Natural Language Processing. Lecture 13: More on CFG Parsing
|
|
|
- Stephanie Morton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Natural Language Processing Lecture 13: More on CFG Parsing
2 Probabilistc/Weighted Parsing
3 Example: ambiguous parse
4 Probabilistc CFG
5 Ambiguous parse w/probabilites P(lef) = 2.2 *10^-6 P(right) = 6.1 *10^-7
6 Review: Context-Free Grammars Vocabulary of terminal symbols, Σ Set of nonterminal symbols (a.k.a. variables), N Special start symbol S N Producton rules of the form X α where X N α (N Σ)* (in CNF: α N Σ)
7 Probabilistc Context-Free Grammars Vocabulary of terminal symbols, Σ Set of nonterminal symbols (a.k.a. variables), N Special start symbol S N Producton rules of the form X α, each with a positve weight p(x α), where X N α (N Σ)* (in CNF: α N 2 Σ) X N, α p(x α) = 1
8 CKY Algorithm: Review for i = 1... n C[i-1, i] = { V V w i } for l = 2... n // width for i = 0... n - l // lef boundary k = i + l // right boundary for j = i k 1 // midpoint C[i, k] = C[i, k] { V V YZ, Y C[i, j], Z C[j, k] } return true if S C[0, n]
9 Weighted CKY Algorithm for i = 1... n, V N C[V, i-1, i] = p(v w i ) for l = 2... n // width of span for i = 0... n - l // lef boundary k = i + l // right boundary for j = i k 1 // midpoint for each binary rule V YZ C[V, i, k] = max{ C[V, i, k], C[Y, i, j] C[Z, j, k] p(v YZ) } return true if S C[,0, n]
10 CKY Algorithm: Review
11 Weighted CKY Algorithm
12 P-CKY algorithm from book
13
14 Parsing as (Weighted) Deducton
15 Earley s Algorithm
16
17 Example Grammar (same for CKY)
18 Earley Parsing Allows arbitrary CFGs Top-down control Fills a table (or chart) in a single sweep over the input Table is length N+1; N is number of words Table entries represent Completed consttuents and their locatons In-progress consttuents Predicted consttuents 02/26/2019 Speech and Language Processing - Jurafsky and Martn 18
19 States The table-entries are called states and are represented with doted-rules. S. VP NP Det. Nominal VP V NP. A VP is predicted An NP is in progress A VP has been found 02/26/2019 Speech and Language Processing - Jurafsky and Martn 19
20 States/Locatons S. VP [0,0] NP Det.Nominal [1,2] VP V NP. [0,3] A VP is predicted at the start of the sentence An NP is in progress; the Det goes from 1 to 2 A VP has been found startng at 0 and ending at 3 02/26/2019 Speech and Language Processing - Jurafsky and Martn 20
21 Earley top-level As with most dynamic programming approaches, the answer is found by looking in the table in the right place. In this case, there should be an S state in the final column that spans from 0 to N and is complete. That is, S α. [0,N] If that s the case, you re done. 02/26/2019 Speech and Language Processing - Jurafsky and Martn 21
22 Earley top-level (2) So sweep through the table from 0 to N New predicted states are created by startng topdown from S New incomplete states are created by advancing existng states as new consttuents are discovered New complete states are created in the same way. 02/26/2019 Speech and Language Processing - Jurafsky and Martn 22
23 Earley top-level (3) More specifically 1. Predict all the states you can upfront 2. Read a word 1. Extend states based on matches 2. Generate new predictons 3. Go to step 2 3. When you re out of words, look at the chart to see if you have a winner 02/26/2019 Speech and Language Processing - Jurafsky and Martn 23
24 Earley code: top-level
25 Earley code: 3 main functons
26 Extended Earley Example Book that fight We should find: an S from 0 to 3 that is a completed state 02/26/2019 Speech and Language Processing - Jurafsky and Martn 26
27
28
29
30
31
32 Earley s Algorithm in equatons We can look at this from the declaratve programming point of view too. ROOT S [0,0] goal: ROOT S [0,n] book the fight through Chicago
33 Earley s Algorithm: PREDICT Given V α Xβ [i, j] and the rule X γ, create X γ [j, j] ROOT S [0,0] S VP S VP [0,0] ROOT S [0,0] S VP [0,0] S NP VP [0,0]... VP V NP [0,0]... NP DT N [0,0]... book the fight through Chicago
34 Earley s Algorithm: SCAN Given V α Tβ [i, j] and the rule T w j+1, create T w j+1 [j, j+1] VP V NP [0,0] V book V book [0,1] ROOT S [0,0] S VP [0,0] S NP VP [0,0]... VP V NP [0,0]... NP DT N [0,0]... V book [0, 1] book the fight through Chicago
35 Earley s Algorithm: COMPLETE Given V α Xβ [i, j] and X γ [j, k], create V αx β [i, k] VP V NP [0,0] V book [0,1] VP V NP [0,1] ROOT S [0,0] S VP [0,0] S NP VP [0,0]... VP V NP [0,0]... NP DT N [0,0]... V book [0, 1] VP V NP [0,1] book the fight through Chicago
36
37 Thought Questons Runtme? O(n 3 ) Memory? O(n 2 ) Can we make it faster? Recovering trees?
38 Make it an Earley Parser
39 Parsing as Search, Again
40 Implementng Recognizers as Search Agenda = { state0 } while(agenda not empty) s = pop a state from Agenda if s is a success-state return s // valid parse tree else if s is not a failure-state: generate new states from s push new states onto Agenda return nil // no parse!
41 Agenda-Based Probabilistc Parsing Agenda = { (item, value) : inital updates from equatons } // items take the form [X, i, j]; values are reals while(agenda not empty) u = pop an update from Agenda if u.item is goal return u.value // valid parse tree else if u.value -> Chart[u.item] store Chart[u.item] u.value if u.item combines with other Chart items: generate new updates from u and items stored in Chart push new updates onto Agenda return nil // no parse!
42 Catalog of CF Parsing Algorithms Recogniton/Boolean vs. parsing/probabilistc Chomsky normal form/cky vs. general/earley s Exhaustve vs. agenda
Context- Free Parsing with CKY. October 16, 2014
 Context- Free Parsing with CKY October 16, 2014 Lecture Plan Parsing as Logical DeducBon Defining the CFG recognibon problem BoHom up vs. top down Quick review of Chomsky normal form The CKY algorithm
Context- Free Parsing with CKY October 16, 2014 Lecture Plan Parsing as Logical DeducBon Defining the CFG recognibon problem BoHom up vs. top down Quick review of Chomsky normal form The CKY algorithm
CKY & Earley Parsing. Ling 571 Deep Processing Techniques for NLP January 13, 2016
 CKY & Earley Parsing Ling 571 Deep Processing Techniques for NLP January 13, 2016 No Class Monday: Martin Luther King Jr. Day CKY Parsing: Finish the parse Recognizer à Parser Roadmap Earley parsing Motivation:
CKY & Earley Parsing Ling 571 Deep Processing Techniques for NLP January 13, 2016 No Class Monday: Martin Luther King Jr. Day CKY Parsing: Finish the parse Recognizer à Parser Roadmap Earley parsing Motivation:
Review. Earley Algorithm Chapter Left Recursion. Left-Recursion. Rule Ordering. Rule Ordering
 Review Earley Algorithm Chapter 13.4 Lecture #9 October 2009 Top-Down vs. Bottom-Up Parsers Both generate too many useless trees Combine the two to avoid over-generation: Top-Down Parsing with Bottom-Up
Review Earley Algorithm Chapter 13.4 Lecture #9 October 2009 Top-Down vs. Bottom-Up Parsers Both generate too many useless trees Combine the two to avoid over-generation: Top-Down Parsing with Bottom-Up
CMPT-825 Natural Language Processing. Why are parsing algorithms important?
 CMPT-825 Natural Language Processing Anoop Sarkar http://www.cs.sfu.ca/ anoop October 26, 2010 1/34 Why are parsing algorithms important? A linguistic theory is implemented in a formal system to generate
CMPT-825 Natural Language Processing Anoop Sarkar http://www.cs.sfu.ca/ anoop October 26, 2010 1/34 Why are parsing algorithms important? A linguistic theory is implemented in a formal system to generate
Parsing with CFGs L445 / L545 / B659. Dept. of Linguistics, Indiana University Spring Parsing with CFGs. Direction of processing
 L445 / L545 / B659 Dept. of Linguistics, Indiana University Spring 2016 1 / 46 : Overview Input: a string Output: a (single) parse tree A useful step in the process of obtaining meaning We can view the
L445 / L545 / B659 Dept. of Linguistics, Indiana University Spring 2016 1 / 46 : Overview Input: a string Output: a (single) parse tree A useful step in the process of obtaining meaning We can view the
Parsing with CFGs. Direction of processing. Top-down. Bottom-up. Left-corner parsing. Chart parsing CYK. Earley 1 / 46.
 : Overview L545 Dept. of Linguistics, Indiana University Spring 2013 Input: a string Output: a (single) parse tree A useful step in the process of obtaining meaning We can view the problem as searching
: Overview L545 Dept. of Linguistics, Indiana University Spring 2013 Input: a string Output: a (single) parse tree A useful step in the process of obtaining meaning We can view the problem as searching
Parsing. Left-Corner Parsing. Laura Kallmeyer. Winter 2017/18. Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf 1 / 17
 Parsing Left-Corner Parsing Laura Kallmeyer Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf Winter 2017/18 1 / 17 Table of contents 1 Motivation 2 Algorithm 3 Look-ahead 4 Chart Parsing 2 / 17 Motivation Problems
Parsing Left-Corner Parsing Laura Kallmeyer Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf Winter 2017/18 1 / 17 Table of contents 1 Motivation 2 Algorithm 3 Look-ahead 4 Chart Parsing 2 / 17 Motivation Problems
Parsing with Context-Free Grammars
 Parsing with Context-Free Grammars Berlin Chen 2005 References: 1. Natural Language Understanding, chapter 3 (3.1~3.4, 3.6) 2. Speech and Language Processing, chapters 9, 10 NLP-Berlin Chen 1 Grammars
Parsing with Context-Free Grammars Berlin Chen 2005 References: 1. Natural Language Understanding, chapter 3 (3.1~3.4, 3.6) 2. Speech and Language Processing, chapters 9, 10 NLP-Berlin Chen 1 Grammars
Handout 8: Computation & Hierarchical parsing II. Compute initial state set S 0 Compute initial state set S 0
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.863J/9.611J, Natural Language Processing, Spring, 2001 Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences Handout
Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.863J/9.611J, Natural Language Processing, Spring, 2001 Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences Handout
Parsing. Probabilistic CFG (PCFG) Laura Kallmeyer. Winter 2017/18. Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf 1 / 22
 Parsing Probabilistic CFG (PCFG) Laura Kallmeyer Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf Winter 2017/18 1 / 22 Table of contents 1 Introduction 2 PCFG 3 Inside and outside probability 4 Parsing Jurafsky
Parsing Probabilistic CFG (PCFG) Laura Kallmeyer Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf Winter 2017/18 1 / 22 Table of contents 1 Introduction 2 PCFG 3 Inside and outside probability 4 Parsing Jurafsky
Introduction to Computational Linguistics
 Introduction to Computational Linguistics Olga Zamaraeva (2018) Based on Bender (prev. years) University of Washington May 3, 2018 1 / 101 Midterm Project Milestone 2: due Friday Assgnments 4& 5 due dates
Introduction to Computational Linguistics Olga Zamaraeva (2018) Based on Bender (prev. years) University of Washington May 3, 2018 1 / 101 Midterm Project Milestone 2: due Friday Assgnments 4& 5 due dates
Grammar formalisms Tree Adjoining Grammar: Formal Properties, Parsing. Part I. Formal Properties of TAG. Outline: Formal Properties of TAG
 Grammar formalisms Tree Adjoining Grammar: Formal Properties, Parsing Laura Kallmeyer, Timm Lichte, Wolfgang Maier Universität Tübingen Part I Formal Properties of TAG 16.05.2007 und 21.05.2007 TAG Parsing
Grammar formalisms Tree Adjoining Grammar: Formal Properties, Parsing Laura Kallmeyer, Timm Lichte, Wolfgang Maier Universität Tübingen Part I Formal Properties of TAG 16.05.2007 und 21.05.2007 TAG Parsing
Statistical Machine Translation
 Statistical Machine Translation -tree-based models (cont.)- Artem Sokolov Computerlinguistik Universität Heidelberg Sommersemester 2015 material from P. Koehn, S. Riezler, D. Altshuler Bottom-Up Decoding
Statistical Machine Translation -tree-based models (cont.)- Artem Sokolov Computerlinguistik Universität Heidelberg Sommersemester 2015 material from P. Koehn, S. Riezler, D. Altshuler Bottom-Up Decoding
A* Search. 1 Dijkstra Shortest Path
 A* Search Consider the eight puzzle. There are eight tiles numbered 1 through 8 on a 3 by three grid with nine locations so that one location is left empty. We can move by sliding a tile adjacent to the
A* Search Consider the eight puzzle. There are eight tiles numbered 1 through 8 on a 3 by three grid with nine locations so that one location is left empty. We can move by sliding a tile adjacent to the
In this chapter, we explore the parsing problem, which encompasses several questions, including:
 Chapter 12 Parsing Algorithms 12.1 Introduction In this chapter, we explore the parsing problem, which encompasses several questions, including: Does L(G) contain w? What is the highest-weight derivation
Chapter 12 Parsing Algorithms 12.1 Introduction In this chapter, we explore the parsing problem, which encompasses several questions, including: Does L(G) contain w? What is the highest-weight derivation
Context-Free Parsing: CKY & Earley Algorithms and Probabilistic Parsing
 Context-Free Parsing: CKY & Earley Algorithms and Probabilistic Parsing Natural Language Processing CS 4120/6120 Spring 2017 Northeastern University David Smith with some slides from Jason Eisner & Andrew
Context-Free Parsing: CKY & Earley Algorithms and Probabilistic Parsing Natural Language Processing CS 4120/6120 Spring 2017 Northeastern University David Smith with some slides from Jason Eisner & Andrew
Everything You Always Wanted to Know About Parsing
 Everything You Always Wanted to Know About Parsing Part V : LR Parsing University of Padua, Italy ESSLLI, August 2013 Introduction Parsing strategies classified by the time the associated PDA commits to
Everything You Always Wanted to Know About Parsing Part V : LR Parsing University of Padua, Italy ESSLLI, August 2013 Introduction Parsing strategies classified by the time the associated PDA commits to
Top-Down Parsing and Intro to Bottom-Up Parsing
 Predictive Parsers op-down Parsing and Intro to Bottom-Up Parsing Lecture 7 Like recursive-descent but parser can predict which production to use By looking at the next few tokens No backtracking Predictive
Predictive Parsers op-down Parsing and Intro to Bottom-Up Parsing Lecture 7 Like recursive-descent but parser can predict which production to use By looking at the next few tokens No backtracking Predictive
Parsing. Weighted Deductive Parsing. Laura Kallmeyer. Winter 2017/18. Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf 1 / 26
 Parsing Weighted Deductive Parsing Laura Kallmeyer Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf Winter 2017/18 1 / 26 Table of contents 1 Idea 2 Algorithm 3 CYK Example 4 Parsing 5 Left Corner Example 2 / 26
Parsing Weighted Deductive Parsing Laura Kallmeyer Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf Winter 2017/18 1 / 26 Table of contents 1 Idea 2 Algorithm 3 CYK Example 4 Parsing 5 Left Corner Example 2 / 26
Pushdown Automata (2015/11/23)
 Chapter 6 Pushdown Automata (2015/11/23) Sagrada Familia, Barcelona, Spain Outline 6.0 Introduction 6.1 Definition of PDA 6.2 The Language of a PDA 6.3 Euivalence of PDA s and CFG s 6.4 Deterministic PDA
Chapter 6 Pushdown Automata (2015/11/23) Sagrada Familia, Barcelona, Spain Outline 6.0 Introduction 6.1 Definition of PDA 6.2 The Language of a PDA 6.3 Euivalence of PDA s and CFG s 6.4 Deterministic PDA
Parsing with Context-Free Grammars
 Parsing with Context-Free Grammars CS 585, Fall 2017 Introduction to Natural Language Processing http://people.cs.umass.edu/~brenocon/inlp2017 Brendan O Connor College of Information and Computer Sciences
Parsing with Context-Free Grammars CS 585, Fall 2017 Introduction to Natural Language Processing http://people.cs.umass.edu/~brenocon/inlp2017 Brendan O Connor College of Information and Computer Sciences
Parsing. Unger s Parser. Laura Kallmeyer. Winter 2016/17. Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf 1 / 21
 Parsing Unger s Parser Laura Kallmeyer Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf Winter 2016/17 1 / 21 Table of contents 1 Introduction 2 The Parser 3 An Example 4 Optimizations 5 Conclusion 2 / 21 Introduction
Parsing Unger s Parser Laura Kallmeyer Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf Winter 2016/17 1 / 21 Table of contents 1 Introduction 2 The Parser 3 An Example 4 Optimizations 5 Conclusion 2 / 21 Introduction
Probabilistic Context-free Grammars
 Probabilistic Context-free Grammars Computational Linguistics Alexander Koller 24 November 2017 The CKY Recognizer S NP VP NP Det N VP V NP V ate NP John Det a N sandwich i = 1 2 3 4 k = 2 3 4 5 S NP John
Probabilistic Context-free Grammars Computational Linguistics Alexander Koller 24 November 2017 The CKY Recognizer S NP VP NP Det N VP V NP V ate NP John Det a N sandwich i = 1 2 3 4 k = 2 3 4 5 S NP John
LECTURER: BURCU CAN Spring
 LECTURER: BURCU CAN 2017-2018 Spring Regular Language Hidden Markov Model (HMM) Context Free Language Context Sensitive Language Probabilistic Context Free Grammar (PCFG) Unrestricted Language PCFGs can
LECTURER: BURCU CAN 2017-2018 Spring Regular Language Hidden Markov Model (HMM) Context Free Language Context Sensitive Language Probabilistic Context Free Grammar (PCFG) Unrestricted Language PCFGs can
Parsing. Based on presentations from Chris Manning s course on Statistical Parsing (Stanford)
 Parsing Based on presentations from Chris Manning s course on Statistical Parsing (Stanford) S N VP V NP D N John hit the ball Levels of analysis Level Morphology/Lexical POS (morpho-synactic), WSD Elements
Parsing Based on presentations from Chris Manning s course on Statistical Parsing (Stanford) S N VP V NP D N John hit the ball Levels of analysis Level Morphology/Lexical POS (morpho-synactic), WSD Elements
Probabilistic Context-Free Grammars. Michael Collins, Columbia University
 Probabilistic Context-Free Grammars Michael Collins, Columbia University Overview Probabilistic Context-Free Grammars (PCFGs) The CKY Algorithm for parsing with PCFGs A Probabilistic Context-Free Grammar
Probabilistic Context-Free Grammars Michael Collins, Columbia University Overview Probabilistic Context-Free Grammars (PCFGs) The CKY Algorithm for parsing with PCFGs A Probabilistic Context-Free Grammar
Pushdown Automata (Pre Lecture)
 Pushdown Automata (Pre Lecture) Dr. Neil T. Dantam CSCI-561, Colorado School of Mines Fall 2017 Dantam (Mines CSCI-561) Pushdown Automata (Pre Lecture) Fall 2017 1 / 41 Outline Pushdown Automata Pushdown
Pushdown Automata (Pre Lecture) Dr. Neil T. Dantam CSCI-561, Colorado School of Mines Fall 2017 Dantam (Mines CSCI-561) Pushdown Automata (Pre Lecture) Fall 2017 1 / 41 Outline Pushdown Automata Pushdown
Probabilistic Context Free Grammars
 1 Defining PCFGs A PCFG G consists of Probabilistic Context Free Grammars 1. A set of terminals: {w k }, k = 1..., V 2. A set of non terminals: { i }, i = 1..., n 3. A designated Start symbol: 1 4. A set
1 Defining PCFGs A PCFG G consists of Probabilistic Context Free Grammars 1. A set of terminals: {w k }, k = 1..., V 2. A set of non terminals: { i }, i = 1..., n 3. A designated Start symbol: 1 4. A set
Section 1 (closed-book) Total points 30
 CS 454 Theory of Computation Fall 2011 Section 1 (closed-book) Total points 30 1. Which of the following are true? (a) a PDA can always be converted to an equivalent PDA that at each step pops or pushes
CS 454 Theory of Computation Fall 2011 Section 1 (closed-book) Total points 30 1. Which of the following are true? (a) a PDA can always be converted to an equivalent PDA that at each step pops or pushes
CPS 220 Theory of Computation Pushdown Automata (PDA)
 CPS 220 Theory of Computation Pushdown Automata (PDA) Nondeterministic Finite Automaton with some extra memory Memory is called the stack, accessed in a very restricted way: in a First-In First-Out fashion
CPS 220 Theory of Computation Pushdown Automata (PDA) Nondeterministic Finite Automaton with some extra memory Memory is called the stack, accessed in a very restricted way: in a First-In First-Out fashion
Context-Free Parsing: CKY & Earley Algorithms and Probabilistic Parsing
 Context-Free Parsing: CKY & Earley Algorithms and Probabilistic Parsing Natural Language Processing! CS 6120 Spring 2014! Northeastern University!! David Smith! with some slides from Jason Eisner & Andrew
Context-Free Parsing: CKY & Earley Algorithms and Probabilistic Parsing Natural Language Processing! CS 6120 Spring 2014! Northeastern University!! David Smith! with some slides from Jason Eisner & Andrew
An Efficient Context-Free Parsing Algorithm. Speakers: Morad Ankri Yaniv Elia
 An Efficient Context-Free Parsing Algorithm Speakers: Morad Ankri Yaniv Elia Yaniv: Introduction Terminology Informal Explanation The Recognizer Morad: Example Time and Space Bounds Empirical results Practical
An Efficient Context-Free Parsing Algorithm Speakers: Morad Ankri Yaniv Elia Yaniv: Introduction Terminology Informal Explanation The Recognizer Morad: Example Time and Space Bounds Empirical results Practical
Prof. Mohamed Hamada Software Engineering Lab. The University of Aizu Japan
 Language Processing Systems Prof. Mohamed Hamada Software Engineering La. The University of izu Japan Syntax nalysis (Parsing) 1. Uses Regular Expressions to define tokens 2. Uses Finite utomata to recognize
Language Processing Systems Prof. Mohamed Hamada Software Engineering La. The University of izu Japan Syntax nalysis (Parsing) 1. Uses Regular Expressions to define tokens 2. Uses Finite utomata to recognize
Einführung in die Computerlinguistik
 Einführung in die Computerlinguistik Context-Free Grammars (CFG) Laura Kallmeyer Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf Summer 2016 1 / 22 CFG (1) Example: Grammar G telescope : Productions: S NP VP NP
Einführung in die Computerlinguistik Context-Free Grammars (CFG) Laura Kallmeyer Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf Summer 2016 1 / 22 CFG (1) Example: Grammar G telescope : Productions: S NP VP NP
MA/CSSE 474 Theory of Computation
 MA/CSSE 474 Theory of Computation CFL Hierarchy CFL Decision Problems Your Questions? Previous class days' material Reading Assignments HW 12 or 13 problems Anything else I have included some slides online
MA/CSSE 474 Theory of Computation CFL Hierarchy CFL Decision Problems Your Questions? Previous class days' material Reading Assignments HW 12 or 13 problems Anything else I have included some slides online
Probabilistic Context Free Grammars. Many slides from Michael Collins and Chris Manning
 Probabilistic Context Free Grammars Many slides from Michael Collins and Chris Manning Overview I Probabilistic Context-Free Grammars (PCFGs) I The CKY Algorithm for parsing with PCFGs A Probabilistic
Probabilistic Context Free Grammars Many slides from Michael Collins and Chris Manning Overview I Probabilistic Context-Free Grammars (PCFGs) I The CKY Algorithm for parsing with PCFGs A Probabilistic
Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 9: Regular Languages Wrap-Up, Context-Free Grammars
 Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 9: Regular Languages Wrap-Up, Context-Free Grammars Salil Vadhan October 2, 2012 Reading: Sipser, 2.1 (except Chomsky Normal Form). Algorithmic questions about regular
Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 9: Regular Languages Wrap-Up, Context-Free Grammars Salil Vadhan October 2, 2012 Reading: Sipser, 2.1 (except Chomsky Normal Form). Algorithmic questions about regular
Parsing. Unger s Parser. Introduction (1) Unger s parser [Grune and Jacobs, 2008] is a CFG parser that is
![Parsing. Unger s Parser. Introduction (1) Unger s parser [Grune and Jacobs, 2008] is a CFG parser that is Parsing. Unger s Parser. Introduction (1) Unger s parser [Grune and Jacobs, 2008] is a CFG parser that is](/thumbs/88/115486668.jpg) Introduction (1) Unger s parser [Grune and Jacobs, 2008] is a CFG parser that is Unger s Parser Laura Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf Wintersemester 2012/2013 a top-down parser: we start with S and
Introduction (1) Unger s parser [Grune and Jacobs, 2008] is a CFG parser that is Unger s Parser Laura Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf Wintersemester 2012/2013 a top-down parser: we start with S and
Introduction to Theory of Computing
 CSCI 2670, Fall 2012 Introduction to Theory of Computing Department of Computer Science University of Georgia Athens, GA 30602 Instructor: Liming Cai www.cs.uga.edu/ cai 0 Lecture Note 3 Context-Free Languages
CSCI 2670, Fall 2012 Introduction to Theory of Computing Department of Computer Science University of Georgia Athens, GA 30602 Instructor: Liming Cai www.cs.uga.edu/ cai 0 Lecture Note 3 Context-Free Languages
Natural Language Processing CS Lecture 06. Razvan C. Bunescu School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
 Natural Language Processing CS 6840 Lecture 06 Razvan C. Bunescu School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science bunescu@ohio.edu Statistical Parsing Define a probabilistic model of syntax P(T S):
Natural Language Processing CS 6840 Lecture 06 Razvan C. Bunescu School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science bunescu@ohio.edu Statistical Parsing Define a probabilistic model of syntax P(T S):
Syntax-Based Decoding
 Syntax-Based Decoding Philipp Koehn 9 November 2017 1 syntax-based models Synchronous Context Free Grammar Rules 2 Nonterminal rules NP DET 1 2 JJ 3 DET 1 JJ 3 2 Terminal rules N maison house NP la maison
Syntax-Based Decoding Philipp Koehn 9 November 2017 1 syntax-based models Synchronous Context Free Grammar Rules 2 Nonterminal rules NP DET 1 2 JJ 3 DET 1 JJ 3 2 Terminal rules N maison house NP la maison
Introduction to Bottom-Up Parsing
 Introduction to Bottom-Up Parsing Outline Review LL parsing Shift-reduce parsing The LR parsing algorithm Constructing LR parsing tables 2 Top-Down Parsing: Review Top-down parsing expands a parse tree
Introduction to Bottom-Up Parsing Outline Review LL parsing Shift-reduce parsing The LR parsing algorithm Constructing LR parsing tables 2 Top-Down Parsing: Review Top-down parsing expands a parse tree
Introduction to Bottom-Up Parsing
 Introduction to Bottom-Up Parsing Outline Review LL parsing Shift-reduce parsing The LR parsing algorithm Constructing LR parsing tables Compiler Design 1 (2011) 2 Top-Down Parsing: Review Top-down parsing
Introduction to Bottom-Up Parsing Outline Review LL parsing Shift-reduce parsing The LR parsing algorithm Constructing LR parsing tables Compiler Design 1 (2011) 2 Top-Down Parsing: Review Top-down parsing
CS Pushdown Automata
 Chap. 6 Pushdown Automata 6.1 Definition of Pushdown Automata Example 6.2 L ww R = {ww R w (0+1) * } Palindromes over {0, 1}. A cfg P 0 1 0P0 1P1. Consider a FA with a stack(= a Pushdown automaton; PDA).
Chap. 6 Pushdown Automata 6.1 Definition of Pushdown Automata Example 6.2 L ww R = {ww R w (0+1) * } Palindromes over {0, 1}. A cfg P 0 1 0P0 1P1. Consider a FA with a stack(= a Pushdown automaton; PDA).
Attendee information. Seven Lectures on Statistical Parsing. Phrase structure grammars = context-free grammars. Assessment.
 even Lectures on tatistical Parsing Christopher Manning LA Linguistic Institute 7 LA Lecture Attendee information Please put on a piece of paper: ame: Affiliation: tatus (undergrad, grad, industry, prof,
even Lectures on tatistical Parsing Christopher Manning LA Linguistic Institute 7 LA Lecture Attendee information Please put on a piece of paper: ame: Affiliation: tatus (undergrad, grad, industry, prof,
Introduction to Bottom-Up Parsing
 Outline Introduction to Bottom-Up Parsing Review LL parsing Shift-reduce parsing he LR parsing algorithm Constructing LR parsing tables 2 op-down Parsing: Review op-down parsing expands a parse tree from
Outline Introduction to Bottom-Up Parsing Review LL parsing Shift-reduce parsing he LR parsing algorithm Constructing LR parsing tables 2 op-down Parsing: Review op-down parsing expands a parse tree from
Administrivia. Test I during class on 10 March. Bottom-Up Parsing. Lecture An Introductory Example
 Administrivia Test I during class on 10 March. Bottom-Up Parsing Lecture 11-12 From slides by G. Necula & R. Bodik) 2/20/08 Prof. Hilfinger CS14 Lecture 11 1 2/20/08 Prof. Hilfinger CS14 Lecture 11 2 Bottom-Up
Administrivia Test I during class on 10 March. Bottom-Up Parsing Lecture 11-12 From slides by G. Necula & R. Bodik) 2/20/08 Prof. Hilfinger CS14 Lecture 11 1 2/20/08 Prof. Hilfinger CS14 Lecture 11 2 Bottom-Up
CS481F01 Prelim 2 Solutions
 CS481F01 Prelim 2 Solutions A. Demers 7 Nov 2001 1 (30 pts = 4 pts each part + 2 free points). For this question we use the following notation: x y means x is a prefix of y m k n means m n k For each of
CS481F01 Prelim 2 Solutions A. Demers 7 Nov 2001 1 (30 pts = 4 pts each part + 2 free points). For this question we use the following notation: x y means x is a prefix of y m k n means m n k For each of
CSCI 1010 Models of Computa3on. Lecture 17 Parsing Context-Free Languages
 CSCI 1010 Models of Computa3on Lecture 17 Parsing Context-Free Languages Overview BoCom-up parsing of CFLs. BoCom-up parsing via the CKY algorithm An O(n 3 ) algorithm John E. Savage CSCI 1010 Lect 17
CSCI 1010 Models of Computa3on Lecture 17 Parsing Context-Free Languages Overview BoCom-up parsing of CFLs. BoCom-up parsing via the CKY algorithm An O(n 3 ) algorithm John E. Savage CSCI 1010 Lect 17
Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 10: CFLs: PDAs, Closure Properties, and Non-CFLs
 Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 10: CFLs: PDAs, Closure Properties, and Non-CFLs Harry Lewis October 8, 2013 Reading: Sipser, pp. 119-128. Pushdown Automata (review) Pushdown Automata = Finite automaton
Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 10: CFLs: PDAs, Closure Properties, and Non-CFLs Harry Lewis October 8, 2013 Reading: Sipser, pp. 119-128. Pushdown Automata (review) Pushdown Automata = Finite automaton
Remembering subresults (Part I): Well-formed substring tables
 Remembering subresults (Part I): Well-formed substring tables Detmar Meurers: Intro to Computational Linguistics I OSU, LING 684.01, 1. February 2005 Problem: Inefficiency of recomputing subresults Two
Remembering subresults (Part I): Well-formed substring tables Detmar Meurers: Intro to Computational Linguistics I OSU, LING 684.01, 1. February 2005 Problem: Inefficiency of recomputing subresults Two
Introduction to Natural Language Processing
 Introduction to Natural Language Processing PARSING: Earley, Bottom-Up Chart Parsing Jean-Cédric Chappelier Jean-Cedric.Chappelier@epfl.ch Artificial Intelligence Laboratory 1/20 Objectives of this lecture
Introduction to Natural Language Processing PARSING: Earley, Bottom-Up Chart Parsing Jean-Cédric Chappelier Jean-Cedric.Chappelier@epfl.ch Artificial Intelligence Laboratory 1/20 Objectives of this lecture
Context-Free Languages (Pre Lecture)
 Context-Free Languages (Pre Lecture) Dr. Neil T. Dantam CSCI-561, Colorado School of Mines Fall 2017 Dantam (Mines CSCI-561) Context-Free Languages (Pre Lecture) Fall 2017 1 / 34 Outline Pumping Lemma
Context-Free Languages (Pre Lecture) Dr. Neil T. Dantam CSCI-561, Colorado School of Mines Fall 2017 Dantam (Mines CSCI-561) Context-Free Languages (Pre Lecture) Fall 2017 1 / 34 Outline Pumping Lemma
Chomsky Normal Form for Context-Free Gramars
 Chomsky Normal Form for Context-Free Gramars Deepak D Souza Department of Computer Science and Automation Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore. 17 September 2014 Outline 1 CNF 2 Converting to CNF 3 Correctness
Chomsky Normal Form for Context-Free Gramars Deepak D Souza Department of Computer Science and Automation Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore. 17 September 2014 Outline 1 CNF 2 Converting to CNF 3 Correctness
Announcements. H6 posted 2 days ago (due on Tue) Midterm went well: Very nice curve. Average 65% High score 74/75
 Announcements H6 posted 2 days ago (due on Tue) Mterm went well: Average 65% High score 74/75 Very nice curve 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 1 6 11 16 21 26 31 36 41 46 51 56 61 66 71 76 81 86 91 96 101 106
Announcements H6 posted 2 days ago (due on Tue) Mterm went well: Average 65% High score 74/75 Very nice curve 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 1 6 11 16 21 26 31 36 41 46 51 56 61 66 71 76 81 86 91 96 101 106
Grammars and Context Free Languages
 Grammars and Context Free Languages H. Geuvers and J. Rot Institute for Computing and Information Sciences Version: fall 2016 H. Geuvers & J. Rot Version: fall 2016 Talen en Automaten 1 / 24 Outline Grammars
Grammars and Context Free Languages H. Geuvers and J. Rot Institute for Computing and Information Sciences Version: fall 2016 H. Geuvers & J. Rot Version: fall 2016 Talen en Automaten 1 / 24 Outline Grammars
A parsing technique for TRG languages
 A parsing technique for TRG languages Daniele Paolo Scarpazza Politecnico di Milano October 15th, 2004 Daniele Paolo Scarpazza A parsing technique for TRG grammars [1]
A parsing technique for TRG languages Daniele Paolo Scarpazza Politecnico di Milano October 15th, 2004 Daniele Paolo Scarpazza A parsing technique for TRG grammars [1]
Plan for 2 nd half. Just when you thought it was safe. Just when you thought it was safe. Theory Hall of Fame. Chomsky Normal Form
 Plan for 2 nd half Pumping Lemma for CFLs The Return of the Pumping Lemma Just when you thought it was safe Return of the Pumping Lemma Recall: With Regular Languages The Pumping Lemma showed that if a
Plan for 2 nd half Pumping Lemma for CFLs The Return of the Pumping Lemma Just when you thought it was safe Return of the Pumping Lemma Recall: With Regular Languages The Pumping Lemma showed that if a
Introduction to Bottom-Up Parsing
 Outline Introduction to Bottom-Up Parsing Review LL parsing Shift-reduce parsing he LR parsing algorithm Constructing LR parsing tables Compiler Design 1 (2011) 2 op-down Parsing: Review op-down parsing
Outline Introduction to Bottom-Up Parsing Review LL parsing Shift-reduce parsing he LR parsing algorithm Constructing LR parsing tables Compiler Design 1 (2011) 2 op-down Parsing: Review op-down parsing
Chapter 14 (Partially) Unsupervised Parsing
 Chapter 14 (Partially) Unsupervised Parsing The linguistically-motivated tree transformations we discussed previously are very effective, but when we move to a new language, we may have to come up with
Chapter 14 (Partially) Unsupervised Parsing The linguistically-motivated tree transformations we discussed previously are very effective, but when we move to a new language, we may have to come up with
Decoding and Inference with Syntactic Translation Models
 Decoding and Inference with Syntactic Translation Models March 5, 2013 CFGs S NP VP VP NP V V NP NP CFGs S NP VP S VP NP V V NP NP CFGs S NP VP S VP NP V NP VP V NP NP CFGs S NP VP S VP NP V NP VP V NP
Decoding and Inference with Syntactic Translation Models March 5, 2013 CFGs S NP VP VP NP V V NP NP CFGs S NP VP S VP NP V V NP NP CFGs S NP VP S VP NP V NP VP V NP NP CFGs S NP VP S VP NP V NP VP V NP
Accept or reject. Stack
 Pushdown Automata CS351 Just as a DFA was equivalent to a regular expression, we have a similar analogy for the context-free grammar. A pushdown automata (PDA) is equivalent in power to contextfree grammars.
Pushdown Automata CS351 Just as a DFA was equivalent to a regular expression, we have a similar analogy for the context-free grammar. A pushdown automata (PDA) is equivalent in power to contextfree grammars.
Grammars and Context Free Languages
 Grammars and Context Free Languages H. Geuvers and A. Kissinger Institute for Computing and Information Sciences Version: fall 2015 H. Geuvers & A. Kissinger Version: fall 2015 Talen en Automaten 1 / 23
Grammars and Context Free Languages H. Geuvers and A. Kissinger Institute for Computing and Information Sciences Version: fall 2015 H. Geuvers & A. Kissinger Version: fall 2015 Talen en Automaten 1 / 23
THEORY OF COMPILATION
 Lecture 04 Syntax analysis: top-down and bottom-up parsing THEORY OF COMPILATION EranYahav 1 You are here Compiler txt Source Lexical Analysis Syntax Analysis Parsing Semantic Analysis Inter. Rep. (IR)
Lecture 04 Syntax analysis: top-down and bottom-up parsing THEORY OF COMPILATION EranYahav 1 You are here Compiler txt Source Lexical Analysis Syntax Analysis Parsing Semantic Analysis Inter. Rep. (IR)
Context-Free Parsing: CKY & Earley Algorithms and Probabilistic Parsing
 Context-Free Parsing: CKY & Earley Algorithms and Probabilistic Parsing Natural Language Processing CS 4120/6120 Spring 2016 Northeastern University David Smith with some slides from Jason Eisner & Andrew
Context-Free Parsing: CKY & Earley Algorithms and Probabilistic Parsing Natural Language Processing CS 4120/6120 Spring 2016 Northeastern University David Smith with some slides from Jason Eisner & Andrew
Shift-Reduce parser E + (E + (E) E [a-z] In each stage, we shift a symbol from the input to the stack, or reduce according to one of the rules.
![Shift-Reduce parser E + (E + (E) E [a-z] In each stage, we shift a symbol from the input to the stack, or reduce according to one of the rules. Shift-Reduce parser E + (E + (E) E [a-z] In each stage, we shift a symbol from the input to the stack, or reduce according to one of the rules.](/thumbs/83/87889808.jpg) Bottom-up Parsing Bottom-up Parsing Until now we started with the starting nonterminal S and tried to derive the input from it. In a way, this isn t the natural thing to do. It s much more logical to start
Bottom-up Parsing Bottom-up Parsing Until now we started with the starting nonterminal S and tried to derive the input from it. In a way, this isn t the natural thing to do. It s much more logical to start
Compiler Principles, PS4
 Top-Down Parsing Compiler Principles, PS4 Parsing problem definition: The general parsing problem is - given set of rules and input stream (in our case scheme token input stream), how to find the parse
Top-Down Parsing Compiler Principles, PS4 Parsing problem definition: The general parsing problem is - given set of rules and input stream (in our case scheme token input stream), how to find the parse
CS626: NLP, Speech and the Web. Pushpak Bhattacharyya CSE Dept., IIT Bombay Lecture 14: Parsing Algorithms 30 th August, 2012
 CS626: NLP, Speech and the Web Pushpak Bhattacharyya CSE Dept., IIT Bombay Lecture 14: Parsing Algorithms 30 th August, 2012 Parsing Problem Semantics Part of Speech Tagging NLP Trinity Morph Analysis
CS626: NLP, Speech and the Web Pushpak Bhattacharyya CSE Dept., IIT Bombay Lecture 14: Parsing Algorithms 30 th August, 2012 Parsing Problem Semantics Part of Speech Tagging NLP Trinity Morph Analysis
CISC4090: Theory of Computation
 CISC4090: Theory of Computation Chapter 2 Context-Free Languages Courtesy of Prof. Arthur G. Werschulz Fordham University Department of Computer and Information Sciences Spring, 2014 Overview In Chapter
CISC4090: Theory of Computation Chapter 2 Context-Free Languages Courtesy of Prof. Arthur G. Werschulz Fordham University Department of Computer and Information Sciences Spring, 2014 Overview In Chapter
Advanced Natural Language Processing Syntactic Parsing
 Advanced Natural Language Processing Syntactic Parsing Alicia Ageno ageno@cs.upc.edu Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya NLP statistical parsing 1 Parsing Review Statistical Parsing SCFG Inside Algorithm
Advanced Natural Language Processing Syntactic Parsing Alicia Ageno ageno@cs.upc.edu Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya NLP statistical parsing 1 Parsing Review Statistical Parsing SCFG Inside Algorithm
Probabilistic Context Free Grammars. Many slides from Michael Collins
 Probabilistic Context Free Grammars Many slides from Michael Collins Overview I Probabilistic Context-Free Grammars (PCFGs) I The CKY Algorithm for parsing with PCFGs A Probabilistic Context-Free Grammar
Probabilistic Context Free Grammars Many slides from Michael Collins Overview I Probabilistic Context-Free Grammars (PCFGs) I The CKY Algorithm for parsing with PCFGs A Probabilistic Context-Free Grammar
Chapter 4: Context-Free Grammars
 Chapter 4: Context-Free Grammars 4.1 Basics of Context-Free Grammars Definition A context-free grammars, or CFG, G is specified by a quadruple (N, Σ, P, S), where N is the nonterminal or variable alphabet;
Chapter 4: Context-Free Grammars 4.1 Basics of Context-Free Grammars Definition A context-free grammars, or CFG, G is specified by a quadruple (N, Σ, P, S), where N is the nonterminal or variable alphabet;
Chapter 1. Formal Definition and View. Lecture Formal Pushdown Automata on the 28th April 2009
 Chapter 1 Formal and View Lecture on the 28th April 2009 Formal of PA Faculty of Information Technology Brno University of Technology 1.1 Aim of the Lecture 1 Define pushdown automaton in a formal way
Chapter 1 Formal and View Lecture on the 28th April 2009 Formal of PA Faculty of Information Technology Brno University of Technology 1.1 Aim of the Lecture 1 Define pushdown automaton in a formal way
CSE302: Compiler Design
 CSE302: Compiler Design Instructor: Dr. Liang Cheng Department of Computer Science and Engineering P.C. Rossin College of Engineering & Applied Science Lehigh University February 27, 2007 Outline Recap
CSE302: Compiler Design Instructor: Dr. Liang Cheng Department of Computer Science and Engineering P.C. Rossin College of Engineering & Applied Science Lehigh University February 27, 2007 Outline Recap
Computability Theory
 CS:4330 Theory of Computation Spring 2018 Computability Theory Decidable Problems of CFLs and beyond Haniel Barbosa Readings for this lecture Chapter 4 of [Sipser 1996], 3rd edition. Section 4.1. Decidable
CS:4330 Theory of Computation Spring 2018 Computability Theory Decidable Problems of CFLs and beyond Haniel Barbosa Readings for this lecture Chapter 4 of [Sipser 1996], 3rd edition. Section 4.1. Decidable
Syntax Analysis (Part 2)
 Syntax Analysis (Part 2) Martin Sulzmann Martin Sulzmann Syntax Analysis (Part 2) 1 / 42 Bottom-Up Parsing Idea Build right-most derivation. Scan input and seek for matching right hand sides. Terminology
Syntax Analysis (Part 2) Martin Sulzmann Martin Sulzmann Syntax Analysis (Part 2) 1 / 42 Bottom-Up Parsing Idea Build right-most derivation. Scan input and seek for matching right hand sides. Terminology
5 Context-Free Languages
 CA320: COMPUTABILITY AND COMPLEXITY 1 5 Context-Free Languages 5.1 Context-Free Grammars Context-Free Grammars Context-free languages are specified with a context-free grammar (CFG). Formally, a CFG G
CA320: COMPUTABILITY AND COMPLEXITY 1 5 Context-Free Languages 5.1 Context-Free Grammars Context-Free Grammars Context-free languages are specified with a context-free grammar (CFG). Formally, a CFG G
Definition: A grammar G = (V, T, P,S) is a context free grammar (cfg) if all productions in P have the form A x where
 Recitation 11 Notes Context Free Grammars Definition: A grammar G = (V, T, P,S) is a context free grammar (cfg) if all productions in P have the form A x A V, and x (V T)*. Examples Problem 1. Given the
Recitation 11 Notes Context Free Grammars Definition: A grammar G = (V, T, P,S) is a context free grammar (cfg) if all productions in P have the form A x A V, and x (V T)*. Examples Problem 1. Given the
CSCI Compiler Construction
 CSCI 742 - Compiler Construction Lecture 12 Cocke-Younger-Kasami (CYK) Algorithm Instructor: Hossein Hojjat February 20, 2017 Recap: Chomsky Normal Form (CNF) A CFG is in Chomsky Normal Form if each rule
CSCI 742 - Compiler Construction Lecture 12 Cocke-Younger-Kasami (CYK) Algorithm Instructor: Hossein Hojjat February 20, 2017 Recap: Chomsky Normal Form (CNF) A CFG is in Chomsky Normal Form if each rule
Statistical Methods for NLP
 Statistical Methods for NLP Stochastic Grammars Joakim Nivre Uppsala University Department of Linguistics and Philology joakim.nivre@lingfil.uu.se Statistical Methods for NLP 1(22) Structured Classification
Statistical Methods for NLP Stochastic Grammars Joakim Nivre Uppsala University Department of Linguistics and Philology joakim.nivre@lingfil.uu.se Statistical Methods for NLP 1(22) Structured Classification
Computational Models - Lecture 4
 Computational Models - Lecture 4 Regular languages: The Myhill-Nerode Theorem Context-free Grammars Chomsky Normal Form Pumping Lemma for context free languages Non context-free languages: Examples Push
Computational Models - Lecture 4 Regular languages: The Myhill-Nerode Theorem Context-free Grammars Chomsky Normal Form Pumping Lemma for context free languages Non context-free languages: Examples Push
CS460/626 : Natural Language
 CS460/626 : Natural Language Processing/Speech, NLP and the Web (Lecture 23, 24 Parsing Algorithms; Parsing in case of Ambiguity; Probabilistic Parsing) Pushpak Bhattacharyya CSE Dept., IIT Bombay 8 th,
CS460/626 : Natural Language Processing/Speech, NLP and the Web (Lecture 23, 24 Parsing Algorithms; Parsing in case of Ambiguity; Probabilistic Parsing) Pushpak Bhattacharyya CSE Dept., IIT Bombay 8 th,
Computational Models - Lecture 5 1
 Computational Models - Lecture 5 1 Handout Mode Iftach Haitner. Tel Aviv University. November 28, 2016 1 Based on frames by Benny Chor, Tel Aviv University, modifying frames by Maurice Herlihy, Brown University.
Computational Models - Lecture 5 1 Handout Mode Iftach Haitner. Tel Aviv University. November 28, 2016 1 Based on frames by Benny Chor, Tel Aviv University, modifying frames by Maurice Herlihy, Brown University.
CS5371 Theory of Computation. Lecture 7: Automata Theory V (CFG, CFL, CNF)
 CS5371 Theory of Computation Lecture 7: Automata Theory V (CFG, CFL, CNF) Announcement Homework 2 will be given soon (before Tue) Due date: Oct 31 (Tue), before class Midterm: Nov 3, (Fri), first hour
CS5371 Theory of Computation Lecture 7: Automata Theory V (CFG, CFL, CNF) Announcement Homework 2 will be given soon (before Tue) Due date: Oct 31 (Tue), before class Midterm: Nov 3, (Fri), first hour
Computing if a token can follow
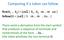 Computing if a token can follow first(b 1... B p ) = {a B 1...B p... aw } follow(x) = {a S......Xa... } There exists a derivation from the start symbol that produces a sequence of terminals and nonterminals
Computing if a token can follow first(b 1... B p ) = {a B 1...B p... aw } follow(x) = {a S......Xa... } There exists a derivation from the start symbol that produces a sequence of terminals and nonterminals
CS311 Computational Structures More about PDAs & Context-Free Languages. Lecture 9. Andrew P. Black Andrew Tolmach
 CS311 Computational Structures More about PDAs & Context-Free Languages Lecture 9 Andrew P. Black Andrew Tolmach 1 Three important results 1. Any CFG can be simulated by a PDA 2. Any PDA can be simulated
CS311 Computational Structures More about PDAs & Context-Free Languages Lecture 9 Andrew P. Black Andrew Tolmach 1 Three important results 1. Any CFG can be simulated by a PDA 2. Any PDA can be simulated
Lecture 11 Sections 4.5, 4.7. Wed, Feb 18, 2009
 The s s The s Lecture 11 Sections 4.5, 4.7 Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Feb 18, 2009 Outline The s s 1 s 2 3 4 5 6 The LR(0) Parsing s The s s There are two tables that we will construct. The action table
The s s The s Lecture 11 Sections 4.5, 4.7 Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Feb 18, 2009 Outline The s s 1 s 2 3 4 5 6 The LR(0) Parsing s The s s There are two tables that we will construct. The action table
Recitation 4: Converting Grammars to Chomsky Normal Form, Simulation of Context Free Languages with Push-Down Automata, Semirings
 Recitation 4: Converting Grammars to Chomsky Normal Form, Simulation of Context Free Languages with Push-Down Automata, Semirings 11-711: Algorithms for NLP October 10, 2014 Conversion to CNF Example grammar
Recitation 4: Converting Grammars to Chomsky Normal Form, Simulation of Context Free Languages with Push-Down Automata, Semirings 11-711: Algorithms for NLP October 10, 2014 Conversion to CNF Example grammar
Natural Language Processing
 SFU NatLangLab Natural Language Processing Anoop Sarkar anoopsarkar.github.io/nlp-class Simon Fraser University September 27, 2018 0 Natural Language Processing Anoop Sarkar anoopsarkar.github.io/nlp-class
SFU NatLangLab Natural Language Processing Anoop Sarkar anoopsarkar.github.io/nlp-class Simon Fraser University September 27, 2018 0 Natural Language Processing Anoop Sarkar anoopsarkar.github.io/nlp-class
Finite Automata and Formal Languages TMV026/DIT321 LP Useful, Useless, Generating and Reachable Symbols
 Finite Automata and Formal Languages TMV026/DIT321 LP4 2012 Lecture 13 Ana Bove May 7th 2012 Overview of today s lecture: Normal Forms for Context-Free Languages Pumping Lemma for Context-Free Languages
Finite Automata and Formal Languages TMV026/DIT321 LP4 2012 Lecture 13 Ana Bove May 7th 2012 Overview of today s lecture: Normal Forms for Context-Free Languages Pumping Lemma for Context-Free Languages
Languages. Languages. An Example Grammar. Grammars. Suppose we have an alphabet V. Then we can write:
 Languages A language is a set (usually infinite) of strings, also known as sentences Each string consists of a sequence of symbols taken from some alphabet An alphabet, V, is a finite set of symbols, e.g.
Languages A language is a set (usually infinite) of strings, also known as sentences Each string consists of a sequence of symbols taken from some alphabet An alphabet, V, is a finite set of symbols, e.g.
Even More on Dynamic Programming
 Algorithms & Models of Computation CS/ECE 374, Fall 2017 Even More on Dynamic Programming Lecture 15 Thursday, October 19, 2017 Sariel Har-Peled (UIUC) CS374 1 Fall 2017 1 / 26 Part I Longest Common Subsequence
Algorithms & Models of Computation CS/ECE 374, Fall 2017 Even More on Dynamic Programming Lecture 15 Thursday, October 19, 2017 Sariel Har-Peled (UIUC) CS374 1 Fall 2017 1 / 26 Part I Longest Common Subsequence
h>p://lara.epfl.ch Compiler Construc/on 2011 CYK Algorithm and Chomsky Normal Form
 h>p://lara.epfl.ch Compiler Construc/on 2011 CYK Algorithm and Chomsky Normal Form S à N ( N S) N ( N ) S S Parsing an Input N S) à S N ) N ( à ( N ) à ) 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 ambiguity N ( N ( N ) N ( N ) N (
h>p://lara.epfl.ch Compiler Construc/on 2011 CYK Algorithm and Chomsky Normal Form S à N ( N S) N ( N ) S S Parsing an Input N S) à S N ) N ( à ( N ) à ) 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 ambiguity N ( N ( N ) N ( N ) N (
CPS 220 Theory of Computation
 CPS 22 Theory of Computation Review - Regular Languages RL - a simple class of languages that can be represented in two ways: 1 Machine description: Finite Automata are machines with a finite number of
CPS 22 Theory of Computation Review - Regular Languages RL - a simple class of languages that can be represented in two ways: 1 Machine description: Finite Automata are machines with a finite number of
CISC 4090 Theory of Computation
 CISC 4090 Theory of Computation Context-Free Languages and Push Down Automata Professor Daniel Leeds dleeds@fordham.edu JMH 332 Languages: Regular and Beyond Regular: Captured by Regular Operations a b
CISC 4090 Theory of Computation Context-Free Languages and Push Down Automata Professor Daniel Leeds dleeds@fordham.edu JMH 332 Languages: Regular and Beyond Regular: Captured by Regular Operations a b
Syntax Analysis Part I
 1 Syntax Analysis Part I Chapter 4 COP5621 Compiler Construction Copyright Robert van Engelen, Florida State University, 2007-2013 2 Position of a Parser in the Compiler Model Source Program Lexical Analyzer
1 Syntax Analysis Part I Chapter 4 COP5621 Compiler Construction Copyright Robert van Engelen, Florida State University, 2007-2013 2 Position of a Parser in the Compiler Model Source Program Lexical Analyzer
Syntactical analysis. Syntactical analysis. Syntactical analysis. Syntactical analysis
 Context-free grammars Derivations Parse Trees Left-recursive grammars Top-down parsing non-recursive predictive parsers construction of parse tables Bottom-up parsing shift/reduce parsers LR parsers GLR
Context-free grammars Derivations Parse Trees Left-recursive grammars Top-down parsing non-recursive predictive parsers construction of parse tables Bottom-up parsing shift/reduce parsers LR parsers GLR
Syntax Analysis Part I
 1 Syntax Analysis Part I Chapter 4 COP5621 Compiler Construction Copyright Robert van Engelen, Florida State University, 2007-2013 2 Position of a Parser in the Compiler Model Source Program Lexical Analyzer
1 Syntax Analysis Part I Chapter 4 COP5621 Compiler Construction Copyright Robert van Engelen, Florida State University, 2007-2013 2 Position of a Parser in the Compiler Model Source Program Lexical Analyzer
Intro to Theory of Computation
 Intro to Theory of Computation LECTURE 7 Last time: Proving a language is not regular Pushdown automata (PDAs) Today: Context-free grammars (CFG) Equivalence of CFGs and PDAs Sofya Raskhodnikova 1/31/2016
Intro to Theory of Computation LECTURE 7 Last time: Proving a language is not regular Pushdown automata (PDAs) Today: Context-free grammars (CFG) Equivalence of CFGs and PDAs Sofya Raskhodnikova 1/31/2016
MTH401A Theory of Computation. Lecture 17
 MTH401A Theory of Computation Lecture 17 Chomsky Normal Form for CFG s Chomsky Normal Form for CFG s For every context free language, L, the language L {ε} has a grammar in which every production looks
MTH401A Theory of Computation Lecture 17 Chomsky Normal Form for CFG s Chomsky Normal Form for CFG s For every context free language, L, the language L {ε} has a grammar in which every production looks
