Cromwell's principle idealized under the theory of large deviations
|
|
|
- Darlene Brown
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Cromwell's principle idealized under the theory of large deviations Seminar, Statistics and Probability Research Group, University of Ottawa Ottawa, Ontario April 27, 2018 David Bickel University of Ottawa
2 Cromwell s principle Cromwell's principle: P(model is wrong) > 0, i.e., the prior probability that the assumptions are incorrect is greater than 0 D. Lindley (2013), Understanding Uncertainty Relevance to Bayesian model checking: Diagnostics often reveal that prior distributions require revision impossible under Bayes's theorem if P(model) = 1 Idealized Cromwell's principle: P(model) vanishes Large deviations version of the infinitesimal probability due to A. Hájek and M. Smithson (2012), Synthese 187, D. R. Bickel (2018), Statistics,
3 Empirical distribution converges to max. entropy Weak convergence to maximum entropy distribution D. R. Bickel (2018), Statistics,
4 Normal-normal CDFs D. R. Bickel (2018), Statistics,
5 models have sufficient evidence
6 Assessing multiple models All models Models in conflict with the data models (of sufficient evidence)
7 Bayesian model assessment Does the prior or parametric family conflict with the data? Yes, if it has relatively low evidence Measures of evidence satisfying the criteria of Bickel, International Statistical Review 81, : Likelihood ratio (limited to comparing two simple models) Bayes factor Penalized likelihood ratio No Yes Use the model for decisions (minimize posterior expected loss) even if other models are adequate Change the model to an adequate model, a model of high evidence
8 Loss function example What act is appropriate? Given multiple priors of sufficient evidence, agreement with the data With or without confidence sets
9 Hurwicz criterion
10 models posteriors Robust Bayes act: Hurwicz criterion Loss function
11 Decisions under robust Bayes rules applied to models of sufficient evidence Robust Bayes acts: models posteriors E-admissible Hurwicz criterion Γ-minimax Bickel, International Journal of Approximate Reasoning 66, Loss function 1 model 1 posterior Bayes act
12 Decisions under the entropy-maximizing model of sufficient evidence models posteriors Bickel, International Journal of Approximate Reasoning 66, Blending Loss function Nested confidence sets 1 posterior Bayes act
13
14
15
16 Decisions under the entropy-maximizing Bayesian model of sufficient evidence models posteriors Bickel, International Journal of Approximate Reasoning 66, Blending Loss function Nested confidence sets 1 posterior Bayes act
17 Pooling methods Good derived a harmonic mean of p-values from Bayes' rule Examples of subjectively weighting each expert's distribution: Minimizing a weighted sum of divergences from the distributions being combined yields a linear combination of the distributions Any linearly combined marginal distribution is the same whether marginalization or combination is carried out first Weighted multiplicative combination of the distributions Externally Bayesian updating
18 Decisions under minimax-redundancy pooling of models of small codelengths Bickel, International Journal of Approximate Reasoning 66, models posteriors Pooling Loss function 1 posterior Minimize expected loss
19 Conflicting probabilities
20 The three players Combiner is you, the statistician who combines the candidate distributions Goal 1: minimize error; Goal 2: beat Chooser Chooser is the imaginary statistician who instead chooses a single candidate distribution Goal 1: minimize error; Goal 2: beat Combiner Nature picks the true distribution among those that are plausible in order to help Chooser
21 Information game Information divergence and inferential gain: Utility paid to Statistician 2 (Combiner or Chooser): Reduction to game of Combiner v. Nature-Chooser Coalition:
22 Decisions under minimax-redundancy pooling of models of small codelengths Bickel, International Journal of Approximate Reasoning 66, models posteriors Pooling Loss function 1 posterior Minimize expected loss
23 models posteriors Robust Bayes acts: E-admissible Hurwicz criterion Γ-minimax Blending Pooling Loss function Nested confidence sets 1 posterior Bayes act Funded by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada
Uncertain Inference and Artificial Intelligence
 March 3, 2011 1 Prepared for a Purdue Machine Learning Seminar Acknowledgement Prof. A. P. Dempster for intensive collaborations on the Dempster-Shafer theory. Jianchun Zhang, Ryan Martin, Duncan Ermini
March 3, 2011 1 Prepared for a Purdue Machine Learning Seminar Acknowledgement Prof. A. P. Dempster for intensive collaborations on the Dempster-Shafer theory. Jianchun Zhang, Ryan Martin, Duncan Ermini
ICES REPORT Model Misspecification and Plausibility
 ICES REPORT 14-21 August 2014 Model Misspecification and Plausibility by Kathryn Farrell and J. Tinsley Odena The Institute for Computational Engineering and Sciences The University of Texas at Austin
ICES REPORT 14-21 August 2014 Model Misspecification and Plausibility by Kathryn Farrell and J. Tinsley Odena The Institute for Computational Engineering and Sciences The University of Texas at Austin
Parametric Models. Dr. Shuang LIANG. School of Software Engineering TongJi University Fall, 2012
 Parametric Models Dr. Shuang LIANG School of Software Engineering TongJi University Fall, 2012 Today s Topics Maximum Likelihood Estimation Bayesian Density Estimation Today s Topics Maximum Likelihood
Parametric Models Dr. Shuang LIANG School of Software Engineering TongJi University Fall, 2012 Today s Topics Maximum Likelihood Estimation Bayesian Density Estimation Today s Topics Maximum Likelihood
Computing Minimax Decisions with Incomplete Observations
 PMLR: Proceedings of Machine Learning Research, vol. 62, 358-369, 207 ISIPTA 7 Computing Minimax Decisions with Incomplete Observations Thijs van Ommen Universiteit van Amsterdam Amsterdam (The Netherlands)
PMLR: Proceedings of Machine Learning Research, vol. 62, 358-369, 207 ISIPTA 7 Computing Minimax Decisions with Incomplete Observations Thijs van Ommen Universiteit van Amsterdam Amsterdam (The Netherlands)
MIT Spring 2016
 MIT 18.655 Dr. Kempthorne Spring 2016 1 MIT 18.655 Outline 1 2 MIT 18.655 3 Decision Problem: Basic Components P = {P θ : θ Θ} : parametric model. Θ = {θ}: Parameter space. A{a} : Action space. L(θ, a)
MIT 18.655 Dr. Kempthorne Spring 2016 1 MIT 18.655 Outline 1 2 MIT 18.655 3 Decision Problem: Basic Components P = {P θ : θ Θ} : parametric model. Θ = {θ}: Parameter space. A{a} : Action space. L(θ, a)
Bayesian Regression Linear and Logistic Regression
 When we want more than point estimates Bayesian Regression Linear and Logistic Regression Nicole Beckage Ordinary Least Squares Regression and Lasso Regression return only point estimates But what if we
When we want more than point estimates Bayesian Regression Linear and Logistic Regression Nicole Beckage Ordinary Least Squares Regression and Lasso Regression return only point estimates But what if we
Hypothesis Testing. Part I. James J. Heckman University of Chicago. Econ 312 This draft, April 20, 2006
 Hypothesis Testing Part I James J. Heckman University of Chicago Econ 312 This draft, April 20, 2006 1 1 A Brief Review of Hypothesis Testing and Its Uses values and pure significance tests (R.A. Fisher)
Hypothesis Testing Part I James J. Heckman University of Chicago Econ 312 This draft, April 20, 2006 1 1 A Brief Review of Hypothesis Testing and Its Uses values and pure significance tests (R.A. Fisher)
Quantifying the Price of Uncertainty in Bayesian Models
 Provided by the author(s) and NUI Galway in accordance with publisher policies. Please cite the published version when available. Title Quantifying the Price of Uncertainty in Bayesian Models Author(s)
Provided by the author(s) and NUI Galway in accordance with publisher policies. Please cite the published version when available. Title Quantifying the Price of Uncertainty in Bayesian Models Author(s)
The Bayesian Choice. Christian P. Robert. From Decision-Theoretic Foundations to Computational Implementation. Second Edition.
 Christian P. Robert The Bayesian Choice From Decision-Theoretic Foundations to Computational Implementation Second Edition With 23 Illustrations ^Springer" Contents Preface to the Second Edition Preface
Christian P. Robert The Bayesian Choice From Decision-Theoretic Foundations to Computational Implementation Second Edition With 23 Illustrations ^Springer" Contents Preface to the Second Edition Preface
Variational Bayesian Logistic Regression
 Variational Bayesian Logistic Regression Sargur N. University at Buffalo, State University of New York USA Topics in Linear Models for Classification Overview 1. Discriminant Functions 2. Probabilistic
Variational Bayesian Logistic Regression Sargur N. University at Buffalo, State University of New York USA Topics in Linear Models for Classification Overview 1. Discriminant Functions 2. Probabilistic
SYDE 372 Introduction to Pattern Recognition. Probability Measures for Classification: Part I
 SYDE 372 Introduction to Pattern Recognition Probability Measures for Classification: Part I Alexander Wong Department of Systems Design Engineering University of Waterloo Outline 1 2 3 4 Why use probability
SYDE 372 Introduction to Pattern Recognition Probability Measures for Classification: Part I Alexander Wong Department of Systems Design Engineering University of Waterloo Outline 1 2 3 4 Why use probability
Should all Machine Learning be Bayesian? Should all Bayesian models be non-parametric?
 Should all Machine Learning be Bayesian? Should all Bayesian models be non-parametric? Zoubin Ghahramani Department of Engineering University of Cambridge, UK zoubin@eng.cam.ac.uk http://learning.eng.cam.ac.uk/zoubin/
Should all Machine Learning be Bayesian? Should all Bayesian models be non-parametric? Zoubin Ghahramani Department of Engineering University of Cambridge, UK zoubin@eng.cam.ac.uk http://learning.eng.cam.ac.uk/zoubin/
Bios 6649: Clinical Trials - Statistical Design and Monitoring
 Bios 6649: Clinical Trials - Statistical Design and Monitoring Spring Semester 2015 John M. Kittelson Department of Biostatistics & nformatics Colorado School of Public Health University of Colorado Denver
Bios 6649: Clinical Trials - Statistical Design and Monitoring Spring Semester 2015 John M. Kittelson Department of Biostatistics & nformatics Colorado School of Public Health University of Colorado Denver
STAT 100C: Linear models
 STAT 100C: Linear models Arash A. Amini June 9, 2018 1 / 21 Model selection Choosing the best model among a collection of models {M 1, M 2..., M N }. What is a good model? 1. fits the data well (model
STAT 100C: Linear models Arash A. Amini June 9, 2018 1 / 21 Model selection Choosing the best model among a collection of models {M 1, M 2..., M N }. What is a good model? 1. fits the data well (model
6.867 Machine learning, lecture 23 (Jaakkola)
 Lecture topics: Markov Random Fields Probabilistic inference Markov Random Fields We will briefly go over undirected graphical models or Markov Random Fields (MRFs) as they will be needed in the context
Lecture topics: Markov Random Fields Probabilistic inference Markov Random Fields We will briefly go over undirected graphical models or Markov Random Fields (MRFs) as they will be needed in the context
A Brief Review of Probability, Bayesian Statistics, and Information Theory
 A Brief Review of Probability, Bayesian Statistics, and Information Theory Brendan Frey Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Toronto frey@psi.toronto.edu http://www.psi.toronto.edu A system
A Brief Review of Probability, Bayesian Statistics, and Information Theory Brendan Frey Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Toronto frey@psi.toronto.edu http://www.psi.toronto.edu A system
New Bayesian methods for model comparison
 Back to the future New Bayesian methods for model comparison Murray Aitkin murray.aitkin@unimelb.edu.au Department of Mathematics and Statistics The University of Melbourne Australia Bayesian Model Comparison
Back to the future New Bayesian methods for model comparison Murray Aitkin murray.aitkin@unimelb.edu.au Department of Mathematics and Statistics The University of Melbourne Australia Bayesian Model Comparison
Classification CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology. M. Soleymani Fall 2012
 Classification CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology M. Soleymani Fall 2012 Topics Discriminant functions Logistic regression Perceptron Generative models Generative vs. discriminative
Classification CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology M. Soleymani Fall 2012 Topics Discriminant functions Logistic regression Perceptron Generative models Generative vs. discriminative
σ(a) = a N (x; 0, 1 2 ) dx. σ(a) = Φ(a) =
 Until now we have always worked with likelihoods and prior distributions that were conjugate to each other, allowing the computation of the posterior distribution to be done in closed form. Unfortunately,
Until now we have always worked with likelihoods and prior distributions that were conjugate to each other, allowing the computation of the posterior distribution to be done in closed form. Unfortunately,
Applied Bayesian Statistics STAT 388/488
 STAT 388/488 Dr. Earvin Balderama Department of Mathematics & Statistics Loyola University Chicago August 29, 207 Course Info STAT 388/488 http://math.luc.edu/~ebalderama/bayes 2 A motivating example (See
STAT 388/488 Dr. Earvin Balderama Department of Mathematics & Statistics Loyola University Chicago August 29, 207 Course Info STAT 388/488 http://math.luc.edu/~ebalderama/bayes 2 A motivating example (See
Machine Learning Lecture 7
 Course Outline Machine Learning Lecture 7 Fundamentals (2 weeks) Bayes Decision Theory Probability Density Estimation Statistical Learning Theory 23.05.2016 Discriminative Approaches (5 weeks) Linear Discriminant
Course Outline Machine Learning Lecture 7 Fundamentals (2 weeks) Bayes Decision Theory Probability Density Estimation Statistical Learning Theory 23.05.2016 Discriminative Approaches (5 weeks) Linear Discriminant
Bayesian inference. Fredrik Ronquist and Peter Beerli. October 3, 2007
 Bayesian inference Fredrik Ronquist and Peter Beerli October 3, 2007 1 Introduction The last few decades has seen a growing interest in Bayesian inference, an alternative approach to statistical inference.
Bayesian inference Fredrik Ronquist and Peter Beerli October 3, 2007 1 Introduction The last few decades has seen a growing interest in Bayesian inference, an alternative approach to statistical inference.
7. Estimation and hypothesis testing. Objective. Recommended reading
 7. Estimation and hypothesis testing Objective In this chapter, we show how the election of estimators can be represented as a decision problem. Secondly, we consider the problem of hypothesis testing
7. Estimation and hypothesis testing Objective In this chapter, we show how the election of estimators can be represented as a decision problem. Secondly, we consider the problem of hypothesis testing
Stochastic population forecast: a supra-bayesian approach to combine experts opinions and observed past forecast errors
 Stochastic population forecast: a supra-bayesian approach to combine experts opinions and observed past forecast errors Rebecca Graziani and Eugenio Melilli 1 Abstract We suggest a method for developing
Stochastic population forecast: a supra-bayesian approach to combine experts opinions and observed past forecast errors Rebecca Graziani and Eugenio Melilli 1 Abstract We suggest a method for developing
Blending Bayesian and frequentist methods. according to the precision of prior information with. applications to hypothesis testing.
 Blending Bayesian and frequentist methods according to the precision of prior information with applications to hypothesis testing July 28, 2012 David R. Bickel Ottawa Institute of Systems Biology Department
Blending Bayesian and frequentist methods according to the precision of prior information with applications to hypothesis testing July 28, 2012 David R. Bickel Ottawa Institute of Systems Biology Department
Strong Lens Modeling (II): Statistical Methods
 Strong Lens Modeling (II): Statistical Methods Chuck Keeton Rutgers, the State University of New Jersey Probability theory multiple random variables, a and b joint distribution p(a, b) conditional distribution
Strong Lens Modeling (II): Statistical Methods Chuck Keeton Rutgers, the State University of New Jersey Probability theory multiple random variables, a and b joint distribution p(a, b) conditional distribution
Experimental Design to Maximize Information
 Experimental Design to Maximize Information P. Sebastiani and H.P. Wynn Department of Mathematics and Statistics University of Massachusetts at Amherst, 01003 MA Department of Statistics, University of
Experimental Design to Maximize Information P. Sebastiani and H.P. Wynn Department of Mathematics and Statistics University of Massachusetts at Amherst, 01003 MA Department of Statistics, University of
CS 630 Basic Probability and Information Theory. Tim Campbell
 CS 630 Basic Probability and Information Theory Tim Campbell 21 January 2003 Probability Theory Probability Theory is the study of how best to predict outcomes of events. An experiment (or trial or event)
CS 630 Basic Probability and Information Theory Tim Campbell 21 January 2003 Probability Theory Probability Theory is the study of how best to predict outcomes of events. An experiment (or trial or event)
Statistical Inference for Food Webs
 Statistical Inference for Food Webs Part I: Bayesian Melding Grace Chiu and Josh Gould Department of Statistics & Actuarial Science CMAR-Hobart Science Seminar, March 6, 2009 1 Outline CMAR-Hobart Science
Statistical Inference for Food Webs Part I: Bayesian Melding Grace Chiu and Josh Gould Department of Statistics & Actuarial Science CMAR-Hobart Science Seminar, March 6, 2009 1 Outline CMAR-Hobart Science
Noninformative Priors for the Ratio of the Scale Parameters in the Inverted Exponential Distributions
 Communications for Statistical Applications and Methods 03, Vol. 0, No. 5, 387 394 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/0.535/csam.03.0.5.387 Noninformative Priors for the Ratio of the Scale Parameters in the Inverted
Communications for Statistical Applications and Methods 03, Vol. 0, No. 5, 387 394 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/0.535/csam.03.0.5.387 Noninformative Priors for the Ratio of the Scale Parameters in the Inverted
More on nuisance parameters
 BS2 Statistical Inference, Lecture 3, Hilary Term 2009 January 30, 2009 Suppose that there is a minimal sufficient statistic T = t(x ) partitioned as T = (S, C) = (s(x ), c(x )) where: C1: the distribution
BS2 Statistical Inference, Lecture 3, Hilary Term 2009 January 30, 2009 Suppose that there is a minimal sufficient statistic T = t(x ) partitioned as T = (S, C) = (s(x ), c(x )) where: C1: the distribution
ST440/540: Applied Bayesian Statistics. (9) Model selection and goodness-of-fit checks
 (9) Model selection and goodness-of-fit checks Objectives In this module we will study methods for model comparisons and checking for model adequacy For model comparisons there are a finite number of candidate
(9) Model selection and goodness-of-fit checks Objectives In this module we will study methods for model comparisons and checking for model adequacy For model comparisons there are a finite number of candidate
STAT 499/962 Topics in Statistics Bayesian Inference and Decision Theory Jan 2018, Handout 01
 STAT 499/962 Topics in Statistics Bayesian Inference and Decision Theory Jan 2018, Handout 01 Nasser Sadeghkhani a.sadeghkhani@queensu.ca There are two main schools to statistical inference: 1-frequentist
STAT 499/962 Topics in Statistics Bayesian Inference and Decision Theory Jan 2018, Handout 01 Nasser Sadeghkhani a.sadeghkhani@queensu.ca There are two main schools to statistical inference: 1-frequentist
ECE521 week 3: 23/26 January 2017
 ECE521 week 3: 23/26 January 2017 Outline Probabilistic interpretation of linear regression - Maximum likelihood estimation (MLE) - Maximum a posteriori (MAP) estimation Bias-variance trade-off Linear
ECE521 week 3: 23/26 January 2017 Outline Probabilistic interpretation of linear regression - Maximum likelihood estimation (MLE) - Maximum a posteriori (MAP) estimation Bias-variance trade-off Linear
Stat 5101 Lecture Notes
 Stat 5101 Lecture Notes Charles J. Geyer Copyright 1998, 1999, 2000, 2001 by Charles J. Geyer May 7, 2001 ii Stat 5101 (Geyer) Course Notes Contents 1 Random Variables and Change of Variables 1 1.1 Random
Stat 5101 Lecture Notes Charles J. Geyer Copyright 1998, 1999, 2000, 2001 by Charles J. Geyer May 7, 2001 ii Stat 5101 (Geyer) Course Notes Contents 1 Random Variables and Change of Variables 1 1.1 Random
Chapter Three. Hypothesis Testing
 3.1 Introduction The final phase of analyzing data is to make a decision concerning a set of choices or options. Should I invest in stocks or bonds? Should a new product be marketed? Are my products being
3.1 Introduction The final phase of analyzing data is to make a decision concerning a set of choices or options. Should I invest in stocks or bonds? Should a new product be marketed? Are my products being
Prediction Using Several Macroeconomic Models
 Gianni Amisano European Central Bank 1 John Geweke University of Technology Sydney, Erasmus University, and University of Colorado European Central Bank May 5, 2012 1 The views expressed do not represent
Gianni Amisano European Central Bank 1 John Geweke University of Technology Sydney, Erasmus University, and University of Colorado European Central Bank May 5, 2012 1 The views expressed do not represent
1 Introduction. 2 AIC versus SBIC. Erik Swanson Cori Saviano Li Zha Final Project
 Erik Swanson Cori Saviano Li Zha Final Project 1 Introduction In analyzing time series data, we are posed with the question of how past events influences the current situation. In order to determine this,
Erik Swanson Cori Saviano Li Zha Final Project 1 Introduction In analyzing time series data, we are posed with the question of how past events influences the current situation. In order to determine this,
David Giles Bayesian Econometrics
 9. Model Selection - Theory David Giles Bayesian Econometrics One nice feature of the Bayesian analysis is that we can apply it to drawing inferences about entire models, not just parameters. Can't do
9. Model Selection - Theory David Giles Bayesian Econometrics One nice feature of the Bayesian analysis is that we can apply it to drawing inferences about entire models, not just parameters. Can't do
Pattern Classification
 Pattern Classification All materials in these slides were taken from Pattern Classification (2nd ed) by R. O. Duda, P. E. Hart and D. G. Stork, John Wiley & Sons, 2000 with the permission of the authors
Pattern Classification All materials in these slides were taken from Pattern Classification (2nd ed) by R. O. Duda, P. E. Hart and D. G. Stork, John Wiley & Sons, 2000 with the permission of the authors
Exact Minimax Predictive Density Estimation and MDL
 Exact Minimax Predictive Density Estimation and MDL Feng Liang and Andrew Barron December 5, 2003 Abstract The problems of predictive density estimation with Kullback-Leibler loss, optimal universal data
Exact Minimax Predictive Density Estimation and MDL Feng Liang and Andrew Barron December 5, 2003 Abstract The problems of predictive density estimation with Kullback-Leibler loss, optimal universal data
MIT Spring 2016
 Decision Theoretic Framework MIT 18.655 Dr. Kempthorne Spring 2016 1 Outline Decision Theoretic Framework 1 Decision Theoretic Framework 2 Decision Problems of Statistical Inference Estimation: estimating
Decision Theoretic Framework MIT 18.655 Dr. Kempthorne Spring 2016 1 Outline Decision Theoretic Framework 1 Decision Theoretic Framework 2 Decision Problems of Statistical Inference Estimation: estimating
Algorithm-Independent Learning Issues
 Algorithm-Independent Learning Issues Selim Aksoy Department of Computer Engineering Bilkent University saksoy@cs.bilkent.edu.tr CS 551, Spring 2007 c 2007, Selim Aksoy Introduction We have seen many learning
Algorithm-Independent Learning Issues Selim Aksoy Department of Computer Engineering Bilkent University saksoy@cs.bilkent.edu.tr CS 551, Spring 2007 c 2007, Selim Aksoy Introduction We have seen many learning
Bayesian Econometrics
 Bayesian Econometrics Christopher A. Sims Princeton University sims@princeton.edu September 20, 2016 Outline I. The difference between Bayesian and non-bayesian inference. II. Confidence sets and confidence
Bayesian Econometrics Christopher A. Sims Princeton University sims@princeton.edu September 20, 2016 Outline I. The difference between Bayesian and non-bayesian inference. II. Confidence sets and confidence
var D (B) = var(b? E D (B)) = var(b)? cov(b; D)(var(D))?1 cov(d; B) (2) Stone [14], and Hartigan [9] are among the rst to discuss the role of such ass
![var D (B) = var(b? E D (B)) = var(b)? cov(b; D)(var(D))?1 cov(d; B) (2) Stone [14], and Hartigan [9] are among the rst to discuss the role of such ass var D (B) = var(b? E D (B)) = var(b)? cov(b; D)(var(D))?1 cov(d; B) (2) Stone [14], and Hartigan [9] are among the rst to discuss the role of such ass](/thumbs/73/69313040.jpg) BAYES LINEAR ANALYSIS [This article appears in the Encyclopaedia of Statistical Sciences, Update volume 3, 1998, Wiley.] The Bayes linear approach is concerned with problems in which we want to combine
BAYES LINEAR ANALYSIS [This article appears in the Encyclopaedia of Statistical Sciences, Update volume 3, 1998, Wiley.] The Bayes linear approach is concerned with problems in which we want to combine
Natural Language Processing. Classification. Features. Some Definitions. Classification. Feature Vectors. Classification I. Dan Klein UC Berkeley
 Natural Language Processing Classification Classification I Dan Klein UC Berkeley Classification Automatically make a decision about inputs Example: document category Example: image of digit digit Example:
Natural Language Processing Classification Classification I Dan Klein UC Berkeley Classification Automatically make a decision about inputs Example: document category Example: image of digit digit Example:
Generalized Linear Models
 Generalized Linear Models Lecture 3. Hypothesis testing. Goodness of Fit. Model diagnostics GLM (Spring, 2018) Lecture 3 1 / 34 Models Let M(X r ) be a model with design matrix X r (with r columns) r n
Generalized Linear Models Lecture 3. Hypothesis testing. Goodness of Fit. Model diagnostics GLM (Spring, 2018) Lecture 3 1 / 34 Models Let M(X r ) be a model with design matrix X r (with r columns) r n
STA 4273H: Statistical Machine Learning
 STA 4273H: Statistical Machine Learning Russ Salakhutdinov Department of Statistics! rsalakhu@utstat.toronto.edu! http://www.utstat.utoronto.ca/~rsalakhu/ Sidney Smith Hall, Room 6002 Lecture 3 Linear
STA 4273H: Statistical Machine Learning Russ Salakhutdinov Department of Statistics! rsalakhu@utstat.toronto.edu! http://www.utstat.utoronto.ca/~rsalakhu/ Sidney Smith Hall, Room 6002 Lecture 3 Linear
Miscellany : Long Run Behavior of Bayesian Methods; Bayesian Experimental Design (Lecture 4)
 Miscellany : Long Run Behavior of Bayesian Methods; Bayesian Experimental Design (Lecture 4) Tom Loredo Dept. of Astronomy, Cornell University http://www.astro.cornell.edu/staff/loredo/bayes/ Bayesian
Miscellany : Long Run Behavior of Bayesian Methods; Bayesian Experimental Design (Lecture 4) Tom Loredo Dept. of Astronomy, Cornell University http://www.astro.cornell.edu/staff/loredo/bayes/ Bayesian
Preliminary Statistics Lecture 2: Probability Theory (Outline) prelimsoas.webs.com
 1 School of Oriental and African Studies September 2015 Department of Economics Preliminary Statistics Lecture 2: Probability Theory (Outline) prelimsoas.webs.com Gujarati D. Basic Econometrics, Appendix
1 School of Oriental and African Studies September 2015 Department of Economics Preliminary Statistics Lecture 2: Probability Theory (Outline) prelimsoas.webs.com Gujarati D. Basic Econometrics, Appendix
Testing Statistical Hypotheses
 E.L. Lehmann Joseph P. Romano Testing Statistical Hypotheses Third Edition 4y Springer Preface vii I Small-Sample Theory 1 1 The General Decision Problem 3 1.1 Statistical Inference and Statistical Decisions
E.L. Lehmann Joseph P. Romano Testing Statistical Hypotheses Third Edition 4y Springer Preface vii I Small-Sample Theory 1 1 The General Decision Problem 3 1.1 Statistical Inference and Statistical Decisions
Penalized Loss functions for Bayesian Model Choice
 Penalized Loss functions for Bayesian Model Choice Martyn International Agency for Research on Cancer Lyon, France 13 November 2009 The pure approach For a Bayesian purist, all uncertainty is represented
Penalized Loss functions for Bayesian Model Choice Martyn International Agency for Research on Cancer Lyon, France 13 November 2009 The pure approach For a Bayesian purist, all uncertainty is represented
Stochastic Population Forecasting based on a Combination of Experts Evaluations and accounting for Correlation of Demographic Components
 Stochastic Population Forecasting based on a Combination of Experts Evaluations and accounting for Correlation of Demographic Components Francesco Billari, Rebecca Graziani and Eugenio Melilli 1 EXTENDED
Stochastic Population Forecasting based on a Combination of Experts Evaluations and accounting for Correlation of Demographic Components Francesco Billari, Rebecca Graziani and Eugenio Melilli 1 EXTENDED
Machine Learning 4771
 Machine Learning 4771 Instructor: Tony Jebara Topic 11 Maximum Likelihood as Bayesian Inference Maximum A Posteriori Bayesian Gaussian Estimation Why Maximum Likelihood? So far, assumed max (log) likelihood
Machine Learning 4771 Instructor: Tony Jebara Topic 11 Maximum Likelihood as Bayesian Inference Maximum A Posteriori Bayesian Gaussian Estimation Why Maximum Likelihood? So far, assumed max (log) likelihood
HST.582J / 6.555J / J Biomedical Signal and Image Processing Spring 2007
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu HST.582J / 6.555J / 16.456J Biomedical Signal and Image Processing Spring 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu HST.582J / 6.555J / 16.456J Biomedical Signal and Image Processing Spring 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
Carl N. Morris. University of Texas
 EMPIRICAL BAYES: A FREQUENCY-BAYES COMPROMISE Carl N. Morris University of Texas Empirical Bayes research has expanded significantly since the ground-breaking paper (1956) of Herbert Robbins, and its province
EMPIRICAL BAYES: A FREQUENCY-BAYES COMPROMISE Carl N. Morris University of Texas Empirical Bayes research has expanded significantly since the ground-breaking paper (1956) of Herbert Robbins, and its province
Robust Monte Carlo Methods for Sequential Planning and Decision Making
 Robust Monte Carlo Methods for Sequential Planning and Decision Making Sue Zheng, Jason Pacheco, & John Fisher Sensing, Learning, & Inference Group Computer Science & Artificial Intelligence Laboratory
Robust Monte Carlo Methods for Sequential Planning and Decision Making Sue Zheng, Jason Pacheco, & John Fisher Sensing, Learning, & Inference Group Computer Science & Artificial Intelligence Laboratory
Model comparison. Christopher A. Sims Princeton University October 18, 2016
 ECO 513 Fall 2008 Model comparison Christopher A. Sims Princeton University sims@princeton.edu October 18, 2016 c 2016 by Christopher A. Sims. This document may be reproduced for educational and research
ECO 513 Fall 2008 Model comparison Christopher A. Sims Princeton University sims@princeton.edu October 18, 2016 c 2016 by Christopher A. Sims. This document may be reproduced for educational and research
Final Examination CS 540-2: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence
 Final Examination CS 540-2: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence May 7, 2017 LAST NAME: SOLUTIONS FIRST NAME: Problem Score Max Score 1 14 2 10 3 6 4 10 5 11 6 9 7 8 9 10 8 12 12 8 Total 100 1 of 11
Final Examination CS 540-2: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence May 7, 2017 LAST NAME: SOLUTIONS FIRST NAME: Problem Score Max Score 1 14 2 10 3 6 4 10 5 11 6 9 7 8 9 10 8 12 12 8 Total 100 1 of 11
Confidence Distribution
 Confidence Distribution Xie and Singh (2013): Confidence distribution, the frequentist distribution estimator of a parameter: A Review Céline Cunen, 15/09/2014 Outline of Article Introduction The concept
Confidence Distribution Xie and Singh (2013): Confidence distribution, the frequentist distribution estimator of a parameter: A Review Céline Cunen, 15/09/2014 Outline of Article Introduction The concept
Chapter 6. Estimation of Confidence Intervals for Nodal Maximum Power Consumption per Customer
 Chapter 6 Estimation of Confidence Intervals for Nodal Maximum Power Consumption per Customer The aim of this chapter is to calculate confidence intervals for the maximum power consumption per customer
Chapter 6 Estimation of Confidence Intervals for Nodal Maximum Power Consumption per Customer The aim of this chapter is to calculate confidence intervals for the maximum power consumption per customer
SRNDNA Model Fitting in RL Workshop
 SRNDNA Model Fitting in RL Workshop yael@princeton.edu Topics: 1. trial-by-trial model fitting (morning; Yael) 2. model comparison (morning; Yael) 3. advanced topics (hierarchical fitting etc.) (afternoon;
SRNDNA Model Fitting in RL Workshop yael@princeton.edu Topics: 1. trial-by-trial model fitting (morning; Yael) 2. model comparison (morning; Yael) 3. advanced topics (hierarchical fitting etc.) (afternoon;
Ch 4. Linear Models for Classification
 Ch 4. Linear Models for Classification Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning, C. M. Bishop, 2006. Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pohang University of Science and echnology 77 Cheongam-ro,
Ch 4. Linear Models for Classification Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning, C. M. Bishop, 2006. Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pohang University of Science and echnology 77 Cheongam-ro,
Curve Fitting Re-visited, Bishop1.2.5
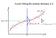 Curve Fitting Re-visited, Bishop1.2.5 Maximum Likelihood Bishop 1.2.5 Model Likelihood differentiation p(t x, w, β) = Maximum Likelihood N N ( t n y(x n, w), β 1). (1.61) n=1 As we did in the case of the
Curve Fitting Re-visited, Bishop1.2.5 Maximum Likelihood Bishop 1.2.5 Model Likelihood differentiation p(t x, w, β) = Maximum Likelihood N N ( t n y(x n, w), β 1). (1.61) n=1 As we did in the case of the
PATTERN RECOGNITION AND MACHINE LEARNING
 PATTERN RECOGNITION AND MACHINE LEARNING Chapter 1. Introduction Shuai Huang April 21, 2014 Outline 1 What is Machine Learning? 2 Curve Fitting 3 Probability Theory 4 Model Selection 5 The curse of dimensionality
PATTERN RECOGNITION AND MACHINE LEARNING Chapter 1. Introduction Shuai Huang April 21, 2014 Outline 1 What is Machine Learning? 2 Curve Fitting 3 Probability Theory 4 Model Selection 5 The curse of dimensionality
Whaddya know? Bayesian and Frequentist approaches to inverse problems
 Whaddya know? Bayesian and Frequentist approaches to inverse problems Philip B. Stark Department of Statistics University of California, Berkeley Inverse Problems: Practical Applications and Advanced Analysis
Whaddya know? Bayesian and Frequentist approaches to inverse problems Philip B. Stark Department of Statistics University of California, Berkeley Inverse Problems: Practical Applications and Advanced Analysis
EC319 Economic Theory and Its Applications, Part II: Lecture 7
 EC319 Economic Theory and Its Applications, Part II: Lecture 7 Leonardo Felli NAB.2.14 27 February 2014 Signalling Games Consider the following Bayesian game: Set of players: N = {N, S, }, Nature N strategy
EC319 Economic Theory and Its Applications, Part II: Lecture 7 Leonardo Felli NAB.2.14 27 February 2014 Signalling Games Consider the following Bayesian game: Set of players: N = {N, S, }, Nature N strategy
MODEL COMPARISON CHRISTOPHER A. SIMS PRINCETON UNIVERSITY
 ECO 513 Fall 2008 MODEL COMPARISON CHRISTOPHER A. SIMS PRINCETON UNIVERSITY SIMS@PRINCETON.EDU 1. MODEL COMPARISON AS ESTIMATING A DISCRETE PARAMETER Data Y, models 1 and 2, parameter vectors θ 1, θ 2.
ECO 513 Fall 2008 MODEL COMPARISON CHRISTOPHER A. SIMS PRINCETON UNIVERSITY SIMS@PRINCETON.EDU 1. MODEL COMPARISON AS ESTIMATING A DISCRETE PARAMETER Data Y, models 1 and 2, parameter vectors θ 1, θ 2.
E. Santovetti lesson 4 Maximum likelihood Interval estimation
 E. Santovetti lesson 4 Maximum likelihood Interval estimation 1 Extended Maximum Likelihood Sometimes the number of total events measurements of the experiment n is not fixed, but, for example, is a Poisson
E. Santovetti lesson 4 Maximum likelihood Interval estimation 1 Extended Maximum Likelihood Sometimes the number of total events measurements of the experiment n is not fixed, but, for example, is a Poisson
David Giles Bayesian Econometrics
 David Giles Bayesian Econometrics 1. General Background 2. Constructing Prior Distributions 3. Properties of Bayes Estimators and Tests 4. Bayesian Analysis of the Multiple Regression Model 5. Bayesian
David Giles Bayesian Econometrics 1. General Background 2. Constructing Prior Distributions 3. Properties of Bayes Estimators and Tests 4. Bayesian Analysis of the Multiple Regression Model 5. Bayesian
Matthias Schubert. Jochen Köhler. Michael H. Faber
 [ 1 International Probabilistic Symposium 2006, Ghent, 28-29 November 2007 Analysis of Tunnel accidents by using Bayesian Networks Matthias Schubert ETH Zürich, Institute for Structural Engineering, Group
[ 1 International Probabilistic Symposium 2006, Ghent, 28-29 November 2007 Analysis of Tunnel accidents by using Bayesian Networks Matthias Schubert ETH Zürich, Institute for Structural Engineering, Group
STA414/2104 Statistical Methods for Machine Learning II
 STA414/2104 Statistical Methods for Machine Learning II Murat A. Erdogdu & David Duvenaud Department of Computer Science Department of Statistical Sciences Lecture 3 Slide credits: Russ Salakhutdinov Announcements
STA414/2104 Statistical Methods for Machine Learning II Murat A. Erdogdu & David Duvenaud Department of Computer Science Department of Statistical Sciences Lecture 3 Slide credits: Russ Salakhutdinov Announcements
Dose-response modeling with bivariate binary data under model uncertainty
 Dose-response modeling with bivariate binary data under model uncertainty Bernhard Klingenberg 1 1 Department of Mathematics and Statistics, Williams College, Williamstown, MA, 01267 and Institute of Statistics,
Dose-response modeling with bivariate binary data under model uncertainty Bernhard Klingenberg 1 1 Department of Mathematics and Statistics, Williams College, Williamstown, MA, 01267 and Institute of Statistics,
Randomized Decision Trees
 Randomized Decision Trees compiled by Alvin Wan from Professor Jitendra Malik s lecture Discrete Variables First, let us consider some terminology. We have primarily been dealing with real-valued data,
Randomized Decision Trees compiled by Alvin Wan from Professor Jitendra Malik s lecture Discrete Variables First, let us consider some terminology. We have primarily been dealing with real-valued data,
WE start with a general discussion. Suppose we have
 646 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INFORMATION THEORY, VOL. 43, NO. 2, MARCH 1997 Minimax Redundancy for the Class of Memoryless Sources Qun Xie and Andrew R. Barron, Member, IEEE Abstract Let X n = (X 1 ; 111;Xn)be
646 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INFORMATION THEORY, VOL. 43, NO. 2, MARCH 1997 Minimax Redundancy for the Class of Memoryless Sources Qun Xie and Andrew R. Barron, Member, IEEE Abstract Let X n = (X 1 ; 111;Xn)be
Bayesian Model Diagnostics and Checking
 Earvin Balderama Quantitative Ecology Lab Department of Forestry and Environmental Resources North Carolina State University April 12, 2013 1 / 34 Introduction MCMCMC 2 / 34 Introduction MCMCMC Steps in
Earvin Balderama Quantitative Ecology Lab Department of Forestry and Environmental Resources North Carolina State University April 12, 2013 1 / 34 Introduction MCMCMC 2 / 34 Introduction MCMCMC Steps in
Parametric Unsupervised Learning Expectation Maximization (EM) Lecture 20.a
 Parametric Unsupervised Learning Expectation Maximization (EM) Lecture 20.a Some slides are due to Christopher Bishop Limitations of K-means Hard assignments of data points to clusters small shift of a
Parametric Unsupervised Learning Expectation Maximization (EM) Lecture 20.a Some slides are due to Christopher Bishop Limitations of K-means Hard assignments of data points to clusters small shift of a
Decision Analysis. An insightful study of the decision-making process under uncertainty and risk
 Decision Analysis An insightful study of the decision-making process under uncertainty and risk Decision Theory A philosophy, articulated by a set of logical axioms and a methodology, for analyzing the
Decision Analysis An insightful study of the decision-making process under uncertainty and risk Decision Theory A philosophy, articulated by a set of logical axioms and a methodology, for analyzing the
Bayesian Brittleness
 Bayesian Brittleness Houman Owhadi Bayesian Brittleness. H. Owhadi, C. Scovel, T. Sullivan. arxiv:1304.6772 Brittleness of Bayesian inference and new Selberg formulas. H. Owhadi, C. Scovel. arxiv:1304.7046
Bayesian Brittleness Houman Owhadi Bayesian Brittleness. H. Owhadi, C. Scovel, T. Sullivan. arxiv:1304.6772 Brittleness of Bayesian inference and new Selberg formulas. H. Owhadi, C. Scovel. arxiv:1304.7046
Lecture Notes 1: Decisions and Data. In these notes, I describe some basic ideas in decision theory. theory is constructed from
 Topics in Data Analysis Steven N. Durlauf University of Wisconsin Lecture Notes : Decisions and Data In these notes, I describe some basic ideas in decision theory. theory is constructed from The Data:
Topics in Data Analysis Steven N. Durlauf University of Wisconsin Lecture Notes : Decisions and Data In these notes, I describe some basic ideas in decision theory. theory is constructed from The Data:
Logistic Regression. Machine Learning Fall 2018
 Logistic Regression Machine Learning Fall 2018 1 Where are e? We have seen the folloing ideas Linear models Learning as loss minimization Bayesian learning criteria (MAP and MLE estimation) The Naïve Bayes
Logistic Regression Machine Learning Fall 2018 1 Where are e? We have seen the folloing ideas Linear models Learning as loss minimization Bayesian learning criteria (MAP and MLE estimation) The Naïve Bayes
Testing Statistical Hypotheses
 E.L. Lehmann Joseph P. Romano, 02LEu1 ttd ~Lt~S Testing Statistical Hypotheses Third Edition With 6 Illustrations ~Springer 2 The Probability Background 28 2.1 Probability and Measure 28 2.2 Integration.........
E.L. Lehmann Joseph P. Romano, 02LEu1 ttd ~Lt~S Testing Statistical Hypotheses Third Edition With 6 Illustrations ~Springer 2 The Probability Background 28 2.1 Probability and Measure 28 2.2 Integration.........
Support Vector Machines
 Support Vector Machines Le Song Machine Learning I CSE 6740, Fall 2013 Naïve Bayes classifier Still use Bayes decision rule for classification P y x = P x y P y P x But assume p x y = 1 is fully factorized
Support Vector Machines Le Song Machine Learning I CSE 6740, Fall 2013 Naïve Bayes classifier Still use Bayes decision rule for classification P y x = P x y P y P x But assume p x y = 1 is fully factorized
Learning Bayesian networks
 1 Lecture topics: Learning Bayesian networks from data maximum likelihood, BIC Bayesian, marginal likelihood Learning Bayesian networks There are two problems we have to solve in order to estimate Bayesian
1 Lecture topics: Learning Bayesian networks from data maximum likelihood, BIC Bayesian, marginal likelihood Learning Bayesian networks There are two problems we have to solve in order to estimate Bayesian
Bayesian Model Comparison
 BS2 Statistical Inference, Lecture 11, Hilary Term 2009 February 26, 2009 Basic result An accurate approximation Asymptotic posterior distribution An integral of form I = b a e λg(y) h(y) dy where h(y)
BS2 Statistical Inference, Lecture 11, Hilary Term 2009 February 26, 2009 Basic result An accurate approximation Asymptotic posterior distribution An integral of form I = b a e λg(y) h(y) dy where h(y)
Expectation Propagation for Approximate Bayesian Inference
 Expectation Propagation for Approximate Bayesian Inference José Miguel Hernández Lobato Universidad Autónoma de Madrid, Computer Science Department February 5, 2007 1/ 24 Bayesian Inference Inference Given
Expectation Propagation for Approximate Bayesian Inference José Miguel Hernández Lobato Universidad Autónoma de Madrid, Computer Science Department February 5, 2007 1/ 24 Bayesian Inference Inference Given
Statistics: Learning models from data
 DS-GA 1002 Lecture notes 5 October 19, 2015 Statistics: Learning models from data Learning models from data that are assumed to be generated probabilistically from a certain unknown distribution is a crucial
DS-GA 1002 Lecture notes 5 October 19, 2015 Statistics: Learning models from data Learning models from data that are assumed to be generated probabilistically from a certain unknown distribution is a crucial
Political Science 236 Hypothesis Testing: Review and Bootstrapping
 Political Science 236 Hypothesis Testing: Review and Bootstrapping Rocío Titiunik Fall 2007 1 Hypothesis Testing Definition 1.1 Hypothesis. A hypothesis is a statement about a population parameter The
Political Science 236 Hypothesis Testing: Review and Bootstrapping Rocío Titiunik Fall 2007 1 Hypothesis Testing Definition 1.1 Hypothesis. A hypothesis is a statement about a population parameter The
Basic Probabilistic Reasoning SEG
 Basic Probabilistic Reasoning SEG 7450 1 Introduction Reasoning under uncertainty using probability theory Dealing with uncertainty is one of the main advantages of an expert system over a simple decision
Basic Probabilistic Reasoning SEG 7450 1 Introduction Reasoning under uncertainty using probability theory Dealing with uncertainty is one of the main advantages of an expert system over a simple decision
STAT 535 Lecture 5 November, 2018 Brief overview of Model Selection and Regularization c Marina Meilă
 STAT 535 Lecture 5 November, 2018 Brief overview of Model Selection and Regularization c Marina Meilă mmp@stat.washington.edu Reading: Murphy: BIC, AIC 8.4.2 (pp 255), SRM 6.5 (pp 204) Hastie, Tibshirani
STAT 535 Lecture 5 November, 2018 Brief overview of Model Selection and Regularization c Marina Meilă mmp@stat.washington.edu Reading: Murphy: BIC, AIC 8.4.2 (pp 255), SRM 6.5 (pp 204) Hastie, Tibshirani
CIS 390 Fall 2016 Robotics: Planning and Perception Final Review Questions
 CIS 390 Fall 2016 Robotics: Planning and Perception Final Review Questions December 14, 2016 Questions Throughout the following questions we will assume that x t is the state vector at time t, z t is the
CIS 390 Fall 2016 Robotics: Planning and Perception Final Review Questions December 14, 2016 Questions Throughout the following questions we will assume that x t is the state vector at time t, z t is the
An introduction to Bayesian reasoning in particle physics
 An introduction to Bayesian reasoning in particle physics Graduiertenkolleg seminar, May 15th 2013 Overview Overview A concrete example Scientific reasoning Probability and the Bayesian interpretation
An introduction to Bayesian reasoning in particle physics Graduiertenkolleg seminar, May 15th 2013 Overview Overview A concrete example Scientific reasoning Probability and the Bayesian interpretation
STA 4273H: Sta-s-cal Machine Learning
 STA 4273H: Sta-s-cal Machine Learning Russ Salakhutdinov Department of Computer Science! Department of Statistical Sciences! rsalakhu@cs.toronto.edu! h0p://www.cs.utoronto.ca/~rsalakhu/ Lecture 2 In our
STA 4273H: Sta-s-cal Machine Learning Russ Salakhutdinov Department of Computer Science! Department of Statistical Sciences! rsalakhu@cs.toronto.edu! h0p://www.cs.utoronto.ca/~rsalakhu/ Lecture 2 In our
What are the Findings?
 What are the Findings? James B. Rawlings Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering University of Wisconsin Madison Madison, Wisconsin April 2010 Rawlings (Wisconsin) Stating the findings 1 / 33
What are the Findings? James B. Rawlings Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering University of Wisconsin Madison Madison, Wisconsin April 2010 Rawlings (Wisconsin) Stating the findings 1 / 33
An Introduction to No Free Lunch Theorems
 February 2, 2012 Table of Contents Induction Learning without direct observation. Generalising from data. Modelling physical phenomena. The Problem of Induction David Hume (1748) How do we know an induced
February 2, 2012 Table of Contents Induction Learning without direct observation. Generalising from data. Modelling physical phenomena. The Problem of Induction David Hume (1748) How do we know an induced
Contents. Set Theory. Functions and its Applications CHAPTER 1 CHAPTER 2. Preface... (v)
 (vii) Preface... (v) CHAPTER 1 Set Theory Definition of Set... 1 Roster, Tabular or Enumeration Form... 1 Set builder Form... 2 Union of Set... 5 Intersection of Sets... 9 Distributive Laws of Unions and
(vii) Preface... (v) CHAPTER 1 Set Theory Definition of Set... 1 Roster, Tabular or Enumeration Form... 1 Set builder Form... 2 Union of Set... 5 Intersection of Sets... 9 Distributive Laws of Unions and
Ellipsoidal Methods for Adaptive Choice-based Conjoint Analysis (CBCA)
 Ellipsoidal Methods for Adaptive Choice-based Conjoint Analysis (CBCA) Juan Pablo Vielma Massachusetts Institute of Technology Joint work with Denis Saure Operations Management Seminar, Rotman School of
Ellipsoidal Methods for Adaptive Choice-based Conjoint Analysis (CBCA) Juan Pablo Vielma Massachusetts Institute of Technology Joint work with Denis Saure Operations Management Seminar, Rotman School of
Confidence Intervals Lecture 2
 Confidence Intervals Lecture 2 First ICFA Instrumentation School/Workshop At Morelia,, Mexico, November 18-29, 2002 Harrison B. rosper Florida State University Recap of Lecture 1 To interpret a confidence
Confidence Intervals Lecture 2 First ICFA Instrumentation School/Workshop At Morelia,, Mexico, November 18-29, 2002 Harrison B. rosper Florida State University Recap of Lecture 1 To interpret a confidence
Using prior knowledge in frequentist tests
 Using prior knowledge in frequentist tests Use of Bayesian posteriors with informative priors as optimal frequentist tests Christian Bartels Email: h.christian.bartels@gmail.com Allschwil, 5. April 2017
Using prior knowledge in frequentist tests Use of Bayesian posteriors with informative priors as optimal frequentist tests Christian Bartels Email: h.christian.bartels@gmail.com Allschwil, 5. April 2017
Class 26: review for final exam 18.05, Spring 2014
 Probability Class 26: review for final eam 8.05, Spring 204 Counting Sets Inclusion-eclusion principle Rule of product (multiplication rule) Permutation and combinations Basics Outcome, sample space, event
Probability Class 26: review for final eam 8.05, Spring 204 Counting Sets Inclusion-eclusion principle Rule of product (multiplication rule) Permutation and combinations Basics Outcome, sample space, event
