19, 20 Phys 631 Instructor R. A. Lindgren 9:00 am 12:00 am No Books or Notes allowed Calculator without access to formulas allowed. The quiz has two parts. The
Quiz 3 July 31, 2007 Chapters 16, 17, 18, 19, 20 Phys 631 Instructor R. A. Lindgren 9:00 am 12:00 am No Books or Notes allowed Calculator without access to formulas allowed. The quiz has two parts. The
A) 120 degrees B) 90 degrees C) 60 degrees D) 45 degrees E) 30 degrees
 Phys10 - First Major 071 Zero Version Q1. Two identical sinusoidal traveling waves are sent along the same string in the same direction. What should be the phase difference between the two waves so that
Phys10 - First Major 071 Zero Version Q1. Two identical sinusoidal traveling waves are sent along the same string in the same direction. What should be the phase difference between the two waves so that
Final Exam. Useful tables. 1 : [10 pts] 2 : [10 pts] 3 : [10 pts] 4 : [10 pts] 5 : [10 pts] 6 : [10 pts] 7 : [10 pts] 8 : [10 pts] TOTAL:
![Final Exam. Useful tables. 1 : [10 pts] 2 : [10 pts] 3 : [10 pts] 4 : [10 pts] 5 : [10 pts] 6 : [10 pts] 7 : [10 pts] 8 : [10 pts] TOTAL: Final Exam. Useful tables. 1 : [10 pts] 2 : [10 pts] 3 : [10 pts] 4 : [10 pts] 5 : [10 pts] 6 : [10 pts] 7 : [10 pts] 8 : [10 pts] TOTAL:](/thumbs/83/87295870.jpg) Final Exam Name Score Please PRINT your name. Read the question carefully. Show your steps. Use letter symbols first if convenient. Give units on final answers. Diagrams help. Do all work on these pages,
Final Exam Name Score Please PRINT your name. Read the question carefully. Show your steps. Use letter symbols first if convenient. Give units on final answers. Diagrams help. Do all work on these pages,
Final Mock Exam PH 221-1D
 Final Mock Exam PH 221-1D April 18, 2015 You will have 2 hours to complete this exam. You must answer 8 questions to make a perfect score of 80. 1 Chapter Concept Summary Equations: Cutnell & Johnson
Final Mock Exam PH 221-1D April 18, 2015 You will have 2 hours to complete this exam. You must answer 8 questions to make a perfect score of 80. 1 Chapter Concept Summary Equations: Cutnell & Johnson
Alternate Midterm Examination Physics 100 Feb. 20, 2014
 Alternate Midterm Examination Physics 100 Feb. 20, 2014 Name/Student #: Instructions: Formulas at the back (you can rip that sheet o ). Questions are on both sides. Calculator permitted. Put your name
Alternate Midterm Examination Physics 100 Feb. 20, 2014 Name/Student #: Instructions: Formulas at the back (you can rip that sheet o ). Questions are on both sides. Calculator permitted. Put your name
Final Exam. June 10, 2008, 1:00pm
 PHYSICS 101: Fundamentals of Physics Final Exam Final Exam Name TA/ Section # June 10, 2008, 1:00pm Recitation Time You have 2 hour to complete the exam. Please answer all questions clearly and completely,
PHYSICS 101: Fundamentals of Physics Final Exam Final Exam Name TA/ Section # June 10, 2008, 1:00pm Recitation Time You have 2 hour to complete the exam. Please answer all questions clearly and completely,
FALL TERM EXAM, PHYS 1211, INTRODUCTORY PHYSICS I Saturday, 14 December 2013, 1PM to 4 PM, AT 1003
 FALL TERM EXAM, PHYS 1211, INTRODUCTORY PHYSICS I Saturday, 14 December 2013, 1PM to 4 PM, AT 1003 NAME: STUDENT ID: INSTRUCTION 1. This exam booklet has 14 pages. Make sure none are missing 2. There is
FALL TERM EXAM, PHYS 1211, INTRODUCTORY PHYSICS I Saturday, 14 December 2013, 1PM to 4 PM, AT 1003 NAME: STUDENT ID: INSTRUCTION 1. This exam booklet has 14 pages. Make sure none are missing 2. There is
Mock Exam III PH 201, PH 221
 Mock Exam III PH 201, PH 221 April 12, 2015 You will have 1 hour to complete this exam, and must answer 7 of the problems correctly to make a perfect score. 1 Chapter Concept Summary Equations: Cutnell
Mock Exam III PH 201, PH 221 April 12, 2015 You will have 1 hour to complete this exam, and must answer 7 of the problems correctly to make a perfect score. 1 Chapter Concept Summary Equations: Cutnell
Physics 101 Hour Exam 1 October 6, 2014
 Physics 101 Hour Exam 1 October 6, 014 Last Name: First Name ID Discussion Section: Discussion TA Name: Instructions Turn off your cell phone and put it away. Calculators cannot be shared. Please keep
Physics 101 Hour Exam 1 October 6, 014 Last Name: First Name ID Discussion Section: Discussion TA Name: Instructions Turn off your cell phone and put it away. Calculators cannot be shared. Please keep
E = K + U. p mv. p i = p f. F dt = p. J t 1. a r = v2. F c = m v2. s = rθ. a t = rα. r 2 dm i. m i r 2 i. I ring = MR 2.
 v = v i + at x = x i + v i t + 1 2 at2 E = K + U p mv p i = p f L r p = Iω τ r F = rf sin θ v 2 = v 2 i + 2a x F = ma = dp dt = U v dx dt a dv dt = d2 x dt 2 A circle = πr 2 A sphere = 4πr 2 V sphere =
v = v i + at x = x i + v i t + 1 2 at2 E = K + U p mv p i = p f L r p = Iω τ r F = rf sin θ v 2 = v 2 i + 2a x F = ma = dp dt = U v dx dt a dv dt = d2 x dt 2 A circle = πr 2 A sphere = 4πr 2 V sphere =
Department of Physics
 Department of Physics PHYS101-051 FINAL EXAM Test Code: 100 Tuesday, 4 January 006 in Building 54 Exam Duration: 3 hrs (from 1:30pm to 3:30pm) Name: Student Number: Section Number: Page 1 1. A car starts
Department of Physics PHYS101-051 FINAL EXAM Test Code: 100 Tuesday, 4 January 006 in Building 54 Exam Duration: 3 hrs (from 1:30pm to 3:30pm) Name: Student Number: Section Number: Page 1 1. A car starts
L = I ω = const. I = 2 3 MR2. When the balloon shrinks (because the air inside it cools down), the moment of inertia decreases, R = 1. L = I ω = I ω.
 PHY 30 K. Solutions for mid-term test #3. Problem 1: Out in space, there are no forces acting on the balloon except gravity and hence no torques (with respect to an axis through the center of mass). Consequently,
PHY 30 K. Solutions for mid-term test #3. Problem 1: Out in space, there are no forces acting on the balloon except gravity and hence no torques (with respect to an axis through the center of mass). Consequently,
7. (2) Of these elements, which has the greatest number of atoms in a mole? a. hydrogen (H) b. oxygen (O) c. iron (Fe) d. gold (Au) e. all tie.
 General Physics I Exam 5 - Chs. 13,14,15 - Heat, Kinetic Theory, Thermodynamics Dec. 14, 2010 Name Rec. Instr. Rec. Time For full credit, make your work clear to the grader. Show formulas used, essential
General Physics I Exam 5 - Chs. 13,14,15 - Heat, Kinetic Theory, Thermodynamics Dec. 14, 2010 Name Rec. Instr. Rec. Time For full credit, make your work clear to the grader. Show formulas used, essential
Final Exam Spring 2014 May 05, 2014
 95.141 Final Exam Spring 2014 May 05, 2014 Section number Section instructor Last/First name Last 3 Digits of Student ID Number: Answer all questions, beginning each new question in the space provided.
95.141 Final Exam Spring 2014 May 05, 2014 Section number Section instructor Last/First name Last 3 Digits of Student ID Number: Answer all questions, beginning each new question in the space provided.
Physics Midterm #2 Two Hours, Closed Book
 Physics 102-1 Midterm #2 Two Hours, Closed Book These are the same instructions as given on the first exam. Instructions for taking the exam in the Science Library: Pick up and return the exam from the
Physics 102-1 Midterm #2 Two Hours, Closed Book These are the same instructions as given on the first exam. Instructions for taking the exam in the Science Library: Pick up and return the exam from the
A B = AB cos θ = 100. = 6t. a(t) = d2 r(t) a(t = 2) = 12 ĵ
 1. A ball is thrown vertically upward from the Earth s surface and falls back to Earth. Which of the graphs below best symbolizes its speed v(t) as a function of time, neglecting air resistance: The answer
1. A ball is thrown vertically upward from the Earth s surface and falls back to Earth. Which of the graphs below best symbolizes its speed v(t) as a function of time, neglecting air resistance: The answer
Physics Exam 2 October 11, 2007
 INSTRUCTIONS: Write your NAME on the front of the blue exam booklet. The exam is closed book, and you may have only pens/pencils and a calculator (no stored equations or programs and no graphing). Show
INSTRUCTIONS: Write your NAME on the front of the blue exam booklet. The exam is closed book, and you may have only pens/pencils and a calculator (no stored equations or programs and no graphing). Show
Figure 1 Answer: = m
 Q1. Figure 1 shows a solid cylindrical steel rod of length =.0 m and diameter D =.0 cm. What will be increase in its length when m = 80 kg block is attached to its bottom end? (Young's modulus of steel
Q1. Figure 1 shows a solid cylindrical steel rod of length =.0 m and diameter D =.0 cm. What will be increase in its length when m = 80 kg block is attached to its bottom end? (Young's modulus of steel
Physics 8, Fall 2011, equation sheet work in progress
 1 year 3.16 10 7 s Physics 8, Fall 2011, equation sheet work in progress circumference of earth 40 10 6 m speed of light c = 2.9979 10 8 m/s mass of proton or neutron 1 amu ( atomic mass unit ) = 1 1.66
1 year 3.16 10 7 s Physics 8, Fall 2011, equation sheet work in progress circumference of earth 40 10 6 m speed of light c = 2.9979 10 8 m/s mass of proton or neutron 1 amu ( atomic mass unit ) = 1 1.66
43. A person sits on a freely spinning lab stool that has no friction in its axle. When this person extends her arms,
 43. A person sits on a freely spinning lab stool that has no friction in its axle. When this person extends her arms, A) her moment of inertia increases and her rotational kinetic energy remains the same.
43. A person sits on a freely spinning lab stool that has no friction in its axle. When this person extends her arms, A) her moment of inertia increases and her rotational kinetic energy remains the same.
Honors Physics. Notes Nov 16, 20 Heat. Persans 1
 Honors Physics Notes Nov 16, 20 Heat Persans 1 Properties of solids Persans 2 Persans 3 Vibrations of atoms in crystalline solids Assuming only nearest neighbor interactions (+Hooke's law) F = C( u! u
Honors Physics Notes Nov 16, 20 Heat Persans 1 Properties of solids Persans 2 Persans 3 Vibrations of atoms in crystalline solids Assuming only nearest neighbor interactions (+Hooke's law) F = C( u! u
Physics UCSB TR 2:00-3:15 lecture Final Exam Wednesday 3/17/2010
 Physics @ UCSB TR :00-3:5 lecture Final Eam Wednesday 3/7/00 Print your last name: Print your first name: Print your perm no.: INSTRUCTIONS: DO NOT START THE EXAM until you are given instructions to do
Physics @ UCSB TR :00-3:5 lecture Final Eam Wednesday 3/7/00 Print your last name: Print your first name: Print your perm no.: INSTRUCTIONS: DO NOT START THE EXAM until you are given instructions to do
Circular Motion, Pt 2: Angular Dynamics. Mr. Velazquez AP/Honors Physics
 Circular Motion, Pt 2: Angular Dynamics Mr. Velazquez AP/Honors Physics Formulas: Angular Kinematics (θ must be in radians): s = rθ Arc Length 360 = 2π rads = 1 rev ω = θ t = v t r Angular Velocity α av
Circular Motion, Pt 2: Angular Dynamics Mr. Velazquez AP/Honors Physics Formulas: Angular Kinematics (θ must be in radians): s = rθ Arc Length 360 = 2π rads = 1 rev ω = θ t = v t r Angular Velocity α av
FOUNDATION STUDIES EXAMINATIONS June PHYSICS Semester One February Main
 1 FOUNDATION STUDIES EXAMINATIONS June 2013 PHYSICS Semester One February Main Time allowed 2 hours for writing 10 minutes for reading This paper consists of 4 questions printed on 10 pages. PLEASE CHECK
1 FOUNDATION STUDIES EXAMINATIONS June 2013 PHYSICS Semester One February Main Time allowed 2 hours for writing 10 minutes for reading This paper consists of 4 questions printed on 10 pages. PLEASE CHECK
Physics 101 Hour Exam 2 November 3, 2014
 Physics 101 Hour Exam 2 November 3, 2014 Last Name: First Name ID Discussion Section: Discussion TA Name: Instructions Turn off your cell phone and put it away. Calculators cannot be shared. Please keep
Physics 101 Hour Exam 2 November 3, 2014 Last Name: First Name ID Discussion Section: Discussion TA Name: Instructions Turn off your cell phone and put it away. Calculators cannot be shared. Please keep
Exam 2. May 21, 2008, 8:00am
 PHYSICS 101: Fundamentals of Physics Exam 2 Exam 2 Name TA/ Section # May 21, 2008, 8:00am Recitation Time You have 1 hour to complete the exam. Please answer all questions clearly and completely, and
PHYSICS 101: Fundamentals of Physics Exam 2 Exam 2 Name TA/ Section # May 21, 2008, 8:00am Recitation Time You have 1 hour to complete the exam. Please answer all questions clearly and completely, and
Physics 8, Fall 2013, equation sheet work in progress
 (Chapter 1: foundations) 1 year 3.16 10 7 s Physics 8, Fall 2013, equation sheet work in progress circumference of earth 40 10 6 m speed of light c = 2.9979 10 8 m/s mass of proton or neutron 1 amu ( atomic
(Chapter 1: foundations) 1 year 3.16 10 7 s Physics 8, Fall 2013, equation sheet work in progress circumference of earth 40 10 6 m speed of light c = 2.9979 10 8 m/s mass of proton or neutron 1 amu ( atomic
SPRING 2003 Final Exam, Part A
 Physics 151 SPRING 2003 Final Exam, Part A Roster No.: Score: 17 pts. possible Exam time limit: 2 hours. You may use calculators and both sides of 2 sheets of notes, handwritten only. Closed book; no collaboration.
Physics 151 SPRING 2003 Final Exam, Part A Roster No.: Score: 17 pts. possible Exam time limit: 2 hours. You may use calculators and both sides of 2 sheets of notes, handwritten only. Closed book; no collaboration.
Physics Final Exam - Summer 2014 Version 31 - Answer Key Page 1 of 20
 Physics 220 - Final Exam - Summer 2014 Version 31 - Answer Key Page 1 of 20 1. A pendulum on the Earth has a period T. The acceleration due to gravity on Mars is less than that on the Earth, and the acceleration
Physics 220 - Final Exam - Summer 2014 Version 31 - Answer Key Page 1 of 20 1. A pendulum on the Earth has a period T. The acceleration due to gravity on Mars is less than that on the Earth, and the acceleration
Translational Motion Rotational Motion Equations Sheet
 PHYSICS 01 Translational Motion Rotational Motion Equations Sheet LINEAR ANGULAR Time t t Displacement x; (x = rθ) θ Velocity v = Δx/Δt; (v = rω) ω = Δθ/Δt Acceleration a = Δv/Δt; (a = rα) α = Δω/Δt (
PHYSICS 01 Translational Motion Rotational Motion Equations Sheet LINEAR ANGULAR Time t t Displacement x; (x = rθ) θ Velocity v = Δx/Δt; (v = rω) ω = Δθ/Δt Acceleration a = Δv/Δt; (a = rα) α = Δω/Δt (
First Name: Last Name: Section: 1 December 20, 2004 Physics 201 FINAL EXAM
 First Name: Last Name: Section: 1 December 20, 2004 Physics 201 FINAL EXAM Print your name and section clearly on all nine pages. (If you do not know your section number, write your TA s name.) Show all
First Name: Last Name: Section: 1 December 20, 2004 Physics 201 FINAL EXAM Print your name and section clearly on all nine pages. (If you do not know your section number, write your TA s name.) Show all
= W Q H. ɛ = T H T C T H = = 0.20 = T C = T H (1 0.20) = = 320 K = 47 C
 1. Four identical 0.18 kg masses are placed at the corners of a 4.0 x 3.0 m rectangle, and are held there by very light connecting rods which form the sides of the rectangle. What is the moment of inertia
1. Four identical 0.18 kg masses are placed at the corners of a 4.0 x 3.0 m rectangle, and are held there by very light connecting rods which form the sides of the rectangle. What is the moment of inertia
Kinematics (special case) Dynamics gravity, tension, elastic, normal, friction. Energy: kinetic, potential gravity, spring + work (friction)
 Kinematics (special case) a = constant 1D motion 2D projectile Uniform circular Dynamics gravity, tension, elastic, normal, friction Motion with a = constant Newton s Laws F = m a F 12 = F 21 Time & Position
Kinematics (special case) a = constant 1D motion 2D projectile Uniform circular Dynamics gravity, tension, elastic, normal, friction Motion with a = constant Newton s Laws F = m a F 12 = F 21 Time & Position
Dr. Gundersen Phy 205DJ Test 2 22 March 2010
 Signature: Idnumber: Name: Do only four out of the five problems. The first problem consists of five multiple choice questions. If you do more only your FIRST four answered problems will be graded. Clearly
Signature: Idnumber: Name: Do only four out of the five problems. The first problem consists of five multiple choice questions. If you do more only your FIRST four answered problems will be graded. Clearly
Measurement p. 1 What Is Physics? p. 2 Measuring Things p. 2 The International System of Units p. 2 Changing Units p. 3 Length p. 4 Time p. 5 Mass p.
 Measurement p. 1 What Is Physics? p. 2 Measuring Things p. 2 The International System of Units p. 2 Changing Units p. 3 Length p. 4 Time p. 5 Mass p. 7 Review & Summary p. 8 Problems p. 8 Motion Along
Measurement p. 1 What Is Physics? p. 2 Measuring Things p. 2 The International System of Units p. 2 Changing Units p. 3 Length p. 4 Time p. 5 Mass p. 7 Review & Summary p. 8 Problems p. 8 Motion Along
Physics 1 Second Midterm Exam (AM) 2/25/2010
 Physics Second Midterm Eam (AM) /5/00. (This problem is worth 40 points.) A roller coaster car of m travels around a vertical loop of radius R. There is no friction and no air resistance. At the top of
Physics Second Midterm Eam (AM) /5/00. (This problem is worth 40 points.) A roller coaster car of m travels around a vertical loop of radius R. There is no friction and no air resistance. At the top of
Static Equilibrium, Gravitation, Periodic Motion
 This test covers static equilibrium, universal gravitation, and simple harmonic motion, with some problems requiring a knowledge of basic calculus. Part I. Multiple Choice 1. 60 A B 10 kg A mass of 10
This test covers static equilibrium, universal gravitation, and simple harmonic motion, with some problems requiring a knowledge of basic calculus. Part I. Multiple Choice 1. 60 A B 10 kg A mass of 10
Winter 2017 PHYSICS 115 MIDTERM EXAM 1 Section X PRACTICE EXAM SOLUTION Seat No
 Winter 2017 PHYSICS 115 MIDTERM EXAM 1 Section X PRACTICE EXAM SOLUTION Seat No Name (Print): Name (Print): Honor Pledge: All work presented here is my own. Signature: Student ID: READ THIS ENTIRE PAGE
Winter 2017 PHYSICS 115 MIDTERM EXAM 1 Section X PRACTICE EXAM SOLUTION Seat No Name (Print): Name (Print): Honor Pledge: All work presented here is my own. Signature: Student ID: READ THIS ENTIRE PAGE
PRACTICE FINAL EXAM SOLUTIONS
 University of California, Berkeley Physics 8A Spring 2007 (Professors Yury Kolomensky and Terry Buehler) Final Review / Practice Final Exam by Brian Shotwell (shotwell@berkeley.edu) PRACTICE FINAL EXAM
University of California, Berkeley Physics 8A Spring 2007 (Professors Yury Kolomensky and Terry Buehler) Final Review / Practice Final Exam by Brian Shotwell (shotwell@berkeley.edu) PRACTICE FINAL EXAM
Phys102 First Major-182 Zero Version Coordinator: A A Naqvi Thursday, February 14, 2019 Page: 1
 Coordinator: A A Naqvi Thursday February 14 2019 Page: 1 Q1. Figure 1 shows a graph of a wave traveling to the left along a string at a speed of 34 m/s. At this instant what is the transverse velocity
Coordinator: A A Naqvi Thursday February 14 2019 Page: 1 Q1. Figure 1 shows a graph of a wave traveling to the left along a string at a speed of 34 m/s. At this instant what is the transverse velocity
PHYSICS 221, FALL 2009 EXAM #1 SOLUTIONS WEDNESDAY, SEPTEMBER 30, 2009
 PHYSICS 221, FALL 2009 EXAM #1 SOLUTIONS WEDNESDAY, SEPTEMBER 30, 2009 Note: The unit vectors in the +x, +y, and +z directions of a right-handed Cartesian coordinate system are î, ĵ, and ˆk, respectively.
PHYSICS 221, FALL 2009 EXAM #1 SOLUTIONS WEDNESDAY, SEPTEMBER 30, 2009 Note: The unit vectors in the +x, +y, and +z directions of a right-handed Cartesian coordinate system are î, ĵ, and ˆk, respectively.
(Heat capacity c is also called specific heat) this means that the heat capacity number c for water is 1 calorie/gram-k.
 Lecture 23: Ideal Gas Law and The First Law of Thermodynamics 1 (REVIEW) Chapter 17: Heat Transfer Origin of the calorie unit A few hundred years ago when people were investigating heat and temperature
Lecture 23: Ideal Gas Law and The First Law of Thermodynamics 1 (REVIEW) Chapter 17: Heat Transfer Origin of the calorie unit A few hundred years ago when people were investigating heat and temperature
Solution to phys101-t112-final Exam
 Solution to phys101-t112-final Exam Q1. An 800-N man stands halfway up a 5.0-m long ladder of negligible weight. The base of the ladder is.0m from the wall as shown in Figure 1. Assuming that the wall-ladder
Solution to phys101-t112-final Exam Q1. An 800-N man stands halfway up a 5.0-m long ladder of negligible weight. The base of the ladder is.0m from the wall as shown in Figure 1. Assuming that the wall-ladder
ω = k/m x = A cos (ωt + ϕ 0 ) L = I ω a x = ω 2 x P = F v P = de sys J = F dt = p w = m g F G = Gm 1m 2 D = 1 2 CρAv2 a r = v2
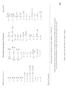 PHYS 2211 A, B, & C Final Exam Formulæ & Constants Spring 2017 Unless otherwise directed, drag is to be neglected and all problems take place on Earth, use the gravitational definition of weight, and all
PHYS 2211 A, B, & C Final Exam Formulæ & Constants Spring 2017 Unless otherwise directed, drag is to be neglected and all problems take place on Earth, use the gravitational definition of weight, and all
Final Review, Day 1. Announcements: Web page:
 Announcements: Final Review, Day 1 Final exam next Wednesday (5/9) at 7:30am in the Coors Event Center. Recitation tomorrow is a review. Please feel free to ask the TA any questions on the course material.
Announcements: Final Review, Day 1 Final exam next Wednesday (5/9) at 7:30am in the Coors Event Center. Recitation tomorrow is a review. Please feel free to ask the TA any questions on the course material.
Final Review Prof. WAN, Xin
 General Physics I Final Review Prof. WAN, Xin xinwan@zju.edu.cn http://zimp.zju.edu.cn/~xinwan/ About the Final Exam Total 6 questions. 40% mechanics, 30% wave and relativity, 30% thermal physics. Pick
General Physics I Final Review Prof. WAN, Xin xinwan@zju.edu.cn http://zimp.zju.edu.cn/~xinwan/ About the Final Exam Total 6 questions. 40% mechanics, 30% wave and relativity, 30% thermal physics. Pick
4. Find the average velocities and average accelerations of a particle moving in 1-D given its position at various times.
 PHYSICS 201: TEST 1 STUDY SHEET 1. Convert a quantity from one set of units to another set of units. 2. Convert a 2-D vector from rectangular form (components) to polar form (magnitude and angle), or from
PHYSICS 201: TEST 1 STUDY SHEET 1. Convert a quantity from one set of units to another set of units. 2. Convert a 2-D vector from rectangular form (components) to polar form (magnitude and angle), or from
Lecture 13 REVIEW. Physics 106 Spring What should we know? What should we know? Newton s Laws
 Lecture 13 REVIEW Physics 106 Spring 2006 http://web.njit.edu/~sirenko/ What should we know? Vectors addition, subtraction, scalar and vector multiplication Trigonometric functions sinθ, cos θ, tan θ,
Lecture 13 REVIEW Physics 106 Spring 2006 http://web.njit.edu/~sirenko/ What should we know? Vectors addition, subtraction, scalar and vector multiplication Trigonometric functions sinθ, cos θ, tan θ,
Write your name legibly on the top right hand corner of this paper
 NAME Phys 631 Summer 2007 Quiz 2 Tuesday July 24, 2007 Instructor R. A. Lindgren 9:00 am 12:00 am Write your name legibly on the top right hand corner of this paper No Books or Notes allowed Calculator
NAME Phys 631 Summer 2007 Quiz 2 Tuesday July 24, 2007 Instructor R. A. Lindgren 9:00 am 12:00 am Write your name legibly on the top right hand corner of this paper No Books or Notes allowed Calculator
PHYSICS 221, FALL 2010 EXAM #1 Solutions WEDNESDAY, SEPTEMBER 29, 2010
 PHYSICS 1, FALL 010 EXAM 1 Solutions WEDNESDAY, SEPTEMBER 9, 010 Note: The unit vectors in the +x, +y, and +z directions of a right-handed Cartesian coordinate system are î, ĵ, and ˆk, respectively. In
PHYSICS 1, FALL 010 EXAM 1 Solutions WEDNESDAY, SEPTEMBER 9, 010 Note: The unit vectors in the +x, +y, and +z directions of a right-handed Cartesian coordinate system are î, ĵ, and ˆk, respectively. In
Version 001 HW 15 Thermodynamics C&J sizemore (21301jtsizemore) 1
 Version 001 HW 15 Thermodynamics C&J sizemore 21301jtsizemore 1 This print-out should have 38 questions. Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page find all choices before answering.
Version 001 HW 15 Thermodynamics C&J sizemore 21301jtsizemore 1 This print-out should have 38 questions. Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page find all choices before answering.
PHYSICS 111 SPRING EXAM 3: April 12, 2016; 8:15pm - 9:45pm
 PHYSICS SPRING 06 EXAM 3: April, 06; 8:5pm - 9:45pm Name (printed): Recitation Instructor: Section # INSTRUCTIONS: This exam contains 0 multiple-choice questions plus extra credit question, each worth
PHYSICS SPRING 06 EXAM 3: April, 06; 8:5pm - 9:45pm Name (printed): Recitation Instructor: Section # INSTRUCTIONS: This exam contains 0 multiple-choice questions plus extra credit question, each worth
Temperature Thermal Expansion Ideal Gas Law Kinetic Theory Heat Heat Transfer Phase Changes Specific Heat Calorimetry Heat Engines
 Temperature Thermal Expansion Ideal Gas Law Kinetic Theory Heat Heat Transfer Phase Changes Specific Heat Calorimetry Heat Engines Zeroeth Law Two systems individually in thermal equilibrium with a third
Temperature Thermal Expansion Ideal Gas Law Kinetic Theory Heat Heat Transfer Phase Changes Specific Heat Calorimetry Heat Engines Zeroeth Law Two systems individually in thermal equilibrium with a third
SPRING GROVE AREA SCHOOL DISTRICT. Course Description. Instructional Strategies, Learning Practices, Activities, and Experiences.
 SPRING GROVE AREA SCHOOL DISTRICT PLANNED COURSE OVERVIEW Course Title: Advanced Placement Physics 1 Grade Level(s): 10-12 Units of Credit: 1.5 credits Classification: Elective Length of Course: 30 cycles
SPRING GROVE AREA SCHOOL DISTRICT PLANNED COURSE OVERVIEW Course Title: Advanced Placement Physics 1 Grade Level(s): 10-12 Units of Credit: 1.5 credits Classification: Elective Length of Course: 30 cycles
General Physics I (aka PHYS 2013)
 General Physics I (aka PHYS 2013) PROF. VANCHURIN (AKA VITALY) University of Minnesota, Duluth (aka UMD) OUTLINE CHAPTER 12 CHAPTER 19 REVIEW CHAPTER 12: FLUID MECHANICS Section 12.1: Density Section 12.2:
General Physics I (aka PHYS 2013) PROF. VANCHURIN (AKA VITALY) University of Minnesota, Duluth (aka UMD) OUTLINE CHAPTER 12 CHAPTER 19 REVIEW CHAPTER 12: FLUID MECHANICS Section 12.1: Density Section 12.2:
Today s lecture. WEST VIRGINIA UNIVERSITY Physics
 Today s lecture Review of chapters 1-14 Note: I m taking for granted that you ll still know SI/cgs units, order-of-magnitude estimates, etc., so I m focusing on problems. Velocity and acceleration (1d)
Today s lecture Review of chapters 1-14 Note: I m taking for granted that you ll still know SI/cgs units, order-of-magnitude estimates, etc., so I m focusing on problems. Velocity and acceleration (1d)
Phys102 First Major- 161 Code: 20 Coordinator: Dr. A. Naqvi Saturday, October 29, 2016 Page: 1
 Coordinator: Dr. A. Naqvi Saturday, October 29, 2016 Page: 1 Q1. FIGURE 1 shows three waves that are separately sent along the same unstretchable string that is kept under constant tension along an x-axis.
Coordinator: Dr. A. Naqvi Saturday, October 29, 2016 Page: 1 Q1. FIGURE 1 shows three waves that are separately sent along the same unstretchable string that is kept under constant tension along an x-axis.
Columbia University Department of Physics QUALIFYING EXAMINATION
 Columbia University Department of Physics QUALIFYING EXAMINATION Friday, January 18, 2013 1:00PM to 3:00PM General Physics (Part I) Section 5. Two hours are permitted for the completion of this section
Columbia University Department of Physics QUALIFYING EXAMINATION Friday, January 18, 2013 1:00PM to 3:00PM General Physics (Part I) Section 5. Two hours are permitted for the completion of this section
On my honor as a Texas A&M University student, I will neither give nor receive unauthorized help on this exam.
 Physics 201, Exam 4 Name (printed) On my honor as a Texas A&M University student, I will neither give nor receive unauthorized help on this exam. Name (signed) The multiple-choice problems carry no partial
Physics 201, Exam 4 Name (printed) On my honor as a Texas A&M University student, I will neither give nor receive unauthorized help on this exam. Name (signed) The multiple-choice problems carry no partial
Learning Objectives for Final Exam Fall, 2012 Physics 2210
 Learning Objectives for Final Exam Fall, 2012 Physics 2210 Operationally defined quantities (They are defined in terms of the operations you perform to, by measurement, compare an object or quantity with
Learning Objectives for Final Exam Fall, 2012 Physics 2210 Operationally defined quantities (They are defined in terms of the operations you perform to, by measurement, compare an object or quantity with
FOUNDATION STUDIES EXAMINATIONS June PHYSICS Semester One February Main
 1 FOUNDATION STUDIES EXAMINATIONS June 2015 PHYSICS Semester One February Main Time allowed 2 hours for writing 10 minutes for reading This paper consists of 6 questions printed on 10 pages. PLEASE CHECK
1 FOUNDATION STUDIES EXAMINATIONS June 2015 PHYSICS Semester One February Main Time allowed 2 hours for writing 10 minutes for reading This paper consists of 6 questions printed on 10 pages. PLEASE CHECK
Pleeeeeeeeeeeeeease mark your UFID, exam number, and name correctly. 20 problems 3 problems from exam 2
 Pleeeeeeeeeeeeeease mark your UFID, exam number, and name correctly. 20 problems 3 problems from exam 1 3 problems from exam 2 6 problems 13.1 14.6 (including 14.5) 8 problems 1.1---9.6 Go through the
Pleeeeeeeeeeeeeease mark your UFID, exam number, and name correctly. 20 problems 3 problems from exam 1 3 problems from exam 2 6 problems 13.1 14.6 (including 14.5) 8 problems 1.1---9.6 Go through the
Version I. Final Exam. May 4, 1999
 Name: Final Exam May 4, 1999 Useful constants: For water: ρ=1000 kg/m 3, c = 1 kcal/kg/ C, latent heat of fusion = 80 kcal/kg, latent heat of vaporization = 540 kcal/kg. G=6.67x10-11 Nm 2 /kg 2, R=8.31
Name: Final Exam May 4, 1999 Useful constants: For water: ρ=1000 kg/m 3, c = 1 kcal/kg/ C, latent heat of fusion = 80 kcal/kg, latent heat of vaporization = 540 kcal/kg. G=6.67x10-11 Nm 2 /kg 2, R=8.31
Grade XI. Physics Exam Preparation Booklet. Chapter-wise Important Questions. #GrowWithGreen
 Grade XI Physics Exam Preparation Booklet Chapter-wise Important Questions #GrowWithGreen Units and Measurements Q1. After reading the physics book, Anamika recalled and noted down the expression for the
Grade XI Physics Exam Preparation Booklet Chapter-wise Important Questions #GrowWithGreen Units and Measurements Q1. After reading the physics book, Anamika recalled and noted down the expression for the
Fall 2004 Physics 3 Tu-Th Section
 Fall 2004 Physics 3 Tu-Th Section Claudio Campagnari Lecture 3: 30 Sep. 2004 Web page: http://hep.ucsb.edu/people/claudio/ph3-04/ 1 Sound Sound = longitudinal wave in a medium. The medium can be anything:
Fall 2004 Physics 3 Tu-Th Section Claudio Campagnari Lecture 3: 30 Sep. 2004 Web page: http://hep.ucsb.edu/people/claudio/ph3-04/ 1 Sound Sound = longitudinal wave in a medium. The medium can be anything:
Physics 53 Summer Final Exam. Solutions
 Final Exam Solutions In questions or problems not requiring numerical answers, express the answers in terms of the symbols given, and standard constants such as g. If numbers are required, use g = 10 m/s
Final Exam Solutions In questions or problems not requiring numerical answers, express the answers in terms of the symbols given, and standard constants such as g. If numbers are required, use g = 10 m/s
Physics 9 Wednesday, February 5, 2014
 Physics 9 Wednesday, February 5, 2014 HW3 (fluids) due Friday. I reserved DRL 3W2 from 6:30pm to 9:30pm on Wednesdays (usually Zoey) and Thursdays (usually Bill) for HW help. Quiz #1 (10 minutes at end
Physics 9 Wednesday, February 5, 2014 HW3 (fluids) due Friday. I reserved DRL 3W2 from 6:30pm to 9:30pm on Wednesdays (usually Zoey) and Thursdays (usually Bill) for HW help. Quiz #1 (10 minutes at end
Physics 213 Spring 2009 Midterm exam. Review Lecture
 Physics 213 Spring 2009 Midterm exam Review Lecture The next two questions pertain to the following situation. A container of air (primarily nitrogen and oxygen molecules) is initially at 300 K and atmospheric
Physics 213 Spring 2009 Midterm exam Review Lecture The next two questions pertain to the following situation. A container of air (primarily nitrogen and oxygen molecules) is initially at 300 K and atmospheric
Chapter 1: Mathematical Concepts and Vectors
 Chapter 1: Mathematical Concepts and Vectors giga G 1 9 mega M 1 6 kilo k 1 3 centi c 1 - milli m 1-3 micro μ 1-6 nano n 1-9 1 in =.54 cm 1 m = 1 cm = 3.81 t 1 mi = 58 t = 169 m 1 hr = 36 s 1 day = 86,4
Chapter 1: Mathematical Concepts and Vectors giga G 1 9 mega M 1 6 kilo k 1 3 centi c 1 - milli m 1-3 micro μ 1-6 nano n 1-9 1 in =.54 cm 1 m = 1 cm = 3.81 t 1 mi = 58 t = 169 m 1 hr = 36 s 1 day = 86,4
PHY 141 Midterm 1 Oct 2, 2014 Version A
 PHY 141 Midterm 1 Oct 2, 2014 Version A Put FULL NAME, ID#, and EXAM VERSION on the front cover of the BLUE BOOKLET! To avoid problems in grading: do all problems in order, write legibly, and show all
PHY 141 Midterm 1 Oct 2, 2014 Version A Put FULL NAME, ID#, and EXAM VERSION on the front cover of the BLUE BOOKLET! To avoid problems in grading: do all problems in order, write legibly, and show all
Homework: 13, 14, 18, 20, 24 (p )
 Homework: 13, 14, 18, 0, 4 (p. 531-53) 13. A sample of an ideal gas is taken through the cyclic process abca shown in the figure below; at point a, T=00 K. (a) How many moles of gas are in the sample?
Homework: 13, 14, 18, 0, 4 (p. 531-53) 13. A sample of an ideal gas is taken through the cyclic process abca shown in the figure below; at point a, T=00 K. (a) How many moles of gas are in the sample?
Grade XI. Physics Exam Preparation Booklet. Chapter-wise Important Questions. #GrowWithGreen
 Grade XI Physics Exam Preparation Booklet Chapter-wise Important Questions #GrowWithGreen Units and Measurements Q1. After reading the physics book, Anamika recalled and noted down the expression for the
Grade XI Physics Exam Preparation Booklet Chapter-wise Important Questions #GrowWithGreen Units and Measurements Q1. After reading the physics book, Anamika recalled and noted down the expression for the
6. (6) Show all the steps of how to convert 50.0 F into its equivalent on the Kelvin scale.
 General Physics I Quiz 8 - Ch. 13 - Temperature & Kinetic Theory July 30, 2009 Name: Make your work clear to the grader. Show formulas used. Give correct units and significant figures. Partial credit is
General Physics I Quiz 8 - Ch. 13 - Temperature & Kinetic Theory July 30, 2009 Name: Make your work clear to the grader. Show formulas used. Give correct units and significant figures. Partial credit is
Chapter 13. Hooke s Law: F = - kx Periodic & Simple Harmonic Motion Springs & Pendula Waves Superposition. Next Week!
 Chapter 13 Hooke s Law: F = - kx Periodic & Simple Harmonic Motion Springs & Pendula Waves Superposition Next Week! Review Physics 2A: Springs, Pendula & Circular Motion Elastic Systems F = kx Small Vibrations
Chapter 13 Hooke s Law: F = - kx Periodic & Simple Harmonic Motion Springs & Pendula Waves Superposition Next Week! Review Physics 2A: Springs, Pendula & Circular Motion Elastic Systems F = kx Small Vibrations
FALL TERM EXAM, PHYS 1211, INTRODUCTORY PHYSICS I Thursday, 11 December 2014, 6 PM to 9 PM, Field House Gym
 FALL TERM EXAM, PHYS 1211, INTRODUCTORY PHYSICS I Thursday, 11 December 2014, 6 PM to 9 PM, Field House Gym NAME: STUDENT ID: INSTRUCTION 1. This exam booklet has 13 pages. Make sure none are missing 2.
FALL TERM EXAM, PHYS 1211, INTRODUCTORY PHYSICS I Thursday, 11 December 2014, 6 PM to 9 PM, Field House Gym NAME: STUDENT ID: INSTRUCTION 1. This exam booklet has 13 pages. Make sure none are missing 2.
Rate of Heating and Cooling
 Rate of Heating and Cooling 35 T [ o C] Example: Heating and cooling of Water E 30 Cooling S 25 Heating exponential decay 20 0 100 200 300 400 t [sec] Newton s Law of Cooling T S > T E : System S cools
Rate of Heating and Cooling 35 T [ o C] Example: Heating and cooling of Water E 30 Cooling S 25 Heating exponential decay 20 0 100 200 300 400 t [sec] Newton s Law of Cooling T S > T E : System S cools
Phys102 Final-132 Zero Version Coordinator: A.A.Naqvi Wednesday, May 21, 2014 Page: 1
 Coordinator: A.A.Naqvi Wednesday, May 1, 014 Page: 1 Q1. What is the potential difference V B -V A in the circuit shown in Figure 1 if R 1 =70.0 Ω, R =105 Ω, R 3 =140 Ω, ε 1 =.0 V and ε =7.0 V? A).3 V
Coordinator: A.A.Naqvi Wednesday, May 1, 014 Page: 1 Q1. What is the potential difference V B -V A in the circuit shown in Figure 1 if R 1 =70.0 Ω, R =105 Ω, R 3 =140 Ω, ε 1 =.0 V and ε =7.0 V? A).3 V
Phys 111 Exam 3 November 14, Name Section University ID
 Phys 111 Exam 3 November 14, 017 Name Section University ID Please fill in your computer answer sheet as follows: 1) In the NAME grid, fill in your last name, leave one blank space, then your first name.
Phys 111 Exam 3 November 14, 017 Name Section University ID Please fill in your computer answer sheet as follows: 1) In the NAME grid, fill in your last name, leave one blank space, then your first name.
Physics 1301, Exam 3 Review
 c V Andersen, 2006 1 Physics 1301, Exam 3 Review The following is a list of things you should definitely know for the exam, however, the list is not exhaustive. You are responsible for all the material
c V Andersen, 2006 1 Physics 1301, Exam 3 Review The following is a list of things you should definitely know for the exam, however, the list is not exhaustive. You are responsible for all the material
First Name: Last Name: Section: 1 December 20, 2004 Physics 201 FINAL EXAM
 First Name: Last Name: Section: 1 December 20, 2004 Physics 201 FINAL EXAM Print your name and section clearly on all nine pages. (If you do not know your section number, write your TA s name.) Show all
First Name: Last Name: Section: 1 December 20, 2004 Physics 201 FINAL EXAM Print your name and section clearly on all nine pages. (If you do not know your section number, write your TA s name.) Show all
1. Types of Waves. There are three main types of waves:
 Chapter 16 WAVES I 1. Types of Waves There are three main types of waves: https://youtu.be/kvc7obkzq9u?t=3m49s 1. Mechanical waves: These are the most familiar waves. Examples include water waves, sound
Chapter 16 WAVES I 1. Types of Waves There are three main types of waves: https://youtu.be/kvc7obkzq9u?t=3m49s 1. Mechanical waves: These are the most familiar waves. Examples include water waves, sound
PHY 2130 EXAM 3 A April 3, 2013
 PHY 130 EXAM 3 A April 3, 013 Name (print): (Last) (First) WSU ID Number (9 digit): Please circle your quiz section: Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday 11:45 AM (K. Dhindsa) 10:40 AM (J. Huang) 11:45 AM
PHY 130 EXAM 3 A April 3, 013 Name (print): (Last) (First) WSU ID Number (9 digit): Please circle your quiz section: Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday 11:45 AM (K. Dhindsa) 10:40 AM (J. Huang) 11:45 AM
V sphere = 4 3 πr3. a c = v2. F c = m v2. F s = k s. F ds. = dw dt. P W t. K linear 1 2 mv2. U s = 1 2 kx2 E = K + U. p mv
 v = v i + at x = x i + v i t + 1 2 at2 v 2 = v 2 i + 2a x F = ma F = dp dt P = mv R = v2 sin(2θ) g v dx dt a dv dt = d2 x dt 2 x = r cos(θ) V sphere = 4 3 πr3 a c = v2 r = rω2 F f = µf n F c = m v2 r =
v = v i + at x = x i + v i t + 1 2 at2 v 2 = v 2 i + 2a x F = ma F = dp dt P = mv R = v2 sin(2θ) g v dx dt a dv dt = d2 x dt 2 x = r cos(θ) V sphere = 4 3 πr3 a c = v2 r = rω2 F f = µf n F c = m v2 r =
Temperature Thermal Expansion Ideal Gas Law Kinetic Theory Heat Heat Transfer Phase Changes Specific Heat Calorimetry
 Temperature Thermal Expansion Ideal Gas Law Kinetic Theory Heat Heat Transfer Phase Changes Specific Heat Calorimetry Zeroeth Law Two systems individually in thermal equilibrium with a third system (such
Temperature Thermal Expansion Ideal Gas Law Kinetic Theory Heat Heat Transfer Phase Changes Specific Heat Calorimetry Zeroeth Law Two systems individually in thermal equilibrium with a third system (such
PHYSICS 221, FALL 2011 EXAM #2 SOLUTIONS WEDNESDAY, NOVEMBER 2, 2011
 PHYSICS 1, FALL 011 EXAM SOLUTIONS WEDNESDAY, NOVEMBER, 011 Note: The unit vectors in the +x, +y, and +z directions of a right-handed Cartesian coordinate system are î, ĵ, and ˆk, respectively. In this
PHYSICS 1, FALL 011 EXAM SOLUTIONS WEDNESDAY, NOVEMBER, 011 Note: The unit vectors in the +x, +y, and +z directions of a right-handed Cartesian coordinate system are î, ĵ, and ˆk, respectively. In this
Solution The light plates are at the same heights. In balance, the pressure at both plates has to be the same. m g A A A F A = F B.
 43. A piece of metal rests in a toy wood boat floating in water in a bathtub. If the metal is removed from the boat, and kept out of the water, what happens to the water level in the tub? A) It does not
43. A piece of metal rests in a toy wood boat floating in water in a bathtub. If the metal is removed from the boat, and kept out of the water, what happens to the water level in the tub? A) It does not
