Testing Without Load Cells - Can Opening Shock Be Estimated From Video Data Only?
|
|
|
- Liliana Wilkerson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Testng Wthout Load Cells - Can Openng Shock Be Estmated From deo Data Only? Paper AIAA Gary Peek & Jean Potvn Physcs Department, Sant Lous Unversty, St. Lous MO Contact: peek@ndustrologc.com potvnj@slu.edu Talk presented at the 19 th AIAA Aerodynamc Decelerator Systems Conerence, Wllamburg, A 22-24, 2007
2 Work unded by Natck Solder Center (Natck, MA U.S. Army contract W9124R-06-P-1068
3 Executve Summary The maxmum drag orce generated by an nlatng parachute can be estmated va these two ormulas: Horzontal trajectores 2m Fmax 1 ( t t descent ertcal trajectores (downwards F max ( t 2m t 1 descent + g ( t t Note the dependence on (t t nlaton duraton (obtaned rom vdeo Such estmate wll work wth most parachute and reeng types Works only or slow-descendng parachute-payload systems (.e. descent < 30t/sec Paper shows the large database that was used to check the range o valdty
4 Executve Summary NOT DISCUSSED IN THIS TALK OR PAPER: The maxmum drag orce generated by an nlatng parachute used at nnte-mass condtons (.e. low mass ratos/wnd tunnels,etc., can be estmated va ths ormula: F U max ck U 20 ck (Horzontal trajectores ρ ( SC 2( t D sd t 3 / 2 For both low- and hgh porosty hemsphercals - unreeed More detals can be ound n: Unversalty Consderatons or Graphng Parachute Openng Shock Factor ersus Mass Rato "; JOA, 44, No. 2, pp , Paper-copy avalable on request.
5 Why s ths a bg deal? The value o the maxmum drag orce s a standard measurement durng the testng phase o most parachute systems (nvolvng load cells and/or accelerometers But what about ndng out durng servce use, say ater unusual deployments and/or unusually hard openngs? Typcally such parachutes are not equpped wth orce-measurng devces. The method dscussed here proposes an estmate, based on general deployment and parachute characterstcs AND on nlaton duraton, whch obtaned rom the vdeo coverage o the openng
6 Man ngredent the Momentum-Impulse Theorem Integraton o Newton s 2 nd law o moton m m = F ( t dt + W cos θ ( t dt D Momentum change Parachute drag Gravtatonal o parachute-payload mpulse mpulse = descent end o nlaton = descent the begnnng o nlaton lne stretch θ(t = lght angle The MI-theorem has been used extensvely to study the maxmum orce on many types o systems. See reerences [1 5] n paper. Paper copes o res. [1] and [4, 5] are avalable here!
7 Man ngredent the Momentum-Impulse Theorem Reormulate n terms o m m = F ( t dt + W cos θ ( t dt D ( m = F + max ( t t I F m W cos θ ( t dt Inlaton duraton Drag ntegral; gauges the shape o the drag vs. tme curve I F = F F max D ( t ( t dt t
8 Man ngredent the Momentum-Impulse Theorem Focus on ether vertcal trajectores (θ(t = 0 and on horzontal downwards trajectores (θ(t = 90 Assume ~ descent (.e. steady-state descent under ully nlated canopy Assume drag ntegral I F ~ 1/2 Extractng rom the MI-theorem under these condtons yelds the man results o ths paper Horzontal ertcal Obtaned rom vdeo coverage 2 = 1/I F F max 2m Fmax 1 ( t t ( t 2m t 1 Froude term descent descent g ( t + t
9 Whch parachute-payload system satsy the condton ~ descent? One can get ~ descent the drag orce s large enough and lasts long enough to generate the requred deceleraton In partcular ths constrant apples to hgh mass rato (R m systems! R m ρ hgh ( SC Why? Consder Netwon s 2 nd law agan (horzontal trajectory and reormulate n terms o the mass rato ma ( t = We get: δ 1 2 ρ hgh ( S ( t C ( SC D ( t 2 D 1/ 2 sd ( t m D ( t 2 ( t a( t = 3 / 2 sd 1 2 R m ( S ( t C ( SC D ( t D sd
10 δ ( SC D ( t 2 1/ 2 sd ( t a( t = 1 2 R m ( S ( t C ( SC D ( t D sd Ths means that the hgher the mass rato R m, the more deceleraton; hgh-r m typcally means R m > 0.1 Note that hgh-mass rato also means slow-descendng R m = 2 g ( SC D 1/ 2 sd ( hgh 2 descent So R m ~ 1.7 means descent ~ 25 t/sec or US. Army T-10, or R m ~ 6.0 means descent ~ 25 t/sec or US Army G-11 (one canopy In what ollows we consder descent < 30 t/sec as a necessary constrant or the estmate to work
11 Whch parachute-payload system satsy the condton I F ~ ½? One can get I F ~ ½ the mass rato s large enough, agan R m > 0.1. Why? The drag ntegral measures the area under the (normalzed drag vs. tme curve Drag ntegral ~ ½ Drag ntegral ~ 1
12 Ds-reeng case (long ater reeed nlaton Drag ntegral ~ ¼. Note: drag ntegral 0 as t ds t ree W/F ds << 1/2
13 When s I F ~ ½? Reerence [1] showed the rst expermental data suggestng ths value whenever R m > 0.1 (or so, on - Slder-reeed paraols - Permanently reeed or un-reeed hemsphercal canopes More expermental data analyzed here show the same trend to be workng also on -rngslottypes - slder-reeed rounds - deep cones - unreeed paraols (not always though; depends on lt Reerence [1] also shows that I F < 1/3 when R m < 0.1, at least or dsk-gap-band types and hemsphercal types Excepton: t seems that I F < 1/3 at both small- and large-r m wth chutes that ds-ree long ater reeed nlaton
14 aldaton Based on a large database (next slde Data must nclude load cell data (to calculate I F and Must also nclude vdeo coverage o each test, n order to obtan the nlaton tme t t (va rame-countng 2m Fmax 1 ( t t descent 2 = 1/I F va standard descent ormula vdeo Load cell F max ( t 2m t 1 descent + g ( t t, smulated or measured
15 Database: 14 canopy-reeng combos & 67 drops total Hemsphercal and sphercal types US Army T-10C (Table 4-1 USAF C-9, unreeed & permanently skrt-reeed (Table 4-2 ½-scale C-9, unreeed & permanently skrt-reeed (Table 4-3 Butler HX-600 (hemsphercal canopy wth slder reeng (Table 4-4 Crucorm, wth and wthout slder-reeng (Table 4-5 US Army 26t rngslot extracton parachute (Table 4-6 Deep-concal types Truncated Cone Decelerator (Table 4-7 Paraol types Unreeed paraols (Table 4-8 BLM Trlobe (Table 4-9 PD Sabre230 (Table 4-10 PDSabre120 (Table 4-11 PD Sabre150 (Table 4-12 PD Stletto150 (Table repeat jumps/drops
16 Results Hard to plot ths data on a sngle graph Data shown n tabular orm
17 US. Army T-10C Table 4-1. US Army T-10C (hemsphercal canopy Canopy specs: 35.0t nomnal dameter. Constructon detals can be ound n reerence [8]. Deployment method: statc lne. Good matches Act ID Drop# Act speed Deploy alttude (eet; MSL W R m Mass rato Estmated (true arspeed at lnestretch; t/sec descent (t/sec / descent I F (Drag ntegral; calculated rom data t -t (sec Traject. type durng nlaton horz Horzontal trajectory Measured vert ertcal trajectory UH-1 Helo Test KIAS ballstc UH-1 Helo Test KIAS ballstc UH-1 Helo Test KIAS ballstc
18 Table 4-4. Butler HX-600 slder-reeed hemsphercal canopy Canopy specs: 27.64t nomnal dameter (low porosty abrc. More constructon detals can be ound n [16]. Slder specs: span = 67n (Sombrero slder - rm dameter. Deployment method: statc lne. Good matches Act ID Drop# Act speed (KIAS Deploy alttude (eet; MSL W R m Mass rato Estmated (true arspeed at lnestretch; t/sec descent (t/sec (C D ~ 0.75 / descent I F (Drag ntegral; calculated rom data t -t (sec Traject. type durng nlaton horz Horzontal trajectory Measured vert ertcal trajectory Beech Kng Ar NW KTSI ballstc Beech Kng Ar NW KTSI ballstc Cessna Super Caravan YPG KTSI ballstc Cessna Super Caravan YPG KTSI ballstc
19 Slder-reeed paraol - note the drop-to-drop varatons n nlaton tme BUT not n I F Table 4-9. US Bureau o Land Management Trlobe slder-reeed, seven cell paraol Wng specs: span = 25.7t & chord = Slder specs: span = 2.08t by 1.83t. Deployment: ater reeall by parachutst (at least 10secs o reeall Reerence [13]. NA = not applcable Good matches Deploy alttude (eet; MSL W R m Mass rato Measured (true arspeed at lne-stretch; t/sec descent (t/sec / descent I F (Drag ntegral; calculated rom data t - t (sec Trajectory type durng nlaton horz Horzontal trajectory Measured vert ertcal trajectory vertcal NA vertcal NA vertcal NA vertcal NA vertcal NA vertcal NA vertcal NA vertcal NA
20 USAF C-9 unreeed (yelds hemsphercal shape Table 4-2. Full-scale USAF C-9 (unreeed and hemsphercally-shaped canopy; Canopy specs: 28.0t nomnal dameter. See reerence [8] or detals. Deployment method: statc lne, rom Cessna Caravan. Good matches Drop# Reeng type Act speed (KIAS Deploy alttude (eet; MSL W R m Mass rato Estmated (true arspeed at lnestretch; t/sec descent (t/sec / descent I F (Drag ntegral; calculated rom data t -t (sec Traj. type durng nl. horz Horzontal trajectory Measured vert ertcal trajectory YPG001 No reeng (80-20 Mea West ballst c YPG004 No reeng ballst c YPG005 No reeng ballst c YPG008 No reeng ballst c
21 USAF C-9 reeed (tght reeng - yelds sphercal shape Table 4-2. Full-scale USAF C-9 (unreeed and hemsphercally-shaped canopy; and permanently reeed and sphercally-shaped canopy Canopy specs: 28.0t nomnal dameter. See reerence [8] or detals. Deployment method: statc lne, rom Cessna Caravan. Good matches YPG011 24%reeng ballst c YPG014 24%reeng ballst c YPG020 24%reeng ballst c YPG024 24%reeng ballst c
22 Hal-scale C-9 unreeed (yelds hemsphercal shape Good to ar matches Table 4-3a. 1/2-scale C-9 canopy (hemsphercal canopy; unreeed Canopy specs: 14.0t nomnal dameter. Constructon detals can be ound n reerence [17] Deployment method: ery wde payload contaner; statc lne; ext rom sde door o Cessna 402 (NW12 and Cessna 411 (all others. Drop# Act speed (KIAS Deploy alttude (eet; MSL W R m Mass rato Estmated (true arspeed at lnestretch; t/sec descent (t/sec / descent I F (Drag ntegral; calculated rom data t -t (sec Traj. type durng nl. horz Horzontal trajectory Measured vert ertcal trajectory NW Mostly horz NW Mostly horz NW Mostly horz NW Mostly horz
23 Hal-scale C-9 reeed (tght reeng - yelds sphercal shape Table 4-3b. 1/2-scale C-9 canopy (permanently skrt-reeed; sphercally-shaped canopy Canopy specs: 14.0t nomnal dameter (unreeed [17]. Deployment method: statc lne, rom Cessna Caravan. NO match! Out o valdty range Drop# Reeng type YPG006 16%reeng YPG009 16%reeng Act speed (KIAS Deploy alttude (eet; MSL W (lbs R m Mass rato Estmated (true arspeed at lne-stretch; t/sec descent (t/sec / descent I F (Drag ntegral; calculated rom data t -t (sec Traj. type dur ng nl. Mos tly hor z. Mos tly hor z. horz Horzontal trajectory Measured Calculate d vert ertcal trajectory YPG012 24%reeng Mos tly hor z YPG015 24%reeng Mos tly hor z YPG018 24%reeng Mos tly hor z
24 Crucorm parachute (3:1 Aspect rato Table 4-5. Crucorm parachutes Full-scale specs: bult rom two 24.84t by- 9.25t rectangular panels (zero-porosty abrc; Hal-scale specs: bult rom two 12.24t-by-4.37t rectangular panels (zero-porosty abrc; Both versons were made o 200 dener nylon abrc (permeablty: 30-45cm. Deployment method: statc lne. Matches good only b/c o error cancellaton (next slde; out o valdty range! Chute ID Act ID Drop# Act speed Deploy alttude W R m Mass rato Estmated (true arspeed at lne-stretch; t/sec descent (t/sec / descent I F (Drag ntegral; calculated rom data t -t (sec Traject. Type durng nlaton Calculate d horz Horzontal trajectory Measur ed vert ertcal trajectory Full scale C-130 Test (no slder 130KIAS 18,000t MSL 1, Ballstc (mostly horz. 11,960 See sect ,416 14,910 Full scale C-130 Test (wth slder 130KIAS 10,000t MSL 1, Ballstc (mostly horz. 5,544 7, Hal scale UH-1 Helo Test (no slder 80 KIAS 1000t MSL ballstc
25 Error cancellaton n R m < 0.2 regme 2 = 1/I F here; 2 -actor should be replaced by a hgher value, snce n realty I F s smaller 2m Fmax 1 ( t t descent >> descent n ths regme; number nsde brackets should be smaller than 1 descent /
26 Concludng remarks Method works well or almost all parachute/reeng desgns Excepton: Parachutes that dsree long ater reeed nlaton has ended All valdaton cases came rom cargo drops or skydvng, where ~ t/sec What about the cases where >>200 t/sec? (ejecton seat, etc. Would the method work R m > 0.1? Yes, t t measures nlaton +post-nlaton deceleraton What about slow deployments? (BASE jumpng Here ~ descent. In prncple the method should work but must be measured very accurately
27 Smple Wndows-based program or manned parachutng Easy to use Free download at descent calculated wth C D0 = 0.7 (rounds or 1.0 (paraol F max ( t 2m t 1 descent + g ( t t
28 Questons?
Testing Without Load Cells - Can Opening Shock Be Estimated From Video Data Only? ##
 Testng thout Load Cells - Can Openng Shock Be Estmated rom Vdeo Data Only? ## Jean Potvn Э Sant Lous Unversty, St. Lous, MO 63103 Gary Peek Ж Industrologc, Inc. St. Charles MO, 63301 Abstract AIAA-2007-51
Testng thout Load Cells - Can Openng Shock Be Estmated rom Vdeo Data Only? ## Jean Potvn Э Sant Lous Unversty, St. Lous, MO 63103 Gary Peek Ж Industrologc, Inc. St. Charles MO, 63301 Abstract AIAA-2007-51
EN40: Dynamics and Vibrations. Homework 4: Work, Energy and Linear Momentum Due Friday March 1 st
 EN40: Dynamcs and bratons Homework 4: Work, Energy and Lnear Momentum Due Frday March 1 st School of Engneerng Brown Unversty 1. The fgure (from ths publcaton) shows the energy per unt area requred to
EN40: Dynamcs and bratons Homework 4: Work, Energy and Lnear Momentum Due Frday March 1 st School of Engneerng Brown Unversty 1. The fgure (from ths publcaton) shows the energy per unt area requred to
Lecture 16. Chapter 11. Energy Dissipation Linear Momentum. Physics I. Department of Physics and Applied Physics
 Lecture 16 Chapter 11 Physcs I Energy Dsspaton Lnear Momentum Course webste: http://aculty.uml.edu/andry_danylov/teachng/physcsi Department o Physcs and Appled Physcs IN IN THIS CHAPTER, you wll learn
Lecture 16 Chapter 11 Physcs I Energy Dsspaton Lnear Momentum Course webste: http://aculty.uml.edu/andry_danylov/teachng/physcsi Department o Physcs and Appled Physcs IN IN THIS CHAPTER, you wll learn
Module 11 Design of Joints for Special Loading. Version 2 ME, IIT Kharagpur
 Module 11 Desgn o Jonts or Specal Loadng Verson ME, IIT Kharagpur Lesson 1 Desgn o Eccentrcally Loaded Bolted/Rveted Jonts Verson ME, IIT Kharagpur Instructonal Objectves: At the end o ths lesson, the
Module 11 Desgn o Jonts or Specal Loadng Verson ME, IIT Kharagpur Lesson 1 Desgn o Eccentrcally Loaded Bolted/Rveted Jonts Verson ME, IIT Kharagpur Instructonal Objectves: At the end o ths lesson, the
TIME OF COMPLETION NAME SOLUTION DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL SCIENCES. PHYS 2211, Exam 2 Section 1 Version 1 October 18, 2013 Total Weight: 100 points
 TIME OF COMPLETION NAME SOLUTION DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL SCIENCES PHYS, Exam Secton Verson October 8, 03 Total Weght: 00 ponts. Check your examnaton or completeness pror to startng. There are a total o nne
TIME OF COMPLETION NAME SOLUTION DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL SCIENCES PHYS, Exam Secton Verson October 8, 03 Total Weght: 00 ponts. Check your examnaton or completeness pror to startng. There are a total o nne
Spring Force and Power
 Lecture 13 Chapter 9 Sprng Force and Power Yeah, energy s better than orces. What s net? Course webste: http://aculty.uml.edu/andry_danylov/teachng/physcsi IN THIS CHAPTER, you wll learn how to solve problems
Lecture 13 Chapter 9 Sprng Force and Power Yeah, energy s better than orces. What s net? Course webste: http://aculty.uml.edu/andry_danylov/teachng/physcsi IN THIS CHAPTER, you wll learn how to solve problems
Chapter 3 and Chapter 4
 Chapter 3 and Chapter 4 Chapter 3 Energy 3. Introducton:Work Work W s energy transerred to or rom an object by means o a orce actng on the object. Energy transerred to the object s postve work, and energy
Chapter 3 and Chapter 4 Chapter 3 Energy 3. Introducton:Work Work W s energy transerred to or rom an object by means o a orce actng on the object. Energy transerred to the object s postve work, and energy
Physics for Scientists and Engineers. Chapter 9 Impulse and Momentum
 Physcs or Scentsts and Engneers Chapter 9 Impulse and Momentum Sprng, 008 Ho Jung Pak Lnear Momentum Lnear momentum o an object o mass m movng wth a velocty v s dened to be p mv Momentum and lnear momentum
Physcs or Scentsts and Engneers Chapter 9 Impulse and Momentum Sprng, 008 Ho Jung Pak Lnear Momentum Lnear momentum o an object o mass m movng wth a velocty v s dened to be p mv Momentum and lnear momentum
EVALUATION OF THE VISCO-ELASTIC PROPERTIES IN ASPHALT RUBBER AND CONVENTIONAL MIXES
 EVALUATION OF THE VISCO-ELASTIC PROPERTIES IN ASPHALT RUBBER AND CONVENTIONAL MIXES Manuel J. C. Mnhoto Polytechnc Insttute of Bragança, Bragança, Portugal E-mal: mnhoto@pb.pt Paulo A. A. Perera and Jorge
EVALUATION OF THE VISCO-ELASTIC PROPERTIES IN ASPHALT RUBBER AND CONVENTIONAL MIXES Manuel J. C. Mnhoto Polytechnc Insttute of Bragança, Bragança, Portugal E-mal: mnhoto@pb.pt Paulo A. A. Perera and Jorge
Physics 2A Chapter 3 HW Solutions
 Phscs A Chapter 3 HW Solutons Chapter 3 Conceptual Queston: 4, 6, 8, Problems: 5,, 8, 7, 3, 44, 46, 69, 70, 73 Q3.4. Reason: (a) C = A+ B onl A and B are n the same drecton. Sze does not matter. (b) C
Phscs A Chapter 3 HW Solutons Chapter 3 Conceptual Queston: 4, 6, 8, Problems: 5,, 8, 7, 3, 44, 46, 69, 70, 73 Q3.4. Reason: (a) C = A+ B onl A and B are n the same drecton. Sze does not matter. (b) C
Linear Momentum. Equation 1
 Lnear Momentum OBJECTIVE Obsere collsons between two carts, testng or the conseraton o momentum. Measure energy changes durng derent types o collsons. Classy collsons as elastc, nelastc, or completely
Lnear Momentum OBJECTIVE Obsere collsons between two carts, testng or the conseraton o momentum. Measure energy changes durng derent types o collsons. Classy collsons as elastc, nelastc, or completely
Opening Shock and Shape of the Drag-vs-Time Curve
 Openng Shock and Shape o he Drag-vs-Te Curve Jean Povn Physcs Deparen, San Lous Unversy, S. Lous MO Conac: povnj@slu.edu 314-977-8424 Talk presened a he 19 h AIAA Aerodynac Deceleraor Syses Conerence Wllasburg,
Openng Shock and Shape o he Drag-vs-Te Curve Jean Povn Physcs Deparen, San Lous Unversy, S. Lous MO Conac: povnj@slu.edu 314-977-8424 Talk presened a he 19 h AIAA Aerodynac Deceleraor Syses Conerence Wllasburg,
Work is the change in energy of a system (neglecting heat transfer). To examine what could
 Work Work s the change n energy o a system (neglectng heat transer). To eamne what could cause work, let s look at the dmensons o energy: L ML E M L F L so T T dmensonally energy s equal to a orce tmes
Work Work s the change n energy o a system (neglectng heat transer). To eamne what could cause work, let s look at the dmensons o energy: L ML E M L F L so T T dmensonally energy s equal to a orce tmes
Chapter 3 Differentiation and Integration
 MEE07 Computer Modelng Technques n Engneerng Chapter Derentaton and Integraton Reerence: An Introducton to Numercal Computatons, nd edton, S. yakowtz and F. zdarovsky, Mawell/Macmllan, 990. Derentaton
MEE07 Computer Modelng Technques n Engneerng Chapter Derentaton and Integraton Reerence: An Introducton to Numercal Computatons, nd edton, S. yakowtz and F. zdarovsky, Mawell/Macmllan, 990. Derentaton
Angular momentum. Instructor: Dr. Hoi Lam TAM ( 譚海嵐 )
 Angular momentum Instructor: Dr. Ho Lam TAM ( 譚海嵐 ) Physcs Enhancement Programme or Gted Students The Hong Kong Academy or Gted Educaton and Department o Physcs, HKBU Department o Physcs Hong Kong Baptst
Angular momentum Instructor: Dr. Ho Lam TAM ( 譚海嵐 ) Physcs Enhancement Programme or Gted Students The Hong Kong Academy or Gted Educaton and Department o Physcs, HKBU Department o Physcs Hong Kong Baptst
Chapter 6. Operational Amplifier. inputs can be defined as the average of the sum of the two signals.
 6 Operatonal mpler Chapter 6 Operatonal mpler CC Symbol: nput nput Output EE () Non-nvertng termnal, () nvertng termnal nput mpedance : Few mega (ery hgh), Output mpedance : Less than (ery low) Derental
6 Operatonal mpler Chapter 6 Operatonal mpler CC Symbol: nput nput Output EE () Non-nvertng termnal, () nvertng termnal nput mpedance : Few mega (ery hgh), Output mpedance : Less than (ery low) Derental
Department of Statistics University of Toronto STA305H1S / 1004 HS Design and Analysis of Experiments Term Test - Winter Solution
 Department of Statstcs Unversty of Toronto STA35HS / HS Desgn and Analyss of Experments Term Test - Wnter - Soluton February, Last Name: Frst Name: Student Number: Instructons: Tme: hours. Ads: a non-programmable
Department of Statstcs Unversty of Toronto STA35HS / HS Desgn and Analyss of Experments Term Test - Wnter - Soluton February, Last Name: Frst Name: Student Number: Instructons: Tme: hours. Ads: a non-programmable
ONE-DIMENSIONAL COLLISIONS
 Purpose Theory ONE-DIMENSIONAL COLLISIONS a. To very the law o conservaton o lnear momentum n one-dmensonal collsons. b. To study conservaton o energy and lnear momentum n both elastc and nelastc onedmensonal
Purpose Theory ONE-DIMENSIONAL COLLISIONS a. To very the law o conservaton o lnear momentum n one-dmensonal collsons. b. To study conservaton o energy and lnear momentum n both elastc and nelastc onedmensonal
OPTIMISATION. Introduction Single Variable Unconstrained Optimisation Multivariable Unconstrained Optimisation Linear Programming
 OPTIMIATION Introducton ngle Varable Unconstraned Optmsaton Multvarable Unconstraned Optmsaton Lnear Programmng Chapter Optmsaton /. Introducton In an engneerng analss, sometmes etremtes, ether mnmum or
OPTIMIATION Introducton ngle Varable Unconstraned Optmsaton Multvarable Unconstraned Optmsaton Lnear Programmng Chapter Optmsaton /. Introducton In an engneerng analss, sometmes etremtes, ether mnmum or
MEASUREMENT OF MOMENT OF INERTIA
 1. measurement MESUREMENT OF MOMENT OF INERTI The am of ths measurement s to determne the moment of nerta of the rotor of an electrc motor. 1. General relatons Rotatng moton and moment of nerta Let us
1. measurement MESUREMENT OF MOMENT OF INERTI The am of ths measurement s to determne the moment of nerta of the rotor of an electrc motor. 1. General relatons Rotatng moton and moment of nerta Let us
Chapter 5. Answers to Even Numbered Problems m kj. 6. (a) 900 J (b) (a) 31.9 J (b) 0 (c) 0 (d) 31.9 J. 10.
 Answers to Even Numbered Problems Chapter 5. 3.6 m 4..6 J 6. (a) 9 J (b).383 8. (a) 3.9 J (b) (c) (d) 3.9 J. 6 m s. (a) 68 J (b) 84 J (c) 5 J (d) 48 J (e) 5.64 m s 4. 9. J 6. (a). J (b) 5. m s (c) 6.3
Answers to Even Numbered Problems Chapter 5. 3.6 m 4..6 J 6. (a) 9 J (b).383 8. (a) 3.9 J (b) (c) (d) 3.9 J. 6 m s. (a) 68 J (b) 84 J (c) 5 J (d) 48 J (e) 5.64 m s 4. 9. J 6. (a). J (b) 5. m s (c) 6.3
Lecture 8 Modal Analysis
 Lecture 8 Modal Analyss 16.0 Release Introducton to ANSYS Mechancal 1 2015 ANSYS, Inc. February 27, 2015 Chapter Overvew In ths chapter free vbraton as well as pre-stressed vbraton analyses n Mechancal
Lecture 8 Modal Analyss 16.0 Release Introducton to ANSYS Mechancal 1 2015 ANSYS, Inc. February 27, 2015 Chapter Overvew In ths chapter free vbraton as well as pre-stressed vbraton analyses n Mechancal
ENGN 40 Dynamics and Vibrations Homework # 7 Due: Friday, April 15
 NGN 40 ynamcs and Vbratons Homework # 7 ue: Frday, Aprl 15 1. Consder a concal hostng drum used n the mnng ndustry to host a mass up/down. A cable of dameter d has the mass connected at one end and s wound/unwound
NGN 40 ynamcs and Vbratons Homework # 7 ue: Frday, Aprl 15 1. Consder a concal hostng drum used n the mnng ndustry to host a mass up/down. A cable of dameter d has the mass connected at one end and s wound/unwound
PHYSICS 203-NYA-05 MECHANICS
 PHYSICS 03-NYA-05 MECHANICS PROF. S.D. MANOLI PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY CHAMPLAIN - ST. LAWRENCE 790 NÉRÉE-TREMBLAY QUÉBEC, QC GV 4K TELEPHONE: 48.656.69 EXT. 449 EMAIL: smanol@slc.qc.ca WEBPAGE: http:/web.slc.qc.ca/smanol/
PHYSICS 03-NYA-05 MECHANICS PROF. S.D. MANOLI PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY CHAMPLAIN - ST. LAWRENCE 790 NÉRÉE-TREMBLAY QUÉBEC, QC GV 4K TELEPHONE: 48.656.69 EXT. 449 EMAIL: smanol@slc.qc.ca WEBPAGE: http:/web.slc.qc.ca/smanol/
Supplemental Material: Causal Entropic Forces
 Supplemental Materal: Causal Entropc Forces A. D. Wssner-Gross 1, 2, and C. E. Freer 3 1 Insttute for Appled Computatonal Scence, Harvard Unversty, Cambrdge, Massachusetts 02138, USA 2 The Meda Laboratory,
Supplemental Materal: Causal Entropc Forces A. D. Wssner-Gross 1, 2, and C. E. Freer 3 1 Insttute for Appled Computatonal Scence, Harvard Unversty, Cambrdge, Massachusetts 02138, USA 2 The Meda Laboratory,
Physics 5153 Classical Mechanics. Principle of Virtual Work-1
 P. Guterrez 1 Introducton Physcs 5153 Classcal Mechancs Prncple of Vrtual Work The frst varatonal prncple we encounter n mechancs s the prncple of vrtual work. It establshes the equlbrum condton of a mechancal
P. Guterrez 1 Introducton Physcs 5153 Classcal Mechancs Prncple of Vrtual Work The frst varatonal prncple we encounter n mechancs s the prncple of vrtual work. It establshes the equlbrum condton of a mechancal
Physics 2A Chapter 9 HW Solutions
 Phscs A Chapter 9 HW Solutons Chapter 9 Conceptual Queston:, 4, 8, 13 Problems: 3, 8, 1, 15, 3, 40, 51, 6 Q9.. Reason: We can nd the change n momentum o the objects b computng the mpulse on them and usng
Phscs A Chapter 9 HW Solutons Chapter 9 Conceptual Queston:, 4, 8, 13 Problems: 3, 8, 1, 15, 3, 40, 51, 6 Q9.. Reason: We can nd the change n momentum o the objects b computng the mpulse on them and usng
PHYS 1441 Section 002 Lecture #16
 PHYS 1441 Secton 00 Lecture #16 Monday, Mar. 4, 008 Potental Energy Conservatve and Non-conservatve Forces Conservaton o Mechancal Energy Power Today s homework s homework #8, due 9pm, Monday, Mar. 31!!
PHYS 1441 Secton 00 Lecture #16 Monday, Mar. 4, 008 Potental Energy Conservatve and Non-conservatve Forces Conservaton o Mechancal Energy Power Today s homework s homework #8, due 9pm, Monday, Mar. 31!!
10/24/2013. PHY 113 C General Physics I 11 AM 12:15 PM TR Olin 101. Plan for Lecture 17: Review of Chapters 9-13, 15-16
 0/4/03 PHY 3 C General Physcs I AM :5 PM T Oln 0 Plan or Lecture 7: evew o Chapters 9-3, 5-6. Comment on exam and advce or preparaton. evew 3. Example problems 0/4/03 PHY 3 C Fall 03 -- Lecture 7 0/4/03
0/4/03 PHY 3 C General Physcs I AM :5 PM T Oln 0 Plan or Lecture 7: evew o Chapters 9-3, 5-6. Comment on exam and advce or preparaton. evew 3. Example problems 0/4/03 PHY 3 C Fall 03 -- Lecture 7 0/4/03
AERODYNAMICS I LECTURE 6 AERODYNAMICS OF A WING FUNDAMENTALS OF THE LIFTING-LINE THEORY
 LECTURE 6 AERODYNAMICS OF A WING FUNDAMENTALS OF THE LIFTING-LINE THEORY The Bot-Savart Law The velocty nduced by the sngular vortex lne wth the crculaton can be determned by means of the Bot- Savart formula
LECTURE 6 AERODYNAMICS OF A WING FUNDAMENTALS OF THE LIFTING-LINE THEORY The Bot-Savart Law The velocty nduced by the sngular vortex lne wth the crculaton can be determned by means of the Bot- Savart formula
Page 1. Clicker Question 9: Physics 131: Lecture 15. Today s Agenda. Clicker Question 9: Energy. Energy is Conserved.
 Physcs 3: Lecture 5 Today s Agenda Intro to Conseraton o Energy Intro to some derent knds o energy Knetc Potental Denton o Mechancal Energy Conseraton o Mechancal Energy Conserate orces Examples Pendulum
Physcs 3: Lecture 5 Today s Agenda Intro to Conseraton o Energy Intro to some derent knds o energy Knetc Potental Denton o Mechancal Energy Conseraton o Mechancal Energy Conserate orces Examples Pendulum
CHAPTER 9 LINEAR MOMENTUM, IMPULSE AND COLLISIONS
 CHAPTER 9 LINEAR MOMENTUM, IMPULSE AND COLLISIONS 103 Phy 1 9.1 Lnear Momentum The prncple o energy conervaton can be ued to olve problem that are harder to olve jut ung Newton law. It ued to decrbe moton
CHAPTER 9 LINEAR MOMENTUM, IMPULSE AND COLLISIONS 103 Phy 1 9.1 Lnear Momentum The prncple o energy conervaton can be ued to olve problem that are harder to olve jut ung Newton law. It ued to decrbe moton
Name: PHYS 110 Dr. McGovern Spring 2018 Exam 1. Multiple Choice: Circle the answer that best evaluates the statement or completes the statement.
 Name: PHYS 110 Dr. McGoern Sprng 018 Exam 1 Multple Choce: Crcle the answer that best ealuates the statement or completes the statement. #1 - I the acceleraton o an object s negate, the object must be
Name: PHYS 110 Dr. McGoern Sprng 018 Exam 1 Multple Choce: Crcle the answer that best ealuates the statement or completes the statement. #1 - I the acceleraton o an object s negate, the object must be
Strength Requirements for Fore Deck Fittings and Equipment
 (Nov 2002) (Rev.1 March 2003) (Corr.1 July 2003) (Rev.2 Nov 2003) (Rev.3 July 2004) (Rev.4 Nov 2004) (Rev.5 May 2010) Strength Requrements for Fore Deck Fttngs and Equpment 1. General 1.1 Ths UR S 27 provdes
(Nov 2002) (Rev.1 March 2003) (Corr.1 July 2003) (Rev.2 Nov 2003) (Rev.3 July 2004) (Rev.4 Nov 2004) (Rev.5 May 2010) Strength Requrements for Fore Deck Fttngs and Equpment 1. General 1.1 Ths UR S 27 provdes
Winter 2008 CS567 Stochastic Linear/Integer Programming Guest Lecturer: Xu, Huan
 Wnter 2008 CS567 Stochastc Lnear/Integer Programmng Guest Lecturer: Xu, Huan Class 2: More Modelng Examples 1 Capacty Expanson Capacty expanson models optmal choces of the tmng and levels of nvestments
Wnter 2008 CS567 Stochastc Lnear/Integer Programmng Guest Lecturer: Xu, Huan Class 2: More Modelng Examples 1 Capacty Expanson Capacty expanson models optmal choces of the tmng and levels of nvestments
Physics 207, Lecture 13, Oct. 15. Energy
 Physcs 07 Lecture 3 Physcs 07, Lecture 3, Oct. 5 Goals: Chapter 0 Understand the relatonshp between moton and energy Dene Potental Energy n a Hooke s Law sprng Deelop and explot conseraton o energy prncple
Physcs 07 Lecture 3 Physcs 07, Lecture 3, Oct. 5 Goals: Chapter 0 Understand the relatonshp between moton and energy Dene Potental Energy n a Hooke s Law sprng Deelop and explot conseraton o energy prncple
Physics 141. Lecture 14. Frank L. H. Wolfs Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Rochester, Lecture 14, Page 1
 Physcs 141. Lecture 14. Frank L. H. Wolfs Department of Physcs and Astronomy, Unversty of Rochester, Lecture 14, Page 1 Physcs 141. Lecture 14. Course Informaton: Lab report # 3. Exam # 2. Mult-Partcle
Physcs 141. Lecture 14. Frank L. H. Wolfs Department of Physcs and Astronomy, Unversty of Rochester, Lecture 14, Page 1 Physcs 141. Lecture 14. Course Informaton: Lab report # 3. Exam # 2. Mult-Partcle
Physics 2A Chapters 6 - Work & Energy Fall 2017
 Physcs A Chapters 6 - Work & Energy Fall 017 These notes are eght pages. A quck summary: The work-energy theorem s a combnaton o Chap and Chap 4 equatons. Work s dened as the product o the orce actng on
Physcs A Chapters 6 - Work & Energy Fall 017 These notes are eght pages. A quck summary: The work-energy theorem s a combnaton o Chap and Chap 4 equatons. Work s dened as the product o the orce actng on
Old Dominion University Physics 420 Spring 2010
 Projects Structure o Project Reports: 1 Introducton. Brely summarze the nature o the physcal system. Theory. Descrbe equatons selected or the project. Dscuss relevance and lmtatons o the equatons. 3 Method.
Projects Structure o Project Reports: 1 Introducton. Brely summarze the nature o the physcal system. Theory. Descrbe equatons selected or the project. Dscuss relevance and lmtatons o the equatons. 3 Method.
Momentum. Momentum. Impulse. Momentum and Collisions
 Momentum Momentum and Collsons From Newton s laws: orce must be present to change an object s elocty (speed and/or drecton) Wsh to consder eects o collsons and correspondng change n elocty Gol ball ntally
Momentum Momentum and Collsons From Newton s laws: orce must be present to change an object s elocty (speed and/or drecton) Wsh to consder eects o collsons and correspondng change n elocty Gol ball ntally
Physics 5153 Classical Mechanics. D Alembert s Principle and The Lagrangian-1
 P. Guterrez Physcs 5153 Classcal Mechancs D Alembert s Prncple and The Lagrangan 1 Introducton The prncple of vrtual work provdes a method of solvng problems of statc equlbrum wthout havng to consder the
P. Guterrez Physcs 5153 Classcal Mechancs D Alembert s Prncple and The Lagrangan 1 Introducton The prncple of vrtual work provdes a method of solvng problems of statc equlbrum wthout havng to consder the
Lagrange Multipliers. A Somewhat Silly Example. Monday, 25 September 2013
 Lagrange Multplers Monday, 5 September 013 Sometmes t s convenent to use redundant coordnates, and to effect the varaton of the acton consstent wth the constrants va the method of Lagrange undetermned
Lagrange Multplers Monday, 5 September 013 Sometmes t s convenent to use redundant coordnates, and to effect the varaton of the acton consstent wth the constrants va the method of Lagrange undetermned
Conservation Laws (Collisions) Phys101 Lab - 04
 Conservaton Laws (Collsons) Phys101 Lab - 04 1.Objectves The objectves o ths experment are to expermentally test the valdty o the laws o conservaton o momentum and knetc energy n elastc collsons. 2. Theory
Conservaton Laws (Collsons) Phys101 Lab - 04 1.Objectves The objectves o ths experment are to expermentally test the valdty o the laws o conservaton o momentum and knetc energy n elastc collsons. 2. Theory
PHYS 1101 Practice problem set 12, Chapter 32: 21, 22, 24, 57, 61, 83 Chapter 33: 7, 12, 32, 38, 44, 49, 76
 PHYS 1101 Practce problem set 1, Chapter 3: 1,, 4, 57, 61, 83 Chapter 33: 7, 1, 3, 38, 44, 49, 76 3.1. Vsualze: Please reer to Fgure Ex3.1. Solve: Because B s n the same drecton as the ntegraton path s
PHYS 1101 Practce problem set 1, Chapter 3: 1,, 4, 57, 61, 83 Chapter 33: 7, 1, 3, 38, 44, 49, 76 3.1. Vsualze: Please reer to Fgure Ex3.1. Solve: Because B s n the same drecton as the ntegraton path s
Chapter 07: Kinetic Energy and Work
 Chapter 07: Knetc Energy and Work Conservaton o Energy s one o Nature s undamental laws that s not volated. Energy can take on derent orms n a gven system. Ths chapter we wll dscuss work and knetc energy.
Chapter 07: Knetc Energy and Work Conservaton o Energy s one o Nature s undamental laws that s not volated. Energy can take on derent orms n a gven system. Ths chapter we wll dscuss work and knetc energy.
Experimental Study on Ultimate Strength of Flexural-Failure-Type RC Beams under Impact Loading
 xpermental Study on Ultmate Strength of Flexural-Falure-Type RC Beams under Impact Loadng N. Ksh 1), O. Nakano 2~, K. G. Matsuoka 1), and T. Ando 1~ 1) Dept. of Cvl ngneerng, Muroran Insttute of Technology,
xpermental Study on Ultmate Strength of Flexural-Falure-Type RC Beams under Impact Loadng N. Ksh 1), O. Nakano 2~, K. G. Matsuoka 1), and T. Ando 1~ 1) Dept. of Cvl ngneerng, Muroran Insttute of Technology,
Amplification and Relaxation of Electron Spin Polarization in Semiconductor Devices
 Amplfcaton and Relaxaton of Electron Spn Polarzaton n Semconductor Devces Yury V. Pershn and Vladmr Prvman Center for Quantum Devce Technology, Clarkson Unversty, Potsdam, New York 13699-570, USA Spn Relaxaton
Amplfcaton and Relaxaton of Electron Spn Polarzaton n Semconductor Devces Yury V. Pershn and Vladmr Prvman Center for Quantum Devce Technology, Clarkson Unversty, Potsdam, New York 13699-570, USA Spn Relaxaton
Gravitational Acceleration: A case of constant acceleration (approx. 2 hr.) (6/7/11)
 Gravtatonal Acceleraton: A case of constant acceleraton (approx. hr.) (6/7/11) Introducton The gravtatonal force s one of the fundamental forces of nature. Under the nfluence of ths force all objects havng
Gravtatonal Acceleraton: A case of constant acceleraton (approx. hr.) (6/7/11) Introducton The gravtatonal force s one of the fundamental forces of nature. Under the nfluence of ths force all objects havng
Physic 231 Lecture 14
 Physc 3 Lecture 4 Man ponts o last lecture: Ipulses: orces that last only a short te Moentu p Ipulse-Moentu theore F t p ( ) Ipulse-Moentu theore ptot, p, p, p, p, ptot, Moentu and external orces F p ext
Physc 3 Lecture 4 Man ponts o last lecture: Ipulses: orces that last only a short te Moentu p Ipulse-Moentu theore F t p ( ) Ipulse-Moentu theore ptot, p, p, p, p, ptot, Moentu and external orces F p ext
Computational Biology Lecture 8: Substitution matrices Saad Mneimneh
 Computatonal Bology Lecture 8: Substtuton matrces Saad Mnemneh As we have ntroduced last tme, smple scorng schemes lke + or a match, - or a msmatch and -2 or a gap are not justable bologcally, especally
Computatonal Bology Lecture 8: Substtuton matrces Saad Mnemneh As we have ntroduced last tme, smple scorng schemes lke + or a match, - or a msmatch and -2 or a gap are not justable bologcally, especally
CHAPTER 8 Potential Energy and Conservation of Energy
 CHAPTER 8 Potental Energy and Conservaton o Energy One orm o energy can be converted nto another orm o energy. Conservatve and non-conservatve orces Physcs 1 Knetc energy: Potental energy: Energy assocated
CHAPTER 8 Potental Energy and Conservaton o Energy One orm o energy can be converted nto another orm o energy. Conservatve and non-conservatve orces Physcs 1 Knetc energy: Potental energy: Energy assocated
Physics 131: Lecture 16. Today s Agenda
 Physcs 131: Lecture 16 Today s Agenda Intro to Conseraton o Energy Intro to some derent knds o energy Knetc Potental Denton t o Mechancal Energy Conseraton o Mechancal Energy Conserate orces Examples Pendulum
Physcs 131: Lecture 16 Today s Agenda Intro to Conseraton o Energy Intro to some derent knds o energy Knetc Potental Denton t o Mechancal Energy Conseraton o Mechancal Energy Conserate orces Examples Pendulum
Semi-Numerical Derivation of the Opening Shock Factor and Inflation Time for Slider-Reefed Parafoils ##
 AIAA-7-58 Semi-Numerical erivation of the Opening Shock actor and Inflation Time for Slider-Reefed Parafoils ## Jean Potvin Э and Benjamin Hurst epartment of Physics, Saint Louis University, St. Louis,
AIAA-7-58 Semi-Numerical erivation of the Opening Shock actor and Inflation Time for Slider-Reefed Parafoils ## Jean Potvin Э and Benjamin Hurst epartment of Physics, Saint Louis University, St. Louis,
36.1 Why is it important to be able to find roots to systems of equations? Up to this point, we have discussed how to find the solution to
 ChE Lecture Notes - D. Keer, 5/9/98 Lecture 6,7,8 - Rootndng n systems o equatons (A) Theory (B) Problems (C) MATLAB Applcatons Tet: Supplementary notes rom Instructor 6. Why s t mportant to be able to
ChE Lecture Notes - D. Keer, 5/9/98 Lecture 6,7,8 - Rootndng n systems o equatons (A) Theory (B) Problems (C) MATLAB Applcatons Tet: Supplementary notes rom Instructor 6. Why s t mportant to be able to
Translational Equations of Motion for A Body Translational equations of motion (centroidal) for a body are m r = f.
 Lesson 12: Equatons o Moton Newton s Laws Frst Law: A artcle remans at rest or contnues to move n a straght lne wth constant seed there s no orce actng on t Second Law: The acceleraton o a artcle s roortonal
Lesson 12: Equatons o Moton Newton s Laws Frst Law: A artcle remans at rest or contnues to move n a straght lne wth constant seed there s no orce actng on t Second Law: The acceleraton o a artcle s roortonal
Indeterminate pin-jointed frames (trusses)
 Indetermnate pn-jonted frames (trusses) Calculaton of member forces usng force method I. Statcal determnacy. The degree of freedom of any truss can be derved as: w= k d a =, where k s the number of all
Indetermnate pn-jonted frames (trusses) Calculaton of member forces usng force method I. Statcal determnacy. The degree of freedom of any truss can be derved as: w= k d a =, where k s the number of all
Thermodynamics and Gases
 hermodynamcs and Gases Last tme Knetc heory o Gases or smple (monatomc) gases Atomc nature o matter Demonstrate deal gas law Atomc knetc energy nternal energy Mean ree path and velocty dstrbutons From
hermodynamcs and Gases Last tme Knetc heory o Gases or smple (monatomc) gases Atomc nature o matter Demonstrate deal gas law Atomc knetc energy nternal energy Mean ree path and velocty dstrbutons From
You will analyze the motion of the block at different moments using the law of conservation of energy.
 Physcs 00A Homework 7 Chapter 8 Where s the Energy? In ths problem, we wll consder the ollowng stuaton as depcted n the dagram: A block o mass m sldes at a speed v along a horzontal smooth table. It next
Physcs 00A Homework 7 Chapter 8 Where s the Energy? In ths problem, we wll consder the ollowng stuaton as depcted n the dagram: A block o mass m sldes at a speed v along a horzontal smooth table. It next
Chapter 11: Angular Momentum
 Chapter 11: ngular Momentum Statc Equlbrum In Chap. 4 we studed the equlbrum of pontobjects (mass m) wth the applcaton of Newton s aws F 0 F x y, 0 Therefore, no lnear (translatonal) acceleraton, a0 For
Chapter 11: ngular Momentum Statc Equlbrum In Chap. 4 we studed the equlbrum of pontobjects (mass m) wth the applcaton of Newton s aws F 0 F x y, 0 Therefore, no lnear (translatonal) acceleraton, a0 For
Chapter 5 Multilevel Models
 Chapter 5 Multlevel Models 5.1 Cross-sectonal multlevel models 5.1.1 Two-level models 5.1.2 Multple level models 5.1.3 Multple level modelng n other felds 5.2 Longtudnal multlevel models 5.2.1 Two-level
Chapter 5 Multlevel Models 5.1 Cross-sectonal multlevel models 5.1.1 Two-level models 5.1.2 Multple level models 5.1.3 Multple level modelng n other felds 5.2 Longtudnal multlevel models 5.2.1 Two-level
CHAPTER 4d. ROOTS OF EQUATIONS
 CHAPTER 4d. ROOTS OF EQUATIONS A. J. Clark School o Engneerng Department o Cvl and Envronmental Engneerng by Dr. Ibrahm A. Assakka Sprng 00 ENCE 03 - Computaton Methods n Cvl Engneerng II Department o
CHAPTER 4d. ROOTS OF EQUATIONS A. J. Clark School o Engneerng Department o Cvl and Envronmental Engneerng by Dr. Ibrahm A. Assakka Sprng 00 ENCE 03 - Computaton Methods n Cvl Engneerng II Department o
Kinematics in 2-Dimensions. Projectile Motion
 Knematcs n -Dmensons Projectle Moton A medeval trebuchet b Kolderer, c1507 http://members.net.net.au/~rmne/ht/ht0.html#5 Readng Assgnment: Chapter 4, Sectons -6 Introducton: In medeval das, people had
Knematcs n -Dmensons Projectle Moton A medeval trebuchet b Kolderer, c1507 http://members.net.net.au/~rmne/ht/ht0.html#5 Readng Assgnment: Chapter 4, Sectons -6 Introducton: In medeval das, people had
Parachute Research, from Computer Simulations to Uses in the Field
 Parachute Research, from Computer Simulations to Uses in the Field Gary Peek & Jean Potvin Parks College Parachute Research Group www.pcprg.com Contact: peek@industrologic.com 800-435-1975 potvinj@slu.edu
Parachute Research, from Computer Simulations to Uses in the Field Gary Peek & Jean Potvin Parks College Parachute Research Group www.pcprg.com Contact: peek@industrologic.com 800-435-1975 potvinj@slu.edu
Experiment 1 Mass, volume and density
 Experment 1 Mass, volume and densty Purpose 1. Famlarze wth basc measurement tools such as verner calper, mcrometer, and laboratory balance. 2. Learn how to use the concepts of sgnfcant fgures, expermental
Experment 1 Mass, volume and densty Purpose 1. Famlarze wth basc measurement tools such as verner calper, mcrometer, and laboratory balance. 2. Learn how to use the concepts of sgnfcant fgures, expermental
GAUTENG DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION SENIOR SECONDARY INTERVENTION PROGRAMME PHYSICAL SCIENCES GRADE 12 SESSION 1 (LEARNER NOTES)
 PHYSICAL SCIENCES GRADE 1 SESSION 1 (LEARNER NOTES) TOPIC 1: MECHANICS PROJECTILE MOTION Learner Note: Always draw a dagram of the stuaton and enter all the numercal alues onto your dagram. Remember to
PHYSICAL SCIENCES GRADE 1 SESSION 1 (LEARNER NOTES) TOPIC 1: MECHANICS PROJECTILE MOTION Learner Note: Always draw a dagram of the stuaton and enter all the numercal alues onto your dagram. Remember to
Dynamics of Rotational Motion
 Dynamcs of Rotatonal Moton Torque: the rotatonal analogue of force Torque = force x moment arm = Fl moment arm = perpendcular dstance through whch the force acts a.k.a. leer arm l F l F l F l F = Fl =
Dynamcs of Rotatonal Moton Torque: the rotatonal analogue of force Torque = force x moment arm = Fl moment arm = perpendcular dstance through whch the force acts a.k.a. leer arm l F l F l F l F = Fl =
Over-Temperature protection for IGBT modules
 Over-Temperature protecton for IGBT modules Ke Wang 1, Yongjun Lao 2, Gaosheng Song 1, Xanku Ma 1 1 Mtsubsh Electrc & Electroncs (Shangha) Co., Ltd., Chna Room2202, Tower 3, Kerry Plaza, No.1-1 Zhongxns
Over-Temperature protecton for IGBT modules Ke Wang 1, Yongjun Lao 2, Gaosheng Song 1, Xanku Ma 1 1 Mtsubsh Electrc & Electroncs (Shangha) Co., Ltd., Chna Room2202, Tower 3, Kerry Plaza, No.1-1 Zhongxns
Week 8: Chapter 9. Linear Momentum. Newton Law and Momentum. Linear Momentum, cont. Conservation of Linear Momentum. Conservation of Momentum, 2
 Lnear omentum Week 8: Chapter 9 Lnear omentum and Collsons The lnear momentum of a partcle, or an object that can be modeled as a partcle, of mass m movng wth a velocty v s defned to be the product of
Lnear omentum Week 8: Chapter 9 Lnear omentum and Collsons The lnear momentum of a partcle, or an object that can be modeled as a partcle, of mass m movng wth a velocty v s defned to be the product of
Effect of loading frequency on the settlement of granular layer
 Effect of loadng frequency on the settlement of granular layer Akko KONO Ralway Techncal Research Insttute, Japan Takash Matsushma Tsukuba Unversty, Japan ABSTRACT: Cyclc loadng tests were performed both
Effect of loadng frequency on the settlement of granular layer Akko KONO Ralway Techncal Research Insttute, Japan Takash Matsushma Tsukuba Unversty, Japan ABSTRACT: Cyclc loadng tests were performed both
Experience with Automatic Generation Control (AGC) Dynamic Simulation in PSS E
 Semens Industry, Inc. Power Technology Issue 113 Experence wth Automatc Generaton Control (AGC) Dynamc Smulaton n PSS E Lu Wang, Ph.D. Staff Software Engneer lu_wang@semens.com Dngguo Chen, Ph.D. Staff
Semens Industry, Inc. Power Technology Issue 113 Experence wth Automatc Generaton Control (AGC) Dynamc Smulaton n PSS E Lu Wang, Ph.D. Staff Software Engneer lu_wang@semens.com Dngguo Chen, Ph.D. Staff
Motion in One Dimension
 Moton n One Dmenson Speed ds tan ce traeled Aerage Speed tme of trael Mr. Wolf dres hs car on a long trp to a physcs store. Gen the dstance and tme data for hs trp, plot a graph of hs dstance ersus tme.
Moton n One Dmenson Speed ds tan ce traeled Aerage Speed tme of trael Mr. Wolf dres hs car on a long trp to a physcs store. Gen the dstance and tme data for hs trp, plot a graph of hs dstance ersus tme.
Chapter 2. Pythagorean Theorem. Right Hand Rule. Position. Distance Formula
 Chapter Moton n One Dmenson Cartesan Coordnate System The most common coordnate system or representng postons n space s one based on three perpendcular spatal axes generally desgnated x, y, and z. Any
Chapter Moton n One Dmenson Cartesan Coordnate System The most common coordnate system or representng postons n space s one based on three perpendcular spatal axes generally desgnated x, y, and z. Any
PHYS 1441 Section 002 Lecture #15
 PHYS 1441 Secton 00 Lecture #15 Monday, March 18, 013 Work wth rcton Potental Energy Gravtatonal Potental Energy Elastc Potental Energy Mechancal Energy Conservaton Announcements Mdterm comprehensve exam
PHYS 1441 Secton 00 Lecture #15 Monday, March 18, 013 Work wth rcton Potental Energy Gravtatonal Potental Energy Elastc Potental Energy Mechancal Energy Conservaton Announcements Mdterm comprehensve exam
Georgia Tech PHYS 6124 Mathematical Methods of Physics I
 Georga Tech PHYS 624 Mathematcal Methods of Physcs I Instructor: Predrag Cvtanovć Fall semester 202 Homework Set #7 due October 30 202 == show all your work for maxmum credt == put labels ttle legends
Georga Tech PHYS 624 Mathematcal Methods of Physcs I Instructor: Predrag Cvtanovć Fall semester 202 Homework Set #7 due October 30 202 == show all your work for maxmum credt == put labels ttle legends
An influence line shows how the force in a particular member changes as a concentrated load is moved along the structure.
 CE 331, Fall 2010 Influence Les for Trusses 1 / 7 An fluence le shows how the force a partcular member changes as a concentrated load s moved along the structure. For eample, say we are desgng the seven
CE 331, Fall 2010 Influence Les for Trusses 1 / 7 An fluence le shows how the force a partcular member changes as a concentrated load s moved along the structure. For eample, say we are desgng the seven
where v means the change in velocity, and t is the
 1 PHYS:100 LECTURE 4 MECHANICS (3) Ths lecture covers the eneral case of moton wth constant acceleraton and free fall (whch s one of the more mportant examples of moton wth constant acceleraton) n a more
1 PHYS:100 LECTURE 4 MECHANICS (3) Ths lecture covers the eneral case of moton wth constant acceleraton and free fall (whch s one of the more mportant examples of moton wth constant acceleraton) n a more
1. Inference on Regression Parameters a. Finding Mean, s.d and covariance amongst estimates. 2. Confidence Intervals and Working Hotelling Bands
 Content. Inference on Regresson Parameters a. Fndng Mean, s.d and covarance amongst estmates.. Confdence Intervals and Workng Hotellng Bands 3. Cochran s Theorem 4. General Lnear Testng 5. Measures of
Content. Inference on Regresson Parameters a. Fndng Mean, s.d and covarance amongst estmates.. Confdence Intervals and Workng Hotellng Bands 3. Cochran s Theorem 4. General Lnear Testng 5. Measures of
Prof. Paolo Colantonio a.a
 Pro. Paolo olantono a.a. 3 4 Let s consder a two ports network o Two ports Network o L For passve network (.e. wthout nternal sources or actve devces), a general representaton can be made by a sutable
Pro. Paolo olantono a.a. 3 4 Let s consder a two ports network o Two ports Network o L For passve network (.e. wthout nternal sources or actve devces), a general representaton can be made by a sutable
Section 8.1 Exercises
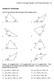 Secton 8.1 Non-rght Trangles: Law of Snes and Cosnes 519 Secton 8.1 Exercses Solve for the unknown sdes and angles of the trangles shown. 10 70 50 1.. 18 40 110 45 5 6 3. 10 4. 75 15 5 6 90 70 65 5. 6.
Secton 8.1 Non-rght Trangles: Law of Snes and Cosnes 519 Secton 8.1 Exercses Solve for the unknown sdes and angles of the trangles shown. 10 70 50 1.. 18 40 110 45 5 6 3. 10 4. 75 15 5 6 90 70 65 5. 6.
AP Physics 1 & 2 Summer Assignment
 AP Physcs 1 & 2 Summer Assgnment AP Physcs 1 requres an exceptonal profcency n algebra, trgonometry, and geometry. It was desgned by a select group of college professors and hgh school scence teachers
AP Physcs 1 & 2 Summer Assgnment AP Physcs 1 requres an exceptonal profcency n algebra, trgonometry, and geometry. It was desgned by a select group of college professors and hgh school scence teachers
Structural Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering
 Structural Dynamcs and Earthuake Engneerng Course 9 Sesmc-resstant desgn of structures (1) Sesmc acton Methods of elastc analyss Course notes are avalable for download at http://www.ct.upt.ro/users/aurelstratan/
Structural Dynamcs and Earthuake Engneerng Course 9 Sesmc-resstant desgn of structures (1) Sesmc acton Methods of elastc analyss Course notes are avalable for download at http://www.ct.upt.ro/users/aurelstratan/
SCHOOL OF COMPUTING, ENGINEERING AND MATHEMATICS SEMESTER 2 EXAMINATIONS 2011/2012 DYNAMICS ME247 DR. N.D.D. MICHÉ
 s SCHOOL OF COMPUTING, ENGINEERING ND MTHEMTICS SEMESTER EXMINTIONS 011/01 DYNMICS ME47 DR. N.D.D. MICHÉ Tme allowed: THREE hours nswer: ny FOUR from SIX questons Each queston carres 5 marks Ths s a CLOSED-BOOK
s SCHOOL OF COMPUTING, ENGINEERING ND MTHEMTICS SEMESTER EXMINTIONS 011/01 DYNMICS ME47 DR. N.D.D. MICHÉ Tme allowed: THREE hours nswer: ny FOUR from SIX questons Each queston carres 5 marks Ths s a CLOSED-BOOK
Lecture Note 3. Eshelby s Inclusion II
 ME340B Elastcty of Mcroscopc Structures Stanford Unversty Wnter 004 Lecture Note 3. Eshelby s Incluson II Chrs Wenberger and We Ca c All rghts reserved January 6, 004 Contents 1 Incluson energy n an nfnte
ME340B Elastcty of Mcroscopc Structures Stanford Unversty Wnter 004 Lecture Note 3. Eshelby s Incluson II Chrs Wenberger and We Ca c All rghts reserved January 6, 004 Contents 1 Incluson energy n an nfnte
Week3, Chapter 4. Position and Displacement. Motion in Two Dimensions. Instantaneous Velocity. Average Velocity
 Week3, Chapter 4 Moton n Two Dmensons Lecture Quz A partcle confned to moton along the x axs moves wth constant acceleraton from x =.0 m to x = 8.0 m durng a 1-s tme nterval. The velocty of the partcle
Week3, Chapter 4 Moton n Two Dmensons Lecture Quz A partcle confned to moton along the x axs moves wth constant acceleraton from x =.0 m to x = 8.0 m durng a 1-s tme nterval. The velocty of the partcle
Modeling motion with VPython Every program that models the motion of physical objects has two main parts:
 1 Modelng moton wth VPython Eery program that models the moton o physcal objects has two man parts: 1. Beore the loop: The rst part o the program tells the computer to: a. Create numercal alues or constants
1 Modelng moton wth VPython Eery program that models the moton o physcal objects has two man parts: 1. Beore the loop: The rst part o the program tells the computer to: a. Create numercal alues or constants
Prof. Dr. I. Nasser T /16/2017
 Pro. Dr. I. Nasser T-171 10/16/017 Chapter Part 1 Moton n one dmenson Sectons -,, 3, 4, 5 - Moton n 1 dmenson We le n a 3-dmensonal world, so why bother analyzng 1-dmensonal stuatons? Bascally, because
Pro. Dr. I. Nasser T-171 10/16/017 Chapter Part 1 Moton n one dmenson Sectons -,, 3, 4, 5 - Moton n 1 dmenson We le n a 3-dmensonal world, so why bother analyzng 1-dmensonal stuatons? Bascally, because
Note 10. Modeling and Simulation of Dynamic Systems
 Lecture Notes of ME 475: Introducton to Mechatroncs Note 0 Modelng and Smulaton of Dynamc Systems Department of Mechancal Engneerng, Unversty Of Saskatchewan, 57 Campus Drve, Saskatoon, SK S7N 5A9, Canada
Lecture Notes of ME 475: Introducton to Mechatroncs Note 0 Modelng and Smulaton of Dynamc Systems Department of Mechancal Engneerng, Unversty Of Saskatchewan, 57 Campus Drve, Saskatoon, SK S7N 5A9, Canada
Introduction to Vapor/Liquid Equilibrium, part 2. Raoult s Law:
 CE304, Sprng 2004 Lecture 4 Introducton to Vapor/Lqud Equlbrum, part 2 Raoult s Law: The smplest model that allows us do VLE calculatons s obtaned when we assume that the vapor phase s an deal gas, and
CE304, Sprng 2004 Lecture 4 Introducton to Vapor/Lqud Equlbrum, part 2 Raoult s Law: The smplest model that allows us do VLE calculatons s obtaned when we assume that the vapor phase s an deal gas, and
Moments of Inertia. and reminds us of the analogous equation for linear momentum p= mv, which is of the form. The kinetic energy of the body is.
 Moments of Inerta Suppose a body s movng on a crcular path wth constant speed Let s consder two quanttes: the body s angular momentum L about the center of the crcle, and ts knetc energy T How are these
Moments of Inerta Suppose a body s movng on a crcular path wth constant speed Let s consder two quanttes: the body s angular momentum L about the center of the crcle, and ts knetc energy T How are these
Physics 207: Lecture 20. Today s Agenda Homework for Monday
 Physcs 207: Lecture 20 Today s Agenda Homework for Monday Recap: Systems of Partcles Center of mass Velocty and acceleraton of the center of mass Dynamcs of the center of mass Lnear Momentum Example problems
Physcs 207: Lecture 20 Today s Agenda Homework for Monday Recap: Systems of Partcles Center of mass Velocty and acceleraton of the center of mass Dynamcs of the center of mass Lnear Momentum Example problems
University of Washington Department of Chemistry Chemistry 452/456 Summer Quarter 2014
 Lecture 12 7/25/14 ERD: 7.1-7.5 Devoe: 8.1.1-8.1.2, 8.2.1-8.2.3, 8.4.1-8.4.3 Unversty o Washngton Department o Chemstry Chemstry 452/456 Summer Quarter 2014 A. Free Energy and Changes n Composton: The
Lecture 12 7/25/14 ERD: 7.1-7.5 Devoe: 8.1.1-8.1.2, 8.2.1-8.2.3, 8.4.1-8.4.3 Unversty o Washngton Department o Chemstry Chemstry 452/456 Summer Quarter 2014 A. Free Energy and Changes n Composton: The
Case A. P k = Ni ( 2L i k 1 ) + (# big cells) 10d 2 P k.
 THE CELLULAR METHOD In ths lecture, we ntroduce the cellular method as an approach to ncdence geometry theorems lke the Szemeréd-Trotter theorem. The method was ntroduced n the paper Combnatoral complexty
THE CELLULAR METHOD In ths lecture, we ntroduce the cellular method as an approach to ncdence geometry theorems lke the Szemeréd-Trotter theorem. The method was ntroduced n the paper Combnatoral complexty
Chapter 8: Potential Energy and The Conservation of Total Energy
 Chapter 8: Potental Energy and The Conservaton o Total Energy Work and knetc energy are energes o moton. K K K mv r v v F dr Potental energy s an energy that depends on locaton. -Dmenson F x d U( x) dx
Chapter 8: Potental Energy and The Conservaton o Total Energy Work and knetc energy are energes o moton. K K K mv r v v F dr Potental energy s an energy that depends on locaton. -Dmenson F x d U( x) dx
Queueing Networks II Network Performance
 Queueng Networks II Network Performance Davd Tpper Assocate Professor Graduate Telecommuncatons and Networkng Program Unversty of Pttsburgh Sldes 6 Networks of Queues Many communcaton systems must be modeled
Queueng Networks II Network Performance Davd Tpper Assocate Professor Graduate Telecommuncatons and Networkng Program Unversty of Pttsburgh Sldes 6 Networks of Queues Many communcaton systems must be modeled
Module 3 LOSSY IMAGE COMPRESSION SYSTEMS. Version 2 ECE IIT, Kharagpur
 Module 3 LOSSY IMAGE COMPRESSION SYSTEMS Verson ECE IIT, Kharagpur Lesson 6 Theory of Quantzaton Verson ECE IIT, Kharagpur Instructonal Objectves At the end of ths lesson, the students should be able to:
Module 3 LOSSY IMAGE COMPRESSION SYSTEMS Verson ECE IIT, Kharagpur Lesson 6 Theory of Quantzaton Verson ECE IIT, Kharagpur Instructonal Objectves At the end of ths lesson, the students should be able to:
EN40: Dynamics and Vibrations. Homework 7: Rigid Body Kinematics
 N40: ynamcs and Vbratons Homewor 7: Rgd Body Knematcs School of ngneerng Brown Unversty 1. In the fgure below, bar AB rotates counterclocwse at 4 rad/s. What are the angular veloctes of bars BC and C?.
N40: ynamcs and Vbratons Homewor 7: Rgd Body Knematcs School of ngneerng Brown Unversty 1. In the fgure below, bar AB rotates counterclocwse at 4 rad/s. What are the angular veloctes of bars BC and C?.
Limited Dependent Variables
 Lmted Dependent Varables. What f the left-hand sde varable s not a contnuous thng spread from mnus nfnty to plus nfnty? That s, gven a model = f (, β, ε, where a. s bounded below at zero, such as wages
Lmted Dependent Varables. What f the left-hand sde varable s not a contnuous thng spread from mnus nfnty to plus nfnty? That s, gven a model = f (, β, ε, where a. s bounded below at zero, such as wages
Bulk Air Flow in a Duct. Hoods and Local Exhaust Ventilation. Inside a ventilation system. System Nomenclature
 Bulk Ar Flow n a Duct Hoods and Local Exhaust Ventlaton Essental pressure and low relatonshps Ar movement always ollows the pressure gradent Flow goes rom hgher (abs) pressure to lower (abs) pressure regons
Bulk Ar Flow n a Duct Hoods and Local Exhaust Ventlaton Essental pressure and low relatonshps Ar movement always ollows the pressure gradent Flow goes rom hgher (abs) pressure to lower (abs) pressure regons
COMPOSITE BEAM WITH WEAK SHEAR CONNECTION SUBJECTED TO THERMAL LOAD
 COMPOSITE BEAM WITH WEAK SHEAR CONNECTION SUBJECTED TO THERMAL LOAD Ákos Jósef Lengyel, István Ecsed Assstant Lecturer, Professor of Mechancs, Insttute of Appled Mechancs, Unversty of Mskolc, Mskolc-Egyetemváros,
COMPOSITE BEAM WITH WEAK SHEAR CONNECTION SUBJECTED TO THERMAL LOAD Ákos Jósef Lengyel, István Ecsed Assstant Lecturer, Professor of Mechancs, Insttute of Appled Mechancs, Unversty of Mskolc, Mskolc-Egyetemváros,
Endogenous timing in a mixed oligopoly consisting of a single public firm and foreign competitors. Abstract
 Endogenous tmng n a mxed olgopoly consstng o a sngle publc rm and oregn compettors Yuanzhu Lu Chna Economcs and Management Academy, Central Unversty o Fnance and Economcs Abstract We nvestgate endogenous
Endogenous tmng n a mxed olgopoly consstng o a sngle publc rm and oregn compettors Yuanzhu Lu Chna Economcs and Management Academy, Central Unversty o Fnance and Economcs Abstract We nvestgate endogenous
