Fluorocarbon C3F8 Properties. Table of Contents
|
|
|
- Linette Stephens
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Fluorocarbon C3F8 Properties (octafluoropropane R218) Table of Contents 1. C3F Saturation line curve for C 3 F logp-h diagram for C 3 F Extended logp-h diagram for C 3 F Table of Saturation properties for C3F Saturation properties by 3M Company Properties of the superheated vapor of the C 3 F Densities [with extended pressure range down to 0.7 bar a ] Specicic heat [with extended pressure range down to 0.7 bar a ] Enthalpy Entropy Thermal conductivity Viscosity Extented Properties of the superheated vapor of the C 3 F Density Specific heat Enthalpy Entropy Thermal conductivity Viscosity Properties of the sub-cooled liquid of the C 3 F Density Specicic heat Enthalpy Entropy Thermal conductivity Viscosity Compatibility of fluorocarbons with materials...33
2 1. C3F8 Some selected thermophysical properties of the C 3 F 8 Fluorocarbon Chem.formula Mean Mol.Wt. 188 Boiling atm [ C] -37 Dens.[g/cm3] Liquid DynamicViscosity [10-3 Pa.s] PF5030 C3F8 C C Liquid Kinematic Viscosity [10-6 m 2 /s] 20 C Surface Tens.[dy/cm] Vapor press.@-10 C [Torr] [bara] Latent Heat Vap. [J/mole] [kj/kg] C Specific Heat [kj/kg.k] 1.05 Thermal conductivity [W/m.K] Liquid Vol. Flow (90 W load) [cm3/s] ~0.8 Gas Vol. Flow (90 W load) [cm3/s] ~50 Liquid-Gas Expansion -10 C ~60 DeltaP max for DeltaT=0.5 C [mbar] ~50
3 1.1 Saturation line curve for C 3 F 8 P - T Diagram for C3F8 Pressure [bar] 100 Pressure [bar] Poly. (Pressure [bar]) 10 1 y = 2E-08x 4 + 9E-06x x x Temperature [C]
4 1.2 logp-h diagram for C3F8
5 1.3 Extended logp-h diagram for C3F8
6 1.4 Table of Saturation properties for C3F8 C3F8 Saturation Properties between -40 and + 45 C By Vic Vacek, March 1999 PAGE1 Temp Pres Dens (L) Dens (V) Enth (L) Enth (V) Entr (L) Entr (V) Cp (L) Cp (V) SoS (L) SoS (V) Visc (L) Visc (V) Th C (L) Th C (V) [C] [bar] [kg/m^3] [kg/m^3] [kj/kg] [kj/kg] [kj/k-kg] [kj/k-kg] [kj/k-kg] [kj/k-kg] [m/s] [m/s] [µpa-s] [µpa-s] [W/m-K] [W/m-K]
7 Table of Saturation properties for C3F8 [continues] C3F8 Saturation Properties between -40 and + 45 C By Vic Vacek, March 1999 Temp Pres Dens (L) Dens (V) Enth (L) Enth (V) Entr (L) Entr (V) Cp (L) Cp (V) SoS (L) SoS (V) Visc (L) Visc (V) Th C (L) [C] [bar] [kg/m^3] [kg/m^3] [kj/kg] [kj/kg] [kj/k-kg] [kj/k-kg] [kj/k-kg] [kj/k-kg] [m/s] [m/s] [µpa-s] [µpa-s] [W/m-K] Reference state values according IIR
8 1.5 Saturation properties by 3M Company TABLE - Saturated Properties of PF C3F8 3M Data, digtalized by Vic Vacek; February 1999 at CERN Page1 T Tr Pvp Pr ρ (L) ρ (V) Vmol (L) Vmol (V) U (L) U (V) H (L) Hvap H (V) S (L) Svap S (V) [K] [-] [bar] [-] [kg/m^3] [kg/m^3] [L/mol] [L/mol] [kj/mol] [kj/mol] [kj/mol] [kj/mol] [kj/mol] [J/mol K] [J/mol K] [J/mol K]
9 TABLE - Saturated Properties of PF C3F8 3M Data, digtalized by Vic Vacek; February 1999 at CERN Page2 T Tr Pvp Pr ρ (L) ρ (V) Vmol (L) Vmol (V) U (L) U (V) H (L) Hvap H (V) S (L) Svap S (V) [K] [-] [bar] [-] [kg/m^3] [kg/m^3] [L/mol] [L/mol] [kj/mol] [kj/mol] [kj/mol] [kj/mol] [kj/mol] [J/mol K] [J/mol K] [J/mol K]
10 TABLE - Saturated Properties of PF C3F8 3M Data, digtalized by Vic Vacek; February 1999 at CERN Page3 T Tr Pvp Pr ρ (L) ρ (V) Vmol (L) Vmol (V) U (L) U (V) H (L) Hvap H (V) S (L) Svap S (V) [K] [-] [bar] [-] [kg/m^3] [kg/m^3] [L/mol] [L/mol] [kj/mol] [kj/mol] [kj/mol] [kj/mol] [kj/mol] [J/mol K] [J/mol K] [J/mol K] REFERENCE: Pure liquid at 180 K SYMBOLS AND UNITS: Pvp = v.p. [bar]; ρ = density [kg/m^3]; V = molar volume [L/mol]; U = int. energy [kj/mol]; H = enthalpy [kj/mol]; S entropy [J/mol.K]; = latent quantity (difference between sat. L and sat. V)
11 1.6 Properties of the superheated vapor of the C 3 F 8 in the pressure range between 1 and 20 bar a and temperature range between 35 ºC and 60 ºC Densities [with extended pressure range down to 0.7 bar a ]
12
13 1.6.2 Specicic heat [with extended pressure range down to 0.7 bar a ]
14
15 1.6.3 Enthalpy
16
17 1.6.4 Entropy
18 1.6.5 Thermal conductivity
19 1.6.6 Viscosity
20 1.7 Extented Properties of the superheated vapor of the C 3 F 8 in the extended pressure range between 15 and 20 bar a and extended temperature range between 40 ºC and 100 ºC Density
21 1.7.2 Specific heat
22 1.7.3 Enthalpy
23 1.7.4 Entropy
24 1.7.5 Thermal conductivity
25 1.7.6 Viscosity
26 1.8 Properties of the sub-cooled liquid of the C 3 F 8 in the pressure range between 1 and 18 bar a and temperature range between 30 ºC and 50 ºC Density
27 1.8.2 Specicic heat
28 1.8.3 Enthalpy
29 1.8.4 Entropy
30 1.8.5 Thermal conductivity
31 1.8.6 Viscosity
32
33 1.9 Compatibility of fluorocarbons with materials Communicated by Lionel Breuilly - 3M FRANCE 3M and various materials manufacturers have been contacted regarding their compatibility with Fluorinert: GOOD Acrylic (Acrylite / Acrysteel / Aristech / Cyrolite / Diakon / Kamax) *possible Buna-N - Nitrile rubber (NBR=Acrylonitrile butadiene rubber - Perbunan-NT / Hycar / Butacril / Chemigum / Isr-N / Stansolv / Sol-Vex) *good Nalgene - Polyurethane (PU/PUR=Polyurethane rubber - Vulkollan / Adiprene) *possible Neoprene W (CR=Polychloroprene rubber - Baypren / Neox / Stanzoil) *prohibited Silicone (SIR=Silicone rubber - Silastic) *possible BAD Nylon (PA=Polyamid - Stanyl / Capron / Ultramid / Maranyl / Zytel / Orgamid / Grilon / Rilsan / Reny / Vestamid) *possible Polypropylene (PP=Polypropylene - Celmar / Coprax / Giacogreen / Hostelen PP / Novolen / Appryl / Lacqtene / Propathene / Ektar FB / Fortilene / Marlex / Polyfine / Pro-Fax / Tenite) *possible PVC (PVC=Polyvinyl chloride - Betaglas / Darvic / Fiberlok / Trovidur / Hostalit / Vestolit / Tygon) *prohibited Teflon (PTFE=Polytetrafluoroethylene - Flubriflon / Fluon / Teflon TFE / Valflon F / Hostaflon TF / Furon / Gortex / Tfm / Rulon) *prohibited Tygon (PVC) *prohibited Viton (FKM=Fluoroelastomer - Fluorel) *prohibited (from our test) EPDM (Ethylene propylene rubber - Keltan / Nordel / Vistalon / Buna-AP / Pyrofil) *possible *CERN IS 41 classification regarding fire
34 C 6 F 14 - PIPING Rad Hard 1 Compatibility 2 Px10 10 (cm 3 mm/cm 2 s cm Hg) Gas Permeability (DATA: Angst+Pfister) GLOBAL RESULT SS Aluminum 1.10 OK 1.11 OK OK (if fluid is pure) 1.12 OK Not well know if fluid is contaminated with H 2 O, O 2, C-H due to F-production 0 OK 0 OK? PEEK rad 1.14 OK (Data: TIS-CFM/MTR/96-17) PUR 10 7 rad (Data: Angst+Pfister) 1.15 OK (Data: 3M) (Data: 3M) 5 N O CO 2 OK OK Polypropylene PP 10 7 rad (Data: Angst+Pfister) 3-5 N 2 ~10 O 2 ~ 35 CO 2? See Note Polyethylene PE Nylon (Polyamide 6) Rilsan (polyamide 11) 10 8 rad (Data: CERN 82-10) 1.16 OK (Data: DELPHI RICH 66) 10 7 rad (Data: CERN 82-10) 1.17 OK (Data: 3M) OK (Data: 3M) Discolaration, Weight loss, but mechanical prop. OK (Data: DELPHI RICH 66) 0.1 N 2 ~ 1 O CO 2 8 H 2 ~ 2 N 2 ~ 1 O CO 2 8 H 2 OK OK BAD Teflon (PTFE) PVC 1.18 BAD 1.19 BAD 10 8 rad (Data: Angst+Pfister) 1.20 Some effect (Data: 3M) 0.3 N 2 ~ 1 O CO 2 33 H 2 Note: one should avoid plastics with the fluorocarbons as they take out the plastiziser and the product becomes brittle. Source: G. Lenzem, DELPHI RICH and 3M. BAD BAD 1 BAD means that material does not show any damage up to the indicated dose. BAD means that it is affected well below 10 5 rad. 2 Effect means change of weight and/or volume after > 72h immersion in C 6 F 14. Some effect means > 1%. BAD means >4%.
35 C6F14 - O-rings How much weight/volume loss/increase is acceptable? SOME EFFECT means > 1%. BAD means > 4%. Suggested by 3M as best choices EPDM Perbunan (NBR) or caoutchouc or nitrile rubber 2. PVDF Neoprene Butyl rubber Kalrez Rad Hard < 10 8 rad (Data: CERN 82-10) 10 8 rad (Data: CERN 82-10) 10 7 rad (Data: CERN 82-10) < 10 5 rad (Data: CERN 82-10) 10 8 rad (Data: Angst+Pfister) 10 6 rad (Data: CERN Compatibility OK (Data: 3M) OK (but some effect) (Data: 3M) OK (Data: 3M) OK (Data: 3M) OK (but some effect) (Data: 3M) GLOBAL RESULT OK OK OK BAD < 10 7 rad Viton BAD BAD (Data: CERN 82-10) (Data: 3M) * Teflon (PTFE & PCTFE) BAD BAD BAD OK * Viton O-rings were used in DELPHI with no leak problems. Source: G. Lenzem, DELPHI RICH
Solkane 134a Thermodynamics
 SOLVAY FLUOR SOLKANE - INFORMATION SERVICE Solkane 134a Thermodynamics SOLVAY FLUOR Technical Service - Refrigerants - PRODUCT BULLETIN NO.: T/09.04/01/E P.O. Box 220 Phone +49/511/857-2653 30002 Hannover
SOLVAY FLUOR SOLKANE - INFORMATION SERVICE Solkane 134a Thermodynamics SOLVAY FLUOR Technical Service - Refrigerants - PRODUCT BULLETIN NO.: T/09.04/01/E P.O. Box 220 Phone +49/511/857-2653 30002 Hannover
Solkane 410 Thermodynamics
 SOLVAY FLUOR SOLKANE - INFORMATION SERVICE Solkane 410 Thermodynamics SOLVAY FLUOR Technical Service - Refrigerants - Product Bulletin no.: T/09.04/04/E P.O. Box 0 Phone +49/511/857-653 3000 Hannover Fax
SOLVAY FLUOR SOLKANE - INFORMATION SERVICE Solkane 410 Thermodynamics SOLVAY FLUOR Technical Service - Refrigerants - Product Bulletin no.: T/09.04/04/E P.O. Box 0 Phone +49/511/857-653 3000 Hannover Fax
Physical Property Data Sheet SI Units
 Physical Property Data Sheet SI Units PHYSICAL PROPERTY DATA FOR KLEA 58 PROPERTY UNITS VALUE Bubble Point (1 atm) C -85.69 Dew Point (1 atm) C -85.68 Bubble Point Pressure (-4 C) bara 8.2 Estimated Critical
Physical Property Data Sheet SI Units PHYSICAL PROPERTY DATA FOR KLEA 58 PROPERTY UNITS VALUE Bubble Point (1 atm) C -85.69 Dew Point (1 atm) C -85.68 Bubble Point Pressure (-4 C) bara 8.2 Estimated Critical
Physical Property Data Sheet SI Units
 Physical Property Data Sheet SI Units PHYSICAL PROPERTY DATA FOR KLEA 407C PROPERTY UNITS VALUE Bubble Point (1 atm) C -44.0 Dew Point (1atm) C -36.8 Bubble Point Pressure (25 C) bara 11.9 Estimated Critical
Physical Property Data Sheet SI Units PHYSICAL PROPERTY DATA FOR KLEA 407C PROPERTY UNITS VALUE Bubble Point (1 atm) C -44.0 Dew Point (1atm) C -36.8 Bubble Point Pressure (25 C) bara 11.9 Estimated Critical
MAE 320 THERODYNAMICS FINAL EXAM - Practice. Name: You are allowed three sheets of notes.
 50 MAE 320 THERODYNAMICS FINAL EXAM - Practice Name: You are allowed three sheets of notes. 1. Fill in the blanks for each of the two (Carnot) cycles below. (a) 5 a) Heat engine or Heat pump/refrigerator
50 MAE 320 THERODYNAMICS FINAL EXAM - Practice Name: You are allowed three sheets of notes. 1. Fill in the blanks for each of the two (Carnot) cycles below. (a) 5 a) Heat engine or Heat pump/refrigerator
Klea 407A Data Sheet SI Units
 Klea 407A Data Sheet SI Units Physical Property Data for Klea 407A Property Units Value Bubble Point 1 (atm) C -45.5 Dew Point (1atm) C -38.9 Bubble Point Pressure (25 C) bara 12.6 Estimated Critical Temperature
Klea 407A Data Sheet SI Units Physical Property Data for Klea 407A Property Units Value Bubble Point 1 (atm) C -45.5 Dew Point (1atm) C -38.9 Bubble Point Pressure (25 C) bara 12.6 Estimated Critical Temperature
KM-1600SWH KM-1600SRH KM-1600SWH3 KM-1600SRH3
 NO. ISSUED: REVISED: 71193 OCT. 2, 2001 JAN. 27, 2003 HOSHIZAKI STACKABLE CRESCENT CUBER MODELS KM-1600SWH KM-1600SRH KM-1600SWH3 KM-1600SRH3 PARTS LIST KM-1600SWH L-0 June, 2001 M-0 Feb., 2002 M-1 Feb.,
NO. ISSUED: REVISED: 71193 OCT. 2, 2001 JAN. 27, 2003 HOSHIZAKI STACKABLE CRESCENT CUBER MODELS KM-1600SWH KM-1600SRH KM-1600SWH3 KM-1600SRH3 PARTS LIST KM-1600SWH L-0 June, 2001 M-0 Feb., 2002 M-1 Feb.,
Appendix A: The Names of Polymers and Polymeric Materials
 Appendix A: The Names of Polymers and Polymeric Materials Every newcomer to the study of polymers is inevitably troubled by the profusion of names for individual polymer materials. Some of the difficulties
Appendix A: The Names of Polymers and Polymeric Materials Every newcomer to the study of polymers is inevitably troubled by the profusion of names for individual polymer materials. Some of the difficulties
There are five problems on the exam. Do all of the problems. Show your work
 CHM 3400 Fundamentals of Physical Chemistry Second Hour Exam March 8, 2017 There are five problems on the exam. Do all of the problems. Show your work R = 0.08206 L atm/mole K N A = 6.022 x 10 23 R = 0.08314
CHM 3400 Fundamentals of Physical Chemistry Second Hour Exam March 8, 2017 There are five problems on the exam. Do all of the problems. Show your work R = 0.08206 L atm/mole K N A = 6.022 x 10 23 R = 0.08314
CHEM Exam 2 - October 11, INFORMATION PAGE (Use for reference and for scratch paper)
 CHEM 5200 - Exam 2 - October 11, 2018 INFORMATION PAGE (Use for reference and for scratch paper) Constants and Conversion Factors: R = 0.082 L-atm/mol-K = 8.31 J/mol-K = 8.31 kpa-l/mol-k 1 L-atm = 101
CHEM 5200 - Exam 2 - October 11, 2018 INFORMATION PAGE (Use for reference and for scratch paper) Constants and Conversion Factors: R = 0.082 L-atm/mol-K = 8.31 J/mol-K = 8.31 kpa-l/mol-k 1 L-atm = 101
Name: Discussion Section:
 CBE 141: Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics, Spring 2018, UC Berkeley Midterm 2 March 22, 2018 Time: 80 minutes, closed-book and closed-notes, one-sided 8 ½ x 11 equation sheet allowed Please show all
CBE 141: Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics, Spring 2018, UC Berkeley Midterm 2 March 22, 2018 Time: 80 minutes, closed-book and closed-notes, one-sided 8 ½ x 11 equation sheet allowed Please show all
ME 201 Thermodynamics
 Spring 01 ME 01 Thermodynamics Property Evaluation Practice Problems II Solutions 1. Air at 100 K and 1 MPa goes to MPa isenthapically. Determine the entropy change. Substance Type: Ideal Gas (air) Process:
Spring 01 ME 01 Thermodynamics Property Evaluation Practice Problems II Solutions 1. Air at 100 K and 1 MPa goes to MPa isenthapically. Determine the entropy change. Substance Type: Ideal Gas (air) Process:
SEM-2017(03HI MECHANICAL ENGINEERING. Paper II. Please read each of the following instructions carefully before attempting questions.
 We RoU No. 700095 Candidate should write his/her Roll No. here. Total No. of Questions : 7 No. of Printed Pages : 7 SEM-2017(03HI MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Paper II Time ; 3 Hours ] [ Total Marks : 0 Instructions
We RoU No. 700095 Candidate should write his/her Roll No. here. Total No. of Questions : 7 No. of Printed Pages : 7 SEM-2017(03HI MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Paper II Time ; 3 Hours ] [ Total Marks : 0 Instructions
Index to Tables in SI Units
 Index to Tables in SI Units Table A-1 Atomic or Molecular Weights and Critical Properties of Selected Elements and Compounds 926 Table A-2 Properties of Saturated Water (Liquid Vapor): Temperature Table
Index to Tables in SI Units Table A-1 Atomic or Molecular Weights and Critical Properties of Selected Elements and Compounds 926 Table A-2 Properties of Saturated Water (Liquid Vapor): Temperature Table
2-412 PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL DATA
 2-412 PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL DATA TABLE 2-304 Saturated Solid/Vapor Water* Volume, Enthalpy, Entropy, Temp., Pressure, ft 3 /lb Btu/lb Btu/(lb)( F) F lb/in 2 abs. Solid Vapor Solid Vapor Solid Vapor 160
2-412 PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL DATA TABLE 2-304 Saturated Solid/Vapor Water* Volume, Enthalpy, Entropy, Temp., Pressure, ft 3 /lb Btu/lb Btu/(lb)( F) F lb/in 2 abs. Solid Vapor Solid Vapor Solid Vapor 160
Lecture No. (1) Introduction of Polymers
 Lecture No. (1) Introduction of Polymers Polymer Structure Polymers are found in nature as proteins, cellulose, silk or synthesized like polyethylene, polystyrene and nylon. Some natural polymers can also
Lecture No. (1) Introduction of Polymers Polymer Structure Polymers are found in nature as proteins, cellulose, silk or synthesized like polyethylene, polystyrene and nylon. Some natural polymers can also
Level 7 Post Graduate Diploma in Engineering Heat and mass transfer
 9210-221 Level 7 Post Graduate Diploma in Engineering Heat and mass transfer 0 You should have the following for this examination one answer book non programmable calculator pen, pencil, drawing instruments
9210-221 Level 7 Post Graduate Diploma in Engineering Heat and mass transfer 0 You should have the following for this examination one answer book non programmable calculator pen, pencil, drawing instruments
O-Ring Handbook. America s Most Responsive Warehouse. Houston, Texas
 14407_APG_CVR 7/12/04 12:33 PM Page 1 O-Ring Handbook America s Most Responsive Warehouse (713) 675-5271 1-800-888-5223 FAX: (713) 675-2730 FAX: 1-800-444-3252 P.O. Box 213 (77001) 6039 Armour Dr. (77020)
14407_APG_CVR 7/12/04 12:33 PM Page 1 O-Ring Handbook America s Most Responsive Warehouse (713) 675-5271 1-800-888-5223 FAX: (713) 675-2730 FAX: 1-800-444-3252 P.O. Box 213 (77001) 6039 Armour Dr. (77020)
III. Evaluating Properties. III. Evaluating Properties
 F. Property Tables 1. What s in the tables and why specific volumes, v (m /kg) (as v, v i, v f, v g ) pressure, P (kpa) temperature, T (C) internal energy, u (kj/kg) (as u, u i, u f, u g, u ig, u fg )
F. Property Tables 1. What s in the tables and why specific volumes, v (m /kg) (as v, v i, v f, v g ) pressure, P (kpa) temperature, T (C) internal energy, u (kj/kg) (as u, u i, u f, u g, u ig, u fg )
Polymer Chemistry POLYMER CHEMISTRY
 Polymer Chemistry POLYMER CHEMISTRY Polymer Chemistry As far back as 1839, Charles Goodyear first improved the elastic properties of natural rubber by heating with sulfur (vulcanization). It was not until
Polymer Chemistry POLYMER CHEMISTRY Polymer Chemistry As far back as 1839, Charles Goodyear first improved the elastic properties of natural rubber by heating with sulfur (vulcanization). It was not until
Thermodynamics Introduction and Basic Concepts
 Thermodynamics Introduction and Basic Concepts by Asst. Prof. Channarong Asavatesanupap Mechanical Engineering Department Faculty of Engineering Thammasat University 2 What is Thermodynamics? Thermodynamics
Thermodynamics Introduction and Basic Concepts by Asst. Prof. Channarong Asavatesanupap Mechanical Engineering Department Faculty of Engineering Thammasat University 2 What is Thermodynamics? Thermodynamics
NO: ISSUED: DEC. 7, 1999 REVISED: SEPT. 4, 2002 HOSHIZAKI MODULAR ICEMAKER F-2000MLF(-C) MODEL (FINAL) PARTS LIST
 NO: 71135 ISSUED: DEC. 7, 1999 REVISED: SEPT. 4, 2002 HOSHIZAKI MODULAR ICEMAKER MODEL F-2000MLF(-C) (FINAL) PARTS LIST H-0 March 1998 J-0 December 1998 K-0 February 2000 K-1 June 2000 L-0 December 2000
NO: 71135 ISSUED: DEC. 7, 1999 REVISED: SEPT. 4, 2002 HOSHIZAKI MODULAR ICEMAKER MODEL F-2000MLF(-C) (FINAL) PARTS LIST H-0 March 1998 J-0 December 1998 K-0 February 2000 K-1 June 2000 L-0 December 2000
The Ultimate Innovators
 Product Over view america, inc. The Ultimate Innovators www.yamadapump.com Yamada Corporation S ince its beginning in 1905, Yamada has been at the forefront in developing the most complete line of air
Product Over view america, inc. The Ultimate Innovators www.yamadapump.com Yamada Corporation S ince its beginning in 1905, Yamada has been at the forefront in developing the most complete line of air
ENGINEERING OF NUCLEAR REACTORS
 22.312 ENGINEERING OF NUCLEAR REACTORS Monday, December 17 th, 2007, 9:00am-12:00 pm FINAL EXAM SOLUTIONS Problem 1 (45%) Analysis of Decay Heat Removal during a Severe Accident i) The energy balance for
22.312 ENGINEERING OF NUCLEAR REACTORS Monday, December 17 th, 2007, 9:00am-12:00 pm FINAL EXAM SOLUTIONS Problem 1 (45%) Analysis of Decay Heat Removal during a Severe Accident i) The energy balance for
Ch 9 Practice Problems
 Ch 9 Practice Problems 1. One mole of an ideal gas is expanded from a volume of 1.50 L to a volume of 10.18 L against a constant external pressure of 1.03 atm. Calculate the work. (1 L atm = 101.3 J) A)
Ch 9 Practice Problems 1. One mole of an ideal gas is expanded from a volume of 1.50 L to a volume of 10.18 L against a constant external pressure of 1.03 atm. Calculate the work. (1 L atm = 101.3 J) A)
The Research of Heat Transfer Area for 55/19 Steam Generator
 Journal of Power and Energy Engineering, 205, 3, 47-422 Published Online April 205 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/jpee http://dx.doi.org/0.4236/jpee.205.34056 The Research of Heat Transfer Area
Journal of Power and Energy Engineering, 205, 3, 47-422 Published Online April 205 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/jpee http://dx.doi.org/0.4236/jpee.205.34056 The Research of Heat Transfer Area
Name: Discussion Section:
 CBE 141: Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics, Spring 2018, UC Berkeley Midterm 2 March 22, 2018 Time: 80 minutes, closed-book and closed-notes, one-sided 8 ½ x 11 equation sheet allowed Please show all
CBE 141: Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics, Spring 2018, UC Berkeley Midterm 2 March 22, 2018 Time: 80 minutes, closed-book and closed-notes, one-sided 8 ½ x 11 equation sheet allowed Please show all
TOPIC 7. Polymeric materials
 Universidad Carlos III de Madrid www.uc3m.es MATERIALS SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING TOPIC 7. Polymeric materials 1. Introduction Definition General characteristics Historic introduction Polymers: Examples 2.
Universidad Carlos III de Madrid www.uc3m.es MATERIALS SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING TOPIC 7. Polymeric materials 1. Introduction Definition General characteristics Historic introduction Polymers: Examples 2.
1. Which molecule will have the strongest intermolecular forces? _D. 2. Which molecule will have the weakest intermolecular forces?
 Use the following information to answer questions 1-5: 1. Which molecule will have the strongest intermolecular forces? _D 2. Which molecule will have the weakest intermolecular forces? _C 3. What is the
Use the following information to answer questions 1-5: 1. Which molecule will have the strongest intermolecular forces? _D 2. Which molecule will have the weakest intermolecular forces? _C 3. What is the
Thermodynamics I Chapter 2 Properties of Pure Substances
 Thermodynamics I Chapter 2 Properties of Pure Substances Mohsin Mohd Sies Fakulti Kejuruteraan Mekanikal, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia Properties of Pure Substances (Motivation) To quantify the changes
Thermodynamics I Chapter 2 Properties of Pure Substances Mohsin Mohd Sies Fakulti Kejuruteraan Mekanikal, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia Properties of Pure Substances (Motivation) To quantify the changes
KM-2000SWE3 KM-2000SRE3
 NO. ISSUED: REVISED: 71090 JUNE 7, 1994 AUG. 7, 2000 HOSHIZAKI STACKABLE CRESCENT CUBER MODEL KM-2000SWE3 KM-2000SRE3 (FINAL) PARTS LIST KM-2000SWE3 D-0 June, 1994 E-1 April, 1995 F-1 May, 1996 F-2 July,
NO. ISSUED: REVISED: 71090 JUNE 7, 1994 AUG. 7, 2000 HOSHIZAKI STACKABLE CRESCENT CUBER MODEL KM-2000SWE3 KM-2000SRE3 (FINAL) PARTS LIST KM-2000SWE3 D-0 June, 1994 E-1 April, 1995 F-1 May, 1996 F-2 July,
FORMULA SHEET (tear off)
 FORMULA SHEET (tear off) N A = 6.022 x 10 23 C = ( 5 / 9 ) ( F - 32) F = ( 9 / 5 )( C) + 32 1 amu = 1.661 x 10-27 kg C = K - 273.15 K = C + 273.15 1 atm = 760 torr = 760 mm Hg 1 atm = 1.013 bar pv = nrt
FORMULA SHEET (tear off) N A = 6.022 x 10 23 C = ( 5 / 9 ) ( F - 32) F = ( 9 / 5 )( C) + 32 1 amu = 1.661 x 10-27 kg C = K - 273.15 K = C + 273.15 1 atm = 760 torr = 760 mm Hg 1 atm = 1.013 bar pv = nrt
Homework Problem Set 8 Solutions
 Chemistry 360 Dr. Jean M. Standard Homework roblem Set 8 Solutions. Starting from G = H S, derive the fundamental equation for G. o begin, we take the differential of G, dg = dh d( S) = dh ds Sd. Next,
Chemistry 360 Dr. Jean M. Standard Homework roblem Set 8 Solutions. Starting from G = H S, derive the fundamental equation for G. o begin, we take the differential of G, dg = dh d( S) = dh ds Sd. Next,
Problem Set 10 Solutions
 Chemistry 360 Dr Jean M Standard Problem Set 10 Solutions 1 Sketch (roughly to scale) a phase diagram for molecular oxygen given the following information: the triple point occurs at 543 K and 114 torr;
Chemistry 360 Dr Jean M Standard Problem Set 10 Solutions 1 Sketch (roughly to scale) a phase diagram for molecular oxygen given the following information: the triple point occurs at 543 K and 114 torr;
Empirical Co - Relations approach for solving problems of convection 10:06:43
 Empirical Co - Relations approach for solving problems of convection 10:06:43 10:06:44 Empirical Corelations for Free Convection Use T f or T b for getting various properties like Re = VL c / ν β = thermal
Empirical Co - Relations approach for solving problems of convection 10:06:43 10:06:44 Empirical Corelations for Free Convection Use T f or T b for getting various properties like Re = VL c / ν β = thermal
Heating and Cooling Curves
 Heating and Cooling Curves $ Under normal circumstances, particles will undergo more than one type of change when heated or cooled $ During a phase change, the temperature will not change $ Parts of the
Heating and Cooling Curves $ Under normal circumstances, particles will undergo more than one type of change when heated or cooled $ During a phase change, the temperature will not change $ Parts of the
Chapter 3 PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES
 Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach Seventh Edition Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2011 Chapter 3 PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach Seventh Edition Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2011 Chapter 3 PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission
Chapter 3 PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES. Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 6 th Edition Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2008
 Chapter 3 PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 6 th Edition Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2008 Objectives Introduce the concept of a pure substance. Discuss
Chapter 3 PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 6 th Edition Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2008 Objectives Introduce the concept of a pure substance. Discuss
Dishwasher. Heater. Homework Solutions ME Thermodynamics I Spring HW-1 (25 points)
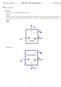 HW-1 (25 points) (a) Given: 1 for writing given, find, EFD, etc., Schematic of a household piping system Find: Identify system and location on the system boundary where the system interacts with the environment
HW-1 (25 points) (a) Given: 1 for writing given, find, EFD, etc., Schematic of a household piping system Find: Identify system and location on the system boundary where the system interacts with the environment
8.21 The Physics of Energy Fall 2009
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 8.21 The Physics of Energy Fall 2009 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 8.21 Lecture 10 Phase Change
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 8.21 The Physics of Energy Fall 2009 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 8.21 Lecture 10 Phase Change
CHAPTER 7 ENTROPY. Copyright Hany A. Al-Ansary and S. I. Abdel-Khalik (2014) 1
 CHAPTER 7 ENTROPY S. I. Abdel-Khalik (2014) 1 ENTROPY The Clausius Inequality The Clausius inequality states that for for all cycles, reversible or irreversible, engines or refrigerators: For internally-reversible
CHAPTER 7 ENTROPY S. I. Abdel-Khalik (2014) 1 ENTROPY The Clausius Inequality The Clausius inequality states that for for all cycles, reversible or irreversible, engines or refrigerators: For internally-reversible
S.E. (Chemical) (Second Semester) EXAMINATION, 2011 HEAT TRANSFER (2008 PATTERN) Time : Three Hours Maximum Marks : 100
 Total No. of Questions 12] [Total No. of Printed Pages 7 [4062]-186 S.E. (Chemical) (Second Semester) EXAMINATION, 2011 HEAT TRANSFER (2008 PATTERN) Time : Three Hours Maximum Marks : 100 N.B. : (i) Answers
Total No. of Questions 12] [Total No. of Printed Pages 7 [4062]-186 S.E. (Chemical) (Second Semester) EXAMINATION, 2011 HEAT TRANSFER (2008 PATTERN) Time : Three Hours Maximum Marks : 100 N.B. : (i) Answers
MAE 110A. Homework 3: Solutions 10/20/2017
 MAE 110A Homework 3: Solutions 10/20/2017 3.10: For H 2O, determine the specified property at the indicated state. Locate the state on a sketch of the T-v diagram. Given a) T 140 C, v 0.5 m 3 kg b) p 30MPa,
MAE 110A Homework 3: Solutions 10/20/2017 3.10: For H 2O, determine the specified property at the indicated state. Locate the state on a sketch of the T-v diagram. Given a) T 140 C, v 0.5 m 3 kg b) p 30MPa,
Review for Exam #1. Review of Mathematics. Weighted Mean
 Review for Exam #1 Review of Mathematics Weighted Mean A certain property of material 1 is P 1 and that of material is P If x 1 amount (weight or volume) of material 1 is mixed with x amount of material,
Review for Exam #1 Review of Mathematics Weighted Mean A certain property of material 1 is P 1 and that of material is P If x 1 amount (weight or volume) of material 1 is mixed with x amount of material,
Review of Mathematics
 Review for Exam #1 Review of Mathematics 2 Weighted Mean A certain property of material 1 is P 1 and that of material 2 is P 2 If x 1 amount (weight or volume) of material 1 is mixed with x 2 amount of
Review for Exam #1 Review of Mathematics 2 Weighted Mean A certain property of material 1 is P 1 and that of material 2 is P 2 If x 1 amount (weight or volume) of material 1 is mixed with x 2 amount of
Review of Mathematics
 Review for Exam #1 Review of Mathematics 2 Weighted Mean A certain property of material 1 is P 1 and that of material 2 is P 2 If x 1 amount (weight or volume) of material 1 is mixed with x 2 amount of
Review for Exam #1 Review of Mathematics 2 Weighted Mean A certain property of material 1 is P 1 and that of material 2 is P 2 If x 1 amount (weight or volume) of material 1 is mixed with x 2 amount of
Fluid Cooling Industrial PF Series
 Fluid Cooling Industrial PF Series 0916 STAINLESS STEEL PLATES CARBON STEEL FRAME Performance Notes Carry bar Gasketed plate style heat exchanger Tie rods Oil to water applications High performance Pressure
Fluid Cooling Industrial PF Series 0916 STAINLESS STEEL PLATES CARBON STEEL FRAME Performance Notes Carry bar Gasketed plate style heat exchanger Tie rods Oil to water applications High performance Pressure
Chapter 3 PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES SUMMARY
 Chapter 3 PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES SUMMARY PURE SUBSTANCE Pure substance: A substance that has a fixed chemical composition throughout. Compressed liquid (sub-cooled liquid): A substance that it is
Chapter 3 PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES SUMMARY PURE SUBSTANCE Pure substance: A substance that has a fixed chemical composition throughout. Compressed liquid (sub-cooled liquid): A substance that it is
O-Rings. Product Description: Part Numbers: O-Rings: Imperial Seals. Quad O-Rings: O-Ring
 Material: Temp. ange Nitrile -40 C to 120 C Low Temp. Nitrile -55 C to 120 C Highly Saturated Nitrile -40 C to 150 C Viton (Fluorocarbon) -25 C to 204 C PTFE -200 C to 250 C Aflas 0 C to 230 C Neoprene
Material: Temp. ange Nitrile -40 C to 120 C Low Temp. Nitrile -55 C to 120 C Highly Saturated Nitrile -40 C to 150 C Viton (Fluorocarbon) -25 C to 204 C PTFE -200 C to 250 C Aflas 0 C to 230 C Neoprene
Evaporation Velocity of Cryogenic Liquid With and Without Spreading
 PetroChemistry 2016 Evaporation Velocity of Cryogenic Liquid With and Without Spreading 2016. 12. 06 Myungbae Kim Korea Institute of Machinery & Materials Contents Introduction Evaporation Model Experimental
PetroChemistry 2016 Evaporation Velocity of Cryogenic Liquid With and Without Spreading 2016. 12. 06 Myungbae Kim Korea Institute of Machinery & Materials Contents Introduction Evaporation Model Experimental
ME 2322 Thermodynamics I PRE-LECTURE Lesson 10 Complete the items below Name:
 Lesson 10 1. (5 pt) If P > P sat (T), the phase is a subcooled liquid. 2. (5 pt) if P < P sat (T), the phase is superheated vapor. 3. (5 pt) if T > T sat (P), the phase is superheated vapor. 4. (5 pt)
Lesson 10 1. (5 pt) If P > P sat (T), the phase is a subcooled liquid. 2. (5 pt) if P < P sat (T), the phase is superheated vapor. 3. (5 pt) if T > T sat (P), the phase is superheated vapor. 4. (5 pt)
ME 201 Thermodynamics
 8 ME 0 Thermodynamics Practice Problems or Property Evaluation For each process described below provide the temperature, pressure, and speciic volume at each state and the change in enthalpy, internal
8 ME 0 Thermodynamics Practice Problems or Property Evaluation For each process described below provide the temperature, pressure, and speciic volume at each state and the change in enthalpy, internal
Chpt 19: Chemical. Thermodynamics. Thermodynamics
 CEM 152 1 Reaction Spontaneity Can we learn anything about the probability of a reaction occurring based on reaction enthaplies? in general, a large, negative reaction enthalpy is indicative of a spontaneous
CEM 152 1 Reaction Spontaneity Can we learn anything about the probability of a reaction occurring based on reaction enthaplies? in general, a large, negative reaction enthalpy is indicative of a spontaneous
 CHEMISTRY 110 EXAM 3 Nov. 11, 2013 ORM A!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!" 1. The cylinder shown below is filled with enough N 2 gas at 25 o C to reach a
CHEMISTRY 110 EXAM 3 Nov. 11, 2013 ORM A!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!" 1. The cylinder shown below is filled with enough N 2 gas at 25 o C to reach a
PROBLEM ρ v (kg/m 3 ) ANALYSIS: The critical heat flux can be estimated by Eq with C = 0.
 PROBLEM 10.10 KNOWN: Fluids at 1 atm: mercury, ethanol, R-14a. FIND: Critical heat flux; compare with value for water also at 1 atm. ASSUMPTIONS: (1) Steady-state conditions, () Nucleate pool boiling.
PROBLEM 10.10 KNOWN: Fluids at 1 atm: mercury, ethanol, R-14a. FIND: Critical heat flux; compare with value for water also at 1 atm. ASSUMPTIONS: (1) Steady-state conditions, () Nucleate pool boiling.
There are five problems on the exam. Do all of the problems. Show your work.
 CHM 3410 - Physical Chemistry 1 Second Hour Exam October 22, 2010 There are five problems on the exam. Do all of the problems. Show your work. R = 0.08206 L. atm/mole. K N A = 6.022 x 10 23 R = 0.08314
CHM 3410 - Physical Chemistry 1 Second Hour Exam October 22, 2010 There are five problems on the exam. Do all of the problems. Show your work. R = 0.08206 L. atm/mole. K N A = 6.022 x 10 23 R = 0.08314
Part 1 Principles of the Fluid Dynamic Design of Packed Columns for Gas/Liquid Systems
 Part 1 Principles of the Fluid Dynamic Design of Packed Columns for Gas/Liquid Systems List of Symbols for Part 1 Formula Variables, Latin Letters a m 2 m 3 geometric surface area of packing per unit volume
Part 1 Principles of the Fluid Dynamic Design of Packed Columns for Gas/Liquid Systems List of Symbols for Part 1 Formula Variables, Latin Letters a m 2 m 3 geometric surface area of packing per unit volume
THERMODYNAMICS, FLUID AND PLANT PROCESSES. The tutorials are drawn from other subjects so the solutions are identified by the appropriate tutorial.
 THERMODYNAMICS, FLUID AND PLANT PROCESSES The tutorials are drawn from other subjects so the solutions are identified by the appropriate tutorial. THERMODYNAMICS TUTORIAL 1 LIQUIDS VAPOURS - GASES SAE
THERMODYNAMICS, FLUID AND PLANT PROCESSES The tutorials are drawn from other subjects so the solutions are identified by the appropriate tutorial. THERMODYNAMICS TUTORIAL 1 LIQUIDS VAPOURS - GASES SAE
Chapter 13 - Polymers Introduction
 Chapter 13 - Polymers Introduction I. Nomenclature A. Polymer/Macromolecule polymer - nonmetallic material consisting of large molecules composed of many repeating units - from Greek: poly (many) and meros
Chapter 13 - Polymers Introduction I. Nomenclature A. Polymer/Macromolecule polymer - nonmetallic material consisting of large molecules composed of many repeating units - from Greek: poly (many) and meros
Pure Substances Phase Change, Property Tables and Diagrams
 Pure Substances Phase Change, Property Tables and Diagrams In this chapter we consider the property values and relationships of a pure substance (such as water) which can exist in three phases - solid,
Pure Substances Phase Change, Property Tables and Diagrams In this chapter we consider the property values and relationships of a pure substance (such as water) which can exist in three phases - solid,
Phase Chemistry. Phase Diagrams and IMF s. Copyright John Sayles 1
 Phase Chemistry Phase Diagrams and IMF s Copyright 2003 - John Sayles 1 C-C Eq n and Phase Diagrams Graph the T and P points that solve the C-C eq n A curve Each point represents a BP The curve is the
Phase Chemistry Phase Diagrams and IMF s Copyright 2003 - John Sayles 1 C-C Eq n and Phase Diagrams Graph the T and P points that solve the C-C eq n A curve Each point represents a BP The curve is the
Chapter Eighteen. Thermodynamics
 Chapter Eighteen Thermodynamics 1 Thermodynamics Study of energy changes during observed processes Purpose: To predict spontaneity of a process Spontaneity: Will process go without assistance? Depends
Chapter Eighteen Thermodynamics 1 Thermodynamics Study of energy changes during observed processes Purpose: To predict spontaneity of a process Spontaneity: Will process go without assistance? Depends
O-Ring Design Guide REGISTERED QMS. ISD
 O-Ring Design Guide ISO 9001 REGISTERED QMS ISD Table of Contents O-Ring Design Guide Hi-Tech Seals Inc. Compound Specifications 3 Machining Specifications 4 O-Ring -Section 4 O-Ring Gland Types 4 ID Stretch/OD
O-Ring Design Guide ISO 9001 REGISTERED QMS ISD Table of Contents O-Ring Design Guide Hi-Tech Seals Inc. Compound Specifications 3 Machining Specifications 4 O-Ring -Section 4 O-Ring Gland Types 4 ID Stretch/OD
This follows from the Clausius inequality as a consequence of the second law of thermodynamics. Therefore. (for reversible process only) (22.
 Entropy Clausius inequality can be used to analyze the cyclic process in a quantitative manner. The second law became a law of wider applicability when Clausius introduced the property called entropy.
Entropy Clausius inequality can be used to analyze the cyclic process in a quantitative manner. The second law became a law of wider applicability when Clausius introduced the property called entropy.
Find: a) Mass of the air, in kg, b) final temperature of the air, in K, and c) amount of entropy produced, in kj/k.
 PROBLEM 6.25 Three m 3 of air in a rigid, insulated container fitted with a paddle wheel is initially at 295 K, 200 kpa. The air receives 1546 kj of work from the paddle wheel. Assuming the ideal gas model,
PROBLEM 6.25 Three m 3 of air in a rigid, insulated container fitted with a paddle wheel is initially at 295 K, 200 kpa. The air receives 1546 kj of work from the paddle wheel. Assuming the ideal gas model,
TankExampleNov2016. Table of contents. Layout
 Table of contents Task... 2 Calculation of heat loss of storage tanks... 3 Properties ambient air Properties of air... 7 Heat transfer outside, roof Heat transfer in flow past a plane wall... 8 Properties
Table of contents Task... 2 Calculation of heat loss of storage tanks... 3 Properties ambient air Properties of air... 7 Heat transfer outside, roof Heat transfer in flow past a plane wall... 8 Properties
Chapter 12 Intermolecular Forces of Attraction
 Chapter 12 Intermolecular Forces of Attraction Intermolecular Forces Attractive or Repulsive Forces between molecules. Molecule - - - - - - Molecule Intramolecular Forces bonding forces within the molecule.
Chapter 12 Intermolecular Forces of Attraction Intermolecular Forces Attractive or Repulsive Forces between molecules. Molecule - - - - - - Molecule Intramolecular Forces bonding forces within the molecule.
Fluid Properties and Units
 Fluid Properties and Units CVEN 311 Continuum Continuum All materials, solid or fluid, are composed of molecules discretely spread and in continuous motion. However, in dealing with fluid-flow flow relations
Fluid Properties and Units CVEN 311 Continuum Continuum All materials, solid or fluid, are composed of molecules discretely spread and in continuous motion. However, in dealing with fluid-flow flow relations
PROBLEM h fg ρ v ρ l σ 10 3 T sat (kj/kg) (kg/m 3 ) (N/m) (K)
 PROBLEM 10.9 KNOWN: Fluids at 1 atm: mercury, ethanol, R-1. FIND: Critical heat flux; compare with value for water also at 1 atm. ASSUMPTIONS: (1) Steady-state conditions, () Nucleate pool boiling. PROPERTIES:
PROBLEM 10.9 KNOWN: Fluids at 1 atm: mercury, ethanol, R-1. FIND: Critical heat flux; compare with value for water also at 1 atm. ASSUMPTIONS: (1) Steady-state conditions, () Nucleate pool boiling. PROPERTIES:
SteamTablesIIE: An ActiveX to Calculate the Thermodynamic Properties of Water
 Proceedings World Geothermal Congress 2010 Bali, Indonesia, 25-29 April 2010 SteamTablesIIE: An ActiveX to Calculate the Thermodynamic Properties of Water Mahendra P. Verma Geotermia, Instituto de Investigaciones
Proceedings World Geothermal Congress 2010 Bali, Indonesia, 25-29 April 2010 SteamTablesIIE: An ActiveX to Calculate the Thermodynamic Properties of Water Mahendra P. Verma Geotermia, Instituto de Investigaciones
Sensible Heat and Enthalpy Calculations
 Sensible Heat and Enthalpy Calculations Sensible Heat - The amount of heat that must be added when a substance undergoes a change in temperature from 298 K to an elevated temperature without a change in
Sensible Heat and Enthalpy Calculations Sensible Heat - The amount of heat that must be added when a substance undergoes a change in temperature from 298 K to an elevated temperature without a change in
1.2 Z 014-A LUG TYPE BUTTERFLY VALVE Z 014-A TECHNICAL DATA
 ug type butterfly valve with threaded holes. This type enables the one-sided lugging of pipes. TECNICA DATA Nominal diameter: 00 ( only PN0/) Face-to-face: EN Series (DIN T ) ISO Series API 0 Table BS
ug type butterfly valve with threaded holes. This type enables the one-sided lugging of pipes. TECNICA DATA Nominal diameter: 00 ( only PN0/) Face-to-face: EN Series (DIN T ) ISO Series API 0 Table BS
Materials of Construction and Chemical Compatibility for Sensing and Control Products
 ADVANCED MATERIALS HANDLING TECHNICAL NOTE Materials of Construction and Compatibility for Sensing and Control Products INTRODUCTION Entegris Sensing and Control products are designed for use in highly
ADVANCED MATERIALS HANDLING TECHNICAL NOTE Materials of Construction and Compatibility for Sensing and Control Products INTRODUCTION Entegris Sensing and Control products are designed for use in highly
Physical Chemistry I Exam points
 Chemistry 360 Fall 2018 Dr. Jean M. tandard October 17, 2018 Name Physical Chemistry I Exam 2 100 points Note: You must show your work on problems in order to receive full credit for any answers. You must
Chemistry 360 Fall 2018 Dr. Jean M. tandard October 17, 2018 Name Physical Chemistry I Exam 2 100 points Note: You must show your work on problems in order to receive full credit for any answers. You must
1. Basic state values of matter
 1. Basic state values of matter Example 1.1 The pressure inside a boiler is p p = 115.10 5 Pa and p v = 9.44.10 4 Pa inside a condenser. Calculate the absolute pressure inside the boiler and condenser
1. Basic state values of matter Example 1.1 The pressure inside a boiler is p p = 115.10 5 Pa and p v = 9.44.10 4 Pa inside a condenser. Calculate the absolute pressure inside the boiler and condenser
Chemistry 2000 Lecture 12: Temperature dependence of the equilibrium constant
 Chemistry 2000 Lecture 12: Temperature dependence of the equilibrium constant Marc R. Roussel February 12, 2019 Marc R. Roussel Temperature dependence of equilibrium February 12, 2019 1 / 15 Temperature
Chemistry 2000 Lecture 12: Temperature dependence of the equilibrium constant Marc R. Roussel February 12, 2019 Marc R. Roussel Temperature dependence of equilibrium February 12, 2019 1 / 15 Temperature
Common Terms, Definitions and Conversion Factors
 1 Common Terms, Definitions and Conversion Factors 1. Force: A force is a push or pull upon an object resulting from the object s interaction with another object. It is defined as Where F = m a F = Force
1 Common Terms, Definitions and Conversion Factors 1. Force: A force is a push or pull upon an object resulting from the object s interaction with another object. It is defined as Where F = m a F = Force
HOSHIZAKI MODULAR CRESCENT CUBER MODEL KM-280MAE KM-280MWE (FINAL) PARTS LIST
 NO. ISSUED: REVISED: 71113 JAN. 12, 1996 APRIL 18, 2000 HOSHIZAKI MODULAR CRESCENT CUBER MODEL KM-280MAE KM-280MWE (FINAL) PARTS LIST KM-280MAE F-1 Feb., 1996 G-0 Dec., 1996 G-1 May, 1997 G-2 June, 1997
NO. ISSUED: REVISED: 71113 JAN. 12, 1996 APRIL 18, 2000 HOSHIZAKI MODULAR CRESCENT CUBER MODEL KM-280MAE KM-280MWE (FINAL) PARTS LIST KM-280MAE F-1 Feb., 1996 G-0 Dec., 1996 G-1 May, 1997 G-2 June, 1997
PROBLEM 6.3. Using the appropriate table, determine the indicated property. In each case, locate the state on sketches of the T-v and T-s diagrams.
 PROBLEM 63 Using the appropriate table, determine the indicated property In each case, locate the state on sketches of the -v and -s diagrams (a) water at p = 040 bar, h = 147714 kj/kg K Find s, in kj/kg
PROBLEM 63 Using the appropriate table, determine the indicated property In each case, locate the state on sketches of the -v and -s diagrams (a) water at p = 040 bar, h = 147714 kj/kg K Find s, in kj/kg
Section A 01. (12 M) (s 2 s 3 ) = 313 s 2 = s 1, h 3 = h 4 (s 1 s 3 ) = kj/kgk. = kj/kgk. 313 (s 3 s 4f ) = ln
 0. (a) Sol: Section A A refrigerator macine uses R- as te working fluid. Te temperature of R- in te evaporator coil is 5C, and te gas leaves te compressor as dry saturated at a temperature of 40C. Te mean
0. (a) Sol: Section A A refrigerator macine uses R- as te working fluid. Te temperature of R- in te evaporator coil is 5C, and te gas leaves te compressor as dry saturated at a temperature of 40C. Te mean
enhancements of immersion cooling of high power chips with nucleate boiling of dielectric liquids
 Advancements in Thermal Management Conference, Denver, CO, 3-4 August 216 enhancements of immersion cooling of high power chips with nucleate boiling of dielectric liquids Mohamed S. El-Genk Regents Professor,
Advancements in Thermal Management Conference, Denver, CO, 3-4 August 216 enhancements of immersion cooling of high power chips with nucleate boiling of dielectric liquids Mohamed S. El-Genk Regents Professor,
CHAPTER. Properties of Pure Substances
 CHAPTER 2 Properties of Pure Substances A Pure Substance Is a substance that is chemically homogenous and fixed in chemical composition.(e.g. water, nitrogen, air & etc.) mixture of oil and water is not
CHAPTER 2 Properties of Pure Substances A Pure Substance Is a substance that is chemically homogenous and fixed in chemical composition.(e.g. water, nitrogen, air & etc.) mixture of oil and water is not
PROBLEM 8.3 ( ) p = kg m 1m s m 1000 m = kg s m = bar < P = N m 0.25 m 4 1m s = 1418 N m s = 1.
 PROBLEM 8.3 KNOWN: Temperature and velocity of water flow in a pipe of prescribed dimensions. FIND: Pressure drop and pump power requirement for (a) a smooth pipe, (b) a cast iron pipe with a clean surface,
PROBLEM 8.3 KNOWN: Temperature and velocity of water flow in a pipe of prescribed dimensions. FIND: Pressure drop and pump power requirement for (a) a smooth pipe, (b) a cast iron pipe with a clean surface,
KNOWN: Data are provided for a closed system undergoing a process involving work, heat transfer, change in elevation, and change in velocity.
 Problem 44 A closed system of mass of 10 kg undergoes a process during which there is energy transfer by work from the system of 0147 kj per kg, an elevation decrease of 50 m, and an increase in velocity
Problem 44 A closed system of mass of 10 kg undergoes a process during which there is energy transfer by work from the system of 0147 kj per kg, an elevation decrease of 50 m, and an increase in velocity
Energy and Energy Balances
 Energy and Energy Balances help us account for the total energy required for a process to run Minimizing wasted energy is crucial in Energy, like mass, is. This is the Components of Total Energy energy
Energy and Energy Balances help us account for the total energy required for a process to run Minimizing wasted energy is crucial in Energy, like mass, is. This is the Components of Total Energy energy
Chapter 3 PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES
 Chapter 3 PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES PURE SUBSTANCE Pure substance: A substance that has a fixed chemical composition throughout. Air is a mixture of several gases, but it is considered to be a pure
Chapter 3 PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES PURE SUBSTANCE Pure substance: A substance that has a fixed chemical composition throughout. Air is a mixture of several gases, but it is considered to be a pure
MATERIALS SCIENCE POLYMERS
 POLYMERS 1) Types of Polymer (a) Plastic Possibly the largest number of different polymeric materials come under the plastic classification. Polyethylene, polypropylene, polyvinyl chloride, polystyrene,
POLYMERS 1) Types of Polymer (a) Plastic Possibly the largest number of different polymeric materials come under the plastic classification. Polyethylene, polypropylene, polyvinyl chloride, polystyrene,
In order to able to perform adequate basic maintenance the following tools are required:
 BASIC MAINTENANCE BASIC MAINTENANCE AND RECOMMENDED SPARE PART 2.14 SPECIAL TOOLS FOR BASIC MAINTENANCE In order to able to perform adequate basic maintenance the following tools are required: - special
BASIC MAINTENANCE BASIC MAINTENANCE AND RECOMMENDED SPARE PART 2.14 SPECIAL TOOLS FOR BASIC MAINTENANCE In order to able to perform adequate basic maintenance the following tools are required: - special
Physical transformations of pure substances Boiling, freezing, and the conversion of graphite to diamond examples of phase transitions changes of
 Physical transformations of pure substances Boiling, freezing, and the conversion of graphite to diamond examples of phase transitions changes of phase without change of chemical composition. In this chapter
Physical transformations of pure substances Boiling, freezing, and the conversion of graphite to diamond examples of phase transitions changes of phase without change of chemical composition. In this chapter
1.2 Z 014-A LUG TYPE BUTTERFLY VALVE Z 014-A TECHNICAL DATA:
 TECNICA DATA: ug type butterfly valve with threaded holes. This type enables the one-sided lugging of pipes. Nominal diameter: Face-to-face: EN Series (DIN T ) ISO Series API 0 Table BS Series NF E -0.
TECNICA DATA: ug type butterfly valve with threaded holes. This type enables the one-sided lugging of pipes. Nominal diameter: Face-to-face: EN Series (DIN T ) ISO Series API 0 Table BS Series NF E -0.
KM-1300SAF KM-1300SWF KM-1300SRF KM-1300SAF3 KM-1300SWF3 KM-1300SRF3
 NO: 71130 ISSUED: OCT. 8, 1998 REVISED: JUNE 14, 2005 HOSHIZAKI STACKABLE CRESCENT CUBER MODEL KM-1300SAF KM-1300SWF KM-1300SRF KM-1300SAF3 KM-1300SWF3 KM-1300SRF3 (FINAL) S LIST 56 KM-1300SAF H-0 JAN.
NO: 71130 ISSUED: OCT. 8, 1998 REVISED: JUNE 14, 2005 HOSHIZAKI STACKABLE CRESCENT CUBER MODEL KM-1300SAF KM-1300SWF KM-1300SRF KM-1300SAF3 KM-1300SWF3 KM-1300SRF3 (FINAL) S LIST 56 KM-1300SAF H-0 JAN.
Refrigeration. 05/04/2011 T.Al-Shemmeri 1
 Refrigeration is a process of controlled removal of heat from a substance to keep it at a temperature below the ambient condition, often below the freezing point of water (0 O C) 05/04/0 T.Al-Shemmeri
Refrigeration is a process of controlled removal of heat from a substance to keep it at a temperature below the ambient condition, often below the freezing point of water (0 O C) 05/04/0 T.Al-Shemmeri
Nickel-Plated Brass Push-In Fittings - NPTF/INCH
 /INCH Tube Connections: External /8, 5/32, /4, 5/6, 3/8, /2 Thread Connections 0-32 UNF, /8, /4, 3/8, /2 Reusable thread seal, PTFE seal ring (Teflon ) - Pro-Fit Standard - Camozzi s all metal fittings
/INCH Tube Connections: External /8, 5/32, /4, 5/6, 3/8, /2 Thread Connections 0-32 UNF, /8, /4, 3/8, /2 Reusable thread seal, PTFE seal ring (Teflon ) - Pro-Fit Standard - Camozzi s all metal fittings
FORMULA SHEET (tear off)
 FORMULA SHEET (tear off) N A = 6.022 x 10 23 C = ( 5 / 9 ) ( F - 32) F = ( 9 / 5 )( C) + 32 1 amu = 1.661 x 10-27 kg C = K - 273.15 K = C + 273.15 1 atm = 760 torr = 760 mm Hg 1 atm = 1.013 bar pv = nrt
FORMULA SHEET (tear off) N A = 6.022 x 10 23 C = ( 5 / 9 ) ( F - 32) F = ( 9 / 5 )( C) + 32 1 amu = 1.661 x 10-27 kg C = K - 273.15 K = C + 273.15 1 atm = 760 torr = 760 mm Hg 1 atm = 1.013 bar pv = nrt
UNIVERSITY OF VICTORIA CHEMISTRY 102 Midterm Test 2 March 13, pm (60 minutes) DISPLAY YOUR STUDENT ID CARD (ONECard) ON TOP OF YOUR DESK NOW
 Version A UNIVERSITY OF VICTORIA CHEMISTRY 102 Midterm Test 2 March 13, 2015 5-6 pm (60 minutes) Version A DISPLAY YOUR STUDENT ID CARD (ONECard) ON TOP OF YOUR DESK NOW Answer all multiple choice questions
Version A UNIVERSITY OF VICTORIA CHEMISTRY 102 Midterm Test 2 March 13, 2015 5-6 pm (60 minutes) Version A DISPLAY YOUR STUDENT ID CARD (ONECard) ON TOP OF YOUR DESK NOW Answer all multiple choice questions
EVALUATING PROPERTIES FOR A PURE SUBSTANCES. By Ertanto Vetra
 EVALUATING PROPERTIES FOR A PURE SUBSTANCES 1 By Ertanto Vetra Outlines - TV, PV, PT, PVT Diagram - Property Tables - Introduction to Enthalpy - Reference State & Reference Values - Ideal Gas Equation
EVALUATING PROPERTIES FOR A PURE SUBSTANCES 1 By Ertanto Vetra Outlines - TV, PV, PT, PVT Diagram - Property Tables - Introduction to Enthalpy - Reference State & Reference Values - Ideal Gas Equation
Sensible Heat and Enthalpy Calculations
 * Sensible Heat and Enthalpy Calculations Sensible Heat - The amount of heat that must be added when a substance undergoes a change in temperature from 298 K to an elevated temperature without a change
* Sensible Heat and Enthalpy Calculations Sensible Heat - The amount of heat that must be added when a substance undergoes a change in temperature from 298 K to an elevated temperature without a change
Non-Newtonian fluids is the fluids in which shear stress is not directly proportional to deformation rate, such as toothpaste,
 CHAPTER1: Basic Definitions, Zeroth, First, and Second Laws of Thermodynamics 1.1. Definitions What does thermodynamic mean? It is a Greeks word which means a motion of the heat. Water is a liquid substance
CHAPTER1: Basic Definitions, Zeroth, First, and Second Laws of Thermodynamics 1.1. Definitions What does thermodynamic mean? It is a Greeks word which means a motion of the heat. Water is a liquid substance
UNIVERSITY OF VICTORIA CHEMISTRY 102 Midterm Test 2 March 13, pm (60 minutes) DISPLAY YOUR STUDENT ID CARD (ONECard) ON TOP OF YOUR DESK NOW
 Version B UNIVERSITY OF VICTORIA CHEMISTRY 102 Midterm Test 2 March 13, 2015 5-6 pm (60 minutes) Version B DISPLAY YOUR STUDENT ID CARD (ONECard) ON TOP OF YOUR DESK NOW Answer all multiple choice questions
Version B UNIVERSITY OF VICTORIA CHEMISTRY 102 Midterm Test 2 March 13, 2015 5-6 pm (60 minutes) Version B DISPLAY YOUR STUDENT ID CARD (ONECard) ON TOP OF YOUR DESK NOW Answer all multiple choice questions
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE
 MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI-621213. Department: Mechanical Subject Code: ME2202 U N IT - 1 Semester: III Subject Name: ENGG. THERMODYNAMICS 1. 1 kg of gas at 1.1 bar, 27 o C is compressed
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI-621213. Department: Mechanical Subject Code: ME2202 U N IT - 1 Semester: III Subject Name: ENGG. THERMODYNAMICS 1. 1 kg of gas at 1.1 bar, 27 o C is compressed
