Newport News, VA Abstract
|
|
|
- Nigel Foster
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 High Current CW Beam Profile Monitors Using Transition Radiation at CEBAF l?ece/ve =J P. Piot, J-C. Denard, P. Adderley, K. Capek, E. Feldl * JM Continuous Electron Beam Accelerator Facility, 12 Jefferson Avenue, 8S7-l Newport News, VA 2366 Abstract One way of measuring the profile of CEBAF s low emittance and high power beam is to use the Optical Transition Radiation (OTR) emitted from a thin foil surface when the electron beam passes through it. We present the design of a monitor using the forward OTR emitted from a.25 pm carbon foil. We believe that the monitor will resolve three main issues :i) whether the maximum temperature of the foil stays below the melting point ii) whether the beam loss remains below.5 %, in order not to trigger the machine protection system iii) and whether the monitor resolution (unlike that of synchrotron radiation monitors) is better than the product X7. It seems that the.most serious limitation for CEBAF is the beam loss due tobbeam scattering. We present results from Keil s theory and simulations from the computer code GEANT as well as measurements with aluminum foils with a 45 MeV electron beam. We also present a measurement of a 3.2 GeV beam profile that is much smaller than X7, supporting Rule & Fiorito s calculations of the OTR resolution limit due to diffraction. INTRODUCTION The Optical Transition Radiation (OTR) phenomenon is a very convenient and reliable means for beam profile and position measurement in a quasi-non destructive way. However, there are limitations in the use of such monitors. Firstly, depending on the beam current of the considered beam, the screen can melt. Secondly, at high temperature, the screen becomes a source of Black Body radiation whose power can be greater than that of the OTR. Finally, the plural scattering that electrons experience while passing through the foil is a source of emittance degradation and beam loss. For the CEBAF electron beam, this last issue is of importance because of the Machine Protection System (MPS) that shuts the injector down when beam losses exceed 1pA out of a total beam current that can reach 2pA. In this paper we describe a monitor which uses the forward OTR produced at the surface of a very thin (.25prn) carbon foil. This device has the potential t o monitor and study the continous electron beam delivered to the experimental halls. *Work Supported by U.S. Department Of Energy contract DEAC584ER OF THlS DOCUMENT IS UNLIMED MASTER
2 DISCLAlMER Portions of this document may be illegible in electronic image products. Images are produced from the best available original document.
3 5 d 2 d v 8 Position (rnrn) Projected Angle (mrad) Figure. 1. Beam scattering angle distribution through thin aluminum foils, measured at 45MeV; before inserting the foil2we set the optics for a minimum vertical beam size at the wire scanner location.(a) Wire scanner vertical profile taken 7.4m after the foil set up, with and without foil; the wire scanner has three 5pm diameter wires (one vertical, one horizontal, and one at 45O).(B) Fraction of the beam contained within the vertical beam scattering angle. In order to deduce these curves from the profiles: (i) we assumed that 1% of the beam has been scanned; (ii) we considered only the right side of the third peak corresponding to the horizontal profile in orde r to reduce the error due to the signal received-by the other wires; (iii) we deconvoluted the relevant profiles with respect to the beam. PLURAL SCATTEFUNG THROUGH FOILS Experimental Results using Aluminum foils In this section, we present the results of the measurements of the scattering angle distribution of an electron beam through thin aluminum foils of various thicknesses, (.25,.8, and 1.5pm). The foils are mounted on a support that is inserted into the beam by mean of a stepping motor. We perform this test in the 45 MeV region of the CEBAF injector. We measure the beam size using a wire scanner installed downstream from the foils. There is no powered quadrupole magnet between the foils and the wire scanner. Therefore by knowing the distance inbetween the two instruments, we can easily calculate the distribution angle of the particles at the exit of the foil from the beam profile distribution measured by the wire scanner. The results (Fig.1B) show that, within the range of the thicknesses tested, the scattering angle containing 7% of the particles decreases in proportion with the foil thickness. However, the angle that contains 9% of the particles does not decrease as much. Measuring angles that contain more than 9% of the beam would require
4 8?I E 4 x f 3 L: - E 2.U a 1 t 9.% 8 e 7 a 1 Thickness (pm) 1 Meon Number Of Collision ( ) Figure. 2. (A) Comparative results of experiment with Keil s model and GEANT computation for thin aluminum foils. The+curvesshow the effects of the foil thickness on the semi-angle containing 7% and 9% of the beam. (B) Projected Scattering angle of highly relativistic electrons in thin foils according to GEANT simulation code and normalized at 1GeV. is the half angle at which the distribution contains the indicated percentage P of the beam. The projected angle of a scattered particle is defined on any plane that contains the incoming trajectory. It is the angle between the incoming and outgoing trajectory projected on that plane. The percentage of the beam foss (1- P) can be computed at any energy for any screen material and thickness, by knowing the machine acceptance angle and the beam energy. scanning larger angles. The curves in Fig.1 are accurate up to 9%; beyond this value we have to use theoretical formulae or Monte-Carlo simulations. Comparative results with Keil s Model and Monte-Carlo Simulation In materials so thin that the mean number of collisions is less than 2 (domain of plural scattering), Molikre s model of multiple scattering is not valid anymore. We used two techniques to calculate the scattering angle distribution. One is a calculation based on Keil s model(l), which is the only analytical model available. The other is a Monte-Carlo technique, GEANT(2) code. The Monte-Carlo code generated angular distribution is narrower than Keil s model by a factor of 2. The measured distribution is narrower than the Monte-Carlo distribution by approximately another factor of 2 (Fig.2A). The beam energy in the transport line ranges from.8gev to 4GeV. The beam scattering angle is inversely proportional to beam momentum. The worst case beam loss occurs at the lowest energy. At.8GeV, CEBAF s beam angle
5 acceptance is around looprad at the location we wish to install a viewer. Table 1 lists various foil materials with their smallest thickness commercially available that can be mounted on a lomm diameter hole, and the corresponding mean number of collisions R per pm. We used the formula: R =.78 x p x (z+ A p is the density in g/cm3, 2 is the atomic number, and A the atomic weight. Material Be Number Of Collis. 7.5 per pm thickness Thinnest foil.25 Available (pm) for 8mm dia. corresponding R C Mg A1 Ti Fe Cu 62 Ag 9 Au Table 1. Survey of the materials commercially available for monitoring intense beams with OTR screens; we excluded the materials with low thermal conductivity and mean number of collisions greater than 3 in their smallest thickness. The best candidates are Beryllium and Carbon; they are equivalent but we prefer the latter because of the toxicity of beryllium. Frpm results of GEANT simulation (Fig.2B), we can estimate the percentage of beam lost at any energy for any screen material and thickness, by knowing the machine acceptance angle. Previous calculations (3) showed that aluminum foils could stand a 2pA continous beam of 5pm rms transverse dimensions. Carbon, with its equivalent thermal conductivity and higher melting point will be even superior. We present the results of a thermal analysis in the last section. OTR PROFILE MONITOR WITH A.25 pm CARBON FOIL Description of the Monitor The backward OTR depends on the reflection characteristics of the surface. There are problems with very thin foils : surface inhomogeneity makes their coefficient of reflection non uniform, and it is also difficult to stretch them enough to obtain a flat surface. Furthermore materials such as aluminum and gold present wrinkles that affect locally both reflection coefficient and angle on the scale of the beam size. These problems disappear with forward OTR since it is emitted around the beam direction regardless of the angle or coefficient of reflection of the foil. There are two additional advantages to the forward over the backward OTR with a foil at 45'. The depth of field error becomes negligeable. The incoming beam at normal incidence has a shorter path through
6 the material which reduces the beam loss due to scattering. We built a profile monitor, shown in Fig.3, which looks at the forward OTR emitted from a.25pm carbon foil mounted on a support that can be inserted into the beam. To prevent the beam from damaging the support, the support is U-shaped and open on the side crossing the beam path. A mirror sends part of the forward OTR to the optical system through a vacuum window. With the OTR that is strongly directional in a l / 7 angular cone, we need to collect the light emitted at small angles from the beam trajectory. We did this by locating the mirror on the same insertion mechanism as the foil. The mirror is 17.5cm downstream from the foil; this insertion mechanism brings its edge close to the beam trajectory (4mm). I ril I, L - & * Figure. 3. Simplified view of the forward OTR Profile Monitor The mirror collects the light and sends it to a Charge Injected Device (CID) camera via two achromatic doublets. Despite its lower sensitivity we preferred a CID camera to the more commonly used Charge Coupled Device (CCD) cameras because of its good radiation resistance (specified to 1 k b d ). The CID array has 768 x 575 square pixels of 11.5pm. The camera is sensitive to the whole visible spectrum. By choosing achromatic lenses, we can improve the monitor's sensitivity without any loss in resolution. We illuminated the support from outside the vacuum chamber so that its lomm square shape can be used to precisely calibrate the CID image. The magnification of the optics is such that the lomm square support encompasses about 5 pixels which yields a pixel size of approximately 2pm in the object plane. I
7 Optical Resolution The beam profile has a gaussian shape with an rms value a N 1 p m. We measured the resolution of the instrument in the laboratory replacing the foil with a resolution target. We found the minimum resolvable distance between two black lines to be about 8prn. We believe the camerais the limiting element since this number is within a factor of 2 of the manufacturer s specifications. The resolution measured with such a target corresponds approximately to the full width of a gaussian beam (4a). Hence, the resolution expressed in terms of one sigma is about 8/4 = 2pm, which is reasonably small compared to the expected beam size. The resolution measurement in the lab does not take into account the pupil function of the transition radiation which has a strong angular dependence. The resolution due to the OTR pupil function is a controversial issue. It has been suggested that it was limited to 1.22 x X7. However, Rule & Fiorito calculated (4) an OTR diffraction limit very close to that of a standard source which has a uniform intensity with angle. Although the mirror center is not on the OTR revolution axis, we believe that the results reported in the following section support their calculations. Experimental -Results We tested the monitor in the transport line of an experimental hall with a 3.2GeV electron beam. Figure 4 shows the horizontal beam profile measured with a 3 p A continuous beam, whose dimension is a, N 1pm. The camera has its maximum sensitivity at 5nm (l.22x7 = 3.9mrn). The l.22x7 product represents the distance between the two minima of the diffraction pattern. A fit to the Airy Diffraction Function with a gaussian distribution yields a a that is 5.8 times smaller than the distance between the two minima of the Airy function. The hypothetical OTR diffraction limit at that beam energy would yield a = 3.9/5.8 =.7mm which is much greater than the O.lmm actually measured. A test done 25pA shows that the beam scattering through the foil does not introduce losses greater than.5 % of the beam. The electrode-sum signals of Beam Position Monitors located upstream and downstream of the foil provided the intensity information for beam loss calculation. With fluctuations of the intensity measurements at the.1% level, we were not able to detect any beam loss. In the near future we will test the monitor in a 18pA continuous beam to confirm that the beam loss is below the MPS threshold of 1pA. THERMAL CONDUCTION An electron beam going through matter deposits ionization energy that heat the foil and knocks out secondary particles. Calculation of the energy deposition ( 5 ) or its computation using the Monte-Carlo code EGS4 (6) yields similar results. The heat is lost through conduction ( 3 ) and radiation. Figure 5 shows the maximum current required to melt various materials. For C E
8 BAF, the maximum tolerable beam loss due to beam scattering limits actually application of OTR to lower currents. CONCLUSION We described an OTR profile monitor that can operate in a 2pA with continuous electron beam, using a very thin carbon foil. The measurement of a looprn (rms radius) beam profile at 3.2GeV supports Rule & Fiorito s calculations and confirms the possibility of imaging micron size beams of high energy. It also supports the concept of using the OTR monitors at CEBAF where the combination of high average beam power, small emittance, and high energy makes other profile diagnostics unsuitable. The present construction of a Free Electron Laser should be an opportunity to test this kind of monitor at higher continuous currents. REFERENCES 1. Scott, W.T., The theory of Small-Angle Multiple Scattering of fast Charged Particles, Rev. Mod. Ph>s. Vol 35 Num 2, pp , April Groosens et Al, GEANT, Detector Description and Simulation Tool, User Guide, CERN Application Software Group, CERN Geneva, Switzerland. 3. Denard, J-C. et A1 Experimental Diagnostics Using Optical Transition Radiation at CEBAF, in AIP Conference Proceedings 333, Beam Instrumentation Workshop, Vancouver, B.C., CANADA, October Rule D.W. and Fiorito R.B., Imaging Micron-Sized Beams with Optical Transition Radiation, in Particles and Fields Series 44, Accelerator Instmentation, 2nd Annual Workshop, Batavia, IL, 199, p Fisher, C., Private Communication, November Nelson, W.R., Hirayama, H., Rogers, D.W.O., The EGS4 Code System, Standford Linear Accelerator Center report SLAC-21, 1978.
9 - 1? V :.-.6 E.5 z ' Distonce (mm) Figure. 4. Horizontal profile of a 3.2GeV, 3pA beam measured with the OTR monitor. Figure. 5. Beam intensity and radius that bring various foil materials to their melting point, taking conduction and radiation phenomena into account. The calculation considers 25mm diameter foils whose outside edge is at ambient temperature, a reasonable assumption for small energy deposition.
SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory FACET & TEST BEAM FACILITIES PROPOSAL
 SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory FACET & TEST BEAM FACILITIES PROPOSAL Date: 6/17/13 A. EXPERIMENT TITLE: Development of Electron Radiography for Material Science B. PROPOSERS & REQUESTED FACILITY:
SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory FACET & TEST BEAM FACILITIES PROPOSAL Date: 6/17/13 A. EXPERIMENT TITLE: Development of Electron Radiography for Material Science B. PROPOSERS & REQUESTED FACILITY:
MEASURING AND CONTROLLING ENERGY SPREAD IN CEBAF
 MEASURING AND CONTROLLING ENERGY SPREAD IN CEBAF Abstract G. A. Krafft, J.-C. Denard, R. W. Dickson, R. Kazimi, V. A. Lebedev, and M. G. Tiefenback TJNAF, Newport News, VA2366, USA As compared to electron
MEASURING AND CONTROLLING ENERGY SPREAD IN CEBAF Abstract G. A. Krafft, J.-C. Denard, R. W. Dickson, R. Kazimi, V. A. Lebedev, and M. G. Tiefenback TJNAF, Newport News, VA2366, USA As compared to electron
object objective lens eyepiece lens
 Advancing Physics G495 June 2015 SET #1 ANSWERS Field and Particle Pictures Seeing with electrons The compound optical microscope Q1. Before attempting this question it may be helpful to review ray diagram
Advancing Physics G495 June 2015 SET #1 ANSWERS Field and Particle Pictures Seeing with electrons The compound optical microscope Q1. Before attempting this question it may be helpful to review ray diagram
Basic structure of SEM
 Table of contents Basis structure of SEM SEM imaging modes Comparison of ordinary SEM and FESEM Electron behavior Electron matter interaction o Elastic interaction o Inelastic interaction o Interaction
Table of contents Basis structure of SEM SEM imaging modes Comparison of ordinary SEM and FESEM Electron behavior Electron matter interaction o Elastic interaction o Inelastic interaction o Interaction
Information about the T9 beam line and experimental facilities
 Information about the T9 beam line and experimental facilities The incoming proton beam from the PS accelerator impinges on the North target and thus produces the particles for the T9 beam line. The collisions
Information about the T9 beam line and experimental facilities The incoming proton beam from the PS accelerator impinges on the North target and thus produces the particles for the T9 beam line. The collisions
Insertion Devices Lecture 2 Wigglers and Undulators. Jim Clarke ASTeC Daresbury Laboratory
 Insertion Devices Lecture 2 Wigglers and Undulators Jim Clarke ASTeC Daresbury Laboratory Summary from Lecture #1 Synchrotron Radiation is emitted by accelerated charged particles The combination of Lorentz
Insertion Devices Lecture 2 Wigglers and Undulators Jim Clarke ASTeC Daresbury Laboratory Summary from Lecture #1 Synchrotron Radiation is emitted by accelerated charged particles The combination of Lorentz
PRELIMINARY TEST OF A LUMINESCENCE PROFILE MONITOR IN THE CERN SPS
 PRELIMINARY TEST OF A LUMINESCENCE PROFILE MONITOR IN THE CERN SPS J. Camas, R. J. Colchester, G. Ferioli, R. Jung, J. Koopman CERN, Geneva, Switzerland Abstract In order to satisfy the tight emittance
PRELIMINARY TEST OF A LUMINESCENCE PROFILE MONITOR IN THE CERN SPS J. Camas, R. J. Colchester, G. Ferioli, R. Jung, J. Koopman CERN, Geneva, Switzerland Abstract In order to satisfy the tight emittance
SRF GUN CHARACTERIZATION - PHASE SPACE AND DARK CURRENT MEASUREMENTS AT ELBE*
 SRF GUN CHARACTERIZATION - PHASE SPACE AND DARK CURRENT MEASUREMENTS AT ELBE* E. Panofski #, A. Jankowiak, T. Kamps, Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin, Berlin, Germany P.N. Lu, J. Teichert, Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf,
SRF GUN CHARACTERIZATION - PHASE SPACE AND DARK CURRENT MEASUREMENTS AT ELBE* E. Panofski #, A. Jankowiak, T. Kamps, Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin, Berlin, Germany P.N. Lu, J. Teichert, Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf,
Light Source I. Takashi TANAKA (RIKEN SPring-8 Center) Cheiron 2012: Light Source I
 Light Source I Takashi TANAKA (RIKEN SPring-8 Center) Light Source I Light Source II CONTENTS Introduction Fundamentals of Light and SR Overview of SR Light Source Characteristics of SR (1) Characteristics
Light Source I Takashi TANAKA (RIKEN SPring-8 Center) Light Source I Light Source II CONTENTS Introduction Fundamentals of Light and SR Overview of SR Light Source Characteristics of SR (1) Characteristics
Measurement of the n_tof beam profile in the second experimental area (EAR2) using a silicon detector
 Measurement of the n_tof beam profile in the second experimental area (EAR) using a silicon detector Fidan Suljik Supervisors: Dr. Massimo Barbagallo & Dr. Federica Mingrone September 8, 7 Abstract A new
Measurement of the n_tof beam profile in the second experimental area (EAR) using a silicon detector Fidan Suljik Supervisors: Dr. Massimo Barbagallo & Dr. Federica Mingrone September 8, 7 Abstract A new
ERL FACILITY AT CERN FOR APPLICATIONS
 ERL FACILITY AT CERN FOR APPLICATIONS Erk Jensen (CERN) Big thanks to contributors: A. Bogacz (JLAB), O. Brüning, R. Calaga, V. Chetvertkova, E. Cormier (CELIA), R. Jones, M. Klein, A. Valloni, D. Pellegrini,
ERL FACILITY AT CERN FOR APPLICATIONS Erk Jensen (CERN) Big thanks to contributors: A. Bogacz (JLAB), O. Brüning, R. Calaga, V. Chetvertkova, E. Cormier (CELIA), R. Jones, M. Klein, A. Valloni, D. Pellegrini,
The Compact Muon Solenoid Experiment. Conference Report. Mailing address: CMS CERN, CH-1211 GENEVA 23, Switzerland
 Available on CMS information server CMS CR -2018/225 The Compact Muon Solenoid Experiment Conference Report Mailing address: CMS CERN, CH-1211 GENEVA 23, Switzerland 27 September 2018 (v2, 19 November
Available on CMS information server CMS CR -2018/225 The Compact Muon Solenoid Experiment Conference Report Mailing address: CMS CERN, CH-1211 GENEVA 23, Switzerland 27 September 2018 (v2, 19 November
Measurement of Beam Profile
 Measurement of Beam Profile The beam width can be changed by focusing via quadruples. Transverse matching between ascending accelerators is done by focusing. Profiles have to be controlled at many locations.
Measurement of Beam Profile The beam width can be changed by focusing via quadruples. Transverse matching between ascending accelerators is done by focusing. Profiles have to be controlled at many locations.
JLEIC forward detector design and performance
 Jefferson Lab E-mail: ryoshida@jlab.org A major part of the physics program at the Electron-Ion Collider being planned in the US is the exploration of nucleon and nuclear structure. This program means
Jefferson Lab E-mail: ryoshida@jlab.org A major part of the physics program at the Electron-Ion Collider being planned in the US is the exploration of nucleon and nuclear structure. This program means
NA62: Ultra-Rare Kaon Decays
 NA62: Ultra-Rare Kaon Decays Phil Rubin George Mason University For the NA62 Collaboration November 10, 2011 The primary goal of the experiment is to reconstruct more than 100 K + π + ν ν events, over
NA62: Ultra-Rare Kaon Decays Phil Rubin George Mason University For the NA62 Collaboration November 10, 2011 The primary goal of the experiment is to reconstruct more than 100 K + π + ν ν events, over
Beam Diagnostics and Instrumentation JUAS, Archamps Peter Forck Gesellschaft für Schwerionenforschnung (GSI)
 Beam Diagnostics and Instrumentation JUAS, Archamps Peter Forck Gesellschaft für Schwerionenforschnung (GSI), 2003, A dedicated proton accelerator for 1p-physics at the future GSI Demands facilities for
Beam Diagnostics and Instrumentation JUAS, Archamps Peter Forck Gesellschaft für Schwerionenforschnung (GSI), 2003, A dedicated proton accelerator for 1p-physics at the future GSI Demands facilities for
II) Experimental Design
 SLAC Experimental Advisory Committee --- September 12 th, 1997 II) Experimental Design Theory and simulations Great promise of significant scientific and technological achievements! How to realize this
SLAC Experimental Advisory Committee --- September 12 th, 1997 II) Experimental Design Theory and simulations Great promise of significant scientific and technological achievements! How to realize this
Electron Energy (MeV)
 A High Resolution Electron Beam Prole Monitor and its Applications W. S. Graves, E. D. Johnson, and S. Ulc Brookhaven National Laboratory, Upton, NY 11973 USA Abstract. A beam diagnostic to measure transverse
A High Resolution Electron Beam Prole Monitor and its Applications W. S. Graves, E. D. Johnson, and S. Ulc Brookhaven National Laboratory, Upton, NY 11973 USA Abstract. A beam diagnostic to measure transverse
Observation of Coherent Optical Transition Radiation in the LCLS Linac
 Observation of Coherent Optical Transition Radiation in the LCLS Linac Henrik Loos, Ron Akre, Franz-Josef Decker, Yuantao Ding, David Dowell, Paul Emma,, Sasha Gilevich, Gregory R. Hays, Philippe Hering,
Observation of Coherent Optical Transition Radiation in the LCLS Linac Henrik Loos, Ron Akre, Franz-Josef Decker, Yuantao Ding, David Dowell, Paul Emma,, Sasha Gilevich, Gregory R. Hays, Philippe Hering,
X-Ray Diagnostics Commissioning at the LCLS
 X-Ray Diagnostics Commissioning at the LCLS - Selected Studies - J. Welch, SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory Aug. 3-27, 2010 Commissioning Studies Microbunching Instability Laser Heater tune-up Gas
X-Ray Diagnostics Commissioning at the LCLS - Selected Studies - J. Welch, SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory Aug. 3-27, 2010 Commissioning Studies Microbunching Instability Laser Heater tune-up Gas
FURTHER UNDERSTANDING THE LCLS INJECTOR EMITTANCE*
 Proceedings of FEL014, Basel, Switzerland FURTHER UNDERSTANDING THE LCLS INJECTOR EMITTANCE* F. Zhou, K. Bane, Y. Ding, Z. Huang, and H. Loos, SLAC, Menlo Park, CA 9405, USA Abstract Coherent optical transition
Proceedings of FEL014, Basel, Switzerland FURTHER UNDERSTANDING THE LCLS INJECTOR EMITTANCE* F. Zhou, K. Bane, Y. Ding, Z. Huang, and H. Loos, SLAC, Menlo Park, CA 9405, USA Abstract Coherent optical transition
Check the LCLS Project website to verify 2 of 6 that this is the correct version prior to use.
 1. Introduction The XTOD Offset Systems are designed to spatially separate the useful FEL radiation from high-energy spontaneous radiation and Bremsstrahlung γ-rays. These unwanted radiations are generated
1. Introduction The XTOD Offset Systems are designed to spatially separate the useful FEL radiation from high-energy spontaneous radiation and Bremsstrahlung γ-rays. These unwanted radiations are generated
PoS(EPS-HEP2017)533. First Physics Results of AWAKE, a Plasma Wakefield Acceleration Experiment at CERN. Patric Muggli, Allen Caldwell
 First Physics Results of AWAKE, a Plasma Wakefield Acceleration Experiment at CERN Patric Muggli, Max Planck Institute for Physics E-mail: muggli@mpp.mpg.de AWAKE is a plasma wakefield acceleration experiment
First Physics Results of AWAKE, a Plasma Wakefield Acceleration Experiment at CERN Patric Muggli, Max Planck Institute for Physics E-mail: muggli@mpp.mpg.de AWAKE is a plasma wakefield acceleration experiment
Diagnostic Systems for High Brightness Electron Injectors
 Diagnostic Systems for High Brightness Electron Injectors Henrik Loos 48 th ICFA Advanced Beam Dynamics Workshop on Future Light Sources SLAC 2010 1 1 Henrik Loos LCLS Injector Injector Diagnostics Characterize
Diagnostic Systems for High Brightness Electron Injectors Henrik Loos 48 th ICFA Advanced Beam Dynamics Workshop on Future Light Sources SLAC 2010 1 1 Henrik Loos LCLS Injector Injector Diagnostics Characterize
Measuring low emittances at FACET
 Measuring low emittances at FACET FACET-II Science Workshop October 18, 2016 Carl A. Lindstrøm PhD Student University of Oslo, Department of Physics Supervisor: Erik Adli Presented by Navid Vafaei-Najafabadi
Measuring low emittances at FACET FACET-II Science Workshop October 18, 2016 Carl A. Lindstrøm PhD Student University of Oslo, Department of Physics Supervisor: Erik Adli Presented by Navid Vafaei-Najafabadi
The photoneutron yield predictions by PICA and comparison with the measurements
 The photoneutron yield predictions by PICA and comparison with the measurements P. K. Job Advanced Photon Source Argonne National Laboratory Argonne, IL 60349 T. G Gabriel OakRidge Detector Center OakRidge
The photoneutron yield predictions by PICA and comparison with the measurements P. K. Job Advanced Photon Source Argonne National Laboratory Argonne, IL 60349 T. G Gabriel OakRidge Detector Center OakRidge
Delta undulator magnet: concept and project status
 Delta undulator magnet: concept and project status Part I: concept and model construction* Alexander Temnykh, CLASSE, Cornell University, Ithaca, New York, USA Part - II: beam test at ATF in BNL + M. Babzien,
Delta undulator magnet: concept and project status Part I: concept and model construction* Alexander Temnykh, CLASSE, Cornell University, Ithaca, New York, USA Part - II: beam test at ATF in BNL + M. Babzien,
A Transverse Profile Imager for SwissFEL Rasmus Ischebeck
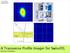 PAUL SCHERRER INSTITUT observer s virtual image d scnitillating crystal primary beam A Transverse Profile Imager for SwissFEL A Transverse Profile Imager for SwissFEL > Profile measurement in FELs observer
PAUL SCHERRER INSTITUT observer s virtual image d scnitillating crystal primary beam A Transverse Profile Imager for SwissFEL A Transverse Profile Imager for SwissFEL > Profile measurement in FELs observer
Diagnostic Systems for Characterizing Electron Sources at the Photo Injector Test Facility at DESY, Zeuthen site
 1 Diagnostic Systems for Characterizing Electron Sources at the Photo Injector Test Facility at DESY, Zeuthen site Sakhorn Rimjaem (on behalf of the PITZ team) Motivation Photo Injector Test Facility at
1 Diagnostic Systems for Characterizing Electron Sources at the Photo Injector Test Facility at DESY, Zeuthen site Sakhorn Rimjaem (on behalf of the PITZ team) Motivation Photo Injector Test Facility at
OPTIMIZATION OF COMPENSATION CHICANES IN THE LCLS-II BEAM DELIVERY SYSTEM
 OPTIMIZATION OF COMPENSATION CHICANES IN THE LCLS-II BEAM DELIVERY SYSTEM LCLS-II TN-15-41 11/23/2015 J. Qiang, M. Venturini November 23, 2015 LCLSII-TN-15-41 1 Introduction L C L S - I I T E C H N I C
OPTIMIZATION OF COMPENSATION CHICANES IN THE LCLS-II BEAM DELIVERY SYSTEM LCLS-II TN-15-41 11/23/2015 J. Qiang, M. Venturini November 23, 2015 LCLSII-TN-15-41 1 Introduction L C L S - I I T E C H N I C
IPBI-TN June 30, 2004
 Spray Electron Beam for Tests of Linear Collider Forward Calorimeter Detectors in SLAC End Station A R. Arnold UMass Amherst, Amherst MA 01003 T. Fieguth Stanford Linear Accelerator Center Menlo Park,
Spray Electron Beam for Tests of Linear Collider Forward Calorimeter Detectors in SLAC End Station A R. Arnold UMass Amherst, Amherst MA 01003 T. Fieguth Stanford Linear Accelerator Center Menlo Park,
A Gaussian Fitter for the CESR-c Fast Luminosity Monitor
 A Gaussian Fitter for the CESR-c Fast Luminosity Monitor Katherine L. Dooley Vassar College, Poughkeepsie, New York 1264 USA (Dated: July 21, 24) The purpose of the CESR-c fast luminosity monitor (FLM)
A Gaussian Fitter for the CESR-c Fast Luminosity Monitor Katherine L. Dooley Vassar College, Poughkeepsie, New York 1264 USA (Dated: July 21, 24) The purpose of the CESR-c fast luminosity monitor (FLM)
Electron Beam Polarimetry at JLab Hall C Dave Gaskell PST 2009 September 7, 2009
 Electron Beam Polarimetry at JLab Hall C Dave Gaskell PST 2009 September 7, 2009 1. Møller Polarimeter 2. Compton Polarimeter 3. Summary JLab Polarimetry Techniques Three different processes used to measure
Electron Beam Polarimetry at JLab Hall C Dave Gaskell PST 2009 September 7, 2009 1. Møller Polarimeter 2. Compton Polarimeter 3. Summary JLab Polarimetry Techniques Three different processes used to measure
2.6 Electron transport lines
 2.6 Electron transport lines 2.6 Electron transport lines Overview The electron transport lines consist of all of the electron beamline segments that are neither part of the Linacs nor part of the injector.
2.6 Electron transport lines 2.6 Electron transport lines Overview The electron transport lines consist of all of the electron beamline segments that are neither part of the Linacs nor part of the injector.
Fall 2014 Mott Target Replacement and Ladder Position Re- Calibration JLAB- TN Joe Grames. September 17, 2014
 Fall 2014 Mott Target Replacement and Ladder Position Re- Calibration JLAB- TN- 14-026 Joe Grames September 17, 2014 Abstract Target foils of gold, silver and copper used in the Spring 2014 re- commissioning
Fall 2014 Mott Target Replacement and Ladder Position Re- Calibration JLAB- TN- 14-026 Joe Grames September 17, 2014 Abstract Target foils of gold, silver and copper used in the Spring 2014 re- commissioning
6/12 GeV CEBAF and HPS beam requirements
 6/12 GeV CEBAF and HPS beam requirements Arne Freyberger Operations Department Accelerator Division JLAB May 26, 2011 APF HPS May 26, 2011 1 / 16 1 12GeV Beam Requirements 2 12GeV Design and Simulation
6/12 GeV CEBAF and HPS beam requirements Arne Freyberger Operations Department Accelerator Division JLAB May 26, 2011 APF HPS May 26, 2011 1 / 16 1 12GeV Beam Requirements 2 12GeV Design and Simulation
Beam Extraction by the Laser Charge Exchange Method Using the 3-MeV LINAC in J-PARC )
 Beam Extraction by the Laser Charge Exchange Method Using the 3-MeV LINAC in J-PARC ) Hayanori TAKEI, Koichiro HIRANO, Kazuyoshi TSUTSUMI 1) and Shin-ichiro MEIGO J-PARC Center, Japan Atomic Energy Agency,
Beam Extraction by the Laser Charge Exchange Method Using the 3-MeV LINAC in J-PARC ) Hayanori TAKEI, Koichiro HIRANO, Kazuyoshi TSUTSUMI 1) and Shin-ichiro MEIGO J-PARC Center, Japan Atomic Energy Agency,
LCLS Injector Prototyping at the GTF
 LCLS Injector Prototyping at at the GTF John John Schmerge, SLAC SLAC November 3, 3, 23 23 GTF GTF Description Summary of of Previous Measurements Longitudinal Emittance Transverse Emittance Active LCLS
LCLS Injector Prototyping at at the GTF John John Schmerge, SLAC SLAC November 3, 3, 23 23 GTF GTF Description Summary of of Previous Measurements Longitudinal Emittance Transverse Emittance Active LCLS
TUNE SPREAD STUDIES AT INJECTION ENERGIES FOR THE CERN PROTON SYNCHROTRON BOOSTER
 TUNE SPREAD STUDIES AT INJECTION ENERGIES FOR THE CERN PROTON SYNCHROTRON BOOSTER B. Mikulec, A. Findlay, V. Raginel, G. Rumolo, G. Sterbini, CERN, Geneva, Switzerland Abstract In the near future, a new
TUNE SPREAD STUDIES AT INJECTION ENERGIES FOR THE CERN PROTON SYNCHROTRON BOOSTER B. Mikulec, A. Findlay, V. Raginel, G. Rumolo, G. Sterbini, CERN, Geneva, Switzerland Abstract In the near future, a new
A Segmented Beam Dump for
 A Segmented Beam Dump for thects Lineat CTF3 M. Olvegård, W. Andreazza, E. Bravin, N. Chritin, A. Dabrowski, M. Duraffourg, T. Lefèvre May10, 2012 Abstract We propose a new segmented beam dump to be installed
A Segmented Beam Dump for thects Lineat CTF3 M. Olvegård, W. Andreazza, E. Bravin, N. Chritin, A. Dabrowski, M. Duraffourg, T. Lefèvre May10, 2012 Abstract We propose a new segmented beam dump to be installed
The low Q 2 chicane and Compton polarimeter at the JLab EIC
 EPJ Web of Conferences 112, 01007 (2016) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 201611201007 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2016 The low Q 2 chicane and Compton polarimeter at the JLab EIC, Alexandre
EPJ Web of Conferences 112, 01007 (2016) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 201611201007 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2016 The low Q 2 chicane and Compton polarimeter at the JLab EIC, Alexandre
Beam diagnostics: Alignment of the beam to prevent for activation. Accelerator physics: using these sensitive particle detectors.
 Beam Loss Monitors When energetic beam particles penetrates matter, secondary particles are emitted: this can be e, γ, protons, neutrons, excited nuclei, fragmented nuclei... Spontaneous radiation and
Beam Loss Monitors When energetic beam particles penetrates matter, secondary particles are emitted: this can be e, γ, protons, neutrons, excited nuclei, fragmented nuclei... Spontaneous radiation and
BEAM PROFILE MONITORS FOR THE HERA PROTON ACCELERATORS
 BEAM PROFILE MONITORS FOR THE HERA PROTON ACCELERATORS V, Hain, F. Hornstra, A. Lazos, G. Miat, G. Samulat, K. Wittenburg DESY, Notkestr. 85, 2000 Hamburg 52, Germany Abstract: Residual gas ionization
BEAM PROFILE MONITORS FOR THE HERA PROTON ACCELERATORS V, Hain, F. Hornstra, A. Lazos, G. Miat, G. Samulat, K. Wittenburg DESY, Notkestr. 85, 2000 Hamburg 52, Germany Abstract: Residual gas ionization
Multi-Purpose Accelerator-Accumulator ITEP-TWAC for Nuclear Physics and Practical Applications
 Multi-Purpose Accelerator-Accumulator ITEP-TWAC for Nuclear Physics and Practical Applications N.N.Alexeev, D.G.Koshkarev and B.Yu.Sharkov Institute for Theoretical and Experimental Physics, B.Cheremushk.
Multi-Purpose Accelerator-Accumulator ITEP-TWAC for Nuclear Physics and Practical Applications N.N.Alexeev, D.G.Koshkarev and B.Yu.Sharkov Institute for Theoretical and Experimental Physics, B.Cheremushk.
Upstream Polarimetry with 4-Magnet Chicane
 2005 International Linear Collider Workshop Stanford, U.S.A. Upstream Polarimetry with 4-Magnet Chicane N. Meyners, V. Gharibyan, K.P. Schüler DESY, Hamburg, Germany We have extended an earlier polarimeter
2005 International Linear Collider Workshop Stanford, U.S.A. Upstream Polarimetry with 4-Magnet Chicane N. Meyners, V. Gharibyan, K.P. Schüler DESY, Hamburg, Germany We have extended an earlier polarimeter
ELIC: A High Luminosity And Efficient Spin Manipulation Electron-Light Ion Collider Based At CEBAF
 ELIC: A High Luminosity And Efficient Spin Manipulation Electron-Light Ion Collider Based At CEBAF Lia Merminga and Yaroslav Derbenev Center for Advanced Studies of Accelerators, Jefferson Laboratory,
ELIC: A High Luminosity And Efficient Spin Manipulation Electron-Light Ion Collider Based At CEBAF Lia Merminga and Yaroslav Derbenev Center for Advanced Studies of Accelerators, Jefferson Laboratory,
New Versatile Platform Based on the Low Energy Electron Beam Delivered by the PHIL Photoinjector
 WDS'13 Proceedings of Contributed Papers, Part III, 33 38, 2013. ISBN 978-80-7378-252-8 MATFYZPRESS New Versatile Platform Based on the Low Energy Electron Beam Delivered by the PHIL Photoinjector S. Barsuk,
WDS'13 Proceedings of Contributed Papers, Part III, 33 38, 2013. ISBN 978-80-7378-252-8 MATFYZPRESS New Versatile Platform Based on the Low Energy Electron Beam Delivered by the PHIL Photoinjector S. Barsuk,
Forward Region, Energy Spectrometer, Polarimeter. Snowmass Klaus Mönig
 Forward Region, Energy Spectrometer, Polarimeter Klaus Mönig Snowmass 2005 1 Klaus Mönig MDI questions related to this talk 9) Is a 2 mrad crossing angle sufficiently small that it does not significantly
Forward Region, Energy Spectrometer, Polarimeter Klaus Mönig Snowmass 2005 1 Klaus Mönig MDI questions related to this talk 9) Is a 2 mrad crossing angle sufficiently small that it does not significantly
L. Bobb 1, 2, M. Billing 3, N. Chritin 2, P. Karataev 1, T. Lefevre 2
 L. Bobb 1, 2, M. Billing 3, N. Chritin 2, P. Karataev 1, T. Lefevre 2 1. John Adams Institute at Royal Holloway, Egham, Surrey, United Kingdom 2. CERN European Organisation for Nuclear Research, CERN,
L. Bobb 1, 2, M. Billing 3, N. Chritin 2, P. Karataev 1, T. Lefevre 2 1. John Adams Institute at Royal Holloway, Egham, Surrey, United Kingdom 2. CERN European Organisation for Nuclear Research, CERN,
RADIATION SOURCES AT SIBERIA-2 STORAGE RING
 RADIATION SOURCES AT SIBERIA-2 STORAGE RING V.N. Korchuganov, N.Yu. Svechnikov, N.V. Smolyakov, S.I. Tomin RRC «Kurchatov Institute», Moscow, Russia Kurchatov Center Synchrotron Radiation undulator undulator
RADIATION SOURCES AT SIBERIA-2 STORAGE RING V.N. Korchuganov, N.Yu. Svechnikov, N.V. Smolyakov, S.I. Tomin RRC «Kurchatov Institute», Moscow, Russia Kurchatov Center Synchrotron Radiation undulator undulator
PIP-II Injector Test s Low Energy Beam Transport: Commissioning and Selected Measurements
 PIP-II Injector Test s Low Energy Beam Transport: Commissioning and Selected Measurements A. Shemyakin 1, M. Alvarez 1, R. Andrews 1, J.-P. Carneiro 1, A. Chen 1, R. D Arcy 2, B. Hanna 1, L. Prost 1, V.
PIP-II Injector Test s Low Energy Beam Transport: Commissioning and Selected Measurements A. Shemyakin 1, M. Alvarez 1, R. Andrews 1, J.-P. Carneiro 1, A. Chen 1, R. D Arcy 2, B. Hanna 1, L. Prost 1, V.
Characterizations and Diagnostics of Compton Light Source
 Characterizations and Diagnostics of Compton Light Source Advance Light Source (ALS) (LBNL) Ying K. Wu Duke Free Electron Laser Laboratory (DFELL) Acknowledgments: DFELL: B. Jia, G. Swift, H. Hao, J. Li,
Characterizations and Diagnostics of Compton Light Source Advance Light Source (ALS) (LBNL) Ying K. Wu Duke Free Electron Laser Laboratory (DFELL) Acknowledgments: DFELL: B. Jia, G. Swift, H. Hao, J. Li,
Particle Physics Homework Assignment 4
 Particle Physics Homework Assignment 4 Prof. Costas Foudas March 01 Problem 1: Show the the momentum, p of a particle moving in a circular trajectory of radius, R, in a magnetic field, B, is given by:
Particle Physics Homework Assignment 4 Prof. Costas Foudas March 01 Problem 1: Show the the momentum, p of a particle moving in a circular trajectory of radius, R, in a magnetic field, B, is given by:
CW POSITRON SOURCE AT CEBAF
 CW POSITRON SOURCE AT CEBAF by Serkan Golge B.S. July 2002, Fatih University M.S. December 2005, Old Dominion University A Dissertation Submitted to the Faculty of Old Dominion University in Partial Fulfillment
CW POSITRON SOURCE AT CEBAF by Serkan Golge B.S. July 2002, Fatih University M.S. December 2005, Old Dominion University A Dissertation Submitted to the Faculty of Old Dominion University in Partial Fulfillment
GEANT4 Emittance Diagnostics Simulations for the ERL Injector Prototype
 GEANT4 Emittance Diagnostics Simulations for the ERL Injector Prototype Colwyn Gulliford Physics Department, New College of Florida, Sarasota, Florida, 34243 (Dated: August 16, 2006) The injector for the
GEANT4 Emittance Diagnostics Simulations for the ERL Injector Prototype Colwyn Gulliford Physics Department, New College of Florida, Sarasota, Florida, 34243 (Dated: August 16, 2006) The injector for the
SURVEY AND ALIGNMENT FOR THE SYNCHROTRON LIGHT SOURCE ELETTRA
 I/49 SURVEY AND ALIGNMENT FOR THE SYNCHROTRON LIGHT SOURCE ELETTRA ABSTRACT: F.Wei, A.Bergamo, P.Furlan, J.Grgic, A.Wrulich Sincrotrone Trieste Padriciano 99, 34012 Trieste, Italy ELETTRA is a third generation
I/49 SURVEY AND ALIGNMENT FOR THE SYNCHROTRON LIGHT SOURCE ELETTRA ABSTRACT: F.Wei, A.Bergamo, P.Furlan, J.Grgic, A.Wrulich Sincrotrone Trieste Padriciano 99, 34012 Trieste, Italy ELETTRA is a third generation
Beam Shape and Halo Monitor Study
 EUROPEAN ORGANISATION FOR NUCLEAR RESEARCH CERN A&B DEPARTMENT AB-Note-2006-047 ABP Beam Shape and Halo Monitor Study J-B. Lallement, E.Z. Sargsyan, M. Hori Abstract The Beam Shape and Halo Monitor, designed
EUROPEAN ORGANISATION FOR NUCLEAR RESEARCH CERN A&B DEPARTMENT AB-Note-2006-047 ABP Beam Shape and Halo Monitor Study J-B. Lallement, E.Z. Sargsyan, M. Hori Abstract The Beam Shape and Halo Monitor, designed
Emittance (Profile) Measurements in the Proton Accelerators at DESY
 Emittance (Profile) Measurements in the Proton Accelerators at DESY Kay Wittenburg, MDI Deutsches Electronen Synchrotron Hamburg, Germany Profile Monitors in the Proton Accelerators DESY III:» Wire Scanner,
Emittance (Profile) Measurements in the Proton Accelerators at DESY Kay Wittenburg, MDI Deutsches Electronen Synchrotron Hamburg, Germany Profile Monitors in the Proton Accelerators DESY III:» Wire Scanner,
σ ε ω 1 /σ ω ε α=ω 2 /ω 1
 The measurement line at the Antiproton Decelerator Ulrik Mikkelsen Institute for Storage Ring Facilities, ISA, University of Aarhus, DK{8000 Aarhus C, Denmark and PS-CA, CERN, CH-1211 Geneva 23, Switzerland
The measurement line at the Antiproton Decelerator Ulrik Mikkelsen Institute for Storage Ring Facilities, ISA, University of Aarhus, DK{8000 Aarhus C, Denmark and PS-CA, CERN, CH-1211 Geneva 23, Switzerland
Imaging principle and experiment results of an 11 MeV low-energy proton radiography system
 NUCLEAR SCIENCE AND TECHNIQUES 25, 060203 (2014) Imaging principle and experiment results of an 11 MeV low-energy proton radiography system LI Yi-Ding ( 李一丁 ), 1, ZHANG Xiao-Ding ( 张小丁 ), 1 WEI Tao ( 魏涛
NUCLEAR SCIENCE AND TECHNIQUES 25, 060203 (2014) Imaging principle and experiment results of an 11 MeV low-energy proton radiography system LI Yi-Ding ( 李一丁 ), 1, ZHANG Xiao-Ding ( 张小丁 ), 1 WEI Tao ( 魏涛
New irradiation zones at the CERN-PS
 Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 426 (1999) 72 77 New irradiation zones at the CERN-PS M. Glaser, L. Durieu, F. Lemeilleur *, M. Tavlet, C. Leroy, P. Roy ROSE/RD48 Collaboration CERN,
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 426 (1999) 72 77 New irradiation zones at the CERN-PS M. Glaser, L. Durieu, F. Lemeilleur *, M. Tavlet, C. Leroy, P. Roy ROSE/RD48 Collaboration CERN,
Experimental study of nonlinear laser-beam Thomson scattering
 Experimental study of nonlinear laser-beam Thomson scattering T. Kumita, Y. Kamiya, T. Hirose Department of Physics, Tokyo Metropolitan University, 1-1 Minami-Ohsawa, Hachioji, Tokyo 192-0397, Japan I.
Experimental study of nonlinear laser-beam Thomson scattering T. Kumita, Y. Kamiya, T. Hirose Department of Physics, Tokyo Metropolitan University, 1-1 Minami-Ohsawa, Hachioji, Tokyo 192-0397, Japan I.
Bethe-Block. Stopping power of positive muons in copper vs βγ = p/mc. The slight dependence on M at highest energies through T max
 Bethe-Block Stopping power of positive muons in copper vs βγ = p/mc. The slight dependence on M at highest energies through T max can be used for PID but typically de/dx depend only on β (given a particle
Bethe-Block Stopping power of positive muons in copper vs βγ = p/mc. The slight dependence on M at highest energies through T max can be used for PID but typically de/dx depend only on β (given a particle
Low slice emittance preservation during bunch compression
 Low slice emittance preservation during bunch compression S. Bettoni M. Aiba, B. Beutner, M. Pedrozzi, E. Prat, S. Reiche, T. Schietinger Outline. Introduction. Experimental studies a. Measurement procedure
Low slice emittance preservation during bunch compression S. Bettoni M. Aiba, B. Beutner, M. Pedrozzi, E. Prat, S. Reiche, T. Schietinger Outline. Introduction. Experimental studies a. Measurement procedure
The FLUKA study of the secondary particles fluence in the AD-Antiproton Decelerator target area.
 2014-01-09 marco.calviani@cern.ch elzbieta.nowak@cern.ch The FLUKA study of the secondary particles fluence in the AD-Antiproton Decelerator target area. M. Calviani and E. Nowak EN/STI CERN, Geneva, Switzerland
2014-01-09 marco.calviani@cern.ch elzbieta.nowak@cern.ch The FLUKA study of the secondary particles fluence in the AD-Antiproton Decelerator target area. M. Calviani and E. Nowak EN/STI CERN, Geneva, Switzerland
Transverse Profiles. Enrico Bravin CERN. CAS - Dourdan, France 28 May 6 June 2008
 Transverse Profiles Enrico Bravin CERN CAS - Dourdan, France 28 May 6 June 2008 Content Coordinate system Transverse space Transverse phase space Interaction of particles with matter Radiation emission
Transverse Profiles Enrico Bravin CERN CAS - Dourdan, France 28 May 6 June 2008 Content Coordinate system Transverse space Transverse phase space Interaction of particles with matter Radiation emission
A gas-filled calorimeter for high intensity beam environments
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Physics Procedia 37 (212 ) 364 371 TIPP 211 - Technology and Instrumentation in Particle Physics 211 A gas-filled calorimeter for high intensity beam environments
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Physics Procedia 37 (212 ) 364 371 TIPP 211 - Technology and Instrumentation in Particle Physics 211 A gas-filled calorimeter for high intensity beam environments
Application of Precision Deformable Mirrors to Space Astronomy
 Application of Precision Deformable Mirrors to Space Astronomy John Trauger, Dwight Moody Brian Gordon, Yekta Gursel (JPL) Mark Ealey, Roger Bagwell (Xinetics) Workshop on Innovative Designs for the Next
Application of Precision Deformable Mirrors to Space Astronomy John Trauger, Dwight Moody Brian Gordon, Yekta Gursel (JPL) Mark Ealey, Roger Bagwell (Xinetics) Workshop on Innovative Designs for the Next
Diagnostics at the MAX IV 3 GeV storage ring during commissioning. PPT-mall 2. Åke Andersson On behalf of the MAX IV team
 Diagnostics at the MAX IV 3 GeV storage ring during commissioning PPT-mall 2 Åke Andersson On behalf of the MAX IV team IBIC Med 2016, linje Barcelona Outline MAX IV facility overview Linac injector mode
Diagnostics at the MAX IV 3 GeV storage ring during commissioning PPT-mall 2 Åke Andersson On behalf of the MAX IV team IBIC Med 2016, linje Barcelona Outline MAX IV facility overview Linac injector mode
LCLS Accelerator Parameters and Tolerances for Low Charge Operations
 LCLS-TN-99-3 May 3, 1999 LCLS Accelerator Parameters and Tolerances for Low Charge Operations P. Emma SLAC 1 Introduction An option to control the X-ray FEL output power of the LCLS [1] by reducing the
LCLS-TN-99-3 May 3, 1999 LCLS Accelerator Parameters and Tolerances for Low Charge Operations P. Emma SLAC 1 Introduction An option to control the X-ray FEL output power of the LCLS [1] by reducing the
Emittance and Quantum Efficiency Measurements from a 1.6 cell S- Band Photocathode RF Gun with Mg Cathode *
 LCLS-TN-4-3 SLAC PUB 763 September, 4 Emittance and Quantum Efficiency Measurements from a.6 cell S- Band Photocathode RF Gun with Mg Cathode * J.F. Schmerge, J.M. Castro, J.E. Clendenin, D.H. Dowell,
LCLS-TN-4-3 SLAC PUB 763 September, 4 Emittance and Quantum Efficiency Measurements from a.6 cell S- Band Photocathode RF Gun with Mg Cathode * J.F. Schmerge, J.M. Castro, J.E. Clendenin, D.H. Dowell,
Measurement of wakefields in hollow plasma channels Carl A. Lindstrøm (University of Oslo)
 Measurement of wakefields in hollow plasma channels Carl A. Lindstrøm (University of Oslo) in collaboration with Spencer Gessner (CERN) presented by Erik Adli (University of Oslo) FACET-II Science Workshop
Measurement of wakefields in hollow plasma channels Carl A. Lindstrøm (University of Oslo) in collaboration with Spencer Gessner (CERN) presented by Erik Adli (University of Oslo) FACET-II Science Workshop
The Very Large Hadron Collider Beam Collimation System
 The Very Large Hadron Collider Beam Collimation System A.I. Drozhdin, N.V. Mokhov, A.A. Sery, Fermilab, P.O. Box 5, Batavia, IL 65 USA INTRODUCTIONS Even in good operational conditions, a finite fraction
The Very Large Hadron Collider Beam Collimation System A.I. Drozhdin, N.V. Mokhov, A.A. Sery, Fermilab, P.O. Box 5, Batavia, IL 65 USA INTRODUCTIONS Even in good operational conditions, a finite fraction
CONCEPTUAL STUDY OF A SELF-SEEDING SCHEME AT FLASH2
 CONCEPTUAL STUDY OF A SELF-SEEDING SCHEME AT FLASH2 T. Plath, L. L. Lazzarino, Universität Hamburg, Hamburg, Germany K. E. Hacker, T.U. Dortmund, Dortmund, Germany Abstract We present a conceptual study
CONCEPTUAL STUDY OF A SELF-SEEDING SCHEME AT FLASH2 T. Plath, L. L. Lazzarino, Universität Hamburg, Hamburg, Germany K. E. Hacker, T.U. Dortmund, Dortmund, Germany Abstract We present a conceptual study
Advanced Storage Photon Ring Source Upgrade Project:
 Advanced Storage Photon Ring Source Upgrade Project: The Shielding World s for Leading the Hard X-ray Light Source Advanced Photon Source - Upgrade Bradley J. Micklich Radiation Physicist Argonne National
Advanced Storage Photon Ring Source Upgrade Project: The Shielding World s for Leading the Hard X-ray Light Source Advanced Photon Source - Upgrade Bradley J. Micklich Radiation Physicist Argonne National
LOLA: Past, present and future operation
 LOLA: Past, present and future operation FLASH Seminar 1/2/29 Christopher Gerth, DESY 8/5/29 FLASH Seminar Christopher Gerth 1 Outline Past Present Future 8/5/29 FLASH Seminar Christopher Gerth 2 Past
LOLA: Past, present and future operation FLASH Seminar 1/2/29 Christopher Gerth, DESY 8/5/29 FLASH Seminar Christopher Gerth 1 Outline Past Present Future 8/5/29 FLASH Seminar Christopher Gerth 2 Past
LITHIUM LENS FOR EFFECTIVE CAPTURE OF POSITRONS
 CBN 07-5 LITHIUM LENS FOR EFFECTIVE CAPTURE OF POSITRONS Alexander Mikhailichenko Cornell University, LEPP, Ithaca, NY 14853 Positron Source Meeting, Jan30-Feb 007, Beijing Efficiency= N e+ /N gammas Angle
CBN 07-5 LITHIUM LENS FOR EFFECTIVE CAPTURE OF POSITRONS Alexander Mikhailichenko Cornell University, LEPP, Ithaca, NY 14853 Positron Source Meeting, Jan30-Feb 007, Beijing Efficiency= N e+ /N gammas Angle
Accuracy of LHC proton loss rate determination by the BLM system
 Accuracy of LHC loss rate determination by the BLM system Eva Barbara Holzer, Bernd Dehning, Christian W. Fabjan, Daniel Kramer, Mariusz Sapinski, and Markus Stockner Abstract Most of the monitors of the
Accuracy of LHC loss rate determination by the BLM system Eva Barbara Holzer, Bernd Dehning, Christian W. Fabjan, Daniel Kramer, Mariusz Sapinski, and Markus Stockner Abstract Most of the monitors of the
Some Sample Calculations for the Far Field Harmonic Power and Angular Pattern in LCLS-1 and LCLS-2
 Some Sample Calculations for the Far Field Harmonic Power and Angular Pattern in LCLS-1 and LCLS-2 W.M. Fawley February 2013 SLAC-PUB-15359 ABSTRACT Calculations with the GINGER FEL simulation code are
Some Sample Calculations for the Far Field Harmonic Power and Angular Pattern in LCLS-1 and LCLS-2 W.M. Fawley February 2013 SLAC-PUB-15359 ABSTRACT Calculations with the GINGER FEL simulation code are
Compressor and Chicane Radiation Studies at the ATF. Gerard Andonian, UCLA High Power Workshop January 14-16, 2009 UCLA
 Compressor and Chicane Radiation Studies at the ATF Gerard Andonian, UCLA High Power Workshop January 14-16, 2009 UCLA Collaboration UCLA PBPL G. Andonian, A. Cook, M. Dunning, E. Hemsing, A. Murokh, S.
Compressor and Chicane Radiation Studies at the ATF Gerard Andonian, UCLA High Power Workshop January 14-16, 2009 UCLA Collaboration UCLA PBPL G. Andonian, A. Cook, M. Dunning, E. Hemsing, A. Murokh, S.
Radiation Safety at LCLS: The Photon Beam s Maximum Capability and Material Damage Potential
 SLAC-PUB-15708 August 2013 Radiation Safety at LCLS: The Photon Beam s Maximum Capability and Material Damage Potential J.M. Bauer *1, J.C. Liu 1, A.A. Prinz 2, and S.H. Rokni 1 1 Radiation Protection
SLAC-PUB-15708 August 2013 Radiation Safety at LCLS: The Photon Beam s Maximum Capability and Material Damage Potential J.M. Bauer *1, J.C. Liu 1, A.A. Prinz 2, and S.H. Rokni 1 1 Radiation Protection
Simulation of Laser-wires at CLIC using BDSIM
 Simulation of Laser-wires at CLIC using BDSIM Grahame A. Blair, Royal Holloway Univ of London, UK. Abstract A laserwire system within the CLIC beam delivery system is simulated using Geant4. The issues
Simulation of Laser-wires at CLIC using BDSIM Grahame A. Blair, Royal Holloway Univ of London, UK. Abstract A laserwire system within the CLIC beam delivery system is simulated using Geant4. The issues
Since the beam from the JNC linac is a very high current, low energy beam, energy loss induced in the material irradiated by the beam becomes very lar
 Proceedings of the Second International Workshop on EGS, 8.-12. August 2000, Tsukuba, Japan KEK Proceedings 200-20, pp.255-263 Beam Dump for High Current Electron Beam at JNC H. Takei and Y. Takeda 1 Japan
Proceedings of the Second International Workshop on EGS, 8.-12. August 2000, Tsukuba, Japan KEK Proceedings 200-20, pp.255-263 Beam Dump for High Current Electron Beam at JNC H. Takei and Y. Takeda 1 Japan
Characterization of an 800 nm SASE FEL at Saturation
 Characterization of an 800 nm SASE FEL at Saturation A.Tremaine*, P. Frigola, A. Murokh, C. Pellegrini, S. Reiche, J. Rosenzweig UCLA, Los Angeles, CA 90095 M. Babzien, I. Ben-Zvi, E. Johnson, R. Malone,
Characterization of an 800 nm SASE FEL at Saturation A.Tremaine*, P. Frigola, A. Murokh, C. Pellegrini, S. Reiche, J. Rosenzweig UCLA, Los Angeles, CA 90095 M. Babzien, I. Ben-Zvi, E. Johnson, R. Malone,
Tuning Techniques And Operator Diagnostics for FACET at SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory. Chris Melton SLAC Accelerator Operations
 Tuning Techniques And Operator Diagnostics for FACET at SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory Chris Melton SLAC Accelerator Operations FACET Tuning And Diagnostics What is FACET? FACET Performance Challenges
Tuning Techniques And Operator Diagnostics for FACET at SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory Chris Melton SLAC Accelerator Operations FACET Tuning And Diagnostics What is FACET? FACET Performance Challenges
The BoNuS Detector. A Radial-Drift GEM TPC. Howard Fenker TPC R&D Meeting LBL, March 24, 2005
 The BoNuS Detector A Radial-Drift GEM TPC Howard Fenker TPC R&D Meeting LBL, March 24, 2005 Barely Off-shell Nucleon Structure This work was partially supported by DOE Contract No. DE-AC05-84ER40150 under
The BoNuS Detector A Radial-Drift GEM TPC Howard Fenker TPC R&D Meeting LBL, March 24, 2005 Barely Off-shell Nucleon Structure This work was partially supported by DOE Contract No. DE-AC05-84ER40150 under
Operational Performance of LCLS Beam Instrumentation. Henrik Loos, SLAC BIW 2010, Santa Fe, NM
 Editor's Note: PDF version of slides from Beam Instrumentation Workshop 21, Santa Fe, NM Operational Performance of LCLS Beam Instrumentation Henrik Loos, SLAC BIW 21, Santa Fe, NM BIW 21 1 1 Henrik Loos
Editor's Note: PDF version of slides from Beam Instrumentation Workshop 21, Santa Fe, NM Operational Performance of LCLS Beam Instrumentation Henrik Loos, SLAC BIW 21, Santa Fe, NM BIW 21 1 1 Henrik Loos
2.24 Simulation Study of K L Beam: K L Rates and Background Ilya Larin Department of Physics Old Dominion University Norfolk, VA 23529, U.S.A.
 2.24 Simulation Study of K L Beam: K L Rates and Background Ilya Larin Department of Physics Old Dominion University Norfolk, VA 23529, U.S.A. Abstract We report our simulation results for K L -beam and
2.24 Simulation Study of K L Beam: K L Rates and Background Ilya Larin Department of Physics Old Dominion University Norfolk, VA 23529, U.S.A. Abstract We report our simulation results for K L -beam and
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A
 Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 712 (2013) 8 112 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/nima
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 712 (2013) 8 112 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/nima
LHC operation in 2015 and prospects for the future
 LHC operation in 2015 and prospects for the future Moriond Workshop La Thuile March 2016 Jörg Wenninger CERN Beams Department Operation group / LHC For the LHC commissioning and operation teams 1 Moriond
LHC operation in 2015 and prospects for the future Moriond Workshop La Thuile March 2016 Jörg Wenninger CERN Beams Department Operation group / LHC For the LHC commissioning and operation teams 1 Moriond
PARTICLE ACCELERATORS
 VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE PARTICLE ACCELERATORS Particle accelerators are used to accelerate elementary particles to very high energies for: Production of radioisotopes Probing the structure of matter There
VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE PARTICLE ACCELERATORS Particle accelerators are used to accelerate elementary particles to very high energies for: Production of radioisotopes Probing the structure of matter There
The Detector Design of the Jefferson Lab EIC
 The Detector Design of the Jefferson Lab EIC Jefferson Lab E-mail: mdiefent@jlab.org The Electron-Ion Collider (EIC) is envisioned as the next-generation U.S. facility to study quarks and gluons in strongly
The Detector Design of the Jefferson Lab EIC Jefferson Lab E-mail: mdiefent@jlab.org The Electron-Ion Collider (EIC) is envisioned as the next-generation U.S. facility to study quarks and gluons in strongly
GTF Transverse and Longitudinal Emittance Data Analysis Technique * J.F. Schmerge, J.E. Clendenin, D.H. Dowell and S.M. Gierman
 LCLS-TN-5-19 July 5 GTF Transverse and Longitudinal Emittance Data Analysis Technique * J.F. Schmerge, J.E. Clendenin, D.H. Dowell and S.M. Gierman Abstract The SSRL Gun Test Facility (GTF) was built to
LCLS-TN-5-19 July 5 GTF Transverse and Longitudinal Emittance Data Analysis Technique * J.F. Schmerge, J.E. Clendenin, D.H. Dowell and S.M. Gierman Abstract The SSRL Gun Test Facility (GTF) was built to
Transverse beam profiles
 Transverse beam profiles E. Bravin CERN, Geneva, Switzerland Abstract The performance and safe operation of a particle accelerator is closely connected to the transverse emittance of the beams it produces.
Transverse beam profiles E. Bravin CERN, Geneva, Switzerland Abstract The performance and safe operation of a particle accelerator is closely connected to the transverse emittance of the beams it produces.
Simulation of the Beam Dump for a High Intensity Electron gun
 EUROPEAN ORGANIZATION FOR NUCLEAR RESEARCH CERN BEAMS DEPARTMENT CERN-BE-2014-007 BI Simulation of the Beam Dump for a High Intensity Electron gun S. Doebert; T. Lefèvre; A, Jeff; CERN Geneva/CH K. Pepitone
EUROPEAN ORGANIZATION FOR NUCLEAR RESEARCH CERN BEAMS DEPARTMENT CERN-BE-2014-007 BI Simulation of the Beam Dump for a High Intensity Electron gun S. Doebert; T. Lefèvre; A, Jeff; CERN Geneva/CH K. Pepitone
SIMULATION STUDY FOR MEIC ELECTRON COOLING*
 SIMULATION STUDY FOR MEIC ELECTRON COOLING* He Zhang #, Yuhong Zhang, JLab, Newport News, VA 23606, USA Abstract Electron cooling of the ion beams is one critical R&D to achieve high luminosities in JLab
SIMULATION STUDY FOR MEIC ELECTRON COOLING* He Zhang #, Yuhong Zhang, JLab, Newport News, VA 23606, USA Abstract Electron cooling of the ion beams is one critical R&D to achieve high luminosities in JLab
ELECTRON DYNAMICS WITH SYNCHROTRON RADIATION
 ELECTRON DYNAMICS WITH SYNCHROTRON RADIATION Lenny Rivkin Ecole Polythechnique Federale de Lausanne (EPFL) and Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI), Switzerland CERN Accelerator School: Introduction to Accelerator
ELECTRON DYNAMICS WITH SYNCHROTRON RADIATION Lenny Rivkin Ecole Polythechnique Federale de Lausanne (EPFL) and Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI), Switzerland CERN Accelerator School: Introduction to Accelerator
LASER-COMPTON SCATTERING AS A POTENTIAL BRIGHT X-RAY SOURCE
 Copyright(C)JCPDS-International Centre for Diffraction Data 2003, Advances in X-ray Analysis, Vol.46 74 ISSN 1097-0002 LASER-COMPTON SCATTERING AS A POTENTIAL BRIGHT X-RAY SOURCE K. Chouffani 1, D. Wells
Copyright(C)JCPDS-International Centre for Diffraction Data 2003, Advances in X-ray Analysis, Vol.46 74 ISSN 1097-0002 LASER-COMPTON SCATTERING AS A POTENTIAL BRIGHT X-RAY SOURCE K. Chouffani 1, D. Wells
On the energy deposition by electrons in air and the accurate determination of the air-fluorescence yield
 arxiv:1207.2913v1 [astro-ph.im] 12 Jul 2012 On the energy deposition by electrons in air and the accurate determination of the air-fluorescence yield J. Rosado, P. Gallego, D. García-Pinto, F. Blanco and
arxiv:1207.2913v1 [astro-ph.im] 12 Jul 2012 On the energy deposition by electrons in air and the accurate determination of the air-fluorescence yield J. Rosado, P. Gallego, D. García-Pinto, F. Blanco and
Coherent Cherenkov radiation from ultra-short electron bunch passing through vacuum channel in conical target
 Coherent Cherenkov radiation from ultra-short electron bunch passing through vacuum channel in conical target A.P. Potylitsyn, S.Yu. Gogolev RREPS_11, London, 2011, Sept.12-16 Motivation Existing experimental
Coherent Cherenkov radiation from ultra-short electron bunch passing through vacuum channel in conical target A.P. Potylitsyn, S.Yu. Gogolev RREPS_11, London, 2011, Sept.12-16 Motivation Existing experimental
