Partial Derivatives for Math 229. Our puropose here is to explain how one computes partial derivatives. We will not attempt
|
|
|
- Marlene Doyle
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Partial Derivatives for Math 229 Our puropose here is to explain how one computes partial derivatives. We will not attempt to explain how they arise or why one would use them; that is left to other courses e.g., multivariate calculus or electromagnetism. Unlike the usual situation in first semester calculus, we start with a function of two or more variables. Two examples of such functions are fx, y = sinxy and gx, y, z = x 2 +xy 2 z 4xyz 2. For each variable there is a corresponding partial derivative. For example, for a function fx, y of the two variables x and y there are two partial derivatives partial derivatives are defined by and = lim fx + h, y fx, y h 0 h = lim h 0 fx, y + h fx, y. h and. Technically speaking these When it comes to computing such things, you need only remember the following: To compute the partial derivative with respect to a variable, you use the same derivative rules and formulas as usual while treating the other variables as constants. The following two examples should help show how one computes partial derivatives. Example 1: Set fx, y = sinxy. To compute the partial derivative we will use the chain rule, constant multiple rule, the formula for the derivative of the sine function and the formula for the derivative of a power. Setting u = xy for the chain rule and treating y as a constant, we have = sinxy = sin u = d sin u du y = cos u y replacing xy with u using the chain rule using a formula and the constant multiple rule = cosxy y replacing u with xy and using another formula. Compare this with how you would compute the derivative of sinπx. Hint: you would use the exact same steps! Example 2: Set gx, y, z = x 2 + xy 2 z 4xyz 2. To compute the partial derivative g we will use the sum/difference rule, constant multiple rule, the formula for the derivative of a constant, 1
2 and the formula for the derivative of a power. Treating both x and z as constants so x 2 and z 2 are constants, too, we have g = x 2 + xy 2 z 4xyz 2 = 2 + xy2 z 4xyz 2 = 0 + xz 2 4xz 2 using the sum/difference rule by formula and the constant multiple rule = 0 + xz 2y 4xz 2 1 by the power formula. Compare this with how you would compute the derivative of e 2 + ey 2 π 4eyπ 2. Just as with usual derivatives in first semester calculus, we have higher order partial derivatives as well. A big difference is that with partial derivatives there are several second derivatives instead of just one. For instance, if we start with a function fx, y of two variables, we have not one, but four ways to partially differentiate twice: 2 2 partially differentiate with respect to x twice, partially differentiate with respect to y twice, partially differentiate with respect to y then x, partially differentiate with respect to x then y. In a more expanded notation, 2 = / 2 = / = / = /. Example 3: Set fx, y = xye x 4x 2 cosx + y. We will compute the four second order 2
3 partial derivatives. First, using u for x + y in the chain rule we have = xye x 4x 2 cosx + y = xyex 4x 2 cosx + y = y xex 4 x 2 cosx + y = y x ex 2 cosx + y + ex 4 x + cosx + y 2 = yxe x + e x 4 x 2 cos u + cosx + y2x = yxe x + e x 4 x 2 d cos u x + y + cosx + y2x du = yxe x + e x 4 x 2 sin u + + cosx + y2x = yxe x + e x 4 x 2 sinx + y cosx + y2x = yxe x + e x + 4x 2 sinx + y 8x cosx + y. Remember we treat y as a constant here. Next = xye x 4x 2 cosx + y = xyex 4x 2 cosx + y Remember we treat x as a constant here. = xe x cosx + y 4x2 = xe x 4x 2 cos u = xe x 4x 2 d cos u x + y du = xe x 4x 2 sin u + = xe x + 4x 2 sinx + y0 + 1 = xe x + 4x 2 sinx + y. Before we compute the second order partial derivatives, we note from above that xe x dx = xe x + e x, and in an entirely similar fashion sinx + y cosx + y = cosx + y and = sinx + y, 3 sinx + y cosx + y = cosx + y. = sinx + y,
4 We have 2 = / = yxe x + e x + 4x 2 sinx + y 8x cosx + y = yxe x + e x + 4x 2 sinx + y 8x cosx + y = y xex + e x + 4 x 2 sinx + y 8 x cosx + y xe x = y + ex 2 sinx + y + 4 x + sinx + y 2 cosx + y 8 x + cosx + y = yxe x + e x + e x + 4x 2 cosx + y + sinx + y2x 8 x sinx + y + cosx + y = yxe x + 2e x + 4x 2 cosx + y + 16x sinx + y 8 cosx + y, using our formulas above. The next three are a little bit simpler: 2 = / = xe x + 4x 2 sinx + y = xex + 4x 2 sinx + y 2 sinx + y = 0 + 4x = 4x 2 cosx + y, = / = xe x + 4x 2 sinx + y = xex + 4x 2 sinx + y = xe x + e x + 4 x 2 sinx + y = xe x + e x 2 sinx + y + 4 x + sinx + y 2 = xe x + e x + 4 x 2 cosx + y + sinx + y2x = xe x + e x + 4x 2 cosx + y + 8x sinx + y, 4
5 and = / = yxe x + e x + 4x 2 sinx + y 8x cosx + y = yxe x + e x + 4x 2 sinx + y 8x cosx + y = xe x + e x sinx + y cosx + y + 4x2 8x = xe x + e x + 4x 2 cosx + y + 8x sinx + y. Notice how the two mixed partials 2 f and 2 f are equal. According to Clairaut s Theorem, this will always be the case when these two mixed partial derivatives are continuous. Any functions you come across in this class will be this way, so you can just assume that 2 f = 2 f. Exercises Find the first partial derivatives of the given function. 1. fx, y = y 5 3xy 2. fx, y = x 4 y 2 + 9x 2 y 3. gx, y = tanxy 2 4. hx, y = x2 +3y x+y 2 5. hx, y, z = x lny + z 2 + e xyz Find all of the second partial derivatives of the given function. 6. gx, y = xy x y 7. hx, y, z = xyz + xy 2 z 3 Verify the conclusion of Clairaut s Theorem, i.e., show that the two mixed partial derivatives are equal, for the following functions. 8. fx, y = e xy sin y 9. gx, y = tan 1 yx 2 + y 2 5
13 Implicit Differentiation
 - 13 Implicit Differentiation This sections highlights the difference between explicit and implicit expressions, and focuses on the differentiation of the latter, which can be a very useful tool in mathematics.
- 13 Implicit Differentiation This sections highlights the difference between explicit and implicit expressions, and focuses on the differentiation of the latter, which can be a very useful tool in mathematics.
Section 5.5 More Integration Formula (The Substitution Method) 2 Lectures. Dr. Abdulla Eid. College of Science. MATHS 101: Calculus I
 Section 5.5 More Integration Formula (The Substitution Method) 2 Lectures College of Science MATHS : Calculus I (University of Bahrain) Integrals / 7 The Substitution Method Idea: To replace a relatively
Section 5.5 More Integration Formula (The Substitution Method) 2 Lectures College of Science MATHS : Calculus I (University of Bahrain) Integrals / 7 The Substitution Method Idea: To replace a relatively
Integration by Parts
 Calculus 2 Lia Vas Integration by Parts Using integration by parts one transforms an integral of a product of two functions into a simpler integral. Divide the initial function into two parts called u
Calculus 2 Lia Vas Integration by Parts Using integration by parts one transforms an integral of a product of two functions into a simpler integral. Divide the initial function into two parts called u
Math 222 Spring 2013 Exam 3 Review Problem Answers
 . (a) By the Chain ule, Math Spring 3 Exam 3 eview Problem Answers w s w x x s + w y y s (y xy)() + (xy x )( ) (( s + 4t) (s 3t)( s + 4t)) ((s 3t)( s + 4t) (s 3t) ) 8s 94st + 3t (b) By the Chain ule, w
. (a) By the Chain ule, Math Spring 3 Exam 3 eview Problem Answers w s w x x s + w y y s (y xy)() + (xy x )( ) (( s + 4t) (s 3t)( s + 4t)) ((s 3t)( s + 4t) (s 3t) ) 8s 94st + 3t (b) By the Chain ule, w
c) xy 3 = cos(7x +5y), y 0 = y3 + 7 sin(7x +5y) 3xy sin(7x +5y) d) xe y = sin(xy), y 0 = ey + y cos(xy) x(e y cos(xy)) e) y = x ln(3x + 5), y 0
 Some Math 35 review problems With answers 2/6/2005 The following problems are based heavily on problems written by Professor Stephen Greenfield for his Math 35 class in spring 2005. His willingness to
Some Math 35 review problems With answers 2/6/2005 The following problems are based heavily on problems written by Professor Stephen Greenfield for his Math 35 class in spring 2005. His willingness to
Solutions to Exam 2, Math 10560
 Solutions to Exam, Math 6. Which of the following expressions gives the partial fraction decomposition of the function x + x + f(x = (x (x (x +? Solution: Notice that (x is not an irreducile factor. If
Solutions to Exam, Math 6. Which of the following expressions gives the partial fraction decomposition of the function x + x + f(x = (x (x (x +? Solution: Notice that (x is not an irreducile factor. If
Section 10.7 Taylor series
 Section 10.7 Taylor series 1. Common Maclaurin series 2. s and approximations with Taylor polynomials 3. Multiplication and division of power series Math 126 Enhanced 10.7 Taylor Series The University
Section 10.7 Taylor series 1. Common Maclaurin series 2. s and approximations with Taylor polynomials 3. Multiplication and division of power series Math 126 Enhanced 10.7 Taylor Series The University
Section 5.6. Integration By Parts. MATH 126 (Section 5.6) Integration By Parts The University of Kansas 1 / 10
 Section 5.6 Integration By Parts MATH 126 (Section 5.6) Integration By Parts The University of Kansas 1 / 10 Integration By Parts Manipulating the Product Rule d dx (f (x) g(x)) = f (x) g (x) + f (x) g(x)
Section 5.6 Integration By Parts MATH 126 (Section 5.6) Integration By Parts The University of Kansas 1 / 10 Integration By Parts Manipulating the Product Rule d dx (f (x) g(x)) = f (x) g (x) + f (x) g(x)
Math 106 Fall 2014 Exam 2.1 October 31, ln(x) x 3 dx = 1. 2 x 2 ln(x) + = 1 2 x 2 ln(x) + 1. = 1 2 x 2 ln(x) 1 4 x 2 + C
 Math 6 Fall 4 Exam. October 3, 4. The following questions have to do with the integral (a) Evaluate dx. Use integration by parts (x 3 dx = ) ( dx = ) x3 x dx = x x () dx = x + x x dx = x + x 3 dx dx =
Math 6 Fall 4 Exam. October 3, 4. The following questions have to do with the integral (a) Evaluate dx. Use integration by parts (x 3 dx = ) ( dx = ) x3 x dx = x x () dx = x + x x dx = x + x 3 dx dx =
Section 3.6 The chain rule 1 Lecture. Dr. Abdulla Eid. College of Science. MATHS 101: Calculus I
 Section 3.6 The chain rule 1 Lecture College of Science MATHS 101: Calculus I (University of Bahrain) Logarithmic Differentiation 1 / 23 Motivation Goal: We want to derive rules to find the derivative
Section 3.6 The chain rule 1 Lecture College of Science MATHS 101: Calculus I (University of Bahrain) Logarithmic Differentiation 1 / 23 Motivation Goal: We want to derive rules to find the derivative
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON. A foreign language dictionary (paper version) is permitted provided it contains no notes, additions or annotations.
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON MATH055W SEMESTER EXAMINATION 03/4 MATHEMATICS FOR ELECTRONIC & ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Duration: 0 min Solutions Only University approved calculators may be used. A foreign language
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON MATH055W SEMESTER EXAMINATION 03/4 MATHEMATICS FOR ELECTRONIC & ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Duration: 0 min Solutions Only University approved calculators may be used. A foreign language
Math 226 Calculus Spring 2016 Practice Exam 1. (1) (10 Points) Let the differentiable function y = f(x) have inverse function x = f 1 (y).
 Math 6 Calculus Spring 016 Practice Exam 1 1) 10 Points) Let the differentiable function y = fx) have inverse function x = f 1 y). a) Write down the formula relating the derivatives f x) and f 1 ) y).
Math 6 Calculus Spring 016 Practice Exam 1 1) 10 Points) Let the differentiable function y = fx) have inverse function x = f 1 y). a) Write down the formula relating the derivatives f x) and f 1 ) y).
Section 3.6 The chain rule 1 Lecture. Dr. Abdulla Eid. College of Science. MATHS 101: Calculus I
 Section 3.6 The chain rule 1 Lecture College of Science MATHS 101: Calculus I (University of Bahrain) Logarithmic Differentiation 1 / 1 Motivation Goal: We want to derive rules to find the derivative of
Section 3.6 The chain rule 1 Lecture College of Science MATHS 101: Calculus I (University of Bahrain) Logarithmic Differentiation 1 / 1 Motivation Goal: We want to derive rules to find the derivative of
23. Implicit differentiation
 23. 23.1. The equation y = x 2 + 3x + 1 expresses a relationship between the quantities x and y. If a value of x is given, then a corresponding value of y is determined. For instance, if x = 1, then y
23. 23.1. The equation y = x 2 + 3x + 1 expresses a relationship between the quantities x and y. If a value of x is given, then a corresponding value of y is determined. For instance, if x = 1, then y
LECTURE 11 - PARTIAL DIFFERENTIATION
 LECTURE 11 - PARTIAL DIFFERENTIATION CHRIS JOHNSON Abstract Partial differentiation is a natural generalization of the differentiation of a function of a single variable that you are familiar with 1 Introduction
LECTURE 11 - PARTIAL DIFFERENTIATION CHRIS JOHNSON Abstract Partial differentiation is a natural generalization of the differentiation of a function of a single variable that you are familiar with 1 Introduction
Math 212-Lecture 8. The chain rule with one independent variable
 Math 212-Lecture 8 137: The multivariable chain rule The chain rule with one independent variable w = f(x, y) If the particle is moving along a curve x = x(t), y = y(t), then the values that the particle
Math 212-Lecture 8 137: The multivariable chain rule The chain rule with one independent variable w = f(x, y) If the particle is moving along a curve x = x(t), y = y(t), then the values that the particle
Chapter 5: Integrals
 Chapter 5: Integrals Section 5.3 The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Sec. 5.3: The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Fundamental Theorem of Calculus: Sec. 5.3: The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Fundamental
Chapter 5: Integrals Section 5.3 The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Sec. 5.3: The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Fundamental Theorem of Calculus: Sec. 5.3: The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Fundamental
Math 250 Skills Assessment Test
 Math 5 Skills Assessment Test Page Math 5 Skills Assessment Test The purpose of this test is purely diagnostic (before beginning your review, it will be helpful to assess both strengths and weaknesses).
Math 5 Skills Assessment Test Page Math 5 Skills Assessment Test The purpose of this test is purely diagnostic (before beginning your review, it will be helpful to assess both strengths and weaknesses).
JUST THE MATHS UNIT NUMBER PARTIAL DIFFERENTIATION 1 (Partial derivatives of the first order) A.J.Hobson
 JUST THE MATHS UNIT NUMBER 14.1 PARTIAL DIFFERENTIATION 1 (Partial derivatives of the first order) by A.J.Hobson 14.1.1 Functions of several variables 14.1.2 The definition of a partial derivative 14.1.3
JUST THE MATHS UNIT NUMBER 14.1 PARTIAL DIFFERENTIATION 1 (Partial derivatives of the first order) by A.J.Hobson 14.1.1 Functions of several variables 14.1.2 The definition of a partial derivative 14.1.3
Taylor and Maclaurin Series
 Taylor and Maclaurin Series MATH 211, Calculus II J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 2018 Background We have seen that some power series converge. When they do, we can think of them as
Taylor and Maclaurin Series MATH 211, Calculus II J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 2018 Background We have seen that some power series converge. When they do, we can think of them as
Math 2163, Practice Exam II, Solution
 Math 63, Practice Exam II, Solution. (a) f =< f s, f t >=< s e t, s e t >, an v v = , so D v f(, ) =< ()e, e > =< 4, 4 > = 4. (b) f =< xy 3, 3x y 4y 3 > an v =< cos π, sin π >=, so
Math 63, Practice Exam II, Solution. (a) f =< f s, f t >=< s e t, s e t >, an v v = , so D v f(, ) =< ()e, e > =< 4, 4 > = 4. (b) f =< xy 3, 3x y 4y 3 > an v =< cos π, sin π >=, so
Lecture 10. (2) Functions of two variables. Partial derivatives. Dan Nichols February 27, 2018
 Lecture 10 Partial derivatives Dan Nichols nichols@math.umass.edu MATH 233, Spring 2018 University of Massachusetts February 27, 2018 Last time: functions of two variables f(x, y) x and y are the independent
Lecture 10 Partial derivatives Dan Nichols nichols@math.umass.edu MATH 233, Spring 2018 University of Massachusetts February 27, 2018 Last time: functions of two variables f(x, y) x and y are the independent
3 Algebraic Methods. we can differentiate both sides implicitly to obtain a differential equation involving x and y:
 3 Algebraic Methods b The first appearance of the equation E Mc 2 in Einstein s handwritten notes. So far, the only general class of differential equations that we know how to solve are directly integrable
3 Algebraic Methods b The first appearance of the equation E Mc 2 in Einstein s handwritten notes. So far, the only general class of differential equations that we know how to solve are directly integrable
4 Partial Differentiation
 4 Partial Differentiation Many equations in engineering, physics and mathematics tie together more than two variables. For example Ohm s Law (V = IR) and the equation for an ideal gas, PV = nrt, which
4 Partial Differentiation Many equations in engineering, physics and mathematics tie together more than two variables. For example Ohm s Law (V = IR) and the equation for an ideal gas, PV = nrt, which
Math Practice Exam 3 - solutions
 Math 181 - Practice Exam 3 - solutions Problem 1 Consider the function h(x) = (9x 2 33x 25)e 3x+1. a) Find h (x). b) Find all values of x where h (x) is zero ( critical values ). c) Using the sign pattern
Math 181 - Practice Exam 3 - solutions Problem 1 Consider the function h(x) = (9x 2 33x 25)e 3x+1. a) Find h (x). b) Find all values of x where h (x) is zero ( critical values ). c) Using the sign pattern
Math 152 Take Home Test 1
 Math 5 Take Home Test Due Monday 5 th October (5 points) The following test will be done at home in order to ensure that it is a fair and representative reflection of your own ability in mathematics I
Math 5 Take Home Test Due Monday 5 th October (5 points) The following test will be done at home in order to ensure that it is a fair and representative reflection of your own ability in mathematics I
Math 113 (Calculus 2) Exam 4
 Math 3 (Calculus ) Exam 4 November 0 November, 009 Sections 0, 3 7 Name Student ID Section Instructor In some cases a series may be seen to converge or diverge for more than one reason. For such problems
Math 3 (Calculus ) Exam 4 November 0 November, 009 Sections 0, 3 7 Name Student ID Section Instructor In some cases a series may be seen to converge or diverge for more than one reason. For such problems
Practice Midterm 2 Math 2153
 Practice Midterm 2 Math 23. Decide if the following statements are TRUE or FALSE and circle your answer. You do NOT need to justify your answers. (a) ( point) If both partial derivatives f x and f y exist
Practice Midterm 2 Math 23. Decide if the following statements are TRUE or FALSE and circle your answer. You do NOT need to justify your answers. (a) ( point) If both partial derivatives f x and f y exist
2. Which of the following is an equation of the line tangent to the graph of f(x) = x 4 + 2x 2 at the point where
 AP Review Chapter Name: Date: Per: 1. The radius of a circle is decreasing at a constant rate of 0.1 centimeter per second. In terms of the circumference C, what is the rate of change of the area of the
AP Review Chapter Name: Date: Per: 1. The radius of a circle is decreasing at a constant rate of 0.1 centimeter per second. In terms of the circumference C, what is the rate of change of the area of the
This practice exam is intended to help you prepare for the final exam for MTH 142 Calculus II.
 MTH 142 Practice Exam Chapters 9-11 Calculus II With Analytic Geometry Fall 2011 - University of Rhode Island This practice exam is intended to help you prepare for the final exam for MTH 142 Calculus
MTH 142 Practice Exam Chapters 9-11 Calculus II With Analytic Geometry Fall 2011 - University of Rhode Island This practice exam is intended to help you prepare for the final exam for MTH 142 Calculus
3 Applications of partial differentiation
 Advanced Calculus Chapter 3 Applications of partial differentiation 37 3 Applications of partial differentiation 3.1 Stationary points Higher derivatives Let U R 2 and f : U R. The partial derivatives
Advanced Calculus Chapter 3 Applications of partial differentiation 37 3 Applications of partial differentiation 3.1 Stationary points Higher derivatives Let U R 2 and f : U R. The partial derivatives
Math 21a Partial Derivatives Fall, 2016
 Math 21a Partial Derivatives Fall, 2016 The solutions are available on our Canvas website (https://canvas.harvard.edu/courses/17064/). Choose Files > Koji s Section. What is the derivative? 1. For each
Math 21a Partial Derivatives Fall, 2016 The solutions are available on our Canvas website (https://canvas.harvard.edu/courses/17064/). Choose Files > Koji s Section. What is the derivative? 1. For each
VANDERBILT UNIVERSITY. MATH 2300 MULTIVARIABLE CALCULUS Practice Test 1 Solutions
 VANDERBILT UNIVERSITY MATH 2300 MULTIVARIABLE CALCULUS Practice Test 1 Solutions Directions. This practice test should be used as a study guide, illustrating the concepts that will be emphasized in the
VANDERBILT UNIVERSITY MATH 2300 MULTIVARIABLE CALCULUS Practice Test 1 Solutions Directions. This practice test should be used as a study guide, illustrating the concepts that will be emphasized in the
M152: Calculus II Midterm Exam Review
 M52: Calculus II Midterm Exam Review Chapter 4. 4.2 : Mean Value Theorem. - Know the statement and idea of Mean Value Theorem. - Know how to find values of c making the theorem true. - Realize the importance
M52: Calculus II Midterm Exam Review Chapter 4. 4.2 : Mean Value Theorem. - Know the statement and idea of Mean Value Theorem. - Know how to find values of c making the theorem true. - Realize the importance
MAS113 CALCULUS II SPRING 2008, QUIZ 5 SOLUTIONS. x 2 dx = 3y + y 3 = x 3 + c. It can be easily verified that the differential equation is exact, as
 MAS113 CALCULUS II SPRING 008, QUIZ 5 SOLUTIONS Quiz 5a Solutions (1) Solve the differential equation y = x 1 + y. (1 + y )y = x = (1 + y ) = x = 3y + y 3 = x 3 + c. () Solve the differential equation
MAS113 CALCULUS II SPRING 008, QUIZ 5 SOLUTIONS Quiz 5a Solutions (1) Solve the differential equation y = x 1 + y. (1 + y )y = x = (1 + y ) = x = 3y + y 3 = x 3 + c. () Solve the differential equation
Limits and Continuity/Partial Derivatives
 Christopher Croke University of Pennsylvania Limits and Continuity/Partial Derivatives Math 115 Limits For (x 0, y 0 ) an interior or a boundary point of the domain of a function f (x, y). Definition:
Christopher Croke University of Pennsylvania Limits and Continuity/Partial Derivatives Math 115 Limits For (x 0, y 0 ) an interior or a boundary point of the domain of a function f (x, y). Definition:
1. The graph of a function f is given above. Answer the question: a. Find the value(s) of x where f is not differentiable. Ans: x = 4, x = 3, x = 2,
 1. The graph of a function f is given above. Answer the question: a. Find the value(s) of x where f is not differentiable. x = 4, x = 3, x = 2, x = 1, x = 1, x = 2, x = 3, x = 4, x = 5 b. Find the value(s)
1. The graph of a function f is given above. Answer the question: a. Find the value(s) of x where f is not differentiable. x = 4, x = 3, x = 2, x = 1, x = 1, x = 2, x = 3, x = 4, x = 5 b. Find the value(s)
Section 4.8 Anti Derivative and Indefinite Integrals 2 Lectures. Dr. Abdulla Eid. College of Science. MATHS 101: Calculus I
 Section 4.8 Anti Derivative and Indefinite Integrals 2 Lectures College of Science MATHS 101: Calculus I (University of Bahrain) 1 / 28 Indefinite Integral Given a function f, if F is a function such that
Section 4.8 Anti Derivative and Indefinite Integrals 2 Lectures College of Science MATHS 101: Calculus I (University of Bahrain) 1 / 28 Indefinite Integral Given a function f, if F is a function such that
Math 180, Exam 2, Practice Fall 2009 Problem 1 Solution. f(x) = arcsin(2x + 1) = sin 1 (3x + 1), lnx
 Math 80, Exam, Practice Fall 009 Problem Solution. Differentiate the functions: (do not simplify) f(x) = x ln(x + ), f(x) = xe x f(x) = arcsin(x + ) = sin (3x + ), f(x) = e3x lnx Solution: For the first
Math 80, Exam, Practice Fall 009 Problem Solution. Differentiate the functions: (do not simplify) f(x) = x ln(x + ), f(x) = xe x f(x) = arcsin(x + ) = sin (3x + ), f(x) = e3x lnx Solution: For the first
1 Lecture 20: Implicit differentiation
 Lecture 20: Implicit ifferentiation. Outline The technique of implicit ifferentiation Tangent lines to a circle Derivatives of inverse functions by implicit ifferentiation Examples.2 Implicit ifferentiation
Lecture 20: Implicit ifferentiation. Outline The technique of implicit ifferentiation Tangent lines to a circle Derivatives of inverse functions by implicit ifferentiation Examples.2 Implicit ifferentiation
24. Partial Differentiation
 24. Partial Differentiation The derivative of a single variable function, d f(x), always assumes that the independent variable dx is increasing in the usual manner. Visually, the derivative s value at
24. Partial Differentiation The derivative of a single variable function, d f(x), always assumes that the independent variable dx is increasing in the usual manner. Visually, the derivative s value at
Lecture 7: Differential Equations
 Math 94 Professor: Padraic Bartlett Lecture 7: Differential Equations Week 7 UCSB 205 This is the seventh week of the Mathematics Subject Test GRE prep course; here, we review various techniques used to
Math 94 Professor: Padraic Bartlett Lecture 7: Differential Equations Week 7 UCSB 205 This is the seventh week of the Mathematics Subject Test GRE prep course; here, we review various techniques used to
February 21 Math 1190 sec. 63 Spring 2017
 February 21 Math 1190 sec. 63 Spring 2017 Chapter 2: Derivatives Let s recall the efinitions an erivative rules we have so far: Let s assume that y = f (x) is a function with c in it s omain. The erivative
February 21 Math 1190 sec. 63 Spring 2017 Chapter 2: Derivatives Let s recall the efinitions an erivative rules we have so far: Let s assume that y = f (x) is a function with c in it s omain. The erivative
Math 221 Exam II Tuesday Mar 23 5:30-7:00 PM Answers
 Math 221 Exam II Tuesday Mar 23 5:30-7:00 PM Answers I. (25 points.) Find. Note: The book sometimes writes D xy for. (a) y = (x 2 x + 1) 7 Answer: Let u = x 2 x + 1. Then y = (x 2 x + 1) 7 = u 7 so = d
Math 221 Exam II Tuesday Mar 23 5:30-7:00 PM Answers I. (25 points.) Find. Note: The book sometimes writes D xy for. (a) y = (x 2 x + 1) 7 Answer: Let u = x 2 x + 1. Then y = (x 2 x + 1) 7 = u 7 so = d
Assignment # 7, Math 370, Fall 2018 SOLUTIONS: y = e x. y = e 3x + 4xe 3x. y = e x cosx.
 Assignment # 7, Math 370, Fall 2018 SOLUTIONS: Problem 1: Solve the equations (a) y 8y + 7y = 0, (i) y(0) = 1, y (0) = 1. Characteristic equation: α 2 8α+7 = 0, = 64 28 = 36 so α 1,2 = (8 ±6)/2 and α 1
Assignment # 7, Math 370, Fall 2018 SOLUTIONS: Problem 1: Solve the equations (a) y 8y + 7y = 0, (i) y(0) = 1, y (0) = 1. Characteristic equation: α 2 8α+7 = 0, = 64 28 = 36 so α 1,2 = (8 ±6)/2 and α 1
8.7 Taylor s Inequality Math 2300 Section 005 Calculus II. f(x) = ln(1 + x) f(0) = 0
 8.7 Taylor s Inequality Math 00 Section 005 Calculus II Name: ANSWER KEY Taylor s Inequality: If f (n+) is continuous and f (n+) < M between the center a and some point x, then f(x) T n (x) M x a n+ (n
8.7 Taylor s Inequality Math 00 Section 005 Calculus II Name: ANSWER KEY Taylor s Inequality: If f (n+) is continuous and f (n+) < M between the center a and some point x, then f(x) T n (x) M x a n+ (n
UNIT 3: DERIVATIVES STUDY GUIDE
 Calculus I UNIT 3: Derivatives REVIEW Name: Date: UNIT 3: DERIVATIVES STUDY GUIDE Section 1: Section 2: Limit Definition (Derivative as the Slope of the Tangent Line) Calculating Rates of Change (Average
Calculus I UNIT 3: Derivatives REVIEW Name: Date: UNIT 3: DERIVATIVES STUDY GUIDE Section 1: Section 2: Limit Definition (Derivative as the Slope of the Tangent Line) Calculating Rates of Change (Average
Chain Rule. MATH 311, Calculus III. J. Robert Buchanan. Spring Department of Mathematics
 3.33pt Chain Rule MATH 311, Calculus III J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 2019 Single Variable Chain Rule Suppose y = g(x) and z = f (y) then dz dx = d (f (g(x))) dx = f (g(x))g (x)
3.33pt Chain Rule MATH 311, Calculus III J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 2019 Single Variable Chain Rule Suppose y = g(x) and z = f (y) then dz dx = d (f (g(x))) dx = f (g(x))g (x)
Graphs of Antiderivatives, Substitution Integrals
 Unit #10 : Graphs of Antiderivatives, Substitution Integrals Goals: Relationship between the graph of f(x) and its anti-derivative F (x) The guess-and-check method for anti-differentiation. The substitution
Unit #10 : Graphs of Antiderivatives, Substitution Integrals Goals: Relationship between the graph of f(x) and its anti-derivative F (x) The guess-and-check method for anti-differentiation. The substitution
Week 1: need to know. November 14, / 20
 Week 1: need to know How to find domains and ranges, operations on functions (addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, composition), behaviors of functions (even/odd/ increasing/decreasing), library
Week 1: need to know How to find domains and ranges, operations on functions (addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, composition), behaviors of functions (even/odd/ increasing/decreasing), library
PARTIAL DIFFERENTIATION
 PARTIAL DIFFERENTIATION CALCULUS 13 INU0115/515 (MATHS 2) Dr Adrian Jannetta MIMA CMath FRAS Partial Differentiation 1/ 15 Adrian Jannetta Functions of many variables The functions and derivatives which
PARTIAL DIFFERENTIATION CALCULUS 13 INU0115/515 (MATHS 2) Dr Adrian Jannetta MIMA CMath FRAS Partial Differentiation 1/ 15 Adrian Jannetta Functions of many variables The functions and derivatives which
If y = f (u) is a differentiable function of u and u = g(x) is a differentiable function of x then dy dx = dy. du du. If y = f (u) then y = f (u) u
 Section 3 4B The Chain Rule If y = f (u) is a differentiable function of u and u = g(x) is a differentiable function of x then dy dx = dy du du dx or If y = f (u) then f (u) u The Chain Rule with the Power
Section 3 4B The Chain Rule If y = f (u) is a differentiable function of u and u = g(x) is a differentiable function of x then dy dx = dy du du dx or If y = f (u) then f (u) u The Chain Rule with the Power
Solutions to Exam 1, Math Solution. Because f(x) is one-to-one, we know the inverse function exists. Recall that (f 1 ) (a) =
 Solutions to Exam, Math 56 The function f(x) e x + x 3 + x is one-to-one (there is no need to check this) What is (f ) ( + e )? Solution Because f(x) is one-to-one, we know the inverse function exists
Solutions to Exam, Math 56 The function f(x) e x + x 3 + x is one-to-one (there is no need to check this) What is (f ) ( + e )? Solution Because f(x) is one-to-one, we know the inverse function exists
MATH 1241 Common Final Exam Fall 2010
 MATH 1241 Common Final Exam Fall 2010 Please print the following information: Name: Instructor: Student ID: Section/Time: The MATH 1241 Final Exam consists of three parts. You have three hours for the
MATH 1241 Common Final Exam Fall 2010 Please print the following information: Name: Instructor: Student ID: Section/Time: The MATH 1241 Final Exam consists of three parts. You have three hours for the
JUST THE MATHS UNIT NUMBER ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS 1 (First order equations (A)) A.J.Hobson
 JUST THE MATHS UNIT NUMBER 5. ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS (First order equations (A)) by A.J.Hobson 5.. Introduction and definitions 5..2 Exact equations 5..3 The method of separation of the variables
JUST THE MATHS UNIT NUMBER 5. ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS (First order equations (A)) by A.J.Hobson 5.. Introduction and definitions 5..2 Exact equations 5..3 The method of separation of the variables
February 11, 2019 LECTURE 5: THE RULES OF DIFFERENTIATION.
 February 11, 2019 LECTURE 5: THE RULES OF DIFFERENTIATION 110211 HONORS MULTIVARIABLE CALCULUS PROFESSOR RICHARD BROWN Synopsis Here, we bring back the rules for differentiation used to derive new functions
February 11, 2019 LECTURE 5: THE RULES OF DIFFERENTIATION 110211 HONORS MULTIVARIABLE CALCULUS PROFESSOR RICHARD BROWN Synopsis Here, we bring back the rules for differentiation used to derive new functions
A = (a + 1) 2 = a 2 + 2a + 1
 A = (a + 1) 2 = a 2 + 2a + 1 1 A = ( (a + b) + 1 ) 2 = (a + b) 2 + 2(a + b) + 1 = a 2 + 2ab + b 2 + 2a + 2b + 1 A = ( (a + b) + 1 ) 2 = (a + b) 2 + 2(a + b) + 1 = a 2 + 2ab + b 2 + 2a + 2b + 1 3 A = (
A = (a + 1) 2 = a 2 + 2a + 1 1 A = ( (a + b) + 1 ) 2 = (a + b) 2 + 2(a + b) + 1 = a 2 + 2ab + b 2 + 2a + 2b + 1 A = ( (a + b) + 1 ) 2 = (a + b) 2 + 2(a + b) + 1 = a 2 + 2ab + b 2 + 2a + 2b + 1 3 A = (
Problem # Max points possible Actual score Total 100
 MIDTERM 1-18.01 - FALL 2014. Name: Email: Please put a check by your recitation section. Instructor Time B.Yang MW 10 M. Hoyois MW 11 M. Hoyois MW 12 X. Sun MW 1 R. Chang MW 2 Problem # Max points possible
MIDTERM 1-18.01 - FALL 2014. Name: Email: Please put a check by your recitation section. Instructor Time B.Yang MW 10 M. Hoyois MW 11 M. Hoyois MW 12 X. Sun MW 1 R. Chang MW 2 Problem # Max points possible
Exam 2 Review Solutions
 Exam Review Solutions 1. True or False, an explain: (a) There exists a function f with continuous secon partial erivatives such that f x (x, y) = x + y f y = x y False. If the function has continuous secon
Exam Review Solutions 1. True or False, an explain: (a) There exists a function f with continuous secon partial erivatives such that f x (x, y) = x + y f y = x y False. If the function has continuous secon
If y = f (u) is a differentiable function of u and u = g(x) is a differentiable function of x then dy dx = dy. du du. If y = f (u) then y = f (u) u
 Section 3 4B Lecture The Chain Rule If y = f (u) is a differentiable function of u and u = g(x) is a differentiable function of x then dy dx = dy du du dx or If y = f (u) then y = f (u) u The Chain Rule
Section 3 4B Lecture The Chain Rule If y = f (u) is a differentiable function of u and u = g(x) is a differentiable function of x then dy dx = dy du du dx or If y = f (u) then y = f (u) u The Chain Rule
MATH 19520/51 Class 5
 MATH 19520/51 Class 5 Minh-Tam Trinh University of Chicago 2017-10-04 1 Definition of partial derivatives. 2 Geometry of partial derivatives. 3 Higher derivatives. 4 Definition of a partial differential
MATH 19520/51 Class 5 Minh-Tam Trinh University of Chicago 2017-10-04 1 Definition of partial derivatives. 2 Geometry of partial derivatives. 3 Higher derivatives. 4 Definition of a partial differential
MATH 1207 R02 MIDTERM EXAM 2 SOLUTION
 MATH 7 R MIDTERM EXAM SOLUTION FALL 6 - MOON Name: Write your answer neatly and show steps. Except calculators, any electronic devices including laptops and cell phones are not allowed. () (5 pts) Find
MATH 7 R MIDTERM EXAM SOLUTION FALL 6 - MOON Name: Write your answer neatly and show steps. Except calculators, any electronic devices including laptops and cell phones are not allowed. () (5 pts) Find
The Relation between the Integral and the Derivative Graphs. Unit #10 : Graphs of Antiderivatives, Substitution Integrals
 Graphs of Antiderivatives - Unit #0 : Graphs of Antiderivatives, Substitution Integrals Goals: Relationship between the graph of f(x) and its anti-derivative F (x) The guess-and-check method for anti-differentiation.
Graphs of Antiderivatives - Unit #0 : Graphs of Antiderivatives, Substitution Integrals Goals: Relationship between the graph of f(x) and its anti-derivative F (x) The guess-and-check method for anti-differentiation.
Chapter 5: Integrals
 Chapter 5: Integrals Section 5.5 The Substitution Rule (u-substitution) Sec. 5.5: The Substitution Rule We know how to find the derivative of any combination of functions Sum rule Difference rule Constant
Chapter 5: Integrals Section 5.5 The Substitution Rule (u-substitution) Sec. 5.5: The Substitution Rule We know how to find the derivative of any combination of functions Sum rule Difference rule Constant
Solutions to Second Midterm(pineapple)
 Math 125 Solutions to Second Midterm(pineapple) 1. Compute each of the derivatives below as indicated. 4 points (a) f(x) = 3x 8 5x 4 + 4x e 3. Solution: f (x) = 24x 7 20x + 4. Don t forget that e 3 is
Math 125 Solutions to Second Midterm(pineapple) 1. Compute each of the derivatives below as indicated. 4 points (a) f(x) = 3x 8 5x 4 + 4x e 3. Solution: f (x) = 24x 7 20x + 4. Don t forget that e 3 is
Spring 2015 Sample Final Exam
 Math 1151 Spring 2015 Sample Final Exam Final Exam on 4/30/14 Name (Print): Time Limit on Final: 105 Minutes Go on carmen.osu.edu to see where your final exam will be. NOTE: This exam is much longer than
Math 1151 Spring 2015 Sample Final Exam Final Exam on 4/30/14 Name (Print): Time Limit on Final: 105 Minutes Go on carmen.osu.edu to see where your final exam will be. NOTE: This exam is much longer than
The Chain Rule. Composition Review. Intuition. = 2(1.5) = 3 times faster than (X)avier.
 The Chain Rule In the previous section we ha to use a trig ientity to etermine the erivative of. h(x) = sin(2x). We can view h(x) as the composition of two functions. Let g(x) = 2x an f (x) = sin x. Then
The Chain Rule In the previous section we ha to use a trig ientity to etermine the erivative of. h(x) = sin(2x). We can view h(x) as the composition of two functions. Let g(x) = 2x an f (x) = sin x. Then
11.5. The Chain Rule. Introduction. Prerequisites. Learning Outcomes
 The Chain Rule 11.5 Introduction In this Section we will see how to obtain the derivative of a composite function (often referred to as a function of a function ). To do this we use the chain rule. This
The Chain Rule 11.5 Introduction In this Section we will see how to obtain the derivative of a composite function (often referred to as a function of a function ). To do this we use the chain rule. This
Math 227 Sample Final Examination 1. Name (print) Name (sign) Bing ID number
 Math 227 Sample Final Examination 1 Name (print) Name (sign) Bing ID number (Your instructor may check your ID during or after the test) No books, notes, or electronic devices (calculators, cell phones,
Math 227 Sample Final Examination 1 Name (print) Name (sign) Bing ID number (Your instructor may check your ID during or after the test) No books, notes, or electronic devices (calculators, cell phones,
Puzzle 1 Puzzle 2 Puzzle 3 Puzzle 4 Puzzle 5 /10 /10 /10 /10 /10
 MATH-65 Puzzle Collection 6 Nov 8 :pm-:pm Name:... 3 :pm Wumaier :pm Njus 5 :pm Wumaier 6 :pm Njus 7 :pm Wumaier 8 :pm Njus This puzzle collection is closed book and closed notes. NO calculators are allowed
MATH-65 Puzzle Collection 6 Nov 8 :pm-:pm Name:... 3 :pm Wumaier :pm Njus 5 :pm Wumaier 6 :pm Njus 7 :pm Wumaier 8 :pm Njus This puzzle collection is closed book and closed notes. NO calculators are allowed
MATH 1231 MATHEMATICS 1B CALCULUS. Section 5: - Power Series and Taylor Series.
 MATH 1231 MATHEMATICS 1B CALCULUS. Section 5: - Power Series and Taylor Series. The objective of this section is to become familiar with the theory and application of power series and Taylor series. By
MATH 1231 MATHEMATICS 1B CALCULUS. Section 5: - Power Series and Taylor Series. The objective of this section is to become familiar with the theory and application of power series and Taylor series. By
PRACTICE PROBLEMS FOR MIDTERM I
 Problem. Find the limits or explain why they do not exist (i) lim x,y 0 x +y 6 x 6 +y ; (ii) lim x,y,z 0 x 6 +y 6 +z 6 x +y +z. (iii) lim x,y 0 sin(x +y ) x +y Problem. PRACTICE PROBLEMS FOR MIDTERM I
Problem. Find the limits or explain why they do not exist (i) lim x,y 0 x +y 6 x 6 +y ; (ii) lim x,y,z 0 x 6 +y 6 +z 6 x +y +z. (iii) lim x,y 0 sin(x +y ) x +y Problem. PRACTICE PROBLEMS FOR MIDTERM I
Math 180, Final Exam, Fall 2012 Problem 1 Solution
 Math 80, Final Exam, Fall 0 Problem Solution. Find the derivatives of the following functions: (a) ln(ln(x)) (b) x 6 + sin(x) e x (c) tan(x ) + cot(x ) (a) We evaluate the derivative using the Chain Rule.
Math 80, Final Exam, Fall 0 Problem Solution. Find the derivatives of the following functions: (a) ln(ln(x)) (b) x 6 + sin(x) e x (c) tan(x ) + cot(x ) (a) We evaluate the derivative using the Chain Rule.
5.5. The Substitution Rule
 INTEGRALS 5 INTEGRALS 5.5 The Substitution Rule In this section, we will learn: To substitute a new variable in place of an existing expression in a function, making integration easier. INTRODUCTION Due
INTEGRALS 5 INTEGRALS 5.5 The Substitution Rule In this section, we will learn: To substitute a new variable in place of an existing expression in a function, making integration easier. INTRODUCTION Due
WeBWorK, Problems 2 and 3
 WeBWorK, Problems 2 and 3 7 dx 2. Evaluate x ln(6x) This can be done using integration by parts or substitution. (Most can not). However, it is much more easily done using substitution. This can be written
WeBWorK, Problems 2 and 3 7 dx 2. Evaluate x ln(6x) This can be done using integration by parts or substitution. (Most can not). However, it is much more easily done using substitution. This can be written
5.4 Variation of Parameters
 202 5.4 Variation of Parameters The method of variation of parameters applies to solve (1) a(x)y + b(x)y + c(x)y = f(x). Continuity of a, b, c and f is assumed, plus a(x) 0. The method is important because
202 5.4 Variation of Parameters The method of variation of parameters applies to solve (1) a(x)y + b(x)y + c(x)y = f(x). Continuity of a, b, c and f is assumed, plus a(x) 0. The method is important because
Math 265 (Butler) Practice Midterm III B (Solutions)
 Math 265 (Butler) Practice Midterm III B (Solutions). Set up (but do not evaluate) an integral for the surface area of the surface f(x, y) x 2 y y over the region x, y 4. We have that the surface are is
Math 265 (Butler) Practice Midterm III B (Solutions). Set up (but do not evaluate) an integral for the surface area of the surface f(x, y) x 2 y y over the region x, y 4. We have that the surface are is
Sec. 14.3: Partial Derivatives. All of the following are ways of representing the derivative. y dx
 Math 2204 Multivariable Calc Chapter 14: Partial Derivatives I. Review from math 1225 A. First Derivative Sec. 14.3: Partial Derivatives 1. Def n : The derivative of the function f with respect to the
Math 2204 Multivariable Calc Chapter 14: Partial Derivatives I. Review from math 1225 A. First Derivative Sec. 14.3: Partial Derivatives 1. Def n : The derivative of the function f with respect to the
Advanced Calculus Math 127B, Winter 2005 Solutions: Final. nx2 1 + n 2 x, g n(x) = n2 x
 . Define f n, g n : [, ] R by f n (x) = Advanced Calculus Math 27B, Winter 25 Solutions: Final nx2 + n 2 x, g n(x) = n2 x 2 + n 2 x. 2 Show that the sequences (f n ), (g n ) converge pointwise on [, ],
. Define f n, g n : [, ] R by f n (x) = Advanced Calculus Math 27B, Winter 25 Solutions: Final nx2 + n 2 x, g n(x) = n2 x 2 + n 2 x. 2 Show that the sequences (f n ), (g n ) converge pointwise on [, ],
Chapter 7: Techniques of Integration
 Chapter 7: Techniques of Integration MATH 206-01: Calculus II Department of Mathematics University of Louisville last corrected September 14, 2013 1 / 43 Chapter 7: Techniques of Integration 7.1. Integration
Chapter 7: Techniques of Integration MATH 206-01: Calculus II Department of Mathematics University of Louisville last corrected September 14, 2013 1 / 43 Chapter 7: Techniques of Integration 7.1. Integration
MATH 15a: Linear Algebra Exam 1, Solutions
 MATH 5a: Linear Algebra Exam, Solutions. Let T : R 3 R 4 be the linear transformation with T( e ) = 2 e + e 2 + 3 e 3 4 e 4, T( e 2 ) = e e 2 +2 e 3 +6 e 4, and T( e 3 ) = 4 e e 2 +7 e 3 +8 e 4. (a) (6
MATH 5a: Linear Algebra Exam, Solutions. Let T : R 3 R 4 be the linear transformation with T( e ) = 2 e + e 2 + 3 e 3 4 e 4, T( e 2 ) = e e 2 +2 e 3 +6 e 4, and T( e 3 ) = 4 e e 2 +7 e 3 +8 e 4. (a) (6
1.4 Techniques of Integration
 .4 Techniques of Integration Recall the following strategy for evaluating definite integrals, which arose from the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus (see Section.3). To calculate b a f(x) dx. Find a function
.4 Techniques of Integration Recall the following strategy for evaluating definite integrals, which arose from the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus (see Section.3). To calculate b a f(x) dx. Find a function
Math 321 Final Exam. 1. Do NOT write your answers on these sheets. Nothing written on the test papers will be graded.
 Math 31 Final Exam Instructions 1 Do NOT write your answers on these sheets Nothing written on the test papers will be graded Please begin each section of questions on a new sheet of paper 3 Do not write
Math 31 Final Exam Instructions 1 Do NOT write your answers on these sheets Nothing written on the test papers will be graded Please begin each section of questions on a new sheet of paper 3 Do not write
M GENERAL MATHEMATICS -2- Dr. Tariq A. AlFadhel 1 Solution of the First Mid-Term Exam First semester H
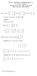 M - GENERAL MATHEMATICS -- Dr. Tariq A. AlFadhel Solution of the First Mid-Term Exam First semester 38-39 H 3 Q. Let A =, B = and C = 3 Compute (if possible) : A+B and BC A+B is impossible. ( ) BC = 3
M - GENERAL MATHEMATICS -- Dr. Tariq A. AlFadhel Solution of the First Mid-Term Exam First semester 38-39 H 3 Q. Let A =, B = and C = 3 Compute (if possible) : A+B and BC A+B is impossible. ( ) BC = 3
Campus Academic Resource Program Chain Rule
 This handout will: Provide a strategy to identify composite functions Provide a strategy to find chain rule by using a substitution method. Identifying Composite Functions This section will provide a strategy
This handout will: Provide a strategy to identify composite functions Provide a strategy to find chain rule by using a substitution method. Identifying Composite Functions This section will provide a strategy
Honors Calculus II [ ] Midterm II
![Honors Calculus II [ ] Midterm II Honors Calculus II [ ] Midterm II](/thumbs/90/103243723.jpg) Honors Calculus II [3-00] Midterm II PRINT NAME: SOLUTIONS Q]...[0 points] Evaluate the following expressions and its. Since you don t have a calculator, square roots, fractions etc. are allowed in your
Honors Calculus II [3-00] Midterm II PRINT NAME: SOLUTIONS Q]...[0 points] Evaluate the following expressions and its. Since you don t have a calculator, square roots, fractions etc. are allowed in your
Even and odd functions
 Connexions module: m15279 1 Even and odd functions Sunil Kumar Singh This work is produced by The Connexions Project and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License Even and odd functions are
Connexions module: m15279 1 Even and odd functions Sunil Kumar Singh This work is produced by The Connexions Project and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License Even and odd functions are
Summer 2017 MATH Solution to Exercise 5
 Summer 07 MATH00 Solution to Exercise 5. Find the partial derivatives of the following functions: (a (xy 5z/( + x, (b x/ x + y, (c arctan y/x, (d log((t + 3 + ts, (e sin(xy z 3, (f x α, x = (x,, x n. (a
Summer 07 MATH00 Solution to Exercise 5. Find the partial derivatives of the following functions: (a (xy 5z/( + x, (b x/ x + y, (c arctan y/x, (d log((t + 3 + ts, (e sin(xy z 3, (f x α, x = (x,, x n. (a
MATH 408N PRACTICE FINAL
 05/05/2012 Bormashenko MATH 408N PRACTICE FINAL Name: TA session: Show your work for all the problems. Good luck! (1) Calculate the following limits, using whatever tools are appropriate. State which results
05/05/2012 Bormashenko MATH 408N PRACTICE FINAL Name: TA session: Show your work for all the problems. Good luck! (1) Calculate the following limits, using whatever tools are appropriate. State which results
Math 221 Notes on Rolle s Theorem, The Mean Value Theorem, l Hôpital s rule, and the Taylor-Maclaurin formula. 1. Two theorems
 Math 221 Notes on Rolle s Theorem, The Mean Value Theorem, l Hôpital s rule, and the Taylor-Maclaurin formula 1. Two theorems Rolle s Theorem. If a function y = f(x) is differentiable for a x b and if
Math 221 Notes on Rolle s Theorem, The Mean Value Theorem, l Hôpital s rule, and the Taylor-Maclaurin formula 1. Two theorems Rolle s Theorem. If a function y = f(x) is differentiable for a x b and if
2.5 The Chain Rule Brian E. Veitch
 2.5 The Chain Rule This is our last ifferentiation rule for this course. It s also one of the most use. The best way to memorize this (along with the other rules) is just by practicing until you can o
2.5 The Chain Rule This is our last ifferentiation rule for this course. It s also one of the most use. The best way to memorize this (along with the other rules) is just by practicing until you can o
Chapter 8: Taylor s theorem and L Hospital s rule
 Chapter 8: Taylor s theorem and L Hospital s rule Theorem: [Inverse Mapping Theorem] Suppose that a < b and f : [a, b] R. Given that f (x) > 0 for all x (a, b) then f 1 is differentiable on (f(a), f(b))
Chapter 8: Taylor s theorem and L Hospital s rule Theorem: [Inverse Mapping Theorem] Suppose that a < b and f : [a, b] R. Given that f (x) > 0 for all x (a, b) then f 1 is differentiable on (f(a), f(b))
Solution to Review Problems for Midterm II
 Solution to Review Problems for Midterm II Midterm II: Monday, October 18 in class Topics: 31-3 (except 34) 1 Use te definition of derivative f f(x+) f(x) (x) lim 0 to find te derivative of te functions
Solution to Review Problems for Midterm II Midterm II: Monday, October 18 in class Topics: 31-3 (except 34) 1 Use te definition of derivative f f(x+) f(x) (x) lim 0 to find te derivative of te functions
Partial Derivatives October 2013
 Partial Derivatives 14.3 02 October 2013 Derivative in one variable. Recall for a function of one variable, f (a) = lim h 0 f (a + h) f (a) h slope f (a + h) f (a) h a a + h Partial derivatives. For a
Partial Derivatives 14.3 02 October 2013 Derivative in one variable. Recall for a function of one variable, f (a) = lim h 0 f (a + h) f (a) h slope f (a + h) f (a) h a a + h Partial derivatives. For a
Math 12 Final Exam Review 1
 Math 12 Final Exam Review 1 Part One Calculators are NOT PERMITTED for this part of the exam. 1. a) The sine of angle θ is 1 What are the 2 possible values of θ in the domain 0 θ 2π? 2 b) Draw these angles
Math 12 Final Exam Review 1 Part One Calculators are NOT PERMITTED for this part of the exam. 1. a) The sine of angle θ is 1 What are the 2 possible values of θ in the domain 0 θ 2π? 2 b) Draw these angles
Name Date Period. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 AB Fall Final Exam Review 200-20 Name Date Period MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Solve the problem. ) The position of a particle
AB Fall Final Exam Review 200-20 Name Date Period MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Solve the problem. ) The position of a particle
Final Exam 2011 Winter Term 2 Solutions
 . (a Find the radius of convergence of the series: ( k k+ x k. Solution: Using the Ratio Test, we get: L = lim a k+ a k = lim ( k+ k+ x k+ ( k k+ x k = lim x = x. Note that the series converges for L
. (a Find the radius of convergence of the series: ( k k+ x k. Solution: Using the Ratio Test, we get: L = lim a k+ a k = lim ( k+ k+ x k+ ( k k+ x k = lim x = x. Note that the series converges for L
Summary: Primer on Integral Calculus:
 Physics 2460 Electricity and Magnetism I, Fall 2006, Primer on Integration: Part I 1 Summary: Primer on Integral Calculus: Part I 1. Integrating over a single variable: Area under a curve Properties of
Physics 2460 Electricity and Magnetism I, Fall 2006, Primer on Integration: Part I 1 Summary: Primer on Integral Calculus: Part I 1. Integrating over a single variable: Area under a curve Properties of
MATH 255 Applied Honors Calculus III Winter Homework 5 Solutions
 MATH 255 Applied Honors Calculus III Winter 2011 Homework 5 Solutions Note: In what follows, numbers in parentheses indicate the problem numbers for users of the sixth edition. A * indicates that this
MATH 255 Applied Honors Calculus III Winter 2011 Homework 5 Solutions Note: In what follows, numbers in parentheses indicate the problem numbers for users of the sixth edition. A * indicates that this
Find the indicated derivative. 1) Find y(4) if y = 3 sin x. A) y(4) = 3 cos x B) y(4) = 3 sin x C) y(4) = - 3 cos x D) y(4) = - 3 sin x
 Assignment 5 Name Find the indicated derivative. ) Find y(4) if y = sin x. ) A) y(4) = cos x B) y(4) = sin x y(4) = - cos x y(4) = - sin x ) y = (csc x + cot x)(csc x - cot x) ) A) y = 0 B) y = y = - csc
Assignment 5 Name Find the indicated derivative. ) Find y(4) if y = sin x. ) A) y(4) = cos x B) y(4) = sin x y(4) = - cos x y(4) = - sin x ) y = (csc x + cot x)(csc x - cot x) ) A) y = 0 B) y = y = - csc
