2. Introduction to quantum mechanics
|
|
|
- Virginia Ryan
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 2. Introduction to quantum mechanics 2.1 Linear algebra Dirac notation Complex conjugate Vector/ket Dual vector/bra Inner product/bracket Tensor product Complex conj. matrix Transpose of matrix Hermitian conj/ adjoint of matrix Inner product
2 Basis, vector representation For a set of vectors spanning The set constitutes a basis for Linear operators A linear operator means Notation
3 Matrix representation For spanning, spanning, a matrix representation of means Numbers form matrix Linear operator (basis given) matrix representation (to be used interchangeably...) Pauli matrices
4 Inner vector product A inner product on is We use notation Hilbert space = inner product space The vectors are orthogonal if The norm of a vector is An orthonormal set of vectors obey
5 Vector representation With respect to an orthonormal basis for the inner product is We thus have (an orthonormal basis will be used unless otherwise stated)
6 Outer vector product The outer product is a linear operator Cauchy-Schwartz inequality For two vectors Completeness relation For vectors forming an orthonormal basis for
7 Eigenvectors and eigenvalues The eigenvector to obeys with the eigenvalue. The diagonal representation of is (for diagonalizable ) in terms of eigenvalues and orthonormal eigenvectors of Hermitian operators The Hermitian conjugate/adjoint of is We have and, An Hermitian operator obeys
8 Projection operator The operator is a projection operator Properties Orthogonal complement Normal operator An operator is normal if An operator is normal if and only if it is diagonalizable. An Hermitian operator is normal.
9 Unitary matrix A matrix/operator is unitary if Positive operator An operator is positive if and real for any vector. Any positive operator is Hermitian Any positive operator has real, positive eigenvalues and a spectral decomposition in terms of eigenvalues and orthonormal eigenvectors of
10 Tensor product A tensor product between vectors in is a vector in Example: A tensor product between operators/matrices is denoted Operation
11 Properties Matrix representation Example: For matrices we have the tensor product
12 Operator functions For a normal operator, written in the spectral decomposition we define the/operator matrix function Trace The trace of a matrix is Cyclic property Outer product formulation
13 Commutators The commutator between two operators/matrices is The anti-commutator between two operators/matrices is Matrix decompositions Polar decomposition: For a linear operator there exists a unitary operator and positive operators so that Singular value decomposition: For a square matrix there exists unitary matrices and a diagonal matrix with non-negative elements (singular values), such that
14 2.2 Postulates of quantum mechanics State space Postulate 1: Associated to any isolated physical system is a Hilbert space, known as the state space of the system. The system is completely described by its state vector, a unit vector in the state space Definitions/names A two-level, qubit state can generally be written as This is a superposition of the two basis states and, with amplitudes and The normalization condition gives
15 Evolution Postulate 2: The evolution of a quantum system is described by a unitary transformation. That is, the state of the system at time is related to the state of the system at time by a unitary operator as Postulate 2 : The evolution of state of a quantum system is described by the Schrödinger equation where is Plancks constant and the Hamiltonian, a Hermitian operator.
16 Closed system For a closed system the Hamiltonian and the system state is is independent on time where we define the unitary time evolution operator The Hamiltonian has the spectral decomposition where are the energy eigenstates and the energy. Effective Hamiltonian for open systems For many open systems we have an effective time dependent Hamiltonian acting on the system The solution to the Schrödinger equation is non-trivial
17 Measurement Projection measurement postulate A projective measurement is described by an observable,, an Hermitian operator on the state space of the system. The observable has the spectral decomposition The possible outcomes correspond to the eigenvalues of. Upon measuring the state is given by, the probability of getting the result Given that has occured, the state immediatelly after the measurement is (wavefunction collapse) Measurement problem?
18 Average and fluctuations The average measured value (over an ensemble of identical states ) The magnitude of the quantum fluctuations are Derivation: Heisenbergs uncertainty principle is
19 General measurement Postulate 3: Quantum measurements are described by a collection of measurement operators, acting on the state space of the system. The index refers to the possible measurement outcomes. Upon measuring the state, the probability of getting the result is given by and the state after the measurement is Generally projection The measurement operators satisfy the completeness relation Probabilities sum to one
20 Composite systems Postulate 4: The state space of a composite system is the tensor product of the state spaces of the component systems. If we have systems numbered through, and system is prepared in state, the state of the total system is General measurement and projection II Derivation: Given projection measurements and an ancilla system, derive the general measurement principles.
21 POVM measurement Common formulation of general measurement postulate. A measurement is described by measurement operators. The probability to get the outcome is given by We define the positive operator which has the properties We call the POVM-elements and the set a POVM. Distinghuishing quantum states Given a single copy of one of two non-orthogonal states not possible to determine which state by any measurement., it is Derivation: The example with
22 Entanglement of two qubits A composite state of two qubits that can not be written as a tensor product of the states of the two qubits is entangled, that is Derivation: Show that the Bell state is entangled Entanglement is the energy for quantum information processing
23 2.3 Superdense coding Suppose that Alice wants to send two bits of classical information to Bob by only sending one qubit. Can she do it? 2 classical bits 1 qubit Alice Bob Derivation: Superdense coding
Lecture 4: Postulates of quantum mechanics
 Lecture 4: Postulates of quantum mechanics Rajat Mittal IIT Kanpur The postulates of quantum mechanics provide us the mathematical formalism over which the physical theory is developed. For people studying
Lecture 4: Postulates of quantum mechanics Rajat Mittal IIT Kanpur The postulates of quantum mechanics provide us the mathematical formalism over which the physical theory is developed. For people studying
Hilbert Space, Entanglement, Quantum Gates, Bell States, Superdense Coding.
 CS 94- Bell States Bell Inequalities 9//04 Fall 004 Lecture Hilbert Space Entanglement Quantum Gates Bell States Superdense Coding 1 One qubit: Recall that the state of a single qubit can be written as
CS 94- Bell States Bell Inequalities 9//04 Fall 004 Lecture Hilbert Space Entanglement Quantum Gates Bell States Superdense Coding 1 One qubit: Recall that the state of a single qubit can be written as
Introduction to Quantum Mechanics
 Introduction to Quantum Mechanics R. J. Renka Department of Computer Science & Engineering University of North Texas 03/19/2018 Postulates of Quantum Mechanics The postulates (axioms) of quantum mechanics
Introduction to Quantum Mechanics R. J. Renka Department of Computer Science & Engineering University of North Texas 03/19/2018 Postulates of Quantum Mechanics The postulates (axioms) of quantum mechanics
Quantum Computing Lecture 3. Principles of Quantum Mechanics. Anuj Dawar
 Quantum Computing Lecture 3 Principles of Quantum Mechanics Anuj Dawar What is Quantum Mechanics? Quantum Mechanics is a framework for the development of physical theories. It is not itself a physical
Quantum Computing Lecture 3 Principles of Quantum Mechanics Anuj Dawar What is Quantum Mechanics? Quantum Mechanics is a framework for the development of physical theories. It is not itself a physical
Quantum Computing Lecture 2. Review of Linear Algebra
 Quantum Computing Lecture 2 Review of Linear Algebra Maris Ozols Linear algebra States of a quantum system form a vector space and their transformations are described by linear operators Vector spaces
Quantum Computing Lecture 2 Review of Linear Algebra Maris Ozols Linear algebra States of a quantum system form a vector space and their transformations are described by linear operators Vector spaces
)j > Riley Tipton Perry University of New South Wales, Australia. World Scientific CHENNAI
 Riley Tipton Perry University of New South Wales, Australia )j > World Scientific NEW JERSEY LONDON. SINGAPORE BEIJING SHANSHAI HONG K0N6 TAIPEI» CHENNAI Contents Acknowledgments xi 1. Introduction 1 1.1
Riley Tipton Perry University of New South Wales, Australia )j > World Scientific NEW JERSEY LONDON. SINGAPORE BEIJING SHANSHAI HONG K0N6 TAIPEI» CHENNAI Contents Acknowledgments xi 1. Introduction 1 1.1
Quantum Mechanics II: Examples
 Quantum Mechanics II: Examples Michael A. Nielsen University of Queensland Goals: 1. To apply the principles introduced in the last lecture to some illustrative examples: superdense coding, and quantum
Quantum Mechanics II: Examples Michael A. Nielsen University of Queensland Goals: 1. To apply the principles introduced in the last lecture to some illustrative examples: superdense coding, and quantum
1 Fundamental physical postulates. C/CS/Phys C191 Quantum Mechanics in a Nutshell I 10/04/07 Fall 2007 Lecture 12
 C/CS/Phys C191 Quantum Mechanics in a Nutshell I 10/04/07 Fall 2007 Lecture 12 In this and the next lecture we summarize the essential physical and mathematical aspects of quantum mechanics relevant to
C/CS/Phys C191 Quantum Mechanics in a Nutshell I 10/04/07 Fall 2007 Lecture 12 In this and the next lecture we summarize the essential physical and mathematical aspects of quantum mechanics relevant to
An Introduction to Quantum Information. By Aditya Jain. Under the Guidance of Dr. Guruprasad Kar PAMU, ISI Kolkata
 An Introduction to Quantum Information By Aditya Jain Under the Guidance of Dr. Guruprasad Kar PAMU, ISI Kolkata 1. Introduction Quantum information is physical information that is held in the state of
An Introduction to Quantum Information By Aditya Jain Under the Guidance of Dr. Guruprasad Kar PAMU, ISI Kolkata 1. Introduction Quantum information is physical information that is held in the state of
1 Mathematical preliminaries
 1 Mathematical preliminaries The mathematical language of quantum mechanics is that of vector spaces and linear algebra. In this preliminary section, we will collect the various definitions and mathematical
1 Mathematical preliminaries The mathematical language of quantum mechanics is that of vector spaces and linear algebra. In this preliminary section, we will collect the various definitions and mathematical
Some Introductory Notes on Quantum Computing
 Some Introductory Notes on Quantum Computing Markus G. Kuhn http://www.cl.cam.ac.uk/~mgk25/ Computer Laboratory University of Cambridge 2000-04-07 1 Quantum Computing Notation Quantum Computing is best
Some Introductory Notes on Quantum Computing Markus G. Kuhn http://www.cl.cam.ac.uk/~mgk25/ Computer Laboratory University of Cambridge 2000-04-07 1 Quantum Computing Notation Quantum Computing is best
CS286.2 Lecture 15: Tsirelson s characterization of XOR games
 CS86. Lecture 5: Tsirelson s characterization of XOR games Scribe: Zeyu Guo We first recall the notion of quantum multi-player games: a quantum k-player game involves a verifier V and k players P,...,
CS86. Lecture 5: Tsirelson s characterization of XOR games Scribe: Zeyu Guo We first recall the notion of quantum multi-player games: a quantum k-player game involves a verifier V and k players P,...,
Introduction to Quantum Computing
 Introduction to Quantum Computing Petros Wallden Lecture 3: Basic Quantum Mechanics 26th September 2016 School of Informatics, University of Edinburgh Resources 1. Quantum Computation and Quantum Information
Introduction to Quantum Computing Petros Wallden Lecture 3: Basic Quantum Mechanics 26th September 2016 School of Informatics, University of Edinburgh Resources 1. Quantum Computation and Quantum Information
Lecture notes on Quantum Computing. Chapter 1 Mathematical Background
 Lecture notes on Quantum Computing Chapter 1 Mathematical Background Vector states of a quantum system with n physical states are represented by unique vectors in C n, the set of n 1 column vectors 1 For
Lecture notes on Quantum Computing Chapter 1 Mathematical Background Vector states of a quantum system with n physical states are represented by unique vectors in C n, the set of n 1 column vectors 1 For
Short Course in Quantum Information Lecture 2
 Short Course in Quantum Information Lecture Formal Structure of Quantum Mechanics Course Info All materials downloadable @ website http://info.phys.unm.edu/~deutschgroup/deutschclasses.html Syllabus Lecture
Short Course in Quantum Information Lecture Formal Structure of Quantum Mechanics Course Info All materials downloadable @ website http://info.phys.unm.edu/~deutschgroup/deutschclasses.html Syllabus Lecture
Quantum Physics II (8.05) Fall 2002 Assignment 3
 Quantum Physics II (8.05) Fall 00 Assignment Readings The readings below will take you through the material for Problem Sets and 4. Cohen-Tannoudji Ch. II, III. Shankar Ch. 1 continues to be helpful. Sakurai
Quantum Physics II (8.05) Fall 00 Assignment Readings The readings below will take you through the material for Problem Sets and 4. Cohen-Tannoudji Ch. II, III. Shankar Ch. 1 continues to be helpful. Sakurai
Chapter 5. Density matrix formalism
 Chapter 5 Density matrix formalism In chap we formulated quantum mechanics for isolated systems. In practice systems interect with their environnement and we need a description that takes this feature
Chapter 5 Density matrix formalism In chap we formulated quantum mechanics for isolated systems. In practice systems interect with their environnement and we need a description that takes this feature
Contents. Preface for the Instructor. Preface for the Student. xvii. Acknowledgments. 1 Vector Spaces 1 1.A R n and C n 2
 Contents Preface for the Instructor xi Preface for the Student xv Acknowledgments xvii 1 Vector Spaces 1 1.A R n and C n 2 Complex Numbers 2 Lists 5 F n 6 Digression on Fields 10 Exercises 1.A 11 1.B Definition
Contents Preface for the Instructor xi Preface for the Student xv Acknowledgments xvii 1 Vector Spaces 1 1.A R n and C n 2 Complex Numbers 2 Lists 5 F n 6 Digression on Fields 10 Exercises 1.A 11 1.B Definition
Introduction to Quantum Information Hermann Kampermann
 Introduction to Quantum Information Hermann Kampermann Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf Theoretische Physik III Summer school Bleubeuren July 014 Contents 1 Quantum Mechanics...........................
Introduction to Quantum Information Hermann Kampermann Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf Theoretische Physik III Summer school Bleubeuren July 014 Contents 1 Quantum Mechanics...........................
DECAY OF SINGLET CONVERSION PROBABILITY IN ONE DIMENSIONAL QUANTUM NETWORKS
 DECAY OF SINGLET CONVERSION PROBABILITY IN ONE DIMENSIONAL QUANTUM NETWORKS SCOTT HOTTOVY Abstract. Quantum networks are used to transmit and process information by using the phenomena of quantum mechanics.
DECAY OF SINGLET CONVERSION PROBABILITY IN ONE DIMENSIONAL QUANTUM NETWORKS SCOTT HOTTOVY Abstract. Quantum networks are used to transmit and process information by using the phenomena of quantum mechanics.
Quantum decoherence. Éric Oliver Paquette (U. Montréal) -Traces Worshop [Ottawa]- April 29 th, Quantum decoherence p. 1/2
![Quantum decoherence. Éric Oliver Paquette (U. Montréal) -Traces Worshop [Ottawa]- April 29 th, Quantum decoherence p. 1/2 Quantum decoherence. Éric Oliver Paquette (U. Montréal) -Traces Worshop [Ottawa]- April 29 th, Quantum decoherence p. 1/2](/thumbs/78/77811482.jpg) Quantum decoherence p. 1/2 Quantum decoherence Éric Oliver Paquette (U. Montréal) -Traces Worshop [Ottawa]- April 29 th, 2007 Quantum decoherence p. 2/2 Outline Quantum decoherence: 1. Basics of quantum
Quantum decoherence p. 1/2 Quantum decoherence Éric Oliver Paquette (U. Montréal) -Traces Worshop [Ottawa]- April 29 th, 2007 Quantum decoherence p. 2/2 Outline Quantum decoherence: 1. Basics of quantum
Physics 215 Quantum Mechanics 1 Assignment 1
 Physics 5 Quantum Mechanics Assignment Logan A. Morrison January 9, 06 Problem Prove via the dual correspondence definition that the hermitian conjugate of α β is β α. By definition, the hermitian conjugate
Physics 5 Quantum Mechanics Assignment Logan A. Morrison January 9, 06 Problem Prove via the dual correspondence definition that the hermitian conjugate of α β is β α. By definition, the hermitian conjugate
C/CS/Phys C191 Quantum Mechanics in a Nutshell 10/06/07 Fall 2009 Lecture 12
 C/CS/Phys C191 Quantum Mechanics in a Nutshell 10/06/07 Fall 2009 Lecture 12 In this lecture we summarize the essential physical and mathematical aspects of quantum mechanics relevant to this course. Topics
C/CS/Phys C191 Quantum Mechanics in a Nutshell 10/06/07 Fall 2009 Lecture 12 In this lecture we summarize the essential physical and mathematical aspects of quantum mechanics relevant to this course. Topics
Lecture: Quantum Information
 Lecture: Quantum Information Transcribed by: Crystal Noel and Da An (Chi Chi) November 10, 016 1 Final Proect Information Find an issue related to class you are interested in and either: read some papers
Lecture: Quantum Information Transcribed by: Crystal Noel and Da An (Chi Chi) November 10, 016 1 Final Proect Information Find an issue related to class you are interested in and either: read some papers
1 Algebra of State Vectors
 J. Rothberg October 6, Introduction to Quantum Mechanics: Part Algebra of State Vectors What does the State Vector mean? A state vector is not a property of a physical system, but rather represents an
J. Rothberg October 6, Introduction to Quantum Mechanics: Part Algebra of State Vectors What does the State Vector mean? A state vector is not a property of a physical system, but rather represents an
Ph 219/CS 219. Exercises Due: Friday 20 October 2006
 1 Ph 219/CS 219 Exercises Due: Friday 20 October 2006 1.1 How far apart are two quantum states? Consider two quantum states described by density operators ρ and ρ in an N-dimensional Hilbert space, and
1 Ph 219/CS 219 Exercises Due: Friday 20 October 2006 1.1 How far apart are two quantum states? Consider two quantum states described by density operators ρ and ρ in an N-dimensional Hilbert space, and
Ph 219/CS 219. Exercises Due: Friday 3 November 2006
 Ph 9/CS 9 Exercises Due: Friday 3 November 006. Fidelity We saw in Exercise. that the trace norm ρ ρ tr provides a useful measure of the distinguishability of the states ρ and ρ. Another useful measure
Ph 9/CS 9 Exercises Due: Friday 3 November 006. Fidelity We saw in Exercise. that the trace norm ρ ρ tr provides a useful measure of the distinguishability of the states ρ and ρ. Another useful measure
. Here we are using the standard inner-product over C k to define orthogonality. Recall that the inner-product of two vectors φ = i α i.
 CS 94- Hilbert Spaces, Tensor Products, Quantum Gates, Bell States 1//07 Spring 007 Lecture 01 Hilbert Spaces Consider a discrete quantum system that has k distinguishable states (eg k distinct energy
CS 94- Hilbert Spaces, Tensor Products, Quantum Gates, Bell States 1//07 Spring 007 Lecture 01 Hilbert Spaces Consider a discrete quantum system that has k distinguishable states (eg k distinct energy
The Postulates of Quantum Mechanics
 p. 1/23 The Postulates of Quantum Mechanics We have reviewed the mathematics (complex linear algebra) necessary to understand quantum mechanics. We will now see how the physics of quantum mechanics fits
p. 1/23 The Postulates of Quantum Mechanics We have reviewed the mathematics (complex linear algebra) necessary to understand quantum mechanics. We will now see how the physics of quantum mechanics fits
PHY305: Notes on Entanglement and the Density Matrix
 PHY305: Notes on Entanglement and the Density Matrix Here follows a short summary of the definitions of qubits, EPR states, entanglement, the density matrix, pure states, mixed states, measurement, and
PHY305: Notes on Entanglement and the Density Matrix Here follows a short summary of the definitions of qubits, EPR states, entanglement, the density matrix, pure states, mixed states, measurement, and
9. Distance measures. 9.1 Classical information measures. Head Tail. How similar/close are two probability distributions? Trace distance.
 9. Distance measures 9.1 Classical information measures How similar/close are two probability distributions? Trace distance Fidelity Example: Flipping two coins, one fair one biased Head Tail Trace distance
9. Distance measures 9.1 Classical information measures How similar/close are two probability distributions? Trace distance Fidelity Example: Flipping two coins, one fair one biased Head Tail Trace distance
C/CS/Phys 191 Quantum Mechanics in a Nutshell I 10/04/05 Fall 2005 Lecture 11
 C/CS/Phys 191 Quantum Mechanics in a Nutshell I 10/04/05 Fall 2005 Lecture 11 In this and the next lecture we summarize the essential physical and mathematical aspects of quantum mechanics relevant to
C/CS/Phys 191 Quantum Mechanics in a Nutshell I 10/04/05 Fall 2005 Lecture 11 In this and the next lecture we summarize the essential physical and mathematical aspects of quantum mechanics relevant to
MP 472 Quantum Information and Computation
 MP 472 Quantum Information and Computation http://www.thphys.may.ie/staff/jvala/mp472.htm Outline Open quantum systems The density operator ensemble of quantum states general properties the reduced density
MP 472 Quantum Information and Computation http://www.thphys.may.ie/staff/jvala/mp472.htm Outline Open quantum systems The density operator ensemble of quantum states general properties the reduced density
Lecture 3: Hilbert spaces, tensor products
 CS903: Quantum computation and Information theory (Special Topics In TCS) Lecture 3: Hilbert spaces, tensor products This lecture will formalize many of the notions introduced informally in the second
CS903: Quantum computation and Information theory (Special Topics In TCS) Lecture 3: Hilbert spaces, tensor products This lecture will formalize many of the notions introduced informally in the second
Quantum Gates, Circuits & Teleportation
 Chapter 3 Quantum Gates, Circuits & Teleportation Unitary Operators The third postulate of quantum physics states that the evolution of a quantum system is necessarily unitary. Geometrically, a unitary
Chapter 3 Quantum Gates, Circuits & Teleportation Unitary Operators The third postulate of quantum physics states that the evolution of a quantum system is necessarily unitary. Geometrically, a unitary
2.0 Basic Elements of a Quantum Information Processor. 2.1 Classical information processing The carrier of information
 QSIT09.L03 Page 1 2.0 Basic Elements of a Quantum Information Processor 2.1 Classical information processing 2.1.1 The carrier of information - binary representation of information as bits (Binary digits).
QSIT09.L03 Page 1 2.0 Basic Elements of a Quantum Information Processor 2.1 Classical information processing 2.1.1 The carrier of information - binary representation of information as bits (Binary digits).
1 Readings. 2 Unitary Operators. C/CS/Phys C191 Unitaries and Quantum Gates 9/22/09 Fall 2009 Lecture 8
 C/CS/Phys C191 Unitaries and Quantum Gates 9//09 Fall 009 Lecture 8 1 Readings Benenti, Casati, and Strini: Classical circuits and computation Ch.1.,.6 Quantum Gates Ch. 3.-3.4 Kaye et al: Ch. 1.1-1.5,
C/CS/Phys C191 Unitaries and Quantum Gates 9//09 Fall 009 Lecture 8 1 Readings Benenti, Casati, and Strini: Classical circuits and computation Ch.1.,.6 Quantum Gates Ch. 3.-3.4 Kaye et al: Ch. 1.1-1.5,
1. Basic rules of quantum mechanics
 1. Basic rules of quantum mechanics How to describe the states of an ideally controlled system? How to describe changes in an ideally controlled system? How to describe measurements on an ideally controlled
1. Basic rules of quantum mechanics How to describe the states of an ideally controlled system? How to describe changes in an ideally controlled system? How to describe measurements on an ideally controlled
A Course in Quantum Information Theory
 A Course in Quantum Information Theory Ofer Shayevitz Spring 2007 Based on lectures given at the Tel Aviv University Edited by Anatoly Khina Version compiled January 9, 2010 Contents 1 Preliminaries 3
A Course in Quantum Information Theory Ofer Shayevitz Spring 2007 Based on lectures given at the Tel Aviv University Edited by Anatoly Khina Version compiled January 9, 2010 Contents 1 Preliminaries 3
1 Dirac Notation for Vector Spaces
 Theoretical Physics Notes 2: Dirac Notation This installment of the notes covers Dirac notation, which proves to be very useful in many ways. For example, it gives a convenient way of expressing amplitudes
Theoretical Physics Notes 2: Dirac Notation This installment of the notes covers Dirac notation, which proves to be very useful in many ways. For example, it gives a convenient way of expressing amplitudes
msqm 2011/8/14 21:35 page 189 #197
 msqm 2011/8/14 21:35 page 189 #197 Bibliography Dirac, P. A. M., The Principles of Quantum Mechanics, 4th Edition, (Oxford University Press, London, 1958). Feynman, R. P. and A. P. Hibbs, Quantum Mechanics
msqm 2011/8/14 21:35 page 189 #197 Bibliography Dirac, P. A. M., The Principles of Quantum Mechanics, 4th Edition, (Oxford University Press, London, 1958). Feynman, R. P. and A. P. Hibbs, Quantum Mechanics
Chapter 2. Mathematical formalism of quantum mechanics. 2.1 Linear algebra in Dirac s notation
 Chapter Mathematical formalism of quantum mechanics Quantum mechanics is the best theory that we have to explain the physical phenomena, except for gravity. The elaboration of the theory has been guided
Chapter Mathematical formalism of quantum mechanics Quantum mechanics is the best theory that we have to explain the physical phenomena, except for gravity. The elaboration of the theory has been guided
Ensembles and incomplete information
 p. 1/32 Ensembles and incomplete information So far in this course, we have described quantum systems by states that are normalized vectors in a complex Hilbert space. This works so long as (a) the system
p. 1/32 Ensembles and incomplete information So far in this course, we have described quantum systems by states that are normalized vectors in a complex Hilbert space. This works so long as (a) the system
SUPERDENSE CODING AND QUANTUM TELEPORTATION
 SUPERDENSE CODING AND QUANTUM TELEPORTATION YAQIAO LI This note tries to rephrase mathematically superdense coding and quantum teleportation explained in [] Section.3 and.3.7, respectively (as if I understood
SUPERDENSE CODING AND QUANTUM TELEPORTATION YAQIAO LI This note tries to rephrase mathematically superdense coding and quantum teleportation explained in [] Section.3 and.3.7, respectively (as if I understood
The following definition is fundamental.
 1. Some Basics from Linear Algebra With these notes, I will try and clarify certain topics that I only quickly mention in class. First and foremost, I will assume that you are familiar with many basic
1. Some Basics from Linear Algebra With these notes, I will try and clarify certain topics that I only quickly mention in class. First and foremost, I will assume that you are familiar with many basic
Lecture 2: Linear operators
 Lecture 2: Linear operators Rajat Mittal IIT Kanpur The mathematical formulation of Quantum computing requires vector spaces and linear operators So, we need to be comfortable with linear algebra to study
Lecture 2: Linear operators Rajat Mittal IIT Kanpur The mathematical formulation of Quantum computing requires vector spaces and linear operators So, we need to be comfortable with linear algebra to study
Introduction to quantum information processing
 Introduction to quantum information processing Measurements and quantum probability Brad Lackey 25 October 2016 MEASUREMENTS AND QUANTUM PROBABILITY 1 of 22 OUTLINE 1 Probability 2 Density Operators 3
Introduction to quantum information processing Measurements and quantum probability Brad Lackey 25 October 2016 MEASUREMENTS AND QUANTUM PROBABILITY 1 of 22 OUTLINE 1 Probability 2 Density Operators 3
Math 108b: Notes on the Spectral Theorem
 Math 108b: Notes on the Spectral Theorem From section 6.3, we know that every linear operator T on a finite dimensional inner product space V has an adjoint. (T is defined as the unique linear operator
Math 108b: Notes on the Spectral Theorem From section 6.3, we know that every linear operator T on a finite dimensional inner product space V has an adjoint. (T is defined as the unique linear operator
Categories and Quantum Informatics: Hilbert spaces
 Categories and Quantum Informatics: Hilbert spaces Chris Heunen Spring 2018 We introduce our main example category Hilb by recalling in some detail the mathematical formalism that underlies quantum theory:
Categories and Quantum Informatics: Hilbert spaces Chris Heunen Spring 2018 We introduce our main example category Hilb by recalling in some detail the mathematical formalism that underlies quantum theory:
Basics on quantum information
 Basics on quantum information Mika Hirvensalo Department of Mathematics and Statistics University of Turku mikhirve@utu.fi Thessaloniki, May 2016 Mika Hirvensalo Basics on quantum information 1 of 52 Brief
Basics on quantum information Mika Hirvensalo Department of Mathematics and Statistics University of Turku mikhirve@utu.fi Thessaloniki, May 2016 Mika Hirvensalo Basics on quantum information 1 of 52 Brief
II. The Machinery of Quantum Mechanics
 II. The Machinery of Quantum Mechanics Based on the results of the experiments described in the previous section, we recognize that real experiments do not behave quite as we expect. This section presents
II. The Machinery of Quantum Mechanics Based on the results of the experiments described in the previous section, we recognize that real experiments do not behave quite as we expect. This section presents
Basic Notation and Background
 Department of Mathematics, The College of William and Mary, Williamsburg, Virginia, USA; Department of Mathematics, Taiyuan University of Technology, Taiyuan, Shanxi, P.R. of China. Hilbert spaces The
Department of Mathematics, The College of William and Mary, Williamsburg, Virginia, USA; Department of Mathematics, Taiyuan University of Technology, Taiyuan, Shanxi, P.R. of China. Hilbert spaces The
A review on quantum teleportation based on: Teleporting an unknown quantum state via dual classical and Einstein- Podolsky-Rosen channels
 JOURNAL OF CHEMISTRY 57 VOLUME NUMBER DECEMBER 8 005 A review on quantum teleportation based on: Teleporting an unknown quantum state via dual classical and Einstein- Podolsky-Rosen channels Miri Shlomi
JOURNAL OF CHEMISTRY 57 VOLUME NUMBER DECEMBER 8 005 A review on quantum teleportation based on: Teleporting an unknown quantum state via dual classical and Einstein- Podolsky-Rosen channels Miri Shlomi
Quantum Computation. Alessandra Di Pierro Computational models (Circuits, QTM) Algorithms (QFT, Quantum search)
 Quantum Computation Alessandra Di Pierro alessandra.dipierro@univr.it 21 Info + Programme Info: http://profs.sci.univr.it/~dipierro/infquant/ InfQuant1.html Preliminary Programme: Introduction and Background
Quantum Computation Alessandra Di Pierro alessandra.dipierro@univr.it 21 Info + Programme Info: http://profs.sci.univr.it/~dipierro/infquant/ InfQuant1.html Preliminary Programme: Introduction and Background
Introduction into Quantum Computations Alexei Ashikhmin Bell Labs
 Introduction into Quantum Computations Alexei Ashikhmin Bell Labs Workshop on Quantum Computing and its Application March 16, 2017 Qubits Unitary transformations Quantum Circuits Quantum Measurements Quantum
Introduction into Quantum Computations Alexei Ashikhmin Bell Labs Workshop on Quantum Computing and its Application March 16, 2017 Qubits Unitary transformations Quantum Circuits Quantum Measurements Quantum
Basics on quantum information
 Basics on quantum information Mika Hirvensalo Department of Mathematics and Statistics University of Turku mikhirve@utu.fi Thessaloniki, May 2014 Mika Hirvensalo Basics on quantum information 1 of 49 Brief
Basics on quantum information Mika Hirvensalo Department of Mathematics and Statistics University of Turku mikhirve@utu.fi Thessaloniki, May 2014 Mika Hirvensalo Basics on quantum information 1 of 49 Brief
The Framework of Quantum Mechanics
 The Framework of Quantum Mechanics We now use the mathematical formalism covered in the last lecture to describe the theory of quantum mechanics. In the first section we outline four axioms that lie at
The Framework of Quantum Mechanics We now use the mathematical formalism covered in the last lecture to describe the theory of quantum mechanics. In the first section we outline four axioms that lie at
Quantum NP - Cont. Classical and Quantum Computation A.Yu Kitaev, A. Shen, M. N. Vyalyi 2002
 Quantum NP - Cont. Classical and Quantum Computation A.Yu Kitaev, A. Shen, M. N. Vyalyi 2002 1 QMA - the quantum analog to MA (and NP). Definition 1 QMA. The complexity class QMA is the class of all languages
Quantum NP - Cont. Classical and Quantum Computation A.Yu Kitaev, A. Shen, M. N. Vyalyi 2002 1 QMA - the quantum analog to MA (and NP). Definition 1 QMA. The complexity class QMA is the class of all languages
Quantum information and quantum computing
 Middle East Technical University, Department of Physics January 7, 009 Outline Measurement 1 Measurement 3 Single qubit gates Multiple qubit gates 4 Distinguishability 5 What s measurement? Quantum measurement
Middle East Technical University, Department of Physics January 7, 009 Outline Measurement 1 Measurement 3 Single qubit gates Multiple qubit gates 4 Distinguishability 5 What s measurement? Quantum measurement
Supplementary information I Hilbert Space, Dirac Notation, and Matrix Mechanics. EE270 Fall 2017
 Supplementary information I Hilbert Space, Dirac Notation, and Matrix Mechanics Properties of Vector Spaces Unit vectors ~xi form a basis which spans the space and which are orthonormal ( if i = j ~xi
Supplementary information I Hilbert Space, Dirac Notation, and Matrix Mechanics Properties of Vector Spaces Unit vectors ~xi form a basis which spans the space and which are orthonormal ( if i = j ~xi
Quantum Information & Quantum Computing
 Math 478, Phys 478, CS4803, February 9, 006 1 Georgia Tech Math, Physics & Computing Math 478, Phys 478, CS4803 Quantum Information & Quantum Computing Problems Set 1 Due February 9, 006 Part I : 1. Read
Math 478, Phys 478, CS4803, February 9, 006 1 Georgia Tech Math, Physics & Computing Math 478, Phys 478, CS4803 Quantum Information & Quantum Computing Problems Set 1 Due February 9, 006 Part I : 1. Read
C/CS/Phys 191 Quantum Gates and Universality 9/22/05 Fall 2005 Lecture 8. a b b d. w. Therefore, U preserves norms and angles (up to sign).
 C/CS/Phys 191 Quantum Gates and Universality 9//05 Fall 005 Lecture 8 1 Readings Benenti, Casati, and Strini: Classical circuits and computation Ch.1.,.6 Quantum Gates Ch. 3.-3.4 Universality Ch. 3.5-3.6
C/CS/Phys 191 Quantum Gates and Universality 9//05 Fall 005 Lecture 8 1 Readings Benenti, Casati, and Strini: Classical circuits and computation Ch.1.,.6 Quantum Gates Ch. 3.-3.4 Universality Ch. 3.5-3.6
Review problems for MA 54, Fall 2004.
 Review problems for MA 54, Fall 2004. Below are the review problems for the final. They are mostly homework problems, or very similar. If you are comfortable doing these problems, you should be fine on
Review problems for MA 54, Fall 2004. Below are the review problems for the final. They are mostly homework problems, or very similar. If you are comfortable doing these problems, you should be fine on
Quantum Computing 1. Multi-Qubit System. Goutam Biswas. Lect 2
 Quantum Computing 1 Multi-Qubit System Quantum Computing State Space of Bits The state space of a single bit is {0,1}. n-bit state space is {0,1} n. These are the vertices of the n-dimensional hypercube.
Quantum Computing 1 Multi-Qubit System Quantum Computing State Space of Bits The state space of a single bit is {0,1}. n-bit state space is {0,1} n. These are the vertices of the n-dimensional hypercube.
Final Exam, Linear Algebra, Fall, 2003, W. Stephen Wilson
 Final Exam, Linear Algebra, Fall, 2003, W. Stephen Wilson Name: TA Name and section: NO CALCULATORS, SHOW ALL WORK, NO OTHER PAPERS ON DESK. There is very little actual work to be done on this exam if
Final Exam, Linear Algebra, Fall, 2003, W. Stephen Wilson Name: TA Name and section: NO CALCULATORS, SHOW ALL WORK, NO OTHER PAPERS ON DESK. There is very little actual work to be done on this exam if
PLEASE LET ME KNOW IF YOU FIND TYPOS (send to
 Teoretisk Fysik KTH Advanced QM (SI2380), Lecture 2 (Summary of concepts) 1 PLEASE LET ME KNOW IF YOU FIND TYPOS (send email to langmann@kth.se) The laws of QM 1. I now discuss the laws of QM and their
Teoretisk Fysik KTH Advanced QM (SI2380), Lecture 2 (Summary of concepts) 1 PLEASE LET ME KNOW IF YOU FIND TYPOS (send email to langmann@kth.se) The laws of QM 1. I now discuss the laws of QM and their
Quantum Mechanics and Quantum Computing: an Introduction. Des Johnston, Notes by Bernd J. Schroers Heriot-Watt University
 Quantum Mechanics and Quantum Computing: an Introduction Des Johnston, Notes by Bernd J. Schroers Heriot-Watt University Contents Preface page Introduction. Quantum mechanics (partly excerpted from Wikipedia).
Quantum Mechanics and Quantum Computing: an Introduction Des Johnston, Notes by Bernd J. Schroers Heriot-Watt University Contents Preface page Introduction. Quantum mechanics (partly excerpted from Wikipedia).
Mathematical foundations - linear algebra
 Mathematical foundations - linear algebra Andrea Passerini passerini@disi.unitn.it Machine Learning Vector space Definition (over reals) A set X is called a vector space over IR if addition and scalar
Mathematical foundations - linear algebra Andrea Passerini passerini@disi.unitn.it Machine Learning Vector space Definition (over reals) A set X is called a vector space over IR if addition and scalar
Tutorial on Quantum Computing. Vwani P. Roychowdhury. Lecture 1: Introduction
 Tutorial on Quantum Computing Vwani P. Roychowdhury Lecture 1: Introduction 1 & ) &! # Fundamentals Qubits A single qubit is a two state system, such as a two level atom we denote two orthogonal states
Tutorial on Quantum Computing Vwani P. Roychowdhury Lecture 1: Introduction 1 & ) &! # Fundamentals Qubits A single qubit is a two state system, such as a two level atom we denote two orthogonal states
Vector spaces and operators
 Vector spaces and operators Sourendu Gupta TIFR, Mumbai, India Quantum Mechanics 1 2013 22 August, 2013 1 Outline 2 Setting up 3 Exploring 4 Keywords and References Quantum states are vectors We saw that
Vector spaces and operators Sourendu Gupta TIFR, Mumbai, India Quantum Mechanics 1 2013 22 August, 2013 1 Outline 2 Setting up 3 Exploring 4 Keywords and References Quantum states are vectors We saw that
3.024 Electrical, Optical, and Magnetic Properties of Materials Spring 2012 Recitation 1. Office Hours: MWF 9am-10am or by appointment
 Adam Floyd Hannon Office Hours: MWF 9am-10am or by e-mail appointment Topic Outline 1. a. Fourier Transform & b. Fourier Series 2. Linear Algebra Review 3. Eigenvalue/Eigenvector Problems 1. a. Fourier
Adam Floyd Hannon Office Hours: MWF 9am-10am or by e-mail appointment Topic Outline 1. a. Fourier Transform & b. Fourier Series 2. Linear Algebra Review 3. Eigenvalue/Eigenvector Problems 1. a. Fourier
Linear Algebra using Dirac Notation: Pt. 2
 Linear Algebra using Dirac Notation: Pt. 2 PHYS 476Q - Southern Illinois University February 6, 2018 PHYS 476Q - Southern Illinois University Linear Algebra using Dirac Notation: Pt. 2 February 6, 2018
Linear Algebra using Dirac Notation: Pt. 2 PHYS 476Q - Southern Illinois University February 6, 2018 PHYS 476Q - Southern Illinois University Linear Algebra using Dirac Notation: Pt. 2 February 6, 2018
Private quantum subsystems and error correction
 Private quantum subsystems and error correction Sarah Plosker Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Brandon University September 26, 2014 Outline 1 Classical Versus Quantum Setting Classical Setting
Private quantum subsystems and error correction Sarah Plosker Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Brandon University September 26, 2014 Outline 1 Classical Versus Quantum Setting Classical Setting
Introduction to Quantum Computing
 Introduction to Quantum Computing Lecture The rules and math of quantum mechanics Enter the Qubit First we start out with the basic block of quantum computing. Analogous to the bit in classical computing,
Introduction to Quantum Computing Lecture The rules and math of quantum mechanics Enter the Qubit First we start out with the basic block of quantum computing. Analogous to the bit in classical computing,
Chapter III. Quantum Computation. Mathematical preliminaries. A.1 Complex numbers. A.2 Linear algebra review
 Chapter III Quantum Computation These lecture notes are exclusively for the use of students in Prof. MacLennan s Unconventional Computation course. c 2017, B. J. MacLennan, EECS, University of Tennessee,
Chapter III Quantum Computation These lecture notes are exclusively for the use of students in Prof. MacLennan s Unconventional Computation course. c 2017, B. J. MacLennan, EECS, University of Tennessee,
CS286.2 Lecture 8: A variant of QPCP for multiplayer entangled games
 CS286.2 Lecture 8: A variant of QPCP for multiplayer entangled games Scribe: Zeyu Guo In the first lecture, we saw three equivalent variants of the classical PCP theorems in terms of CSP, proof checking,
CS286.2 Lecture 8: A variant of QPCP for multiplayer entangled games Scribe: Zeyu Guo In the first lecture, we saw three equivalent variants of the classical PCP theorems in terms of CSP, proof checking,
Ir O D = D = ( ) Section 2.6 Example 1. (Bottom of page 119) dim(v ) = dim(l(v, W )) = dim(v ) dim(f ) = dim(v )
 Section 3.2 Theorem 3.6. Let A be an m n matrix of rank r. Then r m, r n, and, by means of a finite number of elementary row and column operations, A can be transformed into the matrix ( ) Ir O D = 1 O
Section 3.2 Theorem 3.6. Let A be an m n matrix of rank r. Then r m, r n, and, by means of a finite number of elementary row and column operations, A can be transformed into the matrix ( ) Ir O D = 1 O
Basic Calculus Review
 Basic Calculus Review Lorenzo Rosasco ISML Mod. 2 - Machine Learning Vector Spaces Functionals and Operators (Matrices) Vector Space A vector space is a set V with binary operations +: V V V and : R V
Basic Calculus Review Lorenzo Rosasco ISML Mod. 2 - Machine Learning Vector Spaces Functionals and Operators (Matrices) Vector Space A vector space is a set V with binary operations +: V V V and : R V
Qubits vs. bits: a naive account A bit: admits two values 0 and 1, admits arbitrary transformations. is freely readable,
 Qubits vs. bits: a naive account A bit: admits two values 0 and 1, admits arbitrary transformations. is freely readable, A qubit: a sphere of values, which is spanned in projective sense by two quantum
Qubits vs. bits: a naive account A bit: admits two values 0 and 1, admits arbitrary transformations. is freely readable, A qubit: a sphere of values, which is spanned in projective sense by two quantum
Mathematical Introduction
 Chapter 1 Mathematical Introduction HW #1: 164, 165, 166, 181, 182, 183, 1811, 1812, 114 11 Linear Vector Spaces: Basics 111 Field A collection F of elements a,b etc (also called numbers or scalars) with
Chapter 1 Mathematical Introduction HW #1: 164, 165, 166, 181, 182, 183, 1811, 1812, 114 11 Linear Vector Spaces: Basics 111 Field A collection F of elements a,b etc (also called numbers or scalars) with
The quantum state as a vector
 The quantum state as a vector February 6, 27 Wave mechanics In our review of the development of wave mechanics, we have established several basic properties of the quantum description of nature:. A particle
The quantum state as a vector February 6, 27 Wave mechanics In our review of the development of wave mechanics, we have established several basic properties of the quantum description of nature:. A particle
Quantum Physics II (8.05) Fall 2004 Assignment 3
 Quantum Physics II (8.5) Fall 24 Assignment 3 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Physics Department Due September 3, 24 September 23, 24 7:pm This week we continue to study the basic principles of quantum
Quantum Physics II (8.5) Fall 24 Assignment 3 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Physics Department Due September 3, 24 September 23, 24 7:pm This week we continue to study the basic principles of quantum
Lecture #1. Review. Postulates of quantum mechanics (1-3) Postulate 1
 L1.P1 Lecture #1 Review Postulates of quantum mechanics (1-3) Postulate 1 The state of a system at any instant of time may be represented by a wave function which is continuous and differentiable. Specifically,
L1.P1 Lecture #1 Review Postulates of quantum mechanics (1-3) Postulate 1 The state of a system at any instant of time may be represented by a wave function which is continuous and differentiable. Specifically,
Quantum Mechanics is Linear Algebra. Noah Graham Middlebury College February 25, 2014
 Quantum Mechanics is Linear Algebra Noah Graham Middlebury College February 25, 24 Linear Algebra Cheat Sheet Column vector quantum state: v = v v 2. Row vector dual state: w = w w 2... Inner product:
Quantum Mechanics is Linear Algebra Noah Graham Middlebury College February 25, 24 Linear Algebra Cheat Sheet Column vector quantum state: v = v v 2. Row vector dual state: w = w w 2... Inner product:
MP463 QUANTUM MECHANICS
 MP463 QUANTUM MECHANICS Introduction Quantum theory of angular momentum Quantum theory of a particle in a central potential - Hydrogen atom - Three-dimensional isotropic harmonic oscillator (a model of
MP463 QUANTUM MECHANICS Introduction Quantum theory of angular momentum Quantum theory of a particle in a central potential - Hydrogen atom - Three-dimensional isotropic harmonic oscillator (a model of
Basic concepts from quantum theory
 B. BASIC CONCEPTS FROM QUANTUM THEORY 77 B Basic concepts from quantum theory B.1 Introduction B.1.a Bases In quantum mechanics certain physical quantities are quantized, such as the energy of an electron
B. BASIC CONCEPTS FROM QUANTUM THEORY 77 B Basic concepts from quantum theory B.1 Introduction B.1.a Bases In quantum mechanics certain physical quantities are quantized, such as the energy of an electron
Functional Analysis Review
 Outline 9.520: Statistical Learning Theory and Applications February 8, 2010 Outline 1 2 3 4 Vector Space Outline A vector space is a set V with binary operations +: V V V and : R V V such that for all
Outline 9.520: Statistical Learning Theory and Applications February 8, 2010 Outline 1 2 3 4 Vector Space Outline A vector space is a set V with binary operations +: V V V and : R V V such that for all
Chapter 2. Linear Algebra. rather simple and learning them will eventually allow us to explain the strange results of
 Chapter 2 Linear Algebra In this chapter, we study the formal structure that provides the background for quantum mechanics. The basic ideas of the mathematical machinery, linear algebra, are rather simple
Chapter 2 Linear Algebra In this chapter, we study the formal structure that provides the background for quantum mechanics. The basic ideas of the mathematical machinery, linear algebra, are rather simple
Math 307 Learning Goals
 Math 307 Learning Goals May 14, 2018 Chapter 1 Linear Equations 1.1 Solving Linear Equations Write a system of linear equations using matrix notation. Use Gaussian elimination to bring a system of linear
Math 307 Learning Goals May 14, 2018 Chapter 1 Linear Equations 1.1 Solving Linear Equations Write a system of linear equations using matrix notation. Use Gaussian elimination to bring a system of linear
Linear Algebra (Review) Volker Tresp 2017
 Linear Algebra (Review) Volker Tresp 2017 1 Vectors k is a scalar (a number) c is a column vector. Thus in two dimensions, c = ( c1 c 2 ) (Advanced: More precisely, a vector is defined in a vector space.
Linear Algebra (Review) Volker Tresp 2017 1 Vectors k is a scalar (a number) c is a column vector. Thus in two dimensions, c = ( c1 c 2 ) (Advanced: More precisely, a vector is defined in a vector space.
If quantum mechanics hasn t profoundly shocked you, you haven t understood it.
 Quantum Mechanics If quantum mechanics hasn t profoundly shocked you, you haven t understood it. Niels Bohr Today, I will tell you more about quantum mechanics what weird thing it is and why it is so weird.
Quantum Mechanics If quantum mechanics hasn t profoundly shocked you, you haven t understood it. Niels Bohr Today, I will tell you more about quantum mechanics what weird thing it is and why it is so weird.
Quantum Mechanics Solutions
 Quantum Mechanics Solutions (a (i f A and B are Hermitian, since (AB = B A = BA, operator AB is Hermitian if and only if A and B commute So, we know that [A,B] = 0, which means that the Hilbert space H
Quantum Mechanics Solutions (a (i f A and B are Hermitian, since (AB = B A = BA, operator AB is Hermitian if and only if A and B commute So, we know that [A,B] = 0, which means that the Hilbert space H
This is the important completeness relation,
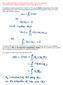 Observable quantities are represented by linear, hermitian operators! Compatible observables correspond to commuting operators! In addition to what was written in eqn 2.1.1, the vector corresponding to
Observable quantities are represented by linear, hermitian operators! Compatible observables correspond to commuting operators! In addition to what was written in eqn 2.1.1, the vector corresponding to
MATH 423 Linear Algebra II Lecture 33: Diagonalization of normal operators.
 MATH 423 Linear Algebra II Lecture 33: Diagonalization of normal operators. Adjoint operator and adjoint matrix Given a linear operator L on an inner product space V, the adjoint of L is a transformation
MATH 423 Linear Algebra II Lecture 33: Diagonalization of normal operators. Adjoint operator and adjoint matrix Given a linear operator L on an inner product space V, the adjoint of L is a transformation
Introduction to Quantum Computing
 Introduction to Quantum Computing Part I Emma Strubell http://cs.umaine.edu/~ema/quantum_tutorial.pdf April 12, 2011 Overview Outline What is quantum computing? Background Caveats Fundamental differences
Introduction to Quantum Computing Part I Emma Strubell http://cs.umaine.edu/~ema/quantum_tutorial.pdf April 12, 2011 Overview Outline What is quantum computing? Background Caveats Fundamental differences
Quantum Teleportation Pt. 1
 Quantum Teleportation Pt. 1 PHYS 500 - Southern Illinois University April 17, 2018 PHYS 500 - Southern Illinois University Quantum Teleportation Pt. 1 April 17, 2018 1 / 13 Types of Communication In the
Quantum Teleportation Pt. 1 PHYS 500 - Southern Illinois University April 17, 2018 PHYS 500 - Southern Illinois University Quantum Teleportation Pt. 1 April 17, 2018 1 / 13 Types of Communication In the
Linear Algebra (Review) Volker Tresp 2018
 Linear Algebra (Review) Volker Tresp 2018 1 Vectors k, M, N are scalars A one-dimensional array c is a column vector. Thus in two dimensions, ( ) c1 c = c 2 c i is the i-th component of c c T = (c 1, c
Linear Algebra (Review) Volker Tresp 2018 1 Vectors k, M, N are scalars A one-dimensional array c is a column vector. Thus in two dimensions, ( ) c1 c = c 2 c i is the i-th component of c c T = (c 1, c
Quantum Mechanics Solutions. λ i λ j v j v j v i v i.
 Quantum Mechanics Solutions 1. (a) If H has an orthonormal basis consisting of the eigenvectors { v i } of A with eigenvalues λ i C, then A can be written in terms of its spectral decomposition as A =
Quantum Mechanics Solutions 1. (a) If H has an orthonormal basis consisting of the eigenvectors { v i } of A with eigenvalues λ i C, then A can be written in terms of its spectral decomposition as A =
A Study of Topological Quantum Error Correcting Codes Part I: From Classical to Quantum ECCs
 A Study of Topological Quantum Error Correcting Codes Part I: From Classical to Quantum ECCs Preetum Nairan preetum@bereley.edu Mar 3, 05 Abstract This survey aims to highlight some interesting ideas in
A Study of Topological Quantum Error Correcting Codes Part I: From Classical to Quantum ECCs Preetum Nairan preetum@bereley.edu Mar 3, 05 Abstract This survey aims to highlight some interesting ideas in
Linear Algebra and Dirac Notation, Pt. 1
 Linear Algebra and Dirac Notation, Pt. 1 PHYS 500 - Southern Illinois University February 1, 2017 PHYS 500 - Southern Illinois University Linear Algebra and Dirac Notation, Pt. 1 February 1, 2017 1 / 13
Linear Algebra and Dirac Notation, Pt. 1 PHYS 500 - Southern Illinois University February 1, 2017 PHYS 500 - Southern Illinois University Linear Algebra and Dirac Notation, Pt. 1 February 1, 2017 1 / 13
