Linear Wire Antennas
|
|
|
- Darren Lambert
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Linear Wire Antennas Ranga Rodrigo August 4, 010 Lecture notes are fully based on Balanis?. Some diagrams and text are directly from the books. Contents 1 Infinitesimal Dipole 1 Small Dipole 7 3 Finite-Length Dipole 9 Wire antennas, linear or curved, are some of the oldest, simplest, cheapest, and in many cases the most versatile for many applications. 1 Infinitesimal Dipole An infinitesimal linear wire l λ) is positioned symmetrically at the origin of the coordinate system and oriented along the z axis. The spatial variation of the current is assumed to be constant and given by I z ) = â z I 0 where I 0 is a constant. 1
2 The source only carries an electric current I e. I m and the potential function F are zero. To find A we write Ax, y, z) = µ I e x, y, z kr e j ) 4π R dl. where x, y, z) : Observation point coordinates. x, y, z ) : Coordinates of the source. C R : The distance from any point on the source to the observation point. C : Path along the length of the source. I e x, y, z ) = â z I 0. x = 0, y = 0, z = 0, for the infinitesimal dipole. R = x x ) + y y ) + z z ) = x + y + z = r constant). dl = d z. µi l/ 0 kr Ax, y, z) = â z e j d z µi 0 l = â z 4π l/ 4π e j kr. z θ x, y, z) x, y, z ) φ y x
3 Next: H A : H A = 1 µ A, E A: H A = J + j ωɛe A. Transformation from rectangular to spherical coordinates: A x = 0, A y = 0, A z 0. A r sinθ cosφ sinθ sinφ cosθ A x A θ = cosθ cosφ cosθ sinφ sinθ A y A φ sinφ cosφ 0 A z A r = A z cosθ = µi j kr A θ = A z sinθ = µi 0l e A φ = 0. A = âr r sinθ θ A φ sinθ) φ A θ H = 1 â φ µ r r r A θ) θ A r H r = H θ = 0. H φ = j ki 0l sinθ E r = η I 0l cosθ πr E θ = j η ki 0l sinθ E φ = 0. cosθ. j kr + âθ 1 r sinθ e j kr. j kr E = E A = 1 j ωɛ H j kr e j kr j kr 1 kr ) φ A r r r A φ) + âφ r r r A θ) θ A r e j kr. The E and H components are valid everywhere except on the source itself. 3
4 z â r, E r, H r â φ, E φ, H φ θ â θ, E θ, H θ φ y x Power Density and Radiation Resistance For a lossless antenna, the real part of the input impedance is designated as the radiation resistance, that power is transferred from the guided wave to the free space wave. W = 1 E H = 1 â r E r + â θ E θ ) ). = 1 â r E θ H φ â θe r H φ W r = η I 0 l sin θ 1 8 λ r 1 j kr ) j W θ = j η k I 0l cosθ sinθ 16π r 3. 1 kr ) â φ H φ The complex power moving int eh radial direction π π P = W d s = â r W r + a θ W θ ) a r r sinθdθdφ S π π = W r r sinθdθdφ 0 0 = η π I 0 l j λ kr ) ).
5 The transverse component W θ does not contribute to the integrals. Thus P does not represent the total complex power radiated by the antenna. W θ is purely imaginary, and does not contribute to any real radiated power. It contributes to the imaginary reactive) power. The reactive power density, which is most dominant for small values of kr, has both radial and transverse components. It merely changes between outward and inward directions to form a standing wave at a rate twice per cycle. It also moves in the transverse direction. Time average power radiated is π ) p rad = η I 0 l 3 λ. For large values of kr kr 1), the reactive power diminishes. For free space η 10π, ) ) π l ) l R rad = η = 80π.. 3 λ λ Near-Field Region kr 1 E r j η I j kr 0l e πkr 3 cosθ. j kr E θ j η I 0l e 4πkr 3 E φ = H r = H θ = 0. H φ I j kr E r and E θ are in time-phase. E r and E θ are in time-phase quadrature with H φ. Therefore, there is no time-average power flow associated with them. Intermediate-Field Region kr > 1 E r η I j kr 0l e πkr cosθ. j kr E θ j η ki 4πkr E φ = H r = H θ = 0. H φ j ki j kr 5
6 E r and E θ approach time-phase quadrature. They form a rotating vector whose tip traces and ellipse in a plane parallel to the direction of propagation: cross field. Far Field kr 1 The ratio of E θ to H φ is equal to E θ j η ki j kr 4πkr E r E φ = H r = H θ = 0. H φ j ki j kr Z w = E θ H φ η. where Z w is the wave impedance and η is the intrinsic impedance πΩ for free-space.) E- and H-field components are perpendicular to each other, transverse to the direction of propagation, and r variations are separable from those of θ and φ. This relationship is applicable in the far-field region of all antennas of finite dimensions. Directivity The average power density The radiation intensity W av = 1 Re E H ) 1 = â r η E θ η = â r ki 0 l sin θ 4π r. U = r W av = η ki 0 l 4π sin θ = r Eθ r,θ,φ). η The maximum value occurs at θ = π/: U max = η ki 0 l 4π. D 0 = 4π U max P rad = 3. 6
7 The maximum effective aperture λ A em = )D 0 = 3λ 4π 8π. P rad = 1 I 0 R rad. ) l. R rad = η π 3 λ Small Dipole The current distribution of the infinitesimal dipole l < λ/50) is I 0, a constant. For a small dipole λ/50 l λ/10) the triangular current distribution approximation must be used. z I 0 I The current distribution is I e x, y, z ) = Ax, y, z) = µ 0 â z I ) e j kr 4π l/ l z R {â z I 0 1 l z ), 0 z l, â z I l z ), l z 0. d z + â z l/ 0 I 0 1 ) e j kr l z R d z. Because the overall length of the dipole is small, the value of R for different values of z along the length of the wire are not much different from r. 7
8 z l/ d z z θ θ R r Pr,θ,φ) l/ φ = φ y x Maximum phase error due to the assumption R r is kl = π 10 = 18 for λ/10. j kr 1 µi0 e A = â z A z = â z, which is one half of that obtained in the previous section for the infinitesimal dipole. Far-Zone Fields, kr 1 E θ j η ki j kr 8πkr E r E φ = H r = H θ = 0. H φ j ki j kr 8πr Directivity and the maximum effective area are the same as for the infinitesimal dipole. R rad = P ) rad l I 0 = 0π λ which is 1/4 of the value for the infinitesimal dipole. 8
9 3 Finite-Length Dipole We can analyze the radiation characteristics of a dipole with any length using magnetic vector potential A. For a thin, center-fed finite-length dipole l λ/10,d λ), the approximate current distribution can be written as I e x = 0, y = 0, z â z I 0 sin k l ) = z ), 0 z l, â z I 0 sin k l + z ), l z 0. In the far field, we have, z r, θ θ. For amplitude: R r. For phase: R r z cosθ. z z l/ d z z θ θ R r Pr,θ,φ) d z z θ θ R r Pr,θ,φ) l/ x φ = φ y x φ = φ y Maximum phase error due to the assumption R r is kl = π 10 = 18 for λ/10. Ax, y, z) = µ 4π C kr µe j Ax, y, z) = C I e x, y, z kr e j ) R dl. I e x, y, z )e j kz cosθ d z. The finite dipole antenna is subdivided into a number of infinitesimal dipoles of length δz. For an infinitesimal dipole of length d z positioned along the z-axis at z de θ j ηki ex, y, z j kr )e sinθd z. 4πR de r de φ = d H r = d H θ = 0 d H φ j ki ex, y, z j kr )e sinθd z. 4πR 9
10 Using the far field approximation de θ j ηki ex, y, z j kr )e sinθe j kz cosθ d z. Summing the contribution from all the infinitesimal elements E θ = l/ l/ kr ke j l/ de θ = j η sinθ I e x, y, z )e j kz cosθ d z l/ Simplifying E θ j η I j kr 0e πr H φ j I j kr 0e πr cos cos kl cosθ ) cos sinθ kl cosθ ) cos sinθ kl kl ) ).. Power Density, Radiation Intensity, and Radiation Resistance W av = 1 Re E H = 1 Re â θ E θ â φ H φ = 1 Re â θ E θ â φ E θ /η 10
Linear Wire Antennas. EE-4382/ Antenna Engineering
 EE-4382/5306 - Antenna Engineering Outline Introduction Infinitesimal Dipole Small Dipole Finite Length Dipole Half-Wave Dipole Ground Effect Constantine A. Balanis, Antenna Theory: Analysis and Design
EE-4382/5306 - Antenna Engineering Outline Introduction Infinitesimal Dipole Small Dipole Finite Length Dipole Half-Wave Dipole Ground Effect Constantine A. Balanis, Antenna Theory: Analysis and Design
ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVE PROPAGATION EC 442. Prof. Darwish Abdel Aziz
 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVE PROPAGATION EC 442 Prof. Darwish Abdel Aziz CHAPTER 6 LINEAR WIRE ANTENNAS INFINITESIMAL DIPOLE INTRODUCTION Wire antennas, linear or curved, are some of the oldest, simplest, cheapest,
ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVE PROPAGATION EC 442 Prof. Darwish Abdel Aziz CHAPTER 6 LINEAR WIRE ANTENNAS INFINITESIMAL DIPOLE INTRODUCTION Wire antennas, linear or curved, are some of the oldest, simplest, cheapest,
Radiation Integrals and Auxiliary Potential Functions
 Radiation Integrals and Auxiliary Potential Functions Ranga Rodrigo June 23, 2010 Lecture notes are fully based on Balanis [?]. Some diagrams and text are directly from the books. Contents 1 The Vector
Radiation Integrals and Auxiliary Potential Functions Ranga Rodrigo June 23, 2010 Lecture notes are fully based on Balanis [?]. Some diagrams and text are directly from the books. Contents 1 The Vector
ANTENNAS. Vector and Scalar Potentials. Maxwell's Equations. E = jωb. H = J + jωd. D = ρ (M3) B = 0 (M4) D = εe
 ANTENNAS Vector and Scalar Potentials Maxwell's Equations E = jωb H = J + jωd D = ρ B = (M) (M) (M3) (M4) D = εe B= µh For a linear, homogeneous, isotropic medium µ and ε are contant. Since B =, there
ANTENNAS Vector and Scalar Potentials Maxwell's Equations E = jωb H = J + jωd D = ρ B = (M) (M) (M3) (M4) D = εe B= µh For a linear, homogeneous, isotropic medium µ and ε are contant. Since B =, there
Arrays. Ranga Rodrigo. August 19, 2010
 Arrays Ranga Rodrigo August 9, 00 Lecture notes are fully based on Balanis [?. Some diagrams and text are directly from the books. Contents Two-Element Array -Element Linear Array: Uniform Amplitude and
Arrays Ranga Rodrigo August 9, 00 Lecture notes are fully based on Balanis [?. Some diagrams and text are directly from the books. Contents Two-Element Array -Element Linear Array: Uniform Amplitude and
Aperture Antennas 1 Introduction
 1 Introduction Very often, we have antennas in aperture forms, for example, the antennas shown below: Pyramidal horn antenna Conical horn antenna 1 Paraboloidal antenna Slot antenna Analysis Method for.1
1 Introduction Very often, we have antennas in aperture forms, for example, the antennas shown below: Pyramidal horn antenna Conical horn antenna 1 Paraboloidal antenna Slot antenna Analysis Method for.1
The most fundamental antenna is the incremental dipole as pictured in Figure 1. a Z. I o δh. a X. Figure 1. Incremental dipole
 . Chapter 13 Antennas Features Used crossp( ), dotp( ), real( ), conj( ), Í, NewProb,, Polar graphs Setup 1 NewFold ant setmode("complex Format", "Polar") This chapter describes how to perform basic antenna
. Chapter 13 Antennas Features Used crossp( ), dotp( ), real( ), conj( ), Í, NewProb,, Polar graphs Setup 1 NewFold ant setmode("complex Format", "Polar") This chapter describes how to perform basic antenna
Linear Wire Antennas Dipoles and Monopoles
 inear Wire Antennas Dipoles and Monopoles The dipole and the monopole are arguably the two most widely used antennas across the UHF, VHF and lower-microwave bands. Arrays of dipoles are commonly used as
inear Wire Antennas Dipoles and Monopoles The dipole and the monopole are arguably the two most widely used antennas across the UHF, VHF and lower-microwave bands. Arrays of dipoles are commonly used as
LECTURE 18: Horn Antennas (Rectangular horn antennas. Circular apertures.)
 LCTUR 18: Horn Antennas (Rectangular horn antennas. Circular apertures.) 1 Rectangular Horn Antennas Horn antennas are popular in the microwave bands (above 1 GHz). Horns provide high gain, low VSWR (with
LCTUR 18: Horn Antennas (Rectangular horn antennas. Circular apertures.) 1 Rectangular Horn Antennas Horn antennas are popular in the microwave bands (above 1 GHz). Horns provide high gain, low VSWR (with
Basics of Electromagnetics Maxwell s Equations (Part - I)
 Basics of Electromagnetics Maxwell s Equations (Part - I) Soln. 1. C A. dl = C. d S [GATE 1994: 1 Mark] A. dl = A. da using Stoke s Theorem = S A. ds 2. The electric field strength at distant point, P,
Basics of Electromagnetics Maxwell s Equations (Part - I) Soln. 1. C A. dl = C. d S [GATE 1994: 1 Mark] A. dl = A. da using Stoke s Theorem = S A. ds 2. The electric field strength at distant point, P,
PHYS 1441 Section 002 Lecture #6
 PHYS 1441 Section 002 Lecture #6 Monday, Sept. 18, 2017 Chapter 21 Motion of a Charged Particle in an Electric Field Electric Dipoles Chapter 22 Electric Flux Gauss Law with many charges What is Gauss
PHYS 1441 Section 002 Lecture #6 Monday, Sept. 18, 2017 Chapter 21 Motion of a Charged Particle in an Electric Field Electric Dipoles Chapter 22 Electric Flux Gauss Law with many charges What is Gauss
Angular Momentum. Classically the orbital angular momentum with respect to a fixed origin is. L = r p. = yp z. L x. zp y L y. = zp x. xpz L z.
 Angular momentum is an important concept in quantum theory, necessary for analyzing motion in 3D as well as intrinsic properties such as spin Classically the orbital angular momentum with respect to a
Angular momentum is an important concept in quantum theory, necessary for analyzing motion in 3D as well as intrinsic properties such as spin Classically the orbital angular momentum with respect to a
Unit 2: Small Antennas + Some Antenna Parameters
 Unit 2: Small Antennas + Some Antenna Parameters Antenna Theory ENGI 9816 Khalid El-Darymli, Ph.D., EIT Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science Memorial
Unit 2: Small Antennas + Some Antenna Parameters Antenna Theory ENGI 9816 Khalid El-Darymli, Ph.D., EIT Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science Memorial
Problem 8.18 For some types of glass, the index of refraction varies with wavelength. A prism made of a material with
 Problem 8.18 For some types of glass, the index of refraction varies with wavelength. A prism made of a material with n = 1.71 4 30 λ 0 (λ 0 in µm), where λ 0 is the wavelength in vacuum, was used to disperse
Problem 8.18 For some types of glass, the index of refraction varies with wavelength. A prism made of a material with n = 1.71 4 30 λ 0 (λ 0 in µm), where λ 0 is the wavelength in vacuum, was used to disperse
EM radiation - Lecture 14
 EM radiation - Lecture 14 1 Review Begin with a review of the potentials, fields, and Poynting vector for a point charge in accelerated motion. The retarded potential forms are given below. The source
EM radiation - Lecture 14 1 Review Begin with a review of the potentials, fields, and Poynting vector for a point charge in accelerated motion. The retarded potential forms are given below. The source
Introduction and Vectors Lecture 1
 1 Introduction Introduction and Vectors Lecture 1 This is a course on classical Electromagnetism. It is the foundation for more advanced courses in modern physics. All physics of the modern era, from quantum
1 Introduction Introduction and Vectors Lecture 1 This is a course on classical Electromagnetism. It is the foundation for more advanced courses in modern physics. All physics of the modern era, from quantum
Antenna Theory Exam No. 1 October 9, 2000
 ntenna Theory Exa No. 1 October 9, 000 Solve the following 4 probles. Each proble is 0% of the grade. To receive full credit, you ust show all work. If you need to assue anything, state your assuptions
ntenna Theory Exa No. 1 October 9, 000 Solve the following 4 probles. Each proble is 0% of the grade. To receive full credit, you ust show all work. If you need to assue anything, state your assuptions
Peeter Joot Fundamental parameters of antennas W = E H. E B.
 Peeter Joot peeter.joot@gmail.com Fundamental parameters of antennas This is my first set of notes for the UofT course ECE1229, Advanced Antenna Theory, taught by Prof. Eleftheriades, covering ch.2 [1]
Peeter Joot peeter.joot@gmail.com Fundamental parameters of antennas This is my first set of notes for the UofT course ECE1229, Advanced Antenna Theory, taught by Prof. Eleftheriades, covering ch.2 [1]
Small Antennas and Some Antenna Parameters
 Unit 2 Small Antennas and Some Antenna Parameters 2.1 The Fundamental Source of Radiated Energy We have seen from Maxwell s equations that a time-varying B field (or H field) implies a time-varying E field
Unit 2 Small Antennas and Some Antenna Parameters 2.1 The Fundamental Source of Radiated Energy We have seen from Maxwell s equations that a time-varying B field (or H field) implies a time-varying E field
Plane Waves Part II. 1. For an electromagnetic wave incident from one medium to a second medium, total reflection takes place when
 Plane Waves Part II. For an electromagnetic wave incident from one medium to a second medium, total reflection takes place when (a) The angle of incidence is equal to the Brewster angle with E field perpendicular
Plane Waves Part II. For an electromagnetic wave incident from one medium to a second medium, total reflection takes place when (a) The angle of incidence is equal to the Brewster angle with E field perpendicular
Antennas Prof. Girish Kumar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay. Module 02 Lecture 08 Dipole Antennas-I
 Antennas Prof. Girish Kumar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Module 02 Lecture 08 Dipole Antennas-I Hello, and welcome to today s lecture. Now in the last lecture
Antennas Prof. Girish Kumar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Module 02 Lecture 08 Dipole Antennas-I Hello, and welcome to today s lecture. Now in the last lecture
( z) ( ) ( )( ) ω ω. Wave equation. Transmission line formulas. = v. Helmholtz equation. Exponential Equation. Trig Formulas = Γ. cos sin 1 1+Γ = VSWR
 Wave equation 1 u tu v u(, t f ( vt + g( + vt Helmholt equation U + ku jk U Ae + Be + jk Eponential Equation γ e + e + γ + γ Trig Formulas sin( + y sin cos y+ sin y cos cos( + y cos cos y sin sin y + cos
Wave equation 1 u tu v u(, t f ( vt + g( + vt Helmholt equation U + ku jk U Ae + Be + jk Eponential Equation γ e + e + γ + γ Trig Formulas sin( + y sin cos y+ sin y cos cos( + y cos cos y sin sin y + cos
Electromagnetic Waves
 Electromagnetic Waves Our discussion on dynamic electromagnetic field is incomplete. I H E An AC current induces a magnetic field, which is also AC and thus induces an AC electric field. H dl Edl J ds
Electromagnetic Waves Our discussion on dynamic electromagnetic field is incomplete. I H E An AC current induces a magnetic field, which is also AC and thus induces an AC electric field. H dl Edl J ds
III. Spherical Waves and Radiation
 III. Spherical Waves and Radiation Antennas radiate spherical waves into free space Receiving antennas, reciprocity, path gain and path loss Noise as a limit to reception Ray model for antennas above a
III. Spherical Waves and Radiation Antennas radiate spherical waves into free space Receiving antennas, reciprocity, path gain and path loss Noise as a limit to reception Ray model for antennas above a
2nd Year Electromagnetism 2012:.Exam Practice
 2nd Year Electromagnetism 2012:.Exam Practice These are sample questions of the type of question that will be set in the exam. They haven t been checked the way exam questions are checked so there may
2nd Year Electromagnetism 2012:.Exam Practice These are sample questions of the type of question that will be set in the exam. They haven t been checked the way exam questions are checked so there may
Solutions: Homework 7
 Solutions: Homework 7 Ex. 7.1: Frustrated Total Internal Reflection a) Consider light propagating from a prism, with refraction index n, into air, with refraction index 1. We fix the angle of incidence
Solutions: Homework 7 Ex. 7.1: Frustrated Total Internal Reflection a) Consider light propagating from a prism, with refraction index n, into air, with refraction index 1. We fix the angle of incidence
EEL 4473 Spectral Domain Techniques and Diffraction Theory. Spectral Domain Techniques and Diffraction Theory - 2-D Fields 1
 EEL 4473 Spectral Domain Techniques and Diffraction Theory Spectral Domain Techniques and Diffraction Theory - 2-D Fields 1 References: 1. *R.H. Clark and J. Brown, Diffraction Theory and Antennas, Wiley,
EEL 4473 Spectral Domain Techniques and Diffraction Theory Spectral Domain Techniques and Diffraction Theory - 2-D Fields 1 References: 1. *R.H. Clark and J. Brown, Diffraction Theory and Antennas, Wiley,
Network Theory and the Array Overlap Integral Formulation
 Chapter 7 Network Theory and the Array Overlap Integral Formulation Classical array antenna theory focuses on the problem of pattern synthesis. There is a vast body of work in the literature on methods
Chapter 7 Network Theory and the Array Overlap Integral Formulation Classical array antenna theory focuses on the problem of pattern synthesis. There is a vast body of work in the literature on methods
Maxwell s Equations & Electromagnetic Waves. The Equations So Far...
 Maxwell s Equations & Electromagnetic Waves Maxwell s equations contain the wave equation Velocity of electromagnetic waves c = 2.99792458 x 1 8 m/s Relationship between E and B in an EM wave Energy in
Maxwell s Equations & Electromagnetic Waves Maxwell s equations contain the wave equation Velocity of electromagnetic waves c = 2.99792458 x 1 8 m/s Relationship between E and B in an EM wave Energy in
Module I: Electromagnetic waves
 Module I: Electromagnetic waves Lecture 9: EM radiation Amol Dighe Outline 1 Electric and magnetic fields: radiation components 2 Energy carried by radiation 3 Radiation from antennas Coming up... 1 Electric
Module I: Electromagnetic waves Lecture 9: EM radiation Amol Dighe Outline 1 Electric and magnetic fields: radiation components 2 Energy carried by radiation 3 Radiation from antennas Coming up... 1 Electric
Integrals in cylindrical, spherical coordinates (Sect. 15.7)
 Integrals in clindrical, spherical coordinates (Sect. 15.7 Integration in spherical coordinates. Review: Clindrical coordinates. Spherical coordinates in space. Triple integral in spherical coordinates.
Integrals in clindrical, spherical coordinates (Sect. 15.7 Integration in spherical coordinates. Review: Clindrical coordinates. Spherical coordinates in space. Triple integral in spherical coordinates.
Uniform Plane Waves. Ranga Rodrigo. University of Moratuwa. November 7, 2008
 Uniform Plane Waves Ranga Rodrigo University of Moratuwa November 7, 2008 Ranga Rodrigo (University of Moratuwa) Uniform Plane Waves November 7, 2008 1 / 51 Summary of Last Week s Lecture Basic Relations
Uniform Plane Waves Ranga Rodrigo University of Moratuwa November 7, 2008 Ranga Rodrigo (University of Moratuwa) Uniform Plane Waves November 7, 2008 1 / 51 Summary of Last Week s Lecture Basic Relations
Module 4. Single-phase AC Circuits. Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1
 Module 4 Single-phase A ircuits ersion EE IIT, Kharagpur esson 4 Solution of urrent in -- Series ircuits ersion EE IIT, Kharagpur In the last lesson, two points were described:. How to represent a sinusoidal
Module 4 Single-phase A ircuits ersion EE IIT, Kharagpur esson 4 Solution of urrent in -- Series ircuits ersion EE IIT, Kharagpur In the last lesson, two points were described:. How to represent a sinusoidal
ELECTROMAGNETISM SUMMARY
 Review of E and B ELECTROMAGNETISM SUMMARY (Rees Chapters 2 and 3) The electric field E is a vector function. E q o q If we place a second test charged q o in the electric field of the charge q, the two
Review of E and B ELECTROMAGNETISM SUMMARY (Rees Chapters 2 and 3) The electric field E is a vector function. E q o q If we place a second test charged q o in the electric field of the charge q, the two
So far, we have considered three basic classes of antennas electrically small, resonant
 Unit 5 Aperture Antennas So far, we have considered three basic classes of antennas electrically small, resonant (narrowband) and broadband (the travelling wave antenna). There are amny other types of
Unit 5 Aperture Antennas So far, we have considered three basic classes of antennas electrically small, resonant (narrowband) and broadband (the travelling wave antenna). There are amny other types of
Electromagnetic Implosion Using an Array
 Sensor and Simulation Notes Note 57 July 2006 Electromagnetic Implosion Using an Array Carl E. Baum University of New Mexico Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Albuquerque New Mexico 873
Sensor and Simulation Notes Note 57 July 2006 Electromagnetic Implosion Using an Array Carl E. Baum University of New Mexico Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Albuquerque New Mexico 873
Fields, sources, forces,
 Phys 208 Summary Fields, sources, forces, etc Applications Materials Math techniques Phys 208 Summary Fields, sources, forces, etc E and charge B and current Fields and forces Charge conservation Potentials
Phys 208 Summary Fields, sources, forces, etc Applications Materials Math techniques Phys 208 Summary Fields, sources, forces, etc E and charge B and current Fields and forces Charge conservation Potentials
Problem Set 10 Solutions
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Physics Physics 87 Fall 25 Problem Set 1 Solutions Problem 1: EM Waves in a Plasma a Transverse electromagnetic waves have, by definition, E = Taking
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Physics Physics 87 Fall 25 Problem Set 1 Solutions Problem 1: EM Waves in a Plasma a Transverse electromagnetic waves have, by definition, E = Taking
INGENIERÍA EN NANOTECNOLOGÍA
 ETAPA DISCIPLINARIA TAREAS 385 TEORÍA ELECTROMAGNÉTICA Prof. E. Efren García G. Ensenada, B.C. México 206 Tarea. Two uniform line charges of ρ l = 4 nc/m each are parallel to the z axis at x = 0, y = ±4
ETAPA DISCIPLINARIA TAREAS 385 TEORÍA ELECTROMAGNÉTICA Prof. E. Efren García G. Ensenada, B.C. México 206 Tarea. Two uniform line charges of ρ l = 4 nc/m each are parallel to the z axis at x = 0, y = ±4
Chapter 1 - The Nature of Light
 David J. Starling Penn State Hazleton PHYS 214 Electromagnetic radiation comes in many forms, differing only in wavelength, frequency or energy. Electromagnetic radiation comes in many forms, differing
David J. Starling Penn State Hazleton PHYS 214 Electromagnetic radiation comes in many forms, differing only in wavelength, frequency or energy. Electromagnetic radiation comes in many forms, differing
PHYS463 Electricity& Magnetism III ( ) Problems Solutions (assignment #3) r n+1
 . (Problem 3.38, p.6) Solution: Use equation (3.95) PHYS463 Electricity& Magnetism (3-4) Problems Solutions (assignment #3) Φ 4π² X n ³ r n Pn ³cos ³ ϑ ρ r dτ r n+ Now λ Q/a a
. (Problem 3.38, p.6) Solution: Use equation (3.95) PHYS463 Electricity& Magnetism (3-4) Problems Solutions (assignment #3) Φ 4π² X n ³ r n Pn ³cos ³ ϑ ρ r dτ r n+ Now λ Q/a a
CHEM-UA 127: Advanced General Chemistry I
 1 CHEM-UA 127: Advanced General Chemistry I Notes for Lecture 11 Nowthatwehaveintroducedthebasicconceptsofquantummechanics, wecanstarttoapplythese conceptsto build up matter, starting from its most elementary
1 CHEM-UA 127: Advanced General Chemistry I Notes for Lecture 11 Nowthatwehaveintroducedthebasicconceptsofquantummechanics, wecanstarttoapplythese conceptsto build up matter, starting from its most elementary
Introduction to Condensed Matter Physics
 Introduction to Condensed Matter Physics Diffraction I Basic Physics M.P. Vaughan Diffraction Electromagnetic waves Geometric wavefront The Principle of Linear Superposition Diffraction regimes Single
Introduction to Condensed Matter Physics Diffraction I Basic Physics M.P. Vaughan Diffraction Electromagnetic waves Geometric wavefront The Principle of Linear Superposition Diffraction regimes Single
EECS 117. Lecture 22: Poynting s Theorem and Normal Incidence. Prof. Niknejad. University of California, Berkeley
 University of California, Berkeley EECS 117 Lecture 22 p. 1/2 EECS 117 Lecture 22: Poynting s Theorem and Normal Incidence Prof. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley University of California, Berkeley
University of California, Berkeley EECS 117 Lecture 22 p. 1/2 EECS 117 Lecture 22: Poynting s Theorem and Normal Incidence Prof. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley University of California, Berkeley
CBE 6333, R. Levicky 1. Orthogonal Curvilinear Coordinates
 CBE 6333, R. Levicky 1 Orthogonal Curvilinear Coordinates Introduction. Rectangular Cartesian coordinates are convenient when solving problems in which the geometry of a problem is well described by the
CBE 6333, R. Levicky 1 Orthogonal Curvilinear Coordinates Introduction. Rectangular Cartesian coordinates are convenient when solving problems in which the geometry of a problem is well described by the
ECE Spring Prof. David R. Jackson ECE Dept. Notes 16
 ECE 6345 Spring 5 Prof. David R. Jackson ECE Dept. Notes 6 Overview In this set of notes we calculate the power radiated into space by the circular patch. This will lead to Q sp of the circular patch.
ECE 6345 Spring 5 Prof. David R. Jackson ECE Dept. Notes 6 Overview In this set of notes we calculate the power radiated into space by the circular patch. This will lead to Q sp of the circular patch.
Electromagnetic Theory: PHAS3201, Winter Maxwell s Equations and EM Waves
 Electromagnetic Theory: PHA3201, Winter 2008 5. Maxwell s Equations and EM Waves 1 Displacement Current We already have most of the pieces that we require for a full statement of Maxwell s Equations; however,
Electromagnetic Theory: PHA3201, Winter 2008 5. Maxwell s Equations and EM Waves 1 Displacement Current We already have most of the pieces that we require for a full statement of Maxwell s Equations; however,
A Review of Radiation and Optics
 A Review of Radiation and Optics Abraham Asfaw 12 aasfaw.student@manhattan.edu May 20, 2011 Abstract This paper attempts to summarize selected topics in Radiation and Optics. It is, by no means, a complete
A Review of Radiation and Optics Abraham Asfaw 12 aasfaw.student@manhattan.edu May 20, 2011 Abstract This paper attempts to summarize selected topics in Radiation and Optics. It is, by no means, a complete
Lecture 6 Scattering theory Partial Wave Analysis. SS2011: Introduction to Nuclear and Particle Physics, Part 2 2
 Lecture 6 Scattering theory Partial Wave Analysis SS2011: Introduction to Nuclear and Particle Physics, Part 2 2 1 The Born approximation for the differential cross section is valid if the interaction
Lecture 6 Scattering theory Partial Wave Analysis SS2011: Introduction to Nuclear and Particle Physics, Part 2 2 1 The Born approximation for the differential cross section is valid if the interaction
Module 4. Single-phase AC circuits. Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur
 Module 4 Single-phase circuits ersion EE T, Kharagpur esson 6 Solution of urrent in Parallel and Seriesparallel ircuits ersion EE T, Kharagpur n the last lesson, the following points were described:. How
Module 4 Single-phase circuits ersion EE T, Kharagpur esson 6 Solution of urrent in Parallel and Seriesparallel ircuits ersion EE T, Kharagpur n the last lesson, the following points were described:. How
Short Wire Antennas: A Simplified Approach Part I: Scaling Arguments. Dan Dobkin version 1.0 July 8, 2005
 Short Wire Antennas: A Simplified Approach Part I: Scaling Arguments Dan Dobkin version 1.0 July 8, 2005 0. Introduction: How does a wire dipole antenna work? How do we find the resistance and the reactance?
Short Wire Antennas: A Simplified Approach Part I: Scaling Arguments Dan Dobkin version 1.0 July 8, 2005 0. Introduction: How does a wire dipole antenna work? How do we find the resistance and the reactance?
mywbut.com Lesson 16 Solution of Current in AC Parallel and Seriesparallel
 esson 6 Solution of urrent in Parallel and Seriesparallel ircuits n the last lesson, the following points were described:. How to compute the total impedance/admittance in series/parallel circuits?. How
esson 6 Solution of urrent in Parallel and Seriesparallel ircuits n the last lesson, the following points were described:. How to compute the total impedance/admittance in series/parallel circuits?. How
D. S. Weile Radiation
 Radiation Daniel S. Weile Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Delaware ELEG 648 Radiation Outline Outline Maxwell Redux Maxwell s Equation s are: 1 E = jωb = jωµh 2 H = J +
Radiation Daniel S. Weile Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Delaware ELEG 648 Radiation Outline Outline Maxwell Redux Maxwell s Equation s are: 1 E = jωb = jωµh 2 H = J +
Problem Set #4: 4.1,4.7,4.9 (Due Monday, March 25th)
 Chapter 4 Multipoles, Dielectrics Problem Set #4: 4.,4.7,4.9 (Due Monday, March 5th 4. Multipole expansion Consider a localized distribution of charges described by ρ(x contained entirely in a sphere of
Chapter 4 Multipoles, Dielectrics Problem Set #4: 4.,4.7,4.9 (Due Monday, March 5th 4. Multipole expansion Consider a localized distribution of charges described by ρ(x contained entirely in a sphere of
Biot-Savart. The equation is this:
 Biot-Savart When a wire carries a current, this current produces a magnetic field in the vicinity of the wire. One way of determining the strength and direction of this field is with the Law of Biot-Savart.
Biot-Savart When a wire carries a current, this current produces a magnetic field in the vicinity of the wire. One way of determining the strength and direction of this field is with the Law of Biot-Savart.
Electric Field and Gauss s law. January 17, 2014 Physics for Scientists & Engineers 2, Chapter 22 1
 Electric Field and Gauss s law January 17, 2014 Physics for Scientists & Engineers 2, Chapter 22 1 Missing clickers! The following clickers are not yet registered! If your clicker number is in this list,
Electric Field and Gauss s law January 17, 2014 Physics for Scientists & Engineers 2, Chapter 22 1 Missing clickers! The following clickers are not yet registered! If your clicker number is in this list,
ECE 222b Applied Electromagnetics Notes Set 5
 ECE b Applied Electomagnetics Notes Set 5 Instucto: Pof. Vitaliy Lomakin Depatment of Electical and Compute Engineeing Univesity of Califonia, San Diego 1 Auxiliay Potential Functions (1) Auxiliay Potential
ECE b Applied Electomagnetics Notes Set 5 Instucto: Pof. Vitaliy Lomakin Depatment of Electical and Compute Engineeing Univesity of Califonia, San Diego 1 Auxiliay Potential Functions (1) Auxiliay Potential
1. A ring of radius α has a charge distribution on it that varies as λ(θ) = λ 0 sin(θ), where λ 0 > 0, as shown in the figure.
 EACH OF THE LECTURE QUESTIONS 1-22 IS WORTH 5 POINTS I. COULOMB S LAW 1. A ring of radius α has a charge distribution on it that varies as λ(θ) = λ 0 sin(θ), where λ 0 > 0, as shown in the figure. What
EACH OF THE LECTURE QUESTIONS 1-22 IS WORTH 5 POINTS I. COULOMB S LAW 1. A ring of radius α has a charge distribution on it that varies as λ(θ) = λ 0 sin(θ), where λ 0 > 0, as shown in the figure. What
Module 4. Single-phase AC Circuits
 Module 4 Single-phase AC Circuits Lesson 14 Solution of Current in R-L-C Series Circuits In the last lesson, two points were described: 1. How to represent a sinusoidal (ac) quantity, i.e. voltage/current
Module 4 Single-phase AC Circuits Lesson 14 Solution of Current in R-L-C Series Circuits In the last lesson, two points were described: 1. How to represent a sinusoidal (ac) quantity, i.e. voltage/current
xy 2 e 2z dx dy dz = 8 3 (1 e 4 ) = 2.62 mc. 12 x2 y 3 e 2z 2 m 2 m 2 m Figure P4.1: Cube of Problem 4.1.
 Problem 4.1 A cube m on a side is located in the first octant in a Cartesian coordinate system, with one of its corners at the origin. Find the total charge contained in the cube if the charge density
Problem 4.1 A cube m on a side is located in the first octant in a Cartesian coordinate system, with one of its corners at the origin. Find the total charge contained in the cube if the charge density
3.4-7 First check to see if the loop is indeed electromagnetically small. Ie sinθ ˆφ H* = 2. ˆrr 2 sinθ dθ dφ =
 ECE 54/4 Spring 17 Assignment.4-7 First check to see if the loop is indeed electromagnetically small f 1 MHz c 1 8 m/s b.5 m λ = c f m b m Yup. (a) You are welcome to use equation (-5), but I don t like
ECE 54/4 Spring 17 Assignment.4-7 First check to see if the loop is indeed electromagnetically small f 1 MHz c 1 8 m/s b.5 m λ = c f m b m Yup. (a) You are welcome to use equation (-5), but I don t like
Electric Flux and Gauss s Law
 Electric Flux and Gauss s Law Electric Flux Figure (1) Consider an electric field that is uniform in both magnitude and direction, as shown in Figure 1. The total number of lines penetrating the surface
Electric Flux and Gauss s Law Electric Flux Figure (1) Consider an electric field that is uniform in both magnitude and direction, as shown in Figure 1. The total number of lines penetrating the surface
Course Name : Physics I Course # PHY 107
 Course Name : Physics I Course # PHY 107 Lecture-2 : Representation of Vectors and the Product Rules Abu Mohammad Khan Department of Mathematics and Physics North South University http://abukhan.weebly.com
Course Name : Physics I Course # PHY 107 Lecture-2 : Representation of Vectors and the Product Rules Abu Mohammad Khan Department of Mathematics and Physics North South University http://abukhan.weebly.com
TC412 Microwave Communications. Lecture 8 Rectangular waveguides and cavity resonator
 TC412 Microwave Communications Lecture 8 Rectangular waveguides and cavity resonator 1 TM waves in rectangular waveguides Finding E and H components in terms of, WG geometry, and modes. From 2 2 2 xye
TC412 Microwave Communications Lecture 8 Rectangular waveguides and cavity resonator 1 TM waves in rectangular waveguides Finding E and H components in terms of, WG geometry, and modes. From 2 2 2 xye
LECTURE 18: Horn Antennas (Rectangular horn antennas. Circular apertures.) Equation Section 18
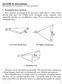 LCTUR 18: Horn Antennas (Rectangular horn antennas. Circular apertures.) quation Section 18 1 Rectangular horn antennas Horn antennas are popular in the microwave band (above 1 GHz). Horns provide high
LCTUR 18: Horn Antennas (Rectangular horn antennas. Circular apertures.) quation Section 18 1 Rectangular horn antennas Horn antennas are popular in the microwave band (above 1 GHz). Horns provide high
Solutions: Homework 5
 Ex. 5.1: Capacitor Solutions: Homework 5 (a) Consider a parallel plate capacitor with large circular plates, radius a, a distance d apart, with a d. Choose cylindrical coordinates (r,φ,z) and let the z
Ex. 5.1: Capacitor Solutions: Homework 5 (a) Consider a parallel plate capacitor with large circular plates, radius a, a distance d apart, with a d. Choose cylindrical coordinates (r,φ,z) and let the z
PLANE WAVE PROPAGATION AND REFLECTION. David R. Jackson Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Houston Houston, TX
 PLANE WAVE PROPAGATION AND REFLECTION David R. Jackson Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Houston Houston, TX 7704-4793 Abstract The basic properties of plane waves propagating
PLANE WAVE PROPAGATION AND REFLECTION David R. Jackson Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Houston Houston, TX 7704-4793 Abstract The basic properties of plane waves propagating
Calculations of Magnetic Fields from Known Current Distributions. B d B2 r 0I B 2 r
 Calculations of Magnetic Fields from Known Current Distributions In the absence of magnetic materials this is a relatively simple problem analogous to finding the electric field with known charge distributions.
Calculations of Magnetic Fields from Known Current Distributions In the absence of magnetic materials this is a relatively simple problem analogous to finding the electric field with known charge distributions.
Winter 2017 Ma 1b Analytical Problem Set 2 Solutions
 1. (5 pts) From Ch. 1.10 in Apostol: Problems 1,3,5,7,9. Also, when appropriate exhibit a basis for S. Solution. (1.10.1) Yes, S is a subspace of V 3 with basis {(0, 0, 1), (0, 1, 0)} and dimension 2.
1. (5 pts) From Ch. 1.10 in Apostol: Problems 1,3,5,7,9. Also, when appropriate exhibit a basis for S. Solution. (1.10.1) Yes, S is a subspace of V 3 with basis {(0, 0, 1), (0, 1, 0)} and dimension 2.
Summary: Applications of Gauss Law
 Physics 2460 Electricity and Magnetism I, Fall 2006, Lecture 15 1 Summary: Applications of Gauss Law 1. Field outside of a uniformly charged sphere of radius a: 2. An infinite, uniformly charged plane
Physics 2460 Electricity and Magnetism I, Fall 2006, Lecture 15 1 Summary: Applications of Gauss Law 1. Field outside of a uniformly charged sphere of radius a: 2. An infinite, uniformly charged plane
dt Now we will look at the E&M force on moving charges to explore the momentum conservation law in E&M.
 . Momentum Conservation.. Momentum in mechanics In classical mechanics p = m v and nd Newton s law d p F = dt If m is constant with time d v F = m = m a dt Now we will look at the &M force on moving charges
. Momentum Conservation.. Momentum in mechanics In classical mechanics p = m v and nd Newton s law d p F = dt If m is constant with time d v F = m = m a dt Now we will look at the &M force on moving charges
1. ELECTRIC CHARGES AND FIELDS
 1. ELECTRIC CHARGES AND FIELDS 1. What are point charges? One mark questions with answers A: Charges whose sizes are very small compared to the distance between them are called point charges 2. The net
1. ELECTRIC CHARGES AND FIELDS 1. What are point charges? One mark questions with answers A: Charges whose sizes are very small compared to the distance between them are called point charges 2. The net
Worked Examples Set 2
 Worked Examples Set 2 Q.1. Application of Maxwell s eqns. [Griffiths Problem 7.42] In a perfect conductor the conductivity σ is infinite, so from Ohm s law J = σe, E = 0. Any net charge must be on the
Worked Examples Set 2 Q.1. Application of Maxwell s eqns. [Griffiths Problem 7.42] In a perfect conductor the conductivity σ is infinite, so from Ohm s law J = σe, E = 0. Any net charge must be on the
1 Chapter 8 Maxwell s Equations
 Electromagnetic Waves ECEN 3410 Prof. Wagner Final Review Questions 1 Chapter 8 Maxwell s Equations 1. Describe the integral form of charge conservation within a volume V through a surface S, and give
Electromagnetic Waves ECEN 3410 Prof. Wagner Final Review Questions 1 Chapter 8 Maxwell s Equations 1. Describe the integral form of charge conservation within a volume V through a surface S, and give
NIU Ph.D. Candidacy Examination Fall 2018 (8/21/2018) Electricity and Magnetism
 NIU Ph.D. Candidacy Examination Fall 2018 (8/21/2018) Electricity and Magnetism You may solve ALL FOUR problems if you choose. The points of the best three problems will be counted towards your final score
NIU Ph.D. Candidacy Examination Fall 2018 (8/21/2018) Electricity and Magnetism You may solve ALL FOUR problems if you choose. The points of the best three problems will be counted towards your final score
Problem set 3. Electromagnetic waves
 Second Year Electromagnetism Michaelmas Term 2017 Caroline Terquem Problem set 3 Electromagnetic waves Problem 1: Poynting vector and resistance heating This problem is not about waves but is useful to
Second Year Electromagnetism Michaelmas Term 2017 Caroline Terquem Problem set 3 Electromagnetic waves Problem 1: Poynting vector and resistance heating This problem is not about waves but is useful to
Physics 214 Course Overview
 Physics 214 Course Overview Lecturer: Mike Kagan Course topics Electromagnetic waves Optics Thin lenses Interference Diffraction Relativity Photons Matter waves Black Holes EM waves Intensity Polarization
Physics 214 Course Overview Lecturer: Mike Kagan Course topics Electromagnetic waves Optics Thin lenses Interference Diffraction Relativity Photons Matter waves Black Holes EM waves Intensity Polarization
4: birefringence and phase matching
 /3/7 4: birefringence and phase matching Polarization states in EM Linear anisotropic response χ () tensor and its symmetry properties Working with the index ellipsoid: angle tuning Phase matching in crystals
/3/7 4: birefringence and phase matching Polarization states in EM Linear anisotropic response χ () tensor and its symmetry properties Working with the index ellipsoid: angle tuning Phase matching in crystals
Dipole Approxima7on Thomson ScaEering
 Feb. 28, 2011 Larmor Formula: radia7on from non- rela7vis7c par7cles Dipole Approxima7on Thomson ScaEering The E, B field at point r and 7me t depends on the retarded posi7on r(ret) and retarded 7me t(ret)
Feb. 28, 2011 Larmor Formula: radia7on from non- rela7vis7c par7cles Dipole Approxima7on Thomson ScaEering The E, B field at point r and 7me t depends on the retarded posi7on r(ret) and retarded 7me t(ret)
MATH 52 MIDTERM 1. April 23, 2004
 MATH 5 MIDTERM April 3, Student ID: Signature: Instructions: Print your name and student ID number and write your signature to indicate that you accept the honor code. During the test, you may not use
MATH 5 MIDTERM April 3, Student ID: Signature: Instructions: Print your name and student ID number and write your signature to indicate that you accept the honor code. During the test, you may not use
Chapter 21. Electric Fields. Lecture 2. Dr. Armen Kocharian
 Chapter 21 Electric Fields Lecture 2 Dr. Armen Kocharian Electric Field Introduction The electric force is a field force Field forces can act through space The effect is produced even with no physical
Chapter 21 Electric Fields Lecture 2 Dr. Armen Kocharian Electric Field Introduction The electric force is a field force Field forces can act through space The effect is produced even with no physical
TECHNO INDIA BATANAGAR
 TECHNO INDIA BATANAGAR ( DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING) QUESTION BANK- 2018 1.Vector Calculus Assistant Professor 9432183958.mukherjee@tib.edu.in 1. When the operator operates on
TECHNO INDIA BATANAGAR ( DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING) QUESTION BANK- 2018 1.Vector Calculus Assistant Professor 9432183958.mukherjee@tib.edu.in 1. When the operator operates on
Physics Letters A 374 (2010) Contents lists available at ScienceDirect. Physics Letters A.
 Physics Letters A 374 (2010) 1063 1067 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Physics Letters A www.elsevier.com/locate/pla Macroscopic far-field observation of the sub-wavelength near-field dipole
Physics Letters A 374 (2010) 1063 1067 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Physics Letters A www.elsevier.com/locate/pla Macroscopic far-field observation of the sub-wavelength near-field dipole
EECS 117. Lecture 23: Oblique Incidence and Reflection. Prof. Niknejad. University of California, Berkeley
 University of California, Berkeley EECS 117 Lecture 23 p. 1/2 EECS 117 Lecture 23: Oblique Incidence and Reflection Prof. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley University of California, Berkeley
University of California, Berkeley EECS 117 Lecture 23 p. 1/2 EECS 117 Lecture 23: Oblique Incidence and Reflection Prof. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley University of California, Berkeley
ECE 6340 Intermediate EM Waves. Fall Prof. David R. Jackson Dept. of ECE. Notes 17
 ECE 634 Intermediate EM Waves Fall 16 Prof. David R. Jacson Dept. of ECE Notes 17 1 General Plane Waves General form of plane wave: E( xz,, ) = Eψ ( xz,, ) where ψ ( xz,, ) = e j( xx+ + zz) The wavenumber
ECE 634 Intermediate EM Waves Fall 16 Prof. David R. Jacson Dept. of ECE Notes 17 1 General Plane Waves General form of plane wave: E( xz,, ) = Eψ ( xz,, ) where ψ ( xz,, ) = e j( xx+ + zz) The wavenumber
RADIATION OF ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES
 Chapter RADIATION OF ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES. Introduction We know that a charge q creates the Coulomb field given by E c 4πɛ 0 q r 2 e r, but a stationary charge cannot radiate electromagnetic waves which
Chapter RADIATION OF ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES. Introduction We know that a charge q creates the Coulomb field given by E c 4πɛ 0 q r 2 e r, but a stationary charge cannot radiate electromagnetic waves which
Antennas and Propagation
 Antennas and Propagation Ranga Rodrigo University of Moratuwa October 20, 2008 Compiled based on Lectures of Prof. (Mrs.) Indra Dayawansa. Ranga Rodrigo (University of Moratuwa) Antennas and Propagation
Antennas and Propagation Ranga Rodrigo University of Moratuwa October 20, 2008 Compiled based on Lectures of Prof. (Mrs.) Indra Dayawansa. Ranga Rodrigo (University of Moratuwa) Antennas and Propagation
SINGLE MATHEMATICS B : Vectors Summary Notes
 Preprint typeset in JHEP style - HYPER VERSION SINGLE MATHEMATICS B : Vectors Summary Notes Ruth Gregory Abstract: These notes sum up all you need to know about the mathematics of vectors at this stage.
Preprint typeset in JHEP style - HYPER VERSION SINGLE MATHEMATICS B : Vectors Summary Notes Ruth Gregory Abstract: These notes sum up all you need to know about the mathematics of vectors at this stage.
ECE 6341 Spring 2016 HW 2
 ECE 6341 Spring 216 HW 2 Assigned problems: 1-6 9-11 13-15 1) Assume that a TEN models a layered structure where the direction (the direction perpendicular to the layers) is the direction that the transmission
ECE 6341 Spring 216 HW 2 Assigned problems: 1-6 9-11 13-15 1) Assume that a TEN models a layered structure where the direction (the direction perpendicular to the layers) is the direction that the transmission
1-2 Vector and scalar potentials
 1-2 Vector and scalar potentials z a f a r q a q J y x f Maxwell's equations μ (1) ε (2) ρ (3) (4) - Derivation of E and H field by source current J Approach 1 : take (1) and plug into (2) μ ε μ μ (5)
1-2 Vector and scalar potentials z a f a r q a q J y x f Maxwell's equations μ (1) ε (2) ρ (3) (4) - Derivation of E and H field by source current J Approach 1 : take (1) and plug into (2) μ ε μ μ (5)
EELE 3332 Electromagnetic II Chapter 11. Transmission Lines. Islamic University of Gaza Electrical Engineering Department Dr.
 EEE 333 Electromagnetic II Chapter 11 Transmission ines Islamic University of Gaza Electrical Engineering Department Dr. Talal Skaik 1 1 11.1 Introduction Wave propagation in unbounded media is used in
EEE 333 Electromagnetic II Chapter 11 Transmission ines Islamic University of Gaza Electrical Engineering Department Dr. Talal Skaik 1 1 11.1 Introduction Wave propagation in unbounded media is used in
Electromagnetic Waves
 Electromagnetic Waves Maxwell s equations predict the propagation of electromagnetic energy away from time-varying sources (current and charge) in the form of waves. Consider a linear, homogeneous, isotropic
Electromagnetic Waves Maxwell s equations predict the propagation of electromagnetic energy away from time-varying sources (current and charge) in the form of waves. Consider a linear, homogeneous, isotropic
POLARISATION. We have not really discussed the direction of the Electric field other that that it is perpendicular to the direction of motion.
 POLARISATION Light is a transverse electromagnetic wave. We have not really discussed the direction of the Electric field other that that it is perpendicular to the direction of motion. If the E field
POLARISATION Light is a transverse electromagnetic wave. We have not really discussed the direction of the Electric field other that that it is perpendicular to the direction of motion. If the E field
Cylindrical Radiation and Scattering
 Cylindrical Radiation and Daniel S. Weile Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Delaware ELEG 648 Radiation and in Cylindrical Coordinates Outline Cylindrical Radiation 1 Cylindrical
Cylindrical Radiation and Daniel S. Weile Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Delaware ELEG 648 Radiation and in Cylindrical Coordinates Outline Cylindrical Radiation 1 Cylindrical
PHY102 Electricity Topic 3 (Lectures 4 & 5) Gauss s Law
 PHY1 Electricity Topic 3 (Lectures 4 & 5) Gauss s Law In this topic, we will cover: 1) Electric Flux ) Gauss s Law, relating flux to enclosed charge 3) Electric Fields and Conductors revisited Reading
PHY1 Electricity Topic 3 (Lectures 4 & 5) Gauss s Law In this topic, we will cover: 1) Electric Flux ) Gauss s Law, relating flux to enclosed charge 3) Electric Fields and Conductors revisited Reading
EM Waves. From previous Lecture. This Lecture More on EM waves EM spectrum Polarization. Displacement currents Maxwell s equations EM Waves
 EM Waves This Lecture More on EM waves EM spectrum Polarization From previous Lecture Displacement currents Maxwell s equations EM Waves 1 Reminders on waves Traveling waves on a string along x obey the
EM Waves This Lecture More on EM waves EM spectrum Polarization From previous Lecture Displacement currents Maxwell s equations EM Waves 1 Reminders on waves Traveling waves on a string along x obey the
Energy conserving coupling through small apertures in an infinite perfect conducting screen
 doi:1.519/ars-13-7-15 Author(s) 15. CC Attribution 3. License. Energy conserving coupling through small apertures in an infinite perfect conducting screen J. Petzold,. Tkachenko, and R. Vick Chair of Electromagnetic
doi:1.519/ars-13-7-15 Author(s) 15. CC Attribution 3. License. Energy conserving coupling through small apertures in an infinite perfect conducting screen J. Petzold,. Tkachenko, and R. Vick Chair of Electromagnetic
Introduction to Polarization
 Phone: Ext 659, E-mail: hcchui@mail.ncku.edu.tw Fall/007 Introduction to Polarization Text Book: A Yariv and P Yeh, Photonics, Oxford (007) 1.6 Polarization States and Representations (Stokes Parameters
Phone: Ext 659, E-mail: hcchui@mail.ncku.edu.tw Fall/007 Introduction to Polarization Text Book: A Yariv and P Yeh, Photonics, Oxford (007) 1.6 Polarization States and Representations (Stokes Parameters
FRACTIONAL DUAL SOLUTIONS AND CORRESPONDING SOURCES
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 5, 3 38, 000 FRACTIONAL DUAL SOLUTIONS AND CORRESPONDING SOURCES Q. A. Naqvi and A. A. Rizvi Communications Lab. Department of Electronics Quaidi-i-Azam University
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 5, 3 38, 000 FRACTIONAL DUAL SOLUTIONS AND CORRESPONDING SOURCES Q. A. Naqvi and A. A. Rizvi Communications Lab. Department of Electronics Quaidi-i-Azam University
Radiation from transmission lines PART I: free space transmission lines
 1 Radiation from transmission lines PART I: free space transmission lines Reuven Ianconescu, Vladimir Vulfin Shenkar College of Engineering and Design, Ramat Gan, Israel, riancon@gmail.com Ben-Gurion University
1 Radiation from transmission lines PART I: free space transmission lines Reuven Ianconescu, Vladimir Vulfin Shenkar College of Engineering and Design, Ramat Gan, Israel, riancon@gmail.com Ben-Gurion University
