Calculus 1 for AE (WI1421LR) Lecture 1: 12.3 The dot product 12.4 The cross product
|
|
|
- Lawrence Goodwin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Calculus 1 for AE (WI1421LR) : 12.3 The dot product 12.4 The cross product
2 About this course Textbook James Stewart, Calculus, Early Transcendentals, 7th edition Course Coordinator Dr. Roelof Koekoek, Department of Applied Mathematics Course documents en.html About me (instructor) Juan Juan Cai: Office: HB , EWI
3 Working schedule Calculus I for AE (wi1421lr), semester 1A James Stewart, Calculus, Early Transcendentals, 7th edition, Brooks/Cole Cengage Learning, 2012 week subjects minimum extra remarks 1 ( 12.1), ( 12.2) : 3, 5, 9, 15, 19, 21, 22, 27, 45, : 3, 5, 7, 17, 19, 27, 31, 37, 43, : 1, 2, 7, 10, 17, 25, 56, 63, : 1, 2, 6, 13, 21, 23, 28, 30, 34, 38, 50 pages : 63, 65, 67, 69, : 64(a), 66(b), 68(b), 70, 72 2 ( 2.2), : 11, 13, 17, 21, : 15, 19, 23, 26, 28 only arcsin, arccos and arctan ( 2.5), : 15, 19, 21, 25, : 17, 23, 26, 27, 37 ( 3.4) 3.4 : 7, 11, 17, : 8, 12, 20, : 1, 3, 7, 15, 29, 35, 51, : 27, 37, 49, 54, : 1, 5, 13, 15, 28, : 3, 11, 17, 26, ( 5.2), ( 5.3) : 9, 11, 17, 23, 25, 35, : 3, 5, 13, 21, 25, 40, 45, 53, 59, 70, : 7, 13, 19, 21, 29, 33, : 1, 4, 7, 20, 30, 33, 38, 44, 66, : 1, 3, 15, 23, 39, 49, : 5, 17, 24, 33, 38, 42, 48, 52 5 ( 7.5) 7.5 : 1, 7, 17, 21, 31, : 9, 23, 42, 43, : 1, 5, 13, 21, 31, 49, 50, 55, : 2, 11, 17, 25, 52, 58, 69, 75 ( 9.1) 9.1 : 1, 3, : 2, 4, : 3, 9, 11, 45, : 1, 5, 12, 46, 48 skip orthogonal trajectories : 3, 7, 9, 13, 17, : 1, 5, 8, 19, 34, 35 7 App. H App. H : 3, 5, 8, 11, 15, 19, 23, 25, 27, 29 App. H : 33, 35, 37, 39, 41, 43, 45, 47 App. H : 1, 9, 12, 16, 17, 20, 21, 22, 26, 28, 31 App. H : 34, 36, 38, 40, 42, 44, 46, 48
4 Introduction on vectors A vector is determined by its magnitude and direction. The two vectors u and v are equivalent: u = v. In 2-dimensional rectangular coordinate system, a :=< a 1, a 2 > denotes the vector initiating at origin O and pointing toward the point P (a 1, a 2 ). The coordinates a 1 and a 2 are called the components of a. A three dimensional vector can be defined similarly.
5 Algebraic operations on vectors Let a :=< a 1, a 2 >, b :=< b 1, b 2 > and c be a real number. Then, a + b =< a 1 + b 1, a 2 + b 2 > a b =< a 1 b 1, a 2 b 2 >. The scalar multiplication of a vector is given by ca =< ca 1, ca 2 >. The operations on three-dimensional vectors are defined in the same way. Triangle Law & Parallelogram Law:
6 Standard basis vectors Two-Dim: i =< 1, 0 > and j =< 0, 1 >. Three-Dim: i =< 1, 0, 0 > and j =< 0, 1, 0 > and k =< 0, 0, 1 >. For a vector a =< a 1, a 2, a 3 >, we can write a = a 1 i + a 2 j + a 3 k. The length of the vector a is denoted by the symbol a or a. < a 1, a 2 > = a a2 2 < a 1, a 2, a 3 > = a a2 2 + a2 3 A vector with length 1 is called unit vector. For instance, the standard basis vectors are unit vectors. The vectors 0 =< 0, 0 > and 0 =< 0, 0, 0 > are called zero vectors.
7 Dot product If a =< a 1, a 2, a 3 > and b =< b 1, b 2, b 3 >, then the dot product of a and b is defined as a b = a 1 b 1 + a 2 b 2 + a 3 b 3. If a =< a 1, a 2 > and b =< b 1, b 2 >, then a b = a 1 b 1 + a 2 b 2. Note that dot product of two vectors is a real number. If a, b and c are vectors and c is a scalar, then 1 a a = a 2 2 a b = b a 3 a (b + c) = a b + a c 4 (ca) b = c(a b) = a (cb) 5 0 a = 0
8 Angles between vectors If θ is the angle between the vectors a and b, then a b = a b cos θ. If vectors a and b both have positive length, then cos θ = a b a b. The angle remains the same while changing the lengths of a and b. Two vectors a and b are orthogonal if and only if a b = 0.
9 Examples If the vectors a and b have lengths 4 and 6, and the angle between them is π/3, find a b. Find the angles between the vectors a =< 2, 2, 1 > and b =< 5, 3, 2 >. Show that 2i + 2j k is perpendicular to 5i 4j + 2k
10 The direction angles of a nonzero vector a are the angles between a and the positive axes, denoted by α, β, and γ. Since the basis vector i represents the direction of positive x-axis, Similarly, we have cos β = a j a j = a 2 a cos α = a i a i = a 1 a. cos γ = a k a k = a 3 a. Hence, it is easy to prove that cos 2 α + cos 2 β + cos 2 γ = 1.
11 Projections Vector projection of b onto a: proj a b = ( a b a 2 ) a. Scalar projection of b onto a: comp a b = a b a = b cos θ. The vector projection is a vector. You can think it as the shadow of b when the light is perpendicular to a. The scalar projection is a real number, the absolute value of which is the length of proj a b.
12 Example Find the scalar projection and vector projection of b =< 1, 1, 2 > onto a =< 2, 3, 1 >.
13 The cross product If a =< a 1, a 2, a 3 > and b =< b 1, b 2, b 3 >, then the cross product of a and b is the vector a b =< a 2 b 3 a 3 b 2, a 3 b 1 a 1 b 3, a 1 b 2 a 2 b 1 >. Note that the cross product is NOT defined for two dimension vectors. The vector a b is orthogonal to both a and b. The length of the cross product a b is equal to the area of the parallelogram determined by a and b: a b = a b sin θ. Two nonzero vectors a and b are parallel if and only if a b = 0.
14 If a, b and c are vectors and c is a scalar, then 1 a b = b a 2 (ca) b = c(a b) = a (cb) 3 a (b + c) = a b + a c 4 (a + b) c = a c + b c 5 a (b c) = (a b) c 6 a (b c) = (a c)b (a b)c The vector a (b c) is called the scalar triple product, the absolute value of which equals to the volume of the parallelepiped determined by the vectors a, b and c.
15 Examples Find a vector perpendicular to the plane that passes through the points P (1, 4, 6), Q( 2, 5, 1), and R(1, 1, 1). Find the area of the triangle with vertices P (1, 4, 6), Q( 2, 5, 1), and R(1, 1, 1). Use the scalar triple product to show that the vectors a =< 1, 4, 7 >, b =< 2, 1, 4 >, and c =< 0, 9, 18 > are coplanar.
What you will learn today
 What you will learn today The Dot Product Equations of Vectors and the Geometry of Space 1/29 Direction angles and Direction cosines Projections Definitions: 1. a : a 1, a 2, a 3, b : b 1, b 2, b 3, a
What you will learn today The Dot Product Equations of Vectors and the Geometry of Space 1/29 Direction angles and Direction cosines Projections Definitions: 1. a : a 1, a 2, a 3, b : b 1, b 2, b 3, a
Quantities which have only magnitude are called scalars. Quantities which have magnitude and direction are called vectors.
 Vectors summary Quantities which have only magnitude are called scalars. Quantities which have magnitude and direction are called vectors. AB is the position vector of B relative to A and is the vector
Vectors summary Quantities which have only magnitude are called scalars. Quantities which have magnitude and direction are called vectors. AB is the position vector of B relative to A and is the vector
The Cross Product. In this section, we will learn about: Cross products of vectors and their applications.
 The Cross Product In this section, we will learn about: Cross products of vectors and their applications. THE CROSS PRODUCT The cross product a x b of two vectors a and b, unlike the dot product, is a
The Cross Product In this section, we will learn about: Cross products of vectors and their applications. THE CROSS PRODUCT The cross product a x b of two vectors a and b, unlike the dot product, is a
MAT 1339-S14 Class 8
 MAT 1339-S14 Class 8 July 28, 2014 Contents 7.2 Review Dot Product........................... 2 7.3 Applications of the Dot Product..................... 4 7.4 Vectors in Three-Space.........................
MAT 1339-S14 Class 8 July 28, 2014 Contents 7.2 Review Dot Product........................... 2 7.3 Applications of the Dot Product..................... 4 7.4 Vectors in Three-Space.........................
MAC Module 5 Vectors in 2-Space and 3-Space II
 MAC 2103 Module 5 Vectors in 2-Space and 3-Space II 1 Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to: 1. Determine the cross product of a vector in R 3. 2. Determine a scalar triple
MAC 2103 Module 5 Vectors in 2-Space and 3-Space II 1 Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to: 1. Determine the cross product of a vector in R 3. 2. Determine a scalar triple
The Cross Product. Philippe B. Laval. Spring 2012 KSU. Philippe B. Laval (KSU) The Cross Product Spring /
 The Cross Product Philippe B Laval KSU Spring 2012 Philippe B Laval (KSU) The Cross Product Spring 2012 1 / 15 Introduction The cross product is the second multiplication operation between vectors we will
The Cross Product Philippe B Laval KSU Spring 2012 Philippe B Laval (KSU) The Cross Product Spring 2012 1 / 15 Introduction The cross product is the second multiplication operation between vectors we will
Math 241, Exam 1 Information.
 Math 241, Exam 1 Information. 2/13/13, LC 310, 11:15-12:05. Exam 1 will be based on: Sections 12.1-12.5, 14.2. The corresponding assigned homework problems (see http://www.math.sc.edu/ boylan/sccourses/241sp13/241.html)
Math 241, Exam 1 Information. 2/13/13, LC 310, 11:15-12:05. Exam 1 will be based on: Sections 12.1-12.5, 14.2. The corresponding assigned homework problems (see http://www.math.sc.edu/ boylan/sccourses/241sp13/241.html)
The Cross Product. MATH 311, Calculus III. J. Robert Buchanan. Fall Department of Mathematics. J. Robert Buchanan The Cross Product
 The Cross Product MATH 311, Calculus III J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2011 Introduction Recall: the dot product of two vectors is a scalar. There is another binary operation on vectors
The Cross Product MATH 311, Calculus III J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2011 Introduction Recall: the dot product of two vectors is a scalar. There is another binary operation on vectors
Review of Coordinate Systems
 Vector in 2 R and 3 R Review of Coordinate Systems Used to describe the position of a point in space Common coordinate systems are: Cartesian Polar Cartesian Coordinate System Also called rectangular coordinate
Vector in 2 R and 3 R Review of Coordinate Systems Used to describe the position of a point in space Common coordinate systems are: Cartesian Polar Cartesian Coordinate System Also called rectangular coordinate
Brief Review of Exam Topics
 Math 32A Discussion Session Week 3 Notes October 17 and 19, 2017 We ll use this week s discussion session to prepare for the first midterm. We ll start with a quick rundown of the relevant topics, and
Math 32A Discussion Session Week 3 Notes October 17 and 19, 2017 We ll use this week s discussion session to prepare for the first midterm. We ll start with a quick rundown of the relevant topics, and
MATH 19520/51 Class 2
 MATH 19520/51 Class 2 Minh-Tam Trinh University of Chicago 2017-09-27 1 Review dot product. 2 Angles between vectors and orthogonality. 3 Projection of one vector onto another. 4 Cross product and its
MATH 19520/51 Class 2 Minh-Tam Trinh University of Chicago 2017-09-27 1 Review dot product. 2 Angles between vectors and orthogonality. 3 Projection of one vector onto another. 4 Cross product and its
Detailed objectives are given in each of the sections listed below. 1. Cartesian Space Coordinates. 2. Displacements, Forces, Velocities and Vectors
 Unit 1 Vectors In this unit, we introduce vectors, vector operations, and equations of lines and planes. Note: Unit 1 is based on Chapter 12 of the textbook, Salas and Hille s Calculus: Several Variables,
Unit 1 Vectors In this unit, we introduce vectors, vector operations, and equations of lines and planes. Note: Unit 1 is based on Chapter 12 of the textbook, Salas and Hille s Calculus: Several Variables,
11.1 Three-Dimensional Coordinate System
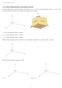 11.1 Three-Dimensional Coordinate System In three dimensions, a point has three coordinates: (x,y,z). The normal orientation of the x, y, and z-axes is shown below. The three axes divide the region into
11.1 Three-Dimensional Coordinate System In three dimensions, a point has three coordinates: (x,y,z). The normal orientation of the x, y, and z-axes is shown below. The three axes divide the region into
Last week we presented the following expression for the angles between two vectors u and v in R n ( ) θ = cos 1 u v
 Orthogonality (I) Last week we presented the following expression for the angles between two vectors u and v in R n ( ) θ = cos 1 u v u v which brings us to the fact that θ = π/2 u v = 0. Definition (Orthogonality).
Orthogonality (I) Last week we presented the following expression for the angles between two vectors u and v in R n ( ) θ = cos 1 u v u v which brings us to the fact that θ = π/2 u v = 0. Definition (Orthogonality).
MATH 255 Applied Honors Calculus III Winter Midterm 1 Review Solutions
 MATH 55 Applied Honors Calculus III Winter 11 Midterm 1 Review Solutions 11.1: #19 Particle starts at point ( 1,, traces out a semicircle in the counterclockwise direction, ending at the point (1,. 11.1:
MATH 55 Applied Honors Calculus III Winter 11 Midterm 1 Review Solutions 11.1: #19 Particle starts at point ( 1,, traces out a semicircle in the counterclockwise direction, ending at the point (1,. 11.1:
Section 13.4 The Cross Product
 Section 13.4 The Cross Product Multiplying Vectors 2 In this section we consider the more technical multiplication which can be defined on vectors in 3-space (but not vectors in 2-space). 1. Basic Definitions
Section 13.4 The Cross Product Multiplying Vectors 2 In this section we consider the more technical multiplication which can be defined on vectors in 3-space (but not vectors in 2-space). 1. Basic Definitions
DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS. MATH 233 SOME SOLUTIONS TO EXAM 1 Fall 2018
 DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS MATH SOME SOLUTIONS TO EXAM 1 Fall 018 Version A refers to the regular exam and Version B to the make-up 1. Version A. Find the center
DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS MATH SOME SOLUTIONS TO EXAM 1 Fall 018 Version A refers to the regular exam and Version B to the make-up 1. Version A. Find the center
R n : The Cross Product
 A FIRST COURSE IN LINEAR ALGEBRA An Open Text by Ken Kuttler R n : The Cross Product Lecture Notes by Karen Seyffarth Adapted by LYRYX SERVICE COURSE SOLUTION Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike (CC BY-NC-SA)
A FIRST COURSE IN LINEAR ALGEBRA An Open Text by Ken Kuttler R n : The Cross Product Lecture Notes by Karen Seyffarth Adapted by LYRYX SERVICE COURSE SOLUTION Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike (CC BY-NC-SA)
Course Notes Math 275 Boise State University. Shari Ultman
 Course Notes Math 275 Boise State University Shari Ultman Fall 2017 Contents 1 Vectors 1 1.1 Introduction to 3-Space & Vectors.............. 3 1.2 Working With Vectors.................... 7 1.3 Introduction
Course Notes Math 275 Boise State University Shari Ultman Fall 2017 Contents 1 Vectors 1 1.1 Introduction to 3-Space & Vectors.............. 3 1.2 Working With Vectors.................... 7 1.3 Introduction
Study guide for Exam 1. by William H. Meeks III October 26, 2012
 Study guide for Exam 1. by William H. Meeks III October 2, 2012 1 Basics. First we cover the basic definitions and then we go over related problems. Note that the material for the actual midterm may include
Study guide for Exam 1. by William H. Meeks III October 2, 2012 1 Basics. First we cover the basic definitions and then we go over related problems. Note that the material for the actual midterm may include
How can we find the distance between a point and a plane in R 3? Between two lines in R 3? Between two planes? Between a plane and a line?
 Overview Yesterday we introduced equations to describe lines and planes in R 3 : r = r 0 + tv The vector equation for a line describes arbitrary points r in terms of a specific point r 0 and the direction
Overview Yesterday we introduced equations to describe lines and planes in R 3 : r = r 0 + tv The vector equation for a line describes arbitrary points r in terms of a specific point r 0 and the direction
(arrows denote positive direction)
 12 Chapter 12 12.1 3-dimensional Coordinate System The 3-dimensional coordinate system we use are coordinates on R 3. The coordinate is presented as a triple of numbers: (a,b,c). In the Cartesian coordinate
12 Chapter 12 12.1 3-dimensional Coordinate System The 3-dimensional coordinate system we use are coordinates on R 3. The coordinate is presented as a triple of numbers: (a,b,c). In the Cartesian coordinate
The Cross Product of Two Vectors
 The Cross roduct of Two Vectors In proving some statements involving surface integrals, there will be a need to approximate areas of segments of the surface by areas of parallelograms. Therefore it is
The Cross roduct of Two Vectors In proving some statements involving surface integrals, there will be a need to approximate areas of segments of the surface by areas of parallelograms. Therefore it is
EGR2013 Tutorial 8. Linear Algebra. Powers of a Matrix and Matrix Polynomial
 EGR1 Tutorial 8 Linear Algebra Outline Powers of a Matrix and Matrix Polynomial Vector Algebra Vector Spaces Powers of a Matrix and Matrix Polynomial If A is a square matrix, then we define the nonnegative
EGR1 Tutorial 8 Linear Algebra Outline Powers of a Matrix and Matrix Polynomial Vector Algebra Vector Spaces Powers of a Matrix and Matrix Polynomial If A is a square matrix, then we define the nonnegative
Exercise Solutions for Introduction to 3D Game Programming with DirectX 10
 Exercise Solutions for Introduction to 3D Game Programming with DirectX 10 Frank Luna, September 6, 009 Solutions to Part I Chapter 1 1. Let u = 1, and v = 3, 4. Perform the following computations and
Exercise Solutions for Introduction to 3D Game Programming with DirectX 10 Frank Luna, September 6, 009 Solutions to Part I Chapter 1 1. Let u = 1, and v = 3, 4. Perform the following computations and
Math Vector Calculus II
 Math 255 - Vector Calculus II Review Notes Vectors We assume the reader is familiar with all the basic concepts regarding vectors and vector arithmetic, such as addition/subtraction of vectors in R n,
Math 255 - Vector Calculus II Review Notes Vectors We assume the reader is familiar with all the basic concepts regarding vectors and vector arithmetic, such as addition/subtraction of vectors in R n,
The Geometry of R n. Supplemental Lecture Notes for Linear Algebra Courses at Georgia Tech
 The Geometry of R n Supplemental Lecture Notes for Linear Algebra Courses at Georgia Tech Contents Vectors in R n. Vectors....................................... The Length and Direction of a Vector......................3
The Geometry of R n Supplemental Lecture Notes for Linear Algebra Courses at Georgia Tech Contents Vectors in R n. Vectors....................................... The Length and Direction of a Vector......................3
CHAPTER 3 : VECTORS. Definition 3.1 A vector is a quantity that has both magnitude and direction.
 EQT 101-Engineering Mathematics I Teaching Module CHAPTER 3 : VECTORS 3.1 Introduction Definition 3.1 A ector is a quantity that has both magnitude and direction. A ector is often represented by an arrow
EQT 101-Engineering Mathematics I Teaching Module CHAPTER 3 : VECTORS 3.1 Introduction Definition 3.1 A ector is a quantity that has both magnitude and direction. A ector is often represented by an arrow
1.3 LECTURE 3. Vector Product
 12 CHAPTER 1. VECTOR ALGEBRA Example. Let L be a line x x 1 a = y y 1 b = z z 1 c passing through a point P 1 and parallel to the vector N = a i +b j +c k. The equation of the plane passing through the
12 CHAPTER 1. VECTOR ALGEBRA Example. Let L be a line x x 1 a = y y 1 b = z z 1 c passing through a point P 1 and parallel to the vector N = a i +b j +c k. The equation of the plane passing through the
Remark 3.2. The cross product only makes sense in R 3.
 3. Cross product Definition 3.1. Let v and w be two vectors in R 3. The cross product of v and w, denoted v w, is the vector defined as follows: the length of v w is the area of the parallelogram with
3. Cross product Definition 3.1. Let v and w be two vectors in R 3. The cross product of v and w, denoted v w, is the vector defined as follows: the length of v w is the area of the parallelogram with
If the pull is downward (Fig. 1), we want C to point into the page. If the pull is upward (Fig. 2), we want C to point out of the page.
 11.5 Cross Product Contemporary Calculus 1 11.5 CROSS PRODUCT This section is the final one about the arithmetic of vectors, and it introduces a second type of vector vector multiplication called the cross
11.5 Cross Product Contemporary Calculus 1 11.5 CROSS PRODUCT This section is the final one about the arithmetic of vectors, and it introduces a second type of vector vector multiplication called the cross
10.2,3,4. Vectors in 3D, Dot products and Cross Products
 Name: Section: 10.2,3,4. Vectors in 3D, Dot products and Cross Products 1. Sketch the plane parallel to the xy-plane through (2, 4, 2) 2. For the given vectors u and v, evaluate the following expressions.
Name: Section: 10.2,3,4. Vectors in 3D, Dot products and Cross Products 1. Sketch the plane parallel to the xy-plane through (2, 4, 2) 2. For the given vectors u and v, evaluate the following expressions.
Lecture 2: Vector-Vector Operations
 Lecture 2: Vector-Vector Operations Vector-Vector Operations Addition of two vectors Geometric representation of addition and subtraction of vectors Vectors and points Dot product of two vectors Geometric
Lecture 2: Vector-Vector Operations Vector-Vector Operations Addition of two vectors Geometric representation of addition and subtraction of vectors Vectors and points Dot product of two vectors Geometric
(1) Recap of Differential Calculus and Integral Calculus (2) Preview of Calculus in three dimensional space (3) Tools for Calculus 3
 Math 127 Introduction and Review (1) Recap of Differential Calculus and Integral Calculus (2) Preview of Calculus in three dimensional space (3) Tools for Calculus 3 MATH 127 Introduction to Calculus III
Math 127 Introduction and Review (1) Recap of Differential Calculus and Integral Calculus (2) Preview of Calculus in three dimensional space (3) Tools for Calculus 3 MATH 127 Introduction to Calculus III
12.1. Cartesian Space
 12.1. Cartesian Space In most of your previous math classes, we worked with functions on the xy-plane only meaning we were working only in 2D. Now we will be working in space, or rather 3D. Now we will
12.1. Cartesian Space In most of your previous math classes, we worked with functions on the xy-plane only meaning we were working only in 2D. Now we will be working in space, or rather 3D. Now we will
Chapter 2: Vector Geometry
 Chapter 2: Vector Geometry Daniel Chan UNSW Semester 1 2018 Daniel Chan (UNSW) Chapter 2: Vector Geometry Semester 1 2018 1 / 32 Goals of this chapter In this chapter, we will answer the following geometric
Chapter 2: Vector Geometry Daniel Chan UNSW Semester 1 2018 Daniel Chan (UNSW) Chapter 2: Vector Geometry Semester 1 2018 1 / 32 Goals of this chapter In this chapter, we will answer the following geometric
CHAPTER 10 VECTORS POINTS TO REMEMBER
 For more important questions visit : www4onocom CHAPTER 10 VECTORS POINTS TO REMEMBER A quantity that has magnitude as well as direction is called a vector It is denoted by a directed line segment Two
For more important questions visit : www4onocom CHAPTER 10 VECTORS POINTS TO REMEMBER A quantity that has magnitude as well as direction is called a vector It is denoted by a directed line segment Two
Workbook. MAT 397: Calculus III
 Workbook MAT 397: Calculus III Instructor: Caleb McWhorter Name: Summer 217 Contents Preface..................................................... 2 1 Spatial Geometry & Vectors 3 1.1 Basic n Euclidean
Workbook MAT 397: Calculus III Instructor: Caleb McWhorter Name: Summer 217 Contents Preface..................................................... 2 1 Spatial Geometry & Vectors 3 1.1 Basic n Euclidean
MATH 12 CLASS 2 NOTES, SEP Contents. 2. Dot product: determining the angle between two vectors 2
 MATH 12 CLASS 2 NOTES, SEP 23 2011 Contents 1. Dot product: definition, basic properties 1 2. Dot product: determining the angle between two vectors 2 Quick links to definitions/theorems Dot product definition
MATH 12 CLASS 2 NOTES, SEP 23 2011 Contents 1. Dot product: definition, basic properties 1 2. Dot product: determining the angle between two vectors 2 Quick links to definitions/theorems Dot product definition
Math 32A Discussion Session Week 2 Notes October 10 and 12, 2017
 Math 32A Discussion Session Week 2 Notes October 10 and 12, 2017 Since we didn t get a chance to discuss parametrized lines last week, we may spend some time discussing those before moving on to the dot
Math 32A Discussion Session Week 2 Notes October 10 and 12, 2017 Since we didn t get a chance to discuss parametrized lines last week, we may spend some time discussing those before moving on to the dot
JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS MTH201 CALCULUS III. 5 Semester Credit Hours. Prepared by: Linda Cook
 JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS MTH201 CALCULUS III 5 Semester Credit Hours Prepared by: Linda Cook Revised Date: December 14, 2006 by Mulavana J Johny Arts & Science Education Dr. Mindy Selsor, Dean
JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS MTH201 CALCULUS III 5 Semester Credit Hours Prepared by: Linda Cook Revised Date: December 14, 2006 by Mulavana J Johny Arts & Science Education Dr. Mindy Selsor, Dean
Main topics for the First Midterm Exam
 Main topics for the First Midterm Exam The final will cover Sections.-.0, 2.-2.5, and 4.. This is roughly the material from first three homeworks and three quizzes, in addition to the lecture on Monday,
Main topics for the First Midterm Exam The final will cover Sections.-.0, 2.-2.5, and 4.. This is roughly the material from first three homeworks and three quizzes, in addition to the lecture on Monday,
F F. proj cos( ) v. v proj v
 Geometric Definition of Dot Product 1.2 The Dot Product Suppose you are pulling up on a rope attached to a box, as shown above. How would you find the force moving the box towards you? As stated above,
Geometric Definition of Dot Product 1.2 The Dot Product Suppose you are pulling up on a rope attached to a box, as shown above. How would you find the force moving the box towards you? As stated above,
Distance Formula in 3-D Given any two points P 1 (x 1, y 1, z 1 ) and P 2 (x 2, y 2, z 2 ) the distance between them is ( ) ( ) ( )
 Vectors and the Geometry of Space Vector Space The 3-D coordinate system (rectangular coordinates ) is the intersection of three perpendicular (orthogonal) lines called coordinate axis: x, y, and z. Their
Vectors and the Geometry of Space Vector Space The 3-D coordinate system (rectangular coordinates ) is the intersection of three perpendicular (orthogonal) lines called coordinate axis: x, y, and z. Their
Math 2433 Notes Week The Dot Product. The angle between two vectors is found with this formula: cosθ = a b
 Math 2433 Notes Week 2 11.3 The Dot Product The angle between two vectors is found with this formula: cosθ = a b a b 3) Given, a = 4i + 4j, b = i - 2j + 3k, c = 2i + 2k Find the angle between a and c Projection
Math 2433 Notes Week 2 11.3 The Dot Product The angle between two vectors is found with this formula: cosθ = a b a b 3) Given, a = 4i + 4j, b = i - 2j + 3k, c = 2i + 2k Find the angle between a and c Projection
Department of Physics, Korea University
 Name: Department: Notice +2 ( 1) points per correct (incorrect) answer. No penalty for an unanswered question. Fill the blank ( ) with (8) if the statement is correct (incorrect).!!!: corrections to an
Name: Department: Notice +2 ( 1) points per correct (incorrect) answer. No penalty for an unanswered question. Fill the blank ( ) with (8) if the statement is correct (incorrect).!!!: corrections to an
SUPPLEMENT I. Example. Graph the vector 4, 3. Definition. Given two points A(x 1, y 1 ) and B(x 2, y 2 ), the vector represented by # AB is # AB =,
 SUPPLEMENT I 1. Vectors Definition. A vector is a quantity that has both a magnitude and a direction. A twodimensional vector is an ordered pair a = a 1, a 2 of real numbers. The numbers a 1 and a 2 are
SUPPLEMENT I 1. Vectors Definition. A vector is a quantity that has both a magnitude and a direction. A twodimensional vector is an ordered pair a = a 1, a 2 of real numbers. The numbers a 1 and a 2 are
Math 261 Lecture Notes: Sections 6.1, 6.2, 6.3 and 6.4 Orthogonal Sets and Projections
 Math 6 Lecture Notes: Sections 6., 6., 6. and 6. Orthogonal Sets and Projections We will not cover general inner product spaces. We will, however, focus on a particular inner product space the inner product
Math 6 Lecture Notes: Sections 6., 6., 6. and 6. Orthogonal Sets and Projections We will not cover general inner product spaces. We will, however, focus on a particular inner product space the inner product
vand v 3. Find the area of a parallelogram that has the given vectors as adjacent sides.
 Name: Date: 1. Given the vectors u and v, find u vand v v. u= 8,6,2, v = 6, 3, 4 u v v v 2. Given the vectors u nd v, find the cross product and determine whether it is orthogonal to both u and v. u= 1,8,
Name: Date: 1. Given the vectors u and v, find u vand v v. u= 8,6,2, v = 6, 3, 4 u v v v 2. Given the vectors u nd v, find the cross product and determine whether it is orthogonal to both u and v. u= 1,8,
The Cross Product The cross product of v = (v 1,v 2,v 3 ) and w = (w 1,w 2,w 3 ) is
 The Cross Product 1-1-2018 The cross product of v = (v 1,v 2,v 3 ) and w = (w 1,w 2,w 3 ) is v w = (v 2 w 3 v 3 w 2 )î+(v 3 w 1 v 1 w 3 )ĵ+(v 1 w 2 v 2 w 1 )ˆk = v 1 v 2 v 3 w 1 w 2 w 3. Strictly speaking,
The Cross Product 1-1-2018 The cross product of v = (v 1,v 2,v 3 ) and w = (w 1,w 2,w 3 ) is v w = (v 2 w 3 v 3 w 2 )î+(v 3 w 1 v 1 w 3 )ĵ+(v 1 w 2 v 2 w 1 )ˆk = v 1 v 2 v 3 w 1 w 2 w 3. Strictly speaking,
Mathematics 2203, Test 1 - Solutions
 Mathematics 220, Test 1 - Solutions F, 2010 Philippe B. Laval Name 1. Determine if each statement below is True or False. If it is true, explain why (cite theorem, rule, property). If it is false, explain
Mathematics 220, Test 1 - Solutions F, 2010 Philippe B. Laval Name 1. Determine if each statement below is True or False. If it is true, explain why (cite theorem, rule, property). If it is false, explain
Multiple Choice. 1.(6 pts) Find symmetric equations of the line L passing through the point (2, 5, 1) and perpendicular to the plane x + 3y z = 9.
 Multiple Choice.(6 pts) Find smmetric equations of the line L passing through the point (, 5, ) and perpendicular to the plane x + 3 z = 9. (a) x = + 5 3 = z (c) (x ) + 3( 3) (z ) = 9 (d) (e) x = 3 5 =
Multiple Choice.(6 pts) Find smmetric equations of the line L passing through the point (, 5, ) and perpendicular to the plane x + 3 z = 9. (a) x = + 5 3 = z (c) (x ) + 3( 3) (z ) = 9 (d) (e) x = 3 5 =
VECTORS IN COMPONENT FORM
 VECTORS IN COMPONENT FORM In Cartesian coordinates any D vector a can be written as a = a x i + a y j + a z k a x a y a x a y a z a z where i, j and k are unit vectors in x, y and z directions. i = j =
VECTORS IN COMPONENT FORM In Cartesian coordinates any D vector a can be written as a = a x i + a y j + a z k a x a y a x a y a z a z where i, j and k are unit vectors in x, y and z directions. i = j =
Objective 1. Lesson 87: The Cross Product of Vectors IBHL - SANTOWSKI FINDING THE CROSS PRODUCT OF TWO VECTORS
 Lesson 87: The Cross Product of Vectors IBHL - SANTOWSKI In this lesson you will learn how to find the cross product of two vectors how to find an orthogonal vector to a plane defined by two vectors how
Lesson 87: The Cross Product of Vectors IBHL - SANTOWSKI In this lesson you will learn how to find the cross product of two vectors how to find an orthogonal vector to a plane defined by two vectors how
APPM 2350 Section Exam points Wednesday September 26, 6:00pm 7:30pm, 2018
 APPM 2350 Section Exam 1 140 points Wednesday September 26, 6:00pm 7:30pm, 2018 ON THE FRONT OF YOUR BLUEBOOK write: (1) your name, (2) your student ID number, (3) lecture section/time (4) your instructor
APPM 2350 Section Exam 1 140 points Wednesday September 26, 6:00pm 7:30pm, 2018 ON THE FRONT OF YOUR BLUEBOOK write: (1) your name, (2) your student ID number, (3) lecture section/time (4) your instructor
MA2081 Vector Calculus and Fluid Dynamics
 MA2081 Vector Calculus and Fluid Dynamics Manolis Georgoulis January 2007 1/76 Course Information Module Webpage http://www.math.le.ac.uk/people/eg64/teaching/ma2081/ma2081.html Contact Details Dr. Manolis
MA2081 Vector Calculus and Fluid Dynamics Manolis Georgoulis January 2007 1/76 Course Information Module Webpage http://www.math.le.ac.uk/people/eg64/teaching/ma2081/ma2081.html Contact Details Dr. Manolis
7.1 Projections and Components
 7. Projections and Components As we have seen, the dot product of two vectors tells us the cosine of the angle between them. So far, we have only used this to find the angle between two vectors, but cosines
7. Projections and Components As we have seen, the dot product of two vectors tells us the cosine of the angle between them. So far, we have only used this to find the angle between two vectors, but cosines
REQUIRED TEXTBOOK/MATERIALS
 Code: MATH 273 Title: CALCULUS III Division: MATHEMATICS Department: MATHEMATICS Course Description: This course, a continuation of MATH 172, Calculus II, completes the study of elementary calculus. Topics
Code: MATH 273 Title: CALCULUS III Division: MATHEMATICS Department: MATHEMATICS Course Description: This course, a continuation of MATH 172, Calculus II, completes the study of elementary calculus. Topics
Brief Review of Vector Algebra
 APPENDIX Brief Review of Vector Algebra A.0 Introduction Vector algebra is used extensively in computational mechanics. The student must thus understand the concepts associated with this subject. The current
APPENDIX Brief Review of Vector Algebra A.0 Introduction Vector algebra is used extensively in computational mechanics. The student must thus understand the concepts associated with this subject. The current
MTH 2310, FALL Introduction
 MTH 2310, FALL 2011 SECTION 6.2: ORTHOGONAL SETS Homework Problems: 1, 5, 9, 13, 17, 21, 23 1, 27, 29, 35 1. Introduction We have discussed previously the benefits of having a set of vectors that is linearly
MTH 2310, FALL 2011 SECTION 6.2: ORTHOGONAL SETS Homework Problems: 1, 5, 9, 13, 17, 21, 23 1, 27, 29, 35 1. Introduction We have discussed previously the benefits of having a set of vectors that is linearly
1. Vectors in the Plane
 CHAPTER 10 Vectors and the Geometry of Space 1. Vectors in the Plane We denote the directed line segment from the point P (initial point) to the!! point Q (terminal point) as P Q. The length of P Q is
CHAPTER 10 Vectors and the Geometry of Space 1. Vectors in the Plane We denote the directed line segment from the point P (initial point) to the!! point Q (terminal point) as P Q. The length of P Q is
Vectors Year 12 Term 1
 Vectors Year 12 Term 1 1 Vectors - A Vector has Two properties Magnitude and Direction - A vector is usually denoted in bold, like vector a, or a, or many others. In 2D - a = xı + yȷ - a = x, y - where,
Vectors Year 12 Term 1 1 Vectors - A Vector has Two properties Magnitude and Direction - A vector is usually denoted in bold, like vector a, or a, or many others. In 2D - a = xı + yȷ - a = x, y - where,
1.1 Single Variable Calculus versus Multivariable Calculus Rectangular Coordinate Systems... 4
 MATH2202 Notebook 1 Fall 2015/2016 prepared by Professor Jenny Baglivo Contents 1 MATH2202 Notebook 1 3 1.1 Single Variable Calculus versus Multivariable Calculus................... 3 1.2 Rectangular Coordinate
MATH2202 Notebook 1 Fall 2015/2016 prepared by Professor Jenny Baglivo Contents 1 MATH2202 Notebook 1 3 1.1 Single Variable Calculus versus Multivariable Calculus................... 3 1.2 Rectangular Coordinate
VECTOR NAME OF THE CHAPTER. By, Srinivasamurthy s.v. Lecturer in mathematics. K.P.C.L.P.U.College. jogfalls PART-B TWO MARKS QUESTIONS
 NAME OF THE CHAPTER VECTOR PART-A ONE MARKS PART-B TWO MARKS PART-C FIVE MARKS PART-D SIX OR FOUR MARKS PART-E TWO OR FOUR 1 1 1 1 1 16 TOTAL MARKS ALLOTED APPROXIMATELY By, Srinivasamurthy s.v Lecturer
NAME OF THE CHAPTER VECTOR PART-A ONE MARKS PART-B TWO MARKS PART-C FIVE MARKS PART-D SIX OR FOUR MARKS PART-E TWO OR FOUR 1 1 1 1 1 16 TOTAL MARKS ALLOTED APPROXIMATELY By, Srinivasamurthy s.v Lecturer
6. Vectors. Given two points, P 0 = (x 0, y 0 ) and P 1 = (x 1, y 1 ), a vector can be drawn with its foot at P 0 and
 6. Vectors For purposes of applications in calculus and physics, a vector has both a direction and a magnitude (length), and is usually represented as an arrow. The start of the arrow is the vector s foot,
6. Vectors For purposes of applications in calculus and physics, a vector has both a direction and a magnitude (length), and is usually represented as an arrow. The start of the arrow is the vector s foot,
A vector in the plane is directed line segment. The directed line segment AB
 Vector: A ector is a matrix that has only one row then we call the matrix a row ector or only one column then we call it a column ector. A row ector is of the form: a a a... A column ector is of the form:
Vector: A ector is a matrix that has only one row then we call the matrix a row ector or only one column then we call it a column ector. A row ector is of the form: a a a... A column ector is of the form:
Worksheet 1.4: Geometry of the Dot and Cross Products
 Boise State Math 275 (Ultman) Worksheet 1.4: Geometry of the Dot and Cross Products From the Toolbox (what you need from previous classes): Basic algebra and trigonometry: be able to solve quadratic equations,
Boise State Math 275 (Ultman) Worksheet 1.4: Geometry of the Dot and Cross Products From the Toolbox (what you need from previous classes): Basic algebra and trigonometry: be able to solve quadratic equations,
Lake-Sumter State College Course Syllabus. South Lake Building 2 Room 339
 Lake-Sumter State College Course Syllabus Course / Prefix Number MAC 2313 Course Title: Calculus with Analytic Geometry III CRN: 20110 20110 Credit: 4 Term: Spring 2015 Course Catalog Description: Instructor:
Lake-Sumter State College Course Syllabus Course / Prefix Number MAC 2313 Course Title: Calculus with Analytic Geometry III CRN: 20110 20110 Credit: 4 Term: Spring 2015 Course Catalog Description: Instructor:
Lecture 3: Linear Algebra Review, Part II
 Lecture 3: Linear Algebra Review, Part II Brian Borchers January 4, Linear Independence Definition The vectors v, v,..., v n are linearly independent if the system of equations c v + c v +...+ c n v n
Lecture 3: Linear Algebra Review, Part II Brian Borchers January 4, Linear Independence Definition The vectors v, v,..., v n are linearly independent if the system of equations c v + c v +...+ c n v n
1 Vectors. c Kun Wang. Math 151, Fall Vector Supplement
 Vector Supplement 1 Vectors A vector is a quantity that has both magnitude and direction. Vectors are drawn as directed line segments and are denoted by boldface letters a or by a. The magnitude of a vector
Vector Supplement 1 Vectors A vector is a quantity that has both magnitude and direction. Vectors are drawn as directed line segments and are denoted by boldface letters a or by a. The magnitude of a vector
Inner products. Theorem (basic properties): Given vectors u, v, w in an inner product space V, and a scalar k, the following properties hold:
 Inner products Definition: An inner product on a real vector space V is an operation (function) that assigns to each pair of vectors ( u, v) in V a scalar u, v satisfying the following axioms: 1. u, v
Inner products Definition: An inner product on a real vector space V is an operation (function) that assigns to each pair of vectors ( u, v) in V a scalar u, v satisfying the following axioms: 1. u, v
Math 110 (S & E) Textbook: Calculus Early Transcendentals by James Stewart, 7 th Edition
 Math 110 (S & E) Textbook: Calculus Early Transcendentals by James Stewart, 7 th Edition 1 Appendix A : Numbers, Inequalities, and Absolute Values Sets A set is a collection of objects with an important
Math 110 (S & E) Textbook: Calculus Early Transcendentals by James Stewart, 7 th Edition 1 Appendix A : Numbers, Inequalities, and Absolute Values Sets A set is a collection of objects with an important
Notes on multivariable calculus
 Notes on multivariable calculus Jonathan Wise February 2, 2010 1 Review of trigonometry Trigonometry is essentially the study of the relationship between polar coordinates and Cartesian coordinates in
Notes on multivariable calculus Jonathan Wise February 2, 2010 1 Review of trigonometry Trigonometry is essentially the study of the relationship between polar coordinates and Cartesian coordinates in
Electromagnetic Field Theory
 University of Babylon College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering Class :2 st Lectures of Electromagnetic Field Theory By ssistant lecturer : hmed Hussein Shatti l-isawi 2014-2015 References
University of Babylon College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering Class :2 st Lectures of Electromagnetic Field Theory By ssistant lecturer : hmed Hussein Shatti l-isawi 2014-2015 References
Prepared by: M. S. KumarSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page
 Prepared by: M S KumarSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - 119 - CHAPTER 10: VECTOR ALGEBRA QUICK REVISION (Important Concepts & Formulae) MARKS WEIGHTAGE 06 marks Vector The line l to the line segment AB, then a
Prepared by: M S KumarSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - 119 - CHAPTER 10: VECTOR ALGEBRA QUICK REVISION (Important Concepts & Formulae) MARKS WEIGHTAGE 06 marks Vector The line l to the line segment AB, then a
MATH1013 Calculus I. Functions I 1
 1 Steward, James, Single Variable Calculus, Early Transcendentals, 7th edition, Brooks/Coles, 2012 Based on Briggs, Cochran and Gillett: Calculus for Scientists and Engineers: Early Transcendentals, Pearson
1 Steward, James, Single Variable Calculus, Early Transcendentals, 7th edition, Brooks/Coles, 2012 Based on Briggs, Cochran and Gillett: Calculus for Scientists and Engineers: Early Transcendentals, Pearson
MAT 272 Test 1 Review. 1. Let P = (1,1) and Q = (2,3). Find the unit vector u that has the same
 11.1 Vectors in the Plane 1. Let P = (1,1) and Q = (2,3). Find the unit vector u that has the same direction as. QP a. u =< 1, 2 > b. u =< 1 5, 2 5 > c. u =< 1, 2 > d. u =< 1 5, 2 5 > 2. If u has magnitude
11.1 Vectors in the Plane 1. Let P = (1,1) and Q = (2,3). Find the unit vector u that has the same direction as. QP a. u =< 1, 2 > b. u =< 1 5, 2 5 > c. u =< 1, 2 > d. u =< 1 5, 2 5 > 2. If u has magnitude
Sept , 17, 23, 29, 37, 41, 45, 47, , 5, 13, 17, 19, 29, 33. Exam Sept 26. Covers Sept 30-Oct 4.
 MATH 23, FALL 2013 Text: Calculus, Early Transcendentals or Multivariable Calculus, 7th edition, Stewart, Brooks/Cole. We will cover chapters 12 through 16, so the multivariable volume will be fine. WebAssign
MATH 23, FALL 2013 Text: Calculus, Early Transcendentals or Multivariable Calculus, 7th edition, Stewart, Brooks/Cole. We will cover chapters 12 through 16, so the multivariable volume will be fine. WebAssign
Exam 1 Review. IEA Section 2 2/5/2018 Section 3 2/5/2018
 Exam 1 Review IEA Section 2 2/5/2018 Section 3 2/5/2018 ALAC review session ALAC will have a review session in preparation for IEA Exam 1 Monday (Today) February 5th 8PM-10PM DCC 330 Test 1 Wednesday 2/7/2018
Exam 1 Review IEA Section 2 2/5/2018 Section 3 2/5/2018 ALAC review session ALAC will have a review session in preparation for IEA Exam 1 Monday (Today) February 5th 8PM-10PM DCC 330 Test 1 Wednesday 2/7/2018
Vector Geometry. Chapter 5
 Chapter 5 Vector Geometry In this chapter we will look more closely at certain geometric aspects of vectors in R n. We will first develop an intuitive understanding of some basic concepts by looking at
Chapter 5 Vector Geometry In this chapter we will look more closely at certain geometric aspects of vectors in R n. We will first develop an intuitive understanding of some basic concepts by looking at
Solutions to Selected Questions from Denis Sevee s Vector Geometry. (Updated )
 Solutions to Selected Questions from Denis Sevee s Vector Geometry. (Updated 24--27) Denis Sevee s Vector Geometry notes appear as Chapter 5 in the current custom textbook used at John Abbott College for
Solutions to Selected Questions from Denis Sevee s Vector Geometry. (Updated 24--27) Denis Sevee s Vector Geometry notes appear as Chapter 5 in the current custom textbook used at John Abbott College for
The Dot Product
 The Dot Product 1-9-017 If = ( 1,, 3 ) and = ( 1,, 3 ) are ectors, the dot product of and is defined algebraically as = 1 1 + + 3 3. Example. (a) Compute the dot product (,3, 7) ( 3,,0). (b) Compute the
The Dot Product 1-9-017 If = ( 1,, 3 ) and = ( 1,, 3 ) are ectors, the dot product of and is defined algebraically as = 1 1 + + 3 3. Example. (a) Compute the dot product (,3, 7) ( 3,,0). (b) Compute the
4.1 Distance and Length
 Chapter Vector Geometry In this chapter we will look more closely at certain geometric aspects of vectors in R n. We will first develop an intuitive understanding of some basic concepts by looking at vectors
Chapter Vector Geometry In this chapter we will look more closely at certain geometric aspects of vectors in R n. We will first develop an intuitive understanding of some basic concepts by looking at vectors
Exercises for Unit I (Topics from linear algebra)
 Exercises for Unit I (Topics from linear algebra) I.0 : Background Note. There is no corresponding section in the course notes, but as noted at the beginning of Unit I these are a few exercises which involve
Exercises for Unit I (Topics from linear algebra) I.0 : Background Note. There is no corresponding section in the course notes, but as noted at the beginning of Unit I these are a few exercises which involve
MATH Calculus III Fall 2009 Homework 1 - Solutions
 MATH 2300 - Calculus III Fall 2009 Homework 1 - Solutions 1. Find the equations of the two spheres that are tangent with equal radii whose centers are ( 3, 1, 2) and (5, 3, 6). SOLUTION: In order for the
MATH 2300 - Calculus III Fall 2009 Homework 1 - Solutions 1. Find the equations of the two spheres that are tangent with equal radii whose centers are ( 3, 1, 2) and (5, 3, 6). SOLUTION: In order for the
web: HOMEWORK 1
 MAT 207 LINEAR ALGEBRA I 2009207 Dokuz Eylül University, Faculty of Science, Department of Mathematics Instructor: Engin Mermut web: http://kisideuedutr/enginmermut/ HOMEWORK VECTORS IN THE n-dimensional
MAT 207 LINEAR ALGEBRA I 2009207 Dokuz Eylül University, Faculty of Science, Department of Mathematics Instructor: Engin Mermut web: http://kisideuedutr/enginmermut/ HOMEWORK VECTORS IN THE n-dimensional
DATE: MATH ANALYSIS 2 CHAPTER 12: VECTORS & DETERMINANTS
 NAME: PERIOD: DATE: MATH ANALYSIS 2 MR. MELLINA CHAPTER 12: VECTORS & DETERMINANTS Sections: v 12.1 Geometric Representation of Vectors v 12.2 Algebraic Representation of Vectors v 12.3 Vector and Parametric
NAME: PERIOD: DATE: MATH ANALYSIS 2 MR. MELLINA CHAPTER 12: VECTORS & DETERMINANTS Sections: v 12.1 Geometric Representation of Vectors v 12.2 Algebraic Representation of Vectors v 12.3 Vector and Parametric
b) The trend is for the average slope at x = 1 to decrease. The slope at x = 1 is 1.
 Chapters 1 to 8 Course Review Chapters 1 to 8 Course Review Question 1 Page 509 a) i) ii) [2(16) 12 + 4][2 3+ 4] 4 1 [2(2.25) 4.5+ 4][2 3+ 4] 1.51 = 21 3 = 7 = 1 0.5 = 2 [2(1.21) 3.3+ 4][2 3+ 4] iii) =
Chapters 1 to 8 Course Review Chapters 1 to 8 Course Review Question 1 Page 509 a) i) ii) [2(16) 12 + 4][2 3+ 4] 4 1 [2(2.25) 4.5+ 4][2 3+ 4] 1.51 = 21 3 = 7 = 1 0.5 = 2 [2(1.21) 3.3+ 4][2 3+ 4] iii) =
Vectors and Vector Arithmetic
 Vectors and Vector Arithmetic Introduction and Goals: The purpose of this lab is to become familiar with the syntax of Maple commands for manipulating and graphing vectors. It will introduce you to basic
Vectors and Vector Arithmetic Introduction and Goals: The purpose of this lab is to become familiar with the syntax of Maple commands for manipulating and graphing vectors. It will introduce you to basic
Linear Algebra: Homework 3
 Linear Algebra: Homework 3 Alvin Lin August 206 - December 206 Section.2 Exercise 48 Find all values of the scalar k for which the two vectors are orthogonal. [ ] [ ] 2 k + u v 3 k u v 0 2(k + ) + 3(k
Linear Algebra: Homework 3 Alvin Lin August 206 - December 206 Section.2 Exercise 48 Find all values of the scalar k for which the two vectors are orthogonal. [ ] [ ] 2 k + u v 3 k u v 0 2(k + ) + 3(k
Properties of Linear Transformations from R n to R m
 Properties of Linear Transformations from R n to R m MATH 322, Linear Algebra I J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 2015 Topic Overview Relationship between the properties of a matrix transformation
Properties of Linear Transformations from R n to R m MATH 322, Linear Algebra I J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 2015 Topic Overview Relationship between the properties of a matrix transformation
NORTHEASTERN UNIVERSITY Department of Mathematics
 NORTHEASTERN UNIVERSITY Department of Mathematics MATH 1342 (Calculus 2 for Engineering and Science) Final Exam Spring 2010 Do not write in these boxes: pg1 pg2 pg3 pg4 pg5 pg6 pg7 pg8 Total (100 points)
NORTHEASTERN UNIVERSITY Department of Mathematics MATH 1342 (Calculus 2 for Engineering and Science) Final Exam Spring 2010 Do not write in these boxes: pg1 pg2 pg3 pg4 pg5 pg6 pg7 pg8 Total (100 points)
MAT 2037 LINEAR ALGEBRA I web:
 MAT 237 LINEAR ALGEBRA I 2625 Dokuz Eylül University, Faculty of Science, Department of Mathematics web: Instructor: Engin Mermut http://kisideuedutr/enginmermut/ HOMEWORK 2 MATRIX ALGEBRA Textbook: Linear
MAT 237 LINEAR ALGEBRA I 2625 Dokuz Eylül University, Faculty of Science, Department of Mathematics web: Instructor: Engin Mermut http://kisideuedutr/enginmermut/ HOMEWORK 2 MATRIX ALGEBRA Textbook: Linear
Unit #17: Spring Trig Unit. A. First Quadrant Notice how the x-values decrease by while the y-values increase by that same amount.
 Name Unit #17: Spring Trig Unit Notes #1: Basic Trig Review I. Unit Circle A circle with center point and radius. A. First Quadrant Notice how the x-values decrease by while the y-values increase by that
Name Unit #17: Spring Trig Unit Notes #1: Basic Trig Review I. Unit Circle A circle with center point and radius. A. First Quadrant Notice how the x-values decrease by while the y-values increase by that
Vectors for Physics. AP Physics C
 Vectors for Physics AP Physics C A Vector is a quantity that has a magnitude (size) AND a direction. can be in one-dimension, two-dimensions, or even three-dimensions can be represented using a magnitude
Vectors for Physics AP Physics C A Vector is a quantity that has a magnitude (size) AND a direction. can be in one-dimension, two-dimensions, or even three-dimensions can be represented using a magnitude
JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS. MTH 201 CALCULUS III 5 Credit Hours. Prepared by: John M Johny August 2012
 JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS MTH 201 CALCULUS III 5 Credit Hours Prepared by: John M Johny August 2012 Dr. Robert Brieler, Division Chair, Math & Science Dr. Shirley Davenport, Dean, Arts & Science
JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS MTH 201 CALCULUS III 5 Credit Hours Prepared by: John M Johny August 2012 Dr. Robert Brieler, Division Chair, Math & Science Dr. Shirley Davenport, Dean, Arts & Science
10.1 Vectors. c Kun Wang. Math 150, Fall 2017
 10.1 Vectors Definition. A vector is a quantity that has both magnitude and direction. A vector is often represented graphically as an arrow where the direction is the direction of the arrow, and the magnitude
10.1 Vectors Definition. A vector is a quantity that has both magnitude and direction. A vector is often represented graphically as an arrow where the direction is the direction of the arrow, and the magnitude
45. The Parallelogram Law states that. product of a and b is the vector a b a 2 b 3 a 3 b 2, a 3 b 1 a 1 b 3, a 1 b 2 a 2 b 1. a c. a 1. b 1.
 SECTION 10.4 THE CROSS PRODUCT 537 42. Suppose that all sides of a quadrilateral are equal in length and opposite sides are parallel. Use vector methods to show that the diagonals are perpendicular. 43.
SECTION 10.4 THE CROSS PRODUCT 537 42. Suppose that all sides of a quadrilateral are equal in length and opposite sides are parallel. Use vector methods to show that the diagonals are perpendicular. 43.
MATH1014. Semester 1 Administrative Overview. Neil Montgomery calculus
 MATH1014 Semester 1 Administrative Overview Lecturers: Scott Morrison linear algebra scott.morrison@anu.edu.au Neil Montgomery calculus neil.montgomery@anu.edu.au Dr Scott Morrison (ANU) MATH1014 Notes
MATH1014 Semester 1 Administrative Overview Lecturers: Scott Morrison linear algebra scott.morrison@anu.edu.au Neil Montgomery calculus neil.montgomery@anu.edu.au Dr Scott Morrison (ANU) MATH1014 Notes
Vectors and Plane Geometry
 Vectors and Plane Geometry Karl Heinz Dovermann Professor of Mathematics University of Hawaii January 7, 0 Preface During the first week of the semester it is difficult to get started with the course
Vectors and Plane Geometry Karl Heinz Dovermann Professor of Mathematics University of Hawaii January 7, 0 Preface During the first week of the semester it is difficult to get started with the course
