Inelastic scattering
|
|
|
- Raymond Kelly
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Inelastic scattering When the scattering is not elastic (new particles are produced) the energy and direction of the scattered electron are independent variables, unlike the elastic scattering situation. W is the mass squared of the produced hadronic system From the measurement of the direction θ (solid angle element dω) and the energy E ' of the scattered electron, the four momentum transfer Q =-q can be calculated. The differential cross-section is determined as a function of E ' and Q. e (k,e) N (P,M) k ' = k q q = 4 EE ' sin θ W = (P + q) = P + P q + q = M + Mν Q e(k',e') γ (q) θ ν = E E' W 004,Torino Aram Kotzinian 1
2 Electron - proton inelastic scattering Bloom et al. (SLAC-MIT group) in 1969 performed an experiment with high-energy electron beams (7-18 GeV). Scattering of electrons from a hydrogen target at 6 0 and Only electrons are detected in the final state - inclusive approach. The data showed peaks when the mass W of the produced hadronic system corresponded to the mass of the known resonances. 004,Torino Aram Kotzinian
3 Inelastic scattering cross-section Similar to the electron-proton elastic scattering, the differential cross-section of electron-proton inelastic scattering can be written in a general form: dσ = α cos θ dωde ' 4E sin 4 θ [ W (ν,q ) +W 1 (ν,q )tan θ ] The cross-section is double differential because θ and E ' are independent variables. The expression contains Mott cross-section as a factor and is analogous to the Rosenbluth formula. It isolates the unknown shape of the nucleon target in two structure functions W 1 and W, which are the functions of two independent variables ν and q. The structure functions correspond to the two possible polarisation states of the virtual photon: longitudinal and transverse. Longitudinal polarisation exists only because photon is virtual and has a mass. For elastic scattering, (P+q) =M and the two variables ν and Q are related by Q =Mν. 004,Torino Aram Kotzinian 3
4 Scaling To determine W 1 and W separately it is necessary to measure the differential cross-section at two values of θ and E ' that correspond to the same values of ν and Q. This is possible by varying the incident energy E. SLAC result: the ratio of σ /σ Mott depends only weakly on Q for high values of W. For small scattering angles σ /σ Mott W. Thus, the structure function W does not depend on Q. 004,Torino Aram Kotzinian 4
5 Scaling Instead, at high values of W the function νw depends on the single variable ω = Mν / Q (at present the variable x=1/ω is widely used) This is the so-called "scaling" behaviour of the cross-section (structure function). It was first proposed by Bjorken in W 1, (ν,q ) W 1, (x) when ν,q. 004,Torino Aram Kotzinian 5
6 Deep Inelastic Scattering (DIS) z-axis to be along the incident lepton beam direction. Kinematic Variables M --The mass of the target hadron. E -- The energy of the incident lepton. k -- The momentum of the initial lepton. W -- The solid angle into which the outgoing lepton is scattered. E -- The energy of the scattered lepton. K -- The momentum of the scattered lepton, K = (E ;E sinqcosφ;e sinqsinf;e cosθ). P -- The momentum of the target, p = (M; 0; 0; 0), for a fixed target experiment. q = k-k -- the momentum transfer in the scattering process, i.e. the momentum of the virtual photon. 004,Torino Aram Kotzinian 6
7 Important variables The invariant mass of the final hadronic system X is 004,Torino Aram Kotzinian 7
8 Some inequalities The invariant mass of X must be at least that of a nucleon, since baryon number is conserved in the scattering process. Since Q and n are both positive, x must also be positive. The lepton energy loss E-E must be between zero and E, so the physically allowed kinematic region is The value x = 1 corresponds to elastic scattering. 004,Torino Aram Kotzinian 8
9 Any fixed hadron state X with invariant mass contributes to the cross-section at the value of x M X In the DIS limit Q, with fixed x So, any hadron state X with fixed invariant mass gets driven to x=1 The experimental measurements give the cross-section as a function of the final lepton energy and scattering angle. The results are often presented instead by giving the differential cross-section as a function of (x, Q ) or (x,y). The Jacobian for converting between these cases is easily worked out using the definitions of the kinematic variables 004,Torino Aram Kotzinian 9
10 Thus the cross-sections are related by x = Q ME Q Q = Mν ME ν E the contours of constant x are straight lines through the origin with slope x. 1 = ( E ν )(1 cosθ ) M the contours of constant angle q are straight lines passing through the point n=e 004,Torino Aram Kotzinian 10
11 For fixed value of x, the maximum allowed value of Q It is useful to have formulae for the different components of q as a function of x and y. This expressions are valid in the Lab frame with z-axis along lepton momentum 004,Torino Aram Kotzinian 11
12 Expression for DIS cross section The scattering amplitude M is given by s l - lepton polarization λ - target polarization 004,Torino Aram Kotzinian 1
13 It is conventional to define the leptonic tensor The definition of the hadronic tensor is slightly more complicated. Inserting a complete set of states gives where the sum on X is a sum over the allowed phase space for the final state X 004,Torino Aram Kotzinian 13
14 Translation invariance implies that 0 0 Only the first term contributes, since p X p and q 0 0 Using leptonic and hadronic tensors we have 004,Torino Aram Kotzinian 14
15 Finally, integrating over azimuth, we get 004,Torino Aram Kotzinian 15
16 Leptonic tensor The polarization of a spin 1/ particle can be described by a spin vector defined in the rest frame of the particle by The spin vector in arbitrary frame is obtained by Lorentz boost 004,Torino Aram Kotzinian 16
17 For a spin-1/ particle at rest with spin along the z-axis, the spin vector is s = mˆ z. This differs from the conventional normalization of s by a factor of the fermion mass m. Here we use the relativistic spinors normalized to E. In the extreme relativistic limit have s=hk, where k is the lepton momentum and H is the lepton helicity. Using trace theorems we obtain for leptonic tensor Unpolarized lepton beam probes only the symmetric part of hadronic tensor 004,Torino Aram Kotzinian 17
18 The Hadronic Tensor for Spin-1/ Targets Using parity, time-reversal invariance, hermiticity and current conservation one can show that Where the structure functions F, F, g and g depend on Q and. 1 1 ν Often another structure functions are used in the literature: 004,Torino Aram Kotzinian 18
19 Scaling The hadronic tensor is dimensionless The structure functions are dimensionless functions of the Lorentz invariant variables p = M, pq and Q It is conventional to write them as functions of x = Q They can be written as dimensionless functions of the dimensionless variables x and Q M In elastic scattering there is a strong dependence on Q M, and the elastic form factors fall o like a power of Q M. Bjorken: in DIS the structure functions only depend on x, and must be independent of Q. pq and Q 004,Torino Aram Kotzinian 19
20 The Cross-Section for Spin-1/ Targets Useful relation: Contracting hadronic and leptonic tensors we get: For a longitudinally polarized lepton beam, the polarization is where = ±1 is the lepton helicity. s l = k 004,Torino Aram Kotzinian 0
21 Longitudinally Polarized Target A target polarized along the incident beam direction: sh = M z ) where = ±1 for a target polarized parallel or antiparallel to the beam. p in the evaluation of the cross-section s h Where the azimuthal angle f has been integrated over since the cross-section is independent on f. 004,Torino Aram Kotzinian 1
22 Transversely Polarized Target The polarization vector of a transversely polarized target can be chosen to point along the x ) axis in the Lab frame. So, the azimuthal angle of scattered lepton is counted from that direction. Then, in this case we get: The structure functions g1 and g are equally important for a transversely polarized target, and so an experiment with a transversely polarized target can be used to determine g, once g1 has been measured using a longitudinally polarized target. 004,Torino Aram Kotzinian
23 Details of derivation for unpolarized DIS Consider the general form of inelastic electron-proton scattering We must construct W only from the available 4-vectors, p and q, µν µ µ and the invariant tensors g and ε µν µναβ. Thus we can write the most general structure in terms of the possible 6 tensors and corresponding form factors 004,Torino Aram Kotzinian 3
24 Leptonic tensor is symmetric and we can ignore the antisymmetric terms in hadronic tensor for unpolarized DIS. Then conservation of the neutral current requires that, or, for arbitrary p, q µ µ Hence the coefficients of p and q µ µ in this equation mustseparately vanish Substituting back into the initial expression we have 004,Torino Aram Kotzinian 4
25 In the laboratory frame we have the following relations between the kinematic quantities 004,Torino Aram Kotzinian 5
26 Finally the definition of the cross section gives 004,Torino Aram Kotzinian 6
Physics at Hadron Colliders Partons and PDFs
 Physics at Hadron Colliders Partons and PDFs Marina Cobal Thanks to D. Bettoni Università di Udine 1 2 How to probe the nucleon / quarks? Scatter high-energy lepton off a proton: Deep-Inelastic Scattering
Physics at Hadron Colliders Partons and PDFs Marina Cobal Thanks to D. Bettoni Università di Udine 1 2 How to probe the nucleon / quarks? Scatter high-energy lepton off a proton: Deep-Inelastic Scattering
The Development of Particle Physics. Dr. Vitaly Kudryavtsev E45, Tel.:
 The Development of Particle Physics Dr. Vitaly Kudryavtsev E45, Tel.: 0114 4531 v.kudryavtsev@sheffield.ac.uk The structure of the nucleon Electron - nucleon elastic scattering Rutherford, Mott cross-sections
The Development of Particle Physics Dr. Vitaly Kudryavtsev E45, Tel.: 0114 4531 v.kudryavtsev@sheffield.ac.uk The structure of the nucleon Electron - nucleon elastic scattering Rutherford, Mott cross-sections
Deep Inelastic Scattering (DIS) Un-ki Yang Dept. of Physics and Astronomy Seoul National University Un-ki Yang - DIS
 Deep Inelastic Scattering (DIS) Un-ki Yang Dept. of Physics and Astronomy Seoul National University ukyang@snu.ac.kr Un-ki Yang - DIS 1 Elastic and Inelastic scattering Electron-Proton Scattering P Electron-proton
Deep Inelastic Scattering (DIS) Un-ki Yang Dept. of Physics and Astronomy Seoul National University ukyang@snu.ac.kr Un-ki Yang - DIS 1 Elastic and Inelastic scattering Electron-Proton Scattering P Electron-proton
High Energy Physics. Lecture 9. Deep Inelastic Scattering Scaling Violation. HEP Lecture 9 1
 High Energy Physics Lecture 9 Deep Inelastic Scattering Scaling Violation HEP Lecture 9 1 Deep Inelastic Scattering: The reaction equation of DIS is written e+ p e+ X where X is a system of outgoing hadrons
High Energy Physics Lecture 9 Deep Inelastic Scattering Scaling Violation HEP Lecture 9 1 Deep Inelastic Scattering: The reaction equation of DIS is written e+ p e+ X where X is a system of outgoing hadrons
DEEP INELASTIC SCATTERING
 DEEP INELASTIC SCATTERING Electron scattering off nucleons (Fig 7.1): 1) Elastic scattering: E = E (θ) 2) Inelastic scattering: No 1-to-1 relationship between E and θ Inelastic scattering: nucleon gets
DEEP INELASTIC SCATTERING Electron scattering off nucleons (Fig 7.1): 1) Elastic scattering: E = E (θ) 2) Inelastic scattering: No 1-to-1 relationship between E and θ Inelastic scattering: nucleon gets
Experimental Aspects of Deep-Inelastic Scattering. Kinematics, Techniques and Detectors
 1 Experimental Aspects of Deep-Inelastic Scattering Kinematics, Techniques and Detectors 2 Outline DIS Structure Function Measurements DIS Kinematics DIS Collider Detectors DIS process description Dirac
1 Experimental Aspects of Deep-Inelastic Scattering Kinematics, Techniques and Detectors 2 Outline DIS Structure Function Measurements DIS Kinematics DIS Collider Detectors DIS process description Dirac
Currents and scattering
 Chapter 4 Currents and scattering The goal of this remaining chapter is to investigate hadronic scattering processes, either with leptons or with other hadrons. These are important for illuminating the
Chapter 4 Currents and scattering The goal of this remaining chapter is to investigate hadronic scattering processes, either with leptons or with other hadrons. These are important for illuminating the
Electron-Positron Annihilation
 Evidence for Quarks The quark model originally arose from the analysis of symmetry patterns using group theory. The octets, nonets, decuplets etc. could easily be explained with coloured quarks and the
Evidence for Quarks The quark model originally arose from the analysis of symmetry patterns using group theory. The octets, nonets, decuplets etc. could easily be explained with coloured quarks and the
8 The structure of the nucleon
 8 The structure of the nucleon Elastic and deep inelastic scattering from nucleons, 1956 1973 Hadronic scattering experiments produced extensive and rich data revealing resonances and regularities of cross
8 The structure of the nucleon Elastic and deep inelastic scattering from nucleons, 1956 1973 Hadronic scattering experiments produced extensive and rich data revealing resonances and regularities of cross
Form Factors with Electrons and Positrons
 HUGS2013, JLab, May 28 June 14, 2013 Form Factors with Electrons and Positrons Part 2: Proton form factor measurements Michael Kohl Hampton University, Hampton, VA 23668 Jefferson Laboratory, Newport News,
HUGS2013, JLab, May 28 June 14, 2013 Form Factors with Electrons and Positrons Part 2: Proton form factor measurements Michael Kohl Hampton University, Hampton, VA 23668 Jefferson Laboratory, Newport News,
What are the Low-Q and Large-x Boundaries of Collinear QCD Factorization Theorems?
 What are the Low-Q and Large-x Boundaries of Collinear QCD Factorization Theorems? Presented by Eric Moffat Paper written in collaboration with Wally Melnitchouk, Ted Rogers, and Nobuo Sato arxiv:1702.03955
What are the Low-Q and Large-x Boundaries of Collinear QCD Factorization Theorems? Presented by Eric Moffat Paper written in collaboration with Wally Melnitchouk, Ted Rogers, and Nobuo Sato arxiv:1702.03955
Standard Model of Particle Physics SS 2012
 Lecture: Standard Model of Particle Physics Heidelberg SS 22 Fermi Theory Standard Model of Particle Physics SS 22 2 Standard Model of Particle Physics SS 22 Fermi Theory Unified description of all kind
Lecture: Standard Model of Particle Physics Heidelberg SS 22 Fermi Theory Standard Model of Particle Physics SS 22 2 Standard Model of Particle Physics SS 22 Fermi Theory Unified description of all kind
2. Hadronic Form Factors
 PHYS 6610: Graduate Nuclear and Particle Physics I H. W. Grießhammer INS Institute for Nuclear Studies The George Washington University Institute for Nuclear Studies Spring 2018 II. Phenomena 2. Hadronic
PHYS 6610: Graduate Nuclear and Particle Physics I H. W. Grießhammer INS Institute for Nuclear Studies The George Washington University Institute for Nuclear Studies Spring 2018 II. Phenomena 2. Hadronic
Outline. Charged Leptonic Weak Interaction. Charged Weak Interactions of Quarks. Neutral Weak Interaction. Electroweak Unification
 Weak Interactions Outline Charged Leptonic Weak Interaction Decay of the Muon Decay of the Neutron Decay of the Pion Charged Weak Interactions of Quarks Cabibbo-GIM Mechanism Cabibbo-Kobayashi-Maskawa
Weak Interactions Outline Charged Leptonic Weak Interaction Decay of the Muon Decay of the Neutron Decay of the Pion Charged Weak Interactions of Quarks Cabibbo-GIM Mechanism Cabibbo-Kobayashi-Maskawa
Standard Model of Particle Physics SS 2013
 Lecture: Standard Model of Particle Physics Heidelberg SS 23 Fermi Theory Standard Model of Particle Physics SS 23 2 Standard Model of Particle Physics SS 23 Weak Force Decay of strange particles Nuclear
Lecture: Standard Model of Particle Physics Heidelberg SS 23 Fermi Theory Standard Model of Particle Physics SS 23 2 Standard Model of Particle Physics SS 23 Weak Force Decay of strange particles Nuclear
Scattering Processes. General Consideration. Kinematics of electron scattering Fermi Golden Rule Rutherford scattering cross section
 Scattering Processes General Consideration Kinematics of electron scattering Fermi Golden Rule Rutherford scattering cross section The form factor Mott scattering Nuclear charge distributions and radii
Scattering Processes General Consideration Kinematics of electron scattering Fermi Golden Rule Rutherford scattering cross section The form factor Mott scattering Nuclear charge distributions and radii
Extraction of Quark Distributions on Transverse Spin of the Nucleon at the HERMES Experiment. Hidekazu Tanaka
 Extraction of Quark Distributions on Transverse Spin of the Nucleon at the HERMES Experiment A Dissertation By Hidekazu Tanaka February 25 Department of Physics Tokyo Institute of Technology Abstract
Extraction of Quark Distributions on Transverse Spin of the Nucleon at the HERMES Experiment A Dissertation By Hidekazu Tanaka February 25 Department of Physics Tokyo Institute of Technology Abstract
arxiv: v1 [hep-ph] 31 Jan 2018
![arxiv: v1 [hep-ph] 31 Jan 2018 arxiv: v1 [hep-ph] 31 Jan 2018](/thumbs/88/115145622.jpg) Noname manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Polarization and dilepton angular distribution in pion-nucleon collisions Miklós Zétényi Enrico Speranza Bengt Friman Received: date / Accepted: date
Noname manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Polarization and dilepton angular distribution in pion-nucleon collisions Miklós Zétényi Enrico Speranza Bengt Friman Received: date / Accepted: date
Radiative Correction Introduction. Hanjie Liu Columbia University 2017 Hall A&C Analysis meeting
 Radiative Correction Introduction Hanjie Liu Columbia University 2017 Hall A&C Analysis meeting 1 Outline internal radiative correction: elastic peak, elastic tail, tail for continuum spectra external
Radiative Correction Introduction Hanjie Liu Columbia University 2017 Hall A&C Analysis meeting 1 Outline internal radiative correction: elastic peak, elastic tail, tail for continuum spectra external
Implications of G p E(Q 2 )/G p M(Q 2 ).
 Implications of G p E(Q 2 )/G p M(Q 2 ). S. Dubnička 1, A. Z. Dubničková 2, OUTLINE: 1. JLab proton polarization data puzzle 2. Existence of two different G p E(t) behaviors in spacelike region 3. Consequences
Implications of G p E(Q 2 )/G p M(Q 2 ). S. Dubnička 1, A. Z. Dubničková 2, OUTLINE: 1. JLab proton polarization data puzzle 2. Existence of two different G p E(t) behaviors in spacelike region 3. Consequences
Review of hadron-hadron interactions
 Chapter 10 Deep inelastic scattering between leptons and nucleons Confirm quarks are more than mathematical objects High momentum transfer from leptons to hadron constituents QCD predicts small coupling
Chapter 10 Deep inelastic scattering between leptons and nucleons Confirm quarks are more than mathematical objects High momentum transfer from leptons to hadron constituents QCD predicts small coupling
Particle Physics. Michaelmas Term 2011 Prof Mark Thomson. Handout 5 : Electron-Proton Elastic Scattering. Electron-Proton Scattering
 Particle Physics Michaelmas Term 2011 Prof Mark Thomson Handout 5 : Electron-Proton Elastic Scattering Prof. M.A. Thomson Michaelmas 2011 149 i.e. the QED part of ( q q) Electron-Proton Scattering In this
Particle Physics Michaelmas Term 2011 Prof Mark Thomson Handout 5 : Electron-Proton Elastic Scattering Prof. M.A. Thomson Michaelmas 2011 149 i.e. the QED part of ( q q) Electron-Proton Scattering In this
Lecture 8. CPT theorem and CP violation
 Lecture 8 CPT theorem and CP violation We have seen that although both charge conjugation and parity are violated in weak interactions, the combination of the two CP turns left-handed antimuon onto right-handed
Lecture 8 CPT theorem and CP violation We have seen that although both charge conjugation and parity are violated in weak interactions, the combination of the two CP turns left-handed antimuon onto right-handed
Nucleon Valence Quark Structure
 Nucleon Valence Quark Structure Z.-E. Meziani, S. Kuhn, O. Rondon, W. Melnitchouk Physics Motivation Nucleon spin and flavor structure High-x quark distributions Spin-flavor separation Moments of structure
Nucleon Valence Quark Structure Z.-E. Meziani, S. Kuhn, O. Rondon, W. Melnitchouk Physics Motivation Nucleon spin and flavor structure High-x quark distributions Spin-flavor separation Moments of structure
Introduction to particle physics Lecture 7
 Introduction to particle physics Lecture 7 Frank Krauss IPPP Durham U Durham, Epiphany term 2009 Outline 1 Deep-inelastic scattering and the structure of protons 2 Elastic scattering Scattering on extended
Introduction to particle physics Lecture 7 Frank Krauss IPPP Durham U Durham, Epiphany term 2009 Outline 1 Deep-inelastic scattering and the structure of protons 2 Elastic scattering Scattering on extended
SPIN STRUCTURE OF THE NUCLEON AND POLARIZATION. Charles Y. Prescott Stanford Linear Accelerator Center Stanford University, Stanford CA 94309
 SLAC-PUB-662 September 1994 (TE) SPIN STRUCTURE OF THE NUCLEON AND POLARIZATION Charles Y. Prescott Stanford Linear Accelerator Center Stanford University, Stanford CA 9439 Work supported by Department
SLAC-PUB-662 September 1994 (TE) SPIN STRUCTURE OF THE NUCLEON AND POLARIZATION Charles Y. Prescott Stanford Linear Accelerator Center Stanford University, Stanford CA 9439 Work supported by Department
Experimental results on nucleon structure Lecture I. National Nuclear Physics Summer School 2013
 Experimental results on nucleon structure Lecture I Barbara Badelek University of Warsaw National Nuclear Physics Summer School 2013 Stony Brook University, July 15 26, 2013 Barbara Badelek (Univ. of Warsaw
Experimental results on nucleon structure Lecture I Barbara Badelek University of Warsaw National Nuclear Physics Summer School 2013 Stony Brook University, July 15 26, 2013 Barbara Badelek (Univ. of Warsaw
QCD and deep inelastic scattering
 QCD and deep inelastic scattering Alex Tapper Slides available at: http://www.hep.ph.ic.ac.uk/~tapper/lecture.html Outline We ll start with some history of the structure of matter and scattering experiments.
QCD and deep inelastic scattering Alex Tapper Slides available at: http://www.hep.ph.ic.ac.uk/~tapper/lecture.html Outline We ll start with some history of the structure of matter and scattering experiments.
Lecture 3. Experimental Methods & Feynman Diagrams
 Lecture 3 Experimental Methods & Feynman Diagrams Natural Units & the Planck Scale Review of Relativistic Kinematics Cross-Sections, Matrix Elements & Phase Space Decay Rates, Lifetimes & Branching Fractions
Lecture 3 Experimental Methods & Feynman Diagrams Natural Units & the Planck Scale Review of Relativistic Kinematics Cross-Sections, Matrix Elements & Phase Space Decay Rates, Lifetimes & Branching Fractions
SECOND PUBLIC EXAMINATION. Honour School of Physics Part C: 4 Year Course. Honour School of Physics and Philosophy Part C C4: PARTICLE PHYSICS
 754 SECOND PUBLIC EXAMINATION Honour School of Physics Part C: 4 Year Course Honour School of Physics and Philosophy Part C C4: PARTICLE PHYSICS TRINITY TERM 04 Thursday, 9 June,.30 pm 5.45 pm 5 minutes
754 SECOND PUBLIC EXAMINATION Honour School of Physics Part C: 4 Year Course Honour School of Physics and Philosophy Part C C4: PARTICLE PHYSICS TRINITY TERM 04 Thursday, 9 June,.30 pm 5.45 pm 5 minutes
Lecture 9. Isospin The quark model
 Lecture 9 Isospin The quark model There is one more symmetry that applies to strong interactions. isospin or isotopic spin It was useful in formulation of the quark picture of known particles. We can consider
Lecture 9 Isospin The quark model There is one more symmetry that applies to strong interactions. isospin or isotopic spin It was useful in formulation of the quark picture of known particles. We can consider
Deuteron from CLAS/EG1B Data. Spin Structure Functions of the OUTLINE. Nevzat Guler (for the CLAS Collaboration) Old Dominion University
 Spin Structure Functions of the Deuteron from CLAS/EGB Data Nevzat Guler (for the CLAS Collaboration) Old Dominion University OULINE Formalism Experimental setup Data analysis Results and Conclusion Motivation
Spin Structure Functions of the Deuteron from CLAS/EGB Data Nevzat Guler (for the CLAS Collaboration) Old Dominion University OULINE Formalism Experimental setup Data analysis Results and Conclusion Motivation
Quark-Hadron Duality in Structure Functions
 Approaches to QCD, Oberwoelz, Austria September 10, 2008 Quark-Hadron Duality in Structure Functions Wally Melnitchouk Outline Bloom-Gilman duality Duality in QCD OPE & higher twists Resonances & local
Approaches to QCD, Oberwoelz, Austria September 10, 2008 Quark-Hadron Duality in Structure Functions Wally Melnitchouk Outline Bloom-Gilman duality Duality in QCD OPE & higher twists Resonances & local
Problem Set # 2 SOLUTIONS
 Wissink P640 Subatomic Physics I Fall 007 Problem Set # SOLUTIONS 1. Easy as π! (a) Consider the decay of a charged pion, the π +, that is at rest in the laboratory frame. Most charged pions decay according
Wissink P640 Subatomic Physics I Fall 007 Problem Set # SOLUTIONS 1. Easy as π! (a) Consider the decay of a charged pion, the π +, that is at rest in the laboratory frame. Most charged pions decay according
A Precision Measurement of Elastic e+p Beam Normal Single Spin Asymmetry and Other Transverse Spin Measurements from Qweak
 A Precision Measurement of Elastic e+p Beam Normal Single Spin Asymmetry and Other Transverse Spin Measurements from Qweak Buddhini P. Waidyawansa For the Qweak Collaboration JLab Users Group Meeting June
A Precision Measurement of Elastic e+p Beam Normal Single Spin Asymmetry and Other Transverse Spin Measurements from Qweak Buddhini P. Waidyawansa For the Qweak Collaboration JLab Users Group Meeting June
An Alternative Approach to the Extraction of Structure Functions in Deep Inelastic e-p Scattering at 5 to 20 GeV
 Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China 39 (2003 pp. 573 578 c International Academic Publishers Vol. 39, No. 5, May 15, 2003 An Alternative Approach to the Extraction of Structure Functions in Deep Inelastic
Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China 39 (2003 pp. 573 578 c International Academic Publishers Vol. 39, No. 5, May 15, 2003 An Alternative Approach to the Extraction of Structure Functions in Deep Inelastic
Using Electron Scattering Superscaling to predict Charge-changing Neutrino Cross Sections in Nuclei
 Using Electron Scattering Superscaling to predict Charge-changing Neutrino Cross Sections in Nuclei Maria B. Barbaro University of Torino (Italy) and INFN Maria B. Barbaro NUFACT05, Frascati, June 21-26,
Using Electron Scattering Superscaling to predict Charge-changing Neutrino Cross Sections in Nuclei Maria B. Barbaro University of Torino (Italy) and INFN Maria B. Barbaro NUFACT05, Frascati, June 21-26,
A Measurement of the Induced polarization of electro-produced Λ(1116) with CLAS
 A Measurement of the Induced polarization of electro-produced Λ(1116) with CLAS Marianna Gabrielyan Florida International University HUGS 2008 Why study electromagnetic production of kaons? Formalism.
A Measurement of the Induced polarization of electro-produced Λ(1116) with CLAS Marianna Gabrielyan Florida International University HUGS 2008 Why study electromagnetic production of kaons? Formalism.
1 Deep Inelastic Scattering
 Deep Inelastic Scattering Introduction Many important development in high energy physics comes from the studies of the properties of the proton which has mass M p 938.3 Mev/c. The diffi culty in the study
Deep Inelastic Scattering Introduction Many important development in high energy physics comes from the studies of the properties of the proton which has mass M p 938.3 Mev/c. The diffi culty in the study
Particles and Deep Inelastic Scattering
 Particles and Deep Inelastic Scattering University HUGS - JLab - June 2010 June 2010 HUGS 1 k q k P P A generic scatter of a lepton off of some target. k µ and k µ are the 4-momenta of the lepton and P
Particles and Deep Inelastic Scattering University HUGS - JLab - June 2010 June 2010 HUGS 1 k q k P P A generic scatter of a lepton off of some target. k µ and k µ are the 4-momenta of the lepton and P
Studying Nuclear Structure
 Microscope for the Studying Nuclear Structure with s School of Physics Seoul National University November 15, 2004 Outline s Microscope for the s Smaller, smaller Quest for basic building blocks of the
Microscope for the Studying Nuclear Structure with s School of Physics Seoul National University November 15, 2004 Outline s Microscope for the s Smaller, smaller Quest for basic building blocks of the
Particle Physics WS 2012/13 ( )
 Particle Physics WS 01/13 (3.11.01) Stephanie Hansmann-Menzemer Physikalisches Institut, INF 6, 3.101 Content of Today Structure of the proton: Inelastic proton scattering can be described by elastic scattering
Particle Physics WS 01/13 (3.11.01) Stephanie Hansmann-Menzemer Physikalisches Institut, INF 6, 3.101 Content of Today Structure of the proton: Inelastic proton scattering can be described by elastic scattering
Donie O Brien Nigel Buttimore
 Spin Observables and Antiproton Polarisation Donie O Brien Nigel Buttimore Trinity College Dublin Email: donie@maths.tcd.ie 17 July 006 CALC 006 Dubna Donie O Brien Introduction Relativistic formulae for
Spin Observables and Antiproton Polarisation Donie O Brien Nigel Buttimore Trinity College Dublin Email: donie@maths.tcd.ie 17 July 006 CALC 006 Dubna Donie O Brien Introduction Relativistic formulae for
Nucleosynthesis. at MAGIX/MESA. Stefan Lunkenheimer MAGIX Collaboration Meeting 2017
 Nucleosynthesis 12 C(α, γ) 16 O at MAGIX/MESA Stefan Lunkenheimer MAGIX Collaboration Meeting 2017 Topics S-Factor Simulation Outlook 2 S-Factor 3 Stages of stellar nucleosynthesis Hydrogen Burning (PPI-III
Nucleosynthesis 12 C(α, γ) 16 O at MAGIX/MESA Stefan Lunkenheimer MAGIX Collaboration Meeting 2017 Topics S-Factor Simulation Outlook 2 S-Factor 3 Stages of stellar nucleosynthesis Hydrogen Burning (PPI-III
Nucleon Electromagnetic Form Factors: Introduction and Overview
 Nucleon Electromagnetic Form Factors: Introduction and Overview Diego Bettoni Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare, Ferrara Scattering and Annihilation Electromagnetic Processes Trento, 18- February 013
Nucleon Electromagnetic Form Factors: Introduction and Overview Diego Bettoni Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare, Ferrara Scattering and Annihilation Electromagnetic Processes Trento, 18- February 013
1 The pion bump in the gamma reay flux
 1 The pion bump in the gamma reay flux Calculation of the gamma ray spectrum generated by an hadronic mechanism (that is by π decay). A pion of energy E π generated a flat spectrum between kinematical
1 The pion bump in the gamma reay flux Calculation of the gamma ray spectrum generated by an hadronic mechanism (that is by π decay). A pion of energy E π generated a flat spectrum between kinematical
Lecture 6 Scattering theory Partial Wave Analysis. SS2011: Introduction to Nuclear and Particle Physics, Part 2 2
 Lecture 6 Scattering theory Partial Wave Analysis SS2011: Introduction to Nuclear and Particle Physics, Part 2 2 1 The Born approximation for the differential cross section is valid if the interaction
Lecture 6 Scattering theory Partial Wave Analysis SS2011: Introduction to Nuclear and Particle Physics, Part 2 2 1 The Born approximation for the differential cross section is valid if the interaction
What are the Low-Q and Large-x Boundaries of Collinear QCD Factorization Theorems?
 What are the Low-Q and Large-x Boundaries of Collinear QCD Factorization Theorems? Presented by Eric Moffat Old Dominion University Paper written in collaboration with Wally Melnitchouk, Ted Rogers, and
What are the Low-Q and Large-x Boundaries of Collinear QCD Factorization Theorems? Presented by Eric Moffat Old Dominion University Paper written in collaboration with Wally Melnitchouk, Ted Rogers, and
Qweak Transverse Asymmetry Measurements
 Qweak Transverse Asymmetry Measurements Buddhini Waidyawansa For the Qweak Collaboration Hall C Collaboration Meeting 02-21-2014 Outline Physics of transverse asymmetries Qweak transverse data set Analysis
Qweak Transverse Asymmetry Measurements Buddhini Waidyawansa For the Qweak Collaboration Hall C Collaboration Meeting 02-21-2014 Outline Physics of transverse asymmetries Qweak transverse data set Analysis
Measurements with Polarized Hadrons
 Aug 15, 003 Lepton-Photon 003 Measurements with Polarized Hadrons T.-A. Shibata Tokyo Institute of Technology Contents: Introduction: Spin of Proton Polarized Deep Inelastic Lepton-Nucleon Scattering 1.
Aug 15, 003 Lepton-Photon 003 Measurements with Polarized Hadrons T.-A. Shibata Tokyo Institute of Technology Contents: Introduction: Spin of Proton Polarized Deep Inelastic Lepton-Nucleon Scattering 1.
Study of Strange Quark in the Nucleon with Neutrino Scattering
 July 28, 2004 NuFact 04, Osaka Study of Strange Quark in the Nucleon with Neutrino Scattering T.-A. Shibata Tokyo Institute of Technology Contents: 3. Physics Motivation --- Quark Structure of the Nucleon
July 28, 2004 NuFact 04, Osaka Study of Strange Quark in the Nucleon with Neutrino Scattering T.-A. Shibata Tokyo Institute of Technology Contents: 3. Physics Motivation --- Quark Structure of the Nucleon
arxiv:hep-ph/ v1 25 Jun 1999
 DESY 99 077 TTP99 29 June 1999 arxiv:hep-ph/9906503v1 25 Jun 1999 Azimuthal Asymmetries in Hadronic Final States at HERA M. Ahmed a,b and T. Gehrmann c a II. Institut für Theoretische Physik, Universität
DESY 99 077 TTP99 29 June 1999 arxiv:hep-ph/9906503v1 25 Jun 1999 Azimuthal Asymmetries in Hadronic Final States at HERA M. Ahmed a,b and T. Gehrmann c a II. Institut für Theoretische Physik, Universität
Subleading-twist effects in single-spin asymmetries in semi-inclusive DIS on a longitudinally polarized hydrogen target
 Subleading-twist effects in single-spin asymmetries in semi-inclusive DIS on a longitudinally polarized hydrogen target G Schnell, H Ohsuga, H Tanaka, T Hasegawa, T Kobayashi, Y Miyachi, T-A Shibata Tokyo
Subleading-twist effects in single-spin asymmetries in semi-inclusive DIS on a longitudinally polarized hydrogen target G Schnell, H Ohsuga, H Tanaka, T Hasegawa, T Kobayashi, Y Miyachi, T-A Shibata Tokyo
Spin Structure of the Nucleon: quark spin dependence
 Spin Structure of the Nucleon: quark spin dependence R. De Vita Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare Electromagnetic Interactions with Nucleons and Nuclei EINN005 Milos September, 005 The discovery of
Spin Structure of the Nucleon: quark spin dependence R. De Vita Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare Electromagnetic Interactions with Nucleons and Nuclei EINN005 Milos September, 005 The discovery of
Partículas Elementares (2015/2016)
 Partículas Elementares (015/016) 11 - Deep inelastic scattering Quarks and Partons Mário Pimenta Lisboa, 10/015 pimenta@lip.pt Elastic scattering kinematics (ep) Lab 1 θ 3 Only one independent variable!
Partículas Elementares (015/016) 11 - Deep inelastic scattering Quarks and Partons Mário Pimenta Lisboa, 10/015 pimenta@lip.pt Elastic scattering kinematics (ep) Lab 1 θ 3 Only one independent variable!
Electroweak Physics and Searches for New Physics at HERA
 Electroweak Physics and Searches for New Physics at HERA Uwe Schneekloth DESY On behalf of the H1 and ZEUS Collaborations 14th Lomonosov Conference on Elementary Particle Physics 5.08.009 Outline Introduction
Electroweak Physics and Searches for New Physics at HERA Uwe Schneekloth DESY On behalf of the H1 and ZEUS Collaborations 14th Lomonosov Conference on Elementary Particle Physics 5.08.009 Outline Introduction
Timelike Compton Scattering
 Timelike Compton Scattering Tanja Horn In collaboration with: Y. Illieva, F.J. Klein, P. Nadel-Turonski, R. Paremuzyan, S. Stepanyan 12 th Int. Conference on Meson-Nucleon Physics and the Structure of
Timelike Compton Scattering Tanja Horn In collaboration with: Y. Illieva, F.J. Klein, P. Nadel-Turonski, R. Paremuzyan, S. Stepanyan 12 th Int. Conference on Meson-Nucleon Physics and the Structure of
arxiv:hep-ph/ v1 4 Feb 1997
 DOUBLE SPIN TRANSVERSE ASYMMETRIES IN DRELL YAN PROCESSES V. Barone a,b, T. Calarco c and A. Drago c a Dipartimento di Fisica Teorica, Università di Torino and INFN, Sezione di Torino, 10125 Torino, Italy
DOUBLE SPIN TRANSVERSE ASYMMETRIES IN DRELL YAN PROCESSES V. Barone a,b, T. Calarco c and A. Drago c a Dipartimento di Fisica Teorica, Università di Torino and INFN, Sezione di Torino, 10125 Torino, Italy
Overview of recent HERMES results
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Overview of recent HERMES results To cite this article: Hrachya Marukyan and 216 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 678 1238 View the article online for updates
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Overview of recent HERMES results To cite this article: Hrachya Marukyan and 216 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 678 1238 View the article online for updates
Charged current DIS with polarised e ± beams at HERA. Alex Tapper
 Charged current DIS with polarised e ± beams at HRA Alex Tapper The HRA accelerator e± p 27.5 GeV 920 GeV s=320 GeV Page 2 Longitudinal polarisation at HRA Longitudinal polarisation of the lepton beam
Charged current DIS with polarised e ± beams at HRA Alex Tapper The HRA accelerator e± p 27.5 GeV 920 GeV s=320 GeV Page 2 Longitudinal polarisation at HRA Longitudinal polarisation of the lepton beam
Form Factors and Structure Functions
 Form Factors and Structure Functions Yury Kolomensky Physics 129, Fall 2010 Standard Model Primer 3 fundamental interactions Electromagnetic: U=q 1 q 2 /r Vector couplings Fine structure constant α=e 2
Form Factors and Structure Functions Yury Kolomensky Physics 129, Fall 2010 Standard Model Primer 3 fundamental interactions Electromagnetic: U=q 1 q 2 /r Vector couplings Fine structure constant α=e 2
BRIEF INTRODUCTION TO HERA PHYSICS
 BRIEF INTRODUCTION TO HERA PHYSICS aim: get to exercises as soon as possible cover: HERA accelarator and experiments DIS kinematics, how to compare theory and data:mc generators ==> next step: use them!
BRIEF INTRODUCTION TO HERA PHYSICS aim: get to exercises as soon as possible cover: HERA accelarator and experiments DIS kinematics, how to compare theory and data:mc generators ==> next step: use them!
1. Kinematics, cross-sections etc
 1. Kinematics, cross-sections etc A study of kinematics is of great importance to any experiment on particle scattering. It is necessary to interpret your measurements, but at an earlier stage to determine
1. Kinematics, cross-sections etc A study of kinematics is of great importance to any experiment on particle scattering. It is necessary to interpret your measurements, but at an earlier stage to determine
Time-like proton form factors and heavy lepton production at the PANDA experiment
 Time-like proton form factors and heavy lepton production at the PANDA experiment IPN-Orsay E-mail: dbeyssi@ipno.in2p3.fr Electromagnetic form factors (FFs) are fundamental quantities which describe the
Time-like proton form factors and heavy lepton production at the PANDA experiment IPN-Orsay E-mail: dbeyssi@ipno.in2p3.fr Electromagnetic form factors (FFs) are fundamental quantities which describe the
Deep Inelastic Scattering in Lepton-Hadron Collisions Probing the Parton Structure of the Nucleon with Leptons Basic Formalism (indep.
 Deep Inelastic Scattering in Lepton-Hadron Collisions Probing the Parton Structure of the Nucleon with Leptons Basic Formalism (indep. of strong dynamics and parton picture) Experimental Development Fixed
Deep Inelastic Scattering in Lepton-Hadron Collisions Probing the Parton Structure of the Nucleon with Leptons Basic Formalism (indep. of strong dynamics and parton picture) Experimental Development Fixed
arxiv: v2 [hep-ph] 19 Feb 2016
![arxiv: v2 [hep-ph] 19 Feb 2016 arxiv: v2 [hep-ph] 19 Feb 2016](/thumbs/94/118270241.jpg) TWIST EXPANSION OF FORWARD DRE YAN PROCESS Tomasz Stebel, eszek Motyka, Mariusz Sadzikowski arxiv:1602.01762v2 [hep-ph] 19 Feb 2016 The Marian Smoluchowski Institute of Physics, Jagiellonian University
TWIST EXPANSION OF FORWARD DRE YAN PROCESS Tomasz Stebel, eszek Motyka, Mariusz Sadzikowski arxiv:1602.01762v2 [hep-ph] 19 Feb 2016 The Marian Smoluchowski Institute of Physics, Jagiellonian University
2 Feynman rules, decay widths and cross sections
 2 Feynman rules, decay widths and cross sections 2.1 Feynman rules Normalization In non-relativistic quantum mechanics, wave functions of free particles are normalized so that there is one particle in
2 Feynman rules, decay widths and cross sections 2.1 Feynman rules Normalization In non-relativistic quantum mechanics, wave functions of free particles are normalized so that there is one particle in
Nucleon Spin. Tyler Corbett
 Nucleon Spin Tyler Corbett Abstract: In 1988 the European Muon Collaboration showed that the quark contribution to spin only accounts for 20-30 percent of the nucleon spin; The "naive quark parton model
Nucleon Spin Tyler Corbett Abstract: In 1988 the European Muon Collaboration showed that the quark contribution to spin only accounts for 20-30 percent of the nucleon spin; The "naive quark parton model
Standard Model of Particle Physics SS 2012
 Lecture: Standard Model of Particle Physics Heidelberg SS 2012 Experimental Tests of QED Part 2 1 Overview PART I Cross Sections and QED tests Accelerator Facilities + Experimental Results and Tests PART
Lecture: Standard Model of Particle Physics Heidelberg SS 2012 Experimental Tests of QED Part 2 1 Overview PART I Cross Sections and QED tests Accelerator Facilities + Experimental Results and Tests PART
Standard Model of Particle Physics SS 2013
 Lecture: Standard Model of Particle Physics Heidelberg SS 013 Weak Interactions II 1 Important Experiments Wu-Experiment (1957): radioactive decay of Co60 Goldhaber-Experiment (1958): radioactive decay
Lecture: Standard Model of Particle Physics Heidelberg SS 013 Weak Interactions II 1 Important Experiments Wu-Experiment (1957): radioactive decay of Co60 Goldhaber-Experiment (1958): radioactive decay
Weak interactions. Chapter 7
 Chapter 7 Weak interactions As already discussed, weak interactions are responsible for many processes which involve the transformation of particles from one type to another. Weak interactions cause nuclear
Chapter 7 Weak interactions As already discussed, weak interactions are responsible for many processes which involve the transformation of particles from one type to another. Weak interactions cause nuclear
Λ and Λ polarization at COMPASS
 and polarization at COMASS onghee Kang Johannes Gutenberg Universität Mainz On behalf of the COMASS collaboration IS XVIII International Workshop on eep Inelastic Scattering Firenze, 1 st April Outline
and polarization at COMASS onghee Kang Johannes Gutenberg Universität Mainz On behalf of the COMASS collaboration IS XVIII International Workshop on eep Inelastic Scattering Firenze, 1 st April Outline
Transverse Target Asymmetry in Exclusive Charged Pion Production at 12 GeV
 Transverse Target Asymmetry in Exclusive Charged Pion Production at 12 GeV Dipangkar Dutta Mississippi State University (with Dave Gaskell & Garth Huber) Polarized Target Workshop: June 17-18, 2010 Outline
Transverse Target Asymmetry in Exclusive Charged Pion Production at 12 GeV Dipangkar Dutta Mississippi State University (with Dave Gaskell & Garth Huber) Polarized Target Workshop: June 17-18, 2010 Outline
SECOND PUBLIC EXAMINATION. Honour School of Physics Part C: 4 Year Course. Honour School of Physics and Philosophy Part C C4: PARTICLE PHYSICS
 A047W SECOND PUBLIC EXAMINATION Honour School of Physics Part C: 4 Year Course Honour School of Physics and Philosophy Part C C4: PARTICLE PHYSICS TRINITY TERM 05 Thursday, 8 June,.30 pm 5.45 pm 5 minutes
A047W SECOND PUBLIC EXAMINATION Honour School of Physics Part C: 4 Year Course Honour School of Physics and Philosophy Part C C4: PARTICLE PHYSICS TRINITY TERM 05 Thursday, 8 June,.30 pm 5.45 pm 5 minutes
Measurement of the photon electroproduction cross section at JLab with the goal of performing a Rosenbluth separation of the DVCS contribution.
 PHD THESIS: Measurement of the photon electroproduction cross section at JLab with the goal of performing a Rosenbluth separation of the DVCS contribution. A Thesis submitted by Alejandro Martí Jiménez-Argüello
PHD THESIS: Measurement of the photon electroproduction cross section at JLab with the goal of performing a Rosenbluth separation of the DVCS contribution. A Thesis submitted by Alejandro Martí Jiménez-Argüello
1 Introduction Background Scaling Elastic Scattering Inelastic Scattering Resonances...
 arxiv:0812.2144v1 [nucl-ex] 10 Dec 2008 Contents 1 Introduction 2 1.1 Background................................ 3 1.2 Scaling................................... 4 1.2.1 Elastic Scattering.........................
arxiv:0812.2144v1 [nucl-ex] 10 Dec 2008 Contents 1 Introduction 2 1.1 Background................................ 3 1.2 Scaling................................... 4 1.2.1 Elastic Scattering.........................
Outline. Charged Leptonic Weak Interaction. Charged Weak Interactions of Quarks. Neutral Weak Interaction. Electroweak Unification
 Weak Interactions Outline Charged Leptonic Weak Interaction Decay of the Muon Decay of the Neutron Decay of the Pion Charged Weak Interactions of Quarks Cabibbo-GIM Mechanism Cabibbo-Kobayashi-Maskawa
Weak Interactions Outline Charged Leptonic Weak Interaction Decay of the Muon Decay of the Neutron Decay of the Pion Charged Weak Interactions of Quarks Cabibbo-GIM Mechanism Cabibbo-Kobayashi-Maskawa
arxiv:nucl-th/ v1 3 Jul 1996
 MKPH-T-96-15 arxiv:nucl-th/9607004v1 3 Jul 1996 POLARIZATION PHENOMENA IN SMALL-ANGLE PHOTOPRODUCTION OF e + e PAIRS AND THE GDH SUM RULE A.I. L VOV a Lebedev Physical Institute, Russian Academy of Sciences,
MKPH-T-96-15 arxiv:nucl-th/9607004v1 3 Jul 1996 POLARIZATION PHENOMENA IN SMALL-ANGLE PHOTOPRODUCTION OF e + e PAIRS AND THE GDH SUM RULE A.I. L VOV a Lebedev Physical Institute, Russian Academy of Sciences,
Semi-inclusive neutrino-nucleus reactions
 Final State Nucleons for Neutrino - Nucleus Interactions Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility May 14th, 2015 Semi-inclusive neutrino-nucleus reactions Oscar Moreno Laboratory for Nuclear Science,
Final State Nucleons for Neutrino - Nucleus Interactions Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility May 14th, 2015 Semi-inclusive neutrino-nucleus reactions Oscar Moreno Laboratory for Nuclear Science,
arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 16 Jun 2008
![arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 16 Jun 2008 arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 16 Jun 2008](/thumbs/94/118537980.jpg) 1 Two-Photon Exchange Contribution to Proton Form Factors in Time-Like region D. Y. Chen 1, H. Q. Zhou 2 and Y. B. Dong 1 arxiv:0806.2489v1 [nucl-th] 16 Jun 2008 1 Institute of High Energy Physics The
1 Two-Photon Exchange Contribution to Proton Form Factors in Time-Like region D. Y. Chen 1, H. Q. Zhou 2 and Y. B. Dong 1 arxiv:0806.2489v1 [nucl-th] 16 Jun 2008 1 Institute of High Energy Physics The
Standard Model of Particle Physics SS 2013
 Lecture: Standard Model of Particle Physics Heidelberg SS 2012 Experimental Tests of QED Part 2 1 Overview PART I Cross Sections and QED tests Accelerator Facilities + Experimental Results and Tests PART
Lecture: Standard Model of Particle Physics Heidelberg SS 2012 Experimental Tests of QED Part 2 1 Overview PART I Cross Sections and QED tests Accelerator Facilities + Experimental Results and Tests PART
QGP Physics from Fixed Target to LHC
 QGP Physics from Fixed Target to LHC 2. Kinematic Variables Prof. Dr. Klaus Reygers, Prof. Dr. Johanna Stachel Physikalisches Institut, Universität Heidelberg SS 2015 1 May 5, 2015: First collisions at
QGP Physics from Fixed Target to LHC 2. Kinematic Variables Prof. Dr. Klaus Reygers, Prof. Dr. Johanna Stachel Physikalisches Institut, Universität Heidelberg SS 2015 1 May 5, 2015: First collisions at
Density Dependence of Parity Violation in Electron Quasi-elastic Scattering
 Journal of the Korean Physical Society, Vol. 66, No. 12, June 2015, pp. 1936 1941 Brief Reports Density Dependence of Parity Violation in Electron Quasi-elastic Scattering K. S. Kim School of Liberal Arts
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, Vol. 66, No. 12, June 2015, pp. 1936 1941 Brief Reports Density Dependence of Parity Violation in Electron Quasi-elastic Scattering K. S. Kim School of Liberal Arts
6. QED. Particle and Nuclear Physics. Dr. Tina Potter. Dr. Tina Potter 6. QED 1
 6. QED Particle and Nuclear Physics Dr. Tina Potter Dr. Tina Potter 6. QED 1 In this section... Gauge invariance Allowed vertices + examples Scattering Experimental tests Running of alpha Dr. Tina Potter
6. QED Particle and Nuclear Physics Dr. Tina Potter Dr. Tina Potter 6. QED 1 In this section... Gauge invariance Allowed vertices + examples Scattering Experimental tests Running of alpha Dr. Tina Potter
PHY492: Nuclear & Particle Physics. Lecture 4 Nature of the nuclear force. Reminder: Investigate
 PHY49: Nuclear & Particle Physics Lecture 4 Nature of the nuclear force Reminder: Investigate www.nndc.bnl.gov Topics to be covered size and shape mass and binding energy charge distribution angular momentum
PHY49: Nuclear & Particle Physics Lecture 4 Nature of the nuclear force Reminder: Investigate www.nndc.bnl.gov Topics to be covered size and shape mass and binding energy charge distribution angular momentum
Installed and commissioned during run 4 To be commissioned Installed/commissioned in run /10/2005 Raimondo Bertini
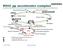 Installed and commissioned during run 4 To be commissioned Installed/commissioned in run 5 9-15/10/005 Raimondo Bertini Transverse Structure Functions Twist- PDFs f 1 g 1L g 1T h 1T Distribution functions
Installed and commissioned during run 4 To be commissioned Installed/commissioned in run 5 9-15/10/005 Raimondo Bertini Transverse Structure Functions Twist- PDFs f 1 g 1L g 1T h 1T Distribution functions
Structure of Hadrons and the parton model
 Structure of Hadrons and the parton model Ben Kilminster University of Zürich - Physik Institut Phenomenology of Particle Physics - PPP2 Lecture: 10/3/2015 Topics in this lecture How do we study the structure
Structure of Hadrons and the parton model Ben Kilminster University of Zürich - Physik Institut Phenomenology of Particle Physics - PPP2 Lecture: 10/3/2015 Topics in this lecture How do we study the structure
Duality in Inclusive Structure Functions: Present and Future. Simona Malace Jefferson Lab
 Duality in Inclusive Structure Functions: Present and Future Simona Malace Jefferson Lab University of Virginia, March 13 2015 What is Quark-hadron duality? Quark-Hadron Duality Quark-hadron duality =
Duality in Inclusive Structure Functions: Present and Future Simona Malace Jefferson Lab University of Virginia, March 13 2015 What is Quark-hadron duality? Quark-Hadron Duality Quark-hadron duality =
Two Photon Exchange in Inclusive and Semi Inclusive DIS
 Two Photon Exchange in Inclusive and Semi Inclusive DIS Marc Schlegel Theory Center, Jefferson Lab In collaboration with Christian Weiss, Andrei Afanasev, Andreas Metz Two Photon Exchange in elastic scattering
Two Photon Exchange in Inclusive and Semi Inclusive DIS Marc Schlegel Theory Center, Jefferson Lab In collaboration with Christian Weiss, Andrei Afanasev, Andreas Metz Two Photon Exchange in elastic scattering
The Quark Parton Model
 The Quark Parton Model Quark Model Pseudoscalar J P = 0 Mesons Vector J P = 1 Mesons Meson Masses J P = 3 /2 + Baryons J P = ½ + Baryons Resonances Resonance Detection Discovery of the ω meson Dalitz Plots
The Quark Parton Model Quark Model Pseudoscalar J P = 0 Mesons Vector J P = 1 Mesons Meson Masses J P = 3 /2 + Baryons J P = ½ + Baryons Resonances Resonance Detection Discovery of the ω meson Dalitz Plots
Measuring Form Factors and Structure Functions With CLAS
 Measuring Form Factors and Structure Functions With CLAS Jerry Gilfoyle for the CLAS Collaboration Physics Department, University of Richmond, Virginia Outline: 1. Jefferson Lab and the CLAS Detector..
Measuring Form Factors and Structure Functions With CLAS Jerry Gilfoyle for the CLAS Collaboration Physics Department, University of Richmond, Virginia Outline: 1. Jefferson Lab and the CLAS Detector..
TMDs in covariant approach
 TMDs in covariant approach Petr Zavada Institute of Physics AS CR, Prague, Czech Rep. (based on collaboration and discussions with A.Efremov, P.Schweitzer and O.Teryaev) Newport News, VA, May, 16-19, 2016
TMDs in covariant approach Petr Zavada Institute of Physics AS CR, Prague, Czech Rep. (based on collaboration and discussions with A.Efremov, P.Schweitzer and O.Teryaev) Newport News, VA, May, 16-19, 2016
Introduction to Elementary Particle Physics I
 Physics 56400 Introduction to Elementary Particle Physics I Lecture 16 Fall 018 Semester Prof. Matthew Jones Review of Lecture 15 When we introduced a (classical) electromagnetic field, the Dirac equation
Physics 56400 Introduction to Elementary Particle Physics I Lecture 16 Fall 018 Semester Prof. Matthew Jones Review of Lecture 15 When we introduced a (classical) electromagnetic field, the Dirac equation
NEW VALUE OF PROTON CHARGE rms RADIUS
 NEW VALUE OF PROTON CHARGE rms RADIUS Institute of Physics SAS, Bratislava and Dept. of Theoretical Physics, Comenius University, Bratislava, Slovakia September 22, 2011 Erice School 2001: From Quarks
NEW VALUE OF PROTON CHARGE rms RADIUS Institute of Physics SAS, Bratislava and Dept. of Theoretical Physics, Comenius University, Bratislava, Slovakia September 22, 2011 Erice School 2001: From Quarks
Helicity amplitudes and crossing relations for antiproton proton reactions
 Helicity amplitudes and crossing relations for antiproton proton reactions arxiv:hep-ph/07048v4 4 Apr 007 N. H. Buttimore and E. Jennings School of Mathematics, Trinity College, Dublin, Ireland February,
Helicity amplitudes and crossing relations for antiproton proton reactions arxiv:hep-ph/07048v4 4 Apr 007 N. H. Buttimore and E. Jennings School of Mathematics, Trinity College, Dublin, Ireland February,
Neutral Current Cross Sections With Polarised Lepton Beam At ZEUS
 Neutral Current Cross Sections With Polarised Lepton Beam At Syed Umer Noor York University, Canada On Behalf of the Collaboration DIS 6, - 4 April 6, Tsukuba, Japan Syed Umer Noor (York University) NC
Neutral Current Cross Sections With Polarised Lepton Beam At Syed Umer Noor York University, Canada On Behalf of the Collaboration DIS 6, - 4 April 6, Tsukuba, Japan Syed Umer Noor (York University) NC
OUTLINE. CHARGED LEPTONIC WEAK INTERACTION - Decay of the Muon - Decay of the Neutron - Decay of the Pion
 Weak Interactions OUTLINE CHARGED LEPTONIC WEAK INTERACTION - Decay of the Muon - Decay of the Neutron - Decay of the Pion CHARGED WEAK INTERACTIONS OF QUARKS - Cabibbo-GIM Mechanism - Cabibbo-Kobayashi-Maskawa
Weak Interactions OUTLINE CHARGED LEPTONIC WEAK INTERACTION - Decay of the Muon - Decay of the Neutron - Decay of the Pion CHARGED WEAK INTERACTIONS OF QUARKS - Cabibbo-GIM Mechanism - Cabibbo-Kobayashi-Maskawa
light-cone (LC) variables
 light-cone (LC) variables 4-vector a µ scalar product metric LC basis : transverse metric 24-Apr-13 1 hadron target at rest inclusive DIS target absorbes momentum from γ * ; for example, if q z P z =0
light-cone (LC) variables 4-vector a µ scalar product metric LC basis : transverse metric 24-Apr-13 1 hadron target at rest inclusive DIS target absorbes momentum from γ * ; for example, if q z P z =0
THE GPD EXPERIMENTAL PROGRAM AT JEFFERSON LAB. C. Muñoz Camacho 1
 Author manuscript, published in "XIX International Baldin Seminar on High Energy Physics Problems, Relativistic Nuclear Physics and Quantum Chromodynamics, Dubna : Russie (8)" THE GPD EXPERIMENTAL PROGRAM
Author manuscript, published in "XIX International Baldin Seminar on High Energy Physics Problems, Relativistic Nuclear Physics and Quantum Chromodynamics, Dubna : Russie (8)" THE GPD EXPERIMENTAL PROGRAM
A SPIN ON THE PROTON FOR SEEKING NUCLEON STRUCTURE. Nigel Buttimore
 A SPIN ON THE PROTON FOR SEEKING NUCLEON STRUCTURE Nigel Buttimore Trinity College Dublin 22 May 2009 DAMTP Cambridge Cavendish Laboratory OUTLINE Introduction to spin and the spin structure of the nucleon
A SPIN ON THE PROTON FOR SEEKING NUCLEON STRUCTURE Nigel Buttimore Trinity College Dublin 22 May 2009 DAMTP Cambridge Cavendish Laboratory OUTLINE Introduction to spin and the spin structure of the nucleon
