Everything You Always Wanted to Know About Parsing
|
|
|
- Trevor Curtis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Everything You Always Wanted to Know About Parsing Part V : LR Parsing University of Padua, Italy ESSLLI, August 2013
2 Introduction Parsing strategies classified by the time the associated PDA commits to a production in the analysis : B A B β Top-Down Bottom-Up Left-Corner
3 Introduction LR parsing discovered in 1965 in an article by Donald Knuth, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, California L stands for left-to-right parsing and R stands for reversed rightmost derivation Works in linear time for deterministic context-free languages The algorithm consists of a shift-reduce, deterministic PDA called LR PDA, realizing a bottom-up parsing strategy Widely used for parsing of programming languages, where LR PDAs are mechanically generated from a formal grammar
4 Introduction parsing (GLR for short) extends the LR method to handle nondeterministic and ambiguous CFGs First discovered in 1985 by Masaru Tomita in his PhD dissertation, Carnegie Mellon University Very popular in computational linguistics in the late eighties
5 Introduction The GLR algorithm consists of the LR PDA as in Knuth original proposal the definition of a technique for simulating the LR PDA, based on a data structure called graph structured stack We disregard the graph structured stack, and apply our tabulation algorithm to simulate the LR PDA The outcome is an optimized version of the original GLR parsing algorithm
6 Stack Symbols Let P be a set of CFG productions; a stack symbol of the LR PDA is a non-empty subset of I P = {A α 1 α 2 (A α 1 α 2 ) P} satisfying some additional property, to be introduced later Informally, a stack symbol represents a disjunction of dotted rules; in this way several alternative parsing analyses can be carried out simultaneously
7 Stack Symbols Example : Stack symbol q = {A B C γ, A C γ } represents two alternative analyses; observe how the strings preceding the dots are suffixes of a common string S S A a 1 a j BC γ a j+1 a i B a 1 a j a j+1 a j A A C γ a j +1 a i
8 Stack Symbols We need a function closure to precompute the closure of the prediction step from the Earley algorithm Let q I P ; closure(q) is the smallest set such that : q closure(q); and if (A α Bα ) closure(q) and (B β) P then (B β) closure(q)
9 Stack Symbols Example : if P consists of the productions : S S + S, S a we have closure({s S + S}) = {S S + S, S S + S, S a}
10 Stack Symbols We need a function goto to precompute the scanner and the completer steps from the Earley algorithm, followed by closure() Let q I P and X N Σ; we have goto(q, X ) = closure({a αx α (A α X α ) q})
11 Stack Symbols Example (cont d) : if P consists of the productions : S S + S, S a we have goto({s S + S, S S + S, S a}, a) = {S a } goto({s S + S, S S + S, S a}, S) = {S S + S, S S +S}
12 Stack Symbols The initial stack symbol of the LR PDA is = closure({s α (S α) P}) The final stack symbol of the LR PDA is a special symbol q fin ;
13 Stack Symbols The stack alphabet Q LR of the LR PDA is the smallest set satisfying : Q LR ; q fin Q LR ; and if q Q LR and goto(q, X ) for some X N Σ, then q Q LR
14 Stack Symbols Example (cont d) : P consists of the productions S S + S and S a The goto function, also called the LR table, excluding q fin : S S S + S S a q 2 S S +S + S S + S S S + S S a q 3 S + S S + S S S +S q 4 a q 1 S a a By construction, in each state the strings preceding the dots are suffixes of a common string
15 LR PDA The LR PDA M LR is constructed from G as follows The input alphabet of M LR is the terminal alphabet of G The stack alphabet of M LR is Q LR, as previously defined
16 LR PDA Set LR contains transitions having one of the following forms : shift q 1 a q 1 q 2 for each q 1, q 2 and a with q 2 = goto(q 1, a) reduce q 0 q 1 q m ε q 0 q for each q 0, q 1,, q m, q and A α with (A α ) q m, α = m and q = goto(q 0, A) reduce (special case) q 1 q m ε q fin for each q 1,, q m and S α with (S α ) q m and α = m
17 LR PDA Each stack symbol of M LR records the set of rules that are compatible with the sequence of nonterminals recognized so far Thus alternative analyses within a stack symbol match suffixes of the sequence of nonterminals recognized so far; we call this the suffix property The implemented strategy is bottom-up : the commitment to a production occurs as late as possible, after all of the production s right-hand side symbols have been recognized
18 Computational Complexity A production A α has exactly Aα dotted items; therefore I P = G It is not difficult to construct a worst case set P such that Q LR = O(exp( G )) M LR = O(exp( G ))
19 M LR Computation Example (cont d) : input string w = a + a + a S S S + S S S S + S S + S a a S + S a a a a
20 M LR Computation Example (cont d) : input string w = a + a + a, first computation reduce S a q 3 q 1 q 2 q 2 a ε
21 M LR Computation Example (cont d) : input string w = a + a + a, first computation reduce S a reduce S S + S q 1 q 4 q 3 q 3 q 3 q 2 q 2 q 2 q 2 a ε ε
22 M LR Computation Example (cont d) : input string w = a + a + a, first computation reduce S a reduce S S + S q 1 q 4 q 3 q 3 q 2 q 2 a ε ε q fin 5 5 5
23 M LR Computation Example (cont d) : input string w = a + a + a, second computation reduce S a q 3 q 1 q 2 q 2 a ε
24 M LR Computation q 1 reduce S a q 3 q 3 q 1 q 4 q 4 q 4 q 3 q 3 q 3 q 3 q 2 q 2 q 2 q 2 a ε + a
25 M LR Computation reduce S a q 4 q 3 q 4 reduce S S + S q 4 q 3 q 3 q 2 q 2 reduce S S + S ε ε ε q fin 5 5 5
26 M E and M LR Comparison Example : Earley PDA on sample rule A 0 A 1 A 2 A 3 (simplified notation) [ A 1A 2A 3] [A 1 A 2A 3] [A 1A 2 A 3] [A 1A 2A 3 ].... i 1 i 2 i 3 i 4
27 M E and M LR Example (cont d) : LR PDAs on sample rule A 0 A 1 A 2 A 3 (simplified notation) {A 1A 2A 3 } {A 1A 2 A 3} {A 1A 2 A 3} {A 1 A 2A 3} {A 1 A 2A 3} {A 1 A 2A 3} { A 1A 2A 3} { A 1A 2A 3} { A 1A 2A 3} { A 1A 2A 3}.... i 1 i 2 i 3 i 4
28 M E and M LR Example (cont d) : M E tabulation on sample rule A 0 A 1 A 2 A 3 A 1 A 2A 3 A 1A 2 A 3 A 1A 2A 3 i 1 A 1 i 2 A 2 i 3 A 3 i 4 No need to reduce
29 M E and M LR Example (cont d) : M LR tabulation on sample rule A 0 A 1 A 2 A 3 reduce A 1A 2A 3 A 1 A 2A 3 A 1A 2 A 3 A 1A 2A 3 i 1 A 1 i 2 A 2 i 3 A 3 i 4 Single step reduction should be avoided; this issue will be addressed later
30 Remarks M LR is deterministic only for so-called deterministic context-free languages For general CFGs, M LR is strictly nondeterministic, with an exponential proliferation of computations in the length of the input string But this needs not concern us : the only purpose of M LR is to specify a parsing strategy nondeterminism can be simulated using (an extension of) our deterministic tabulation algorithm
31 GLR Algorithm We derive the GLR algorithm by tabulation of the LR PDA Items in the GLR algorithm have the form (q, j, q, i) In this case we can not drop the first item component as we did for the CKY and Earley algorithm
32 Deduction Rules We overview the GLR tabular algorithm using inference rules M LR starts with in the stack. This corresponds to the init step of the tabular algorithm (, 0,, 0) (, ) 0
33 Deduction Rules The shift transition q 1 a q 1 q 2 can be implemented as (q, j, q 1, i 1) (q 1, i 1, q 2, i) { a = ai (q, q 1 ) (q 1, q 2 ) j i 1 a i
34 Deduction Rules The reduce transition (q 0 q 1 q m 1 q m ε q 0 q ) is in a form more general than the reduce transition available for our tabulation algorithm This reduction can be implemented as (q 0, j 0, q 1, j 1 ) (q 1, j 1, q 2, j 2 ). (q m 1, j m 1, q m, j m ) (q 0, j 0, q, j m )
35 Deduction Rules The deduction rule for the reduce transition (q 0 q 1 q m 1 q m ε q 0 q ) can be graphically represented as (q 0, q ) (q 0, q 1) (q 1, q 2) j 0 j 1 j 2 (q m 1, q m) i m 1 i m
36 GLR Pseudocode Algorithm 5 GLR Algorithm (from Tabulation of LR PDA) 1: T {(, 0,, 0)} 2: for i 1,..., n do edges with right end at i 3: D 4: for each (q, j, q 1, i 1) T do 5: for each (q 1 ai q 1 q 2 ) do shift step 6: T T {(q 1, i 1, q 2, i)} 7: D D {(q 1, i 1, q 2, i)} 8: end for 9: end for
37 Pseudocode 10: while D do 11: pop (q m 1, j m 1, q m, j m ) from D 12: for each (q 0 q 1 q m ε q 0 q ) do reduce step 13: for each (q 0, j 0, q 1, j 1 ), (q 1, j 1, q 2, j 2 ),..., (q m 2, j m 2, q m 1, j m 1 ) T do 14: if (q 0, j 0, q, j m ) T then 15: T T {(q 0, j 0, q, j m )} 16: D D {(q 0, j 0, q, j m )} 17: end if 18: end for 19: end for
38 Pseudocode 20: for each ( q 1 q m ε q fin ) do reduce step 21: for each (, 0,, 0), (, 0, q 1, j 1 ),..., (q m 2, j m 2, q m 1, j m 1 ) T do 22: if (, 0, q fin, j m ) T then 23: T T {(, 0, q fin, j m )} 24: D D {(, 0, q fin, j m )} 25: end if 26: end for 27: end for 28: end while 29: end for 30: accept iff (, 0, q fin, n) T
39 Computational Complexity There are two different sources of complexity in the GLR algorithm The first is related to the worst case exponential size of the set of stack symbols Q LR ; see our previous analysis This effect can be alleviated by using optimization techniques that simplify item representation for certain rules
40 Computational Complexity The second source of complexity is related to the length of the input string; let m be the length of the longest rule in the grammar The reduce step involves m + 1 indices and can be instantiated a number of times O( w m+1 ), resulting in exponential time complexity in the grammar size Such an exponential behavior can be avoided by factorizing each reduce transition into a sequence of pop transitions with only two stack symbols in the left-hand side
Everything You Always Wanted to Know About Parsing
 Everything You Always Wanted to Know About Parsing Part IV : Parsing University of Padua, Italy ESSLLI, August 2013 Introduction First published in 1968 by Jay in his PhD dissertation, Carnegie Mellon
Everything You Always Wanted to Know About Parsing Part IV : Parsing University of Padua, Italy ESSLLI, August 2013 Introduction First published in 1968 by Jay in his PhD dissertation, Carnegie Mellon
Einführung in die Computerlinguistik
 Einführung in die Computerlinguistik Context-Free Grammars (CFG) Laura Kallmeyer Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf Summer 2016 1 / 22 CFG (1) Example: Grammar G telescope : Productions: S NP VP NP
Einführung in die Computerlinguistik Context-Free Grammars (CFG) Laura Kallmeyer Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf Summer 2016 1 / 22 CFG (1) Example: Grammar G telescope : Productions: S NP VP NP
COM364 Automata Theory Lecture Note 2 - Nondeterminism
 COM364 Automata Theory Lecture Note 2 - Nondeterminism Kurtuluş Küllü March 2018 The FA we saw until now were deterministic FA (DFA) in the sense that for each state and input symbol there was exactly
COM364 Automata Theory Lecture Note 2 - Nondeterminism Kurtuluş Küllü March 2018 The FA we saw until now were deterministic FA (DFA) in the sense that for each state and input symbol there was exactly
CPS 220 Theory of Computation Pushdown Automata (PDA)
 CPS 220 Theory of Computation Pushdown Automata (PDA) Nondeterministic Finite Automaton with some extra memory Memory is called the stack, accessed in a very restricted way: in a First-In First-Out fashion
CPS 220 Theory of Computation Pushdown Automata (PDA) Nondeterministic Finite Automaton with some extra memory Memory is called the stack, accessed in a very restricted way: in a First-In First-Out fashion
60-354, Theory of Computation Fall Asish Mukhopadhyay School of Computer Science University of Windsor
 60-354, Theory of Computation Fall 2013 Asish Mukhopadhyay School of Computer Science University of Windsor Pushdown Automata (PDA) PDA = ε-nfa + stack Acceptance ε-nfa enters a final state or Stack is
60-354, Theory of Computation Fall 2013 Asish Mukhopadhyay School of Computer Science University of Windsor Pushdown Automata (PDA) PDA = ε-nfa + stack Acceptance ε-nfa enters a final state or Stack is
Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 10: Ambiguity, Pushdown Automata
 Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 10: Ambiguity, Pushdown Automata Salil Vadhan October 4, 2012 Reading: Sipser, 2.2. Another example of a CFG (with proof) L = {x {a, b} : x has the same # of a s and
Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 10: Ambiguity, Pushdown Automata Salil Vadhan October 4, 2012 Reading: Sipser, 2.2. Another example of a CFG (with proof) L = {x {a, b} : x has the same # of a s and
MA/CSSE 474 Theory of Computation
 MA/CSSE 474 Theory of Computation CFL Hierarchy CFL Decision Problems Your Questions? Previous class days' material Reading Assignments HW 12 or 13 problems Anything else I have included some slides online
MA/CSSE 474 Theory of Computation CFL Hierarchy CFL Decision Problems Your Questions? Previous class days' material Reading Assignments HW 12 or 13 problems Anything else I have included some slides online
Pushdown Automata (Pre Lecture)
 Pushdown Automata (Pre Lecture) Dr. Neil T. Dantam CSCI-561, Colorado School of Mines Fall 2017 Dantam (Mines CSCI-561) Pushdown Automata (Pre Lecture) Fall 2017 1 / 41 Outline Pushdown Automata Pushdown
Pushdown Automata (Pre Lecture) Dr. Neil T. Dantam CSCI-561, Colorado School of Mines Fall 2017 Dantam (Mines CSCI-561) Pushdown Automata (Pre Lecture) Fall 2017 1 / 41 Outline Pushdown Automata Pushdown
Push-down Automata = FA + Stack
 Push-down Automata = FA + Stack PDA Definition A push-down automaton M is a tuple M = (Q,, Γ, δ, q0, F) where Q is a finite set of states is the input alphabet (of terminal symbols, terminals) Γ is the
Push-down Automata = FA + Stack PDA Definition A push-down automaton M is a tuple M = (Q,, Γ, δ, q0, F) where Q is a finite set of states is the input alphabet (of terminal symbols, terminals) Γ is the
Parsing. Context-Free Grammars (CFG) Laura Kallmeyer. Winter 2017/18. Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf 1 / 26
 Parsing Context-Free Grammars (CFG) Laura Kallmeyer Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf Winter 2017/18 1 / 26 Table of contents 1 Context-Free Grammars 2 Simplifying CFGs Removing useless symbols Eliminating
Parsing Context-Free Grammars (CFG) Laura Kallmeyer Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf Winter 2017/18 1 / 26 Table of contents 1 Context-Free Grammars 2 Simplifying CFGs Removing useless symbols Eliminating
Pushdown Automata: Introduction (2)
 Pushdown Automata: Introduction Pushdown automaton (PDA) M = (K, Σ, Γ,, s, A) where K is a set of states Σ is an input alphabet Γ is a set of stack symbols s K is the start state A K is a set of accepting
Pushdown Automata: Introduction Pushdown automaton (PDA) M = (K, Σ, Γ,, s, A) where K is a set of states Σ is an input alphabet Γ is a set of stack symbols s K is the start state A K is a set of accepting
LR2: LR(0) Parsing. LR Parsing. CMPT 379: Compilers Instructor: Anoop Sarkar. anoopsarkar.github.io/compilers-class
 LR2: LR(0) Parsing LR Parsing CMPT 379: Compilers Instructor: Anoop Sarkar anoopsarkar.github.io/compilers-class Parsing - Roadmap Parser: decision procedure: builds a parse tree Top-down vs. bottom-up
LR2: LR(0) Parsing LR Parsing CMPT 379: Compilers Instructor: Anoop Sarkar anoopsarkar.github.io/compilers-class Parsing - Roadmap Parser: decision procedure: builds a parse tree Top-down vs. bottom-up
NPDA, CFG equivalence
 NPDA, CFG equivalence Theorem A language L is recognized by a NPDA iff L is described by a CFG. Must prove two directions: ( ) L is recognized by a NPDA implies L is described by a CFG. ( ) L is described
NPDA, CFG equivalence Theorem A language L is recognized by a NPDA iff L is described by a CFG. Must prove two directions: ( ) L is recognized by a NPDA implies L is described by a CFG. ( ) L is described
Parsing -3. A View During TD Parsing
 Parsing -3 Deterministic table-driven parsing techniques Pictorial view of TD and BU parsing BU (shift-reduce) Parsing Handle, viable prefix, items, closures, goto s LR(k): SLR(1), LR(1) Problems with
Parsing -3 Deterministic table-driven parsing techniques Pictorial view of TD and BU parsing BU (shift-reduce) Parsing Handle, viable prefix, items, closures, goto s LR(k): SLR(1), LR(1) Problems with
SCHEME FOR INTERNAL ASSESSMENT TEST 3
 SCHEME FOR INTERNAL ASSESSMENT TEST 3 Max Marks: 40 Subject& Code: Automata Theory & Computability (15CS54) Sem: V ISE (A & B) Note: Answer any FIVE full questions, choosing one full question from each
SCHEME FOR INTERNAL ASSESSMENT TEST 3 Max Marks: 40 Subject& Code: Automata Theory & Computability (15CS54) Sem: V ISE (A & B) Note: Answer any FIVE full questions, choosing one full question from each
CPS 220 Theory of Computation
 CPS 22 Theory of Computation Review - Regular Languages RL - a simple class of languages that can be represented in two ways: 1 Machine description: Finite Automata are machines with a finite number of
CPS 22 Theory of Computation Review - Regular Languages RL - a simple class of languages that can be represented in two ways: 1 Machine description: Finite Automata are machines with a finite number of
1. Draw a parse tree for the following derivation: S C A C C A b b b b A b b b b B b b b b a A a a b b b b a b a a b b 2. Show on your parse tree u,
 1. Draw a parse tree for the following derivation: S C A C C A b b b b A b b b b B b b b b a A a a b b b b a b a a b b 2. Show on your parse tree u, v, x, y, z as per the pumping theorem. 3. Prove that
1. Draw a parse tree for the following derivation: S C A C C A b b b b A b b b b B b b b b a A a a b b b b a b a a b b 2. Show on your parse tree u, v, x, y, z as per the pumping theorem. 3. Prove that
Lecture 11 Sections 4.5, 4.7. Wed, Feb 18, 2009
 The s s The s Lecture 11 Sections 4.5, 4.7 Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Feb 18, 2009 Outline The s s 1 s 2 3 4 5 6 The LR(0) Parsing s The s s There are two tables that we will construct. The action table
The s s The s Lecture 11 Sections 4.5, 4.7 Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Feb 18, 2009 Outline The s s 1 s 2 3 4 5 6 The LR(0) Parsing s The s s There are two tables that we will construct. The action table
(pp ) PDAs and CFGs (Sec. 2.2)
 (pp. 117-124) PDAs and CFGs (Sec. 2.2) A language is context free iff all strings in L can be generated by some context free grammar Theorem 2.20: L is Context Free iff a PDA accepts it I.e. if L is context
(pp. 117-124) PDAs and CFGs (Sec. 2.2) A language is context free iff all strings in L can be generated by some context free grammar Theorem 2.20: L is Context Free iff a PDA accepts it I.e. if L is context
Shift-Reduce parser E + (E + (E) E [a-z] In each stage, we shift a symbol from the input to the stack, or reduce according to one of the rules.
![Shift-Reduce parser E + (E + (E) E [a-z] In each stage, we shift a symbol from the input to the stack, or reduce according to one of the rules. Shift-Reduce parser E + (E + (E) E [a-z] In each stage, we shift a symbol from the input to the stack, or reduce according to one of the rules.](/thumbs/83/87889808.jpg) Bottom-up Parsing Bottom-up Parsing Until now we started with the starting nonterminal S and tried to derive the input from it. In a way, this isn t the natural thing to do. It s much more logical to start
Bottom-up Parsing Bottom-up Parsing Until now we started with the starting nonterminal S and tried to derive the input from it. In a way, this isn t the natural thing to do. It s much more logical to start
CSE 105 THEORY OF COMPUTATION
 CSE 105 THEORY OF COMPUTATION Spring 2017 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/sp17/cse105-ab/ Review of CFG, CFL, ambiguity What is the language generated by the CFG below: G 1 = ({S,T 1,T 2 }, {0,1,2}, { S
CSE 105 THEORY OF COMPUTATION Spring 2017 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/sp17/cse105-ab/ Review of CFG, CFL, ambiguity What is the language generated by the CFG below: G 1 = ({S,T 1,T 2 }, {0,1,2}, { S
PUSHDOWN AUTOMATA (PDA)
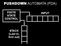 PUSHDOWN AUTOMATA (PDA) FINITE STATE CONTROL INPUT STACK (Last in, first out) input pop push ε,ε $ 0,ε 0 1,0 ε ε,$ ε 1,0 ε PDA that recognizes L = { 0 n 1 n n 0 } Definition: A (non-deterministic) PDA
PUSHDOWN AUTOMATA (PDA) FINITE STATE CONTROL INPUT STACK (Last in, first out) input pop push ε,ε $ 0,ε 0 1,0 ε ε,$ ε 1,0 ε PDA that recognizes L = { 0 n 1 n n 0 } Definition: A (non-deterministic) PDA
CS 406: Bottom-Up Parsing
 CS 406: Bottom-Up Parsing Stefan D. Bruda Winter 2016 BOTTOM-UP PUSH-DOWN AUTOMATA A different way to construct a push-down automaton equivalent to a given grammar = shift-reduce parser: Given G = (N,
CS 406: Bottom-Up Parsing Stefan D. Bruda Winter 2016 BOTTOM-UP PUSH-DOWN AUTOMATA A different way to construct a push-down automaton equivalent to a given grammar = shift-reduce parser: Given G = (N,
Definition: A grammar G = (V, T, P,S) is a context free grammar (cfg) if all productions in P have the form A x where
 Recitation 11 Notes Context Free Grammars Definition: A grammar G = (V, T, P,S) is a context free grammar (cfg) if all productions in P have the form A x A V, and x (V T)*. Examples Problem 1. Given the
Recitation 11 Notes Context Free Grammars Definition: A grammar G = (V, T, P,S) is a context free grammar (cfg) if all productions in P have the form A x A V, and x (V T)*. Examples Problem 1. Given the
CSE 105 THEORY OF COMPUTATION
 CSE 105 THEORY OF COMPUTATION Spring 2016 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/sp16/cse105-ab/ Today's learning goals Sipser Ch 2 Define push down automata Trace the computation of a push down automaton Design
CSE 105 THEORY OF COMPUTATION Spring 2016 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/sp16/cse105-ab/ Today's learning goals Sipser Ch 2 Define push down automata Trace the computation of a push down automaton Design
CISC4090: Theory of Computation
 CISC4090: Theory of Computation Chapter 2 Context-Free Languages Courtesy of Prof. Arthur G. Werschulz Fordham University Department of Computer and Information Sciences Spring, 2014 Overview In Chapter
CISC4090: Theory of Computation Chapter 2 Context-Free Languages Courtesy of Prof. Arthur G. Werschulz Fordham University Department of Computer and Information Sciences Spring, 2014 Overview In Chapter
Parsing. Left-Corner Parsing. Laura Kallmeyer. Winter 2017/18. Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf 1 / 17
 Parsing Left-Corner Parsing Laura Kallmeyer Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf Winter 2017/18 1 / 17 Table of contents 1 Motivation 2 Algorithm 3 Look-ahead 4 Chart Parsing 2 / 17 Motivation Problems
Parsing Left-Corner Parsing Laura Kallmeyer Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf Winter 2017/18 1 / 17 Table of contents 1 Motivation 2 Algorithm 3 Look-ahead 4 Chart Parsing 2 / 17 Motivation Problems
Outline. CS21 Decidability and Tractability. Machine view of FA. Machine view of FA. Machine view of FA. Machine view of FA.
 Outline CS21 Decidability and Tractability Lecture 5 January 16, 219 and Languages equivalence of NPDAs and CFGs non context-free languages January 16, 219 CS21 Lecture 5 1 January 16, 219 CS21 Lecture
Outline CS21 Decidability and Tractability Lecture 5 January 16, 219 and Languages equivalence of NPDAs and CFGs non context-free languages January 16, 219 CS21 Lecture 5 1 January 16, 219 CS21 Lecture
(pp ) PDAs and CFGs (Sec. 2.2)
 (pp. 117-124) PDAs and CFGs (Sec. 2.2) A language is context free iff all strings in L can be generated by some context free grammar Theorem 2.20: L is Context Free iff a PDA accepts it I.e. if L is context
(pp. 117-124) PDAs and CFGs (Sec. 2.2) A language is context free iff all strings in L can be generated by some context free grammar Theorem 2.20: L is Context Free iff a PDA accepts it I.e. if L is context
Context-Free Languages (Pre Lecture)
 Context-Free Languages (Pre Lecture) Dr. Neil T. Dantam CSCI-561, Colorado School of Mines Fall 2017 Dantam (Mines CSCI-561) Context-Free Languages (Pre Lecture) Fall 2017 1 / 34 Outline Pumping Lemma
Context-Free Languages (Pre Lecture) Dr. Neil T. Dantam CSCI-561, Colorado School of Mines Fall 2017 Dantam (Mines CSCI-561) Context-Free Languages (Pre Lecture) Fall 2017 1 / 34 Outline Pumping Lemma
Introduction to Formal Languages, Automata and Computability p.1/42
 Introduction to Formal Languages, Automata and Computability Pushdown Automata K. Krithivasan and R. Rama Introduction to Formal Languages, Automata and Computability p.1/42 Introduction We have considered
Introduction to Formal Languages, Automata and Computability Pushdown Automata K. Krithivasan and R. Rama Introduction to Formal Languages, Automata and Computability p.1/42 Introduction We have considered
Context-Free and Noncontext-Free Languages
 Examples: Context-Free and Noncontext-Free Languages a*b* is regular. A n B n = {a n b n : n 0} is context-free but not regular. A n B n C n = {a n b n c n : n 0} is not context-free The Regular and the
Examples: Context-Free and Noncontext-Free Languages a*b* is regular. A n B n = {a n b n : n 0} is context-free but not regular. A n B n C n = {a n b n c n : n 0} is not context-free The Regular and the
Final exam study sheet for CS3719 Turing machines and decidability.
 Final exam study sheet for CS3719 Turing machines and decidability. A Turing machine is a finite automaton with an infinite memory (tape). Formally, a Turing machine is a 6-tuple M = (Q, Σ, Γ, δ, q 0,
Final exam study sheet for CS3719 Turing machines and decidability. A Turing machine is a finite automaton with an infinite memory (tape). Formally, a Turing machine is a 6-tuple M = (Q, Σ, Γ, δ, q 0,
Pushdown Automata (2015/11/23)
 Chapter 6 Pushdown Automata (2015/11/23) Sagrada Familia, Barcelona, Spain Outline 6.0 Introduction 6.1 Definition of PDA 6.2 The Language of a PDA 6.3 Euivalence of PDA s and CFG s 6.4 Deterministic PDA
Chapter 6 Pushdown Automata (2015/11/23) Sagrada Familia, Barcelona, Spain Outline 6.0 Introduction 6.1 Definition of PDA 6.2 The Language of a PDA 6.3 Euivalence of PDA s and CFG s 6.4 Deterministic PDA
CFGs and PDAs are Equivalent. We provide algorithms to convert a CFG to a PDA and vice versa.
 CFGs and PDAs are Equivalent We provide algorithms to convert a CFG to a PDA and vice versa. CFGs and PDAs are Equivalent We now prove that a language is generated by some CFG if and only if it is accepted
CFGs and PDAs are Equivalent We provide algorithms to convert a CFG to a PDA and vice versa. CFGs and PDAs are Equivalent We now prove that a language is generated by some CFG if and only if it is accepted
Bottom-Up Parsing. Ÿ rm E + F *idÿ rm E +id*idÿ rm T +id*id. Ÿ rm F +id*id Ÿ rm id + id * id
 Bottom-Up Parsing Attempts to traverse a parse tree bottom up (post-order traversal) Reduces a sequence of tokens to the start symbol At each reduction step, the RHS of a production is replaced with LHS
Bottom-Up Parsing Attempts to traverse a parse tree bottom up (post-order traversal) Reduces a sequence of tokens to the start symbol At each reduction step, the RHS of a production is replaced with LHS
Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 10: CFLs: PDAs, Closure Properties, and Non-CFLs
 Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 10: CFLs: PDAs, Closure Properties, and Non-CFLs Harry Lewis October 8, 2013 Reading: Sipser, pp. 119-128. Pushdown Automata (review) Pushdown Automata = Finite automaton
Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 10: CFLs: PDAs, Closure Properties, and Non-CFLs Harry Lewis October 8, 2013 Reading: Sipser, pp. 119-128. Pushdown Automata (review) Pushdown Automata = Finite automaton
THEORY OF COMPUTATION (AUBER) EXAM CRIB SHEET
 THEORY OF COMPUTATION (AUBER) EXAM CRIB SHEET Regular Languages and FA A language is a set of strings over a finite alphabet Σ. All languages are finite or countably infinite. The set of all languages
THEORY OF COMPUTATION (AUBER) EXAM CRIB SHEET Regular Languages and FA A language is a set of strings over a finite alphabet Σ. All languages are finite or countably infinite. The set of all languages
Deterministic Finite Automata. Non deterministic finite automata. Non-Deterministic Finite Automata (NFA) Non-Deterministic Finite Automata (NFA)
 Deterministic Finite Automata Non deterministic finite automata Automata we ve been dealing with have been deterministic For every state and every alphabet symbol there is exactly one move that the machine
Deterministic Finite Automata Non deterministic finite automata Automata we ve been dealing with have been deterministic For every state and every alphabet symbol there is exactly one move that the machine
Theory of Computation (IV) Yijia Chen Fudan University
 Theory of Computation (IV) Yijia Chen Fudan University Review language regular context-free machine DFA/ NFA PDA syntax regular expression context-free grammar Pushdown automata Definition A pushdown automaton
Theory of Computation (IV) Yijia Chen Fudan University Review language regular context-free machine DFA/ NFA PDA syntax regular expression context-free grammar Pushdown automata Definition A pushdown automaton
October 6, Equivalence of Pushdown Automata with Context-Free Gramm
 Equivalence of Pushdown Automata with Context-Free Grammar October 6, 2013 Motivation Motivation CFG and PDA are equivalent in power: a CFG generates a context-free language and a PDA recognizes a context-free
Equivalence of Pushdown Automata with Context-Free Grammar October 6, 2013 Motivation Motivation CFG and PDA are equivalent in power: a CFG generates a context-free language and a PDA recognizes a context-free
Introduction to Bottom-Up Parsing
 Introduction to Bottom-Up Parsing Outline Review LL parsing Shift-reduce parsing The LR parsing algorithm Constructing LR parsing tables 2 Top-Down Parsing: Review Top-down parsing expands a parse tree
Introduction to Bottom-Up Parsing Outline Review LL parsing Shift-reduce parsing The LR parsing algorithm Constructing LR parsing tables 2 Top-Down Parsing: Review Top-down parsing expands a parse tree
Lecture 17: Language Recognition
 Lecture 17: Language Recognition Finite State Automata Deterministic and Non-Deterministic Finite Automata Regular Expressions Push-Down Automata Turing Machines Modeling Computation When attempting to
Lecture 17: Language Recognition Finite State Automata Deterministic and Non-Deterministic Finite Automata Regular Expressions Push-Down Automata Turing Machines Modeling Computation When attempting to
Chapter 4: Bottom-up Analysis 106 / 338
 Syntactic Analysis Chapter 4: Bottom-up Analysis 106 / 338 Bottom-up Analysis Attention: Many grammars are not LL(k)! A reason for that is: Definition Grammar G is called left-recursive, if A + A β for
Syntactic Analysis Chapter 4: Bottom-up Analysis 106 / 338 Bottom-up Analysis Attention: Many grammars are not LL(k)! A reason for that is: Definition Grammar G is called left-recursive, if A + A β for
Introduction to Bottom-Up Parsing
 Introduction to Bottom-Up Parsing Outline Review LL parsing Shift-reduce parsing The LR parsing algorithm Constructing LR parsing tables Compiler Design 1 (2011) 2 Top-Down Parsing: Review Top-down parsing
Introduction to Bottom-Up Parsing Outline Review LL parsing Shift-reduce parsing The LR parsing algorithm Constructing LR parsing tables Compiler Design 1 (2011) 2 Top-Down Parsing: Review Top-down parsing
CS Pushdown Automata
 Chap. 6 Pushdown Automata 6.1 Definition of Pushdown Automata Example 6.2 L ww R = {ww R w (0+1) * } Palindromes over {0, 1}. A cfg P 0 1 0P0 1P1. Consider a FA with a stack(= a Pushdown automaton; PDA).
Chap. 6 Pushdown Automata 6.1 Definition of Pushdown Automata Example 6.2 L ww R = {ww R w (0+1) * } Palindromes over {0, 1}. A cfg P 0 1 0P0 1P1. Consider a FA with a stack(= a Pushdown automaton; PDA).
Pushdown Automata. We have seen examples of context-free languages that are not regular, and hence can not be recognized by finite automata.
 Pushdown Automata We have seen examples of context-free languages that are not regular, and hence can not be recognized by finite automata. Next we consider a more powerful computation model, called a
Pushdown Automata We have seen examples of context-free languages that are not regular, and hence can not be recognized by finite automata. Next we consider a more powerful computation model, called a
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages. Pushdown Automata Parsing
 CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Pushdown Automata Parsing Chomsky Hierarchy Categorization of various languages and grammars Each is strictly more restrictive than the previous First described
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Pushdown Automata Parsing Chomsky Hierarchy Categorization of various languages and grammars Each is strictly more restrictive than the previous First described
5 Context-Free Languages
 CA320: COMPUTABILITY AND COMPLEXITY 1 5 Context-Free Languages 5.1 Context-Free Grammars Context-Free Grammars Context-free languages are specified with a context-free grammar (CFG). Formally, a CFG G
CA320: COMPUTABILITY AND COMPLEXITY 1 5 Context-Free Languages 5.1 Context-Free Grammars Context-Free Grammars Context-free languages are specified with a context-free grammar (CFG). Formally, a CFG G
CMPT-825 Natural Language Processing. Why are parsing algorithms important?
 CMPT-825 Natural Language Processing Anoop Sarkar http://www.cs.sfu.ca/ anoop October 26, 2010 1/34 Why are parsing algorithms important? A linguistic theory is implemented in a formal system to generate
CMPT-825 Natural Language Processing Anoop Sarkar http://www.cs.sfu.ca/ anoop October 26, 2010 1/34 Why are parsing algorithms important? A linguistic theory is implemented in a formal system to generate
Theory of Computation (VI) Yijia Chen Fudan University
 Theory of Computation (VI) Yijia Chen Fudan University Review Forced handles Definition A handle h of a valid string v = xhy is a forced handle if h is the unique handle in every valid string xhŷ where
Theory of Computation (VI) Yijia Chen Fudan University Review Forced handles Definition A handle h of a valid string v = xhy is a forced handle if h is the unique handle in every valid string xhŷ where
Introduction to Bottom-Up Parsing
 Outline Introduction to Bottom-Up Parsing Review LL parsing Shift-reduce parsing he LR parsing algorithm Constructing LR parsing tables 2 op-down Parsing: Review op-down parsing expands a parse tree from
Outline Introduction to Bottom-Up Parsing Review LL parsing Shift-reduce parsing he LR parsing algorithm Constructing LR parsing tables 2 op-down Parsing: Review op-down parsing expands a parse tree from
SYLLABUS. Introduction to Finite Automata, Central Concepts of Automata Theory. CHAPTER - 3 : REGULAR EXPRESSIONS AND LANGUAGES
 Contents i SYLLABUS UNIT - I CHAPTER - 1 : AUT UTOMA OMATA Introduction to Finite Automata, Central Concepts of Automata Theory. CHAPTER - 2 : FINITE AUT UTOMA OMATA An Informal Picture of Finite Automata,
Contents i SYLLABUS UNIT - I CHAPTER - 1 : AUT UTOMA OMATA Introduction to Finite Automata, Central Concepts of Automata Theory. CHAPTER - 2 : FINITE AUT UTOMA OMATA An Informal Picture of Finite Automata,
Administrivia. Test I during class on 10 March. Bottom-Up Parsing. Lecture An Introductory Example
 Administrivia Test I during class on 10 March. Bottom-Up Parsing Lecture 11-12 From slides by G. Necula & R. Bodik) 2/20/08 Prof. Hilfinger CS14 Lecture 11 1 2/20/08 Prof. Hilfinger CS14 Lecture 11 2 Bottom-Up
Administrivia Test I during class on 10 March. Bottom-Up Parsing Lecture 11-12 From slides by G. Necula & R. Bodik) 2/20/08 Prof. Hilfinger CS14 Lecture 11 1 2/20/08 Prof. Hilfinger CS14 Lecture 11 2 Bottom-Up
Introduction to Bottom-Up Parsing
 Outline Introduction to Bottom-Up Parsing Review LL parsing Shift-reduce parsing he LR parsing algorithm Constructing LR parsing tables Compiler Design 1 (2011) 2 op-down Parsing: Review op-down parsing
Outline Introduction to Bottom-Up Parsing Review LL parsing Shift-reduce parsing he LR parsing algorithm Constructing LR parsing tables Compiler Design 1 (2011) 2 op-down Parsing: Review op-down parsing
Foundations of Informatics: a Bridging Course
 Foundations of Informatics: a Bridging Course Week 3: Formal Languages and Semantics Thomas Noll Lehrstuhl für Informatik 2 RWTH Aachen University noll@cs.rwth-aachen.de http://www.b-it-center.de/wob/en/view/class211_id948.html
Foundations of Informatics: a Bridging Course Week 3: Formal Languages and Semantics Thomas Noll Lehrstuhl für Informatik 2 RWTH Aachen University noll@cs.rwth-aachen.de http://www.b-it-center.de/wob/en/view/class211_id948.html
Pushdown automata. Twan van Laarhoven. Institute for Computing and Information Sciences Intelligent Systems Radboud University Nijmegen
 Pushdown automata Twan van Laarhoven Institute for Computing and Information Sciences Intelligent Systems Version: fall 2014 T. van Laarhoven Version: fall 2014 Formal Languages, Grammars and Automata
Pushdown automata Twan van Laarhoven Institute for Computing and Information Sciences Intelligent Systems Version: fall 2014 T. van Laarhoven Version: fall 2014 Formal Languages, Grammars and Automata
MA/CSSE 474 Theory of Computation
 MA/CSSE 474 Theory of Computation Bottom-up parsing Pumping Theorem for CFLs Recap: Going One Way Lemma: Each context-free language is accepted by some PDA. Proof (by construction): The idea: Let the stack
MA/CSSE 474 Theory of Computation Bottom-up parsing Pumping Theorem for CFLs Recap: Going One Way Lemma: Each context-free language is accepted by some PDA. Proof (by construction): The idea: Let the stack
FORMAL LANGUAGES, AUTOMATA AND COMPUTABILITY
 15-453 FORMAL LANGUAGES, AUTOMATA AND COMPUTABILITY REVIEW for MIDTERM 1 THURSDAY Feb 6 Midterm 1 will cover everything we have seen so far The PROBLEMS will be from Sipser, Chapters 1, 2, 3 It will be
15-453 FORMAL LANGUAGES, AUTOMATA AND COMPUTABILITY REVIEW for MIDTERM 1 THURSDAY Feb 6 Midterm 1 will cover everything we have seen so far The PROBLEMS will be from Sipser, Chapters 1, 2, 3 It will be
Miscellaneous. Closure Properties Decision Properties
 Miscellaneous Closure Properties Decision Properties 1 Closure Properties of CFL s CFL s are closed under union, concatenation, and Kleene closure. Also, under reversal, homomorphisms and inverse homomorphisms.
Miscellaneous Closure Properties Decision Properties 1 Closure Properties of CFL s CFL s are closed under union, concatenation, and Kleene closure. Also, under reversal, homomorphisms and inverse homomorphisms.
Compiler Construction
 Compiler Construction Thomas Noll Software Modeling and Verification Group RWTH Aachen University https://moves.rwth-aachen.de/teaching/ss-16/cc/ Recap: LR(0) Grammars LR(0) Grammars The case k = 0 is
Compiler Construction Thomas Noll Software Modeling and Verification Group RWTH Aachen University https://moves.rwth-aachen.de/teaching/ss-16/cc/ Recap: LR(0) Grammars LR(0) Grammars The case k = 0 is
Computational Models - Lecture 4
 Computational Models - Lecture 4 Regular languages: The Myhill-Nerode Theorem Context-free Grammars Chomsky Normal Form Pumping Lemma for context free languages Non context-free languages: Examples Push
Computational Models - Lecture 4 Regular languages: The Myhill-Nerode Theorem Context-free Grammars Chomsky Normal Form Pumping Lemma for context free languages Non context-free languages: Examples Push
CS481F01 Prelim 2 Solutions
 CS481F01 Prelim 2 Solutions A. Demers 7 Nov 2001 1 (30 pts = 4 pts each part + 2 free points). For this question we use the following notation: x y means x is a prefix of y m k n means m n k For each of
CS481F01 Prelim 2 Solutions A. Demers 7 Nov 2001 1 (30 pts = 4 pts each part + 2 free points). For this question we use the following notation: x y means x is a prefix of y m k n means m n k For each of
An Efficient Context-Free Parsing Algorithm. Speakers: Morad Ankri Yaniv Elia
 An Efficient Context-Free Parsing Algorithm Speakers: Morad Ankri Yaniv Elia Yaniv: Introduction Terminology Informal Explanation The Recognizer Morad: Example Time and Space Bounds Empirical results Practical
An Efficient Context-Free Parsing Algorithm Speakers: Morad Ankri Yaniv Elia Yaniv: Introduction Terminology Informal Explanation The Recognizer Morad: Example Time and Space Bounds Empirical results Practical
UNIT-VIII COMPUTABILITY THEORY
 CONTEXT SENSITIVE LANGUAGE UNIT-VIII COMPUTABILITY THEORY A Context Sensitive Grammar is a 4-tuple, G = (N, Σ P, S) where: N Set of non terminal symbols Σ Set of terminal symbols S Start symbol of the
CONTEXT SENSITIVE LANGUAGE UNIT-VIII COMPUTABILITY THEORY A Context Sensitive Grammar is a 4-tuple, G = (N, Σ P, S) where: N Set of non terminal symbols Σ Set of terminal symbols S Start symbol of the
HKN CS/ECE 374 Midterm 1 Review. Nathan Bleier and Mahir Morshed
 HKN CS/ECE 374 Midterm 1 Review Nathan Bleier and Mahir Morshed For the most part, all about strings! String induction (to some extent) Regular languages Regular expressions (regexps) Deterministic finite
HKN CS/ECE 374 Midterm 1 Review Nathan Bleier and Mahir Morshed For the most part, all about strings! String induction (to some extent) Regular languages Regular expressions (regexps) Deterministic finite
THEORY OF COMPILATION
 Lecture 04 Syntax analysis: top-down and bottom-up parsing THEORY OF COMPILATION EranYahav 1 You are here Compiler txt Source Lexical Analysis Syntax Analysis Parsing Semantic Analysis Inter. Rep. (IR)
Lecture 04 Syntax analysis: top-down and bottom-up parsing THEORY OF COMPILATION EranYahav 1 You are here Compiler txt Source Lexical Analysis Syntax Analysis Parsing Semantic Analysis Inter. Rep. (IR)
Handout 8: Computation & Hierarchical parsing II. Compute initial state set S 0 Compute initial state set S 0
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.863J/9.611J, Natural Language Processing, Spring, 2001 Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences Handout
Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.863J/9.611J, Natural Language Processing, Spring, 2001 Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences Handout
Theory of Computation (I) Yijia Chen Fudan University
 Theory of Computation (I) Yijia Chen Fudan University Instructor Yijia Chen Homepage: http://basics.sjtu.edu.cn/~chen Email: yijiachen@fudan.edu.cn Textbook Introduction to the Theory of Computation Michael
Theory of Computation (I) Yijia Chen Fudan University Instructor Yijia Chen Homepage: http://basics.sjtu.edu.cn/~chen Email: yijiachen@fudan.edu.cn Textbook Introduction to the Theory of Computation Michael
Pushdown Automata. Reading: Chapter 6
 Pushdown Automata Reading: Chapter 6 1 Pushdown Automata (PDA) Informally: A PDA is an NFA-ε with a infinite stack. Transitions are modified to accommodate stack operations. Questions: What is a stack?
Pushdown Automata Reading: Chapter 6 1 Pushdown Automata (PDA) Informally: A PDA is an NFA-ε with a infinite stack. Transitions are modified to accommodate stack operations. Questions: What is a stack?
Lecture 1: Finite State Automaton
 Lecture 1: Finite State Automaton Instructor: Ketan Mulmuley Scriber: Yuan Li January 6, 2015 1 Deterministic Finite Automaton Informally, a deterministic finite automaton (DFA) has finite number of s-
Lecture 1: Finite State Automaton Instructor: Ketan Mulmuley Scriber: Yuan Li January 6, 2015 1 Deterministic Finite Automaton Informally, a deterministic finite automaton (DFA) has finite number of s-
LR(1) Parsers Part III Last Parsing Lecture. Copyright 2010, Keith D. Cooper & Linda Torczon, all rights reserved.
 LR(1) Parsers Part III Last Parsing Lecture Copyright 2010, Keith D. Cooper & Linda Torczon, all rights reserved. LR(1) Parsers A table-driven LR(1) parser looks like source code Scanner Table-driven Parser
LR(1) Parsers Part III Last Parsing Lecture Copyright 2010, Keith D. Cooper & Linda Torczon, all rights reserved. LR(1) Parsers A table-driven LR(1) parser looks like source code Scanner Table-driven Parser
Theory of Computation (II) Yijia Chen Fudan University
 Theory of Computation (II) Yijia Chen Fudan University Review A language L is a subset of strings over an alphabet Σ. Our goal is to identify those languages that can be recognized by one of the simplest
Theory of Computation (II) Yijia Chen Fudan University Review A language L is a subset of strings over an alphabet Σ. Our goal is to identify those languages that can be recognized by one of the simplest
Functions on languages:
 MA/CSSE 474 Final Exam Notation and Formulas page Name (turn this in with your exam) Unless specified otherwise, r,s,t,u,v,w,x,y,z are strings over alphabet Σ; while a, b, c, d are individual alphabet
MA/CSSE 474 Final Exam Notation and Formulas page Name (turn this in with your exam) Unless specified otherwise, r,s,t,u,v,w,x,y,z are strings over alphabet Σ; while a, b, c, d are individual alphabet
Section 1 (closed-book) Total points 30
 CS 454 Theory of Computation Fall 2011 Section 1 (closed-book) Total points 30 1. Which of the following are true? (a) a PDA can always be converted to an equivalent PDA that at each step pops or pushes
CS 454 Theory of Computation Fall 2011 Section 1 (closed-book) Total points 30 1. Which of the following are true? (a) a PDA can always be converted to an equivalent PDA that at each step pops or pushes
Introduction to Theory of Computing
 CSCI 2670, Fall 2012 Introduction to Theory of Computing Department of Computer Science University of Georgia Athens, GA 30602 Instructor: Liming Cai www.cs.uga.edu/ cai 0 Lecture Note 3 Context-Free Languages
CSCI 2670, Fall 2012 Introduction to Theory of Computing Department of Computer Science University of Georgia Athens, GA 30602 Instructor: Liming Cai www.cs.uga.edu/ cai 0 Lecture Note 3 Context-Free Languages
Lecture VII Part 2: Syntactic Analysis Bottom-up Parsing: LR Parsing. Prof. Bodik CS Berkley University 1
 Lecture VII Part 2: Syntactic Analysis Bottom-up Parsing: LR Parsing. Prof. Bodik CS 164 -- Berkley University 1 Bottom-Up Parsing Bottom-up parsing is more general than topdown parsing And just as efficient
Lecture VII Part 2: Syntactic Analysis Bottom-up Parsing: LR Parsing. Prof. Bodik CS 164 -- Berkley University 1 Bottom-Up Parsing Bottom-up parsing is more general than topdown parsing And just as efficient
Generalized Bottom Up Parsers With Reduced Stack Activity
 The Author 2005. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of The British Computer Society. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oupjournals.org Advance Access
The Author 2005. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of The British Computer Society. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oupjournals.org Advance Access
CS5371 Theory of Computation. Lecture 7: Automata Theory V (CFG, CFL, CNF)
 CS5371 Theory of Computation Lecture 7: Automata Theory V (CFG, CFL, CNF) Announcement Homework 2 will be given soon (before Tue) Due date: Oct 31 (Tue), before class Midterm: Nov 3, (Fri), first hour
CS5371 Theory of Computation Lecture 7: Automata Theory V (CFG, CFL, CNF) Announcement Homework 2 will be given soon (before Tue) Due date: Oct 31 (Tue), before class Midterm: Nov 3, (Fri), first hour
Introduction to Finite-State Automata
 Introduction to Finite-State Automata John McDonough Language Technologies Institute, Machine Learning for Signal Processing Group, Carnegie Mellon University March 26, 2012 Introduction In this lecture,
Introduction to Finite-State Automata John McDonough Language Technologies Institute, Machine Learning for Signal Processing Group, Carnegie Mellon University March 26, 2012 Introduction In this lecture,
Automata and Languages
 Automata and Languages Prof. Mohamed Hamada Software Engineering Lab. The University of Aizu Japan Nondeterministic Finite Automata with empty moves (-NFA) Definition A nondeterministic finite automaton
Automata and Languages Prof. Mohamed Hamada Software Engineering Lab. The University of Aizu Japan Nondeterministic Finite Automata with empty moves (-NFA) Definition A nondeterministic finite automaton
Pushdown Automata. Chapter 12
 Pushdown Automata Chapter 12 Recognizing Context-Free Languages We need a device similar to an FSM except that it needs more power. The insight: Precisely what it needs is a stack, which gives it an unlimited
Pushdown Automata Chapter 12 Recognizing Context-Free Languages We need a device similar to an FSM except that it needs more power. The insight: Precisely what it needs is a stack, which gives it an unlimited
St.MARTIN S ENGINEERING COLLEGE Dhulapally, Secunderabad
 St.MARTIN S ENGINEERING COLLEGE Dhulapally, Secunderabad-500 014 Subject: FORMAL LANGUAGES AND AUTOMATA THEORY Class : CSE II PART A (SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS) UNIT- I 1 Explain transition diagram, transition
St.MARTIN S ENGINEERING COLLEGE Dhulapally, Secunderabad-500 014 Subject: FORMAL LANGUAGES AND AUTOMATA THEORY Class : CSE II PART A (SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS) UNIT- I 1 Explain transition diagram, transition
Parsing beyond context-free grammar: Parsing Multiple Context-Free Grammars
 Parsing beyond context-free grammar: Parsing Multiple Context-Free Grammars Laura Kallmeyer, Wolfgang Maier University of Tübingen ESSLLI Course 2008 Parsing beyond CFG 1 MCFG Parsing Multiple Context-Free
Parsing beyond context-free grammar: Parsing Multiple Context-Free Grammars Laura Kallmeyer, Wolfgang Maier University of Tübingen ESSLLI Course 2008 Parsing beyond CFG 1 MCFG Parsing Multiple Context-Free
CDM Parsing and Decidability
 CDM Parsing and Decidability 1 Parsing Klaus Sutner Carnegie Mellon Universality 65-parsing 2017/12/15 23:17 CFGs and Decidability Pushdown Automata The Recognition Problem 3 What Could Go Wrong? 4 Problem:
CDM Parsing and Decidability 1 Parsing Klaus Sutner Carnegie Mellon Universality 65-parsing 2017/12/15 23:17 CFGs and Decidability Pushdown Automata The Recognition Problem 3 What Could Go Wrong? 4 Problem:
Languages. Languages. An Example Grammar. Grammars. Suppose we have an alphabet V. Then we can write:
 Languages A language is a set (usually infinite) of strings, also known as sentences Each string consists of a sequence of symbols taken from some alphabet An alphabet, V, is a finite set of symbols, e.g.
Languages A language is a set (usually infinite) of strings, also known as sentences Each string consists of a sequence of symbols taken from some alphabet An alphabet, V, is a finite set of symbols, e.g.
Context-Free Grammars and Languages. Reading: Chapter 5
 Context-Free Grammars and Languages Reading: Chapter 5 1 Context-Free Languages The class of context-free languages generalizes the class of regular languages, i.e., every regular language is a context-free
Context-Free Grammars and Languages Reading: Chapter 5 1 Context-Free Languages The class of context-free languages generalizes the class of regular languages, i.e., every regular language is a context-free
Computability and Complexity
 Computability and Complexity Lecture 10 More examples of problems in P Closure properties of the class P The class NP given by Jiri Srba Lecture 10 Computability and Complexity 1/12 Example: Relatively
Computability and Complexity Lecture 10 More examples of problems in P Closure properties of the class P The class NP given by Jiri Srba Lecture 10 Computability and Complexity 1/12 Example: Relatively
Compiler Design 1. LR Parsing. Goutam Biswas. Lect 7
 Compiler Design 1 LR Parsing Compiler Design 2 LR(0) Parsing An LR(0) parser can take shift-reduce decisions entirely on the basis of the states of LR(0) automaton a of the grammar. Consider the following
Compiler Design 1 LR Parsing Compiler Design 2 LR(0) Parsing An LR(0) parser can take shift-reduce decisions entirely on the basis of the states of LR(0) automaton a of the grammar. Consider the following
CS20a: summary (Oct 24, 2002)
 CS20a: summary (Oct 24, 2002) Context-free languages Grammars G = (V, T, P, S) Pushdown automata N-PDA = CFG D-PDA < CFG Today What languages are context-free? Pumping lemma (similar to pumping lemma for
CS20a: summary (Oct 24, 2002) Context-free languages Grammars G = (V, T, P, S) Pushdown automata N-PDA = CFG D-PDA < CFG Today What languages are context-free? Pumping lemma (similar to pumping lemma for
Accept or reject. Stack
 Pushdown Automata CS351 Just as a DFA was equivalent to a regular expression, we have a similar analogy for the context-free grammar. A pushdown automata (PDA) is equivalent in power to contextfree grammars.
Pushdown Automata CS351 Just as a DFA was equivalent to a regular expression, we have a similar analogy for the context-free grammar. A pushdown automata (PDA) is equivalent in power to contextfree grammars.
Properties of Context-Free Languages. Closure Properties Decision Properties
 Properties of Context-Free Languages Closure Properties Decision Properties 1 Closure Properties of CFL s CFL s are closed under union, concatenation, and Kleene closure. Also, under reversal, homomorphisms
Properties of Context-Free Languages Closure Properties Decision Properties 1 Closure Properties of CFL s CFL s are closed under union, concatenation, and Kleene closure. Also, under reversal, homomorphisms
Grammar formalisms Tree Adjoining Grammar: Formal Properties, Parsing. Part I. Formal Properties of TAG. Outline: Formal Properties of TAG
 Grammar formalisms Tree Adjoining Grammar: Formal Properties, Parsing Laura Kallmeyer, Timm Lichte, Wolfgang Maier Universität Tübingen Part I Formal Properties of TAG 16.05.2007 und 21.05.2007 TAG Parsing
Grammar formalisms Tree Adjoining Grammar: Formal Properties, Parsing Laura Kallmeyer, Timm Lichte, Wolfgang Maier Universität Tübingen Part I Formal Properties of TAG 16.05.2007 und 21.05.2007 TAG Parsing
Computational Models - Lecture 5 1
 Computational Models - Lecture 5 1 Handout Mode Iftach Haitner and Yishay Mansour. Tel Aviv University. April 10/22, 2013 1 Based on frames by Benny Chor, Tel Aviv University, modifying frames by Maurice
Computational Models - Lecture 5 1 Handout Mode Iftach Haitner and Yishay Mansour. Tel Aviv University. April 10/22, 2013 1 Based on frames by Benny Chor, Tel Aviv University, modifying frames by Maurice
EXAM. CS331 Compiler Design Spring Please read all instructions, including these, carefully
 EXAM Please read all instructions, including these, carefully There are 7 questions on the exam, with multiple parts. You have 3 hours to work on the exam. The exam is open book, open notes. Please write
EXAM Please read all instructions, including these, carefully There are 7 questions on the exam, with multiple parts. You have 3 hours to work on the exam. The exam is open book, open notes. Please write
Natural Language Processing. Lecture 13: More on CFG Parsing
 Natural Language Processing Lecture 13: More on CFG Parsing Probabilistc/Weighted Parsing Example: ambiguous parse Probabilistc CFG Ambiguous parse w/probabilites 0.05 0.05 0.20 0.10 0.30 0.20 0.60 0.75
Natural Language Processing Lecture 13: More on CFG Parsing Probabilistc/Weighted Parsing Example: ambiguous parse Probabilistc CFG Ambiguous parse w/probabilites 0.05 0.05 0.20 0.10 0.30 0.20 0.60 0.75
CISC 4090 Theory of Computation
 CISC 4090 Theory of Computation Context-Free Languages and Push Down Automata Professor Daniel Leeds dleeds@fordham.edu JMH 332 Languages: Regular and Beyond Regular: a b c b d e a Not-regular: c n bd
CISC 4090 Theory of Computation Context-Free Languages and Push Down Automata Professor Daniel Leeds dleeds@fordham.edu JMH 332 Languages: Regular and Beyond Regular: a b c b d e a Not-regular: c n bd
Pushdown Automata. Pushdown Automata. Pushdown Automata. Pushdown Automata. Pushdown Automata. Pushdown Automata. The stack
 A pushdown automata (PDA) is essentially: An NFA with a stack A move of a PDA will depend upon Current state of the machine Current symbol being read in Current symbol popped off the top of the stack With
A pushdown automata (PDA) is essentially: An NFA with a stack A move of a PDA will depend upon Current state of the machine Current symbol being read in Current symbol popped off the top of the stack With
Intro to Theory of Computation
 Intro to Theory of Computation LECTURE 7 Last time: Proving a language is not regular Pushdown automata (PDAs) Today: Context-free grammars (CFG) Equivalence of CFGs and PDAs Sofya Raskhodnikova 1/31/2016
Intro to Theory of Computation LECTURE 7 Last time: Proving a language is not regular Pushdown automata (PDAs) Today: Context-free grammars (CFG) Equivalence of CFGs and PDAs Sofya Raskhodnikova 1/31/2016
MTH401A Theory of Computation. Lecture 17
 MTH401A Theory of Computation Lecture 17 Chomsky Normal Form for CFG s Chomsky Normal Form for CFG s For every context free language, L, the language L {ε} has a grammar in which every production looks
MTH401A Theory of Computation Lecture 17 Chomsky Normal Form for CFG s Chomsky Normal Form for CFG s For every context free language, L, the language L {ε} has a grammar in which every production looks
