CALCULUS REVIS ITED PART 2 A Self-study Course
|
|
|
- Roland Page
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CALCULUS REVIS ITED PART 2 A Self-study Course STUDY GUIDE Block 3 Partial Derivatives Herbert I. Gross Senior Lecturer Center for Advanced Engineering Study Massachusetts Institute of Technology
2 by Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge, Massachusetts All rights reserved. No part of this book may be reproduced in any form or by any means without permission in writing from the Center for Advanced Engineering Study, M.I.T.
3 CONTENTS Studv Guide Pretest Unit 2: An Introduction to Partial Derivatives Unit 3: Differentiability and the Gradient Unit 4: The Directional Derivative in n-dimensional Vector Spaces (Optional) Unit 5: The Chain Rule, Part 1 Unit 6: The Chain Rule, Part 2 Unit 7: More on Derivatives of Integrals Unit 8: The Total Differential Quiz Solutions Pretest Unit 2: An Introduction to Partial Derivatives Unit 3: Differentiability and the Gradient Unit 4: The Directional Derivative in n-dimensional Vector Spaces (Optional) Unit 5: The Chain Rule, Part 1 Unit 6: The Chain Rule, Part 2 Unit 7: More on Derivatives of Integrals Unit 8: The Total Differential Quiz iii
4 I BLOCK 3: PARTIAL DERIVATIVES
5 Pretest 1. Let w = f (x,y) = 2Xy 2, (x,y) # (0.0). Show that x +Y lim f(x,y) depends on the path by which (x,y) approaches (x,y)+(o,o) 2. Find the equation of the plane which is tangent to the surface x4 + y 6 z + xyz5 = 3 at ~ ~, ~, ~ ~. I. Suppose w depends on r but not on 8, say w = h(r), and that h is a twice-differentiable function of r. Determine -a'w + -a ;, expressed ax a~ in terms of r. rn,. L 4. Find the equation of the curve C if C passes through the origin and has its slope at each point (x,y) given by Given that g(y) = i1 b dx where y > b > -1, determine gl(y).
6 Unit '1: Functions of More Than One Variable 1. Lecture 3.010
7 2. Read Supplementary Notes, Chapter Read Thomas, Section (Optional) Read Thomas, Sections and (These sections will help you feel more at home with equations of surfaces. The idea is that just as the graphs of functions of a single variable are curves in the xy-plane, the graphs of functions of two real variables are surfaces in space. Except for any peace-of-mind that you get in feeling at home with the various equations, it should be noted that we can survive the remainder of this course without recourse to accurate graphs just as was the case in functions of a single real variable.) 5. Exercises : Define as the Minkowski metric. That is, if -x = (xl,...,xn), then IlxIl - = max~lxll...i xnil. a. Show that 1. 1k1) >/ 0 for all x 2- IIx + yll 4 lkll + Ikll 3. IlaxII = lal IkII - and llxll - = 0 if and only if - x = - 0. b. Compute -x *~,llxllr and llrll (where we are still using the Minkowski metric) if 5 = (2,4,1) and 4~ = (4,4,5). From this conclude that it need not be true that ~ -X - ~ 6I l l ~ l l Ilu_ll. Mimic the proof of the corresponding 1-dimensional case to prove lim 1i m that if - x and -a belong to E" and x-rg f (x) = L1 while x,a g (5) = L2, then lim [f (x) + g(x)i - x-rg = L1 + L2
8 a. Using the Minkowski metric, suppose E>O is given; find 6 such that for this choice of 6 b. Interpret the answer in (a) geometrically and explain why the same value of 6 as in (a) would have sufficed had we used the Euclidean metric rather than the Minkowski metric (L) Let -x = (xl,x2,x3,x4) and let -1 = (1,1,1,1). Define f by 3 2 f(x) = x12 + 2x2 + x3 + x4. Prove that f is continuous at = Let f, -x and such that -1 be as in Exercise For a given E>O, find (L) Let f be defined by a. b. c. Is f continuous at (0,0)? lim lim Compute both lim limf(x,y)l. y+q [x+o f (x,y)l and x+o ry+(, Investigate the behaviour of in more detail by introducing polar coordinates.
9 Let f be defined by a. Show that lim f(x,y) depends on the path by which (xiy) (x,y)+(o,o) approaches (0,O. 1i m b. Compute (x,y)+(o,o) f (x,y) if (x,y) approaches (0,O) along the 71 ray t3 = - 4. c. Show that if (x,y) approaches (0,O) either along the x-axis or the y-axis then lim f(x,y) = 0. Define g by r l. a. Show that g is not continuous at (0,O). b. Show that lim g(x,y) = g(o,o) if (x,y) is allowed to (x,y)+(o,o) approach (0,O) along either axis. Let the function :E~-+E be continuous. Prove that f cannot be 1-1. Comment The following two exercises are optional. They may be omitted without loss of continuity to our present discussion. Their main purpose is to supply the interested reader with a few clues as to how analytic proofs are carried out in n-dimensional vector spaces (with n greater than three) using the ordinary properties of real number arithmetic.
10 lock 3: Partial Derivatives Let -a and b belong to E 4. Prove that our definition of -a = b_ is an equivalence relation because a the fact that "ordinary" equality is an equivalence relation on the set of real numbers. Let a, 2 and -c be elements of E 4. With the dot product as defined in our supplementary notes, prove that
11 MIT OpenCourseWare Resource: Calculus Revisited: Multivariable Calculus Prof. Herbert Gross The following may not correspond to a particular course on MIT OpenCourseWare, but has been provided by the author as an individual learning resource. For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit:
The Double Sum as an Iterated Integral
 Unit 2: The Double Sum as an Iterated Integral 1. Overview In Part 1 of our course, we showed that there was a relationship between a certain infinite sum known as the definite integral and the inverse
Unit 2: The Double Sum as an Iterated Integral 1. Overview In Part 1 of our course, we showed that there was a relationship between a certain infinite sum known as the definite integral and the inverse
reason is that from a gaametrical point of view, as we shall show in the exercises, tha study of complex functions of a
 Study Guide Block 1: Rn Introduction to Functions of a Complex Variable Unit 4: Comulex Functions of a Cmlex Variable 1. overview The main aim of this Black is to study the calculus of functions of a complex
Study Guide Block 1: Rn Introduction to Functions of a Complex Variable Unit 4: Comulex Functions of a Cmlex Variable 1. overview The main aim of this Black is to study the calculus of functions of a complex
Study Guide Block 2: Ordinary Differential Equations. Unit 4: Linear Differential Equations. Overview
 Overview Unless a first order differential equation has a rather special form, we often have to resort to numerical methods in order to solve the equation. Even when the equation has the special form,
Overview Unless a first order differential equation has a rather special form, we often have to resort to numerical methods in order to solve the equation. Even when the equation has the special form,
1. (Optional) Read Thomas, Section (See Preface to ~xercise for an explanation.)
 1. (Optional) Read Thomas, Section 15.1. (See Preface to ~xercise 3.6. for an explanation.). Exercises: 3.6.1(L) Suppose w = f(x,y) where f is a continuously differentiable function of x and y. Assume
1. (Optional) Read Thomas, Section 15.1. (See Preface to ~xercise 3.6. for an explanation.). Exercises: 3.6.1(L) Suppose w = f(x,y) where f is a continuously differentiable function of x and y. Assume
a (x,y,z) dvs. a (u,v,w)
 1. Overview In Unit 3 we discussed the role of the Jacobian determinant in evaluating double integrals involving a change of variables. technique generalizes very nicely to triple integrals. In fact, except
1. Overview In Unit 3 we discussed the role of the Jacobian determinant in evaluating double integrals involving a change of variables. technique generalizes very nicely to triple integrals. In fact, except
Study Guide Block 2: Ordinary Differential Equations. Unit 9: The Laplace Transform, Part Overview
 Unit 9: The Laplace Transform, Part 1 1. Overview ~ The Laplace transform has application far beyond its present role in this block of being a useful device for solving certain types of linear differential
Unit 9: The Laplace Transform, Part 1 1. Overview ~ The Laplace transform has application far beyond its present role in this block of being a useful device for solving certain types of linear differential
Student Session Topic: Average and Instantaneous Rates of Change
 Student Session Topic: Average and Instantaneous Rates of Change The concepts of average rates of change and instantaneous rates of change are the building blocks of differential calculus. The AP exams
Student Session Topic: Average and Instantaneous Rates of Change The concepts of average rates of change and instantaneous rates of change are the building blocks of differential calculus. The AP exams
Linear Systems Series. Instructor s Guide. Table of Contents
 Linear Approximation Linear Systems Series Instructor s Guide Table of duction.... 2 When to Use this Video.... 2 Learning Objectives.... 2 Motivation.... 2 Student Experience.... 2 Key Information....
Linear Approximation Linear Systems Series Instructor s Guide Table of duction.... 2 When to Use this Video.... 2 Learning Objectives.... 2 Motivation.... 2 Student Experience.... 2 Key Information....
Study Guide Block 3: Selected Topics in Linear Algebra. Unit 8: Fourier Series
 1. Overview We conclude our present course with a brief excursion into Fourier series. Aside from their.great practical value, Fourier series give us a chance to see an excellent application of the dot
1. Overview We conclude our present course with a brief excursion into Fourier series. Aside from their.great practical value, Fourier series give us a chance to see an excellent application of the dot
Solutions Block 5: Multiple Integration. Pretest 1. 54
 Pretest 1. 54 lock 5: Multiple Integration In the expression (kai j), it is assumed that in the pareni=1 j=1 thesized-sum, i is treated as being constant (notice the "flavor" of the notion of independent
Pretest 1. 54 lock 5: Multiple Integration In the expression (kai j), it is assumed that in the pareni=1 j=1 thesized-sum, i is treated as being constant (notice the "flavor" of the notion of independent
Tangent Planes, Linear Approximations and Differentiability
 Jim Lambers MAT 80 Spring Semester 009-10 Lecture 5 Notes These notes correspond to Section 114 in Stewart and Section 3 in Marsden and Tromba Tangent Planes, Linear Approximations and Differentiability
Jim Lambers MAT 80 Spring Semester 009-10 Lecture 5 Notes These notes correspond to Section 114 in Stewart and Section 3 in Marsden and Tromba Tangent Planes, Linear Approximations and Differentiability
Module 5 : Linear and Quadratic Approximations, Error Estimates, Taylor's Theorem, Newton and Picard Methods
 Module 5 : Linear and Quadratic Approximations, Error Estimates, Taylor's Theorem, Newton and Picard Methods Lecture 14 : Taylor's Theorem [Section 141] Objectives In this section you will learn the following
Module 5 : Linear and Quadratic Approximations, Error Estimates, Taylor's Theorem, Newton and Picard Methods Lecture 14 : Taylor's Theorem [Section 141] Objectives In this section you will learn the following
A, then the function g defined by g:s+b such that g(s) - = f(s) - for each s&s is called the restriction of f to S. Pictorially,
 The main aim of this exercise is to review the basic principles taught in this unit in terms of a rather simple computational exercise. To begin with, we should observe that the definition of f makes it
The main aim of this exercise is to review the basic principles taught in this unit in terms of a rather simple computational exercise. To begin with, we should observe that the definition of f makes it
18.01 Single Variable Calculus Fall 2006
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 18.01 Single Variable Calculus Fall 2006 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. Lecture 14: Mean Value
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 18.01 Single Variable Calculus Fall 2006 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. Lecture 14: Mean Value
Unit #24 - Lagrange Multipliers Section 15.3
 Unit #24 - Lagrange Multipliers Section 1.3 Some material from Calculus, Single and MultiVariable by Hughes-Hallett, Gleason, McCallum et. al. Copyright 200 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. This material is
Unit #24 - Lagrange Multipliers Section 1.3 Some material from Calculus, Single and MultiVariable by Hughes-Hallett, Gleason, McCallum et. al. Copyright 200 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. This material is
18.02 Multivariable Calculus Fall 2007
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 18.02 Multivariable Calculus Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. V11. Line Integrals in Space
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 18.02 Multivariable Calculus Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. V11. Line Integrals in Space
Math 163: Lecture notes
 Math 63: Lecture notes Professor Monika Nitsche March 2, 2 Special functions that are inverses of known functions. Inverse functions (Day ) Go over: early exam, hw, quizzes, grading scheme, attendance
Math 63: Lecture notes Professor Monika Nitsche March 2, 2 Special functions that are inverses of known functions. Inverse functions (Day ) Go over: early exam, hw, quizzes, grading scheme, attendance
February 4, 2019 LECTURE 4: THE DERIVATIVE.
 February 4, 29 LECTURE 4: THE DERIVATIVE 2 HONORS MULTIVARIABLE CALCULUS PROFESSOR RICHARD BROWN Synopsis Today, we finish our discussion on its and pass through the concept of continuity Really, there
February 4, 29 LECTURE 4: THE DERIVATIVE 2 HONORS MULTIVARIABLE CALCULUS PROFESSOR RICHARD BROWN Synopsis Today, we finish our discussion on its and pass through the concept of continuity Really, there
Take-Home Exam 1: pick up on Thursday, June 8, return Monday,
 SYLLABUS FOR 18.089 1. Overview This course is a review of calculus. We will start with a week-long review of single variable calculus, and move on for the remaining five weeks to multivariable calculus.
SYLLABUS FOR 18.089 1. Overview This course is a review of calculus. We will start with a week-long review of single variable calculus, and move on for the remaining five weeks to multivariable calculus.
DEVELOPMENT OF THE COMPLEX NUMBERS
 2 DEVELOPMENT OF THE COMPLEX NUMBERS In this chapter, we shall try to motivate how the structure of the complex number system developed. We shall investigate this develop- ment both from an algebraic and
2 DEVELOPMENT OF THE COMPLEX NUMBERS In this chapter, we shall try to motivate how the structure of the complex number system developed. We shall investigate this develop- ment both from an algebraic and
11.11 Applications of Taylor Polynomials. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 11.11 Applications of Taylor Polynomials Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Approximating Functions by Polynomials 2 Approximating Functions by Polynomials Suppose that f(x) is equal to the
11.11 Applications of Taylor Polynomials Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Approximating Functions by Polynomials 2 Approximating Functions by Polynomials Suppose that f(x) is equal to the
The main aim of this exercise is to stress the structure of matrix arithmetic. a. If we had been given the equation
 The main aim of this exercise is to stress the structure of matrix arithmetic. a. If we had been given the equation where XI A, B, and C were numbers, we would have at once concluded that X = 3 (AB + C).
The main aim of this exercise is to stress the structure of matrix arithmetic. a. If we had been given the equation where XI A, B, and C were numbers, we would have at once concluded that X = 3 (AB + C).
Taylor and Maclaurin Series. Approximating functions using Polynomials.
 Taylor and Maclaurin Series Approximating functions using Polynomials. Approximating f x = e x near x = 0 In order to approximate the function f x = e x near x = 0, we can use the tangent line (The Linear
Taylor and Maclaurin Series Approximating functions using Polynomials. Approximating f x = e x near x = 0 In order to approximate the function f x = e x near x = 0, we can use the tangent line (The Linear
Math 212-Lecture 8. The chain rule with one independent variable
 Math 212-Lecture 8 137: The multivariable chain rule The chain rule with one independent variable w = f(x, y) If the particle is moving along a curve x = x(t), y = y(t), then the values that the particle
Math 212-Lecture 8 137: The multivariable chain rule The chain rule with one independent variable w = f(x, y) If the particle is moving along a curve x = x(t), y = y(t), then the values that the particle
MTH4100 Calculus I. Week 6 (Thomas Calculus Sections 3.5 to 4.2) Rainer Klages. School of Mathematical Sciences Queen Mary, University of London
 MTH4100 Calculus I Week 6 (Thomas Calculus Sections 3.5 to 4.2) Rainer Klages School of Mathematical Sciences Queen Mary, University of London Autumn 2008 R. Klages (QMUL) MTH4100 Calculus 1 Week 6 1 /
MTH4100 Calculus I Week 6 (Thomas Calculus Sections 3.5 to 4.2) Rainer Klages School of Mathematical Sciences Queen Mary, University of London Autumn 2008 R. Klages (QMUL) MTH4100 Calculus 1 Week 6 1 /
MTH4101 CALCULUS II REVISION NOTES. 1. COMPLEX NUMBERS (Thomas Appendix 7 + lecture notes) ax 2 + bx + c = 0. x = b ± b 2 4ac 2a. i = 1.
 MTH4101 CALCULUS II REVISION NOTES 1. COMPLEX NUMBERS (Thomas Appendix 7 + lecture notes) 1.1 Introduction Types of numbers (natural, integers, rationals, reals) The need to solve quadratic equations:
MTH4101 CALCULUS II REVISION NOTES 1. COMPLEX NUMBERS (Thomas Appendix 7 + lecture notes) 1.1 Introduction Types of numbers (natural, integers, rationals, reals) The need to solve quadratic equations:
Vector Multiplication. Directional Derivatives and the Gradient
 Vector Multiplication - 1 Unit # : Goals: Directional Derivatives and the Gradient To learn about dot and scalar products of vectors. To introduce the directional derivative and the gradient vector. To
Vector Multiplication - 1 Unit # : Goals: Directional Derivatives and the Gradient To learn about dot and scalar products of vectors. To introduce the directional derivative and the gradient vector. To
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY 6.265/15.070J Fall 2013 Lecture 7 9/25/2013
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY 6.65/15.070J Fall 013 Lecture 7 9/5/013 The Reflection Principle. The Distribution of the Maximum. Brownian motion with drift Content. 1. Quick intro to stopping times.
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY 6.65/15.070J Fall 013 Lecture 7 9/5/013 The Reflection Principle. The Distribution of the Maximum. Brownian motion with drift Content. 1. Quick intro to stopping times.
VANDERBILT UNIVERSITY. MATH 2300 MULTIVARIABLE CALCULUS Practice Test 1 Solutions
 VANDERBILT UNIVERSITY MATH 2300 MULTIVARIABLE CALCULUS Practice Test 1 Solutions Directions. This practice test should be used as a study guide, illustrating the concepts that will be emphasized in the
VANDERBILT UNIVERSITY MATH 2300 MULTIVARIABLE CALCULUS Practice Test 1 Solutions Directions. This practice test should be used as a study guide, illustrating the concepts that will be emphasized in the
Math 527 Lecture Notes Topics in Calculus and Analysis Northern Illinois University Spring, Prof. Richard Blecksmith
 Math 527 Lecture Notes Topics in Calculus and Analysis Northern Illinois University Spring, 2014 Prof. Richard Blecksmith Contents Module 4. Further Applications of Derivatives 47 1. Direction of a Curve
Math 527 Lecture Notes Topics in Calculus and Analysis Northern Illinois University Spring, 2014 Prof. Richard Blecksmith Contents Module 4. Further Applications of Derivatives 47 1. Direction of a Curve
Course Name : Physics I Course # PHY 107. Note - 3 : Motion in One Dimension
 Course Name : Physics I Course # PHY 107 Note - 3 : Motion in One Dimension Abu Mohammad Khan Department of Mathematics and Physics North South University https://abukhan.weebly.com Copyright: It is unlawful
Course Name : Physics I Course # PHY 107 Note - 3 : Motion in One Dimension Abu Mohammad Khan Department of Mathematics and Physics North South University https://abukhan.weebly.com Copyright: It is unlawful
MITOCW MITRES_18-007_Part3_lec5_300k.mp4
 MITOCW MITRES_18-007_Part3_lec5_300k.mp4 The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources
MITOCW MITRES_18-007_Part3_lec5_300k.mp4 The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources
Directional Derivatives and the Gradient
 Unit #20 : Directional Derivatives and the Gradient Goals: To learn about dot and scalar products of vectors. To introduce the directional derivative and the gradient vector. To learn how to compute the
Unit #20 : Directional Derivatives and the Gradient Goals: To learn about dot and scalar products of vectors. To introduce the directional derivative and the gradient vector. To learn how to compute the
MAT 1332: CALCULUS FOR LIFE SCIENCES
 MAT 1332: CALCULUS FOR LIFE SCIENCES JING LI Contents 1 Review: Functions of several variables I: Partial derivatives 1 2 Function of several variables II: Vector-valued functions 2 21 Introductory example
MAT 1332: CALCULUS FOR LIFE SCIENCES JING LI Contents 1 Review: Functions of several variables I: Partial derivatives 1 2 Function of several variables II: Vector-valued functions 2 21 Introductory example
Differentiation - Quick Review From Calculus
 Differentiation - Quick Review From Calculus Philippe B. Laval KSU Current Semester Philippe B. Laval (KSU) Differentiation - Quick Review From Calculus Current Semester 1 / 13 Introduction In this section,
Differentiation - Quick Review From Calculus Philippe B. Laval KSU Current Semester Philippe B. Laval (KSU) Differentiation - Quick Review From Calculus Current Semester 1 / 13 Introduction In this section,
MATH 19520/51 Class 5
 MATH 19520/51 Class 5 Minh-Tam Trinh University of Chicago 2017-10-04 1 Definition of partial derivatives. 2 Geometry of partial derivatives. 3 Higher derivatives. 4 Definition of a partial differential
MATH 19520/51 Class 5 Minh-Tam Trinh University of Chicago 2017-10-04 1 Definition of partial derivatives. 2 Geometry of partial derivatives. 3 Higher derivatives. 4 Definition of a partial differential
D(f/g)(P ) = D(f)(P )g(p ) f(p )D(g)(P ). g 2 (P )
 We first record a very useful: 11. Higher derivatives Theorem 11.1. Let A R n be an open subset. Let f : A R m and g : A R m be two functions and suppose that P A. Let λ A be a scalar. If f and g are differentiable
We first record a very useful: 11. Higher derivatives Theorem 11.1. Let A R n be an open subset. Let f : A R m and g : A R m be two functions and suppose that P A. Let λ A be a scalar. If f and g are differentiable
The Comparison Test & Limit Comparison Test
 The Comparison Test & Limit Comparison Test Math4 Department of Mathematics, University of Kentucky February 5, 207 Math4 Lecture 3 / 3 Summary of (some of) what we have learned about series... Math4 Lecture
The Comparison Test & Limit Comparison Test Math4 Department of Mathematics, University of Kentucky February 5, 207 Math4 Lecture 3 / 3 Summary of (some of) what we have learned about series... Math4 Lecture
DIFFERENTIATION RULES
 3 DIFFERENTIATION RULES DIFFERENTIATION RULES We have: Seen how to interpret derivatives as slopes and rates of change Seen how to estimate derivatives of functions given by tables of values Learned how
3 DIFFERENTIATION RULES DIFFERENTIATION RULES We have: Seen how to interpret derivatives as slopes and rates of change Seen how to estimate derivatives of functions given by tables of values Learned how
Lecture 10. (2) Functions of two variables. Partial derivatives. Dan Nichols February 27, 2018
 Lecture 10 Partial derivatives Dan Nichols nichols@math.umass.edu MATH 233, Spring 2018 University of Massachusetts February 27, 2018 Last time: functions of two variables f(x, y) x and y are the independent
Lecture 10 Partial derivatives Dan Nichols nichols@math.umass.edu MATH 233, Spring 2018 University of Massachusetts February 27, 2018 Last time: functions of two variables f(x, y) x and y are the independent
Kinematics and One Dimensional Motion
 Kinematics and One Dimensional Motion Kinematics Vocabulary Kinema means movement Mathematical description of motion Position Time Interval Displacement Velocity; absolute value: speed Acceleration Averages
Kinematics and One Dimensional Motion Kinematics Vocabulary Kinema means movement Mathematical description of motion Position Time Interval Displacement Velocity; absolute value: speed Acceleration Averages
(1) Recap of Differential Calculus and Integral Calculus (2) Preview of Calculus in three dimensional space (3) Tools for Calculus 3
 Math 127 Introduction and Review (1) Recap of Differential Calculus and Integral Calculus (2) Preview of Calculus in three dimensional space (3) Tools for Calculus 3 MATH 127 Introduction to Calculus III
Math 127 Introduction and Review (1) Recap of Differential Calculus and Integral Calculus (2) Preview of Calculus in three dimensional space (3) Tools for Calculus 3 MATH 127 Introduction to Calculus III
NOTES ON MULTIVARIABLE CALCULUS: DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS
 NOTES ON MULTIVARIABLE CALCULUS: DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS SAMEER CHAVAN Abstract. This is the first part of Notes on Multivariable Calculus based on the classical texts [6] and [5]. We present here the geometric
NOTES ON MULTIVARIABLE CALCULUS: DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS SAMEER CHAVAN Abstract. This is the first part of Notes on Multivariable Calculus based on the classical texts [6] and [5]. We present here the geometric
Calculus Example Exam Solutions
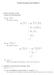 Calculus Example Exam Solutions. Limits (8 points, 6 each) Evaluate the following limits: p x 2 (a) lim x 4 We compute as follows: lim p x 2 x 4 p p x 2 x +2 x 4 p x +2 x 4 (x 4)( p x + 2) p x +2 = p 4+2
Calculus Example Exam Solutions. Limits (8 points, 6 each) Evaluate the following limits: p x 2 (a) lim x 4 We compute as follows: lim p x 2 x 4 p p x 2 x +2 x 4 p x +2 x 4 (x 4)( p x + 2) p x +2 = p 4+2
Directional Derivatives and Gradient Vectors. Suppose we want to find the rate of change of a function z = f x, y at the point in the
 14.6 Directional Derivatives and Gradient Vectors 1. Partial Derivates are nice, but they only tell us the rate of change of a function z = f x, y in the i and j direction. What if we are interested in
14.6 Directional Derivatives and Gradient Vectors 1. Partial Derivates are nice, but they only tell us the rate of change of a function z = f x, y in the i and j direction. What if we are interested in
AP CALCULUS BC 2009 SCORING GUIDELINES
 AP CALCULUS BC 2009 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 5 x 2 5 8 1 f ( x ) 1 4 2 6 Let f be a function that is twice differentiable for all real numbers. The table above gives values of f for selected points
AP CALCULUS BC 2009 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 5 x 2 5 8 1 f ( x ) 1 4 2 6 Let f be a function that is twice differentiable for all real numbers. The table above gives values of f for selected points
18.01 EXERCISES. Unit 3. Integration. 3A. Differentials, indefinite integration. 3A-1 Compute the differentials df(x) of the following functions.
 8. EXERCISES Unit 3. Integration 3A. Differentials, indefinite integration 3A- Compute the differentials df(x) of the following functions. a) d(x 7 + sin ) b) d x c) d(x 8x + 6) d) d(e 3x sin x) e) Express
8. EXERCISES Unit 3. Integration 3A. Differentials, indefinite integration 3A- Compute the differentials df(x) of the following functions. a) d(x 7 + sin ) b) d x c) d(x 8x + 6) d) d(e 3x sin x) e) Express
P1 Calculus II. Partial Differentiation & Multiple Integration. Prof David Murray. dwm/courses/1pd
 P1 2017 1 / 39 P1 Calculus II Partial Differentiation & Multiple Integration Prof David Murray david.murray@eng.ox.ac.uk www.robots.ox.ac.uk/ dwm/courses/1pd 4 lectures, MT 2017 P1 2017 2 / 39 Motivation
P1 2017 1 / 39 P1 Calculus II Partial Differentiation & Multiple Integration Prof David Murray david.murray@eng.ox.ac.uk www.robots.ox.ac.uk/ dwm/courses/1pd 4 lectures, MT 2017 P1 2017 2 / 39 Motivation
6.2 Their Derivatives
 Exponential Functions and 6.2 Their Derivatives Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Exponential Functions and Their Derivatives The function f(x) = 2 x is called an exponential function because
Exponential Functions and 6.2 Their Derivatives Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Exponential Functions and Their Derivatives The function f(x) = 2 x is called an exponential function because
Student Study Session. Theorems
 Students should be able to apply and have a geometric understanding of the following: Intermediate Value Theorem Mean Value Theorem for derivatives Extreme Value Theorem Name Formal Statement Restatement
Students should be able to apply and have a geometric understanding of the following: Intermediate Value Theorem Mean Value Theorem for derivatives Extreme Value Theorem Name Formal Statement Restatement
EXAM 3 MAT 167 Calculus I Spring is a composite function of two functions y = e u and u = 4 x + x 2. By the. dy dx = dy du = e u x + 2x.
 EXAM MAT 67 Calculus I Spring 20 Name: Section: I Each answer must include either supporting work or an explanation of your reasoning. These elements are considered to be the main part of each answer and
EXAM MAT 67 Calculus I Spring 20 Name: Section: I Each answer must include either supporting work or an explanation of your reasoning. These elements are considered to be the main part of each answer and
MATH 2400: PRACTICE PROBLEMS FOR EXAM 1
 MATH 2400: PRACTICE PROBLEMS FOR EXAM 1 PETE L. CLARK 1) Find all real numbers x such that x 3 = x. Prove your answer! Solution: If x 3 = x, then 0 = x 3 x = x(x + 1)(x 1). Earlier we showed using the
MATH 2400: PRACTICE PROBLEMS FOR EXAM 1 PETE L. CLARK 1) Find all real numbers x such that x 3 = x. Prove your answer! Solution: If x 3 = x, then 0 = x 3 x = x(x + 1)(x 1). Earlier we showed using the
February 27, 2019 LECTURE 10: VECTOR FIELDS.
 February 27, 209 LECTURE 0: VECTOR FIELDS 02 HONORS MULTIVARIABLE CALCULUS PROFESSOR RICHARD BROWN Synopsis Vector fields, as geometric objects and/or functions, provide a backbone in which all of physics
February 27, 209 LECTURE 0: VECTOR FIELDS 02 HONORS MULTIVARIABLE CALCULUS PROFESSOR RICHARD BROWN Synopsis Vector fields, as geometric objects and/or functions, provide a backbone in which all of physics
Caculus 221. Possible questions for Exam II. March 19, 2002
 Caculus 221 Possible questions for Exam II March 19, 2002 These notes cover the recent material in a style more like the lecture than the book. The proofs in the book are in section 1-11. At the end there
Caculus 221 Possible questions for Exam II March 19, 2002 These notes cover the recent material in a style more like the lecture than the book. The proofs in the book are in section 1-11. At the end there
Science One Integral Calculus
 Science One Integral Calculus January 018 Happy New Year! Differential Calculus central idea: The Derivative What is the derivative f (x) of a function f(x)? Differential Calculus central idea: The Derivative
Science One Integral Calculus January 018 Happy New Year! Differential Calculus central idea: The Derivative What is the derivative f (x) of a function f(x)? Differential Calculus central idea: The Derivative
MATH 1210 Assignment 3 Solutions 17R-T2
 MATH 1210 Assignment 3 Solutions 17R-T2 This assignment is optional and does not need to be handed in. Attempt all questions, write out nicely written solutions (showing all your work), and the solutions
MATH 1210 Assignment 3 Solutions 17R-T2 This assignment is optional and does not need to be handed in. Attempt all questions, write out nicely written solutions (showing all your work), and the solutions
 AP Calculus BC 2003 Free-Response Questions The materials included in these files are intended for use by AP teachers for course and exam preparation; permission for any other use must be sought from the
AP Calculus BC 2003 Free-Response Questions The materials included in these files are intended for use by AP teachers for course and exam preparation; permission for any other use must be sought from the
Parametric Equations and Polar Coordinates
 Parametric Equations and Polar Coordinates Parametrizations of Plane Curves In previous chapters, we have studied curves as the graphs of functions or equations involving the two variables x and y. Another
Parametric Equations and Polar Coordinates Parametrizations of Plane Curves In previous chapters, we have studied curves as the graphs of functions or equations involving the two variables x and y. Another
Slope Fields and Differential Equations. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 Slope Fields and Differential Equations Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Review verifying solutions to differential equations. Review solving differential equations. Review using
Slope Fields and Differential Equations Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Review verifying solutions to differential equations. Review solving differential equations. Review using
JUST THE MATHS UNIT NUMBER NUMERICAL MATHEMATICS 6 (Numerical solution) of (ordinary differential equations (A)) A.J.Hobson
 JUST THE MATHS UNIT NUMBER 17.6 NUMERICAL MATHEMATICS 6 (Numerical solution) of (ordinary differential equations (A)) by A.J.Hobson 17.6.1 Euler s unmodified method 17.6.2 Euler s modified method 17.6.3
JUST THE MATHS UNIT NUMBER 17.6 NUMERICAL MATHEMATICS 6 (Numerical solution) of (ordinary differential equations (A)) by A.J.Hobson 17.6.1 Euler s unmodified method 17.6.2 Euler s modified method 17.6.3
Prague, II.2. Integrability (existence of the Riemann integral) sufficient conditions... 37
 Mathematics II Prague, 1998 ontents Introduction.................................................................... 3 I. Functions of Several Real Variables (Stanislav Kračmar) II. I.1. Euclidean space
Mathematics II Prague, 1998 ontents Introduction.................................................................... 3 I. Functions of Several Real Variables (Stanislav Kračmar) II. I.1. Euclidean space
MATH The Derivative as a Function - Section 3.2. The derivative of f is the function. f x h f x. f x lim
 MATH 90 - The Derivative as a Function - Section 3.2 The derivative of f is the function f x lim h 0 f x h f x h for all x for which the limit exists. The notation f x is read "f prime of x". Note that
MATH 90 - The Derivative as a Function - Section 3.2 The derivative of f is the function f x lim h 0 f x h f x h for all x for which the limit exists. The notation f x is read "f prime of x". Note that
Math 233. Directional Derivatives and Gradients Basics
 Math 233. Directional Derivatives and Gradients Basics Given a function f(x, y) and a unit vector u = a, b we define the directional derivative of f at (x 0, y 0 ) in the direction u by f(x 0 + ta, y 0
Math 233. Directional Derivatives and Gradients Basics Given a function f(x, y) and a unit vector u = a, b we define the directional derivative of f at (x 0, y 0 ) in the direction u by f(x 0 + ta, y 0
MIDTERM EXAMINATION. Spring MTH301- Calculus II (Session - 3)
 ASSALAM O ALAIKUM All Dear fellows ALL IN ONE MTH3 Calculus II Midterm solved papers Created BY Ali Shah From Sahiwal BSCS th semester alaoudin.bukhari@gmail.com Remember me in your prayers MIDTERM EXAMINATION
ASSALAM O ALAIKUM All Dear fellows ALL IN ONE MTH3 Calculus II Midterm solved papers Created BY Ali Shah From Sahiwal BSCS th semester alaoudin.bukhari@gmail.com Remember me in your prayers MIDTERM EXAMINATION
CHAPTER 2. The Derivative
 CHAPTER The Derivative Section.1 Tangent Lines and Rates of Change Suggested Time Allocation: 1 to 1 1 lectures Slides Available on the Instructor Companion Site for this Text: Figures.1.1,.1.,.1.7,.1.11
CHAPTER The Derivative Section.1 Tangent Lines and Rates of Change Suggested Time Allocation: 1 to 1 1 lectures Slides Available on the Instructor Companion Site for this Text: Figures.1.1,.1.,.1.7,.1.11
Lecture 7 - Separable Equations
 Lecture 7 - Separable Equations Separable equations is a very special type of differential equations where you can separate the terms involving only y on one side of the equation and terms involving only
Lecture 7 - Separable Equations Separable equations is a very special type of differential equations where you can separate the terms involving only y on one side of the equation and terms involving only
AP Calculus AB 1998 Free-Response Questions
 AP Calculus AB 1998 Free-Response Questions These materials are intended for non-commercial use by AP teachers for course and exam preparation; permission for any other use must be sought from the Advanced
AP Calculus AB 1998 Free-Response Questions These materials are intended for non-commercial use by AP teachers for course and exam preparation; permission for any other use must be sought from the Advanced
AP Calculus BC 1998 Free-Response Questions
 AP Calculus BC 1998 Free-Response Questions These materials are intended for non-commercial use by AP teachers for course and exam preparation; permission for any other use must be sought from the Advanced
AP Calculus BC 1998 Free-Response Questions These materials are intended for non-commercial use by AP teachers for course and exam preparation; permission for any other use must be sought from the Advanced
2006 AP6 CALCULUS AB FREE-RESPONSE QUESTIONS
 2006 AP6 CALCULUS AB FREE-RESPONSE QUESTIONS dy 1+ y 5. Consider th e differential equation =, where x 0. dx x (a) On the axes provided, sketch a slope field for the given differential equation at the
2006 AP6 CALCULUS AB FREE-RESPONSE QUESTIONS dy 1+ y 5. Consider th e differential equation =, where x 0. dx x (a) On the axes provided, sketch a slope field for the given differential equation at the
Vector Calculus - GATE Study Material in PDF
 Vector Calculus - GATE Study Material in PDF In previous articles, we have already seen the basics of Calculus Differentiation and Integration and applications. In GATE 2018 Study Notes, we will be introduced
Vector Calculus - GATE Study Material in PDF In previous articles, we have already seen the basics of Calculus Differentiation and Integration and applications. In GATE 2018 Study Notes, we will be introduced
Method of Lagrange Multipliers
 Method of Lagrange Multipliers A. Salih Department of Aerospace Engineering Indian Institute of Space Science and Technology, Thiruvananthapuram September 2013 Lagrange multiplier method is a technique
Method of Lagrange Multipliers A. Salih Department of Aerospace Engineering Indian Institute of Space Science and Technology, Thiruvananthapuram September 2013 Lagrange multiplier method is a technique
Metric Spaces Lecture 17
 Metric Spaces Lecture 17 Homeomorphisms At the end of last lecture an example was given of a bijective continuous function f such that f 1 is not continuous. For another example, consider the sets T =
Metric Spaces Lecture 17 Homeomorphisms At the end of last lecture an example was given of a bijective continuous function f such that f 1 is not continuous. For another example, consider the sets T =
CHAPTER 7. An Introduction to Numerical Methods for. Linear and Nonlinear ODE s
 A SERIES OF CLASS NOTES FOR 2005-2006 TO INTRODUCE LINEAR AND NONLINEAR PROBLEMS TO ENGINEERS, SCIENTISTS, AND APPLIED MATHEMATICIANS DE CLASS NOTES 1 A COLLECTION OF HANDOUTS ON FIRST ORDER ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL
A SERIES OF CLASS NOTES FOR 2005-2006 TO INTRODUCE LINEAR AND NONLINEAR PROBLEMS TO ENGINEERS, SCIENTISTS, AND APPLIED MATHEMATICIANS DE CLASS NOTES 1 A COLLECTION OF HANDOUTS ON FIRST ORDER ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL
We have seen that for a function the partial derivatives whenever they exist, play an important role. This motivates the following definition.
 \ Module 12 : Total differential, Tangent planes and normals Lecture 34 : Gradient of a scaler field [Section 34.1] Objectives In this section you will learn the following : The notions gradient vector
\ Module 12 : Total differential, Tangent planes and normals Lecture 34 : Gradient of a scaler field [Section 34.1] Objectives In this section you will learn the following : The notions gradient vector
LECTURE 2. Convexity and related notions. Last time: mutual information: definitions and properties. Lecture outline
 LECTURE 2 Convexity and related notions Last time: Goals and mechanics of the class notation entropy: definitions and properties mutual information: definitions and properties Lecture outline Convexity
LECTURE 2 Convexity and related notions Last time: Goals and mechanics of the class notation entropy: definitions and properties mutual information: definitions and properties Lecture outline Convexity
IB Mathematics Standard Level Revision guide
 IB Mathematics Standard Level Revision guide F.G. Groeneveld TopClassTutors.ORG Copyright 2016 by F. Groeneveld All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, distributed, or transmitted
IB Mathematics Standard Level Revision guide F.G. Groeneveld TopClassTutors.ORG Copyright 2016 by F. Groeneveld All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, distributed, or transmitted
One Variable Calculus: Foundations and Applications
 One Variable Calculus: Foundations and Applications Prof. Manuela Pedio 20550 Quantitative Methods for Finance August 2018 About myself I graduated from Bocconi s MSc in Finance in 2013 (yes, I remember
One Variable Calculus: Foundations and Applications Prof. Manuela Pedio 20550 Quantitative Methods for Finance August 2018 About myself I graduated from Bocconi s MSc in Finance in 2013 (yes, I remember
Partial Derivatives for Math 229. Our puropose here is to explain how one computes partial derivatives. We will not attempt
 Partial Derivatives for Math 229 Our puropose here is to explain how one computes partial derivatives. We will not attempt to explain how they arise or why one would use them; that is left to other courses
Partial Derivatives for Math 229 Our puropose here is to explain how one computes partial derivatives. We will not attempt to explain how they arise or why one would use them; that is left to other courses
Chapter 7. Extremal Problems. 7.1 Extrema and Local Extrema
 Chapter 7 Extremal Problems No matter in theoretical context or in applications many problems can be formulated as problems of finding the maximum or minimum of a function. Whenever this is the case, advanced
Chapter 7 Extremal Problems No matter in theoretical context or in applications many problems can be formulated as problems of finding the maximum or minimum of a function. Whenever this is the case, advanced
NO CALCULATOR 1. Find the interval or intervals on which the function whose graph is shown is increasing:
 AP Calculus AB PRACTICE MIDTERM EXAM Read each choice carefully and find the best answer. Your midterm exam will be made up of 5 of these questions. I reserve the right to change numbers and answers on
AP Calculus AB PRACTICE MIDTERM EXAM Read each choice carefully and find the best answer. Your midterm exam will be made up of 5 of these questions. I reserve the right to change numbers and answers on
ALGEBRA. COPYRIGHT 1996 Mark Twain Media, Inc. ISBN Printing No EB
 ALGEBRA By Don Blattner and Myrl Shireman COPYRIGHT 1996 Mark Twain Media, Inc. ISBN 978-1-58037-826-0 Printing No. 1874-EB Mark Twain Media, Inc., Publishers Distributed by Carson-Dellosa Publishing Company,
ALGEBRA By Don Blattner and Myrl Shireman COPYRIGHT 1996 Mark Twain Media, Inc. ISBN 978-1-58037-826-0 Printing No. 1874-EB Mark Twain Media, Inc., Publishers Distributed by Carson-Dellosa Publishing Company,
Lecture Notes for MATH6106. March 25, 2010
 Lecture Notes for MATH66 March 25, 2 Contents Vectors 4. Points in Space.......................... 4.2 Distance between Points..................... 4.3 Scalars and Vectors........................ 5.4 Vectors
Lecture Notes for MATH66 March 25, 2 Contents Vectors 4. Points in Space.......................... 4.2 Distance between Points..................... 4.3 Scalars and Vectors........................ 5.4 Vectors
MATH 18.01, FALL PROBLEM SET # 2
 MATH 18.01, FALL 2012 - PROBLEM SET # 2 Professor: Jared Speck Due: by Thursday 4:00pm on 9-20-12 (in the boxes outside of Room 2-255 during the day; stick it under the door if the room is locked; write
MATH 18.01, FALL 2012 - PROBLEM SET # 2 Professor: Jared Speck Due: by Thursday 4:00pm on 9-20-12 (in the boxes outside of Room 2-255 during the day; stick it under the door if the room is locked; write
Math 180, Final Exam, Fall 2007 Problem 1 Solution
 Problem Solution. Differentiate with respect to x. Write your answers showing the use of the appropriate techniques. Do not simplify. (a) x 27 x 2/3 (b) (x 2 2x + 2)e x (c) ln(x 2 + 4) (a) Use the Power
Problem Solution. Differentiate with respect to x. Write your answers showing the use of the appropriate techniques. Do not simplify. (a) x 27 x 2/3 (b) (x 2 2x + 2)e x (c) ln(x 2 + 4) (a) Use the Power
Name (print): Question 4. exercise 1.24 (compute the union, then the intersection of two sets)
 MTH299 - Homework 1 Question 1. exercise 1.10 (compute the cardinality of a handful of finite sets) Solution. Write your answer here. Question 2. exercise 1.20 (compute the union of two sets) Question
MTH299 - Homework 1 Question 1. exercise 1.10 (compute the cardinality of a handful of finite sets) Solution. Write your answer here. Question 2. exercise 1.20 (compute the union of two sets) Question
MA102: Multivariable Calculus
 MA102: Multivariable Calculus Rupam Barman and Shreemayee Bora Department of Mathematics IIT Guwahati Differentiability of f : U R n R m Definition: Let U R n be open. Then f : U R n R m is differentiable
MA102: Multivariable Calculus Rupam Barman and Shreemayee Bora Department of Mathematics IIT Guwahati Differentiability of f : U R n R m Definition: Let U R n be open. Then f : U R n R m is differentiable
Sec. 14.3: Partial Derivatives. All of the following are ways of representing the derivative. y dx
 Math 2204 Multivariable Calc Chapter 14: Partial Derivatives I. Review from math 1225 A. First Derivative Sec. 14.3: Partial Derivatives 1. Def n : The derivative of the function f with respect to the
Math 2204 Multivariable Calc Chapter 14: Partial Derivatives I. Review from math 1225 A. First Derivative Sec. 14.3: Partial Derivatives 1. Def n : The derivative of the function f with respect to the
26. Directional Derivatives & The Gradient
 26. Directional Derivatives & The Gradient Given a multivariable function z = f(x, y) and a point on the xy-plane P 0 = (x 0, y 0 ) at which f is differentiable (i.e. it is smooth with no discontinuities,
26. Directional Derivatives & The Gradient Given a multivariable function z = f(x, y) and a point on the xy-plane P 0 = (x 0, y 0 ) at which f is differentiable (i.e. it is smooth with no discontinuities,
Lecture 5 - Logarithms, Slope of a Function, Derivatives
 Lecture 5 - Logarithms, Slope of a Function, Derivatives 5. Logarithms Note the graph of e x This graph passes the horizontal line test, so f(x) = e x is one-to-one and therefore has an inverse function.
Lecture 5 - Logarithms, Slope of a Function, Derivatives 5. Logarithms Note the graph of e x This graph passes the horizontal line test, so f(x) = e x is one-to-one and therefore has an inverse function.
Logarithmic, Exponential, and Other Transcendental Functions. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 5 Logarithmic, Exponential, and Other Transcendental Functions Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 5.5 Bases Other Than e and Applications Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
5 Logarithmic, Exponential, and Other Transcendental Functions Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 5.5 Bases Other Than e and Applications Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
Section 2.1: The Derivative and the Tangent Line Problem Goals for this Section:
 Section 2.1: The Derivative and the Tangent Line Problem Goals for this Section: Find the slope of the tangent line to a curve at a point. Day 1 Use the limit definition to find the derivative of a function.
Section 2.1: The Derivative and the Tangent Line Problem Goals for this Section: Find the slope of the tangent line to a curve at a point. Day 1 Use the limit definition to find the derivative of a function.
Calculus. Weijiu Liu. Department of Mathematics University of Central Arkansas 201 Donaghey Avenue, Conway, AR 72035, USA
 Calculus Weijiu Liu Department of Mathematics University of Central Arkansas 201 Donaghey Avenue, Conway, AR 72035, USA 1 Opening Welcome to your Calculus I class! My name is Weijiu Liu. I will guide you
Calculus Weijiu Liu Department of Mathematics University of Central Arkansas 201 Donaghey Avenue, Conway, AR 72035, USA 1 Opening Welcome to your Calculus I class! My name is Weijiu Liu. I will guide you
NO CALCULATOR 1. Find the interval or intervals on which the function whose graph is shown is increasing:
 AP Calculus AB PRACTICE MIDTERM EXAM Read each choice carefully and find the best answer. Your midterm exam will be made up of 8 of these questions. I reserve the right to change numbers and answers on
AP Calculus AB PRACTICE MIDTERM EXAM Read each choice carefully and find the best answer. Your midterm exam will be made up of 8 of these questions. I reserve the right to change numbers and answers on
AB.Q103.NOTES: Chapter 2.4, 3.1, 3.2 LESSON 1. Discovering the derivative at x = a: Slopes of secants and tangents to a curve
 AB.Q103.NOTES: Chapter 2.4, 3.1, 3.2 LESSON 1 Discovering the derivative at x = a: Slopes of secants and tangents to a curve 1 1. Instantaneous rate of change versus average rate of change Equation of
AB.Q103.NOTES: Chapter 2.4, 3.1, 3.2 LESSON 1 Discovering the derivative at x = a: Slopes of secants and tangents to a curve 1 1. Instantaneous rate of change versus average rate of change Equation of
AP CALCULUS AB 2004 SCORING GUIDELINES (Form B)
 AP CALCULUS AB 004 SCORING GUIDELINES (Form B) Question 4 The figure above shows the graph of f, the derivative of the function f, on the closed interval 1 x 5. The graph of f has horizontal tangent lines
AP CALCULUS AB 004 SCORING GUIDELINES (Form B) Question 4 The figure above shows the graph of f, the derivative of the function f, on the closed interval 1 x 5. The graph of f has horizontal tangent lines
Math 251 Midterm II Information Spring 2018
 Math 251 Midterm II Information Spring 2018 WHEN: Thursday, April 12 (in class). You will have the entire period (125 minutes) to work on the exam. RULES: No books or notes. You may bring a non-graphing
Math 251 Midterm II Information Spring 2018 WHEN: Thursday, April 12 (in class). You will have the entire period (125 minutes) to work on the exam. RULES: No books or notes. You may bring a non-graphing
LECTURE 5, FRIDAY
 LECTURE 5, FRIDAY 20.02.04 FRANZ LEMMERMEYER Before we start with the arithmetic of elliptic curves, let us talk a little bit about multiplicities, tangents, and singular points. 1. Tangents How do we
LECTURE 5, FRIDAY 20.02.04 FRANZ LEMMERMEYER Before we start with the arithmetic of elliptic curves, let us talk a little bit about multiplicities, tangents, and singular points. 1. Tangents How do we
Announcements. Topics: Homework:
 Topics: Announcements - section 2.6 (limits at infinity [skip Precise Definitions (middle of pg. 134 end of section)]) - sections 2.1 and 2.7 (rates of change, the derivative) - section 2.8 (the derivative
Topics: Announcements - section 2.6 (limits at infinity [skip Precise Definitions (middle of pg. 134 end of section)]) - sections 2.1 and 2.7 (rates of change, the derivative) - section 2.8 (the derivative
Math 216 Calculus 3 Directional derivatives. Math 216 Calculus 3 Directional derivatives 1 / 6
 Math 216 Calculus 3 Directional derivatives Math 216 Calculus 3 Directional derivatives 1 / 6 How fast does f (x, y) change if you change (x, y) in the direction v The partial derivatives f x and f y measure
Math 216 Calculus 3 Directional derivatives Math 216 Calculus 3 Directional derivatives 1 / 6 How fast does f (x, y) change if you change (x, y) in the direction v The partial derivatives f x and f y measure
