Transactions on the Built Environment vol 22, 1996 WIT Press, ISSN
|
|
|
- Josephine Hill
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A simplified procedure for analysis of flask impact J. Marti"''', F. Martinez", F. Mayoral'' "Principia-EQE, Velazquez 94, 28006, Madrid, Spain School ofmines, Rios Rosas 21, 28003, Madrid, Spain ABSTRACT Licencing requirements, as well as reasonable engineering considerations, imply the necessity of analysing spent fuel flasks against impact events. Such analyses must generally be conducted using explicit integration procedures, large threedimensional meshes and realistic non-linear behaviour of the materials involved they must also incorporate the appropriate bolt stresses, internal pressures and thermal conditions prior to impact. This procedure implies considerable time and expense and, at some point, carrying it out becomes inevitable In spite of this inevitability, it would be very convenient to have at hand faster and cheaper procedures, able to generate some information about flask impacts without having to conduct the full analyses. The present paper proposes simplified procedures which are suitable for assessment of impacts of bare flasks against rigid planes. The procedures allow conducting immediate assessments of the impact duration, the time history of forces generated during the impact, the mean decelerations of the flask internals and the spatial extension of flask crushing. The proposed procedures are suitable, in principle, for all impact attitudes of interest: bottom drop, lid drop, side drop and corner/edge drop. They apply to flasks devoid of shock absorbers or design features intended to provide some impact limiting capacity. The paper presents some comparisons with full three dimensional calculations and experiments to support a discussion about the applicability and reliability of the simplified prediction tools proposed.
2 752 Structures Under Shock And Impact 1 INTRODUCTION The transport and storage of radioactive materials give rise to a number of potential impact problems. Most national requirements on transport flasks are based on the updated IAEA [1] guidelines. They usually demand that the flask sustain successfully all 9 m drops onto unyielding plane targets and all 1 m drops onto 15 cm square punches. All impact attitudes must be taken into account, including the possibility that design singularities (such as lifting trunions, cooling fins or other local features) be directly involved in the impact. Thermal and other conditions at impact must be the most pessimistic ones It has been mentioned that the flask must sustain "successfully" the prescribed impacts. From a conceptual viewpoint, success is usually assessed on the basis of three different concurrent criteria: a) No gross structural damage must occur; in other words, the flask must maintain its structural integrity. b) The isolation of the contents must also be preserved. This requirement can be stated either in terms of tolerances at the seals or dosage in the proximity of the flask. c) Damage to the contents must be limited and not lead to thermal, criticality or other problems. This is often replaced by establishing an upper bound on the accelerations felt at the centre of gravity of the flask. Some of the ideas in the present paper were already advanced recently by Marti [2] in a chapter dedicated to flask impact studies. However, that chapter was dedicated to the generalities of the impact problem and did not include the simplified plastic considerations proposed here. 2. ASSUMPTIONS AND METHODOLOGY Flasks are very stiff and competent structures; also, when they drop, regulations usually assign infinite rigidity to the target in an attempt to remain conservative. For the purposes of this paper, only impacts on rigid planes will be considered. A simplified treatment of any problem requires accounting for the most important governing mechanisms. From this viewpoint, it is important to subdivide flask impacts into two different categories:
3 Structures Under Shock And Impact 153 Impacts which occur essentially within the elastic regime of the materials: base drops, lid drops and face drops in cubical flasks. Impacts governed by local plastic straining: side and edge drops in cylindrical flasks, as well as corner and edge drops in cubical flasks Quasi-elastic impacts By nature, such impacts are very rigid. Since a large contact area is available from the beginning, the momentum exchange is very rapid and efficient. For simplicity, only base drops of cylindrical flasks will be discussed here, but the concepts are analogous in lid drops or, in case of cubical flasks, in any purely translational base, lid or side drop For such impacts, even in bare cask 9 m drops, very little plasticity is developed in the flask materials. The elastic impact stresses a developed upon impact would be: where p is the density of the material c is the speed of wave propagation in the material v is the impact velocity a = pcv (1) Waves transmitting this stress level (or a somewhat smaller one limited by material yield) travel at around 5 km/sec across the base thickness and along the flask walls. These waves rebound quickly from their travel across the base thickness (on the order of 0.1 msec), but take longer to return from their longitudinal travel along the flask. In a first approximation, the impact force developed can be idealized (Figure 1) as a short pulse with amplitude FI lasting f/, followed by a longer pulse of amplitude Fj lasting fe, where: FI = <%4/, where A/ is the total cross section of the flask // = 2//c, where / is the base thickness F2= cra2, where /U is the cross section of theflaskwalls h = 2L/c, where L is the total length of the flask and the remaining variables retain their former meaning. The rebound of the base plate leads to a half-cycle oscillation in its natural frequency, during which the base centre loses contact with the impacted plane. If h exceeds that half-cycle duration, the base will impact the plane a second time. Multiple base rebounds are possible in sufficiently long flasks.
4 154 Structures Under Shock And Impact FORCE F2 tl t2 Fig. 1 Idealized contact force history developed in the course of base and lid impacts The previous considerations allow conducting a quick assessment by hand of many of the main characteristics of the impact event: force time history, mean deceleration of internals and impact duration As will be seen later, this assessment is in reasonable agreement with more detailed calculations. Base drops are often noisy impacts; the fast times involved and the quasi-elastic behaviour of the materials contribute to the activation of high-frequency vibrations of the flask structure. It is worth noticing that, the wave propagation along the walls may be slightly slower than across the base because of the lack of radial confinement. The effects on the lid(s) are analogous to those discussed for the base, except that full oscillation cycles are developed in the case of the lids since there is no target plane arresting the motion after one half-cycle. It should be noticed that restraining forces must be developed in order to keep the lid from abandoning contact with the flask walls. These forces will initially generate from a decrease in the lid pre-compression (given by bolt pretensioning); but, if that is exceeded, the excess would have to be taken as an additional load by the lid bolts, as was already mentioned earlier Generally, base drops imply little threat on the flask structural integrity because of the symmetries of the configuration and the large contact area available. However, they are a potential source of problems on three counts: The impact duration is minimal (typically 3-4 msec in 100 ton flasks). This leads to high deceleration values, with whatever implications this may have for the flask internals (possible buckling, etc.) The high decelerations also maximise lead slumping effects in flasks which incorporate this material Some attention must be given to lid bolts.
5 2.2. Plastic impacts Structures Under Shock And Impact 155 Greater damage to the flask structure occurs when the flask attitude at impact is such that only a small contact area is initially available for momentum exchange between the flask and the target plane Two types of impacts are of interest Translational impacts on a corner/edge with the centre of gravity directly above the impact point. Mixed translational-rotational impacts resulting from the overturning of a flask during storage or in handling operations The procedure will be described here as applied to a corner drop in a cylindrical flask, but it is readily applicable to corner, edge and some overturning impacts in both cylindrical and cubical flasks Some such applications will be presented and discussed in later sections An important feature of these impacts is the fact that the initial contact area is infinitesimal. Hence, any finite exchange of momentum must be accompanied by plastmg flattening of the impacted edge/corner Acceptability criteria for the flask must therefore take account of this inescapable fact Plastic straining of the edge/corner leads to a gradual increase of the effective contact area between the flask and the target plane Regarding momentum exchange, this is felt as a progressive stiffening of the contact, thus providing a certain shock absorbing capacity The assumption made here is that, at any time the contact force F can be calculated as: I- aa(x) (2) where a is a stress, intermediate between the yield and ultimate stresses A(x) is an area, which is a function of the displacement x accumulated by the flask's centre since the impact started The value of A(x) is calculated as the area of intersection of the flask and the plane when their relative distance is shortened by an amount x following initial contact The determination of A(x) is a simple exercise in geometry and calculus for both cylindrical and cubical flasks The history of movements of the flask's centre of gravity and the history of
6 756 Structures Under Shock And Impact the impact force can then be easily calculated by integrating the scalar equation of motion of the flask as a point mass. jc - oa(x) m (3) where x is the acceleration of the flask's centre of gravity m is the mass of the flask The equation, provided with the appropriate initial conditions (at t = 0, x = 0 and x - -vo), can be solved by simple explicit integration or other similar procedures. The integration must continue until the flask's velocity x changes sign. At that time, the unloading process begins followed by results in the rebound of the flask. In this process, the easiest realistic assumption is to decrease the impact load linearly to zero over a half-period of longitudinal vibration of the flask i.e. about the time required by pressure waves to travel along the length of the flask The contact force history developed in these impacts is approximately made of two traces such as idealized in Figure 2 The first one (not necessarily linear) is associated with the increase in contact area resulting from local flattening. The second one represents the elastic rebound This impact is about an order of magnitude longer in duration than the corresponding base/lid drops, lasting typically msec. Because this time is equivalent to several flask periods in its first vibrational mode, the impact is far less dynamic than in the case of base/lid drops. The impact tends to be less noisy and oscillatory deviations in the response are only moderate FORCE Fig. 2 Idealized contact force history developed in corner and similar impacts As already indicated, corner/edge impacts are more demanding from the viewpoint of the integrity of the flask, which suffers major local deformations. But, although this effect is serious, it is only local; as compensation, this local sacrifice drastically limits deleterious effects elsewhere in the flask
7 3. VALIDATIONS AND APPLICABILITY Structures Under Shock And Impact 157 The interest of any simplified procedures lies in their ability to reproduce one or more aspects of the actual problem. Several cases will be discussed here in order to assess the reliability of the drastic simplifications proposed Base drop The concepts presented in the previous section have been used to study the problem of a low height drop of a reai cylindrical flask. The flask, known as the STC (Storage Transport Cask) in the United States and DPT (Dual-Purpose Inllo),n Spam, is a joint development of both countries, intended for both transport and storage functions. The accident studied here is a storage related accident, othenvise the flask would have been provided with transpon shock absorbers. In storage operations, the drop height cannot exceed 0.38 m, which is the height for which the present analysis has been conducted. The flask is cylindrical with internal and external diameters of about 1 78 m and 2.18 m, respectively. The overall length is 5.02 m and the base thickness is approximately 0.31 m The total weight of the flask, including lead shielding in the walls and the flask internals, is 1045 kn. * Fig. 3 Mesh used in the finite element simulation of the STC/DPT flask The base drop from 0.38 m has been modelled with DYNA3D [3] using the complex threedimensional mesh shown in Figure 3. The resulting history of calculated forces is plotted together with the estimates based on the procedure proposed in section 2.1 (see Figure 4). As can be seen, the agreement is very reasonable: estimates for impact duration, force history and, consequently, mean deceleration of the contents are certainly adequate for a first assessment of the consequences of the impact, both on the flask and on the impacted structure.
8 158 Structures Under Shock And Impact 500 T Finite elements Simplified procedure Fig 4 Comparison of force-time histories in a base drop of the STC/DPT flask. The double peak appearing in the first impact of the flask's base occurs because the base is actually made of two steel plates with a softer intermediate material. This feature was taken into account in the finite element calculations It is interesting to notice that, in this particular case, the base impacts the plane twice while the walls maintain continuous contact with it A third impact occurs when the flask is loosing contact; actually, as suggested by the time history, this third impact occurs just as the walls leave contact with the plane Some approximations have been adopted in the calculation of the simplified force history Firstly, since the walls include both lead and steel, homogeneized stiffness and density properties have been used for estimating wave propagation velocities Second, the period of oscillation of the base has been taken as that of a simply supported circular plate. 3.2 Corner/edge impacts This example corresponds to an 18m drop of the Magnox flask (Figure 5). This is a cubical flask with overall dimensions of 2 2 m, 26 m and 2.2 m and a total weight of 420 kn. This flask impact was modelled in three dimensions by Kalsi and Dowling [4] using PR3D [5] and was subjected to a full-scale drop test [6]. Figure 6 shows the force histories arising from the three-dimensional calculations, the actual experiment and the proposed simplified procedure The latter curve
9 Structures Under Shock And Impact 159 Fig. 5 Corner impact of the Magnox flask 200 g Z 150 o I UJ d 100 -Physical test "Simplified procedure ' Finite elements TIME (msec) Fig. 6 Comparison of force-time histories in a comer drop of the Magnox flask is perfectly consistent with the finite element calculations and indeed with the experimental measurements. The internal dynamic oscillations obviously cannot be predicted in a model which reduces the flask to "a single mass point No attempt has been made to evaluate the unloading slope of the force history since for a cubicai Oask m a comer impact, no simplified procedures are easily available tor estimating the corresponding natural frequency.
10 760 Structures Under Shock And Impact 4 CONCLUSIONS Simplified procedures have been proposed for producing quick estimates of some of the basic characteristics of flask impacts They cover primarily elastic impacts (bottom and lid drops), as well as those which elicit considerable plastic response (corner/edge drops, side drops and overturning impacts). The main characteristics that can be estimated are impact duration, peak impact force, histories of impact forces and mean decelerations, extent of flask crushing and rebound velocity. The comparisons performed between the predictions of the simplified procedures, experimental measurements and finite element calculations indicate that the quality of the simplified predictions is more than adequate for a first assessment of the problem. The results are very good for primarily elastic impacts, such as base drops, and for primarily plastic impacts, such as corner drops REFERENCES [1] IAEA. Regulations for the safe transport of radioactive materials, International Atomic Energy Agency, Safety Standards no 6 Viena, 1985 Edition (as amended 1990). [2] Marti, J. Impact analysis of transport flasks, in Shock and Impact on Structures by C Brebbia and V Sanchez (eds), Wessex Institute of Technology, [3] Whirley, R.G and Engelman, BE DYNA3D A non-linear, explicit, threedimensional finite element code for solid and structural mechanics, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, 1993 [4] Kalsi, G.S. and Dowling, A R Three dimensionalfinitedifference analysis of a corner drop of the Magnox nuclear fuel transport flask, 9th International Conference on Structural Mechanics in Reactor Technology, Lausanne, Switzerland, vol. L, pp , A.A Balkema, 1987 [5] Marti, J. and Kalsi, G. PR3D Program manuals, Principia Mechanica Ltd, 1983 [6] Institution of Mechanical Engineers The resistance to impact of spent Magnox fuel transport flasks, Proceedings of the Seminar, London, April 30 - May 1,1985
Parametric study of the force acting on a target during an aircraft impact
 Parametric study of the force acting on a target during an aircraft impact Lili Eszter Laczák * and György Károlyi ** * Department of Structural Engineering, Budapest University of Technology and Economics,
Parametric study of the force acting on a target during an aircraft impact Lili Eszter Laczák * and György Károlyi ** * Department of Structural Engineering, Budapest University of Technology and Economics,
Reply to Dr. Greening
 Reply to Dr. Greening Author: The author of this work, Gordon Ross, was born in Dundee, Scotland. He holds degrees in both Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering, graduating from Liverpool John Moores
Reply to Dr. Greening Author: The author of this work, Gordon Ross, was born in Dundee, Scotland. He holds degrees in both Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering, graduating from Liverpool John Moores
ASSESSMENT OF DYNAMICALLY LOADED CRACKS IN FILLETS
 ASSESSMENT OF DNAMICALL LOADED CRACKS IN FILLETS Uwe Zencker, Linan Qiao, Bernhard Droste Federal Institute for Materials Research and Testing (BAM) 12200 Berlin, Germany e-mail: zencker@web.de Abstract
ASSESSMENT OF DNAMICALL LOADED CRACKS IN FILLETS Uwe Zencker, Linan Qiao, Bernhard Droste Federal Institute for Materials Research and Testing (BAM) 12200 Berlin, Germany e-mail: zencker@web.de Abstract
Impact Simulation of Extreme Wind Generated Missiles on Radioactive Waste Storage Facilities
 Impact Simulation of Extreme Wind Generated Missiles on Radioactive Waste Storage Facilities Gianluca Barbella Sogin S.p.A. Structural Design Department barbella@sogin.it Rotterdam - october 24, 2013 Outline
Impact Simulation of Extreme Wind Generated Missiles on Radioactive Waste Storage Facilities Gianluca Barbella Sogin S.p.A. Structural Design Department barbella@sogin.it Rotterdam - october 24, 2013 Outline
PLATE GIRDERS II. Load. Web plate Welds A Longitudinal elevation. Fig. 1 A typical Plate Girder
 16 PLATE GIRDERS II 1.0 INTRODUCTION This chapter describes the current practice for the design of plate girders adopting meaningful simplifications of the equations derived in the chapter on Plate Girders
16 PLATE GIRDERS II 1.0 INTRODUCTION This chapter describes the current practice for the design of plate girders adopting meaningful simplifications of the equations derived in the chapter on Plate Girders
MODELING SLAB-COLUMN CONNECTIONS REINFORCED WITH GFRP UNDER LOCALIZED IMPACT
 MODELING SLAB-COLUMN CONNECTIONS REINFORCED WITH GFRP UNDER LOCALIZED IMPACT QI ZHANG and AMGAD HUSSEIN Faculty of Engineering, Memorial University of Newfoundland St. John s, Newfoundland, Canada, A1B
MODELING SLAB-COLUMN CONNECTIONS REINFORCED WITH GFRP UNDER LOCALIZED IMPACT QI ZHANG and AMGAD HUSSEIN Faculty of Engineering, Memorial University of Newfoundland St. John s, Newfoundland, Canada, A1B
STEEL JOINTS - COMPONENT METHOD APPLICATION
 Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Vol. 5 (54) - 2012 Series 1: Special Issue No. 1 STEEL JOINTS - COPONENT ETHOD APPLICATION D. RADU 1 Abstract: As long as the rotation joint stiffness
Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Vol. 5 (54) - 2012 Series 1: Special Issue No. 1 STEEL JOINTS - COPONENT ETHOD APPLICATION D. RADU 1 Abstract: As long as the rotation joint stiffness
Compact energy absorbing cellular structure
 Structures Under Shock and Impact IX 413 Compact energy absorbing cellular structure M. Ali 1, A. Qamhiyah 2, D. Flugrad 1 & M. Shakoor 1 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Iowa State University,
Structures Under Shock and Impact IX 413 Compact energy absorbing cellular structure M. Ali 1, A. Qamhiyah 2, D. Flugrad 1 & M. Shakoor 1 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Iowa State University,
The Dynamical Loading of the WWER440/V213 Reactor Pressure Vessel Internals during LOCA Accident in Hot and Cold Leg of the Primary Circuit
 The Dynamical Loading of the WWER440/V213 Reactor Pressure Vessel Internals during LOCA Accident in Hot and Cold Leg of the Primary Circuit ABSTRACT Peter Hermansky, Marian Krajčovič VUJE, Inc. Okružná
The Dynamical Loading of the WWER440/V213 Reactor Pressure Vessel Internals during LOCA Accident in Hot and Cold Leg of the Primary Circuit ABSTRACT Peter Hermansky, Marian Krajčovič VUJE, Inc. Okružná
ANALYTICAL PENDULUM METHOD USED TO PREDICT THE ROLLOVER BEHAVIOR OF A BODY STRUCTURE
 The 3rd International Conference on Computational Mechanics and Virtual Engineering COMEC 2009 29 30 OCTOBER 2009, Brasov, Romania ANALYTICAL PENDULUM METHOD USED TO PREDICT THE ROLLOVER BEHAVIOR OF A
The 3rd International Conference on Computational Mechanics and Virtual Engineering COMEC 2009 29 30 OCTOBER 2009, Brasov, Romania ANALYTICAL PENDULUM METHOD USED TO PREDICT THE ROLLOVER BEHAVIOR OF A
D : SOLID MECHANICS. Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. Q.1 Find the force (in kn) in the member BH of the truss shown.
 D : SOLID MECHANICS Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. Q.1 Find the force (in kn) in the member BH of the truss shown. Q.2 Consider the forces of magnitude F acting on the sides of the regular hexagon having
D : SOLID MECHANICS Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. Q.1 Find the force (in kn) in the member BH of the truss shown. Q.2 Consider the forces of magnitude F acting on the sides of the regular hexagon having
Ultimate shear strength of FPSO stiffened panels after supply vessel collision
 Ultimate shear strength of FPSO stiffened panels after supply vessel collision Nicolau Antonio dos Santos Rizzo PETROBRAS Rio de Janeiro Brazil Marcelo Caire SINTEF do Brasil Rio de Janeiro Brazil Carlos
Ultimate shear strength of FPSO stiffened panels after supply vessel collision Nicolau Antonio dos Santos Rizzo PETROBRAS Rio de Janeiro Brazil Marcelo Caire SINTEF do Brasil Rio de Janeiro Brazil Carlos
SEISMIC BASE ISOLATION
 SEISMIC BASE ISOLATION DESIGN OF BASE ISOLATION SYSTEMS IN BUILDINGS FILIPE RIBEIRO DE FIGUEIREDO SUMMARY The current paper aims to present the results of a study for the comparison of different base isolation
SEISMIC BASE ISOLATION DESIGN OF BASE ISOLATION SYSTEMS IN BUILDINGS FILIPE RIBEIRO DE FIGUEIREDO SUMMARY The current paper aims to present the results of a study for the comparison of different base isolation
EARTHQUAKE SAFETY OF AN ARCH-GRAVITY DAM WITH A HORIZONTAL CRACK IN THE UPPER PORTION OF THE DAM
 EARTHQUAKE SAFETY OF AN ARCH-GRAVITY DAM WITH A HORIZONTAL CRACK IN THE UPPER PORTION OF THE DAM Martin WIELAND 1 And Sujan MALLA 2 SUMMARY A horizontal crack first appeared along the downstream wall of
EARTHQUAKE SAFETY OF AN ARCH-GRAVITY DAM WITH A HORIZONTAL CRACK IN THE UPPER PORTION OF THE DAM Martin WIELAND 1 And Sujan MALLA 2 SUMMARY A horizontal crack first appeared along the downstream wall of
SIMPLE MODEL FOR PRYING FORCES IN T-HANGER CONNECTIONS WITH SNUG TIGHTENED BOLTS
 SIMPLE MODEL FOR PRYING FORCES IN T-HANGER CONNECTIONS WITH SNUG TIGHTENED BOLTS By Fathy Abdelmoniem Abdelfattah Faculty of Engineering at Shoubra, Zagazig University, Banha Branch Mohamed Salah A. Soliman
SIMPLE MODEL FOR PRYING FORCES IN T-HANGER CONNECTIONS WITH SNUG TIGHTENED BOLTS By Fathy Abdelmoniem Abdelfattah Faculty of Engineering at Shoubra, Zagazig University, Banha Branch Mohamed Salah A. Soliman
Influence of residual stresses in the structural behavior of. tubular columns and arches. Nuno Rocha Cima Gomes
 October 2014 Influence of residual stresses in the structural behavior of Abstract tubular columns and arches Nuno Rocha Cima Gomes Instituto Superior Técnico, Universidade de Lisboa, Portugal Contact:
October 2014 Influence of residual stresses in the structural behavior of Abstract tubular columns and arches Nuno Rocha Cima Gomes Instituto Superior Técnico, Universidade de Lisboa, Portugal Contact:
Expansion of circular tubes by rigid tubes as impact energy absorbers: experimental and theoretical investigation
 Expansion of circular tubes by rigid tubes as impact energy absorbers: experimental and theoretical investigation M Shakeri, S Salehghaffari and R. Mirzaeifar Department of Mechanical Engineering, Amirkabir
Expansion of circular tubes by rigid tubes as impact energy absorbers: experimental and theoretical investigation M Shakeri, S Salehghaffari and R. Mirzaeifar Department of Mechanical Engineering, Amirkabir
Modal Analysis: What it is and is not Gerrit Visser
 Modal Analysis: What it is and is not Gerrit Visser What is a Modal Analysis? What answers do we get out of it? How is it useful? What does it not tell us? In this article, we ll discuss where a modal
Modal Analysis: What it is and is not Gerrit Visser What is a Modal Analysis? What answers do we get out of it? How is it useful? What does it not tell us? In this article, we ll discuss where a modal
Finite element prediction of the ultimate axial load capacity of V-section band clamps
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series Finite element prediction of the ultimate axial load capacity of V-section band clamps To cite this article: S M Barrans and M Muller 2009 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 181
Journal of Physics: Conference Series Finite element prediction of the ultimate axial load capacity of V-section band clamps To cite this article: S M Barrans and M Muller 2009 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 181
This document downloaded from vulcanhammer.net vulcanhammer.info Chet Aero Marine
 This document downloaded from vulcanhammer.net vulcanhammer.info Chet Aero Marine Don t forget to visit our companion site http://www.vulcanhammer.org Use subject to the terms and conditions of the respective
This document downloaded from vulcanhammer.net vulcanhammer.info Chet Aero Marine Don t forget to visit our companion site http://www.vulcanhammer.org Use subject to the terms and conditions of the respective
CAPACITY DESIGN FOR TALL BUILDINGS WITH MIXED SYSTEM
 13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 24 Paper No. 2367 CAPACITY DESIGN FOR TALL BUILDINGS WITH MIXED SYSTEM M.UMA MAHESHWARI 1 and A.R.SANTHAKUMAR 2 SUMMARY
13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 24 Paper No. 2367 CAPACITY DESIGN FOR TALL BUILDINGS WITH MIXED SYSTEM M.UMA MAHESHWARI 1 and A.R.SANTHAKUMAR 2 SUMMARY
Stress Concentrations, Fatigue, Fracture
 Stress Concentrations, Fatigue, Fracture The fundamental topic in this document is the development of cracks in steel. For structures subjected to cyclic loads, such cracks can develop over time and ultimately
Stress Concentrations, Fatigue, Fracture The fundamental topic in this document is the development of cracks in steel. For structures subjected to cyclic loads, such cracks can develop over time and ultimately
FURTHER RESEARCH ON CHORD LENGTH AND BOUNDARY CONDITIONS OF CHS T- AND X-JOINTS
 Advanced Steel Construction Vol. 6, No. 3, pp. 879-89 (1) 879 FURTHER RESEARCH ON CHORD LENGTH AND BOUNDARY CONDITIONS OF CHS T- AND X-JOINTS G.J. van der Vegte 1, * and Y. Makino 1 Delft University of
Advanced Steel Construction Vol. 6, No. 3, pp. 879-89 (1) 879 FURTHER RESEARCH ON CHORD LENGTH AND BOUNDARY CONDITIONS OF CHS T- AND X-JOINTS G.J. van der Vegte 1, * and Y. Makino 1 Delft University of
Nonlinear Analysis of Reinforced Concrete Shells Subjected to Impact Loads
 Transactions of the 7 th International Conference on Structural Mechanics in Reactor Technology (SMiRT 7) Prague, Czech Republic, August 7, 00 Paper # J0- Nonlinear Analysis of Reinforced Concrete Shells
Transactions of the 7 th International Conference on Structural Mechanics in Reactor Technology (SMiRT 7) Prague, Czech Republic, August 7, 00 Paper # J0- Nonlinear Analysis of Reinforced Concrete Shells
Lecture 3: Stresses in Rigid Pavements
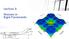 Lecture 3: Stresses in Rigid Pavements Nature of Responses under Flexible and Rigid Plates Flexible plate: Uniform Contact Pressure Variable Deflection Profile Flexible Plate Rigid Plate plate: Non-Uniform
Lecture 3: Stresses in Rigid Pavements Nature of Responses under Flexible and Rigid Plates Flexible plate: Uniform Contact Pressure Variable Deflection Profile Flexible Plate Rigid Plate plate: Non-Uniform
Collapse modes of structures under strong motions of earthquake
 ANNALS OF GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 45, N. 6, December 2002 Collapse modes of structures under strong motions of earthquake Hiroshi Akiyama Real Estate Science, School of Science and Technology, Nihon University,
ANNALS OF GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 45, N. 6, December 2002 Collapse modes of structures under strong motions of earthquake Hiroshi Akiyama Real Estate Science, School of Science and Technology, Nihon University,
Acceleration levels of dropped objects. Technical paper 321
 Acceleration levels of dropped objects Technical paper 31 Acceleration levels of dropped objects Introduction This paper is intended to provide an overview of drop shock testing, which is defined as the
Acceleration levels of dropped objects Technical paper 31 Acceleration levels of dropped objects Introduction This paper is intended to provide an overview of drop shock testing, which is defined as the
COMPARISON BETWEEN 2D AND 3D ANALYSES OF SEISMIC STABILITY OF DETACHED BLOCKS IN AN ARCH DAM
 COMPARISON BETWEEN 2D AND 3D ANALYSES OF SEISMIC STABILITY OF DETACHED BLOCKS IN AN ARCH DAM Sujan MALLA 1 ABSTRACT The seismic safety of the 147 m high Gigerwald arch dam in Switzerland was assessed for
COMPARISON BETWEEN 2D AND 3D ANALYSES OF SEISMIC STABILITY OF DETACHED BLOCKS IN AN ARCH DAM Sujan MALLA 1 ABSTRACT The seismic safety of the 147 m high Gigerwald arch dam in Switzerland was assessed for
Finite Element Modelling with Plastic Hinges
 01/02/2016 Marco Donà Finite Element Modelling with Plastic Hinges 1 Plastic hinge approach A plastic hinge represents a concentrated post-yield behaviour in one or more degrees of freedom. Hinges only
01/02/2016 Marco Donà Finite Element Modelling with Plastic Hinges 1 Plastic hinge approach A plastic hinge represents a concentrated post-yield behaviour in one or more degrees of freedom. Hinges only
MODULE C: COMPRESSION MEMBERS
 MODULE C: COMPRESSION MEMBERS This module of CIE 428 covers the following subjects Column theory Column design per AISC Effective length Torsional and flexural-torsional buckling Built-up members READING:
MODULE C: COMPRESSION MEMBERS This module of CIE 428 covers the following subjects Column theory Column design per AISC Effective length Torsional and flexural-torsional buckling Built-up members READING:
NUMERICAL EVALUATION OF THE ROTATIONAL CAPACITY OF STEEL BEAMS AT ELEVATED TEMPERATURES
 8 th GRACM International Congress on Computational Mechanics Volos, 12 July 15 July 2015 NUMERICAL EVALUATION OF THE ROTATIONAL CAPACITY OF STEEL BEAMS AT ELEVATED TEMPERATURES Savvas Akritidis, Daphne
8 th GRACM International Congress on Computational Mechanics Volos, 12 July 15 July 2015 NUMERICAL EVALUATION OF THE ROTATIONAL CAPACITY OF STEEL BEAMS AT ELEVATED TEMPERATURES Savvas Akritidis, Daphne
7.6 Stress in symmetrical elastic beam transmitting both shear force and bending moment
 7.6 Stress in symmetrical elastic beam transmitting both shear force and bending moment à It is more difficult to obtain an exact solution to this problem since the presence of the shear force means that
7.6 Stress in symmetrical elastic beam transmitting both shear force and bending moment à It is more difficult to obtain an exact solution to this problem since the presence of the shear force means that
Numerical modelling of induced tensile stresses in rock in response to impact loading
 Numerical modelling of induced tensile stresses in rock in response to impact loading M.T. Mnisi, D.P. Roberts and J.S. Kuijpers Council for Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR): Natural Resources
Numerical modelling of induced tensile stresses in rock in response to impact loading M.T. Mnisi, D.P. Roberts and J.S. Kuijpers Council for Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR): Natural Resources
Deep Foundations 2. Load Capacity of a Single Pile
 Deep Foundations 2 Load Capacity of a Single Pile All calculations of pile capacity are approximate because it is almost impossible to account for the variability of soil types and the differences in the
Deep Foundations 2 Load Capacity of a Single Pile All calculations of pile capacity are approximate because it is almost impossible to account for the variability of soil types and the differences in the
A NEW ROCK BOLT CONCEPT FOR UNDERGROUND EXCAVATIONS UNDER HIGH STRESS CONDITIONS
 A NEW ROCK BOLT CONCEPT FOR UNDERGROUND EXCAVATIONS UNDER HIGH STRESS CONDITIONS François Charette 1 and Michel Plouffe 2 1 Atlas Copco MAI, 2 CANMET-MMSL, Natural Resources Canada Abstract This paper
A NEW ROCK BOLT CONCEPT FOR UNDERGROUND EXCAVATIONS UNDER HIGH STRESS CONDITIONS François Charette 1 and Michel Plouffe 2 1 Atlas Copco MAI, 2 CANMET-MMSL, Natural Resources Canada Abstract This paper
Chapter Two: Mechanical Properties of materials
 Chapter Two: Mechanical Properties of materials Time : 16 Hours An important consideration in the choice of a material is the way it behave when subjected to force. The mechanical properties of a material
Chapter Two: Mechanical Properties of materials Time : 16 Hours An important consideration in the choice of a material is the way it behave when subjected to force. The mechanical properties of a material
METHODOLOGICAL ASPECTS FOR NUMERICAL ANALYSIS OF LID SYSTEMS FOR SNF AND HLW TRANSPORT PACKAGES
 Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on the Packaging and Transportation of Radioactive Materials PATRAM 23 August 8-23, 23, San Francisco, CA, USA METHODOLOGICAL ASPECTS FOR NUMERICAL ANALYSIS
Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on the Packaging and Transportation of Radioactive Materials PATRAM 23 August 8-23, 23, San Francisco, CA, USA METHODOLOGICAL ASPECTS FOR NUMERICAL ANALYSIS
Mechanics of Materials II. Chapter III. A review of the fundamental formulation of stress, strain, and deflection
 Mechanics of Materials II Chapter III A review of the fundamental formulation of stress, strain, and deflection Outline Introduction Assumtions and limitations Axial loading Torsion of circular shafts
Mechanics of Materials II Chapter III A review of the fundamental formulation of stress, strain, and deflection Outline Introduction Assumtions and limitations Axial loading Torsion of circular shafts
ME 2570 MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
 ME 2570 MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Chapter III. Mechanical Properties of Materials 1 Tension and Compression Test The strength of a material depends on its ability to sustain a load without undue deformation
ME 2570 MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Chapter III. Mechanical Properties of Materials 1 Tension and Compression Test The strength of a material depends on its ability to sustain a load without undue deformation
ESTIMATION OF THE TRANSVERSE CRUSH RESISTANCE OF A SECTION OF THE T23 FRIGATE
 ESTIMATION OF THE TRANSVERSE CRUSH RESISTANCE OF A SECTION OF THE T23 FRIGATE Dr. GS Kalsi Royal Military College of Science, Cranfield University, UK Introduction Ocean-going vessels are very complex
ESTIMATION OF THE TRANSVERSE CRUSH RESISTANCE OF A SECTION OF THE T23 FRIGATE Dr. GS Kalsi Royal Military College of Science, Cranfield University, UK Introduction Ocean-going vessels are very complex
Buckling Resistance Assessment of a Slender Cylindrical Shell Axially Compressed
 Mechanics and Mechanical Engineering Vol. 14, No. 2 (2010) 309 316 c Technical University of Lodz Buckling Resistance Assessment of a Slender Cylindrical Shell Axially Compressed Jakub Marcinowski Institute
Mechanics and Mechanical Engineering Vol. 14, No. 2 (2010) 309 316 c Technical University of Lodz Buckling Resistance Assessment of a Slender Cylindrical Shell Axially Compressed Jakub Marcinowski Institute
ENCE 455 Design of Steel Structures. III. Compression Members
 ENCE 455 Design of Steel Structures III. Compression Members C. C. Fu, Ph.D., P.E. Civil and Environmental Engineering Department University of Maryland Compression Members Following subjects are covered:
ENCE 455 Design of Steel Structures III. Compression Members C. C. Fu, Ph.D., P.E. Civil and Environmental Engineering Department University of Maryland Compression Members Following subjects are covered:
RULES PUBLICATION NO. 17/P ZONE STRENGTH ANALYSIS OF HULL STRUCTURE OF ROLL ON/ROLL OFF SHIP
 RULES PUBLICATION NO. 17/P ZONE STRENGTH ANALYSIS OF HULL STRUCTURE OF ROLL ON/ROLL OFF SHIP 1995 Publications P (Additional Rule Requirements), issued by Polski Rejestr Statków, complete or extend the
RULES PUBLICATION NO. 17/P ZONE STRENGTH ANALYSIS OF HULL STRUCTURE OF ROLL ON/ROLL OFF SHIP 1995 Publications P (Additional Rule Requirements), issued by Polski Rejestr Statków, complete or extend the
Self-weight loading of horizontal hydraulic cylinders with axial load
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Self-weight loading of horizontal hydraulic cylinders with axial load Related content - Stability analysis of large slenderness ratio horizontal
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Self-weight loading of horizontal hydraulic cylinders with axial load Related content - Stability analysis of large slenderness ratio horizontal
Transactions on the Built Environment vol 22, 1996 WIT Press, ISSN
 A shock damage potential approach to shock testing D.H. Trepess Mechanical Subject Group, School of Engineering, Coventry University, Coventry CVl 5FB, UK A shock damage (excitation capacity) approach
A shock damage potential approach to shock testing D.H. Trepess Mechanical Subject Group, School of Engineering, Coventry University, Coventry CVl 5FB, UK A shock damage (excitation capacity) approach
Contact pressure distribution in joints formed by V-band clamps Simon M Barrans 1,a, Goodarz Khodabakhshi 1,b and Qiang Xu 1,c
 Contact pressure distribution in joints formed by V-band clamps Simon M Barrans 1,a, Goodarz Khodabakhshi 1,b and Qiang Xu 1,c 1 School of Computing and Engineering, University of Huddersfield, Queensgate,
Contact pressure distribution in joints formed by V-band clamps Simon M Barrans 1,a, Goodarz Khodabakhshi 1,b and Qiang Xu 1,c 1 School of Computing and Engineering, University of Huddersfield, Queensgate,
NIST AND DR. BAZANT - A SIMULTANEOUS FAILURE
 NIST AND DR. BAZANT - A SIMULTANEOUS FAILURE The author of this work, Gordon Ross, was born in Dundee, Scotland. He holds degrees in both Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering, graduating from Liverpool
NIST AND DR. BAZANT - A SIMULTANEOUS FAILURE The author of this work, Gordon Ross, was born in Dundee, Scotland. He holds degrees in both Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering, graduating from Liverpool
Investigation into the Self-loosening Trend of Bolt Joints on the Tower Crane ShengChun Wang1,a, PeiWei Ni1,b, Ye Zhang1,c and MingXiao Dong1,2,d
 2nd International Conference on Advances in Mechanical Engineering and Industrial Informatics (AMEII 2016) Investigation into the Self-loosening Trend of Bolt Joints on the Tower Crane ShengChun Wang1,a,
2nd International Conference on Advances in Mechanical Engineering and Industrial Informatics (AMEII 2016) Investigation into the Self-loosening Trend of Bolt Joints on the Tower Crane ShengChun Wang1,a,
FEA A Guide to Good Practice. What to expect when you re expecting FEA A guide to good practice
 FEA A Guide to Good Practice What to expect when you re expecting FEA A guide to good practice 1. Background Finite Element Analysis (FEA) has transformed design procedures for engineers. Allowing more
FEA A Guide to Good Practice What to expect when you re expecting FEA A guide to good practice 1. Background Finite Element Analysis (FEA) has transformed design procedures for engineers. Allowing more
Sabah Shawkat Cabinet of Structural Engineering Walls carrying vertical loads should be designed as columns. Basically walls are designed in
 Sabah Shawkat Cabinet of Structural Engineering 17 3.6 Shear walls Walls carrying vertical loads should be designed as columns. Basically walls are designed in the same manner as columns, but there are
Sabah Shawkat Cabinet of Structural Engineering 17 3.6 Shear walls Walls carrying vertical loads should be designed as columns. Basically walls are designed in the same manner as columns, but there are
Stresses Analysis of Petroleum Pipe Finite Element under Internal Pressure
 ISSN : 48-96, Vol. 6, Issue 8, ( Part -4 August 06, pp.3-38 RESEARCH ARTICLE Stresses Analysis of Petroleum Pipe Finite Element under Internal Pressure Dr.Ragbe.M.Abdusslam Eng. Khaled.S.Bagar ABSTRACT
ISSN : 48-96, Vol. 6, Issue 8, ( Part -4 August 06, pp.3-38 RESEARCH ARTICLE Stresses Analysis of Petroleum Pipe Finite Element under Internal Pressure Dr.Ragbe.M.Abdusslam Eng. Khaled.S.Bagar ABSTRACT
Lecture #2: Split Hopkinson Bar Systems
 Lecture #2: Split Hopkinson Bar Systems by Dirk Mohr ETH Zurich, Department of Mechanical and Process Engineering, Chair of Computational Modeling of Materials in Manufacturing 2015 1 1 1 Uniaxial Compression
Lecture #2: Split Hopkinson Bar Systems by Dirk Mohr ETH Zurich, Department of Mechanical and Process Engineering, Chair of Computational Modeling of Materials in Manufacturing 2015 1 1 1 Uniaxial Compression
HVTT 11: Truck Occupant Protection Considerations in Heavy Truck Crashes
 TRUCK OCCUPANT PROTECTION CONSIDERATIONS IN HEAVYVEHICLE CRASHES Peter Hart graduated with a PhD in electrical engineering from Monash University in 1990. He is the principal of Hartwood Consulting Pty
TRUCK OCCUPANT PROTECTION CONSIDERATIONS IN HEAVYVEHICLE CRASHES Peter Hart graduated with a PhD in electrical engineering from Monash University in 1990. He is the principal of Hartwood Consulting Pty
Special edition paper
 Development of New Aseismatic Structure Using Escalators Kazunori Sasaki* Atsushi Hayashi* Hajime Yoshida** Toru Masuda* Aseismatic reinforcement work is often carried out in parallel with improvement
Development of New Aseismatic Structure Using Escalators Kazunori Sasaki* Atsushi Hayashi* Hajime Yoshida** Toru Masuda* Aseismatic reinforcement work is often carried out in parallel with improvement
Reliability analysis of different structure parameters of PCBA under drop impact
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Reliability analysis of different structure parameters of PCBA under drop impact To cite this article: P S Liu et al 2018 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 986
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Reliability analysis of different structure parameters of PCBA under drop impact To cite this article: P S Liu et al 2018 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 986
Fatigue-Ratcheting Study of Pressurized Piping System under Seismic Load
 Fatigue-Ratcheting Study of Pressurized Piping System under Seismic Load A. Ravi Kiran, M. K. Agrawal, G. R. Reddy, R. K. Singh, K. K. Vaze, A. K. Ghosh and H. S. Kushwaha Reactor Safety Division, Bhabha
Fatigue-Ratcheting Study of Pressurized Piping System under Seismic Load A. Ravi Kiran, M. K. Agrawal, G. R. Reddy, R. K. Singh, K. K. Vaze, A. K. Ghosh and H. S. Kushwaha Reactor Safety Division, Bhabha
End forming of thin-walled tubes
 Journal of Materials Processing Technology 177 (2006) 183 187 End forming of thin-walled tubes M.L. Alves a, B.P.P. Almeida b, P.A.R. Rosa b, P.A.F. Martins b, a Escola Superior de Tecnologia e Gestão
Journal of Materials Processing Technology 177 (2006) 183 187 End forming of thin-walled tubes M.L. Alves a, B.P.P. Almeida b, P.A.R. Rosa b, P.A.F. Martins b, a Escola Superior de Tecnologia e Gestão
Weak Rock - Controlling Ground Deformations
 EOSC 547: Tunnelling & Underground Design Topic 7: Ground Characteristic & Support Reaction Curves 1 of 35 Tunnelling Grad Class (2014) Dr. Erik Eberhardt Weak Rock - Controlling Ground Deformations To
EOSC 547: Tunnelling & Underground Design Topic 7: Ground Characteristic & Support Reaction Curves 1 of 35 Tunnelling Grad Class (2014) Dr. Erik Eberhardt Weak Rock - Controlling Ground Deformations To
The Simulation of Dropped Objects on the Offshore Structure Liping SUN 1,a, Gang MA 1,b, Chunyong NIE 2,c, Zihan WANG 1,d
 Advanced Materials Research Online: 2011-09-02 ISSN: 1662-8985, Vol. 339, pp 553-556 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/amr.339.553 2011 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland The Simulation of Dropped Objects
Advanced Materials Research Online: 2011-09-02 ISSN: 1662-8985, Vol. 339, pp 553-556 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/amr.339.553 2011 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland The Simulation of Dropped Objects
NONLINEAR SEISMIC SOIL-STRUCTURE (SSI) ANALYSIS USING AN EFFICIENT COMPLEX FREQUENCY APPROACH
 NONLINEAR SEISMIC SOIL-STRUCTURE (SSI) ANALYSIS USING AN EFFICIENT COMPLEX FREQUENCY APPROACH Dan M. GHIOCEL 1 ABSTRACT The paper introduces a novel approach for modeling nonlinear hysteretic behavior
NONLINEAR SEISMIC SOIL-STRUCTURE (SSI) ANALYSIS USING AN EFFICIENT COMPLEX FREQUENCY APPROACH Dan M. GHIOCEL 1 ABSTRACT The paper introduces a novel approach for modeling nonlinear hysteretic behavior
AN IMPORTANT PITFALL OF PSEUDO-STATIC FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS
 AN IMPORTANT PITFALL OF PSEUDO-STATIC FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS S. Kontoe, L. Pelecanos & D.M. Potts ABSTRACT: Finite Element (FE) pseudo-static analysis can provide a good compromise between simplified
AN IMPORTANT PITFALL OF PSEUDO-STATIC FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS S. Kontoe, L. Pelecanos & D.M. Potts ABSTRACT: Finite Element (FE) pseudo-static analysis can provide a good compromise between simplified
PREDICTION OF THE CYCLIC BEHAVIOR OF MOMENT RESISTANT BEAM-TO-COLUMN JOINTS OF COMPOSITE STRUCTURAL ELEMENTS
 SDSS Rio 21 STABILITY AND DUCTILITY OF STEEL STRUCTURES E. Batista, P. Vellasco, L. de Lima (Eds.) Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, September 8-1, 21 PREDICTION OF THE CYCLIC BEHAVIOR OF MOMENT RESISTANT BEAM-TO-COLUMN
SDSS Rio 21 STABILITY AND DUCTILITY OF STEEL STRUCTURES E. Batista, P. Vellasco, L. de Lima (Eds.) Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, September 8-1, 21 PREDICTION OF THE CYCLIC BEHAVIOR OF MOMENT RESISTANT BEAM-TO-COLUMN
Harmonized European standards for construction in Egypt
 Harmonized European standards for construction in Egypt EN 1998 - Design of structures for earthquake resistance Jean-Armand Calgaro Chairman of CEN/TC250 Organised with the support of the Egyptian Organization
Harmonized European standards for construction in Egypt EN 1998 - Design of structures for earthquake resistance Jean-Armand Calgaro Chairman of CEN/TC250 Organised with the support of the Egyptian Organization
Safety Margin Ratio-Based Design of Isolation Gap Size for Base-isolated Structures
 Safety Margin Ratio-Based Design of Isolation Gap Size for Base-isolated Structures T. Nakazawa Tokyo Kenchiku Structural Engineers, Co. Ltd., Japan S. Kishiki Osaka Institute of Technology, Japan Z. u
Safety Margin Ratio-Based Design of Isolation Gap Size for Base-isolated Structures T. Nakazawa Tokyo Kenchiku Structural Engineers, Co. Ltd., Japan S. Kishiki Osaka Institute of Technology, Japan Z. u
Appendix G Analytical Studies of Columns
 Appendix G Analytical Studies of Columns G.1 Introduction Analytical parametric studies were performed to evaluate a number of issues related to the use of ASTM A103 steel as longitudinal and transverse
Appendix G Analytical Studies of Columns G.1 Introduction Analytical parametric studies were performed to evaluate a number of issues related to the use of ASTM A103 steel as longitudinal and transverse
4. Objectives of Research work
 4. Objectives of Research work 4.1 Objectives of Study: The design of bellows is challenging looking to varieties of applications and evaluation of stresses is further difficult to approximate due to its
4. Objectives of Research work 4.1 Objectives of Study: The design of bellows is challenging looking to varieties of applications and evaluation of stresses is further difficult to approximate due to its
Design of Beams (Unit - 8)
 Design of Beams (Unit - 8) Contents Introduction Beam types Lateral stability of beams Factors affecting lateral stability Behaviour of simple and built - up beams in bending (Without vertical stiffeners)
Design of Beams (Unit - 8) Contents Introduction Beam types Lateral stability of beams Factors affecting lateral stability Behaviour of simple and built - up beams in bending (Without vertical stiffeners)
Structural Integrity Assessment of a Rupture Disc Housing with Explicit FE- Simulation
 20th International Conference on Structural Mechanics in Reactor Technology (SMiRT 20) Espoo, Finland, August 9-14, 2009 SMiRT 20-Division 2, Paper 2503 Structural Integrity Assessment of a Rupture Disc
20th International Conference on Structural Mechanics in Reactor Technology (SMiRT 20) Espoo, Finland, August 9-14, 2009 SMiRT 20-Division 2, Paper 2503 Structural Integrity Assessment of a Rupture Disc
THE EFFECTS OF LOCAL BUCKLING ON THE CRASH ENERGY ABSORPTION OF THIN-WALLED EXPANSION TUBES
 THE EFFECTS OF LOCAL BUCKLING ON THE CRASH ENERGY ABSORPTION OF THIN-WALLED EXPANSION TUBES Kwanghyun Ahn, Jin Sung Kim, Hoon Huh * School of Mechanical, Aerospace and System Engineering, KAIST, 335 Gwahangno,
THE EFFECTS OF LOCAL BUCKLING ON THE CRASH ENERGY ABSORPTION OF THIN-WALLED EXPANSION TUBES Kwanghyun Ahn, Jin Sung Kim, Hoon Huh * School of Mechanical, Aerospace and System Engineering, KAIST, 335 Gwahangno,
Tolerance Ring Improvement for Reducing Metal Scratch
 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 2, Issue 11, November 2012 1 Tolerance Ring Improvement for Reducing Metal Scratch Pattaraweerin Woraratsoontorn*, Pitikhate Sooraksa**
International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 2, Issue 11, November 2012 1 Tolerance Ring Improvement for Reducing Metal Scratch Pattaraweerin Woraratsoontorn*, Pitikhate Sooraksa**
INFLUENCE OF FLANGE STIFFNESS ON DUCTILITY BEHAVIOUR OF PLATE GIRDER
 International Journal of Civil Structural 6 Environmental And Infrastructure Engineering Research Vol.1, Issue.1 (2011) 1-15 TJPRC Pvt. Ltd.,. INFLUENCE OF FLANGE STIFFNESS ON DUCTILITY BEHAVIOUR OF PLATE
International Journal of Civil Structural 6 Environmental And Infrastructure Engineering Research Vol.1, Issue.1 (2011) 1-15 TJPRC Pvt. Ltd.,. INFLUENCE OF FLANGE STIFFNESS ON DUCTILITY BEHAVIOUR OF PLATE
Advanced Strength of Materials Prof S. K. Maiti Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay. Lecture 27
 Advanced Strength of Materials Prof S. K. Maiti Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture 27 Last time we considered Griffith theory of brittle fracture, where in it was considered
Advanced Strength of Materials Prof S. K. Maiti Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture 27 Last time we considered Griffith theory of brittle fracture, where in it was considered
Introduction to Continuous Systems. Continuous Systems. Strings, Torsional Rods and Beams.
 Outline of Continuous Systems. Introduction to Continuous Systems. Continuous Systems. Strings, Torsional Rods and Beams. Vibrations of Flexible Strings. Torsional Vibration of Rods. Bernoulli-Euler Beams.
Outline of Continuous Systems. Introduction to Continuous Systems. Continuous Systems. Strings, Torsional Rods and Beams. Vibrations of Flexible Strings. Torsional Vibration of Rods. Bernoulli-Euler Beams.
Analytical Strip Method for Thin Isotropic Cylindrical Shells
 IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 2278-1684,p-ISSN: 2320-334X, Volume 14, Issue 4 Ver. III (Jul. Aug. 2017), PP 24-38 www.iosrjournals.org Analytical Strip Method for
IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 2278-1684,p-ISSN: 2320-334X, Volume 14, Issue 4 Ver. III (Jul. Aug. 2017), PP 24-38 www.iosrjournals.org Analytical Strip Method for
Reliability of Traditional Retaining Wall Design
 Reliability of Traditional Retaining Wall Design by Gordon A. Fenton 1, D. V. Griffiths 2, and M. B. Williams 3 in Géotechique, Vol. 55, No. 1, pp. 55-62, 2005 Keywords: retaining walls, earth pressure,
Reliability of Traditional Retaining Wall Design by Gordon A. Fenton 1, D. V. Griffiths 2, and M. B. Williams 3 in Géotechique, Vol. 55, No. 1, pp. 55-62, 2005 Keywords: retaining walls, earth pressure,
LINEAR AND NONLINEAR BUCKLING ANALYSIS OF STIFFENED CYLINDRICAL SUBMARINE HULL
 LINEAR AND NONLINEAR BUCKLING ANALYSIS OF STIFFENED CYLINDRICAL SUBMARINE HULL SREELATHA P.R * M.Tech. Student, Computer Aided Structural Engineering, M A College of Engineering, Kothamangalam 686 666,
LINEAR AND NONLINEAR BUCKLING ANALYSIS OF STIFFENED CYLINDRICAL SUBMARINE HULL SREELATHA P.R * M.Tech. Student, Computer Aided Structural Engineering, M A College of Engineering, Kothamangalam 686 666,
Mechanics of Materials Primer
 Mechanics of Materials rimer Notation: A = area (net = with holes, bearing = in contact, etc...) b = total width of material at a horizontal section d = diameter of a hole D = symbol for diameter E = modulus
Mechanics of Materials rimer Notation: A = area (net = with holes, bearing = in contact, etc...) b = total width of material at a horizontal section d = diameter of a hole D = symbol for diameter E = modulus
Compression Members. ENCE 455 Design of Steel Structures. III. Compression Members. Introduction. Compression Members (cont.)
 ENCE 455 Design of Steel Structures III. Compression Members C. C. Fu, Ph.D., P.E. Civil and Environmental Engineering Department University of Maryland Compression Members Following subjects are covered:
ENCE 455 Design of Steel Structures III. Compression Members C. C. Fu, Ph.D., P.E. Civil and Environmental Engineering Department University of Maryland Compression Members Following subjects are covered:
Cone-shaped socket connections for cylindrical members
 NSCC2009 Cone-shaped socket connections for cylindrical members H. Kuwamura 1 & T. Ito 2 1 Department of Architecture, The University of Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan 2 Department of Architecture, Tokyo University
NSCC2009 Cone-shaped socket connections for cylindrical members H. Kuwamura 1 & T. Ito 2 1 Department of Architecture, The University of Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan 2 Department of Architecture, Tokyo University
3 Shearing stress. 3.1 Introduction
 3 Shearing stress 3.1 Introduction In Chapter 1 we made a study of tensile and compressive stresses, which we called direct stresses. There is another type of stress which plays a vital role in the behaviour
3 Shearing stress 3.1 Introduction In Chapter 1 we made a study of tensile and compressive stresses, which we called direct stresses. There is another type of stress which plays a vital role in the behaviour
LATERAL STABILITY OF BEAMS WITH ELASTIC END RESTRAINTS
 LATERAL STABILITY OF BEAMS WITH ELASTIC END RESTRAINTS By John J. Zahn, 1 M. ASCE ABSTRACT: In the analysis of the lateral buckling of simply supported beams, the ends are assumed to be rigidly restrained
LATERAL STABILITY OF BEAMS WITH ELASTIC END RESTRAINTS By John J. Zahn, 1 M. ASCE ABSTRACT: In the analysis of the lateral buckling of simply supported beams, the ends are assumed to be rigidly restrained
Job No. Sheet 1 of 6 Rev B. Made by IR Date Oct Checked by FH/NB Date Oct Revised by MEB Date April 2006
 Job No. Sheet 1 of 6 Rev B, Route de Limours Tel : (0)1 0 85 5 00 Fax : (0)1 0 5 75 8 Revised by MEB Date April 006 DESIGN EXAMPLE 6 BOLTED JOINT A 0 0 angle loaded in tension is to be connected to a gusset
Job No. Sheet 1 of 6 Rev B, Route de Limours Tel : (0)1 0 85 5 00 Fax : (0)1 0 5 75 8 Revised by MEB Date April 006 DESIGN EXAMPLE 6 BOLTED JOINT A 0 0 angle loaded in tension is to be connected to a gusset
NORMAL STRESS. The simplest form of stress is normal stress/direct stress, which is the stress perpendicular to the surface on which it acts.
 NORMAL STRESS The simplest form of stress is normal stress/direct stress, which is the stress perpendicular to the surface on which it acts. σ = force/area = P/A where σ = the normal stress P = the centric
NORMAL STRESS The simplest form of stress is normal stress/direct stress, which is the stress perpendicular to the surface on which it acts. σ = force/area = P/A where σ = the normal stress P = the centric
ON THE PREDICTION OF EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS FROM TWO PILE TESTS UNDER FORCED VIBRATIONS
 Transactions, SMiRT-24 ON THE PREDICTION OF EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS FROM TWO PILE TESTS UNDER FORCED VIBRATIONS 1 Principal Engineer, MTR & Associates, USA INTRODUCTION Mansour Tabatabaie 1 Dynamic response
Transactions, SMiRT-24 ON THE PREDICTION OF EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS FROM TWO PILE TESTS UNDER FORCED VIBRATIONS 1 Principal Engineer, MTR & Associates, USA INTRODUCTION Mansour Tabatabaie 1 Dynamic response
Members Subjected to Torsional Loads
 Members Subjected to Torsional Loads Torsion of circular shafts Definition of Torsion: Consider a shaft rigidly clamped at one end and twisted at the other end by a torque T = F.d applied in a plane perpendicular
Members Subjected to Torsional Loads Torsion of circular shafts Definition of Torsion: Consider a shaft rigidly clamped at one end and twisted at the other end by a torque T = F.d applied in a plane perpendicular
The Design of Reactor Internals Hold-Down Spring
 MATEC Web of Conferences 40, 02002 ( 2016) DOI: 10.1051/ matecconf/ 2016400200 2 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2016 The Design of Reactor Internals Hold-Down Spring Xue Guohong 1,a,
MATEC Web of Conferences 40, 02002 ( 2016) DOI: 10.1051/ matecconf/ 2016400200 2 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2016 The Design of Reactor Internals Hold-Down Spring Xue Guohong 1,a,
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK. Subject code/name: ME2254/STRENGTH OF MATERIALS Year/Sem:II / IV
 KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Subject code/name: ME2254/STRENGTH OF MATERIALS Year/Sem:II / IV UNIT I STRESS, STRAIN DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS PART A (2 MARKS)
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Subject code/name: ME2254/STRENGTH OF MATERIALS Year/Sem:II / IV UNIT I STRESS, STRAIN DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS PART A (2 MARKS)
Collapse behaviour and simplified modeling of triangular cross-section columns
 Indian Journal of ngineering & Materials Sciences Vol. 16, April 2009, pp. 71-78 Collapse behaviour and simplified ing of triangular cross-section columns Yucheng Liu* Department of Mechanical ngineering,
Indian Journal of ngineering & Materials Sciences Vol. 16, April 2009, pp. 71-78 Collapse behaviour and simplified ing of triangular cross-section columns Yucheng Liu* Department of Mechanical ngineering,
BUCKLING MODE CLASSIFICATION OF MEMBERS WITH OPEN THIN-WALLED CROSS-SECTIONS
 CIMS 4 Fourth International Conference on Coupled Instabilities in Metal Structures Rome, Italy, 27-29 September, 24 BUCKLING MODE CLASSIFICATION OF MEMBERS WITH OPEN THIN-WALLED CROSS-SECTIONS S. ÁDÁNY,
CIMS 4 Fourth International Conference on Coupled Instabilities in Metal Structures Rome, Italy, 27-29 September, 24 BUCKLING MODE CLASSIFICATION OF MEMBERS WITH OPEN THIN-WALLED CROSS-SECTIONS S. ÁDÁNY,
Chapter 5 CENTRIC TENSION OR COMPRESSION ( AXIAL LOADING )
 Chapter 5 CENTRIC TENSION OR COMPRESSION ( AXIAL LOADING ) 5.1 DEFINITION A construction member is subjected to centric (axial) tension or compression if in any cross section the single distinct stress
Chapter 5 CENTRIC TENSION OR COMPRESSION ( AXIAL LOADING ) 5.1 DEFINITION A construction member is subjected to centric (axial) tension or compression if in any cross section the single distinct stress
EUROCODE EN SEISMIC DESIGN OF BRIDGES
 Brussels, 18-20 February 2008 Dissemination of information workshop 1 EUROCODE EN1998-2 SEISMIC DESIGN OF BRIDGES Basil Kolias Basic Requirements Brussels, 18-20 February 2008 Dissemination of information
Brussels, 18-20 February 2008 Dissemination of information workshop 1 EUROCODE EN1998-2 SEISMIC DESIGN OF BRIDGES Basil Kolias Basic Requirements Brussels, 18-20 February 2008 Dissemination of information
Cyclic Behavior of Sand and Cyclic Triaxial Tests. Hsin-yu Shan Dept. of Civil Engineering National Chiao Tung University
 Cyclic Behavior of Sand and Cyclic Triaxial Tests Hsin-yu Shan Dept. of Civil Engineering National Chiao Tung University Causes of Pore Pressure Buildup due to Cyclic Stress Application Stress are due
Cyclic Behavior of Sand and Cyclic Triaxial Tests Hsin-yu Shan Dept. of Civil Engineering National Chiao Tung University Causes of Pore Pressure Buildup due to Cyclic Stress Application Stress are due
EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA SCIENCE FOR TECHNICIANS OUTCOME 1 - STATIC AND DYNAMIC FORCES TUTORIAL 3 STRESS AND STRAIN
 EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA SCIENCE FOR TECHNICIANS OUTCOME 1 - STATIC AND DYNAMIC FORCES TUTORIAL 3 STRESS AND STRAIN 1 Static and dynamic forces Forces: definitions of: matter, mass, weight,
EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA SCIENCE FOR TECHNICIANS OUTCOME 1 - STATIC AND DYNAMIC FORCES TUTORIAL 3 STRESS AND STRAIN 1 Static and dynamic forces Forces: definitions of: matter, mass, weight,
Module 5: Failure Criteria of Rock and Rock masses. Contents Hydrostatic compression Deviatoric compression
 FAILURE CRITERIA OF ROCK AND ROCK MASSES Contents 5.1 Failure in rocks 5.1.1 Hydrostatic compression 5.1.2 Deviatoric compression 5.1.3 Effect of confining pressure 5.2 Failure modes in rocks 5.3 Complete
FAILURE CRITERIA OF ROCK AND ROCK MASSES Contents 5.1 Failure in rocks 5.1.1 Hydrostatic compression 5.1.2 Deviatoric compression 5.1.3 Effect of confining pressure 5.2 Failure modes in rocks 5.3 Complete
Figure 2-1: Stresses under axisymmetric circular loading
 . Stresses in Pavements.1. Stresses in Fleible Pavements.1.1. Stresses in Homogeneous Mass Boussinesq formulated models for the stresses inside an elastic half-space due to a concentrated load applied
. Stresses in Pavements.1. Stresses in Fleible Pavements.1.1. Stresses in Homogeneous Mass Boussinesq formulated models for the stresses inside an elastic half-space due to a concentrated load applied
PARAMETRIC STUDY OF THE STRUCTURAL CAPACITY OF REINFORCED CONCRETE CONTAINMENT SUBJECTED TO LARGE COMMERICAL AIRCRFAT IMPACT
 Transactions, SMiRT-23, Paper 285 PARAMETRIC STUDY OF THE STRUCTURAL CAPACITY OF REINFORCED CONCRETE CONTAINMENT SUBJECTED TO LARGE COMMERICAL AIRCRFAT IMPACT Marin Kostov 1, Milko Miloshev 2, Zhivko Nikolov
Transactions, SMiRT-23, Paper 285 PARAMETRIC STUDY OF THE STRUCTURAL CAPACITY OF REINFORCED CONCRETE CONTAINMENT SUBJECTED TO LARGE COMMERICAL AIRCRFAT IMPACT Marin Kostov 1, Milko Miloshev 2, Zhivko Nikolov
ANALYSIS AND SIMULATION OF AN AIRPLANE SEAT DURING VERTICAL IMPACTS
 ANALYSIS AND SIMULATION OF AN AIRPLANE SEAT DURING VERTICAL IMPACTS ABSTRACT Luís Carlos das Neves Ferreira luis.neves.ferreira@ist.utl.pt Instituto Superior Técnico, Universidade de Lisboa, Portugal December
ANALYSIS AND SIMULATION OF AN AIRPLANE SEAT DURING VERTICAL IMPACTS ABSTRACT Luís Carlos das Neves Ferreira luis.neves.ferreira@ist.utl.pt Instituto Superior Técnico, Universidade de Lisboa, Portugal December
Section Forces Within Earth. 8 th Grade Earth & Space Science - Class Notes
 Section 19.1 - Forces Within Earth 8 th Grade Earth & Space Science - Class Notes Stress and Strain Stress - is the total force acting on crustal rocks per unit of area (cause) Strain deformation of materials
Section 19.1 - Forces Within Earth 8 th Grade Earth & Space Science - Class Notes Stress and Strain Stress - is the total force acting on crustal rocks per unit of area (cause) Strain deformation of materials
3-D Numerical simulation of shake-table tests on piles subjected to lateral spreading
 3-D Numerical simulation of shake-table tests on piles subjected to lateral spreading M. Cubrinovski 1, H. Sugita 2, K. Tokimatsu 3, M. Sato 4, K. Ishihara 5, Y. Tsukamoto 5, T. Kamata 5 1 Department of
3-D Numerical simulation of shake-table tests on piles subjected to lateral spreading M. Cubrinovski 1, H. Sugita 2, K. Tokimatsu 3, M. Sato 4, K. Ishihara 5, Y. Tsukamoto 5, T. Kamata 5 1 Department of
Application of cyclic accumulation models for undrained and partially drained general boundary value problems
 Application of cyclic accumulation models for undrained and partially drained general boundary value problems A. M. Page Risueño Yngres Dag 2014, May 15 th 2014 Introduction Cyclic loads in geotechnical
Application of cyclic accumulation models for undrained and partially drained general boundary value problems A. M. Page Risueño Yngres Dag 2014, May 15 th 2014 Introduction Cyclic loads in geotechnical
