Appendix A. Appendices. A.1 ɛ ijk and cross products. Vector Operations: δ ij and ɛ ijk
|
|
|
- Johnathan Terry
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Appendix A Appendices A1 ɛ and coss poducts A11 Vecto Opeations: δ ij and ɛ These ae some notes on the use of the antisymmetic symbol ɛ fo expessing coss poducts This is an extemely poweful tool fo manipulating coss poducts and thei genealizations in highe dimensions, and although many low level couses avoid the use of ɛ, I think this is a mistake and I want you to become poficient with it In a catesian coodinate system a vecto V has components V i along each of the thee othonomal basis vectos ê i,ov = i V i ê i The dot poduct of two vectos, A B, is bilinea and can theefoe be witten as A B = ( A i ê i ) B j ê j (A1) i j = A i B j ê i ê j (A2) i j = A i B j δ ij, (A3) i j whee the Konecke delta δ ij is defined to be 1 if i = j and 0 othewise As the basis vectos ê k ae othonomal, ie othogonal to each othe and of unit length, we have ê i ê j = δ ij Doing a sum ove an index j of an expession involving a δ ij is vey simple, because the only tem in the sum which contibutes is the one with j = i Thus j F (i, j)δ ij = F (i, i), which is to say, one just eplaces j with i in all 263
2 264 APPENDIX A APPENDICES the othe factos, and dops the δ ij and the summation ove j So we have A B = i A i B i, the standad expession fo the dot poduct 1 We now conside the coss poduct of two vectos, A B, which is also a bilinea expession, so we must have A B =( i A i ê i ) ( j B j ê j )= i j A i B j (ê i ê j ) The coss poduct ê i ê j is a vecto, which can theefoe be witten as V = k V k ê k But the vecto esult depends also on the two input vectos, so the coefficients V k eally depend on i and j as well Define them to be ɛ,so ê i ê j = ɛ kij ê k k It is easy to evaluate the 27 coefficients ɛ kij, because the coss poduct of two othogonal unit vectos is a unit vecto othogonal to both of them Thus ê 1 ê 2 =ê 3,soɛ 312 =1andɛ k12 =0ifk = 1 o 2 Applying the same agument to ê 2 ê 3 and ê 3 ê 1, and using the antisymmety of the coss poduct, A B = B A, we see that ɛ 123 = ɛ 231 = ɛ 312 =1; ɛ 132 = ɛ 213 = ɛ 321 = 1, and ɛ = 0 fo all othe values of the indices, ie ɛ = 0 wheneve any two of the indices ae equal Note that ɛ changes sign not only when the last two indices ae intechanged (a consequence of the antisymmety of the coss poduct), but wheneve any two of its indices ae intechanged Thus ɛ is zeo unless (1, 2, 3) (i, j, k) is a pemutation, and is equal to the sign of the pemutation if it exists Now that we have an expession fo ê i ê j, we can evaluate A B = i A i B j (ê i ê j )= j i ɛ kij A i B j ê k j k (A4) Much of the usefulness of expessing coss poducts in tems of ɛ s comes fom the identity ɛ kij ɛ klm = δ il δ jm δ im δ jl, (A5) k which can be shown as follows To get a contibution to the sum, k must be diffeent fom the unequal indices i and j, and also diffeent fom l and m Thus we get 0 unless the pai (i, j) and the pai (l, m) ae the same pai of 1 Note that this only holds because we have expessed ou vectos in tems of othonomal basis vectos
3 A1 ɛ IJK AND CROSS PRODUCTS 265 diffeent indices Thee ae only two ways that can happen, as given by the two tems, and we only need to veify the coefficients If i = l and j = m, the two ɛ s ae equal and the squae is 1, so the fist tem has the pope coefficient of 1 The second tem diffes by one tansposition of two indices on one epsilon, so it must have the opposite sign We now tun to some applications Let us fist evaluate A ( B C)= i A i ɛ B j C k = ɛ A i B j C k jk (A6) Note that A ( B C) is, up to sign, the volume of the paallelopiped fomed by the vectos A, B, and C Fom the fact that the ɛ changes sign unde tanspositions of any two indices, we see that the same is tue fo tansposing the vectos, so that A ( B C)= A ( C B) = B ( C A)= B ( A C) = C ( A B)= C ( B A) Now conside V = A ( B C) Using ou fomulas, V = ɛ kij ê k A i ( B C) j = ɛ kij ê k A i ɛ jlm B l C m lm Notice that the sum on j involves only the two epsilons, and we can use ɛ kij ɛ jlm = j j ɛ jki ɛ jlm = δ kl δ im δ km δ il Thus V k = ( ilm j ɛ kij ɛ jlm )A i B l C m = ilm(δ kl δ im δ km δ il )A i B l C m = δ kl δ im A i B l C m δ km δ il A i B l C m ilm ilm = i A i B k C i i A i B i C k = A C B k A B C k, so A ( B C)= B A C C A B (A7) This is sometimes known as the bac-cab fomula
4 266 APPENDIX A APPENDICES Execise: Using (A5) fo the manipulation of coss poducts, show that ( A B) ( C D)= A C B D A D B C The deteminant of a matix can be defined using the ɛ symbol Fo a 3 3 matix A, det A = ɛ A 1i A 2j A 3k = ɛ A i1 A j2 A k3 Fom the second definition, we see that the deteminant is the volume of the paallelopiped fomed fom the images unde the linea map A of the thee unit vectos ê i,as (Aê 1 ) ((Aê 2 ) (Aê 3 )) = det A In highe dimensions, the coss poduct is not a vecto, but thee is a genealization of ɛ which emains vey useful In an n-dimensional space, ɛ i1 i 2 i n has n indices and is defined as the sign of the pemutation (1, 2,,n) (i 1 i 2 i n ), if the indices ae all unequal, and zeo othewise The analog of (A5) has (n 1)! tems fom all the pemutations of the unsummed indices on the second ɛ The deteminant of an n n matix is defined as det A = n ɛ i1 i 2 i n A p,ip i 1,,i n p=1 A2 The gadient opeato We can define the gadient opeato = i ê i (A8) While this looks like an odinay vecto, the coefficients ae not numbes V i but ae opeatos, which do not commute with functions of the coodinates x i We can still wite out the components staightfowadly, but we must be caeful to keep the ode of the opeatos and the fields coect The gadient of a scala field Φ( ) is simply evaluated by distibuting the gadient opeato Φ =( i ê i )Φ( ) = i ê i Φ (A9)
5 A2 THE GRADIENT OPERATOR 267 Because the individual components obey the Leibnitz ule AB so does the gadient, so if A and B ae scala fields, AB =( A)B + A B = A B+A B, (A10) The geneal application of the gadient opeato to a vecto A gives an object with coefficients with two indices, a tenso Some pats of this tenso, howeve, can be simplified The fist (which is the tace of the tenso) is called the divegence of the vecto, witten and defined by A = ( i ê i ) ( j ê j B j )= ij ê i ê j B j = ij δ ij B j = B i (A11) i In asking about Leibnitz ule, we must emembe to apply the divegence opeato only to vectos One possibility is to apply it to the vecto V =ΦA, with components V i =ΦA i Thus (Φ A) = i (ΦA i ) = i Φ A i +Φ i A i = ( Φ) A +Φ A (A12) We could also apply the divegence to the coss poduct of two vectos, ( A B) = i ( A B) i = i ( jk ɛ A j B k ) = ɛ (A j B k ) = A j ɛ B k + B k ɛ A j (A13) This is expessible in tems of the culs of A and B The cul is like a coss poduct with the fist vecto eplaced by the diffeential opeato, so we may wite the i th component as ( A) i = ɛ A k (A14) jk x j We see that the last expession in (A13) is ( A j ɛ kij )B k B k A j ɛ jik =( ij j x A) B A ( B) (A15) i k ik
6 268 APPENDIX A APPENDICES whee the sign which changed did so due to the tanspositions in the indices on the ɛ, which we have done in ode to put things in the fom of the definition of the cul Thus ( A B)=( A) B A ( B) (A16) Vecto algeba identities apply to the cul as to any odinay vecto, except that one must be caeful not to change, by eodeing, what the diffeential opeatos act on In paticula, Eq A7 is A ( B)= i A i Bi i A i B (A17) A3 Gadient in Spheical Coodinates The tansfomation between Catesian and spheical coodinates is given by = (x 2 + y 2 + z 2 ) 1 2 x= sin θ cos φ θ= cos 1 (z/) y= sin θ sin φ φ= tan 1 (y/x) z= cos θ The basis vectos {ê, ê θ, ê φ } at the point (, θ, φ) ae given in tems of the catesian basis vectos by ê = sin θ cos φ ê x + sin θ sin φ ê y + cos θ ê z ê θ = cos θ cos φ ê x + cos θ sin φ ê y sin θ ê z ê φ = sin φ ê x + cos φ ê y By the chain ule, if we have two sets of coodinates, say s i and c i,andwe know the fom a function f(s i ) and the dependence of s i on c j, we can find f c i = j f s s j c s j c i, whee s means hold the othe s s fixed while vaying s j In ou case, the s j ae the spheical coodinates, θ, φ, while the c i ae x, y, z Thus f = f ê θφ x yz φ x yz θ x x yz + f ê θφ y xz φ y xz y (A18) θ y xz
7 A3 GRADIENT IN SPHERICAL COORDINATES f θφ z xy φ z xy θ z xy ê z We will need all the patial deivatives s j c i Fom 2 = x 2 + y 2 + z 2 we see that = x = y = z x yz y xz z xy Fom cos θ = z/ = z/ x 2 + y 2 + z 2, sin θ = x yz zx (x 2 + y 2 + z 2 ) = 2 cos θ sin θ cos φ 3/2 3 so Similaly, = x yz = y xz cos θ cos φ cos θ sin φ Thee is an exta tem when diffeentiating wt z, fom the numeato, so sin θ = 1 z xy z2 = 1 cos2 θ = 1 sin 2 θ, 3 so = 1 sin θ z xy Finally, the deivatives of φ can easily be found fom diffeentiating tan φ = y/x Using diffeentials, sec 2 φdφ = dy x ydx x 2 = dy dx sin θ sin φ sin θ cos φ sin 2 θ cos 2 φ so = 1 sin φ x yz sin θ = 1 y xz cos φ sin θ =0 z xy
8 270 APPENDIX A APPENDICES Now we ae eady to plug this all into (A18) Gouping togethe the tems involving each of the thee patial deivatives, we find f = f ( x θφ êx + y êy + z êz) ( cos θ cos φ cos θ sin φ ê x + ê y sin θ ) φ êz ( 1 sin φ θ sin θ êx + 1 ) cos φ sin θ êy = f ê + 1 f ê θφ θ + 1 f ê φ sin θ φ θ Thus we have deived the fom fo the gadient in spheical coodinates
As is natural, our Aerospace Structures will be described in a Euclidean three-dimensional space R 3.
 Appendix A Vecto Algeba As is natual, ou Aeospace Stuctues will be descibed in a Euclidean thee-dimensional space R 3. A.1 Vectos A vecto is used to epesent quantities that have both magnitude and diection.
Appendix A Vecto Algeba As is natual, ou Aeospace Stuctues will be descibed in a Euclidean thee-dimensional space R 3. A.1 Vectos A vecto is used to epesent quantities that have both magnitude and diection.
Vector d is a linear vector function of vector d when the following relationships hold:
 Appendix 4 Dyadic Analysis DEFINITION ecto d is a linea vecto function of vecto d when the following elationships hold: d x = a xxd x + a xy d y + a xz d z d y = a yxd x + a yy d y + a yz d z d z = a zxd
Appendix 4 Dyadic Analysis DEFINITION ecto d is a linea vecto function of vecto d when the following elationships hold: d x = a xxd x + a xy d y + a xz d z d y = a yxd x + a yy d y + a yz d z d z = a zxd
J. N. R E DDY ENERGY PRINCIPLES AND VARIATIONAL METHODS APPLIED MECHANICS
 J. N. E DDY ENEGY PINCIPLES AND VAIATIONAL METHODS IN APPLIED MECHANICS T H I D E DI T IO N JN eddy - 1 MEEN 618: ENEGY AND VAIATIONAL METHODS A EVIEW OF VECTOS AND TENSOS ead: Chapte 2 CONTENTS Physical
J. N. E DDY ENEGY PINCIPLES AND VAIATIONAL METHODS IN APPLIED MECHANICS T H I D E DI T IO N JN eddy - 1 MEEN 618: ENEGY AND VAIATIONAL METHODS A EVIEW OF VECTOS AND TENSOS ead: Chapte 2 CONTENTS Physical
ENGI 4430 Non-Cartesian Coordinates Page xi Fy j Fzk from Cartesian coordinates z to another orthonormal coordinate system u, v, ˆ i ˆ ˆi
 ENGI 44 Non-Catesian Coodinates Page 7-7. Conesions between Coodinate Systems In geneal, the conesion of a ecto F F xi Fy j Fzk fom Catesian coodinates x, y, z to anothe othonomal coodinate system u,,
ENGI 44 Non-Catesian Coodinates Page 7-7. Conesions between Coodinate Systems In geneal, the conesion of a ecto F F xi Fy j Fzk fom Catesian coodinates x, y, z to anothe othonomal coodinate system u,,
PHZ 3113 Fall 2017 Homework #5, Due Friday, October 13
 PHZ 3113 Fall 2017 Homewok #5, Due Fiday, Octobe 13 1. Genealize the poduct ule (fg) = f g +f g to wite the divegence Ö (Ù Ú) of the coss poduct of the vecto fields Ù and Ú in tems of the cul of Ù and
PHZ 3113 Fall 2017 Homewok #5, Due Fiday, Octobe 13 1. Genealize the poduct ule (fg) = f g +f g to wite the divegence Ö (Ù Ú) of the coss poduct of the vecto fields Ù and Ú in tems of the cul of Ù and
3D-Central Force Problems I
 5.73 Lectue #1 1-1 Roadmap 1. define adial momentum 3D-Cental Foce Poblems I Read: C-TDL, pages 643-660 fo next lectue. All -Body, 3-D poblems can be educed to * a -D angula pat that is exactly and univesally
5.73 Lectue #1 1-1 Roadmap 1. define adial momentum 3D-Cental Foce Poblems I Read: C-TDL, pages 643-660 fo next lectue. All -Body, 3-D poblems can be educed to * a -D angula pat that is exactly and univesally
Question 1: The dipole
 Septembe, 08 Conell Univesity, Depatment of Physics PHYS 337, Advance E&M, HW #, due: 9/5/08, :5 AM Question : The dipole Conside a system as discussed in class and shown in Fig.. in Heald & Maion.. Wite
Septembe, 08 Conell Univesity, Depatment of Physics PHYS 337, Advance E&M, HW #, due: 9/5/08, :5 AM Question : The dipole Conside a system as discussed in class and shown in Fig.. in Heald & Maion.. Wite
DonnishJournals
 DonnishJounals 041-1189 Donnish Jounal of Educational Reseach and Reviews. Vol 1(1) pp. 01-017 Novembe, 014. http:///dje Copyight 014 Donnish Jounals Oiginal Reseach Pape Vecto Analysis Using MAXIMA Savaş
DonnishJounals 041-1189 Donnish Jounal of Educational Reseach and Reviews. Vol 1(1) pp. 01-017 Novembe, 014. http:///dje Copyight 014 Donnish Jounals Oiginal Reseach Pape Vecto Analysis Using MAXIMA Savaş
Math 124B February 02, 2012
 Math 24B Febuay 02, 202 Vikto Gigoyan 8 Laplace s equation: popeties We have aleady encounteed Laplace s equation in the context of stationay heat conduction and wave phenomena. Recall that in two spatial
Math 24B Febuay 02, 202 Vikto Gigoyan 8 Laplace s equation: popeties We have aleady encounteed Laplace s equation in the context of stationay heat conduction and wave phenomena. Recall that in two spatial
PROBLEM SET #1 SOLUTIONS by Robert A. DiStasio Jr.
 POBLM S # SOLUIONS by obet A. DiStasio J. Q. he Bon-Oppenheime appoximation is the standad way of appoximating the gound state of a molecula system. Wite down the conditions that detemine the tonic and
POBLM S # SOLUIONS by obet A. DiStasio J. Q. he Bon-Oppenheime appoximation is the standad way of appoximating the gound state of a molecula system. Wite down the conditions that detemine the tonic and
Homework # 3 Solution Key
 PHYSICS 631: Geneal Relativity Homewok # 3 Solution Key 1. You e on you hono not to do this one by hand. I ealize you can use a compute o simply look it up. Please don t. In a flat space, the metic in
PHYSICS 631: Geneal Relativity Homewok # 3 Solution Key 1. You e on you hono not to do this one by hand. I ealize you can use a compute o simply look it up. Please don t. In a flat space, the metic in
PHYS 705: Classical Mechanics. Small Oscillations
 PHYS 705: Classical Mechanics Small Oscillations Fomulation of the Poblem Assumptions: V q - A consevative system with depending on position only - The tansfomation equation defining does not dep on time
PHYS 705: Classical Mechanics Small Oscillations Fomulation of the Poblem Assumptions: V q - A consevative system with depending on position only - The tansfomation equation defining does not dep on time
3. Electromagnetic Waves II
 Lectue 3 - Electomagnetic Waves II 9 3. Electomagnetic Waves II Last time, we discussed the following. 1. The popagation of an EM wave though a macoscopic media: We discussed how the wave inteacts with
Lectue 3 - Electomagnetic Waves II 9 3. Electomagnetic Waves II Last time, we discussed the following. 1. The popagation of an EM wave though a macoscopic media: We discussed how the wave inteacts with
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL CHAPTER 7 A (2 ) B. a x + bx + c dx
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL 613 7.6.3 CHAPTER 7 ( px + q) a x + bx + c dx. We choose constants A and B such that d px + q A ( ax + bx + c) + B dx A(ax + b) + B Compaing the coefficients of x and the constant
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL 613 7.6.3 CHAPTER 7 ( px + q) a x + bx + c dx. We choose constants A and B such that d px + q A ( ax + bx + c) + B dx A(ax + b) + B Compaing the coefficients of x and the constant
Auchmuty High School Mathematics Department Advanced Higher Notes Teacher Version
 The Binomial Theoem Factoials Auchmuty High School Mathematics Depatment The calculations,, 6 etc. often appea in mathematics. They ae called factoials and have been given the notation n!. e.g. 6! 6!!!!!
The Binomial Theoem Factoials Auchmuty High School Mathematics Depatment The calculations,, 6 etc. often appea in mathematics. They ae called factoials and have been given the notation n!. e.g. 6! 6!!!!!
Classical Mechanics Homework set 7, due Nov 8th: Solutions
 Classical Mechanics Homewok set 7, due Nov 8th: Solutions 1. Do deivation 8.. It has been asked what effect does a total deivative as a function of q i, t have on the Hamiltonian. Thus, lets us begin with
Classical Mechanics Homewok set 7, due Nov 8th: Solutions 1. Do deivation 8.. It has been asked what effect does a total deivative as a function of q i, t have on the Hamiltonian. Thus, lets us begin with
(read nabla or del) is defined by, k. (9.7.1*)
 9.7 Gadient of a scala field. Diectional deivative Some of the vecto fields in applications can be obtained fom scala fields. This is vey advantageous because scala fields can be handled moe easily. The
9.7 Gadient of a scala field. Diectional deivative Some of the vecto fields in applications can be obtained fom scala fields. This is vey advantageous because scala fields can be handled moe easily. The
EM Boundary Value Problems
 EM Bounday Value Poblems 10/ 9 11/ By Ilekta chistidi & Lee, Seung-Hyun A. Geneal Desciption : Maxwell Equations & Loentz Foce We want to find the equations of motion of chaged paticles. The way to do
EM Bounday Value Poblems 10/ 9 11/ By Ilekta chistidi & Lee, Seung-Hyun A. Geneal Desciption : Maxwell Equations & Loentz Foce We want to find the equations of motion of chaged paticles. The way to do
S7: Classical mechanics problem set 2
 J. Magoian MT 9, boowing fom J. J. Binney s 6 couse S7: Classical mechanics poblem set. Show that if the Hamiltonian is indepdent of a genealized co-odinate q, then the conjugate momentum p is a constant
J. Magoian MT 9, boowing fom J. J. Binney s 6 couse S7: Classical mechanics poblem set. Show that if the Hamiltonian is indepdent of a genealized co-odinate q, then the conjugate momentum p is a constant
AE301 Aerodynamics I UNIT B: Theory of Aerodynamics
 AE301 Aeodynamics I UNIT B: Theoy of Aeodynamics ROAD MAP... B-1: Mathematics fo Aeodynamics B-2: Flow Field Repesentations B-3: Potential Flow Analysis B-4: Applications of Potential Flow Analysis AE301
AE301 Aeodynamics I UNIT B: Theoy of Aeodynamics ROAD MAP... B-1: Mathematics fo Aeodynamics B-2: Flow Field Repesentations B-3: Potential Flow Analysis B-4: Applications of Potential Flow Analysis AE301
MATH 220: SECOND ORDER CONSTANT COEFFICIENT PDE. We consider second order constant coefficient scalar linear PDEs on R n. These have the form
 MATH 220: SECOND ORDER CONSTANT COEFFICIENT PDE ANDRAS VASY We conside second ode constant coefficient scala linea PDEs on R n. These have the fom Lu = f L = a ij xi xj + b i xi + c i whee a ij b i and
MATH 220: SECOND ORDER CONSTANT COEFFICIENT PDE ANDRAS VASY We conside second ode constant coefficient scala linea PDEs on R n. These have the fom Lu = f L = a ij xi xj + b i xi + c i whee a ij b i and
15 Solving the Laplace equation by Fourier method
 5 Solving the Laplace equation by Fouie method I aleady intoduced two o thee dimensional heat equation, when I deived it, ecall that it taes the fom u t = α 2 u + F, (5.) whee u: [0, ) D R, D R is the
5 Solving the Laplace equation by Fouie method I aleady intoduced two o thee dimensional heat equation, when I deived it, ecall that it taes the fom u t = α 2 u + F, (5.) whee u: [0, ) D R, D R is the
1 Spherical multipole moments
 Jackson notes 9 Spheical multipole moments Suppose we have a chage distibution ρ (x) wheeallofthechageiscontained within a spheical egion of adius R, as shown in the diagam. Then thee is no chage in the
Jackson notes 9 Spheical multipole moments Suppose we have a chage distibution ρ (x) wheeallofthechageiscontained within a spheical egion of adius R, as shown in the diagam. Then thee is no chage in the
The Strain Compatibility Equations in Polar Coordinates RAWB, Last Update 27/12/07
 The Stain Compatibility Equations in Pola Coodinates RAWB Last Update 7//7 In D thee is just one compatibility equation. In D polas it is (Equ.) whee denotes the enineein shea (twice the tensoial shea)
The Stain Compatibility Equations in Pola Coodinates RAWB Last Update 7//7 In D thee is just one compatibility equation. In D polas it is (Equ.) whee denotes the enineein shea (twice the tensoial shea)
MATH 417 Homework 3 Instructor: D. Cabrera Due June 30. sin θ v x = v r cos θ v θ r. (b) Then use the Cauchy-Riemann equations in polar coordinates
 MATH 417 Homewok 3 Instucto: D. Cabea Due June 30 1. Let a function f(z) = u + iv be diffeentiable at z 0. (a) Use the Chain Rule and the fomulas x = cosθ and y = to show that u x = u cosθ u θ, v x = v
MATH 417 Homewok 3 Instucto: D. Cabea Due June 30 1. Let a function f(z) = u + iv be diffeentiable at z 0. (a) Use the Chain Rule and the fomulas x = cosθ and y = to show that u x = u cosθ u θ, v x = v
1 MathematicalPreliminaries
 1 MathematicalPeliminaies The enomous usefulness of mathematics in the natual sciences is something bodeing on the mysteious. Eugene Wigne (1960 1.1 Intoduction This chapte pesents a collection of mathematical
1 MathematicalPeliminaies The enomous usefulness of mathematics in the natual sciences is something bodeing on the mysteious. Eugene Wigne (1960 1.1 Intoduction This chapte pesents a collection of mathematical
PHYS 301 HOMEWORK #10 (Optional HW)
 PHYS 301 HOMEWORK #10 (Optional HW) 1. Conside the Legende diffeential equation : 1 - x 2 y'' - 2xy' + m m + 1 y = 0 Make the substitution x = cos q and show the Legende equation tansfoms into d 2 y 2
PHYS 301 HOMEWORK #10 (Optional HW) 1. Conside the Legende diffeential equation : 1 - x 2 y'' - 2xy' + m m + 1 y = 0 Make the substitution x = cos q and show the Legende equation tansfoms into d 2 y 2
3D-Central Force Problems II
 5.73 ectue # - 1 3D-Cental Foce Poblems II ast time: [x,p] vecto commutation ules: genealize fom 1-D to 3-D conugate position and momentum components in Catesian coodinates Coespondence Pinciple Recipe
5.73 ectue # - 1 3D-Cental Foce Poblems II ast time: [x,p] vecto commutation ules: genealize fom 1-D to 3-D conugate position and momentum components in Catesian coodinates Coespondence Pinciple Recipe
THE LAPLACE EQUATION. The Laplace (or potential) equation is the equation. u = 0. = 2 x 2. x y 2 in R 2
 THE LAPLACE EQUATION The Laplace (o potential) equation is the equation whee is the Laplace opeato = 2 x 2 u = 0. in R = 2 x 2 + 2 y 2 in R 2 = 2 x 2 + 2 y 2 + 2 z 2 in R 3 The solutions u of the Laplace
THE LAPLACE EQUATION The Laplace (o potential) equation is the equation whee is the Laplace opeato = 2 x 2 u = 0. in R = 2 x 2 + 2 y 2 in R 2 = 2 x 2 + 2 y 2 + 2 z 2 in R 3 The solutions u of the Laplace
5.61 Physical Chemistry Lecture #23 page 1 MANY ELECTRON ATOMS
 5.6 Physical Chemisty Lectue #3 page MAY ELECTRO ATOMS At this point, we see that quantum mechanics allows us to undestand the helium atom, at least qualitatively. What about atoms with moe than two electons,
5.6 Physical Chemisty Lectue #3 page MAY ELECTRO ATOMS At this point, we see that quantum mechanics allows us to undestand the helium atom, at least qualitatively. What about atoms with moe than two electons,
A Relativistic Electron in a Coulomb Potential
 A Relativistic Electon in a Coulomb Potential Alfed Whitehead Physics 518, Fall 009 The Poblem Solve the Diac Equation fo an electon in a Coulomb potential. Identify the conseved quantum numbes. Specify
A Relativistic Electon in a Coulomb Potential Alfed Whitehead Physics 518, Fall 009 The Poblem Solve the Diac Equation fo an electon in a Coulomb potential. Identify the conseved quantum numbes. Specify
Stress, Cauchy s equation and the Navier-Stokes equations
 Chapte 3 Stess, Cauchy s equation and the Navie-Stokes equations 3. The concept of taction/stess Conside the volume of fluid shown in the left half of Fig. 3.. The volume of fluid is subjected to distibuted
Chapte 3 Stess, Cauchy s equation and the Navie-Stokes equations 3. The concept of taction/stess Conside the volume of fluid shown in the left half of Fig. 3.. The volume of fluid is subjected to distibuted
Multipole Radiation. February 29, The electromagnetic field of an isolated, oscillating source
 Multipole Radiation Febuay 29, 26 The electomagnetic field of an isolated, oscillating souce Conside a localized, oscillating souce, located in othewise empty space. We know that the solution fo the vecto
Multipole Radiation Febuay 29, 26 The electomagnetic field of an isolated, oscillating souce Conside a localized, oscillating souce, located in othewise empty space. We know that the solution fo the vecto
Question Bank. Section A. is skew-hermitian matrix. is diagonalizable. (, ) , Evaluate (, ) 12 about = 1 and = Find, if
 Subject: Mathematics-I Question Bank Section A T T. Find the value of fo which the matix A = T T has ank one. T T i. Is the matix A = i is skew-hemitian matix. i. alculate the invese of the matix = 5 7
Subject: Mathematics-I Question Bank Section A T T. Find the value of fo which the matix A = T T has ank one. T T i. Is the matix A = i is skew-hemitian matix. i. alculate the invese of the matix = 5 7
Qualifying Examination Electricity and Magnetism Solutions January 12, 2006
 1 Qualifying Examination Electicity and Magnetism Solutions Januay 12, 2006 PROBLEM EA. a. Fist, we conside a unit length of cylinde to find the elationship between the total chage pe unit length λ and
1 Qualifying Examination Electicity and Magnetism Solutions Januay 12, 2006 PROBLEM EA. a. Fist, we conside a unit length of cylinde to find the elationship between the total chage pe unit length λ and
dq 1 (5) q 1 where the previously mentioned limit has been taken.
 1 Vecto Calculus And Continuum Consevation Equations In Cuvilinea Othogonal Coodinates Robet Maska: Novembe 25, 2008 In ode to ewite the consevation equations(continuit, momentum, eneg) to some cuvilinea
1 Vecto Calculus And Continuum Consevation Equations In Cuvilinea Othogonal Coodinates Robet Maska: Novembe 25, 2008 In ode to ewite the consevation equations(continuit, momentum, eneg) to some cuvilinea
c n ψ n (r)e ient/ h (2) where E n = 1 mc 2 α 2 Z 2 ψ(r) = c n ψ n (r) = c n = ψn(r)ψ(r)d 3 x e 2r/a0 1 πa e 3r/a0 r 2 dr c 1 2 = 2 9 /3 6 = 0.
 Poblem {a} Fo t : Ψ(, t ψ(e iet/ h ( whee E mc α (α /7 ψ( e /a πa Hee we have used the gound state wavefunction fo Z. Fo t, Ψ(, t can be witten as a supeposition of Z hydogenic wavefunctions ψ n (: Ψ(,
Poblem {a} Fo t : Ψ(, t ψ(e iet/ h ( whee E mc α (α /7 ψ( e /a πa Hee we have used the gound state wavefunction fo Z. Fo t, Ψ(, t can be witten as a supeposition of Z hydogenic wavefunctions ψ n (: Ψ(,
working pages for Paul Richards class notes; do not copy or circulate without permission from PGR 2004/11/3 10:50
 woking pages fo Paul Richads class notes; do not copy o ciculate without pemission fom PGR 2004/11/3 10:50 CHAPTER7 Solid angle, 3D integals, Gauss s Theoem, and a Delta Function We define the solid angle,
woking pages fo Paul Richads class notes; do not copy o ciculate without pemission fom PGR 2004/11/3 10:50 CHAPTER7 Solid angle, 3D integals, Gauss s Theoem, and a Delta Function We define the solid angle,
B da = 0. Q E da = ε. E da = E dv
 lectomagnetic Theo Pof Ruiz, UNC Asheville, doctophs on YouTube Chapte Notes The Maxwell quations in Diffeential Fom 1 The Maxwell quations in Diffeential Fom We will now tansfom the integal fom of the
lectomagnetic Theo Pof Ruiz, UNC Asheville, doctophs on YouTube Chapte Notes The Maxwell quations in Diffeential Fom 1 The Maxwell quations in Diffeential Fom We will now tansfom the integal fom of the
I. CONSTRUCTION OF THE GREEN S FUNCTION
 I. CONSTRUCTION OF THE GREEN S FUNCTION The Helmohltz equation in 4 dimensions is 4 + k G 4 x, x = δ 4 x x. In this equation, G is the Geen s function and 4 efes to the dimensionality. In the vey end,
I. CONSTRUCTION OF THE GREEN S FUNCTION The Helmohltz equation in 4 dimensions is 4 + k G 4 x, x = δ 4 x x. In this equation, G is the Geen s function and 4 efes to the dimensionality. In the vey end,
Part V: Closed-form solutions to Loop Closure Equations
 Pat V: Closed-fom solutions to Loop Closue Equations This section will eview the closed-fom solutions techniques fo loop closue equations. The following thee cases will be consideed. ) Two unknown angles
Pat V: Closed-fom solutions to Loop Closue Equations This section will eview the closed-fom solutions techniques fo loop closue equations. The following thee cases will be consideed. ) Two unknown angles
2. Electrostatics. Dr. Rakhesh Singh Kshetrimayum 8/11/ Electromagnetic Field Theory by R. S. Kshetrimayum
 2. Electostatics D. Rakhesh Singh Kshetimayum 1 2.1 Intoduction In this chapte, we will study how to find the electostatic fields fo vaious cases? fo symmetic known chage distibution fo un-symmetic known
2. Electostatics D. Rakhesh Singh Kshetimayum 1 2.1 Intoduction In this chapte, we will study how to find the electostatic fields fo vaious cases? fo symmetic known chage distibution fo un-symmetic known
COORDINATE TRANSFORMATIONS - THE JACOBIAN DETERMINANT
 COORDINATE TRANSFORMATIONS - THE JACOBIAN DETERMINANT Link to: phsicspages home page. To leave a comment o epot an eo, please use the auilia blog. Refeence: d Inveno, Ra, Intoducing Einstein s Relativit
COORDINATE TRANSFORMATIONS - THE JACOBIAN DETERMINANT Link to: phsicspages home page. To leave a comment o epot an eo, please use the auilia blog. Refeence: d Inveno, Ra, Intoducing Einstein s Relativit
Do not turn over until you are told to do so by the Invigilator.
 UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Mathematics Main Seies UG Examination 2015 16 FLUID DYNAMICS WITH ADVANCED TOPICS MTH-MD59 Time allowed: 3 Hous Attempt QUESTIONS 1 and 2, and THREE othe questions.
UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Mathematics Main Seies UG Examination 2015 16 FLUID DYNAMICS WITH ADVANCED TOPICS MTH-MD59 Time allowed: 3 Hous Attempt QUESTIONS 1 and 2, and THREE othe questions.
MODULE 5a and 5b (Stewart, Sections 12.2, 12.3) INTRO: In MATH 1114 vectors were written either as rows (a1, a2,..., an) or as columns a 1 a. ...
 MODULE 5a and 5b (Stewat, Sections 2.2, 2.3) INTRO: In MATH 4 vectos wee witten eithe as ows (a, a2,..., an) o as columns a a 2... a n and the set of all such vectos of fixed length n was called the vecto
MODULE 5a and 5b (Stewat, Sections 2.2, 2.3) INTRO: In MATH 4 vectos wee witten eithe as ows (a, a2,..., an) o as columns a a 2... a n and the set of all such vectos of fixed length n was called the vecto
arxiv: v1 [physics.pop-ph] 3 Jun 2013
![arxiv: v1 [physics.pop-ph] 3 Jun 2013 arxiv: v1 [physics.pop-ph] 3 Jun 2013](/thumbs/89/100795062.jpg) A note on the electostatic enegy of two point chages axiv:1306.0401v1 [physics.pop-ph] 3 Jun 013 A C Tot Instituto de Física Univesidade Fedeal do io de Janeio Caixa Postal 68.58; CEP 1941-97 io de Janeio,
A note on the electostatic enegy of two point chages axiv:1306.0401v1 [physics.pop-ph] 3 Jun 013 A C Tot Instituto de Física Univesidade Fedeal do io de Janeio Caixa Postal 68.58; CEP 1941-97 io de Janeio,
f(k) e p 2 (k) e iax 2 (k a) r 2 e a x a a 2 + k 2 e a2 x 1 2 H(x) ik p (k) 4 r 3 cos Y 2 = 4
 Fouie tansfom pais: f(x) 1 f(k) e p 2 (k) p e iax 2 (k a) 2 e a x a a 2 + k 2 e a2 x 1 2, a > 0 a p k2 /4a2 e 2 1 H(x) ik p 2 + 2 (k) The fist few Y m Y 0 0 = Y 0 1 = Y ±1 1 = l : 1 Y2 0 = 4 3 ±1 cos Y
Fouie tansfom pais: f(x) 1 f(k) e p 2 (k) p e iax 2 (k a) 2 e a x a a 2 + k 2 e a2 x 1 2, a > 0 a p k2 /4a2 e 2 1 H(x) ik p 2 + 2 (k) The fist few Y m Y 0 0 = Y 0 1 = Y ±1 1 = l : 1 Y2 0 = 4 3 ±1 cos Y
Analytic Evaluation of two-electron Atomic Integrals involving Extended Hylleraas-CI functions with STO basis
 Analytic Evaluation of two-electon Atomic Integals involving Extended Hylleaas-CI functions with STO basis B PADHY (Retd.) Faculty Membe Depatment of Physics, Khalikote (Autonomous) College, Behampu-760001,
Analytic Evaluation of two-electon Atomic Integals involving Extended Hylleaas-CI functions with STO basis B PADHY (Retd.) Faculty Membe Depatment of Physics, Khalikote (Autonomous) College, Behampu-760001,
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Physics Department Physics 8.07: Electromagnetism II September 15, 2012 Prof. Alan Guth PROBLEM SET 2
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Physics Depatment Physics 8.07: Electomagnetism II Septembe 5, 202 Pof. Alan Guth PROBLEM SET 2 DUE DATE: Monday, Septembe 24, 202. Eithe hand it in at the lectue,
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Physics Depatment Physics 8.07: Electomagnetism II Septembe 5, 202 Pof. Alan Guth PROBLEM SET 2 DUE DATE: Monday, Septembe 24, 202. Eithe hand it in at the lectue,
Vector Calculus Identities
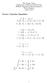 The Coope Union Depatment of Electical Engineeing ECE135 Engineeing Electomagnetics Vecto Analysis Mach 8, 2012 Vecto Calculus Identities A B B A A B C B C A C A B A B C B A C C A B fg f g + g f fg f G
The Coope Union Depatment of Electical Engineeing ECE135 Engineeing Electomagnetics Vecto Analysis Mach 8, 2012 Vecto Calculus Identities A B B A A B C B C A C A B A B C B A C C A B fg f g + g f fg f G
BASIC ALGEBRA OF VECTORS
 Fomulae Fo u Vecto Algeba By Mi Mohammed Abbas II PCMB 'A' Impotant Tems, Definitions & Fomulae 01 Vecto - Basic Intoduction: A quantity having magnitude as well as the diection is called vecto It is denoted
Fomulae Fo u Vecto Algeba By Mi Mohammed Abbas II PCMB 'A' Impotant Tems, Definitions & Fomulae 01 Vecto - Basic Intoduction: A quantity having magnitude as well as the diection is called vecto It is denoted
Math 2263 Solutions for Spring 2003 Final Exam
 Math 6 Solutions fo Sping Final Exam ) A staightfowad appoach to finding the tangent plane to a suface at a point ( x, y, z ) would be to expess the cuve as an explicit function z = f ( x, y ), calculate
Math 6 Solutions fo Sping Final Exam ) A staightfowad appoach to finding the tangent plane to a suface at a point ( x, y, z ) would be to expess the cuve as an explicit function z = f ( x, y ), calculate
Partition Functions. Chris Clark July 18, 2006
 Patition Functions Chis Clak July 18, 2006 1 Intoduction Patition functions ae useful because it is easy to deive expectation values of paametes of the system fom them. Below is a list of the mao examples.
Patition Functions Chis Clak July 18, 2006 1 Intoduction Patition functions ae useful because it is easy to deive expectation values of paametes of the system fom them. Below is a list of the mao examples.
18.06 Problem Set 4 Solution
 8.6 Poblem Set 4 Solution Total: points Section 3.5. Poblem 2: (Recommended) Find the lagest possible numbe of independent vectos among ) ) ) v = v 4 = v 5 = v 6 = v 2 = v 3 =. Solution (4 points): Since
8.6 Poblem Set 4 Solution Total: points Section 3.5. Poblem 2: (Recommended) Find the lagest possible numbe of independent vectos among ) ) ) v = v 4 = v 5 = v 6 = v 2 = v 3 =. Solution (4 points): Since
MAC Module 12 Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors
 MAC 23 Module 2 Eigenvalues and Eigenvectos Leaning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to:. Solve the eigenvalue poblem by finding the eigenvalues and the coesponding eigenvectos
MAC 23 Module 2 Eigenvalues and Eigenvectos Leaning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to:. Solve the eigenvalue poblem by finding the eigenvalues and the coesponding eigenvectos
Physics 505 Homework No. 9 Solutions S9-1
 Physics 505 Homewok No 9 s S9-1 1 As pomised, hee is the tick fo summing the matix elements fo the Stak effect fo the gound state of the hydogen atom Recall, we need to calculate the coection to the gound
Physics 505 Homewok No 9 s S9-1 1 As pomised, hee is the tick fo summing the matix elements fo the Stak effect fo the gound state of the hydogen atom Recall, we need to calculate the coection to the gound
Vectors, Vector Calculus, and Coordinate Systems
 Apil 5, 997 A Quick Intoduction to Vectos, Vecto Calculus, and Coodinate Systems David A. Randall Depatment of Atmospheic Science Coloado State Univesity Fot Collins, Coloado 80523. Scalas and vectos Any
Apil 5, 997 A Quick Intoduction to Vectos, Vecto Calculus, and Coodinate Systems David A. Randall Depatment of Atmospheic Science Coloado State Univesity Fot Collins, Coloado 80523. Scalas and vectos Any
Berkeley Math Circle AIME Preparation March 5, 2013
 Algeba Toolkit Rules of Thumb. Make sue that you can pove all fomulas you use. This is even bette than memoizing the fomulas. Although it is best to memoize, as well. Stive fo elegant, economical methods.
Algeba Toolkit Rules of Thumb. Make sue that you can pove all fomulas you use. This is even bette than memoizing the fomulas. Although it is best to memoize, as well. Stive fo elegant, economical methods.
Solutions to Exercises in Notes 1., multiplying byg kl, and using [ ]
![Solutions to Exercises in Notes 1., multiplying byg kl, and using [ ] Solutions to Exercises in Notes 1., multiplying byg kl, and using [ ]](/thumbs/96/127738252.jpg) Fo any vecto fields X, Y and Z that Solutions to Execises in Notes. 2g ( X Y, Z) = X (g (Y, Z)) + Y (g (X, Z)) Z (g (X, Y )) () + g ([X, Y ], Z) g ([X, Z], Y ) g ([Y, Z], X). Applying this to X =, Y =,
Fo any vecto fields X, Y and Z that Solutions to Execises in Notes. 2g ( X Y, Z) = X (g (Y, Z)) + Y (g (X, Z)) Z (g (X, Y )) () + g ([X, Y ], Z) g ([X, Z], Y ) g ([Y, Z], X). Applying this to X =, Y =,
Quantum theory of angular momentum
 Quantum theoy of angula momentum Igo Mazets igo.mazets+e141@tuwien.ac.at (Atominstitut TU Wien, Stadionallee 2, 1020 Wien Time: Fiday, 13:00 14:30 Place: Feihaus, Sem.R. DA gün 06B (exception date 18 Nov.:
Quantum theoy of angula momentum Igo Mazets igo.mazets+e141@tuwien.ac.at (Atominstitut TU Wien, Stadionallee 2, 1020 Wien Time: Fiday, 13:00 14:30 Place: Feihaus, Sem.R. DA gün 06B (exception date 18 Nov.:
16 Modeling a Language by a Markov Process
 K. Pommeening, Language Statistics 80 16 Modeling a Language by a Makov Pocess Fo deiving theoetical esults a common model of language is the intepetation of texts as esults of Makov pocesses. This model
K. Pommeening, Language Statistics 80 16 Modeling a Language by a Makov Pocess Fo deiving theoetical esults a common model of language is the intepetation of texts as esults of Makov pocesses. This model
Class #16 Monday, March 20, 2017
 D. Pogo Class #16 Monday, Mach 0, 017 D Non-Catesian Coodinate Systems A point in space can be specified by thee numbes:, y, and z. O, it can be specified by 3 diffeent numbes:,, and z, whee = cos, y =
D. Pogo Class #16 Monday, Mach 0, 017 D Non-Catesian Coodinate Systems A point in space can be specified by thee numbes:, y, and z. O, it can be specified by 3 diffeent numbes:,, and z, whee = cos, y =
6 Vector Operators. 6.1 The Gradient Operator
 6 Vecto Opeatos 6. The Gadient Opeato In the B2 couse ou wee intoduced to the gadient opeato in Catesian coodinates. Fo an diffeentiable scala function f(x,, z), we can define a vecto function though (
6 Vecto Opeatos 6. The Gadient Opeato In the B2 couse ou wee intoduced to the gadient opeato in Catesian coodinates. Fo an diffeentiable scala function f(x,, z), we can define a vecto function though (
Chapter 3: Theory of Modular Arithmetic 38
 Chapte 3: Theoy of Modula Aithmetic 38 Section D Chinese Remainde Theoem By the end of this section you will be able to pove the Chinese Remainde Theoem apply this theoem to solve simultaneous linea conguences
Chapte 3: Theoy of Modula Aithmetic 38 Section D Chinese Remainde Theoem By the end of this section you will be able to pove the Chinese Remainde Theoem apply this theoem to solve simultaneous linea conguences
Preliminary Exam: Quantum Physics 1/14/2011, 9:00-3:00
 Peliminay Exam: Quantum Physics /4/ 9:-: Answe a total of SIX questions of which at least TWO ae fom section A and at least THREE ae fom section B Fo you answes you can use eithe the blue books o individual
Peliminay Exam: Quantum Physics /4/ 9:-: Answe a total of SIX questions of which at least TWO ae fom section A and at least THREE ae fom section B Fo you answes you can use eithe the blue books o individual
The Poisson bracket and magnetic monopoles
 FYST420 Advanced electodynamics Olli Aleksante Koskivaaa Final poject ollikoskivaaa@gmail.com The Poisson backet and magnetic monopoles Abstact: In this wok magnetic monopoles ae studied using the Poisson
FYST420 Advanced electodynamics Olli Aleksante Koskivaaa Final poject ollikoskivaaa@gmail.com The Poisson backet and magnetic monopoles Abstact: In this wok magnetic monopoles ae studied using the Poisson
I( x) t e. is the total mean free path in the medium, [cm] tis the total cross section in the medium, [cm ] A M
![I( x) t e. is the total mean free path in the medium, [cm] tis the total cross section in the medium, [cm ] A M I( x) t e. is the total mean free path in the medium, [cm] tis the total cross section in the medium, [cm ] A M](/thumbs/79/79663309.jpg) t I ( x) I e x x t Ie (1) whee: 1 t is the total mean fee path in the medium, [cm] N t t -1 tis the total coss section in the medium, [cm ] A M 3 is the density of the medium [gm/cm ] v 3 N= is the nuclea
t I ( x) I e x x t Ie (1) whee: 1 t is the total mean fee path in the medium, [cm] N t t -1 tis the total coss section in the medium, [cm ] A M 3 is the density of the medium [gm/cm ] v 3 N= is the nuclea
0606 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS 0606/01 Paper 1, maximum raw mark 80
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Intenational Geneal Cetificate of Seconday Education MARK SCHEME fo the Octobe/Novembe 009 question pape fo the guidance of teaches 0606 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Intenational Geneal Cetificate of Seconday Education MARK SCHEME fo the Octobe/Novembe 009 question pape fo the guidance of teaches 0606 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS
When two numbers are written as the product of their prime factors, they are in factored form.
 10 1 Study Guide Pages 420 425 Factos Because 3 4 12, we say that 3 and 4 ae factos of 12. In othe wods, factos ae the numbes you multiply to get a poduct. Since 2 6 12, 2 and 6 ae also factos of 12. The
10 1 Study Guide Pages 420 425 Factos Because 3 4 12, we say that 3 and 4 ae factos of 12. In othe wods, factos ae the numbes you multiply to get a poduct. Since 2 6 12, 2 and 6 ae also factos of 12. The
PHYS 110B - HW #7 Spring 2004, Solutions by David Pace Any referenced equations are from Griffiths Problem statements are paraphrased
 PHYS 0B - HW #7 Sping 2004, Solutions by David Pace Any efeenced euations ae fom Giffiths Poblem statements ae paaphased. Poblem 0.3 fom Giffiths A point chage,, moves in a loop of adius a. At time t 0
PHYS 0B - HW #7 Sping 2004, Solutions by David Pace Any efeenced euations ae fom Giffiths Poblem statements ae paaphased. Poblem 0.3 fom Giffiths A point chage,, moves in a loop of adius a. At time t 0
-Δ u = λ u. u(x,y) = u 1. (x) u 2. (y) u(r,θ) = R(r) Θ(θ) Δu = 2 u + 2 u. r = x 2 + y 2. tan(θ) = y/x. r cos(θ) = cos(θ) r.
 The Laplace opeato in pola coodinates We now conside the Laplace opeato with Diichlet bounday conditions on a cicula egion Ω {(x,y) x + y A }. Ou goal is to compute eigenvalues and eigenfunctions of the
The Laplace opeato in pola coodinates We now conside the Laplace opeato with Diichlet bounday conditions on a cicula egion Ω {(x,y) x + y A }. Ou goal is to compute eigenvalues and eigenfunctions of the
Lecture 16 Root Systems and Root Lattices
 1.745 Intoduction to Lie Algebas Novembe 1, 010 Lectue 16 Root Systems and Root Lattices Pof. Victo Kac Scibe: Michael Cossley Recall that a oot system is a pai (V, ), whee V is a finite dimensional Euclidean
1.745 Intoduction to Lie Algebas Novembe 1, 010 Lectue 16 Root Systems and Root Lattices Pof. Victo Kac Scibe: Michael Cossley Recall that a oot system is a pai (V, ), whee V is a finite dimensional Euclidean
of the contestants play as Falco, and 1 6
 JHMT 05 Algeba Test Solutions 4 Febuay 05. In a Supe Smash Bothes tounament, of the contestants play as Fox, 3 of the contestants play as Falco, and 6 of the contestants play as Peach. Given that thee
JHMT 05 Algeba Test Solutions 4 Febuay 05. In a Supe Smash Bothes tounament, of the contestants play as Fox, 3 of the contestants play as Falco, and 6 of the contestants play as Peach. Given that thee
Lecture 23. Representation of the Dirac delta function in other coordinate systems
 Lectue 23 Repesentation of the Diac delta function in othe coodinate systems In a geneal sense, one can wite, ( ) = (x x ) (y y ) (z z ) = (u u ) (v v ) (w w ) J Whee J epesents the Jacobian of the tansfomation.
Lectue 23 Repesentation of the Diac delta function in othe coodinate systems In a geneal sense, one can wite, ( ) = (x x ) (y y ) (z z ) = (u u ) (v v ) (w w ) J Whee J epesents the Jacobian of the tansfomation.
e.g: If A = i 2 j + k then find A. A = Ax 2 + Ay 2 + Az 2 = ( 2) = 6
 MOTION IN A PLANE 1. Scala Quantities Physical quantities that have only magnitude and no diection ae called scala quantities o scalas. e.g. Mass, time, speed etc. 2. Vecto Quantities Physical quantities
MOTION IN A PLANE 1. Scala Quantities Physical quantities that have only magnitude and no diection ae called scala quantities o scalas. e.g. Mass, time, speed etc. 2. Vecto Quantities Physical quantities
Math Notes on Kepler s first law 1. r(t) kp(t)
 Math 7 - Notes on Keple s fist law Planetay motion and Keple s Laws We conside the motion of a single planet about the sun; fo simplicity, we assign coodinates in R 3 so that the position of the sun is
Math 7 - Notes on Keple s fist law Planetay motion and Keple s Laws We conside the motion of a single planet about the sun; fo simplicity, we assign coodinates in R 3 so that the position of the sun is
(A) 2log( tan cot ) [ ], 2 MATHEMATICS. 1. Which of the following is correct?
![(A) 2log( tan cot ) [ ], 2 MATHEMATICS. 1. Which of the following is correct? (A) 2log( tan cot ) [ ], 2 MATHEMATICS. 1. Which of the following is correct?](/thumbs/76/73747145.jpg) MATHEMATICS. Which of the following is coect? A L.P.P always has unique solution Evey L.P.P has an optimal solution A L.P.P admits two optimal solutions If a L.P.P admits two optimal solutions then it
MATHEMATICS. Which of the following is coect? A L.P.P always has unique solution Evey L.P.P has an optimal solution A L.P.P admits two optimal solutions If a L.P.P admits two optimal solutions then it
On the integration of the equations of hydrodynamics
 Uebe die Integation de hydodynamischen Gleichungen J f eine u angew Math 56 (859) -0 On the integation of the equations of hydodynamics (By A Clebsch at Calsuhe) Tanslated by D H Delphenich In a pevious
Uebe die Integation de hydodynamischen Gleichungen J f eine u angew Math 56 (859) -0 On the integation of the equations of hydodynamics (By A Clebsch at Calsuhe) Tanslated by D H Delphenich In a pevious
Quantum Chemistry Notes:
 Quantum Chemisty otes: Hatee-Fock equations The Hatee-Fock method is the undelying appoximation to nealy all methods of computational chemisty, both ab initio and semi-empiical. Theefoe, a clea undestanding
Quantum Chemisty otes: Hatee-Fock equations The Hatee-Fock method is the undelying appoximation to nealy all methods of computational chemisty, both ab initio and semi-empiical. Theefoe, a clea undestanding
Quantum Mechanics II
 Quantum Mechanics II Pof. Bois Altshule Apil 25, 2 Lectue 25 We have been dicussing the analytic popeties of the S-matix element. Remembe the adial wave function was u kl () = R kl () e ik iπl/2 S l (k)e
Quantum Mechanics II Pof. Bois Altshule Apil 25, 2 Lectue 25 We have been dicussing the analytic popeties of the S-matix element. Remembe the adial wave function was u kl () = R kl () e ik iπl/2 S l (k)e
Review: Electrostatics and Magnetostatics
 Review: Electostatics and Magnetostatics In the static egime, electomagnetic quantities do not vay as a function of time. We have two main cases: ELECTROSTATICS The electic chages do not change postion
Review: Electostatics and Magnetostatics In the static egime, electomagnetic quantities do not vay as a function of time. We have two main cases: ELECTROSTATICS The electic chages do not change postion
transformation Earth V-curve (meridian) λ Conical projection. u,v curves on the datum surface projected as U,V curves on the projection surface
 . CONICAL PROJECTIONS In elementay texts on map pojections, the pojection sufaces ae often descibed as developable sufaces, such as the cylinde (cylindical pojections) and the cone (conical pojections),
. CONICAL PROJECTIONS In elementay texts on map pojections, the pojection sufaces ae often descibed as developable sufaces, such as the cylinde (cylindical pojections) and the cone (conical pojections),
A New Approach to General Relativity
 Apeion, Vol. 14, No. 3, July 7 7 A New Appoach to Geneal Relativity Ali Rıza Şahin Gaziosmanpaşa, Istanbul Tukey E-mail: aizasahin@gmail.com Hee we pesent a new point of view fo geneal elativity and/o
Apeion, Vol. 14, No. 3, July 7 7 A New Appoach to Geneal Relativity Ali Rıza Şahin Gaziosmanpaşa, Istanbul Tukey E-mail: aizasahin@gmail.com Hee we pesent a new point of view fo geneal elativity and/o
Scattering in Three Dimensions
 Scatteing in Thee Dimensions Scatteing expeiments ae an impotant souce of infomation about quantum systems, anging in enegy fom vey low enegy chemical eactions to the highest possible enegies at the LHC.
Scatteing in Thee Dimensions Scatteing expeiments ae an impotant souce of infomation about quantum systems, anging in enegy fom vey low enegy chemical eactions to the highest possible enegies at the LHC.
Physics Tutorial V1 2D Vectors
 Physics Tutoial V1 2D Vectos 1 Resolving Vectos & Addition of Vectos A vecto quantity has both magnitude and diection. Thee ae two ways commonly used to mathematically descibe a vecto. y (a) The pola fom:,
Physics Tutoial V1 2D Vectos 1 Resolving Vectos & Addition of Vectos A vecto quantity has both magnitude and diection. Thee ae two ways commonly used to mathematically descibe a vecto. y (a) The pola fom:,
Markscheme May 2017 Calculus Higher level Paper 3
 M7/5/MATHL/HP3/ENG/TZ0/SE/M Makscheme May 07 Calculus Highe level Pape 3 pages M7/5/MATHL/HP3/ENG/TZ0/SE/M This makscheme is the popety of the Intenational Baccalaueate and must not be epoduced o distibuted
M7/5/MATHL/HP3/ENG/TZ0/SE/M Makscheme May 07 Calculus Highe level Pape 3 pages M7/5/MATHL/HP3/ENG/TZ0/SE/M This makscheme is the popety of the Intenational Baccalaueate and must not be epoduced o distibuted
A Crash Course in (2 2) Matrices
 A Cash Couse in ( ) Matices Seveal weeks woth of matix algeba in an hou (Relax, we will only stuy the simplest case, that of matices) Review topics: What is a matix (pl matices)? A matix is a ectangula
A Cash Couse in ( ) Matices Seveal weeks woth of matix algeba in an hou (Relax, we will only stuy the simplest case, that of matices) Review topics: What is a matix (pl matices)? A matix is a ectangula
Vectors, Vector Calculus, and Coordinate Systems
 ! Revised Apil 11, 2017 1:48 PM! 1 Vectos, Vecto Calculus, and Coodinate Systems David Randall Physical laws and coodinate systems Fo the pesent discussion, we define a coodinate system as a tool fo descibing
! Revised Apil 11, 2017 1:48 PM! 1 Vectos, Vecto Calculus, and Coodinate Systems David Randall Physical laws and coodinate systems Fo the pesent discussion, we define a coodinate system as a tool fo descibing
Problem Set 10 Solutions
 Chemisty 6 D. Jean M. Standad Poblem Set 0 Solutions. Give the explicit fom of the Hamiltonian opeato (in atomic units) fo the lithium atom. You expession should not include any summations (expand them
Chemisty 6 D. Jean M. Standad Poblem Set 0 Solutions. Give the explicit fom of the Hamiltonian opeato (in atomic units) fo the lithium atom. You expession should not include any summations (expand them
Solution to HW 3, Ma 1a Fall 2016
 Solution to HW 3, Ma a Fall 206 Section 2. Execise 2: Let C be a subset of the eal numbes consisting of those eal numbes x having the popety that evey digit in the decimal expansion of x is, 3, 5, o 7.
Solution to HW 3, Ma a Fall 206 Section 2. Execise 2: Let C be a subset of the eal numbes consisting of those eal numbes x having the popety that evey digit in the decimal expansion of x is, 3, 5, o 7.
Lecture 8 - Gauss s Law
 Lectue 8 - Gauss s Law A Puzzle... Example Calculate the potential enegy, pe ion, fo an infinite 1D ionic cystal with sepaation a; that is, a ow of equally spaced chages of magnitude e and altenating sign.
Lectue 8 - Gauss s Law A Puzzle... Example Calculate the potential enegy, pe ion, fo an infinite 1D ionic cystal with sepaation a; that is, a ow of equally spaced chages of magnitude e and altenating sign.
3.6 Applied Optimization
 .6 Applied Optimization Section.6 Notes Page In this section we will be looking at wod poblems whee it asks us to maimize o minimize something. Fo all the poblems in this section you will be taking the
.6 Applied Optimization Section.6 Notes Page In this section we will be looking at wod poblems whee it asks us to maimize o minimize something. Fo all the poblems in this section you will be taking the
Let us next consider how one can calculate one- electron elements of the long- range nuclear- electron potential:
 Hatee- Fock Long Range In the following assume the patition of 1/ into shot ange and long ance components 1 efc( / a) ef ( / a) + Hee a is a paamete detemining the patitioning between shot ange and long
Hatee- Fock Long Range In the following assume the patition of 1/ into shot ange and long ance components 1 efc( / a) ef ( / a) + Hee a is a paamete detemining the patitioning between shot ange and long
sinγ(h y > ) exp(iωt iqx)dωdq
 Lectue 9/28/5 Can we ecove a ay pictue fom the above G fo a membane stip? Such a pictue would be complementay to the above expansion in a seies of integals along the many banches of the dispesion elation.
Lectue 9/28/5 Can we ecove a ay pictue fom the above G fo a membane stip? Such a pictue would be complementay to the above expansion in a seies of integals along the many banches of the dispesion elation.
Chapter 5 Linear Equations: Basic Theory and Practice
 Chapte 5 inea Equations: Basic Theoy and actice In this chapte and the next, we ae inteested in the linea algebaic equation AX = b, (5-1) whee A is an m n matix, X is an n 1 vecto to be solved fo, and
Chapte 5 inea Equations: Basic Theoy and actice In this chapte and the next, we ae inteested in the linea algebaic equation AX = b, (5-1) whee A is an m n matix, X is an n 1 vecto to be solved fo, and
Right-handed screw dislocation in an isotropic solid
 Dislocation Mechanics Elastic Popeties of Isolated Dislocations Ou study of dislocations to this point has focused on thei geomety and thei ole in accommodating plastic defomation though thei motion. We
Dislocation Mechanics Elastic Popeties of Isolated Dislocations Ou study of dislocations to this point has focused on thei geomety and thei ole in accommodating plastic defomation though thei motion. We
Transformation of the Navier-Stokes Equations in Curvilinear Coordinate Systems with Maple
 Global Jounal of Pue and Applied Mathematics. ISSN 0973-1768 Volume 12, Numbe 4 2016, pp. 3315 3325 Reseach India Publications http://www.ipublication.com/gjpam.htm Tansfomation of the Navie-Stokes Equations
Global Jounal of Pue and Applied Mathematics. ISSN 0973-1768 Volume 12, Numbe 4 2016, pp. 3315 3325 Reseach India Publications http://www.ipublication.com/gjpam.htm Tansfomation of the Navie-Stokes Equations
Hopefully Helpful Hints for Gauss s Law
 Hopefully Helpful Hints fo Gauss s Law As befoe, thee ae things you need to know about Gauss s Law. In no paticula ode, they ae: a.) In the context of Gauss s Law, at a diffeential level, the electic flux
Hopefully Helpful Hints fo Gauss s Law As befoe, thee ae things you need to know about Gauss s Law. In no paticula ode, they ae: a.) In the context of Gauss s Law, at a diffeential level, the electic flux
= e2. = 2e2. = 3e2. V = Ze2. where Z is the atomic numnber. Thus, we take as the Hamiltonian for a hydrogenic. H = p2 r. (19.4)
 Chapte 9 Hydogen Atom I What is H int? That depends on the physical system and the accuacy with which it is descibed. A natual stating point is the fom H int = p + V, (9.) µ which descibes a two-paticle
Chapte 9 Hydogen Atom I What is H int? That depends on the physical system and the accuacy with which it is descibed. A natual stating point is the fom H int = p + V, (9.) µ which descibes a two-paticle
ATMO 551a Fall 08. Diffusion
 Diffusion Diffusion is a net tanspot of olecules o enegy o oentu o fo a egion of highe concentation to one of lowe concentation by ando olecula) otion. We will look at diffusion in gases. Mean fee path
Diffusion Diffusion is a net tanspot of olecules o enegy o oentu o fo a egion of highe concentation to one of lowe concentation by ando olecula) otion. We will look at diffusion in gases. Mean fee path
