Quantum operator methods QM (quantum mouse) version (ALR mods) p. 1
|
|
|
- George Brooks
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Quantum operator methods QM (quantum mouse) version (ALR mods) p. 1 I. The quantum mouse and operators SETUP: Consider a quantum object (a "quantum lab mouse") and some new properties we can measure. E.g., suppose "quantum weight", W, is a hermitian operator. The corresponding physical measurement is "put the mouse on a quantum scale". Interestingly, this scale reads either 1 (skinny mice) or 10 (heavy ones), but nothing else (!) W > = >, W > = 10 >. (Because I'm no artist, I will simplify the icons for skinny and heavy mice to > and > respectively) Note! Being skinny or heavy is normal. In fact, let us assume it is orthonormal (and complete). Stare at these two eigen-equations and make sure you, and your group, understand the notation: which symbols are the eigenvectors here, what are the eigenvalues, in those equations? What can you say about, e.g. < >? (Explain) Quantum mood, M, is also Hermitian. The corresponding physical measurement is look at the mouse s expression, yielding either a smile (mood = +1, or happy), or frown (mood = 1, or unhappy/sad) ĤˆM Ĥ ˆM > = >, but > = - > Note! Being happy or unhappy is normal. (Again, orthonormal, and complete.) Again, make sure you follow this notation: what are the possible outcomes of a measurement of M? Which symbols are the eigenvectors here, what are the eigenvalues? What is?
2 Quantum operator methods QM (quantum mouse) version (ALR mods) p. 2 1 Lastly, let us suppose that > = > + > 5 5 I guess this means skinny quantum-mice are a little stressed. (Do you see this from the equation?) Let's see some consequences of the above assumptions! A) In this quantum world, suppose I give you a mouse, you measure W and get eigenvalue 1. i) What quantum state is the mouse in? Is there any ambiguity at this point? 2 ii) If you now remeasure W on this state, what results can you get, with what probabilities? After this second measurement of W, what state will you be in? (Is there any ambiguity at this point?) iii) Following the above, what is the probability that a subsequent measurement of M will yield a result of 1, i.e. unhappy? Explain.
3 Quantum operator methods QM (quantum mouse) version (ALR mods) p. 3 B) i) Use orthonormality and completeness to expand the W=10 eigenstate in the "mood basis": > = a > + b > i.e. find the numerical constants a and b. Is your answer unique? (If not, does it matter?) ii) Suppose I give you a quantum mouse, and you measure M and find eigenvalue 1. What state is it in after your measurement? (Is there any ambiguity at this point?) iii) What is the probability that a subsequent measurement of W will yield a result of 1, i.e. light? (Don t intuit answers at this point, work it out from the postulates of quantum mechanics!) C) If I have an ensemble of happy mice, and measure W on all of them, do they each get the same result? Explain. What is the average result (i.e., expectation value) of measuring weight of this ensemble of happy mice?
4 Quantum operator methods QM (quantum mouse) version (ALR mods) p. 4 II. The quantum mouse (Part II) D) Use orthonormality and completeness to expand the M=±1 (happy and sad) eigenstates in the weight basis :
5 Quantum operator methods QM (quantum mouse) version (ALR mods) p. 5 Now, let P be the feed a quantum pizza operator. This curious operator does the following: ˆP ˆP > = >, but > = 0 This means pizza makes a skinny mouse heavy, but kills the heavy mice. (it gives back 0, nothing) E) Are skinny mice eigenstates of P? Are heavy mice? F) Show that P is NOT a Hermitian operator Can you observe mice eating pizza in this quantum world? Explain. G) What would P do to a heavy mouse? What would it do to a skinny mouse? This is tricky, work it out! Based on the above, in the spirit of this Tutorial, make up a plausible name for the P operator.
6 Quantum operator methods QM (quantum mouse) version (ALR mods) p. 6 Simultaneous measurements: H) i) Do M and W commute? (Again, tricky. If they DO commute, then MW gives the same result as WM for any state, and the matrix elements φ MW ψ = φ WM ψ are equal for all φ and ψ. A single counterexample will disprove it! Consider, for example, letting φ and ψ be a fat and skinny state.) ii) Based on the above, does measuring the quantum weight of a mouse affect the outcome of a future measurement of its quantum happiness? (Vice versa?) I) Given a mouse in the +1 happiness state, if you then measure weight, what is the probability that you will measure 1? (Colloquially, we might phrase this what is the probability that a happy mouse is skinny? )
7 Quantum operator methods QM (quantum mouse) version (ALR mods) p. 7 Time evolution Now suppose that the mouse Hamiltonian, H, commutes with W (One way to think of this would be if the energy of a mouse is proportional to its measured weight) Suppose I give you a mouse which I have carefully prepared. I know what state it is in, but I don t tell you. It might be in a superposition of skinny and heavy states! J) You can measure weight at any time you like. Does the probability that your measurement will yield 10 (i.e. heavy) depend on the amount of time that you wait before measuring? Explain. K) Suppose instead that you chose NOT to measure W but instead to measure M. Does the probability that your measurement will yield +1 (i.e, that it s happy) depend on the amount of time that you wait before measuring? Explain. (You might consider the simple case that I handed you a particle prepared in a happy state at t=0.)
Quantum operator methods QM (quantum mouse) version p. 1
 Quantum operator methods QM (quantum mouse) version p. 1 SETUP: Consider a quantum object (a "quantum lab mouse") and some new properties we can measure. E.g., suppose "quantum weight", W, is a hermitian
Quantum operator methods QM (quantum mouse) version p. 1 SETUP: Consider a quantum object (a "quantum lab mouse") and some new properties we can measure. E.g., suppose "quantum weight", W, is a hermitian
1 Measurement and expectation values
 C/CS/Phys 191 Measurement and expectation values, Intro to Spin 2/15/05 Spring 2005 Lecture 9 1 Measurement and expectation values Last time we discussed how useful it is to work in the basis of energy
C/CS/Phys 191 Measurement and expectation values, Intro to Spin 2/15/05 Spring 2005 Lecture 9 1 Measurement and expectation values Last time we discussed how useful it is to work in the basis of energy
Quantum Mechanics crash course (For the scholar with an higher education in mathematics) Fabio Grazioso :48
 Quantum Mechanics crash course (For the scholar with an higher education in mathematics) Fabio Grazioso 2015-03-23 19:48 1 Contents 1 Mathematical definitions 3 11 Hilbert space 3 12 Operators on the Hilbert
Quantum Mechanics crash course (For the scholar with an higher education in mathematics) Fabio Grazioso 2015-03-23 19:48 1 Contents 1 Mathematical definitions 3 11 Hilbert space 3 12 Operators on the Hilbert
Physics 342 Lecture 17. Midterm I Recap. Lecture 17. Physics 342 Quantum Mechanics I
 Physics 342 Lecture 17 Midterm I Recap Lecture 17 Physics 342 Quantum Mechanics I Monday, March 1th, 28 17.1 Introduction In the context of the first midterm, there are a few points I d like to make about
Physics 342 Lecture 17 Midterm I Recap Lecture 17 Physics 342 Quantum Mechanics I Monday, March 1th, 28 17.1 Introduction In the context of the first midterm, there are a few points I d like to make about
1 Mathematical preliminaries
 1 Mathematical preliminaries The mathematical language of quantum mechanics is that of vector spaces and linear algebra. In this preliminary section, we will collect the various definitions and mathematical
1 Mathematical preliminaries The mathematical language of quantum mechanics is that of vector spaces and linear algebra. In this preliminary section, we will collect the various definitions and mathematical
Topic 2: The mathematical formalism and the standard way of thin
 The mathematical formalism and the standard way of thinking about it http://www.wuthrich.net/ MA Seminar: Philosophy of Physics Vectors and vector spaces Vectors and vector spaces Operators Albert, Quantum
The mathematical formalism and the standard way of thinking about it http://www.wuthrich.net/ MA Seminar: Philosophy of Physics Vectors and vector spaces Vectors and vector spaces Operators Albert, Quantum
Introduction to Quantum Mechanics Physics Thursday February 21, Problem # 1 (10pts) We are given the operator U(m, n) defined by
 Department of Physics Introduction to Quantum Mechanics Physics 5701 Temple University Z.-E. Meziani Thursday February 1, 017 Problem # 1 10pts We are given the operator Um, n defined by Ûm, n φ m >< φ
Department of Physics Introduction to Quantum Mechanics Physics 5701 Temple University Z.-E. Meziani Thursday February 1, 017 Problem # 1 10pts We are given the operator Um, n defined by Ûm, n φ m >< φ
The Schrodinger Equation and Postulates Common operators in QM: Potential Energy. Often depends on position operator: Kinetic Energy 1-D case:
 The Schrodinger Equation and Postulates Common operators in QM: Potential Energy Often depends on position operator: Kinetic Energy 1-D case: 3-D case Time Total energy = Hamiltonian To find out about
The Schrodinger Equation and Postulates Common operators in QM: Potential Energy Often depends on position operator: Kinetic Energy 1-D case: 3-D case Time Total energy = Hamiltonian To find out about
1.1 Quantum mechanics of one particle
 1 Second quantization 1.1 Quantum mechanics of one particle In quantum mechanics the physical state of a particle is described in terms of a ket Ψ. This ket belongs to a Hilbert space which is nothing
1 Second quantization 1.1 Quantum mechanics of one particle In quantum mechanics the physical state of a particle is described in terms of a ket Ψ. This ket belongs to a Hilbert space which is nothing
3.5 Finite Rotations in 3D Euclidean Space and Angular Momentum in QM
 3.5 Finite Rotations in 3D Euclidean Space and Angular Momentum in QM An active rotation in 3D position space is defined as the rotation of a vector about some point in a fixed coordinate system (a passive
3.5 Finite Rotations in 3D Euclidean Space and Angular Momentum in QM An active rotation in 3D position space is defined as the rotation of a vector about some point in a fixed coordinate system (a passive
Quantum Mechanics I Physics 5701
 Quantum Mechanics I Physics 5701 Z. E. Meziani 02/23//2017 Physics 5701 Lecture Outline 1 General Formulation of Quantum Mechanics 2 Measurement of physical quantities and observables 3 Representations
Quantum Mechanics I Physics 5701 Z. E. Meziani 02/23//2017 Physics 5701 Lecture Outline 1 General Formulation of Quantum Mechanics 2 Measurement of physical quantities and observables 3 Representations
4.3 Lecture 18: Quantum Mechanics
 CHAPTER 4. QUANTUM SYSTEMS 73 4.3 Lecture 18: Quantum Mechanics 4.3.1 Basics Now that we have mathematical tools of linear algebra we are ready to develop a framework of quantum mechanics. The framework
CHAPTER 4. QUANTUM SYSTEMS 73 4.3 Lecture 18: Quantum Mechanics 4.3.1 Basics Now that we have mathematical tools of linear algebra we are ready to develop a framework of quantum mechanics. The framework
8.04: Quantum Mechanics Professor Allan Adams Massachusetts Institute of Technology Tuesday March 19. Problem Set 6. Due Wednesday April 3 at 10.
 8.04: Quantum Mechanics Professor Allan Adams Massachusetts Institute of Technology Tuesday March 19 Problem Set 6 Due Wednesday April 3 at 10.00AM Assigned Reading: E&R 6 all, G, H Li. 7 1 9, 8 1 Ga.
8.04: Quantum Mechanics Professor Allan Adams Massachusetts Institute of Technology Tuesday March 19 Problem Set 6 Due Wednesday April 3 at 10.00AM Assigned Reading: E&R 6 all, G, H Li. 7 1 9, 8 1 Ga.
PLEASE LET ME KNOW IF YOU FIND TYPOS (send to
 Teoretisk Fysik KTH Advanced QM (SI2380), Lecture 2 (Summary of concepts) 1 PLEASE LET ME KNOW IF YOU FIND TYPOS (send email to langmann@kth.se) The laws of QM 1. I now discuss the laws of QM and their
Teoretisk Fysik KTH Advanced QM (SI2380), Lecture 2 (Summary of concepts) 1 PLEASE LET ME KNOW IF YOU FIND TYPOS (send email to langmann@kth.se) The laws of QM 1. I now discuss the laws of QM and their
0.1 Schrödinger Equation in 2-dimensional system
 0.1 Schrödinger Equation in -dimensional system In HW problem set 5, we introduced a simpleminded system describing the ammonia (NH 3 ) molecule, consisting of a plane spanned by the 3 hydrogen atoms and
0.1 Schrödinger Equation in -dimensional system In HW problem set 5, we introduced a simpleminded system describing the ammonia (NH 3 ) molecule, consisting of a plane spanned by the 3 hydrogen atoms and
Lecture 4: Equations of motion and canonical quantization Read Sakurai Chapter 1.6 and 1.7
 Lecture 4: Equations of motion and canonical quantization Read Sakurai Chapter 1.6 and 1.7 In Lecture 1 and 2, we have discussed how to represent the state of a quantum mechanical system based the superposition
Lecture 4: Equations of motion and canonical quantization Read Sakurai Chapter 1.6 and 1.7 In Lecture 1 and 2, we have discussed how to represent the state of a quantum mechanical system based the superposition
PHYS Concept Tests Fall 2009
 PHYS 30 Concept Tests Fall 009 In classical mechanics, given the state (i.e. position and velocity) of a particle at a certain time instant, the state of the particle at a later time A) cannot be determined
PHYS 30 Concept Tests Fall 009 In classical mechanics, given the state (i.e. position and velocity) of a particle at a certain time instant, the state of the particle at a later time A) cannot be determined
Quantum Mechanics C (130C) Winter 2014 Final exam
 University of California at San Diego Department of Physics Prof. John McGreevy Quantum Mechanics C (130C Winter 014 Final exam Please remember to put your name on your exam booklet. This is a closed-book
University of California at San Diego Department of Physics Prof. John McGreevy Quantum Mechanics C (130C Winter 014 Final exam Please remember to put your name on your exam booklet. This is a closed-book
II. The Machinery of Quantum Mechanics
 II. The Machinery of Quantum Mechanics Based on the results of the experiments described in the previous section, we recognize that real experiments do not behave quite as we expect. This section presents
II. The Machinery of Quantum Mechanics Based on the results of the experiments described in the previous section, we recognize that real experiments do not behave quite as we expect. This section presents
This is the important completeness relation,
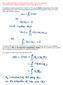 Observable quantities are represented by linear, hermitian operators! Compatible observables correspond to commuting operators! In addition to what was written in eqn 2.1.1, the vector corresponding to
Observable quantities are represented by linear, hermitian operators! Compatible observables correspond to commuting operators! In addition to what was written in eqn 2.1.1, the vector corresponding to
Theoretical Physics II B Quantum Mechanics. Lecture 5
 Theoretical Physics II B Quantum Mechanics Lecture 5 Frank Krauss February 11, 2014 Solutions to previous control questions 4.1 Determine first the transformation matrix ˆT through ( ˆT ij = ψ i φ j =
Theoretical Physics II B Quantum Mechanics Lecture 5 Frank Krauss February 11, 2014 Solutions to previous control questions 4.1 Determine first the transformation matrix ˆT through ( ˆT ij = ψ i φ j =
The Postulates of Quantum Mechanics
 p. 1/23 The Postulates of Quantum Mechanics We have reviewed the mathematics (complex linear algebra) necessary to understand quantum mechanics. We will now see how the physics of quantum mechanics fits
p. 1/23 The Postulates of Quantum Mechanics We have reviewed the mathematics (complex linear algebra) necessary to understand quantum mechanics. We will now see how the physics of quantum mechanics fits
E = hν light = hc λ = ( J s)( m/s) m = ev J = ev
 Problem The ionization potential tells us how much energy we need to use to remove an electron, so we know that any energy left afterwards will be the kinetic energy of the ejected electron. So first we
Problem The ionization potential tells us how much energy we need to use to remove an electron, so we know that any energy left afterwards will be the kinetic energy of the ejected electron. So first we
Tutorial for PhET Sim Quantum Bound States
 Tutorial for PhET Sim Quantum Bound States J. Mathias Weber * JILA and Department of Chemistry & Biochemistry, University of Colorado at Boulder With this PhET Sim, we will explore the properties of some
Tutorial for PhET Sim Quantum Bound States J. Mathias Weber * JILA and Department of Chemistry & Biochemistry, University of Colorado at Boulder With this PhET Sim, we will explore the properties of some
2. Introduction to quantum mechanics
 2. Introduction to quantum mechanics 2.1 Linear algebra Dirac notation Complex conjugate Vector/ket Dual vector/bra Inner product/bracket Tensor product Complex conj. matrix Transpose of matrix Hermitian
2. Introduction to quantum mechanics 2.1 Linear algebra Dirac notation Complex conjugate Vector/ket Dual vector/bra Inner product/bracket Tensor product Complex conj. matrix Transpose of matrix Hermitian
Quantum Mechanics: Postulates
 Quantum Mechanics: Postulates 25th March 2008 I. Physical meaning of the Wavefunction Postulate 1: The wavefunction attempts to describe a quantum mechanical entity (photon, electron, x-ray, etc.) through
Quantum Mechanics: Postulates 25th March 2008 I. Physical meaning of the Wavefunction Postulate 1: The wavefunction attempts to describe a quantum mechanical entity (photon, electron, x-ray, etc.) through
Ensembles and incomplete information
 p. 1/32 Ensembles and incomplete information So far in this course, we have described quantum systems by states that are normalized vectors in a complex Hilbert space. This works so long as (a) the system
p. 1/32 Ensembles and incomplete information So far in this course, we have described quantum systems by states that are normalized vectors in a complex Hilbert space. This works so long as (a) the system
The Postulates of Quantum Mechanics Common operators in QM: Potential Energy. Often depends on position operator: Kinetic Energy 1-D case: 3-D case
 The Postulates of Quantum Mechanics Common operators in QM: Potential Energy Often depends on position operator: Kinetic Energy 1-D case: 3-D case Time Total energy = Hamiltonian To find out about the
The Postulates of Quantum Mechanics Common operators in QM: Potential Energy Often depends on position operator: Kinetic Energy 1-D case: 3-D case Time Total energy = Hamiltonian To find out about the
An operator is a transformation that takes a function as an input and produces another function (usually).
 Formalism of Quantum Mechanics Operators Engel 3.2 An operator is a transformation that takes a function as an input and produces another function (usually). Example: In QM, most operators are linear:
Formalism of Quantum Mechanics Operators Engel 3.2 An operator is a transformation that takes a function as an input and produces another function (usually). Example: In QM, most operators are linear:
Rotations in Quantum Mechanics
 Rotations in Quantum Mechanics We have seen that physical transformations are represented in quantum mechanics by unitary operators acting on the Hilbert space. In this section, we ll think about the specific
Rotations in Quantum Mechanics We have seen that physical transformations are represented in quantum mechanics by unitary operators acting on the Hilbert space. In this section, we ll think about the specific
The Schroedinger equation
 The Schroedinger equation After Planck, Einstein, Bohr, de Broglie, and many others (but before Born), the time was ripe for a complete theory that could be applied to any problem involving nano-scale
The Schroedinger equation After Planck, Einstein, Bohr, de Broglie, and many others (but before Born), the time was ripe for a complete theory that could be applied to any problem involving nano-scale
Quantum Mechanics I Physics 5701
 Quantum Mechanics I Physics 5701 Z. E. Meziani 02/24//2017 Physics 5701 Lecture Commutation of Observables and First Consequences of the Postulates Outline 1 Commutation Relations 2 Uncertainty Relations
Quantum Mechanics I Physics 5701 Z. E. Meziani 02/24//2017 Physics 5701 Lecture Commutation of Observables and First Consequences of the Postulates Outline 1 Commutation Relations 2 Uncertainty Relations
Page 684. Lecture 40: Coordinate Transformations: Time Transformations Date Revised: 2009/02/02 Date Given: 2009/02/02
 Page 684 Lecture 40: Coordinate Transformations: Time Transformations Date Revised: 2009/02/02 Date Given: 2009/02/02 Time Transformations Section 12.5 Symmetries: Time Transformations Page 685 Time Translation
Page 684 Lecture 40: Coordinate Transformations: Time Transformations Date Revised: 2009/02/02 Date Given: 2009/02/02 Time Transformations Section 12.5 Symmetries: Time Transformations Page 685 Time Translation
Continuous quantum states, Particle on a line and Uncertainty relations
 Continuous quantum states, Particle on a line and Uncertainty relations So far we have considered k-level (discrete) quantum systems. Now we turn our attention to continuous quantum systems, such as a
Continuous quantum states, Particle on a line and Uncertainty relations So far we have considered k-level (discrete) quantum systems. Now we turn our attention to continuous quantum systems, such as a
ECE 501b Homework #4 Due: 10/22/2012
 1. Game Strategy: Consider a multiplayer boardgame that takes place on the following board and with the following rules: 7 8 9 10 6 11 5 12 4 3 2 1 The board contains six squares that are property (the
1. Game Strategy: Consider a multiplayer boardgame that takes place on the following board and with the following rules: 7 8 9 10 6 11 5 12 4 3 2 1 The board contains six squares that are property (the
Physics 215 Quantum Mechanics 1 Assignment 1
 Physics 5 Quantum Mechanics Assignment Logan A. Morrison January 9, 06 Problem Prove via the dual correspondence definition that the hermitian conjugate of α β is β α. By definition, the hermitian conjugate
Physics 5 Quantum Mechanics Assignment Logan A. Morrison January 9, 06 Problem Prove via the dual correspondence definition that the hermitian conjugate of α β is β α. By definition, the hermitian conjugate
04. Five Principles of Quantum Mechanics
 04. Five Principles of Quantum Mechanics () States are represented by vectors of length. A physical system is represented by a linear vector space (the space of all its possible states). () Properties
04. Five Principles of Quantum Mechanics () States are represented by vectors of length. A physical system is represented by a linear vector space (the space of all its possible states). () Properties
Chem 3502/4502 Physical Chemistry II (Quantum Mechanics) 3 Credits Spring Semester 2006 Christopher J. Cramer. Lecture 7, February 1, 2006
 Chem 350/450 Physical Chemistry II (Quantum Mechanics) 3 Credits Spring Semester 006 Christopher J. Cramer ecture 7, February 1, 006 Solved Homework We are given that A is a Hermitian operator such that
Chem 350/450 Physical Chemistry II (Quantum Mechanics) 3 Credits Spring Semester 006 Christopher J. Cramer ecture 7, February 1, 006 Solved Homework We are given that A is a Hermitian operator such that
Quantum Mechanics is Linear Algebra. Noah Graham Middlebury College February 25, 2014
 Quantum Mechanics is Linear Algebra Noah Graham Middlebury College February 25, 24 Linear Algebra Cheat Sheet Column vector quantum state: v = v v 2. Row vector dual state: w = w w 2... Inner product:
Quantum Mechanics is Linear Algebra Noah Graham Middlebury College February 25, 24 Linear Algebra Cheat Sheet Column vector quantum state: v = v v 2. Row vector dual state: w = w w 2... Inner product:
Physics 741 Graduate Quantum Mechanics 1 Solutions to Midterm Exam, Fall x i x dx i x i x x i x dx
 Physics 74 Graduate Quantum Mechanics Solutions to Midterm Exam, Fall 4. [ points] Consider the wave function x Nexp x ix (a) [6] What is the correct normaliation N? The normaliation condition is. exp,
Physics 74 Graduate Quantum Mechanics Solutions to Midterm Exam, Fall 4. [ points] Consider the wave function x Nexp x ix (a) [6] What is the correct normaliation N? The normaliation condition is. exp,
A Simple Model of Quantum Trajectories. Todd A. Brun University of Southern California
 A Simple Model of Quantum Trajectories Todd A. Brun University of Southern California Outline 1. Review projective and generalized measurements. 2. A simple model of indirect measurement. 3. Weak measurements--jump-like
A Simple Model of Quantum Trajectories Todd A. Brun University of Southern California Outline 1. Review projective and generalized measurements. 2. A simple model of indirect measurement. 3. Weak measurements--jump-like
Master Projects (EPFL) Philosophical perspectives on the exact sciences and their history
 Master Projects (EPFL) Philosophical perspectives on the exact sciences and their history Some remarks on the measurement problem in quantum theory (Davide Romano) 1. An introduction to the quantum formalism
Master Projects (EPFL) Philosophical perspectives on the exact sciences and their history Some remarks on the measurement problem in quantum theory (Davide Romano) 1. An introduction to the quantum formalism
Physics 3220 Homework 13 Due Dec. 7, 2012
 This homework set concentrates on the spin ½ system and the closely related two-level system. All of quantum mechanics is right here, without a single differential equation. Have fun! 1. Spin 1/ system
This homework set concentrates on the spin ½ system and the closely related two-level system. All of quantum mechanics is right here, without a single differential equation. Have fun! 1. Spin 1/ system
in terms of the classical frequency, ω = , puts the classical Hamiltonian in the form H = p2 2m + mω2 x 2
 One of the most important problems in quantum mechanics is the simple harmonic oscillator, in part because its properties are directly applicable to field theory. The treatment in Dirac notation is particularly
One of the most important problems in quantum mechanics is the simple harmonic oscillator, in part because its properties are directly applicable to field theory. The treatment in Dirac notation is particularly
Angular Momentum set II
 Angular Momentum set II PH - QM II Sem, 7-8 Problem : Using the commutation relations for the angular momentum operators, prove the Jacobi identity Problem : [ˆL x, [ˆL y, ˆL z ]] + [ˆL y, [ˆL z, ˆL x
Angular Momentum set II PH - QM II Sem, 7-8 Problem : Using the commutation relations for the angular momentum operators, prove the Jacobi identity Problem : [ˆL x, [ˆL y, ˆL z ]] + [ˆL y, [ˆL z, ˆL x
Introduction to Quantum Mechanics PVK - Solutions. Nicolas Lanzetti
 Introduction to Quantum Mechanics PVK - Solutions Nicolas Lanzetti lnicolas@student.ethz.ch 1 Contents 1 The Wave Function and the Schrödinger Equation 3 1.1 Quick Checks......................................
Introduction to Quantum Mechanics PVK - Solutions Nicolas Lanzetti lnicolas@student.ethz.ch 1 Contents 1 The Wave Function and the Schrödinger Equation 3 1.1 Quick Checks......................................
Quantum Mechanics Basics II
 Quantum Mechanics Basics II VBS/MRC Quantum Mechanics Basics II 0 Basic Postulates of Quantum Mechanics 1. State of a Particle Wave Functions 2. Physical Observables Hermitian Operators 3. Outcome of Experiment
Quantum Mechanics Basics II VBS/MRC Quantum Mechanics Basics II 0 Basic Postulates of Quantum Mechanics 1. State of a Particle Wave Functions 2. Physical Observables Hermitian Operators 3. Outcome of Experiment
2 Quantum Mechanics. 2.1 The Strange Lives of Electrons
 2 Quantum Mechanics A philosopher once said, It is necessary for the very existence of science that the same conditions always produce the same results. Well, they don t! Richard Feynman Today, we re going
2 Quantum Mechanics A philosopher once said, It is necessary for the very existence of science that the same conditions always produce the same results. Well, they don t! Richard Feynman Today, we re going
Physics 342 Lecture 26. Angular Momentum. Lecture 26. Physics 342 Quantum Mechanics I
 Physics 342 Lecture 26 Angular Momentum Lecture 26 Physics 342 Quantum Mechanics I Friday, April 2nd, 2010 We know how to obtain the energy of Hydrogen using the Hamiltonian operator but given a particular
Physics 342 Lecture 26 Angular Momentum Lecture 26 Physics 342 Quantum Mechanics I Friday, April 2nd, 2010 We know how to obtain the energy of Hydrogen using the Hamiltonian operator but given a particular
Hilbert Space, Entanglement, Quantum Gates, Bell States, Superdense Coding.
 CS 94- Bell States Bell Inequalities 9//04 Fall 004 Lecture Hilbert Space Entanglement Quantum Gates Bell States Superdense Coding 1 One qubit: Recall that the state of a single qubit can be written as
CS 94- Bell States Bell Inequalities 9//04 Fall 004 Lecture Hilbert Space Entanglement Quantum Gates Bell States Superdense Coding 1 One qubit: Recall that the state of a single qubit can be written as
HW5 computer problem: modelling a dye molecule Objectives By the end of this lab you should: Know how to manipulate complex numbers and matrices. Prog
 HW5 computer problem: modelling a dye molecule Objectives By the end of this lab you should: Know how to manipulate complex numbers and matrices. Programming environment: Spyder. To implement this, do
HW5 computer problem: modelling a dye molecule Objectives By the end of this lab you should: Know how to manipulate complex numbers and matrices. Programming environment: Spyder. To implement this, do
1. Quantum Mechanics, Cohen Tannoudji, Chapters Linear Algebra, Schaum Series 3. Quantum Chemistry Ch. 6
 Lecture # Today s Program 1. Recap: Classical States, Hamiltonians and time evolution. First postulate The description of a state of a system. 3. Second postulate physical quantities. 4. Linear operators.
Lecture # Today s Program 1. Recap: Classical States, Hamiltonians and time evolution. First postulate The description of a state of a system. 3. Second postulate physical quantities. 4. Linear operators.
1 Quantum field theory and Green s function
 1 Quantum field theory and Green s function Condensed matter physics studies systems with large numbers of identical particles (e.g. electrons, phonons, photons) at finite temperature. Quantum field theory
1 Quantum field theory and Green s function Condensed matter physics studies systems with large numbers of identical particles (e.g. electrons, phonons, photons) at finite temperature. Quantum field theory
2. As we shall see, we choose to write in terms of σ x because ( X ) 2 = σ 2 x.
 Section 5.1 Simple One-Dimensional Problems: The Free Particle Page 9 The Free Particle Gaussian Wave Packets The Gaussian wave packet initial state is one of the few states for which both the { x } and
Section 5.1 Simple One-Dimensional Problems: The Free Particle Page 9 The Free Particle Gaussian Wave Packets The Gaussian wave packet initial state is one of the few states for which both the { x } and
Vector Spaces for Quantum Mechanics J. P. Leahy January 30, 2012
 PHYS 20602 Handout 1 Vector Spaces for Quantum Mechanics J. P. Leahy January 30, 2012 Handout Contents Examples Classes Examples for Lectures 1 to 4 (with hints at end) Definitions of groups and vector
PHYS 20602 Handout 1 Vector Spaces for Quantum Mechanics J. P. Leahy January 30, 2012 Handout Contents Examples Classes Examples for Lectures 1 to 4 (with hints at end) Definitions of groups and vector
MP463 QUANTUM MECHANICS
 MP463 QUANTUM MECHANICS Introduction Quantum theory of angular momentum Quantum theory of a particle in a central potential - Hydrogen atom - Three-dimensional isotropic harmonic oscillator (a model of
MP463 QUANTUM MECHANICS Introduction Quantum theory of angular momentum Quantum theory of a particle in a central potential - Hydrogen atom - Three-dimensional isotropic harmonic oscillator (a model of
The quantum state as a vector
 The quantum state as a vector February 6, 27 Wave mechanics In our review of the development of wave mechanics, we have established several basic properties of the quantum description of nature:. A particle
The quantum state as a vector February 6, 27 Wave mechanics In our review of the development of wave mechanics, we have established several basic properties of the quantum description of nature:. A particle
Recitation 1 (Sep. 15, 2017)
 Lecture 1 8.321 Quantum Theory I, Fall 2017 1 Recitation 1 (Sep. 15, 2017) 1.1 Simultaneous Diagonalization In the last lecture, we discussed the situations in which two operators can be simultaneously
Lecture 1 8.321 Quantum Theory I, Fall 2017 1 Recitation 1 (Sep. 15, 2017) 1.1 Simultaneous Diagonalization In the last lecture, we discussed the situations in which two operators can be simultaneously
1 Fundamental physical postulates. C/CS/Phys C191 Quantum Mechanics in a Nutshell I 10/04/07 Fall 2007 Lecture 12
 C/CS/Phys C191 Quantum Mechanics in a Nutshell I 10/04/07 Fall 2007 Lecture 12 In this and the next lecture we summarize the essential physical and mathematical aspects of quantum mechanics relevant to
C/CS/Phys C191 Quantum Mechanics in a Nutshell I 10/04/07 Fall 2007 Lecture 12 In this and the next lecture we summarize the essential physical and mathematical aspects of quantum mechanics relevant to
Coordinate and Momentum Representation. Commuting Observables and Simultaneous Measurements. January 30, 2012
 Coordinate and Momentum Representation. Commuting Observables and Simultaneous Measurements. January 30, 2012 1 Coordinate and Momentum Representations Let us consider an eigenvalue problem for a Hermitian
Coordinate and Momentum Representation. Commuting Observables and Simultaneous Measurements. January 30, 2012 1 Coordinate and Momentum Representations Let us consider an eigenvalue problem for a Hermitian
Lecture 4 (Sep. 18, 2017)
 Lecture 4 8.3 Quantum Theory I, Fall 07 Lecture 4 (Sep. 8, 07) 4. Measurement 4.. Spin- Systems Last time, we said that a general state in a spin- system can be written as ψ = c + + + c, (4.) where +,
Lecture 4 8.3 Quantum Theory I, Fall 07 Lecture 4 (Sep. 8, 07) 4. Measurement 4.. Spin- Systems Last time, we said that a general state in a spin- system can be written as ψ = c + + + c, (4.) where +,
d 3 r d 3 vf( r, v) = N (2) = CV C = n where n N/V is the total number of molecules per unit volume. Hence e βmv2 /2 d 3 rd 3 v (5)
 LECTURE 12 Maxwell Velocity Distribution Suppose we have a dilute gas of molecules, each with mass m. If the gas is dilute enough, we can ignore the interactions between the molecules and the energy will
LECTURE 12 Maxwell Velocity Distribution Suppose we have a dilute gas of molecules, each with mass m. If the gas is dilute enough, we can ignore the interactions between the molecules and the energy will
10 Time-Independent Perturbation Theory
 S.K. Saiin Oct. 6, 009 Lecture 0 0 Time-Independent Perturbation Theory Content: Non-degenerate case. Degenerate case. Only a few quantum mechanical problems can be solved exactly. However, if the system
S.K. Saiin Oct. 6, 009 Lecture 0 0 Time-Independent Perturbation Theory Content: Non-degenerate case. Degenerate case. Only a few quantum mechanical problems can be solved exactly. However, if the system
Harmonic Oscillator I
 Physics 34 Lecture 7 Harmonic Oscillator I Lecture 7 Physics 34 Quantum Mechanics I Monday, February th, 008 We can manipulate operators, to a certain extent, as we would algebraic expressions. By considering
Physics 34 Lecture 7 Harmonic Oscillator I Lecture 7 Physics 34 Quantum Mechanics I Monday, February th, 008 We can manipulate operators, to a certain extent, as we would algebraic expressions. By considering
Lecture #1. Review. Postulates of quantum mechanics (1-3) Postulate 1
 L1.P1 Lecture #1 Review Postulates of quantum mechanics (1-3) Postulate 1 The state of a system at any instant of time may be represented by a wave function which is continuous and differentiable. Specifically,
L1.P1 Lecture #1 Review Postulates of quantum mechanics (1-3) Postulate 1 The state of a system at any instant of time may be represented by a wave function which is continuous and differentiable. Specifically,
Quantum Mechanics II
 Quantum Mechanics II Prof. Boris Altshuler March 8, 011 1 Lecture 19 1.1 Second Quantization Recall our results from simple harmonic oscillator. We know the Hamiltonian very well so no need to repeat here.
Quantum Mechanics II Prof. Boris Altshuler March 8, 011 1 Lecture 19 1.1 Second Quantization Recall our results from simple harmonic oscillator. We know the Hamiltonian very well so no need to repeat here.
PHY305: Notes on Entanglement and the Density Matrix
 PHY305: Notes on Entanglement and the Density Matrix Here follows a short summary of the definitions of qubits, EPR states, entanglement, the density matrix, pure states, mixed states, measurement, and
PHY305: Notes on Entanglement and the Density Matrix Here follows a short summary of the definitions of qubits, EPR states, entanglement, the density matrix, pure states, mixed states, measurement, and
Chapter 2 Approximation Methods Can be Used When Exact Solutions to the Schrödinger Equation Can Not be Found.
 Chapter 2 Approximation Methods Can be Used When Exact Solutions to the Schrödinger Equation Can Not be Found. In applying quantum mechanics to 'real' chemical problems, one is usually faced with a Schrödinger
Chapter 2 Approximation Methods Can be Used When Exact Solutions to the Schrödinger Equation Can Not be Found. In applying quantum mechanics to 'real' chemical problems, one is usually faced with a Schrödinger
Quantum Mechanics Solutions. λ i λ j v j v j v i v i.
 Quantum Mechanics Solutions 1. (a) If H has an orthonormal basis consisting of the eigenvectors { v i } of A with eigenvalues λ i C, then A can be written in terms of its spectral decomposition as A =
Quantum Mechanics Solutions 1. (a) If H has an orthonormal basis consisting of the eigenvectors { v i } of A with eigenvalues λ i C, then A can be written in terms of its spectral decomposition as A =
The Quantum Theory of Atoms and Molecules
 The Quantum Theory of Atoms and Molecules The postulates of quantum mechanics Dr Grant Ritchie The postulates.. 1. Associated with any particle moving in a conservative field of force is a wave function,
The Quantum Theory of Atoms and Molecules The postulates of quantum mechanics Dr Grant Ritchie The postulates.. 1. Associated with any particle moving in a conservative field of force is a wave function,
arxiv:quant-ph/ v2 23 Mar 2001
 A PHYSICAL EXPLANATION FOR THE TILDE SYSTEM IN THERMO FIELD DYNAMICS DONG MI, HE-SHAN SONG Department of Physics, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian 116024, P.R.China arxiv:quant-ph/0102127v2 23 Mar
A PHYSICAL EXPLANATION FOR THE TILDE SYSTEM IN THERMO FIELD DYNAMICS DONG MI, HE-SHAN SONG Department of Physics, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian 116024, P.R.China arxiv:quant-ph/0102127v2 23 Mar
C/CS/Phys C191 Quantum Mechanics in a Nutshell 10/06/07 Fall 2009 Lecture 12
 C/CS/Phys C191 Quantum Mechanics in a Nutshell 10/06/07 Fall 2009 Lecture 12 In this lecture we summarize the essential physical and mathematical aspects of quantum mechanics relevant to this course. Topics
C/CS/Phys C191 Quantum Mechanics in a Nutshell 10/06/07 Fall 2009 Lecture 12 In this lecture we summarize the essential physical and mathematical aspects of quantum mechanics relevant to this course. Topics
Review of the Formalism of Quantum Mechanics
 Review of the Formalism of Quantum Mechanics The postulates of quantum mechanics are often stated in textbooks. There are two main properties of physics upon which these postulates are based: 1)the probability
Review of the Formalism of Quantum Mechanics The postulates of quantum mechanics are often stated in textbooks. There are two main properties of physics upon which these postulates are based: 1)the probability
Name Solutions Linear Algebra; Test 3. Throughout the test simplify all answers except where stated otherwise.
 Name Solutions Linear Algebra; Test 3 Throughout the test simplify all answers except where stated otherwise. 1) Find the following: (10 points) ( ) Or note that so the rows are linearly independent, so
Name Solutions Linear Algebra; Test 3 Throughout the test simplify all answers except where stated otherwise. 1) Find the following: (10 points) ( ) Or note that so the rows are linearly independent, so
C/CS/Phys C191 Particle-in-a-box, Spin 10/02/08 Fall 2008 Lecture 11
 C/CS/Phys C191 Particle-in-a-box, Spin 10/0/08 Fall 008 Lecture 11 Last time we saw that the time dependent Schr. eqn. can be decomposed into two equations, one in time (t) and one in space (x): space
C/CS/Phys C191 Particle-in-a-box, Spin 10/0/08 Fall 008 Lecture 11 Last time we saw that the time dependent Schr. eqn. can be decomposed into two equations, one in time (t) and one in space (x): space
Lecture 6 Quantum Mechanical Systems and Measurements
 Lecture 6 Quantum Mechanical Systems and Measurements Today s Program: 1. Simple Harmonic Oscillator (SHO). Principle of spectral decomposition. 3. Predicting the results of measurements, fourth postulate
Lecture 6 Quantum Mechanical Systems and Measurements Today s Program: 1. Simple Harmonic Oscillator (SHO). Principle of spectral decomposition. 3. Predicting the results of measurements, fourth postulate
POSTULATES OF QUANTUM MECHANICS
 POSTULATES OF QUANTUM MECHANICS Quantum-mechanical states - In the coordinate representation, the state of a quantum-mechanical system is described by the wave function ψ(q, t) = ψ(q 1,..., q f, t) (in
POSTULATES OF QUANTUM MECHANICS Quantum-mechanical states - In the coordinate representation, the state of a quantum-mechanical system is described by the wave function ψ(q, t) = ψ(q 1,..., q f, t) (in
Are these states normalized? A) Yes
 QMII-. Consider two kets and their corresponding column vectors: Ψ = φ = Are these two state orthogonal? Is ψ φ = 0? A) Yes ) No Answer: A Are these states normalized? A) Yes ) No Answer: (each state has
QMII-. Consider two kets and their corresponding column vectors: Ψ = φ = Are these two state orthogonal? Is ψ φ = 0? A) Yes ) No Answer: A Are these states normalized? A) Yes ) No Answer: (each state has
BASICS OF QUANTUM MECHANICS. Reading: QM Course packet Ch 5
 BASICS OF QUANTUM MECHANICS 1 Reading: QM Course packet Ch 5 Interesting things happen when electrons are confined to small regions of space (few nm). For one thing, they can behave as if they are in an
BASICS OF QUANTUM MECHANICS 1 Reading: QM Course packet Ch 5 Interesting things happen when electrons are confined to small regions of space (few nm). For one thing, they can behave as if they are in an
Ch 125a Problem Set 1
 Ch 5a Problem Set Due Monday, Oct 5, 05, am Problem : Bra-ket notation (Dirac notation) Bra-ket notation is a standard and convenient way to describe quantum state vectors For example, φ is an abstract
Ch 5a Problem Set Due Monday, Oct 5, 05, am Problem : Bra-ket notation (Dirac notation) Bra-ket notation is a standard and convenient way to describe quantum state vectors For example, φ is an abstract
Identical Particles in Quantum Mechanics
 Identical Particles in Quantum Mechanics Chapter 20 P. J. Grandinetti Chem. 4300 Nov 17, 2017 P. J. Grandinetti (Chem. 4300) Identical Particles in Quantum Mechanics Nov 17, 2017 1 / 20 Wolfgang Pauli
Identical Particles in Quantum Mechanics Chapter 20 P. J. Grandinetti Chem. 4300 Nov 17, 2017 P. J. Grandinetti (Chem. 4300) Identical Particles in Quantum Mechanics Nov 17, 2017 1 / 20 Wolfgang Pauli
1 Algebra of State Vectors
 J. Rothberg October 6, Introduction to Quantum Mechanics: Part Algebra of State Vectors What does the State Vector mean? A state vector is not a property of a physical system, but rather represents an
J. Rothberg October 6, Introduction to Quantum Mechanics: Part Algebra of State Vectors What does the State Vector mean? A state vector is not a property of a physical system, but rather represents an
Select/Special Topics in Atomic Physics Prof. P. C. Deshmukh Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras
 Select/Special Topics in Atomic Physics Prof. P. C. Deshmukh Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 9 Angular Momentum in Quantum Mechanics Dimensionality of the Direct-Product
Select/Special Topics in Atomic Physics Prof. P. C. Deshmukh Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 9 Angular Momentum in Quantum Mechanics Dimensionality of the Direct-Product
QM and Angular Momentum
 Chapter 5 QM and Angular Momentum 5. Angular Momentum Operators In your Introductory Quantum Mechanics (QM) course you learned about the basic properties of low spin systems. Here we want to review that
Chapter 5 QM and Angular Momentum 5. Angular Momentum Operators In your Introductory Quantum Mechanics (QM) course you learned about the basic properties of low spin systems. Here we want to review that
Quantum field theory and Green s function
 1 Quantum field theory and Green s function Condensed matter physics studies systems with large numbers of identical particles (e.g. electrons, phonons, photons) at finite temperature. Quantum field theory
1 Quantum field theory and Green s function Condensed matter physics studies systems with large numbers of identical particles (e.g. electrons, phonons, photons) at finite temperature. Quantum field theory
On the Postulates of Quantum Mechanics and their Interpretation.
 On the Postulates of Quantum Mechanics and their Interpretation. Marcel Nooijen University of Waterloo One arrives at very implausible theoretical conceptions, if one attempts to maintain the thesis that
On the Postulates of Quantum Mechanics and their Interpretation. Marcel Nooijen University of Waterloo One arrives at very implausible theoretical conceptions, if one attempts to maintain the thesis that
MODELING MATTER AT NANOSCALES. 4. Introduction to quantum treatments Outline of the principles and the method of quantum mechanics
 MODELING MATTER AT NANOSCALES 4. Introduction to quantum treatments 4.01. Outline of the principles and the method of quantum mechanics 1 Why quantum mechanics? Physics and sizes in universe Knowledge
MODELING MATTER AT NANOSCALES 4. Introduction to quantum treatments 4.01. Outline of the principles and the method of quantum mechanics 1 Why quantum mechanics? Physics and sizes in universe Knowledge
PHYS-454 The position and momentum representations
 PHYS-454 The position and momentum representations 1 Τhe continuous spectrum-a n So far we have seen problems where the involved operators have a discrete spectrum of eigenfunctions and eigenvalues.! n
PHYS-454 The position and momentum representations 1 Τhe continuous spectrum-a n So far we have seen problems where the involved operators have a discrete spectrum of eigenfunctions and eigenvalues.! n
Statistical Interpretation
 Physics 342 Lecture 15 Statistical Interpretation Lecture 15 Physics 342 Quantum Mechanics I Friday, February 29th, 2008 Quantum mechanics is a theory of probability densities given that we now have an
Physics 342 Lecture 15 Statistical Interpretation Lecture 15 Physics 342 Quantum Mechanics I Friday, February 29th, 2008 Quantum mechanics is a theory of probability densities given that we now have an
Non-Hermitian systems with PT symmetry
 Author: Facultat de Física, Universitat de Barcelona, Diagonal 645, 08028 Barcelona, Spain. Advisor: Oleg Bulashenko Abstract: We discuss the possibility to build the formalism of quantum mechanics based
Author: Facultat de Física, Universitat de Barcelona, Diagonal 645, 08028 Barcelona, Spain. Advisor: Oleg Bulashenko Abstract: We discuss the possibility to build the formalism of quantum mechanics based
Quantum mechanics in one hour
 Chapter 2 Quantum mechanics in one hour 2.1 Introduction The purpose of this chapter is to refresh your knowledge of quantum mechanics and to establish notation. Depending on your background you might
Chapter 2 Quantum mechanics in one hour 2.1 Introduction The purpose of this chapter is to refresh your knowledge of quantum mechanics and to establish notation. Depending on your background you might
Short Course in Quantum Information Lecture 2
 Short Course in Quantum Information Lecture Formal Structure of Quantum Mechanics Course Info All materials downloadable @ website http://info.phys.unm.edu/~deutschgroup/deutschclasses.html Syllabus Lecture
Short Course in Quantum Information Lecture Formal Structure of Quantum Mechanics Course Info All materials downloadable @ website http://info.phys.unm.edu/~deutschgroup/deutschclasses.html Syllabus Lecture
Quantum Gates, Circuits & Teleportation
 Chapter 3 Quantum Gates, Circuits & Teleportation Unitary Operators The third postulate of quantum physics states that the evolution of a quantum system is necessarily unitary. Geometrically, a unitary
Chapter 3 Quantum Gates, Circuits & Teleportation Unitary Operators The third postulate of quantum physics states that the evolution of a quantum system is necessarily unitary. Geometrically, a unitary
Introduction to quantum information processing
 Introduction to quantum information processing Measurements and quantum probability Brad Lackey 25 October 2016 MEASUREMENTS AND QUANTUM PROBABILITY 1 of 22 OUTLINE 1 Probability 2 Density Operators 3
Introduction to quantum information processing Measurements and quantum probability Brad Lackey 25 October 2016 MEASUREMENTS AND QUANTUM PROBABILITY 1 of 22 OUTLINE 1 Probability 2 Density Operators 3
PHY413 Quantum Mechanics B Duration: 2 hours 30 minutes
 BSc/MSci Examination by Course Unit Thursday nd May 4 : - :3 PHY43 Quantum Mechanics B Duration: hours 3 minutes YOU ARE NOT PERMITTED TO READ THE CONTENTS OF THIS QUESTION PAPER UNTIL INSTRUCTED TO DO
BSc/MSci Examination by Course Unit Thursday nd May 4 : - :3 PHY43 Quantum Mechanics B Duration: hours 3 minutes YOU ARE NOT PERMITTED TO READ THE CONTENTS OF THIS QUESTION PAPER UNTIL INSTRUCTED TO DO
Page 404. Lecture 22: Simple Harmonic Oscillator: Energy Basis Date Given: 2008/11/19 Date Revised: 2008/11/19
 Page 404 Lecture : Simple Harmonic Oscillator: Energy Basis Date Given: 008/11/19 Date Revised: 008/11/19 Coordinate Basis Section 6. The One-Dimensional Simple Harmonic Oscillator: Coordinate Basis Page
Page 404 Lecture : Simple Harmonic Oscillator: Energy Basis Date Given: 008/11/19 Date Revised: 008/11/19 Coordinate Basis Section 6. The One-Dimensional Simple Harmonic Oscillator: Coordinate Basis Page
Angular momentum. Quantum mechanics. Orbital angular momentum
 Angular momentum 1 Orbital angular momentum Consider a particle described by the Cartesian coordinates (x, y, z r and their conjugate momenta (p x, p y, p z p. The classical definition of the orbital angular
Angular momentum 1 Orbital angular momentum Consider a particle described by the Cartesian coordinates (x, y, z r and their conjugate momenta (p x, p y, p z p. The classical definition of the orbital angular
Lecture 20. Parity and Time Reversal
 Lecture 20 Parity and Time Reversal November 15, 2009 Lecture 20 Time Translation ( ψ(t + ɛ) = Û[T (ɛ)] ψ(t) = I iɛ ) h Ĥ ψ(t) Ĥ is the generator of time translations. Û[T (ɛ)] = I iɛ h Ĥ [Ĥ, Ĥ] = 0 time
Lecture 20 Parity and Time Reversal November 15, 2009 Lecture 20 Time Translation ( ψ(t + ɛ) = Û[T (ɛ)] ψ(t) = I iɛ ) h Ĥ ψ(t) Ĥ is the generator of time translations. Û[T (ɛ)] = I iɛ h Ĥ [Ĥ, Ĥ] = 0 time
General Physical Chemistry II
 General Physical Chemistry II Lecture 3 Aleksey Kocherzhenko September 2, 2014" Last time " The time-independent Schrödinger equation" Erwin Schrödinger " ~ 2 2m d 2 (x) dx 2 The wavefunction:" (x) The
General Physical Chemistry II Lecture 3 Aleksey Kocherzhenko September 2, 2014" Last time " The time-independent Schrödinger equation" Erwin Schrödinger " ~ 2 2m d 2 (x) dx 2 The wavefunction:" (x) The
ECE 487 Lecture 6 : Time-Dependent Quantum Mechanics I Class Outline:
 ECE 487 Lecture 6 : Time-Dependent Quantum Mechanics I Class Outline: Time-Dependent Schrödinger Equation Solutions to thetime-dependent Schrödinger Equation Expansion of Energy Eigenstates Things you
ECE 487 Lecture 6 : Time-Dependent Quantum Mechanics I Class Outline: Time-Dependent Schrödinger Equation Solutions to thetime-dependent Schrödinger Equation Expansion of Energy Eigenstates Things you
