J. N. R E DDY ENERGY PRINCIPLES AND VARIATIONAL METHODS APPLIED MECHANICS
|
|
|
- Phillip Simmons
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 J. N. E DDY ENEGY PINCIPLES AND VAIATIONAL METHODS IN APPLIED MECHANICS T H I D E DI T IO N
2 JN eddy - 1 MEEN 618: ENEGY AND VAIATIONAL METHODS A EVIEW OF VECTOS AND TENSOS ead: Chapte 2 CONTENTS Physical vecto Axioms of mathematical vecto Scala and vecto poducts Tiple poducts of vectos Components of vectos Summation convention Second-ode tensos Tansfomation of components The del opeato and calculus of vectos and tensos Cylindical and spheical coodinates systems J. N. eddy VECTOS&TENSOS -
3 JN eddy - 2 A EVIEW OF VECTOS AND TENSOS Much of the mateial included heein is taken fom the instucto s two books exhibited hee (both published by the Cambidge Univesity Pess) J. N. eddy VECTOS&TENSOS - 2
4 JN eddy - 3 PHYSICAL VECTOS Physical vecto: A diected line segment with an aow head. Examples: foce, displacement, velocity, weight Unit vecto along a given vecto A: A The unit vecto, ê A ( A 0) A is that vecto which has the same P A ê A Q diection as A but has a magnitude that is unity. J. N. eddy VECTOS&TENSOS - 3
5 JN eddy - 4 MATHEMATICAL VECTOS ules o Axioms Vecto addition: (i) A + B = B+A (commutative) (ii) (A + B)+C = A+(B+C) (associative) (iii) A+0=A (zeo vecto) (iv) A+( A) = 0 (negative vecto) Scala multiplication of a vecto: (i) α(βa)= αβ (A) (associative) (ii) (α + β)a = α A+ βa (distibutive w..t. scala addition) (iii) α (A+B)=αA+αB (distibutive w..t. vecto addition) (iv) 1. A=A. 1 A B B A A+B=B+A J. N. eddy VECTOS&TENSOS - 4
6 JN eddy - 5 VECTOS (continued) Wok done Magnitude of the foce multiplied by the magnitude of the displacement in the diection of the foce: F u WD F cosu F u WD F u cos J. N. eddy VECTOS&TENSOS - 5
7 JN eddy - 6 VECTOS (continued) Inne poduct (o scala poduct) of two vectos is defined as A B A B cos AB cos A = A A = A B = B A A J. N. eddy VECTOS&TENSOS - 6
8 JN eddy - 7 VECTOS (continued) Moment of a foce Magnitude of the foce multiplied by the magnitude of the pependicula distance to the action of the foce: M F, M sinf M F F e M F O P θ M O θ sin sin J. N. eddy VECTOS&TENSOS - 7
9 JN eddy - 8 VECTOS (continued) Vecto poduct of two vectos is defined as AB A B sin e ˆ AB sin AB AB A AB B J. N. eddy VECTOS&TENSOS - 8
10 JN eddy - 9 PLANE AEA AS A VECTO The magnitude of the vecto C = A B is equal to the aea of the paallelogam fomed by the vectos A and B. C = A B B ê θ S A S S nˆ In fact, the vecto C may be consideed to epesent both the magnitude and the diection of the poduct of A and B. Thus, a plane aea in space may be looked upon as possessing a diection in addition to a magnitude, the diectional chaacte aising out of the need to specify an oientation of the plane aea in space. epesentation of an aea as a vecto has many uses in mechanics, as will be seen in the sequel. ˆn J. N. eddy VECTOS&TENSOS - 9
11 JN eddy - 10 SCALA TIPLE PODUCT The poduct A. (B C) is a scala and it is temed the scala tiple poduct. It can be seen fom the figue that the poduct A. (B C), except fo the algebaic sign, is the volume of the paallelepiped fomed by the vectos A, B, and C. B C A C B A. (B C) J. N. eddy VECTOS&TENSOS -10
12 JN eddy - 11 EXECISES ON VECTOS 1. If two vectos ae such that what can we conclude? 2. If two vectos ae such that what can we conclude? 3. Pove that ABCABC AB0 AB0 4. If thee vectos ae such that ABC 0 what can we conclude? 5. The velocity vecto in a flow field is v 2 i ˆ 3 ˆ j (m/ s). Detemine (a) the velocity vecto nomal to the plane 3 ˆ v n n i-4ˆ k passing though the point, (b) the angle between v and v n, (c) tangential velocity vecto on the plane, and (d) The mass flow ate acoss the plane though an aea A m if the fluid density is 10 kg/ m and the flow is unifom. J. N. eddy VECTOS&TENSOS -11
13 JN eddy - 12 COMPONENTS OF VECTOS Components of a vecto e ˆ e z ˆ3 e ˆ e ˆ y 2 ˆ e x ˆ1 e z x 3 A x x 1 y x 2 1, 0, 0, , 0, 1, ,,, ,, A A A A x x y y z z A A A n ˆ n n n x x y y z z n n n z x 3 A A 1 A 2 A 3 i x x 1 y x 2 A A i J. N. eddy VECTOS&TENSOS -12
14 JN eddy - 13 SUMMATION CONVENTION Omit the summation sign and undestand that a epeated index is to be summed ove its ange: A A A A i1 A A (summation convention) i i i i Dummy index A A A Dummy indices Scala poduct i i j j A ˆ B ˆ AB e e AB i i j j i j i j AB AB i j ij i i 0, if i 1, if i ij i j J. N. eddy VECTOS&TENSOS -13 j j
15 JN eddy - 14 Vecto poduct SUMMATION CONVENTION (continued) AB AB sin A B AB AB AB i i j j i j i j i j ijk k AB A A A B B B ijk 2 i j j k k i i j ijk k 0, if any twoindicesaethesame 1, if i j k, and they pemute inanatual ode 1, if i j k,and they pemute opposite toanatual ode ijk i j k i j k 1 J. N. eddy VECTOS&TENSOS -14
16 JN eddy - 15 SUMMATION CONVENTION (continued) Contaction of indices: The Konecke delta ij modifies (o contacts) the subscipts in the coefficients of an expession in which it appeas: A A, AB AB AB, i ij j i j ij i i j j ij ik jk Coect expessions: F ABC, G H ( 23AB) PQF i i j j k k i i j j k Fee indices Incoect expessions: A BC, A B and F ABC i j k i j k i j k J. N. eddy VECTOS&TENSOS -15
17 JN eddy - 16 SUMMATION CONVENTION (continued) One must be caeful when substituting a quantity with an index into an expession with indices o solving fo one quantity with index in tems of the othes with indices in an equation. Fo example, conside the equations It is coect to wite p abc and c deq i i j j k i i k but it is incoect to wite pi bc j j ai which has a totally diffeent meaning bc a i pi bc p p p i j j ai a1 a2 a3 J. N. eddy VECTOS&TENSOS -16 j j p
18 JN eddy - 17 SUMMATION CONVENTION (continued) The pemutation symbol and the Konecke delta pove to be vey useful in establishing vecto identities. Since a vecto fom of any identity is invaiant (i.e., valid in any coodinate system), it suffices to pove it in one coodinate system. The following identity is useful: - Identity: ijk imn jm kn jn km J. N. eddy VECTOS&TENSOS -17
19 JN eddy - 18 EXECISES ON INDEX NOTATION Execise-1: Check which one of the following expessions ae valid: (a) abc( df); (b) abc( df) m s m m s m s s (c) a bc( d f); (d) x x i j i i i m m (e) a 3; (f)? i ij jk ki Execise-2: Pove A A A ABCijkABC i j k B B B C C C Execise-3: Simplify the expession ( AB)( CD) Execise-4: Simplify the expession A( BC) Execise-5: ewite the expession in vecto fom ABC D J. N. eddy VECTOS&TENSOS ê mni i j m n j
20 JN eddy - 19 SECOND-ODE TENSOS A second-ode tenso is one that has two basis vectos standing next to each othe, and they satisfy the same ules as those of a vecto (hence, mathematically, tensos ae also called vectos). A second-ode tenso and its tanspose can be expessed in tems of ectangula Catesian base vectos as T S S ee ˆˆ S ee ˆˆ; S S ee ˆˆ S ee ˆˆ ij i j ji j i ji i j ij j i A second-ode tenso is symmetic only if SS T Sij Sji Second-ode identity tenso has the fom I ij ˆ i e j J. N. eddy VECTOS&TENSOS -19
21 JN eddy - 20 SECOND-ODE TENSOS We note that ST T S tensos) because (whee S and T ae second-ode ST S ee ˆˆ T ST STee ˆˆ ij i j kl k l ij kl i j k l ij jl i l TS T ee ˆˆ S TS STee ˆˆ ij i j kl k l ij kl i j k l jl ij i l We also note that (whee S and T ae second-ode tensos and A is a vecto) ST S ee ˆˆ T ST ST ee ˆˆ ij i j kl k l ij kl i j k l ij kl jkp i p l SA Sˆ e A SA SA ij i j k k ij k i j k ij j i SA See ˆˆ A SA SA ee ˆˆ ij i j k k ij k i j k ij k jkp i p J. N. eddy VECTOS&TENSOS -20
22 JN eddy - 21 CAUCHY STESS TENSO Stess tenso is a good example of a second-ode tenso. The two basis vectos epesent the diection and the plane on which they act. The Cauchy stess tenso is defined by the Cauchy fomula (to be established): t 1 x 1 t 3 σ ê 1 x 3 ê 3 T ˆ ˆ o ti ij nj t n n σ ê 2 t2 x 2 t i j ji ji j 13 t ee ˆˆ ee ˆˆ t t ˆ ˆ ˆ 2 e112 e222 e332 i i ji j i ij i j J. N. eddy VECTOS&TENSOS t
23 JN eddy - 22 CAUCHY S FOMULA t at1 a1t2 a2t3 a3ρ vf ρ va anˆ a ˆ ˆ ˆ 1e1a2e2a3e3 0 a ( nˆ) a, a ( nˆ) a h a ˆ ˆ 3 ( e3n) a, v a 3 F 1 F 2 t ( 2) F 3 a 2 = t2 h t t1( 1nˆ) t2( 2nˆ) t3( 3nˆ) ( af) 3 As h 0, we obtain 2 x 1 t ˆn t Inteio of the body x 3 ê 3 ê ê 2 1 t t1( 1nˆ) t2( 2nˆ) t3( 3nˆ) t nˆ nˆ i i 3 ˆn On the bounday a t 1 t 2 a 1 ( 1) t = t 1 t t ( 3) a 3 = t ˆn 3 1 ( nˆ ) x 3 x 2 t t 3 ˆn x 2 x 1 J. N. eddy VECTOS&TENSOS -22
24 JN eddy - 23 HIGHE-ODE TENSOS A n th -ode tenso is one that has n basis vectos standing next to each othe, and they satisfy the same ules as those of a vecto. A n th -ode tenso T can be expessed in tems of ectangula Catesian base vectos as T T ˆˆ e e ijkp i j k p ; C ε n subs eee ˆˆˆ eee ˆˆˆ base vectos The pemutation tenso is a thid-ode tenso J. N. eddy VECTOS&TENSOS -23 n ijk i j k The elasticity tenso is a fouth-ode tenso C ijkl i j k l
25 JN eddy - 24 TANSFOMATION OF TENSO COMPONENTS A second-ode Catesian tenso S (i.e., tenso with Catesian components) may be epesented in baed ( x and unbaed Catesian coodinate 1, x2, x3) ( x1, x2, x3) systems as S s ee ˆ ˆ s ij i j mn m n The unit base vectos in the unbaed and baed systems ae elated by and, j ij i i ij j ij i j Thus the components of a second-ode tenso tansfom accoding to s s ij im jn mn J. N. eddy VECTOS&TENSOS -24
26 THE DEL OPEATO AND ITS POPETIES IN ECTANGULA CATESIAN SYSTEM JN eddy - 25 Del opeato: i xi x x x Laplace opeato: 2 xixi x x x Gadient opeation: F F ê i, whee F isa scala function x i Gad F defines both the diection and magnitude of the maximum ate of incease of F at any point. J. N. eddy VECTOS&TENSOS -25
27 THE DEL OPEATO AND ITS POPETIES IN ECTANGULA CATESIAN SYSTEM JN eddy - 26 F F nˆ, whee nˆ isa unit vecto nomal n to the suface F constant F F We also have nˆ and nˆ F F n Divegence opeation: Gi G i jg j, whee Gisavecto function x x i The divegence of a vecto function epesents the volume density of the outwad flux of the vecto field. i J. N. eddy VECTOS&TENSOS -26
28 THE DEL OPEATO AND ITS POPETIES IN ECTANGULA CATESIAN SYSTEM JN eddy - 27 Cul opeation: Gj G i jg j ijk k, x ε x i whee Gisavecto function. The cul of a vecto function epesents its otation. If the vecto field is the velocity of a fluid, cul of the velocity epesents the otation of the fluid at the point. i J. N. eddy VECTOS&TENSOS -27
29 JN eddy - 28 CYLINDICAL COODINATE SYSTEM 0 cos sin x sin cos 0 y z z 0 x cos sin sin cos 0 y z z A A A A z z Del opeato in cylindical coodinates 1 z z J. N. eddy VECTOS&TENSOS -28 x z θ y, z z x ê z y
30 JN eddy - 29 CYLINDICAL COODINATE SYSTEM 1 ( A ) A A z A z 1 1 z Az A A A z 1( A) A A z z A A 1 A Az A A ee ˆ ˆ ee ˆ ˆ A ee ˆ ˆ ee ˆ ˆ ee ˆ ˆ z 1 A 1A A ee ˆ ˆ ee ˆ ˆ J. N. eddy VECTOS&TENSOS -29 z z z Hee A is a vecto: A A A A Veify these elations to youself A z z z ee ˆ ˆ A z ee ˆ ˆ z z z z z z
31 JN eddy - 30 SPHEICAL COODINATE SYSTEM sin cos sin sin cos x cos cos cos sin sin y sin cos 0 z x sincos coscos sine ˆ y sinsin cossin cos z cos sin 0 A A A A Del opeato 1 1 sin J. N. eddy VECTOS&TENSOS -30 x z x y z 2 2 Line paallel to ê θ y, sin, cos sin z θ x ê ê cos y Line paallel to ê
32 JN eddy - 31 SPHEICAL COODINATE SYSTEM sin sin sin A 1 ( sin ) A A 1 A A sin sin 1 (sin A ) A 1 1 ( ) 1 ( A ) A A A A sin sin A A 1 A A 1 A A sin A A sin 1 A 1 A 1 A A ee ˆ ˆ ee ˆ ˆ cos ee ˆ ˆ A sin 1 A A sin cos ee ˆ ˆ A sin J. N. eddy VECTOS&TENSOS -31
33 JN eddy - 32 EXECISES ON VECTO CALCULUS Establish the following identities (using ectangula Catesian components and index notation): 1. ( ) n 2. ( ) n n2 3. ( F ) 0 4. ( FG) A A A ( ) ( ) AB ABBA A( A) ( AA) AA. 1 2 J. N. eddy VECTOS&TENSOS -32
34 JN eddy - 33 Execise: Check appopiate box Quantity Vecto Scala Nonsense ( f ) ( F) ( f ) ( F) ( F) ( f ) f scala; F vecto J. N. eddy VECTOS&TENSOS -33
35 JN eddy - 34 INTEGAL THEOEMS involving the del opeato d nˆ ds Ad nˆ Ads Ad nˆ Ads y ˆj y ˆi n yˆ j nˆ n xˆ i ds x (Gadient theoem) (Divegence theoem) (Cul theoem) nˆ n ˆin ˆj x J. N. eddy VECTOS&TENSOS -34 n n x y n x x y y n
36 J. N. eddy VECTOS&TENSOS -35 EXECISES ON INTEGAL IDENTITIES n n ˆ ˆ. volume ( ).... ( ) d d d d n d d n d d n n d d n n Establish the following identities using the integal theoems: JN eddy - 35
As is natural, our Aerospace Structures will be described in a Euclidean three-dimensional space R 3.
 Appendix A Vecto Algeba As is natual, ou Aeospace Stuctues will be descibed in a Euclidean thee-dimensional space R 3. A.1 Vectos A vecto is used to epesent quantities that have both magnitude and diection.
Appendix A Vecto Algeba As is natual, ou Aeospace Stuctues will be descibed in a Euclidean thee-dimensional space R 3. A.1 Vectos A vecto is used to epesent quantities that have both magnitude and diection.
Appendix A. Appendices. A.1 ɛ ijk and cross products. Vector Operations: δ ij and ɛ ijk
 Appendix A Appendices A1 ɛ and coss poducts A11 Vecto Opeations: δ ij and ɛ These ae some notes on the use of the antisymmetic symbol ɛ fo expessing coss poducts This is an extemely poweful tool fo manipulating
Appendix A Appendices A1 ɛ and coss poducts A11 Vecto Opeations: δ ij and ɛ These ae some notes on the use of the antisymmetic symbol ɛ fo expessing coss poducts This is an extemely poweful tool fo manipulating
BASIC ALGEBRA OF VECTORS
 Fomulae Fo u Vecto Algeba By Mi Mohammed Abbas II PCMB 'A' Impotant Tems, Definitions & Fomulae 01 Vecto - Basic Intoduction: A quantity having magnitude as well as the diection is called vecto It is denoted
Fomulae Fo u Vecto Algeba By Mi Mohammed Abbas II PCMB 'A' Impotant Tems, Definitions & Fomulae 01 Vecto - Basic Intoduction: A quantity having magnitude as well as the diection is called vecto It is denoted
(read nabla or del) is defined by, k. (9.7.1*)
 9.7 Gadient of a scala field. Diectional deivative Some of the vecto fields in applications can be obtained fom scala fields. This is vey advantageous because scala fields can be handled moe easily. The
9.7 Gadient of a scala field. Diectional deivative Some of the vecto fields in applications can be obtained fom scala fields. This is vey advantageous because scala fields can be handled moe easily. The
Stress, Cauchy s equation and the Navier-Stokes equations
 Chapte 3 Stess, Cauchy s equation and the Navie-Stokes equations 3. The concept of taction/stess Conside the volume of fluid shown in the left half of Fig. 3.. The volume of fluid is subjected to distibuted
Chapte 3 Stess, Cauchy s equation and the Navie-Stokes equations 3. The concept of taction/stess Conside the volume of fluid shown in the left half of Fig. 3.. The volume of fluid is subjected to distibuted
AE301 Aerodynamics I UNIT B: Theory of Aerodynamics
 AE301 Aeodynamics I UNIT B: Theoy of Aeodynamics ROAD MAP... B-1: Mathematics fo Aeodynamics B-2: Flow Field Repesentations B-3: Potential Flow Analysis B-4: Applications of Potential Flow Analysis AE301
AE301 Aeodynamics I UNIT B: Theoy of Aeodynamics ROAD MAP... B-1: Mathematics fo Aeodynamics B-2: Flow Field Repesentations B-3: Potential Flow Analysis B-4: Applications of Potential Flow Analysis AE301
Vectors, Vector Calculus, and Coordinate Systems
 Apil 5, 997 A Quick Intoduction to Vectos, Vecto Calculus, and Coodinate Systems David A. Randall Depatment of Atmospheic Science Coloado State Univesity Fot Collins, Coloado 80523. Scalas and vectos Any
Apil 5, 997 A Quick Intoduction to Vectos, Vecto Calculus, and Coodinate Systems David A. Randall Depatment of Atmospheic Science Coloado State Univesity Fot Collins, Coloado 80523. Scalas and vectos Any
2 Governing Equations
 2 Govening Equations This chapte develops the govening equations of motion fo a homogeneous isotopic elastic solid, using the linea thee-dimensional theoy of elasticity in cylindical coodinates. At fist,
2 Govening Equations This chapte develops the govening equations of motion fo a homogeneous isotopic elastic solid, using the linea thee-dimensional theoy of elasticity in cylindical coodinates. At fist,
Vector d is a linear vector function of vector d when the following relationships hold:
 Appendix 4 Dyadic Analysis DEFINITION ecto d is a linea vecto function of vecto d when the following elationships hold: d x = a xxd x + a xy d y + a xz d z d y = a yxd x + a yy d y + a yz d z d z = a zxd
Appendix 4 Dyadic Analysis DEFINITION ecto d is a linea vecto function of vecto d when the following elationships hold: d x = a xxd x + a xy d y + a xz d z d y = a yxd x + a yy d y + a yz d z d z = a zxd
2. Electrostatics. Dr. Rakhesh Singh Kshetrimayum 8/11/ Electromagnetic Field Theory by R. S. Kshetrimayum
 2. Electostatics D. Rakhesh Singh Kshetimayum 1 2.1 Intoduction In this chapte, we will study how to find the electostatic fields fo vaious cases? fo symmetic known chage distibution fo un-symmetic known
2. Electostatics D. Rakhesh Singh Kshetimayum 1 2.1 Intoduction In this chapte, we will study how to find the electostatic fields fo vaious cases? fo symmetic known chage distibution fo un-symmetic known
ECE 3318 Applied Electricity and Magnetism. Spring Prof. David R. Jackson ECE Dept. Notes 13
 ECE 338 Applied Electicity and Magnetism ping 07 Pof. David R. Jackson ECE Dept. Notes 3 Divegence The Physical Concept Find the flux going outwad though a sphee of adius. x ρ v0 z a y ψ = D nˆ d = D ˆ
ECE 338 Applied Electicity and Magnetism ping 07 Pof. David R. Jackson ECE Dept. Notes 3 Divegence The Physical Concept Find the flux going outwad though a sphee of adius. x ρ v0 z a y ψ = D nˆ d = D ˆ
EELE 3331 Electromagnetic I Chapter 4. Electrostatic fields. Islamic University of Gaza Electrical Engineering Department Dr.
 EELE 3331 Electomagnetic I Chapte 4 Electostatic fields Islamic Univesity of Gaza Electical Engineeing Depatment D. Talal Skaik 212 1 Electic Potential The Gavitational Analogy Moving an object upwad against
EELE 3331 Electomagnetic I Chapte 4 Electostatic fields Islamic Univesity of Gaza Electical Engineeing Depatment D. Talal Skaik 212 1 Electic Potential The Gavitational Analogy Moving an object upwad against
University Physics (PHY 2326)
 Chapte Univesity Physics (PHY 6) Lectue lectostatics lectic field (cont.) Conductos in electostatic euilibium The oscilloscope lectic flux and Gauss s law /6/5 Discuss a techniue intoduced by Kal F. Gauss
Chapte Univesity Physics (PHY 6) Lectue lectostatics lectic field (cont.) Conductos in electostatic euilibium The oscilloscope lectic flux and Gauss s law /6/5 Discuss a techniue intoduced by Kal F. Gauss
Question Bank. Section A. is skew-hermitian matrix. is diagonalizable. (, ) , Evaluate (, ) 12 about = 1 and = Find, if
 Subject: Mathematics-I Question Bank Section A T T. Find the value of fo which the matix A = T T has ank one. T T i. Is the matix A = i is skew-hemitian matix. i. alculate the invese of the matix = 5 7
Subject: Mathematics-I Question Bank Section A T T. Find the value of fo which the matix A = T T has ank one. T T i. Is the matix A = i is skew-hemitian matix. i. alculate the invese of the matix = 5 7
working pages for Paul Richards class notes; do not copy or circulate without permission from PGR 2004/11/3 10:50
 woking pages fo Paul Richads class notes; do not copy o ciculate without pemission fom PGR 2004/11/3 10:50 CHAPTER7 Solid angle, 3D integals, Gauss s Theoem, and a Delta Function We define the solid angle,
woking pages fo Paul Richads class notes; do not copy o ciculate without pemission fom PGR 2004/11/3 10:50 CHAPTER7 Solid angle, 3D integals, Gauss s Theoem, and a Delta Function We define the solid angle,
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL CHAPTER 7 A (2 ) B. a x + bx + c dx
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL 613 7.6.3 CHAPTER 7 ( px + q) a x + bx + c dx. We choose constants A and B such that d px + q A ( ax + bx + c) + B dx A(ax + b) + B Compaing the coefficients of x and the constant
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL 613 7.6.3 CHAPTER 7 ( px + q) a x + bx + c dx. We choose constants A and B such that d px + q A ( ax + bx + c) + B dx A(ax + b) + B Compaing the coefficients of x and the constant
Physics 235 Chapter 5. Chapter 5 Gravitation
 Chapte 5 Gavitation In this Chapte we will eview the popeties of the gavitational foce. The gavitational foce has been discussed in geat detail in you intoductoy physics couses, and we will pimaily focus
Chapte 5 Gavitation In this Chapte we will eview the popeties of the gavitational foce. The gavitational foce has been discussed in geat detail in you intoductoy physics couses, and we will pimaily focus
Vectors, Vector Calculus, and Coordinate Systems
 ! Revised Apil 11, 2017 1:48 PM! 1 Vectos, Vecto Calculus, and Coodinate Systems David Randall Physical laws and coodinate systems Fo the pesent discussion, we define a coodinate system as a tool fo descibing
! Revised Apil 11, 2017 1:48 PM! 1 Vectos, Vecto Calculus, and Coodinate Systems David Randall Physical laws and coodinate systems Fo the pesent discussion, we define a coodinate system as a tool fo descibing
Liquid gas interface under hydrostatic pressure
 Advances in Fluid Mechanics IX 5 Liquid gas inteface unde hydostatic pessue A. Gajewski Bialystok Univesity of Technology, Faculty of Civil Engineeing and Envionmental Engineeing, Depatment of Heat Engineeing,
Advances in Fluid Mechanics IX 5 Liquid gas inteface unde hydostatic pessue A. Gajewski Bialystok Univesity of Technology, Faculty of Civil Engineeing and Envionmental Engineeing, Depatment of Heat Engineeing,
1 Spherical multipole moments
 Jackson notes 9 Spheical multipole moments Suppose we have a chage distibution ρ (x) wheeallofthechageiscontained within a spheical egion of adius R, as shown in the diagam. Then thee is no chage in the
Jackson notes 9 Spheical multipole moments Suppose we have a chage distibution ρ (x) wheeallofthechageiscontained within a spheical egion of adius R, as shown in the diagam. Then thee is no chage in the
DonnishJournals
 DonnishJounals 041-1189 Donnish Jounal of Educational Reseach and Reviews. Vol 1(1) pp. 01-017 Novembe, 014. http:///dje Copyight 014 Donnish Jounals Oiginal Reseach Pape Vecto Analysis Using MAXIMA Savaş
DonnishJounals 041-1189 Donnish Jounal of Educational Reseach and Reviews. Vol 1(1) pp. 01-017 Novembe, 014. http:///dje Copyight 014 Donnish Jounals Oiginal Reseach Pape Vecto Analysis Using MAXIMA Savaş
Review: Electrostatics and Magnetostatics
 Review: Electostatics and Magnetostatics In the static egime, electomagnetic quantities do not vay as a function of time. We have two main cases: ELECTROSTATICS The electic chages do not change postion
Review: Electostatics and Magnetostatics In the static egime, electomagnetic quantities do not vay as a function of time. We have two main cases: ELECTROSTATICS The electic chages do not change postion
Chapter 2: Basic Physics and Math Supplements
 Chapte 2: Basic Physics and Math Supplements Decembe 1, 215 1 Supplement 2.1: Centipetal Acceleation This supplement expands on a topic addessed on page 19 of the textbook. Ou task hee is to calculate
Chapte 2: Basic Physics and Math Supplements Decembe 1, 215 1 Supplement 2.1: Centipetal Acceleation This supplement expands on a topic addessed on page 19 of the textbook. Ou task hee is to calculate
PROBLEM SET #1 SOLUTIONS by Robert A. DiStasio Jr.
 POBLM S # SOLUIONS by obet A. DiStasio J. Q. he Bon-Oppenheime appoximation is the standad way of appoximating the gound state of a molecula system. Wite down the conditions that detemine the tonic and
POBLM S # SOLUIONS by obet A. DiStasio J. Q. he Bon-Oppenheime appoximation is the standad way of appoximating the gound state of a molecula system. Wite down the conditions that detemine the tonic and
CHAPTER 25 ELECTRIC POTENTIAL
 CHPTE 5 ELECTIC POTENTIL Potential Diffeence and Electic Potential Conside a chaged paticle of chage in a egion of an electic field E. This filed exets an electic foce on the paticle given by F=E. When
CHPTE 5 ELECTIC POTENTIL Potential Diffeence and Electic Potential Conside a chaged paticle of chage in a egion of an electic field E. This filed exets an electic foce on the paticle given by F=E. When
3 VECTOR CALCULUS I. 3.1 Divergence and curl of vector fields. 3.2 Important identities
 3 VECTOR CALCULU I 3.1 Divegence and cul of vecto fields Let = ( x, y, z ). eveal popeties of φ fo scala φ wee intoduced in section 1.2. The gadient opeato may also be applied to vecto fields. Let F =
3 VECTOR CALCULU I 3.1 Divegence and cul of vecto fields Let = ( x, y, z ). eveal popeties of φ fo scala φ wee intoduced in section 1.2. The gadient opeato may also be applied to vecto fields. Let F =
F Q E v B MAGNETOSTATICS. Creation of magnetic field B. Effect of B on a moving charge. On moving charges only. Stationary and moving charges
 MAGNETOSTATICS Ceation of magnetic field. Effect of on a moving chage. Take the second case: F Q v mag On moving chages only F QE v Stationay and moving chages dw F dl Analysis on F mag : mag mag Qv. vdt
MAGNETOSTATICS Ceation of magnetic field. Effect of on a moving chage. Take the second case: F Q v mag On moving chages only F QE v Stationay and moving chages dw F dl Analysis on F mag : mag mag Qv. vdt
Electric field generated by an electric dipole
 Electic field geneated by an electic dipole ( x) 2 (22-7) We will detemine the electic field E geneated by the electic dipole shown in the figue using the pinciple of supeposition. The positive chage geneates
Electic field geneated by an electic dipole ( x) 2 (22-7) We will detemine the electic field E geneated by the electic dipole shown in the figue using the pinciple of supeposition. The positive chage geneates
MAGNETIC FIELD INTRODUCTION
 MAGNETIC FIELD INTRODUCTION It was found when a magnet suspended fom its cente, it tends to line itself up in a noth-south diection (the compass needle). The noth end is called the Noth Pole (N-pole),
MAGNETIC FIELD INTRODUCTION It was found when a magnet suspended fom its cente, it tends to line itself up in a noth-south diection (the compass needle). The noth end is called the Noth Pole (N-pole),
dq 1 (5) q 1 where the previously mentioned limit has been taken.
 1 Vecto Calculus And Continuum Consevation Equations In Cuvilinea Othogonal Coodinates Robet Maska: Novembe 25, 2008 In ode to ewite the consevation equations(continuit, momentum, eneg) to some cuvilinea
1 Vecto Calculus And Continuum Consevation Equations In Cuvilinea Othogonal Coodinates Robet Maska: Novembe 25, 2008 In ode to ewite the consevation equations(continuit, momentum, eneg) to some cuvilinea
B. Spherical Wave Propagation
 11/8/007 Spheical Wave Popagation notes 1/1 B. Spheical Wave Popagation Evey antenna launches a spheical wave, thus its powe density educes as a function of 1, whee is the distance fom the antenna. We
11/8/007 Spheical Wave Popagation notes 1/1 B. Spheical Wave Popagation Evey antenna launches a spheical wave, thus its powe density educes as a function of 1, whee is the distance fom the antenna. We
The Divergence Theorem
 13.8 The ivegence Theoem Back in 13.5 we ewote Geen s Theoem in vecto fom as C F n ds= div F x, y da ( ) whee C is the positively-oiented bounday cuve of the plane egion (in the xy-plane). Notice this
13.8 The ivegence Theoem Back in 13.5 we ewote Geen s Theoem in vecto fom as C F n ds= div F x, y da ( ) whee C is the positively-oiented bounday cuve of the plane egion (in the xy-plane). Notice this
AP-C WEP. h. Students should be able to recognize and solve problems that call for application both of conservation of energy and Newton s Laws.
 AP-C WEP 1. Wok a. Calculate the wok done by a specified constant foce on an object that undegoes a specified displacement. b. Relate the wok done by a foce to the aea unde a gaph of foce as a function
AP-C WEP 1. Wok a. Calculate the wok done by a specified constant foce on an object that undegoes a specified displacement. b. Relate the wok done by a foce to the aea unde a gaph of foce as a function
Quiz 6--Work, Gravitation, Circular Motion, Torque. (60 pts available, 50 points possible)
 Name: Class: Date: ID: A Quiz 6--Wok, Gavitation, Cicula Motion, Toque. (60 pts available, 50 points possible) Multiple Choice, 2 point each Identify the choice that best completes the statement o answes
Name: Class: Date: ID: A Quiz 6--Wok, Gavitation, Cicula Motion, Toque. (60 pts available, 50 points possible) Multiple Choice, 2 point each Identify the choice that best completes the statement o answes
TUTORIAL 9. Static magnetic field
 TUTOIAL 9 Static magnetic field Vecto magnetic potential Null Identity % & %$ A # Fist postulation # " B such that: Vecto magnetic potential Vecto Poisson s equation The solution is: " Substitute it into
TUTOIAL 9 Static magnetic field Vecto magnetic potential Null Identity % & %$ A # Fist postulation # " B such that: Vecto magnetic potential Vecto Poisson s equation The solution is: " Substitute it into
4. Electrodynamic fields
 4. Electodynamic fields D. Rakhesh Singh Kshetimayum 1 4.1 Intoduction Electodynamics Faaday s law Maxwell s equations Wave equations Lenz s law Integal fom Diffeential fom Phaso fom Bounday conditions
4. Electodynamic fields D. Rakhesh Singh Kshetimayum 1 4.1 Intoduction Electodynamics Faaday s law Maxwell s equations Wave equations Lenz s law Integal fom Diffeential fom Phaso fom Bounday conditions
Electrostatics (Electric Charges and Field) #2 2010
 Electic Field: The concept of electic field explains the action at a distance foce between two chaged paticles. Evey chage poduces a field aound it so that any othe chaged paticle expeiences a foce when
Electic Field: The concept of electic field explains the action at a distance foce between two chaged paticles. Evey chage poduces a field aound it so that any othe chaged paticle expeiences a foce when
Physics 2212 GH Quiz #2 Solutions Spring 2016
 Physics 2212 GH Quiz #2 Solutions Sping 216 I. 17 points) Thee point chages, each caying a chage Q = +6. nc, ae placed on an equilateal tiangle of side length = 3. mm. An additional point chage, caying
Physics 2212 GH Quiz #2 Solutions Sping 216 I. 17 points) Thee point chages, each caying a chage Q = +6. nc, ae placed on an equilateal tiangle of side length = 3. mm. An additional point chage, caying
Lecture 23. Representation of the Dirac delta function in other coordinate systems
 Lectue 23 Repesentation of the Diac delta function in othe coodinate systems In a geneal sense, one can wite, ( ) = (x x ) (y y ) (z z ) = (u u ) (v v ) (w w ) J Whee J epesents the Jacobian of the tansfomation.
Lectue 23 Repesentation of the Diac delta function in othe coodinate systems In a geneal sense, one can wite, ( ) = (x x ) (y y ) (z z ) = (u u ) (v v ) (w w ) J Whee J epesents the Jacobian of the tansfomation.
2. Plane Elasticity Problems
 S0 Solid Mechanics Fall 009. Plane lasticity Poblems Main Refeence: Theoy of lasticity by S.P. Timoshenko and J.N. Goodie McGaw-Hill New Yok. Chaptes 3..1 The plane-stess poblem A thin sheet of an isotopic
S0 Solid Mechanics Fall 009. Plane lasticity Poblems Main Refeence: Theoy of lasticity by S.P. Timoshenko and J.N. Goodie McGaw-Hill New Yok. Chaptes 3..1 The plane-stess poblem A thin sheet of an isotopic
e.g: If A = i 2 j + k then find A. A = Ax 2 + Ay 2 + Az 2 = ( 2) = 6
 MOTION IN A PLANE 1. Scala Quantities Physical quantities that have only magnitude and no diection ae called scala quantities o scalas. e.g. Mass, time, speed etc. 2. Vecto Quantities Physical quantities
MOTION IN A PLANE 1. Scala Quantities Physical quantities that have only magnitude and no diection ae called scala quantities o scalas. e.g. Mass, time, speed etc. 2. Vecto Quantities Physical quantities
Cartesian Coordinate System and Vectors
 Catesian Coodinate System and Vectos Coodinate System Coodinate system: used to descibe the position of a point in space and consists of 1. An oigin as the efeence point 2. A set of coodinate axes with
Catesian Coodinate System and Vectos Coodinate System Coodinate system: used to descibe the position of a point in space and consists of 1. An oigin as the efeence point 2. A set of coodinate axes with
1 MathematicalPreliminaries
 1 MathematicalPeliminaies The enomous usefulness of mathematics in the natual sciences is something bodeing on the mysteious. Eugene Wigne (1960 1.1 Intoduction This chapte pesents a collection of mathematical
1 MathematicalPeliminaies The enomous usefulness of mathematics in the natual sciences is something bodeing on the mysteious. Eugene Wigne (1960 1.1 Intoduction This chapte pesents a collection of mathematical
THE LAPLACE EQUATION. The Laplace (or potential) equation is the equation. u = 0. = 2 x 2. x y 2 in R 2
 THE LAPLACE EQUATION The Laplace (o potential) equation is the equation whee is the Laplace opeato = 2 x 2 u = 0. in R = 2 x 2 + 2 y 2 in R 2 = 2 x 2 + 2 y 2 + 2 z 2 in R 3 The solutions u of the Laplace
THE LAPLACE EQUATION The Laplace (o potential) equation is the equation whee is the Laplace opeato = 2 x 2 u = 0. in R = 2 x 2 + 2 y 2 in R 2 = 2 x 2 + 2 y 2 + 2 z 2 in R 3 The solutions u of the Laplace
PHYS 1444 Section 501 Lecture #7
 PHYS 1444 Section 51 Lectue #7 Wednesday, Feb. 8, 26 Equi-potential Lines and Sufaces Electic Potential Due to Electic Dipole E detemined fom V Electostatic Potential Enegy of a System of Chages Capacitos
PHYS 1444 Section 51 Lectue #7 Wednesday, Feb. 8, 26 Equi-potential Lines and Sufaces Electic Potential Due to Electic Dipole E detemined fom V Electostatic Potential Enegy of a System of Chages Capacitos
Module 05: Gauss s s Law a
 Module 05: Gauss s s Law a 1 Gauss s Law The fist Maxwell Equation! And a vey useful computational technique to find the electic field E when the souce has enough symmety. 2 Gauss s Law The Idea The total
Module 05: Gauss s s Law a 1 Gauss s Law The fist Maxwell Equation! And a vey useful computational technique to find the electic field E when the souce has enough symmety. 2 Gauss s Law The Idea The total
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS
 DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS TSOKOS LESSON 10-1 DESCRIBING FIELDS Essential Idea: Electic chages and masses each influence the space aound them and that influence can be epesented
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS TSOKOS LESSON 10-1 DESCRIBING FIELDS Essential Idea: Electic chages and masses each influence the space aound them and that influence can be epesented
7.2.1 Basic relations for Torsion of Circular Members
 Section 7. 7. osion In this section, the geomety to be consideed is that of a long slende cicula ba and the load is one which twists the ba. Such poblems ae impotant in the analysis of twisting components,
Section 7. 7. osion In this section, the geomety to be consideed is that of a long slende cicula ba and the load is one which twists the ba. Such poblems ae impotant in the analysis of twisting components,
1 Equations of linear elasticity
 C5.2 Elasticity & Plasticity Daft date: 17 Januay 2017 1 1 1 Equations of linea elasticity 1.1 Hooke s law Robet Hooke (1678 wote... it is... evident that the ule o law of natue in evey spinging body is
C5.2 Elasticity & Plasticity Daft date: 17 Januay 2017 1 1 1 Equations of linea elasticity 1.1 Hooke s law Robet Hooke (1678 wote... it is... evident that the ule o law of natue in evey spinging body is
CALCULUS II Vectors. Paul Dawkins
 CALCULUS II Vectos Paul Dawkins Table of Contents Peface... ii Vectos... 3 Intoduction... 3 Vectos The Basics... 4 Vecto Aithmetic... 8 Dot Poduct... 13 Coss Poduct... 21 2007 Paul Dawkins i http://tutoial.math.lama.edu/tems.aspx
CALCULUS II Vectos Paul Dawkins Table of Contents Peface... ii Vectos... 3 Intoduction... 3 Vectos The Basics... 4 Vecto Aithmetic... 8 Dot Poduct... 13 Coss Poduct... 21 2007 Paul Dawkins i http://tutoial.math.lama.edu/tems.aspx
B da = 0. Q E da = ε. E da = E dv
 lectomagnetic Theo Pof Ruiz, UNC Asheville, doctophs on YouTube Chapte Notes The Maxwell quations in Diffeential Fom 1 The Maxwell quations in Diffeential Fom We will now tansfom the integal fom of the
lectomagnetic Theo Pof Ruiz, UNC Asheville, doctophs on YouTube Chapte Notes The Maxwell quations in Diffeential Fom 1 The Maxwell quations in Diffeential Fom We will now tansfom the integal fom of the
Math 124B February 02, 2012
 Math 24B Febuay 02, 202 Vikto Gigoyan 8 Laplace s equation: popeties We have aleady encounteed Laplace s equation in the context of stationay heat conduction and wave phenomena. Recall that in two spatial
Math 24B Febuay 02, 202 Vikto Gigoyan 8 Laplace s equation: popeties We have aleady encounteed Laplace s equation in the context of stationay heat conduction and wave phenomena. Recall that in two spatial
Physics Tutorial V1 2D Vectors
 Physics Tutoial V1 2D Vectos 1 Resolving Vectos & Addition of Vectos A vecto quantity has both magnitude and diection. Thee ae two ways commonly used to mathematically descibe a vecto. y (a) The pola fom:,
Physics Tutoial V1 2D Vectos 1 Resolving Vectos & Addition of Vectos A vecto quantity has both magnitude and diection. Thee ae two ways commonly used to mathematically descibe a vecto. y (a) The pola fom:,
Gauss Law. Physics 231 Lecture 2-1
 Gauss Law Physics 31 Lectue -1 lectic Field Lines The numbe of field lines, also known as lines of foce, ae elated to stength of the electic field Moe appopiately it is the numbe of field lines cossing
Gauss Law Physics 31 Lectue -1 lectic Field Lines The numbe of field lines, also known as lines of foce, ae elated to stength of the electic field Moe appopiately it is the numbe of field lines cossing
IX INDUCTANCE AND MAGNETIC FIELDS
 IX INDUCTNCE ND MGNETIC FIELDS 9. Field in a solenoid vaying cuent in a conducto will poduce a vaying magnetic field. nd this vaying magnetic field then has the capability of inducing an EMF o voltage
IX INDUCTNCE ND MGNETIC FIELDS 9. Field in a solenoid vaying cuent in a conducto will poduce a vaying magnetic field. nd this vaying magnetic field then has the capability of inducing an EMF o voltage
Final Review of AerE 243 Class
 Final Review of AeE 4 Class Content of Aeodynamics I I Chapte : Review of Multivaiable Calculus Chapte : Review of Vectos Chapte : Review of Fluid Mechanics Chapte 4: Consevation Equations Chapte 5: Simplifications
Final Review of AeE 4 Class Content of Aeodynamics I I Chapte : Review of Multivaiable Calculus Chapte : Review of Vectos Chapte : Review of Fluid Mechanics Chapte 4: Consevation Equations Chapte 5: Simplifications
ELECTRODYNAMICS: PHYS 30441
 ELETRODYNAMIS: PHYS 44. Electomagnetic Field Equations. Maxwell s Equations Analysis in space (vacuum). oulomb Bon June 4, 76 Angoulême, Fance Died August 2, 86 Pais, Fance In 785 oulomb pesented his thee
ELETRODYNAMIS: PHYS 44. Electomagnetic Field Equations. Maxwell s Equations Analysis in space (vacuum). oulomb Bon June 4, 76 Angoulême, Fance Died August 2, 86 Pais, Fance In 785 oulomb pesented his thee
EM Boundary Value Problems
 EM Bounday Value Poblems 10/ 9 11/ By Ilekta chistidi & Lee, Seung-Hyun A. Geneal Desciption : Maxwell Equations & Loentz Foce We want to find the equations of motion of chaged paticles. The way to do
EM Bounday Value Poblems 10/ 9 11/ By Ilekta chistidi & Lee, Seung-Hyun A. Geneal Desciption : Maxwell Equations & Loentz Foce We want to find the equations of motion of chaged paticles. The way to do
Math 2263 Solutions for Spring 2003 Final Exam
 Math 6 Solutions fo Sping Final Exam ) A staightfowad appoach to finding the tangent plane to a suface at a point ( x, y, z ) would be to expess the cuve as an explicit function z = f ( x, y ), calculate
Math 6 Solutions fo Sping Final Exam ) A staightfowad appoach to finding the tangent plane to a suface at a point ( x, y, z ) would be to expess the cuve as an explicit function z = f ( x, y ), calculate
PHYS 1444 Lecture #5
 Shot eview Chapte 24 PHYS 1444 Lectue #5 Tuesday June 19, 212 D. Andew Bandt Capacitos and Capacitance 1 Coulom s Law The Fomula QQ Q Q F 1 2 1 2 Fomula 2 2 F k A vecto quantity. Newtons Diection of electic
Shot eview Chapte 24 PHYS 1444 Lectue #5 Tuesday June 19, 212 D. Andew Bandt Capacitos and Capacitance 1 Coulom s Law The Fomula QQ Q Q F 1 2 1 2 Fomula 2 2 F k A vecto quantity. Newtons Diection of electic
Voltage ( = Electric Potential )
 V-1 of 10 Voltage ( = lectic Potential ) An electic chage altes the space aound it. Thoughout the space aound evey chage is a vecto thing called the electic field. Also filling the space aound evey chage
V-1 of 10 Voltage ( = lectic Potential ) An electic chage altes the space aound it. Thoughout the space aound evey chage is a vecto thing called the electic field. Also filling the space aound evey chage
ENGI 4430 Non-Cartesian Coordinates Page xi Fy j Fzk from Cartesian coordinates z to another orthonormal coordinate system u, v, ˆ i ˆ ˆi
 ENGI 44 Non-Catesian Coodinates Page 7-7. Conesions between Coodinate Systems In geneal, the conesion of a ecto F F xi Fy j Fzk fom Catesian coodinates x, y, z to anothe othonomal coodinate system u,,
ENGI 44 Non-Catesian Coodinates Page 7-7. Conesions between Coodinate Systems In geneal, the conesion of a ecto F F xi Fy j Fzk fom Catesian coodinates x, y, z to anothe othonomal coodinate system u,,
Chapter 3 Optical Systems with Annular Pupils
 Chapte 3 Optical Systems with Annula Pupils 3 INTRODUCTION In this chapte, we discuss the imaging popeties of a system with an annula pupil in a manne simila to those fo a system with a cicula pupil The
Chapte 3 Optical Systems with Annula Pupils 3 INTRODUCTION In this chapte, we discuss the imaging popeties of a system with an annula pupil in a manne simila to those fo a system with a cicula pupil The
Vector Calculus Identities
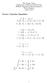 The Coope Union Depatment of Electical Engineeing ECE135 Engineeing Electomagnetics Vecto Analysis Mach 8, 2012 Vecto Calculus Identities A B B A A B C B C A C A B A B C B A C C A B fg f g + g f fg f G
The Coope Union Depatment of Electical Engineeing ECE135 Engineeing Electomagnetics Vecto Analysis Mach 8, 2012 Vecto Calculus Identities A B B A A B C B C A C A B A B C B A C C A B fg f g + g f fg f G
Review for Midterm-1
 Review fo Midtem-1 Midtem-1! Wednesday Sept. 24th at 6pm Section 1 (the 4:10pm class) exam in BCC N130 (Business College) Section 2 (the 6:00pm class) exam in NR 158 (Natual Resouces) Allowed one sheet
Review fo Midtem-1 Midtem-1! Wednesday Sept. 24th at 6pm Section 1 (the 4:10pm class) exam in BCC N130 (Business College) Section 2 (the 6:00pm class) exam in NR 158 (Natual Resouces) Allowed one sheet
INTRODUCTION. 2. Vectors in Physics 1
 INTRODUCTION Vectos ae used in physics to extend the study of motion fom one dimension to two dimensions Vectos ae indispensable when a physical quantity has a diection associated with it As an example,
INTRODUCTION Vectos ae used in physics to extend the study of motion fom one dimension to two dimensions Vectos ae indispensable when a physical quantity has a diection associated with it As an example,
Flux. Area Vector. Flux of Electric Field. Gauss s Law
 Gauss s Law Flux Flux in Physics is used to two distinct ways. The fist meaning is the ate of flow, such as the amount of wate flowing in a ive, i.e. volume pe unit aea pe unit time. O, fo light, it is
Gauss s Law Flux Flux in Physics is used to two distinct ways. The fist meaning is the ate of flow, such as the amount of wate flowing in a ive, i.e. volume pe unit aea pe unit time. O, fo light, it is
[Griffiths Ch.1-3] 2008/11/18, 10:10am 12:00am, 1. (6%, 7%, 7%) Suppose the potential at the surface of a hollow hemisphere is specified, as shown
![[Griffiths Ch.1-3] 2008/11/18, 10:10am 12:00am, 1. (6%, 7%, 7%) Suppose the potential at the surface of a hollow hemisphere is specified, as shown [Griffiths Ch.1-3] 2008/11/18, 10:10am 12:00am, 1. (6%, 7%, 7%) Suppose the potential at the surface of a hollow hemisphere is specified, as shown](/thumbs/80/81190242.jpg) [Giffiths Ch.-] 8//8, :am :am, Useful fomulas V ˆ ˆ V V V = + θ+ φ ˆ and v = ( v ) + (sin θvθ ) + v θ sinθ φ sinθ θ sinθ φ φ. (6%, 7%, 7%) Suppose the potential at the suface of a hollow hemisphee is specified,
[Giffiths Ch.-] 8//8, :am :am, Useful fomulas V ˆ ˆ V V V = + θ+ φ ˆ and v = ( v ) + (sin θvθ ) + v θ sinθ φ sinθ θ sinθ φ φ. (6%, 7%, 7%) Suppose the potential at the suface of a hollow hemisphee is specified,
Newton s Laws, Kepler s Laws, and Planetary Orbits
 Newton s Laws, Keple s Laws, and Planetay Obits PROBLEM SET 4 DUE TUESDAY AT START OF LECTURE 28 Septembe 2017 ASTRONOMY 111 FALL 2017 1 Newton s & Keple s laws and planetay obits Unifom cicula motion
Newton s Laws, Keple s Laws, and Planetay Obits PROBLEM SET 4 DUE TUESDAY AT START OF LECTURE 28 Septembe 2017 ASTRONOMY 111 FALL 2017 1 Newton s & Keple s laws and planetay obits Unifom cicula motion
3D-Central Force Problems I
 5.73 Lectue #1 1-1 Roadmap 1. define adial momentum 3D-Cental Foce Poblems I Read: C-TDL, pages 643-660 fo next lectue. All -Body, 3-D poblems can be educed to * a -D angula pat that is exactly and univesally
5.73 Lectue #1 1-1 Roadmap 1. define adial momentum 3D-Cental Foce Poblems I Read: C-TDL, pages 643-660 fo next lectue. All -Body, 3-D poblems can be educed to * a -D angula pat that is exactly and univesally
1 Fundamental Solutions to the Wave Equation
 1 Fundamental Solutions to the Wave Equation Physical insight in the sound geneation mechanism can be gained by consideing simple analytical solutions to the wave equation. One example is to conside acoustic
1 Fundamental Solutions to the Wave Equation Physical insight in the sound geneation mechanism can be gained by consideing simple analytical solutions to the wave equation. One example is to conside acoustic
17.1 Electric Potential Energy. Equipotential Lines. PE = energy associated with an arrangement of objects that exert forces on each other
 Electic Potential Enegy, PE Units: Joules Electic Potential, Units: olts 17.1 Electic Potential Enegy Electic foce is a consevative foce and so we can assign an electic potential enegy (PE) to the system
Electic Potential Enegy, PE Units: Joules Electic Potential, Units: olts 17.1 Electic Potential Enegy Electic foce is a consevative foce and so we can assign an electic potential enegy (PE) to the system
AST 121S: The origin and evolution of the Universe. Introduction to Mathematical Handout 1
 Please ead this fist... AST S: The oigin and evolution of the Univese Intoduction to Mathematical Handout This is an unusually long hand-out and one which uses in places mathematics that you may not be
Please ead this fist... AST S: The oigin and evolution of the Univese Intoduction to Mathematical Handout This is an unusually long hand-out and one which uses in places mathematics that you may not be
Physics 122, Fall October 2012
 Today in Physics 1: electostatics eview David Blaine takes the pactical potion of his electostatics midtem (Gawke). 11 Octobe 01 Physics 1, Fall 01 1 Electostatics As you have pobably noticed, electostatics
Today in Physics 1: electostatics eview David Blaine takes the pactical potion of his electostatics midtem (Gawke). 11 Octobe 01 Physics 1, Fall 01 1 Electostatics As you have pobably noticed, electostatics
Chapter 21: Gauss s Law
 Chapte : Gauss s Law Gauss s law : intoduction The total electic flux though a closed suface is equal to the total (net) electic chage inside the suface divided by ε Gauss s law is equivalent to Coulomb
Chapte : Gauss s Law Gauss s law : intoduction The total electic flux though a closed suface is equal to the total (net) electic chage inside the suface divided by ε Gauss s law is equivalent to Coulomb
Transformation of the Navier-Stokes Equations in Curvilinear Coordinate Systems with Maple
 Global Jounal of Pue and Applied Mathematics. ISSN 0973-1768 Volume 12, Numbe 4 2016, pp. 3315 3325 Reseach India Publications http://www.ipublication.com/gjpam.htm Tansfomation of the Navie-Stokes Equations
Global Jounal of Pue and Applied Mathematics. ISSN 0973-1768 Volume 12, Numbe 4 2016, pp. 3315 3325 Reseach India Publications http://www.ipublication.com/gjpam.htm Tansfomation of the Navie-Stokes Equations
A Tutorial on Multiple Integrals (for Natural Sciences / Computer Sciences Tripos Part IA Maths)
 A Tutoial on Multiple Integals (fo Natual Sciences / Compute Sciences Tipos Pat IA Maths) Coections to D Ian Rud (http://people.ds.cam.ac.uk/ia/contact.html) please. This tutoial gives some bief eamples
A Tutoial on Multiple Integals (fo Natual Sciences / Compute Sciences Tipos Pat IA Maths) Coections to D Ian Rud (http://people.ds.cam.ac.uk/ia/contact.html) please. This tutoial gives some bief eamples
A dual-reciprocity boundary element method for axisymmetric thermoelastodynamic deformations in functionally graded solids
 APCOM & ISCM 11-14 th Decembe, 013, Singapoe A dual-ecipocity bounday element method fo axisymmetic themoelastodynamic defomations in functionally gaded solids *W. T. Ang and B. I. Yun Division of Engineeing
APCOM & ISCM 11-14 th Decembe, 013, Singapoe A dual-ecipocity bounday element method fo axisymmetic themoelastodynamic defomations in functionally gaded solids *W. T. Ang and B. I. Yun Division of Engineeing
( ) Make-up Tests. From Last Time. Electric Field Flux. o The Electric Field Flux through a bit of area is
 Mon., 3/23 Wed., 3/25 Thus., 3/26 Fi., 3/27 Mon., 3/30 Tues., 3/31 21.4-6 Using Gauss s & nto to Ampee s 21.7-9 Maxwell s, Gauss s, and Ampee s Quiz Ch 21, Lab 9 Ampee s Law (wite up) 22.1-2,10 nto to
Mon., 3/23 Wed., 3/25 Thus., 3/26 Fi., 3/27 Mon., 3/30 Tues., 3/31 21.4-6 Using Gauss s & nto to Ampee s 21.7-9 Maxwell s, Gauss s, and Ampee s Quiz Ch 21, Lab 9 Ampee s Law (wite up) 22.1-2,10 nto to
Math Notes on Kepler s first law 1. r(t) kp(t)
 Math 7 - Notes on Keple s fist law Planetay motion and Keple s Laws We conside the motion of a single planet about the sun; fo simplicity, we assign coodinates in R 3 so that the position of the sun is
Math 7 - Notes on Keple s fist law Planetay motion and Keple s Laws We conside the motion of a single planet about the sun; fo simplicity, we assign coodinates in R 3 so that the position of the sun is
Phys-272 Lecture 17. Motional Electromotive Force (emf) Induced Electric Fields Displacement Currents Maxwell s Equations
 Phys-7 Lectue 17 Motional Electomotive Foce (emf) Induced Electic Fields Displacement Cuents Maxwell s Equations Fom Faaday's Law to Displacement Cuent AC geneato Magnetic Levitation Tain Review of Souces
Phys-7 Lectue 17 Motional Electomotive Foce (emf) Induced Electic Fields Displacement Cuents Maxwell s Equations Fom Faaday's Law to Displacement Cuent AC geneato Magnetic Levitation Tain Review of Souces
MODULE 5a and 5b (Stewart, Sections 12.2, 12.3) INTRO: In MATH 1114 vectors were written either as rows (a1, a2,..., an) or as columns a 1 a. ...
 MODULE 5a and 5b (Stewat, Sections 2.2, 2.3) INTRO: In MATH 4 vectos wee witten eithe as ows (a, a2,..., an) o as columns a a 2... a n and the set of all such vectos of fixed length n was called the vecto
MODULE 5a and 5b (Stewat, Sections 2.2, 2.3) INTRO: In MATH 4 vectos wee witten eithe as ows (a, a2,..., an) o as columns a a 2... a n and the set of all such vectos of fixed length n was called the vecto
anubhavclasses.wordpress.com CBSE Solved Test Papers PHYSICS Class XII Chapter : Electrostatics
 CBS Solved Test Papes PHYSICS Class XII Chapte : lectostatics CBS TST PAPR-01 CLASS - XII PHYSICS (Unit lectostatics) 1. Show does the foce between two point chages change if the dielectic constant of
CBS Solved Test Papes PHYSICS Class XII Chapte : lectostatics CBS TST PAPR-01 CLASS - XII PHYSICS (Unit lectostatics) 1. Show does the foce between two point chages change if the dielectic constant of
3. Magnetostatic fields
 3. Magnetostatic fields D. Rakhesh Singh Kshetimayum 1 Electomagnetic Field Theoy by R. S. Kshetimayum 3.1 Intoduction to electic cuents Electic cuents Ohm s law Kichoff s law Joule s law Bounday conditions
3. Magnetostatic fields D. Rakhesh Singh Kshetimayum 1 Electomagnetic Field Theoy by R. S. Kshetimayum 3.1 Intoduction to electic cuents Electic cuents Ohm s law Kichoff s law Joule s law Bounday conditions
But for simplicity, we ll define significant as the time it takes a star to lose all memory of its original trajectory, i.e.,
 Stella elaxation Time [Chandasekha 1960, Pinciples of Stella Dynamics, Chap II] [Ostike & Davidson 1968, Ap.J., 151, 679] Do stas eve collide? Ae inteactions between stas (as opposed to the geneal system
Stella elaxation Time [Chandasekha 1960, Pinciples of Stella Dynamics, Chap II] [Ostike & Davidson 1968, Ap.J., 151, 679] Do stas eve collide? Ae inteactions between stas (as opposed to the geneal system
6 Vector Operators. 6.1 The Gradient Operator
 6 Vecto Opeatos 6. The Gadient Opeato In the B2 couse ou wee intoduced to the gadient opeato in Catesian coodinates. Fo an diffeentiable scala function f(x,, z), we can define a vecto function though (
6 Vecto Opeatos 6. The Gadient Opeato In the B2 couse ou wee intoduced to the gadient opeato in Catesian coodinates. Fo an diffeentiable scala function f(x,, z), we can define a vecto function though (
TheWaveandHelmholtzEquations
 TheWaveandHelmholtzEquations Ramani Duaiswami The Univesity of Mayland, College Pak Febuay 3, 2006 Abstact CMSC828D notes (adapted fom mateial witten with Nail Gumeov). Wok in pogess 1 Acoustic Waves 1.1
TheWaveandHelmholtzEquations Ramani Duaiswami The Univesity of Mayland, College Pak Febuay 3, 2006 Abstact CMSC828D notes (adapted fom mateial witten with Nail Gumeov). Wok in pogess 1 Acoustic Waves 1.1
arxiv: v1 [physics.pop-ph] 3 Jun 2013
![arxiv: v1 [physics.pop-ph] 3 Jun 2013 arxiv: v1 [physics.pop-ph] 3 Jun 2013](/thumbs/89/100795062.jpg) A note on the electostatic enegy of two point chages axiv:1306.0401v1 [physics.pop-ph] 3 Jun 013 A C Tot Instituto de Física Univesidade Fedeal do io de Janeio Caixa Postal 68.58; CEP 1941-97 io de Janeio,
A note on the electostatic enegy of two point chages axiv:1306.0401v1 [physics.pop-ph] 3 Jun 013 A C Tot Instituto de Física Univesidade Fedeal do io de Janeio Caixa Postal 68.58; CEP 1941-97 io de Janeio,
MAGNETIC FIELD AROUND TWO SEPARATED MAGNETIZING COILS
 The 8 th Intenational Confeence of the Slovenian Society fo Non-Destuctive Testing»pplication of Contempoay Non-Destuctive Testing in Engineeing«Septembe 1-3, 5, Potoož, Slovenia, pp. 17-1 MGNETIC FIELD
The 8 th Intenational Confeence of the Slovenian Society fo Non-Destuctive Testing»pplication of Contempoay Non-Destuctive Testing in Engineeing«Septembe 1-3, 5, Potoož, Slovenia, pp. 17-1 MGNETIC FIELD
Lecture 8 - Gauss s Law
 Lectue 8 - Gauss s Law A Puzzle... Example Calculate the potential enegy, pe ion, fo an infinite 1D ionic cystal with sepaation a; that is, a ow of equally spaced chages of magnitude e and altenating sign.
Lectue 8 - Gauss s Law A Puzzle... Example Calculate the potential enegy, pe ion, fo an infinite 1D ionic cystal with sepaation a; that is, a ow of equally spaced chages of magnitude e and altenating sign.
Electrostatics. 1. Show does the force between two point charges change if the dielectric constant of the medium in which they are kept increase?
 Electostatics 1. Show does the foce between two point chages change if the dielectic constant of the medium in which they ae kept incease? 2. A chaged od P attacts od R whee as P epels anothe chaged od
Electostatics 1. Show does the foce between two point chages change if the dielectic constant of the medium in which they ae kept incease? 2. A chaged od P attacts od R whee as P epels anothe chaged od
Chapter 13 Gravitation
 Chapte 13 Gavitation In this chapte we will exploe the following topics: -Newton s law of gavitation, which descibes the attactive foce between two point masses and its application to extended objects
Chapte 13 Gavitation In this chapte we will exploe the following topics: -Newton s law of gavitation, which descibes the attactive foce between two point masses and its application to extended objects
FREE Download Study Package from website: &
 .. Linea Combinations: (a) (b) (c) (d) Given a finite set of vectos a b c,,,... then the vecto xa + yb + zc +... is called a linea combination of a, b, c,... fo any x, y, z... R. We have the following
.. Linea Combinations: (a) (b) (c) (d) Given a finite set of vectos a b c,,,... then the vecto xa + yb + zc +... is called a linea combination of a, b, c,... fo any x, y, z... R. We have the following
Physics 2A Chapter 10 - Moment of Inertia Fall 2018
 Physics Chapte 0 - oment of netia Fall 08 The moment of inetia of a otating object is a measue of its otational inetia in the same way that the mass of an object is a measue of its inetia fo linea motion.
Physics Chapte 0 - oment of netia Fall 08 The moment of inetia of a otating object is a measue of its otational inetia in the same way that the mass of an object is a measue of its inetia fo linea motion.
Section 1: Main results of Electrostatics and Magnetostatics. Electrostatics
 Chage density ection 1: ain esults of Electostatics and agnetostatics Electostatics The most fundamental quantity of electostatics is electic chage. Chage comes in two vaieties, which ae called positive
Chage density ection 1: ain esults of Electostatics and agnetostatics Electostatics The most fundamental quantity of electostatics is electic chage. Chage comes in two vaieties, which ae called positive
Supplementary material for the paper Platonic Scattering Cancellation for Bending Waves on a Thin Plate. Abstract
 Supplementay mateial fo the pape Platonic Scatteing Cancellation fo Bending Waves on a Thin Plate M. Fahat, 1 P.-Y. Chen, 2 H. Bağcı, 1 S. Enoch, 3 S. Guenneau, 3 and A. Alù 2 1 Division of Compute, Electical,
Supplementay mateial fo the pape Platonic Scatteing Cancellation fo Bending Waves on a Thin Plate M. Fahat, 1 P.-Y. Chen, 2 H. Bağcı, 1 S. Enoch, 3 S. Guenneau, 3 and A. Alù 2 1 Division of Compute, Electical,
Physics 111 Lecture 5 (Walker: 3.3-6) Vectors & Vector Math Motion Vectors Sept. 11, 2009
 Physics 111 Lectue 5 (Walke: 3.3-6) Vectos & Vecto Math Motion Vectos Sept. 11, 2009 Quiz Monday - Chap. 2 1 Resolving a vecto into x-component & y- component: Pola Coodinates Catesian Coodinates x y =
Physics 111 Lectue 5 (Walke: 3.3-6) Vectos & Vecto Math Motion Vectos Sept. 11, 2009 Quiz Monday - Chap. 2 1 Resolving a vecto into x-component & y- component: Pola Coodinates Catesian Coodinates x y =
Math 259 Winter Handout 6: In-class Review for the Cumulative Final Exam
 Math 259 Winte 2009 Handout 6: In-class Review fo the Cumulative Final Exam The topics coveed by the cumulative final exam include the following: Paametic cuves. Finding fomulas fo paametic cuves. Dawing
Math 259 Winte 2009 Handout 6: In-class Review fo the Cumulative Final Exam The topics coveed by the cumulative final exam include the following: Paametic cuves. Finding fomulas fo paametic cuves. Dawing
POISSON S EQUATION 2 V 0
 POISSON S EQUATION We have seen how to solve the equation but geneally we have V V4k We now look at a vey geneal way of attacking this poblem though Geen s Functions. It tuns out that this poblem has applications
POISSON S EQUATION We have seen how to solve the equation but geneally we have V V4k We now look at a vey geneal way of attacking this poblem though Geen s Functions. It tuns out that this poblem has applications
Welcome to Physics 272
 Welcome to Physics 7 Bob Mose mose@phys.hawaii.edu http://www.phys.hawaii.edu/~mose/physics7.html To do: Sign into Masteing Physics phys-7 webpage Registe i-clickes (you i-clicke ID to you name on class-list)
Welcome to Physics 7 Bob Mose mose@phys.hawaii.edu http://www.phys.hawaii.edu/~mose/physics7.html To do: Sign into Masteing Physics phys-7 webpage Registe i-clickes (you i-clicke ID to you name on class-list)
