Stability of an Adaptive Switched Controller for Power System Oscillation Damping using Remote Synchrophasor Signals
|
|
|
- Alyson Dean
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Stablty of an Adaptve Swtched Controller for Power Sytem Ocllaton Dampng ung Remote Synchrophaor Sgnal Farhad R. Pour Safae 1, Scott G. Ghocel 2, João P. Hepanha 1, and Joe H. Chow 3 Abtract Th paper concerned wth the tablty of an adaptve wtched controller for nterarea power ytem ocllaton dampng ung remote gnal. Thee gnal ntroduce varable latency nto the dampng control ytem due to phaor proceng and communcaton network delay. In prevou work, we degned an adaptve controller that dynamcally wtche among dfferent compenator dependng on the latency of the ncomng meaurement. To prevent wtchng ntablty, a long reet tme wa mplemented. We demontrated the tablty of the adaptve ytem ung mulaton. In th work, we ue the concept of average dwell tme (ADT) of wtched control ytem to develop a uffcent condton that guarantee the tablty of our adaptve wtchng algorthm. Ung th condton, we formulate a feablty problem to compute the mnmum average dwell tme for the et of degned compenator. We apply the algorthm to a thyrtor-controlled ere compenator on a two-area power ytem and how that the adaptve controller table for tme-varyng latency. I. INTRODUCTION The advent of ynchronzed phaor meaurement unt (PMU) at many locaton acro power grd enable the ue of uch remote gnal for nterarea ocllaton dampng. Unlke local gnal, remote meaurement can provde better obervablty of nterarea mode and thu more effectve control ung power-electronc-baed devce uch a a thyrtor-controller ere compenator (TCSC). However, communcaton of data from remote PMU can ntroduce data lo, corrupton, and latency. Data lo and corrupton can be partally mtgated ung data recontructon method or tate etmaton technque [1]. On the other hand, latency nherent n remote gnal and ncreaed by uch data proceng algorthm. Dfferent level of congeton n communcaton network produce varyng amount of meaurement latency to be compenated. In prevou work [2], we developed an adaptve wtched controller to damp nterarea ocllaton for a two-area power ytem ung remote PMU gnal. The controller conted of everal compenator, each degned for a pecfc amount of data latency n the PMU. Thu the adaptve cheme would Th work at RPI wa upported n part by the Engneerng Reearch Center Program of the Natonal Scence Foundaton and the Department of Energy under NSF Award Number EEC and the CURENT Indutry Partnerhp Program. Th reearch at UCSB wa upported by the Inttute for Collaboratve Botechnologe through grant W911NF from the U.S. Army Reearch Offce. 1 F. R. Pour Safae (farhad@ece.ucb.edu) and J. P. Hepanha (hepanha@ece.ucb.edu) are wth the Dept. of Electrcal and Computer Eng., Unverty of Calforna, Santa Barbara, CA. 2 S. G. Ghocel (ghocel@exponent.com) wth the Electrcal Engneerng and Computer Scence Practce, Exponent, Inc., New York, NY. 3 J. H. Chow (chowj@rp.edu) wth the Dept. of Electrcal, Computer, and Sytem Eng., Renelaer Polytechnc Inttute, Troy, NY. wtch among the compenator dependng on the meaured latency of the nput gnal. To prevent ntablty due to wtchng among the dfferent compenator, we degned the algorthm to have a uffcently long reet tme, much longer than the typcal decay tme of the ocllaton. Through mulaton, we howed that the wtchng algorthm exhbted tablty. In th work, we formally demontrate the tablty of the adaptve controller degn ung a theoretcal reult for wtched ytem. We employ the concept of average dwell tme (ADT) wtchng equence to contruct a tablty proof for our degned adaptve controller. Ung thee theoretcal reult, we compute the mnmum average dwell tme to guarantee tablty for a elected et of compenator under our adaptve control cheme. We how that the reet tme choen n our prevou work uffcent to enure table operaton. Other reearcher have alo condered tablty of networked control ytem wth tme varyng delay [3]. However, the man drawback of [3] that t more computatonally expenve compared to the algorthm ntroduced n th paper. II. PMU DATA LATENCY Phaor meaurement unt (PMU) are dtrbuted acro wde geographcal regon and the data tranmtted acro long communcaton lnk. Generally the data frt collected by a local utlte at ther phaor data concentrator (PDC), then treamed to the central PDC of the regonal ytem operator. An example of th herarchcal arrangement hown n Fgure 1. The phaor meaurement face a number of delay along the gnal path. Frt, the frequency etmaton and phaor calculaton algorthm typcally requre multple cycle of meaured data to compute the phaor quantte. Th type of fxed delay et a floor for the overall tme-varyng meaurement latency. After the phaor computed, the data tranmtted acro communcaton network to the local PDC and fnally to the central PDC. In addton to the delay acro the communcaton network nfratructure, whch can be calculated baed on the type of communcaton lnk [4], the data alo encounter mall delay at each PDC due to proceng. A an example, we lt the etmated delay for the Quebec power ytem n Table I [5]. We model the meaurement latency ung the ame approach a n our prevou work, namely a mnmum delay wth a varable component, takng the approach ued n [6] to calculate total tme delay T ld a T ld = T + T b + T p + T r
2 Phaor Meaurement Unt Hgh-voltage Subtaton A GPS Sgnal 3-phae current and voltage Hundred of km apart Local Phaor Data Concentrator Phaor Meaurement Unt Hgh-voltage Subtaton B PMU data GPS Sgnal 3-phae current and voltage Internet Local Phaor Data Concentrator Internet PMU data Central Phaor Data Concentrator Dampng Controller PMU data GPS Sgnal Control actuaton Fg. 1. PMU Data Communcaton Path 0 + u TABLE I PMU DATA LATENCY IN THE QUEBEC POWER SYSTEM PMU proceng tme 73 m Local data concentraton 16 m 2,000 km n optcal fber m Central data concentraton m Total etmated data latency 9 m TW 1+ TW Fg. 2. ( 1+ T ) 2 δ Delay d( t) Glead (, T ) d d( t) TCSC Adaptve Control Sytem Power Sytem where T = P /D r the eral delay, P the packet ze n bt, D r the tranmon rate of the lnk n bt/, and T b the delay between data packet. Moreover, T p = L/ν the propagaton delay, where L the lnk length n km and ν the propagaton peed n the lnk n km/, and T r the routng delay. III. CONTROL DESIGN The adaptve controller follow a mlar control degn a n [2] wth ome mnor change to reflect a more practcal mplementaton. For dampng control wth a thyrtorcontroller ere compenator (TCSC), we typcally ue a dervatve flter wth a mall tme contant T δ n addton to the wahout flter and thu no addtonal phae lead requred. For our controller degn, we adapt the controller from [7] and add a phae lead compenator to counteract the phae lag caued by data latency. The overall controller G c (, T d ) = K(T d ) 1+Tnum(T d) 1+T den (T d ) (1+T δ ) 2 T w 1+T w (1) and the ytem hown n Fgure 2. Note that we wtch among everal phae lead compenator whch are each degned for a pecfc level of delay T d. A the nput gnal latency d(t) vare, we ue the adaptve algorthm from [2] to elect the controller delay T d uch that T d d(t), but wth dwell tme conderaton to prevent wtchng ntablty. The algorthm can be ummarzed a follow: Adaptve Control Algorthm Prepecfy a et of T d value: 0 < T d1 < T d2 < < T dn. At tme t = t k, where t the tme at the controller, the tme delay T d ued to et the controller. for t = t k + t, where t the amplng perod of the PMU data f the next data pont already n the nput data buffer, or the ncremental tme of arrval of the next data pont f the nput data buffer empty. f the data delay larger than the T d, wtch to a controller wth the lowet latency T dj whch hgher than the data delay. elef the maxmum latency of all the data n the lat T r le than T dj, where T dj < T d, wtch n the controller wth a lower latency T dj. ele contnue wth the ame controller. end End algorthm Note that the reet tme T r ued to lmt rapd wtchng and prevent ntablty. In the next ecton, we wll derve a uffcent condton to guarantee tablty of the cloed-loop wtched ytem. IV. STABILITY OF THE SWITCHED SYSTEM It well-known [8] that a wtched ytem mght be table under uffcently low wtchng equence, uch that the tranent effect dpate after each wtch. The mplet way to pecfy low wtchng equence to retrct the cla of admble wtchng gnal to atfy a dwell tme contrant. That to ntroduce a number τ d > 0 uch that
3 the wtchng tme atfy the nequalty t k+1 t k τ d. Specfyng a dwell tme contrant may be too retrctve n the context of controlled wtchng. Thu, one can conder an enlarged famly of wtchng gnal that occaonally have conecutve dcontnute eparated by le than τ d, but for whch the average nterval between dcontnute no le than τ d. Th concept wa frt formalzed n [9] a average dwell tme. Let N σ (t, T ) denote the number of dcontnute of a wtchng gnal σ on the tme nterval (t, T ). We ay that σ ha average dwell tme τ d f there ext potve number N 0 and τ d uch that N σ (t, T ) N 0 + T t τ d T t 0. Our goal to etablh a tablty crtera for a cla of wtched delay ytem under an average dwell tme contrant. We conder a cla of wtched delay ytem of the form ẋ(t) = A σ(t) x(t) + B σ(t) x(t d t ), (2) where x R n denote the tate of the ytem, σ(t) : [0, ) S = {1, 2,..., N} the pecewe contant wtchng gnal. We propoe a uffcent condton that guarantee the tablty of the adaptve wtchng mechanm n [2]. We formulate the problem for arbtrary number of mode. Let u denote the latency of the arrvng data by d t [0, d max ]. Aume that controller ha been degned to work n the range of d t [0, d ] for S wth d +1 > d and d N = d max. We conder the followng wtchng mechanm. In mode, If the data latency larger than d, wtch to the controller wth the mallet delay d j whch greater than the data latency. If the data latency maller than d j where d j < d, wtch to the controller wth a lower delay, conderng that the average tme between wtche at leat τ d. Our goal to fnd a mnmum value of τ d for whch the wtched ytem reman table. The followng theorem provde a lower bound for τ d. We defne F := [ A 0 ] and H := [ ] 0 B. Theorem 1: Conder the delayed wtched ytem (2) wth d t [0, d max ). Aume that controller ha been degned to work n the range of d t [0, d ] for S wth d +1 > d and d N = d max. If there ext potve defnte ymmetrc matrce P, Z R n n, matrce N R 2n n and a contant µ 1 uch that wth P µp j Z µz j, j S (3) [ ] φ N Φ := N d 1 < 0 (4) Z [ φ = F P 0 ] + [ P 0 ] F [ + H P 0 ] + [ P 0 ] H + d max (F + H ) Z (F + H ) [ ] [ ] N I I I I N then the ytem table for any average dwell tme wtchng equence wth τ d > log µ α where α gven by α = mn λ mn ((φ + d N Z 1 N )) max λ max (P ) + d2 max 2 max λ max (Z ). (5) It worth notng that for a fxed value of µ 1, (3)-(4) are lnear matrx nequalty condton. By performng a lne earch on µ, one hould look for the mallet µ for whch (3)-(4) are feable. Proof: Aume that the ytem n the th mode for t [t k, t k+1 ]. We have ẋ(t) = A x(t) + B x(t d t ) + B x(t) B x(t) = (A + B )x(t) B ẋ() d. We chooe the Lyapunov functon V (t) = V 1 (t) + V 2 (t), V 1 (t) = x(t) P σ(t) x(t), V 2 (t) = 0 d max t+θ ẋ() Z σ() ẋ() d dθ. Let u compute V (t) for t [t k, t k+1 ). We aume that n th tme nterval σ(t) = V 1 (t) = x(t) ((A + B ) P + P (A + B )) x(t) 2x(t) P B ẋ() d V 2 (t) = d max ẋ(t) Z ẋ(t) ẋ() Z ẋ() d td max Therefore, V (t) x(t) ((A + B ) P + P (A + B )) x(t) 2x(t) P B + d max ẋ(t) Z ẋ(t) ẋ() d ẋ() Z ẋ() d = x(t) ((A + B ) P + P (A + B )) x(t) 2x(t) P B ẋ() d + d max (A x(t) + B x(t d t )) Z ( A x(t) + + B x(t d t ) ) ẋ() Z ẋ() d = x(t) ((A + B ) P + P (A + B )) x(t) 2x(t) P B (x(t) x(t d t )) + d max x(t) A Z A x(t) + 2d max x(t) A Z B x(t d t ) + d max x(t d t ) B Z B x(t d t ) ẋ() Z ẋ() d (6)
4 TABLE II PHASE LEAD COMPENSATORS G c() Controller # Delay (T d ) Lag (Delay) Lead Damp. K T N T D 1 m % m % m % m % m % Defnng ξ(t) := [ x(t) N, we have 2ξ N [ I I ] ξ = 2ξ N x(t d t ) ], For any et of matrce + ẋ() d d(t)ξ N Z 1 N ξ Combnng (6) and (7), we have ẋ() Z ẋ() d. (7) V (t) x(t) ((A + B ) P + P (A + B )) x(t) 2x(t) P B (x(t) x(t d t )) + d max x(t)a Z A x(t) + 2d max x(t) A Z B x(t d t ) + d max x(t d t ) B Z B x(t d t ) 2ξ [ ] N I I ξ + d ξ N Z 1 N ξ = ξ (F [ P 0 ] + [ P 0 ] F + H [ P 0 ] + [ P 0 ] H + d max (F + H ) Z (F + H ) [ ] [ ] N I I I I N + d N Z 1 N )ξ Thu, we have V (t) ξ (φ + d N Z 1 n (5), one can how that V (t) αv (t). N )ξ. Wth α gven Therefore, the Lyapunov functon decreae between wtchng. Followng (3), at a wtchng ntant t k, we have V σ(tk )(t k ) µv σ(t k )(t k ). Ung the reult of [8, Theorem 3.2], we conclude that the ytem table for any average dwell tme wtchng wth τ d > log µ α. It worth notng that the number of decon varable n (4) a lnear functon of the number of mode. However the number of decon varable n [3] grow quadratcally wth the number of mode. In partcular, f N denote the number of mode and n the dmenon of the cloed-loop ytem, the number of decon varable n (4) N(3n 2 + n) whle [3] requre N(5N + 1)n(n + 1)/2 decon varable. A. Two-Area Power Sytem V. SIMULATION RESULTS To llutrate the capablty of our degn, we conder a two-area, four-generator ytem adapted from [] and hown n Fgure 3. We ue the ame parameter from [2], uch that the ytem ha gnfcant nterarea power tranfer and prone to untable ocllaton followng a hort crcut fault. In th ytem, Generator 1 and 2 n Area 1 are coherent and Generator 11 and n Area 2 are coherent and all generator are repreented ung detaled machne model wth exctaton ytem. Gen 1 Gen 2 Area Load 4 Load 14 Fg. 3. Four-Machne, Two-Area Sytem Area Gen 11 Gen The TCSC located n ere wth one of the nterarea lne, and a hort crcut fault appled near Bu 999 to excte the ytem. We chooe the dfference between the averaged angle θ a n each area a our nput gnal θ a = 0.5(θ 1 + θ 2 ) 0.5(θ 11 + θ ) where θ the phae angle of the voltage at Bu. Th nput gnal exhbt good obervablty of the nterarea mode, and often preent n PMU deployment. Further dcuon on the choce of nput gnal can be found n [2]. B. Multple Compenator for Tme-Varyng Data Latency In degnng an adaptve controller for tme-varyng latency, we elect delay level tartng at 50 m, at ncrement of 50 m, up to 250 m. We alo nclude a delay level of m to how the nearly-deal cae. We mplement the overall controller from (1), where the tme contant of the hgh-pa wahout flter T w = and the tme contant of the dervatve flter T δ = 0.04, the ame a n [7]. The adaptve parameter K(T d ), T 1 (T d ), and T 2 (T d ) are gven n Table II. C. Average Dwell Tme Baed on Theorem 1, we formulate a lnear matrx nequalty (LMI) feablty problem and calculate the ADT for the degned controller n Table II. The LMI feablty problem become prohbtvely large a the number of wtched controller and ytem tate ncreae. To mprove the optmzaton convergence and obtan a oluton n a reaonable amount of tme, we reduce the tate-pace model
5 of the power ytem before applyng the TCSC controller. There are two part to the proce. Frt, we remove the ytem mode, whch are located at the orgn of the root-locu. Thee pole correpond to the fact that the machne angle have multple table oluton wth perodcty 2π. We perform a mple tranformaton on the angle to elmnate thee pole, whch ha the effect of lghtly hftng the frequency of the nterarea mode. The econd tep to reduce the order of the power ytem dynamc model. After removng the 2 ytem mode, we have a plant wth 35 tate. We then perform a balanced reducton to reduce the ytem to 3rd order. Becaue the nterarea mode untable and the TCSC doe not gnfcantly affect the other tate, the nterarea mode kept n the 3rd order ytem and t behavor cloely reemble the orgnal ytem. Fgure 4 compare the root-locu plot of the reduced model and orgnal ytem. TABLE III AVERAGE DWELL TIME RESULTS Controller # Delay (m) Mn. ADT () (4,5) (150,200) (3,4,5) (0,150,200) (2,3,4,5) (50,0,150,200) (1,2,3,4,5) (,50,0,150,200) mulate data latency wth varable arrval tme baed on a Poon tochatc proce, wth a mnmum latency of 90 m. The parameter of the probablty dtrbuton functon are choen uch that the data latency n the range d(t) [90, 1] m n 99% of cae. For a 1- nterval durng the dturbance, latency varablty ncreaed to repreent a bref congeton. We et the mnmum reet tme to T r =, uch that t gnfcantly larger than the mnmum average dwell tme. Imagnary Ax (econd -1 ) Orgnal Sytem Reduced Model Root Locu Angle Dff. (degree) Angle Dfference (Input) Sgnal Actual Value Delayed Sgnal Controller Input Tme () 0 Fg Real Ax (econd -1 ) Root-Locu Plot for Orgnal and Reduced Sytem Let (A p, B p, C p, 0) and (A c, Bc, Cc, Dc) be the tate pace realzaton for the reduced plant and the controller n mode, repectvely. Aume that A p R n pl n pl and A c R ncn ncn. The matrce n (2) whch correpond to the cloed-loop matrce are gven by [ ] A A = p B p Cc 0 ncn n pl A c [ ] Bp D B = cc p 0 npl n cn BcC. p 0 ncn n cn Ung Theorem 1, we can how that for the group of controller n Table III, the decrbed wtchng mechanm tablze the cloed-loop ytem. Note that a addtonal controller are combned, the mnmum average dwell tme ncreae to guarantee tablty. D. Adaptve Controller Performance Th adaptve algorthm appled to the 2-area ytem for the ame hort-crcut dturbance. The adaptve control performance hown n Fgure 5. In th 15-econd mulaton, a data buffer functon created n PST. We Fg. 5. Dampng Performance of the Adaptve Controller Fgure 5 how the angle dfference gnal θ a meaured ntantaneouly at the bue, the tme that the gnal θ a actually arrve at the controller, and the θ a waveform that ued a the dampng controller nput. A cloe-up hown n Fgure 6. Note the ntal delay for the phaor data θ a to be pcked up by the data buffer. In Fgure 7, we how the phae compenaton electon by the adaptve algorthm. The algorthm tart wth T d = 0 m compenator and wtche to the T d = 200 m Angle Dff. (degree) Fg. 6. Actual Value Delayed Sgnal Controller Input Tme () Performance wth Data Latency and Controller Delay
6 Delay (m) Angle Dff. (degree) X: Y: 200 Sgnal delay Controller delay Tme () Fg. 8. Fg. 7. Adaptve Compenator Selecton Actual Value Delayed Sgnal Controller Input Tme () Cloe-Up of Input Sgnal durng Compenator Swtchng compenator before the fault and t doe not affect the performance. At t = 1.588, a data pont arrve wth greater than 150 m latency, o the algorthm wtche to the T d = 200 m compenator. We ee that 150 m later (at t = ), the controller hold the lat data pont n nput queue for 50 m whle t wtche to the T d = 200 m compenator (Fgure 8). After wtchng n the 200 m latency compenator, the controller performance tll excellent. To damp the ocllaton, the controller aturate a t drve the effectve reactance of the TCSC branch connecton Bue 3 and 13 to a mnmum, a hown n Fgure 9. X eq (p.u.) VI. CONCLUSION In th paper, we analyzed the tablty of an adaptve control cheme for a power ytem nterarea dampng controller ung remote PMU data wth tme-varyng latency. The adaptve control cont of a controller wtchng algorthm baed on the latency of PMU data, and a phae compenaton degn of the controller for a gven et of latency. Latency requre addng phae lead compenaton, and we ue a bank of phae-lead controller governed by a latency-montorng, adaptve algorthm to wtch among them. We developed a uffcent condton to guarantee that th wtched control ytem table a long a an average dwell tme contant met. Fnally, we llutrated the control degn and demontrated the performance ung a 2-area power ytem. Future work nclude the development and analy of adaptve control algorthm for multple actuator conderng packet lo, late data arrval, and cooperatve control. Another topc for future reearch to degn a et of controller that are robut both to the nput gnal delay and to the varaton n the operatng condton of the ytem. REFERENCES [1] S. Ghocel, J. Chow, G. Stefopoulo, B. Fardaneh, D. Maragal, B. Blanchard, M. Razanouky, and D. Bertagnoll, Phaormeaurement-baed tate etmaton for ynchrophaor data qualty mprovement and power tranfer nterface montorng, Power Sytem, IEEE Tranacton on, vol. 29, no. 2, pp , March [2] J. H. Chow and S. G. Ghocel, An adaptve wde-area power ytem dampng controller ung ynchrophaor data, n Control and Optmzaton Method for Electrc Smart Grd, er. Power Electronc and Power Sytem, A. Chakrabortty and M. D. Ilc, Ed. Sprnger New York, 20, vol. 3, pp [3] B. Demrel, C. Brat, and M. Johanon, Determntc and tochatc approache to upervory control degn for networked ytem wth tme-varyng communcaton delay, CoRR, vol. ab/ , [4] J. Kuroe and K. Ro, Computer Networkng: A Top-Down Approach, 5th ed. New York: Addon-Weley, 20. [5] C. Cyr and I. Kamwa, WACS degn at Hydro-Quebec, n Proc. of IEEE PES General Meetng, Mnneapol, MN, July 20. [6] J.W. Stahlhut, T.J. Browne, G.T. Heydt, and V. Vttal, Latency vewed a a tochatc proce and t mpact on wde area power ytem control gnal, IEEE Tran. Power Syt., vol. 23, pp , Feb [7] E.V. Laren, J.J. Sanchez-Gaca, and J.H. Chow, Concept for degn of FACTS controller to damp power wng, IEEE Tran. Power Syt., vol., pp , May [8] D. Lberzon, Swtchng n Sytem and Control. Boton: Brkhäuer, [9] J. Hepanha and A. More, Stablty of wtched ytem wth average dwell-tme, n Proc. 38th IEEE Conf. on Decon and Control, 1999, pp [] M. Klen, G.J. Roger, and P. Kundur, A fundamental tudy of nterarea ocllaton n power ytem, IEEE Tran. Power Syt., vol. 6, pp , Aug Tme () Fg. 9. TCSC Control Acton
Root Locus Techniques
 Root Locu Technque ELEC 32 Cloed-Loop Control The control nput u t ynthezed baed on the a pror knowledge of the ytem plant, the reference nput r t, and the error gnal, e t The control ytem meaure the output,
Root Locu Technque ELEC 32 Cloed-Loop Control The control nput u t ynthezed baed on the a pror knowledge of the ytem plant, the reference nput r t, and the error gnal, e t The control ytem meaure the output,
Additional File 1 - Detailed explanation of the expression level CPD
 Addtonal Fle - Detaled explanaton of the expreon level CPD A mentoned n the man text, the man CPD for the uterng model cont of two ndvdual factor: P( level gen P( level gen P ( level gen 2 (.).. CPD factor
Addtonal Fle - Detaled explanaton of the expreon level CPD A mentoned n the man text, the man CPD for the uterng model cont of two ndvdual factor: P( level gen P( level gen P ( level gen 2 (.).. CPD factor
Small signal analysis
 Small gnal analy. ntroducton Let u conder the crcut hown n Fg., where the nonlnear retor decrbed by the equaton g v havng graphcal repreentaton hown n Fg.. ( G (t G v(t v Fg. Fg. a D current ource wherea
Small gnal analy. ntroducton Let u conder the crcut hown n Fg., where the nonlnear retor decrbed by the equaton g v havng graphcal repreentaton hown n Fg.. ( G (t G v(t v Fg. Fg. a D current ource wherea
Hybrid State Feedback Controller Design of Networked Switched Control Systems with Packet Dropout
 Amercan Control Conference Marrott Waterfront, Baltmore, MD, USA June 3-July, WeB6.6 Hybrd State Feedbac Controller Degn of etwored Swtched Control Sytem wth Pacet Dropout Dan Ma, Georg M. Dmrov and Jun
Amercan Control Conference Marrott Waterfront, Baltmore, MD, USA June 3-July, WeB6.6 Hybrd State Feedbac Controller Degn of etwored Swtched Control Sytem wth Pacet Dropout Dan Ma, Georg M. Dmrov and Jun
Harmonic oscillator approximation
 armonc ocllator approxmaton armonc ocllator approxmaton Euaton to be olved We are fndng a mnmum of the functon under the retrcton where W P, P,..., P, Q, Q,..., Q P, P,..., P, Q, Q,..., Q lnwgner functon
armonc ocllator approxmaton armonc ocllator approxmaton Euaton to be olved We are fndng a mnmum of the functon under the retrcton where W P, P,..., P, Q, Q,..., Q P, P,..., P, Q, Q,..., Q lnwgner functon
Improvements on Waring s Problem
 Improvement on Warng Problem L An-Png Bejng, PR Chna apl@nacom Abtract By a new recurve algorthm for the auxlary equaton, n th paper, we wll gve ome mprovement for Warng problem Keyword: Warng Problem,
Improvement on Warng Problem L An-Png Bejng, PR Chna apl@nacom Abtract By a new recurve algorthm for the auxlary equaton, n th paper, we wll gve ome mprovement for Warng problem Keyword: Warng Problem,
Start Point and Trajectory Analysis for the Minimal Time System Design Algorithm
 Start Pont and Trajectory Analy for the Mnmal Tme Sytem Degn Algorthm ALEXANDER ZEMLIAK, PEDRO MIRANDA Department of Phyc and Mathematc Puebla Autonomou Unverty Av San Claudo /n, Puebla, 757 MEXICO Abtract:
Start Pont and Trajectory Analy for the Mnmal Tme Sytem Degn Algorthm ALEXANDER ZEMLIAK, PEDRO MIRANDA Department of Phyc and Mathematc Puebla Autonomou Unverty Av San Claudo /n, Puebla, 757 MEXICO Abtract:
Distributed Control for the Parallel DC Linked Modular Shunt Active Power Filters under Distorted Utility Voltage Condition
 Dtrbted Control for the Parallel DC Lnked Modlar Shnt Actve Power Flter nder Dtorted Utlty Voltage Condton Reearch Stdent: Adl Salman Spervor: Dr. Malabka Ba School of Electrcal and Electronc Engneerng
Dtrbted Control for the Parallel DC Lnked Modlar Shnt Actve Power Flter nder Dtorted Utlty Voltage Condton Reearch Stdent: Adl Salman Spervor: Dr. Malabka Ba School of Electrcal and Electronc Engneerng
Variable Structure Control ~ Basics
 Varable Structure Control ~ Bac Harry G. Kwatny Department of Mechancal Engneerng & Mechanc Drexel Unverty Outlne A prelmnary example VS ytem, ldng mode, reachng Bac of dcontnuou ytem Example: underea
Varable Structure Control ~ Bac Harry G. Kwatny Department of Mechancal Engneerng & Mechanc Drexel Unverty Outlne A prelmnary example VS ytem, ldng mode, reachng Bac of dcontnuou ytem Example: underea
Specification -- Assumptions of the Simple Classical Linear Regression Model (CLRM) 1. Introduction
 ECONOMICS 35* -- NOTE ECON 35* -- NOTE Specfcaton -- Aumpton of the Smple Clacal Lnear Regreon Model (CLRM). Introducton CLRM tand for the Clacal Lnear Regreon Model. The CLRM alo known a the tandard lnear
ECONOMICS 35* -- NOTE ECON 35* -- NOTE Specfcaton -- Aumpton of the Smple Clacal Lnear Regreon Model (CLRM). Introducton CLRM tand for the Clacal Lnear Regreon Model. The CLRM alo known a the tandard lnear
Chapter 6 The Effect of the GPS Systematic Errors on Deformation Parameters
 Chapter 6 The Effect of the GPS Sytematc Error on Deformaton Parameter 6.. General Beutler et al., (988) dd the frt comprehenve tudy on the GPS ytematc error. Baed on a geometrc approach and aumng a unform
Chapter 6 The Effect of the GPS Sytematc Error on Deformaton Parameter 6.. General Beutler et al., (988) dd the frt comprehenve tudy on the GPS ytematc error. Baed on a geometrc approach and aumng a unform
Chapter 11. Supplemental Text Material. The method of steepest ascent can be derived as follows. Suppose that we have fit a firstorder
 S-. The Method of Steepet cent Chapter. Supplemental Text Materal The method of teepet acent can be derved a follow. Suppoe that we have ft a frtorder model y = β + β x and we wh to ue th model to determne
S-. The Method of Steepet cent Chapter. Supplemental Text Materal The method of teepet acent can be derved a follow. Suppoe that we have ft a frtorder model y = β + β x and we wh to ue th model to determne
Solution Methods for Time-indexed MIP Models for Chemical Production Scheduling
 Ian Davd Lockhart Bogle and Mchael Farweather (Edtor), Proceedng of the 22nd European Sympoum on Computer Aded Proce Engneerng, 17-2 June 212, London. 212 Elever B.V. All rght reerved. Soluton Method for
Ian Davd Lockhart Bogle and Mchael Farweather (Edtor), Proceedng of the 22nd European Sympoum on Computer Aded Proce Engneerng, 17-2 June 212, London. 212 Elever B.V. All rght reerved. Soluton Method for
A Novel Approach for Testing Stability of 1-D Recursive Digital Filters Based on Lagrange Multipliers
 Amercan Journal of Appled Scence 5 (5: 49-495, 8 ISSN 546-939 8 Scence Publcaton A Novel Approach for Tetng Stablty of -D Recurve Dgtal Flter Baed on Lagrange ultpler KRSanth, NGangatharan and Ponnavakko
Amercan Journal of Appled Scence 5 (5: 49-495, 8 ISSN 546-939 8 Scence Publcaton A Novel Approach for Tetng Stablty of -D Recurve Dgtal Flter Baed on Lagrange ultpler KRSanth, NGangatharan and Ponnavakko
728. Mechanical and electrical elements in reduction of vibrations
 78. Mechancal and electrcal element n reducton of vbraton Katarzyna BIAŁAS The Slean Unverty of Technology, Faculty of Mechancal Engneerng Inttute of Engneerng Procee Automaton and Integrated Manufacturng
78. Mechancal and electrcal element n reducton of vbraton Katarzyna BIAŁAS The Slean Unverty of Technology, Faculty of Mechancal Engneerng Inttute of Engneerng Procee Automaton and Integrated Manufacturng
Electrical Circuits II (ECE233b)
 Electrcal Crcut II (ECE33b) Applcaton of Laplace Tranform to Crcut Analy Anet Dounav The Unverty of Wetern Ontaro Faculty of Engneerng Scence Crcut Element Retance Tme Doman (t) v(t) R v(t) = R(t) Frequency
Electrcal Crcut II (ECE33b) Applcaton of Laplace Tranform to Crcut Analy Anet Dounav The Unverty of Wetern Ontaro Faculty of Engneerng Scence Crcut Element Retance Tme Doman (t) v(t) R v(t) = R(t) Frequency
Improvements on Waring s Problem
 Imrovement on Warng Problem L An-Png Bejng 85, PR Chna al@nacom Abtract By a new recurve algorthm for the auxlary equaton, n th aer, we wll gve ome mrovement for Warng roblem Keyword: Warng Problem, Hardy-Lttlewood
Imrovement on Warng Problem L An-Png Bejng 85, PR Chna al@nacom Abtract By a new recurve algorthm for the auxlary equaton, n th aer, we wll gve ome mrovement for Warng roblem Keyword: Warng Problem, Hardy-Lttlewood
Two Approaches to Proving. Goldbach s Conjecture
 Two Approache to Provng Goldbach Conecture By Bernard Farley Adved By Charle Parry May 3 rd 5 A Bref Introducton to Goldbach Conecture In 74 Goldbach made h mot famou contrbuton n mathematc wth the conecture
Two Approache to Provng Goldbach Conecture By Bernard Farley Adved By Charle Parry May 3 rd 5 A Bref Introducton to Goldbach Conecture In 74 Goldbach made h mot famou contrbuton n mathematc wth the conecture
Method Of Fundamental Solutions For Modeling Electromagnetic Wave Scattering Problems
 Internatonal Workhop on MehFree Method 003 1 Method Of Fundamental Soluton For Modelng lectromagnetc Wave Scatterng Problem Der-Lang Young (1) and Jhh-We Ruan (1) Abtract: In th paper we attempt to contruct
Internatonal Workhop on MehFree Method 003 1 Method Of Fundamental Soluton For Modelng lectromagnetc Wave Scatterng Problem Der-Lang Young (1) and Jhh-We Ruan (1) Abtract: In th paper we attempt to contruct
Computer Control Systems
 Computer Control ytem In th chapter we preent the element and the bac concept of computercontrolled ytem. The dcretaton and choce of amplng frequency wll be frt examned, followed by a tudy of dcrete-tme
Computer Control ytem In th chapter we preent the element and the bac concept of computercontrolled ytem. The dcretaton and choce of amplng frequency wll be frt examned, followed by a tudy of dcrete-tme
Scattering of two identical particles in the center-of. of-mass frame. (b)
 Lecture # November 5 Scatterng of two dentcal partcle Relatvtc Quantum Mechanc: The Klen-Gordon equaton Interpretaton of the Klen-Gordon equaton The Drac equaton Drac repreentaton for the matrce α and
Lecture # November 5 Scatterng of two dentcal partcle Relatvtc Quantum Mechanc: The Klen-Gordon equaton Interpretaton of the Klen-Gordon equaton The Drac equaton Drac repreentaton for the matrce α and
Team. Outline. Statistics and Art: Sampling, Response Error, Mixed Models, Missing Data, and Inference
 Team Stattc and Art: Samplng, Repone Error, Mxed Model, Mng Data, and nference Ed Stanek Unverty of Maachuett- Amhert, USA 9/5/8 9/5/8 Outlne. Example: Doe-repone Model n Toxcology. ow to Predct Realzed
Team Stattc and Art: Samplng, Repone Error, Mxed Model, Mng Data, and nference Ed Stanek Unverty of Maachuett- Amhert, USA 9/5/8 9/5/8 Outlne. Example: Doe-repone Model n Toxcology. ow to Predct Realzed
On the SO 2 Problem in Thermal Power Plants. 2.Two-steps chemical absorption modeling
 Internatonal Journal of Engneerng Reearch ISSN:39-689)(onlne),347-53(prnt) Volume No4, Iue No, pp : 557-56 Oct 5 On the SO Problem n Thermal Power Plant Two-tep chemcal aborpton modelng hr Boyadjev, P
Internatonal Journal of Engneerng Reearch ISSN:39-689)(onlne),347-53(prnt) Volume No4, Iue No, pp : 557-56 Oct 5 On the SO Problem n Thermal Power Plant Two-tep chemcal aborpton modelng hr Boyadjev, P
CHAPTER 5 NUMERICAL EVALUATION OF DYNAMIC RESPONSE
 CHAPTER 5 NUMERICAL EVALUATION OF DYNAMIC RESPONSE Analytcal soluton s usually not possble when exctaton vares arbtrarly wth tme or f the system s nonlnear. Such problems can be solved by numercal tmesteppng
CHAPTER 5 NUMERICAL EVALUATION OF DYNAMIC RESPONSE Analytcal soluton s usually not possble when exctaton vares arbtrarly wth tme or f the system s nonlnear. Such problems can be solved by numercal tmesteppng
Comparative Study on Electromagnetic and Electromechanical Transient Model for Grid-connected Photovoltaic Power System
 Energy and Power Engneerng, 13, 5, 47-5 do:1.436/epe.13.54b48 Publhed Onlne July 13 (http://www.crp.org/journal/epe) Comparatve Study on and Tranent Model for Grd-connected Photovoltac Power Sytem Man
Energy and Power Engneerng, 13, 5, 47-5 do:1.436/epe.13.54b48 Publhed Onlne July 13 (http://www.crp.org/journal/epe) Comparatve Study on and Tranent Model for Grd-connected Photovoltac Power Sytem Man
Digital Simulation of Power Systems and Power Electronics using the MATLAB Power System Blockset 筑龙网
 Dgtal Smulaton of Power Sytem and Power Electronc ung the MATAB Power Sytem Blocket Power Sytem Blocket Htory Deeloped by IREQ (HydroQuébec) n cooperaton wth Teqm, Unerté aal (Québec), and École de Technologe
Dgtal Smulaton of Power Sytem and Power Electronc ung the MATAB Power Sytem Blocket Power Sytem Blocket Htory Deeloped by IREQ (HydroQuébec) n cooperaton wth Teqm, Unerté aal (Québec), and École de Technologe
Estimation of Finite Population Total under PPS Sampling in Presence of Extra Auxiliary Information
 Internatonal Journal of Stattc and Analy. ISSN 2248-9959 Volume 6, Number 1 (2016), pp. 9-16 Reearch Inda Publcaton http://www.rpublcaton.com Etmaton of Fnte Populaton Total under PPS Samplng n Preence
Internatonal Journal of Stattc and Analy. ISSN 2248-9959 Volume 6, Number 1 (2016), pp. 9-16 Reearch Inda Publcaton http://www.rpublcaton.com Etmaton of Fnte Populaton Total under PPS Samplng n Preence
SUBTRACTION METHOD FOR REMOVING POWERLINE INTERFERENCE
 SUBTRACTION METHOD OR REMOVING POWERLINE INTERERENCE ROM ECG IN CASE O REQUENCY DEVIATION Georgy Slavtchev Mhov, Ratcho Marnov Ivanov, Chavdar Lev Levkov aculty of Electronc Engneerng and Technologe (ETT),
SUBTRACTION METHOD OR REMOVING POWERLINE INTERERENCE ROM ECG IN CASE O REQUENCY DEVIATION Georgy Slavtchev Mhov, Ratcho Marnov Ivanov, Chavdar Lev Levkov aculty of Electronc Engneerng and Technologe (ETT),
Resonant FCS Predictive Control of Power Converter in Stationary Reference Frame
 Preprnt of the 9th World Congre The Internatonal Federaton of Automatc Control Cape Town, South Afrca. Augut -9, Reonant FCS Predctve Control of Power Converter n Statonary Reference Frame Lupng Wang K
Preprnt of the 9th World Congre The Internatonal Federaton of Automatc Control Cape Town, South Afrca. Augut -9, Reonant FCS Predctve Control of Power Converter n Statonary Reference Frame Lupng Wang K
Module 5. Cables and Arches. Version 2 CE IIT, Kharagpur
 odule 5 Cable and Arche Veron CE IIT, Kharagpur Leon 33 Two-nged Arch Veron CE IIT, Kharagpur Intructonal Objectve: After readng th chapter the tudent wll be able to 1. Compute horzontal reacton n two-hnged
odule 5 Cable and Arche Veron CE IIT, Kharagpur Leon 33 Two-nged Arch Veron CE IIT, Kharagpur Intructonal Objectve: After readng th chapter the tudent wll be able to 1. Compute horzontal reacton n two-hnged
The multivariate Gaussian probability density function for random vector X (X 1,,X ) T. diagonal term of, denoted
 Appendx Proof of heorem he multvarate Gauan probablty denty functon for random vector X (X,,X ) px exp / / x x mean and varance equal to the th dagonal term of, denoted he margnal dtrbuton of X Gauan wth
Appendx Proof of heorem he multvarate Gauan probablty denty functon for random vector X (X,,X ) px exp / / x x mean and varance equal to the th dagonal term of, denoted he margnal dtrbuton of X Gauan wth
Joint Source Coding and Higher-Dimension Modulation
 Jont Codng and Hgher-Dmenon Modulaton Tze C. Wong and Huck M. Kwon Electrcal Engneerng and Computer Scence Wchta State Unvert, Wchta, Kana 676, USA {tcwong; huck.kwon}@wchta.edu Abtract Th paper propoe
Jont Codng and Hgher-Dmenon Modulaton Tze C. Wong and Huck M. Kwon Electrcal Engneerng and Computer Scence Wchta State Unvert, Wchta, Kana 676, USA {tcwong; huck.kwon}@wchta.edu Abtract Th paper propoe
MODELLING OF TRANSIENT HEAT TRANSPORT IN TWO-LAYERED CRYSTALLINE SOLID FILMS USING THE INTERVAL LATTICE BOLTZMANN METHOD
 Journal o Appled Mathematc and Computatonal Mechanc 7, 6(4), 57-65 www.amcm.pcz.pl p-issn 99-9965 DOI:.75/jamcm.7.4.6 e-issn 353-588 MODELLING OF TRANSIENT HEAT TRANSPORT IN TWO-LAYERED CRYSTALLINE SOLID
Journal o Appled Mathematc and Computatonal Mechanc 7, 6(4), 57-65 www.amcm.pcz.pl p-issn 99-9965 DOI:.75/jamcm.7.4.6 e-issn 353-588 MODELLING OF TRANSIENT HEAT TRANSPORT IN TWO-LAYERED CRYSTALLINE SOLID
Pythagorean triples. Leen Noordzij.
 Pythagorean trple. Leen Noordz Dr.l.noordz@leennoordz.nl www.leennoordz.me Content A Roadmap for generatng Pythagorean Trple.... Pythagorean Trple.... 3 Dcuon Concluon.... 5 A Roadmap for generatng Pythagorean
Pythagorean trple. Leen Noordz Dr.l.noordz@leennoordz.nl www.leennoordz.me Content A Roadmap for generatng Pythagorean Trple.... Pythagorean Trple.... 3 Dcuon Concluon.... 5 A Roadmap for generatng Pythagorean
CHAPTER 9 LINEAR MOMENTUM, IMPULSE AND COLLISIONS
 CHAPTER 9 LINEAR MOMENTUM, IMPULSE AND COLLISIONS 103 Phy 1 9.1 Lnear Momentum The prncple o energy conervaton can be ued to olve problem that are harder to olve jut ung Newton law. It ued to decrbe moton
CHAPTER 9 LINEAR MOMENTUM, IMPULSE AND COLLISIONS 103 Phy 1 9.1 Lnear Momentum The prncple o energy conervaton can be ued to olve problem that are harder to olve jut ung Newton law. It ued to decrbe moton
Confidence intervals for the difference and the ratio of Lognormal means with bounded parameters
 Songklanakarn J. Sc. Technol. 37 () 3-40 Mar.-Apr. 05 http://www.jt.pu.ac.th Orgnal Artcle Confdence nterval for the dfference and the rato of Lognormal mean wth bounded parameter Sa-aat Nwtpong* Department
Songklanakarn J. Sc. Technol. 37 () 3-40 Mar.-Apr. 05 http://www.jt.pu.ac.th Orgnal Artcle Confdence nterval for the dfference and the rato of Lognormal mean wth bounded parameter Sa-aat Nwtpong* Department
Modeling of Wave Behavior of Substrate Noise Coupling for Mixed-Signal IC Design
 Modelng of Wave Behavor of Subtrate Noe Couplng for Mxed-Sgnal IC Degn Georgo Veron, Y-Chang Lu, and Robert W. Dutton Center for Integrated Sytem, Stanford Unverty, Stanford, CA 9435 yorgo@gloworm.tanford.edu
Modelng of Wave Behavor of Subtrate Noe Couplng for Mxed-Sgnal IC Degn Georgo Veron, Y-Chang Lu, and Robert W. Dutton Center for Integrated Sytem, Stanford Unverty, Stanford, CA 9435 yorgo@gloworm.tanford.edu
Transfer Functions. Convenient representation of a linear, dynamic model. A transfer function (TF) relates one input and one output: ( ) system
 Transfer Functons Convenent representaton of a lnear, dynamc model. A transfer functon (TF) relates one nput and one output: x t X s y t system Y s The followng termnology s used: x y nput output forcng
Transfer Functons Convenent representaton of a lnear, dynamc model. A transfer functon (TF) relates one nput and one output: x t X s y t system Y s The followng termnology s used: x y nput output forcng
ROBUST MODEL PREDICTIVE CONTROL FOR PIECEWISE AFFINE SYSTEMS SUBJECT TO BOUNDED DISTURBANCES
 ROBUST MODEL PREDICTIE CONTROL FOR PIECEWISE FFINE SYSTEMS SUBJECT TO BOUNDED DISTURBNCES ( J. Thoma, ( S. Olaru, (3 J. Buon and ( D. Dumur ( Indutral Educaton College Ben Swef, Egypt Phone : + ( 5 63
ROBUST MODEL PREDICTIE CONTROL FOR PIECEWISE FFINE SYSTEMS SUBJECT TO BOUNDED DISTURBNCES ( J. Thoma, ( S. Olaru, (3 J. Buon and ( D. Dumur ( Indutral Educaton College Ben Swef, Egypt Phone : + ( 5 63
Introduction to Interfacial Segregation. Xiaozhe Zhang 10/02/2015
 Introducton to Interfacal Segregaton Xaozhe Zhang 10/02/2015 Interfacal egregaton Segregaton n materal refer to the enrchment of a materal conttuent at a free urface or an nternal nterface of a materal.
Introducton to Interfacal Segregaton Xaozhe Zhang 10/02/2015 Interfacal egregaton Segregaton n materal refer to the enrchment of a materal conttuent at a free urface or an nternal nterface of a materal.
KEY POINTS FOR NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF INCLINATION OF BUILDINGS ON LIQUEFIABLE SOIL LAYERS
 KY POINTS FOR NUMRICAL SIMULATION OF INCLINATION OF BUILDINGS ON LIQUFIABL SOIL LAYRS Jn Xu 1, Xaomng Yuan, Jany Zhang 3,Fanchao Meng 1 1 Student, Dept. of Geotechncal ngneerng, Inttute of ngneerng Mechanc,
KY POINTS FOR NUMRICAL SIMULATION OF INCLINATION OF BUILDINGS ON LIQUFIABL SOIL LAYRS Jn Xu 1, Xaomng Yuan, Jany Zhang 3,Fanchao Meng 1 1 Student, Dept. of Geotechncal ngneerng, Inttute of ngneerng Mechanc,
m = 4 n = 9 W 1 N 1 x 1 R D 4 s x i
 GREEDY WIRE-SIZING IS LINEAR TIME Chr C. N. Chu D. F. Wong cnchu@c.utexa.edu wong@c.utexa.edu Department of Computer Scence, Unverty of Texa at Autn, Autn, T 787. ABSTRACT In nterconnect optmzaton by wre-zng,
GREEDY WIRE-SIZING IS LINEAR TIME Chr C. N. Chu D. F. Wong cnchu@c.utexa.edu wong@c.utexa.edu Department of Computer Scence, Unverty of Texa at Autn, Autn, T 787. ABSTRACT In nterconnect optmzaton by wre-zng,
A New Virtual Indexing Method for Measuring Host Connection Degrees
 A New Vrtual Indexng Method for Meaurng ot Connecton Degree Pnghu Wang, Xaohong Guan,, Webo Gong 3, and Don Towley 4 SKLMS Lab and MOE KLINNS Lab, X an Jaotong Unverty, X an, Chna Department of Automaton
A New Vrtual Indexng Method for Meaurng ot Connecton Degree Pnghu Wang, Xaohong Guan,, Webo Gong 3, and Don Towley 4 SKLMS Lab and MOE KLINNS Lab, X an Jaotong Unverty, X an, Chna Department of Automaton
Extended Prigogine Theorem: Method for Universal Characterization of Complex System Evolution
 Extended Prgogne Theorem: Method for Unveral Characterzaton of Complex Sytem Evoluton Sergey amenhchkov* Mocow State Unverty of M.V. Lomonoov, Phycal department, Rua, Mocow, Lennke Gory, 1/, 119991 Publhed
Extended Prgogne Theorem: Method for Unveral Characterzaton of Complex Sytem Evoluton Sergey amenhchkov* Mocow State Unverty of M.V. Lomonoov, Phycal department, Rua, Mocow, Lennke Gory, 1/, 119991 Publhed
Distributed Adaptive Fault-Tolerant Control of Nonlinear Uncertain Second-order Multi-agent Systems
 Dtrbuted Adaptve Fault-Tolerant Control of Nonlnear Uncertan Second-order ult-agent Sytem ohen Khall, Xaodong Zhang, Yongcan Cao, aro. Polycarpou, and Thoma Parn Abtract Th paper preent an adaptve fault-tolerant
Dtrbuted Adaptve Fault-Tolerant Control of Nonlnear Uncertan Second-order ult-agent Sytem ohen Khall, Xaodong Zhang, Yongcan Cao, aro. Polycarpou, and Thoma Parn Abtract Th paper preent an adaptve fault-tolerant
This is a repository copy of An iterative orthogonal forward regression algorithm.
 Th a repotory copy of An teratve orthogonal forward regreon algorthm. Whte Roe Reearch Onlne URL for th paper: http://eprnt.whteroe.ac.uk/0735/ Veron: Accepted Veron Artcle: Guo, Y., Guo, L. Z., Bllng,
Th a repotory copy of An teratve orthogonal forward regreon algorthm. Whte Roe Reearch Onlne URL for th paper: http://eprnt.whteroe.ac.uk/0735/ Veron: Accepted Veron Artcle: Guo, Y., Guo, L. Z., Bllng,
Energy Saving for Automatic Train Control in. Moving Block Signaling System
 Energy Savng for Automatc Tran Control n Movng Block Sgnalng Sytem Qng Gu, Xao-Yun Lu and Tao Tang Abtract Wth rapd development of the ralway traffc, the movng block gnalng ytem (MBS) method ha become
Energy Savng for Automatc Tran Control n Movng Block Sgnalng Sytem Qng Gu, Xao-Yun Lu and Tao Tang Abtract Wth rapd development of the ralway traffc, the movng block gnalng ytem (MBS) method ha become
ELG3336: Op Amp-based Active Filters
 ELG6: Op Amp-baed Actve Flter Advantage: educed ze and weght, and thereore paratc. Increaed relablty and mproved perormance. Smpler degn than or pave lter and can realze a wder range o uncton a well a
ELG6: Op Amp-baed Actve Flter Advantage: educed ze and weght, and thereore paratc. Increaed relablty and mproved perormance. Smpler degn than or pave lter and can realze a wder range o uncton a well a
PCI-697: DISTILLATION CONTROL. Department of Chemical Engineering KFUPM
 PCI-697: DISTILLATION CONTROL Department of Chemcal Engneerng KFUPM Topc: Dtllaton Prncple and Dynamc Dr. Houam Bnou Objectve of dtllaton control Operate n Safe, Stable Manner Operate Wthn Equpment Contrant
PCI-697: DISTILLATION CONTROL Department of Chemcal Engneerng KFUPM Topc: Dtllaton Prncple and Dynamc Dr. Houam Bnou Objectve of dtllaton control Operate n Safe, Stable Manner Operate Wthn Equpment Contrant
The Essential Dynamics Algorithm: Essential Results
 @ MIT maachuett nttute of technology artfcal ntellgence laboratory The Eental Dynamc Algorthm: Eental Reult Martn C. Martn AI Memo 003-014 May 003 003 maachuett nttute of technology, cambrdge, ma 0139
@ MIT maachuett nttute of technology artfcal ntellgence laboratory The Eental Dynamc Algorthm: Eental Reult Martn C. Martn AI Memo 003-014 May 003 003 maachuett nttute of technology, cambrdge, ma 0139
EEL 6266 Power System Operation and Control. Chapter 3 Economic Dispatch Using Dynamic Programming
 EEL 6266 Power System Operaton and Control Chapter 3 Economc Dspatch Usng Dynamc Programmng Pecewse Lnear Cost Functons Common practce many utltes prefer to represent ther generator cost functons as sngle-
EEL 6266 Power System Operaton and Control Chapter 3 Economc Dspatch Usng Dynamc Programmng Pecewse Lnear Cost Functons Common practce many utltes prefer to represent ther generator cost functons as sngle-
Problem #1. Known: All required parameters. Schematic: Find: Depth of freezing as function of time. Strategy:
 BEE 3500 013 Prelm Soluton Problem #1 Known: All requred parameter. Schematc: Fnd: Depth of freezng a functon of tme. Strategy: In thee mplfed analy for freezng tme, a wa done n cla for a lab geometry,
BEE 3500 013 Prelm Soluton Problem #1 Known: All requred parameter. Schematc: Fnd: Depth of freezng a functon of tme. Strategy: In thee mplfed analy for freezng tme, a wa done n cla for a lab geometry,
Quick Visit to Bernoulli Land
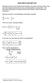 Although we have een the Bernoull equaton and een t derved before, th next note how t dervaton for an uncopreble & nvcd flow. The dervaton follow that of Kuethe &Chow ot cloely (I lke t better than Anderon).
Although we have een the Bernoull equaton and een t derved before, th next note how t dervaton for an uncopreble & nvcd flow. The dervaton follow that of Kuethe &Chow ot cloely (I lke t better than Anderon).
Decomposing Travel Times Measured by Probe-based Traffic Monitoring Systems to Individual Road Segments
 Decompong Travel Tme Meaured by Probe-baed Traffc Montorng Sytem to Indvdual Road Segment Correpondng Author Bruce Hellnga PhD PEng Aocate Profeor Dept. of Cvl and Envronmental Engneerng Unverty of Waterloo
Decompong Travel Tme Meaured by Probe-baed Traffc Montorng Sytem to Indvdual Road Segment Correpondng Author Bruce Hellnga PhD PEng Aocate Profeor Dept. of Cvl and Envronmental Engneerng Unverty of Waterloo
Batch RL Via Least Squares Policy Iteration
 Batch RL Va Leat Square Polcy Iteraton Alan Fern * Baed n part on lde by Ronald Parr Overvew Motvaton LSPI Dervaton from LSTD Expermental reult Onlne veru Batch RL Onlne RL: ntegrate data collecton and
Batch RL Va Leat Square Polcy Iteraton Alan Fern * Baed n part on lde by Ronald Parr Overvew Motvaton LSPI Dervaton from LSTD Expermental reult Onlne veru Batch RL Onlne RL: ntegrate data collecton and
MULTIPLE REGRESSION ANALYSIS For the Case of Two Regressors
 MULTIPLE REGRESSION ANALYSIS For the Cae of Two Regreor In the followng note, leat-quare etmaton developed for multple regreon problem wth two eplanator varable, here called regreor (uch a n the Fat Food
MULTIPLE REGRESSION ANALYSIS For the Cae of Two Regreor In the followng note, leat-quare etmaton developed for multple regreon problem wth two eplanator varable, here called regreor (uch a n the Fat Food
Wind - Induced Vibration Control of Long - Span Bridges by Multiple Tuned Mass Dampers
 Tamkang Journal of Scence and Engneerng, Vol. 3, o., pp. -3 (000) Wnd - Induced Vbraton Control of Long - Span Brdge by Multple Tuned Ma Damper Yuh-Y Ln, Ch-Mng Cheng and Davd Sun Department of Cvl Engneerng
Tamkang Journal of Scence and Engneerng, Vol. 3, o., pp. -3 (000) Wnd - Induced Vbraton Control of Long - Span Brdge by Multple Tuned Ma Damper Yuh-Y Ln, Ch-Mng Cheng and Davd Sun Department of Cvl Engneerng
Gain and Phase Margins Based Delay Dependent Stability Analysis of Two- Area LFC System with Communication Delays
 Gain and Phae Margin Baed Delay Dependent Stability Analyi of Two- Area LFC Sytem with Communication Delay Şahin Sönmez and Saffet Ayaun Department of Electrical Engineering, Niğde Ömer Halidemir Univerity,
Gain and Phae Margin Baed Delay Dependent Stability Analyi of Two- Area LFC Sytem with Communication Delay Şahin Sönmez and Saffet Ayaun Department of Electrical Engineering, Niğde Ömer Halidemir Univerity,
376 CHAPTER 6. THE FREQUENCY-RESPONSE DESIGN METHOD. D(s) = we get the compensated system with :
 376 CHAPTER 6. THE FREQUENCY-RESPONSE DESIGN METHOD Therefore by applying the lead compenator with ome gain adjutment : D() =.12 4.5 +1 9 +1 we get the compenated ytem with : PM =65, ω c = 22 rad/ec, o
376 CHAPTER 6. THE FREQUENCY-RESPONSE DESIGN METHOD Therefore by applying the lead compenator with ome gain adjutment : D() =.12 4.5 +1 9 +1 we get the compenated ytem with : PM =65, ω c = 22 rad/ec, o
Linear Feature Engineering 11
 Lnear Feature Engneerng 11 2 Least-Squares 2.1 Smple least-squares Consder the followng dataset. We have a bunch of nputs x and correspondng outputs y. The partcular values n ths dataset are x y 0.23 0.19
Lnear Feature Engneerng 11 2 Least-Squares 2.1 Smple least-squares Consder the followng dataset. We have a bunch of nputs x and correspondng outputs y. The partcular values n ths dataset are x y 0.23 0.19
A Preliminary Study on Material Utilization of Stiffened Cylindrical Shells
 Reearch Journal of Appled Scence, Engneerng and echnology 6(5): 757-763, 03 ISSN: 040-7459; e-issn: 040-7467 Maxwell Scentfc Organzaton, 03 Submtted: December 8, 0 Accepted: February 08, 03 Publhed: Augut
Reearch Journal of Appled Scence, Engneerng and echnology 6(5): 757-763, 03 ISSN: 040-7459; e-issn: 040-7467 Maxwell Scentfc Organzaton, 03 Submtted: December 8, 0 Accepted: February 08, 03 Publhed: Augut
Module 3 LOSSY IMAGE COMPRESSION SYSTEMS. Version 2 ECE IIT, Kharagpur
 Module 3 LOSSY IMAGE COMPRESSION SYSTEMS Verson ECE IIT, Kharagpur Lesson 6 Theory of Quantzaton Verson ECE IIT, Kharagpur Instructonal Objectves At the end of ths lesson, the students should be able to:
Module 3 LOSSY IMAGE COMPRESSION SYSTEMS Verson ECE IIT, Kharagpur Lesson 6 Theory of Quantzaton Verson ECE IIT, Kharagpur Instructonal Objectves At the end of ths lesson, the students should be able to:
Physics 120. Exam #1. April 15, 2011
 Phyc 120 Exam #1 Aprl 15, 2011 Name Multple Choce /16 Problem #1 /28 Problem #2 /28 Problem #3 /28 Total /100 PartI:Multple Choce:Crclethebetanwertoeachqueton.Anyothermark wllnotbegvencredt.eachmultple
Phyc 120 Exam #1 Aprl 15, 2011 Name Multple Choce /16 Problem #1 /28 Problem #2 /28 Problem #3 /28 Total /100 PartI:Multple Choce:Crclethebetanwertoeachqueton.Anyothermark wllnotbegvencredt.eachmultple
Time Synchronization for Wireless Sensor Networks
 3 Tme Synchronzaton for Wrele Senor etwork Kyoung-Lae oh Texa A&M Unverty Yk-Chung Wu The Unverty of Hong Kong Khald Qaraqe Texa A&M Unverty Erchn Serpedn Texa A&M Unverty 3. Introducton... 373 3. Sgnal
3 Tme Synchronzaton for Wrele Senor etwork Kyoung-Lae oh Texa A&M Unverty Yk-Chung Wu The Unverty of Hong Kong Khald Qaraqe Texa A&M Unverty Erchn Serpedn Texa A&M Unverty 3. Introducton... 373 3. Sgnal
Pop-Click Noise Detection Using Inter-Frame Correlation for Improved Portable Auditory Sensing
 Advanced Scence and Technology Letters, pp.164-168 http://dx.do.org/10.14257/astl.2013 Pop-Clc Nose Detecton Usng Inter-Frame Correlaton for Improved Portable Audtory Sensng Dong Yun Lee, Kwang Myung Jeon,
Advanced Scence and Technology Letters, pp.164-168 http://dx.do.org/10.14257/astl.2013 Pop-Clc Nose Detecton Usng Inter-Frame Correlaton for Improved Portable Audtory Sensng Dong Yun Lee, Kwang Myung Jeon,
A Complexity-Based Approach in Image Compression using Neural Networks
 Internatonal Journal of Sgnal Proceng 5; www.waet.org Sprng 009 A Complexty-Baed Approach n Image Compreon ung eural etwork Had Ve, Manour Jamzad Abtract In th paper we preent an adaptve method for mage
Internatonal Journal of Sgnal Proceng 5; www.waet.org Sprng 009 A Complexty-Baed Approach n Image Compreon ung eural etwork Had Ve, Manour Jamzad Abtract In th paper we preent an adaptve method for mage
Outline. Communication. Bellman Ford Algorithm. Bellman Ford Example. Bellman Ford Shortest Path [1]
![Outline. Communication. Bellman Ford Algorithm. Bellman Ford Example. Bellman Ford Shortest Path [1] Outline. Communication. Bellman Ford Algorithm. Bellman Ford Example. Bellman Ford Shortest Path [1]](/thumbs/81/84170417.jpg) DYNAMIC SHORTEST PATH SEARCH AND SYNCHRONIZED TASK SWITCHING Jay Wagenpfel, Adran Trachte 2 Outlne Shortest Communcaton Path Searchng Bellmann Ford algorthm Algorthm for dynamc case Modfcatons to our algorthm
DYNAMIC SHORTEST PATH SEARCH AND SYNCHRONIZED TASK SWITCHING Jay Wagenpfel, Adran Trachte 2 Outlne Shortest Communcaton Path Searchng Bellmann Ford algorthm Algorthm for dynamc case Modfcatons to our algorthm
Circuit Theorems. Introduction
 //5 Crcut eorem ntroducton nearty Property uperpoton ource Tranformaton eenn eorem orton eorem Maxmum Power Tranfer ummary ntroducton To deelop analy technque applcable to lnear crcut. To mplfy crcut analy
//5 Crcut eorem ntroducton nearty Property uperpoton ource Tranformaton eenn eorem orton eorem Maxmum Power Tranfer ummary ntroducton To deelop analy technque applcable to lnear crcut. To mplfy crcut analy
Digital Control System
 Digital Control Sytem - A D D A Micro ADC DAC Proceor Correction Element Proce Clock Meaurement A: Analog D: Digital Continuou Controller and Digital Control Rt - c Plant yt Continuou Controller Digital
Digital Control Sytem - A D D A Micro ADC DAC Proceor Correction Element Proce Clock Meaurement A: Analog D: Digital Continuou Controller and Digital Control Rt - c Plant yt Continuou Controller Digital
Statistical Properties of the OLS Coefficient Estimators. 1. Introduction
 ECOOMICS 35* -- OTE 4 ECO 35* -- OTE 4 Stattcal Properte of the OLS Coeffcent Etmator Introducton We derved n ote the OLS (Ordnary Leat Square etmator ˆβ j (j, of the regreon coeffcent βj (j, n the mple
ECOOMICS 35* -- OTE 4 ECO 35* -- OTE 4 Stattcal Properte of the OLS Coeffcent Etmator Introducton We derved n ote the OLS (Ordnary Leat Square etmator ˆβ j (j, of the regreon coeffcent βj (j, n the mple
The Study of Teaching-learning-based Optimization Algorithm
 Advanced Scence and Technology Letters Vol. (AST 06), pp.05- http://dx.do.org/0.57/astl.06. The Study of Teachng-learnng-based Optmzaton Algorthm u Sun, Yan fu, Lele Kong, Haolang Q,, Helongang Insttute
Advanced Scence and Technology Letters Vol. (AST 06), pp.05- http://dx.do.org/0.57/astl.06. The Study of Teachng-learnng-based Optmzaton Algorthm u Sun, Yan fu, Lele Kong, Haolang Q,, Helongang Insttute
Tokyo Institute of Technology Periodic Sequencing Control over Multi Communication Channels with Packet Losses
 oyo Insttute of echnology Fujta Laboratory oyo Insttute of echnology erodc Sequencng Control over Mult Communcaton Channels wth acet Losses FL6-7- /8/6 zwrman Gusrald oyo Insttute of echnology Fujta Laboratory
oyo Insttute of echnology Fujta Laboratory oyo Insttute of echnology erodc Sequencng Control over Mult Communcaton Channels wth acet Losses FL6-7- /8/6 zwrman Gusrald oyo Insttute of echnology Fujta Laboratory
Supervised Learning. Neural Networks and Back-Propagation Learning. Credit Assignment Problem. Feedforward Network. Adaptive System.
 Part 7: Neura Networ & earnng /2/05 Superved earnng Neura Networ and Bac-Propagaton earnng Produce dered output for tranng nput Generaze reaonaby & appropratey to other nput Good exampe: pattern recognton
Part 7: Neura Networ & earnng /2/05 Superved earnng Neura Networ and Bac-Propagaton earnng Produce dered output for tranng nput Generaze reaonaby & appropratey to other nput Good exampe: pattern recognton
EECE 301 Signals & Systems Prof. Mark Fowler
 -T Sytem: Ung Bode Plot EEE 30 Sgnal & Sytem Pro. Mark Fowler Note Set #37 /3 Bode Plot Idea an Help Vualze What rcut Do Lowpa Flter Break Pont = / H ( ) j /3 Hghpa Flter c = / L Bandpa Flter n nn ( a)
-T Sytem: Ung Bode Plot EEE 30 Sgnal & Sytem Pro. Mark Fowler Note Set #37 /3 Bode Plot Idea an Help Vualze What rcut Do Lowpa Flter Break Pont = / H ( ) j /3 Hghpa Flter c = / L Bandpa Flter n nn ( a)
This appendix presents the derivations and proofs omitted from the main text.
 Onlne Appendx A Appendx: Omtted Dervaton and Proof Th appendx preent the dervaton and proof omtted from the man text A Omtted dervaton n Secton Mot of the analy provded n the man text Here, we formally
Onlne Appendx A Appendx: Omtted Dervaton and Proof Th appendx preent the dervaton and proof omtted from the man text A Omtted dervaton n Secton Mot of the analy provded n the man text Here, we formally
CHAPTER 8 OBSERVER BASED REDUCED ORDER CONTROLLER DESIGN FOR LARGE SCALE LINEAR DISCRETE-TIME CONTROL SYSTEMS
 CHAPTER 8 OBSERVER BASED REDUCED ORDER CONTROLLER DESIGN FOR LARGE SCALE LINEAR DISCRETE-TIME CONTROL SYSTEMS 8.1 INTRODUCTION 8.2 REDUCED ORDER MODEL DESIGN FOR LINEAR DISCRETE-TIME CONTROL SYSTEMS 8.3
CHAPTER 8 OBSERVER BASED REDUCED ORDER CONTROLLER DESIGN FOR LARGE SCALE LINEAR DISCRETE-TIME CONTROL SYSTEMS 8.1 INTRODUCTION 8.2 REDUCED ORDER MODEL DESIGN FOR LINEAR DISCRETE-TIME CONTROL SYSTEMS 8.3
A Hybrid Evolution Algorithm with Application Based on Chaos Genetic Algorithm and Particle Swarm Optimization
 Natonal Conference on Informaton Technology and Computer Scence (CITCS ) A Hybrd Evoluton Algorthm wth Applcaton Baed on Chao Genetc Algorthm and Partcle Swarm Optmzaton Fu Yu School of Computer & Informaton
Natonal Conference on Informaton Technology and Computer Scence (CITCS ) A Hybrd Evoluton Algorthm wth Applcaton Baed on Chao Genetc Algorthm and Partcle Swarm Optmzaton Fu Yu School of Computer & Informaton
No! Yes! Only if reactions occur! Yes! Ideal Gas, change in temperature or pressure. Survey Results. Class 15. Is the following possible?
 Survey Reult Chapter 5-6 (where we are gong) % of Student 45% 40% 35% 30% 25% 20% 15% 10% 5% 0% Hour Spent on ChE 273 1-2 3-4 5-6 7-8 9-10 11+ Hour/Week 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2017 F17
Survey Reult Chapter 5-6 (where we are gong) % of Student 45% 40% 35% 30% 25% 20% 15% 10% 5% 0% Hour Spent on ChE 273 1-2 3-4 5-6 7-8 9-10 11+ Hour/Week 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2017 F17
Makoto SAKANE GS Yuasa Power Electronics Ltd Osaka ,Japan. U d
 Dtrbuted Parallel Operaton of Modfed Deadbeat Controlled UPS Inverter Meng WAG, Fangheng LI, Yadong LIU, Lpe HUAG State Key Lab of Power Sytem Department of Electrcal Engneerng, nghua Unverty Bejng, 100084,
Dtrbuted Parallel Operaton of Modfed Deadbeat Controlled UPS Inverter Meng WAG, Fangheng LI, Yadong LIU, Lpe HUAG State Key Lab of Power Sytem Department of Electrcal Engneerng, nghua Unverty Bejng, 100084,
DEPARTMENT MATHEMATIK SCHWERPUNKT MATHEMATISCHE STATISTIK UND STOCHASTISCHE PROZESSE
 U N I V E R S I T Ä T H A M B U R G Strong and Weak Approxmaton Method for Stochatc Dfferental Equaton Some Recent Development Andrea Rößler Preprnt No. - Februar DEPARTMENT MATHEMATIK SCHWERPUNKT MATHEMATISCHE
U N I V E R S I T Ä T H A M B U R G Strong and Weak Approxmaton Method for Stochatc Dfferental Equaton Some Recent Development Andrea Rößler Preprnt No. - Februar DEPARTMENT MATHEMATIK SCHWERPUNKT MATHEMATISCHE
Chapter 7 Four-Wave Mixing phenomena
 Chapter 7 Four-Wave Mx phenomena We wll dcu n th chapter the general nonlnear optcal procee wth four nteract electromagnetc wave n a NLO medum. Frt note that FWM procee are allowed n all meda (nveron or
Chapter 7 Four-Wave Mx phenomena We wll dcu n th chapter the general nonlnear optcal procee wth four nteract electromagnetc wave n a NLO medum. Frt note that FWM procee are allowed n all meda (nveron or
Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineeing Imperial College London. E4.20 Digital IC Design. Median Filter Project Specification
 Desgn Project Specfcaton Medan Flter Department of Electrcal & Electronc Engneeng Imperal College London E4.20 Dgtal IC Desgn Medan Flter Project Specfcaton A medan flter s used to remove nose from a sampled
Desgn Project Specfcaton Medan Flter Department of Electrcal & Electronc Engneeng Imperal College London E4.20 Dgtal IC Desgn Medan Flter Project Specfcaton A medan flter s used to remove nose from a sampled
Lectures on Multivariable Feedback Control
 Lecture on Multvarable Feedback Control Al Karmpour Department of Electrcal Engneerng, Faculty of Engneerng, Ferdow Unverty of Mahhad September 9 Chapter : Introducton to Multvarable Control - Multvarable
Lecture on Multvarable Feedback Control Al Karmpour Department of Electrcal Engneerng, Faculty of Engneerng, Ferdow Unverty of Mahhad September 9 Chapter : Introducton to Multvarable Control - Multvarable
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen the world leadng publher of Open Acce book Bult by centt for centt 4 116 12M Open acce book avalable Internatonal author and edtor Download Our author are among the 154 Countre delvered
We are IntechOpen the world leadng publher of Open Acce book Bult by centt for centt 4 116 12M Open acce book avalable Internatonal author and edtor Download Our author are among the 154 Countre delvered
Adaptive sliding mode reliable excitation control design for power systems
 Acta Technca 6, No. 3B/17, 593 6 c 17 Insttute of Thermomechancs CAS, v.v.. Adaptve sldng mode relable exctaton control desgn for power systems Xuetng Lu 1, 3, Yanchao Yan Abstract. In ths paper, the problem
Acta Technca 6, No. 3B/17, 593 6 c 17 Insttute of Thermomechancs CAS, v.v.. Adaptve sldng mode relable exctaton control desgn for power systems Xuetng Lu 1, 3, Yanchao Yan Abstract. In ths paper, the problem
Chapter - 2. Distribution System Power Flow Analysis
 Chapter - 2 Dstrbuton System Power Flow Analyss CHAPTER - 2 Radal Dstrbuton System Load Flow 2.1 Introducton Load flow s an mportant tool [66] for analyzng electrcal power system network performance. Load
Chapter - 2 Dstrbuton System Power Flow Analyss CHAPTER - 2 Radal Dstrbuton System Load Flow 2.1 Introducton Load flow s an mportant tool [66] for analyzng electrcal power system network performance. Load
AP Statistics Ch 3 Examining Relationships
 Introducton To tud relatonhp between varable, we mut meaure the varable on the ame group of ndvdual. If we thnk a varable ma eplan or even caue change n another varable, then the eplanator varable and
Introducton To tud relatonhp between varable, we mut meaure the varable on the ame group of ndvdual. If we thnk a varable ma eplan or even caue change n another varable, then the eplanator varable and
GREY PREDICTIVE PROCESS CONTROL CHARTS
 The 4th Internatonal Conference on Qualty Relablty Augut 9-th, 2005 Bejng, Chna GREY PREDICTIVE PROCESS CONTROL CHARTS RENKUAN GUO, TIM DUNNE Department of Stattcal Scence, Unverty of Cape Town, Prvate
The 4th Internatonal Conference on Qualty Relablty Augut 9-th, 2005 Bejng, Chna GREY PREDICTIVE PROCESS CONTROL CHARTS RENKUAN GUO, TIM DUNNE Department of Stattcal Scence, Unverty of Cape Town, Prvate
Batch Reinforcement Learning
 Batch Renforcement Learnng Alan Fern * Baed n part on lde by Ronald Parr Overvew What batch renforcement learnng? Leat Square Polcy Iteraton Ftted Q-teraton Batch DQN Onlne veru Batch RL Onlne RL: ntegrate
Batch Renforcement Learnng Alan Fern * Baed n part on lde by Ronald Parr Overvew What batch renforcement learnng? Leat Square Polcy Iteraton Ftted Q-teraton Batch DQN Onlne veru Batch RL Onlne RL: ntegrate
Alpha Risk of Taguchi Method with L 18 Array for NTB Type QCH by Simulation
 Proceedng of the World Congre on Engneerng 00 Vol II WCE 00, July -, 00, London, U.K. Alpha Rk of Taguch Method wth L Array for NTB Type QCH by Smulaton A. Al-Refae and M.H. L Abtract Taguch method a wdely
Proceedng of the World Congre on Engneerng 00 Vol II WCE 00, July -, 00, London, U.K. Alpha Rk of Taguch Method wth L Array for NTB Type QCH by Smulaton A. Al-Refae and M.H. L Abtract Taguch method a wdely
CHAPTER 4 DESIGN OF STATE FEEDBACK CONTROLLERS AND STATE OBSERVERS USING REDUCED ORDER MODEL
 98 CHAPTER DESIGN OF STATE FEEDBACK CONTROLLERS AND STATE OBSERVERS USING REDUCED ORDER MODEL INTRODUCTION The deign of ytem uing tate pace model for the deign i called a modern control deign and it i
98 CHAPTER DESIGN OF STATE FEEDBACK CONTROLLERS AND STATE OBSERVERS USING REDUCED ORDER MODEL INTRODUCTION The deign of ytem uing tate pace model for the deign i called a modern control deign and it i
The Price of Anarchy in a Network Pricing Game
 The Prce of Anarchy n a Network Prcng Game John Muaccho and Shuang Wu Abtract We analyze a game theoretc model of competng network ervce provder that trategcally prce ther ervce n the preence of elatc
The Prce of Anarchy n a Network Prcng Game John Muaccho and Shuang Wu Abtract We analyze a game theoretc model of competng network ervce provder that trategcally prce ther ervce n the preence of elatc
Lecture 10 Support Vector Machines II
 Lecture 10 Support Vector Machnes II 22 February 2016 Taylor B. Arnold Yale Statstcs STAT 365/665 1/28 Notes: Problem 3 s posted and due ths upcomng Frday There was an early bug n the fake-test data; fxed
Lecture 10 Support Vector Machnes II 22 February 2016 Taylor B. Arnold Yale Statstcs STAT 365/665 1/28 Notes: Problem 3 s posted and due ths upcomng Frday There was an early bug n the fake-test data; fxed
Not at Steady State! Yes! Only if reactions occur! Yes! Ideal Gas, change in temperature or pressure. Yes! Class 15. Is the following possible?
 Chapter 5-6 (where we are gong) Ideal gae and lqud (today) Dente Partal preure Non-deal gae (next tme) Eqn. of tate Reduced preure and temperature Compreblty chart (z) Vapor-lqud ytem (Ch. 6) Vapor preure
Chapter 5-6 (where we are gong) Ideal gae and lqud (today) Dente Partal preure Non-deal gae (next tme) Eqn. of tate Reduced preure and temperature Compreblty chart (z) Vapor-lqud ytem (Ch. 6) Vapor preure
STOCHASTIC BEHAVIOUR OF COMMUNICATION SUBSYSTEM OF COMMUNICATION SATELLITE
 IJS 4 () July Sharma & al ehavour of Subytem of ommuncaton Satellte SOHSI HVIOU O OMMUNIION SUSYSM O OMMUNIION SLLI SK Mttal eepankar Sharma & Neelam Sharma 3 S he author n th paper have dcued the tochatc
IJS 4 () July Sharma & al ehavour of Subytem of ommuncaton Satellte SOHSI HVIOU O OMMUNIION SUSYSM O OMMUNIION SLLI SK Mttal eepankar Sharma & Neelam Sharma 3 S he author n th paper have dcued the tochatc
FREE VIBRATION ANALYSIS OF CLAMPED-FREE COMPOSITE CYLINDRICAL SHELLS WITH AN INTERIOR RECTANGULAR PLATE
 FREE VIBRATION ANALYSIS OF CLAPED-FREE COPOSITE CYLINDRICAL SHELLS WITH AN INTERIOR RECTANGULAR PLATE Young-Shn Lee and young-hwan Cho Department of echancal Degn Engneerng, Chungnam Natonal Unverty, 0
FREE VIBRATION ANALYSIS OF CLAPED-FREE COPOSITE CYLINDRICAL SHELLS WITH AN INTERIOR RECTANGULAR PLATE Young-Shn Lee and young-hwan Cho Department of echancal Degn Engneerng, Chungnam Natonal Unverty, 0
Analytical and Empirical Study of Particle Swarm Optimization with a Sigmoid Decreasing Inertia W eight
 Electrcal and Electronc 47 Analytcal and Emprcal Study of Partcle Sarm Optmzaton th a Sgmod Decreang Inerta W eght And Adranyah, Shamudn H. M. Amn Departmentof Electrcal, Faculty ofindutral Engneerng,
Electrcal and Electronc 47 Analytcal and Emprcal Study of Partcle Sarm Optmzaton th a Sgmod Decreang Inerta W eght And Adranyah, Shamudn H. M. Amn Departmentof Electrcal, Faculty ofindutral Engneerng,
NUMERICAL DIFFERENTIATION
 NUMERICAL DIFFERENTIATION 1 Introducton Dfferentaton s a method to compute the rate at whch a dependent output y changes wth respect to the change n the ndependent nput x. Ths rate of change s called the
NUMERICAL DIFFERENTIATION 1 Introducton Dfferentaton s a method to compute the rate at whch a dependent output y changes wth respect to the change n the ndependent nput x. Ths rate of change s called the
Operating conditions of a mine fan under conditions of variable resistance
 Paper No. 11 ISMS 216 Operatng condtons of a mne fan under condtons of varable resstance Zhang Ynghua a, Chen L a, b, Huang Zhan a, *, Gao Yukun a a State Key Laboratory of Hgh-Effcent Mnng and Safety
Paper No. 11 ISMS 216 Operatng condtons of a mne fan under condtons of varable resstance Zhang Ynghua a, Chen L a, b, Huang Zhan a, *, Gao Yukun a a State Key Laboratory of Hgh-Effcent Mnng and Safety
DEADLOCK INDEX ANALYSIS OF MULTI-LEVEL QUEUE SCHEDULING IN OPERATING SYSTEM USING DATA MODEL APPROACH
 GESJ: Computer Scence and Telecommuncaton 2 No.(29 ISSN 2-232 DEADLOCK INDEX ANALYSIS OF MULTI-LEVEL QUEUE SCHEDULING IN OPERATING SYSTEM USING DATA MODEL APPROACH D. Shukla, Shweta Ojha 2 Deptt. of Mathematc
GESJ: Computer Scence and Telecommuncaton 2 No.(29 ISSN 2-232 DEADLOCK INDEX ANALYSIS OF MULTI-LEVEL QUEUE SCHEDULING IN OPERATING SYSTEM USING DATA MODEL APPROACH D. Shukla, Shweta Ojha 2 Deptt. of Mathematc
