Major Concepts Calorimetry (from last time)
|
|
|
- Oliver Lang
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Major Concepts Calorimetry (from last time) Heat capacity Molar heat capacity (per mole) Specific heat capacity (per mass) Standard state enthalpies: Hº Physical Changes Chemical Changes Hess's Law Balancing chemical reactions & energies Standard state enthalpies: Hº Calculating H s tables of Hº Heats of Reaction and Formation Temperature Dependence in r Hº(T) Kirkhoff s Law 9/9/10 Thermochemistry (lec7) 1
2 Calorimetry is: the science of measuring heat based on observing the temperature change when a body absorbs or discharges energy as heat Calorimeters: Calorimetry Constant-Pressure Calorimeters, e.g., the coffee cup calorimeter Differential Scanning Calorimeters (DSC) The device has an overall heat capacity, and is otherwise insulating 9/9/10 Thermochemistry (lec7) 2
3 Recall: Heat Capacity Heat Capacity, C P, is the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of a substance by one degree at constant pressure. Heat Capacity = C P = where Heat Capacity vs. Molar Heat Capacity: C p = q ΔT c p = C p n = ( units are J ) K q nδt q ΔT = heat absorbed ΔT = dh dt P C P denotes Heat Capacity at constant pressure units are J K mole ( ) ΔT = T f -T i 9/9/10 Thermochemistry (lec7) 3
4 Properties of Heat Capacity C P = dh dt P and c P = C P is always a positive number d( H ) n dt q and ΔT must be both negative or positive If q is negative, then heat is evolved or given off and the temperature decreases If q is positive, then heat is absorbed and the temperature increases Heat flows from High to Low Temperature P 9/9/10 Thermochemistry (lec7) 4
5 Specific Heat Capacity The word Specific before the name of a physical quantity very often means divided by the mass Specific Heat Capacity is the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of one gram of material by one degree Kelvin (at constant pressure) cs = C P m units are JK -1 g -1 9/9/10 Thermochemistry (lec7) 5
6 Calorimetry: Balancing Chemical Equations with Enthalpy Changes (by example) CO (g) + ½ O 2 (g) CO 2 (g) ΔH= -283kJ An exothermic reaction If Quantities doubled (x2), then double ΔH 2CO (g) + 1 O 2 (g) 2 CO 2 (g) ΔH= -566kJ If the original reaction is reversed, then change sign of H CO 2 (g) CO (g) + ½ O 2 (g) ΔH= +283kJ An endothermic reaction 9/9/10 Thermochemistry (lec7) 6
7 Skill: Calculating Heat Changes for a Reaction How much heat energy is needed to decompose 9.74g of HBr(g) (M =80.9 g/mol) into its elements? Given: H 2 (g) + Br 2 (g) 2HBr (g) ΔH = kj mol -1 Strategy: Decomposition is actually the reverse reaction ΔH to decompose 2 moles of HBr is +72.8kJ/mol 9/9/10 Thermochemistry (lec7) 7
8 Skill: Calculating Heat Chances for a Reaction How much heat energy is needed to decompose 9.74g of HBr(g) (M =80.9 g/mol) into its elements? Given: H 2 (g) + Br 2 (g) 2HBr (g) ΔH = kj mol -1 Solution : Decomposition is actually the reverse reaction 2HBr (g) H 2 (g) + Br 2 (g) ΔH = kj mol -1 q = ΔH = 72.8 kj 2 moles HBr = 4.38 kj 9.74 g HBr g HBr mole 9/9/10 Thermochemistry (lec7) 8
9 Standard State Enthalpies: Hº(T) Designated using a superscript (pronounced naught) This is needed because Enthalpy varies with conditions Is written as ΔH ΔH 25 o C or ΔH K If no temperature is indicated in the sub-script, assume 25 C. In this course, the standard pressure is 1 bar. (Warning: in some text books, the standard pressure is 1 atm.) Standard State conditions All concentrations are 1M or 1 mol/l All partial pressures are 1 atm or ΔH 9/9/10 Thermochemistry (lec7) 9
10 Refer to Slide 7.2 Standard Enthalpy Changes 9/9/10 Thermochemistry (lec7) 10
11 Solid, liquid & vapor regions Normal: Melting point Freezing point Triple point Critical point Supercritical fluid region Phase Diagram of Water 9/9/10 Thermochemistry (lec7) 11
12 Hess s Law Sometimes its difficult or even impossible to conduct some experiments in the lab. Because Enthalpy (H) is a State Property, it doesn t matter what path is taken as long as the initial reactants lead to the final product. Hess s Law is about adding or subtracting equations and enthalpies. Hess s Law: If two or more chemical equations are added to give a new equation, then adding the enthalpies of the reactions that they represent gives the enthalpy of the new reaction. 9/9/10 Thermochemistry (lec7) 12
13 Enthalpy Changes for Formation & Reaction Refer to Slide 7.3 9/9/10 Thermochemistry (lec7) 13
14 Skill: Using Hess's law (by example) Rxn #2 N 2 (g) + O 2 (g) 2 NO ΔH 2 = +180 kj Rxn #3 2 NO (g) + O 2 (g) 2 NO 2 ΔH 3 = 112 kj Rxn #1 N 2 (g) + 2 O 2 (g) 2 NO 2 ΔH 1 = +68kJ 9/9/10 Thermochemistry (lec7) 14
15 Temperature Dependence in Hº(T) Refer to Slide 7.4 9/9/10 Thermochemistry (lec7) 15
10-1 Heat 10-2 Calorimetry 10-3 Enthalpy 10-4 Standard-State Enthalpies 10-5 Bond Enthalpies 10-6 The First Law of Thermodynamics
 Chapter 10 Thermochemistry 10-1 Heat 10-2 Calorimetry 10-3 Enthalpy 10-4 Standard-State Enthalpies 10-5 Bond Enthalpies 10-6 The First Law of Thermodynamics OFB Chap. 10 1 Chapter 10 Thermochemistry Heat
Chapter 10 Thermochemistry 10-1 Heat 10-2 Calorimetry 10-3 Enthalpy 10-4 Standard-State Enthalpies 10-5 Bond Enthalpies 10-6 The First Law of Thermodynamics OFB Chap. 10 1 Chapter 10 Thermochemistry Heat
10-1 Heat 10-2 Calorimetry 10-3 Enthalpy 10-4 Standard-State Enthalpies 10-5 Bond Enthalpies 10-6 The First Law of Thermodynamics
 Chapter 10 Thermochemistry 10-1 Heat 10-2 Calorimetry 10-3 Enthalpy 10-4 Standard-State Enthalpies 10-5 Bond Enthalpies 10-6 The First Law of Thermodynamics OFB Chap. 10 1 OFB Chap. 10 2 Thermite Reaction
Chapter 10 Thermochemistry 10-1 Heat 10-2 Calorimetry 10-3 Enthalpy 10-4 Standard-State Enthalpies 10-5 Bond Enthalpies 10-6 The First Law of Thermodynamics OFB Chap. 10 1 OFB Chap. 10 2 Thermite Reaction
CHEM 1105 S10 March 11 & 14, 2014
 CHEM 1105 S10 March 11 & 14, 2014 Today s topics: Thermochemistry (Chapter 6) Basic definitions Calorimetry Enthalpy Thermochemical equations Calculating heats of reaction Hess s Law Energy and Heat Some
CHEM 1105 S10 March 11 & 14, 2014 Today s topics: Thermochemistry (Chapter 6) Basic definitions Calorimetry Enthalpy Thermochemical equations Calculating heats of reaction Hess s Law Energy and Heat Some
First Law of Thermodynamics
 Energy Energy: ability to do work or produce heat. Types of energy 1) Potential energy - energy possessed by objects due to position or arrangement of particles. Forms of potential energy - electrical,
Energy Energy: ability to do work or produce heat. Types of energy 1) Potential energy - energy possessed by objects due to position or arrangement of particles. Forms of potential energy - electrical,
Learning Check. How much heat, q, is required to raise the temperature of 1000 kg of iron and 1000 kg of water from 25 C to 75 C?
 Learning Check q = c * m * ΔT How much heat, q, is required to raise the temperature of 1000 kg of iron and 1000 kg of water from 25 C to 75 C? (c water =4.184 J/ C g, c iron =0.450 J/ C g) q Fe = 0.450
Learning Check q = c * m * ΔT How much heat, q, is required to raise the temperature of 1000 kg of iron and 1000 kg of water from 25 C to 75 C? (c water =4.184 J/ C g, c iron =0.450 J/ C g) q Fe = 0.450
8.6 The Thermodynamic Standard State
 8.6 The Thermodynamic Standard State The value of H reported for a reaction depends on the number of moles of reactants...or how much matter is contained in the system C 3 H 8 (g) + 5O 2 (g) > 3CO 2 (g)
8.6 The Thermodynamic Standard State The value of H reported for a reaction depends on the number of moles of reactants...or how much matter is contained in the system C 3 H 8 (g) + 5O 2 (g) > 3CO 2 (g)
Review of Terms. Additional Review. Energy, Enthalpy, & Thermochemistry
 Energy, Enthalpy, & Thermochemistry 9.1 The Nature of Energy 9. Enthalpy 9. Thermodynamics of Ideal Gases 9.4 alorimetry 9.5 Hess s Law 9.6 Standard Enthalpies of Formation 9.7 Present Sources of Energy
Energy, Enthalpy, & Thermochemistry 9.1 The Nature of Energy 9. Enthalpy 9. Thermodynamics of Ideal Gases 9.4 alorimetry 9.5 Hess s Law 9.6 Standard Enthalpies of Formation 9.7 Present Sources of Energy
Chapter 11. Thermochemistry: Heat & Chemical Change
 Chapter 11 Thermochemistry: Heat & Chemical Change The Flow of Energy Thermochemistry: Study of heat changes that occur during physical processes and chemical reactions Energy Energy is the capacity to
Chapter 11 Thermochemistry: Heat & Chemical Change The Flow of Energy Thermochemistry: Study of heat changes that occur during physical processes and chemical reactions Energy Energy is the capacity to
Chapter 11. Thermochemistry. 1. Let s begin by previewing the chapter (Page 292). 2. We will partner read Pages
 Chapter 11 Thermochemistry 1. Let s begin by previewing the chapter (Page 292). 2. We will partner read Pages 293-94 The Flow of energy - heat Thermochemistry concerned with the heat changes that occur
Chapter 11 Thermochemistry 1. Let s begin by previewing the chapter (Page 292). 2. We will partner read Pages 293-94 The Flow of energy - heat Thermochemistry concerned with the heat changes that occur
The Nature of Energy. Chapter Six: Kinetic vs. Potential Energy. Energy and Work. Temperature vs. Heat
 The Nature of Energy Chapter Six: THERMOCHEMISTRY Thermodynamics is the study of energy and its transformations. Thermochemistry is the study of the relationship between chemical reactions and energy changes
The Nature of Energy Chapter Six: THERMOCHEMISTRY Thermodynamics is the study of energy and its transformations. Thermochemistry is the study of the relationship between chemical reactions and energy changes
Types of Energy Calorimetry q = mc T Thermochemical Equations Hess s Law Spontaneity, Entropy, Gibb s Free energy
 Unit 7: Energy Outline Types of Energy Calorimetry q = mc T Thermochemical Equations Hess s Law Spontaneity, Entropy, Gibb s Free energy Energy Energy is the ability to do work or produce heat. The energy
Unit 7: Energy Outline Types of Energy Calorimetry q = mc T Thermochemical Equations Hess s Law Spontaneity, Entropy, Gibb s Free energy Energy Energy is the ability to do work or produce heat. The energy
Ch. 17 Thermochemistry
 Ch. 17 Thermochemistry 17.1 The Flow of Energy Energy Transformations Thermochemistry: study of energy changes in chemical reactions and changes in state Chemical potential energy: energy stored in bonds
Ch. 17 Thermochemistry 17.1 The Flow of Energy Energy Transformations Thermochemistry: study of energy changes in chemical reactions and changes in state Chemical potential energy: energy stored in bonds
Thermochemistry. Energy. 1st Law of Thermodynamics. Enthalpy / Calorimetry. Enthalpy of Formation
 THERMOCHEMISTRY Thermochemistry Energy 1st Law of Thermodynamics Enthalpy / Calorimetry Hess' Law Enthalpy of Formation The Nature of Energy Kinetic Energy and Potential Energy Kinetic energy is the energy
THERMOCHEMISTRY Thermochemistry Energy 1st Law of Thermodynamics Enthalpy / Calorimetry Hess' Law Enthalpy of Formation The Nature of Energy Kinetic Energy and Potential Energy Kinetic energy is the energy
Chapter 6: Thermochemistry
 Chapter 6: Thermochemistry 1. Light the Furnace: The Nature of Energy and Its Transformations a. Thermochemistry is the study of the relationships between chemistry and energy i. This means that we will
Chapter 6: Thermochemistry 1. Light the Furnace: The Nature of Energy and Its Transformations a. Thermochemistry is the study of the relationships between chemistry and energy i. This means that we will
Thermochemistry: the study of energy (in the from of heat) changes that accompany physical & chemical changes
 Thermochemistry Thermochemistry: the study of energy (in the from of heat) changes that accompany physical & chemical changes heat flows from high to low (hot cool) endothermic reactions: absorb energy
Thermochemistry Thermochemistry: the study of energy (in the from of heat) changes that accompany physical & chemical changes heat flows from high to low (hot cool) endothermic reactions: absorb energy
Enthalpy and Internal Energy
 Enthalpy and Internal Energy H or ΔH is used to symbolize enthalpy. The mathematical expression of the First Law of Thermodynamics is: ΔE = q + w, where ΔE is the change in internal energy, q is heat and
Enthalpy and Internal Energy H or ΔH is used to symbolize enthalpy. The mathematical expression of the First Law of Thermodynamics is: ΔE = q + w, where ΔE is the change in internal energy, q is heat and
Chapter 5 Thermochemistry
 Chapter 5 Thermochemistry Learning Outcomes: Interconvert energy units Distinguish between the system and the surroundings in thermodynamics Calculate internal energy from heat and work and state sign
Chapter 5 Thermochemistry Learning Outcomes: Interconvert energy units Distinguish between the system and the surroundings in thermodynamics Calculate internal energy from heat and work and state sign
The Nature of Energy Energy is the ability to do work or produce Heat, q or Q, is ; flows due to temperature differences (always to )
 CP Chapter 17 Thermochemistry 2014-2015 Thermochemistry Thermochemistry is the study of energy that occur during chemical and physical changes (changes of state) The Nature of Energy Energy is the ability
CP Chapter 17 Thermochemistry 2014-2015 Thermochemistry Thermochemistry is the study of energy that occur during chemical and physical changes (changes of state) The Nature of Energy Energy is the ability
Chapter 8. Thermochemistry 강의개요. 8.1 Principles of Heat Flow. 2) Magnitude of Heat Flow. 1) State Properties. Basic concepts : study of heat flow
 강의개요 Basic concepts : study of heat flow Chapter 8 Thermochemistry Calorimetry : experimental measurement of the magnitude and direction of heat flow Thermochemical Equations Copyright 2005 연세대학교이학계열일반화학및실험
강의개요 Basic concepts : study of heat flow Chapter 8 Thermochemistry Calorimetry : experimental measurement of the magnitude and direction of heat flow Thermochemical Equations Copyright 2005 연세대학교이학계열일반화학및실험
Energy. Different types of energy exist (heat, potential, kinetic, chemical, nuclear etc.)
 Change in Energy Energy Different types of energy exist (heat, potential, kinetic, chemical, nuclear etc.) Heat - the energy transferred between objects that are at different temperatures. Unit of heat
Change in Energy Energy Different types of energy exist (heat, potential, kinetic, chemical, nuclear etc.) Heat - the energy transferred between objects that are at different temperatures. Unit of heat
Chapter 8 Thermochemistry
 William L Masterton Cecile N. Hurley http://academic.cengage.com/chemistry/masterton Chapter 8 Thermochemistry Edward J. Neth University of Connecticut Outline 1. Principles of heat flow 2. Measurement
William L Masterton Cecile N. Hurley http://academic.cengage.com/chemistry/masterton Chapter 8 Thermochemistry Edward J. Neth University of Connecticut Outline 1. Principles of heat flow 2. Measurement
Exothermic process is any process that gives off heat transfers thermal energy from the system to the surroundings. H 2 O (l) + energy
 Exothermic process is any process that gives off heat transfers thermal energy from the system to the surroundings. H 2 O (g) H 2 O (l) + energy Endothermic process is any process in which heat has to
Exothermic process is any process that gives off heat transfers thermal energy from the system to the surroundings. H 2 O (g) H 2 O (l) + energy Endothermic process is any process in which heat has to
Thermochemistry-Part 1
 Brad Collins Thermochemistry-Part 1 Chapter 7 Thermochemistry Thermodynamics: The study of energy Thermochemistry: The study of energy in chemical reactions Energy: The capacity to do work Work = force
Brad Collins Thermochemistry-Part 1 Chapter 7 Thermochemistry Thermodynamics: The study of energy Thermochemistry: The study of energy in chemical reactions Energy: The capacity to do work Work = force
Chapter 6 Thermochemistry 許富銀
 Chapter 6 Thermochemistry 許富銀 6.1 Chemical Hand Warmers Thermochemistry: the study of the relationships between chemistry and energy Hand warmers use the oxidation of iron as the exothermic reaction: Nature
Chapter 6 Thermochemistry 許富銀 6.1 Chemical Hand Warmers Thermochemistry: the study of the relationships between chemistry and energy Hand warmers use the oxidation of iron as the exothermic reaction: Nature
Chapter 5 Thermochemistry
 Chapter 5 Thermochemistry Section 17.1 The Flow of Energy Heat and Work OBJECTIVES: Explain how energy, heat, and work are related. 2 Section 17.1 The Flow of Energy Heat and Work OBJECTIVES: Classify
Chapter 5 Thermochemistry Section 17.1 The Flow of Energy Heat and Work OBJECTIVES: Explain how energy, heat, and work are related. 2 Section 17.1 The Flow of Energy Heat and Work OBJECTIVES: Classify
33. a. Heat is absorbed from the water (it gets colder) as KBr dissolves, so this is an endothermic process.
 31. This is an endothermic reaction so heat must be absorbed in order to convert reactants into products. The high temperature environment of internal combustion engines provides the heat. 33. a. Heat
31. This is an endothermic reaction so heat must be absorbed in order to convert reactants into products. The high temperature environment of internal combustion engines provides the heat. 33. a. Heat
Chemistry Chapter 16. Reaction Energy
 Chemistry Reaction Energy Section 16.1.I Thermochemistry Objectives Define temperature and state the units in which it is measured. Define heat and state its units. Perform specific-heat calculations.
Chemistry Reaction Energy Section 16.1.I Thermochemistry Objectives Define temperature and state the units in which it is measured. Define heat and state its units. Perform specific-heat calculations.
I. The Nature of Energy A. Energy
 I. The Nature of Energy A. Energy is the ability to do work or produce heat. It exists in 2 forms: 1. Potential energy is energy due to the composition or position of an object. 2. Kinetic energy is energy
I. The Nature of Energy A. Energy is the ability to do work or produce heat. It exists in 2 forms: 1. Potential energy is energy due to the composition or position of an object. 2. Kinetic energy is energy
Chemistry: The Central Science. Chapter 5: Thermochemistry
 Chemistry: The Central Science Chapter 5: Thermochemistry Study of energy and its transformations is called thermodynamics Portion of thermodynamics that involves the relationships between chemical and
Chemistry: The Central Science Chapter 5: Thermochemistry Study of energy and its transformations is called thermodynamics Portion of thermodynamics that involves the relationships between chemical and
Energy Transformations
 Thermochemistry Energy Transformations Thermochemistry - concerned with heat changes that occur during chemical reactions Energy - capacity for doing work or supplying heat weightless, odorless, tasteless
Thermochemistry Energy Transformations Thermochemistry - concerned with heat changes that occur during chemical reactions Energy - capacity for doing work or supplying heat weightless, odorless, tasteless
Chapter 8. Thermochemistry
 Chapter 8 Thermochemistry Copyright 2001 by Harcourt, Inc. All rights reserved. Requests for permission to make copies of any part of the work should be mailed to the following address: Permissions Department,
Chapter 8 Thermochemistry Copyright 2001 by Harcourt, Inc. All rights reserved. Requests for permission to make copies of any part of the work should be mailed to the following address: Permissions Department,
Ch. 6 Enthalpy Changes
 Ch. 6 Enthalpy Changes Energy: The capacity to do work. In Physics, there are 2 main types of energy Kinetic (energy of motion) = ½ mv 2 Potential (energy of position due to gravity)= mgh In Chemistry,
Ch. 6 Enthalpy Changes Energy: The capacity to do work. In Physics, there are 2 main types of energy Kinetic (energy of motion) = ½ mv 2 Potential (energy of position due to gravity)= mgh In Chemistry,
Slide 1 / Objects can possess energy as: (a) endothermic energy (b) potential energy (c) kinetic energy. a only b only c only a and c b and c
 Slide 1 / 84 1 Objects can possess energy as: (a) endothermic energy (b) potential energy (c) kinetic energy A B C D E a only b only c only a and c b and c Slide 2 / 84 2 The internal energy of a system
Slide 1 / 84 1 Objects can possess energy as: (a) endothermic energy (b) potential energy (c) kinetic energy A B C D E a only b only c only a and c b and c Slide 2 / 84 2 The internal energy of a system
Thermochemistry is the study of the relationships between chemical reactions and energy changes involving heat.
 CHEM134- F18 Dr. Al- Qaisi Chapter 06: Thermodynamics Thermochemistry is the study of the relationships between chemical reactions and energy changes involving heat. Energy is anything that has the capacity
CHEM134- F18 Dr. Al- Qaisi Chapter 06: Thermodynamics Thermochemistry is the study of the relationships between chemical reactions and energy changes involving heat. Energy is anything that has the capacity
Name: Class: Date: ID: A
 Name: Class: _ Date: _ ID: A Chpter 17 review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of these phase changes is an endothermic process? a.
Name: Class: _ Date: _ ID: A Chpter 17 review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of these phase changes is an endothermic process? a.
I. Chemical Reactions that Involve Heat
 Unit 12 Energy I. Chemical Reactions that Involve Heat Thermochemistry: study of changes in heat in chemical reactions. Endothermic: absorbs heat; temp. goes down Exothermic: releases heat; temp. goes
Unit 12 Energy I. Chemical Reactions that Involve Heat Thermochemistry: study of changes in heat in chemical reactions. Endothermic: absorbs heat; temp. goes down Exothermic: releases heat; temp. goes
Chapter 17 Thermochemistry
 Chapter 17 Thermochemistry Section 17.1 The Flow of Energy Heat and Work OBJECTIVES: Explain how energy, heat, and work are related. 2 Section 17.1 The Flow of Energy Heat and Work OBJECTIVES: Classify
Chapter 17 Thermochemistry Section 17.1 The Flow of Energy Heat and Work OBJECTIVES: Explain how energy, heat, and work are related. 2 Section 17.1 The Flow of Energy Heat and Work OBJECTIVES: Classify
Name Date Class THE FLOW OF ENERGY HEAT AND WORK
 17.1 THE FLOW OF ENERGY HEAT AND WORK Section Review Objectives Explain the relationship between energy, heat, and work Distinguish between exothermic and endothermic processes Distinguish between heat
17.1 THE FLOW OF ENERGY HEAT AND WORK Section Review Objectives Explain the relationship between energy, heat, and work Distinguish between exothermic and endothermic processes Distinguish between heat
5/14/14. How can you measure the amount of heat released when a match burns?
 CHEMISTRY & YOU Chapter 7 Thermochemistry How can you measure the amount of heat released when a match burns? 7. The Flow of Energy 7.3 Heat in Changes of State 7.4 Calculating Heats of Reaction Remember:
CHEMISTRY & YOU Chapter 7 Thermochemistry How can you measure the amount of heat released when a match burns? 7. The Flow of Energy 7.3 Heat in Changes of State 7.4 Calculating Heats of Reaction Remember:
measure ΔT in water to get q = q surroundings and use q system = q surroundings
 example using water: Calculate the amount of energy required to heat 95.0 g of water from 22.5 C to 95.5 C. q = s m ΔT ( C (4.184 J g 1 C 1 ) (95.0 g) (73.0 = = 2.90 x 10 4 J or 29.0 kj Constant Pressure
example using water: Calculate the amount of energy required to heat 95.0 g of water from 22.5 C to 95.5 C. q = s m ΔT ( C (4.184 J g 1 C 1 ) (95.0 g) (73.0 = = 2.90 x 10 4 J or 29.0 kj Constant Pressure
Thermochemistry HW. PSI Chemistry
 Thermochemistry HW PSI Chemistry Name Energy 1) Objects can possess energy as: (a) endothermic energy (b) potential energy A) a only B) b only C) c only D) a and c E) b and c (c) kinetic energy 2) The
Thermochemistry HW PSI Chemistry Name Energy 1) Objects can possess energy as: (a) endothermic energy (b) potential energy A) a only B) b only C) c only D) a and c E) b and c (c) kinetic energy 2) The
Chapter 6. Heat Flow
 Chapter 6 Thermochemistry Heat Flow Heat (q): energy transferred from body at high T to body at low T Two definitions: System: part of universe we are interested in Surrounding: the rest of the universe
Chapter 6 Thermochemistry Heat Flow Heat (q): energy transferred from body at high T to body at low T Two definitions: System: part of universe we are interested in Surrounding: the rest of the universe
Thermochemistry: Energy Flow and Chemical Reactions
 Thermochemistry: Energy Flow and Chemical Reactions Outline thermodynamics internal energy definition, first law enthalpy definition, energy diagrams, calorimetry, theoretical calculation (heats of formation
Thermochemistry: Energy Flow and Chemical Reactions Outline thermodynamics internal energy definition, first law enthalpy definition, energy diagrams, calorimetry, theoretical calculation (heats of formation
Thermochemistry Notes
 Name: Thermochemistry Notes I. Thermochemistry deals with the changes in energy that accompany a chemical reaction. Energy is measured in a quantity called enthalpy, represented as H. The change in energy
Name: Thermochemistry Notes I. Thermochemistry deals with the changes in energy that accompany a chemical reaction. Energy is measured in a quantity called enthalpy, represented as H. The change in energy
Thermochemistry Chapter 4
 Thermochemistry Chapter 4 Thermochemistry is the study of energy changes that occur during chemical reactions Focus is on heat and matter transfer between the system and the surroundings Energy The ability
Thermochemistry Chapter 4 Thermochemistry is the study of energy changes that occur during chemical reactions Focus is on heat and matter transfer between the system and the surroundings Energy The ability
Energy Relationships in Chemical Reactions
 Energy Relationships in Chemical Reactions What is heat? What is a state function? What is enthalpy? Is enthalpy a state function? What does this mean? How can we calculate this? How are the methods the
Energy Relationships in Chemical Reactions What is heat? What is a state function? What is enthalpy? Is enthalpy a state function? What does this mean? How can we calculate this? How are the methods the
CP Chapter 17 Thermochemistry
 CP Chapter 17 Thermochemistry Thermochemistry Thermochemistry is the study of energy that occur during chemical reactions and phase changes (changes of state) The Nature of Energy Energy is the ability
CP Chapter 17 Thermochemistry Thermochemistry Thermochemistry is the study of energy that occur during chemical reactions and phase changes (changes of state) The Nature of Energy Energy is the ability
Enthalpies of Reaction
 Enthalpies of Reaction Enthalpy is an extensive property Magnitude of H is directly related to the amount of reactant used up in a process. CH 4 (g) + 2O 2 (g) CO 2 (g) + 2H 2 O(l) H = 890 kj 2CH 4 (g)
Enthalpies of Reaction Enthalpy is an extensive property Magnitude of H is directly related to the amount of reactant used up in a process. CH 4 (g) + 2O 2 (g) CO 2 (g) + 2H 2 O(l) H = 890 kj 2CH 4 (g)
Chapter 6. Thermochemistry
 Chapter 6 Thermochemistry Section 5.6 The Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases http://www.scuc.txed.net/webpages/dmackey/files /chap06notes.pdf ..\..\..\..\..\..\Videos\AP Videos\Thermochemistry\AP
Chapter 6 Thermochemistry Section 5.6 The Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases http://www.scuc.txed.net/webpages/dmackey/files /chap06notes.pdf ..\..\..\..\..\..\Videos\AP Videos\Thermochemistry\AP
17.2 Thermochemical Equations
 17.2. Thermochemical Equations www.ck12.org 17.2 Thermochemical Equations Lesson Objectives Define enthalpy, and know the conditions under which the enthalpy change in a reaction is equal to the heat absorbed
17.2. Thermochemical Equations www.ck12.org 17.2 Thermochemical Equations Lesson Objectives Define enthalpy, and know the conditions under which the enthalpy change in a reaction is equal to the heat absorbed
Chapter 5. Thermochemistry
 Chapter 5 Thermochemistry Energy Thermodynamics Study of the relationship between heat, work, and other forms of energy Thermochemistry A branch of thermodynamics Focuses on the study of heat given off
Chapter 5 Thermochemistry Energy Thermodynamics Study of the relationship between heat, work, and other forms of energy Thermochemistry A branch of thermodynamics Focuses on the study of heat given off
Calorimetry. Enthalpy of Neutralization
 Calorimetry Enthalpy of Neutralization Introduction A calorimeter is a device that can measure the heat absorbed or released by a reaction (Petrucci, 2011). A calorimeter is thermally insulated from its
Calorimetry Enthalpy of Neutralization Introduction A calorimeter is a device that can measure the heat absorbed or released by a reaction (Petrucci, 2011). A calorimeter is thermally insulated from its
This reaction is ENDOTHERMIC. Energy is being transferred from the room/flask/etc. (the SURROUNDINGS) to the reaction itself (the SYSTEM).
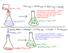 151 This reaction is EXOTHERMIC. Energy is transferred from the reactants and products (the SYSTEM) to the water in the flask, the flask, etc. (the SURROUNDINGS) This reaction is ENDOTHERMIC. Energy is
151 This reaction is EXOTHERMIC. Energy is transferred from the reactants and products (the SYSTEM) to the water in the flask, the flask, etc. (the SURROUNDINGS) This reaction is ENDOTHERMIC. Energy is
Energy, Heat and Chemical Change
 Energy, Heat and Chemical Change Chemistry 35 Fall 2000 Thermochemistry A part of Thermodynamics dealing with energy changes associated with physical and chemical reactions Why do we care? -will a reaction
Energy, Heat and Chemical Change Chemistry 35 Fall 2000 Thermochemistry A part of Thermodynamics dealing with energy changes associated with physical and chemical reactions Why do we care? -will a reaction
Thermodynamics. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Thermodynamics Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Thermodynamics is the scientific study of the interconversion of heat and other kinds of energy.
Thermodynamics Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Thermodynamics is the scientific study of the interconversion of heat and other kinds of energy.
Topic 5: Energetics. Heat & Calorimetry. Thursday, March 22, 2012
 Topic 5: Energetics Heat & Calorimetry 1 Heat is energy that is transferred from one object to another due to a difference in temperature Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of a body
Topic 5: Energetics Heat & Calorimetry 1 Heat is energy that is transferred from one object to another due to a difference in temperature Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of a body
Chapter 6. Energy Thermodynamics
 Chapter 6 Energy Thermodynamics 1 Energy is... The ability to do work. Conserved. made of heat and work. a state function. independent of the path, or how you get from point A to B. Work is a force acting
Chapter 6 Energy Thermodynamics 1 Energy is... The ability to do work. Conserved. made of heat and work. a state function. independent of the path, or how you get from point A to B. Work is a force acting
THE ENERGY OF THE UNIVERSE IS CONSTANT.
 Chapter 6 Thermochemistry.notebook Chapter 6: Thermochemistry Jan 29 1:37 PM 6.1 The Nature of Energy Thermodynamics: The study of energy and its interconversions Energy: the capacity to do work or to
Chapter 6 Thermochemistry.notebook Chapter 6: Thermochemistry Jan 29 1:37 PM 6.1 The Nature of Energy Thermodynamics: The study of energy and its interconversions Energy: the capacity to do work or to
Lecture 2. Review of Basic Concepts
 Lecture 2 Review of Basic Concepts Thermochemistry Enthalpy H heat content H Changes with all physical and chemical changes H Standard enthalpy (25 C, 1 atm) (H=O for all elements in their standard forms
Lecture 2 Review of Basic Concepts Thermochemistry Enthalpy H heat content H Changes with all physical and chemical changes H Standard enthalpy (25 C, 1 atm) (H=O for all elements in their standard forms
Thermochemistry. Energy (and Thermochemistry) World of Chemistry Chapter 10. Energy. Energy
 Thermochemistry Thermodynamics is the science of the relationship between heat and other forms of energy. (and Thermochemistry) World of Chemistry Chapter 10 is defined as the ability to do work or produce
Thermochemistry Thermodynamics is the science of the relationship between heat and other forms of energy. (and Thermochemistry) World of Chemistry Chapter 10 is defined as the ability to do work or produce
Ch. 14 Notes ENERGY AND CHEMICAL CHANGE NOTE: Vocabulary terms are in boldface and underlined. Supporting details are in italics.
 Ch. 14 Notes ENERGY AND CHEMICAL CHANGE NOTE: Vocabulary terms are in boldface and underlined. Supporting details are in italics. I. Energy the capacity to do work or produce heat A. two basic types of
Ch. 14 Notes ENERGY AND CHEMICAL CHANGE NOTE: Vocabulary terms are in boldface and underlined. Supporting details are in italics. I. Energy the capacity to do work or produce heat A. two basic types of
Advanced Chemistry Practice Problems
 Thermodynamics: Review of Thermochemistry 1. Question: What is the sign of DH for an exothermic reaction? An endothermic reaction? Answer: ΔH is negative for an exothermic reaction and positive for an
Thermodynamics: Review of Thermochemistry 1. Question: What is the sign of DH for an exothermic reaction? An endothermic reaction? Answer: ΔH is negative for an exothermic reaction and positive for an
_ + Units of Energy. Energy in Thermochemistry. Thermochemistry. Energy flow between system and surroundings. 100º C heat 50º C
 Units of Energy Like we saw with pressure, many different units are used throughout the world for energy. SI unit for energy 1kg m 1J = 2 s 2 Joule (J) calorie (cal) erg (erg) electron volts (ev) British
Units of Energy Like we saw with pressure, many different units are used throughout the world for energy. SI unit for energy 1kg m 1J = 2 s 2 Joule (J) calorie (cal) erg (erg) electron volts (ev) British
CHEMISTRY. Chapter 5 Thermochemistry
 CHEMISTRY The Central Science 8 th Edition Chapter 5 Thermochemistry Dr. Kozet YAPSAKLI The Nature of Energy Kinetic and Potential Energy Potential energy can be converted into kinetic energy. E p = mgh
CHEMISTRY The Central Science 8 th Edition Chapter 5 Thermochemistry Dr. Kozet YAPSAKLI The Nature of Energy Kinetic and Potential Energy Potential energy can be converted into kinetic energy. E p = mgh
Thermochemistry: Heat and Chemical Change
 Thermochemistry: Heat and Chemical Change 1 Heat or Thermal Energy (q) Heat is a form of energy Is heat the same as temperature? Heat flows between two objects at different temperatures. Hot Cold 2 Chemical
Thermochemistry: Heat and Chemical Change 1 Heat or Thermal Energy (q) Heat is a form of energy Is heat the same as temperature? Heat flows between two objects at different temperatures. Hot Cold 2 Chemical
Thermochemistry. Mr.V
 Thermochemistry Mr.V Introduction to Energy changes System Surroundings Exothermic Endothermic Internal energy Enthalpy Definitions System A specified part of the universe which is under investigation
Thermochemistry Mr.V Introduction to Energy changes System Surroundings Exothermic Endothermic Internal energy Enthalpy Definitions System A specified part of the universe which is under investigation
Thermodynamics - Energy Relationships in Chemical Reactions:
 Thermodynamics - Energy Relationships in Chemical Reactions: energy - The capacity to do work. Types of Energy: radiant-energy from the sun. potential-energy due to an objects position. chemical-energy
Thermodynamics - Energy Relationships in Chemical Reactions: energy - The capacity to do work. Types of Energy: radiant-energy from the sun. potential-energy due to an objects position. chemical-energy
Chemical Thermodynamics
 Chemical Thermodynamics 1 Thermodynamics Thermodynamics is a Greek term which means, heat power. Thermodynamics is the study of energy and its transformations. 2 Thermodynamics Thermochemistry how we observe,
Chemical Thermodynamics 1 Thermodynamics Thermodynamics is a Greek term which means, heat power. Thermodynamics is the study of energy and its transformations. 2 Thermodynamics Thermochemistry how we observe,
AAE THERMOCHEMISTRY BASICS
 5.4 THERMOCHEMISTRY BASICS Ch5 23 Energies in Chemical Reactions Enthalpy of Combustion (Reactions): Q CV H in = H reactant H out = H product REACTANTS Stoichiometric fuel-oxidizer (air) mixture at standard
5.4 THERMOCHEMISTRY BASICS Ch5 23 Energies in Chemical Reactions Enthalpy of Combustion (Reactions): Q CV H in = H reactant H out = H product REACTANTS Stoichiometric fuel-oxidizer (air) mixture at standard
Chemistry 163B. Thermochemistry. Chapter 4 Engel & Reid
 Chemistry 163B Thermochemistry Chapter 4 Engel & Reid 3 heats of reactions (constant volume; bomb calorimeter) ΔU V = q V ΔU= U products -U reactants 4 heats of reactions (constant volume; fig 4.3 E&R)
Chemistry 163B Thermochemistry Chapter 4 Engel & Reid 3 heats of reactions (constant volume; bomb calorimeter) ΔU V = q V ΔU= U products -U reactants 4 heats of reactions (constant volume; fig 4.3 E&R)
Chapter 6 Problems: 9, 19, 24, 25, 26, 27, 31-33, 37, 39, 43, 45, 47, 48, 53, 55, 57, 59, 65, 67, 73, 78-82, 85, 89, 93
 Chapter 6 Problems: 9, 19, 24, 25, 26, 27, 31-33, 37, 39, 43, 45, 47, 48, 53, 55, 57, 59, 65, 67, 73, 78-82, 85, 89, 93 Chapter 6 Thermochemistry The study of chemical reactions and the energy changes
Chapter 6 Problems: 9, 19, 24, 25, 26, 27, 31-33, 37, 39, 43, 45, 47, 48, 53, 55, 57, 59, 65, 67, 73, 78-82, 85, 89, 93 Chapter 6 Thermochemistry The study of chemical reactions and the energy changes
ENERGY (THERMOCHEMISTRY) Ch 1.5, 6, 9.10, , 13.3
 ENERGY (THERMOCHEMISTRY) Ch 1.5, 6, 9.10, 11.5-11.7, 13.3 Thermochemistry Prediction and measurement of energy transfer, in the form of heat, that accompanies chemical and physical processes. Chemical
ENERGY (THERMOCHEMISTRY) Ch 1.5, 6, 9.10, 11.5-11.7, 13.3 Thermochemistry Prediction and measurement of energy transfer, in the form of heat, that accompanies chemical and physical processes. Chemical
CHM 1046 FINAL REVIEW
 CHM 1046 FINAL REVIEW Prepared & Presented By: Marian Ayoub PART I Chapter Description 6 Thermochemistry 11 States of Matter; Liquids and Solids 12 Solutions 13 Rates of Reactions 18 Thermodynamics and
CHM 1046 FINAL REVIEW Prepared & Presented By: Marian Ayoub PART I Chapter Description 6 Thermochemistry 11 States of Matter; Liquids and Solids 12 Solutions 13 Rates of Reactions 18 Thermodynamics and
Energy and Chemical Change
 Energy and Chemical Change Section 15.1 Energy Section 15.2 Heat Section 15.3 Thermochemical Equations Section 15.4 Calculating Enthalpy Change Section 15.5 Reaction Spontaneity Click a hyperlink or folder
Energy and Chemical Change Section 15.1 Energy Section 15.2 Heat Section 15.3 Thermochemical Equations Section 15.4 Calculating Enthalpy Change Section 15.5 Reaction Spontaneity Click a hyperlink or folder
Thermodynamics- Chapter 19 Schedule and Notes
 Thermodynamics- Chapter 19 Schedule and Notes Date Topics Video cast DUE Assignment during class time One Review of thermodynamics ONE and TWO Review of thermo Wksheet Two 19.1-4; state function THREE
Thermodynamics- Chapter 19 Schedule and Notes Date Topics Video cast DUE Assignment during class time One Review of thermodynamics ONE and TWO Review of thermo Wksheet Two 19.1-4; state function THREE
47 people in recitation yesterday. Expect quizzes there and in class.
 Announcements 47 people in recitation yesterday. Expect quizzes there and in class. Chapter 6 Problems: 6.9, 6.11, 6.13(except c), 6.19, 6.23, 6.34, 6.38, 6.42, 6.51, 6.53, 6.54, 6.57, 6.64, 6.66, 6.69,
Announcements 47 people in recitation yesterday. Expect quizzes there and in class. Chapter 6 Problems: 6.9, 6.11, 6.13(except c), 6.19, 6.23, 6.34, 6.38, 6.42, 6.51, 6.53, 6.54, 6.57, 6.64, 6.66, 6.69,
Chapter 5: Thermochemistry. Molecular Kinetic Energy -Translational energy E k, translational = 1/2mv 2 -Rotational energy 5.
 Chapter 5: Thermochemistry 1. Thermodynamics 2. Energy 3. Specific Heat 4. Enthalpy 5. Enthalpies of Reactions 6. Hess s Law 7. State Functions 8. Standard Enthalpies of Formation 9. Determining Enthalpies
Chapter 5: Thermochemistry 1. Thermodynamics 2. Energy 3. Specific Heat 4. Enthalpy 5. Enthalpies of Reactions 6. Hess s Law 7. State Functions 8. Standard Enthalpies of Formation 9. Determining Enthalpies
Introduction to Thermochemistry. Thermochemistry Unit. Definition. Terminology. Terminology. Terminology 07/04/2016. Chemistry 30
 Thermochemistry Unit Introduction to Thermochemistry Chemistry 30 Definition Thermochemistry is the branch of chemistry concerned with the heat produced and used in chemical reactions. Most of thermochemistry
Thermochemistry Unit Introduction to Thermochemistry Chemistry 30 Definition Thermochemistry is the branch of chemistry concerned with the heat produced and used in chemical reactions. Most of thermochemistry
Thermodynamics: Enthalpy
 Name: Band: Date: Thermodynamics: Enthalpy Big Idea: Spontaneity A spontaneous change is a change that occurs without outside intervention. All spontaneous changes lead to equilibrium. Identify each change
Name: Band: Date: Thermodynamics: Enthalpy Big Idea: Spontaneity A spontaneous change is a change that occurs without outside intervention. All spontaneous changes lead to equilibrium. Identify each change
Chapter 5 Thermochemistry. 許富銀 ( Hsu Fu-Yin)
 Chapter 5 Thermochemistry 許富銀 ( Hsu Fu-Yin) 1 Thermodynamics The study of energy and its transformations is known as thermodynamics The relationships between chemical reactions and energy changes that
Chapter 5 Thermochemistry 許富銀 ( Hsu Fu-Yin) 1 Thermodynamics The study of energy and its transformations is known as thermodynamics The relationships between chemical reactions and energy changes that
Chemistry 123: Physical and Organic Chemistry Topic 2: Thermochemistry
 Topic 2: Introduction, Topic 2: Thermochemistry Text: Chapter 7 and 19 (~ 3 weeks) 2.0 Introduction, terminology and scope 2.1 Enthalapy and Energy Change in a chemical process; 1st law of Thermodynamics
Topic 2: Introduction, Topic 2: Thermochemistry Text: Chapter 7 and 19 (~ 3 weeks) 2.0 Introduction, terminology and scope 2.1 Enthalapy and Energy Change in a chemical process; 1st law of Thermodynamics
Section 9: Thermodynamics and Energy
 Section 9: Thermodynamics and Energy The following maps the videos in this section to the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Science TAC 112.35(c). 9.01 Law of Conservation of Energy Chemistry (11)(A)
Section 9: Thermodynamics and Energy The following maps the videos in this section to the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Science TAC 112.35(c). 9.01 Law of Conservation of Energy Chemistry (11)(A)
THERMOCHEMISTRY CHAPTER 11
 THERMOCHEMISTRY CHAPTER 11 ENERGY AND HEAT nthermochemistry: The study of the energy changes that accompany chemical reactions and changes in the physical states of matter. ENERGY AND HEAT nwork: Energy
THERMOCHEMISTRY CHAPTER 11 ENERGY AND HEAT nthermochemistry: The study of the energy changes that accompany chemical reactions and changes in the physical states of matter. ENERGY AND HEAT nwork: Energy
Mr Chiasson Advanced Chemistry 12 / Chemistry 12 1 Unit B: Thermochemical Changes
 Mr Chiasson Advanced Chemistry 12 / Chemistry 12 1 Unit B: Thermochemical Changes Students will be expected to: Compare the molar enthalpies of several combustion reactions involving organic compounds.
Mr Chiasson Advanced Chemistry 12 / Chemistry 12 1 Unit B: Thermochemical Changes Students will be expected to: Compare the molar enthalpies of several combustion reactions involving organic compounds.
Enthalpy. Enthalpy. Enthalpy. Enthalpy. E = q + w. Internal Energy at Constant Volume SYSTEM. heat transfer in (endothermic), +q
 heat transfer in (endothermic), +q heat transfer out (exothermic), -q SYSTEM E = q + w w transfer in (+w) w transfer out (-w) Internal Energy at Constant Volume E = KE + PE ΔE = q + w Because most systems,
heat transfer in (endothermic), +q heat transfer out (exothermic), -q SYSTEM E = q + w w transfer in (+w) w transfer out (-w) Internal Energy at Constant Volume E = KE + PE ΔE = q + w Because most systems,
Name: Thermochemistry. Practice Test C. General Chemistry Honors Chemistry
 Name: Thermochemistry C Practice Test C General Chemistry Honors Chemistry 1 Objective 1: Use the relationship between mass, specific heat, and temperature change to calculate the heat flow during a chemical
Name: Thermochemistry C Practice Test C General Chemistry Honors Chemistry 1 Objective 1: Use the relationship between mass, specific heat, and temperature change to calculate the heat flow during a chemical
Thermochemistry Enthalpy & Hess Law. Packet #35
 Thermochemistry Enthalpy & Hess Law Packet #35 Introduction I Thermochemistry, is the branch of chemistry that, investigates the amount of energy that is gained or lost during a chemical reaction. Introduction
Thermochemistry Enthalpy & Hess Law Packet #35 Introduction I Thermochemistry, is the branch of chemistry that, investigates the amount of energy that is gained or lost during a chemical reaction. Introduction
Thermochemistry. Questions to ponder. Because 4/20/14. an ice-cube? an ice-cube? Part 2: Calorimetry. But I KNOW. Q=mc T, but T=0
 Thermochemistry Part 2: Calorimetry p p If you leave your keys and your chemistry book sitting in the sun on a hot summer day, which one is hotter? Why is there a difference in temperature between the
Thermochemistry Part 2: Calorimetry p p If you leave your keys and your chemistry book sitting in the sun on a hot summer day, which one is hotter? Why is there a difference in temperature between the
Lecture 26: Liquids 1: phase changes & heat capacity
 Lecture 26: Liquids 1: phase changes & heat capacity Read: BLB 5.5; 11.4 HW: BLB 5:48,49,51; 11:33,37,39 Know: viscosity, surface tension cohesive & adhesive forces phase changes heat capacity calorimetry
Lecture 26: Liquids 1: phase changes & heat capacity Read: BLB 5.5; 11.4 HW: BLB 5:48,49,51; 11:33,37,39 Know: viscosity, surface tension cohesive & adhesive forces phase changes heat capacity calorimetry
3.2 Calorimetry and Enthalpy
 3.2 Calorimetry and Enthalpy Heat Capacity Specific heat capacity (c) is the quantity of thermal energy required to raise the temperature of 1 g of a substance by 1 C. The SI units for specific heat capacity
3.2 Calorimetry and Enthalpy Heat Capacity Specific heat capacity (c) is the quantity of thermal energy required to raise the temperature of 1 g of a substance by 1 C. The SI units for specific heat capacity
First Law of Thermodynamics: energy cannot be created or destroyed.
 1 CHEMICAL THERMODYNAMICS ANSWERS energy = anything that has the capacity to do work work = force acting over a distance Energy (E) = Work = Force x Distance First Law of Thermodynamics: energy cannot
1 CHEMICAL THERMODYNAMICS ANSWERS energy = anything that has the capacity to do work work = force acting over a distance Energy (E) = Work = Force x Distance First Law of Thermodynamics: energy cannot
Chemistry 212 THE ENTHALPY OF FORMATION OF MAGNESIUM OXIDE LEARNING OBJECTIVES
 Chemistry 212 THE ENTHALPY OF FORMATION OF MAGNESIUM OXIDE The learning objectives of this experiment are LEARNING OBJECTIVES A simple coffee cup calorimeter will be used to determine the enthalpy of formation
Chemistry 212 THE ENTHALPY OF FORMATION OF MAGNESIUM OXIDE The learning objectives of this experiment are LEARNING OBJECTIVES A simple coffee cup calorimeter will be used to determine the enthalpy of formation
Thermochemistry. Energy. 1st Law of Thermodynamics. Enthalpy / Calorimetry. Enthalpy of Formation
 Thermochemistry Energy 1st Law of Thermodynamics Enthalpy / Calorimetry Hess' Law Enthalpy of Formation The Nature of Energy Kinetic Energy and Potential Energy Kinetic energy is the energy of motion:
Thermochemistry Energy 1st Law of Thermodynamics Enthalpy / Calorimetry Hess' Law Enthalpy of Formation The Nature of Energy Kinetic Energy and Potential Energy Kinetic energy is the energy of motion:
Chapter 6: Thermochemistry
 Chapter 6: Thermochemistry Section 6.1: Introduction to Thermochemistry Thermochemistry refers to the study of heat flow or heat energy in a chemical reaction. In a study of Thermochemistry the chemical
Chapter 6: Thermochemistry Section 6.1: Introduction to Thermochemistry Thermochemistry refers to the study of heat flow or heat energy in a chemical reaction. In a study of Thermochemistry the chemical
Thermochemistry: Part of Thermodynamics
 Thermochemistry: Part of Thermodynamics Dr. Vickie M. Williamson @vmwilliamson Student Version 1 Chemical Thermodynamics! Thermodynamics: study of the energy changes associated with physical and chemical
Thermochemistry: Part of Thermodynamics Dr. Vickie M. Williamson @vmwilliamson Student Version 1 Chemical Thermodynamics! Thermodynamics: study of the energy changes associated with physical and chemical
Measuring and Expressing Enthalpy Changes. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall. Measuring and Expressing Enthalpy Changes. Calorimetry
 Measuring and Expressing Enthalpy Changes A burning match releases heat to its surroundings in all directions. How much heat does this exothermic reaction release? You will learn to measure heat flow in
Measuring and Expressing Enthalpy Changes A burning match releases heat to its surroundings in all directions. How much heat does this exothermic reaction release? You will learn to measure heat flow in
Chemistry. Friday, March 30 th Monday, April 9 th, 2018
 Chemistry Friday, March 30 th Monday, April 9 th, 2018 Do-Now: BrainPOP: Heat 1. Write down today s FLT 2. Distinguish between exothermic and endothermic processes. 3. What is the specific heat of water?
Chemistry Friday, March 30 th Monday, April 9 th, 2018 Do-Now: BrainPOP: Heat 1. Write down today s FLT 2. Distinguish between exothermic and endothermic processes. 3. What is the specific heat of water?
Heat. Heat Terminology 04/12/2017. System Definitions. System Definitions
 System Definitions Heat Physical Science 20 Ms. Hayduk Heat Terminology System: the part of the universe being studied (big Earth, or small one atom) Surroundings: the part of the universe outside the
System Definitions Heat Physical Science 20 Ms. Hayduk Heat Terminology System: the part of the universe being studied (big Earth, or small one atom) Surroundings: the part of the universe outside the
Energy & Chemistry. Internal Energy (E) Energy and Chemistry. Potential Energy. Kinetic Energy. Energy and Chemical Reactions: Thermochemistry or
 Page III-5-1 / Chapter Five Lecture Notes Energy & Chemistry Energy and Chemical Reactions: Thermochemistry or Thermodynamics Chapter Five Burning peanuts supplies sufficient energy to boil a cup of water
Page III-5-1 / Chapter Five Lecture Notes Energy & Chemistry Energy and Chemical Reactions: Thermochemistry or Thermodynamics Chapter Five Burning peanuts supplies sufficient energy to boil a cup of water
Name: General Chemistry Chapter 11 Thermochemistry- Heat and Chemical Change
 Name: General Chemistry Chapter 11 Thermochemistry- Heat and Chemical Change Notepack 1 Section 11.1: The Flow of Energy Heat (Pages 293 299) 1. Define the following terms: a. Thermochemistry b. Energy
Name: General Chemistry Chapter 11 Thermochemistry- Heat and Chemical Change Notepack 1 Section 11.1: The Flow of Energy Heat (Pages 293 299) 1. Define the following terms: a. Thermochemistry b. Energy
