Slope Fields and Differential Equations. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
|
|
|
- Jonathan Lee
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Slope Fields and Differential Equations Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
2 Objectives Review verifying solutions to differential equations. Review solving differential equations. Review using initial conditions to find particular solutions of differential equations. Use slope fields to approximate solutions of differential equations. 2
3 Verifying Solutions of Differential Equations 3
4 Verifying Solutions A differential equation in x and y is an equation that involves x, y, and derivatives of y. A function y = f(x) is called a solution of a differential equation if the equation is satisfied when y and its derivatives are replaced by f(x) and its derivatives. 4
5 Example 1 Verifying Solutions Determine whether the function is a solution of the differential equation y'' y = 0. a. y = sin x b. y = 4e x c. y = Ce x Solution: a. Because y = sin x, y' = cos x, and y'' = sin x, it follows that y'' y = sin x sin x = 2sin x 0. So, y = sin x is not a solution. 5
6 Example 1 Solution cont d b. Because y = 4e x, y' = 4e x, and y'' = 4e x, it follows that y'' y = 4e x 4e x = 0. So, y = 4e x is a solution. c. Because y = Ce x, y' = Ce x, and y'' = Ce x, it follows that y'' y = Ce x Ce x = 0. So, y = Ce x is a solution for any value of C. 6
7 General and Particular Solutions 7
8 General and Particular Solutions Differentiation and substitution would show that y = e 2x is a solution of the differential equation y' + 2y = 0. It can be shown that every solution of this differential equation is of the form y = Ce 2x General solution of y ' + 2y = 0 where C is any real number. This solution is called the general solution. 8
9 General and Particular Solutions Show how to find the general solution of the differential equation y' + 2y = 0. 9
10 General and Particular Solutions *The order of a differential equation is determined by the highest-order derivative in the equation. For instance, y' = 4y is a first-order differential equation. *It can be shown that a differential equation of order n has a general solution with n arbitrary constants. *Example: Find the general solution of the second-order differential equation s''(t) =
11 General and Particular Solutions Particular solutions of a differential equation are obtained from initial conditions that give the values of the dependent variable or one of its derivatives for particular values of the independent variable. 11
12 General and Particular Solutions The term initial condition stems from the fact that, often in problems involving time, the value of the dependent variable or one of its derivatives is known at the initial time t = 0. Example: Find the particular solution for the differential equation s''(t) = 32 having initial conditions s(0) = 80 and s'(0) =
13 General and Particular Solutions Geometrically, the general solution of a first-order differential equation represents a family of curves known as solution curves, one for each value assigned to the arbitrary constant. For instance, you can verify that every function of the form is a solution of the differential equation xy' + y = 0. 13
14 General and Particular Solutions Figure 6.1 shows four of the solution curves corresponding to different values of C. Particular solutions of a differential equation are obtained from initial conditions that give the values of the dependent variable or one of its derivatives for particular values of the independent variable. Figure
15 Example 2 Finding a Particular Solution For the differential equation xy' 3y = 0, verify that y = Cx 3 is a solution, and find the particular solution determined by the initial condition y = 2 when x = 3. Solution: You know that y = Cx 3 is a solution because y' = 3Cx 2 and xy' 3y = x(3cx 2 ) 3(Cx 3 ) = 0. 15
16 Example 2 Solution cont d Furthermore, the initial condition y = 2 when x = 3 yields y = Cx 3 General solution 2 = C( 3) 3 Substitute initial condition. Solve for C and you can conclude that the particular solution is Particular solution Try checking this solution by substituting for y and y' in the original differential equation. 16
17 Slope Fields 17
18 Slope Fields Solving a differential equation analytically can be difficult or even impossible. However, there is a graphical approach you can use to learn a lot about the solution of a differential equation. Consider a differential equation of the form y' = F(x, y) Differential equation where F(x, y) is some expression in x and y. At each point (x, y) in the xy plane where F is defined, the differential equation determines the slope y' = F(x, y) of the solution at that point. 18
19 Slope Fields If you draw short line segments with slope F(x, y) at selected points (x, y) in the domain of F, then these line segments form a slope field, or a direction field, for the differential equation y' = F(x, y). Each line segment has the same slope as the solution curve through that point. A slope field shows the general shape of all the solutions and can be helpful in getting a visual perspective of the directions of the solutions of a differential equation. 19
20 Example 3 Sketching a Slope Field Sketch a slope field for the differential equation y' = x y for the points ( 1, 1), (0, 1), and (1, 1). Solution: The slope of the solution curve at any point (x, y) is F (x, y) = x y. So, the slope at ( 1, 1) is y' = 1 1 = 2, the slope at (0, 1) is y' = 0 1 = 1, and the slope at (1, 1) is y' = 1 1 = 0. 20
21 Example 3 Solution cont d Draw short line segments at the three points with their respective slopes, as shown in Figure 6.2. Figure
22 General and Particular Solutions Make a slope field for the differential equation xy' + y = 0. Now find the general solution for the same equation. 22
23 General and Particular Solutions See how the slope field represents all the general solutions of the differential equation. Figure
Analytic Trigonometry. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 Analytic Trigonometry Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 7.4 Basic Trigonometric Equations Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Basic Trigonometric Equations Solving
Analytic Trigonometry Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 7.4 Basic Trigonometric Equations Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Basic Trigonometric Equations Solving
Logarithmic, Exponential, and Other Transcendental Functions
 5 Logarithmic, Exponential, and Other Transcendental Functions Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 1 5.3 Inverse Functions Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 2 Objectives Verify
5 Logarithmic, Exponential, and Other Transcendental Functions Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 1 5.3 Inverse Functions Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 2 Objectives Verify
Integration. Antiderivatives and Indefinite Integration 3/9/2015. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 Integration Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Antiderivatives and Indefinite Integration Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 1 Objectives Write the general solution of a differential
Integration Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Antiderivatives and Indefinite Integration Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 1 Objectives Write the general solution of a differential
Logarithmic, Exponential, and Other Transcendental Functions. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 5 Logarithmic, Exponential, and Other Transcendental Functions Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 5.5 Bases Other Than e and Applications Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
5 Logarithmic, Exponential, and Other Transcendental Functions Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 5.5 Bases Other Than e and Applications Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
6.2 Their Derivatives
 Exponential Functions and 6.2 Their Derivatives Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Exponential Functions and Their Derivatives The function f(x) = 2 x is called an exponential function because
Exponential Functions and 6.2 Their Derivatives Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Exponential Functions and Their Derivatives The function f(x) = 2 x is called an exponential function because
Infinite Series. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 Infinite Series Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Taylor and Maclaurin Series Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Find a Taylor or Maclaurin series for a function.
Infinite Series Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Taylor and Maclaurin Series Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Find a Taylor or Maclaurin series for a function.
11.4 The Comparison Tests. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 11.4 The Comparison Tests Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. The Comparison Tests In the comparison tests the idea is to compare a given series with a series that is known to be convergent
11.4 The Comparison Tests Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. The Comparison Tests In the comparison tests the idea is to compare a given series with a series that is known to be convergent
9.1 Circles and Parabolas. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 9.1 Circles and Parabolas Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn Recognize a conic as the intersection of a plane and a double-napped cone. Write equations of circles in
9.1 Circles and Parabolas Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn Recognize a conic as the intersection of a plane and a double-napped cone. Write equations of circles in
4 Integration. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 4 Integration Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 4.1 Antiderivatives and Indefinite Integration Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives! Write the general solution of
4 Integration Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 4.1 Antiderivatives and Indefinite Integration Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives! Write the general solution of
Integration. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 4 Integration Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 1 4.3 Riemann Sums and Definite Integrals Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 2 Objectives Understand the definition of a Riemann
4 Integration Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 1 4.3 Riemann Sums and Definite Integrals Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 2 Objectives Understand the definition of a Riemann
Functions. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 Functions Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 2.1 What is a Function? Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Functions All Around Us Definition of Function Evaluating
Functions Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 2.1 What is a Function? Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Functions All Around Us Definition of Function Evaluating
Taylor and Maclaurin Series. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 11.10 Taylor and Maclaurin Series Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. We start by supposing that f is any function that can be represented by a power series f(x)= c 0 +c 1 (x a)+c 2 (x a)
11.10 Taylor and Maclaurin Series Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. We start by supposing that f is any function that can be represented by a power series f(x)= c 0 +c 1 (x a)+c 2 (x a)
TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 12 TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 12.2 The Trigonometric Functions Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. The Trigonometric Functions and Their Graphs
12 TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 12.2 The Trigonometric Functions Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. The Trigonometric Functions and Their Graphs
Analytic Trigonometry. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 Analytic Trigonometry Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 7.1 Trigonometric Identities Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Simplifying Trigonometric Expressions Proving
Analytic Trigonometry Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 7.1 Trigonometric Identities Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Simplifying Trigonometric Expressions Proving
5.3 SOLVING TRIGONOMETRIC EQUATIONS
 5.3 SOLVING TRIGONOMETRIC EQUATIONS Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn Use standard algebraic techniques to solve trigonometric equations. Solve trigonometric equations
5.3 SOLVING TRIGONOMETRIC EQUATIONS Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn Use standard algebraic techniques to solve trigonometric equations. Solve trigonometric equations
Fundamentals. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 Fundamentals Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 1.11 Making Models Using Variation Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Direct Variation Inverse Variation Joint Variation
Fundamentals Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 1.11 Making Models Using Variation Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Direct Variation Inverse Variation Joint Variation
AFFINE COMBINATIONS, BARYCENTRIC COORDINATES, AND CONVEX COMBINATIONS
 On-Line Geometric Modeling Notes AFFINE COMBINATIONS, BARYCENTRIC COORDINATES, AND CONVEX COMBINATIONS Kenneth I. Joy Visualization and Graphics Research Group Department of Computer Science University
On-Line Geometric Modeling Notes AFFINE COMBINATIONS, BARYCENTRIC COORDINATES, AND CONVEX COMBINATIONS Kenneth I. Joy Visualization and Graphics Research Group Department of Computer Science University
Integration. Tuesday, December 3, 13
 4 Integration 4.3 Riemann Sums and Definite Integrals Objectives n Understand the definition of a Riemann sum. n Evaluate a definite integral using properties of definite integrals. 3 Riemann Sums 4 Riemann
4 Integration 4.3 Riemann Sums and Definite Integrals Objectives n Understand the definition of a Riemann sum. n Evaluate a definite integral using properties of definite integrals. 3 Riemann Sums 4 Riemann
Derivation of Euler's Method - Numerical Methods for Solving Differential Equations
 Derivation of Euler's Method - Numerical Methods for Solving Differential Equations Let s start with a general first order Initial Value Problem dx = f(x, y) y(x 0) = y 0 (1) where f(x, y) is a known function
Derivation of Euler's Method - Numerical Methods for Solving Differential Equations Let s start with a general first order Initial Value Problem dx = f(x, y) y(x 0) = y 0 (1) where f(x, y) is a known function
Polynomial and Rational Functions. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 2 Polynomial and Rational Functions Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 2.2 Polynomial Functions of Higher Degree Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn Use
2 Polynomial and Rational Functions Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 2.2 Polynomial Functions of Higher Degree Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn Use
Infinite Series. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 Infinite Series Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Sequences Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives List the terms of a sequence. Determine whether a sequence converges
Infinite Series Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Sequences Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives List the terms of a sequence. Determine whether a sequence converges
Polynomial and Rational Functions. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 2 Polynomial and Rational Functions Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 2.6 Rational Functions and Asymptotes Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn Find the
2 Polynomial and Rational Functions Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 2.6 Rational Functions and Asymptotes Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn Find the
1.7 Inequalities. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 1.7 Inequalities Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Solving Linear Inequalities Solving Nonlinear Inequalities Absolute Value Inequalities Modeling with Inequalities 2 Inequalities
1.7 Inequalities Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Solving Linear Inequalities Solving Nonlinear Inequalities Absolute Value Inequalities Modeling with Inequalities 2 Inequalities
Key Point. The nth order linear homogeneous equation with constant coefficients
 General Solutions of Higher-Order Linear Equations In section 3.1, we saw the following fact: Key Point. The nth order linear homogeneous equation with constant coefficients a n y (n) +... + a 2 y + a
General Solutions of Higher-Order Linear Equations In section 3.1, we saw the following fact: Key Point. The nth order linear homogeneous equation with constant coefficients a n y (n) +... + a 2 y + a
Chapter 6. Additional Topics in Trigonometry. 6.6 Vectors. Copyright 2014, 2010, 2007 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 6 Additional Topics in Trigonometry 6.6 Vectors Copyright 2014, 2010, 2007 Pearson Education, Inc. 1 Obectives: Use magnitude and direction to show vectors are equal. Visualize scalar multiplication,
Chapter 6 Additional Topics in Trigonometry 6.6 Vectors Copyright 2014, 2010, 2007 Pearson Education, Inc. 1 Obectives: Use magnitude and direction to show vectors are equal. Visualize scalar multiplication,
15.9. Triple Integrals in Spherical Coordinates. Spherical Coordinates. Spherical Coordinates. Spherical Coordinates. Multiple Integrals
 15 Multiple Integrals 15.9 Triple Integrals in Spherical Coordinates Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Triple Integrals in Another useful
15 Multiple Integrals 15.9 Triple Integrals in Spherical Coordinates Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Triple Integrals in Another useful
11.11 Applications of Taylor Polynomials. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 11.11 Applications of Taylor Polynomials Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Approximating Functions by Polynomials 2 Approximating Functions by Polynomials Suppose that f(x) is equal to the
11.11 Applications of Taylor Polynomials Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Approximating Functions by Polynomials 2 Approximating Functions by Polynomials Suppose that f(x) is equal to the
2.2. Polynomial Functions of Higher Degree. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 Warm-ups 1 2.2 Polynomial Functions of Higher Degree Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Use transformations to sketch graphs of polynomial functions. Use the Leading Coefficient
Warm-ups 1 2.2 Polynomial Functions of Higher Degree Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Use transformations to sketch graphs of polynomial functions. Use the Leading Coefficient
Chapter. Triangles. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 3 Triangles Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 3.5 Inequalities in a Triangle Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Inequalities in a Triangle Important inequality relationships
Chapter 3 Triangles Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 3.5 Inequalities in a Triangle Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Inequalities in a Triangle Important inequality relationships
In mathematics (and physics...) such quantities are called vectors and are represented by a directed line segment.
 12.2 1 12.2 Vectors Some things that we measure are determined simply by their magnitude, e.g., length, time, mass, etc. Others require more information. For example, to describe velocity one needs the
12.2 1 12.2 Vectors Some things that we measure are determined simply by their magnitude, e.g., length, time, mass, etc. Others require more information. For example, to describe velocity one needs the
7.6 The Inverse of a Square Matrix
 7.6 The Inverse of a Square Matrix Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn Verify that two matrices are inverses of each other. Use Gauss-Jordan elimination to find inverses
7.6 The Inverse of a Square Matrix Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn Verify that two matrices are inverses of each other. Use Gauss-Jordan elimination to find inverses
BARYCENTRIC COORDINATES
 Computer Graphics Notes BARYCENTRIC COORDINATES Kenneth I. Joy Institute for Data Analysis and Visualization Department of Computer Science University of California, Davis Overview If we are given a frame
Computer Graphics Notes BARYCENTRIC COORDINATES Kenneth I. Joy Institute for Data Analysis and Visualization Department of Computer Science University of California, Davis Overview If we are given a frame
Complex Numbers. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 4 Complex Numbers Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 4.1 Complex Numbers Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Use the imaginary unit i to write complex numbers. Add,
4 Complex Numbers Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 4.1 Complex Numbers Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Use the imaginary unit i to write complex numbers. Add,
GUIDED NOTES 4.1 LINEAR FUNCTIONS
 GUIDED NOTES 4.1 LINEAR FUNCTIONS LEARNING OBJECTIVES In this section, you will: Represent a linear function. Determine whether a linear function is increasing, decreasing, or constant. Interpret slope
GUIDED NOTES 4.1 LINEAR FUNCTIONS LEARNING OBJECTIVES In this section, you will: Represent a linear function. Determine whether a linear function is increasing, decreasing, or constant. Interpret slope
2.3 Differentiation Formulas. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 2.3 Differentiation Formulas Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Differentiation Formulas Let s start with the simplest of all functions, the constant function f (x) = c. The graph of this
2.3 Differentiation Formulas Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Differentiation Formulas Let s start with the simplest of all functions, the constant function f (x) = c. The graph of this
MA 102 Mathematics II Lecture Feb, 2015
 MA 102 Mathematics II Lecture 1 20 Feb, 2015 Differential Equations An equation containing derivatives is called a differential equation. The origin of differential equations Many of the laws of nature
MA 102 Mathematics II Lecture 1 20 Feb, 2015 Differential Equations An equation containing derivatives is called a differential equation. The origin of differential equations Many of the laws of nature
2.1 Functions and Their Graphs. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 2.1 Functions and Their Graphs Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Functions A manufacturer would like to know how his company s profit is related to its production level; a biologist would
2.1 Functions and Their Graphs Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Functions A manufacturer would like to know how his company s profit is related to its production level; a biologist would
Linear Systems and Matrices. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 7 Linear Systems and Matrices Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 7.1 Solving Systems of Equations Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn Use the methods of
7 Linear Systems and Matrices Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 7.1 Solving Systems of Equations Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn Use the methods of
CHAPTER 7 FUNCTIONS. Alessandro Artale UniBZ - artale/
 CHAPTER 7 FUNCTIONS Alessandro Artale UniBZ - http://www.inf.unibz.it/ artale/ SECTION 7.1 Functions Defined on General Sets Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Functions Defined on General
CHAPTER 7 FUNCTIONS Alessandro Artale UniBZ - http://www.inf.unibz.it/ artale/ SECTION 7.1 Functions Defined on General Sets Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Functions Defined on General
Exponential and Logarithmic Functions. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 3 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 3.2 Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn
3 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 3.2 Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn
Sections 8.1 & 8.2 Systems of Linear Equations in Two Variables
 Sections 8.1 & 8.2 Systems of Linear Equations in Two Variables Department of Mathematics Porterville College September 7, 2014 Systems of Linear Equations in Two Variables Learning Objectives: Solve Systems
Sections 8.1 & 8.2 Systems of Linear Equations in Two Variables Department of Mathematics Porterville College September 7, 2014 Systems of Linear Equations in Two Variables Learning Objectives: Solve Systems
3.3 Dividing Polynomials. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 3.3 Dividing Polynomials Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Long Division of Polynomials Synthetic Division The Remainder and Factor Theorems 2 Dividing Polynomials In this section
3.3 Dividing Polynomials Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Long Division of Polynomials Synthetic Division The Remainder and Factor Theorems 2 Dividing Polynomials In this section
Correlation and Regression
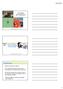 Correlation and Regression 8 9 Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Section 9.2 Linear Regression and the Coefficient of Determination Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Focus
Correlation and Regression 8 9 Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Section 9.2 Linear Regression and the Coefficient of Determination Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Focus
Math 122 Fall Handout 11: Summary of Euler s Method, Slope Fields and Symbolic Solutions of Differential Equations
 1 Math 122 Fall 2008 Handout 11: Summary of Euler s Method, Slope Fields and Symbolic Solutions of Differential Equations The purpose of this handout is to review the techniques that you will learn for
1 Math 122 Fall 2008 Handout 11: Summary of Euler s Method, Slope Fields and Symbolic Solutions of Differential Equations The purpose of this handout is to review the techniques that you will learn for
CONVERSION OF COORDINATES BETWEEN FRAMES
 ECS 178 Course Notes CONVERSION OF COORDINATES BETWEEN FRAMES Kenneth I. Joy Institute for Data Analysis and Visualization Department of Computer Science University of California, Davis Overview Frames
ECS 178 Course Notes CONVERSION OF COORDINATES BETWEEN FRAMES Kenneth I. Joy Institute for Data Analysis and Visualization Department of Computer Science University of California, Davis Overview Frames
The Definite Integral. Day 6 Motion Problems Strategies for Finding Total Area
 The Definite Integral Day 6 Motion Problems Strategies for Finding Total Area ARRIVAL---HW Questions Working in PODS Additional Practice Packet p. 13 and 14 Make good use of your time! Practice makes perfect!
The Definite Integral Day 6 Motion Problems Strategies for Finding Total Area ARRIVAL---HW Questions Working in PODS Additional Practice Packet p. 13 and 14 Make good use of your time! Practice makes perfect!
2.1 Differential Equations and Solutions. Blerina Xhabli
 2.1 Math 3331 Differential Equations 2.1 Differential Equations and Solutions Blerina Xhabli Department of Mathematics, University of Houston blerina@math.uh.edu math.uh.edu/ blerina/teaching.html Blerina
2.1 Math 3331 Differential Equations 2.1 Differential Equations and Solutions Blerina Xhabli Department of Mathematics, University of Houston blerina@math.uh.edu math.uh.edu/ blerina/teaching.html Blerina
MAC Learning Objectives. Learning Objectives. Module 1 Introduction to Functions and Graphs
 MAC 1140 Module 1 Introduction to Functions and Graphs Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to 1. recognize common sets of numbers. 2. understand scientific notation and
MAC 1140 Module 1 Introduction to Functions and Graphs Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to 1. recognize common sets of numbers. 2. understand scientific notation and
DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
 DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Basic Terminology A differential equation is an equation that contains an unknown function together with one or more of its derivatives. 1 Examples: 1. y = 2x + cos x 2. dy dt =
DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Basic Terminology A differential equation is an equation that contains an unknown function together with one or more of its derivatives. 1 Examples: 1. y = 2x + cos x 2. dy dt =
22 Approximations - the method of least squares (1)
 22 Approximations - the method of least squares () Suppose that for some y, the equation Ax = y has no solutions It may happpen that this is an important problem and we can t just forget about it If we
22 Approximations - the method of least squares () Suppose that for some y, the equation Ax = y has no solutions It may happpen that this is an important problem and we can t just forget about it If we
APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION
 4 APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION Many applications of calculus depend on our ability to deduce facts about a function f from information concerning its derivatives. APPLICATIONS
4 APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION Many applications of calculus depend on our ability to deduce facts about a function f from information concerning its derivatives. APPLICATIONS
Parametric Functions and Vector Functions (BC Only)
 Parametric Functions and Vector Functions (BC Only) Parametric Functions Parametric functions are another way of viewing functions. This time, the values of x and y are both dependent on another independent
Parametric Functions and Vector Functions (BC Only) Parametric Functions Parametric functions are another way of viewing functions. This time, the values of x and y are both dependent on another independent
LINEAR PROGRAMMING: A GEOMETRIC APPROACH. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 3 LINEAR PROGRAMMING: A GEOMETRIC APPROACH Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 3.4 Sensitivity Analysis Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Sensitivity Analysis In this section,
3 LINEAR PROGRAMMING: A GEOMETRIC APPROACH Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 3.4 Sensitivity Analysis Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Sensitivity Analysis In this section,
7.5 Operations with Matrices. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 7.5 Operations with Matrices Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn Decide whether two matrices are equal. Add and subtract matrices and multiply matrices by scalars. Multiply
7.5 Operations with Matrices Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn Decide whether two matrices are equal. Add and subtract matrices and multiply matrices by scalars. Multiply
means Name a function whose derivative is 2x. x 4, and so forth.
 AP Slope Fields Worksheet Slope fields give us a great wa to visualize a famil of antiderivatives, solutions of differential equations. d Solving means Name a function whose derivative is. d Answers might
AP Slope Fields Worksheet Slope fields give us a great wa to visualize a famil of antiderivatives, solutions of differential equations. d Solving means Name a function whose derivative is. d Answers might
. For each initial condition y(0) = y 0, there exists a. unique solution. In fact, given any point (x, y), there is a unique curve through this point,
 1.2. Direction Fields: Graphical Representation of the ODE and its Solution Section Objective(s): Constructing Direction Fields. Interpreting Direction Fields. Definition 1.2.1. A first order ODE of the
1.2. Direction Fields: Graphical Representation of the ODE and its Solution Section Objective(s): Constructing Direction Fields. Interpreting Direction Fields. Definition 1.2.1. A first order ODE of the
Section 14.1 Vector Functions and Space Curves
 Section 14.1 Vector Functions and Space Curves Functions whose range does not consists of numbers A bulk of elementary mathematics involves the study of functions - rules that assign to a given input a
Section 14.1 Vector Functions and Space Curves Functions whose range does not consists of numbers A bulk of elementary mathematics involves the study of functions - rules that assign to a given input a
Unit #16 : Differential Equations
 Unit #16 : Differential Equations Goals: To introduce the concept of a differential equation. Discuss the relationship between differential equations and slope fields. Discuss Euler s method for solving
Unit #16 : Differential Equations Goals: To introduce the concept of a differential equation. Discuss the relationship between differential equations and slope fields. Discuss Euler s method for solving
Math 131. The Derivative and the Tangent Line Problem Larson Section 2.1
 Math 131. The Derivative and the Tangent Line Problem Larson Section.1 From precalculus, the secant line through the two points (c, f(c)) and (c +, f(c + )) is given by m sec = rise f(c + ) f(c) f(c +
Math 131. The Derivative and the Tangent Line Problem Larson Section.1 From precalculus, the secant line through the two points (c, f(c)) and (c +, f(c + )) is given by m sec = rise f(c + ) f(c) f(c +
dt 2 The Order of a differential equation is the order of the highest derivative that occurs in the equation. Example The differential equation
 Lecture 18 : Direction Fields and Euler s Method A Differential Equation is an equation relating an unknown function and one or more of its derivatives. Examples Population growth : dp dp = kp, or = kp
Lecture 18 : Direction Fields and Euler s Method A Differential Equation is an equation relating an unknown function and one or more of its derivatives. Examples Population growth : dp dp = kp, or = kp
Math 2 Variable Manipulation Part 7 Absolute Value & Inequalities
 Math 2 Variable Manipulation Part 7 Absolute Value & Inequalities 1 MATH 1 REVIEW SOLVING AN ABSOLUTE VALUE EQUATION Absolute value is a measure of distance; how far a number is from zero. In practice,
Math 2 Variable Manipulation Part 7 Absolute Value & Inequalities 1 MATH 1 REVIEW SOLVING AN ABSOLUTE VALUE EQUATION Absolute value is a measure of distance; how far a number is from zero. In practice,
14.3 Partial Derivatives
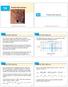 14 14.3 Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. On a hot day, extreme humidity makes us think the temperature is higher than it really is, whereas
14 14.3 Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. On a hot day, extreme humidity makes us think the temperature is higher than it really is, whereas
Section 4.2: The Mean Value Theorem
 Section 4.2: The Mean Value Theorem Before we continue with the problem of describing graphs using calculus we shall briefly pause to examine some interesting applications of the derivative. In previous
Section 4.2: The Mean Value Theorem Before we continue with the problem of describing graphs using calculus we shall briefly pause to examine some interesting applications of the derivative. In previous
APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION
 4 APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION 4.9 Antiderivatives In this section, we will learn about: Antiderivatives and how they are useful in solving certain scientific problems.
4 APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION 4.9 Antiderivatives In this section, we will learn about: Antiderivatives and how they are useful in solving certain scientific problems.
Algebra II: Strand 2. Linear Functions; Topic 2. Slope and Rate of Change; Task 2.2.1
 1 TASK 2.2.1: AVERAGE RATES OF CHANGE Solutions One of the ways in which we describe functions is by whether they are increasing, decreasing, or constant on an interval in their domain. If the graph of
1 TASK 2.2.1: AVERAGE RATES OF CHANGE Solutions One of the ways in which we describe functions is by whether they are increasing, decreasing, or constant on an interval in their domain. If the graph of
CONTROL POLYGONS FOR CUBIC CURVES
 On-Line Geometric Modeling Notes CONTROL POLYGONS FOR CUBIC CURVES Kenneth I. Joy Visualization and Graphics Research Group Department of Computer Science University of California, Davis Overview B-Spline
On-Line Geometric Modeling Notes CONTROL POLYGONS FOR CUBIC CURVES Kenneth I. Joy Visualization and Graphics Research Group Department of Computer Science University of California, Davis Overview B-Spline
0, otherwise. Find each of the following limits, or explain that the limit does not exist.
 Midterm Solutions 1, y x 4 1. Let f(x, y) = 1, y 0 0, otherwise. Find each of the following limits, or explain that the limit does not exist. (a) (b) (c) lim f(x, y) (x,y) (0,1) lim f(x, y) (x,y) (2,3)
Midterm Solutions 1, y x 4 1. Let f(x, y) = 1, y 0 0, otherwise. Find each of the following limits, or explain that the limit does not exist. (a) (b) (c) lim f(x, y) (x,y) (0,1) lim f(x, y) (x,y) (2,3)
Topics Covered in Math 115
 Topics Covered in Math 115 Basic Concepts Integer Exponents Use bases and exponents. Evaluate exponential expressions. Apply the product, quotient, and power rules. Polynomial Expressions Perform addition
Topics Covered in Math 115 Basic Concepts Integer Exponents Use bases and exponents. Evaluate exponential expressions. Apply the product, quotient, and power rules. Polynomial Expressions Perform addition
Numerical method for approximating the solution of an IVP. Euler Algorithm (the simplest approximation method)
 Section 2.7 Euler s Method (Computer Approximation) Key Terms/ Ideas: Numerical method for approximating the solution of an IVP Linear Approximation; Tangent Line Euler Algorithm (the simplest approximation
Section 2.7 Euler s Method (Computer Approximation) Key Terms/ Ideas: Numerical method for approximating the solution of an IVP Linear Approximation; Tangent Line Euler Algorithm (the simplest approximation
The geometry of least squares
 The geometry of least squares We can think of a vector as a point in space, where the elements of the vector are the coordinates of the point. Consider for example, the following vector s: t = ( 4, 0),
The geometry of least squares We can think of a vector as a point in space, where the elements of the vector are the coordinates of the point. Consider for example, the following vector s: t = ( 4, 0),
8.1 Supplement: Differential Equations and Slope Fields
 Math 131 -copyright Angela Allen, Spring 2008 1 8.1 Supplement: Differential Equations and Slope Fields Note: Several of these examples come from your textbook Calculus Concepts: An Applied Approach to
Math 131 -copyright Angela Allen, Spring 2008 1 8.1 Supplement: Differential Equations and Slope Fields Note: Several of these examples come from your textbook Calculus Concepts: An Applied Approach to
Exercises * on Functions
 Exercises * on Functions Laurenz Wiskott Institut für Neuroinformatik Ruhr-Universität Bochum, Germany, EU 2 February 2017 Contents 1 Scalar functions in one variable 3 1.1 Elementary transformations.....................................
Exercises * on Functions Laurenz Wiskott Institut für Neuroinformatik Ruhr-Universität Bochum, Germany, EU 2 February 2017 Contents 1 Scalar functions in one variable 3 1.1 Elementary transformations.....................................
Fundamentals. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 Fundamentals Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 1.2 Exponents and Radicals Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Integer Exponents Rules for Working with Exponents Scientific
Fundamentals Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 1.2 Exponents and Radicals Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Integer Exponents Rules for Working with Exponents Scientific
Approximations - the method of least squares (1)
 Approximations - the method of least squares () In many applications, we have to consider the following problem: Suppose that for some y, the equation Ax = y has no solutions It could be that this is an
Approximations - the method of least squares () In many applications, we have to consider the following problem: Suppose that for some y, the equation Ax = y has no solutions It could be that this is an
Sequences and Series
 Sequences and Series What do you think of when you read the title of our next unit? In case your answers are leading us off track, let's review the following IB problems. 1 November 2013 HL 2 3 November
Sequences and Series What do you think of when you read the title of our next unit? In case your answers are leading us off track, let's review the following IB problems. 1 November 2013 HL 2 3 November
MAT 311 Midterm #1 Show your work! 1. The existence and uniqueness theorem says that, given a point (x 0, y 0 ) the ODE. y = (1 x 2 y 2 ) 1/3
 MAT 3 Midterm # Show your work!. The existence and uniqueness theorem says that, given a point (x 0, y 0 ) the ODE y = ( x 2 y 2 ) /3 has a unique (local) solution with initial condition y(x 0 ) = y 0
MAT 3 Midterm # Show your work!. The existence and uniqueness theorem says that, given a point (x 0, y 0 ) the ODE y = ( x 2 y 2 ) /3 has a unique (local) solution with initial condition y(x 0 ) = y 0
MAT01A1: Functions and Mathematical Models
 MAT01A1: Functions and Mathematical Models Dr Craig 21 February 2017 Introduction Who: Dr Craig What: Lecturer & course coordinator for MAT01A1 Where: C-Ring 508 acraig@uj.ac.za Web: http://andrewcraigmaths.wordpress.com
MAT01A1: Functions and Mathematical Models Dr Craig 21 February 2017 Introduction Who: Dr Craig What: Lecturer & course coordinator for MAT01A1 Where: C-Ring 508 acraig@uj.ac.za Web: http://andrewcraigmaths.wordpress.com
15.5. Applications of Double Integrals. Density and Mass. Density and Mass. Density and Mass. Density and Mass. Multiple Integrals
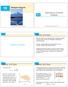 15 Multiple Integrals 15.5 Applications of Double Integrals Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. We were able to use single integrals to compute
15 Multiple Integrals 15.5 Applications of Double Integrals Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. We were able to use single integrals to compute
Taylor and Maclaurin Series. Approximating functions using Polynomials.
 Taylor and Maclaurin Series Approximating functions using Polynomials. Approximating f x = e x near x = 0 In order to approximate the function f x = e x near x = 0, we can use the tangent line (The Linear
Taylor and Maclaurin Series Approximating functions using Polynomials. Approximating f x = e x near x = 0 In order to approximate the function f x = e x near x = 0, we can use the tangent line (The Linear
Student Study Session Topic: Interpreting Graphs
 Student Study Session Topic: Interpreting Graphs Starting with the graph of a function or its derivative, you may be asked all kinds of questions without having (or needing) and equation to work with.
Student Study Session Topic: Interpreting Graphs Starting with the graph of a function or its derivative, you may be asked all kinds of questions without having (or needing) and equation to work with.
DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
 DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Chapter 1 Introduction and Basic Terminology Most of the phenomena studied in the sciences and engineering involve processes that change with time. For example, it is well known
DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Chapter 1 Introduction and Basic Terminology Most of the phenomena studied in the sciences and engineering involve processes that change with time. For example, it is well known
Exponential and Logarithmic Functions. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 3 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 3.1 Exponential Functions and Their Graphs Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn
3 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 3.1 Exponential Functions and Their Graphs Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn
Taylor and Maclaurin Series. Approximating functions using Polynomials.
 Taylor and Maclaurin Series Approximating functions using Polynomials. Approximating f x = e x near x = 0 In order to approximate the function f x = e x near x = 0, we can use the tangent line (The Linear
Taylor and Maclaurin Series Approximating functions using Polynomials. Approximating f x = e x near x = 0 In order to approximate the function f x = e x near x = 0, we can use the tangent line (The Linear
Period: Date: Lesson 3B: Properties of Dilations and Equations of lines
 Name: Period: Date: : Properties of Dilations and Equations of lines Learning Targets I can identify the properties of dilation mentioned as followed: dilation takes a line not passing through the center
Name: Period: Date: : Properties of Dilations and Equations of lines Learning Targets I can identify the properties of dilation mentioned as followed: dilation takes a line not passing through the center
1.3 Algebraic Expressions. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 1.3 Algebraic Expressions Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Adding and Subtracting Polynomials Multiplying Algebraic Expressions Special Product Formulas Factoring Common Factors
1.3 Algebraic Expressions Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Adding and Subtracting Polynomials Multiplying Algebraic Expressions Special Product Formulas Factoring Common Factors
Math 651 Introduction to Numerical Analysis I Fall SOLUTIONS: Homework Set 1
 ath 651 Introduction to Numerical Analysis I Fall 2010 SOLUTIONS: Homework Set 1 1. Consider the polynomial f(x) = x 2 x 2. (a) Find P 1 (x), P 2 (x) and P 3 (x) for f(x) about x 0 = 0. What is the relation
ath 651 Introduction to Numerical Analysis I Fall 2010 SOLUTIONS: Homework Set 1 1. Consider the polynomial f(x) = x 2 x 2. (a) Find P 1 (x), P 2 (x) and P 3 (x) for f(x) about x 0 = 0. What is the relation
2. Use the relationship between the probability of an event and and the probability of its complement.
 ACT NON NEGOTIABLE STANDARDS- TO BE TAUGHT: 1. Solve one-step equations having integer or decimal answers 2. Use the relationship between the probability of an event and and the probability of its complement.
ACT NON NEGOTIABLE STANDARDS- TO BE TAUGHT: 1. Solve one-step equations having integer or decimal answers 2. Use the relationship between the probability of an event and and the probability of its complement.
Sequences and Series. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 Sequences and Series Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 12.1 Sequences and Summation Notation Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Sequences Recursively Defined Sequences
Sequences and Series Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 12.1 Sequences and Summation Notation Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Sequences Recursively Defined Sequences
Chapter 6: The Definite Integral
 Name: Date: Period: AP Calc AB Mr. Mellina Chapter 6: The Definite Integral v v Sections: v 6.1 Estimating with Finite Sums v 6.5 Trapezoidal Rule v 6.2 Definite Integrals 6.3 Definite Integrals and Antiderivatives
Name: Date: Period: AP Calc AB Mr. Mellina Chapter 6: The Definite Integral v v Sections: v 6.1 Estimating with Finite Sums v 6.5 Trapezoidal Rule v 6.2 Definite Integrals 6.3 Definite Integrals and Antiderivatives
AP Calculus Worksheet: Chapter 2 Review Part I
 AP Calculus Worksheet: Chapter 2 Review Part I 1. Given y = f(x), what is the average rate of change of f on the interval [a, b]? What is the graphical interpretation of your answer? 2. The derivative
AP Calculus Worksheet: Chapter 2 Review Part I 1. Given y = f(x), what is the average rate of change of f on the interval [a, b]? What is the graphical interpretation of your answer? 2. The derivative
56 CHAPTER 3. POLYNOMIAL FUNCTIONS
 56 CHAPTER 3. POLYNOMIAL FUNCTIONS Chapter 4 Rational functions and inequalities 4.1 Rational functions Textbook section 4.7 4.1.1 Basic rational functions and asymptotes As a first step towards understanding
56 CHAPTER 3. POLYNOMIAL FUNCTIONS Chapter 4 Rational functions and inequalities 4.1 Rational functions Textbook section 4.7 4.1.1 Basic rational functions and asymptotes As a first step towards understanding
Polynomial and Rational Functions. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 2 Polynomial and Rational Functions Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 2.4 Complex Numbers Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn Use the imaginary unit i
2 Polynomial and Rational Functions Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 2.4 Complex Numbers Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn Use the imaginary unit i
ELEMENTARY NUMBER THEORY AND METHODS OF PROOF
 CHAPTER 4 ELEMENTARY NUMBER THEORY AND METHODS OF PROOF Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. SECTION 4.3 Direct Proof and Counterexample III: Divisibility Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights
CHAPTER 4 ELEMENTARY NUMBER THEORY AND METHODS OF PROOF Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. SECTION 4.3 Direct Proof and Counterexample III: Divisibility Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights
Note: Final Exam is at 10:45 on Tuesday, 5/3/11 (This is the Final Exam time reserved for our labs). From Practice Test I
 MA Practice Final Answers in Red 4/8/ and 4/9/ Name Note: Final Exam is at :45 on Tuesday, 5// (This is the Final Exam time reserved for our labs). From Practice Test I Consider the integral 5 x dx. Sketch
MA Practice Final Answers in Red 4/8/ and 4/9/ Name Note: Final Exam is at :45 on Tuesday, 5// (This is the Final Exam time reserved for our labs). From Practice Test I Consider the integral 5 x dx. Sketch
c n (x a) n c 0 c 1 (x a) c 2 (x a) 2...
 3 CHAPTER 6 SERIES SOLUTIONS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS 6. REVIEW OF POWER SERIES REVIEW MATERIAL Infinite series of constants, p-series, harmonic series, alternating harmonic series, geometric series, tests
3 CHAPTER 6 SERIES SOLUTIONS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS 6. REVIEW OF POWER SERIES REVIEW MATERIAL Infinite series of constants, p-series, harmonic series, alternating harmonic series, geometric series, tests
Solutions of Equations in One Variable. Newton s Method
 Solutions of Equations in One Variable Newton s Method Numerical Analysis (9th Edition) R L Burden & J D Faires Beamer Presentation Slides prepared by John Carroll Dublin City University c 2011 Brooks/Cole,
Solutions of Equations in One Variable Newton s Method Numerical Analysis (9th Edition) R L Burden & J D Faires Beamer Presentation Slides prepared by John Carroll Dublin City University c 2011 Brooks/Cole,
Chapter 6 Additional Topics in Trigonometry, Part II
 Chapter 6 Additional Topics in Trigonometry, Part II Section 3 Section 4 Section 5 Vectors in the Plane Vectors and Dot Products Trigonometric Form of a Complex Number Vocabulary Directed line segment
Chapter 6 Additional Topics in Trigonometry, Part II Section 3 Section 4 Section 5 Vectors in the Plane Vectors and Dot Products Trigonometric Form of a Complex Number Vocabulary Directed line segment
Math 225 Differential Equations Notes Chapter 1
 Math 225 Differential Equations Notes Chapter 1 Michael Muscedere September 9, 2004 1 Introduction 1.1 Background In science and engineering models are used to describe physical phenomena. Often these
Math 225 Differential Equations Notes Chapter 1 Michael Muscedere September 9, 2004 1 Introduction 1.1 Background In science and engineering models are used to describe physical phenomena. Often these
Introduction to systems of equations
 Introduction to systems of equations A system of equations is a collection of two or more equations that contains the same variables. This is a system of two equations with two variables: In solving a
Introduction to systems of equations A system of equations is a collection of two or more equations that contains the same variables. This is a system of two equations with two variables: In solving a
Parametric Equations and Polar Coordinates
 Parametric Equations and Polar Coordinates Parametrizations of Plane Curves In previous chapters, we have studied curves as the graphs of functions or equations involving the two variables x and y. Another
Parametric Equations and Polar Coordinates Parametrizations of Plane Curves In previous chapters, we have studied curves as the graphs of functions or equations involving the two variables x and y. Another
