PHYSICS: the study of matter and its motion through space and time, along with related concepts such as energy and force.
|
|
|
- Darren Greene
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Car materials: 2 toilet paper rolls 8 water bottle caps 2 straws masking tape 2 4-inch bamboo skewers 5 paper clips 10 toothpicks PHYSICS: the study of matter and its motion through space and time, along with related concepts such as energy and force.
2 MOTION Do Now: Be as still as possible. Even if you don't move a muscle you are still moving. Explain. ENDURING UNDERSTANDINGS * An object is in motion if its distance from a reference point is changing. * Speed is the distance traveled divided by the time traveled. V = d / t * Acceleration is the rate at which velocity changes.
3 RELATIVE MOTION * Relative Motion depends on your point of view. position change must be in relation to a reference point SPEED * Speed is the distance traveled divided by the time speed = distance / time s = d/t Speed video * Instantaneous speed is the rate an object is moving at a given instant in time.
4 5 GRAPHING MOTION February 11, 2014 * When graphing motion, time is on the x-axis and distance on the y-axis. * The faster the motion, the steeper the slope of the straight line. * Slope is calculated as the rise (distance on the y-axis) divided by run (distance on the x-axis). GRAPHING SPEED * A graph of speed shows separate line segments, each with a slope relating distance covered during that particular time period. * A horizontal line shows an object is not moving as time passes.
5 Velocity Velocity is speed in a given direction. It is calculated by dividing distance by time also. A measurement of velocity must include a direction in the units Example: Todd's speed was 5 m/s but his velocity was 5 m/s East
6 Try it... Sam rides his bike 4 miles to Sylvan s house. It takes him 20 minutes. What was Sam s average speed? S = V = 4 mi / 20 min V =.2 mi/min What is Sam s speed in miles per hour?.2 mi 60 min V = x = 12.0 mi/hr 1 min 1 hr S = If Sylvan rode to Sam s house averaging 15 mi/hr, how long would it take him to go the 4 miles?
7 D S T Resultant Velocity (Combined velocity) 2 m/s East 5 m/s West the train is moving 20 m/s East ( ) What is the resultant velocity of Mr. A and the train? What is the resultant velocity of Ms. B and the train? What is the resultant velocity of Mr. C and the train? How would you define resultant velocity?
8 PRACTICE PROBLEMS : 1. Calculate the speed of a dog running through a field if he is covering 23.7 meters in 54 seconds. 2. If a cross country runner covers a distance of 347 meters in 134 seconds what is her speed? 3. What is the speed of a baseball that travels 49 meters in 2.4 seconds? 4. Calculate the velocity of a car that travels 556 kilometers northeast in 3.4 hours. Leave your answer in kilometers per hour. Speed Graph Do Now: This is a graph showing a person walking through a park. Distance (in meters; moving North) What can you tell about this person motion and speed for each colored segment? time in second
9 ACCELERATION * Acceleration is any change in velocity * Acceleration can be a decrease in speed, increase in speed, or a change in direc CALCULATING ACCELERATION To determine acceleration, calculate the change in speed per unit of time or as in the following equation: Acceleration = final speed - initial speed time For example: a = = 5 m/s 2 20 m/s - 5 m/s 3 s
10 February 11, 2014
11
12 GRAPHING ACCELERATION Constant acceleration forms a straight line on a speed vs time graph. Constant acceleration forms a curve on a distance vs time graph
13
14 Do Now: What is the acceleration of a car that is speeding up from 20 m/s East to 25 m/s East in 2 seconds? What is the acceleration of a rocket that was moving at 100m/s then, after 10 seconds, it crashes? Acceleration Graph Do Now: what do you think this graph is showing? speed (in meters/sec) time in second
15 Do Now: On a blank piece of paper, copy the following questions and leave 2-4 lines after. DO NOT ANSWER THEM! What is motion? What is a reference point? What is speed? What are the units we measure distance in? What are the units we measure time in? How can you measure the speed of a toy car? What is acceleration? What are 3 ways something can accelerate? How can we find the acceleration of something? *What are the 4 states of matter? *How do the atoms differ in each state? *How is the periodic table organized? *What are the 3 main types of elements on the periodic table? *What is the law of conservation of mass? *What does this law have to do with balancing equations?
16 1 The change in position relative to a reference point is A B C D speed motion velocity car parts 2 What is an object that is used to determine if an object is in motion? A B C point of contact motion point reference point
17 3 What is the distance travelled in a certain amount of time known as? 4 What is the one factor that makes speed different from velocity?
18 5 the rate of change in velocity is 6 what are the three ways an object can accelerate?
19 7 what is the equation to determine an object's acceleration? 8 what are the 4 states of matter?
20 9 How do the atoms behave in each state of matter? 10 How is the periodic table organized?
21
Position, Speed and Velocity Position is a variable that gives your location relative to an origin. The origin is the place where position equals 0.
 Position, Speed and Velocity Position is a variable that gives your location relative to an origin. The origin is the place where position equals 0. The position of this car at 50 cm describes where the
Position, Speed and Velocity Position is a variable that gives your location relative to an origin. The origin is the place where position equals 0. The position of this car at 50 cm describes where the
MOTION, DISTANCE, AND DISPLACEMENT Q: What is motion? A: Motion is any change in the position or place of an object. is the study of motion (without
 MOTION, DISTANCE, AND DISPLACEMENT Q: What is motion? A: Motion is any change in the position or place of an object. is the study of motion (without considering the cause of the motion). Distance vs. Displacement
MOTION, DISTANCE, AND DISPLACEMENT Q: What is motion? A: Motion is any change in the position or place of an object. is the study of motion (without considering the cause of the motion). Distance vs. Displacement
Physical Science Chapter 11. Motion
 Physical Science Chapter 11 Motion Motion Definition An object is in motion when its distance from another object is changing. Relative Motion Relative motion is movement in relation to a REFERENCE POINT.
Physical Science Chapter 11 Motion Motion Definition An object is in motion when its distance from another object is changing. Relative Motion Relative motion is movement in relation to a REFERENCE POINT.
Forces and Motion Study Guide
 Forces and Motion Study Guide Name 8 th Grade PSI 1. A snail travels 10 m in 3000 seconds. What is the snail s average speed? a. 60000 m/s b. 0.02 m/s c. 600 m/s d. 0.003 m/s 2. A blimp travels at 3 m/s
Forces and Motion Study Guide Name 8 th Grade PSI 1. A snail travels 10 m in 3000 seconds. What is the snail s average speed? a. 60000 m/s b. 0.02 m/s c. 600 m/s d. 0.003 m/s 2. A blimp travels at 3 m/s
AP Physics 1 Summer Assignment (2014)
 Name: Date: AP Physics 1 Summer Assignment (2014) Instructions: 1. Read and study Chapter 2 Describing Motion: Kinematics in One Dimension. 2. Answer the questions below. 3. Submit your answers online
Name: Date: AP Physics 1 Summer Assignment (2014) Instructions: 1. Read and study Chapter 2 Describing Motion: Kinematics in One Dimension. 2. Answer the questions below. 3. Submit your answers online
Section Distance and displacment
 Chapter 11 Motion Section 11.1 Distance and displacment Choosing a Frame of Reference What is needed to describe motion completely? A frame of reference is a system of objects that are not moving with
Chapter 11 Motion Section 11.1 Distance and displacment Choosing a Frame of Reference What is needed to describe motion completely? A frame of reference is a system of objects that are not moving with
Kinematics 7 Solutions. 7.1 Represent and Reason a) The bike is moving at a constant velocity of 4 m/s towards the east
 Kinematics 7 Solutions 7.1 Represent and Reason a) The bike is moving at a constant velocity of 4 m/s towards the east b) For the same motion, a position versus time graph would be a straight line at a
Kinematics 7 Solutions 7.1 Represent and Reason a) The bike is moving at a constant velocity of 4 m/s towards the east b) For the same motion, a position versus time graph would be a straight line at a
Motion Unit Review 1. To create real-time graphs of an object s displacement versus time and velocity versus time, a student would need to use a
 Motion Unit Review 1. To create real-time graphs of an object s displacement versus time and velocity versus time, a student would need to use a A motion sensor.b low- g accelerometer. C potential difference
Motion Unit Review 1. To create real-time graphs of an object s displacement versus time and velocity versus time, a student would need to use a A motion sensor.b low- g accelerometer. C potential difference
Motion Chapter 3, Section 1: Distance, Displacement, Speed, Velocity
 3 Motion Chapter 3, Section 1: Distance, Displacement, Speed, Velocity Distance An important part of describing the motion of an object is to describe how far it has moved, which is distance. The SI unit
3 Motion Chapter 3, Section 1: Distance, Displacement, Speed, Velocity Distance An important part of describing the motion of an object is to describe how far it has moved, which is distance. The SI unit
Distance vs. Displacement, Speed vs. Velocity, Acceleration, Free-fall, Average vs. Instantaneous quantities, Motion diagrams, Motion graphs,
 Distance vs. Displacement, Speed vs. Velocity, Acceleration, Free-fall, Average vs. Instantaneous quantities, Motion diagrams, Motion graphs, Kinematic formulas. A Distance Tells how far an object is from
Distance vs. Displacement, Speed vs. Velocity, Acceleration, Free-fall, Average vs. Instantaneous quantities, Motion diagrams, Motion graphs, Kinematic formulas. A Distance Tells how far an object is from
Unit 2 mid term review
 Unit 2 mid term review Modified True/False Indicate whether the sentence or statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the sentence or statement true. 1. Motion
Unit 2 mid term review Modified True/False Indicate whether the sentence or statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the sentence or statement true. 1. Motion
Which car/s is/are undergoing an acceleration?
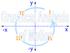 Which car/s is/are undergoing an acceleration? Which car experiences the greatest acceleration? Match a Graph Consider the position-time graphs below. Each one of the 3 lines on the position-time graph
Which car/s is/are undergoing an acceleration? Which car experiences the greatest acceleration? Match a Graph Consider the position-time graphs below. Each one of the 3 lines on the position-time graph
Motion and Forces study Guide
 Motion and Forces study Guide Completion Complete each statement. 1. The motion of an object looks different to observers in different. 2. The SI unit for measuring is the meter. 3. The direction and length
Motion and Forces study Guide Completion Complete each statement. 1. The motion of an object looks different to observers in different. 2. The SI unit for measuring is the meter. 3. The direction and length
Describing Mo tion. Speed and Velocity. What is speed?
 CHAPTER 1 LESSON 2 Describing Mo tion Speed and Velocity Key Concepts What is speed? How can you use a dis tance-time graph to calculate average speed? What are ways velocity can change? What do you think?
CHAPTER 1 LESSON 2 Describing Mo tion Speed and Velocity Key Concepts What is speed? How can you use a dis tance-time graph to calculate average speed? What are ways velocity can change? What do you think?
Introduction to Kinematics. Motion, Forces and Energy
 Introduction to Kinematics Motion, Forces and Energy Mechanics: The study of motion Kinematics The description of how things move 1-D and 2-D motion Dynamics The study of the forces that cause motion Newton
Introduction to Kinematics Motion, Forces and Energy Mechanics: The study of motion Kinematics The description of how things move 1-D and 2-D motion Dynamics The study of the forces that cause motion Newton
Problem: What affect does the force of launch have on the average speed of a straw rocket?
 Describing Motion and Measuring Speed A Straw Rocket Lab Background: An object is in motion when its distance from another object is changing. Whether an object is moving or not depends on your point of
Describing Motion and Measuring Speed A Straw Rocket Lab Background: An object is in motion when its distance from another object is changing. Whether an object is moving or not depends on your point of
MOTION. Chapter 2: Sections 1 and 2
 MOTION Chapter 2: Sections 1 and 2 Vocab: Ch 2.1-2.2 Distance Displacement Speed Average speed Instantaneous speed Velocity Acceleration Describing Motion Motion is an object s change in position relative
MOTION Chapter 2: Sections 1 and 2 Vocab: Ch 2.1-2.2 Distance Displacement Speed Average speed Instantaneous speed Velocity Acceleration Describing Motion Motion is an object s change in position relative
AP Physics 1- Kinematics Practice Problems (version 2)
 AP Physics 1- Kinematics Practice Problems (version 2) FACT: Kinematics is the branch of Newtonian mechanics concerned with the motion of objects without reference to the forces that cause the motion.
AP Physics 1- Kinematics Practice Problems (version 2) FACT: Kinematics is the branch of Newtonian mechanics concerned with the motion of objects without reference to the forces that cause the motion.
Describing Motion Verbally with Distance and Displacement
 Describing Motion Verbally with Distance and Displacement Read from Lesson 1 of the 1-D Kinematics chapter at The Physics Classroom: http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/1dkin/u1l1a.cfm http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/1dkin/u1l1b.cfm
Describing Motion Verbally with Distance and Displacement Read from Lesson 1 of the 1-D Kinematics chapter at The Physics Classroom: http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/1dkin/u1l1a.cfm http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/1dkin/u1l1b.cfm
Physics #1 - Motion Notebook
 Name Hour Group # Test Date Physics #1 - Motion Notebook Physics #1 - LEARNING Targets Physics #1 Vocabulary: You re The Scientist #1 Getting to Know a Physicist! You will research a physicist and create
Name Hour Group # Test Date Physics #1 - Motion Notebook Physics #1 - LEARNING Targets Physics #1 Vocabulary: You re The Scientist #1 Getting to Know a Physicist! You will research a physicist and create
The key difference between speed and velocity is the. object s motion, while velocity designates an object s speed plus the direction of its motion.
 Article retrieved from Brittanica, Retrieved 6/27/2016 Velocity Velocity has a scientific meaning that is slightly different from that of speed. Speed is the rate of an object s motion, while velocity
Article retrieved from Brittanica, Retrieved 6/27/2016 Velocity Velocity has a scientific meaning that is slightly different from that of speed. Speed is the rate of an object s motion, while velocity
Each dot represents an object moving, between constant intervals of time. Describe the motion that you see. equation symbol: units: Velocity
 What is displacement, velocity and acceleration? what units do they have? vector vs scalar? One dimensional motion, and graphing Moving man worksheet moving man doc - todo Introduction to simple graphing
What is displacement, velocity and acceleration? what units do they have? vector vs scalar? One dimensional motion, and graphing Moving man worksheet moving man doc - todo Introduction to simple graphing
FACT: Kinematics is the branch of Newtonian mechanics concerned with the motion of objects without reference to the forces that cause the motion.
 AP Physics 1- Kinematics Practice Problems FACT: Kinematics is the branch of Newtonian mechanics concerned with the motion of objects without reference to the forces that cause the motion. FACT: Displacement
AP Physics 1- Kinematics Practice Problems FACT: Kinematics is the branch of Newtonian mechanics concerned with the motion of objects without reference to the forces that cause the motion. FACT: Displacement
Speed. Change of Distance (in meters) Change of Time (in seconds) T 5 sec. Step 2: Formula D. 100m in 10sec. 200m in 10sec T.
 Speed Unit 6:1 Speed Speed is how fast something is moving. Precisely, it is how far an object travels in a certain amount of time. The standard metric units are meters per second (m/s), but any units
Speed Unit 6:1 Speed Speed is how fast something is moving. Precisely, it is how far an object travels in a certain amount of time. The standard metric units are meters per second (m/s), but any units
Fall 2008 RED Barcode Here Physics 105, sections 1 and 2 Please write your CID Colton
 Fall 008 RED Barcode Here Physics 105, sections 1 and Exam 1 Please write your CID Colton -3669 3 hour time limit. One 3 5 handwritten note card permitted (both sides). Calculators permitted. No books.
Fall 008 RED Barcode Here Physics 105, sections 1 and Exam 1 Please write your CID Colton -3669 3 hour time limit. One 3 5 handwritten note card permitted (both sides). Calculators permitted. No books.
Forces and Motion in One Dimension. Chapter 3
 Forces and Motion in One Dimension Chapter 3 Constant velocity on an x-versus-t graph Velocity and Position In general, the average velocity is the slope of the line segment that connects the positions
Forces and Motion in One Dimension Chapter 3 Constant velocity on an x-versus-t graph Velocity and Position In general, the average velocity is the slope of the line segment that connects the positions
Motion in One Dimension
 Motion in One Dimension Much of the physics we ll learn this semester will deal with the motion of objects We start with the simple case of one-dimensional motion Or, motion in x: As always, we begin by
Motion in One Dimension Much of the physics we ll learn this semester will deal with the motion of objects We start with the simple case of one-dimensional motion Or, motion in x: As always, we begin by
RECAP!! Paul is a safe driver who always drives the speed limit. Here is a record of his driving on a straight road. Time (s)
 RECAP!! What is uniform motion? > Motion in a straight line > Moving at a constant speed Yes or No? Yes or No? Paul is a safe driver who always drives the speed limit. Here is a record of his driving on
RECAP!! What is uniform motion? > Motion in a straight line > Moving at a constant speed Yes or No? Yes or No? Paul is a safe driver who always drives the speed limit. Here is a record of his driving on
Introduction to Kinematics. Motion, Forces and Energy
 Introduction to Kinematics Motion, Forces and Energy Mechanics: The study of motion Kinematics The description of how things move 1-D and 2-D motion Dynamics The study of the forces that cause motion Newton
Introduction to Kinematics Motion, Forces and Energy Mechanics: The study of motion Kinematics The description of how things move 1-D and 2-D motion Dynamics The study of the forces that cause motion Newton
Speed ( v ) is the distance an object travels during a given time interval divided by the time interval.
 v 8.2 Average Velocity Speed ( v ) is the distance an object travels during a given time interval divided by the time interval. Speed is a scalar quantity. The SI unit for speed is metres per second (m/s).
v 8.2 Average Velocity Speed ( v ) is the distance an object travels during a given time interval divided by the time interval. Speed is a scalar quantity. The SI unit for speed is metres per second (m/s).
( ) for t 0. Rectilinear motion CW. ( ) = t sin t ( Calculator)
 Rectilinear motion CW 1997 ( Calculator) 1) A particle moves along the x-axis so that its velocity at any time t is given by v(t) = 3t 2 2t 1. The position x(t) is 5 for t = 2. a) Write a polynomial expression
Rectilinear motion CW 1997 ( Calculator) 1) A particle moves along the x-axis so that its velocity at any time t is given by v(t) = 3t 2 2t 1. The position x(t) is 5 for t = 2. a) Write a polynomial expression
Speed. Change of Distance (in meters) Change of Time (in seconds) Step 2: Formula. 100m in 10sec. 200m in 10sec T. 200m in 20sec.
 Speed Unit 6:1 Speed Speed is how fast something is moving. Precisely, it is how far an object travels in a certain amount of time. The standard metric units are meters per second (m/s), but any units
Speed Unit 6:1 Speed Speed is how fast something is moving. Precisely, it is how far an object travels in a certain amount of time. The standard metric units are meters per second (m/s), but any units
Physics 30S Unit 2 Motion Graphs. Mrs. Kornelsen Teulon Collegiate Institute
 Physics 30S Unit 2 Motion Graphs Mrs. Kornelsen Teulon Collegiate Institute 1 Grade 11 Physics Graphing Properties Property d-t Graph v-t Graph a-t Graph Not Moving Does Not Apply Constant Velocity Change
Physics 30S Unit 2 Motion Graphs Mrs. Kornelsen Teulon Collegiate Institute 1 Grade 11 Physics Graphing Properties Property d-t Graph v-t Graph a-t Graph Not Moving Does Not Apply Constant Velocity Change
CHAPTER 2. Motion Notes
 CHAPTER 2 Motion Notes DISTANCE AND DISPLACEMENT Distance and displacement are two quantities which may seem to mean the same thing, yet have distinctly different definitions and meanings. DISTANCE Distance
CHAPTER 2 Motion Notes DISTANCE AND DISPLACEMENT Distance and displacement are two quantities which may seem to mean the same thing, yet have distinctly different definitions and meanings. DISTANCE Distance
Particle Motion. Typically, if a particle is moving along the x-axis at any time, t, x()
 Typically, if a particle is moving along the x-axis at any time, t, x() t represents the position of the particle; along the y-axis, yt () is often used; along another straight line, st () is often used.
Typically, if a particle is moving along the x-axis at any time, t, x() t represents the position of the particle; along the y-axis, yt () is often used; along another straight line, st () is often used.
SECTION 2 - VELOCITY
 MOTION SECTION 2 - VELOCITY How fast do you think we are traveling (orbiting) around the sun? 67,0672 mph How fast do you think we are spinning around our axis as we move around the sun? 1,041.67 mph Why
MOTION SECTION 2 - VELOCITY How fast do you think we are traveling (orbiting) around the sun? 67,0672 mph How fast do you think we are spinning around our axis as we move around the sun? 1,041.67 mph Why
Physics 2A. Lecture 2A. "You must learn from the mistakes of others. You can't possibly live long enough to make them all yourself.
 Physics 2A Lecture 2A "You must learn from the mistakes of others. You can't possibly live long enough to make them all yourself." --Sam Levenson 1 Motion Chapter 2 will focus on motion in one dimension.
Physics 2A Lecture 2A "You must learn from the mistakes of others. You can't possibly live long enough to make them all yourself." --Sam Levenson 1 Motion Chapter 2 will focus on motion in one dimension.
Page 1 / 15. Motion Unit Test. Name: Motion ONLY, no forces. Question 1 (1 point) Examine the graphs below:
 Motion Unit Test Motion ONLY, no forces Name: Question 1 (1 point) Examine the graphs below: Which of the four graphs shows the runner with the fastest speed? A. Graph A B. Graph B C. Graph C D. Graph
Motion Unit Test Motion ONLY, no forces Name: Question 1 (1 point) Examine the graphs below: Which of the four graphs shows the runner with the fastest speed? A. Graph A B. Graph B C. Graph C D. Graph
Vectors. Coordinates & Vectors. Chapter 2 One-Dimensional Kinematics. Chapter 2 One-Dimensional Kinematics
 Chapter 2 One-Dimensional Kinematics Chapter 2 One-Dimensional Kinematics James Walker, Physics, 2 nd Ed. Prentice Hall One dimensional kinematics refers to motion along a straight line. Even though we
Chapter 2 One-Dimensional Kinematics Chapter 2 One-Dimensional Kinematics James Walker, Physics, 2 nd Ed. Prentice Hall One dimensional kinematics refers to motion along a straight line. Even though we
Chapter 2: 1-D Kinematics. Paul E. Tippens, Professor of Physics Southern Polytechnic State University Editing by Mr. Gehman
 Chapter 2: 1-D Kinematics Paul E. Tippens, Professor of Physics Southern Polytechnic State University Editing by Mr. Gehman 2007 The Cheetah: A cat that is built for speed. Its strength and agility allow
Chapter 2: 1-D Kinematics Paul E. Tippens, Professor of Physics Southern Polytechnic State University Editing by Mr. Gehman 2007 The Cheetah: A cat that is built for speed. Its strength and agility allow
To conduct the experiment, each person in your group should be given a role:
 Varying Motion NAME In this activity, your group of 3 will collect data based on one person s motion. From this data, you will create graphs comparing displacement, velocity, and acceleration to time.
Varying Motion NAME In this activity, your group of 3 will collect data based on one person s motion. From this data, you will create graphs comparing displacement, velocity, and acceleration to time.
4.1 Implicit Differentiation
 4.1 Implicit Differentiation Learning Objectives A student will be able to: Find the derivative of variety of functions by using the technique of implicit differentiation. Consider the equation We want
4.1 Implicit Differentiation Learning Objectives A student will be able to: Find the derivative of variety of functions by using the technique of implicit differentiation. Consider the equation We want
Lesson 3A: How Fast Are You Moving?
 Lesson 3A: How Fast Are You Moving? 3.1 Observe and represent Decide on a starting point. You will need 2 cars (or other moving objects). For each car, you will mark its position at each second. Make sure
Lesson 3A: How Fast Are You Moving? 3.1 Observe and represent Decide on a starting point. You will need 2 cars (or other moving objects). For each car, you will mark its position at each second. Make sure
Chapter 2 Describing Motion
 Chapter 2 Describing Motion Chapter 2 Overview In chapter 2, we will try to accomplish two primary goals. 1. Understand and describe the motion of objects. Define concepts like speed, velocity, acceleration,
Chapter 2 Describing Motion Chapter 2 Overview In chapter 2, we will try to accomplish two primary goals. 1. Understand and describe the motion of objects. Define concepts like speed, velocity, acceleration,
Physic 231 Lecture 3. Main points of today s lecture. for constant acceleration: a = a; assuming also t0. v = lim
 Physic 231 Lecture 3 Main points of today s lecture Δx v = ; Δ t = t t0 for constant acceleration: a = a; assuming also t0 = 0 Δ x = v v= v0 + at Δx 1 v = lim Δ x = Δ t 0 ( v+ vo ) t 2 Δv 1 2 a = ; Δ v=
Physic 231 Lecture 3 Main points of today s lecture Δx v = ; Δ t = t t0 for constant acceleration: a = a; assuming also t0 = 0 Δ x = v v= v0 + at Δx 1 v = lim Δ x = Δ t 0 ( v+ vo ) t 2 Δv 1 2 a = ; Δ v=
Chapter 2: 2-Dimensional Motion
 Chapter 2: 2-Dimensional Motion Chapter 2: 2-Dimensional Motion Chapter 2: 2-Dimensional Motion 2.1 Position 2.2 Distance and Displacement 2.3 Average Speed and Average Velocity 2.4 Instant Speed and Instant
Chapter 2: 2-Dimensional Motion Chapter 2: 2-Dimensional Motion Chapter 2: 2-Dimensional Motion 2.1 Position 2.2 Distance and Displacement 2.3 Average Speed and Average Velocity 2.4 Instant Speed and Instant
v t 2 2t 8. Fig. 7 (i) Write down the velocity of the insect when t 0. (ii) Show that the insect is instantaneously at rest when t 2and when t 4.
 1 Fig. 7 is a sketch of part of the velocity-time graph for the motion of an insect walking in a straight line. Its velocity, v ms 1, at time t seconds for the time interval 3 t 5 is given by v ms -1 v
1 Fig. 7 is a sketch of part of the velocity-time graph for the motion of an insect walking in a straight line. Its velocity, v ms 1, at time t seconds for the time interval 3 t 5 is given by v ms -1 v
A B C D. Unit 6 (1-Dimensional Motion) Practice Assessment
 Unit 6 (1-Dimensional Motion) Practice Assessment Choose the best answer to the following questions. Indicate the confidence in your answer by writing C (Confident), S (So-so), or G (Guessed) next to the
Unit 6 (1-Dimensional Motion) Practice Assessment Choose the best answer to the following questions. Indicate the confidence in your answer by writing C (Confident), S (So-so), or G (Guessed) next to the
Wednesday 9/27. Please open quizizz
 Wednesday 9/27 Please open quizizz Graphing Acceleration VT Graphs VELOCITY m/s VELOCITY TIME GRAPHS Moving in a positive direction, SPEEDING UP Constant speed NO ACCELERATION Moving in a positive direction,
Wednesday 9/27 Please open quizizz Graphing Acceleration VT Graphs VELOCITY m/s VELOCITY TIME GRAPHS Moving in a positive direction, SPEEDING UP Constant speed NO ACCELERATION Moving in a positive direction,
Table of Contents. Motion. Section 1 Describing Motion. Section 2 Velocity and Momentum. Section 3 Acceleration
 Table of Contents Motion 1 Describing Motion 2 Velocity and Momentum 3 Acceleration 1 Describing Motion Motion Are distance and time important in describing running events at the track-and-field meets
Table of Contents Motion 1 Describing Motion 2 Velocity and Momentum 3 Acceleration 1 Describing Motion Motion Are distance and time important in describing running events at the track-and-field meets
BELL RINGER: Define Displacement. Define Velocity. Define Speed. Define Acceleration. Give an example of constant acceleration.
 BELL RINGER: Define Displacement. Define Velocity. Define Speed. Define Acceleration. Give an example of constant acceleration. What does the below equation tell us? v = d t NOTES 2.1: ONE-DIMENSIONAL
BELL RINGER: Define Displacement. Define Velocity. Define Speed. Define Acceleration. Give an example of constant acceleration. What does the below equation tell us? v = d t NOTES 2.1: ONE-DIMENSIONAL
Chapter 3: Introduction to Motion
 Chapter 3: Introduction to Motion Motion... Particle Models Vectors vs. Scalars Position, Displacement and Distance Velocity vs. Speed Instantaneous vs. Average Acceleration start time Particle motion
Chapter 3: Introduction to Motion Motion... Particle Models Vectors vs. Scalars Position, Displacement and Distance Velocity vs. Speed Instantaneous vs. Average Acceleration start time Particle motion
Vector and Relative motion discussion/ in class notes. Projectile Motion discussion and launch angle problem. Finish 2 d motion and review for test
 AP Physics 1 Unit 2: 2 Dimensional Kinematics Name: Date In Class Homework to completed that evening (before coming to next class period) 9/6 Tue (B) 9/7 Wed (C) 1D Kinematics Test Unit 2 Video 1: Vectors
AP Physics 1 Unit 2: 2 Dimensional Kinematics Name: Date In Class Homework to completed that evening (before coming to next class period) 9/6 Tue (B) 9/7 Wed (C) 1D Kinematics Test Unit 2 Video 1: Vectors
2/18/2019. Position-versus-Time Graphs. Below is a motion diagram, made at 1 frame per minute, of a student walking to school.
 Position-versus-Time Graphs Below is a motion diagram, made at 1 frame per minute, of a student walking to school. A motion diagram is one way to represent the student s motion. Another way is to make
Position-versus-Time Graphs Below is a motion diagram, made at 1 frame per minute, of a student walking to school. A motion diagram is one way to represent the student s motion. Another way is to make
Be ready to take a few more Notes (Chapter 10 Section 3) Chapter 10 Quiz next Tuesday. If you were absent yesterday - graph review page - Exit ticket
 February 6 Be ready to take a few more Notes (Chapter 10 Section 3) Chapter 10 Quiz next Tuesday If you were absent yesterday - graph review page - Exit ticket Chapter 10 Section 3 Acceleration measures
February 6 Be ready to take a few more Notes (Chapter 10 Section 3) Chapter 10 Quiz next Tuesday If you were absent yesterday - graph review page - Exit ticket Chapter 10 Section 3 Acceleration measures
One Dimensional Motion. Motion in x or y only
 One Dimensional Motion Motion in x or y only Scalar vs. Vector Scalar Defined as quantity with magnitude (size) only Example: 3 m, 62 seconds, 4.2 miles EASY Math!!! Vector Defined as quantity with magnitude
One Dimensional Motion Motion in x or y only Scalar vs. Vector Scalar Defined as quantity with magnitude (size) only Example: 3 m, 62 seconds, 4.2 miles EASY Math!!! Vector Defined as quantity with magnitude
1) If the acceleration of an object is negative, the object must be slowing down. A) True B) False Answer: B Var: 1
 University Physics, 13e (Young/Freedman) Chapter 2 Motion Along a Straight Line 2.1 Conceptual Questions 1) If the acceleration of an object is negative, the object must be slowing down. A) True B) False
University Physics, 13e (Young/Freedman) Chapter 2 Motion Along a Straight Line 2.1 Conceptual Questions 1) If the acceleration of an object is negative, the object must be slowing down. A) True B) False
SECTION 3 - VELOCITY
 UNIT 2 MOTION SECTION 3 - VELOCITY How fast do you think we are traveling (orbiting) around the sun? 67,0672 mph How fast do you think we are spinning around our axis as we move around the sun? 1,041.67
UNIT 2 MOTION SECTION 3 - VELOCITY How fast do you think we are traveling (orbiting) around the sun? 67,0672 mph How fast do you think we are spinning around our axis as we move around the sun? 1,041.67
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) If the acceleration of an object is negative, the object must be slowing down. A) True B) False
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) If the acceleration of an object is negative, the object must be slowing down. A) True B) False
AP Physics 1 Summer Assignment 2018 Mrs. DeMaio
 AP Physics 1 Summer Assignment 2018 Mrs. DeMaio demaiod@middletownk12.org Welcome to AP Physics 1 for the 2018-2019 school year. AP Physics 1 is an algebra based, introductory college-level physics course.
AP Physics 1 Summer Assignment 2018 Mrs. DeMaio demaiod@middletownk12.org Welcome to AP Physics 1 for the 2018-2019 school year. AP Physics 1 is an algebra based, introductory college-level physics course.
1. Complete the following table: Term Definition Unit Examples Speed Velocity Scalar Vector Displacement Distance
 Motion Review Name: Answer ALL questions on separate paper. Draw diagrams to help you visualize each scenario. Show all steps, as we have in class, to solve math questions. 1. Complete the following table:
Motion Review Name: Answer ALL questions on separate paper. Draw diagrams to help you visualize each scenario. Show all steps, as we have in class, to solve math questions. 1. Complete the following table:
Describing Motion. Motion. Are distance and time important in describing running events at the track-and-field meets in the Olympics?
 Describing Motion Section 1 Motion Are distance and time important in describing running events at the track-and-field meets in the Olympics? Comstock/JupiterImages Describing Motion Section 1 Motion Distance
Describing Motion Section 1 Motion Are distance and time important in describing running events at the track-and-field meets in the Olympics? Comstock/JupiterImages Describing Motion Section 1 Motion Distance
Describing and Measuring Motion
 Describing and Measuring Motion End of Chapter Project In lieu of a test, you are going to write a formal lab report A formal lab report is what scientists use to describe their research in a reproducible
Describing and Measuring Motion End of Chapter Project In lieu of a test, you are going to write a formal lab report A formal lab report is what scientists use to describe their research in a reproducible
? 4. Like number bonds, a formula is useful because it helps us know what operation to use depending on which pieces of information we have.
 UNIT SIX DECIMALS LESSON 168 PROBLEM-SOLVING You ve covered quite a distance in your journey through our number system, from whole numbers through fractions, to decimals. Today s math mysteries all have
UNIT SIX DECIMALS LESSON 168 PROBLEM-SOLVING You ve covered quite a distance in your journey through our number system, from whole numbers through fractions, to decimals. Today s math mysteries all have
Four Types of Motion We ll Study
 Four Types of Motion We ll Study The branch of mechanics that studies the motion of a body without caring about what caused the motion. Kinematics definitions Kinematics branch of physics; study of motion
Four Types of Motion We ll Study The branch of mechanics that studies the motion of a body without caring about what caused the motion. Kinematics definitions Kinematics branch of physics; study of motion
chapter M otion 1 15
 Motion chapter 1 15 What is Motion? Standard 1: Students will understand how to measure, calculate, and describe the motion of an object in terms of position, time, velocity, and acceleration. Standard
Motion chapter 1 15 What is Motion? Standard 1: Students will understand how to measure, calculate, and describe the motion of an object in terms of position, time, velocity, and acceleration. Standard
4.1 Motion Is Relative. An object is moving if its position relative to a fixed point is changing. You can describe the motion of an object by its
 4.1 Motion Is Relative You can describe the motion of an object by its position, speed, direction, and acceleration. An object is moving if its position relative to a fixed point is changing. 4.1 Motion
4.1 Motion Is Relative You can describe the motion of an object by its position, speed, direction, and acceleration. An object is moving if its position relative to a fixed point is changing. 4.1 Motion
A. VOCABULARY REVIEWS On the line, write the term that correctly completes each statement. Use each term once.
 PART III. KINEMATICS A. VOCABULARY REVIEWS On the line, write the term that correctly completes each statement. Use each term once. 1. rise (Δy) The vertical separation of any two points on a curve is
PART III. KINEMATICS A. VOCABULARY REVIEWS On the line, write the term that correctly completes each statement. Use each term once. 1. rise (Δy) The vertical separation of any two points on a curve is
Physics Essentials Homework Packet
 Name Date Hour Physics Essentials Homework Packet Unit 3: Motion 1 P age Speed Practice Problems Answer the questions below using the formulas for speed and velocity as discussed in class. Be sure to show
Name Date Hour Physics Essentials Homework Packet Unit 3: Motion 1 P age Speed Practice Problems Answer the questions below using the formulas for speed and velocity as discussed in class. Be sure to show
AP Physics 1: Summer Assignment
 AP Physics 1: Summer Assignment- Part 1 AP Physics 1: Summer Assignment Welcome to AP Physics 1! Attached is the summer assignment, which consists of two parts. The first part is an easy read about the
AP Physics 1: Summer Assignment- Part 1 AP Physics 1: Summer Assignment Welcome to AP Physics 1! Attached is the summer assignment, which consists of two parts. The first part is an easy read about the
Position-versus-Time Graphs
 Position-versus-Time Graphs Below is a motion diagram, made at 1 frame per minute, of a student walking to school. A motion diagram is one way to represent the student s motion. Another way is to make
Position-versus-Time Graphs Below is a motion diagram, made at 1 frame per minute, of a student walking to school. A motion diagram is one way to represent the student s motion. Another way is to make
Acceleration. 3. Changing Direction occurs when the velocity and acceleration are neither parallel nor anti-parallel
 Acceleration When the velocity of an object changes, we say that the object is accelerating. This acceleration can take one of three forms: 1. Speeding Up occurs when the object s velocity and acceleration
Acceleration When the velocity of an object changes, we say that the object is accelerating. This acceleration can take one of three forms: 1. Speeding Up occurs when the object s velocity and acceleration
scalar: quantity described by magnitude (size) only vector: quantity described by both magnitude AND direction
 Unit I: Motion Subunit A: Constant Velocity Chapter 2 Section 1 Texas Physics p. 38-45 Equations Variables, Units NOTES: scalar: quantity described by magnitude (size) only vector: quantity described by
Unit I: Motion Subunit A: Constant Velocity Chapter 2 Section 1 Texas Physics p. 38-45 Equations Variables, Units NOTES: scalar: quantity described by magnitude (size) only vector: quantity described by
Position and Displacement
 Position and Displacement Ch. in your text book Objectives Students will be able to: ) Explain the difference between a scalar and a vector quantity ) Explain the difference between total distance traveled
Position and Displacement Ch. in your text book Objectives Students will be able to: ) Explain the difference between a scalar and a vector quantity ) Explain the difference between total distance traveled
New HW : complete handout work on lab (due Tuesday) review new notes on website (pdf)
 Physics HW due Today a. Read in book: pages 43 51 b. define/explain in notes: particle model, position vector, vector quantity, scalar quantity, displacement, distance c. p.60: 2 3 4 5 d. Write this list
Physics HW due Today a. Read in book: pages 43 51 b. define/explain in notes: particle model, position vector, vector quantity, scalar quantity, displacement, distance c. p.60: 2 3 4 5 d. Write this list
1. Type your first name. * 2. Type your last name. * 3. Choose the block I teach you for science. * Mark only one oval. Block 1.
 Hippenmeyer Physics Assessment 1 Your email address (khippenmeyer@ncmcs.net) will be recorded when you submit this form. Not khippenmeyer? Sign out * Required 1. Type your first name. * 2. Type your last
Hippenmeyer Physics Assessment 1 Your email address (khippenmeyer@ncmcs.net) will be recorded when you submit this form. Not khippenmeyer? Sign out * Required 1. Type your first name. * 2. Type your last
PHYSICS Kinematics in One Dimension
 PHYSICS Kinematics in One Dimension August 13, 2012 www.njctl.org 1 Motion in One Dimension Return to Table of Contents 2 Distance We all know what the distance between two objects is... So what is it?
PHYSICS Kinematics in One Dimension August 13, 2012 www.njctl.org 1 Motion in One Dimension Return to Table of Contents 2 Distance We all know what the distance between two objects is... So what is it?
What does the lab partner observe during the instant the student pushes off?
 Motion Unit Review State Test Questions 1. To create real-time graphs of an object s displacement versus time and velocity versus time, a student would need to use a A motion sensor.b low- g accelerometer.
Motion Unit Review State Test Questions 1. To create real-time graphs of an object s displacement versus time and velocity versus time, a student would need to use a A motion sensor.b low- g accelerometer.
The Mean Value Theorem Rolle s Theorem
 The Mean Value Theorem In this section, we will look at two more theorems that tell us about the way that derivatives affect the shapes of graphs: Rolle s Theorem and the Mean Value Theorem. Rolle s Theorem
The Mean Value Theorem In this section, we will look at two more theorems that tell us about the way that derivatives affect the shapes of graphs: Rolle s Theorem and the Mean Value Theorem. Rolle s Theorem
What is a Vector? A vector is a mathematical object which describes magnitude and direction
 What is a Vector? A vector is a mathematical object which describes magnitude and direction We frequently use vectors when solving problems in Physics Example: Change in position (displacement) Velocity
What is a Vector? A vector is a mathematical object which describes magnitude and direction We frequently use vectors when solving problems in Physics Example: Change in position (displacement) Velocity
Motion in One Dimension
 Motion in One Dimension Chapter 2 Physics Table of Contents Position and Displacement Velocity Acceleration Motion with Constant Acceleration Falling Objects The Big Idea Displacement is a change of position
Motion in One Dimension Chapter 2 Physics Table of Contents Position and Displacement Velocity Acceleration Motion with Constant Acceleration Falling Objects The Big Idea Displacement is a change of position
7-7A. Describing a Function from its Graph. Vocabulary. Lesson
 Chapter 7 Lesson 7-7A Describing a Function from its Graph Vocabular increasing decreasing constant function BIG IDEA eamining its graph. Man attributes of a function can be determined b In companies that
Chapter 7 Lesson 7-7A Describing a Function from its Graph Vocabular increasing decreasing constant function BIG IDEA eamining its graph. Man attributes of a function can be determined b In companies that
Conceptual Physics 11 th Edition
 Conceptual Physics 11 th Edition Chapter 3: LINEAR MOTION This lecture will help you understand: Motion Is Relative Speed : Average and Instantaneous Velocity Acceleration Free Fall Motion Is Relative
Conceptual Physics 11 th Edition Chapter 3: LINEAR MOTION This lecture will help you understand: Motion Is Relative Speed : Average and Instantaneous Velocity Acceleration Free Fall Motion Is Relative
If we plot the position of a moving object at increasing time intervals, we get a position time graph. This is sometimes called a distance time graph.
 Physics Lecture #2: Position Time Graphs If we plot the position of a moving object at increasing time intervals, we get a position time graph. This is sometimes called a distance time graph. Suppose a
Physics Lecture #2: Position Time Graphs If we plot the position of a moving object at increasing time intervals, we get a position time graph. This is sometimes called a distance time graph. Suppose a
C 2. The average speed of a car that travels 500 km in 5 hours is a. 10 km/h. b km/h. c. 100 km/h. d. 1,000 km/h
 Name: KEY IP 644 lock: Date: / / Review Packet: Position, Distance, Displacement, Motion, Speed and Velocity Multiple Choice C 1. When a driver checks her speedometer, she is checking a. acceleration.
Name: KEY IP 644 lock: Date: / / Review Packet: Position, Distance, Displacement, Motion, Speed and Velocity Multiple Choice C 1. When a driver checks her speedometer, she is checking a. acceleration.
VEL A Distance & Displacement & VEL B Speed and Velocity 1. You run from your house to a friend's house that is 3 miles away. You then walk home.
 VEL A Distance & Displacement & VEL B Speed and Velocity 1. You run from your house to a friend's house that is 3 miles away. You then walk home. a. What distance did you travel? b. What was the displacement
VEL A Distance & Displacement & VEL B Speed and Velocity 1. You run from your house to a friend's house that is 3 miles away. You then walk home. a. What distance did you travel? b. What was the displacement
RATES AND UNIT RATES
 RATES AND UNIT RATES 7.. 7.. Rate of change is a ratio that describes how one quantity is changing with respect to another. Unit rate is a rate that compares the change in one quantity to a one-unit change
RATES AND UNIT RATES 7.. 7.. Rate of change is a ratio that describes how one quantity is changing with respect to another. Unit rate is a rate that compares the change in one quantity to a one-unit change
Definitions. Mechanics: The study of motion. Kinematics: The mathematical description of motion in 1-D and 2-D motion.
 Lecture 2 Definitions Mechanics: The study of motion. Kinematics: The mathematical description of motion in 1-D and 2-D motion. Dynamics: The study of the forces that cause motion. Chapter Outline Consider
Lecture 2 Definitions Mechanics: The study of motion. Kinematics: The mathematical description of motion in 1-D and 2-D motion. Dynamics: The study of the forces that cause motion. Chapter Outline Consider
Particle Motion. Typically, if a particle is moving along the x-axis at any time, t, x()
 Typically, if a particle is moving along the x-axis at any time, t, x() t represents the position of the particle; along the y-axis, yt () is often used; along another straight line, st () is often used.
Typically, if a particle is moving along the x-axis at any time, t, x() t represents the position of the particle; along the y-axis, yt () is often used; along another straight line, st () is often used.
Four Basic Types of Motion Pearson Education, Inc.
 Four Basic Types of Motion Making a Motion Diagram An easy way to study motion is to make a video of a moving object. A video camera takes images at a fixed rate, typically 30 every second. Each separate
Four Basic Types of Motion Making a Motion Diagram An easy way to study motion is to make a video of a moving object. A video camera takes images at a fixed rate, typically 30 every second. Each separate
9/4/2017. Motion: Acceleration
 Velocity Velocity (m/s) Position Velocity Position 9/4/217 Motion: Acceleration Summary Last : Find your clicker! Scalars: Distance, Speed Vectors: Position velocity Speed = Distance covered/time taken
Velocity Velocity (m/s) Position Velocity Position 9/4/217 Motion: Acceleration Summary Last : Find your clicker! Scalars: Distance, Speed Vectors: Position velocity Speed = Distance covered/time taken
Physics I Exam 1 Spring 2015 (version A)
 95.141 Physics I Exam 1 Spring 015 (version A) Section Number Section instructor Last/First Name (PRINT) / Last 3 Digits of Student ID Number: Answer all questions, beginning each new question in the space
95.141 Physics I Exam 1 Spring 015 (version A) Section Number Section instructor Last/First Name (PRINT) / Last 3 Digits of Student ID Number: Answer all questions, beginning each new question in the space
Practice Ace Problems
 Unit 5: Moving Straight Ahead Investigation 1: Walking Rates Practice Ace Problems Directions: Please complete the necessary problems to earn a maximum of 11 points according to the chart below. Show all
Unit 5: Moving Straight Ahead Investigation 1: Walking Rates Practice Ace Problems Directions: Please complete the necessary problems to earn a maximum of 11 points according to the chart below. Show all
Physics. Chapter 3 Linear Motion
 Physics Chapter 3 Linear Motion Motion is Relative How fast are you moving? We can only speak of how fast in relation to some other thing. Unless otherwise specified, we will assume motion relative to
Physics Chapter 3 Linear Motion Motion is Relative How fast are you moving? We can only speak of how fast in relation to some other thing. Unless otherwise specified, we will assume motion relative to
Representing Motion Chapter 2
 Phenomena Representing Motion Chapter 2 Pop Quiz! How fast are you moving at this moment? o A.) 0m/s o B.) 783 mi/h o C.) 350m/s o D.) 30 km/s Pop Quiz! How fast are you moving? oa.) 0m/s ob.) 783 mi/h
Phenomena Representing Motion Chapter 2 Pop Quiz! How fast are you moving at this moment? o A.) 0m/s o B.) 783 mi/h o C.) 350m/s o D.) 30 km/s Pop Quiz! How fast are you moving? oa.) 0m/s ob.) 783 mi/h
Progressive Science Initiative. Click to go to website:
 Slide 1 / 129 New Jersey Center for Teaching and Learning Progressive Science Initiative This material is made freely available at www.njctl.org and is intended for the non-commercial use of students and
Slide 1 / 129 New Jersey Center for Teaching and Learning Progressive Science Initiative This material is made freely available at www.njctl.org and is intended for the non-commercial use of students and
Particle Motion Problems
 Particle Motion Problems Particle motion problems deal with particles that are moving along the x or y axis. Thus, we are speaking of horizontal or vertical movement. The position, velocity, or acceleration
Particle Motion Problems Particle motion problems deal with particles that are moving along the x or y axis. Thus, we are speaking of horizontal or vertical movement. The position, velocity, or acceleration
Analyzing Motion: Enrichment
 Chapter 2 Analyzing Motion: Enrichment Note to Teachers: The concepts involved in motion position, velocity, acceleration, and time should be developed using the four modes of representation: visual, numeric,
Chapter 2 Analyzing Motion: Enrichment Note to Teachers: The concepts involved in motion position, velocity, acceleration, and time should be developed using the four modes of representation: visual, numeric,
Unit 2 - Motion. Chapter 3 - Distance and Speed. Unit 2 - Motion 1 / 76
 Unit 2 - Motion Chapter 3 - Distance and Speed Unit 2 - Motion 1 / 76 Precision and Accuracy Precision is a measure of how closely individual measurements agree with one another. Accuracy refers to how
Unit 2 - Motion Chapter 3 - Distance and Speed Unit 2 - Motion 1 / 76 Precision and Accuracy Precision is a measure of how closely individual measurements agree with one another. Accuracy refers to how
Graphing and Physical Quantities
 Show all work on a separate sheet of paper. 3.1 Observe and Describe Graphing and Physical Quantities Claire recorded the position of a motorized toy car using the origin as her reference point. She wrote
Show all work on a separate sheet of paper. 3.1 Observe and Describe Graphing and Physical Quantities Claire recorded the position of a motorized toy car using the origin as her reference point. She wrote
