Variable Selection in High Dimensional Convex Regression
|
|
|
- Antony Nelson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Sensing and Analysis of High-Dimensional Data UCL-Duke Workshop September 4 & 5, 2014 Variable Selection in High Dimensional Convex Regression John Lafferty Department of Statistics & Department of Computer Science University of Chicago
2 Collaborators Min Xu CMU / UChicago Minhua Chen Duke / UChicago / Amazon 2
3 Collaborators Sabyasachi Chatterjee Yale / UChicago YJ Choe UChicago 3
4 Outline Nonparametric additive models Faithful variable selection in convex regression Algorithm using convex and concave additive models Finite sample analysis Convexity pattern decoding 4
5 Context Great progress in recent years on high dimensional models We have been trying to push nonparametric methods further Shape-constrained approaches are attractive for many reasons 5
6 High Dimensional Variable Selection Fully nonparametric models appear hopeless Logarithmic scaling, p = log n (e.g., Rodeo L. and Wasserman, 2008) Additive models are useful compromise Exponential scaling, p = exp(n c ) (e.g., SpAM Ravikumar et al., 2009) But do not give faithful variable selection 6
7 Additive Models Figure Bone Mineral Density Data Age Bmi Map Tc Difficulty: ChoosingFigure smoothing Diabetes parameters Data 7
8 Convex Regression: High Level Convex regression is fully nonparametric, with no tuning parameters. Shape constraints often natural in economics, marketing, reinforcement learning, etc. Estimation is a convex optimization problem. Efficient, scalable QP algorithms. We can recover sparsity pattern for convex regression assuming an (incorrect) additive model 21st century version of the 4 B s (Efron) Barlow, Bartholomew, Bremner and Brunk (1972), Statistical inference under order restrictions 8
9 Convex Regression The infinite-dimensional nonparametric convex regression (y i f (x i )) 2 min f convex is equivalent to the finite dimensional QP (y i f i ) 2 min f,β i i such that f j f i + β T i (x j x i ) Guntuboyina (2012): minimax analysis for support functions. Rate n 4/(3+p) equivalent to requiring two derivatives Minimax analysis for convex regression not yet complete; new results by Guntuboyina and Sen (2013) in 1-d setting 9
10 Other Previous Work N. Pya and S. Wood, Shape constrained additive models, Statistics and Computing, February Uses P-splines and requires smoothing parameters L. Hannah and D. Dunson, (1) Multivariate convex regression with adaptive partitioning, JMLR, 2013; (2) Bayesian nonparametric convex regression, (1) partitions data and constructs linear estimates (2) places prior over piecewise planar functions 10
11 Variable Selection in Convex Regression: Results Variable selection using a (potentially mis-specified) convex additive model is faithful no false negatives Sparsistent variable selection achievable with sample complexity n 4/5 Cs 5 σ 2 log 2 p where s is the number of relevant variables. 11
12 Faithfulness Additive approximation is { [( {fk }, µ := arg min f 1,...,f p,µ E f (X) p k=1 ) 2 ] f k (X k ) µ } : Ef k (X k ) = 0. We say f is additively faithful in case fk depend on coordinate k. = 0 implies that f does not 12
13 Nonconvex and Unfaithful Egg carton: f (x 1, x 2 ) = sin(2πx 1 ) sin(2πx 2 ). An additive approximation would set f 1 = 0 and f 2 = 0 13
14 Nonconvex and Unfaithful Tilting slope: f (x 1, x 2 ) = x 1 x 2 for x 1 [ 1, 1] and x 2 [0, 1]. An additive approximation would set f 2 = 0 14
15 Faithfulness under Convexity Theorem. Suppose the data density is supported on [0, 1] p and satisfies the boundary points condition p(x j x j ) = 2 p(x j x j ) x j xj 2 = 0 at x j = 0, x j = 1. If f is convex and twice differentiable, then f is additively faithful with respect to p. 15
16 Intuition Suppose the underlying distribution has a product density. Then the additive approximation zeroes out k when, fixing x k, every slice of f integrates to zero. The proof of this result shows that slices of convex functions that integrate to zero cannot be glued together while still maintaining convexity. 16
17 Using Shape Constraints Difficult to estimate optimal additive functions fk need not be convex When can a convex additive model be used? We need to couple with fitting concave functions on the residuals: ( gk {E = arg min f (X) 2 } fk (X k k) ) g : gk -C 1, Eg k (X k ) = 0. k k 17
18 Faithful Variable Screening Theorem. Suppose the density satisfies the boundary points condition, and f is convex and twice differentiable. Then fk = 0 and gk = 0 implies that f does not depend on x k. 18
19 ACEDC Algorithm 1 AC Stage: Estimate an additive convex model { f k }, µ = 1 arg min f 1,...,f p C 1, µ R n n i=1 ( y i µ p ) 2 p f k (x ik ) + λ f k k=1 k=1 2 DC Stage: If f k = 0, estimate decoupled concave function: 1 ĝ k = arg min g k -C 1 n n i=1 ( y i µ k fk (x ik ) g k (x ik )) 2 + λ gk 3 Estimated support Ŝn = {k : f k > 0 or ĝ k > 0} 19
20 Example simulation 20
21 ACEDC Sparsity Recovery Curves 21
22 Finite Sample Analysis: Assumptions A1: f 0 convex, twice differentiable A2: f 0 sb A3: sub-gaussian noise A4: X S and X S c are independent A5: boundary points condition 22
23 Finite Sample Analysis: Signal-to-Noise Define α + = inf {E ( f 0 (X) f (X) ) 2 ( E f0 (X) f (X) ) } 2 f C p 1 : k, f k 0 f k =0 Smallest excess approximation error if a relevant variable is omitted in AC stage. If α + is small, false negatives may occur in the AC stage. Plays role of smallest coefficient in lasso theory. 23
24 Finite Sample Analysis: Signal-to-Noise Define α = { min E ( f 0 (X) f (X) ) 2 ( E f0 (X) f (X) g k S : gk 0 k (X k) ) } 2. Smallest excess approximation error if a relevant variable is omitted in DC stage. If α is small, false negatives may occur in the DC stage. 24
25 Finite Sample Analysis: Sparsistency Theorem. Suppose that the regularization level is σ λ n = c 1 sb 2 log 2 np n and the signal-to-noise ratio satisfies α ( + σ, α ) 2 c2 B 3 s 5 log 2 np σ n 4/5. Then for n 4/5 c 3 σ 2 s 5 log 2 p, the AC/DC algorithm outputs a support set Ŝn satisfying P(Ŝn = S) 1 1 n. 25
26 Finite Sample Analysis: Sparsistency Allows exponential scaling p = O(exp(n c )) in ambient dimension Allows intrinsic dimension to scale as S s = o(n 4/25 ) Gives n = O(poly(s)) sample complexity. Comminges and Dalalyan (2012) show that under traditional smoothness constraints, consistent variable selection in high dimensions is only possible if n exp(s). 26
27 Finite Sample Analysis: Proof The proof exploits recent bracketing number bounds for convex function classes by Kim and Samworth (2014). Specifically, we bound W, f f f using bracketing entropy, where W is the noise. This removes some of the limitations of covering number bounds developed by Guntuboyina and Sen (2013). 27
28 Current Work: Convexity Pattern Decoding Suppose we have an additive model with a sum of convex and concave functions Estimation is a QP with no smoothing parameters What if we don t know the convexity pattern which functions are convex and which are concave? Can it be learned? 28
29 Convexity Pattern Decoding Model: Problem: Y = p z j f j (x j ) + ε j=1 z j { 1, 1}, f j convex Given data {(X i, Y i )} n i=1, X i R p, Y i R, decode z = (z 1,..., z p ) { 1, 1} p Solving this problem will lead to a new, useful approach to high-dimensional nonparametric estimation with no tuning parameters. 29
30 Mixed Integer SOCP Formulation min f,g,z,w such that n ( Y i i=1 p (f ij + g ij ) j=1 ) 2 convexity constraints on f j concavity constraints on g j n fij 2 z j B i=1 n gij 2 w j B i=1 z j + w j 1 z j, w j {0, 1}. 30
31 A Better, Convex Approach min f,g,β,γ,z,w such that n ( Y i i=1 p (f ij + g ij ) j=1 ) 2 convexity constraints on f j concavity constraints on g j p { } β(n)j β (1)j + γ (1)j γ (n)j L j=1 β (1)j, β (n)j, γ (1)j, γ (n)j are first and last subgradient vectors of f j and g j A nonstandard type of lasso. Works well requires special analysis. 31
32 Summary Gave conditions for additive faithfulness in convex function estimation Proposed AC/DC algorithm for variable selection using convex additive models Analyzed finite sample behavior, giving sparsistency rate of convergence Introduced problem of convexity pattern decoding 32
Computational and Statistical Aspects of Statistical Machine Learning. John Lafferty Department of Statistics Retreat Gleacher Center
 Computational and Statistical Aspects of Statistical Machine Learning John Lafferty Department of Statistics Retreat Gleacher Center Outline Modern nonparametric inference for high dimensional data Nonparametric
Computational and Statistical Aspects of Statistical Machine Learning John Lafferty Department of Statistics Retreat Gleacher Center Outline Modern nonparametric inference for high dimensional data Nonparametric
Thesis Proposal Shape-Constrained Estimation in High Dimensions
 January 22, 204 Thesis Proposal Shape-Constrained Estimation in High Dimensions Min Xu January 204 School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University Pittsburgh, PA 523 Thesis Committee: John Lafferty,
January 22, 204 Thesis Proposal Shape-Constrained Estimation in High Dimensions Min Xu January 204 School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University Pittsburgh, PA 523 Thesis Committee: John Lafferty,
Shape-Constrained Estimation in High Dimensions
 Shape-Constrained Estimation in High Dimensions Min Xu June 205 CMU-ML-4-XXX Machine Learning Department School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University Pittsburgh, PA 523 Thesis Committee: John
Shape-Constrained Estimation in High Dimensions Min Xu June 205 CMU-ML-4-XXX Machine Learning Department School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University Pittsburgh, PA 523 Thesis Committee: John
Variations on Nonparametric Additive Models: Computational and Statistical Aspects
 Variations on Nonparametric Additive Models: Computational and Statistical Aspects John Lafferty Department of Statistics & Department of Computer Science University of Chicago Collaborators Sivaraman
Variations on Nonparametric Additive Models: Computational and Statistical Aspects John Lafferty Department of Statistics & Department of Computer Science University of Chicago Collaborators Sivaraman
Sparsity Models. Tong Zhang. Rutgers University. T. Zhang (Rutgers) Sparsity Models 1 / 28
 Sparsity Models Tong Zhang Rutgers University T. Zhang (Rutgers) Sparsity Models 1 / 28 Topics Standard sparse regression model algorithms: convex relaxation and greedy algorithm sparse recovery analysis:
Sparsity Models Tong Zhang Rutgers University T. Zhang (Rutgers) Sparsity Models 1 / 28 Topics Standard sparse regression model algorithms: convex relaxation and greedy algorithm sparse recovery analysis:
Probabilistic Graphical Models
 School of Computer Science Probabilistic Graphical Models Gaussian graphical models and Ising models: modeling networks Eric Xing Lecture 0, February 7, 04 Reading: See class website Eric Xing @ CMU, 005-04
School of Computer Science Probabilistic Graphical Models Gaussian graphical models and Ising models: modeling networks Eric Xing Lecture 0, February 7, 04 Reading: See class website Eric Xing @ CMU, 005-04
Sparse Nonparametric Density Estimation in High Dimensions Using the Rodeo
 Outline in High Dimensions Using the Rodeo Han Liu 1,2 John Lafferty 2,3 Larry Wasserman 1,2 1 Statistics Department, 2 Machine Learning Department, 3 Computer Science Department, Carnegie Mellon University
Outline in High Dimensions Using the Rodeo Han Liu 1,2 John Lafferty 2,3 Larry Wasserman 1,2 1 Statistics Department, 2 Machine Learning Department, 3 Computer Science Department, Carnegie Mellon University
Sliced Inverse Regression
 Sliced Inverse Regression Ge Zhao gzz13@psu.edu Department of Statistics The Pennsylvania State University Outline Background of Sliced Inverse Regression (SIR) Dimension Reduction Definition of SIR Inversed
Sliced Inverse Regression Ge Zhao gzz13@psu.edu Department of Statistics The Pennsylvania State University Outline Background of Sliced Inverse Regression (SIR) Dimension Reduction Definition of SIR Inversed
High-dimensional Statistical Models
 High-dimensional Statistical Models Pradeep Ravikumar UT Austin MLSS 2014 1 Curse of Dimensionality Statistical Learning: Given n observations from p(x; θ ), where θ R p, recover signal/parameter θ. For
High-dimensional Statistical Models Pradeep Ravikumar UT Austin MLSS 2014 1 Curse of Dimensionality Statistical Learning: Given n observations from p(x; θ ), where θ R p, recover signal/parameter θ. For
25 : Graphical induced structured input/output models
 10-708: Probabilistic Graphical Models 10-708, Spring 2016 25 : Graphical induced structured input/output models Lecturer: Eric P. Xing Scribes: Raied Aljadaany, Shi Zong, Chenchen Zhu Disclaimer: A large
10-708: Probabilistic Graphical Models 10-708, Spring 2016 25 : Graphical induced structured input/output models Lecturer: Eric P. Xing Scribes: Raied Aljadaany, Shi Zong, Chenchen Zhu Disclaimer: A large
Statistical Machine Learning for Structured and High Dimensional Data
 Statistical Machine Learning for Structured and High Dimensional Data (FA9550-09- 1-0373) PI: Larry Wasserman (CMU) Co- PI: John Lafferty (UChicago and CMU) AFOSR Program Review (Jan 28-31, 2013, Washington,
Statistical Machine Learning for Structured and High Dimensional Data (FA9550-09- 1-0373) PI: Larry Wasserman (CMU) Co- PI: John Lafferty (UChicago and CMU) AFOSR Program Review (Jan 28-31, 2013, Washington,
Sparse Additive Functional and kernel CCA
 Sparse Additive Functional and kernel CCA Sivaraman Balakrishnan* Kriti Puniyani* John Lafferty *Carnegie Mellon University University of Chicago Presented by Miao Liu 5/3/2013 Canonical correlation analysis
Sparse Additive Functional and kernel CCA Sivaraman Balakrishnan* Kriti Puniyani* John Lafferty *Carnegie Mellon University University of Chicago Presented by Miao Liu 5/3/2013 Canonical correlation analysis
Regression, Ridge Regression, Lasso
 Regression, Ridge Regression, Lasso Fabio G. Cozman - fgcozman@usp.br October 2, 2018 A general definition Regression studies the relationship between a response variable Y and covariates X 1,..., X n.
Regression, Ridge Regression, Lasso Fabio G. Cozman - fgcozman@usp.br October 2, 2018 A general definition Regression studies the relationship between a response variable Y and covariates X 1,..., X n.
High-dimensional Statistics
 High-dimensional Statistics Pradeep Ravikumar UT Austin Outline 1. High Dimensional Data : Large p, small n 2. Sparsity 3. Group Sparsity 4. Low Rank 1 Curse of Dimensionality Statistical Learning: Given
High-dimensional Statistics Pradeep Ravikumar UT Austin Outline 1. High Dimensional Data : Large p, small n 2. Sparsity 3. Group Sparsity 4. Low Rank 1 Curse of Dimensionality Statistical Learning: Given
Gaussian Processes. Le Song. Machine Learning II: Advanced Topics CSE 8803ML, Spring 2012
 Gaussian Processes Le Song Machine Learning II: Advanced Topics CSE 8803ML, Spring 01 Pictorial view of embedding distribution Transform the entire distribution to expected features Feature space Feature
Gaussian Processes Le Song Machine Learning II: Advanced Topics CSE 8803ML, Spring 01 Pictorial view of embedding distribution Transform the entire distribution to expected features Feature space Feature
Convex-constrained Sparse Additive Modeling and Its Extensions
 Convex-constrained Sparse Additive Modeling and Its Extensions Jung Yin Eller College of Management University of Arizona Tucson, AZ 857 Yaoliang Yu School of Computer Science University of Waterloo Waterloo,
Convex-constrained Sparse Additive Modeling and Its Extensions Jung Yin Eller College of Management University of Arizona Tucson, AZ 857 Yaoliang Yu School of Computer Science University of Waterloo Waterloo,
Learning and Testing Structured Distributions
 Learning and Testing Structured Distributions Ilias Diakonikolas University of Edinburgh Simons Institute March 2015 This Talk Algorithmic Framework for Distribution Estimation: Leads to fast & robust
Learning and Testing Structured Distributions Ilias Diakonikolas University of Edinburgh Simons Institute March 2015 This Talk Algorithmic Framework for Distribution Estimation: Leads to fast & robust
High-dimensional covariance estimation based on Gaussian graphical models
 High-dimensional covariance estimation based on Gaussian graphical models Shuheng Zhou Department of Statistics, The University of Michigan, Ann Arbor IMA workshop on High Dimensional Phenomena Sept. 26,
High-dimensional covariance estimation based on Gaussian graphical models Shuheng Zhou Department of Statistics, The University of Michigan, Ann Arbor IMA workshop on High Dimensional Phenomena Sept. 26,
Dimension Reduction Techniques. Presented by Jie (Jerry) Yu
 Dimension Reduction Techniques Presented by Jie (Jerry) Yu Outline Problem Modeling Review of PCA and MDS Isomap Local Linear Embedding (LLE) Charting Background Advances in data collection and storage
Dimension Reduction Techniques Presented by Jie (Jerry) Yu Outline Problem Modeling Review of PCA and MDS Isomap Local Linear Embedding (LLE) Charting Background Advances in data collection and storage
An Introduction to Sparse Approximation
 An Introduction to Sparse Approximation Anna C. Gilbert Department of Mathematics University of Michigan Basic image/signal/data compression: transform coding Approximate signals sparsely Compress images,
An Introduction to Sparse Approximation Anna C. Gilbert Department of Mathematics University of Michigan Basic image/signal/data compression: transform coding Approximate signals sparsely Compress images,
PATTERN RECOGNITION AND MACHINE LEARNING
 PATTERN RECOGNITION AND MACHINE LEARNING Chapter 1. Introduction Shuai Huang April 21, 2014 Outline 1 What is Machine Learning? 2 Curve Fitting 3 Probability Theory 4 Model Selection 5 The curse of dimensionality
PATTERN RECOGNITION AND MACHINE LEARNING Chapter 1. Introduction Shuai Huang April 21, 2014 Outline 1 What is Machine Learning? 2 Curve Fitting 3 Probability Theory 4 Model Selection 5 The curse of dimensionality
Decision-making, inference, and learning theory. ECE 830 & CS 761, Spring 2016
 Decision-making, inference, and learning theory ECE 830 & CS 761, Spring 2016 1 / 22 What do we have here? Given measurements or observations of some physical process, we ask the simple question what do
Decision-making, inference, and learning theory ECE 830 & CS 761, Spring 2016 1 / 22 What do we have here? Given measurements or observations of some physical process, we ask the simple question what do
COS513: FOUNDATIONS OF PROBABILISTIC MODELS LECTURE 10
 COS53: FOUNDATIONS OF PROBABILISTIC MODELS LECTURE 0 MELISSA CARROLL, LINJIE LUO. BIAS-VARIANCE TRADE-OFF (CONTINUED FROM LAST LECTURE) If V = (X n, Y n )} are observed data, the linear regression problem
COS53: FOUNDATIONS OF PROBABILISTIC MODELS LECTURE 0 MELISSA CARROLL, LINJIE LUO. BIAS-VARIANCE TRADE-OFF (CONTINUED FROM LAST LECTURE) If V = (X n, Y n )} are observed data, the linear regression problem
Convex Optimization and l 1 -minimization
 Convex Optimization and l 1 -minimization Sangwoon Yun Computational Sciences Korea Institute for Advanced Study December 11, 2009 2009 NIMS Thematic Winter School Outline I. Convex Optimization II. l
Convex Optimization and l 1 -minimization Sangwoon Yun Computational Sciences Korea Institute for Advanced Study December 11, 2009 2009 NIMS Thematic Winter School Outline I. Convex Optimization II. l
Approximating high-dimensional posteriors with nuisance parameters via integrated rotated Gaussian approximation (IRGA)
 Approximating high-dimensional posteriors with nuisance parameters via integrated rotated Gaussian approximation (IRGA) Willem van den Boom Department of Statistics and Applied Probability National University
Approximating high-dimensional posteriors with nuisance parameters via integrated rotated Gaussian approximation (IRGA) Willem van den Boom Department of Statistics and Applied Probability National University
Causal Inference: Discussion
 Causal Inference: Discussion Mladen Kolar The University of Chicago Booth School of Business Sept 23, 2016 Types of machine learning problems Based on the information available: Supervised learning Reinforcement
Causal Inference: Discussion Mladen Kolar The University of Chicago Booth School of Business Sept 23, 2016 Types of machine learning problems Based on the information available: Supervised learning Reinforcement
ECE G: Special Topics in Signal Processing: Sparsity, Structure, and Inference
 ECE 18-898G: Special Topics in Signal Processing: Sparsity, Structure, and Inference Sparse Recovery using L1 minimization - algorithms Yuejie Chi Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Spring
ECE 18-898G: Special Topics in Signal Processing: Sparsity, Structure, and Inference Sparse Recovery using L1 minimization - algorithms Yuejie Chi Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Spring
27: Case study with popular GM III. 1 Introduction: Gene association mapping for complex diseases 1
 10-708: Probabilistic Graphical Models, Spring 2015 27: Case study with popular GM III Lecturer: Eric P. Xing Scribes: Hyun Ah Song & Elizabeth Silver 1 Introduction: Gene association mapping for complex
10-708: Probabilistic Graphical Models, Spring 2015 27: Case study with popular GM III Lecturer: Eric P. Xing Scribes: Hyun Ah Song & Elizabeth Silver 1 Introduction: Gene association mapping for complex
Unlabeled Data: Now It Helps, Now It Doesn t
 institution-logo-filena A. Singh, R. D. Nowak, and X. Zhu. In NIPS, 2008. 1 Courant Institute, NYU April 21, 2015 Outline institution-logo-filena 1 Conflicting Views in Semi-supervised Learning The Cluster
institution-logo-filena A. Singh, R. D. Nowak, and X. Zhu. In NIPS, 2008. 1 Courant Institute, NYU April 21, 2015 Outline institution-logo-filena 1 Conflicting Views in Semi-supervised Learning The Cluster
STATISTICAL MACHINE LEARNING FOR STRUCTURED AND HIGH DIMENSIONAL DATA
 AFRL-OSR-VA-TR-2014-0234 STATISTICAL MACHINE LEARNING FOR STRUCTURED AND HIGH DIMENSIONAL DATA Larry Wasserman CARNEGIE MELLON UNIVERSITY 0 Final Report DISTRIBUTION A: Distribution approved for public
AFRL-OSR-VA-TR-2014-0234 STATISTICAL MACHINE LEARNING FOR STRUCTURED AND HIGH DIMENSIONAL DATA Larry Wasserman CARNEGIE MELLON UNIVERSITY 0 Final Report DISTRIBUTION A: Distribution approved for public
Curve Fitting Re-visited, Bishop1.2.5
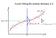 Curve Fitting Re-visited, Bishop1.2.5 Maximum Likelihood Bishop 1.2.5 Model Likelihood differentiation p(t x, w, β) = Maximum Likelihood N N ( t n y(x n, w), β 1). (1.61) n=1 As we did in the case of the
Curve Fitting Re-visited, Bishop1.2.5 Maximum Likelihood Bishop 1.2.5 Model Likelihood differentiation p(t x, w, β) = Maximum Likelihood N N ( t n y(x n, w), β 1). (1.61) n=1 As we did in the case of the
Sparsity Regularization
 Sparsity Regularization Bangti Jin Course Inverse Problems & Imaging 1 / 41 Outline 1 Motivation: sparsity? 2 Mathematical preliminaries 3 l 1 solvers 2 / 41 problem setup finite-dimensional formulation
Sparsity Regularization Bangti Jin Course Inverse Problems & Imaging 1 / 41 Outline 1 Motivation: sparsity? 2 Mathematical preliminaries 3 l 1 solvers 2 / 41 problem setup finite-dimensional formulation
Cross-Validation with Confidence
 Cross-Validation with Confidence Jing Lei Department of Statistics, Carnegie Mellon University WHOA-PSI Workshop, St Louis, 2017 Quotes from Day 1 and Day 2 Good model or pure model? Occam s razor We really
Cross-Validation with Confidence Jing Lei Department of Statistics, Carnegie Mellon University WHOA-PSI Workshop, St Louis, 2017 Quotes from Day 1 and Day 2 Good model or pure model? Occam s razor We really
Gaussian processes. Chuong B. Do (updated by Honglak Lee) November 22, 2008
 Gaussian processes Chuong B Do (updated by Honglak Lee) November 22, 2008 Many of the classical machine learning algorithms that we talked about during the first half of this course fit the following pattern:
Gaussian processes Chuong B Do (updated by Honglak Lee) November 22, 2008 Many of the classical machine learning algorithms that we talked about during the first half of this course fit the following pattern:
Cross-Validation with Confidence
 Cross-Validation with Confidence Jing Lei Department of Statistics, Carnegie Mellon University UMN Statistics Seminar, Mar 30, 2017 Overview Parameter est. Model selection Point est. MLE, M-est.,... Cross-validation
Cross-Validation with Confidence Jing Lei Department of Statistics, Carnegie Mellon University UMN Statistics Seminar, Mar 30, 2017 Overview Parameter est. Model selection Point est. MLE, M-est.,... Cross-validation
Using Multiple Kernel-based Regularization for Linear System Identification
 Using Multiple Kernel-based Regularization for Linear System Identification What are the Structure Issues in System Identification? with coworkers; see last slide Reglerteknik, ISY, Linköpings Universitet
Using Multiple Kernel-based Regularization for Linear System Identification What are the Structure Issues in System Identification? with coworkers; see last slide Reglerteknik, ISY, Linköpings Universitet
1 Regression with High Dimensional Data
 6.883 Learning with Combinatorial Structure ote for Lecture 11 Instructor: Prof. Stefanie Jegelka Scribe: Xuhong Zhang 1 Regression with High Dimensional Data Consider the following regression problem:
6.883 Learning with Combinatorial Structure ote for Lecture 11 Instructor: Prof. Stefanie Jegelka Scribe: Xuhong Zhang 1 Regression with High Dimensional Data Consider the following regression problem:
Course Outline. FRTN10 Multivariable Control, Lecture 13. General idea for Lectures Lecture 13 Outline. Example 1 (Doyle Stein, 1979)
 Course Outline FRTN Multivariable Control, Lecture Automatic Control LTH, 6 L-L Specifications, models and loop-shaping by hand L6-L8 Limitations on achievable performance L9-L Controller optimization:
Course Outline FRTN Multivariable Control, Lecture Automatic Control LTH, 6 L-L Specifications, models and loop-shaping by hand L6-L8 Limitations on achievable performance L9-L Controller optimization:
VARIABLE SELECTION AND INDEPENDENT COMPONENT
 VARIABLE SELECTION AND INDEPENDENT COMPONENT ANALYSIS, PLUS TWO ADVERTS Richard Samworth University of Cambridge Joint work with Rajen Shah and Ming Yuan My core research interests A broad range of methodological
VARIABLE SELECTION AND INDEPENDENT COMPONENT ANALYSIS, PLUS TWO ADVERTS Richard Samworth University of Cambridge Joint work with Rajen Shah and Ming Yuan My core research interests A broad range of methodological
Cheng Soon Ong & Christian Walder. Canberra February June 2018
 Cheng Soon Ong & Christian Walder Research Group and College of Engineering and Computer Science Canberra February June 2018 (Many figures from C. M. Bishop, "Pattern Recognition and ") 1of 254 Part V
Cheng Soon Ong & Christian Walder Research Group and College of Engineering and Computer Science Canberra February June 2018 (Many figures from C. M. Bishop, "Pattern Recognition and ") 1of 254 Part V
Boosting Methods: Why They Can Be Useful for High-Dimensional Data
 New URL: http://www.r-project.org/conferences/dsc-2003/ Proceedings of the 3rd International Workshop on Distributed Statistical Computing (DSC 2003) March 20 22, Vienna, Austria ISSN 1609-395X Kurt Hornik,
New URL: http://www.r-project.org/conferences/dsc-2003/ Proceedings of the 3rd International Workshop on Distributed Statistical Computing (DSC 2003) March 20 22, Vienna, Austria ISSN 1609-395X Kurt Hornik,
The Frank-Wolfe Algorithm:
 The Frank-Wolfe Algorithm: New Results, and Connections to Statistical Boosting Paul Grigas, Robert Freund, and Rahul Mazumder http://web.mit.edu/rfreund/www/talks.html Massachusetts Institute of Technology
The Frank-Wolfe Algorithm: New Results, and Connections to Statistical Boosting Paul Grigas, Robert Freund, and Rahul Mazumder http://web.mit.edu/rfreund/www/talks.html Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Practical Bayesian Optimization of Machine Learning. Learning Algorithms
 Practical Bayesian Optimization of Machine Learning Algorithms CS 294 University of California, Berkeley Tuesday, April 20, 2016 Motivation Machine Learning Algorithms (MLA s) have hyperparameters that
Practical Bayesian Optimization of Machine Learning Algorithms CS 294 University of California, Berkeley Tuesday, April 20, 2016 Motivation Machine Learning Algorithms (MLA s) have hyperparameters that
Probabilistic Graphical Models
 School of Computer Science Probabilistic Graphical Models Gaussian graphical models and Ising models: modeling networks Eric Xing Lecture 0, February 5, 06 Reading: See class website Eric Xing @ CMU, 005-06
School of Computer Science Probabilistic Graphical Models Gaussian graphical models and Ising models: modeling networks Eric Xing Lecture 0, February 5, 06 Reading: See class website Eric Xing @ CMU, 005-06
FRTN10 Multivariable Control, Lecture 13. Course outline. The Q-parametrization (Youla) Example: Spring-mass System
 FRTN Multivariable Control, Lecture 3 Anders Robertsson Automatic Control LTH, Lund University Course outline The Q-parametrization (Youla) L-L5 Purpose, models and loop-shaping by hand L6-L8 Limitations
FRTN Multivariable Control, Lecture 3 Anders Robertsson Automatic Control LTH, Lund University Course outline The Q-parametrization (Youla) L-L5 Purpose, models and loop-shaping by hand L6-L8 Limitations
Statistical Measures of Uncertainty in Inverse Problems
 Statistical Measures of Uncertainty in Inverse Problems Workshop on Uncertainty in Inverse Problems Institute for Mathematics and Its Applications Minneapolis, MN 19-26 April 2002 P.B. Stark Department
Statistical Measures of Uncertainty in Inverse Problems Workshop on Uncertainty in Inverse Problems Institute for Mathematics and Its Applications Minneapolis, MN 19-26 April 2002 P.B. Stark Department
BAGUS: Bayesian Regularization for Graphical Models with Unequal Shrinkage
 BAGUS: Bayesian Regularization for Graphical Models with Unequal Shrinkage Lingrui Gan, Naveen N. Narisetty, Feng Liang Department of Statistics University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Problem Statement
BAGUS: Bayesian Regularization for Graphical Models with Unequal Shrinkage Lingrui Gan, Naveen N. Narisetty, Feng Liang Department of Statistics University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Problem Statement
Optimization and Gradient Descent
 Optimization and Gradient Descent INFO-4604, Applied Machine Learning University of Colorado Boulder September 12, 2017 Prof. Michael Paul Prediction Functions Remember: a prediction function is the function
Optimization and Gradient Descent INFO-4604, Applied Machine Learning University of Colorado Boulder September 12, 2017 Prof. Michael Paul Prediction Functions Remember: a prediction function is the function
STAT 518 Intro Student Presentation
 STAT 518 Intro Student Presentation Wen Wei Loh April 11, 2013 Title of paper Radford M. Neal [1999] Bayesian Statistics, 6: 475-501, 1999 What the paper is about Regression and Classification Flexible
STAT 518 Intro Student Presentation Wen Wei Loh April 11, 2013 Title of paper Radford M. Neal [1999] Bayesian Statistics, 6: 475-501, 1999 What the paper is about Regression and Classification Flexible
41903: Introduction to Nonparametrics
 41903: Notes 5 Introduction Nonparametrics fundamentally about fitting flexible models: want model that is flexible enough to accommodate important patterns but not so flexible it overspecializes to specific
41903: Notes 5 Introduction Nonparametrics fundamentally about fitting flexible models: want model that is flexible enough to accommodate important patterns but not so flexible it overspecializes to specific
High-dimensional graphical model selection: Practical and information-theoretic limits
 1 High-dimensional graphical model selection: Practical and information-theoretic limits Martin Wainwright Departments of Statistics, and EECS UC Berkeley, California, USA Based on joint work with: John
1 High-dimensional graphical model selection: Practical and information-theoretic limits Martin Wainwright Departments of Statistics, and EECS UC Berkeley, California, USA Based on joint work with: John
Composite Loss Functions and Multivariate Regression; Sparse PCA
 Composite Loss Functions and Multivariate Regression; Sparse PCA G. Obozinski, B. Taskar, and M. I. Jordan (2009). Joint covariate selection and joint subspace selection for multiple classification problems.
Composite Loss Functions and Multivariate Regression; Sparse PCA G. Obozinski, B. Taskar, and M. I. Jordan (2009). Joint covariate selection and joint subspace selection for multiple classification problems.
High-dimensional regression with unknown variance
 High-dimensional regression with unknown variance Christophe Giraud Ecole Polytechnique march 2012 Setting Gaussian regression with unknown variance: Y i = f i + ε i with ε i i.i.d. N (0, σ 2 ) f = (f
High-dimensional regression with unknown variance Christophe Giraud Ecole Polytechnique march 2012 Setting Gaussian regression with unknown variance: Y i = f i + ε i with ε i i.i.d. N (0, σ 2 ) f = (f
Efficient Estimation in Convex Single Index Models 1
 1/28 Efficient Estimation in Convex Single Index Models 1 Rohit Patra University of Florida http://arxiv.org/abs/1708.00145 1 Joint work with Arun K. Kuchibhotla (UPenn) and Bodhisattva Sen (Columbia)
1/28 Efficient Estimation in Convex Single Index Models 1 Rohit Patra University of Florida http://arxiv.org/abs/1708.00145 1 Joint work with Arun K. Kuchibhotla (UPenn) and Bodhisattva Sen (Columbia)
Lasso: Algorithms and Extensions
 ELE 538B: Sparsity, Structure and Inference Lasso: Algorithms and Extensions Yuxin Chen Princeton University, Spring 2017 Outline Proximal operators Proximal gradient methods for lasso and its extensions
ELE 538B: Sparsity, Structure and Inference Lasso: Algorithms and Extensions Yuxin Chen Princeton University, Spring 2017 Outline Proximal operators Proximal gradient methods for lasso and its extensions
Constrained optimization
 Constrained optimization DS-GA 1013 / MATH-GA 2824 Optimization-based Data Analysis http://www.cims.nyu.edu/~cfgranda/pages/obda_fall17/index.html Carlos Fernandez-Granda Compressed sensing Convex constrained
Constrained optimization DS-GA 1013 / MATH-GA 2824 Optimization-based Data Analysis http://www.cims.nyu.edu/~cfgranda/pages/obda_fall17/index.html Carlos Fernandez-Granda Compressed sensing Convex constrained
Machine Learning for Big Data CSE547/STAT548, University of Washington Emily Fox February 4 th, Emily Fox 2014
 Case Study 3: fmri Prediction Fused LASSO LARS Parallel LASSO Solvers Machine Learning for Big Data CSE547/STAT548, University of Washington Emily Fox February 4 th, 2014 Emily Fox 2014 1 LASSO Regression
Case Study 3: fmri Prediction Fused LASSO LARS Parallel LASSO Solvers Machine Learning for Big Data CSE547/STAT548, University of Washington Emily Fox February 4 th, 2014 Emily Fox 2014 1 LASSO Regression
The Q-parametrization (Youla) Lecture 13: Synthesis by Convex Optimization. Lecture 13: Synthesis by Convex Optimization. Example: Spring-mass System
 The Q-parametrization (Youla) Lecture 3: Synthesis by Convex Optimization controlled variables z Plant distubances w Example: Spring-mass system measurements y Controller control inputs u Idea for lecture
The Q-parametrization (Youla) Lecture 3: Synthesis by Convex Optimization controlled variables z Plant distubances w Example: Spring-mass system measurements y Controller control inputs u Idea for lecture
A New Combined Approach for Inference in High-Dimensional Regression Models with Correlated Variables
 A New Combined Approach for Inference in High-Dimensional Regression Models with Correlated Variables Niharika Gauraha and Swapan Parui Indian Statistical Institute Abstract. We consider the problem of
A New Combined Approach for Inference in High-Dimensional Regression Models with Correlated Variables Niharika Gauraha and Swapan Parui Indian Statistical Institute Abstract. We consider the problem of
Concentration behavior of the penalized least squares estimator
 Concentration behavior of the penalized least squares estimator Penalized least squares behavior arxiv:1511.08698v2 [math.st] 19 Oct 2016 Alan Muro and Sara van de Geer {muro,geer}@stat.math.ethz.ch Seminar
Concentration behavior of the penalized least squares estimator Penalized least squares behavior arxiv:1511.08698v2 [math.st] 19 Oct 2016 Alan Muro and Sara van de Geer {muro,geer}@stat.math.ethz.ch Seminar
Statistics: Learning models from data
 DS-GA 1002 Lecture notes 5 October 19, 2015 Statistics: Learning models from data Learning models from data that are assumed to be generated probabilistically from a certain unknown distribution is a crucial
DS-GA 1002 Lecture notes 5 October 19, 2015 Statistics: Learning models from data Learning models from data that are assumed to be generated probabilistically from a certain unknown distribution is a crucial
Optimization methods
 Lecture notes 3 February 8, 016 1 Introduction Optimization methods In these notes we provide an overview of a selection of optimization methods. We focus on methods which rely on first-order information,
Lecture notes 3 February 8, 016 1 Introduction Optimization methods In these notes we provide an overview of a selection of optimization methods. We focus on methods which rely on first-order information,
Model Selection. Frank Wood. December 10, 2009
 Model Selection Frank Wood December 10, 2009 Standard Linear Regression Recipe Identify the explanatory variables Decide the functional forms in which the explanatory variables can enter the model Decide
Model Selection Frank Wood December 10, 2009 Standard Linear Regression Recipe Identify the explanatory variables Decide the functional forms in which the explanatory variables can enter the model Decide
Compressed Sensing and Neural Networks
 and Jan Vybíral (Charles University & Czech Technical University Prague, Czech Republic) NOMAD Summer Berlin, September 25-29, 2017 1 / 31 Outline Lasso & Introduction Notation Training the network Applications
and Jan Vybíral (Charles University & Czech Technical University Prague, Czech Republic) NOMAD Summer Berlin, September 25-29, 2017 1 / 31 Outline Lasso & Introduction Notation Training the network Applications
A Survey of L 1. Regression. Céline Cunen, 20/10/2014. Vidaurre, Bielza and Larranaga (2013)
 A Survey of L 1 Regression Vidaurre, Bielza and Larranaga (2013) Céline Cunen, 20/10/2014 Outline of article 1.Introduction 2.The Lasso for Linear Regression a) Notation and Main Concepts b) Statistical
A Survey of L 1 Regression Vidaurre, Bielza and Larranaga (2013) Céline Cunen, 20/10/2014 Outline of article 1.Introduction 2.The Lasso for Linear Regression a) Notation and Main Concepts b) Statistical
Nonparametric estimation of. s concave and log-concave densities: alternatives to maximum likelihood
 Nonparametric estimation of s concave and log-concave densities: alternatives to maximum likelihood Jon A. Wellner University of Washington, Seattle Cowles Foundation Seminar, Yale University November
Nonparametric estimation of s concave and log-concave densities: alternatives to maximum likelihood Jon A. Wellner University of Washington, Seattle Cowles Foundation Seminar, Yale University November
High dimensional thresholded regression and shrinkage effect
 J. R. Statist. Soc. B (014) 76, Part 3, pp. 67 649 High dimensional thresholded regression and shrinkage effect Zemin Zheng, Yingying Fan and Jinchi Lv University of Southern California, Los Angeles, USA
J. R. Statist. Soc. B (014) 76, Part 3, pp. 67 649 High dimensional thresholded regression and shrinkage effect Zemin Zheng, Yingying Fan and Jinchi Lv University of Southern California, Los Angeles, USA
CPSC 540: Machine Learning
 CPSC 540: Machine Learning Undirected Graphical Models Mark Schmidt University of British Columbia Winter 2016 Admin Assignment 3: 2 late days to hand it in today, Thursday is final day. Assignment 4:
CPSC 540: Machine Learning Undirected Graphical Models Mark Schmidt University of British Columbia Winter 2016 Admin Assignment 3: 2 late days to hand it in today, Thursday is final day. Assignment 4:
Graph Partitioning Using Random Walks
 Graph Partitioning Using Random Walks A Convex Optimization Perspective Lorenzo Orecchia Computer Science Why Spectral Algorithms for Graph Problems in practice? Simple to implement Can exploit very efficient
Graph Partitioning Using Random Walks A Convex Optimization Perspective Lorenzo Orecchia Computer Science Why Spectral Algorithms for Graph Problems in practice? Simple to implement Can exploit very efficient
COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF ORTHOGONAL MATCHING PURSUIT AND LEAST ANGLE REGRESSION
 COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF ORTHOGONAL MATCHING PURSUIT AND LEAST ANGLE REGRESSION By Mazin Abdulrasool Hameed A THESIS Submitted to Michigan State University in partial fulfillment of the requirements for
COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF ORTHOGONAL MATCHING PURSUIT AND LEAST ANGLE REGRESSION By Mazin Abdulrasool Hameed A THESIS Submitted to Michigan State University in partial fulfillment of the requirements for
A Test for Order Restriction of Several Multivariate Normal Mean Vectors against all Alternatives when the Covariance Matrices are Unknown but Common
 Journal of Statistical Theory and Applications Volume 11, Number 1, 2012, pp. 23-45 ISSN 1538-7887 A Test for Order Restriction of Several Multivariate Normal Mean Vectors against all Alternatives when
Journal of Statistical Theory and Applications Volume 11, Number 1, 2012, pp. 23-45 ISSN 1538-7887 A Test for Order Restriction of Several Multivariate Normal Mean Vectors against all Alternatives when
Integrated Non-Factorized Variational Inference
 Integrated Non-Factorized Variational Inference Shaobo Han, Xuejun Liao and Lawrence Carin Duke University February 27, 2014 S. Han et al. Integrated Non-Factorized Variational Inference February 27, 2014
Integrated Non-Factorized Variational Inference Shaobo Han, Xuejun Liao and Lawrence Carin Duke University February 27, 2014 S. Han et al. Integrated Non-Factorized Variational Inference February 27, 2014
Lecture 3. Linear Regression II Bastian Leibe RWTH Aachen
 Advanced Machine Learning Lecture 3 Linear Regression II 02.11.2015 Bastian Leibe RWTH Aachen http://www.vision.rwth-aachen.de/ leibe@vision.rwth-aachen.de This Lecture: Advanced Machine Learning Regression
Advanced Machine Learning Lecture 3 Linear Regression II 02.11.2015 Bastian Leibe RWTH Aachen http://www.vision.rwth-aachen.de/ leibe@vision.rwth-aachen.de This Lecture: Advanced Machine Learning Regression
Motivation Sparse Signal Recovery is an interesting area with many potential applications. Methods developed for solving sparse signal recovery proble
 Bayesian Methods for Sparse Signal Recovery Bhaskar D Rao 1 University of California, San Diego 1 Thanks to David Wipf, Zhilin Zhang and Ritwik Giri Motivation Sparse Signal Recovery is an interesting
Bayesian Methods for Sparse Signal Recovery Bhaskar D Rao 1 University of California, San Diego 1 Thanks to David Wipf, Zhilin Zhang and Ritwik Giri Motivation Sparse Signal Recovery is an interesting
Statistical Inference
 Statistical Inference Liu Yang Florida State University October 27, 2016 Liu Yang, Libo Wang (Florida State University) Statistical Inference October 27, 2016 1 / 27 Outline The Bayesian Lasso Trevor Park
Statistical Inference Liu Yang Florida State University October 27, 2016 Liu Yang, Libo Wang (Florida State University) Statistical Inference October 27, 2016 1 / 27 Outline The Bayesian Lasso Trevor Park
SOLVING NON-CONVEX LASSO TYPE PROBLEMS WITH DC PROGRAMMING. Gilles Gasso, Alain Rakotomamonjy and Stéphane Canu
 SOLVING NON-CONVEX LASSO TYPE PROBLEMS WITH DC PROGRAMMING Gilles Gasso, Alain Rakotomamonjy and Stéphane Canu LITIS - EA 48 - INSA/Universite de Rouen Avenue de l Université - 768 Saint-Etienne du Rouvray
SOLVING NON-CONVEX LASSO TYPE PROBLEMS WITH DC PROGRAMMING Gilles Gasso, Alain Rakotomamonjy and Stéphane Canu LITIS - EA 48 - INSA/Universite de Rouen Avenue de l Université - 768 Saint-Etienne du Rouvray
Approximation. Inderjit S. Dhillon Dept of Computer Science UT Austin. SAMSI Massive Datasets Opening Workshop Raleigh, North Carolina.
 Using Quadratic Approximation Inderjit S. Dhillon Dept of Computer Science UT Austin SAMSI Massive Datasets Opening Workshop Raleigh, North Carolina Sept 12, 2012 Joint work with C. Hsieh, M. Sustik and
Using Quadratic Approximation Inderjit S. Dhillon Dept of Computer Science UT Austin SAMSI Massive Datasets Opening Workshop Raleigh, North Carolina Sept 12, 2012 Joint work with C. Hsieh, M. Sustik and
Pathwise coordinate optimization
 Stanford University 1 Pathwise coordinate optimization Jerome Friedman, Trevor Hastie, Holger Hoefling, Robert Tibshirani Stanford University Acknowledgements: Thanks to Stephen Boyd, Michael Saunders,
Stanford University 1 Pathwise coordinate optimization Jerome Friedman, Trevor Hastie, Holger Hoefling, Robert Tibshirani Stanford University Acknowledgements: Thanks to Stephen Boyd, Michael Saunders,
Plug-in Approach to Active Learning
 Plug-in Approach to Active Learning Stanislav Minsker Stanislav Minsker (Georgia Tech) Plug-in approach to active learning 1 / 18 Prediction framework Let (X, Y ) be a random couple in R d { 1, +1}. X
Plug-in Approach to Active Learning Stanislav Minsker Stanislav Minsker (Georgia Tech) Plug-in approach to active learning 1 / 18 Prediction framework Let (X, Y ) be a random couple in R d { 1, +1}. X
Cheng Soon Ong & Christian Walder. Canberra February June 2018
 Cheng Soon Ong & Christian Walder Research Group and College of Engineering and Computer Science Canberra February June 2018 Outlines Overview Introduction Linear Algebra Probability Linear Regression
Cheng Soon Ong & Christian Walder Research Group and College of Engineering and Computer Science Canberra February June 2018 Outlines Overview Introduction Linear Algebra Probability Linear Regression
Learning discrete graphical models via generalized inverse covariance matrices
 Learning discrete graphical models via generalized inverse covariance matrices Duzhe Wang, Yiming Lv, Yongjoon Kim, Young Lee Department of Statistics University of Wisconsin-Madison {dwang282, lv23, ykim676,
Learning discrete graphical models via generalized inverse covariance matrices Duzhe Wang, Yiming Lv, Yongjoon Kim, Young Lee Department of Statistics University of Wisconsin-Madison {dwang282, lv23, ykim676,
High-dimensional Ordinary Least-squares Projection for Screening Variables
 1 / 38 High-dimensional Ordinary Least-squares Projection for Screening Variables Chenlei Leng Joint with Xiangyu Wang (Duke) Conference on Nonparametric Statistics for Big Data and Celebration to Honor
1 / 38 High-dimensional Ordinary Least-squares Projection for Screening Variables Chenlei Leng Joint with Xiangyu Wang (Duke) Conference on Nonparametric Statistics for Big Data and Celebration to Honor
Dimension Reduction in Abundant High Dimensional Regressions
 Dimension Reduction in Abundant High Dimensional Regressions Dennis Cook University of Minnesota 8th Purdue Symposium June 2012 In collaboration with Liliana Forzani & Adam Rothman, Annals of Statistics,
Dimension Reduction in Abundant High Dimensional Regressions Dennis Cook University of Minnesota 8th Purdue Symposium June 2012 In collaboration with Liliana Forzani & Adam Rothman, Annals of Statistics,
High dimensional Ising model selection
 High dimensional Ising model selection Pradeep Ravikumar UT Austin (based on work with John Lafferty, Martin Wainwright) Sparse Ising model US Senate 109th Congress Banerjee et al, 2008 Estimate a sparse
High dimensional Ising model selection Pradeep Ravikumar UT Austin (based on work with John Lafferty, Martin Wainwright) Sparse Ising model US Senate 109th Congress Banerjee et al, 2008 Estimate a sparse
Nonconcave Penalized Likelihood with A Diverging Number of Parameters
 Nonconcave Penalized Likelihood with A Diverging Number of Parameters Jianqing Fan and Heng Peng Presenter: Jiale Xu March 12, 2010 Jianqing Fan and Heng Peng Presenter: JialeNonconcave Xu () Penalized
Nonconcave Penalized Likelihood with A Diverging Number of Parameters Jianqing Fan and Heng Peng Presenter: Jiale Xu March 12, 2010 Jianqing Fan and Heng Peng Presenter: JialeNonconcave Xu () Penalized
Adaptive Piecewise Polynomial Estimation via Trend Filtering
 Adaptive Piecewise Polynomial Estimation via Trend Filtering Liubo Li, ShanShan Tu The Ohio State University li.2201@osu.edu, tu.162@osu.edu October 1, 2015 Liubo Li, ShanShan Tu (OSU) Trend Filtering
Adaptive Piecewise Polynomial Estimation via Trend Filtering Liubo Li, ShanShan Tu The Ohio State University li.2201@osu.edu, tu.162@osu.edu October 1, 2015 Liubo Li, ShanShan Tu (OSU) Trend Filtering
Analysis of Greedy Algorithms
 Analysis of Greedy Algorithms Jiahui Shen Florida State University Oct.26th Outline Introduction Regularity condition Analysis on orthogonal matching pursuit Analysis on forward-backward greedy algorithm
Analysis of Greedy Algorithms Jiahui Shen Florida State University Oct.26th Outline Introduction Regularity condition Analysis on orthogonal matching pursuit Analysis on forward-backward greedy algorithm
The lasso, persistence, and cross-validation
 The lasso, persistence, and cross-validation Daniel J. McDonald Department of Statistics Indiana University http://www.stat.cmu.edu/ danielmc Joint work with: Darren Homrighausen Colorado State University
The lasso, persistence, and cross-validation Daniel J. McDonald Department of Statistics Indiana University http://www.stat.cmu.edu/ danielmc Joint work with: Darren Homrighausen Colorado State University
Is the test error unbiased for these programs? 2017 Kevin Jamieson
 Is the test error unbiased for these programs? 2017 Kevin Jamieson 1 Is the test error unbiased for this program? 2017 Kevin Jamieson 2 Simple Variable Selection LASSO: Sparse Regression Machine Learning
Is the test error unbiased for these programs? 2017 Kevin Jamieson 1 Is the test error unbiased for this program? 2017 Kevin Jamieson 2 Simple Variable Selection LASSO: Sparse Regression Machine Learning
Generative v. Discriminative classifiers Intuition
 Logistic Regression (Continued) Generative v. Discriminative Decision rees Machine Learning 10701/15781 Carlos Guestrin Carnegie Mellon University January 31 st, 2007 2005-2007 Carlos Guestrin 1 Generative
Logistic Regression (Continued) Generative v. Discriminative Decision rees Machine Learning 10701/15781 Carlos Guestrin Carnegie Mellon University January 31 st, 2007 2005-2007 Carlos Guestrin 1 Generative
Nonparametric Regression 10/ Larry Wasserman
 Nonparametric Regression 10/36-702 Larry Wasserman 1 Introduction Now we focus on the following problem: Given a sample (X 1, Y 1 ),..., (X n, Y n ), where X i R d and Y i R, estimate the regression function
Nonparametric Regression 10/36-702 Larry Wasserman 1 Introduction Now we focus on the following problem: Given a sample (X 1, Y 1 ),..., (X n, Y n ), where X i R d and Y i R, estimate the regression function
Lecture 6: September 19
 36-755: Advanced Statistical Theory I Fall 2016 Lecture 6: September 19 Lecturer: Alessandro Rinaldo Scribe: YJ Choe Note: LaTeX template courtesy of UC Berkeley EECS dept. Disclaimer: These notes have
36-755: Advanced Statistical Theory I Fall 2016 Lecture 6: September 19 Lecturer: Alessandro Rinaldo Scribe: YJ Choe Note: LaTeX template courtesy of UC Berkeley EECS dept. Disclaimer: These notes have
Probabilistic numerics for deep learning
 Presenter: Shijia Wang Department of Engineering Science, University of Oxford rning (RLSS) Summer School, Montreal 2017 Outline 1 Introduction Probabilistic Numerics 2 Components Probabilistic modeling
Presenter: Shijia Wang Department of Engineering Science, University of Oxford rning (RLSS) Summer School, Montreal 2017 Outline 1 Introduction Probabilistic Numerics 2 Components Probabilistic modeling
Reconstruction from Anisotropic Random Measurements
 Reconstruction from Anisotropic Random Measurements Mark Rudelson and Shuheng Zhou The University of Michigan, Ann Arbor Coding, Complexity, and Sparsity Workshop, 013 Ann Arbor, Michigan August 7, 013
Reconstruction from Anisotropic Random Measurements Mark Rudelson and Shuheng Zhou The University of Michigan, Ann Arbor Coding, Complexity, and Sparsity Workshop, 013 Ann Arbor, Michigan August 7, 013
Extended Bayesian Information Criteria for Gaussian Graphical Models
 Extended Bayesian Information Criteria for Gaussian Graphical Models Rina Foygel University of Chicago rina@uchicago.edu Mathias Drton University of Chicago drton@uchicago.edu Abstract Gaussian graphical
Extended Bayesian Information Criteria for Gaussian Graphical Models Rina Foygel University of Chicago rina@uchicago.edu Mathias Drton University of Chicago drton@uchicago.edu Abstract Gaussian graphical
Dimension Reduction. David M. Blei. April 23, 2012
 Dimension Reduction David M. Blei April 23, 2012 1 Basic idea Goal: Compute a reduced representation of data from p -dimensional to q-dimensional, where q < p. x 1,...,x p z 1,...,z q (1) We want to do
Dimension Reduction David M. Blei April 23, 2012 1 Basic idea Goal: Compute a reduced representation of data from p -dimensional to q-dimensional, where q < p. x 1,...,x p z 1,...,z q (1) We want to do
Grouping Pursuit in regression. Xiaotong Shen
 Grouping Pursuit in regression Xiaotong Shen School of Statistics University of Minnesota Email xshen@stat.umn.edu Joint with Hsin-Cheng Huang (Sinica, Taiwan) Workshop in honor of John Hartigan Innovation
Grouping Pursuit in regression Xiaotong Shen School of Statistics University of Minnesota Email xshen@stat.umn.edu Joint with Hsin-Cheng Huang (Sinica, Taiwan) Workshop in honor of John Hartigan Innovation
Sparse Proteomics Analysis (SPA)
 Sparse Proteomics Analysis (SPA) Toward a Mathematical Theory for Feature Selection from Forward Models Martin Genzel Technische Universität Berlin Winter School on Compressed Sensing December 5, 2015
Sparse Proteomics Analysis (SPA) Toward a Mathematical Theory for Feature Selection from Forward Models Martin Genzel Technische Universität Berlin Winter School on Compressed Sensing December 5, 2015
Sparse, stable gene regulatory network recovery via convex optimization
 Sparse, stable gene regulatory network recovery via convex optimization Arwen Meister June, 11 Gene regulatory networks Gene expression regulation allows cells to control protein levels in order to live
Sparse, stable gene regulatory network recovery via convex optimization Arwen Meister June, 11 Gene regulatory networks Gene expression regulation allows cells to control protein levels in order to live
