Surface x(u, v) and curve α(t) on it given by u(t) & v(t). Math 4140/5530: Differential Geometry
|
|
|
- Wilfrid Cummings
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Surface x(u, v) and curve α(t) on it given by u(t) & v(t). α du dv (t) x u dt + x v dt
2 Surface x(u, v) and curve α(t) on it given by u(t) & v(t). α du dv (t) x u dt + x v dt ( ds dt )2
3 Surface x(u, v) and curve α(t) on it given by u(t) & v(t). α du dv (t) x u dt + x v dt ( ds dt )2 α (t) 2 α (t) α du (t) ( x u dt + x v dv dt ) ( x u du dt + x v dv dt )
4 Surface x(u, v) and curve α(t) on it given by u(t) & v(t). α du dv (t) x u dt + x v dt ( ds dt )2 α (t) 2 α (t) α (t) ( x u du dt + x v dv x u x u ( du dt )2 du + 2 x u x v dt dv dt + x v x v ( dv dt )2 dt ) ( x u du dt + x v dv dt )
5 Surface x(u, v) and curve α(t) on it given by u(t) & v(t). α du dv (t) x u dt + x v dt ( ds dt )2 α (t) 2 α (t) α (t) ( x u du dt + x v dv x u x u ( du dt )2 du + 2 x u x v dt E( du dt )2 + 2F du dt dv dt + G( dv dt )2 dv dt + x v x v ( dv dt )2 dt ) ( x u du dt + x v dv E, F, G play important roles in many intrinsic properties of a surface like length, area and angles Example 1: x(u, v) (u, v, 0) dt )
6 [ ] [ ] g11 g Matrix representation: g ij 12 E F g 21 g 22 F G g ij determines dot products of tangent vectors
7 [ ] [ ] g11 g Matrix representation: g ij 12 E F g 21 g 22 F G g ij determines dot products of tangent vectors E, F, G play important roles in many intrinsic properties of a surface like length, area and angles (ds ) 2 (du ) 2 du dv E + 2F dt dt dt dt + G( dv ) 2 dt ds 2 g 11 du 1 du 1 +g 12 du 1 du 2 +g 21 du 2 du 1 +g 22 du 2 du 2 i,j g ij du i du j
8 [ ] [ ] g11 g Matrix representation: g ij 12 E F g 21 g 22 F G g ij determines dot products of tangent vectors w 1, w 2 in T p M { x u, x v } is a basis: w 1 a x u + b x v, w 2 c x u + d x v w 1 w 2 foil
9 [ ] [ ] g11 g Matrix representation: g ij 12 E F g 21 g 22 F G g ij determines dot products of tangent vectors w 1, w 2 in T p M { x u, x v } is a basis: w 1 a x u + b x v, w 2 c x u + d x v foil w 1 w 2 ac x u x u + (ad + bc) x u x v + bd x v x v ace + (ad + bc)f + bdg
10 [ ] [ ] g11 g Matrix representation: g ij 12 E F g 21 g 22 F G g ij determines dot products of tangent vectors w 1, w 2 in T p M { x u, x v } is a basis: w 1 a x u + b x v, w 2 c x u + d x v foil w 1 w 2 ac x u x u + (ad + bc) x u x v + bd x v x v ace + (ad + bc)f + bdg a(ce + df) + b(cf + dg) [ a b ] [ ] ce + df cf + dg
11 [ ] [ ] g11 g Matrix representation: g ij 12 E F g 21 g 22 F G g ij determines dot products of tangent vectors w 1, w 2 in T p M { x u, x v } is a basis: w 1 a x u + b x v, w 2 c x u + d x v foil w 1 w 2 ac x u x u + (ad + bc) x u x v + bd x v x v ace + (ad + bc)f + bdg a(ce + df) + b(cf + dg) [ a b ] [ ] ce + df cf + dg [ a b ] [ ] [ ] E F c F G d
12 [ ] [ ] g11 g Matrix representation: g ij 12 E F g 21 g 22 F G g ij determines dot products of tangent vectors w 1, w 2 in T p M { x u, x v } is a basis: w 1 a x u + b x v, w 2 c x u + d x v foil w 1 w 2 ac x u x u + (ad + bc) x u x v + bd x v x v ace + (ad + bc)f + bdg a(ce + df) + b(cf + dg) [ a b ] [ ] ce + df cf + dg [ a b ] [ ] [ ] E F c F G d w 1 w 2 w 1 w 2 cos θ E, F, G play important roles in many intrinsic properties of a surface like length ( ds dt )2, area (det) and angles (above)
13
14 2nd Fundamental Form l x uu U, m x uv U, n x vv U 2nd picture: The Center of Population of the United States curve: κ, τ rate of change of unit vector fields T & B ( N). surface: U unit vector field. Whole plane of directions rates of change of U are measured, not numerically, but by a linear operator called the shape operator, which captures the bending of a surface.
15 2nd Fundamental Form l x uu U, m x uv U, n x vv U 2nd picture: The Center of Population of the United States curve: κ, τ rate of change of unit vector fields T & B ( N). surface: U unit vector field. Whole plane of directions rates of change of U are measured, not numerically, but by a linear operator called the shape operator, which captures the bending of a surface. S p ( w) w U S( x u ) x u x uu U l, S( x u ) x v x uv U m, S( x v ) x v x vv U n eigenvalues of the shape operator: max and min normal curvature at p, called the principal curvatures κ 1 and κ 2
The First Fundamental Form
 The First Fundamental Form Outline 1. Bilinear Forms Let V be a vector space. A bilinear form on V is a function V V R that is linear in each variable separately. That is,, is bilinear if αu + β v, w αu,
The First Fundamental Form Outline 1. Bilinear Forms Let V be a vector space. A bilinear form on V is a function V V R that is linear in each variable separately. That is,, is bilinear if αu + β v, w αu,
CS Tutorial 5 - Differential Geometry I - Surfaces
 236861 Numerical Geometry of Images Tutorial 5 Differential Geometry II Surfaces c 2009 Parameterized surfaces A parameterized surface X : U R 2 R 3 a differentiable map 1 X from an open set U R 2 to R
236861 Numerical Geometry of Images Tutorial 5 Differential Geometry II Surfaces c 2009 Parameterized surfaces A parameterized surface X : U R 2 R 3 a differentiable map 1 X from an open set U R 2 to R
Lecture 13 The Fundamental Forms of a Surface
 Lecture 13 The Fundamental Forms of a Surface In the following we denote by F : O R 3 a parametric surface in R 3, F(u, v) = (x(u, v), y(u, v), z(u, v)). We denote partial derivatives with respect to the
Lecture 13 The Fundamental Forms of a Surface In the following we denote by F : O R 3 a parametric surface in R 3, F(u, v) = (x(u, v), y(u, v), z(u, v)). We denote partial derivatives with respect to the
1 The Differential Geometry of Surfaces
 1 The Differential Geometry of Surfaces Three-dimensional objects are bounded by surfaces. This section reviews some of the basic definitions and concepts relating to the geometry of smooth surfaces. 1.1
1 The Differential Geometry of Surfaces Three-dimensional objects are bounded by surfaces. This section reviews some of the basic definitions and concepts relating to the geometry of smooth surfaces. 1.1
Notes on Cartan s Method of Moving Frames
 Math 553 σιι June 4, 996 Notes on Cartan s Method of Moving Frames Andrejs Treibergs The method of moving frames is a very efficient way to carry out computations on surfaces Chern s Notes give an elementary
Math 553 σιι June 4, 996 Notes on Cartan s Method of Moving Frames Andrejs Treibergs The method of moving frames is a very efficient way to carry out computations on surfaces Chern s Notes give an elementary
HOMEWORK 3 MA1132: ADVANCED CALCULUS, HILARY 2017
 HOMEWORK MA112: ADVANCED CALCULUS, HILARY 2017 (1) A particle moves along a curve in R with position function given by r(t) = (e t, t 2 + 1, t). Find the velocity v(t), the acceleration a(t), the speed
HOMEWORK MA112: ADVANCED CALCULUS, HILARY 2017 (1) A particle moves along a curve in R with position function given by r(t) = (e t, t 2 + 1, t). Find the velocity v(t), the acceleration a(t), the speed
Chapter 4. The First Fundamental Form (Induced Metric)
 Chapter 4. The First Fundamental Form (Induced Metric) We begin with some definitions from linear algebra. Def. Let V be a vector space (over IR). A bilinear form on V is a map of the form B : V V IR which
Chapter 4. The First Fundamental Form (Induced Metric) We begin with some definitions from linear algebra. Def. Let V be a vector space (over IR). A bilinear form on V is a map of the form B : V V IR which
Hyperbolic Geometry on Geometric Surfaces
 Mathematics Seminar, 15 September 2010 Outline Introduction Hyperbolic geometry Abstract surfaces The hemisphere model as a geometric surface The Poincaré disk model as a geometric surface Conclusion Introduction
Mathematics Seminar, 15 September 2010 Outline Introduction Hyperbolic geometry Abstract surfaces The hemisphere model as a geometric surface The Poincaré disk model as a geometric surface Conclusion Introduction
Math 115 ( ) Yum-Tong Siu 1. Euler-Lagrange Equations for Many Functions and Variables and High-Order Derivatives
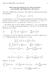 Math 115 006-007 Yum-Tong Siu 1 Euler-Lagrange Equations for Many Functions and Variables and High-Order Derivatives The Case of High-Order Derivatives. The context is to find the extremal for the functional
Math 115 006-007 Yum-Tong Siu 1 Euler-Lagrange Equations for Many Functions and Variables and High-Order Derivatives The Case of High-Order Derivatives. The context is to find the extremal for the functional
Chapter 14. Basics of The Differential Geometry of Surfaces. Introduction. Parameterized Surfaces. The First... Home Page. Title Page.
 Chapter 14 Basics of The Differential Geometry of Surfaces Page 649 of 681 14.1. Almost all of the material presented in this chapter is based on lectures given by Eugenio Calabi in an upper undergraduate
Chapter 14 Basics of The Differential Geometry of Surfaces Page 649 of 681 14.1. Almost all of the material presented in this chapter is based on lectures given by Eugenio Calabi in an upper undergraduate
MATH 332: Vector Analysis Summer 2005 Homework
 MATH 332, (Vector Analysis), Summer 2005: Homework 1 Instructor: Ivan Avramidi MATH 332: Vector Analysis Summer 2005 Homework Set 1. (Scalar Product, Equation of a Plane, Vector Product) Sections: 1.9,
MATH 332, (Vector Analysis), Summer 2005: Homework 1 Instructor: Ivan Avramidi MATH 332: Vector Analysis Summer 2005 Homework Set 1. (Scalar Product, Equation of a Plane, Vector Product) Sections: 1.9,
A PROOF OF THE GAUSS-BONNET THEOREM. Contents. 1. Introduction. 2. Regular Surfaces
 A PROOF OF THE GAUSS-BONNET THEOREM AARON HALPER Abstract. In this paper I will provide a proof of the Gauss-Bonnet Theorem. I will start by briefly explaining regular surfaces and move on to the first
A PROOF OF THE GAUSS-BONNET THEOREM AARON HALPER Abstract. In this paper I will provide a proof of the Gauss-Bonnet Theorem. I will start by briefly explaining regular surfaces and move on to the first
Chapter 5. The Second Fundamental Form
 Chapter 5. The Second Fundamental Form Directional Derivatives in IR 3. Let f : U IR 3 IR be a smooth function defined on an open subset of IR 3. Fix p U and X T p IR 3. The directional derivative of f
Chapter 5. The Second Fundamental Form Directional Derivatives in IR 3. Let f : U IR 3 IR be a smooth function defined on an open subset of IR 3. Fix p U and X T p IR 3. The directional derivative of f
Tangent and Normal Vectors
 Tangent and Normal Vectors MATH 311, Calculus III J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2011 Navigation When an observer is traveling along with a moving point, for example the passengers in
Tangent and Normal Vectors MATH 311, Calculus III J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2011 Navigation When an observer is traveling along with a moving point, for example the passengers in
CHAPTER 3. Gauss map. In this chapter we will study the Gauss map of surfaces in R 3.
 CHAPTER 3 Gauss map In this chapter we will study the Gauss map of surfaces in R 3. 3.1. Surfaces in R 3 Let S R 3 be a submanifold of dimension 2. Let {U i, ϕ i } be a DS on S. For any p U i we have a
CHAPTER 3 Gauss map In this chapter we will study the Gauss map of surfaces in R 3. 3.1. Surfaces in R 3 Let S R 3 be a submanifold of dimension 2. Let {U i, ϕ i } be a DS on S. For any p U i we have a
d F = (df E 3 ) E 3. (4.1)
 4. The Second Fundamental Form In the last section we developed the theory of intrinsic geometry of surfaces by considering the covariant differential d F, that is, the tangential component of df for a
4. The Second Fundamental Form In the last section we developed the theory of intrinsic geometry of surfaces by considering the covariant differential d F, that is, the tangential component of df for a
9.1 Mean and Gaussian Curvatures of Surfaces
 Chapter 9 Gauss Map II 9.1 Mean and Gaussian Curvatures of Surfaces in R 3 We ll assume that the curves are in R 3 unless otherwise noted. We start off by quoting the following useful theorem about self
Chapter 9 Gauss Map II 9.1 Mean and Gaussian Curvatures of Surfaces in R 3 We ll assume that the curves are in R 3 unless otherwise noted. We start off by quoting the following useful theorem about self
HOMEWORK 2 SOLUTIONS
 HOMEWORK SOLUTIONS MA11: ADVANCED CALCULUS, HILARY 17 (1) Find parametric equations for the tangent line of the graph of r(t) = (t, t + 1, /t) when t = 1. Solution: A point on this line is r(1) = (1,,
HOMEWORK SOLUTIONS MA11: ADVANCED CALCULUS, HILARY 17 (1) Find parametric equations for the tangent line of the graph of r(t) = (t, t + 1, /t) when t = 1. Solution: A point on this line is r(1) = (1,,
Introduction to Algebraic and Geometric Topology Week 14
 Introduction to Algebraic and Geometric Topology Week 14 Domingo Toledo University of Utah Fall 2016 Computations in coordinates I Recall smooth surface S = {f (x, y, z) =0} R 3, I rf 6= 0 on S, I Chart
Introduction to Algebraic and Geometric Topology Week 14 Domingo Toledo University of Utah Fall 2016 Computations in coordinates I Recall smooth surface S = {f (x, y, z) =0} R 3, I rf 6= 0 on S, I Chart
Intrinsic Surface Geometry
 Chapter 7 Intrinsic Surface Geometry The second fundamental form of a regular surface M R 3 helps to describe precisely how M sits inside the Euclidean space R 3. The first fundamental form of M, on the
Chapter 7 Intrinsic Surface Geometry The second fundamental form of a regular surface M R 3 helps to describe precisely how M sits inside the Euclidean space R 3. The first fundamental form of M, on the
Report submitted to Prof. P. Shipman for Math 641, Spring 2012
 Dynamics at the Horsetooth Volume 4, 2012. The Weierstrass-Enneper Representations Department of Mathematics Colorado State University mylak@rams.colostate.edu drpackar@rams.colostate.edu Report submitted
Dynamics at the Horsetooth Volume 4, 2012. The Weierstrass-Enneper Representations Department of Mathematics Colorado State University mylak@rams.colostate.edu drpackar@rams.colostate.edu Report submitted
Metrics and Curvature
 Metrics and Curvature How to measure curvature? Metrics Euclidian/Minkowski Curved spaces General 4 dimensional space Cosmological principle Homogeneity and isotropy: evidence Robertson-Walker metrics
Metrics and Curvature How to measure curvature? Metrics Euclidian/Minkowski Curved spaces General 4 dimensional space Cosmological principle Homogeneity and isotropy: evidence Robertson-Walker metrics
THE LOWELL LEDGER. INDEPENDENT NOT NEUTRAL. NPRAKER BLOCK SOLI)
 D DD U X X 2 U UD U 2 90 x F D D F & U [V U 2 225 00 U D?? - F V D VV U F D «- U 20 -! - - > - U ( >»!( - > ( - - < x V ) - - F 8 F z F < : V - x x F - ) V V ( V x V V x V D 6 0 ( F - V x x z F 5-- - F
D DD U X X 2 U UD U 2 90 x F D D F & U [V U 2 225 00 U D?? - F V D VV U F D «- U 20 -! - - > - U ( >»!( - > ( - - < x V ) - - F 8 F z F < : V - x x F - ) V V ( V x V V x V D 6 0 ( F - V x x z F 5-- - F
t f(u)g (u) g(u)f (u) du,
 Chapter 2 Notation. Recall that F(R 3 ) denotes the set of all differentiable real-valued functions f : R 3 R and V(R 3 ) denotes the set of all differentiable vector fields on R 3. 2.1 7. The problem
Chapter 2 Notation. Recall that F(R 3 ) denotes the set of all differentiable real-valued functions f : R 3 R and V(R 3 ) denotes the set of all differentiable vector fields on R 3. 2.1 7. The problem
DIFFERENTIAL GEOMETRY HW 4. Show that a catenoid and helicoid are locally isometric.
 DIFFERENTIAL GEOMETRY HW 4 CLAY SHONKWILER Show that a catenoid and helicoid are locally isometric. 3 Proof. Let X(u, v) = (a cosh v cos u, a cosh v sin u, av) be the parametrization of the catenoid and
DIFFERENTIAL GEOMETRY HW 4 CLAY SHONKWILER Show that a catenoid and helicoid are locally isometric. 3 Proof. Let X(u, v) = (a cosh v cos u, a cosh v sin u, av) be the parametrization of the catenoid and
Definition of Derivative
 Definition of Derivative The derivative of the function f with respect to the variable x is the function ( ) fʹ x whose value at xis ( x) fʹ = lim provided the limit exists. h 0 ( + ) ( ) f x h f x h Slide
Definition of Derivative The derivative of the function f with respect to the variable x is the function ( ) fʹ x whose value at xis ( x) fʹ = lim provided the limit exists. h 0 ( + ) ( ) f x h f x h Slide
Geometric Modelling Summer 2016
 Geometric Modelling Summer 2016 Exercises Benjamin Karer M.Sc. http://gfx.uni-kl.de/~gm Benjamin Karer M.Sc. Geometric Modelling Summer 2016 1 Dierential Geometry Benjamin Karer M.Sc. Geometric Modelling
Geometric Modelling Summer 2016 Exercises Benjamin Karer M.Sc. http://gfx.uni-kl.de/~gm Benjamin Karer M.Sc. Geometric Modelling Summer 2016 1 Dierential Geometry Benjamin Karer M.Sc. Geometric Modelling
Topic 5.6: Surfaces and Surface Elements
 Math 275 Notes Topic 5.6: Surfaces and Surface Elements Textbook Section: 16.6 From the Toolbox (what you need from previous classes): Using vector valued functions to parametrize curves. Derivatives of
Math 275 Notes Topic 5.6: Surfaces and Surface Elements Textbook Section: 16.6 From the Toolbox (what you need from previous classes): Using vector valued functions to parametrize curves. Derivatives of
Normal Curvature, Geodesic Curvature and Gauss Formulas
 Title Normal Curvature, Geodesic Curvature and Gauss Formulas MATH 2040 December 20, 2016 MATH 2040 Normal and Geodesic Curvature December 20, 2016 1 / 12 Readings Readings Readings: 4.4 MATH 2040 Normal
Title Normal Curvature, Geodesic Curvature and Gauss Formulas MATH 2040 December 20, 2016 MATH 2040 Normal and Geodesic Curvature December 20, 2016 1 / 12 Readings Readings Readings: 4.4 MATH 2040 Normal
Week 3: Differential Geometry of Curves
 Week 3: Differential Geometry of Curves Introduction We now know how to differentiate and integrate along curves. This week we explore some of the geometrical properties of curves that can be addressed
Week 3: Differential Geometry of Curves Introduction We now know how to differentiate and integrate along curves. This week we explore some of the geometrical properties of curves that can be addressed
Review for the Final Exam
 Math 171 Review for the Final Exam 1 Find the limits (4 points each) (a) lim 4x 2 3; x x (b) lim ( x 2 x x 1 )x ; (c) lim( 1 1 ); x 1 ln x x 1 sin (x 2) (d) lim x 2 x 2 4 Solutions (a) The limit lim 4x
Math 171 Review for the Final Exam 1 Find the limits (4 points each) (a) lim 4x 2 3; x x (b) lim ( x 2 x x 1 )x ; (c) lim( 1 1 ); x 1 ln x x 1 sin (x 2) (d) lim x 2 x 2 4 Solutions (a) The limit lim 4x
Getting started: CFD notation
 PDE of p-th order Getting started: CFD notation f ( u,x, t, u x 1,..., u x n, u, 2 u x 1 x 2,..., p u p ) = 0 scalar unknowns u = u(x, t), x R n, t R, n = 1,2,3 vector unknowns v = v(x, t), v R m, m =
PDE of p-th order Getting started: CFD notation f ( u,x, t, u x 1,..., u x n, u, 2 u x 1 x 2,..., p u p ) = 0 scalar unknowns u = u(x, t), x R n, t R, n = 1,2,3 vector unknowns v = v(x, t), v R m, m =
Math 20E Midterm II(ver. a)
 Name: olutions tudent ID No.: Discussion ection: Math 20E Midterm IIver. a) Fall 2018 Problem core 1 /24 2 /25 3 /26 4 /25 Total /100 1. 24 Points.) Consider the force field F 5y ı + 3y 2 j. Compute the
Name: olutions tudent ID No.: Discussion ection: Math 20E Midterm IIver. a) Fall 2018 Problem core 1 /24 2 /25 3 /26 4 /25 Total /100 1. 24 Points.) Consider the force field F 5y ı + 3y 2 j. Compute the
Geodesics: Minimizing Distance on a Surface
 Geodesics: Minimizing Distance on a Surface Seth Donahue 5/13/13 Abstract Geodesics use the principles of differential geometry. The system of differential equations and the analysis of these will be done
Geodesics: Minimizing Distance on a Surface Seth Donahue 5/13/13 Abstract Geodesics use the principles of differential geometry. The system of differential equations and the analysis of these will be done
Inner Product Spaces 6.1 Length and Dot Product in R n
 Inner Product Spaces 6.1 Length and Dot Product in R n Summer 2017 Goals We imitate the concept of length and angle between two vectors in R 2, R 3 to define the same in the n space R n. Main topics are:
Inner Product Spaces 6.1 Length and Dot Product in R n Summer 2017 Goals We imitate the concept of length and angle between two vectors in R 2, R 3 to define the same in the n space R n. Main topics are:
Sec. 1.1: Basics of Vectors
 Sec. 1.1: Basics of Vectors Notation for Euclidean space R n : all points (x 1, x 2,..., x n ) in n-dimensional space. Examples: 1. R 1 : all points on the real number line. 2. R 2 : all points (x 1, x
Sec. 1.1: Basics of Vectors Notation for Euclidean space R n : all points (x 1, x 2,..., x n ) in n-dimensional space. Examples: 1. R 1 : all points on the real number line. 2. R 2 : all points (x 1, x
MTH 277 Test 4 review sheet Chapter , 14.7, 14.8 Chalmeta
 MTH 77 Test 4 review sheet Chapter 13.1-13.4, 14.7, 14.8 Chalmeta Multiple Choice 1. Let r(t) = 3 sin t i + 3 cos t j + αt k. What value of α gives an arc length of 5 from t = 0 to t = 1? (a) 6 (b) 5 (c)
MTH 77 Test 4 review sheet Chapter 13.1-13.4, 14.7, 14.8 Chalmeta Multiple Choice 1. Let r(t) = 3 sin t i + 3 cos t j + αt k. What value of α gives an arc length of 5 from t = 0 to t = 1? (a) 6 (b) 5 (c)
Final Exam Topic Outline
 Math 442 - Differential Geometry of Curves and Surfaces Final Exam Topic Outline 30th November 2010 David Dumas Note: There is no guarantee that this outline is exhaustive, though I have tried to include
Math 442 - Differential Geometry of Curves and Surfaces Final Exam Topic Outline 30th November 2010 David Dumas Note: There is no guarantee that this outline is exhaustive, though I have tried to include
DIFFERENTIAL GEOMETRY OF CURVES AND SURFACES 5. The Second Fundamental Form of a Surface
 DIFFERENTIAL GEOMETRY OF CURVES AND SURFACES 5. The Second Fundamental Form of a Surface The main idea of this chapter is to try to measure to which extent a surface S is different from a plane, in other
DIFFERENTIAL GEOMETRY OF CURVES AND SURFACES 5. The Second Fundamental Form of a Surface The main idea of this chapter is to try to measure to which extent a surface S is different from a plane, in other
WORKSHEET #13 MATH 1260 FALL 2014
 WORKSHEET #3 MATH 26 FALL 24 NOT DUE. Short answer: (a) Find the equation of the tangent plane to z = x 2 + y 2 at the point,, 2. z x (, ) = 2x = 2, z y (, ) = 2y = 2. So then the tangent plane equation
WORKSHEET #3 MATH 26 FALL 24 NOT DUE. Short answer: (a) Find the equation of the tangent plane to z = x 2 + y 2 at the point,, 2. z x (, ) = 2x = 2, z y (, ) = 2y = 2. So then the tangent plane equation
Lectures 18: Gauss's Remarkable Theorem II. Table of contents
 Math 348 Fall 27 Lectures 8: Gauss's Remarkable Theorem II Disclaimer. As we have a textbook, this lecture note is for guidance and supplement only. It should not be relied on when preparing for exams.
Math 348 Fall 27 Lectures 8: Gauss's Remarkable Theorem II Disclaimer. As we have a textbook, this lecture note is for guidance and supplement only. It should not be relied on when preparing for exams.
ON CHRISTOFFEL SYMBOLS AND TEOREMA EGREGIUM
 ON CHRISTOFFEL SYMBOLS AND TEOREMA EGREGIUM LISBETH FAJSTRUP 1. CHRISTOFFEL SYMBOLS Thisisasectiononatechnicaldevicewhichisindispensableboth in the proof of Gauss Theorema egregium and when handling geodesics
ON CHRISTOFFEL SYMBOLS AND TEOREMA EGREGIUM LISBETH FAJSTRUP 1. CHRISTOFFEL SYMBOLS Thisisasectiononatechnicaldevicewhichisindispensableboth in the proof of Gauss Theorema egregium and when handling geodesics
Totally quasi-umbilic timelike surfaces in R 1,2
 Totally quasi-umbilic timelike surfaces in R 1,2 Jeanne N. Clelland, University of Colorado AMS Central Section Meeting Macalester College April 11, 2010 Definition: Three-dimensional Minkowski space R
Totally quasi-umbilic timelike surfaces in R 1,2 Jeanne N. Clelland, University of Colorado AMS Central Section Meeting Macalester College April 11, 2010 Definition: Three-dimensional Minkowski space R
Math 497C Mar 3, Curves and Surfaces Fall 2004, PSU
 Math 497C Mar 3, 2004 1 Curves and Surfaces Fall 2004, PSU Lecture Notes 10 2.3 Meaning of Gaussian Curvature In the previous lecture we gave a formal definition for Gaussian curvature K in terms of the
Math 497C Mar 3, 2004 1 Curves and Surfaces Fall 2004, PSU Lecture Notes 10 2.3 Meaning of Gaussian Curvature In the previous lecture we gave a formal definition for Gaussian curvature K in terms of the
Indeterminate Analysis Force Method 1
 Indeterminate Analysis Force Method 1 The force (flexibility) method expresses the relationships between displacements and forces that exist in a structure. Primary objective of the force method is to
Indeterminate Analysis Force Method 1 The force (flexibility) method expresses the relationships between displacements and forces that exist in a structure. Primary objective of the force method is to
x + ye z2 + ze y2, y + xe z2 + ze x2, z and where T is the
 1.(8pts) Find F ds where F = x + ye z + ze y, y + xe z + ze x, z and where T is the T surface in the pictures. (The two pictures are two views of the same surface.) The boundary of T is the unit circle
1.(8pts) Find F ds where F = x + ye z + ze y, y + xe z + ze x, z and where T is the T surface in the pictures. (The two pictures are two views of the same surface.) The boundary of T is the unit circle
Solutions for Math 348 Assignment #4 1
 Solutions for Math 348 Assignment #4 1 (1) Do the following: (a) Show that the intersection of two spheres S 1 = {(x, y, z) : (x x 1 ) 2 + (y y 1 ) 2 + (z z 1 ) 2 = r 2 1} S 2 = {(x, y, z) : (x x 2 ) 2
Solutions for Math 348 Assignment #4 1 (1) Do the following: (a) Show that the intersection of two spheres S 1 = {(x, y, z) : (x x 1 ) 2 + (y y 1 ) 2 + (z z 1 ) 2 = r 2 1} S 2 = {(x, y, z) : (x x 2 ) 2
Topics. CS Advanced Computer Graphics. Differential Geometry Basics. James F. O Brien. Vector and Tensor Fields.
 CS 94-3 Advanced Computer Graphics Differential Geometry Basics James F. O Brien Associate Professor U.C. Berkeley Topics Vector and Tensor Fields Divergence, curl, etc. Parametric Curves Tangents, curvature,
CS 94-3 Advanced Computer Graphics Differential Geometry Basics James F. O Brien Associate Professor U.C. Berkeley Topics Vector and Tensor Fields Divergence, curl, etc. Parametric Curves Tangents, curvature,
Practice Final Solutions
 Practice Final Solutions Math 1, Fall 17 Problem 1. Find a parameterization for the given curve, including bounds on the parameter t. Part a) The ellipse in R whose major axis has endpoints, ) and 6, )
Practice Final Solutions Math 1, Fall 17 Problem 1. Find a parameterization for the given curve, including bounds on the parameter t. Part a) The ellipse in R whose major axis has endpoints, ) and 6, )
M435: INTRODUCTION TO DIFFERENTIAL GEOMETRY
 M435: INTODUCTION TO DIFFNTIAL GOMTY MAK POWLL Contents 7. The Gauss-Bonnet Theorem 1 7.1. Statement of local Gauss-Bonnet theorem 1 7.2. Area of geodesic triangles 2 7.3. Special case of the plane 2 7.4.
M435: INTODUCTION TO DIFFNTIAL GOMTY MAK POWLL Contents 7. The Gauss-Bonnet Theorem 1 7.1. Statement of local Gauss-Bonnet theorem 1 7.2. Area of geodesic triangles 2 7.3. Special case of the plane 2 7.4.
Dierential Geometry Curves and surfaces Local properties Geometric foundations (critical for visual modeling and computing) Quantitative analysis Algo
 Dierential Geometry Curves and surfaces Local properties Geometric foundations (critical for visual modeling and computing) Quantitative analysis Algorithm development Shape control and interrogation Curves
Dierential Geometry Curves and surfaces Local properties Geometric foundations (critical for visual modeling and computing) Quantitative analysis Algorithm development Shape control and interrogation Curves
Calculus III. Math 233 Spring Final exam May 3rd. Suggested solutions
 alculus III Math 33 pring 7 Final exam May 3rd. uggested solutions This exam contains twenty problems numbered 1 through. All problems are multiple choice problems, and each counts 5% of your total score.
alculus III Math 33 pring 7 Final exam May 3rd. uggested solutions This exam contains twenty problems numbered 1 through. All problems are multiple choice problems, and each counts 5% of your total score.
5.2 The Levi-Civita Connection on Surfaces. 1 Parallel transport of vector fields on a surface M
 5.2 The Levi-Civita Connection on Surfaces In this section, we define the parallel transport of vector fields on a surface M, and then we introduce the concept of the Levi-Civita connection, which is also
5.2 The Levi-Civita Connection on Surfaces In this section, we define the parallel transport of vector fields on a surface M, and then we introduce the concept of the Levi-Civita connection, which is also
Affine invariant Fourier descriptors
 Affine invariant Fourier descriptors Sought: a generalization of the previously introduced similarityinvariant Fourier descriptors H. Burkhardt, Institut für Informatik, Universität Freiburg ME-II, Kap.
Affine invariant Fourier descriptors Sought: a generalization of the previously introduced similarityinvariant Fourier descriptors H. Burkhardt, Institut für Informatik, Universität Freiburg ME-II, Kap.
Math 433 Outline for Final Examination
 Math 433 Outline for Final Examination Richard Koch May 3, 5 Curves From the chapter on curves, you should know. the formula for arc length of a curve;. the definition of T (s), N(s), B(s), and κ(s) for
Math 433 Outline for Final Examination Richard Koch May 3, 5 Curves From the chapter on curves, you should know. the formula for arc length of a curve;. the definition of T (s), N(s), B(s), and κ(s) for
5.3 Surface Theory with Differential Forms
 5.3 Surface Theory with Differential Forms 1 Differential forms on R n, Click here to see more details Differential forms provide an approach to multivariable calculus (Click here to see more detailes)
5.3 Surface Theory with Differential Forms 1 Differential forms on R n, Click here to see more details Differential forms provide an approach to multivariable calculus (Click here to see more detailes)
Arbitrary-Speed Curves
 Arbitrary-Speed Curves (Com S 477/577 Notes) Yan-Bin Jia Oct 12, 2017 The Frenet formulas are valid only for unit-speed curves; they tell the rate of change of the orthonormal vectors T, N, B with respect
Arbitrary-Speed Curves (Com S 477/577 Notes) Yan-Bin Jia Oct 12, 2017 The Frenet formulas are valid only for unit-speed curves; they tell the rate of change of the orthonormal vectors T, N, B with respect
Lectures 15: Parallel Transport. Table of contents
 Lectures 15: Parallel Transport Disclaimer. As we have a textbook, this lecture note is for guidance and supplement only. It should not be relied on when preparing for exams. In this lecture we study the
Lectures 15: Parallel Transport Disclaimer. As we have a textbook, this lecture note is for guidance and supplement only. It should not be relied on when preparing for exams. In this lecture we study the
of all two dimensional curvatures found by considering the intersection of the surface and a plane that contains the surface normal. Or, more simply,
 A Proof that the Divergence of a Surface Normal Is Equal to the Sum of the Principal Curvatures Patience Henson May 5, 000 Motivation In solving problems that include an interface it is often important
A Proof that the Divergence of a Surface Normal Is Equal to the Sum of the Principal Curvatures Patience Henson May 5, 000 Motivation In solving problems that include an interface it is often important
Motion in Space. MATH 311, Calculus III. J. Robert Buchanan. Fall Department of Mathematics. J. Robert Buchanan Motion in Space
 Motion in Space MATH 311, Calculus III J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2011 Background Suppose the position vector of a moving object is given by r(t) = f (t), g(t), h(t), Background
Motion in Space MATH 311, Calculus III J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2011 Background Suppose the position vector of a moving object is given by r(t) = f (t), g(t), h(t), Background
Math 1501 Calc I Summer 2015 QUP SOUP w/ GTcourses
 Math 1501 Calc I Summer 2015 QUP SOUP w/ GTcourses Instructor: Sal Barone School of Mathematics Georgia Tech May 22, 2015 (updated May 22, 2015) Covered sections: 3.3 & 3.5 Exam 1 (Ch.1 - Ch.3) Thursday,
Math 1501 Calc I Summer 2015 QUP SOUP w/ GTcourses Instructor: Sal Barone School of Mathematics Georgia Tech May 22, 2015 (updated May 22, 2015) Covered sections: 3.3 & 3.5 Exam 1 (Ch.1 - Ch.3) Thursday,
2009 Applied Mathematics. Advanced Higher Mechanics. Finalised Marking Instructions
 2009 Applied Mathematics Advanced Higher Mechanics Finalised Marking Instructions Scottish Qualifications Authority 2009 The information in this publication may be reproduced to support SQA qualifications
2009 Applied Mathematics Advanced Higher Mechanics Finalised Marking Instructions Scottish Qualifications Authority 2009 The information in this publication may be reproduced to support SQA qualifications
Map Projections. Jim Emery. Revision 7/21/ The Earth Ellipsoid 2. 2 The Fundamental Quadratic Forms of a Surface 6
 Map Projections Jim Emery Revision 7/21/2004 Contents 1 The Earth Ellipsoid 2 2 The Fundamental Quadratic Forms of a Surface 6 3 Principal Directions On A Surface 9 4 Principal Normal Curvatures on the
Map Projections Jim Emery Revision 7/21/2004 Contents 1 The Earth Ellipsoid 2 2 The Fundamental Quadratic Forms of a Surface 6 3 Principal Directions On A Surface 9 4 Principal Normal Curvatures on the
GEOMETRY HW Consider the parametrized surface (Enneper s surface)
 GEOMETRY HW 4 CLAY SHONKWILER 3.3.5 Consider the parametrized surface (Enneper s surface φ(u, v (x u3 3 + uv2, v v3 3 + vu2, u 2 v 2 show that (a The coefficients of the first fundamental form are E G
GEOMETRY HW 4 CLAY SHONKWILER 3.3.5 Consider the parametrized surface (Enneper s surface φ(u, v (x u3 3 + uv2, v v3 3 + vu2, u 2 v 2 show that (a The coefficients of the first fundamental form are E G
Dust devils, water spouts, tornados
 Balanced flow Things we know Primitive equations are very comprehensive, but there may be a number of vast simplifications that may be relevant (e.g., geostrophic balance). Seems that there are things
Balanced flow Things we know Primitive equations are very comprehensive, but there may be a number of vast simplifications that may be relevant (e.g., geostrophic balance). Seems that there are things
HOMEWORK 3 - GEOMETRY OF CURVES AND SURFACES. where ν is the unit normal consistent with the orientation of α (right hand rule).
 HOMEWORK 3 - GEOMETRY OF CURVES AND SURFACES ANDRÉ NEVES ) If α : I R 2 is a curve on the plane parametrized by arc length and θ is the angle that α makes with the x-axis, show that α t) = dθ dt ν, where
HOMEWORK 3 - GEOMETRY OF CURVES AND SURFACES ANDRÉ NEVES ) If α : I R 2 is a curve on the plane parametrized by arc length and θ is the angle that α makes with the x-axis, show that α t) = dθ dt ν, where
Calculus 1: A Large and In Charge Review Solutions
 Calculus : A Large and n Charge Review Solutions use the symbol which is shorthand for the phrase there eists.. We use the formula that Average Rate of Change is given by f(b) f(a) b a (a) (b) 5 = 3 =
Calculus : A Large and n Charge Review Solutions use the symbol which is shorthand for the phrase there eists.. We use the formula that Average Rate of Change is given by f(b) f(a) b a (a) (b) 5 = 3 =
Math 340 Final Exam December 16, 2006
 Math 34 Final Exam December 6, 6. () Suppose A 3 4. a) Find the row-reduced echelon form of A. 3 4 so the row reduced echelon form is b) What is rank(a)? 3 4 4 The rank is two since there are two pivots.
Math 34 Final Exam December 6, 6. () Suppose A 3 4. a) Find the row-reduced echelon form of A. 3 4 so the row reduced echelon form is b) What is rank(a)? 3 4 4 The rank is two since there are two pivots.
Homework 2. Solutions T =
 Homework. s Let {e x, e y, e z } be an orthonormal basis in E. Consider the following ordered triples: a) {e x, e x + e y, 5e z }, b) {e y, e x, 5e z }, c) {e y, e x, e z }, d) {e y, e x, 5e z }, e) {
Homework. s Let {e x, e y, e z } be an orthonormal basis in E. Consider the following ordered triples: a) {e x, e x + e y, 5e z }, b) {e y, e x, 5e z }, c) {e y, e x, e z }, d) {e y, e x, 5e z }, e) {
Allen Cahn Equation in Two Spatial Dimension
 Allen Cahn Equation in Two Spatial Dimension Yoichiro Mori April 25, 216 Consider the Allen Cahn equation in two spatial dimension: ɛ u = ɛ2 u + fu) 1) where ɛ > is a small parameter and fu) is of cubic
Allen Cahn Equation in Two Spatial Dimension Yoichiro Mori April 25, 216 Consider the Allen Cahn equation in two spatial dimension: ɛ u = ɛ2 u + fu) 1) where ɛ > is a small parameter and fu) is of cubic
Rational Bézier Patch Differentiation using the Rational Forward Difference Operator
 Rational Bézier Patch Differentiation using the Rational Forward Difference Operator Xianming Chen, Richard F. Riesenfeld, Elaine Cohen School of Computing, University of Utah Abstract This paper introduces
Rational Bézier Patch Differentiation using the Rational Forward Difference Operator Xianming Chen, Richard F. Riesenfeld, Elaine Cohen School of Computing, University of Utah Abstract This paper introduces
Surfaces of Revolution with Constant Mean Curvature H = c in Hyperbolic 3-Space H 3 ( c 2 )
 Surfaces of Revolution with Constant Mean Curvature H = c in Hyerbolic 3-Sace H 3 ( c 2 Kinsey-Ann Zarske Deartment of Mathematics, University of Southern Mississii, Hattiesburg, MS 39406, USA E-mail:
Surfaces of Revolution with Constant Mean Curvature H = c in Hyerbolic 3-Sace H 3 ( c 2 Kinsey-Ann Zarske Deartment of Mathematics, University of Southern Mississii, Hattiesburg, MS 39406, USA E-mail:
HILBERT S THEOREM ON THE HYPERBOLIC PLANE
 HILBET S THEOEM ON THE HYPEBOLIC PLANE MATTHEW D. BOWN Abstract. We recount a proof of Hilbert s result that a complete geometric surface of constant negative Gaussian curvature cannot be isometrically
HILBET S THEOEM ON THE HYPEBOLIC PLANE MATTHEW D. BOWN Abstract. We recount a proof of Hilbert s result that a complete geometric surface of constant negative Gaussian curvature cannot be isometrically
OHSx XM521 Multivariable Differential Calculus: Homework Solutions 14.1
 OHSx XM5 Multivariable Differential Calculus: Homework Solutions 4. (8) Describe the graph of the equation. r = i + tj + (t )k. Solution: Let y(t) = t, so that z(t) = t = y. In the yz-plane, this is just
OHSx XM5 Multivariable Differential Calculus: Homework Solutions 4. (8) Describe the graph of the equation. r = i + tj + (t )k. Solution: Let y(t) = t, so that z(t) = t = y. In the yz-plane, this is just
Chapter 14: Vector Calculus
 Chapter 14: Vector Calculus Introduction to Vector Functions Section 14.1 Limits, Continuity, Vector Derivatives a. Limit of a Vector Function b. Limit Rules c. Component By Component Limits d. Continuity
Chapter 14: Vector Calculus Introduction to Vector Functions Section 14.1 Limits, Continuity, Vector Derivatives a. Limit of a Vector Function b. Limit Rules c. Component By Component Limits d. Continuity
Christoffel symbols and Gauss Theorema Egregium
 Durham University Pavel Tumarkin Epiphany 207 Dierential Geometry III, Solutions 5 (Week 5 Christoel symbols and Gauss Theorema Egregium 5.. Show that the Gauss curvature K o the surace o revolution locally
Durham University Pavel Tumarkin Epiphany 207 Dierential Geometry III, Solutions 5 (Week 5 Christoel symbols and Gauss Theorema Egregium 5.. Show that the Gauss curvature K o the surace o revolution locally
A local characterization for constant curvature metrics in 2-dimensional Lorentz manifolds
 A local characterization for constant curvature metrics in -dimensional Lorentz manifolds Ivo Terek Couto Alexandre Lymberopoulos August 9, 8 arxiv:65.7573v [math.dg] 4 May 6 Abstract In this paper we
A local characterization for constant curvature metrics in -dimensional Lorentz manifolds Ivo Terek Couto Alexandre Lymberopoulos August 9, 8 arxiv:65.7573v [math.dg] 4 May 6 Abstract In this paper we
Theorema Egregium, Intrinsic Curvature
 Theorema Egregium, Intrinsic Curvature Cartan s second structural equation dω 12 = K θ 1 θ 2, (1) is, as we have seen, a powerful tool for computing curvature. But it also has far reaching theoretical
Theorema Egregium, Intrinsic Curvature Cartan s second structural equation dω 12 = K θ 1 θ 2, (1) is, as we have seen, a powerful tool for computing curvature. But it also has far reaching theoretical
Alignment processes on the sphere
 Alignment processes on the sphere Amic Frouvelle CEREMADE Université Paris Dauphine Joint works with : Pierre Degond (Imperial College London) and Gaël Raoul (École Polytechnique) Jian-Guo Liu (Duke University)
Alignment processes on the sphere Amic Frouvelle CEREMADE Université Paris Dauphine Joint works with : Pierre Degond (Imperial College London) and Gaël Raoul (École Polytechnique) Jian-Guo Liu (Duke University)
Mathematical Notation Math Calculus & Analytic Geometry III
 Name : Mathematical Notation Math 221 - alculus & Analytic Geometry III Use Word or WordPerect to recreate the ollowing documents. Each article is worth 10 points and can e printed and given to the instructor
Name : Mathematical Notation Math 221 - alculus & Analytic Geometry III Use Word or WordPerect to recreate the ollowing documents. Each article is worth 10 points and can e printed and given to the instructor
MATH107 Vectors and Matrices
 School of Mathematics, KSU 20/11/16 Vector valued functions Let D be a set of real numbers D R. A vector-valued functions r with domain D is a correspondence that assigns to each number t in D exactly
School of Mathematics, KSU 20/11/16 Vector valued functions Let D be a set of real numbers D R. A vector-valued functions r with domain D is a correspondence that assigns to each number t in D exactly
Part IB. Geometry. Year
 Part IB Year 2017 2016 2015 2014 2013 2012 2011 2010 2009 2008 2007 2006 2005 2004 2003 2002 2001 2017 17 Paper 1, Section I 3G Give the definition for the area of a hyperbolic triangle with interior angles
Part IB Year 2017 2016 2015 2014 2013 2012 2011 2010 2009 2008 2007 2006 2005 2004 2003 2002 2001 2017 17 Paper 1, Section I 3G Give the definition for the area of a hyperbolic triangle with interior angles
Surfaces of Arbitrary Constant Negative Gaussian Curvature and Related Sine-Gordon Equations
 Mathematica Aeterna, Vol.1, 011, no. 01, 1-11 Surfaces of Arbitrary Constant Negative Gaussian Curvature and Related Sine-Gordon Equations Paul Bracken Department of Mathematics, University of Texas, Edinburg,
Mathematica Aeterna, Vol.1, 011, no. 01, 1-11 Surfaces of Arbitrary Constant Negative Gaussian Curvature and Related Sine-Gordon Equations Paul Bracken Department of Mathematics, University of Texas, Edinburg,
Exercise 1 (Formula for connection 1-forms) Using the first structure equation, show that
 1 Stokes s Theorem Let D R 2 be a connected compact smooth domain, so that D is a smooth embedded circle. Given a smooth function f : D R, define fdx dy fdxdy, D where the left-hand side is the integral
1 Stokes s Theorem Let D R 2 be a connected compact smooth domain, so that D is a smooth embedded circle. Given a smooth function f : D R, define fdx dy fdxdy, D where the left-hand side is the integral
Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors
 /88 Chia-Ping Chen Department of Computer Science and Engineering National Sun Yat-sen University Linear Algebra Eigenvalue Problem /88 Eigenvalue Equation By definition, the eigenvalue equation for matrix
/88 Chia-Ping Chen Department of Computer Science and Engineering National Sun Yat-sen University Linear Algebra Eigenvalue Problem /88 Eigenvalue Equation By definition, the eigenvalue equation for matrix
Molding surfaces and Liouville s equation
 Molding surfaces and Liouville s equation Naoya Ando Abstract According to [9], a molding surface has a property that a family of lines of curvature consists of geodesics. In the present paper, we will
Molding surfaces and Liouville s equation Naoya Ando Abstract According to [9], a molding surface has a property that a family of lines of curvature consists of geodesics. In the present paper, we will
Riemannian geometry of surfaces
 Riemannian geometry of surfaces In this note, we will learn how to make sense of the concepts of differential geometry on a surface M, which is not necessarily situated in R 3. This intrinsic approach
Riemannian geometry of surfaces In this note, we will learn how to make sense of the concepts of differential geometry on a surface M, which is not necessarily situated in R 3. This intrinsic approach
Course on Inverse Problems
 Stanford University School of Earth Sciences Course on Inverse Problems Albert Tarantola Third Lesson: Probability (Elementary Notions) Let u and v be two Cartesian parameters (then, volumetric probabilities
Stanford University School of Earth Sciences Course on Inverse Problems Albert Tarantola Third Lesson: Probability (Elementary Notions) Let u and v be two Cartesian parameters (then, volumetric probabilities
1 + f 2 x + f 2 y dy dx, where f(x, y) = 2 + 3x + 4y, is
 1. The value of the double integral (a) 15 26 (b) 15 8 (c) 75 (d) 105 26 5 4 0 1 1 + f 2 x + f 2 y dy dx, where f(x, y) = 2 + 3x + 4y, is 2. What is the value of the double integral interchange the order
1. The value of the double integral (a) 15 26 (b) 15 8 (c) 75 (d) 105 26 5 4 0 1 1 + f 2 x + f 2 y dy dx, where f(x, y) = 2 + 3x + 4y, is 2. What is the value of the double integral interchange the order
1 Vector algebra in R 3.
 ECE 298JA VC #1 Version 3.03 November 14, 2017 Fall 2017 Univ. of Illinois Due Mon, Dec 4, 2017 Prof. Allen Topic of this homework: Vector algebra and fields in R 3 ; Gradient and scalar Laplacian operator;
ECE 298JA VC #1 Version 3.03 November 14, 2017 Fall 2017 Univ. of Illinois Due Mon, Dec 4, 2017 Prof. Allen Topic of this homework: Vector algebra and fields in R 3 ; Gradient and scalar Laplacian operator;
Differential calculus. Background mathematics review
 Differential calculus Background mathematics review David Miller Differential calculus First derivative Background mathematics review David Miller First derivative For some function y The (first) derivative
Differential calculus Background mathematics review David Miller Differential calculus First derivative Background mathematics review David Miller First derivative For some function y The (first) derivative
Mathematics Review Exercises. (answers at end)
 Brock University Physics 1P21/1P91 Mathematics Review Exercises (answers at end) Work each exercise without using a calculator. 1. Express each number in scientific notation. (a) 437.1 (b) 563, 000 (c)
Brock University Physics 1P21/1P91 Mathematics Review Exercises (answers at end) Work each exercise without using a calculator. 1. Express each number in scientific notation. (a) 437.1 (b) 563, 000 (c)
Exact Solutions of the Einstein Equations
 Notes from phz 6607, Special and General Relativity University of Florida, Fall 2004, Detweiler Exact Solutions of the Einstein Equations These notes are not a substitute in any manner for class lectures.
Notes from phz 6607, Special and General Relativity University of Florida, Fall 2004, Detweiler Exact Solutions of the Einstein Equations These notes are not a substitute in any manner for class lectures.
Part IB Geometry. Theorems. Based on lectures by A. G. Kovalev Notes taken by Dexter Chua. Lent 2016
 Part IB Geometry Theorems Based on lectures by A. G. Kovalev Notes taken by Dexter Chua Lent 2016 These notes are not endorsed by the lecturers, and I have modified them (often significantly) after lectures.
Part IB Geometry Theorems Based on lectures by A. G. Kovalev Notes taken by Dexter Chua Lent 2016 These notes are not endorsed by the lecturers, and I have modified them (often significantly) after lectures.
UNIVERSITY OF DUBLIN
 UNIVERSITY OF DUBLIN TRINITY COLLEGE JS & SS Mathematics SS Theoretical Physics SS TSM Mathematics Faculty of Engineering, Mathematics and Science school of mathematics Trinity Term 2015 Module MA3429
UNIVERSITY OF DUBLIN TRINITY COLLEGE JS & SS Mathematics SS Theoretical Physics SS TSM Mathematics Faculty of Engineering, Mathematics and Science school of mathematics Trinity Term 2015 Module MA3429
THE TRANSLATION PLANES OF ORDER 49 AND THEIR AUTOMORPHISM GROUPS
 MATHEMATICS OF COMPUTATION Volume 67, Number 223, July 1998, Pages 1207 1224 S 0025-5718(98)00961-2 THE TRANSLATION PLANES OF ORDER 49 AND THEIR AUTOMORPHISM GROUPS C. CHARNES AND U. DEMPWOLFF Abstract.
MATHEMATICS OF COMPUTATION Volume 67, Number 223, July 1998, Pages 1207 1224 S 0025-5718(98)00961-2 THE TRANSLATION PLANES OF ORDER 49 AND THEIR AUTOMORPHISM GROUPS C. CHARNES AND U. DEMPWOLFF Abstract.
Look out for typos! Homework 1: Review of Calc 1 and 2. Problem 1. Sketch the graphs of the following functions:
 Math 226 homeworks, Fall 2016 General Info All homeworks are due mostly on Tuesdays, occasionally on Thursdays, at the discussion section. No late submissions will be accepted. If you need to miss the
Math 226 homeworks, Fall 2016 General Info All homeworks are due mostly on Tuesdays, occasionally on Thursdays, at the discussion section. No late submissions will be accepted. If you need to miss the
Lecture 31 INTEGRATION
 Lecture 3 INTEGRATION Substitution. Example. x (let u = x 3 +5 x3 +5 du =3x = 3x 3 x 3 +5 = du 3 u du =3x ) = 3 u du = 3 u = 3 u = 3 x3 +5+C. Example. du (let u =3x +5 3x+5 = 3 3 3x+5 =3 du =3.) = 3 du
Lecture 3 INTEGRATION Substitution. Example. x (let u = x 3 +5 x3 +5 du =3x = 3x 3 x 3 +5 = du 3 u du =3x ) = 3 u du = 3 u = 3 u = 3 x3 +5+C. Example. du (let u =3x +5 3x+5 = 3 3 3x+5 =3 du =3.) = 3 du
Lectures on Quantum sine-gordon Models
 Lectures on Quantum sine-gordon Models Juan Mateos Guilarte 1, 1 Departamento de Física Fundamental (Universidad de Salamanca) IUFFyM (Universidad de Salamanca) Universidade Federal de Matto Grosso Cuiabá,
Lectures on Quantum sine-gordon Models Juan Mateos Guilarte 1, 1 Departamento de Física Fundamental (Universidad de Salamanca) IUFFyM (Universidad de Salamanca) Universidade Federal de Matto Grosso Cuiabá,
Fronts of Whitney umbrella a differential geometric approach via blowing up
 Journal of Singularities Volume 4 (202), 35-67 received 3 October 20 in revised form 9 January 202 DOI: 0.5427/jsing.202.4c Fronts of Whitney umbrella a differential geometric approach via blowing up Toshizumi
Journal of Singularities Volume 4 (202), 35-67 received 3 October 20 in revised form 9 January 202 DOI: 0.5427/jsing.202.4c Fronts of Whitney umbrella a differential geometric approach via blowing up Toshizumi
