Note on the application of complex integration to the equation of Conduction of Heat, with special reference to Dr Peddie's problem.
|
|
|
- Liliana Walker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 50 Note on the application of complex integration to the equation of Conduction of Heat, with special reference to Dr Peddie's problem. By OHN DOUGALL, M.A. 1. In Dr Peddie's problem of a sphere cooling in a well-stirred liquid, the conditions to be satisfied by the temperature v(r, t) are (i) For every positive t, and every r from 0 to a, v is to be finite and one-valued, and is to possess finite derivatives dv dv drr.,. -j- > j-, -jr. i satisfying dv idrv 2 < d,, dtdv ' dr* x (ii) For every positive t, and r = a, dv pa dv where p = I (capacity of liquid)/(capacity of sphere). (iii) Limit v(r, t) = a. given arbitrary function f(r), for every r less than o. (iv) Limit v(a, t) = initial temperature of liquid = 0 suppose. The classical method of Fourier, which Dr Peddie applies to the problem, is simple and beautiful so far as it goes, but it is open to the very serious objection that it leaves unverified the fundamental condition (iii). A complete, though necessarily more tedious treatment, can be given by means of Cauchy's Theory of Residues, which I applied to some Potential problems in a paper published in last year's Proceedings. I have to thank Dr Peddie for kindly permitting me to illustrate this method by a discussion of his very pretty problem.
2 51 2. In order to avoid a certain difficulty arising out of condition (iv), I suppose to begin with that/(r) is zero from r = b to r = a, where b<a ; this restriction is afterwards removed. Then a function satisfying (i; and (iii) is V = ]_ f P/(p)\e 2r \litkt o L This is, in fact, the known expression for the temperature at time t in an infinite solid, when the initial temperature is f(r) from 0 to b, and zero for all values of r greater than b. We may write t being positive, or 2 f* f» _ 2/ V = p/(p)dp e sinar sinap da, nrj o o l"v»> where 2 Too _ 2, U = e Ka sinar sinap da. vro If now we can find a function U, satisfying (i), such that Limit U 1 = 0 for every r from 0 to a inclusive, and every p from 0 (=0 to 6 inclusive; and such that U + Uj satisfies the surface condition rb (ii); then v = p(p)(u + Tdp is obviously the solution of our o problem. 3. In order to obtain V 1 it is necessary to express U as a complex integral. We have U - f + -X- e " KaH sinap e ior da -»> wr = the complex integral -e-kah sinap e iar da, VKT the path being the whole of the real axis from West to East. This path we now displace into the upper half of the a plane. The precise position of the new path need not be specified, the only
3 52 essential being that the ultimate directions of its ends must not make greater angles than r/4 With the real axis, since e~ Kat is infinite if the phase of a lie between rr/4 and 3n-/4. For the sake of definiteness, however, we shall suppose the displaced path to be symmetrical about the axis of imaginaries, and to be ultimately inclined to the axis of reals at an angle ir/8; this path we shall call the path toe. Hence U = - e ~ Kat nrrj sinao e' ar da, path we; oi'u= uda, path we ; where u = - e~ Ka ~ sinu<ie' ar %-rrr Take u 1 = - e " Ka sinap sinar, which satisfies (i), choosing the %TTT constant A, so that u + <t, satisfies (ii)..., (parar - iaa + 1 )e aa 11ns gives A = - ih TT-- ', (pa-a~ +1) sinaa - aa cosaa 1 - KO?I (pa"ar + l)sina(a - r) - aa cosa(a - r) and» + it, = - ee Ka l s m sa p m y i ^a^ ' p ^ i ^ - ;. iirr (pa-a* + 1) sinaa - aa cosaa Then i«,'ia, path we, is the function U, we require. For (u + u t )da satisfies the surface condition ; also Limit u y da '"0 is zero for all values of p and r in question. To prove the latter statement, we have f If KO,v.. (pav-icuh-l)e iaa u.da -. e sinup sinar- ^, : ' da, IT;r (pa-a-+ l)smaa - aacoma path we, and the integral at both ends of the path converges uniformly with respect to t right up to t = 0, provided p + r < 2a. Hence Limit «,c?a may be found by putting I = 0 in the integrand. (»0 But this gives a zero integral, there being no singularities of the new integrand in the part of the «plane above the path we.
4 Hence 53 U + U, fe ' H sinap s i {P n a +1)sina{a p { P 7 7 V) " ^ ^ ^ ~ r) da, vrrr (parar (par + l)sinaa l)sinaa - aa aa cosaa cosaa path we. If w^i be the image of the path we in the real axis, this integral is the same, element for element, as the integral over the path e- l w i (from right to left), for the integrand is an odd function of a. Thus U + U, = I ("(path e,»e,) + ("(path ive). These two patlis are equivalent to.1 complete circuit, in the negative direction, embracing the real axis. The singularities within this circuit are the zeros of the function {pa?d* + l)sino.a - aa cosaa, which, as will be shown immediately, are all real and simple, viz., a = 0, a = + a u etc. Hence, replacing the integral by - (2ri) (sum of residues at poles within circuit), we obtain T7 + T, xa-i. sina;' (pira 1 ~ CT : C Sin«/>.. - ;, (P+ } s) n ' > d /..,.,. }! (/«-«-+l)sinua - ua cosaa!- Gt ft v. the summation extending over the positive roots of the equation (pa?ar + 1) sinaa - ao cosno = (E) The solution of the original problem is p/(p)(u + \ l )dp, but o the series for U + U, manifestly converges uniformly with respect to p, provided t is greater than zero. Hence the integration can be performed term by term, and we have 2 V - Ka? t sinar p-a*a* + (2p + l)a'-a" + 1 [...., H ^e.. ~,:., pf(p) sinan ilp. a r p 2 a 4 o 4 + (3p + l)av- o where we have simplified the general term by means of the equation (E).
5 54 4. The roots of (E) are all real and simple. (1) Suppose, if possible, that ft. = m + in is a root, then v = m - in is also a root. and 1? = e r are solutions of the equation of conduction, and by Green's Theorem. / dv du\ 1 f a / dv du\ t., Airarl it v r-1 = I u v-z- 14-rr'rdr \ dr dr/ r=a K O\ dt dt! dv du\ ("«/ dv du or (/x 2 - v 2 ) {paxvy)^ + fvuvdr} = 0. e This is obviously impossible if /A 2, V 2 are different, since p is positive, and IT, V are conjugate complexes, so that UV is positive. %v (2) Suppose, if possible, that a = is a pure imaginary root. Cb Then (pr - 1) sinhv + v coshv = 0. The derivative with respect to v of the function on the left is pv- coshv + (2p +l)vsinhv, which is constantly positive if v is real and positive. Hence the function, starting from zero for v = 0, can never again become zero. (3) If a = is a repeated root, then, as we have shown, v is real. We must have, simultaneously, (pv* + l)sinv = vcosv (2p +l)sinv= -pvcosv Therefore (pv> + l)(2p + l)sin 2 i/ +pi^cos-v = 0, which cannot be if p is positive, unless v = 0, which is obviously excluded. A more searching investigation will show that the roots are all real as long as p > --, but that if p < - I;, there are two pure imaginary roots.
6 55 5. If b be put equal to a in the investigation of 3, it will be seen that one point requires examination. It was proved that Limit u^da 0, if p + r < 2a. If p and r each be equal to a, this (-0 condition is violated, and the limit is in fact infinite. Limit uda (=0 is infinite at the same time, but it is easy to prove that Limit («i + u)da is finite, and the investigation stands. however, verify in another way that the function We shall, 2 /fa= / sinar/av + (2p+l)oa-(-l f,.,., p/(p)smapdp a r p-a'a" + (6p + 1 )a*a' o satisfies the condition Limit via, t) = 0. For if t> 0, v obviously satisfies (i) and (ii). Integrating (ii) over the surface, we have *dv &ira 3 p tdv\ ~dr + K \dl) o ~ ' r> by Green's Theorem and (i), iw. -=-dr + v a = 0, n K at K dt so that I r-vdr + pa?v a I = 0 ra and r*vdr+ pa?v a is constant for all positive values of /. o n Hence the limits of r*vdr+pa 3 v a for t = 0 and for t = a> are the o same. The limit for t = «is The limit for t = 0 is = r j; p2 f(p)dp +pa s Limit v a. o «=o Hence Limit v a = 0. '=0
7 56 Another point may be noted in connection with condition (iv), as it explains the form of Dr Peddie's eliminating factor. If the initial temperature is sinar sinaa, a being a root of (E), then the temperature at time t is _ KaSf sinar sinnfc for this satisfies all the conditions (i) to (iv). Comparing this with the general solution, we see that the coefficients of all the terras must vanish, except that corresponding to the root a. Hence (sinao sinual &mfipdp = Q, o* «/ if /8 is a different root from a. Pi. If the solution given in i; o is to be verified a posteriori, the only condition causing any trouble is that of (iii). Writing the series for r(r, 1) in ;"> in the contracted form we have to prove that as I continuously approaches zero, the series continuously approaches f(r), or more shortly that Limit 1'e ~ *"»\ n {r) =/(r) (A). t 0 It is well enough known, but it seems desirable to recall, that this is not quite the same thing as to prove S».M=/(r) (B) although it is the latter theorem which is usually attacked by writers on the subject, from Fourier onwards. We may, it is true, deduce (A) from (B), with the help of a theorem analogous to the celebrated theorem of Abel's on the continuity of a power series, but even then we lose something: in fact not only is (B) more difficult to prove than (A), but it cannot, so far as I know, be proved at all for functions with an unlimited number of turning points, though, so far as (A) is concerned, these present no difficulty whatever.
(z + n) 2. n=0. 2 (z + 2) (z + n). 2 We d like to compute this as an integral. To this end, we d like a function with residues
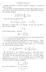 8. Stirling Formula Stirling s Formula is a classical formula to compute n! accurately when n is large. We will derive a version of Stirling s formula using complex analysis and residues. Recall the formula
8. Stirling Formula Stirling s Formula is a classical formula to compute n! accurately when n is large. We will derive a version of Stirling s formula using complex analysis and residues. Recall the formula
e iωt dt and explained why δ(ω) = 0 for ω 0 but δ(0) =. A crucial property of the delta function, however, is that
 Phys 531 Fourier Transforms In this handout, I will go through the derivations of some of the results I gave in class (Lecture 14, 1/11). I won t reintroduce the concepts though, so you ll want to refer
Phys 531 Fourier Transforms In this handout, I will go through the derivations of some of the results I gave in class (Lecture 14, 1/11). I won t reintroduce the concepts though, so you ll want to refer
f (t) K(t, u) d t. f (t) K 1 (t, u) d u. Integral Transform Inverse Fourier Transform
 Integral Transforms Massoud Malek An integral transform maps an equation from its original domain into another domain, where it might be manipulated and solved much more easily than in the original domain.
Integral Transforms Massoud Malek An integral transform maps an equation from its original domain into another domain, where it might be manipulated and solved much more easily than in the original domain.
Section 14.1 Vector Functions and Space Curves
 Section 14.1 Vector Functions and Space Curves Functions whose range does not consists of numbers A bulk of elementary mathematics involves the study of functions - rules that assign to a given input a
Section 14.1 Vector Functions and Space Curves Functions whose range does not consists of numbers A bulk of elementary mathematics involves the study of functions - rules that assign to a given input a
Higher Order Linear Equations
 C H A P T E R 4 Higher Order Linear Equations 4.1 1. The differential equation is in standard form. Its coefficients, as well as the function g(t) = t, are continuous everywhere. Hence solutions are valid
C H A P T E R 4 Higher Order Linear Equations 4.1 1. The differential equation is in standard form. Its coefficients, as well as the function g(t) = t, are continuous everywhere. Hence solutions are valid
Part IB. Further Analysis. Year
 Year 2004 2003 2002 2001 10 2004 2/I/4E Let τ be the topology on N consisting of the empty set and all sets X N such that N \ X is finite. Let σ be the usual topology on R, and let ρ be the topology on
Year 2004 2003 2002 2001 10 2004 2/I/4E Let τ be the topology on N consisting of the empty set and all sets X N such that N \ X is finite. Let σ be the usual topology on R, and let ρ be the topology on
Department of Mathematics
 INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, BOMBAY Department of Mathematics MA 04 - Complex Analysis & PDE s Solutions to Tutorial No.13 Q. 1 (T) Assuming that term-wise differentiation is permissible, show that
INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, BOMBAY Department of Mathematics MA 04 - Complex Analysis & PDE s Solutions to Tutorial No.13 Q. 1 (T) Assuming that term-wise differentiation is permissible, show that
MATH 185: COMPLEX ANALYSIS FALL 2009/10 PROBLEM SET 10 SOLUTIONS. f(z) = a n. h(z) := a n+m (z a) n. f(z) = h(z) + (z a) m n. =: e h(z) F (z).
 MATH 85: COMPLEX ANALYSIS FALL 29/ PROBLEM SET SOLUTIONS. (a) Show that if f has a pole or an essential singularity at a, then e f has an essential singularity at a. Solution. If f has a pole of order
MATH 85: COMPLEX ANALYSIS FALL 29/ PROBLEM SET SOLUTIONS. (a) Show that if f has a pole or an essential singularity at a, then e f has an essential singularity at a. Solution. If f has a pole of order
The RC Circuit: An Approach with Fourier Transforms
 The RC Circuit: An Approach with Fourier Transforms In this article we shall mathematically analyse the Resistor- Capacitor RC) circuit with the help of Fourier transforms FT). This very general technique
The RC Circuit: An Approach with Fourier Transforms In this article we shall mathematically analyse the Resistor- Capacitor RC) circuit with the help of Fourier transforms FT). This very general technique
Boundary value problems for partial differential equations
 Boundary value problems for partial differential equations Henrik Schlichtkrull March 11, 213 1 Boundary value problem 2 1 Introduction This note contains a brief introduction to linear partial differential
Boundary value problems for partial differential equations Henrik Schlichtkrull March 11, 213 1 Boundary value problem 2 1 Introduction This note contains a brief introduction to linear partial differential
Notes on uniform convergence
 Notes on uniform convergence Erik Wahlén erik.wahlen@math.lu.se January 17, 2012 1 Numerical sequences We begin by recalling some properties of numerical sequences. By a numerical sequence we simply mean
Notes on uniform convergence Erik Wahlén erik.wahlen@math.lu.se January 17, 2012 1 Numerical sequences We begin by recalling some properties of numerical sequences. By a numerical sequence we simply mean
1 Res z k+1 (z c), 0 =
 32. COMPLEX ANALYSIS FOR APPLICATIONS Mock Final examination. (Monday June 7..am 2.pm) You may consult your handwritten notes, the book by Gamelin, and the solutions and handouts provided during the Quarter.
32. COMPLEX ANALYSIS FOR APPLICATIONS Mock Final examination. (Monday June 7..am 2.pm) You may consult your handwritten notes, the book by Gamelin, and the solutions and handouts provided during the Quarter.
a 11 x 1 + a 12 x a 1n x n = b 1 a 21 x 1 + a 22 x a 2n x n = b 2.
 Chapter 1 LINEAR EQUATIONS 11 Introduction to linear equations A linear equation in n unknowns x 1, x,, x n is an equation of the form a 1 x 1 + a x + + a n x n = b, where a 1, a,, a n, b are given real
Chapter 1 LINEAR EQUATIONS 11 Introduction to linear equations A linear equation in n unknowns x 1, x,, x n is an equation of the form a 1 x 1 + a x + + a n x n = b, where a 1, a,, a n, b are given real
Th n nt T p n n th V ll f x Th r h l l r r h nd xpl r t n rr d nt ff t b Pr f r ll N v n d r n th r 8 l t p t, n z n l n n th n rth t rn p rt n f th v
 Th n nt T p n n th V ll f x Th r h l l r r h nd xpl r t n rr d nt ff t b Pr f r ll N v n d r n th r 8 l t p t, n z n l n n th n rth t rn p rt n f th v ll f x, h v nd d pr v n t fr tf l t th f nt r n r
Th n nt T p n n th V ll f x Th r h l l r r h nd xpl r t n rr d nt ff t b Pr f r ll N v n d r n th r 8 l t p t, n z n l n n th n rth t rn p rt n f th v ll f x, h v nd d pr v n t fr tf l t th f nt r n r
e iωt dt and explained why δ(ω) = 0 for ω 0 but δ(0) =. A crucial property of the delta function, however, is that
 Phys 53 Fourier Transforms In this handout, I will go through the derivations of some of the results I gave in class (Lecture 4, /). I won t reintroduce the concepts though, so if you haven t seen the
Phys 53 Fourier Transforms In this handout, I will go through the derivations of some of the results I gave in class (Lecture 4, /). I won t reintroduce the concepts though, so if you haven t seen the
Complex Analysis for Applications, Math 132/1, Home Work Solutions-II Masamichi Takesaki
 Page 48, Problem. Complex Analysis for Applications, Math 3/, Home Work Solutions-II Masamichi Takesaki Γ Γ Γ 0 Page 9, Problem. If two contours Γ 0 and Γ are respectively shrunkable to single points in
Page 48, Problem. Complex Analysis for Applications, Math 3/, Home Work Solutions-II Masamichi Takesaki Γ Γ Γ 0 Page 9, Problem. If two contours Γ 0 and Γ are respectively shrunkable to single points in
2 Write down the range of values of α (real) or β (complex) for which the following integrals converge. (i) e z2 dz where {γ : z = se iα, < s < }
 Mathematical Tripos Part II Michaelmas term 2007 Further Complex Methods, Examples sheet Dr S.T.C. Siklos Comments and corrections: e-mail to stcs@cam. Sheet with commentary available for supervisors.
Mathematical Tripos Part II Michaelmas term 2007 Further Complex Methods, Examples sheet Dr S.T.C. Siklos Comments and corrections: e-mail to stcs@cam. Sheet with commentary available for supervisors.
ELEMENTARY LINEAR ALGEBRA
 ELEMENTARY LINEAR ALGEBRA K R MATTHEWS DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS UNIVERSITY OF QUEENSLAND First Printing, 99 Chapter LINEAR EQUATIONS Introduction to linear equations A linear equation in n unknowns x,
ELEMENTARY LINEAR ALGEBRA K R MATTHEWS DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS UNIVERSITY OF QUEENSLAND First Printing, 99 Chapter LINEAR EQUATIONS Introduction to linear equations A linear equation in n unknowns x,
Math 20C Homework 2 Partial Solutions
 Math 2C Homework 2 Partial Solutions Problem 1 (12.4.14). Calculate (j k) (j + k). Solution. The basic properties of the cross product are found in Theorem 2 of Section 12.4. From these properties, we
Math 2C Homework 2 Partial Solutions Problem 1 (12.4.14). Calculate (j k) (j + k). Solution. The basic properties of the cross product are found in Theorem 2 of Section 12.4. From these properties, we
A NEW METHOD OF INVERSION OF THE LAPLACE TRANSFORM* ATHANASIOS PAPOULIS. Polytechnic Institute of Brooklyn
 405 A NEW METHOD OF INVERSION OF THE LAPLACE TRANSFORM* BY ATHANASIOS PAPOULIS Polytechnic Institute of Brooklyn Introduction. In determining a function r(t) from its Laplace transform R(p) R(p) = [ e"'r(t)
405 A NEW METHOD OF INVERSION OF THE LAPLACE TRANSFORM* BY ATHANASIOS PAPOULIS Polytechnic Institute of Brooklyn Introduction. In determining a function r(t) from its Laplace transform R(p) R(p) = [ e"'r(t)
A tricky node-voltage situation
 A tricky node-voltage situation The node-method will always work you can always generate enough equations to determine all of the node voltages. The method we have outlined well in almost all cases, but
A tricky node-voltage situation The node-method will always work you can always generate enough equations to determine all of the node voltages. The method we have outlined well in almost all cases, but
ζ (s) = s 1 s {u} [u] ζ (s) = s 0 u 1+sdu, {u} Note how the integral runs from 0 and not 1.
![ζ (s) = s 1 s {u} [u] ζ (s) = s 0 u 1+sdu, {u} Note how the integral runs from 0 and not 1. ζ (s) = s 1 s {u} [u] ζ (s) = s 0 u 1+sdu, {u} Note how the integral runs from 0 and not 1.](/thumbs/94/118787137.jpg) Problem Sheet 3. From Theorem 3. we have ζ (s) = + s s {u} u+sdu, (45) valid for Res > 0. i) Deduce that for Res >. [u] ζ (s) = s u +sdu ote the integral contains [u] in place of {u}. ii) Deduce that for
Problem Sheet 3. From Theorem 3. we have ζ (s) = + s s {u} u+sdu, (45) valid for Res > 0. i) Deduce that for Res >. [u] ζ (s) = s u +sdu ote the integral contains [u] in place of {u}. ii) Deduce that for
Solutions to Homework 1, Introduction to Differential Equations, 3450: , Dr. Montero, Spring y(x) = ce 2x + e x
 Solutions to Homewor 1, Introduction to Differential Equations, 3450:335-003, Dr. Montero, Spring 2009 problem 2. The problem says that the function yx = ce 2x + e x solves the ODE y + 2y = e x, and ass
Solutions to Homewor 1, Introduction to Differential Equations, 3450:335-003, Dr. Montero, Spring 2009 problem 2. The problem says that the function yx = ce 2x + e x solves the ODE y + 2y = e x, and ass
(Refer Slide Time: 01:30)
 Networks and Systems Prof V.G K.Murti Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 11 Fourier Series (5) Continuing our discussion of Fourier series today, we will
Networks and Systems Prof V.G K.Murti Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 11 Fourier Series (5) Continuing our discussion of Fourier series today, we will
An Introduction to Partial Differential Equations in the Undergraduate Curriculum
 An Introduction to Partial Differential Equations in the Undergraduate Curriculum John C. Polking LECTURE 12 Heat Transfer in the Ball 12.1. Outline of Lecture The problem The problem for radial temperatures
An Introduction to Partial Differential Equations in the Undergraduate Curriculum John C. Polking LECTURE 12 Heat Transfer in the Ball 12.1. Outline of Lecture The problem The problem for radial temperatures
MAT389 Fall 2016, Problem Set 11
 MAT389 Fall 216, Problem Set 11 Improper integrals 11.1 In each of the following cases, establish the convergence of the given integral and calculate its value. i) x 2 x 2 + 1) 2 ii) x x 2 + 1)x 2 + 2x
MAT389 Fall 216, Problem Set 11 Improper integrals 11.1 In each of the following cases, establish the convergence of the given integral and calculate its value. i) x 2 x 2 + 1) 2 ii) x x 2 + 1)x 2 + 2x
,. *â â > V>V. â ND * 828.
 BL D,. *â â > V>V Z V L. XX. J N R â J N, 828. LL BL D, D NB R H â ND T. D LL, TR ND, L ND N. * 828. n r t d n 20 2 2 0 : 0 T http: hdl.h ndl.n t 202 dp. 0 02802 68 Th N : l nd r.. N > R, L X. Fn r f,
BL D,. *â â > V>V Z V L. XX. J N R â J N, 828. LL BL D, D NB R H â ND T. D LL, TR ND, L ND N. * 828. n r t d n 20 2 2 0 : 0 T http: hdl.h ndl.n t 202 dp. 0 02802 68 Th N : l nd r.. N > R, L X. Fn r f,
Polynomial expansions in the Borel region
 Polynomial expansions in the Borel region By J. T. HURT and L. R. FORD, Rice Institute, Houston, Texas. (Received 22nd August, 1936. Read 6th November, 1936.) This paper deals with certain expansions of
Polynomial expansions in the Borel region By J. T. HURT and L. R. FORD, Rice Institute, Houston, Texas. (Received 22nd August, 1936. Read 6th November, 1936.) This paper deals with certain expansions of
A L A BA M A L A W R E V IE W
 A L A BA M A L A W R E V IE W Volume 52 Fall 2000 Number 1 B E F O R E D I S A B I L I T Y C I V I L R I G HT S : C I V I L W A R P E N S I O N S A N D TH E P O L I T I C S O F D I S A B I L I T Y I N
A L A BA M A L A W R E V IE W Volume 52 Fall 2000 Number 1 B E F O R E D I S A B I L I T Y C I V I L R I G HT S : C I V I L W A R P E N S I O N S A N D TH E P O L I T I C S O F D I S A B I L I T Y I N
We start with a simple result from Fourier analysis. Given a function f : [0, 1] C, we define the Fourier coefficients of f by
![We start with a simple result from Fourier analysis. Given a function f : [0, 1] C, we define the Fourier coefficients of f by We start with a simple result from Fourier analysis. Given a function f : [0, 1] C, we define the Fourier coefficients of f by](/thumbs/74/71304729.jpg) Chapter 9 The functional equation for the Riemann zeta function We will eventually deduce a functional equation, relating ζ(s to ζ( s. There are various methods to derive this functional equation, see
Chapter 9 The functional equation for the Riemann zeta function We will eventually deduce a functional equation, relating ζ(s to ζ( s. There are various methods to derive this functional equation, see
Chapter 8. Rigid transformations
 Chapter 8. Rigid transformations We are about to start drawing figures in 3D. There are no built-in routines for this purpose in PostScript, and we shall have to start more or less from scratch in extending
Chapter 8. Rigid transformations We are about to start drawing figures in 3D. There are no built-in routines for this purpose in PostScript, and we shall have to start more or less from scratch in extending
THE FIVE GROUPS OF AXIOMS.
 2 THE FIVE GROUPS OF AXIOMS. 1. THE ELEMENTS OF GEOMETRY AND THE FIVE GROUPS OF AXIOMS. Let us consider three distinct systems of things. The things composing the first system, we will call points and
2 THE FIVE GROUPS OF AXIOMS. 1. THE ELEMENTS OF GEOMETRY AND THE FIVE GROUPS OF AXIOMS. Let us consider three distinct systems of things. The things composing the first system, we will call points and
d 1 µ 2 Θ = 0. (4.1) consider first the case of m = 0 where there is no azimuthal dependence on the angle φ.
 4 Legendre Functions In order to investigate the solutions of Legendre s differential equation d ( µ ) dθ ] ] + l(l + ) m dµ dµ µ Θ = 0. (4.) consider first the case of m = 0 where there is no azimuthal
4 Legendre Functions In order to investigate the solutions of Legendre s differential equation d ( µ ) dθ ] ] + l(l + ) m dµ dµ µ Θ = 0. (4.) consider first the case of m = 0 where there is no azimuthal
PROOF OF POINCARE'S GEOMETRIC THEOREM
 PROOF OF POINCARE'S GEOMETRIC THEOREM BY GEORGE D. BIRKHOFF* In a paper recently published in the Rendiconti del Circolo Matemático di Palermo (vol. 33, 1912, pp. 375-407) and entitled Sur un théorème
PROOF OF POINCARE'S GEOMETRIC THEOREM BY GEORGE D. BIRKHOFF* In a paper recently published in the Rendiconti del Circolo Matemático di Palermo (vol. 33, 1912, pp. 375-407) and entitled Sur un théorème
23.6. The Complex Form. Introduction. Prerequisites. Learning Outcomes
 he Complex Form 3.6 Introduction In this Section we show how a Fourier series can be expressed more concisely if we introduce the complex number i where i =. By utilising the Euler relation: e iθ cos θ
he Complex Form 3.6 Introduction In this Section we show how a Fourier series can be expressed more concisely if we introduce the complex number i where i =. By utilising the Euler relation: e iθ cos θ
Ninth Meeting, July KM, On the form in Polar co-ordinates of oertain expressions occurring in Elastic Solids and in Hydrodynamics.
 109 Ninth Meeting, July KM, 1885. A. J. G. BARCLAY, Esq., M.A., President, in thr Chair. On the form in Polar co-ordinates of oertain expressions occurring in Elastic Solids and in Hydrodynamics. By CHARLES
109 Ninth Meeting, July KM, 1885. A. J. G. BARCLAY, Esq., M.A., President, in thr Chair. On the form in Polar co-ordinates of oertain expressions occurring in Elastic Solids and in Hydrodynamics. By CHARLES
Some Fun with Divergent Series
 Some Fun with Divergent Series 1. Preliminary Results We begin by examining the (divergent) infinite series S 1 = 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 + 6 + = k=1 k S 2 = 1 2 + 2 2 + 3 2 + 4 2 + 5 2 + 6 2 + = k=1 k 2 (i)
Some Fun with Divergent Series 1. Preliminary Results We begin by examining the (divergent) infinite series S 1 = 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 + 6 + = k=1 k S 2 = 1 2 + 2 2 + 3 2 + 4 2 + 5 2 + 6 2 + = k=1 k 2 (i)
EXERCISES. a b = a + b l aq b = ab - (a + b) + 2. a b = a + b + 1 n0i) = oii + ii + fi. A. Examples of Rings. C. Ring of 2 x 2 Matrices
 / rings definitions and elementary properties 171 EXERCISES A. Examples of Rings In each of the following, a set A with operations of addition and multiplication is given. Prove that A satisfies all the
/ rings definitions and elementary properties 171 EXERCISES A. Examples of Rings In each of the following, a set A with operations of addition and multiplication is given. Prove that A satisfies all the
THE HEAVISIDE OPERATIONAL CALCULUS* BY H. W. MARCH
 1927.I HEAVISIDE OPERATIONAL CALCULUS 311 Again, generally fit^f. Under what condition will /i /'? From (2) and (3) we see that the dual of a function is the same as the negative of the function if each
1927.I HEAVISIDE OPERATIONAL CALCULUS 311 Again, generally fit^f. Under what condition will /i /'? From (2) and (3) we see that the dual of a function is the same as the negative of the function if each
Chemical Process Dynamics and Control. Aisha Osman Mohamed Ahmed Department of Chemical Engineering Faculty of Engineering, Red Sea University
 Chemical Process Dynamics and Control Aisha Osman Mohamed Ahmed Department of Chemical Engineering Faculty of Engineering, Red Sea University 1 Chapter 4 System Stability 2 Chapter Objectives End of this
Chemical Process Dynamics and Control Aisha Osman Mohamed Ahmed Department of Chemical Engineering Faculty of Engineering, Red Sea University 1 Chapter 4 System Stability 2 Chapter Objectives End of this
A FIRST COURSE IN LINEAR ALGEBRA. An Open Text by Ken Kuttler. Matrix Arithmetic
 A FIRST COURSE IN LINEAR ALGEBRA An Open Text by Ken Kuttler Matrix Arithmetic Lecture Notes by Karen Seyffarth Adapted by LYRYX SERVICE COURSE SOLUTION Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike (CC BY-NC-SA)
A FIRST COURSE IN LINEAR ALGEBRA An Open Text by Ken Kuttler Matrix Arithmetic Lecture Notes by Karen Seyffarth Adapted by LYRYX SERVICE COURSE SOLUTION Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike (CC BY-NC-SA)
Fun and Fascinating Bible Reference for Kids Ages 8 to 12. starts on page 3! starts on page 163!
 F a Faa R K 8 12 a a 3! a a 163! 2013 a P, I. ISN 978-1-62416-216-9. N a a a a a, a,. C a a a a P, a 500 a a aa a. W, : F G: K Fa a Q &, a P, I. U. L aa a a a Fa a Q & a. C a 2 (M) Ta H P M (K) Wa P a
F a Faa R K 8 12 a a 3! a a 163! 2013 a P, I. ISN 978-1-62416-216-9. N a a a a a, a,. C a a a a P, a 500 a a aa a. W, : F G: K Fa a Q &, a P, I. U. L aa a a a Fa a Q & a. C a 2 (M) Ta H P M (K) Wa P a
Chern forms and the Fredholm determinant
 CHAPTER 10 Chern forms and the Fredholm determinant Lecture 10: 20 October, 2005 I showed in the lecture before last that the topological group G = G (Y ;E) for any compact manifold of positive dimension,
CHAPTER 10 Chern forms and the Fredholm determinant Lecture 10: 20 October, 2005 I showed in the lecture before last that the topological group G = G (Y ;E) for any compact manifold of positive dimension,
MATH 205C: STATIONARY PHASE LEMMA
 MATH 205C: STATIONARY PHASE LEMMA For ω, consider an integral of the form I(ω) = e iωf(x) u(x) dx, where u Cc (R n ) complex valued, with support in a compact set K, and f C (R n ) real valued. Thus, I(ω)
MATH 205C: STATIONARY PHASE LEMMA For ω, consider an integral of the form I(ω) = e iωf(x) u(x) dx, where u Cc (R n ) complex valued, with support in a compact set K, and f C (R n ) real valued. Thus, I(ω)
Chapter 2 Carnot Principle
 Chapter 2 Carnot Principle 2.1 Temperature 2.1.1 Isothermal Process When two bodies are placed in thermal contact, the hotter body gives off heat to the colder body. As long as the temperatures are different,
Chapter 2 Carnot Principle 2.1 Temperature 2.1.1 Isothermal Process When two bodies are placed in thermal contact, the hotter body gives off heat to the colder body. As long as the temperatures are different,
MODULE 8 Topics: Null space, range, column space, row space and rank of a matrix
 MODULE 8 Topics: Null space, range, column space, row space and rank of a matrix Definition: Let L : V 1 V 2 be a linear operator. The null space N (L) of L is the subspace of V 1 defined by N (L) = {x
MODULE 8 Topics: Null space, range, column space, row space and rank of a matrix Definition: Let L : V 1 V 2 be a linear operator. The null space N (L) of L is the subspace of V 1 defined by N (L) = {x
CHAPTER III THE CURVE AND THE EQUATION. The bisectors of the adjacent angles formed by two lines is. To solve any locus problem involves two things :
 CHAPTER III THE CURVE AND THE EQUATION 24. Locus of a point satisfying a given condition. The curve* (or group of curves) passing through all points which satisfy a given condition, and through no other
CHAPTER III THE CURVE AND THE EQUATION 24. Locus of a point satisfying a given condition. The curve* (or group of curves) passing through all points which satisfy a given condition, and through no other
Math 320-2: Final Exam Practice Solutions Northwestern University, Winter 2015
 Math 30-: Final Exam Practice Solutions Northwestern University, Winter 015 1. Give an example of each of the following. No justification is needed. (a) A closed and bounded subset of C[0, 1] which is
Math 30-: Final Exam Practice Solutions Northwestern University, Winter 015 1. Give an example of each of the following. No justification is needed. (a) A closed and bounded subset of C[0, 1] which is
A Basic Course in Real Analysis Prof. P. D. Srivastava Department of Mathematics Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 A Basic Course in Real Analysis Prof. P. D. Srivastava Department of Mathematics Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 36 Application of MVT, Darbou Theorem, L Hospital Rule (Refer Slide
A Basic Course in Real Analysis Prof. P. D. Srivastava Department of Mathematics Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 36 Application of MVT, Darbou Theorem, L Hospital Rule (Refer Slide
4.4 Uniform Convergence of Sequences of Functions and the Derivative
 4.4 Uniform Convergence of Sequences of Functions and the Derivative Say we have a sequence f n (x) of functions defined on some interval, [a, b]. Let s say they converge in some sense to a function f
4.4 Uniform Convergence of Sequences of Functions and the Derivative Say we have a sequence f n (x) of functions defined on some interval, [a, b]. Let s say they converge in some sense to a function f
Calculus II. Philippe Rukimbira. Department of Mathematics Florida International University PR (FIU) MAC / 1
 Calculus II Philippe Rukimbira Department of Mathematics Florida International University PR (FIU) MAC 2312 1 / 1 5.4. Sigma notation; The definition of area as limit Assignment: page 350, #11-15, 27,
Calculus II Philippe Rukimbira Department of Mathematics Florida International University PR (FIU) MAC 2312 1 / 1 5.4. Sigma notation; The definition of area as limit Assignment: page 350, #11-15, 27,
Basic Thermodynamics Prof. S. K. Som Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Basic Thermodynamics Prof. S. K. Som Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 09 Second Law and its Corollaries-IV Good afternoon to all of you to this session
Basic Thermodynamics Prof. S. K. Som Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 09 Second Law and its Corollaries-IV Good afternoon to all of you to this session
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Chemistry 5.76 Revised February, 1982 NOTES ON MATRIX METHODS
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Chemistry 5.76 Revised February, 198 NOTES ON MATRIX METHODS 1. Matrix Algebra Margenau and Murphy, The Mathematics of Physics and Chemistry, Chapter 10, give almost
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Chemistry 5.76 Revised February, 198 NOTES ON MATRIX METHODS 1. Matrix Algebra Margenau and Murphy, The Mathematics of Physics and Chemistry, Chapter 10, give almost
Chapter 3. Integration. 3.1 Indefinite Integration
 Chapter 3 Integration 3. Indefinite Integration Integration is the reverse of differentiation. Consider a function f(x) and suppose that there exists another function F (x) such that df f(x). (3.) For
Chapter 3 Integration 3. Indefinite Integration Integration is the reverse of differentiation. Consider a function f(x) and suppose that there exists another function F (x) such that df f(x). (3.) For
ON THE NUMBER OF REPRESENTATIONS OF 2n AS A SUM OF 2r SQUARES.
 1919.] REPEESENTATION AS SUM OF SQUARES. 19 ON THE NUMBER OF REPRESENTATIONS OF 2n AS A SUM OF 2r SQUARES. BY PEOFESSOR E. T. BELL. (Read before the San Francisco Section of the American Mathematical Society
1919.] REPEESENTATION AS SUM OF SQUARES. 19 ON THE NUMBER OF REPRESENTATIONS OF 2n AS A SUM OF 2r SQUARES. BY PEOFESSOR E. T. BELL. (Read before the San Francisco Section of the American Mathematical Society
MOMENTS OF HYPERGEOMETRIC HURWITZ ZETA FUNCTIONS
 MOMENTS OF HYPERGEOMETRIC HURWITZ ZETA FUNCTIONS ABDUL HASSEN AND HIEU D. NGUYEN Abstract. This paper investigates a generalization the classical Hurwitz zeta function. It is shown that many of the properties
MOMENTS OF HYPERGEOMETRIC HURWITZ ZETA FUNCTIONS ABDUL HASSEN AND HIEU D. NGUYEN Abstract. This paper investigates a generalization the classical Hurwitz zeta function. It is shown that many of the properties
Taylor Series and Asymptotic Expansions
 Taylor Series and Asymptotic Epansions The importance of power series as a convenient representation, as an approimation tool, as a tool for solving differential equations and so on, is pretty obvious.
Taylor Series and Asymptotic Epansions The importance of power series as a convenient representation, as an approimation tool, as a tool for solving differential equations and so on, is pretty obvious.
Groups. s t or s t or even st rather than f(s,t).
 Groups Definition. A binary operation on a set S is a function which takes a pair of elements s,t S and produces another element f(s,t) S. That is, a binary operation is a function f : S S S. Binary operations
Groups Definition. A binary operation on a set S is a function which takes a pair of elements s,t S and produces another element f(s,t) S. That is, a binary operation is a function f : S S S. Binary operations
3. On the grid below, sketch and label graphs of the following functions: y = sin x, y = cos x, and y = sin(x π/2). π/2 π 3π/2 2π 5π/2
 AP Physics C Calculus C.1 Name Trigonometric Functions 1. Consider the right triangle to the right. In terms of a, b, and c, write the expressions for the following: c a sin θ = cos θ = tan θ =. Using
AP Physics C Calculus C.1 Name Trigonometric Functions 1. Consider the right triangle to the right. In terms of a, b, and c, write the expressions for the following: c a sin θ = cos θ = tan θ =. Using
F = m a. t 2. stress = k(x) strain
 The Wave Equation Consider a bar made of an elastic material. The bar hangs down vertically from an attachment point = and can vibrate vertically but not horizontally. Since chapter 5 is the chapter on
The Wave Equation Consider a bar made of an elastic material. The bar hangs down vertically from an attachment point = and can vibrate vertically but not horizontally. Since chapter 5 is the chapter on
FIITJEE JEE(Main)
 AITS-FT-II-PCM-Sol.-JEE(Main)/7 In JEE Advanced 06, FIITJEE Students bag 6 in Top 00 AIR, 75 in Top 00 AIR, 8 in Top 500 AIR. 54 Students from Long Term Classroom/ Integrated School Program & 44 Students
AITS-FT-II-PCM-Sol.-JEE(Main)/7 In JEE Advanced 06, FIITJEE Students bag 6 in Top 00 AIR, 75 in Top 00 AIR, 8 in Top 500 AIR. 54 Students from Long Term Classroom/ Integrated School Program & 44 Students
Hence. The second law describes the direction of energy transfer in spontaneous processes
 * Heat and Work The first law of thermodynamics states that: Although energy has many forms, the total quantity of energy is constant. When energy disappears in one form, it appears simultaneously in other
* Heat and Work The first law of thermodynamics states that: Although energy has many forms, the total quantity of energy is constant. When energy disappears in one form, it appears simultaneously in other
Ordinary Differential Equations Prof. A. K. Nandakumaran Department of Mathematics Indian Institute of Science Bangalore
 Ordinary Differential Equations Prof. A. K. Nandakumaran Department of Mathematics Indian Institute of Science Bangalore Module - 3 Lecture - 10 First Order Linear Equations (Refer Slide Time: 00:33) Welcome
Ordinary Differential Equations Prof. A. K. Nandakumaran Department of Mathematics Indian Institute of Science Bangalore Module - 3 Lecture - 10 First Order Linear Equations (Refer Slide Time: 00:33) Welcome
Mathematical Methods for Physics and Engineering
 Mathematical Methods for Physics and Engineering Lecture notes for PDEs Sergei V. Shabanov Department of Mathematics, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL 32611 USA CHAPTER 1 The integration theory
Mathematical Methods for Physics and Engineering Lecture notes for PDEs Sergei V. Shabanov Department of Mathematics, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL 32611 USA CHAPTER 1 The integration theory
27. The pole diagram and the Laplace transform
 124 27. The pole diagram and the Laplace transform When working with the Laplace transform, it is best to think of the variable s in F (s) as ranging over the complex numbers. In the first section below
124 27. The pole diagram and the Laplace transform When working with the Laplace transform, it is best to think of the variable s in F (s) as ranging over the complex numbers. In the first section below
4 8 N v btr 20, 20 th r l f ff nt f l t. r t pl n f r th n tr t n f h h v lr d b n r d t, rd n t h h th t b t f l rd n t f th rld ll b n tr t d n R th
 n r t d n 20 2 :24 T P bl D n, l d t z d http:.h th tr t. r pd l 4 8 N v btr 20, 20 th r l f ff nt f l t. r t pl n f r th n tr t n f h h v lr d b n r d t, rd n t h h th t b t f l rd n t f th rld ll b n
n r t d n 20 2 :24 T P bl D n, l d t z d http:.h th tr t. r pd l 4 8 N v btr 20, 20 th r l f ff nt f l t. r t pl n f r th n tr t n f h h v lr d b n r d t, rd n t h h th t b t f l rd n t f th rld ll b n
tom.h.wilson Dept. Geology and Geography West Virginia University Tom Wilson, Department of Geology and Geography
 tom.h.wilson tom.wilson@mail.wvu.edu Dept. Geology and Geography West Virginia University Heat flow problems to accompany the example in Chapter 9 Consider heat conduction through a thick glass window
tom.h.wilson tom.wilson@mail.wvu.edu Dept. Geology and Geography West Virginia University Heat flow problems to accompany the example in Chapter 9 Consider heat conduction through a thick glass window
CHAPTER 3 Applications of Differentiation
 CHAPTER Applications of Differentiation Section. Etrema on an Interval................... 0 Section. Rolle s Theorem and the Mean Value Theorem...... 0 Section. Increasing and Decreasing Functions and
CHAPTER Applications of Differentiation Section. Etrema on an Interval................... 0 Section. Rolle s Theorem and the Mean Value Theorem...... 0 Section. Increasing and Decreasing Functions and
DIVERGENCE AND CURL THEOREMS
 This document is stored in Documents/4C/Gausstokes.tex. with LaTex. Compile it November 29, 2014 Hans P. Paar DIVERGENCE AND CURL THEOREM 1 Introduction We discuss the theorems of Gauss and tokes also
This document is stored in Documents/4C/Gausstokes.tex. with LaTex. Compile it November 29, 2014 Hans P. Paar DIVERGENCE AND CURL THEOREM 1 Introduction We discuss the theorems of Gauss and tokes also
DIRECTED STUDIES IN MATHEMATICS - FINAL REPORT. 1. Introduction
 DIRECTED STUDIES IN MATHEMATICS - FINAL REPORT ZHANG YONGQUAN 1. Introduction The factorial function n!, usually defined as the number of permutations of n distinct objects (or equivalently the product
DIRECTED STUDIES IN MATHEMATICS - FINAL REPORT ZHANG YONGQUAN 1. Introduction The factorial function n!, usually defined as the number of permutations of n distinct objects (or equivalently the product
13 Definite integrals
 3 Definite integrals Read: Boas h. 4. 3. Laurent series: Def.: Laurent series (LS). If f() is analytic in a region R, then converges in R, with a n = πi f() = a n ( ) n + n= n= f() ; b ( ) n+ n = πi b
3 Definite integrals Read: Boas h. 4. 3. Laurent series: Def.: Laurent series (LS). If f() is analytic in a region R, then converges in R, with a n = πi f() = a n ( ) n + n= n= f() ; b ( ) n+ n = πi b
General Inner Product and The Fourier Series
 A Linear Algebra Approach Department of Mathematics University of Puget Sound 4-20-14 / Spring Semester Outline 1 2 Inner Product The inner product is an algebraic operation that takes two vectors and
A Linear Algebra Approach Department of Mathematics University of Puget Sound 4-20-14 / Spring Semester Outline 1 2 Inner Product The inner product is an algebraic operation that takes two vectors and
(3) 6(t) = /(* /(* ~ t), *(0 - /(* + 0 ~ /(* ~t)-l,
 ON THE BEHAVIOR OF FOURIER COEFFICIENTS R. MOHANTY AND M. NANDA 1. Let/(0 be integrable L in ( ir,ir) periodic with period 2ir, let 1 00 1 00 (1) f(t) ~ oo + E (a* cos ni + bn sin nt) = a0 + E ^n(0-2 i
ON THE BEHAVIOR OF FOURIER COEFFICIENTS R. MOHANTY AND M. NANDA 1. Let/(0 be integrable L in ( ir,ir) periodic with period 2ir, let 1 00 1 00 (1) f(t) ~ oo + E (a* cos ni + bn sin nt) = a0 + E ^n(0-2 i
Solutions to Calculus problems. b k A = limsup n. a n limsup b k,
 Solutions to Calculus problems. We will prove the statement. Let {a n } be the sequence and consider limsupa n = A [, ]. If A = ±, we can easily find a nondecreasing (nonincreasing) subsequence of {a n
Solutions to Calculus problems. We will prove the statement. Let {a n } be the sequence and consider limsupa n = A [, ]. If A = ±, we can easily find a nondecreasing (nonincreasing) subsequence of {a n
x by so in other words ( )
 Math 154. Norm and trace An interesting application of Galois theory is to help us understand properties of two special constructions associated to field extensions, the norm and trace. If L/k is a finite
Math 154. Norm and trace An interesting application of Galois theory is to help us understand properties of two special constructions associated to field extensions, the norm and trace. If L/k is a finite
Theorem 5.3. Let E/F, E = F (u), be a simple field extension. Then u is algebraic if and only if E/F is finite. In this case, [E : F ] = deg f u.
![Theorem 5.3. Let E/F, E = F (u), be a simple field extension. Then u is algebraic if and only if E/F is finite. In this case, [E : F ] = deg f u. Theorem 5.3. Let E/F, E = F (u), be a simple field extension. Then u is algebraic if and only if E/F is finite. In this case, [E : F ] = deg f u.](/thumbs/81/83685479.jpg) 5. Fields 5.1. Field extensions. Let F E be a subfield of the field E. We also describe this situation by saying that E is an extension field of F, and we write E/F to express this fact. If E/F is a field
5. Fields 5.1. Field extensions. Let F E be a subfield of the field E. We also describe this situation by saying that E is an extension field of F, and we write E/F to express this fact. If E/F is a field
Physics 451/551 Theoretical Mechanics. G. A. Krafft Old Dominion University Jefferson Lab Lecture 18
 Physics 451/551 Theoretical Mechanics G. A. Krafft Old Dominion University Jefferson Lab Lecture 18 Theoretical Mechanics Fall 18 Properties of Sound Sound Waves Requires medium for propagation Mainly
Physics 451/551 Theoretical Mechanics G. A. Krafft Old Dominion University Jefferson Lab Lecture 18 Theoretical Mechanics Fall 18 Properties of Sound Sound Waves Requires medium for propagation Mainly
On a Formula of Mellin and Its Application to the Study of the Riemann Zeta-function
 Journal of Mathematics Research; Vol. 4, No. 6; 22 ISSN 96-9795 E-ISSN 96-989 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education On a Formula of Mellin and Its Application to the Study of the Riemann
Journal of Mathematics Research; Vol. 4, No. 6; 22 ISSN 96-9795 E-ISSN 96-989 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education On a Formula of Mellin and Its Application to the Study of the Riemann
4 Uniform convergence
 4 Uniform convergence In the last few sections we have seen several functions which have been defined via series or integrals. We now want to develop tools that will allow us to show that these functions
4 Uniform convergence In the last few sections we have seen several functions which have been defined via series or integrals. We now want to develop tools that will allow us to show that these functions
Contents. MATH 32B-2 (18W) (L) G. Liu / (TA) A. Zhou Calculus of Several Variables. 1 Multiple Integrals 3. 2 Vector Fields 9
 MATH 32B-2 (8W) (L) G. Liu / (TA) A. Zhou Calculus of Several Variables Contents Multiple Integrals 3 2 Vector Fields 9 3 Line and Surface Integrals 5 4 The Classical Integral Theorems 9 MATH 32B-2 (8W)
MATH 32B-2 (8W) (L) G. Liu / (TA) A. Zhou Calculus of Several Variables Contents Multiple Integrals 3 2 Vector Fields 9 3 Line and Surface Integrals 5 4 The Classical Integral Theorems 9 MATH 32B-2 (8W)
An Analytic Basis for Heat Conduction in a Fuel Rods
 An Analytic Basis for Heat Conduction in a Fuel Rods Dan Shields December 15, 211 Introduction It is important in nuclear science and engineering to understand heat flow in and around fuel in reactors.
An Analytic Basis for Heat Conduction in a Fuel Rods Dan Shields December 15, 211 Introduction It is important in nuclear science and engineering to understand heat flow in and around fuel in reactors.
CHAPTER 3 Applications of Differentiation
 CHAPTER Applications of Differentiation Section. Etrema on an Interval.............. Section. Rolle s Theorem and the Mean Value Theorem. 7 Section. Increasing and Decreasing Functions and the First Derivative
CHAPTER Applications of Differentiation Section. Etrema on an Interval.............. Section. Rolle s Theorem and the Mean Value Theorem. 7 Section. Increasing and Decreasing Functions and the First Derivative
2.5 Linear Applications 99 Two-Tank Mixing. Two tanks A and B are assumed to contain A 0 and B 0 liters of brine at t = 0. Let the input for the rst t
 98 First Order Dierential Equations 2.5 Linear Applications This collection of applications for the linear equation y 0 + p(x)y = r(x) includes mixing problems, especially brine tanks in single and multiple
98 First Order Dierential Equations 2.5 Linear Applications This collection of applications for the linear equation y 0 + p(x)y = r(x) includes mixing problems, especially brine tanks in single and multiple
ON THE NON-LINEAR VIBRATION PROBLEM OF THE ELASTIC STRING* G. F. CARRIER
 157 ON THE NON-LINEAR VIBRATION PROBLEM OF THE ELASTIC STRING* BY G. F. CARRIER Harvard University 1. Introduction. It is well known that the classical linearized analysis of the vibrating string can lead
157 ON THE NON-LINEAR VIBRATION PROBLEM OF THE ELASTIC STRING* BY G. F. CARRIER Harvard University 1. Introduction. It is well known that the classical linearized analysis of the vibrating string can lead
A-LEVEL Mathematics. MPC4 Pure Core 4 Mark scheme June Version: 1.0 Final
 A-LEVEL Mathematics MPC4 Pure Core 4 Mark scheme 660 June 06 Version:.0 Final Mark schemes are prepared by the Lead Assessment Writer and considered, together with the relevant questions, by a panel of
A-LEVEL Mathematics MPC4 Pure Core 4 Mark scheme 660 June 06 Version:.0 Final Mark schemes are prepared by the Lead Assessment Writer and considered, together with the relevant questions, by a panel of
Ch 4 Differentiation
 Ch 1 Partial fractions Ch 6 Integration Ch 2 Coordinate geometry C4 Ch 5 Vectors Ch 3 The binomial expansion Ch 4 Differentiation Chapter 1 Partial fractions We can add (or take away) two fractions only
Ch 1 Partial fractions Ch 6 Integration Ch 2 Coordinate geometry C4 Ch 5 Vectors Ch 3 The binomial expansion Ch 4 Differentiation Chapter 1 Partial fractions We can add (or take away) two fractions only
Merton College Maths for Physics Prelims October 3, 2010 MT I. Calculus. { y(x + δx) y(x) dx 2 + x dy
 Merton College Maths for Physics Prelims October 3, 2010 1. From the definition of the derivative, dy = lim δx 0 MT I Calculus { y(x + δx) y(x) evaluate d(x 2 )/. In the same way evaluate d(sin x)/. 2.
Merton College Maths for Physics Prelims October 3, 2010 1. From the definition of the derivative, dy = lim δx 0 MT I Calculus { y(x + δx) y(x) evaluate d(x 2 )/. In the same way evaluate d(sin x)/. 2.
ELEMENTARY LINEAR ALGEBRA
 ELEMENTARY LINEAR ALGEBRA K. R. MATTHEWS DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS UNIVERSITY OF QUEENSLAND Second Online Version, December 1998 Comments to the author at krm@maths.uq.edu.au Contents 1 LINEAR EQUATIONS
ELEMENTARY LINEAR ALGEBRA K. R. MATTHEWS DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS UNIVERSITY OF QUEENSLAND Second Online Version, December 1998 Comments to the author at krm@maths.uq.edu.au Contents 1 LINEAR EQUATIONS
Lecture 16 and 17 Application to Evaluation of Real Integrals. R a (f)η(γ; a)
 Lecture 16 and 17 Application to Evaluation of Real Integrals Theorem 1 Residue theorem: Let Ω be a simply connected domain and A be an isolated subset of Ω. Suppose f : Ω\A C is a holomorphic function.
Lecture 16 and 17 Application to Evaluation of Real Integrals Theorem 1 Residue theorem: Let Ω be a simply connected domain and A be an isolated subset of Ω. Suppose f : Ω\A C is a holomorphic function.
Math 127: Course Summary
 Math 27: Course Summary Rich Schwartz October 27, 2009 General Information: M27 is a course in functional analysis. Functional analysis deals with normed, infinite dimensional vector spaces. Usually, these
Math 27: Course Summary Rich Schwartz October 27, 2009 General Information: M27 is a course in functional analysis. Functional analysis deals with normed, infinite dimensional vector spaces. Usually, these
Fourier Theory on the Complex Plane II Weak Convergence, Classification and Factorization of Singularities
 Fourier Theory on the Complex Plane II Weak Convergence, Classification and Factorization of Singularities Jorge L. delyra Department of Mathematical Physics Physics Institute University of São Paulo April
Fourier Theory on the Complex Plane II Weak Convergence, Classification and Factorization of Singularities Jorge L. delyra Department of Mathematical Physics Physics Institute University of São Paulo April
MAGIC058 & MATH64062: Partial Differential Equations 1
 MAGIC58 & MATH6462: Partial Differential Equations Section 6 Fourier transforms 6. The Fourier integral formula We have seen from section 4 that, if a function f(x) satisfies the Dirichlet conditions,
MAGIC58 & MATH6462: Partial Differential Equations Section 6 Fourier transforms 6. The Fourier integral formula We have seen from section 4 that, if a function f(x) satisfies the Dirichlet conditions,
3 rd class Mech. Eng. Dept. hamdiahmed.weebly.com Fourier Series
 Definition 1 Fourier Series A function f is said to be piecewise continuous on [a, b] if there exists finitely many points a = x 1 < x 2
Definition 1 Fourier Series A function f is said to be piecewise continuous on [a, b] if there exists finitely many points a = x 1 < x 2
Taylor and Laurent Series
 Chapter 4 Taylor and Laurent Series 4.. Taylor Series 4... Taylor Series for Holomorphic Functions. In Real Analysis, the Taylor series of a given function f : R R is given by: f (x + f (x (x x + f (x
Chapter 4 Taylor and Laurent Series 4.. Taylor Series 4... Taylor Series for Holomorphic Functions. In Real Analysis, the Taylor series of a given function f : R R is given by: f (x + f (x (x x + f (x
f(w) f(a) = 1 2πi w a Proof. There exists a number r such that the disc D(a,r) is contained in I(γ). For any ǫ < r, w a dw
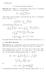 Proof[section] 5. Cauchy integral formula Theorem 5.. Suppose f is holomorphic inside and on a positively oriented curve. Then if a is a point inside, f(a) = w a dw. Proof. There exists a number r such
Proof[section] 5. Cauchy integral formula Theorem 5.. Suppose f is holomorphic inside and on a positively oriented curve. Then if a is a point inside, f(a) = w a dw. Proof. There exists a number r such
Summary of various integrals
 ummary of various integrals Here s an arbitrary compilation of information about integrals Moisés made on a cold ecember night. 1 General things o not mix scalars and vectors! In particular ome integrals
ummary of various integrals Here s an arbitrary compilation of information about integrals Moisés made on a cold ecember night. 1 General things o not mix scalars and vectors! In particular ome integrals
Solutions for the Practice Final - Math 23B, 2016
 olutions for the Practice Final - Math B, 6 a. True. The area of a surface is given by the expression d, and since we have a parametrization φ x, y x, y, f x, y with φ, this expands as d T x T y da xy
olutions for the Practice Final - Math B, 6 a. True. The area of a surface is given by the expression d, and since we have a parametrization φ x, y x, y, f x, y with φ, this expands as d T x T y da xy
1 Assignment 1: Nonlinear dynamics (due September
 Assignment : Nonlinear dynamics (due September 4, 28). Consider the ordinary differential equation du/dt = cos(u). Sketch the equilibria and indicate by arrows the increase or decrease of the solutions.
Assignment : Nonlinear dynamics (due September 4, 28). Consider the ordinary differential equation du/dt = cos(u). Sketch the equilibria and indicate by arrows the increase or decrease of the solutions.
Entropy and the second law of thermodynamics
 Chapter 4 Entropy and the second law of thermodynamics 4.1 Heat engines In a cyclic transformation the final state of a system is by definition identical to the initial state. he overall change of the
Chapter 4 Entropy and the second law of thermodynamics 4.1 Heat engines In a cyclic transformation the final state of a system is by definition identical to the initial state. he overall change of the
12.7 Heat Equation: Modeling Very Long Bars.
 568 CHAP. Partial Differential Equations (PDEs).7 Heat Equation: Modeling Very Long Bars. Solution by Fourier Integrals and Transforms Our discussion of the heat equation () u t c u x in the last section
568 CHAP. Partial Differential Equations (PDEs).7 Heat Equation: Modeling Very Long Bars. Solution by Fourier Integrals and Transforms Our discussion of the heat equation () u t c u x in the last section
