= 1 T 4 T 1 T 3 T 2. W net V max V min. = (k 1) ln ( v 2. v min
|
|
|
- Randell Hodges
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SUMMARY OF GAS POWER CYCLES-CHAPTER 9 OTTO CYCLE GASOLINE ENGINES Useful Wor, Thermal Efficiency 1-2 Isentropic Compression (s 1=s Isochoric Heat Addition (v 2= v Isentropic Expansion (s 3=s Isochoric-Heat Rejection (v 4= v 1 For isochoric process 1-2 Q 12 = Q Added Heat = m(u 3 u 1 = mc v (T 3 T 2 = c v (T 3 T 2 For isochoric process 4-1 Q 41 = Q Rejection = m(u 4 u 1 = mc v (T 4 q out = c v (T 4 η th Otto = W net = q out In the isentropic process: ds = 0 = 1 T 4 T 3 T 2 ds = du T + P T dv du + Pdv = 0 for ideal gas: c vdt + Pdv = 0 P = RT v, MEP = W net V max V min dt + RT dv = 0 dt vc v T + R dv c v v = 0 R = c p c v dt T = (1 c p dv c v v Integrating dt T = ( 1 dv v yields: is the specific heat ratio = c p c v ln T 2 = ( 1 ln ( v 2 v 1 T 2 = ( v 2 v 1, η th Otto = 1 1 r where r = v max v min = v 1 v 2 T-s diagram P-v College of Engineering Taibah University 1
2 DIESEL CYCLE DIESEL ENGINES Useful Wor, Thermal Efficiency 1-2 Isentropic Compression (s 1=s Isochoric Heat Addition (v 2= v Isentropic Expansion (s 3=s Isochoric-Heat Rejection (v 4= v 1 For isochoric process 1-2 = P 2 (v 3 v 2 + (u 3 u 2 = h 3 h 2 = c p (T 3 T 2 q out = (u 4 u 1 = c v (T 4 η Diesel = W net = 1 T 4 (T 3 T 2 Thermal Efficiency ( T 4 T 1 = 1 1 T 2 ( T, 3 T 1 2 P 1 v 3 = RT 3, P 1 v 1 = R r c = v 3, r = v 1 Max. Volume = v 2 v 2 Mini. Volume r c is a Cutt off Ratio is the ratio of the cylinder volumes and after and beforethe combustion proces. The efficiency becomes: η Diesel = W net P 4 v 4 = RT 4, P 2 v 2 = RT 2 = 1 T 4 (T 3 T 2 = 1 r c 1 r (r c 1 DUAL CYCLE DIESEL+GASOLINE ENGINES The dual cycle is a diesel and a gasoline cycle which has a constant pressure and a constant volume at the heat addition College of Engineering Taibah University 2
3 1-2 Isentropic Compression process (s 1=s Isochoric and Isobaric Heat Addition process (v 2= v X, P 3=P x 3-4 Isentropic Expansion process (s 3=s Isochoric-Heat Rejection process (v 4= v 1 = c v (T X T 2 + c p (T 3 T X q out = (u 4 u 1 = c v (T 4 η Dual = W net P-v diagram BRAYTON CYCLE TURBOJET ENGINES = h 3 h 2 = c p (T 3 T 2 P 2 = P 3 q out = h 4 h 1 = c p (T 4 Isentropic process: P 2 = P 3 and P 1 = P 4 T 2 = ( P 2 \\\\ P 1 ( η Brayton and T 3 T 4 = ( P 3 P 4 = 1 = 1 1 r P ( T 4 1 T 2 ( T 3 T 2 1, r P = P 2 P 1 The actual cycle of Brayton cycle: η C = h 2s h 1 h 2a h 1 η T = h 3 h 4a h 3 h College of Engineering Taibah University 3
4 A. Brayton Cycle with Regeneration q regen, act = h 5 h 2, andq regen, max = h 5 h 2 = h 4 h 2 The extent to which a regenerator approaches and ideal regenerator is called and is defined as = h 5 h 2 h 4 h 2 η Brayton, generation = (1 ( r T P 3 Regeneration cycle B. Brayton Cycle with intercooling, Reheating, and Regeneration P 2 P 1 = P 4 P 3, and P 6 P 7 = P 8 P 6 Closed Gas- Turbine Regenerator with reheating and intercooler College of Engineering Taibah University 4
5 College of Engineering Jet Propulsion Ideal Engines: 1-3 Isentropic Compression (s 1=s Isobaric Heat Addition (P 3= P Isentropic Expansion (s 4=s Isobaric-Heat Rejection (P 6= P 1 The thrust net force can be calculated as: F thurst = m (V eixt V inlet Propulsive efficiency: η P = W P Q in W comp = W Turbine T 3 = T 4 T 6 ( No inetic or Potentail Energy h 1 + V = h 2 + V = T 2 + V V 1 2c p 1-3 Isentropic Compression (s 1=s 2 T 4, also T 3 = ( P 3 P 1 T 6 = ( P 4 P 6 Stirling and Ericson Cycles Stirling Cycle: 1-2 T= constant expansion (heat addition from the external source 2-3 v = constant regeneration (internal heat transfer from the woring fluid to the regenerator 3-4 T= constant compression (heat rejection to the external tan 4-1 v = constant regeneration (internal heat transfer from the regenerator bac to the woring College of Engineering Taibah University 5
6 W net = mr(t H T L ln ( V max = mr(t V H T L ln ( v 3 min v 4 Q regen = m c v (T 2 T 3 = mc v ( T 4 T H is at P max = P 1 and T L is at P in = P 3. = c v (T H T L + w 34 w 34 = RT 4 ln ( P 4 P 3 η th = w net Ericson Cycle: Q regen = m c p (T 2 T 3 = mc p ( T 4 W net = mr(t H T L ln ( V max V min = mr(t H T L ln ( v 2 v College of Engineering Taibah University 6
Week 4. Gas Power Cycles IV. GENESYS Laboratory
 Week 4. Gas Power Cycles IV Objecties. Ealuate the performance of gas power cycles for which the working fluid remains a gas throughout the entire cycle 2. Deelop simplifying assumptions applicable to
Week 4. Gas Power Cycles IV Objecties. Ealuate the performance of gas power cycles for which the working fluid remains a gas throughout the entire cycle 2. Deelop simplifying assumptions applicable to
T222 T194. c Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq (BUET) Gas Power Cycles ME 6101 (2017) 2 / 20 T225 T226
 The Carnot Gas Power Cycle Gas Power Cycles 1 2 : Reversible, isothermal expansion at T H 2 3 : Reversible, adiabatic expansion from T H to T L 3 4 : Reversible, isothermal compression at T L Dr. Md. Zahurul
The Carnot Gas Power Cycle Gas Power Cycles 1 2 : Reversible, isothermal expansion at T H 2 3 : Reversible, adiabatic expansion from T H to T L 3 4 : Reversible, isothermal compression at T L Dr. Md. Zahurul
OVERVIEW. Air-Standard Power Cycles (open cycle)
 OVERVIEW OWER CYCLE The Rankine Cycle thermal efficiency effects of pressure and temperature Reheat cycle Regenerative cycle Losses and Cogeneration Air-Standard ower Cycles (open cycle) The Brayton cycle
OVERVIEW OWER CYCLE The Rankine Cycle thermal efficiency effects of pressure and temperature Reheat cycle Regenerative cycle Losses and Cogeneration Air-Standard ower Cycles (open cycle) The Brayton cycle
1. (10) Calorically perfect ideal air at 300 K, 100 kpa, 1000 m/s, is brought to rest isentropically. Determine its final temperature.
 AME 5053 Intermediate Thermodynamics Examination Prof J M Powers 30 September 0 0 Calorically perfect ideal air at 300 K, 00 kpa, 000 m/s, is brought to rest isentropically Determine its final temperature
AME 5053 Intermediate Thermodynamics Examination Prof J M Powers 30 September 0 0 Calorically perfect ideal air at 300 K, 00 kpa, 000 m/s, is brought to rest isentropically Determine its final temperature
Lecture 40: Air standard cycle, internal combustion engines, Otto cycle
 ME 200 Thermodynamics I Spring 206 Lecture 40: Air standard cycle, internal combustion engines, Otto cycle Yong Li Shanghai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Chuan
ME 200 Thermodynamics I Spring 206 Lecture 40: Air standard cycle, internal combustion engines, Otto cycle Yong Li Shanghai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Chuan
Teaching schedule *15 18
 Teaching schedule Session *15 18 19 21 22 24 Topics 5. Gas power cycles Basic considerations in the analysis of power cycle; Carnot cycle; Air standard cycle; Reciprocating engines; Otto cycle; Diesel
Teaching schedule Session *15 18 19 21 22 24 Topics 5. Gas power cycles Basic considerations in the analysis of power cycle; Carnot cycle; Air standard cycle; Reciprocating engines; Otto cycle; Diesel
Chapter Five Applications of Thermodynamic Cycle
 Chapter Five Applications of hermodynamic Cycle Updated on 4// Power cycles: Power generation by converting heat to wor. Uses: Power generation, Propulsion. Cycles: Carnot cycle, Otto cycle, Diesel cycle,
Chapter Five Applications of hermodynamic Cycle Updated on 4// Power cycles: Power generation by converting heat to wor. Uses: Power generation, Propulsion. Cycles: Carnot cycle, Otto cycle, Diesel cycle,
9.1 Basic considerations in power cycle analysis. Thermal efficiency of a power cycle : th = Wnet/Qin
 Chapter 9 GAS POWER CYCLES 9.1 Basic considerations in power cycle analysis. Thermal efficiency of a power cycle : th = Wnet/Qin Gas-power cycles vs. vapor-power cycles: T p 1 p 2 p 3 Vapor cycle Gas cycle
Chapter 9 GAS POWER CYCLES 9.1 Basic considerations in power cycle analysis. Thermal efficiency of a power cycle : th = Wnet/Qin Gas-power cycles vs. vapor-power cycles: T p 1 p 2 p 3 Vapor cycle Gas cycle
Course: MECH-341 Thermodynamics II Semester: Fall 2006
 FINAL EXAM Date: Thursday, December 21, 2006, 9 am 12 am Examiner: Prof. E. Timofeev Associate Examiner: Prof. D. Frost READ CAREFULLY BEFORE YOU PROCEED: Course: MECH-341 Thermodynamics II Semester: Fall
FINAL EXAM Date: Thursday, December 21, 2006, 9 am 12 am Examiner: Prof. E. Timofeev Associate Examiner: Prof. D. Frost READ CAREFULLY BEFORE YOU PROCEED: Course: MECH-341 Thermodynamics II Semester: Fall
Lecture 44: Review Thermodynamics I
 ME 00 Thermodynamics I Lecture 44: Review Thermodynamics I Yong Li Shanghai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Chuan Road Shanghai, 0040, P. R. China Email : liyo@sjtu.edu.cn
ME 00 Thermodynamics I Lecture 44: Review Thermodynamics I Yong Li Shanghai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Chuan Road Shanghai, 0040, P. R. China Email : liyo@sjtu.edu.cn
Stirling Cycle. Ab Hashemi
 Stirling Cycle Ab Hashemi Stirling Cycle T-s and P-v Diagrams 3 Tmax =constant 3 4 2 T min =constant 4 1 2 1 Ab Hashemi 2 Stirling Cycle Stirling cycle is made up of four totally reversible processes:
Stirling Cycle Ab Hashemi Stirling Cycle T-s and P-v Diagrams 3 Tmax =constant 3 4 2 T min =constant 4 1 2 1 Ab Hashemi 2 Stirling Cycle Stirling cycle is made up of four totally reversible processes:
AME 436. Energy and Propulsion. Lecture 7 Unsteady-flow (reciprocating) engines 2: Using P-V and T-s diagrams
 AME 46 Energy and ropulsion Lecture 7 Unsteady-flow (reciprocating) engines : Using - and -s diagrams Outline! Air cycles! What are they?! Why use - and -s diagrams?! Using - and -s diagrams for air cycles!!!!!!
AME 46 Energy and ropulsion Lecture 7 Unsteady-flow (reciprocating) engines : Using - and -s diagrams Outline! Air cycles! What are they?! Why use - and -s diagrams?! Using - and -s diagrams for air cycles!!!!!!
ME 2322 Thermodynamics I PRE-LECTURE Lesson 23 Complete the items below Name:
 Lesson 23 1. (10 pt) Write the equation for the thermal efficiency of a Carnot heat engine below: 1 L H 2. (10 pt) Can the thermal efficiency of an actual engine ever exceed that of an equivalent Carnot
Lesson 23 1. (10 pt) Write the equation for the thermal efficiency of a Carnot heat engine below: 1 L H 2. (10 pt) Can the thermal efficiency of an actual engine ever exceed that of an equivalent Carnot
Entropy balance special forms. Quasiequilibrium (QE) process. QE process is reversible. dt Tk = = +
 Entropy balance Outline Closed systems Open systems Reversible steady flow wor Minimizing compressor wor Isentropic efficiencies Examples Entropy balance Sin Sout + Sgen = Ssys Entropy balance Entropy
Entropy balance Outline Closed systems Open systems Reversible steady flow wor Minimizing compressor wor Isentropic efficiencies Examples Entropy balance Sin Sout + Sgen = Ssys Entropy balance Entropy
8.21 The Physics of Energy Fall 2009
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 8.21 The Physics of Energy Fall 2009 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 8.21 Lecture 9 Heat Engines
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 8.21 The Physics of Energy Fall 2009 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 8.21 Lecture 9 Heat Engines
ME 300 Thermodynamics II Spring 2015 Exam 3. Son Jain Lucht 8:30AM 11:30AM 2:30PM
 NAME: PUID#: ME 300 Thermodynamics II Spring 05 Exam 3 Circle your section (-5 points for not circling correct section): Son Jain Lucht 8:30AM :30AM :30PM Instructions: This is a closed book/note exam.
NAME: PUID#: ME 300 Thermodynamics II Spring 05 Exam 3 Circle your section (-5 points for not circling correct section): Son Jain Lucht 8:30AM :30AM :30PM Instructions: This is a closed book/note exam.
Applied Thermodynamics for Marine Systems Prof. P. K. Das Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Applied Thermodynamics for Marine Systems Prof. P. K. Das Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 8 Introduction to Vapour Power Cycle Today, we will continue
Applied Thermodynamics for Marine Systems Prof. P. K. Das Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 8 Introduction to Vapour Power Cycle Today, we will continue
Thermodynamics. Mechanical Engineering. For
 Thermodynamics For Mechanical Engineering By www.thegateacademy.com Syllabus Syllabus for Thermodynamics Zeroth, First and Second Laws of Thermodynamics, Thermodynamic System and rocesses, Carnot Cycle.
Thermodynamics For Mechanical Engineering By www.thegateacademy.com Syllabus Syllabus for Thermodynamics Zeroth, First and Second Laws of Thermodynamics, Thermodynamic System and rocesses, Carnot Cycle.
Jet Aircraft Propulsion Prof. Bhaskar Roy Prof. A.M. Pradeep Department of Aerospace Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay
 Jet Aircraft Propulsion Prof. Bhaskar Roy Prof. A.M. Pradeep Department of Aerospace Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Module No. # 01 Lecture No. # 06 Ideal and Real Brayton Cycles Hello
Jet Aircraft Propulsion Prof. Bhaskar Roy Prof. A.M. Pradeep Department of Aerospace Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Module No. # 01 Lecture No. # 06 Ideal and Real Brayton Cycles Hello
MAE 11. Homework 8: Solutions 11/30/2018
 MAE 11 Homework 8: Solutions 11/30/2018 MAE 11 Fall 2018 HW #8 Due: Friday, November 30 (beginning of class at 12:00p) Requirements:: Include T s diagram for all cycles. Also include p v diagrams for Ch
MAE 11 Homework 8: Solutions 11/30/2018 MAE 11 Fall 2018 HW #8 Due: Friday, November 30 (beginning of class at 12:00p) Requirements:: Include T s diagram for all cycles. Also include p v diagrams for Ch
Theoretical & Derivation based Questions and Answer. Unit Derive the condition for exact differentials. Solution:
 Theoretical & Derivation based Questions and Answer Unit 01 1. Derive the condition for exact differentials. Solution: 2*. Derive the Maxwell relations and explain their importance in thermodynamics. Solution:
Theoretical & Derivation based Questions and Answer Unit 01 1. Derive the condition for exact differentials. Solution: 2*. Derive the Maxwell relations and explain their importance in thermodynamics. Solution:
Previous lecture. Today lecture
 Previous lecture ds relations (derive from steady energy balance) Gibb s equations Entropy change in liquid and solid Equations of & v, & P, and P & for steady isentropic process of ideal gas Isentropic
Previous lecture ds relations (derive from steady energy balance) Gibb s equations Entropy change in liquid and solid Equations of & v, & P, and P & for steady isentropic process of ideal gas Isentropic
Section 4.1: Introduction to Jet Propulsion. MAE Propulsion Systems II
 Section 4.1: Introduction to Jet Propulsion Jet Propulsion Basics Squeeze Bang Blow Suck Credit: USAF Test Pilot School 2 Basic Types of Jet Engines Ramjet High Speed, Supersonic Propulsion, Passive Compression/Expansion
Section 4.1: Introduction to Jet Propulsion Jet Propulsion Basics Squeeze Bang Blow Suck Credit: USAF Test Pilot School 2 Basic Types of Jet Engines Ramjet High Speed, Supersonic Propulsion, Passive Compression/Expansion
ME Thermodynamics I. Lecture Notes and Example Problems
 ME 227.3 Thermodynamics I Lecture Notes and Example Problems James D. Bugg September 2018 Department of Mechanical Engineering Introduction Part I: Lecture Notes This part contains handout versions of
ME 227.3 Thermodynamics I Lecture Notes and Example Problems James D. Bugg September 2018 Department of Mechanical Engineering Introduction Part I: Lecture Notes This part contains handout versions of
Thermodynamics Fundamentals for Energy Conversion Systems Renewable Energy Applications
 Thermodynamics Fundamentals for Energy Conversion Systems Renewable Energy Applications The study of the laws that govern the conversion of energy from one form to the other Energy Conversion Concerned
Thermodynamics Fundamentals for Energy Conversion Systems Renewable Energy Applications The study of the laws that govern the conversion of energy from one form to the other Energy Conversion Concerned
Chapter One Reviews of Thermodynamics Update on 2013/9/13
 Chapter One Reviews of Thermodynamics Update on 2013/9/13 (1.1). Thermodynamic system An isolated system is a system that exchanges neither mass nor energy with its environment. An insulated rigid tank
Chapter One Reviews of Thermodynamics Update on 2013/9/13 (1.1). Thermodynamic system An isolated system is a system that exchanges neither mass nor energy with its environment. An insulated rigid tank
Part III: Planes, Trains, and Automobiles: Making Heat Work for You
 Contents at a Glance Introduction... 1 Part I: Covering the Basics in Thermodynamics... 7 Chapter 1: Thermodynamics in Everyday Life...9 Chapter 2: Laying the Foundation of Thermodynamics...15 Chapter
Contents at a Glance Introduction... 1 Part I: Covering the Basics in Thermodynamics... 7 Chapter 1: Thermodynamics in Everyday Life...9 Chapter 2: Laying the Foundation of Thermodynamics...15 Chapter
CHAPTER 2 ENERGY INTERACTION (HEAT AND WORK)
 CHATER ENERGY INTERACTION (HEAT AND WORK) Energy can cross the boundary of a closed system in two ways: Heat and Work. WORK The work is done by a force as it acts upon a body moving in direction of force.
CHATER ENERGY INTERACTION (HEAT AND WORK) Energy can cross the boundary of a closed system in two ways: Heat and Work. WORK The work is done by a force as it acts upon a body moving in direction of force.
Lecture 43: Aircraft Propulsion
 Lecture 43: Aircraft Propulsion Turbojet Engine: 1 3 4 fuel in air in exhaust gases Diffuser Compressor Combustor Turbine Nozzle 43.1 T Ideal Ccle: w T,s = w C,s s 1 s w T,s w C,s 3 4 s s Processes: 1:
Lecture 43: Aircraft Propulsion Turbojet Engine: 1 3 4 fuel in air in exhaust gases Diffuser Compressor Combustor Turbine Nozzle 43.1 T Ideal Ccle: w T,s = w C,s s 1 s w T,s w C,s 3 4 s s Processes: 1:
I.C. Engine Cycles. Thermodynamic Analysis
 I.C. Engine Cycles Thermodynamic Analysis AIR STANDARD CYCLES Air as a perfect gas All processes ideal and reversible Mass same throughout Constant Specific Heat. OTTO CYCLE OTTO CYCLE Efficiency is
I.C. Engine Cycles Thermodynamic Analysis AIR STANDARD CYCLES Air as a perfect gas All processes ideal and reversible Mass same throughout Constant Specific Heat. OTTO CYCLE OTTO CYCLE Efficiency is
HEAT TRANSFER EFFECTS ON THE PERFORMANCE OF AN AIR STANDARD OTTO CYCLE. Havva Demirpolat, Ali Ates, S.Orkun Demirpolat, Ali Kahraman
 HEAT TRANSFER EFFECTS ON THE PERFORMANCE OF AN AIR STANDARD OTTO CYCLE Havva Demirpolat, Ali Ates, S.Orkun Demirpolat, Ali Kahraman University of Selçuk, TURKEY Abstract There are heat losses during the
HEAT TRANSFER EFFECTS ON THE PERFORMANCE OF AN AIR STANDARD OTTO CYCLE Havva Demirpolat, Ali Ates, S.Orkun Demirpolat, Ali Kahraman University of Selçuk, TURKEY Abstract There are heat losses during the
Fundamentals of Thermodynamics Applied to Thermal Power Plants
 Fundamentals of Thermodynamics Applied to Thermal Power Plants José R. Simões-Moreira Abstract In this chapter it is reviewed the fundamental principles of Thermodynamics aiming at its application to power
Fundamentals of Thermodynamics Applied to Thermal Power Plants José R. Simões-Moreira Abstract In this chapter it is reviewed the fundamental principles of Thermodynamics aiming at its application to power
NOTE: Only CHANGE in internal energy matters
 The First Law of Thermodynamics The First Law of Thermodynamics is a special case of the Law of Conservation of Energy It takes into account changes in internal energy and energy transfers by heat and
The First Law of Thermodynamics The First Law of Thermodynamics is a special case of the Law of Conservation of Energy It takes into account changes in internal energy and energy transfers by heat and
Turbine D P. Example 5.6 Air-standard Brayton cycle thermal efficiency
 Section 5.6 Engines 5.6 ENGINES ombustion Gas Turbine (Brayton ycle) The typical approach for analysis of air standard cycles is illustrated by the Brayton ycle in Fig. S-5.. To understand the cycle, the
Section 5.6 Engines 5.6 ENGINES ombustion Gas Turbine (Brayton ycle) The typical approach for analysis of air standard cycles is illustrated by the Brayton ycle in Fig. S-5.. To understand the cycle, the
AE1104 Physics 1. List of equations. Made by: E. Bruins Slot
 i AE04 Physics List of equations Made by: E. Bruins Slot Chapter Introduction and basic concepts Newton s second law Weight F = M a (N) W = m g J = N m (N) Density Specific volume ρ = m V m 3 v = V m =
i AE04 Physics List of equations Made by: E. Bruins Slot Chapter Introduction and basic concepts Newton s second law Weight F = M a (N) W = m g J = N m (N) Density Specific volume ρ = m V m 3 v = V m =
Physical Fundamentals of Global Change Processes
 University of Applied Sciences Eberswalde Master Study Program Global Change Management Manfred Stock Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research Module: Physical Fundamentals of Global Change Processes
University of Applied Sciences Eberswalde Master Study Program Global Change Management Manfred Stock Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research Module: Physical Fundamentals of Global Change Processes
ME Thermodynamics I
 Homework - Week 01 HW-01 (25 points) Given: 5 Schematic of the solar cell/solar panel Find: 5 Identify the system and the heat/work interactions associated with it. Show the direction of the interactions.
Homework - Week 01 HW-01 (25 points) Given: 5 Schematic of the solar cell/solar panel Find: 5 Identify the system and the heat/work interactions associated with it. Show the direction of the interactions.
Chapter 2 Carnot Principle
 Chapter 2 Carnot Principle 2.1 Temperature 2.1.1 Isothermal Process When two bodies are placed in thermal contact, the hotter body gives off heat to the colder body. As long as the temperatures are different,
Chapter 2 Carnot Principle 2.1 Temperature 2.1.1 Isothermal Process When two bodies are placed in thermal contact, the hotter body gives off heat to the colder body. As long as the temperatures are different,
Chapter 1 Introduction and Basic Concepts
 Chapter 1 Introduction and Basic Concepts 1-1 Thermodynamics and Energy Application Areas of Thermodynamics 1-2 Importance of Dimensions and Units Some SI and English Units Dimensional Homogeneity Unity
Chapter 1 Introduction and Basic Concepts 1-1 Thermodynamics and Energy Application Areas of Thermodynamics 1-2 Importance of Dimensions and Units Some SI and English Units Dimensional Homogeneity Unity
The exergy of asystemis the maximum useful work possible during a process that brings the system into equilibrium with aheat reservoir. (4.
 Energy Equation Entropy equation in Chapter 4: control mass approach The second law of thermodynamics Availability (exergy) The exergy of asystemis the maximum useful work possible during a process that
Energy Equation Entropy equation in Chapter 4: control mass approach The second law of thermodynamics Availability (exergy) The exergy of asystemis the maximum useful work possible during a process that
ME 440 Aerospace Engineering Fundamentals
 Fall 00 ME 440 Aerospace Engineering Fundamentals Propulsion Examples Example: Compressor Turbine Determine the outlet temperature and pressure for a turbine whose purpose is to power the compressor described
Fall 00 ME 440 Aerospace Engineering Fundamentals Propulsion Examples Example: Compressor Turbine Determine the outlet temperature and pressure for a turbine whose purpose is to power the compressor described
Analysis (a) Process 1-2: isentropic compression. p = 755K. R7] h87kpa.m 3/kg.K }30~ = O.906m 3/kg = V max
![Analysis (a) Process 1-2: isentropic compression. p = 755K. R7] h87kpa.m 3/kg.K }30~ = O.906m 3/kg = V max Analysis (a) Process 1-2: isentropic compression. p = 755K. R7] h87kpa.m 3/kg.K }30~ = O.906m 3/kg = V max](/thumbs/85/92734469.jpg) ~ Chapter 8 Gas Power Cycles Analysis (a) Process 1-2: isentropic compression. p - f ii, f T2=1j ( - VI = (300KX8)0.4 = 689K k-l I V2 - ~..., I ~=~ T2 Process 2-3: v = constant heat addition. q23,in =U3
~ Chapter 8 Gas Power Cycles Analysis (a) Process 1-2: isentropic compression. p - f ii, f T2=1j ( - VI = (300KX8)0.4 = 689K k-l I V2 - ~..., I ~=~ T2 Process 2-3: v = constant heat addition. q23,in =U3
+ m B1 = 1. u A1. u B1. - m B1 = V A. /v A = , u B1 + V B. = 5.5 kg => = V tot. Table B.1.
 5.6 A rigid tank is divided into two rooms by a membrane, both containing water, shown in Fig. P5.6. Room A is at 200 kpa, v = 0.5 m3/kg, VA = m3, and room B contains 3.5 kg at 0.5 MPa, 400 C. The membrane
5.6 A rigid tank is divided into two rooms by a membrane, both containing water, shown in Fig. P5.6. Room A is at 200 kpa, v = 0.5 m3/kg, VA = m3, and room B contains 3.5 kg at 0.5 MPa, 400 C. The membrane
Thermodynamics is the Science of Energy and Entropy
 Definition of Thermodynamics: Thermodynamics is the Science of Energy and Entropy - Some definitions. - The zeroth law. - Properties of pure substances. - Ideal gas law. - Entropy and the second law. Some
Definition of Thermodynamics: Thermodynamics is the Science of Energy and Entropy - Some definitions. - The zeroth law. - Properties of pure substances. - Ideal gas law. - Entropy and the second law. Some
10. Heat devices: heat engines and refrigerators (Hiroshi Matsuoka)
 10 Heat devices: heat engines and refrigerators (Hiroshi Matsuoka) 1 In this chapter we will discuss how heat devices work Heat devices convert heat into work or work into heat and include heat engines
10 Heat devices: heat engines and refrigerators (Hiroshi Matsuoka) 1 In this chapter we will discuss how heat devices work Heat devices convert heat into work or work into heat and include heat engines
Computational Tools to Enhance the Study of Gas Power Cycles in Mechanical Engineering Courses
 Computational Tools to Enhance the Study of Gas Power Cycles in Mechanical Engineering Courses Alta A. Knizley and Pedro J. Mago Department of Mechanical Engineering, Mississippi State University Abstract
Computational Tools to Enhance the Study of Gas Power Cycles in Mechanical Engineering Courses Alta A. Knizley and Pedro J. Mago Department of Mechanical Engineering, Mississippi State University Abstract
Introduction to Thermodynamic Cycles Part 1 1 st Law of Thermodynamics and Gas Power Cycles
 Introduction to Thermodynamic Cycles Part 1 1 st Law of Thermodynamics and Gas Power Cycles by James Doane, PhD, PE Contents 1.0 Course Oeriew... 4.0 Basic Concepts of Thermodynamics... 4.1 Temperature
Introduction to Thermodynamic Cycles Part 1 1 st Law of Thermodynamics and Gas Power Cycles by James Doane, PhD, PE Contents 1.0 Course Oeriew... 4.0 Basic Concepts of Thermodynamics... 4.1 Temperature
Modeling and Analysis of Dynamic Systems
 Modeling and Analysis of Dynamic Systems Dr. Guillaume Ducard Fall 2017 Institute for Dynamic Systems and Control ETH Zurich, Switzerland G. Ducard c 1 / 34 Outline 1 Lecture 7: Recall on Thermodynamics
Modeling and Analysis of Dynamic Systems Dr. Guillaume Ducard Fall 2017 Institute for Dynamic Systems and Control ETH Zurich, Switzerland G. Ducard c 1 / 34 Outline 1 Lecture 7: Recall on Thermodynamics
Existing Resources: Supplemental/reference for students with thermodynamics background and interests:
 Existing Resources: Masters, G. (1991) Introduction to Environmental Engineering and Science (Prentice Hall: NJ), pages 15 29. [ Masters_1991_Energy.pdf] Supplemental/reference for students with thermodynamics
Existing Resources: Masters, G. (1991) Introduction to Environmental Engineering and Science (Prentice Hall: NJ), pages 15 29. [ Masters_1991_Energy.pdf] Supplemental/reference for students with thermodynamics
PART 2 POWER AND PROPULSION CYCLES
 PAR 2 POWER AND PROPULSION CYCLES PAR 2 POWER AND PROPULSION CYCLES 2A Gas Power and Propulsion Cycles [SB&VW -.8,.9,.,.,.2,.3,.4] In this section we analyze several gas cycles used in practical applications
PAR 2 POWER AND PROPULSION CYCLES PAR 2 POWER AND PROPULSION CYCLES 2A Gas Power and Propulsion Cycles [SB&VW -.8,.9,.,.,.2,.3,.4] In this section we analyze several gas cycles used in practical applications
Chapter 1: FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS OF THERMODYNAMICS AND VARIOUS THERMODYMIC PROCESSES
 Chapter 1: FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS OF THERMODYNAMICS AND VARIOUS THERMODYMIC PROCESSES Thermodynamics is that branch of science which deals with energy transfer A system may be closed, open or isolated system
Chapter 1: FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS OF THERMODYNAMICS AND VARIOUS THERMODYMIC PROCESSES Thermodynamics is that branch of science which deals with energy transfer A system may be closed, open or isolated system
= T. (kj/k) (kj/k) 0 (kj/k) int rev. Chapter 6 SUMMARY
 Capter 6 SUMMARY e second la of termodynamics leads to te definition of a ne property called entropy ic is a quantitative measure of microscopic disorder for a system. e definition of entropy is based
Capter 6 SUMMARY e second la of termodynamics leads to te definition of a ne property called entropy ic is a quantitative measure of microscopic disorder for a system. e definition of entropy is based
Heat Engines and Refrigerators
 Lecture 26, Dec. 1 Goals: Chapter 19 Understand the relationship between work and heat in a cycling process Follow the physics of basic heat engines and refrigerators. Recognize some practical applications
Lecture 26, Dec. 1 Goals: Chapter 19 Understand the relationship between work and heat in a cycling process Follow the physics of basic heat engines and refrigerators. Recognize some practical applications
Minimizing and maximizing compressor and turbine work respectively
 Minimizing and maximizing compressor and turbine ork respectively Reversible steady-flo ork In Chapter 3, Work Done during a rocess as found to be W b dv Work Done during a rocess It depends on the path
Minimizing and maximizing compressor and turbine ork respectively Reversible steady-flo ork In Chapter 3, Work Done during a rocess as found to be W b dv Work Done during a rocess It depends on the path
Theory and Applica>on of Gas Turbine Systems
 Theory and Applica>on of Gas Turbine Systems Part I: Ideal Sha- Power Cycles Munich Summer School at University of Applied Sciences Prof. Kim A. Shollenberger Outline for Theory of Gas Turbine Systems
Theory and Applica>on of Gas Turbine Systems Part I: Ideal Sha- Power Cycles Munich Summer School at University of Applied Sciences Prof. Kim A. Shollenberger Outline for Theory of Gas Turbine Systems
VEER SURENDRA SAI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY BURLA, ODISHA DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS.
 VEER SURENDRA SAI UNIVERSIY OF ECHNOLOGY BURLA, ODISHA DEPARMEN OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ENGINEERING HERMODYNAMICS Lecture Notes Disclaimer his document does not claim any originality and cannot be used
VEER SURENDRA SAI UNIVERSIY OF ECHNOLOGY BURLA, ODISHA DEPARMEN OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ENGINEERING HERMODYNAMICS Lecture Notes Disclaimer his document does not claim any originality and cannot be used
Week 5. Energy Analysis of Closed Systems. GENESYS Laboratory
 Week 5. Energy Analysis of Closed Systems Objectives 1. Examine the moving boundary work or PdV work commonly encountered in reciprocating devices such as automotive engines and compressors 2. Identify
Week 5. Energy Analysis of Closed Systems Objectives 1. Examine the moving boundary work or PdV work commonly encountered in reciprocating devices such as automotive engines and compressors 2. Identify
Preface Acknowledgments Nomenclature
 CONTENTS Preface Acknowledgments Nomenclature page xv xvii xix 1 BASIC CONCEPTS 1 1.1 Overview 1 1.2 Thermodynamic Systems 3 1.3 States and Properties 4 1.3.1 State of a System 4 1.3.2 Measurable and Derived
CONTENTS Preface Acknowledgments Nomenclature page xv xvii xix 1 BASIC CONCEPTS 1 1.1 Overview 1 1.2 Thermodynamic Systems 3 1.3 States and Properties 4 1.3.1 State of a System 4 1.3.2 Measurable and Derived
CHAPTER 8 THERMODYNAMICS. Common Data For Q. 3 and Q.4. Steam enters an adiabatic turbine operating at steady state with an enthalpy of 3251.
 CHAPER 8 HERMODYNAMICS YEAR 0 ONE MARK MCQ 8. MCQ 8. Steam enters an adiabatic turbine operating at steady state with an enthalpy of 35.0 kj/ kg and leaves as a saturated mixture at 5 kpa with quality
CHAPER 8 HERMODYNAMICS YEAR 0 ONE MARK MCQ 8. MCQ 8. Steam enters an adiabatic turbine operating at steady state with an enthalpy of 35.0 kj/ kg and leaves as a saturated mixture at 5 kpa with quality
Comparative analysis of the Atkinson and the Otto cycles with heat transfer, friction and variable specific heats of working fluid
 همایش ملي مهندسي مکانیک 9 خرداد 939 (3 May, 3) Comparative analysis of the Atkinson and the Otto cycles with heat transfer, friction and variable specific heats of working fluid Mohammad Mehdi Rashidi,
همایش ملي مهندسي مکانیک 9 خرداد 939 (3 May, 3) Comparative analysis of the Atkinson and the Otto cycles with heat transfer, friction and variable specific heats of working fluid Mohammad Mehdi Rashidi,
Details on the Carnot Cycle
 Details on the Carnot Cycle he isothermal expansion (ab) and compression (cd): 0 ( is constant and U() is a function U isothermal of only for an Ideal Gas.) V b QH Wab nrh ln Va (ab : isothermal expansion)
Details on the Carnot Cycle he isothermal expansion (ab) and compression (cd): 0 ( is constant and U() is a function U isothermal of only for an Ideal Gas.) V b QH Wab nrh ln Va (ab : isothermal expansion)
Propulsion Thermodynamics
 Chapter 1 Propulsion Thermodynamics 1.1 Introduction The Figure below shows a cross-section of a Pratt and Whitney JT9D-7 high bypass ratio turbofan engine. The engine is depicted without any inlet, nacelle
Chapter 1 Propulsion Thermodynamics 1.1 Introduction The Figure below shows a cross-section of a Pratt and Whitney JT9D-7 high bypass ratio turbofan engine. The engine is depicted without any inlet, nacelle
Boundary. Surroundings
 Thermodynamics Thermodynamics describes the physics of matter using the concept of the thermodynamic system, a region of the universe that is under study. All quantities, such as pressure or mechanical
Thermodynamics Thermodynamics describes the physics of matter using the concept of the thermodynamic system, a region of the universe that is under study. All quantities, such as pressure or mechanical
On thermodynamic cycles for detonation engines
 On thermodynamic cycles for detonation engines R. Vutthivithayarak, E.M. Braun, and F.K. Lu 1 Introduction Detonation engines are considered to potentially yield better performance than existing turbo-engines
On thermodynamic cycles for detonation engines R. Vutthivithayarak, E.M. Braun, and F.K. Lu 1 Introduction Detonation engines are considered to potentially yield better performance than existing turbo-engines
An introduction to thermodynamics applied to Organic Rankine Cycles
 An introduction to thermodynamics applied to Organic Rankine Cycles By : Sylvain Quoilin PhD Student at the University of Liège November 2008 1 Definition of a few thermodynamic variables 1.1 Main thermodynamics
An introduction to thermodynamics applied to Organic Rankine Cycles By : Sylvain Quoilin PhD Student at the University of Liège November 2008 1 Definition of a few thermodynamic variables 1.1 Main thermodynamics
Thermodynamics Fundamental for TKE
 L/O/G/O EKNIK KONVERSI & KONSERVASI ENERGI F 091324 / 4 SKS / Smt. 6 Dosen : Syamsul Arifin syamsul@ep.its.ac.id K5 hermodynamics Fundamental for KE http://share.its.ac.id eknik Konversi Energi Fasilitator
L/O/G/O EKNIK KONVERSI & KONSERVASI ENERGI F 091324 / 4 SKS / Smt. 6 Dosen : Syamsul Arifin syamsul@ep.its.ac.id K5 hermodynamics Fundamental for KE http://share.its.ac.id eknik Konversi Energi Fasilitator
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ESE TOPICWISE OBJECTIVE SOLVED PAPER-I FROM (1995-2018) UPSC Engineering Services Examination State Engineering Service Examination & Public Sector Examination. IES MASTER PUBLICATION
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ESE TOPICWISE OBJECTIVE SOLVED PAPER-I FROM (1995-2018) UPSC Engineering Services Examination State Engineering Service Examination & Public Sector Examination. IES MASTER PUBLICATION
THERMODYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF COMBUSTION PROCESSES FOR PROPULSION SYSTEMS
 2nd AIAA Aerospace Sciences Paper 2-33 Meeting and Exhibit January -8, 2, Reno, NV THERMODYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF COMBUSTION PROCESSES FOR PROPULSION SYSTEMS E. Wintenberger and J. E. Shepherd Graduate Aeronautical
2nd AIAA Aerospace Sciences Paper 2-33 Meeting and Exhibit January -8, 2, Reno, NV THERMODYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF COMBUSTION PROCESSES FOR PROPULSION SYSTEMS E. Wintenberger and J. E. Shepherd Graduate Aeronautical
Irreversible Processes
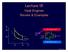 Lecture 15 Heat Engines Review & Examples p p b b Hot reservoir at T h p a a c adiabats Heat leak Heat pump Q h Q c W d V 1 V 2 V Cold reservoir at T c Lecture 15, p 1 Irreversible Processes Entropy-increasing
Lecture 15 Heat Engines Review & Examples p p b b Hot reservoir at T h p a a c adiabats Heat leak Heat pump Q h Q c W d V 1 V 2 V Cold reservoir at T c Lecture 15, p 1 Irreversible Processes Entropy-increasing
CHAPTER 8 ENTROPY. Blank
 CHAPER 8 ENROPY Blank SONNAG/BORGNAKKE SUDY PROBLEM 8-8. A heat engine efficiency from the inequality of Clausius Consider an actual heat engine with efficiency of η working between reservoirs at and L.
CHAPER 8 ENROPY Blank SONNAG/BORGNAKKE SUDY PROBLEM 8-8. A heat engine efficiency from the inequality of Clausius Consider an actual heat engine with efficiency of η working between reservoirs at and L.
Thermodynamics: The Laws
 Thermodynamics: The Laws Resources: Serway The Laws of Thermodynamics: 12 AP Physics B Videos Physics B Lesson 29: Laws of Thermodynamics Thermodynamics Thermodynamics is the study of heat and thermal
Thermodynamics: The Laws Resources: Serway The Laws of Thermodynamics: 12 AP Physics B Videos Physics B Lesson 29: Laws of Thermodynamics Thermodynamics Thermodynamics is the study of heat and thermal
Consequences of Second Law of Thermodynamics. Entropy. Clausius Inequity
 onsequences of Second Law of hermodynamics Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & echnology BUE Dhaka-000, Bangladesh zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd
onsequences of Second Law of hermodynamics Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & echnology BUE Dhaka-000, Bangladesh zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd
Chapter 20 The Second Law of Thermodynamics
 Chapter 20 The Second Law of Thermodynamics When we previously studied the first law of thermodynamics, we observed how conservation of energy provided us with a relationship between U, Q, and W, namely
Chapter 20 The Second Law of Thermodynamics When we previously studied the first law of thermodynamics, we observed how conservation of energy provided us with a relationship between U, Q, and W, namely
Summarizing, Key Point: An irreversible process is either spontaneous (ΔS universe > 0) or does not occur (ΔS universe < 0)
 Summarizing, Key Point: An irreversible process is either spontaneous (ΔS universe > 0) or does not occur (ΔS universe < 0) Key Point: ΔS universe allows us to distinguish between reversible and irreversible
Summarizing, Key Point: An irreversible process is either spontaneous (ΔS universe > 0) or does not occur (ΔS universe < 0) Key Point: ΔS universe allows us to distinguish between reversible and irreversible
Unit Workbook 2 - Level 5 ENG U64 Thermofluids 2018 UniCourse Ltd. All Rights Reserved. Sample
 Pearson BTEC Level 5 Higher Nationals in Engineering (RQF) Unit 64: Thermofluids Unit Workbook 2 in a series of 4 for this unit Learning Outcome 2 Vapour Power Cycles Page 1 of 26 2.1 Power Cycles Unit
Pearson BTEC Level 5 Higher Nationals in Engineering (RQF) Unit 64: Thermofluids Unit Workbook 2 in a series of 4 for this unit Learning Outcome 2 Vapour Power Cycles Page 1 of 26 2.1 Power Cycles Unit
Lecture 3 Evaluation of Entropy
 Lecture 3 Evaluation of Entropy If we wish to designate S by a proper name we can say of it that it is the transformation content of the body, in the same way that we say of the quantity U that it is the
Lecture 3 Evaluation of Entropy If we wish to designate S by a proper name we can say of it that it is the transformation content of the body, in the same way that we say of the quantity U that it is the
Jet Aircraft Propulsion Prof. Bhaskar Roy Prof A M Pradeep Department of Aerospace Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay
 Jet Aircraft Propulsion Prof. Bhaskar Roy Prof A M Pradeep Department of Aerospace Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Module No. #01 Lecture No. # 07 Jet Engine Cycles For Aircraft propulsion
Jet Aircraft Propulsion Prof. Bhaskar Roy Prof A M Pradeep Department of Aerospace Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Module No. #01 Lecture No. # 07 Jet Engine Cycles For Aircraft propulsion
Heat Machines (Chapters 18.6, 19)
 eat Machines (hapters 8.6, 9) eat machines eat engines eat pumps The Second Law of thermodynamics Entropy Ideal heat engines arnot cycle Other cycles: Brayton, Otto, Diesel eat Machines Description The
eat Machines (hapters 8.6, 9) eat machines eat engines eat pumps The Second Law of thermodynamics Entropy Ideal heat engines arnot cycle Other cycles: Brayton, Otto, Diesel eat Machines Description The
FUNDAMENTALS OF THERMODYNAMICS
 FUNDAMENTALS OF THERMODYNAMICS SEVENTH EDITION CLAUS BORGNAKKE RICHARD E. SONNTAG University of Michigan John Wiley & Sons, Inc. PUBLISHER ASSOCIATE PUBLISHER ACQUISITIONS EDITOR SENIOR PRODUCTION EDITOR
FUNDAMENTALS OF THERMODYNAMICS SEVENTH EDITION CLAUS BORGNAKKE RICHARD E. SONNTAG University of Michigan John Wiley & Sons, Inc. PUBLISHER ASSOCIATE PUBLISHER ACQUISITIONS EDITOR SENIOR PRODUCTION EDITOR
Not so black. Black Hole Thermodynamics. Nobel Prize 2017: Rainer Weiss, Kip Thorne, and Barry Barish.
 Not so black Nobel Prize 2017: Rainer Weiss, Kip Thorne, and Barry Barish. Black Hole Thermodynamics Zeroth Law of thermodynamics requires that black holes are round *. First law of thermodynamics requires
Not so black Nobel Prize 2017: Rainer Weiss, Kip Thorne, and Barry Barish. Black Hole Thermodynamics Zeroth Law of thermodynamics requires that black holes are round *. First law of thermodynamics requires
Chapter 1: FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS OF THERMODYNAMICS AND VARIOUS THERMODYMIC PROCESSES
 Chapter 1: FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS OF THERMODYNAMICS AND VARIOUS THERMODYMIC PROCESSES Thermodynamics is that branch of science which deals with energy transfer A system may be closed, open or isolated system
Chapter 1: FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS OF THERMODYNAMICS AND VARIOUS THERMODYMIC PROCESSES Thermodynamics is that branch of science which deals with energy transfer A system may be closed, open or isolated system
Exercise 8 - Turbocompressors
 Exercise 8 - Turbocompressors A turbocompressor TC) or turbocharger is a mechanical device used in internal combustion engines to enhance their power output. The basic idea of a TC is to force additional
Exercise 8 - Turbocompressors A turbocompressor TC) or turbocharger is a mechanical device used in internal combustion engines to enhance their power output. The basic idea of a TC is to force additional
AAE COMBUSTION AND THERMOCHEMISTRY
 5. COMBUSTIO AD THERMOCHEMISTRY Ch5 1 Overview Definition & mathematical determination of chemical equilibrium, Definition/determination of adiabatic flame temperature, Prediction of composition and temperature
5. COMBUSTIO AD THERMOCHEMISTRY Ch5 1 Overview Definition & mathematical determination of chemical equilibrium, Definition/determination of adiabatic flame temperature, Prediction of composition and temperature
Thermodynamics of solids 5. Unary systems. Kwangheon Park Kyung Hee University Department of Nuclear Engineering
 Thermodynamics of solids 5. Unary systems Kwangheon ark Kyung Hee University Department of Nuclear Engineering 5.1. Unary heterogeneous system definition Unary system: one component system. Unary heterogeneous
Thermodynamics of solids 5. Unary systems Kwangheon ark Kyung Hee University Department of Nuclear Engineering 5.1. Unary heterogeneous system definition Unary system: one component system. Unary heterogeneous
Thermodynamic system is classified into the following three systems. (ii) Closed System It exchanges only energy (not matter) with surroundings.
 1 P a g e The branch of physics which deals with the study of transformation of heat energy into other forms of energy and vice-versa. A thermodynamical system is said to be in thermal equilibrium when
1 P a g e The branch of physics which deals with the study of transformation of heat energy into other forms of energy and vice-versa. A thermodynamical system is said to be in thermal equilibrium when
Dishwasher. Heater. Homework Solutions ME Thermodynamics I Spring HW-1 (25 points)
 HW-1 (25 points) (a) Given: 1 for writing given, find, EFD, etc., Schematic of a household piping system Find: Identify system and location on the system boundary where the system interacts with the environment
HW-1 (25 points) (a) Given: 1 for writing given, find, EFD, etc., Schematic of a household piping system Find: Identify system and location on the system boundary where the system interacts with the environment
ME 200 Thermodynamics 1 Fall 2016 Final Exam
 Last Name: First Name: Thermo no. ME 200 Thermodynamics 1 Fall 2016 Final Exam Circle your instructor s last name Ardekani Bae Fisher olloway Jackson Meyer Sojka INSTRUCTIONS This is a closed book and
Last Name: First Name: Thermo no. ME 200 Thermodynamics 1 Fall 2016 Final Exam Circle your instructor s last name Ardekani Bae Fisher olloway Jackson Meyer Sojka INSTRUCTIONS This is a closed book and
(prev) (top) (next) (Throughout, we will assume the processes involve an ideal gas with constant n.)
 1 of 9 8/22/12 9:51 PM (prev) (top) (next) Thermodynamics 1 Thermodynamic processes can be: 2 isothermal processes, ΔT = 0 (so P ~ 1 / V); isobaric processes, ΔP = 0 (so T ~ V); isovolumetric or isochoric
1 of 9 8/22/12 9:51 PM (prev) (top) (next) Thermodynamics 1 Thermodynamic processes can be: 2 isothermal processes, ΔT = 0 (so P ~ 1 / V); isobaric processes, ΔP = 0 (so T ~ V); isovolumetric or isochoric
The need for something else: Entropy
 Lecture 27 Goals: Ch. 18 ualitatively understand 2 nd Law of Thermodynamics Ch. 19 Understand the relationship between work and heat in a cycling process Follow the physics of basic heat engines and refrigerators.
Lecture 27 Goals: Ch. 18 ualitatively understand 2 nd Law of Thermodynamics Ch. 19 Understand the relationship between work and heat in a cycling process Follow the physics of basic heat engines and refrigerators.
열과유체, 에너지와친해지기 KAIST 기계공학과정상권
 열과유체, 에너지와친해지기 KAIST 기계공학과정상권 이번시간에는! 열역학 - 세상을움직이는스마트한법칙 물과공기로움직이는기계 사라지지않는에너지 / 증가하는엔트로피 열역학 - 세상을움직이는스마트한법칙 KAIST 기계공학과정상권 [ 학습목차 ] Thermofluids Energy conservation principle Energy Work (boundary work)
열과유체, 에너지와친해지기 KAIST 기계공학과정상권 이번시간에는! 열역학 - 세상을움직이는스마트한법칙 물과공기로움직이는기계 사라지지않는에너지 / 증가하는엔트로피 열역학 - 세상을움직이는스마트한법칙 KAIST 기계공학과정상권 [ 학습목차 ] Thermofluids Energy conservation principle Energy Work (boundary work)
1. Second Law of Thermodynamics
 1. Second Law of hermodynamics he first law describes how the state of a system changes in response to work it performs and heat absorbed. he second law deals with direction of thermodynamic processes
1. Second Law of hermodynamics he first law describes how the state of a system changes in response to work it performs and heat absorbed. he second law deals with direction of thermodynamic processes
Internal Energy (example)
 Internal Energy (example) A bucket of water KEs: translational: rotational: vibrational: PEs: within molecules: between molecules: @ rest on the table molecular bonds dipole-dipole interactions Internal
Internal Energy (example) A bucket of water KEs: translational: rotational: vibrational: PEs: within molecules: between molecules: @ rest on the table molecular bonds dipole-dipole interactions Internal
Today lecture. 1. Entropy change in an isolated system 2. Exergy
 Today lecture 1. Entropy change in an isolated system. Exergy - What is exergy? - Reversible Work & Irreversibility - Second-Law Efficiency - Exergy change of a system For a fixed mass For a flow stream
Today lecture 1. Entropy change in an isolated system. Exergy - What is exergy? - Reversible Work & Irreversibility - Second-Law Efficiency - Exergy change of a system For a fixed mass For a flow stream
Chapter 5: The First Law of Thermodynamics: Closed Systems
 Chapter 5: The First Law of Thermodynamics: Closed Systems The first law of thermodynamics can be simply stated as follows: during an interaction between a system and its surroundings, the amount of energy
Chapter 5: The First Law of Thermodynamics: Closed Systems The first law of thermodynamics can be simply stated as follows: during an interaction between a system and its surroundings, the amount of energy
Civil aeroengines for subsonic cruise have convergent nozzles (page 83):
 120 Civil aeroengines for subsonic cruise have convergent nozzles (page 83): Choked convergent nozzle must be sonic at the exit A N. Consequently, the pressure (p 19 ) at the nozzle exit will be above
120 Civil aeroengines for subsonic cruise have convergent nozzles (page 83): Choked convergent nozzle must be sonic at the exit A N. Consequently, the pressure (p 19 ) at the nozzle exit will be above
ÂF = Ù. ı s. Ù u(ru) nds PRODUCTION OF THRUST. For x-component of vectors:
 PRODUCTION OF THRUST Newton s 2 nd Law (e.g. S F = d/dt (mv)) for a control volume of fixed mass with steady flow in and out and no acceleration of the frame of reference relative to inertial coordinates:
PRODUCTION OF THRUST Newton s 2 nd Law (e.g. S F = d/dt (mv)) for a control volume of fixed mass with steady flow in and out and no acceleration of the frame of reference relative to inertial coordinates:
OPTIMIZATION OF AN IRREVERSIBLE OTTO AND DIESEL CYCLES BASED ON ECOLOGICAL FUNCTION. Paraná Federal Institute, Jacarezinho, Paraná, Brasil.
 OPIMIZAION OF AN IRREVERSIBE OO AND DIESE CYCES BASED ON ECOOGICA FUNCION André. S. MOSCAO *, Santiago D. R. OIVEIRA, Vicente. SCAON, Alcides PADIA * Paraná Federal Institute, Jacarezinho, Paraná, Brasil.
OPIMIZAION OF AN IRREVERSIBE OO AND DIESE CYCES BASED ON ECOOGICA FUNCION André. S. MOSCAO *, Santiago D. R. OIVEIRA, Vicente. SCAON, Alcides PADIA * Paraná Federal Institute, Jacarezinho, Paraná, Brasil.
Thermodynamics part III.
 Thermodynamics part III. a.) Fenomenological thermodynamics macroscopic description b.) Molecular thermodynamics microscopic description b1.) kinetical gas theory b2.) statistical thermodynamics Laws of
Thermodynamics part III. a.) Fenomenological thermodynamics macroscopic description b.) Molecular thermodynamics microscopic description b1.) kinetical gas theory b2.) statistical thermodynamics Laws of
Chapter 19 The First Law of Thermodynamics
 Chapter 19 The First Law of Thermodynamics The first law of thermodynamics is an extension of the principle of conservation of energy. It includes the transfer of both mechanical and thermal energy. First
Chapter 19 The First Law of Thermodynamics The first law of thermodynamics is an extension of the principle of conservation of energy. It includes the transfer of both mechanical and thermal energy. First
Irreversible Processes
 Lecture 15 Heat Engines Review & Examples p p b b Hot reservoir at T h p a a c adiabats Heat leak Heat pump Q h Q c W d V 1 V 2 V Cold reservoir at T c Lecture 15, p 1 Irreversible Processes Entropy-increasing
Lecture 15 Heat Engines Review & Examples p p b b Hot reservoir at T h p a a c adiabats Heat leak Heat pump Q h Q c W d V 1 V 2 V Cold reservoir at T c Lecture 15, p 1 Irreversible Processes Entropy-increasing
