Scale-free structural organization of oxygen interstitials in La 2 CuO 4+y
|
|
|
- June Hawkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Scale-free structural organization of oxygen interstitials in La 2 CuO 4+y Michela Fratini 1,*, Nicola Poccia 1, Alessandro Ricci 1, Gaetano Campi 1,2, Manfred Burghammer 3, Gabriel Aeppli 4 & Antonio Bianconi 1 1 Department of Physics, Sapienza University of Rome, Piazzale Aldo Moro 2, Roma, Italy. 2 Institute of Crystallography, CNR, Via Salaria Km , Monterotondo Stazione, Roma, I-00016, Italy. 3 European Synchrotron Radiation Facility, B.P. 220, F Grenoble Cedex, France. 4 London Centre for Nanotechnology and Department of Physics and Astronomy, University College London, Gordon Street, London WC1H 0AH, UK. * Present address: Institute for Photonic and Nanotechnologies, CNR, Via Cineto Romano 42, It is well known that the microstructures of the transition-metal oxides 1 3, including the high-transition-temperature (high-t c ) copper oxide superconductors 4 7, are complex. This is particularly so when there are oxygen interstitials or vacancies 8, which influence the bulk properties. For example, the oxygen interstitials in the spacer layers separating the superconducting CuO 2 planes undergo ordering phenomena in Sr 2 O 1+y CuO 2 (ref. 9), YBa 2 Cu 3 O 6+y (ref. 10) and La 2 CuO 4+y (refs 11 15) that induce enhancements in the transition temperatures with no changes in hole concentrations. It is also known that complex systems often have a scaleinvariant structural organization 16, but hitherto none had been found in high- T c materials. Here we report that the ordering of oxygen interstitials in the La 2 O 2+y spacer layers of La 2 CuO 4+y high-t c superconductors is characterized by a fractal distribution up to a maximum limiting size of 400 mm. Intriguingly, these fractal distributions of dopants seem to enhance superconductivity at high temperature. Scale-free structural organization of oxygen interstitials in La 2 CuO 4+y pag. 1
2 To make progress in the engineering and science of multiscale phase separation, visualization is essential. Momentum-space probes such as X-ray diffraction (XRD), angle-resolved photoelectron spectroscopy and inelastic neutron scattering are excellent for characterizing order and coherent excitations but are highly ambiguous when different phases coexist. Therefore, to image micrometre-scale lattice fluctuations in high-temperature superconductors due to the ordering of oxygen interstitials (i-o), we have used scanning synchrotron radiation X-ray microdiffraction (µxrd) 17 19, which combines high wavenumber resolution with micrometre-scale spatial resolution, made possible by twin revolutions in X-ray optics and electron-accelerator-based X-ray sources. The technique examines the same bulk, showing interesting material functionalities such as superconductivity, but also gives a wavelet 20 mixed real- and reciprocal-space representation of the sample, where the nanostructure associated with short- and medium-range oxygen order is captured by means of diffraction and the microstructure is recorded in real space. Optimally doped La 2 CuO 4+y is ideal for the investigation of intrinsic multiscale heterogeneity in copper oxides because the i-o are mobile 8 in the La 2 O 2+y layers intercalated between the super- conducting CuO 2 planes, forming a superlattice with the largest misfit strain in the copper oxides 21,22. Therefore, the order parameters associated with mobile i-o in the spacer layers maintaining charge neutrality are expected to track the microscale phase separation in the CuO 2 planes. In the optimum doping range, 0.1 < y < 0.12, a single T c = 40 K superconducting phase appears but many experiments 11 15,23,24 indicate a complex magnetic, electronic and structural phase separation. Annealing the sample at 370 K, where i- O does not escape from the sample, followed by quenching below 200 K, yields a mixed state, displaying two critical temperatures 11,12, 32< T c1 < 36 K and T c2 =16 K; we therefore call this state the T c =16+32 K phase. The mixed state has been thought to originate from the coexistence of regions with the same average doping level but with two different orderings of the dopants, with some unknown i-o selforganization; also, no information is available on the relation between this unknown superstructure and the high-temperature superconducting phase. Scale-free structural organization of oxygen interstitials in La 2 CuO 4+y pag. 2
3 Our single-crystal samples of La 2 CuO 4+y are cleaved with their surfaces parallel to the CuO 2 planes and then mounted on the x y translator of the µxrd instrument (Fig. 1a). The main XRD reflections of the single crystal (orthorhombic Fmmm space group) show no splitting or spatial spot-to-spot change. The reciprocal-space image recorded by the CCD on the right in Fig. 1a reveals the known satellite peaks, associated with the three-dimensional Q2 superstructure of the ordered i-o dopants 14,15, displaced from the main crystal reflections by the wavevector q2 with components Δl = (0.497 ± 0.005)c*, Δk = (0.247 ± 0.003)b* and Δh = (0.087 ± 0.004)a*, where a*, b* and c* are the reciprocal-lattice units; there is also a strong second harmonic displaced by 2q2. Mapping the x y position dependence of the integrated satellite peak intensity (Fig. 1b) provides our key experimental discovery, namely that on the micrometre scale probed, the i-o order with nanometre-scale wavelength in real space (Fig. 1c), which is responsible for the satellite peaks, is highly inhomogeneous, even for an optimal (T c = 40 K) superconducting sample of La 2 CuO 4.1. The micrometre-scale inhomogeneity depends on the sample preparation history, which also controls the superconducting properties. In fact, the x y position dependence of the Q2 superstructure intensity for two typical samples with T c = 40 K (Fig. 2a) and T c = K (Fig. 2b), respectively, is quite different. We quantify the difference by looking at the distribution of intensities as well as the distancedependent intensity correlations. The probability distribution (Fig. 2c) of XRD intensities shows a fat tail above the average Q2 intensity, <I>, extending to intensities 20 times larger than the average intensity. In this range, the data show a clear power-law distribution according to standard statistical physics criteria 25. The difference between the probability distributions of the two sets of samples is also obvious from fitting the data using a power law P x) " x!# exp(! x / x ). The outcome ( 0 is that the power-law exponent, α, is always indistinguishable from 2.6 and that the cut-off, x 0, is less than 10 for the T c = K materials and greater than 10 for the high-t c (40 K) materials. r r The spatial intensity correlation function, G(r) (Fig. 2d), where r = R i! R is the distance between x y positions R r k on the sample, as in Fig. 2a,b, does not exhibit exponential behaviour but follows a power law with a cut-off, as expected, near a j Scale-free structural organization of oxygen interstitials in La 2 CuO 4+y pag. 3
4 " critical point: G ( r) $ r # exp( # r /! ), with η = 0.3 ± 0.1 for all five samples. The correlation length,ξ, increases with increasing <I>, varying between 50 and 250 mm for the T c = K samples and taking the respective values 400 ± 30 µm and 350 ± 30 µm for the two T c = 40 K samples. The results for both the intensity distribution and the two-point correlation function show that the unexpected fractal nature, associated with the measured power laws, of i-o ordering is robust, approaching a pure scale-free distribution in the sample with higher critical temperature. A decade of work at the Elettra storage ring in Trieste shows that thermal treatments (Fig. 3) can control the i-o self-assembly and detailed superconducting properties while maintaining constant oxygen content. In particular, the probability of ordered i-o domains can be suppressed by annealing at K and enhanced by annealing at K. After quenching the sample from 370 K to 300 K and keeping the temperature constant at 300 K, the Q2 XRD signal, spatially averaged over the full sample surface, increases rapidly as a function of time in the first few days, after which it increases slowly over very much longer durations. The superconducting transitions of samples with different levels of average ordered Q2 volume have been established using contactless single-coil inductance. The data clearly demonstrate that the low-t c (16 K) phase disappears with the fully disordered i-o produced after annealing above 370 K followed by rapid quenching. Modest annealing at K induces weak Q2 XRD superstructure spots and an additional superconducting signature with T c = 16 K. On further annealing, the average intensity of the Q2 superstructure rises and the T c = 16 K superconducting phase gains prominence. After a very long annealing time, the integrated volume of the ordered i-o domains increases, the T c = 16 K phase disappears and a single superconducting phase with T c = K finally dominates. Our work puts the copper oxides into the same category as other heterogeneous transition-metal oxides 1,2, where a key parameter is the misfit strain parameter of the superlattice 21,22, and better superconductivity is associated with critical percolation of oxygen order. Unexplained effects of disorder, photoexcitation, pressure 11 and misfit strain in high-temperature superconductors (and also pnictides 26 ) can now be explored as potentially being due to granular fractal microstructure. The data also raise the more intriguing question of whether the oxygen defects order on fractal networks because the electrons that form the Scale-free structural organization of oxygen interstitials in La 2 CuO 4+y pag. 4
5 strange metal constitute a fractal glue, perhaps generated as a photographic-like image of the quantum critical charge fluctuations 27 sampled during annealing (at temperatures well within the non-fermi-liquid regime). Another possibility is that fractal defect structure promotes superconductivity, by means of either conventional percolation or the more unconventional mechanism of Feshbach-like shape resonances 28 associated with anisotropic superconducting gaps in granular heterostructures 29. Acknowledgements We are grateful to the ID13 beamline staff at ESRF, R. Davies, S. Agrestini, V. Palmisano, E. J. Sarria, L. Simonelli and A. Vittorini Orgeas for help in the early stage of this research project. We thank J. Zaanen and G. Bianconi for suggestions, comments and help with the data analysis. This experimental work has been carried out with the financial support of the European STREP project Controlling Mesoscopic Phase Separation (COMEPHS) ( ) and Sapienza University of Rome, research project Stripes and High-T c Superconductivity. References 1. Dagotto, E. Complexity in strongly correlated electronic systems. Science 309, (2005). 2. Tokura, Y. Critical features of colossal magnetoresistive manganites. Rep. Prog. Phys. 69, (2006). 3. Wadhawan, V. K. Smart Structures: Blurring the Distinction Between the Living and the Nonliving (Monogr. Phys. Chem. Mater. 65, Oxford Univ. Press, 2007). 4. Bishop, A. R. HTC oxides: a collusion of spin, charge and lattice. J. Phys. Conf. Ser.108, (2008). 5. Müller, K. A. in Superconductivity in Complex Systems (eds Muller, K. A. & Bussmann- Holder, A.) 1 11 (Structure and Bonding 114, Springer, 2005). Scale-free structural organization of oxygen interstitials in La 2 CuO 4+y pag. 5
6 6. Bednorz, J. G. & Muller, K. A. Possible high T c superconductivity in the Ba 2 La 2 Cu 2 O system. Z. Phys. B 64, (1986). 7. Phillips, J. C. Percolative theories of strongly disordered ceramic high temperature superconductors. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 107, (2010). 8. Skinner, S. J. & Kilner, J. A. Oxygen ion conductors. Mater. Today 6, (2003). 9. Liu, Q. Q. et al. Enhancement of the superconducting critical temperature of Sr 2 CuO 3+δ up to 95 K by ordering dopant atoms. Phys. Rev. B 74, (R) (2006). 10. Frello, T. et al. Dynamics of oxygen ordering in YBa 2 Cu 3 O 61x studied by neutron and high-energy synchrotron X-ray diffraction. Physica C , (1997). 11. Lorenz, B., Li, Z. G., Honma, T. & Hor, P. H. An intrinsic tendency of electronic phase separation into two superconducting states in La 2-x Sr x CuO 4+y. Phys. Rev. B 65, (2002). 12. Liu, L., Che, G., Zhao, J. & Zhao, Z. Thermal treatment effect of the oxidized La 2 CuO 4 : the access of continuous and discontinuous. Physica C 425, (2005). 13. Mohottala, H. E. et al. Phase separation in superoxygenated La 2-x Sr x CuO 4+ y. Nature Mater. 5, (2006). 14. Kusmartsev, F. et al. Transformation of strings into an inhomogeneous phase of stripes and itinerant carriers. Phys. Lett. A 275, (2000). 15. Lee, Y. S. et al. Neutron scattering study of the effects of dopant disorder on the superconductivity and magnetic order in stage-4 La 2 CuO 4+y. Phys. Rev. B 69, (R) (2004). 16. Barabasi, A.-L. & Stanley, H. E. Fractal Concepts in Surface Growth (Cambridge Univ. Press, 1995). 17. Soh, Y.-A. et al. Local mapping of strain at grain boundaries in colossal magnetoresistive films using X-ray microdiffraction. J. Appl. Phys. 91, (2002). 18. Evans, P. G., Isaacs, E. D., Aeppli, G., Cai, Z. & Lai, B. X-ray microdiffraction images of antiferromagnetic domain evolution in chromium. Science 295, (2002). 19. Cojoc, D. et al. Scanning X-ray microdiffraction of optically manipulated liposomes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 91, (2007). Scale-free structural organization of oxygen interstitials in La 2 CuO 4+y pag. 6
7 20. Daubechies, I. Ten Lectures on Wavelets (CBMS-NSF Regional Conf. Ser. Appl. Math. 61, Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, 1992). 21. Poccia, N., Ricci, A. & Bianconi, A. Misfit strain in superlattices controlling the electron-lattice interaction via microstrain in active layers. Adv. Condens. Matter Phys. 2010, (2010). 22. Agrestini, S., Saini, N. L., Bianconi, G. & Bianconi, A. The strain of CuO 2 lattice: the second variable for the phase diagram of cuprate perovskites. J. Phys. Math. Gen. 36, (2003). 23. Hammel, P. C. et al. Localized holes in superconducting lanthanum cuprate. Phys. Rev. B 57, R712 R715 (1998). 24. Savici, A. T. et al. Muon spin relaxation studies of incommensurate magnetism and superconductivity in stage-4 La 2 CuO 4.11 and La 1.88 Sr 0.12 CuO 4. Phys. Rev. B 66, (2002). 25. Clauset, A., Shalizi, C. R. & Newman, M. E. J. Power-law distributions in empirical data. SIAM Rev. 51, (2009). 26. Caivano, R. et al. Feshbach resonance and mesoscopic phase separation near a quantum critical point in multiband FeAs-based superconductors. Superconduct. Sci. Technol. 22, (2009). 27. Cubrovic, M., Zaanen, J. & Schalm, K. String theory, quantum phase transitions, and the emergent Fermi liquid. Science 325, (2009). 28. Bianconi, A. Feshbach shape resonance in multiband superconductivity in heterostructures. J. Superconduct. Novel Magnet. 18, (2005). 29. Bianconi, A., Valletta, A., Perali, A. & Saini, N. L. Superconductivity of a striped phase at the atomic limit. Physica C 296, (1998). Scale-free structural organization of oxygen interstitials in La 2 CuO 4+y pag. 7
8 Figure 1. Mixed real- and reciprocal-space images of dopant ordering. a, The X-ray microdiffraction apparatus is located at the European Synchrotron Radiation Facility (ESRF) and features an electron undulator providing keV X-rays to crystal optics followed by a tapered glass capillary, which produces a 1 µm 2 beam spot at the sample. A charge coupled area detector (CCD; right hand side) records the X-rays scattered by the sample. The intensity, I(Q2), of the superstructure satellites due to the Q2 ordering of oxygen interstitials in the La 2 CuO 4.1 crystal is integrated over square subareas of the images recorded by the CCD detector in reciprocal-lattice units (r.l.u.) and then normalized to the intensity (I 0 ) of the tail of the main crystalline reflections at each point (x, y) of the sample reached by the translator. b, Incommensurate order is highly inhomogeneous, even for an optimal (T c = 40 K) superconducting sample of La 2 CuO 4.1. The intensities of the superstructure satellites are presented on a logarithmic scale as a false-colour image. The scale bar corresponds to 100 µm. The intense red yellow peaks in the two-dimensional colour map represent locations in the sample with high strength of the three-dimensional i-o ordering, and dark blue indicates spots of disordered i-o domains. The scanning images show few regions with intense satellite µxrd reflections and many regions with weak satellite µxrd reflections. c, Realspace view of the ordered domains that give rise to the Q2 superstructure imaged on the CCD detector. It highlights the i-o ions (blue dots) in the c b plane of the Fmmm crystal structure of La 2 CuO 4. The i-o located at the (1/4, 1/4, 1/4) site in the La 2 O 2+y spacer layers pair to form linear stripes in the orthorhombic a direction with a period of nearly four lattice units along the b axis in the a b plane. The stripes alternate in different layers with a c-axis periodicity of two lattice units. The red octahedra indicate the CuO 6 octahedral coordination units in the CuO 2 plane. Scale-free structural organization of oxygen interstitials in La 2 CuO 4+y pag. 8
9 Figure 2. Scale-free fractal distribution and power-law statistical analysis of ordered i-o domains. a, b, The position dependence of the Q2 superstructure intensity I(Q2)/I 0 for two typical samples obtained by following different annealing quenching protocols, resulting in T c = 40 K (a) and T c K (b) phases. Visual inspection of a and b shows that the spikes corresponding to ordered microdomains are more isolated for the more disordered sample with lower T c than for the high-t c sample, indicating that the nucleation and growth of Q2 regions proceeds to smaller length scales for shorter annealing times. c, The probability distribution, P(x), of the Q2 XRD intensity x = I(Q2)/I 0 scales at sufficiently high intensity as a power-law distribution with exponential cut-off x 0. The data are fitted by the function described in the text. The fitted power-law exponent is given by α = 2.6 ± 0.2 independently of the sample critical temperature, and the cut-off increases from 7 < x 0 < 9 for the T c = K samples to 28 < x 0 < 33 for the T c = 40 K samples. In the plot, we show that the P(x) distributions, when properly rescaled, collapse on the same universal r r curve (solid line). d, Spatial correlation function, G(r), where r = R i! R j, calculated for the intensities at the spots R r mapped in a and b. The spatial correlation function does not have k " the standard exponential behaviour but instead obeys a power law, G ( r) $ r # exp( # r /! ), with cut-off ξ, as expected, near a critical point (see text for details). The correlation length, ξ, increases with increasing <I>, and in the illustrated cases for T c = K and 40 K has respective values 180 ± 30 µm and 400 ± 30 µm. Scale-free structural organization of oxygen interstitials in La 2 CuO 4+y pag. 9
10 Figure 3. Nucleation and growth of i-o superstructures. a, The integrated intensity, <I>, of the Q2 superstructure satellite reflections as a function of temperature measured using a large (200 µm diameter) beam at the Elettra storage ring. Starting from 300 K, we warmed the sample at a slow heating rate, 10 K h 21. The decreasing <I> becomes indistinguishable from zero at 350 K, indicating a continuous order-to-disorder phase transition in the K range. A rapid quench from the disordered phase to below 200 K produces a stable sample with randomly distributed i-o (dashed red arrow). Heating the sample very slowly induces a disorder-to-order transition in the K range. Annealing the random i-o sample for a long time at constant temperature in the K range (following the green vertical arrow) allows the i-o ordering to reach the maximum allowed intensity of the Q2 superstructure (we used annealing process A to produce the sample image in Fig. 2a). Using annealing process B in the K range followed by quenching process B produces samples with reduced i-o domain order (we used annealing process B for the sample in Fig. 2b). b, Temperature-dependent complex conductivity of doped La 2 CuO 4.1 superconducting crystals. We used a single-coil inductance method recording ( /!( T ) 2!, where ω(t) is the 0 ) resonance frequency of an LC circuit, L is the inductance of the submillimetre coil placed near the surface of the superconducting sample and ω 0 is the reference resonance frequency for a non-superconducting sample. The lower part of the figure shows the derivatives of ( /!( T ) 2!. The yellow, orange and red curves are for the two T c = K samples, 0 ) where T c1 = 16 K, 32 <T c2 < 36 K and <I> = <I(Q2)/I 0 > is small (annealing process B), and the green curves are for the T c = 40 K samples, where <I> = <I(Q2)/I 0 > is large (annealing process A). Scale-free structural organization of oxygen interstitials in La 2 CuO 4+y pag. 10
The Misfit Strain Critical Point in the 3D Phase Diagrams of Cuprates. Abstract
 The Misfit Strain Critical Point in the 3D Phase Diagrams of Cuprates Nicola Poccia, Michela Fratini Department of Physics, Sapienza University of Rome, P. Aldo Moro 2, 00185 Roma, Italy E-mail: nicola.poccia@roma1.infn.it
The Misfit Strain Critical Point in the 3D Phase Diagrams of Cuprates Nicola Poccia, Michela Fratini Department of Physics, Sapienza University of Rome, P. Aldo Moro 2, 00185 Roma, Italy E-mail: nicola.poccia@roma1.infn.it
Nanoscale phase separations in correlated materials by micro-xanes
 Nanoscale phase separations in correlated materials by micro-xanes A. Marcelli INFN - LNF USTC - NSRL & RICMASS marcelli@lnf.infn.it May 19, 2015 Layout Introduction phase separation scenario and mesophysics
Nanoscale phase separations in correlated materials by micro-xanes A. Marcelli INFN - LNF USTC - NSRL & RICMASS marcelli@lnf.infn.it May 19, 2015 Layout Introduction phase separation scenario and mesophysics
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SI - N. Poccia et al. Evolution and Control of Oxygen Order in a Cuprate Superconductor SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION 1. X-ray diffraction experiments The diffraction data were collected on the x-ray diffraction
SI - N. Poccia et al. Evolution and Control of Oxygen Order in a Cuprate Superconductor SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION 1. X-ray diffraction experiments The diffraction data were collected on the x-ray diffraction
DISORDER TO ORDER-LIKE TRANSITION IN La 2 CuO 4.1 SUPERCONDUCTOR INDUCED BY HIGH INTENSITY X-RAYS
 International Journal of Modern Physics B, Vol. 16, Nos. 11 & 12 (2002) 1627 1632 c World Scientific Publishing Company DISORDER TO ORDER-LIKE TRANSITION IN La 2 CuO 4.1 SUPERCONDUCTOR INDUCED BY HIGH
International Journal of Modern Physics B, Vol. 16, Nos. 11 & 12 (2002) 1627 1632 c World Scientific Publishing Company DISORDER TO ORDER-LIKE TRANSITION IN La 2 CuO 4.1 SUPERCONDUCTOR INDUCED BY HIGH
SESSION 2. (September 26, 2000) B. Lake Spin-gap and magnetic coherence in a high-temperature superconductor
 SESSION 2 (September 26, 2000) Spin fluctuations and stripes - I S2-I G. Shirane Stripes in Sr doped La 2 CuO 4 insulators and superconductors S2-II B. Lake Spin-gap and magnetic coherence in a high-temperature
SESSION 2 (September 26, 2000) Spin fluctuations and stripes - I S2-I G. Shirane Stripes in Sr doped La 2 CuO 4 insulators and superconductors S2-II B. Lake Spin-gap and magnetic coherence in a high-temperature
Electron State and Lattice Effects in Cuprate High Temperature Superconductors
 Electron State and Lattice Effects in Cuprate High Temperature Superconductors - The True Story Revealed by Fermi Surface and Unconventional Lattice Effects- October 27-28, 2005 Headquarters and Information
Electron State and Lattice Effects in Cuprate High Temperature Superconductors - The True Story Revealed by Fermi Surface and Unconventional Lattice Effects- October 27-28, 2005 Headquarters and Information
Striping in Cuprates. Michael Bertolli. Solid State II Elbio Dagotto Spring 2008 Department of Physics, Univ. of Tennessee
 Striping in Cuprates Michael Bertolli Solid State II Elbio Dagotto Spring 2008 Department of Physics, Univ. of Tennessee Outline Introduction Basics of Striping Implications to Superconductivity Experimental
Striping in Cuprates Michael Bertolli Solid State II Elbio Dagotto Spring 2008 Department of Physics, Univ. of Tennessee Outline Introduction Basics of Striping Implications to Superconductivity Experimental
YBCO. CuO 2. the CuO 2. planes is controlled. from deviation from. neutron. , blue star for. Hg12011 (this work) for T c = 72
 Supplementary Figure 1 Crystal structures and joint phase diagram of Hg1201 and YBCO. (a) Hg1201 features tetragonal symmetry and one CuO 2 plane per primitive cell. In the superconducting (SC) doping
Supplementary Figure 1 Crystal structures and joint phase diagram of Hg1201 and YBCO. (a) Hg1201 features tetragonal symmetry and one CuO 2 plane per primitive cell. In the superconducting (SC) doping
High temperature superconductivity
 High temperature superconductivity Applications to the maglev industry Elsa Abreu April 30, 2009 Outline Historical overview of superconductivity Copper oxide high temperature superconductors Angle Resolved
High temperature superconductivity Applications to the maglev industry Elsa Abreu April 30, 2009 Outline Historical overview of superconductivity Copper oxide high temperature superconductors Angle Resolved
Neutron scattering from quantum materials
 Neutron scattering from quantum materials Bernhard Keimer Max Planck Institute for Solid State Research Max Planck UBC UTokyo Center for Quantum Materials Detection of bosonic elementary excitations in
Neutron scattering from quantum materials Bernhard Keimer Max Planck Institute for Solid State Research Max Planck UBC UTokyo Center for Quantum Materials Detection of bosonic elementary excitations in
Magnetism in correlated-electron materials
 Magnetism in correlated-electron materials B. Keimer Max-Planck-Institute for Solid State Research focus on delocalized electrons in metals and superconductors localized electrons: Hinkov talk outline
Magnetism in correlated-electron materials B. Keimer Max-Planck-Institute for Solid State Research focus on delocalized electrons in metals and superconductors localized electrons: Hinkov talk outline
Imaging Self-Organized Domains at the Micron Scale in Antiferromagnetic Elemental Cr Using Magnetic X-ray Microscopy
 Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 690 2002 Materials Research Society Imaging Self-Organized Domains at the Micron Scale in Antiferromagnetic Elemental Cr Using Magnetic X-ray Microscopy P. G. Evans, 1 E.
Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 690 2002 Materials Research Society Imaging Self-Organized Domains at the Micron Scale in Antiferromagnetic Elemental Cr Using Magnetic X-ray Microscopy P. G. Evans, 1 E.
Scale free networks of superconducting striped grains tuned at Fano resonances for high T c
 Scale free networks of superconducting striped grains tuned at Fano resonances for high T c Antonio Bianconi 1 Rome International Center for Materials Science Superstripes RICMASS Via dei Sabelli 119A,
Scale free networks of superconducting striped grains tuned at Fano resonances for high T c Antonio Bianconi 1 Rome International Center for Materials Science Superstripes RICMASS Via dei Sabelli 119A,
Tuning order in cuprate superconductors
 Tuning order in cuprate superconductors arxiv:cond-mat/0201401 v1 23 Jan 2002 Subir Sachdev 1 and Shou-Cheng Zhang 2 1 Department of Physics, Yale University, P.O. Box 208120, New Haven, CT 06520-8120,
Tuning order in cuprate superconductors arxiv:cond-mat/0201401 v1 23 Jan 2002 Subir Sachdev 1 and Shou-Cheng Zhang 2 1 Department of Physics, Yale University, P.O. Box 208120, New Haven, CT 06520-8120,
Oliver Portugall Laboratoire National des Champs Magnétiques Intenses (LNCMI) Toulouse & Grenoble, France
 Oliver Portugall Laboratoire National des Champs Magnétiques Intenses (LNCMI) Toulouse & Grenoble, France 1 Building & Infrastructure 2 3 Industrial building (steel panel construction) 6 explosion proof
Oliver Portugall Laboratoire National des Champs Magnétiques Intenses (LNCMI) Toulouse & Grenoble, France 1 Building & Infrastructure 2 3 Industrial building (steel panel construction) 6 explosion proof
What's so unusual about high temperature superconductors? UBC 2005
 What's so unusual about high temperature superconductors? UBC 2005 Everything... 1. Normal State - doped Mott insulator 2. Pairing Symmetry - d-wave 2. Short Coherence Length - superconducting fluctuations
What's so unusual about high temperature superconductors? UBC 2005 Everything... 1. Normal State - doped Mott insulator 2. Pairing Symmetry - d-wave 2. Short Coherence Length - superconducting fluctuations
Supplementary Figure 1. Spin-spin relaxation curves for three La 1.8-x Eu 0.2 Sr x CuO 4 samples.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Spin-spin relaxation curves for three La 1.8-x Eu 0.2 Sr x CuO 4 samples. The data here are raw nuclear quadrupole resonance (NQR) data multiplied by temperature to compensate for
Supplementary Figure 1. Spin-spin relaxation curves for three La 1.8-x Eu 0.2 Sr x CuO 4 samples. The data here are raw nuclear quadrupole resonance (NQR) data multiplied by temperature to compensate for
NEURON SCATTERING STUDIES OF THE MAGNETIC FLUCTUATIONS IN YBa 2 Cu 3 O 7¹d
 Pergamon PII: S0022-3697(98)00196-6 J. Phys. Chem Solids Vol 59, No. 10 12, pp. 2140 2144, 1998 0022-3697/98/$ - see front matter 1998 Elsevier Science Ltd. All rights reserved NEURON SCATTERING STUDIES
Pergamon PII: S0022-3697(98)00196-6 J. Phys. Chem Solids Vol 59, No. 10 12, pp. 2140 2144, 1998 0022-3697/98/$ - see front matter 1998 Elsevier Science Ltd. All rights reserved NEURON SCATTERING STUDIES
SESSION 3. Lattice fluctuations and stripes - I. (September 26, 2000) S3-I S3-II S3-III S3-IV S3-V. E. Kaldis New aspects of Ca doping in 123
 SESSION 3 (September 26, 2000) Lattice fluctuations and stripes - I S3-I E. Kaldis New aspects of Ca doping in 123 S3-II H. Oyanagi Local lattice distortions in YBa 2 Cu 3 O y single crystal: Phase separation
SESSION 3 (September 26, 2000) Lattice fluctuations and stripes - I S3-I E. Kaldis New aspects of Ca doping in 123 S3-II H. Oyanagi Local lattice distortions in YBa 2 Cu 3 O y single crystal: Phase separation
Time-Resolved and Momentum-Resolved Resonant Soft X-ray Scattering on Strongly Correlated Systems
 Time-Resolved and Momentum-Resolved Resonant Soft X-ray Scattering on Strongly Correlated Systems Wei-Sheng Lee Stanford Institute of Material and Energy Science (SIMES) SLAC & Stanford University Collaborators
Time-Resolved and Momentum-Resolved Resonant Soft X-ray Scattering on Strongly Correlated Systems Wei-Sheng Lee Stanford Institute of Material and Energy Science (SIMES) SLAC & Stanford University Collaborators
Dipolar clusters and ferroelectricity in high T c superconductors
 July, 0 : IJMPB S000 page International Journal of Modern Physics B Vol., No. 0 (0) 00 ( pages) c World Scientific Publishing Company DOI: 0./S000 Dipolar clusters and ferroelectricity in high T c superconductors
July, 0 : IJMPB S000 page International Journal of Modern Physics B Vol., No. 0 (0) 00 ( pages) c World Scientific Publishing Company DOI: 0./S000 Dipolar clusters and ferroelectricity in high T c superconductors
Synchrotron Methods in Nanomaterials Research
 Synchrotron Methods in Nanomaterials Research Marcel MiGLiERiNi Slovak University of Technology in Bratislava and Centre for Nanomaterials Research, Olomouc marcel.miglierini@stuba.sk www.nuc.elf.stuba.sk/bruno
Synchrotron Methods in Nanomaterials Research Marcel MiGLiERiNi Slovak University of Technology in Bratislava and Centre for Nanomaterials Research, Olomouc marcel.miglierini@stuba.sk www.nuc.elf.stuba.sk/bruno
Crystal growth and annealing study of the hightemperature superconductor HgBa 2 CuO 4+δ
 Nagarajan 1 Crystal growth and annealing study of the hightemperature superconductor HgBa 2 CuO 4+δ Vikram Nagarajan University of Minnesota, Twin Cities Greven Lab Supervisor: Martin Greven The flux crystal-growth
Nagarajan 1 Crystal growth and annealing study of the hightemperature superconductor HgBa 2 CuO 4+δ Vikram Nagarajan University of Minnesota, Twin Cities Greven Lab Supervisor: Martin Greven The flux crystal-growth
Quantum dynamics in many body systems
 Quantum dynamics in many body systems Eugene Demler Harvard University Collaborators: David Benjamin (Harvard), Israel Klich (U. Virginia), D. Abanin (Perimeter), K. Agarwal (Harvard), E. Dalla Torre (Harvard)
Quantum dynamics in many body systems Eugene Demler Harvard University Collaborators: David Benjamin (Harvard), Israel Klich (U. Virginia), D. Abanin (Perimeter), K. Agarwal (Harvard), E. Dalla Torre (Harvard)
Dynamics of fluctuations in high temperature superconductors far from equilibrium. L. Perfetti, Laboratoire des Solides Irradiés, Ecole Polytechnique
 Dynamics of fluctuations in high temperature superconductors far from equilibrium L. Perfetti, Laboratoire des Solides Irradiés, Ecole Polytechnique Superconductors display amazing properties: Dissipation-less
Dynamics of fluctuations in high temperature superconductors far from equilibrium L. Perfetti, Laboratoire des Solides Irradiés, Ecole Polytechnique Superconductors display amazing properties: Dissipation-less
Solid Surfaces, Interfaces and Thin Films
 Hans Lüth Solid Surfaces, Interfaces and Thin Films Fifth Edition With 427 Figures.2e Springer Contents 1 Surface and Interface Physics: Its Definition and Importance... 1 Panel I: Ultrahigh Vacuum (UHV)
Hans Lüth Solid Surfaces, Interfaces and Thin Films Fifth Edition With 427 Figures.2e Springer Contents 1 Surface and Interface Physics: Its Definition and Importance... 1 Panel I: Ultrahigh Vacuum (UHV)
J. D. Thompson with Tuson Park, Zohar Nussinov, John L. Sarrao Los Alamos National Laboratory and Sang-Wook Cheong Rutgers University
 Dielectric Glassiness in Hole-Doped but Insulating Cuprates and Nickelates J. D. Thompson with Tuson Park, Zohar Nussinov, John L. Sarrao Los Alamos National Laboratory and Sang-Wook Cheong Rutgers University
Dielectric Glassiness in Hole-Doped but Insulating Cuprates and Nickelates J. D. Thompson with Tuson Park, Zohar Nussinov, John L. Sarrao Los Alamos National Laboratory and Sang-Wook Cheong Rutgers University
Neutron and x-ray spectroscopy
 Neutron and x-ray spectroscopy B. Keimer Max-Planck-Institute for Solid State Research outline 1. self-contained introduction neutron scattering and spectroscopy x-ray scattering and spectroscopy 2. application
Neutron and x-ray spectroscopy B. Keimer Max-Planck-Institute for Solid State Research outline 1. self-contained introduction neutron scattering and spectroscopy x-ray scattering and spectroscopy 2. application
arxiv: [cond-mat.supr-con] Scanning micro X-ray diffraction unveils the distribution of oxygen chains nano-puddles in YBa 2 Cu 3 O 6.
![arxiv: [cond-mat.supr-con] Scanning micro X-ray diffraction unveils the distribution of oxygen chains nano-puddles in YBa 2 Cu 3 O 6. arxiv: [cond-mat.supr-con] Scanning micro X-ray diffraction unveils the distribution of oxygen chains nano-puddles in YBa 2 Cu 3 O 6.](/thumbs/88/114802019.jpg) Scanning micro X-ray diffraction unveils the distribution of oxygen chains nano-puddles in YBa 2 Cu 3 O 6.33 Gaetano Campi 1, Alessandro Ricci 2, Nicola Poccia 3, Luisa Barba 4, Gianmichele Arrighetti
Scanning micro X-ray diffraction unveils the distribution of oxygen chains nano-puddles in YBa 2 Cu 3 O 6.33 Gaetano Campi 1, Alessandro Ricci 2, Nicola Poccia 3, Luisa Barba 4, Gianmichele Arrighetti
Simultaneous emergence of superconductivity, inter-pocket scattering and. nematic fluctuation in potassium-coated FeSe superconductor., and Y.
 Simultaneous emergence of superconductivity, inter-pocket scattering and nematic fluctuation in potassium-coated FeSe superconductor Z. R. Ye 1,, C. F. Zhang 2, 3,, H. L. Ning 1, W. Li 2, 3, L. Chen 1,
Simultaneous emergence of superconductivity, inter-pocket scattering and nematic fluctuation in potassium-coated FeSe superconductor Z. R. Ye 1,, C. F. Zhang 2, 3,, H. L. Ning 1, W. Li 2, 3, L. Chen 1,
Superconducting Stripes
 Superconducting Stripes By: Nick Vence I. Introduction In 1972 Bardeen, Cooper, and Schrieffer shared the Nobel prize in physics for describing a mechanism of superconductivity. Their BCS theory describes
Superconducting Stripes By: Nick Vence I. Introduction In 1972 Bardeen, Cooper, and Schrieffer shared the Nobel prize in physics for describing a mechanism of superconductivity. Their BCS theory describes
The Chemical Control of Superconductivity in Bi 2 Sr 2 (Ca 1 x Y x )Cu 2 O 8+±
 CHINESE JOURNAL OF PHYSICS VOL. 38, NO. 2-II APRIL 2000 The Chemical Control of Superconductivity in Bi 2 Sr 2 (Ca 1 x Y x )Cu 2 O 8+± R. S. Liu 1, I. J. Hsu 1, J. M. Chen 2, and R. G. Liu 2 1 Department
CHINESE JOURNAL OF PHYSICS VOL. 38, NO. 2-II APRIL 2000 The Chemical Control of Superconductivity in Bi 2 Sr 2 (Ca 1 x Y x )Cu 2 O 8+± R. S. Liu 1, I. J. Hsu 1, J. M. Chen 2, and R. G. Liu 2 1 Department
Quantum phase transitions in Mott insulators and d-wave superconductors
 Quantum phase transitions in Mott insulators and d-wave superconductors Subir Sachdev Matthias Vojta (Augsburg) Ying Zhang Science 286, 2479 (1999). Transparencies on-line at http://pantheon.yale.edu/~subir
Quantum phase transitions in Mott insulators and d-wave superconductors Subir Sachdev Matthias Vojta (Augsburg) Ying Zhang Science 286, 2479 (1999). Transparencies on-line at http://pantheon.yale.edu/~subir
Origin of the anomalous low temperature upturn in resistivity in the electron-doped cuprates.
 Origin of the anomalous low temperature upturn in resistivity in the electron-doped cuprates. Y. Dagan 1, A. Biswas 2, M. C. Barr 1, W. M. Fisher 1, and R. L. Greene 1. 1 Center for Superconductivity Research,
Origin of the anomalous low temperature upturn in resistivity in the electron-doped cuprates. Y. Dagan 1, A. Biswas 2, M. C. Barr 1, W. M. Fisher 1, and R. L. Greene 1. 1 Center for Superconductivity Research,
High T C copper oxide superconductors and CMR:
 High T C copper oxide superconductors and CMR: Ram Seshadri (seshadri@mrl.ucsb.edu) The Ruddlesden-Popper phases: Ruddlesden-Popper phases are intergrowths of perovskite slabs with rock salt slabs. First
High T C copper oxide superconductors and CMR: Ram Seshadri (seshadri@mrl.ucsb.edu) The Ruddlesden-Popper phases: Ruddlesden-Popper phases are intergrowths of perovskite slabs with rock salt slabs. First
Core Level Spectroscopies
 Core Level Spectroscopies Spectroscopies involving core levels are element-sensitive, and that makes them very useful for understanding chemical bonding, as well as for the study of complex materials.
Core Level Spectroscopies Spectroscopies involving core levels are element-sensitive, and that makes them very useful for understanding chemical bonding, as well as for the study of complex materials.
Phases of Na x CoO 2
 Phases of Na x CoO 2 by Aakash Pushp (pushp@uiuc.edu) Abstract This paper deals with the various phases of Na x CoO 2 ranging from charge ordered insulator to Curie-Weiss metal to superconductor as the
Phases of Na x CoO 2 by Aakash Pushp (pushp@uiuc.edu) Abstract This paper deals with the various phases of Na x CoO 2 ranging from charge ordered insulator to Curie-Weiss metal to superconductor as the
Time Resolved (Pump Probe) Experiment to watch structural dynamics by using the pulsed nature of synchrotron radiation
 SESAME-JSPS School November 14-16, 2011 Amman, Jordan Time Resolved (Pump Probe) Experiment to watch structural dynamics by using the pulsed nature of synchrotron radiation Shin-ichi Adachi (Photon Factory,
SESAME-JSPS School November 14-16, 2011 Amman, Jordan Time Resolved (Pump Probe) Experiment to watch structural dynamics by using the pulsed nature of synchrotron radiation Shin-ichi Adachi (Photon Factory,
Bipartite magnetic parent phases in the iron oxypnictide superconductor
 M. Hiraishi 1, S. Iimura 2, K. M. Kojima 1,3*, J. Yamaura 4, H. Hiraka 1, K. Ikeda 1, P. Miao 1,3, Y. Ishikawa 1, S. Torii 1, M. Miyazaki 1, I. Yamauchi 1, A. Koda 1,3, K. Ishii 5, M. Yoshida 5,6, J. Mizuki
M. Hiraishi 1, S. Iimura 2, K. M. Kojima 1,3*, J. Yamaura 4, H. Hiraka 1, K. Ikeda 1, P. Miao 1,3, Y. Ishikawa 1, S. Torii 1, M. Miyazaki 1, I. Yamauchi 1, A. Koda 1,3, K. Ishii 5, M. Yoshida 5,6, J. Mizuki
Magnetic Circular Dichroism spectroscopy in epitaxial La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 thin films
 Magnetic Circular Dichroism spectroscopy in epitaxial La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 thin films T. K. Nath 1 and J. R. Neal 2, G. A. Gehring 2 1 Dept. of Physics and Meteorology, Indian Institute Technology of Kharagpur,
Magnetic Circular Dichroism spectroscopy in epitaxial La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 thin films T. K. Nath 1 and J. R. Neal 2, G. A. Gehring 2 1 Dept. of Physics and Meteorology, Indian Institute Technology of Kharagpur,
arxiv:cond-mat/ v3 [cond-mat.supr-con] 23 May 2000
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v3 [cond-mat.supr-con] 23 May 2000 arxiv:cond-mat/ v3 [cond-mat.supr-con] 23 May 2000](/thumbs/75/71950529.jpg) Electronic Structure of La 2 x Sr x CuO 4 in the Vicinity of the Superconductor-Insulator Transition arxiv:cond-mat/99248v3 [cond-mat.supr-con] 23 May 2 A. Ino, C. Kim 2, M. Nakamura 3, T. Yoshida, T.
Electronic Structure of La 2 x Sr x CuO 4 in the Vicinity of the Superconductor-Insulator Transition arxiv:cond-mat/99248v3 [cond-mat.supr-con] 23 May 2 A. Ino, C. Kim 2, M. Nakamura 3, T. Yoshida, T.
Structure and Dynamics : An Atomic View of Materials
 Structure and Dynamics : An Atomic View of Materials MARTIN T. DOVE Department ofearth Sciences University of Cambridge OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Observations 1 1.1.1 Microscopic
Structure and Dynamics : An Atomic View of Materials MARTIN T. DOVE Department ofearth Sciences University of Cambridge OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Observations 1 1.1.1 Microscopic
Impact of disorder and topology in two dimensional systems at low carrier densities
 Impact of disorder and topology in two dimensional systems at low carrier densities A Thesis Submitted For the Degree of Doctor of Philosophy in the Faculty of Science by Mohammed Ali Aamir Department
Impact of disorder and topology in two dimensional systems at low carrier densities A Thesis Submitted For the Degree of Doctor of Philosophy in the Faculty of Science by Mohammed Ali Aamir Department
μsr Studies on Magnetism and Superconductivity
 The 14 th International Conference on Muon Spin Rotation, Relaxation and Resonance (μsr217) School (June 25-3, 217, Sapporo) μsr Studies on Magnetism and Superconductivity Y. Koike Dept. of Applied Physics,
The 14 th International Conference on Muon Spin Rotation, Relaxation and Resonance (μsr217) School (June 25-3, 217, Sapporo) μsr Studies on Magnetism and Superconductivity Y. Koike Dept. of Applied Physics,
Electronic Noise Due to Thermal Stripe Switching
 Electronic Noise Due to Thermal Stripe Switching E. W. Carlson B. Phillabaum Y. L. Loh D. X. Yao Research Corporation Solid Liquid Gas www.stonecropgallery.com/artists/caleb/01-solidliquidgas.jpg Crystals
Electronic Noise Due to Thermal Stripe Switching E. W. Carlson B. Phillabaum Y. L. Loh D. X. Yao Research Corporation Solid Liquid Gas www.stonecropgallery.com/artists/caleb/01-solidliquidgas.jpg Crystals
Anisotropic Magnetic Structures in Iron-Based Superconductors
 Anisotropic Magnetic Structures in Iron-Based Superconductors Chi-Cheng Lee, Weiguo Yin & Wei Ku CM-Theory, CMPMSD, Brookhaven National Lab Department of Physics, SUNY Stony Brook Another example of SC
Anisotropic Magnetic Structures in Iron-Based Superconductors Chi-Cheng Lee, Weiguo Yin & Wei Ku CM-Theory, CMPMSD, Brookhaven National Lab Department of Physics, SUNY Stony Brook Another example of SC
Supplementary Figure 1: Fitting of the x-ray diffraction data by FULLPROF method. (a) O-LPCMO and (b) R-LPCMO. The orange (red) line is the x-ray
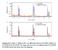 Supplementary Figure 1: Fitting of the x-ray diffraction data by FULLPROF method. (a) O-LPCMO and (b) R-LPCMO. The orange (red) line is the x-ray diffraction data of O-LPCMO (R-LPCMO) and the blue (black)
Supplementary Figure 1: Fitting of the x-ray diffraction data by FULLPROF method. (a) O-LPCMO and (b) R-LPCMO. The orange (red) line is the x-ray diffraction data of O-LPCMO (R-LPCMO) and the blue (black)
Visualizing the evolution from the Mott insulator to a charge-ordered insulator in lightly doped cuprates
 Visualizing the evolution from the Mott insulator to a charge-ordered insulator in lightly doped cuprates Peng Cai 1, Wei Ruan 1, Yingying Peng, Cun Ye 1, Xintong Li 1, Zhenqi Hao 1, Xingjiang Zhou,5,
Visualizing the evolution from the Mott insulator to a charge-ordered insulator in lightly doped cuprates Peng Cai 1, Wei Ruan 1, Yingying Peng, Cun Ye 1, Xintong Li 1, Zhenqi Hao 1, Xingjiang Zhou,5,
Structural dynamics of PZT thin films at the nanoscale
 Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 902E 2006 Materials Research Society 0902-T06-09.1 Structural dynamics of PZT thin films at the nanoscale Alexei Grigoriev 1, Dal-Hyun Do 1, Dong Min Kim 1, Chang-Beom
Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 902E 2006 Materials Research Society 0902-T06-09.1 Structural dynamics of PZT thin films at the nanoscale Alexei Grigoriev 1, Dal-Hyun Do 1, Dong Min Kim 1, Chang-Beom
Magnetic Order versus superconductivity in the Iron-based
 Magnetic Order versus superconductivity in the Iron-based layered La(O 1-x F x )FeAs systems Clarina de la Cruz 1,2, Q. Huang 3, J. W. Lynn 3, Jiying Li 3,4, W. Ratcliff II 3, J. L. Zarestky 5, H. A. Mook
Magnetic Order versus superconductivity in the Iron-based layered La(O 1-x F x )FeAs systems Clarina de la Cruz 1,2, Q. Huang 3, J. W. Lynn 3, Jiying Li 3,4, W. Ratcliff II 3, J. L. Zarestky 5, H. A. Mook
ARPES studies of cuprates. Inna Vishik Physics 250 (Special topics: spectroscopies of quantum materials) UC Davis, Fall 2016
 ARPES studies of cuprates Inna Vishik Physics 250 (Special topics: spectroscopies of quantum materials) UC Davis, Fall 2016 Goals of lecture Understand why gaps are important and various ways that gap
ARPES studies of cuprates Inna Vishik Physics 250 (Special topics: spectroscopies of quantum materials) UC Davis, Fall 2016 Goals of lecture Understand why gaps are important and various ways that gap
Harald Ibach Hans Lüth SOLID-STATE PHYSICS. An Introduction to Theory and Experiment
 Harald Ibach Hans Lüth SOLID-STATE PHYSICS An Introduction to Theory and Experiment With 230 Figures Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg New York London Paris Tokyo Hong Kong Barcelona Budapest Contents
Harald Ibach Hans Lüth SOLID-STATE PHYSICS An Introduction to Theory and Experiment With 230 Figures Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg New York London Paris Tokyo Hong Kong Barcelona Budapest Contents
Spin correlations in YBa 2 Cu 3 O 6+x bulk vs. interface
 Spin correlations in YBa 2 Cu 3 O 6+x bulk vs. interface B. Keimer Max-Planck-Institute for Solid State Research outline new quantum states in bulk? yes, good evidence for electronic nematic phase new
Spin correlations in YBa 2 Cu 3 O 6+x bulk vs. interface B. Keimer Max-Planck-Institute for Solid State Research outline new quantum states in bulk? yes, good evidence for electronic nematic phase new
Superconducting Single-photon Detectors
 : Quantum Cryptography Superconducting Single-photon Detectors Hiroyuki Shibata Abstract This article describes the fabrication and properties of a single-photon detector made of a superconducting NbN
: Quantum Cryptography Superconducting Single-photon Detectors Hiroyuki Shibata Abstract This article describes the fabrication and properties of a single-photon detector made of a superconducting NbN
File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures, Supplementary Notes, Supplementary Tables, Supplementary References
 File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures, Supplementary Notes, Supplementary Tables, Supplementary References Supplementary Figure 1 Illustration of the reaction chamber
File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures, Supplementary Notes, Supplementary Tables, Supplementary References Supplementary Figure 1 Illustration of the reaction chamber
Energy Spectroscopy. Ex.: Fe/MgO
 Energy Spectroscopy Spectroscopy gives access to the electronic properties (and thus chemistry, magnetism,..) of the investigated system with thickness dependence Ex.: Fe/MgO Fe O Mg Control of the oxidation
Energy Spectroscopy Spectroscopy gives access to the electronic properties (and thus chemistry, magnetism,..) of the investigated system with thickness dependence Ex.: Fe/MgO Fe O Mg Control of the oxidation
Universal Post-quench Dynamics at a Quantum Critical Point
 Universal Post-quench Dynamics at a Quantum Critical Point Peter P. Orth University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, USA Rutgers University, 10 March 2016 References: P. Gagel, P. P. Orth, J. Schmalian Phys.
Universal Post-quench Dynamics at a Quantum Critical Point Peter P. Orth University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, USA Rutgers University, 10 March 2016 References: P. Gagel, P. P. Orth, J. Schmalian Phys.
2) Atom manipulation. Xe / Ni(110) Model: Experiment:
 2) Atom manipulation D. Eigler & E. Schweizer, Nature 344, 524 (1990) Xe / Ni(110) Model: Experiment: G.Meyer, et al. Applied Physics A 68, 125 (1999) First the tip is approached close to the adsorbate
2) Atom manipulation D. Eigler & E. Schweizer, Nature 344, 524 (1990) Xe / Ni(110) Model: Experiment: G.Meyer, et al. Applied Physics A 68, 125 (1999) First the tip is approached close to the adsorbate
Strong interplay between stripe spin fluctuations, nematicity and superconductivity in FeSe
 Strong interplay between stripe spin fluctuations, nematicity and superconductivity in FeSe Qisi Wang 1, Yao Shen 1, Bingying Pan 1, Yiqing ao 1, Mingwei Ma 2, Fang Zhou 2, P. Steens 3,. Schmalzl 4, T.
Strong interplay between stripe spin fluctuations, nematicity and superconductivity in FeSe Qisi Wang 1, Yao Shen 1, Bingying Pan 1, Yiqing ao 1, Mingwei Ma 2, Fang Zhou 2, P. Steens 3,. Schmalzl 4, T.
Ohoyama., TEM, neutron diffraction, ordered perovskite, CE structure. Abstract An A-site ordered manganese perovskite YBaMn 2
 New Stacking Variations of the CE-type Structure in the Metal-Ordered Manganite YBaMn 2 1 H. Kageyama, 1 T. Nakajima, 1 M. Ichihara, 1 Y. Ueda, and 2 H. Yoshizawa, 3 K. Ohoyama 1 Material Design and Characterization
New Stacking Variations of the CE-type Structure in the Metal-Ordered Manganite YBaMn 2 1 H. Kageyama, 1 T. Nakajima, 1 M. Ichihara, 1 Y. Ueda, and 2 H. Yoshizawa, 3 K. Ohoyama 1 Material Design and Characterization
SECOND PUBLIC EXAMINATION. Honour School of Physics Part C: 4 Year Course. Honour School of Physics and Philosophy Part C C3: CONDENSED MATTER PHYSICS
 A11046W1 SECOND PUBLIC EXAMINATION Honour School of Physics Part C: 4 Year Course Honour School of Physics and Philosophy Part C C3: CONDENSED MATTER PHYSICS TRINITY TERM 2015 Wednesday, 17 June, 2.30
A11046W1 SECOND PUBLIC EXAMINATION Honour School of Physics Part C: 4 Year Course Honour School of Physics and Philosophy Part C C3: CONDENSED MATTER PHYSICS TRINITY TERM 2015 Wednesday, 17 June, 2.30
New perspectives in superconductors. E. Bascones Instituto de Ciencia de Materiales de Madrid (ICMM-CSIC)
 New perspectives in superconductors E. Bascones Instituto de Ciencia de Materiales de Madrid (ICMM-CSIC) E. Bascones leni@icmm.csic.es Outline Talk I: Correlations in iron superconductors Introduction
New perspectives in superconductors E. Bascones Instituto de Ciencia de Materiales de Madrid (ICMM-CSIC) E. Bascones leni@icmm.csic.es Outline Talk I: Correlations in iron superconductors Introduction
Nanomaterials and their Optical Applications
 Nanomaterials and their Optical Applications Winter Semester 2013 Lecture 02 rachel.grange@uni-jena.de http://www.iap.uni-jena.de/multiphoton Lecture 2: outline 2 Introduction to Nanophotonics Theoretical
Nanomaterials and their Optical Applications Winter Semester 2013 Lecture 02 rachel.grange@uni-jena.de http://www.iap.uni-jena.de/multiphoton Lecture 2: outline 2 Introduction to Nanophotonics Theoretical
Observation of ferroelectric domains in bismuth ferrite using coherent diffraction techniques
 Observation of ferroelectric domains in bismuth ferrite using coherent diffraction techniques James Vale October 25, 2011 Abstract Multiferroic materials have significant potential for both the scientific
Observation of ferroelectric domains in bismuth ferrite using coherent diffraction techniques James Vale October 25, 2011 Abstract Multiferroic materials have significant potential for both the scientific
Spin-orbital separation in the quasi-one-dimensional Mott insulator Sr 2 CuO 3 Splitting the electron
 Spin-orbital separation in the quasi-one-dimensional Mott insulator Sr 2 CuO 3 Splitting the electron James Gloudemans, Suraj Hegde, Ian Gilbert, and Gregory Hart December 7, 2012 The paper We describe
Spin-orbital separation in the quasi-one-dimensional Mott insulator Sr 2 CuO 3 Splitting the electron James Gloudemans, Suraj Hegde, Ian Gilbert, and Gregory Hart December 7, 2012 The paper We describe
Synchrotron powder X-ray diffraction and structural analysis of Eu0.5La0.5FBiS2-xSex
 Synchrotron powder X-ray diffraction and structural analysis of Eu0.5La0.5FBiS2-xSex K. Nagasaka 1, G. Jinno 1, O. Miura 1, A. Miura 2, C. Moriyoshi 3, Y. Kuroiwa 3, Y. Mizuguchi 1 * 1. Department of Electrical
Synchrotron powder X-ray diffraction and structural analysis of Eu0.5La0.5FBiS2-xSex K. Nagasaka 1, G. Jinno 1, O. Miura 1, A. Miura 2, C. Moriyoshi 3, Y. Kuroiwa 3, Y. Mizuguchi 1 * 1. Department of Electrical
Superconductivity in Cu x Bi 2 Se 3 and its Implications for Pairing in the Undoped Topological Insulator
 Superconductivity in Cu x Bi 2 Se 3 and its Implications for Pairing in the Undoped Topological Insulator Y. S. Hor, A. J. Williams, J. G. Checkelsky, P. Roushan, J. Seo, Q. Xu, H. W. Zandbergen, A. Yazdani,
Superconductivity in Cu x Bi 2 Se 3 and its Implications for Pairing in the Undoped Topological Insulator Y. S. Hor, A. J. Williams, J. G. Checkelsky, P. Roushan, J. Seo, Q. Xu, H. W. Zandbergen, A. Yazdani,
Strongly Correlated Systems:
 M.N.Kiselev Strongly Correlated Systems: High Temperature Superconductors Heavy Fermion Compounds Organic materials 1 Strongly Correlated Systems: High Temperature Superconductors 2 Superconductivity:
M.N.Kiselev Strongly Correlated Systems: High Temperature Superconductors Heavy Fermion Compounds Organic materials 1 Strongly Correlated Systems: High Temperature Superconductors 2 Superconductivity:
Understanding interlayer interaction in layered supercoducting materials. Eugenio Paris University La Sapienza of Rome
 Understanding interlayer interaction in layered supercoducting materials Eugenio Paris University La Sapienza of Rome My PhD Thesis project Study of local structure, local disorder and interlayer interaction
Understanding interlayer interaction in layered supercoducting materials Eugenio Paris University La Sapienza of Rome My PhD Thesis project Study of local structure, local disorder and interlayer interaction
Angle-Resolved Two-Photon Photoemission of Mott Insulator
 Angle-Resolved Two-Photon Photoemission of Mott Insulator Takami Tohyama Institute for Materials Research (IMR) Tohoku University, Sendai Collaborators IMR: H. Onodera, K. Tsutsui, S. Maekawa H. Onodera
Angle-Resolved Two-Photon Photoemission of Mott Insulator Takami Tohyama Institute for Materials Research (IMR) Tohoku University, Sendai Collaborators IMR: H. Onodera, K. Tsutsui, S. Maekawa H. Onodera
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures Supplementary figure S1: Characterisation of the electron beam intensity profile. (a) A 3D plot of beam intensity (grey value) with position, (b) the beam
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures Supplementary figure S1: Characterisation of the electron beam intensity profile. (a) A 3D plot of beam intensity (grey value) with position, (b) the beam
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.supr-con] 28 May 2003
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.supr-con] 28 May 2003 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.supr-con] 28 May 2003](/thumbs/96/128981112.jpg) arxiv:cond-mat/0305637v1 [cond-mat.supr-con] 28 May 2003 The superconducting state in a single CuO 2 layer: Experimental findings and scenario Rushan Han, Wei Guo School of Physics, Peking University,
arxiv:cond-mat/0305637v1 [cond-mat.supr-con] 28 May 2003 The superconducting state in a single CuO 2 layer: Experimental findings and scenario Rushan Han, Wei Guo School of Physics, Peking University,
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 XRD patterns and TEM image of the SrNbO 3 film grown on LaAlO 3(001) substrate. The film was deposited under oxygen partial pressure of 5 10-6 Torr. (a) θ-2θ scan, where * indicates
Supplementary Figure 1 XRD patterns and TEM image of the SrNbO 3 film grown on LaAlO 3(001) substrate. The film was deposited under oxygen partial pressure of 5 10-6 Torr. (a) θ-2θ scan, where * indicates
Plasmonics. The long wavelength of light ( μm) creates a problem for extending optoelectronics into the nanometer regime.
 Plasmonics The long wavelength of light ( μm) creates a problem for extending optoelectronics into the nanometer regime. A possible way out is the conversion of light into plasmons. They have much shorter
Plasmonics The long wavelength of light ( μm) creates a problem for extending optoelectronics into the nanometer regime. A possible way out is the conversion of light into plasmons. They have much shorter
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature09910 Supplementary Online Material METHODS Single crystals were made at Kyoto University by the electrooxidation of BEDT-TTF in an 1,1,2- tetrachloroethylene solution of KCN, CuCN, and
doi:10.1038/nature09910 Supplementary Online Material METHODS Single crystals were made at Kyoto University by the electrooxidation of BEDT-TTF in an 1,1,2- tetrachloroethylene solution of KCN, CuCN, and
Electronic inhomogeneity, magnetic order & superconductivity probed by NMR in cuprates and pnictides
 Electronic inhomogeneity, magnetic order & superconductivity probed by NMR in cuprates and pnictides Marc-Henri Julien Laboratoire de Spectrométrie Physique Université J. Fourier Grenoble I Acknowledgments
Electronic inhomogeneity, magnetic order & superconductivity probed by NMR in cuprates and pnictides Marc-Henri Julien Laboratoire de Spectrométrie Physique Université J. Fourier Grenoble I Acknowledgments
Superconductivity Induced Transparency
 Superconductivity Induced Transparency Coskun Kocabas In this paper I will discuss the effect of the superconducting phase transition on the optical properties of the superconductors. Firstly I will give
Superconductivity Induced Transparency Coskun Kocabas In this paper I will discuss the effect of the superconducting phase transition on the optical properties of the superconductors. Firstly I will give
SECOND PUBLIC EXAMINATION. Honour School of Physics Part C: 4 Year Course. Honour School of Physics and Philosophy Part C C3: CONDENSED MATTER PHYSICS
 2753 SECOND PUBLIC EXAMINATION Honour School of Physics Part C: 4 Year Course Honour School of Physics and Philosophy Part C C3: CONDENSED MATTER PHYSICS TRINITY TERM 2011 Wednesday, 22 June, 9.30 am 12.30
2753 SECOND PUBLIC EXAMINATION Honour School of Physics Part C: 4 Year Course Honour School of Physics and Philosophy Part C C3: CONDENSED MATTER PHYSICS TRINITY TERM 2011 Wednesday, 22 June, 9.30 am 12.30
Citation PHYSICAL REVIEW LETTERS (2000), 85( RightCopyright 2000 American Physical So
 Title Discriminating the superconducting Bi2Sr2CaCu2O8+delta by interlayer t Author(s) Suzuki, M; Watanabe, T Citation PHYSICAL REVIEW LETTERS (2), 85( Issue Date 2-11-27 URL http://hdl.handle.net/2433/39919
Title Discriminating the superconducting Bi2Sr2CaCu2O8+delta by interlayer t Author(s) Suzuki, M; Watanabe, T Citation PHYSICAL REVIEW LETTERS (2), 85( Issue Date 2-11-27 URL http://hdl.handle.net/2433/39919
Chemistry Institute B6, SUPRATECS, University of Liège, Sart-Tilman, B-4000 Liège, Belgium b
 Synthesis and characterization of Bi 2 Sr 2 CaCu 2 O 8 ceramics prepared in presence of sodium S. Rahier a*, S. Stassen a, R. Cloots a and M. Ausloos b a Chemistry Institute B6, SUPRATECS, University of
Synthesis and characterization of Bi 2 Sr 2 CaCu 2 O 8 ceramics prepared in presence of sodium S. Rahier a*, S. Stassen a, R. Cloots a and M. Ausloos b a Chemistry Institute B6, SUPRATECS, University of
TRANSVERSE SPIN TRANSPORT IN GRAPHENE
 International Journal of Modern Physics B Vol. 23, Nos. 12 & 13 (2009) 2641 2646 World Scientific Publishing Company TRANSVERSE SPIN TRANSPORT IN GRAPHENE TARIQ M. G. MOHIUDDIN, A. A. ZHUKOV, D. C. ELIAS,
International Journal of Modern Physics B Vol. 23, Nos. 12 & 13 (2009) 2641 2646 World Scientific Publishing Company TRANSVERSE SPIN TRANSPORT IN GRAPHENE TARIQ M. G. MOHIUDDIN, A. A. ZHUKOV, D. C. ELIAS,
Studies of Iron-Based Superconductor Thin Films
 MBE Growth and STM Studies of Iron-Based Superconductor Thin Films Wei Li 1, Canli Song 1,2, Xucun Ma 2, Xi Chen 1*, Qi-Kun Xu 1 State Key Laboratory of Low-Dimensional Quantum Physics, Department of Physics,
MBE Growth and STM Studies of Iron-Based Superconductor Thin Films Wei Li 1, Canli Song 1,2, Xucun Ma 2, Xi Chen 1*, Qi-Kun Xu 1 State Key Laboratory of Low-Dimensional Quantum Physics, Department of Physics,
Resonant Inelastic X-ray Scattering on elementary excitations
 Resonant Inelastic X-ray Scattering on elementary excitations Jeroen van den Brink Ament, van Veenendaal, Devereaux, Hill & JvdB Rev. Mod. Phys. 83, 705 (2011) Autumn School in Correlated Electrons Jülich
Resonant Inelastic X-ray Scattering on elementary excitations Jeroen van den Brink Ament, van Veenendaal, Devereaux, Hill & JvdB Rev. Mod. Phys. 83, 705 (2011) Autumn School in Correlated Electrons Jülich
Structural characterization. Part 1
 Structural characterization Part 1 Experimental methods X-ray diffraction Electron diffraction Neutron diffraction Light diffraction EXAFS-Extended X- ray absorption fine structure XANES-X-ray absorption
Structural characterization Part 1 Experimental methods X-ray diffraction Electron diffraction Neutron diffraction Light diffraction EXAFS-Extended X- ray absorption fine structure XANES-X-ray absorption
Scientific opportunities with ultrafast electron diffraction & microscopy
 Scientific opportunities with ultrafast electron diffraction & microscopy Jim Cao Frontier of ultrafast science MeV UED Transition pathways Rate and time scale Elementary steps Probe dynamics on the atomic
Scientific opportunities with ultrafast electron diffraction & microscopy Jim Cao Frontier of ultrafast science MeV UED Transition pathways Rate and time scale Elementary steps Probe dynamics on the atomic
Studying Metal to Insulator Transitions in Solids using Synchrotron Radiation-based Spectroscopies.
 PY482 Lecture. February 28 th, 2013 Studying Metal to Insulator Transitions in Solids using Synchrotron Radiation-based Spectroscopies. Kevin E. Smith Department of Physics Department of Chemistry Division
PY482 Lecture. February 28 th, 2013 Studying Metal to Insulator Transitions in Solids using Synchrotron Radiation-based Spectroscopies. Kevin E. Smith Department of Physics Department of Chemistry Division
Materials 218/UCSB: Superconductivity and High T C copper oxide superconductors:
 Materials 218/UCSB: Superconductivity and High T C copper oxide superconductors: Ram Seshadri (seshadri@mrl.ucsb.edu) The Ruddlesden-Popper phases: Ruddlesden-Popper phases are intergrowths of perovskite
Materials 218/UCSB: Superconductivity and High T C copper oxide superconductors: Ram Seshadri (seshadri@mrl.ucsb.edu) The Ruddlesden-Popper phases: Ruddlesden-Popper phases are intergrowths of perovskite
SOLID STATE PHYSICS. Second Edition. John Wiley & Sons. J. R. Hook H. E. Hall. Department of Physics, University of Manchester
 SOLID STATE PHYSICS Second Edition J. R. Hook H. E. Hall Department of Physics, University of Manchester John Wiley & Sons CHICHESTER NEW YORK BRISBANE TORONTO SINGAPORE Contents Flow diagram Inside front
SOLID STATE PHYSICS Second Edition J. R. Hook H. E. Hall Department of Physics, University of Manchester John Wiley & Sons CHICHESTER NEW YORK BRISBANE TORONTO SINGAPORE Contents Flow diagram Inside front
III.1. MICROSCOPIC PHASE SEPARATION AND TWO TYPE OF QUASIPARTICLES IN LIGHTLY DOPED La 2-x Sr x CuO 4 OBSERVED BY ELECTRON PARAMAGNETIC RESONANCE
 A. Bianconi (ed.) Symmetry and Heterogeneity in High Temperature Superconductors, 105-116 NATO Science Series II Mathematics,Physics and Chemistry Vol. 214 2006 Springer, Dordrecht, The Netherlands III.1
A. Bianconi (ed.) Symmetry and Heterogeneity in High Temperature Superconductors, 105-116 NATO Science Series II Mathematics,Physics and Chemistry Vol. 214 2006 Springer, Dordrecht, The Netherlands III.1
Principles of Electron Tunneling Spectroscopy
 Principles of Electron Tunneling Spectroscopy Second Edition E. L. Wolf Polytechnic Institute of New York University, USA OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents 1 Introduction 1.1 Concepts of quantum mechanical
Principles of Electron Tunneling Spectroscopy Second Edition E. L. Wolf Polytechnic Institute of New York University, USA OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents 1 Introduction 1.1 Concepts of quantum mechanical
Superconductivity and Electron Correlations in Ruthenates
 University of St Andrews School of Physics and Astronomy Superconductivity and Electron Correlations in Ruthenates Andy Mackenzie University of St Andrews, UK Key collaborator: Yoshi Maeno, Kyoto University
University of St Andrews School of Physics and Astronomy Superconductivity and Electron Correlations in Ruthenates Andy Mackenzie University of St Andrews, UK Key collaborator: Yoshi Maeno, Kyoto University
Out-of-equilibrium electron dynamics in photoexcited topological insulators studied by TR-ARPES
 Cliquez et modifiez le titre Out-of-equilibrium electron dynamics in photoexcited topological insulators studied by TR-ARPES Laboratoire de Physique des Solides Orsay, France June 15, 2016 Workshop Condensed
Cliquez et modifiez le titre Out-of-equilibrium electron dynamics in photoexcited topological insulators studied by TR-ARPES Laboratoire de Physique des Solides Orsay, France June 15, 2016 Workshop Condensed
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Point-contact spectra of a Pt-Ir tip/lto film junction. The main panel shows differential conductance at 2, 12, 13, 16 K (0 T), and 10 K (2 T) to demonstrate
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Point-contact spectra of a Pt-Ir tip/lto film junction. The main panel shows differential conductance at 2, 12, 13, 16 K (0 T), and 10 K (2 T) to demonstrate
The Tetragonal to Orthorhombic structural phase transition in multiband FeAs-based superconductors
 The Tetragonal to Orthorhombic structural phase transition in multiband FeAs-based superconductors Alessandro Ricci, Michela Fratini and Antonio Bianconi Department of Physics, Sapienza University of Rome,
The Tetragonal to Orthorhombic structural phase transition in multiband FeAs-based superconductors Alessandro Ricci, Michela Fratini and Antonio Bianconi Department of Physics, Sapienza University of Rome,
Universal scaling relation in high-temperature superconductors
 SLAC-PUB-10699 cond-mat/0404216 September 2004 Universal scaling relation in high-temperature superconductors C. C. Homes 1, S. V. Dordevic 1, M. Strongin 1, D. A. Bonn 2, Ruixing Liang 2, W. N. Hardy
SLAC-PUB-10699 cond-mat/0404216 September 2004 Universal scaling relation in high-temperature superconductors C. C. Homes 1, S. V. Dordevic 1, M. Strongin 1, D. A. Bonn 2, Ruixing Liang 2, W. N. Hardy
Refinement of X-ray Fluorescence Holography for Determination of Local Atomic Environment
 Materials Transactions, Vol. 43, No. 7 (2002) pp. 1464 to 1468 Special Issue on Grain Boundaries, Interfaces, Defects and Localized Quantum Structure in Ceramics c 2002 The Japan Institute of Metals Refinement
Materials Transactions, Vol. 43, No. 7 (2002) pp. 1464 to 1468 Special Issue on Grain Boundaries, Interfaces, Defects and Localized Quantum Structure in Ceramics c 2002 The Japan Institute of Metals Refinement
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Yi et al..73/pnas.55728 SI Text Study of k z Dispersion Effect on Anisotropy of Fermi Surface Topology. In angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy (ARPES), the electronic structure
Supporting Information Yi et al..73/pnas.55728 SI Text Study of k z Dispersion Effect on Anisotropy of Fermi Surface Topology. In angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy (ARPES), the electronic structure
V.3. SUPERCONDUCTIVITY VERSUS ANTIFERERROMAGNETIC SDW ORDER IN THE CUPRATES AND RELATED SYSTEMS Inhomogeneities and Electron Correlation
 A. Bianconi (ed.) Symmetry and Heterogeneity in High Temperature Superconductors, 217-228 NATO Science Series II Mathematics,Physics and Chemistry Vol. 214 2006 Springer, Dordrecht, The Netherlands V.3
A. Bianconi (ed.) Symmetry and Heterogeneity in High Temperature Superconductors, 217-228 NATO Science Series II Mathematics,Physics and Chemistry Vol. 214 2006 Springer, Dordrecht, The Netherlands V.3
Superconductivity in Fe-based ladder compound BaFe 2 S 3
 02/24/16 QMS2016 @ Incheon Superconductivity in Fe-based ladder compound BaFe 2 S 3 Tohoku University Kenya OHGUSHI Outline Introduction Fe-based ladder material BaFe 2 S 3 Basic physical properties High-pressure
02/24/16 QMS2016 @ Incheon Superconductivity in Fe-based ladder compound BaFe 2 S 3 Tohoku University Kenya OHGUSHI Outline Introduction Fe-based ladder material BaFe 2 S 3 Basic physical properties High-pressure
Electrostatic Tuning of Superconductivity. Allen M. Goldman School of Physics and Astronomy University of Minnesota
 Electrostatic Tuning of Superconductivity Allen M. Goldman School of Physics and Astronomy University of Minnesota Paarticipating Graduate Students Yen-Hsiang Lin Kevin Parendo (US Patent Office) Sarwa
Electrostatic Tuning of Superconductivity Allen M. Goldman School of Physics and Astronomy University of Minnesota Paarticipating Graduate Students Yen-Hsiang Lin Kevin Parendo (US Patent Office) Sarwa
