Cyclic Processes. water
|
|
|
- Winifred Powell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Name Cyclic Processes Cyclic Processes A fixed quantity of ideal gas is contained within a metal cylinder that is sealed with a movable, frictionless, insulating piston. (The piston can move up or down without the slightest resistance from friction, but no gas can enter or leave the cylinder. The piston is heavy, but there can be no heat transfer to or from the piston itself.) The cylinder is surrounded by a large container of water with high walls as shown. We are going to describe two separate processes, Process #1 and Process #2. movable piston Time A ideal gas water Entire system at room temperature. At initial time A, the gas, cylinder, and water have all been sitting in a room for a long period of time, and all of them are at room temperature. Step 1. We now begin Process #1: The water container is gradually heated, and the piston very slowly moves upward. At time B the heating of the water stops, and the piston stops moving when it is in the position shown in the diagram below: Time B Piston in new position. Temperature of system has changed. Question #1: During the process that occurs from time A to time B, which of the following is true: (a) positive work is done on the gas by the environment, (b) positive work is done by the gas on the environment, (c) no net work is done on or by the gas. Question #2: During the process that occurs from time A to time B, the gas absorbs x joules of energy from the water. Which of the following is true: The total kinetic energy of all of the gas molecules (a) increases by more than x joules; (b) increases by x joules; (c) increases, but by less than x joules; (d) remains unchanged; (e) decreases by less than x joules; (f) decreases by x joules; (g) decreases by more than x joules. Explain your answer: 1
2 Step 2. Now, empty containers are placed on top of the piston as shown. Small lead weights are gradually placed in the containers, one by one, and the piston is observed to move down slowly. While this happens, the temperature of the water is nearly unchanged, and the gas temperature remains practically constant. (That is, it remains at the temperature it reached at time B, after the water had been heated up.) containers lead weight weights being added Piston moves down slowly. Temperature remains same as at time B. Step 3. At time C we stop adding lead weights to the container and the piston stops moving. (The weights that we have already added up until now are still in the containers.) The piston is now found to be at exactly the same position it was at time A. Time C Weights in containers. Piston in same position as at time A. Temperature same as at time B. Question #3: During the process that occurs from time B to time C, does the total kinetic energy of all the gas molecules increase, decrease, or remain unchanged? Question #4: During the process that occurs from time B to time C, is there any net energy flow between the gas and the water? If no, explain why not. If yes, is there a net flow of energy from gas to water, or from water to gas? Explain your answer: 2
3 Step 4. Now, the piston is locked into place so it cannot move; the weights are removed from the piston. The system is left to sit in the room for many hours, and eventually the entire system cools back down to the same room temperature it had at time A. When this finally happens, it is time D. Time D Piston in same position as at time A. Temperature same as at time A. Question #5: During the process that occurs from time C to time D, the water absorbs y joules of energy from the gas. Which of the following is true: The total kinetic energy of all of the gas molecules (a) increases by more than y joules; (b) increases by y joules; (c) increases, but by less than y joules; (d) remains unchanged; (e) decreases, by less than y joules; (f) decreases by y joules; (g) decreases by more than y joules. Question #6: Consider the entire process from time A to time D. (i) Is the net work done by the gas on the environment during that process (a) greater than zero, (b) equal to zero, or (c) less than zero? Explain your answer: (ii) Is the total heat transfer to the gas during that process (a) greater than zero, (b) equal to zero, or (c) less than zero? Explain your answer: 3
4 Now let us begin Process #2. The piston is unlocked so it is again free to move. We start from the same initial situation as shown at time A and D (i.e., same temperature and position of the piston). Just as before, we heat the water and watch as the piston rises. However, this time, we will heat the water for a longer period of time. As a result, the piston ends up higher than it was at time B. Step 5. Step 6. Now, weights are added to the piston and it begins to move down. (Temperature does not change during this process.) However, this time, more weights than before must be added to get the piston back to the position it had at time C. Again, the piston is locked and the weights are removed. After many hours, the system returns to the same temperature that it had at time A and time D (and the piston is in the same position as it was at those times). This final state occurs at time E. Question #7: Consider the total kinetic energy of all of the gas molecules at times A, D, and E; call those E A, E D, and E E. Rank these in order of magnitude (greatest to least, using > or < signs). If two or more of these are equal, indicate that with an = sign. Explain your answer: Question #8: Consider the following positive quantities: Q 1, Q2, W1, W2. These represent the absolute values of the total heat transfer to the gas during Process #1 and Process #2, and of the net work done by the gas during Processes #1 and #2. Rank these four quantities from largest to smallest. If two or more are equal, indicate with = sign. Explain your answer: Question #9: Sketch a P-V diagram of Process #1 and Process #2 on the same set of axes; label (with the appropriate letter) the states that occur at times A, B, C, D, and E. (Use the other side of this sheet if necessary.) Explain how you can use the diagram to justify your answer to Question #8. 4
5 Question #10: A. For the process A B: i. Is the work done by the system (W AB ) positive, negative, or zero? ii. Is heat transferred to the system, away from the system, or is there no heat transfer? iii. Does the internal energy increase, decrease, or remain the same? Explain. B. For the process B C: i. Is the work done by the system (W BC ) positive, negative, or zero? ii. Is heat transferred to the system, away from the system, or is there no heat transfer? iii. Does the internal energy increase, decrease, or remain the same? Explain. C. For the process C D: i. Is the work done by the system (W CD ) positive, negative, or zero? ii. Is heat transferred to the system, away from the system, or is there no heat transfer? iii. Does the internal energy increase, decrease, or remain the same? Explain. 5
6 Question #11: Rank the absolute values W AB, W BC, and W CD from largest to smallest; if two or more are equal, indicate with an = sign. largest smallest Explain your reasoning. Question #12: Rank the absolute values of internal energy change U AB, U BC, and U CD from largest to smallest; if two or more are equal, indicate with an = sign. largest smallest Explain your reasoning. Question #13: Rank the absolute values of heat transfer Q AB, Q BC, and Q CD from largest to smallest; if two or more are equal, indicate with an = sign. Assume that the low temperature is 300 K, and the high temperature is 600 K. largest smallest Explain your reasoning. 6
7 Question #14: Are your answers to Questions #11, 12, and 13 consistent with your answers to parts (i) and (ii) of Question #6? Explain. Question #15: Is the net change in volume from time A to time D (V D V A ) greater than zero, equal to zero, or less than zero? Is this consistent with your answers to Questions #6(i) and #14? Explain. Question #16: Is the net change in temperature from time A to time D (T D T A ) greater than zero, equal to zero, or less than zero? Is this consistent with your answers to Questions #6(ii) and #14? Explain. 7
8 A Sample Cyclic Process A thermodynamic system undergoes a three-step process. An adiabatic expansion takes it from state 1 to state 2; heat is added at constant pressure to move the system to state 3; and an isothermal compression returns the system to state 1. The system consists of a diatomic ideal gas with C V = 5R/2. The number of moles is chosen so nr = 100 J/K. The following information is known about states 2 and 3. Pressure: P 2 = P 3 = 100 kpa Volume: V 3 = 0.5 m 3 What is the temperature of the system in state 3? The system does J of work in the constant pressure process that takes it from state 2 to state 3. What is the volume and temperature of the system in state 2? V 2 = T 2 = Complete the table below, filling in the missing numerical values, with units of joules. The total work done by the system in the cycle is J. Note that there is a way to do this without integrating or using logarithms. Process Q E W int Complete cycle Step 1: First fill in all the terms that are zero. Remember that each row in the table satisfies the First Law of Thermodynamics. Also remember that Eint = ncv T. Chapter 15 The Laws of Thermodynamics Page 9
Process Nature of Process
 AP Physics Free Response Practice Thermodynamics 1983B. The pv-diagram above represents the states of an ideal gas during one cycle of operation of a reversible heat engine. The cycle consists of the following
AP Physics Free Response Practice Thermodynamics 1983B. The pv-diagram above represents the states of an ideal gas during one cycle of operation of a reversible heat engine. The cycle consists of the following
1985B4. A kilogram sample of a material is initially a solid at a temperature of 20 C. Heat is added to the sample at a constant rate of 100
 1985B4. A 0.020-kilogram sample of a material is initially a solid at a temperature of 20 C. Heat is added to the sample at a constant rate of 100 joules per second until the temperature increases to 60
1985B4. A 0.020-kilogram sample of a material is initially a solid at a temperature of 20 C. Heat is added to the sample at a constant rate of 100 joules per second until the temperature increases to 60
TB [103 marks] The damping of the system is now increased. Which describes the change in ƒ 0 and the change in A 0?
![TB [103 marks] The damping of the system is now increased. Which describes the change in ƒ 0 and the change in A 0? TB [103 marks] The damping of the system is now increased. Which describes the change in ƒ 0 and the change in A 0?](/thumbs/87/96952878.jpg) TB [103 marks] 1. A periodic driving force of frequency ƒ acts on a system which undergoes forced oscillations of amplitude A. The graph below shows the variation with ƒ of A. The maximum amplitude A 0
TB [103 marks] 1. A periodic driving force of frequency ƒ acts on a system which undergoes forced oscillations of amplitude A. The graph below shows the variation with ƒ of A. The maximum amplitude A 0
Physics 202 Homework 5
 Physics 202 Homework 5 Apr 29, 2013 1. A nuclear-fueled electric power plant utilizes a so-called boiling water reac- 5.8 C tor. In this type of reactor, nuclear energy causes water under pressure to boil
Physics 202 Homework 5 Apr 29, 2013 1. A nuclear-fueled electric power plant utilizes a so-called boiling water reac- 5.8 C tor. In this type of reactor, nuclear energy causes water under pressure to boil
The Kinetic Theory of Gases
 PHYS102 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 19 The Kinetic Theory of Gases Ideal gas RMS speed Internal energy Isothermal process Isobaric process Isochoric process Adiabatic process General process 1. Figure
PHYS102 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 19 The Kinetic Theory of Gases Ideal gas RMS speed Internal energy Isothermal process Isobaric process Isochoric process Adiabatic process General process 1. Figure
Chapter 19: The Kinetic Theory of Gases Questions and Example Problems
 Chapter 9: The Kinetic Theory of Gases Questions and Example Problems N M V f N M Vo sam n pv nrt Nk T W nrt ln B A molar nmv RT k T rms B p v K k T λ rms avg B V M m πd N/V Q nc T Q nc T C C + R E nc
Chapter 9: The Kinetic Theory of Gases Questions and Example Problems N M V f N M Vo sam n pv nrt Nk T W nrt ln B A molar nmv RT k T rms B p v K k T λ rms avg B V M m πd N/V Q nc T Q nc T C C + R E nc
THERMODYNAMICS CONCEPTUAL PROBLEMS
 THERMODYNAMICS CONCEPTUAL PROBLEMS Q-01 Is the heat supplied to a system always equal to the increases in its internal energy? Ans Acc. to first law of thermo- dynamics If heat is supplied in such a manner
THERMODYNAMICS CONCEPTUAL PROBLEMS Q-01 Is the heat supplied to a system always equal to the increases in its internal energy? Ans Acc. to first law of thermo- dynamics If heat is supplied in such a manner
Distinguish between an isothermal process and an adiabatic process as applied to an ideal gas (2)
 1. This question is about thermodynamic processes. (a) Distinguish between an isothermal process and an adiabatic process as applied to an ideal gas.......... An ideal gas is held in a container by a moveable
1. This question is about thermodynamic processes. (a) Distinguish between an isothermal process and an adiabatic process as applied to an ideal gas.......... An ideal gas is held in a container by a moveable
Chapter 19. First Law of Thermodynamics. Dr. Armen Kocharian, 04/04/05
 Chapter 19 First Law of Thermodynamics Dr. Armen Kocharian, 04/04/05 Heat and Work Work during volume change Work in Thermodynamics Work can be done on a deformable system, such as a gas Consider a cylinder
Chapter 19 First Law of Thermodynamics Dr. Armen Kocharian, 04/04/05 Heat and Work Work during volume change Work in Thermodynamics Work can be done on a deformable system, such as a gas Consider a cylinder
, is placed in thermal contact with object B, with mass m, specific heat c B. and initially at temperature T B
 4C_PLC http://www.cabrillo.edu/~jmccullough/physics4c/files/4c_plc/4c_plc.htm Page 1 of 8 /6/201 1. The heat capacity at constant volume and the heat capacity at constant pressure have different values
4C_PLC http://www.cabrillo.edu/~jmccullough/physics4c/files/4c_plc/4c_plc.htm Page 1 of 8 /6/201 1. The heat capacity at constant volume and the heat capacity at constant pressure have different values
A thermodynamic system is taken from an initial state X along the path XYZX as shown in the PV-diagram.
 AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Thermodynamics 1. The maximum efficiency of a heat engine that operates between temperatures of 1500 K in the firing chamber and 600 K in the exhaust chamber is most
AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Thermodynamics 1. The maximum efficiency of a heat engine that operates between temperatures of 1500 K in the firing chamber and 600 K in the exhaust chamber is most
The first law of thermodynamics continued
 Lecture 7 The first law of thermodynamics continued Pre-reading: 19.5 Where we are The pressure p, volume V, and temperature T are related by an equation of state. For an ideal gas, pv = nrt = NkT For
Lecture 7 The first law of thermodynamics continued Pre-reading: 19.5 Where we are The pressure p, volume V, and temperature T are related by an equation of state. For an ideal gas, pv = nrt = NkT For
Survey of Thermodynamic Processes and First and Second Laws
 Survey of Thermodynamic Processes and First and Second Laws Please select only one of the five choices, (a)-(e) for each of the 33 questions. All temperatures T are absolute temperatures. All experiments
Survey of Thermodynamic Processes and First and Second Laws Please select only one of the five choices, (a)-(e) for each of the 33 questions. All temperatures T are absolute temperatures. All experiments
Chapter 20. Heat Engines, Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics. Dr. Armen Kocharian
 Chapter 20 Heat Engines, Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics Dr. Armen Kocharian First Law of Thermodynamics Review Review: The first law states that a change in internal energy in a system can
Chapter 20 Heat Engines, Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics Dr. Armen Kocharian First Law of Thermodynamics Review Review: The first law states that a change in internal energy in a system can
Chapter 19 The First Law of Thermodynamics
 Chapter 19 The First Law of Thermodynamics The first law of thermodynamics is an extension of the principle of conservation of energy. It includes the transfer of both mechanical and thermal energy. First
Chapter 19 The First Law of Thermodynamics The first law of thermodynamics is an extension of the principle of conservation of energy. It includes the transfer of both mechanical and thermal energy. First
Unit 05 Kinetic Theory of Gases
 Unit 05 Kinetic Theory of Gases Unit Concepts: A) A bit more about temperature B) Ideal Gas Law C) Molar specific heats D) Using them all Unit 05 Kinetic Theory, Slide 1 Temperature and Velocity Recall:
Unit 05 Kinetic Theory of Gases Unit Concepts: A) A bit more about temperature B) Ideal Gas Law C) Molar specific heats D) Using them all Unit 05 Kinetic Theory, Slide 1 Temperature and Velocity Recall:
The goal of thermodynamics is to understand how heat can be converted to work. Not all the heat energy can be converted to mechanical energy
 Thermodynamics The goal of thermodynamics is to understand how heat can be converted to work Main lesson: Not all the heat energy can be converted to mechanical energy This is because heat energy comes
Thermodynamics The goal of thermodynamics is to understand how heat can be converted to work Main lesson: Not all the heat energy can be converted to mechanical energy This is because heat energy comes
Speed Distribution at CONSTANT Temperature is given by the Maxwell Boltzmann Speed Distribution
 Temperature ~ Average KE of each particle Particles have different speeds Gas Particles are in constant RANDOM motion Average KE of each particle is: 3/2 kt Pressure is due to momentum transfer Speed Distribution
Temperature ~ Average KE of each particle Particles have different speeds Gas Particles are in constant RANDOM motion Average KE of each particle is: 3/2 kt Pressure is due to momentum transfer Speed Distribution
Conservation of Energy
 Conservation of Energy Energy can neither by created nor destroyed, but only transferred from one system to another and transformed from one form to another. Conservation of Energy Consider at a gas in
Conservation of Energy Energy can neither by created nor destroyed, but only transferred from one system to another and transformed from one form to another. Conservation of Energy Consider at a gas in
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 CH. 19 PRACTICE Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) When a fixed amount of ideal gas goes through an isobaric expansion, A) its
CH. 19 PRACTICE Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) When a fixed amount of ideal gas goes through an isobaric expansion, A) its
AP PHYSICS 2 WHS-CH-15 Thermodynamics Show all your work, equations used, and box in your answers!
 AP PHYSICS 2 WHS-CH-15 Thermodynamics Show all your work, equations used, and box in your answers! Nicolas Léonard Sadi Carnot (1796-1832) Sadi Carnot was a French military engineer and physicist, often
AP PHYSICS 2 WHS-CH-15 Thermodynamics Show all your work, equations used, and box in your answers! Nicolas Léonard Sadi Carnot (1796-1832) Sadi Carnot was a French military engineer and physicist, often
Chapter 14 Thermal Physics: A Microscopic View
 Chapter 14 Thermal Physics: Microscopic View The main focus of this chapter is the application of some of the basic principles we learned earlier to thermal physics. This will give us some important insights
Chapter 14 Thermal Physics: Microscopic View The main focus of this chapter is the application of some of the basic principles we learned earlier to thermal physics. This will give us some important insights
Heat and Thermodynamics. February. 2, Solution of Recitation 2. Consider the first case when air is allowed to expand isothermally.
 Heat and Thermodynamics. February., 0 Solution of Recitation Answer : We have given that, Initial volume of air = = 0.4 m 3 Initial pressure of air = P = 04 kpa = 04 0 3 Pa Final pressure of air = P =
Heat and Thermodynamics. February., 0 Solution of Recitation Answer : We have given that, Initial volume of air = = 0.4 m 3 Initial pressure of air = P = 04 kpa = 04 0 3 Pa Final pressure of air = P =
Answer: Volume of water heated = 3.0 litre per minute Mass of water heated, m = 3000 g per minute Increase in temperature,
 Question A geyser heats water flowing at the rate of 3.0 litres per minute from 2 7 C to 77 C. If the geyser operates on a gas burner, what is the rate of consumption of the fuel if its heat of combustion
Question A geyser heats water flowing at the rate of 3.0 litres per minute from 2 7 C to 77 C. If the geyser operates on a gas burner, what is the rate of consumption of the fuel if its heat of combustion
Speed Distribution at CONSTANT Temperature is given by the Maxwell Boltzmann Speed Distribution
 Temperature ~ Average KE of each particle Particles have different speeds Gas Particles are in constant RANDOM motion Average KE of each particle is: 3/2 kt Pressure is due to momentum transfer Speed Distribution
Temperature ~ Average KE of each particle Particles have different speeds Gas Particles are in constant RANDOM motion Average KE of each particle is: 3/2 kt Pressure is due to momentum transfer Speed Distribution
CH 15. Zeroth and First Law of Thermodynamics
 CH 15 Zeroth and First Law of Thermodynamics THERMODYNAMICS Thermodynamics Branch of Physics that is built upon the fundamental laws that heat and work obey. Central Heating Objectives: After finishing
CH 15 Zeroth and First Law of Thermodynamics THERMODYNAMICS Thermodynamics Branch of Physics that is built upon the fundamental laws that heat and work obey. Central Heating Objectives: After finishing
First Law of Thermodynamics Second Law of Thermodynamics Mechanical Equivalent of Heat Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics Thermal Expansion of Solids
 Slide 1 / 66 1 What is the name of the following statement: "When two systems are in thermal equilibrium with a third system, then they are in thermal equilibrium with each other"? A B C D E First Law
Slide 1 / 66 1 What is the name of the following statement: "When two systems are in thermal equilibrium with a third system, then they are in thermal equilibrium with each other"? A B C D E First Law
Thermodynamics: The Laws
 Thermodynamics: The Laws Resources: Serway The Laws of Thermodynamics: 12 AP Physics B Videos Physics B Lesson 29: Laws of Thermodynamics Thermodynamics Thermodynamics is the study of heat and thermal
Thermodynamics: The Laws Resources: Serway The Laws of Thermodynamics: 12 AP Physics B Videos Physics B Lesson 29: Laws of Thermodynamics Thermodynamics Thermodynamics is the study of heat and thermal
THERMODYNAMICS. Zeroth law of thermodynamics. Isotherm
 12 THERMODYNAMICS Zeroth law of thermodynamics Two systems separately in thermal equilibrium with a third system are in thermal equilibrium with each other. Isotherm It is the graph connecting pressure
12 THERMODYNAMICS Zeroth law of thermodynamics Two systems separately in thermal equilibrium with a third system are in thermal equilibrium with each other. Isotherm It is the graph connecting pressure
Chapter 19. Heat Engines
 Chapter 19 Heat Engines Thermo Processes Eint = Q+ W Adiabatic No heat exchanged Q = 0 and E int = W Isobaric Constant pressure W = P (V f V i ) and E int = Q + W Isochoric Constant Volume W = 0 and E
Chapter 19 Heat Engines Thermo Processes Eint = Q+ W Adiabatic No heat exchanged Q = 0 and E int = W Isobaric Constant pressure W = P (V f V i ) and E int = Q + W Isochoric Constant Volume W = 0 and E
11/22/11. If you add some heat to a substance, is it possible for the temperature of the substance to remain unchanged?
 Physics 101 Tuesday 11/22/11 Class 26" Chapter 17.2, 17.5, 17.6, 18.1, 18.2" Kinetic Theory" Latent Heat" Phase changes" 1 st law of thermodynamics" " Which one is not the assumption in kinetic theory
Physics 101 Tuesday 11/22/11 Class 26" Chapter 17.2, 17.5, 17.6, 18.1, 18.2" Kinetic Theory" Latent Heat" Phase changes" 1 st law of thermodynamics" " Which one is not the assumption in kinetic theory
 第 1 頁, 共 6 頁 Chap20 1. Test Bank, Question 5 Which of the following is NOT a state variable? Work Internal energy Entropy Temperature Pressure 2. Test Bank, Question 18 Let denote the change in entropy
第 1 頁, 共 6 頁 Chap20 1. Test Bank, Question 5 Which of the following is NOT a state variable? Work Internal energy Entropy Temperature Pressure 2. Test Bank, Question 18 Let denote the change in entropy
The first law of thermodynamics. U = internal energy. Q = amount of heat energy transfer
 Thermodynamics Investigation of the energy transfer by heat and work and how natural systems behave (Q) Heat transfer of energy due to temp differences. (W) Work transfer of energy through mechanical means.
Thermodynamics Investigation of the energy transfer by heat and work and how natural systems behave (Q) Heat transfer of energy due to temp differences. (W) Work transfer of energy through mechanical means.
Downloaded from
 Chapter 12 (Thermodynamics) Multiple Choice Questions Single Correct Answer Type Q1. An ideal gas undergoes four different processes from the same initial state (figure). Four processes are adiabatic,
Chapter 12 (Thermodynamics) Multiple Choice Questions Single Correct Answer Type Q1. An ideal gas undergoes four different processes from the same initial state (figure). Four processes are adiabatic,
CHAPTER - 12 THERMODYNAMICS
 CHAPER - HERMODYNAMICS ONE MARK QUESIONS. What is hermodynamics?. Mention the Macroscopic variables to specify the thermodynamics. 3. How does thermodynamics differ from Mechanics? 4. What is thermodynamic
CHAPER - HERMODYNAMICS ONE MARK QUESIONS. What is hermodynamics?. Mention the Macroscopic variables to specify the thermodynamics. 3. How does thermodynamics differ from Mechanics? 4. What is thermodynamic
Version 001 HW 15 Thermodynamics C&J sizemore (21301jtsizemore) 1
 Version 001 HW 15 Thermodynamics C&J sizemore 21301jtsizemore 1 This print-out should have 38 questions. Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page find all choices before answering.
Version 001 HW 15 Thermodynamics C&J sizemore 21301jtsizemore 1 This print-out should have 38 questions. Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page find all choices before answering.
S15--AP Phys Q4--Heat-Thermo Ch13_14_15 PRACTICE
 Name: Class: Date: S5--AP Phys Q4--Heat-Thermo Ch3_4_5 PRACTICE Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.. Which of the following is a thermodynamic
Name: Class: Date: S5--AP Phys Q4--Heat-Thermo Ch3_4_5 PRACTICE Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.. Which of the following is a thermodynamic
08/26/09 PHYSICS 223 Exam-2 NAME Please write down your name also on the back side of this exam
 08/6/09 PHYSICS 3 Exam- NAME Please write down your name also on the back side of this exam 1. The figure shows a container-a holding an ideal gas at pressure 3.0 x 10 5 N/m and a temperature of 300K.
08/6/09 PHYSICS 3 Exam- NAME Please write down your name also on the back side of this exam 1. The figure shows a container-a holding an ideal gas at pressure 3.0 x 10 5 N/m and a temperature of 300K.
NOTE: Only CHANGE in internal energy matters
 The First Law of Thermodynamics The First Law of Thermodynamics is a special case of the Law of Conservation of Energy It takes into account changes in internal energy and energy transfers by heat and
The First Law of Thermodynamics The First Law of Thermodynamics is a special case of the Law of Conservation of Energy It takes into account changes in internal energy and energy transfers by heat and
2/18/2019. Ideal-Gas Processes. Thermodynamics systems. Thermodynamics systems
 Thermodynamics systems A thermodynamic system is any collection of objects that may exchange energy with its surroundings. The popcorn in the pot is a thermodynamic system. In the thermodynamic process
Thermodynamics systems A thermodynamic system is any collection of objects that may exchange energy with its surroundings. The popcorn in the pot is a thermodynamic system. In the thermodynamic process
Thermodynamics systems
 Thermodynamics systems A thermodynamic system is any collection of objects that may exchange energy with its surroundings. The popcorn in the pot is a thermodynamic system. In the thermodynamic process
Thermodynamics systems A thermodynamic system is any collection of objects that may exchange energy with its surroundings. The popcorn in the pot is a thermodynamic system. In the thermodynamic process
Temperature Thermal Expansion Ideal Gas Law Kinetic Theory Heat Heat Transfer Phase Changes Specific Heat Calorimetry Heat Engines
 Temperature Thermal Expansion Ideal Gas Law Kinetic Theory Heat Heat Transfer Phase Changes Specific Heat Calorimetry Heat Engines Zeroeth Law Two systems individually in thermal equilibrium with a third
Temperature Thermal Expansion Ideal Gas Law Kinetic Theory Heat Heat Transfer Phase Changes Specific Heat Calorimetry Heat Engines Zeroeth Law Two systems individually in thermal equilibrium with a third
Chapter 19. Heat Engines
 Chapter 19 Heat Engines QuickCheck 19.11 The efficiency of this Carnot heat engine is A. Less than 0.5. B. 0.5. C. Between 0.5 and 1.0. D. 2.0. E. Can t say without knowing Q H. 2013 Pearson Education,
Chapter 19 Heat Engines QuickCheck 19.11 The efficiency of this Carnot heat engine is A. Less than 0.5. B. 0.5. C. Between 0.5 and 1.0. D. 2.0. E. Can t say without knowing Q H. 2013 Pearson Education,
a. 4.2x10-4 m 3 b. 5.5x10-4 m 3 c. 1.2x10-4 m 3 d. 1.4x10-5 m 3 e. 8.8x10-5 m 3
 The following two problems refer to this situation: #1 A cylindrical chamber containing an ideal diatomic gas is sealed by a movable piston with cross-sectional area A = 0.0015 m 2. The volume of the chamber
The following two problems refer to this situation: #1 A cylindrical chamber containing an ideal diatomic gas is sealed by a movable piston with cross-sectional area A = 0.0015 m 2. The volume of the chamber
Physics 111. Thursday, Dec. 9, 3-5pm and 7-9pm. Announcements. Thursday, December 9, 2004
 ics day, ember 9, 2004 Ch 18: diagrams isobaric process isochoric process isothermal process adiabatic process 2nd Law of Thermodynamics Class Reviews/Evaluations For the rest of the semester day,. 9,
ics day, ember 9, 2004 Ch 18: diagrams isobaric process isochoric process isothermal process adiabatic process 2nd Law of Thermodynamics Class Reviews/Evaluations For the rest of the semester day,. 9,
AP Physics Thermodynamics Wrapup
 AP Physics hermodynamics Wrapup Here are your basic equations for thermodynamics. here s a bunch of them. l l 0 Q ml Q his is the equation for the change in length of an object as a function of temperature.
AP Physics hermodynamics Wrapup Here are your basic equations for thermodynamics. here s a bunch of them. l l 0 Q ml Q his is the equation for the change in length of an object as a function of temperature.
Physics 4C Chapter 19: The Kinetic Theory of Gases
 Physics 4C Chapter 19: The Kinetic Theory of Gases Whether you think you can or think you can t, you re usually right. Henry Ford The only thing in life that is achieved without effort is failure. Source
Physics 4C Chapter 19: The Kinetic Theory of Gases Whether you think you can or think you can t, you re usually right. Henry Ford The only thing in life that is achieved without effort is failure. Source
PHY 206 SPRING Problem #1 NAME: SIGNATURE: UM ID: Problem #2. Problem #3. Total. Prof. Massimiliano Galeazzi. Midterm #2 March 8, 2006
 PHY 06 SPRING 006 Prof. Massimiliano Galeazzi Midterm # March 8, 006 NAME: Problem # SIGNAURE: UM ID: Problem # Problem # otal Some useful relations: st lat of thermodynamic: U Q - W Heat in an isobaric
PHY 06 SPRING 006 Prof. Massimiliano Galeazzi Midterm # March 8, 006 NAME: Problem # SIGNAURE: UM ID: Problem # Problem # otal Some useful relations: st lat of thermodynamic: U Q - W Heat in an isobaric
MCQs THERMODYNAMICS. Physics Without Fear.
 MCQs THERMODYNAMICS Physics Without Fear Thermodynamics: At a glance Zeroth law of thermodynamics: Two systems A and B each in thermal equilibrium with a third system C are in thermal equilibrium with
MCQs THERMODYNAMICS Physics Without Fear Thermodynamics: At a glance Zeroth law of thermodynamics: Two systems A and B each in thermal equilibrium with a third system C are in thermal equilibrium with
Part I: Basic Concepts of Thermodynamics
 Part I: Basic Concepts of Thermodynamics Lecture 3: Heat and Work Kinetic Theory of Gases Ideal Gases 3-1 HEAT AND WORK Here we look in some detail at how heat and work are exchanged between a system and
Part I: Basic Concepts of Thermodynamics Lecture 3: Heat and Work Kinetic Theory of Gases Ideal Gases 3-1 HEAT AND WORK Here we look in some detail at how heat and work are exchanged between a system and
Entropy & the Second Law of Thermodynamics
 PHYS102 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 20 Entropy & the Second Law of Thermodynamics Entropy gases Entropy solids & liquids Heat engines Refrigerators Second law of thermodynamics 1. The efficiency of
PHYS102 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 20 Entropy & the Second Law of Thermodynamics Entropy gases Entropy solids & liquids Heat engines Refrigerators Second law of thermodynamics 1. The efficiency of
19-9 Adiabatic Expansion of an Ideal Gas
 19-9 Adiabatic Expansion of an Ideal Gas Learning Objectives 19.44 On a p-v diagram, sketch an adiabatic expansion (or contraction) and identify that there is no heat exchange Q with the environment. 19.45
19-9 Adiabatic Expansion of an Ideal Gas Learning Objectives 19.44 On a p-v diagram, sketch an adiabatic expansion (or contraction) and identify that there is no heat exchange Q with the environment. 19.45
Physics 5D PRACTICE FINAL EXAM Fall 2013
 Print your name: Physics 5D PRACTICE FINAL EXAM Fall 2013 Real Exam is Wednesday December 11 Thimann Lecture 3 4:00-7:00 pm Closed book exam two 8.5x11 sheets of notes ok Note: Avogadro s number N A =
Print your name: Physics 5D PRACTICE FINAL EXAM Fall 2013 Real Exam is Wednesday December 11 Thimann Lecture 3 4:00-7:00 pm Closed book exam two 8.5x11 sheets of notes ok Note: Avogadro s number N A =
Chapter 12. The Laws of Thermodynamics
 Chapter 12 The Laws of Thermodynamics First Law of Thermodynamics The First Law of Thermodynamics tells us that the internal energy of a system can be increased by Adding energy to the system Doing work
Chapter 12 The Laws of Thermodynamics First Law of Thermodynamics The First Law of Thermodynamics tells us that the internal energy of a system can be increased by Adding energy to the system Doing work
Unified Quiz: Thermodynamics
 Unified Quiz: Thermodynamics October 14, 2005 Calculators allowed. No books or notes allowed. A list of equations is provided. Put your ID number on each page of the exam. Read all questions carefully.
Unified Quiz: Thermodynamics October 14, 2005 Calculators allowed. No books or notes allowed. A list of equations is provided. Put your ID number on each page of the exam. Read all questions carefully.
First Law of Thermodynamics
 First Law of Thermodynamics E int = Q + W other state variables E int is a state variable, so only depends on condition (P, V, T, ) of system. Therefore, E int only depends on initial and final states
First Law of Thermodynamics E int = Q + W other state variables E int is a state variable, so only depends on condition (P, V, T, ) of system. Therefore, E int only depends on initial and final states
The laws of Thermodynamics. Work in thermodynamic processes
 The laws of Thermodynamics ork in thermodynamic processes The work done on a gas in a cylinder is directly proportional to the force and the displacement. = F y = PA y It can be also expressed in terms
The laws of Thermodynamics ork in thermodynamic processes The work done on a gas in a cylinder is directly proportional to the force and the displacement. = F y = PA y It can be also expressed in terms
Physics 115. Specific heats revisited Entropy. General Physics II. Session 13
 Physics 115 General Physics II Session 13 Specific heats revisited Entropy R. J. Wilkes Email: phy115a@u.washington.edu Home page: http://courses.washington.edu/phy115a/ 4/22/14 Physics 115 1 Lecture Schedule
Physics 115 General Physics II Session 13 Specific heats revisited Entropy R. J. Wilkes Email: phy115a@u.washington.edu Home page: http://courses.washington.edu/phy115a/ 4/22/14 Physics 115 1 Lecture Schedule
Irreversible Processes
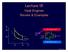 Lecture 15 Heat Engines Review & Examples p p b b Hot reservoir at T h p a a c adiabats Heat leak Heat pump Q h Q c W d V 1 V 2 V Cold reservoir at T c Lecture 15, p 1 Irreversible Processes Entropy-increasing
Lecture 15 Heat Engines Review & Examples p p b b Hot reservoir at T h p a a c adiabats Heat leak Heat pump Q h Q c W d V 1 V 2 V Cold reservoir at T c Lecture 15, p 1 Irreversible Processes Entropy-increasing
Classification following properties of the system in Intensive and Extensive
 Unit I Classification following properties of the system in Intensive and Extensive Extensive : mass, weight, volume, potential energy, Kinetic energy, Internal energy, entropy, exergy, energy, magnetization
Unit I Classification following properties of the system in Intensive and Extensive Extensive : mass, weight, volume, potential energy, Kinetic energy, Internal energy, entropy, exergy, energy, magnetization
Ideal Gases. 247 minutes. 205 marks. theonlinephysicstutor.com. facebook.com/theonlinephysicstutor. Name: Class: Date: Time: Marks: Comments:
 Ideal Gases Name: Class: Date: Time: 247 minutes Marks: 205 marks Comments: Page 1 of 48 1 Which one of the graphs below shows the relationship between the internal energy of an ideal gas (y-axis) and
Ideal Gases Name: Class: Date: Time: 247 minutes Marks: 205 marks Comments: Page 1 of 48 1 Which one of the graphs below shows the relationship between the internal energy of an ideal gas (y-axis) and
UNIVERSITY COLLEGE LONDON. University of London EXAMINATION FOR INTERNAL STUDENTS. For The Following Qualifications:-
 UNIVERSITY COLLEGE LONDON University of London EXAMINATION FOR INTERNAL STUDENTS For The Following Qualifications:- B.Sc. M.Sci. Physics 1B28: Thermal Physics COURSE CODE : PHYSIB28 UNIT VALUE : 0.50 DATE
UNIVERSITY COLLEGE LONDON University of London EXAMINATION FOR INTERNAL STUDENTS For The Following Qualifications:- B.Sc. M.Sci. Physics 1B28: Thermal Physics COURSE CODE : PHYSIB28 UNIT VALUE : 0.50 DATE
Inconsistency of Carnot Principle and Second Law of Thermodynamics. Charanjeet Singh Bansrao. Abstract
 Inconsistency of Carnot Principle and Second Law of Thermodynamics Charanjeet Singh Bansrao bansraos@yahoo.co.in Abstract We know that internal energy of an ideal gas is a state function and it solely
Inconsistency of Carnot Principle and Second Law of Thermodynamics Charanjeet Singh Bansrao bansraos@yahoo.co.in Abstract We know that internal energy of an ideal gas is a state function and it solely
FINAL EXAM. ME 200 Thermodynamics I, Spring 2013 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW:
 ME 200 Thermodynamics I, Spring 2013 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: Div. 5 7:30 am Div. 2 10:30 am Div. 4 12:30 am Prof. Naik Prof. Braun Prof. Bae Div. 3 2:30 pm Div. 1 4:30 pm Div. 6 4:30 pm Prof. Chen Prof.
ME 200 Thermodynamics I, Spring 2013 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: Div. 5 7:30 am Div. 2 10:30 am Div. 4 12:30 am Prof. Naik Prof. Braun Prof. Bae Div. 3 2:30 pm Div. 1 4:30 pm Div. 6 4:30 pm Prof. Chen Prof.
ADIABATIC PROCESS Q = 0
 THE KINETIC THEORY OF GASES Mono-atomic Fig.1 1 3 Average kinetic energy of a single particle Fig.2 INTERNAL ENERGY U and EQUATION OF STATE For a mono-atomic gas, we will assume that the total energy
THE KINETIC THEORY OF GASES Mono-atomic Fig.1 1 3 Average kinetic energy of a single particle Fig.2 INTERNAL ENERGY U and EQUATION OF STATE For a mono-atomic gas, we will assume that the total energy
HEAT- I Part - A C D A B. Te m p. Heat input
 e m p HE- I Part -. solid material is supplied with heat at a constant rate. he temperature of the material is changing with heat input as shown in the graph. Study the graph carefully and answer the following
e m p HE- I Part -. solid material is supplied with heat at a constant rate. he temperature of the material is changing with heat input as shown in the graph. Study the graph carefully and answer the following
Phys 22: Homework 10 Solutions W A = 5W B Q IN QIN B QOUT A = 2Q OUT 2 QOUT B QIN B A = 3Q IN = QIN B QOUT. e A = W A e B W B A Q IN.
 HRK 26.7 Summarizing the information given in the question One way of doing this is as follows. W A = 5W Q IN A = Q IN Q OU A = 2Q OU Use e A = W A Q IN = QIN A QOU Q IN A A A and e = W Q IN = QIN QOU
HRK 26.7 Summarizing the information given in the question One way of doing this is as follows. W A = 5W Q IN A = Q IN Q OU A = 2Q OU Use e A = W A Q IN = QIN A QOU Q IN A A A and e = W Q IN = QIN QOU
PHYS102 Previous Exam Problems. Temperature, Heat & The First Law of Thermodynamics
 PHYS102 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 18 Temperature, Heat & The First Law of Thermodynamics Equilibrium & temperature scales Thermal expansion Exchange of heat First law of thermodynamics Heat conduction
PHYS102 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 18 Temperature, Heat & The First Law of Thermodynamics Equilibrium & temperature scales Thermal expansion Exchange of heat First law of thermodynamics Heat conduction
Thermal Physics. Topics to be covered. Slide 2 / 105. Slide 1 / 105. Slide 3 / 105. Slide 4 / 105. Slide 5 / 105. Slide 6 / 105.
 Slide 1 / 105 Slide 2 / 105 Topics to be covered Thermal Physics Temperature and Thermal quilibrium Gas Laws Internal nergy Heat Work Laws of Thermodynamics Heat ngines Slide 3 / 105 Thermodynamics System
Slide 1 / 105 Slide 2 / 105 Topics to be covered Thermal Physics Temperature and Thermal quilibrium Gas Laws Internal nergy Heat Work Laws of Thermodynamics Heat ngines Slide 3 / 105 Thermodynamics System
Renewable Energy. Theory: The Ideal Gas Law The equation of state for an ideal gas is written: PV = nrt
 Lab 3 Gas Laws and Heat Engines Fall 2010 Introduction/Purpose: In this exercise you will test some of the aspects of the ideal gas law under conditions of constant pressure, constant temperature, and
Lab 3 Gas Laws and Heat Engines Fall 2010 Introduction/Purpose: In this exercise you will test some of the aspects of the ideal gas law under conditions of constant pressure, constant temperature, and
THERMODYNAMICS b) If the temperatures of two bodies are equal then they are said to be in thermal equilibrium.
 THERMODYNAMICS Important Points:. Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics: a) This law gives the concept of temperature. b) If the temperatures of two bodies are equal then they are said to be in thermal equilibrium.
THERMODYNAMICS Important Points:. Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics: a) This law gives the concept of temperature. b) If the temperatures of two bodies are equal then they are said to be in thermal equilibrium.
Simpo PDF Merge and Split Unregistered Version -
 74. The rate of heat flow by conduction through a slab does NOT depend upon the: A. temperature difference between opposite faces of the slab B. thermal conductivity of the slab C. slab thickness D. cross-sectional
74. The rate of heat flow by conduction through a slab does NOT depend upon the: A. temperature difference between opposite faces of the slab B. thermal conductivity of the slab C. slab thickness D. cross-sectional
Irreversible Processes
 Lecture 15 Heat Engines Review & Examples p p b b Hot reservoir at T h p a a c adiabats Heat leak Heat pump Q h Q c W d V 1 V 2 V Cold reservoir at T c Lecture 15, p 1 Irreversible Processes Entropy-increasing
Lecture 15 Heat Engines Review & Examples p p b b Hot reservoir at T h p a a c adiabats Heat leak Heat pump Q h Q c W d V 1 V 2 V Cold reservoir at T c Lecture 15, p 1 Irreversible Processes Entropy-increasing
Three special ideal gas processes: one of, W or Q is 0
 Lecture 12 1st Law for isochoric, isothermal and adiabatic process Temperature change: specific heat Phase change: heat of transformation Calorimetry: calculating heat exchanges Specific heats of gases
Lecture 12 1st Law for isochoric, isothermal and adiabatic process Temperature change: specific heat Phase change: heat of transformation Calorimetry: calculating heat exchanges Specific heats of gases
12.1 Work in Thermodynamic Processes
 Name APPH7_Notes3key Page 1 of 6 AP Physics Date Notes: Thermodynamics 12.1 Work in Thermodynamic Processes First Law of Thermodynamics The First Law of Thermodynamics tells us that the internal energy
Name APPH7_Notes3key Page 1 of 6 AP Physics Date Notes: Thermodynamics 12.1 Work in Thermodynamic Processes First Law of Thermodynamics The First Law of Thermodynamics tells us that the internal energy
Materials at Equilibrium. G. Ceder Fall 2001 COURSE 3.20: THERMODYNAMICS OF MATERIALS. FINAL EXAM, Dec 18, 2001
 NAME: COURSE 3.20: THERMODYNAMICS OF MATERIALS FINAL EXAM, Dec 18, 2001 PROBLEM 1 (15 POINTS) PROBLEM 2 (15 POINTS) PROBLEM 3 (10 POINTS) PROBLEM 4 (20 POINTS) PROBLEM 5 (14 POINTS) PROBLEM 6 (14 POINTS)
NAME: COURSE 3.20: THERMODYNAMICS OF MATERIALS FINAL EXAM, Dec 18, 2001 PROBLEM 1 (15 POINTS) PROBLEM 2 (15 POINTS) PROBLEM 3 (10 POINTS) PROBLEM 4 (20 POINTS) PROBLEM 5 (14 POINTS) PROBLEM 6 (14 POINTS)
Topic 3 &10 Review Thermodynamics
 Name: Date: Topic 3 &10 Review Thermodynamics 1. The kelvin temperature of an object is a measure of A. the total energy of the molecules of the object. B. the total kinetic energy of the molecules of
Name: Date: Topic 3 &10 Review Thermodynamics 1. The kelvin temperature of an object is a measure of A. the total energy of the molecules of the object. B. the total kinetic energy of the molecules of
Heat Engines and the Second Law of Thermodynamics
 Heat Engines and the Second Law of hermodynamics here are three equivalent forms of the second law of thermodynamics; will state all three, discuss: I. (Kelvin-Planck) It is impossible to construct an
Heat Engines and the Second Law of hermodynamics here are three equivalent forms of the second law of thermodynamics; will state all three, discuss: I. (Kelvin-Planck) It is impossible to construct an
Physics 231. Topic 14: Laws of Thermodynamics. Alex Brown Dec MSU Physics 231 Fall
 Physics 231 Topic 14: Laws of Thermodynamics Alex Brown Dec 7-11 2015 MSU Physics 231 Fall 2015 1 8 th 10 pm correction for 3 rd exam 9 th 10 pm attitude survey (1% for participation) 10 th 10 pm concept
Physics 231 Topic 14: Laws of Thermodynamics Alex Brown Dec 7-11 2015 MSU Physics 231 Fall 2015 1 8 th 10 pm correction for 3 rd exam 9 th 10 pm attitude survey (1% for participation) 10 th 10 pm concept
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON PHYS1013W1 SEMESTER 2 EXAMINATION 2014-2015 ENERGY AND MATTER Duration: 120 MINS (2 hours) This paper contains 8 questions. Answers to Section A and Section B must be in separate
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON PHYS1013W1 SEMESTER 2 EXAMINATION 2014-2015 ENERGY AND MATTER Duration: 120 MINS (2 hours) This paper contains 8 questions. Answers to Section A and Section B must be in separate
THERMODYNAMICS. Chapter Twelve MCQ I
 Chapter welve HERMODYNAMICS MCQ I. An ideal gas undergoes four different processes from the same initial state (Fig..). Four processes are adiabatic, isothermal, isobaric and isochoric. Out of,, and 4
Chapter welve HERMODYNAMICS MCQ I. An ideal gas undergoes four different processes from the same initial state (Fig..). Four processes are adiabatic, isothermal, isobaric and isochoric. Out of,, and 4
Handout 12: Thermodynamics. Zeroth law of thermodynamics
 1 Handout 12: Thermodynamics Zeroth law of thermodynamics When two objects with different temperature are brought into contact, heat flows from the hotter body to a cooler one Heat flows until the temperatures
1 Handout 12: Thermodynamics Zeroth law of thermodynamics When two objects with different temperature are brought into contact, heat flows from the hotter body to a cooler one Heat flows until the temperatures
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 1
 PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 1 Q1. In an experiment to measure the temperature of the flame of a Bunsen burner, a lump of copper of mass 0.12 kg is heated in the flame for several minutes. The copper is then
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 1 Q1. In an experiment to measure the temperature of the flame of a Bunsen burner, a lump of copper of mass 0.12 kg is heated in the flame for several minutes. The copper is then
C e. Negative. In a clockwise cycle, the work done on the gas is negative. Or for the cycle Qnet = +600 J and U = 0 so W = Q = 600 J
 AP Physics Free Response Practice Thermodynamics ANSWERS 1983B4 Since T is constant, pbv B = p 0 V 0 and V B = 2V 0 gives p B = ½ p0 U = Q + W, since AB is isothermal, U = 0 and W = Q = 1000 J c. The entropy
AP Physics Free Response Practice Thermodynamics ANSWERS 1983B4 Since T is constant, pbv B = p 0 V 0 and V B = 2V 0 gives p B = ½ p0 U = Q + W, since AB is isothermal, U = 0 and W = Q = 1000 J c. The entropy
First Name: Last Name: Section: 1 December 20, 2004 Physics 201 FINAL EXAM
 First Name: Last Name: Section: 1 December 20, 2004 Physics 201 FINAL EXAM Print your name and section clearly on all nine pages. (If you do not know your section number, write your TA s name.) Show all
First Name: Last Name: Section: 1 December 20, 2004 Physics 201 FINAL EXAM Print your name and section clearly on all nine pages. (If you do not know your section number, write your TA s name.) Show all
Lecture 25 Goals: Chapter 18 Understand the molecular basis for pressure and the idealgas
 Lecture 5 Goals: Chapter 18 Understand the molecular basis for pressure and the idealgas law. redict the molar specific heats of gases and solids. Understand how heat is transferred via molecular collisions
Lecture 5 Goals: Chapter 18 Understand the molecular basis for pressure and the idealgas law. redict the molar specific heats of gases and solids. Understand how heat is transferred via molecular collisions
Chapter 17. Work, Heat, and the First Law of Thermodynamics Topics: Chapter Goal: Conservation of Energy Work in Ideal-Gas Processes
 Chapter 17. Work, Heat, and the First Law of Thermodynamics This false-color thermal image (an infrared photo) shows where heat energy is escaping from a house. In this chapter we investigate the connection
Chapter 17. Work, Heat, and the First Law of Thermodynamics This false-color thermal image (an infrared photo) shows where heat energy is escaping from a house. In this chapter we investigate the connection
Niraj Sir THERMODYNAMICS
 THERMODYNAMICS Thermal Equilibrium:- Two systems are said to be in thermal equilibrium with each other if they have the same temperature. Thermo dynamical system:- An assembly of large numbers of particles
THERMODYNAMICS Thermal Equilibrium:- Two systems are said to be in thermal equilibrium with each other if they have the same temperature. Thermo dynamical system:- An assembly of large numbers of particles
Summarizing, Key Point: An irreversible process is either spontaneous (ΔS universe > 0) or does not occur (ΔS universe < 0)
 Summarizing, Key Point: An irreversible process is either spontaneous (ΔS universe > 0) or does not occur (ΔS universe < 0) Key Point: ΔS universe allows us to distinguish between reversible and irreversible
Summarizing, Key Point: An irreversible process is either spontaneous (ΔS universe > 0) or does not occur (ΔS universe < 0) Key Point: ΔS universe allows us to distinguish between reversible and irreversible
Physics 2 week 7. Chapter 3 The Kinetic Theory of Gases
 Physics week 7 Chapter 3 The Kinetic Theory of Gases 3.1. Ideal Gases 3.1.1. Experimental Laws and the Equation of State 3.1.. Molecular Model of an Ideal Gas 3.. Mean Free Path 3.3. The Boltzmann Distribution
Physics week 7 Chapter 3 The Kinetic Theory of Gases 3.1. Ideal Gases 3.1.1. Experimental Laws and the Equation of State 3.1.. Molecular Model of an Ideal Gas 3.. Mean Free Path 3.3. The Boltzmann Distribution
Unified Thermodynamics Quiz 1
 Unified Thermodynamics Quiz 1 November 22, 2006 Calculators allowed. No books or notes allowed. A list of equations is provided. Put your ID number on each page of the exam. Read all questions carefully.
Unified Thermodynamics Quiz 1 November 22, 2006 Calculators allowed. No books or notes allowed. A list of equations is provided. Put your ID number on each page of the exam. Read all questions carefully.
(f ) From the graph, obtain the height of the tube given the mass of the dart is 20 grams and the constant force applied in the tube is 2 newtons.
 1. Bowling Ball A is dropped from a point halfway up a cliff. A second identical bowling ball, B, is dropped simultaneously from the top of the cliff. Comparing the bowling balls at the instant they reach
1. Bowling Ball A is dropped from a point halfway up a cliff. A second identical bowling ball, B, is dropped simultaneously from the top of the cliff. Comparing the bowling balls at the instant they reach
S6. (a) State what is meant by an ideal gas...
 IB PHYSICS Name: DEVIL PHYSICS Period: Date: BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS TSOKOS CHAPTER 3 TEST REVIEW S1. Thermal energy is transferred through the glass windows of a house mainly by A. conduction. B. radiation.
IB PHYSICS Name: DEVIL PHYSICS Period: Date: BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS TSOKOS CHAPTER 3 TEST REVIEW S1. Thermal energy is transferred through the glass windows of a house mainly by A. conduction. B. radiation.
Regents Chemistry: Thermodynamics and Gas Laws Test [Practice]
![Regents Chemistry: Thermodynamics and Gas Laws Test [Practice] Regents Chemistry: Thermodynamics and Gas Laws Test [Practice]](/thumbs/80/81934728.jpg) Name Date Regents Chemistry: Thermodynamics and Gas Laws Test [Practice] 1. In a laboratory where the air temperature is 22 C, a steel cylinder at 100. C is submerged in a sample of water at 40. C. In
Name Date Regents Chemistry: Thermodynamics and Gas Laws Test [Practice] 1. In a laboratory where the air temperature is 22 C, a steel cylinder at 100. C is submerged in a sample of water at 40. C. In
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON PHYS1013W1 SEMESTER 2 EXAMINATION 2014-2015 ENERGY AND MATTER Duration: 120 MINS (2 hours) This paper contains 8 questions. Answers to Section A and Section B must be in separate
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON PHYS1013W1 SEMESTER 2 EXAMINATION 2014-2015 ENERGY AND MATTER Duration: 120 MINS (2 hours) This paper contains 8 questions. Answers to Section A and Section B must be in separate
Chapter 1: FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS OF THERMODYNAMICS AND VARIOUS THERMODYMIC PROCESSES
 Chapter 1: FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS OF THERMODYNAMICS AND VARIOUS THERMODYMIC PROCESSES Thermodynamics is that branch of science which deals with energy transfer A system may be closed, open or isolated system
Chapter 1: FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS OF THERMODYNAMICS AND VARIOUS THERMODYMIC PROCESSES Thermodynamics is that branch of science which deals with energy transfer A system may be closed, open or isolated system
HEAT, WORK, AND THE FIRST LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
 HET, WORK, ND THE FIRST LW OF THERMODYNMICS 8 EXERCISES Section 8. The First Law of Thermodynamics 5. INTERPRET We identify the system as the water in the insulated container. The problem involves calculating
HET, WORK, ND THE FIRST LW OF THERMODYNMICS 8 EXERCISES Section 8. The First Law of Thermodynamics 5. INTERPRET We identify the system as the water in the insulated container. The problem involves calculating
More Thermodynamics. Specific Specific Heats of a Gas Equipartition of Energy Reversible and Irreversible Processes
 More Thermodynamics Specific Specific Heats of a Gas Equipartition of Energy Reversible and Irreversible Processes Carnot Cycle Efficiency of Engines Entropy More Thermodynamics 1 Specific Heat of Gases
More Thermodynamics Specific Specific Heats of a Gas Equipartition of Energy Reversible and Irreversible Processes Carnot Cycle Efficiency of Engines Entropy More Thermodynamics 1 Specific Heat of Gases
Handout 12: Thermodynamics. Zeroth law of thermodynamics
 1 Handout 12: Thermodynamics Zeroth law of thermodynamics When two objects with different temperature are brought into contact, heat flows from the hotter body to a cooler one Heat flows until the temperatures
1 Handout 12: Thermodynamics Zeroth law of thermodynamics When two objects with different temperature are brought into contact, heat flows from the hotter body to a cooler one Heat flows until the temperatures
(Heat capacity c is also called specific heat) this means that the heat capacity number c for water is 1 calorie/gram-k.
 Lecture 23: Ideal Gas Law and The First Law of Thermodynamics 1 (REVIEW) Chapter 17: Heat Transfer Origin of the calorie unit A few hundred years ago when people were investigating heat and temperature
Lecture 23: Ideal Gas Law and The First Law of Thermodynamics 1 (REVIEW) Chapter 17: Heat Transfer Origin of the calorie unit A few hundred years ago when people were investigating heat and temperature
