[Kumar*, 5(2): February, 2016] ISSN: (I2OR), Publication Impact Factor: 3.785
|
|
|
- Darcy James
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 [Kumar*, 5(): February, 6] ISSN: (IOR), Publication Impact Factor: IJESRT INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES & RESEARCH TECHNOLOGY THERMOSOLUTAL CONVECTION IN A HETEROGENEOUS VISCO-ELASTIC (OLDROYDIAN) FLUID LAYER IN A POROUS MEDIUM Suhir Kumar Associate Professor, S.D. (PG) College, Muzaffarnagar (UP). ABSTRACT The paper critically examines, within the framework of linear stability analysis, the thermosolutal convection in a heterogeneous visco-elastic (Olroyian) flui layer in a porous meium. In the present paper, stationery, oscillatory an non-oscillatory convection have been iscusse in etails. A variational principle is establishe for the present problem. Some Results are iscusse numerically also. Also, principle of exchange of stabilities is not vali in the present problems. KEYWORDS: Thermosolutal instability, Heterogeneous flui, Olroyian flui, Porous Meium. INTRODUCTION The problem of onset of convection in a horizontal layer of flui heate from below, when buoyancy forces arise from ensity ifference ue to variation in temperature, was stuie by Benar [] an Rayleigh [] an the problem, uner varying assumptions of hyromagnetics, has been treate in etail by Chanrashekhar [3], Investigations of thermosolutal convection, when buoyancy forces arise also from variations in solute concentration apart from those ue to variation in temperature, are motivate by its irect relevance to the hyroynamics of oceans, as well as its interesting complexities, as a ouble-iffusion phenomenon. Stomell et al. [4] i the pioneering work in this irection. Since then the problem of thermohaline or thermosolutal convection has been stuie in three basic configurations by Stern [5], Veronis [6] an Niel [7] respectively, when the flui layer heate an solute from above, heate an solute from below an heate from below an solute form above. An experimental emonstration by Toms an Strabrige [8] has reveale that a ilute solution of methyl methacrylate in n-butyl acetate agrees well with the theoretical moel of Olroyian visco-elastic flui propose by Olroy [9]. Sharma [] has stuie the instability of the plane interface between two Olroyian visco-elastic superpose conucting fluis in the presence of a uniform magnetic fiel. In view of the fact that the stuy of visco-elastic flui in a porous meium fins, applications in geophysics an chemical technology, a number of researchers have contribute in this irection. However, the thermosolutal convection in a heterogeneous visco-elastic (Olroyian) flui layer in a porous meium seems, to the best, of our knowlege, uninvestigate so far. In this paper, therefore, we have examine the stability of a visco-elastic [Olroyian] flui layer heate an solute from below in a porous meium first stuie by Khare an Sahai [] leaing to an averse temperature graient an a solute concentration graient with free bounaries when the initial non-homogeneity is present in the flui. Hence it can be looke upon as an extension of thermosolutal convection in a homogenous flui layer in porous meium iscusse by Khare an Sahai. CONSTITUTIVE EQUATIONS AND THE EQUATIONS OF MOTION Let T ij ij, e ij ij, p, q i, T an C enote respectively the total stress tensor, shear stress tensor, rate of strain tensor, Kronecker elta, scalar pressure, velocity vector of the flui, viscosity, stress relaxation time, strain retaration time, temperature fiel an concentration fiel. Then the Olroyian visco-elastic flui is escribe by the constitutive equations [578]
2 [Kumar*, 5(): February, 6] ISSN: (IOR), Publication Impact Factor: Tij pij ij ij eij t t () q q i j an eij x j xi where q. is the total erivative being the sum of local an convective erivatives. t t Let us consier a horizontal layer of saturate porous meium of thickness between two free-bounaries z = an z =, z-axis being vertically upwar. Let the interstitial flui (flui in the porous meium) be visco-elastic, f(z), where f(z) is a monotonic function of z with f() = an is such that f z is constant. The layer is infinite in horizontal irections an is heate an solute from below leaing to an averse temperature graient uniform solutal graient (T T ) an a (S S ), where T an T are the constant temperatures of the lower an upper bounaries with T > T an also S an S are the constant solute concentrations of the lower an upper surfaces with S > S. The effective ensity is the superposition of inhomogeneity escribe by (a) f(z) an (b) T) S)] which is cause by temperature an solute graients. This leas to the effective ensity [f(z) (T T) (S S)]. () When the flui flows through a porous meium, the gross effect is represente by Darcy's law. As a result, the usual viscous term is replace by the resistance term permeability an the filter velocity. Hence, the basic equations are Dq V, where k an V enote respectively the meium k t t [ t p X i] k, t q (3). q (4) an ( q. ), t (5) T (. )T k q T T, t (6) C (. )C k q S C, t (7) [579]
3 [Kumar*, 5(): February, 6] ISSN: (IOR), Publication Impact Factor: where q an are respectively the velocity an kinematic viscosity of the flui respectively, k is the intrinsic permeability of the meium an k correspons to non-porous meium. BASIC STATE AND THE PERTURBATION EQUATIONS The initial stationary state, whose stability we wish to examine is that of an incompressible, viscous, visco-elastic (Olroyian) flui arrange in a horizontal strata in a non-homogeneous an isotropic porous meium. The system is acte upon by a temperature T, concentration C an the gravity fiel g (,, g). The initial state whose stability we wish to examine is thus characterize by z q (,, ), T T z, C C z, [f(z) z z]an p p gz. (8) where p. Following the usual proceure an normal moe technique given by F(z) exp.[i(k x k y) nt], (9) x y where k kx ky is the real wave number of propagation an n is the frequency of arbitrary isturbance. We get Ra [ FP ] [ (D a )(D a P )][ (D a ) P ]w [D a P ] P [ (D a ) P ]w R a [ (D a ) P ]w R a (D a P ) w P [ F P ][D a P ][ (D a ) P ]w. () where 4 g R kt is the thermal Rayleigh number, P is the thermal Prantl number, kt 4 g k R kt is the concentration Rayleigh number, S is the Lewis number, kt 4 f g k F T z is the elastic parameter, R,P an. kt k Equation () can also be written as [ FP ][ P (D a )(D a P )][ (D a ) P ]w Ra [D a P ] [ (D a ) P ]w P Ra [ (D a ) P ]w P R a (D a P ) w P P [ F P ][D a P ][ (D a ) P ]w. () The solution of the equation () is to be obtaine uner the following bounary conitions : w = D an z =. () [58]
4 [Kumar*, 5(): February, 6] ISSN: (IOR), Publication Impact Factor: RESULTS AND DISCUSSION (A) Stationary Convection Hence for stationary convection, equation () becomes R a a ) w =. (3) Multiplying equation (3) by w* an integrating over the range of z, we have Ra (D a ) ww *z 4 or Ra ( D w a a Dw )z (4) In view of the bounary conitions () an following Chanrashekhar [3] only possible solutions. Thus, we observe that the hypothesis that initial state solutions are perturbe is contraicte. Therefore, the instability can not set in as stationary convection, or in other wors the Principle of Exchange of Stabilities (PES) is not vali for the problem uner investigation. (B) Oscillatory Convection Now for the proper solution of equation () for w belonging to the lowest moe, we follow Chanrashekhar [3] an assume that solution w satisfying the bounary conitions is given by w = w Equation () yiels [ FP ] [ P (D a )(D a P )][ (D a ) P ]w Ra [D a P ] [ (D a ) P ]w P Ra [ (D a ) P ]w P R a (D a P ) w P P [ F P ](D a )[D a P ][ (D a ) P ]w. Let I [D a ][D a P ][ (D a ) P ]w, I 3 [ (D a ) P ]w an I 4 [D a P ]w. Substituting w = w, I, I 3 an I 4, we get I [D a ][D a P ][ (D a ) P ]w sin z [ ( a ) P ][ a P ][ a ]wsin z I [D a P ][ (D a ) P ]wsin z, [ ( a ) P ][ a P ]wsin z, I 3 [ (D a ) P ]wsin z [ ( a ) P ] an I 4 [D wsin z a wsin z P wsin z], [ a P ]wsin z Substituting for I, I, I 3 an I 4 from (6) to (9) into equation (5), we have (5) I [D a P ][ (D a ) P ]w, (6) (7) (8) (9) P [ FP ][ a ][ a P ][ ( a ) P ] R a [ FP ][ a P ] [58]
5 [Kumar*, 5(): February, 6] ISSN: (IOR), Publication Impact Factor: [ ( a ) P ] P Ra [ ( a ) P ][ FP ] P R a [ a P ] [ FP ] P P [ FP ][ a ][ a P ][ ( a ) P ]. () Moreover, equation () can be rewritten as Ra Ra [ a P ] [ a ][ a P ] [ a P ] Ra P [ ( a ) P ] P ( a )[ a P ][ FP ] [ FP ] RX 3 R4X[ X P ] [ X][ X P ] [ X P ] RX P [ ( X) P ] P ( X)[ X P ][ FP ] () [ FP ] where R R R a F R 3,R 4,R 4 4,X, an F 4. As iscusse earlier, the Principle of Exchange of Stabilities being not vali for the present problem, the marginal i i i in equation (), the equation at the marginal state is obtaine as RX [ X][( X)i 3 i i P ] [i[ X] ip ] RX ip R4X[ ( X) i P ] iip [ X][ ] PX[ X] [ [ X] i P ] [ F P i ] 3 3 [[ X] [ X]F P i F P i ( ) i( i P [ X]F P i ( ) F P i ] () The real part of equation () is given by R4X[ ( X) i P ] R [ X] i P R3X X [ [ X] ip ] P [ X] [[ X] [ X]F P i F P i ( )] (3) [ F P i ] Also, the imaginary part of equation () is given by R3X[ X] R4Xi P [ X][ ] [ X] i ip i [ [ X] ip ] 3 3 P [ X][ i P i [ X]F P i( ) F P i ] [ F P i ] This leas to the following sixth egree equation in i : 6 4 i i i A B C D, (4) [58]
6 [Kumar*, 5(): February, 6] ISSN: (IOR), Publication Impact Factor: where, A ( X) P F [( X) P P F ] B ( X) P ( X) F P R3X( X)F P R4 X[( X)( )F P ( ) ( X) PF P ( ), 4 3 C ( X) P R3X( X) [P F P ] R4P X( X)( ) PP ( X)[ F ( X)( )]. An D = R 3 X[ + X] 3. i is given by equation (4). We now iscuss the existence of overstable marginal state uner various situations. Case : The case when f (i) R 3 > z An (iii) Observe that (i) an (ii) R 3 > i for which (ii) k k i S T is positive (see equation (4)). It follows that the overstability cannot occur at the marginal state. However, the situation contrary to our assume conitions in this case, in general, oes not automatically guarantee the occurrence of overstability. In fact, for R 3 (i) may exist. (ii) If R 3 -elastic parameter F is so large that it makes either of B or C negative an satisfying the inequality 4[BD C ][AC B ] > [AD BC]. Thus, we see that the visco-elasticity has an effective role in instability criteria as there is a sufficient room for the existence of marginal state even if R 3 Case : When R 3 <, one of the roots of equation (4) is always positive irrespective of the other parameters. Therefore the marginal state an overstability essentially occur. (C) Nature of Non-Oscillating Moes : For R 3 >, k S > k T non- i r r r an w = w D r D r D r D3 r D4 r D5, where D P ( a )F, 3 D P ( a )[ P F P F( a )( )], 3 3 D3 FP a ( a )[R( ) R R ] P P ( a )[F ( a ) ( )] (5) D FP a (R R R) ( a ) P [( a ) P F ( )] P P ( a )], [583]
7 [Kumar*, 5(): February, 6] ISSN: (IOR), Publication Impact Factor: P ( a ) P a (R R R ), D4 P a ( a )[R R R( )] P ( a )[a RF P ( a )] an D5 Ra ( a ). r with real coefficients an thus has five roots, which may be real. Since R 3 5 in the characteristic equation being negative, hence has at least one positive real root an thus making the system unstable. Thus, we conclue that non-oscillatory moes are unstable in nature. VARIATIONAL PRINCIPLE A variational principle can be establishe for the present problem following Chanrashekhar [3]. Let one of the characteristic values be n i an let the corresponing solutions be enote by a subscript i, then ( n) k L n Dw k ( n) g f [ an n] DL nw w g g w, n z k [ n] (6) (7) From equation (6), we have, g f [ n ] DL n w w g g w, i i i i i i i ni z k [ n i] i Also from equation (7) ( n) k L i n Dwi (9) k ( n) Let n j be a characteristic value ifferent from n i, an let subscript j istinguishes the corresponing solutions. We multiply equations (8) an (9) respectively by w j an DW j an integrate them with respect to z from z = an z = using the bounary conitions w D w X Dz at z = an z =. (3) We have g f ( n i) (DL i)w jz ni wiw jz ni z k ( n i) g w z g w z (3) i j i j ( n i) an k L i(dw j)z ni DwiDw jz. (3) k i ( n i) Substituting the characteristic values n j, w j j i i respectively, integrating the same from z = an z = uner the bounary conitions (3) an substituting the results in equation (3), we get g f ( n i) L i(dw j)z ni wiw jz ni z k ( n i) (8) [584]
8 [Kumar*, 5(): February, 6] ISSN: (IOR), Publication Impact Factor: g [k T D i D j k T k ij n ji j ]z g [ksdid j ksk i j n ji j]z (33) Also integrating the L.H.S. of equation (3) by parts an using the bounary conitions (3), we get ( n i) k L i(dw j)z ni DwiDw jz. (34) k ( n i) Putting i = j an suppressing the subscript, equations (33) an (34) yiel ( n) nw (Dw) z (w (Dw) z k ( n) k k g f g gkt w z n z [(D ) k ( ) ]z n z g gks z [(D ) k ( ) ]z (35) Equation (35) provies a basis for the variational formulation of the problem as iscusse below: Let J w (Dw) z, J w (Dw) z, k k k f g J3 w z, J4 z, z (36) g gk T J5 z,j 6 [(D ) k ( ) ]z, gk S an J 7 [(D ) k ( ) ]z, With the help of equation (36), equation (35) can be written as ( n) g nj J J 3 (J4 J 5) n J6 J7 ( n) n g n n[j J4 J 5] J3 J J6 J7 (37) n n n in respectively. ' the corresponing changes in Js, i enote by gives ' Ji s. We can analyse these changes with the help of equation which [585]
9 [Kumar*, 5(): February, 6] ISSN: (IOR), Publication Impact Factor: g ( ) g n n J J4 J5 J 3 J J J4 J5 J3 J n ( n) n n J6 J7 (38) ' ' We, now use the expressions for Ji sgiven by (36) to evaluate Ji s. Integrating by parts a suitable number of times an using (3), we fin J (D w )wz, J (D k ) w z, k kk f g J 3 (w).wz, J 4 ( ) z, z (39) g gkt J 5 ( ) z, J 6 (D k ) z, gk S an J 7 (D k ) z. Combining equations (38) an (39) an using equations (3) to (37) in it an rearranging the terms, we get n g J J4 J6 J 3 J g (w w) z n ( n) g (w w) z (4) Multiplying equation of magnetic fiel by an integrating w.r.t. z from z = to z =, we get nz [ktk k T(D ) ]z wz. (4) an z =, we get n z nz [ktk ktd ]z wz. (4) Subtracting equation (4) from equation (4) an integrating by parts, using bounary conitions (3), we get after some rearrangement of the terms g [w w]z nj4 (43) Proceeing similarly, we get g [w w]z nj5 (44) Using equations (43) an (44) equation (4) reuces to n g ( ) J J4 J6 J 3 J. (45) n ( n) [586]
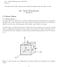
10 [Kumar*, 5(): February, 6] ISSN: (IOR), Publication Impact Factor: Now, it is evient from equation (37) that the quantity within [ ] on the L.H.S. of equation (45) can not vanish. Therefore, equation (35) provies a basis for the variational formulation of the problem uner investigation. NUMERICAL COMPUTATIONS The effect of various parameters on the instability criteria is stuie with the help of numerical computations using variational principle. sin lz an sin lz, where w The substitution of the trial solution in equation (35) an its further simplification ultimately gives, in imensionless where 3 A PF( y ), A P ( y )[ P P F( y )( )] P ( y )P P Fy (R R R5 p b )], 4 3 A 3 ( y ) z[ P PF P Fy ( )[R R Rb p ( )] P P ( y ) ( ) P y (R R R5b p ) A 4 ( y ) P Rb y P ( y )( F( y ) ( )] y ( )(R R ) 5 an A5 Rb y ( y ). where the quantities have been non-imensionalize as k n k y, b,, P S,, l l k kt g g g P, R, R an R 5. k kt kt The roots of equation (46) have been locate for ifferent values of b, y, R, R an P by making use of numerical A A A A A A, (46) stabilizing effect on the system. [587]
11 [Kumar*, 5(): February, 6] ISSN: (IOR), Publication Impact Factor: P =.5, F =, P = 3, t=.5 R =, R = 5, R 5=, b =.5, p = Unstable a c Stable e Critical Wave Number a cvs. e Fig..4 P =.5, e=.5, P = 3, t=.5 R =, R = 5, R 5 =, b =.5, p = Unstable.5 ac..5 Stable Critical Wave Number a c Vs. F Fig. F CONCLUSION An analysis of the problem an the iscussions of the results lea to the conclusion that the Principle of Exchange of Stability is not vali for this problem an the frequency of oscillations an the Rayleigh number in the marginal state are given by equation (3) an equation (4). [588]
12 [Kumar*, 5(): February, 6] ISSN: (IOR), Publication Impact Factor: Further, we fin for ensity istribution with positive graient an for k s >k T, the overstable marginal state oes not exist an we have only non-oscillatory moes which make the system unstable. For ensity istribution with negative graient, the marginal state an overstabse solution exist, irrespective of the values of other parameters. REFERENCES [] Benar, H. : Revue generale es sciences pures et apliques, : 6-7 an 39-8 (9). [] Rayleigh, L. : Phil. Mag. 3 : 59 (96). [3] Chanrashekhar, S. : Hyroynamic an Hyromagnetic Stability, Oxfor University Press, Lonon (96). [4] Stomell, H., Arones, A. B. an Bhanchor, D. : Deep Sea Res. 3 : 5 (956). [5] Stern, M.E. : Tellus : 7 (96). [6] Veronis, G. : J. Flui Mech. 3 : (965). [7] Niel, D.A. : J. Flui Mech. 9 : 545 (967). [8] Toms, B.A. an Strabrige, D. J. : Trans. Faraay Soc., 49 : 5 (953). [9] Olroy, J. G. : Proc. Roy. Soc. (Lonon), A45, (958). [] Sharma, R. C. : J. Maths. Phys. Sci. : 63 (978). [] Khare, H. C. an Sahai, A. K. : Proc. Nat. Aca. Sci. Inia 6(A), IV, (99). [589]
Effect of Rotation on Thermosolutal Convection. in a Rivlin-Ericksen Fluid Permeated with. Suspended Particles in Porous Medium
 Av. Theor. Appl. Mech., Vol. 3,, no. 4, 77-88 Effect of Rotation on Thermosolutal Convection in a Rivlin-Ericksen Flui Permeate with Suspene Particles in Porous Meium A. K. Aggarwal Department of Mathematics
Av. Theor. Appl. Mech., Vol. 3,, no. 4, 77-88 Effect of Rotation on Thermosolutal Convection in a Rivlin-Ericksen Flui Permeate with Suspene Particles in Porous Meium A. K. Aggarwal Department of Mathematics
Stability of Stratified Couple-Stress Dusty Fluid in the Presence of Magnetic Field through Porous Medium
 vailable at http://pvamu.eu/aam ppl. ppl. Math. ISSN: 93-9466 Vol. 6, Issue (December ), pp. 5 5 pplications pplie Mathematics: n International Journal (M) Stability of Stratifie Couple-Stress Dusty Flui
vailable at http://pvamu.eu/aam ppl. ppl. Math. ISSN: 93-9466 Vol. 6, Issue (December ), pp. 5 5 pplications pplie Mathematics: n International Journal (M) Stability of Stratifie Couple-Stress Dusty Flui
Thermal Modulation of Rayleigh-Benard Convection
 Thermal Moulation of Rayleigh-Benar Convection B. S. Bhaauria Department of Mathematics an Statistics, Jai Narain Vyas University, Johpur, Inia-3400 Reprint requests to Dr. B. S.; E-mail: bsbhaauria@reiffmail.com
Thermal Moulation of Rayleigh-Benar Convection B. S. Bhaauria Department of Mathematics an Statistics, Jai Narain Vyas University, Johpur, Inia-3400 Reprint requests to Dr. B. S.; E-mail: bsbhaauria@reiffmail.com
arxiv: v1 [physics.flu-dyn] 8 May 2014
![arxiv: v1 [physics.flu-dyn] 8 May 2014 arxiv: v1 [physics.flu-dyn] 8 May 2014](/thumbs/87/97199974.jpg) Energetics of a flui uner the Boussinesq approximation arxiv:1405.1921v1 [physics.flu-yn] 8 May 2014 Kiyoshi Maruyama Department of Earth an Ocean Sciences, National Defense Acaemy, Yokosuka, Kanagawa
Energetics of a flui uner the Boussinesq approximation arxiv:1405.1921v1 [physics.flu-yn] 8 May 2014 Kiyoshi Maruyama Department of Earth an Ocean Sciences, National Defense Acaemy, Yokosuka, Kanagawa
Chapter 2 Governing Equations
 Chapter 2 Governing Equations In the present an the subsequent chapters, we shall, either irectly or inirectly, be concerne with the bounary-layer flow of an incompressible viscous flui without any involvement
Chapter 2 Governing Equations In the present an the subsequent chapters, we shall, either irectly or inirectly, be concerne with the bounary-layer flow of an incompressible viscous flui without any involvement
Brief Note V. SHARMA, SUNIL 1), U. GUPTA 2) Notations. Himachal Pradesh University, Summer Hill Shimla , India
 Arch. Mech., 58, 1, pp. 187 197, Warszawa 006 Brief Note Stability of stratified elastico-viscous Walters (Model B ) fluid in the presence of horizontal magnetic field and rotation in porous medium V.
Arch. Mech., 58, 1, pp. 187 197, Warszawa 006 Brief Note Stability of stratified elastico-viscous Walters (Model B ) fluid in the presence of horizontal magnetic field and rotation in porous medium V.
Hydrodynamic and Hydromagnetic Stability of Two. Superposed Walters B' Viscoelastic Fluids. in Porous Medium
 Adv. Theor. Appl. Mech., Vol. 4, 0, no. 3, 3 - Hydrodynamic and Hydromagnetic Stability of Two Superposed Walters B' Viscoelastic Fluids in Porous Medium S. K. Kango Department of Mathematics, Govt. College,
Adv. Theor. Appl. Mech., Vol. 4, 0, no. 3, 3 - Hydrodynamic and Hydromagnetic Stability of Two Superposed Walters B' Viscoelastic Fluids in Porous Medium S. K. Kango Department of Mathematics, Govt. College,
Thermosolutal convection in a viscoelastic dusty fluid with hall currents in porous medium
 HOSTED BY Available online at www.scienceirect.com ScienceDirect journal homepage: http://ees.elsevier.com/ejbas/efault.asp Full Length Article Thermosolutal convection in a viscoelastic usty flui with
HOSTED BY Available online at www.scienceirect.com ScienceDirect journal homepage: http://ees.elsevier.com/ejbas/efault.asp Full Length Article Thermosolutal convection in a viscoelastic usty flui with
Convective heat transfer
 CHAPTER VIII Convective heat transfer The previous two chapters on issipative fluis were evote to flows ominate either by viscous effects (Chap. VI) or by convective motion (Chap. VII). In either case,
CHAPTER VIII Convective heat transfer The previous two chapters on issipative fluis were evote to flows ominate either by viscous effects (Chap. VI) or by convective motion (Chap. VII). In either case,
A STABILITY STUDY OF NON-NEWTONIAN FLUID FLOWS
 U.P.B. Sci. Bull., Series A, Vol. 71, Iss. 4, 009 ISSN 13-707 A STABILITY STUDY OF NON-NEWTONIAN FLUID FLOWS Corina CIPU 1, Carmen PRICINĂ, Victor ŢIGOIU 3 Se stuiază problema e curgere a unui flui Olroy
U.P.B. Sci. Bull., Series A, Vol. 71, Iss. 4, 009 ISSN 13-707 A STABILITY STUDY OF NON-NEWTONIAN FLUID FLOWS Corina CIPU 1, Carmen PRICINĂ, Victor ŢIGOIU 3 Se stuiază problema e curgere a unui flui Olroy
Lecture 2 Lagrangian formulation of classical mechanics Mechanics
 Lecture Lagrangian formulation of classical mechanics 70.00 Mechanics Principle of stationary action MATH-GA To specify a motion uniquely in classical mechanics, it suffices to give, at some time t 0,
Lecture Lagrangian formulation of classical mechanics 70.00 Mechanics Principle of stationary action MATH-GA To specify a motion uniquely in classical mechanics, it suffices to give, at some time t 0,
TOWARDS THERMOELASTICITY OF FRACTAL MEDIA
 ownloae By: [University of Illinois] At: 21:04 17 August 2007 Journal of Thermal Stresses, 30: 889 896, 2007 Copyright Taylor & Francis Group, LLC ISSN: 0149-5739 print/1521-074x online OI: 10.1080/01495730701495618
ownloae By: [University of Illinois] At: 21:04 17 August 2007 Journal of Thermal Stresses, 30: 889 896, 2007 Copyright Taylor & Francis Group, LLC ISSN: 0149-5739 print/1521-074x online OI: 10.1080/01495730701495618
Chapter 4. Electrostatics of Macroscopic Media
 Chapter 4. Electrostatics of Macroscopic Meia 4.1 Multipole Expansion Approximate potentials at large istances 3 x' x' (x') x x' x x Fig 4.1 We consier the potential in the far-fiel region (see Fig. 4.1
Chapter 4. Electrostatics of Macroscopic Meia 4.1 Multipole Expansion Approximate potentials at large istances 3 x' x' (x') x x' x x Fig 4.1 We consier the potential in the far-fiel region (see Fig. 4.1
Onset of convection of a reacting fluid layer in a porous medium with temperature-dependent heat source
 AMERICAN JOURNAL OF SCIENTIFIC AND INDUSTRIAL RESEARCH 2011, Science Huβ, http://www.scihub.org/ajsir ISSN: 2153-649X doi:10.5251/ajsir.2011.2.6.860.864 Onset of convection of a reacting fluid layer in
AMERICAN JOURNAL OF SCIENTIFIC AND INDUSTRIAL RESEARCH 2011, Science Huβ, http://www.scihub.org/ajsir ISSN: 2153-649X doi:10.5251/ajsir.2011.2.6.860.864 Onset of convection of a reacting fluid layer in
The effect of nonvertical shear on turbulence in a stably stratified medium
 The effect of nonvertical shear on turbulence in a stably stratifie meium Frank G. Jacobitz an Sutanu Sarkar Citation: Physics of Fluis (1994-present) 10, 1158 (1998); oi: 10.1063/1.869640 View online:
The effect of nonvertical shear on turbulence in a stably stratifie meium Frank G. Jacobitz an Sutanu Sarkar Citation: Physics of Fluis (1994-present) 10, 1158 (1998); oi: 10.1063/1.869640 View online:
Chapter 6: Energy-Momentum Tensors
 49 Chapter 6: Energy-Momentum Tensors This chapter outlines the general theory of energy an momentum conservation in terms of energy-momentum tensors, then applies these ieas to the case of Bohm's moel.
49 Chapter 6: Energy-Momentum Tensors This chapter outlines the general theory of energy an momentum conservation in terms of energy-momentum tensors, then applies these ieas to the case of Bohm's moel.
Application of the homotopy perturbation method to a magneto-elastico-viscous fluid along a semi-infinite plate
 Freun Publishing House Lt., International Journal of Nonlinear Sciences & Numerical Simulation, (9), -, 9 Application of the homotopy perturbation metho to a magneto-elastico-viscous flui along a semi-infinite
Freun Publishing House Lt., International Journal of Nonlinear Sciences & Numerical Simulation, (9), -, 9 Application of the homotopy perturbation metho to a magneto-elastico-viscous flui along a semi-infinite
Conservation Laws. Chapter Conservation of Energy
 20 Chapter 3 Conservation Laws In orer to check the physical consistency of the above set of equations governing Maxwell-Lorentz electroynamics [(2.10) an (2.12) or (1.65) an (1.68)], we examine the action
20 Chapter 3 Conservation Laws In orer to check the physical consistency of the above set of equations governing Maxwell-Lorentz electroynamics [(2.10) an (2.12) or (1.65) an (1.68)], we examine the action
5-4 Electrostatic Boundary Value Problems
 11/8/4 Section 54 Electrostatic Bounary Value Problems blank 1/ 5-4 Electrostatic Bounary Value Problems Reaing Assignment: pp. 149-157 Q: A: We must solve ifferential equations, an apply bounary conitions
11/8/4 Section 54 Electrostatic Bounary Value Problems blank 1/ 5-4 Electrostatic Bounary Value Problems Reaing Assignment: pp. 149-157 Q: A: We must solve ifferential equations, an apply bounary conitions
AN INTRODUCTION TO AIRCRAFT WING FLUTTER Revision A
 AN INTRODUCTION TO AIRCRAFT WIN FLUTTER Revision A By Tom Irvine Email: tomirvine@aol.com January 8, 000 Introuction Certain aircraft wings have experience violent oscillations uring high spee flight.
AN INTRODUCTION TO AIRCRAFT WIN FLUTTER Revision A By Tom Irvine Email: tomirvine@aol.com January 8, 000 Introuction Certain aircraft wings have experience violent oscillations uring high spee flight.
NUMERICAL STUDY OF THERMAL RADIATIONS AND THERMAL STRATIFICATION MECHANISMS IN MHD CASSON FLUID FLOW. and Sardar Muhammad BILAL c
 NUMERICAL STUDY OF THERMAL RADIATIONS AND THERMAL STRATIFICATION MECHANISMS IN MHD CASSON FLUID FLOW Khalil Ur REHMAN b c * Noor Ul SABA b Iffat ZEHRA c Muhamma Yousaf MALIK ab an Sarar Muhamma BILAL c
NUMERICAL STUDY OF THERMAL RADIATIONS AND THERMAL STRATIFICATION MECHANISMS IN MHD CASSON FLUID FLOW Khalil Ur REHMAN b c * Noor Ul SABA b Iffat ZEHRA c Muhamma Yousaf MALIK ab an Sarar Muhamma BILAL c
Introduction to the Vlasov-Poisson system
 Introuction to the Vlasov-Poisson system Simone Calogero 1 The Vlasov equation Consier a particle with mass m > 0. Let x(t) R 3 enote the position of the particle at time t R an v(t) = ẋ(t) = x(t)/t its
Introuction to the Vlasov-Poisson system Simone Calogero 1 The Vlasov equation Consier a particle with mass m > 0. Let x(t) R 3 enote the position of the particle at time t R an v(t) = ẋ(t) = x(t)/t its
EXPONENTIAL FOURIER INTEGRAL TRANSFORM METHOD FOR STRESS ANALYSIS OF BOUNDARY LOAD ON SOIL
 Tome XVI [18] Fascicule 3 [August] 1. Charles Chinwuba IKE EXPONENTIAL FOURIER INTEGRAL TRANSFORM METHOD FOR STRESS ANALYSIS OF BOUNDARY LOAD ON SOIL 1. Department of Civil Engineering, Enugu State University
Tome XVI [18] Fascicule 3 [August] 1. Charles Chinwuba IKE EXPONENTIAL FOURIER INTEGRAL TRANSFORM METHOD FOR STRESS ANALYSIS OF BOUNDARY LOAD ON SOIL 1. Department of Civil Engineering, Enugu State University
Agmon Kolmogorov Inequalities on l 2 (Z d )
 Journal of Mathematics Research; Vol. 6, No. ; 04 ISSN 96-9795 E-ISSN 96-9809 Publishe by Canaian Center of Science an Eucation Agmon Kolmogorov Inequalities on l (Z ) Arman Sahovic Mathematics Department,
Journal of Mathematics Research; Vol. 6, No. ; 04 ISSN 96-9795 E-ISSN 96-9809 Publishe by Canaian Center of Science an Eucation Agmon Kolmogorov Inequalities on l (Z ) Arman Sahovic Mathematics Department,
An analytical investigation into filmwise condensation on a horizontal tube in a porous medium with suction at the tube surface
 Heat Mass Transfer (29) 45:355 361 DOI 1.17/s231-8-436-y ORIGINAL An analytical investigation into filmwise conensation on a horizontal tube in a porous meium with suction at the tube surface Tong Bou
Heat Mass Transfer (29) 45:355 361 DOI 1.17/s231-8-436-y ORIGINAL An analytical investigation into filmwise conensation on a horizontal tube in a porous meium with suction at the tube surface Tong Bou
The total derivative. Chapter Lagrangian and Eulerian approaches
 Chapter 5 The total erivative 51 Lagrangian an Eulerian approaches The representation of a flui through scalar or vector fiels means that each physical quantity uner consieration is escribe as a function
Chapter 5 The total erivative 51 Lagrangian an Eulerian approaches The representation of a flui through scalar or vector fiels means that each physical quantity uner consieration is escribe as a function
( ), such motions are possible, and in particular PES is valid.
 Int. Jnl. of Multiphysics Volume 6 Number 4 4 A semi-circle theorem in couple-stress fluid in the presence of rotation Ajaib S. Banyal* Department of Mathematics Govt. College Nadaun Hamirpur (HP) INDIA
Int. Jnl. of Multiphysics Volume 6 Number 4 4 A semi-circle theorem in couple-stress fluid in the presence of rotation Ajaib S. Banyal* Department of Mathematics Govt. College Nadaun Hamirpur (HP) INDIA
Stability of Two Superposed Viscoelastic (Walters B') Fluid-Particle Mixtures in Porous Medium
 Stability of Two Superposed Viscoelastic (Walters B') Fluid-Particle Mixtures in Porous Medium Pardeep Kumar Department of Mathematics, Himachal Pradesh University, Summer-Hill, Shimla-171005, India Reprint
Stability of Two Superposed Viscoelastic (Walters B') Fluid-Particle Mixtures in Porous Medium Pardeep Kumar Department of Mathematics, Himachal Pradesh University, Summer-Hill, Shimla-171005, India Reprint
Thermal conductivity of graded composites: Numerical simulations and an effective medium approximation
 JOURNAL OF MATERIALS SCIENCE 34 (999)5497 5503 Thermal conuctivity of grae composites: Numerical simulations an an effective meium approximation P. M. HUI Department of Physics, The Chinese University
JOURNAL OF MATERIALS SCIENCE 34 (999)5497 5503 Thermal conuctivity of grae composites: Numerical simulations an an effective meium approximation P. M. HUI Department of Physics, The Chinese University
Completely passive natural convection
 Early View publication on wileyonlinelibrary.com (issue an page numbers not yet assigne; citable using Digital Object Ientifier DOI) ZAMM Z. Angew. Math. Mech., 1 6 (2011) / DOI 10.1002/zamm.201000030
Early View publication on wileyonlinelibrary.com (issue an page numbers not yet assigne; citable using Digital Object Ientifier DOI) ZAMM Z. Angew. Math. Mech., 1 6 (2011) / DOI 10.1002/zamm.201000030
Prototype Instabilities
 Prototype Instabilities David Randall Introduction Broadly speaking, a growing atmospheric disturbance can draw its kinetic energy from two possible sources: the kinetic and available potential energies
Prototype Instabilities David Randall Introduction Broadly speaking, a growing atmospheric disturbance can draw its kinetic energy from two possible sources: the kinetic and available potential energies
05 The Continuum Limit and the Wave Equation
 Utah State University DigitalCommons@USU Founations of Wave Phenomena Physics, Department of 1-1-2004 05 The Continuum Limit an the Wave Equation Charles G. Torre Department of Physics, Utah State University,
Utah State University DigitalCommons@USU Founations of Wave Phenomena Physics, Department of 1-1-2004 05 The Continuum Limit an the Wave Equation Charles G. Torre Department of Physics, Utah State University,
Math 342 Partial Differential Equations «Viktor Grigoryan
 Math 342 Partial Differential Equations «Viktor Grigoryan 6 Wave equation: solution In this lecture we will solve the wave equation on the entire real line x R. This correspons to a string of infinite
Math 342 Partial Differential Equations «Viktor Grigoryan 6 Wave equation: solution In this lecture we will solve the wave equation on the entire real line x R. This correspons to a string of infinite
Effect of Uniform Horizontal Magnetic Field on Thermal Instability in A Rotating Micropolar Fluid Saturating A Porous Medium
 IOSR Journal of Mathematics (IOSR-JM) e-issn: 78-578, p-issn: 39-765X. Volume, Issue Ver. III (Jan. - Fe. 06), 5-65 www.iosrjournals.org Effect of Uniform Horizontal Magnetic Field on Thermal Instaility
IOSR Journal of Mathematics (IOSR-JM) e-issn: 78-578, p-issn: 39-765X. Volume, Issue Ver. III (Jan. - Fe. 06), 5-65 www.iosrjournals.org Effect of Uniform Horizontal Magnetic Field on Thermal Instaility
Surface tension driven oscillatory instability in a rotating fluid layer
 J. Fluid Mech. (1969), wol. 39, part 1, pp. 49-55 Printed in Great Britain 49 Surface tension driven oscillatory instability in a rotating fluid layer By G. A. McCONAGHYT AND B. A. FINLAYSON University
J. Fluid Mech. (1969), wol. 39, part 1, pp. 49-55 Printed in Great Britain 49 Surface tension driven oscillatory instability in a rotating fluid layer By G. A. McCONAGHYT AND B. A. FINLAYSON University
Dusty Plasma Void Dynamics in Unmoving and Moving Flows
 7 TH EUROPEAN CONFERENCE FOR AERONAUTICS AND SPACE SCIENCES (EUCASS) Dusty Plasma Voi Dynamics in Unmoving an Moving Flows O.V. Kravchenko*, O.A. Azarova**, an T.A. Lapushkina*** *Scientific an Technological
7 TH EUROPEAN CONFERENCE FOR AERONAUTICS AND SPACE SCIENCES (EUCASS) Dusty Plasma Voi Dynamics in Unmoving an Moving Flows O.V. Kravchenko*, O.A. Azarova**, an T.A. Lapushkina*** *Scientific an Technological
1 dx. where is a large constant, i.e., 1, (7.6) and Px is of the order of unity. Indeed, if px is given by (7.5), the inequality (7.
 Lectures Nine an Ten The WKB Approximation The WKB metho is a powerful tool to obtain solutions for many physical problems It is generally applicable to problems of wave propagation in which the frequency
Lectures Nine an Ten The WKB Approximation The WKB metho is a powerful tool to obtain solutions for many physical problems It is generally applicable to problems of wave propagation in which the frequency
PAijpam.eu RELATIVE HEAT LOSS REDUCTION FORMULA FOR WINDOWS WITH MULTIPLE PANES Cassandra Reed 1, Jean Michelet Jean-Michel 2
 International Journal of Pure an Applie Mathematics Volume 97 No. 4 2014 543-549 ISSN: 1311-8080 (printe version); ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.ijpam.eu oi: http://x.oi.org/10.12732/ijpam.v97i4.13
International Journal of Pure an Applie Mathematics Volume 97 No. 4 2014 543-549 ISSN: 1311-8080 (printe version); ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.ijpam.eu oi: http://x.oi.org/10.12732/ijpam.v97i4.13
6 General properties of an autonomous system of two first order ODE
 6 General properties of an autonomous system of two first orer ODE Here we embark on stuying the autonomous system of two first orer ifferential equations of the form ẋ 1 = f 1 (, x 2 ), ẋ 2 = f 2 (, x
6 General properties of an autonomous system of two first orer ODE Here we embark on stuying the autonomous system of two first orer ifferential equations of the form ẋ 1 = f 1 (, x 2 ), ẋ 2 = f 2 (, x
arxiv: v1 [physics.class-ph] 20 Dec 2017
![arxiv: v1 [physics.class-ph] 20 Dec 2017 arxiv: v1 [physics.class-ph] 20 Dec 2017](/thumbs/77/74715823.jpg) arxiv:1712.07328v1 [physics.class-ph] 20 Dec 2017 Demystifying the constancy of the Ermakov-Lewis invariant for a time epenent oscillator T. Pamanabhan IUCAA, Post Bag 4, Ganeshkhin, Pune - 411 007, Inia.
arxiv:1712.07328v1 [physics.class-ph] 20 Dec 2017 Demystifying the constancy of the Ermakov-Lewis invariant for a time epenent oscillator T. Pamanabhan IUCAA, Post Bag 4, Ganeshkhin, Pune - 411 007, Inia.
'HVLJQ &RQVLGHUDWLRQ LQ 0DWHULDO 6HOHFWLRQ 'HVLJQ 6HQVLWLYLW\,1752'8&7,21
 Large amping in a structural material may be either esirable or unesirable, epening on the engineering application at han. For example, amping is a esirable property to the esigner concerne with limiting
Large amping in a structural material may be either esirable or unesirable, epening on the engineering application at han. For example, amping is a esirable property to the esigner concerne with limiting
Transactions on Engineering Sciences vol 5, 1994 WIT Press, ISSN
 Generalize heat conuction transfer functions in two imensional linear systems of assigne geometry F. Marcotullio & A. Ponticiello Dipartimento i Energetica- Universit i L 'Aquila Monteluco i Roio - 67100
Generalize heat conuction transfer functions in two imensional linear systems of assigne geometry F. Marcotullio & A. Ponticiello Dipartimento i Energetica- Universit i L 'Aquila Monteluco i Roio - 67100
Proof of SPNs as Mixture of Trees
 A Proof of SPNs as Mixture of Trees Theorem 1. If T is an inuce SPN from a complete an ecomposable SPN S, then T is a tree that is complete an ecomposable. Proof. Argue by contraiction that T is not a
A Proof of SPNs as Mixture of Trees Theorem 1. If T is an inuce SPN from a complete an ecomposable SPN S, then T is a tree that is complete an ecomposable. Proof. Argue by contraiction that T is not a
Strength Analysis of CFRP Composite Material Considering Multiple Fracture Modes
 5--XXXX Strength Analysis of CFRP Composite Material Consiering Multiple Fracture Moes Author, co-author (Do NOT enter this information. It will be pulle from participant tab in MyTechZone) Affiliation
5--XXXX Strength Analysis of CFRP Composite Material Consiering Multiple Fracture Moes Author, co-author (Do NOT enter this information. It will be pulle from participant tab in MyTechZone) Affiliation
Asymptotics of a Small Liquid Drop on a Cone and Plate Rheometer
 Asymptotics of a Small Liqui Drop on a Cone an Plate Rheometer Vincent Cregan, Stephen B.G. O Brien, an Sean McKee Abstract A cone an a plate rheometer is a laboratory apparatus use to measure the viscosity
Asymptotics of a Small Liqui Drop on a Cone an Plate Rheometer Vincent Cregan, Stephen B.G. O Brien, an Sean McKee Abstract A cone an a plate rheometer is a laboratory apparatus use to measure the viscosity
Assignment 1. g i (x 1,..., x n ) dx i = 0. i=1
 Assignment 1 Golstein 1.4 The equations of motion for the rolling isk are special cases of general linear ifferential equations of constraint of the form g i (x 1,..., x n x i = 0. i=1 A constraint conition
Assignment 1 Golstein 1.4 The equations of motion for the rolling isk are special cases of general linear ifferential equations of constraint of the form g i (x 1,..., x n x i = 0. i=1 A constraint conition
Onset of Darcy-Brinkman Convection in a Maxwell Fluid Saturated Anisotropic Porous Layer
 Journal of Applie Flui Mechanics Vol. 9 No. 4 pp. 1709-170 016. Available online at www.jafmonline.net IN 1735-357 EIN 1735-3645. DOI: 10.18869/acapub.jafm.68.35.4634 Onset of Darcy-Brinkman Convection
Journal of Applie Flui Mechanics Vol. 9 No. 4 pp. 1709-170 016. Available online at www.jafmonline.net IN 1735-357 EIN 1735-3645. DOI: 10.18869/acapub.jafm.68.35.4634 Onset of Darcy-Brinkman Convection
Stable and compact finite difference schemes
 Center for Turbulence Research Annual Research Briefs 2006 2 Stable an compact finite ifference schemes By K. Mattsson, M. Svär AND M. Shoeybi. Motivation an objectives Compact secon erivatives have long
Center for Turbulence Research Annual Research Briefs 2006 2 Stable an compact finite ifference schemes By K. Mattsson, M. Svär AND M. Shoeybi. Motivation an objectives Compact secon erivatives have long
Chapter 2 Lagrangian Modeling
 Chapter 2 Lagrangian Moeling The basic laws of physics are use to moel every system whether it is electrical, mechanical, hyraulic, or any other energy omain. In mechanics, Newton s laws of motion provie
Chapter 2 Lagrangian Moeling The basic laws of physics are use to moel every system whether it is electrical, mechanical, hyraulic, or any other energy omain. In mechanics, Newton s laws of motion provie
A SIMPLE ENGINEERING MODEL FOR SPRINKLER SPRAY INTERACTION WITH FIRE PRODUCTS
 International Journal on Engineering Performance-Base Fire Coes, Volume 4, Number 3, p.95-3, A SIMPLE ENGINEERING MOEL FOR SPRINKLER SPRAY INTERACTION WITH FIRE PROCTS V. Novozhilov School of Mechanical
International Journal on Engineering Performance-Base Fire Coes, Volume 4, Number 3, p.95-3, A SIMPLE ENGINEERING MOEL FOR SPRINKLER SPRAY INTERACTION WITH FIRE PROCTS V. Novozhilov School of Mechanical
Homework 7 Due 18 November at 6:00 pm
 Homework 7 Due 18 November at 6:00 pm 1. Maxwell s Equations Quasi-statics o a An air core, N turn, cylinrical solenoi of length an raius a, carries a current I Io cos t. a. Using Ampere s Law, etermine
Homework 7 Due 18 November at 6:00 pm 1. Maxwell s Equations Quasi-statics o a An air core, N turn, cylinrical solenoi of length an raius a, carries a current I Io cos t. a. Using Ampere s Law, etermine
Poroelasticity and tidal loading
 Chapter 6: Poroelasticity an tial loaing 63 Chapter 6: Poroelasticity an tial loaing 6. Introuction It is establishe above, in Chapter 4, that there are many known examples of the tial moulation of seafloor
Chapter 6: Poroelasticity an tial loaing 63 Chapter 6: Poroelasticity an tial loaing 6. Introuction It is establishe above, in Chapter 4, that there are many known examples of the tial moulation of seafloor
Conservation laws a simple application to the telegraph equation
 J Comput Electron 2008 7: 47 51 DOI 10.1007/s10825-008-0250-2 Conservation laws a simple application to the telegraph equation Uwe Norbrock Reinhol Kienzler Publishe online: 1 May 2008 Springer Scienceusiness
J Comput Electron 2008 7: 47 51 DOI 10.1007/s10825-008-0250-2 Conservation laws a simple application to the telegraph equation Uwe Norbrock Reinhol Kienzler Publishe online: 1 May 2008 Springer Scienceusiness
A Universal Model for Bingham Fluids with Two Characteristic Yield Stresses
 A Universal Moel for Bingham Fluis with Two Characteristic Yiel Stresses NGDomostroeva 1 an NNTrunov DIMeneleyev Institute for Metrology Russia, StPetersburg 195 Moskovsky pr 19 February, 4, 9 Abstract:
A Universal Moel for Bingham Fluis with Two Characteristic Yiel Stresses NGDomostroeva 1 an NNTrunov DIMeneleyev Institute for Metrology Russia, StPetersburg 195 Moskovsky pr 19 February, 4, 9 Abstract:
GLOBAL SOLUTIONS FOR 2D COUPLED BURGERS-COMPLEX-GINZBURG-LANDAU EQUATIONS
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 015 015), No. 99, pp. 1 14. ISSN: 107-6691. URL: http://eje.math.txstate.eu or http://eje.math.unt.eu ftp eje.math.txstate.eu GLOBAL SOLUTIONS FOR D COUPLED
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 015 015), No. 99, pp. 1 14. ISSN: 107-6691. URL: http://eje.math.txstate.eu or http://eje.math.unt.eu ftp eje.math.txstate.eu GLOBAL SOLUTIONS FOR D COUPLED
Two Dimensional Numerical Simulator for Modeling NDC Region in SNDC Devices
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Two Dimensional Numerical Simulator for Moeling NDC Region in SNDC Devices To cite this article: Dheeraj Kumar Sinha et al 2016 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser.
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Two Dimensional Numerical Simulator for Moeling NDC Region in SNDC Devices To cite this article: Dheeraj Kumar Sinha et al 2016 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser.
1 Heisenberg Representation
 1 Heisenberg Representation What we have been ealing with so far is calle the Schröinger representation. In this representation, operators are constants an all the time epenence is carrie by the states.
1 Heisenberg Representation What we have been ealing with so far is calle the Schröinger representation. In this representation, operators are constants an all the time epenence is carrie by the states.
EXACT TRAVELING WAVE SOLUTIONS FOR A NEW NON-LINEAR HEAT TRANSFER EQUATION
 THERMAL SCIENCE, Year 017, Vol. 1, No. 4, pp. 1833-1838 1833 EXACT TRAVELING WAVE SOLUTIONS FOR A NEW NON-LINEAR HEAT TRANSFER EQUATION by Feng GAO a,b, Xiao-Jun YANG a,b,* c, an Yu-Feng ZHANG a School
THERMAL SCIENCE, Year 017, Vol. 1, No. 4, pp. 1833-1838 1833 EXACT TRAVELING WAVE SOLUTIONS FOR A NEW NON-LINEAR HEAT TRANSFER EQUATION by Feng GAO a,b, Xiao-Jun YANG a,b,* c, an Yu-Feng ZHANG a School
A new proof of the sharpness of the phase transition for Bernoulli percolation on Z d
 A new proof of the sharpness of the phase transition for Bernoulli percolation on Z Hugo Duminil-Copin an Vincent Tassion October 8, 205 Abstract We provie a new proof of the sharpness of the phase transition
A new proof of the sharpness of the phase transition for Bernoulli percolation on Z Hugo Duminil-Copin an Vincent Tassion October 8, 205 Abstract We provie a new proof of the sharpness of the phase transition
Buoyancy Driven Convection in Micropolar Fluid with Controller and Variable Boundaries
 Buoyancy Driven Convection in Micropolar Fluid with Controller and Variable Boundaries. F. M. MOKHTAR a,b *, I. K. KHALID a,. M. ARIFI b a Department of Mathematics Universiti Putra Malaysia 43400 UPM,
Buoyancy Driven Convection in Micropolar Fluid with Controller and Variable Boundaries. F. M. MOKHTAR a,b *, I. K. KHALID a,. M. ARIFI b a Department of Mathematics Universiti Putra Malaysia 43400 UPM,
Table of Common Derivatives By David Abraham
 Prouct an Quotient Rules: Table of Common Derivatives By Davi Abraham [ f ( g( ] = [ f ( ] g( + f ( [ g( ] f ( = g( [ f ( ] g( g( f ( [ g( ] Trigonometric Functions: sin( = cos( cos( = sin( tan( = sec
Prouct an Quotient Rules: Table of Common Derivatives By Davi Abraham [ f ( g( ] = [ f ( ] g( + f ( [ g( ] f ( = g( [ f ( ] g( g( f ( [ g( ] Trigonometric Functions: sin( = cos( cos( = sin( tan( = sec
A Model of Electron-Positron Pair Formation
 Volume PROGRESS IN PHYSICS January, 8 A Moel of Electron-Positron Pair Formation Bo Lehnert Alfvén Laboratory, Royal Institute of Technology, S-44 Stockholm, Sween E-mail: Bo.Lehnert@ee.kth.se The elementary
Volume PROGRESS IN PHYSICS January, 8 A Moel of Electron-Positron Pair Formation Bo Lehnert Alfvén Laboratory, Royal Institute of Technology, S-44 Stockholm, Sween E-mail: Bo.Lehnert@ee.kth.se The elementary
APPROXIMATE SOLUTION FOR TRANSIENT HEAT TRANSFER IN STATIC TURBULENT HE II. B. Baudouy. CEA/Saclay, DSM/DAPNIA/STCM Gif-sur-Yvette Cedex, France
 APPROXIMAE SOLUION FOR RANSIEN HEA RANSFER IN SAIC URBULEN HE II B. Bauouy CEA/Saclay, DSM/DAPNIA/SCM 91191 Gif-sur-Yvette Ceex, France ABSRAC Analytical solution in one imension of the heat iffusion equation
APPROXIMAE SOLUION FOR RANSIEN HEA RANSFER IN SAIC URBULEN HE II B. Bauouy CEA/Saclay, DSM/DAPNIA/SCM 91191 Gif-sur-Yvette Ceex, France ABSRAC Analytical solution in one imension of the heat iffusion equation
Relation between the propagator matrix of geodesic deviation and the second-order derivatives of the characteristic function
 Journal of Electromagnetic Waves an Applications 203 Vol. 27 No. 3 589 60 http://x.oi.org/0.080/0920507.203.808595 Relation between the propagator matrix of geoesic eviation an the secon-orer erivatives
Journal of Electromagnetic Waves an Applications 203 Vol. 27 No. 3 589 60 http://x.oi.org/0.080/0920507.203.808595 Relation between the propagator matrix of geoesic eviation an the secon-orer erivatives
Qubit channels that achieve capacity with two states
 Qubit channels that achieve capacity with two states Dominic W. Berry Department of Physics, The University of Queenslan, Brisbane, Queenslan 4072, Australia Receive 22 December 2004; publishe 22 March
Qubit channels that achieve capacity with two states Dominic W. Berry Department of Physics, The University of Queenslan, Brisbane, Queenslan 4072, Australia Receive 22 December 2004; publishe 22 March
TRIPLE-DIFFUSIVE CONVECTION IN WALTERS (MODEL B') FLUID WITH VARYING GRAVITY FIELD SATURATING A POROUS MEDIUM
 Studia Geotechnica et Mechanica, Vol. XXXV, No. 3, 3 DOI:.478/sgem-3-9 TRILE-DIFFUSIVE CONVECTION IN WALTERS (MODEL B') FLUID WITH VARYING GRAVITY FIELD SATURATING A OROUS MEDIUM S.K. KANGO Department
Studia Geotechnica et Mechanica, Vol. XXXV, No. 3, 3 DOI:.478/sgem-3-9 TRILE-DIFFUSIVE CONVECTION IN WALTERS (MODEL B') FLUID WITH VARYING GRAVITY FIELD SATURATING A OROUS MEDIUM S.K. KANGO Department
Lower Bounds for the Smoothed Number of Pareto optimal Solutions
 Lower Bouns for the Smoothe Number of Pareto optimal Solutions Tobias Brunsch an Heiko Röglin Department of Computer Science, University of Bonn, Germany brunsch@cs.uni-bonn.e, heiko@roeglin.org Abstract.
Lower Bouns for the Smoothe Number of Pareto optimal Solutions Tobias Brunsch an Heiko Röglin Department of Computer Science, University of Bonn, Germany brunsch@cs.uni-bonn.e, heiko@roeglin.org Abstract.
2.20 Marine Hydrodynamics Lecture 3
 2.20 Marine Hyroynamics, Fall 2018 Lecture 3 Copyright c 2018 MIT - Department of Mechanical Engineering, All rights reserve. 1.7 Stress Tensor 2.20 Marine Hyroynamics Lecture 3 1.7.1 Stress Tensor τ ij
2.20 Marine Hyroynamics, Fall 2018 Lecture 3 Copyright c 2018 MIT - Department of Mechanical Engineering, All rights reserve. 1.7 Stress Tensor 2.20 Marine Hyroynamics Lecture 3 1.7.1 Stress Tensor τ ij
(2012) , ISBN
 Cregan, V. an O'Brien, Stephen B.G. an McKee, Sean (2012) Asymptotics of a small liqui rop on a cone an plate rheometer. In: Progress in Inustrial Mathematics at ECMI 2010. Mathematics in Inustry: Progress
Cregan, V. an O'Brien, Stephen B.G. an McKee, Sean (2012) Asymptotics of a small liqui rop on a cone an plate rheometer. In: Progress in Inustrial Mathematics at ECMI 2010. Mathematics in Inustry: Progress
Lectures - Week 10 Introduction to Ordinary Differential Equations (ODES) First Order Linear ODEs
 Lectures - Week 10 Introuction to Orinary Differential Equations (ODES) First Orer Linear ODEs When stuying ODEs we are consiering functions of one inepenent variable, e.g., f(x), where x is the inepenent
Lectures - Week 10 Introuction to Orinary Differential Equations (ODES) First Orer Linear ODEs When stuying ODEs we are consiering functions of one inepenent variable, e.g., f(x), where x is the inepenent
3-D FEM Modeling of fiber/matrix interface debonding in UD composites including surface effects
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science an Engineering 3-D FEM Moeling of fiber/matrix interface eboning in UD composites incluing surface effects To cite this article: A Pupurs an J Varna 2012 IOP Conf.
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science an Engineering 3-D FEM Moeling of fiber/matrix interface eboning in UD composites incluing surface effects To cite this article: A Pupurs an J Varna 2012 IOP Conf.
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 9 Jan 2012
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 9 Jan 2012 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 9 Jan 2012](/thumbs/89/98753494.jpg) arxiv:1201.1836v1 [con-mat.stat-mech] 9 Jan 2012 Externally riven one-imensional Ising moel Amir Aghamohammai a 1, Cina Aghamohammai b 2, & Mohamma Khorrami a 3 a Department of Physics, Alzahra University,
arxiv:1201.1836v1 [con-mat.stat-mech] 9 Jan 2012 Externally riven one-imensional Ising moel Amir Aghamohammai a 1, Cina Aghamohammai b 2, & Mohamma Khorrami a 3 a Department of Physics, Alzahra University,
A note on the Mooney-Rivlin material model
 A note on the Mooney-Rivlin material moel I-Shih Liu Instituto e Matemática Universiae Feeral o Rio e Janeiro 2945-97, Rio e Janeiro, Brasil Abstract In finite elasticity, the Mooney-Rivlin material moel
A note on the Mooney-Rivlin material moel I-Shih Liu Instituto e Matemática Universiae Feeral o Rio e Janeiro 2945-97, Rio e Janeiro, Brasil Abstract In finite elasticity, the Mooney-Rivlin material moel
Approaches for Predicting Collection Efficiency of Fibrous Filters
 Volume 5, Issue, Summer006 Approaches for Preicting Collection Efficiency of Fibrous Filters Q. Wang, B. Maze, H. Vahei Tafreshi, an B. Poureyhimi Nonwovens Cooperative esearch Center, North Carolina State
Volume 5, Issue, Summer006 Approaches for Preicting Collection Efficiency of Fibrous Filters Q. Wang, B. Maze, H. Vahei Tafreshi, an B. Poureyhimi Nonwovens Cooperative esearch Center, North Carolina State
The Principle of Least Action
 Chapter 7. The Principle of Least Action 7.1 Force Methos vs. Energy Methos We have so far stuie two istinct ways of analyzing physics problems: force methos, basically consisting of the application of
Chapter 7. The Principle of Least Action 7.1 Force Methos vs. Energy Methos We have so far stuie two istinct ways of analyzing physics problems: force methos, basically consisting of the application of
Dust Acoustic Compressive Waves in a Warm Dusty Plasma Having Non-Thermal Ions and Non-Isothermal Electrons
 Plasma Science an Technology, Vol.17, No.9, Sep. 015 Dust Acoustic Compressive Waves in a Warm Dusty Plasma Having Non-Thermal Ions an Non-Isothermal Electrons Apul N. DEV 1, Manoj K. DEKA, Rajesh SUBEDI
Plasma Science an Technology, Vol.17, No.9, Sep. 015 Dust Acoustic Compressive Waves in a Warm Dusty Plasma Having Non-Thermal Ions an Non-Isothermal Electrons Apul N. DEV 1, Manoj K. DEKA, Rajesh SUBEDI
ensembles When working with density operators, we can use this connection to define a generalized Bloch vector: v x Tr x, v y Tr y
 Ph195a lecture notes, 1/3/01 Density operators for spin- 1 ensembles So far in our iscussion of spin- 1 systems, we have restricte our attention to the case of pure states an Hamiltonian evolution. Toay
Ph195a lecture notes, 1/3/01 Density operators for spin- 1 ensembles So far in our iscussion of spin- 1 systems, we have restricte our attention to the case of pure states an Hamiltonian evolution. Toay
INFLUENCE OF SURFACE ROUGHNESS THROUGH A SERIES OF FLOW FACTORS ON THE PERFORMANCE OF A LONGITUDINALLY ROUGH FINITE SLIDER BEARING
 ANNALS of Faculty Engineering Huneoara International Journal of Engineering Tome XIV [2016] Fascicule 2 [May] ISSN: 1584-2665 [print; online] ISSN: 1584-2673 [CD-Rom; online] a free-accessmultiisciplinarypublication
ANNALS of Faculty Engineering Huneoara International Journal of Engineering Tome XIV [2016] Fascicule 2 [May] ISSN: 1584-2665 [print; online] ISSN: 1584-2673 [CD-Rom; online] a free-accessmultiisciplinarypublication
Fluid Mechanics EBS 189a. Winter quarter, 4 units, CRN Lecture TWRF 12:10-1:00, Chemistry 166; Office hours TH 2-3, WF 4-5; 221 Veihmeyer Hall.
 Flui Mechanics EBS 189a. Winter quarter, 4 units, CRN 52984. Lecture TWRF 12:10-1:00, Chemistry 166; Office hours TH 2-3, WF 4-5; 221 eihmeyer Hall. Course Description: xioms of flui mechanics, flui statics,
Flui Mechanics EBS 189a. Winter quarter, 4 units, CRN 52984. Lecture TWRF 12:10-1:00, Chemistry 166; Office hours TH 2-3, WF 4-5; 221 eihmeyer Hall. Course Description: xioms of flui mechanics, flui statics,
On the number of isolated eigenvalues of a pair of particles in a quantum wire
 On the number of isolate eigenvalues of a pair of particles in a quantum wire arxiv:1812.11804v1 [math-ph] 31 Dec 2018 Joachim Kerner 1 Department of Mathematics an Computer Science FernUniversität in
On the number of isolate eigenvalues of a pair of particles in a quantum wire arxiv:1812.11804v1 [math-ph] 31 Dec 2018 Joachim Kerner 1 Department of Mathematics an Computer Science FernUniversität in
Sources and Sinks of Available Potential Energy in a Moist Atmosphere. Olivier Pauluis 1. Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences
 Sources an Sinks of Available Potential Energy in a Moist Atmosphere Olivier Pauluis 1 Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences New York University Submitte to the Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences
Sources an Sinks of Available Potential Energy in a Moist Atmosphere Olivier Pauluis 1 Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences New York University Submitte to the Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences
Chapter 9 Method of Weighted Residuals
 Chapter 9 Metho of Weighte Resiuals 9- Introuction Metho of Weighte Resiuals (MWR) is an approimate technique for solving bounary value problems. It utilizes a trial functions satisfying the prescribe
Chapter 9 Metho of Weighte Resiuals 9- Introuction Metho of Weighte Resiuals (MWR) is an approimate technique for solving bounary value problems. It utilizes a trial functions satisfying the prescribe
Momentum and Energy. Chapter Conservation Principles
 Chapter 2 Momentum an Energy In this chapter we present some funamental results of continuum mechanics. The formulation is base on the principles of conservation of mass, momentum, angular momentum, an
Chapter 2 Momentum an Energy In this chapter we present some funamental results of continuum mechanics. The formulation is base on the principles of conservation of mass, momentum, angular momentum, an
LATTICE-BASED D-OPTIMUM DESIGN FOR FOURIER REGRESSION
 The Annals of Statistics 1997, Vol. 25, No. 6, 2313 2327 LATTICE-BASED D-OPTIMUM DESIGN FOR FOURIER REGRESSION By Eva Riccomagno, 1 Rainer Schwabe 2 an Henry P. Wynn 1 University of Warwick, Technische
The Annals of Statistics 1997, Vol. 25, No. 6, 2313 2327 LATTICE-BASED D-OPTIMUM DESIGN FOR FOURIER REGRESSION By Eva Riccomagno, 1 Rainer Schwabe 2 an Henry P. Wynn 1 University of Warwick, Technische
Dissipative numerical methods for the Hunter-Saxton equation
 Dissipative numerical methos for the Hunter-Saton equation Yan Xu an Chi-Wang Shu Abstract In this paper, we present further evelopment of the local iscontinuous Galerkin (LDG) metho esigne in [] an a
Dissipative numerical methos for the Hunter-Saton equation Yan Xu an Chi-Wang Shu Abstract In this paper, we present further evelopment of the local iscontinuous Galerkin (LDG) metho esigne in [] an a
Generalization of the persistent random walk to dimensions greater than 1
 PHYSICAL REVIEW E VOLUME 58, NUMBER 6 DECEMBER 1998 Generalization of the persistent ranom walk to imensions greater than 1 Marián Boguñá, Josep M. Porrà, an Jaume Masoliver Departament e Física Fonamental,
PHYSICAL REVIEW E VOLUME 58, NUMBER 6 DECEMBER 1998 Generalization of the persistent ranom walk to imensions greater than 1 Marián Boguñá, Josep M. Porrà, an Jaume Masoliver Departament e Física Fonamental,
5.3 Inviscid instability mechanism of parallel flows
 1 Lecture Notes on Flui Dynamics 1.63J/2.21J) by Chiang C. Mei, 27 5.3 Invisci instability mechanism of parallel flows We now turn to an oler problem of the instability of parallel flow without stratification
1 Lecture Notes on Flui Dynamics 1.63J/2.21J) by Chiang C. Mei, 27 5.3 Invisci instability mechanism of parallel flows We now turn to an oler problem of the instability of parallel flow without stratification
A Simple Model for the Calculation of Plasma Impedance in Atmospheric Radio Frequency Discharges
 Plasma Science an Technology, Vol.16, No.1, Oct. 214 A Simple Moel for the Calculation of Plasma Impeance in Atmospheric Raio Frequency Discharges GE Lei ( ) an ZHANG Yuantao ( ) Shanong Provincial Key
Plasma Science an Technology, Vol.16, No.1, Oct. 214 A Simple Moel for the Calculation of Plasma Impeance in Atmospheric Raio Frequency Discharges GE Lei ( ) an ZHANG Yuantao ( ) Shanong Provincial Key
3-dimensional Evolution of an Emerging Flux Tube in the Sun. T. Magara
 3-imensional Evolution of an Emerging Flux Tube in the Sun T. Magara (Montana State University) February 6, 2002 Introuction of the stuy Dynamical evolution of emerging fiel lines Physical process working
3-imensional Evolution of an Emerging Flux Tube in the Sun T. Magara (Montana State University) February 6, 2002 Introuction of the stuy Dynamical evolution of emerging fiel lines Physical process working
ANALYSIS OF A GENERAL FAMILY OF REGULARIZED NAVIER-STOKES AND MHD MODELS
 ANALYSIS OF A GENERAL FAMILY OF REGULARIZED NAVIER-STOKES AND MHD MODELS MICHAEL HOLST, EVELYN LUNASIN, AND GANTUMUR TSOGTGEREL ABSTRACT. We consier a general family of regularize Navier-Stokes an Magnetohyroynamics
ANALYSIS OF A GENERAL FAMILY OF REGULARIZED NAVIER-STOKES AND MHD MODELS MICHAEL HOLST, EVELYN LUNASIN, AND GANTUMUR TSOGTGEREL ABSTRACT. We consier a general family of regularize Navier-Stokes an Magnetohyroynamics
Efficient Macro-Micro Scale Coupled Modeling of Batteries
 A00 Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 15 10 A00-A008 005 0013-651/005/1510/A00/7/$7.00 The Electrochemical Society, Inc. Efficient Macro-Micro Scale Couple Moeling of Batteries Venkat. Subramanian,*,z
A00 Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 15 10 A00-A008 005 0013-651/005/1510/A00/7/$7.00 The Electrochemical Society, Inc. Efficient Macro-Micro Scale Couple Moeling of Batteries Venkat. Subramanian,*,z
Schrödinger s equation.
 Physics 342 Lecture 5 Schröinger s Equation Lecture 5 Physics 342 Quantum Mechanics I Wenesay, February 3r, 2010 Toay we iscuss Schröinger s equation an show that it supports the basic interpretation of
Physics 342 Lecture 5 Schröinger s Equation Lecture 5 Physics 342 Quantum Mechanics I Wenesay, February 3r, 2010 Toay we iscuss Schröinger s equation an show that it supports the basic interpretation of
The derivative of a function f(x) is another function, defined in terms of a limiting expression: f(x + δx) f(x)
 Y. D. Chong (2016) MH2801: Complex Methos for the Sciences 1. Derivatives The erivative of a function f(x) is another function, efine in terms of a limiting expression: f (x) f (x) lim x δx 0 f(x + δx)
Y. D. Chong (2016) MH2801: Complex Methos for the Sciences 1. Derivatives The erivative of a function f(x) is another function, efine in terms of a limiting expression: f (x) f (x) lim x δx 0 f(x + δx)
THE VAN KAMPEN EXPANSION FOR LINKED DUFFING LINEAR OSCILLATORS EXCITED BY COLORED NOISE
 Journal of Soun an Vibration (1996) 191(3), 397 414 THE VAN KAMPEN EXPANSION FOR LINKED DUFFING LINEAR OSCILLATORS EXCITED BY COLORED NOISE E. M. WEINSTEIN Galaxy Scientific Corporation, 2500 English Creek
Journal of Soun an Vibration (1996) 191(3), 397 414 THE VAN KAMPEN EXPANSION FOR LINKED DUFFING LINEAR OSCILLATORS EXCITED BY COLORED NOISE E. M. WEINSTEIN Galaxy Scientific Corporation, 2500 English Creek
Hyperbolic Systems of Equations Posed on Erroneous Curved Domains
 Hyperbolic Systems of Equations Pose on Erroneous Curve Domains Jan Norström a, Samira Nikkar b a Department of Mathematics, Computational Mathematics, Linköping University, SE-58 83 Linköping, Sween (
Hyperbolic Systems of Equations Pose on Erroneous Curve Domains Jan Norström a, Samira Nikkar b a Department of Mathematics, Computational Mathematics, Linköping University, SE-58 83 Linköping, Sween (
12.11 Laplace s Equation in Cylindrical and
 SEC. 2. Laplace s Equation in Cylinrical an Spherical Coorinates. Potential 593 2. Laplace s Equation in Cylinrical an Spherical Coorinates. Potential One of the most important PDEs in physics an engineering
SEC. 2. Laplace s Equation in Cylinrical an Spherical Coorinates. Potential 593 2. Laplace s Equation in Cylinrical an Spherical Coorinates. Potential One of the most important PDEs in physics an engineering
Homotopy Perturbation Method for Solving Twelfth Order Boundary Value Problems
 International Journal of Research an Reviews in Applie Sciences ISSN: 276-734X, EISSN: 276-7366 Volume 1, Issue 2(November 29) Homotopy Perturbation Metho for Solving Twelfth Orer Bounary Value Problems
International Journal of Research an Reviews in Applie Sciences ISSN: 276-734X, EISSN: 276-7366 Volume 1, Issue 2(November 29) Homotopy Perturbation Metho for Solving Twelfth Orer Bounary Value Problems
How the potentials in different gauges yield the same retarded electric and magnetic fields
 How the potentials in ifferent gauges yiel the same retare electric an magnetic fiels José A. Heras a Departamento e Física, E. S. F. M., Instituto Politécnico Nacional, México D. F. México an Department
How the potentials in ifferent gauges yiel the same retare electric an magnetic fiels José A. Heras a Departamento e Física, E. S. F. M., Instituto Politécnico Nacional, México D. F. México an Department
ON THE OPTIMALITY SYSTEM FOR A 1 D EULER FLOW PROBLEM
 ON THE OPTIMALITY SYSTEM FOR A D EULER FLOW PROBLEM Eugene M. Cliff Matthias Heinkenschloss y Ajit R. Shenoy z Interisciplinary Center for Applie Mathematics Virginia Tech Blacksburg, Virginia 46 Abstract
ON THE OPTIMALITY SYSTEM FOR A D EULER FLOW PROBLEM Eugene M. Cliff Matthias Heinkenschloss y Ajit R. Shenoy z Interisciplinary Center for Applie Mathematics Virginia Tech Blacksburg, Virginia 46 Abstract
Characterization of lead zirconate titanate piezoceramic using high frequency ultrasonic spectroscopy
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS VOLUME 85, NUMBER 1 15 JUNE 1999 Characterization of lea zirconate titanate piezoceramic using high frequency ultrasonic spectroscopy Haifeng Wang, Wenhua Jiang, a) an Wenwu
JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS VOLUME 85, NUMBER 1 15 JUNE 1999 Characterization of lea zirconate titanate piezoceramic using high frequency ultrasonic spectroscopy Haifeng Wang, Wenhua Jiang, a) an Wenwu
