Hartmut Buhmann. Physikalisches Institut, EP3 Universität Würzburg Germany
|
|
|
- Clinton Adams
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Hartmut Buhmann Physikalisches Institut, EP3 Universität Würzburg Germany
2 Outline Insulators and Topological Insulators HgTe quantum well structures Two-Dimensional TI Quantum Spin Hall Effect experimental observations: quantized conductivity non-locality spin polarization Three-Dimensional TI Quantum Hall Effect
3 The Insulating States Topologically Generalized C.L.Kane and E.J.Mele, PRL 95, (25) C.L.Kane and E.J.Mele, PRL 95, (25) A.Bernevig and S.-C. Zhang, PRL 96, 1682 (26) C.L.Kane and E.J. Mele, Science 314, 1692 (26)
4 The Usual Boring Insulating State Characterized by energy gap: absence of low energy electronic excitations Covalent Insulator e.g. intrinsic semiconductor Atomic Insulator e.g. solid Ar The vacuum electron E gap ~ 1 ev 4s E gap ~ 1 ev 3p Dirac Vacuum E gap = 2 m e c 2 ~ 1 6 ev Silicon positron ~ hole
5 The Insulating State Topologically Generalized C.L.Kane and E.J.Mele, PRL 95, (25) C.L.Kane and E.J.Mele, PRL 95, (25) A.Bernevig and S.-C. Zhang, PRL 96, 1682 (26) C.L.Kane and E.J. Mele, Science 314, 1692 (26)
6 The Integer Quantum Hall State 2D Cyclotron Motion, Landau Levels E E gap c Energy gap, but NOT an insulator
7 Edge States Quantized Hall conductivity : bulk insulating J E y xy x 2 xy n e h Integer accurate to 1-9
8 Perfect Conductor magnetic field 1d dispersion E k F k F k The QHE state spatially separates the right and left moving states (spinless 1D liquid) suppressed backscattering first example of a new Topological Insulator
9 Topological Insulator
10 Topological Band Theory The distinction between a conventional insulator and the quantum Hall state is a topological property of the manifold of occupied states H( k) : Brillouin zone (torus) Bloch Hamiltonians with energy gap Classified by Chern (or TKNN) integer topological invariant (Thouless et al, 1982) 1 2 n d u u 2i BZ k k k ( k) ( k) u(k) = Bloch wavefunction Insulator : n = IQHE state : xy = n e 2 /h
11 Geometry and Topology Gauss and Bonnet topological 1 2 S KdA 2(1 g) geometric Example: Mug to Torus S: surface K -1 : product of the two radii of curvatures da: area element g: number of handles
12 Edge States The TKNN invariant can only change at a phase transition where the energy gap goes to zero Vacuum Vacuum n = n = 3 n = Dn = # Chiral Edge Modes This approach can actually be generalized to a spinfull QHE at zero magnetic field: the Quantum Spin Hall Effect
13 The Insulating State Topologically Generalized C.L.Kane and E.J.Mele, PRL 95, (25) C.L.Kane and E.J.Mele, PRL 95, (25) A.Bernevig and S.-C. Zhang, PRL 96, 1682 (26) C.L.Kane and E.J. Mele, Science 314, 1692 (26)
14 A two-dimensional topological insulator B quantum Hall effect topological invariant broken time reversal symmetry (TRS)
15 A two-dimensional topological insulator B
16 A two-dimensional topological insulator B helical edge states invariant under time reversal
17 Protected Edge States suppressed backscattering:
18 Protected Edge States suppressed backscattering: spin rotation: Dj = 2 Interference is destructive
19 Quantum Spin Hall Effect Stability of Helical Edge States: x 2e h G QSHE 2 x backscattering is only possible by time reversal symmetry breaking processes (for example external magnetic fields) or if more states are present k s k, s, 2 1, x x x x
20 Topological Insulator : A New B= Phase
21 Topological Insulator : A New B= Phase There are 2 classes of 2D time reversal invariant band structures Z 2 topological invariant: n =,1 Edge States for <k</a n= : Conventional Insulator n=1 : Topological Insulator Kramers degenerate at time reversal invariant momenta k* = k* + G k*= k*=/a k*= k*=/a even number of bands crossing Fermi energy odd number of bands crossing Fermi energy
22 QSHE in Graphene Graphene edge states gap C.L.Kane and E.J.Mele, PRL 95, (25) Graphene spin-orbit coupling strength is too weak gap only about 3 mev. not accessible in experiments
23 QSHE in HgTe Helical edge states for inverted HgTe QW E H1 E1 k B.A Bernevig, T.L. Hughes, S.C. Zhang, Science 314, 1757 (26)
24
25 HgTe band structure semi-metal 1 5 E (mev) -5 D 8 6 E g k (.1 ) 7 semiconductor D.J. Chadi et al. PRB, 358 (1972) fundamental energy gap 6 8 E E 3 mev
26 CdTe and HgTe CdTe HgTe H = H 1 + H D + H mv + H so
27 E (mev) E (mev) HgTe-Quantum Wells QW Barrier 1 HgTe Hg.32 Cd.68 Te VBO k (.1 ) 7 7 k (.1 ) VBO = 57 mev
28 HgTe-Quantum Wells Typ-III QW d 6 HgCdTe HH1 E1 HgTe HgCdTe 8 inverted normal band structure
29 Bandstructure 6 HgTe HgCdTe 6 Zero Gap for 6.3 nm QW structures HgTe HgCdTe 8 8
30 E [mev] E [mev] Dirac Band Structure 8 E2 d c 4 E1 H1-4 H2 H3-8 H d [nm] E1 H1 in-plane direction (k x,k y )=(1,) (k x,k y )=(1,1) -1 H k [nm -1 ]
31 xx [ xx [ Zero Gap B = 1 T 8k 7k 7 6 B = 5 T 3k xy [e²/h] k 5k 4k 3k 2k xy [e²/h] k 1k 1k -1 -,5,,5 1, V G - V Dirac [V] V G - V Dirac [V] B. Büttner et al., Nature Physics 7, 418 (211)
32 LL-Dispersion Kane model effective model LLchart Parameters: M ~ (-.35 mev) D = mev nm² G = mev nm² A = mev nm E(VG) conversion taken from appropriate Kane model B. Büttner et al., Nature Physics 7, 418 (211)
33 Finite Mobility 1.4 xx 8k 6k xx,min =.36 e²/h 1.2 measurement theory 1. 4k 2k DV G xx in e 2 /h V G -V Dirac [V] T [K] B. Büttner et al., Nature Physics 7, 418 (211)
34 Bandstructure 6 HgTe HgCdTe 6 HgTe HgCdTe 8 8 B.A Bernevig et al., Science 314, 1757 (26)
35 Effective Tight Binding Model square lattice with 4 orbitals per site s,, s,, ( p ip ),, ( p ip ), x y x y nearest neighbor hopping integral basis: E1, H1, E1, H1 hk ( ) Heff ( kx, ky) * h ( k)
36 Effective Tight Binding Model square lattice with 4 orbitals per site s,, s,, ( p ip ),, ( p ip ), x y x y nearest neighbor hopping integral basis: E1, H1, E1, H1 hk ( ) Heff ( kx, ky) * h ( k) at the -point k A k h( k) A relativistic Dirac equation 2 M ( k) k Asin k sin x i kx sin kx isin kx M ( k) k 2 M ( k) Ak x ikx x ikx M ( k) HgTe M normalqw for M inverted QW with tunable parameter M (band-gap)
37 Mass domain wall inverted band structure E H1 E1 k states localized on the domain wall which disperse along the x-direction y M> M< y M> x M< M x M> helical edge states
38 Quantum Spin Hall Effect M > M < normal insulator QSHE bulk entire sample insulating bulk insulating
39
40 x G 2e h 2 x
41 Experiment e e k k
42 Small Samples L W (L x W) mm 2. x 1. mm 1. x 1. mm 1. x.5 mm
43 QSHE Size Dependence 1 6 (1 x 1) mm 2 non-inverted R xx / (2 x 1) mm 2 (1 x 1) mm 2 G = 2 e 2 /h 1 3 (1 x.5) mm (V Gate - V thr ) / V König et al., Science 318, 766 (27)
44 R 2-8, 9-11 (k) QSHE Temperature Dependence Q2367 Microhallbar 1 x 1 mm 2 I(2-8), U(9-11); B= T; T= variabel; T = 1.8 K T = 2.5 K T = 4.2 K T = 6.4 K T = 9.8 K T = 19 K T = 28 K T = 48 K U G (V)
45 R (kohm) QSHE Excitation Voltage Dependence mV 14mV 12mV 1mV 8mV 6mV 4mV 2mV U g (V)
46 Conductance Quantization in 4-terminal geometry!? 2 18 V 16 R xx / k G = 2 e 2 /h I (V Gate - V thr ) / V
47 Small Samples
48 Role of Ohmic Contacts n-type metallic contact areas and leads areas where scattering takes place spin relaxation
49 Multi-Terminal Probe T t t I e G h I e G h m m m m generally ) ( e h n R t 3 exp 4 2 t t R R h e G t 2,exp 4 2 Landauer-Büttiker Formalism normal conducting contacts no QSHE ji j ij i ii i i T R M h e I m m 2
50 QSHE in inverted HgTe-QWs 4 35 G = 2/3 e 2 /h V I 4 R xx (k V 3 I G = 2 e 2 /h (2 x 1) mm 2 (1 x.5) mm (V Gate - V thr ) (V) R R 2t 4t 3
51 Non-locality mm 2 mm 6 5 4
52 I (na) Rnl (k) Non-locality I: 1-4 V nl :2-3 V V 3 I mk U Gate [ V ] A. Roth, HB et al., Science 325,295 (29)
53 R (k) Non-locality I: 1-3 V nl : LB: 8.6 k 12 V 1 8 G=3 e 2 /h 4-terminal V* (V) A. Roth, HB et al., Science 325,295 (29)
54 Non-locality 1 2 I: 1-4 V nl :2-3 V LB: 6.4 k 5 G=4 e 2 /h R 14,23 / k V gate / V A. Roth, HB et al., Science 325,295 (29)
55 R nl (k) Non-locality V LB: 4.3 k , -5,5-5, -4,5-4, -3,5-3, V (V) A. Roth, HB et al., Science 325,295 (29)
56 Back Scattering potential fluctuations introduce areas of normal metallic (n- or p-) conductance in which back scattering becomes possible QSHE The potential landscape is modified by gate (density) sweeps!
57 Back Scattering area of raised or lowered chem. Pot. the probalility for back scatterring increases strength length additional ohmic contact transition from a two to a three terminal device
58 Additional Scattering Potential Transition from scattering strength 2 e 2 /h 3/2 e 2 /h A. Roth, HB et al., Science 325,295 (29)
59 Additional Scattering Potential R 14,23 / k V gate / V A. Roth, HB et al., Science 325,295 (29)
60 Rnl (kw) Potential Fluctuations V LB: 4.3 k one additional contact: between 2 and k 4 3 V x A. Roth, HB et al., Science 325,295 (29)
61 V Potential Fluctuations different gate sweep direction V x LB: 22.1 k R nl / k 15 1 LB: 12.9 k V g / V Hysteresis effects due to charging of trap states at the SC-insulator interface J. Hinz, HB et al., Semicond. Sci. Technol. 21 (26) 51 56
62 metal insulator QW HgTe Quantum Well Structures layer structure impurity states discharging charging gate insulator Au 1 nm Si N /SiO cap layer doping layer barrier quantum well barrier doping layer buffer substrate 25 nm HgCdTe x =.7 1 nm HgCdTe x =.7 9 nm HgCdTe with I 1 nm HgCdTe x = nm HgTe 1 nm HgCdTe x =.7 9 nm HgCdTe with I 1 nm HgCdTe x =.7 25 nm CdTe CdZnTe(1) hysteresis effects: J. Hinz et al., Semicond. Sci. Technol. 21 (26) 51 56
63
64 Spin Polarizer
65 Spin Polarizer 5% 1 : 4 5%
66 Spin Polarizer 1% 1 % 5% 1%
67 Spin Injector 1% spin injection 1 % even with backscattering!
68 Spin Detection 1% Dm spin detector 1 %
69 QSHE SHE QSHE Spin Hall Effect as creator and analyzer of spin polarized electrons SHE -1
70 Split Gate H-Bar
71 QSHE Spin-Detector x n-type injector.8.6 5x QSHI-type detector detector sweep QSHE.2 p-type injector SHE V detector-gate / V 4 QSHI-type detector R 34,12 / k V injector-gate / V injector sweep
72 n-regime Q2198 p-regime E / mev n = cm -2 n H1 dl = cm -2 E1 H k / nm -1 E F E / mev p = cm -2 n dl = cm -2 H1 Dk E1 H k / nm -1 E F eex j s, y pf pf Dk 16m J.Sinova et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 92, (24) Intrinsic Spin Hall Effekt Nature Physics 6, 448 (21)
73 QSHE Spin-Injector x n-type detector.8.6 5x QSHI-type detector injector sweep QSHE.2 p-type detector SHE QSHI-type injector R 12,34 / k V detector-gate / V detector sweep
74 n-type 1 detector sweep 1 V 8 8 V R nonloc / 6 4 R nonloc / U gate / V p-type U gate / V R nonloc / 6 4 R nonloc / U gate / V U gate / V
75 Spin-Current Switch I 2 I 1
76 Spin-Current Switch I 2 I 1
77 Spin-Current Switch I 2 I 1 QSHE
78 Spin-Current Switch I 2 I 1 ballistic injection
79 I [na] ballstic 5, 9/1 11/12 1/2 4,5 4, 3,5 B I A C D F I E 3, 8/7 6/5 4/3 2,5 2, 1,5 QSHE 1, -3, -2,5-2, -1,5-1, -,5, U (Gate ACDF) [V]
80 I [na] I [na] /1 11/12 1/ B I A C D F I E 1 5, 9 4,5-3, -2,5-2, -1,5-1, -,5, U (Gate ACDF) [V] 8/7 6/5 4/3 4, 3,5 3, 2,5 2, 1,5 1, -3, -2,5-2, -1,5-1, -,5, U (Gate ACDF) [V]
81
82
83
84 ¼ Graphene
85
86 E, mev Bulk HgTe 2 1 E F fully strained 7 nm HgTe on CdTe substrate ,3 -,2 -,1,,1,2,3 k, nm -1 band structure - gap openning - two Dirac cones on different surfaces Qy*1(rlu) x-ray diffraction (115 reflex) Q2424-map_1.xrdml Qx*1(rlu)
87 R xx in Ohm R xy in Ohm n= n=3 n= R xx (SdH) R xy (Hall) B in Tesla 4 2
88 R xx [k] xy [e 2 /h] B [T] R xy [k] B [T] Brüne et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 16, (211)
89 R xx in Ohm DOS Density of states for two independent surfaces with slightly different density 1 8 n n cm 11-2 cm B in Tesla
90 Brüne et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 16, (211)
91 Summary the QSH effect which consists of an insulating bulk and two counter propagating spin polarized edge channels (Kramers doublet) quantized edge channel transport the QSH effect can be used as an effective spin injector and spin detector with 1 % spin polarization properties Strained HgTe bulk exhibits two-dimensional surface states
92 Acknowledgements Quantum Transport Group (Würzburg, ) C. Brüne C. Ames P. Leubner Ex-QT: C.R. Becker T. Beringer M. Lebrecht J. Schneider S. Wiedmann N. Eikenberg R. Rommel F. Gerhard B. Krefft A. Roth B. Büttner R. Pfeuffer L. Maier M. Mühlbauer A. Friedel Stanford University S.-C. Zhang X.L. Qi J. Maciejko T. L. Hughes M. König C. Thienel H. Thierschmann R. Schaller J. Mutterer A. Astakhova CX Liu Lehrstuhl für Experimentelle Physik 3: L.W. Molenkamp Collaborations: Texas A&M University J. Sinova Univ. Würzburg Inst. f. Theoretische Physik E.M. Hankiewicz B. Trautzettel
93 Quantum Spin Hall Effekt Science 318, 766 (27) The Quantum Spin Hall Effect: Theory and Experiment J. Phys. Soc. Jap. Vol. 77, 317 (28) Nonlocal edge state transport in the quantum spin Hall state Science 325, 294 (29) Intrinsic Spin Hall Effekt Nature Physics 6, 448 (21) Quantum Hall Effect from the Topological Surface States of Strained Bulk HgTe Phys. Rev. Lett. 16, (211)
Hartmut Buhmann. Physikalisches Institut, EP3 Universität Würzburg Germany
 Hartmut Buhmann Physikalisches Institut, EP3 Universität Würzburg Germany Part I and II Insulators and Topological Insulators HgTe crystal structure Part III quantum wells Two-Dimensional TI Quantum Spin
Hartmut Buhmann Physikalisches Institut, EP3 Universität Würzburg Germany Part I and II Insulators and Topological Insulators HgTe crystal structure Part III quantum wells Two-Dimensional TI Quantum Spin
Spin-orbit Effects in Semiconductor Spintronics. Laurens Molenkamp Physikalisches Institut (EP3) University of Würzburg
 Spin-orbit Effects in Semiconductor Spintronics Laurens Molenkamp Physikalisches Institut (EP3) University of Würzburg Collaborators Hartmut Buhmann, Charlie Becker, Volker Daumer, Yongshen Gui Matthias
Spin-orbit Effects in Semiconductor Spintronics Laurens Molenkamp Physikalisches Institut (EP3) University of Würzburg Collaborators Hartmut Buhmann, Charlie Becker, Volker Daumer, Yongshen Gui Matthias
The Quantum Spin Hall Effect
 The Quantum Spin Hall Effect Shou-Cheng Zhang Stanford University with Andrei Bernevig, Taylor Hughes Science, 314,1757 2006 Molenamp et al, Science, 318, 766 2007 XL Qi, T. Hughes, SCZ preprint The quantum
The Quantum Spin Hall Effect Shou-Cheng Zhang Stanford University with Andrei Bernevig, Taylor Hughes Science, 314,1757 2006 Molenamp et al, Science, 318, 766 2007 XL Qi, T. Hughes, SCZ preprint The quantum
Topological insulators
 http://www.physik.uni-regensburg.de/forschung/fabian Topological insulators Jaroslav Fabian Institute for Theoretical Physics University of Regensburg Stara Lesna, 21.8.212 DFG SFB 689 what are topological
http://www.physik.uni-regensburg.de/forschung/fabian Topological insulators Jaroslav Fabian Institute for Theoretical Physics University of Regensburg Stara Lesna, 21.8.212 DFG SFB 689 what are topological
Laurens W. Molenkamp. Physikalisches Institut, EP3 Universität Würzburg
 Laurens W. Molenkamp Physikalisches Institut, EP3 Universität Würzburg Overview - HgTe/CdTe bandstructure, quantum spin Hall effect: 2D TI - Dirac surface states of strained bulk HgTe: 3D TI - Topological
Laurens W. Molenkamp Physikalisches Institut, EP3 Universität Würzburg Overview - HgTe/CdTe bandstructure, quantum spin Hall effect: 2D TI - Dirac surface states of strained bulk HgTe: 3D TI - Topological
InAs/GaSb A New 2D Topological Insulator
 InAs/GaSb A New 2D Topological Insulator 1. Old Material for New Physics 2. Quantized Edge Modes 3. Adreev Reflection 4. Summary Rui-Rui Du Rice University Superconductor Hybrids Villard de Lans, France
InAs/GaSb A New 2D Topological Insulator 1. Old Material for New Physics 2. Quantized Edge Modes 3. Adreev Reflection 4. Summary Rui-Rui Du Rice University Superconductor Hybrids Villard de Lans, France
What is a topological insulator? Ming-Che Chang Dept of Physics, NTNU
 What is a topological insulator? Ming-Che Chang Dept of Physics, NTNU A mini course on topology extrinsic curvature K vs intrinsic (Gaussian) curvature G K 0 G 0 G>0 G=0 K 0 G=0 G
What is a topological insulator? Ming-Che Chang Dept of Physics, NTNU A mini course on topology extrinsic curvature K vs intrinsic (Gaussian) curvature G K 0 G 0 G>0 G=0 K 0 G=0 G
Notes on Topological Insulators and Quantum Spin Hall Effect. Jouko Nieminen Tampere University of Technology.
 Notes on Topological Insulators and Quantum Spin Hall Effect Jouko Nieminen Tampere University of Technology. Not so much discussed concept in this session: topology. In math, topology discards small details
Notes on Topological Insulators and Quantum Spin Hall Effect Jouko Nieminen Tampere University of Technology. Not so much discussed concept in this session: topology. In math, topology discards small details
Introductory lecture on topological insulators. Reza Asgari
 Introductory lecture on topological insulators Reza Asgari Workshop on graphene and topological insulators, IPM. 19-20 Oct. 2011 Outlines -Introduction New phases of materials, Insulators -Theory quantum
Introductory lecture on topological insulators Reza Asgari Workshop on graphene and topological insulators, IPM. 19-20 Oct. 2011 Outlines -Introduction New phases of materials, Insulators -Theory quantum
Topological Insulators
 Topological Insulators Aira Furusai (Condensed Matter Theory Lab.) = topological insulators (3d and 2d) Outline Introduction: band theory Example of topological insulators: integer quantum Hall effect
Topological Insulators Aira Furusai (Condensed Matter Theory Lab.) = topological insulators (3d and 2d) Outline Introduction: band theory Example of topological insulators: integer quantum Hall effect
Introduction to topological insulators. Jennifer Cano
 Introduction to topological insulators Jennifer Cano Adapted from Charlie Kane s Windsor Lectures: http://www.physics.upenn.edu/~kane/ Review article: Hasan & Kane Rev. Mod. Phys. 2010 What is an insulator?
Introduction to topological insulators Jennifer Cano Adapted from Charlie Kane s Windsor Lectures: http://www.physics.upenn.edu/~kane/ Review article: Hasan & Kane Rev. Mod. Phys. 2010 What is an insulator?
Topological insulator (TI)
 Topological insulator (TI) Haldane model: QHE without Landau level Quantized spin Hall effect: 2D topological insulators: Kane-Mele model for graphene HgTe quantum well InAs/GaSb quantum well 3D topological
Topological insulator (TI) Haldane model: QHE without Landau level Quantized spin Hall effect: 2D topological insulators: Kane-Mele model for graphene HgTe quantum well InAs/GaSb quantum well 3D topological
Quantum Spin Hall Insulator State in HgTe Quantum Wells
 SLAC-PUB-15949 Quantum Spin Hall Insulator State in HgTe Quantum Wells Markus König 1, Steffen Wiedmann 1, Christoph Brüne 1, Andreas Roth 1, Hartmut Buhmann 1, Laurens W. Molenkamp 1,, Xiao-Liang Qi 2
SLAC-PUB-15949 Quantum Spin Hall Insulator State in HgTe Quantum Wells Markus König 1, Steffen Wiedmann 1, Christoph Brüne 1, Andreas Roth 1, Hartmut Buhmann 1, Laurens W. Molenkamp 1,, Xiao-Liang Qi 2
InAs/GaSb A New Quantum Spin Hall Insulator
 InAs/GaSb A New Quantum Spin Hall Insulator Rui-Rui Du Rice University 1. Old Material for New Physics 2. Quantized Edge Modes 3. Andreev Reflection 4. Summary KITP Workshop on Topological Insulator/Superconductor
InAs/GaSb A New Quantum Spin Hall Insulator Rui-Rui Du Rice University 1. Old Material for New Physics 2. Quantized Edge Modes 3. Andreev Reflection 4. Summary KITP Workshop on Topological Insulator/Superconductor
Quantum Spin Hall Effect: a theoretical and experimental introduction at kindergarten level, non-shown version
 Quantum Spin Hall Effect: a theoretical and experimental introduction at kindergarten level, non-shown version Ze-Yang Li 1, Jia-Chen Yu 2 and Shang-Jie Xue 3 December 21, 2015 1 光学所 2 凝聚态所 3 量 材料中 Historical
Quantum Spin Hall Effect: a theoretical and experimental introduction at kindergarten level, non-shown version Ze-Yang Li 1, Jia-Chen Yu 2 and Shang-Jie Xue 3 December 21, 2015 1 光学所 2 凝聚态所 3 量 材料中 Historical
Topological insulators
 Oddelek za fiziko Seminar 1 b 1. letnik, II. stopnja Topological insulators Author: Žiga Kos Supervisor: prof. dr. Dragan Mihailović Ljubljana, June 24, 2013 Abstract In the seminar, the basic ideas behind
Oddelek za fiziko Seminar 1 b 1. letnik, II. stopnja Topological insulators Author: Žiga Kos Supervisor: prof. dr. Dragan Mihailović Ljubljana, June 24, 2013 Abstract In the seminar, the basic ideas behind
Topological Insulators and Superconductors
 Topological Insulators and Superconductors Lecture #1: Topology and Band Theory Lecture #: Topological Insulators in and 3 dimensions Lecture #3: Topological Superconductors, Majorana Fermions an Topological
Topological Insulators and Superconductors Lecture #1: Topology and Band Theory Lecture #: Topological Insulators in and 3 dimensions Lecture #3: Topological Superconductors, Majorana Fermions an Topological
Topological Insulators and Superconductors. Tokyo 2010 Shoucheng Zhang, Stanford University
 Topological Insulators and Superconductors Tokyo 2010 Shoucheng Zhang, Stanford University Colloborators Stanford group: Xiaoliang Qi, Andrei Bernevig, Congjun Wu, Chaoxing Liu, Taylor Hughes, Sri Raghu,
Topological Insulators and Superconductors Tokyo 2010 Shoucheng Zhang, Stanford University Colloborators Stanford group: Xiaoliang Qi, Andrei Bernevig, Congjun Wu, Chaoxing Liu, Taylor Hughes, Sri Raghu,
Topological Insulators
 Topological Insulators A new state of matter with three dimensional topological electronic order L. Andrew Wray Lawrence Berkeley National Lab Princeton University Surface States (Topological Order in
Topological Insulators A new state of matter with three dimensional topological electronic order L. Andrew Wray Lawrence Berkeley National Lab Princeton University Surface States (Topological Order in
Spatially resolved study of backscattering in the quantum spin Hall state SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL
 Spatially resolved study of backscattering in the quantum spin Hall state SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Markus König 1,2, Matthias Baenninger 1,2, Andrei G. F. Garcia 1, Nahid Harjee 3, Beth L. Pruitt 4, C. Ames
Spatially resolved study of backscattering in the quantum spin Hall state SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Markus König 1,2, Matthias Baenninger 1,2, Andrei G. F. Garcia 1, Nahid Harjee 3, Beth L. Pruitt 4, C. Ames
Basics of topological insulator
 011/11/18 @ NTU Basics of topological insulator Ming-Che Chang Dept of Physics, NTNU A brief history of insulators Band insulator (Wilson, Bloch) Mott insulator Anderson insulator Quantum Hall insulator
011/11/18 @ NTU Basics of topological insulator Ming-Che Chang Dept of Physics, NTNU A brief history of insulators Band insulator (Wilson, Bloch) Mott insulator Anderson insulator Quantum Hall insulator
Topological Insulator Surface States and Electrical Transport. Alexander Pearce Intro to Topological Insulators: Week 11 February 2, / 21
 Topological Insulator Surface States and Electrical Transport Alexander Pearce Intro to Topological Insulators: Week 11 February 2, 2017 1 / 21 This notes are predominately based on: J.K. Asbóth, L. Oroszlány
Topological Insulator Surface States and Electrical Transport Alexander Pearce Intro to Topological Insulators: Week 11 February 2, 2017 1 / 21 This notes are predominately based on: J.K. Asbóth, L. Oroszlány
Topological insulators and the quantum anomalous Hall state. David Vanderbilt Rutgers University
 Topological insulators and the quantum anomalous Hall state David Vanderbilt Rutgers University Outline Berry curvature and topology 2D quantum anomalous Hall (QAH) insulator TR-invariant insulators (Z
Topological insulators and the quantum anomalous Hall state David Vanderbilt Rutgers University Outline Berry curvature and topology 2D quantum anomalous Hall (QAH) insulator TR-invariant insulators (Z
Topological insulator with time-reversal symmetry
 Phys620.nb 101 7 Topological insulator with time-reversal symmetry Q: Can we get a topological insulator that preserves the time-reversal symmetry? A: Yes, with the help of the spin degree of freedom.
Phys620.nb 101 7 Topological insulator with time-reversal symmetry Q: Can we get a topological insulator that preserves the time-reversal symmetry? A: Yes, with the help of the spin degree of freedom.
Spin orbit interaction in graphene monolayers & carbon nanotubes
 Spin orbit interaction in graphene monolayers & carbon nanotubes Reinhold Egger Institut für Theoretische Physik, Düsseldorf Alessandro De Martino Andreas Schulz, Artur Hütten MPI Dresden, 25.10.2011 Overview
Spin orbit interaction in graphene monolayers & carbon nanotubes Reinhold Egger Institut für Theoretische Physik, Düsseldorf Alessandro De Martino Andreas Schulz, Artur Hütten MPI Dresden, 25.10.2011 Overview
Lecture notes on topological insulators
 Lecture notes on topological insulators Ming-Che Chang Department of Physics, National Taiwan Normal University, Taipei, Taiwan (Dated: November 1, 18) Contents I. D Topological insulator 1 A. General
Lecture notes on topological insulators Ming-Che Chang Department of Physics, National Taiwan Normal University, Taipei, Taiwan (Dated: November 1, 18) Contents I. D Topological insulator 1 A. General
Local currents in a two-dimensional topological insulator
 Local currents in a two-dimensional topological insulator Xiaoqian Dang, J. D. Burton and Evgeny Y. Tsymbal Department of Physics and Astronomy Nebraska Center for Materials and Nanoscience University
Local currents in a two-dimensional topological insulator Xiaoqian Dang, J. D. Burton and Evgeny Y. Tsymbal Department of Physics and Astronomy Nebraska Center for Materials and Nanoscience University
Topological Physics in Band Insulators II
 Topological Physics in Band Insulators II Gene Mele University of Pennsylvania Topological Insulators in Two and Three Dimensions The canonical list of electric forms of matter is actually incomplete Conductor
Topological Physics in Band Insulators II Gene Mele University of Pennsylvania Topological Insulators in Two and Three Dimensions The canonical list of electric forms of matter is actually incomplete Conductor
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 19 Dec 2008
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 19 Dec 2008 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 19 Dec 2008](/thumbs/72/67207946.jpg) Ballistic Intrinsic Spin-Hall Effect in HgTe Nanostructures C. Brüne 1, A. Roth 1, E.G. Novik 1, M. König 1, H. Buhmann 1, E.M. Hankiewicz, W. Hanke, J. Sinova 3, and L. W. Molenkamp 1 1 Physikalisches
Ballistic Intrinsic Spin-Hall Effect in HgTe Nanostructures C. Brüne 1, A. Roth 1, E.G. Novik 1, M. König 1, H. Buhmann 1, E.M. Hankiewicz, W. Hanke, J. Sinova 3, and L. W. Molenkamp 1 1 Physikalisches
From graphene to Z2 topological insulator
 From graphene to Z2 topological insulator single Dirac topological AL mass U U valley WL ordinary mass or ripples WL U WL AL AL U AL WL Rashba Ken-Ichiro Imura Condensed-Matter Theory / Tohoku Univ. Dirac
From graphene to Z2 topological insulator single Dirac topological AL mass U U valley WL ordinary mass or ripples WL U WL AL AL U AL WL Rashba Ken-Ichiro Imura Condensed-Matter Theory / Tohoku Univ. Dirac
5 Topological insulator with time-reversal symmetry
 Phys62.nb 63 5 Topological insulator with time-reversal symmetry It is impossible to have quantum Hall effect without breaking the time-reversal symmetry. xy xy. If we want xy to be invariant under, xy
Phys62.nb 63 5 Topological insulator with time-reversal symmetry It is impossible to have quantum Hall effect without breaking the time-reversal symmetry. xy xy. If we want xy to be invariant under, xy
Quantum Hall effect. Quantization of Hall resistance is incredibly precise: good to 1 part in I believe. WHY?? G xy = N e2 h.
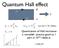 Quantum Hall effect V1 V2 R L I I x = N e2 h V y V x =0 G xy = N e2 h n.b. h/e 2 = 25 kohms Quantization of Hall resistance is incredibly precise: good to 1 part in 10 10 I believe. WHY?? Robustness Why
Quantum Hall effect V1 V2 R L I I x = N e2 h V y V x =0 G xy = N e2 h n.b. h/e 2 = 25 kohms Quantization of Hall resistance is incredibly precise: good to 1 part in 10 10 I believe. WHY?? Robustness Why
Symmetries in Quantum Transport : From Random Matrix Theory to Topological Insulators. Philippe Jacquod. U of Arizona
 Symmetries in Quantum Transport : From Random Matrix Theory to Topological Insulators Philippe Jacquod U of Arizona UA Phys colloquium - feb 1, 2013 Continuous symmetries and conservation laws Noether
Symmetries in Quantum Transport : From Random Matrix Theory to Topological Insulators Philippe Jacquod U of Arizona UA Phys colloquium - feb 1, 2013 Continuous symmetries and conservation laws Noether
Topological Kondo Insulator SmB 6. Tetsuya Takimoto
 Topological Kondo Insulator SmB 6 J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 80 123720, (2011). Tetsuya Takimoto Department of Physics, Hanyang University Collaborator: Ki-Hoon Lee (POSTECH) Content 1. Introduction of SmB 6 in-gap
Topological Kondo Insulator SmB 6 J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 80 123720, (2011). Tetsuya Takimoto Department of Physics, Hanyang University Collaborator: Ki-Hoon Lee (POSTECH) Content 1. Introduction of SmB 6 in-gap
Disordered topological insulators with time-reversal symmetry: Z 2 invariants
 Keio Topo. Science (2016/11/18) Disordered topological insulators with time-reversal symmetry: Z 2 invariants Hosho Katsura Department of Physics, UTokyo Collaborators: Yutaka Akagi (UTokyo) Tohru Koma
Keio Topo. Science (2016/11/18) Disordered topological insulators with time-reversal symmetry: Z 2 invariants Hosho Katsura Department of Physics, UTokyo Collaborators: Yutaka Akagi (UTokyo) Tohru Koma
Organizing Principles for Understanding Matter
 Organizing Principles for Understanding Matter Symmetry Conceptual simplification Conservation laws Distinguish phases of matter by pattern of broken symmetries Topology Properties insensitive to smooth
Organizing Principles for Understanding Matter Symmetry Conceptual simplification Conservation laws Distinguish phases of matter by pattern of broken symmetries Topology Properties insensitive to smooth
Symmetry, Topology and Phases of Matter
 Symmetry, Topology and Phases of Matter E E k=λ a k=λ b k=λ a k=λ b Topological Phases of Matter Many examples of topological band phenomena States adiabatically connected to independent electrons: - Quantum
Symmetry, Topology and Phases of Matter E E k=λ a k=λ b k=λ a k=λ b Topological Phases of Matter Many examples of topological band phenomena States adiabatically connected to independent electrons: - Quantum
Quantum anomalous Hall states on decorated magnetic surfaces
 Quantum anomalous Hall states on decorated magnetic surfaces David Vanderbilt Rutgers University Kevin Garrity & D.V. Phys. Rev. Lett.110, 116802 (2013) Recently: Topological insulators (TR-invariant)
Quantum anomalous Hall states on decorated magnetic surfaces David Vanderbilt Rutgers University Kevin Garrity & D.V. Phys. Rev. Lett.110, 116802 (2013) Recently: Topological insulators (TR-invariant)
Effective Field Theories of Topological Insulators
 Effective Field Theories of Topological Insulators Eduardo Fradkin University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Workshop on Field Theoretic Computer Simulations for Particle Physics and Condensed Matter
Effective Field Theories of Topological Insulators Eduardo Fradkin University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Workshop on Field Theoretic Computer Simulations for Particle Physics and Condensed Matter
First-Principles Calculation of Topological Invariants (Wannier Functions Approach) Alexey A. Soluyanov
 First-Principles Calculation of Topological Invariants (Wannier Functions Approach) Alexey A. Soluyanov ES'12, WFU, June 8, 212 The present work was done in collaboration with David Vanderbilt Outline:
First-Principles Calculation of Topological Invariants (Wannier Functions Approach) Alexey A. Soluyanov ES'12, WFU, June 8, 212 The present work was done in collaboration with David Vanderbilt Outline:
Topological insulators. Pavel Buividovich (Regensburg)
 Topological insulators Pavel Buividovich (Regensburg) Hall effect Classical treatment Dissipative motion for point-like particles (Drude theory) Steady motion Classical Hall effect Cyclotron frequency
Topological insulators Pavel Buividovich (Regensburg) Hall effect Classical treatment Dissipative motion for point-like particles (Drude theory) Steady motion Classical Hall effect Cyclotron frequency
2D Materials with Strong Spin-orbit Coupling: Topological and Electronic Transport Properties
 2D Materials with Strong Spin-orbit Coupling: Topological and Electronic Transport Properties Artem Pulkin California Institute of Technology (Caltech), Pasadena, CA 91125, US Institute of Physics, Ecole
2D Materials with Strong Spin-orbit Coupling: Topological and Electronic Transport Properties Artem Pulkin California Institute of Technology (Caltech), Pasadena, CA 91125, US Institute of Physics, Ecole
Spin Hall and quantum spin Hall effects. Shuichi Murakami Department of Physics, Tokyo Institute of Technology PRESTO, JST
 YKIS2007 (Kyoto) Nov.16, 2007 Spin Hall and quantum spin Hall effects Shuichi Murakami Department of Physics, Tokyo Institute of Technology PRESTO, JST Introduction Spin Hall effect spin Hall effect in
YKIS2007 (Kyoto) Nov.16, 2007 Spin Hall and quantum spin Hall effects Shuichi Murakami Department of Physics, Tokyo Institute of Technology PRESTO, JST Introduction Spin Hall effect spin Hall effect in
Zürich. Transport in InAs-GaSb quantum wells. Klaus Ensslin
 Transport in InAs-GaSb quantum wells Klaus Ensslin Solid State Physics the material system ambipolar behavior non-local transport inverted bandstructure Zürich Collaborators: S. Müller, M. Karalic, C.
Transport in InAs-GaSb quantum wells Klaus Ensslin Solid State Physics the material system ambipolar behavior non-local transport inverted bandstructure Zürich Collaborators: S. Müller, M. Karalic, C.
Supplementary Online Information : Images of edge current in InAs/GaSb quantum wells
 Supplementary Online Information : Images of edge current in InAs/GaSb quantum wells Eric M. Spanton, 1, 2 Katja C. Nowack, 1, 3 Lingjie Du, 4 Gerard Sullivan, 5 Rui-Rui Du, 4 1, 2, 3 and Kathryn A. Moler
Supplementary Online Information : Images of edge current in InAs/GaSb quantum wells Eric M. Spanton, 1, 2 Katja C. Nowack, 1, 3 Lingjie Du, 4 Gerard Sullivan, 5 Rui-Rui Du, 4 1, 2, 3 and Kathryn A. Moler
POEM: Physics of Emergent Materials
 POEM: Physics of Emergent Materials Nandini Trivedi L1: Spin Orbit Coupling L2: Topology and Topological Insulators Tutorials: May 24, 25 (2017) Scope of Lectures and Anchor Points: 1.Spin-Orbit Interaction
POEM: Physics of Emergent Materials Nandini Trivedi L1: Spin Orbit Coupling L2: Topology and Topological Insulators Tutorials: May 24, 25 (2017) Scope of Lectures and Anchor Points: 1.Spin-Orbit Interaction
ARPES experiments on 3D topological insulators. Inna Vishik Physics 250 (Special topics: spectroscopies of quantum materials) UC Davis, Fall 2016
 ARPES experiments on 3D topological insulators Inna Vishik Physics 250 (Special topics: spectroscopies of quantum materials) UC Davis, Fall 2016 Outline Using ARPES to demonstrate that certain materials
ARPES experiments on 3D topological insulators Inna Vishik Physics 250 (Special topics: spectroscopies of quantum materials) UC Davis, Fall 2016 Outline Using ARPES to demonstrate that certain materials
Proximity-induced magnetization dynamics, interaction effects, and phase transitions on a topological surface
 Proximity-induced magnetization dynamics, interaction effects, and phase transitions on a topological surface Ilya Eremin Theoretische Physik III, Ruhr-Uni Bochum Work done in collaboration with: F. Nogueira
Proximity-induced magnetization dynamics, interaction effects, and phase transitions on a topological surface Ilya Eremin Theoretische Physik III, Ruhr-Uni Bochum Work done in collaboration with: F. Nogueira
Topological Insulators and Ferromagnets: appearance of flat surface bands
 Topological Insulators and Ferromagnets: appearance of flat surface bands Thomas Dahm University of Bielefeld T. Paananen and T. Dahm, PRB 87, 195447 (2013) T. Paananen et al, New J. Phys. 16, 033019 (2014)
Topological Insulators and Ferromagnets: appearance of flat surface bands Thomas Dahm University of Bielefeld T. Paananen and T. Dahm, PRB 87, 195447 (2013) T. Paananen et al, New J. Phys. 16, 033019 (2014)
Physics of Semiconductors
 Physics of Semiconductors 13 th 2016.7.11 Shingo Katsumoto Department of Physics and Institute for Solid State Physics University of Tokyo Outline today Laughlin s justification Spintronics Two current
Physics of Semiconductors 13 th 2016.7.11 Shingo Katsumoto Department of Physics and Institute for Solid State Physics University of Tokyo Outline today Laughlin s justification Spintronics Two current
Bloch, Landau, and Dirac: Hofstadter s Butterfly in Graphene. Philip Kim. Physics Department, Columbia University
 Bloch, Landau, and Dirac: Hofstadter s Butterfly in Graphene Philip Kim Physics Department, Columbia University Acknowledgment Prof. Cory Dean (now at CUNY) Lei Wang Patrick Maher Fereshte Ghahari Carlos
Bloch, Landau, and Dirac: Hofstadter s Butterfly in Graphene Philip Kim Physics Department, Columbia University Acknowledgment Prof. Cory Dean (now at CUNY) Lei Wang Patrick Maher Fereshte Ghahari Carlos
New Quantum Transport Results in Type-II InAs/GaSb Quantum Wells
 New Quantum Transport Results in Type-II InAs/GaSb Quantum Wells Wei Pan Sandia National Laboratories Sandia National Laboratories is a multi-program laboratory managed and operated by Sandia Corporation,
New Quantum Transport Results in Type-II InAs/GaSb Quantum Wells Wei Pan Sandia National Laboratories Sandia National Laboratories is a multi-program laboratory managed and operated by Sandia Corporation,
Room temperature topological insulators
 Room temperature topological insulators Ronny Thomale Julius-Maximilians Universität Würzburg ERC Topolectrics SFB Tocotronics Synquant Workshop, KITP, UC Santa Barbara, Nov. 22 2016 Correlated electron
Room temperature topological insulators Ronny Thomale Julius-Maximilians Universität Würzburg ERC Topolectrics SFB Tocotronics Synquant Workshop, KITP, UC Santa Barbara, Nov. 22 2016 Correlated electron
Berry s phase in Hall Effects and Topological Insulators
 Lecture 6 Berry s phase in Hall Effects and Topological Insulators Given the analogs between Berry s phase and vector potentials, it is not surprising that Berry s phase can be important in the Hall effect.
Lecture 6 Berry s phase in Hall Effects and Topological Insulators Given the analogs between Berry s phase and vector potentials, it is not surprising that Berry s phase can be important in the Hall effect.
Time Reversal Invariant Ζ 2 Topological Insulator
 Time Reversal Invariant Ζ Topological Insulator D Bloch Hamiltonians subject to the T constraint 1 ( ) ΘH Θ = H( ) with Θ = 1 are classified by a Ζ topological invariant (ν =,1) Understand via Bul-Boundary
Time Reversal Invariant Ζ Topological Insulator D Bloch Hamiltonians subject to the T constraint 1 ( ) ΘH Θ = H( ) with Θ = 1 are classified by a Ζ topological invariant (ν =,1) Understand via Bul-Boundary
Observation of neutral modes in the fractional quantum hall effect regime. Aveek Bid
 Observation of neutral modes in the fractional quantum hall effect regime Aveek Bid Department of Physics, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Nature 585 466 (2010) Quantum Hall Effect Magnetic field
Observation of neutral modes in the fractional quantum hall effect regime Aveek Bid Department of Physics, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Nature 585 466 (2010) Quantum Hall Effect Magnetic field
Graphite, graphene and relativistic electrons
 Graphite, graphene and relativistic electrons Introduction Physics of E. graphene Y. Andrei Experiments Rutgers University Transport electric field effect Quantum Hall Effect chiral fermions STM Dirac
Graphite, graphene and relativistic electrons Introduction Physics of E. graphene Y. Andrei Experiments Rutgers University Transport electric field effect Quantum Hall Effect chiral fermions STM Dirac
POEM: Physics of Emergent Materials
 POEM: Physics of Emergent Materials Nandini Trivedi L1: Spin Orbit Coupling L2: Topology and Topological Insulators Reference: Bernevig Topological Insulators and Topological Superconductors Tutorials:
POEM: Physics of Emergent Materials Nandini Trivedi L1: Spin Orbit Coupling L2: Topology and Topological Insulators Reference: Bernevig Topological Insulators and Topological Superconductors Tutorials:
Field Theory Description of Topological States of Matter. Andrea Cappelli INFN, Florence (w. E. Randellini, J. Sisti)
 Field Theory Description of Topological States of Matter Andrea Cappelli INFN, Florence (w. E. Randellini, J. Sisti) Topological States of Matter System with bulk gap but non-trivial at energies below
Field Theory Description of Topological States of Matter Andrea Cappelli INFN, Florence (w. E. Randellini, J. Sisti) Topological States of Matter System with bulk gap but non-trivial at energies below
Topological Properties of Quantum States of Condensed Matter: some recent surprises.
 Topological Properties of Quantum States of Condensed Matter: some recent surprises. F. D. M. Haldane Princeton University and Instituut Lorentz 1. Berry phases, zero-field Hall effect, and one-way light
Topological Properties of Quantum States of Condensed Matter: some recent surprises. F. D. M. Haldane Princeton University and Instituut Lorentz 1. Berry phases, zero-field Hall effect, and one-way light
Topological thermoelectrics
 Topological thermoelectrics JAIRO SINOVA Texas A&M University Institute of Physics ASCR Oleg Tretiakov, Artem Abanov, Suichi Murakami Great job candidate MRS Spring Meeting San Francisco April 28th 2011
Topological thermoelectrics JAIRO SINOVA Texas A&M University Institute of Physics ASCR Oleg Tretiakov, Artem Abanov, Suichi Murakami Great job candidate MRS Spring Meeting San Francisco April 28th 2011
Two Dimensional Chern Insulators, the Qi-Wu-Zhang and Haldane Models
 Two Dimensional Chern Insulators, the Qi-Wu-Zhang and Haldane Models Matthew Brooks, Introduction to Topological Insulators Seminar, Universität Konstanz Contents QWZ Model of Chern Insulators Haldane
Two Dimensional Chern Insulators, the Qi-Wu-Zhang and Haldane Models Matthew Brooks, Introduction to Topological Insulators Seminar, Universität Konstanz Contents QWZ Model of Chern Insulators Haldane
Quantum Hall Effect in Graphene p-n Junctions
 Quantum Hall Effect in Graphene p-n Junctions Dima Abanin (MIT) Collaboration: Leonid Levitov, Patrick Lee, Harvard and Columbia groups UIUC January 14, 2008 Electron transport in graphene monolayer New
Quantum Hall Effect in Graphene p-n Junctions Dima Abanin (MIT) Collaboration: Leonid Levitov, Patrick Lee, Harvard and Columbia groups UIUC January 14, 2008 Electron transport in graphene monolayer New
Quantum Spin Hall Effect in Inverted Type II Semiconductors
 Quantum Spin Hall Effect in Inverted Type II Semiconductors Chaoxing Liu 1,2, Taylor L. Hughes 2, Xiao-Liang Qi 2, Kang Wang 3 and Shou-Cheng Zhang 2 1 Center for Advanced Study, Tsinghua University,Beijing,
Quantum Spin Hall Effect in Inverted Type II Semiconductors Chaoxing Liu 1,2, Taylor L. Hughes 2, Xiao-Liang Qi 2, Kang Wang 3 and Shou-Cheng Zhang 2 1 Center for Advanced Study, Tsinghua University,Beijing,
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.other] 20 Apr 2010
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.other] 20 Apr 2010 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.other] 20 Apr 2010](/thumbs/93/114512366.jpg) Characterization of 3d topological insulators by 2d invariants Rahul Roy Rudolf Peierls Centre for Theoretical Physics, 1 Keble Road, Oxford, OX1 3NP, UK arxiv:1004.3507v1 [cond-mat.other] 20 Apr 2010
Characterization of 3d topological insulators by 2d invariants Rahul Roy Rudolf Peierls Centre for Theoretical Physics, 1 Keble Road, Oxford, OX1 3NP, UK arxiv:1004.3507v1 [cond-mat.other] 20 Apr 2010
Quantum Spin Hall Effect and Topological Phase Transition in HgTe Quantum Wells
 arxiv:cond-mat/0611399v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 15 Nov 006 Quantum Spin Hall Effect and Topological Phase Transition in HgTe Quantum Wells B. Andrei Bernevig, 1, Taylor L. Hughes, 1 and Shou-Cheng Zhang 1
arxiv:cond-mat/0611399v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 15 Nov 006 Quantum Spin Hall Effect and Topological Phase Transition in HgTe Quantum Wells B. Andrei Bernevig, 1, Taylor L. Hughes, 1 and Shou-Cheng Zhang 1
Les états de bord d un. isolant de Hall atomique
 Les états de bord d un isolant de Hall atomique séminaire Atomes Froids 2/9/22 Nathan Goldman (ULB), Jérôme Beugnon and Fabrice Gerbier Outline Quantum Hall effect : bulk Landau levels and edge states
Les états de bord d un isolant de Hall atomique séminaire Atomes Froids 2/9/22 Nathan Goldman (ULB), Jérôme Beugnon and Fabrice Gerbier Outline Quantum Hall effect : bulk Landau levels and edge states
Konstantin Y. Bliokh, Daria Smirnova, Franco Nori. Center for Emergent Matter Science, RIKEN, Japan. Science 348, 1448 (2015)
 Konstantin Y. Bliokh, Daria Smirnova, Franco Nori Center for Emergent Matter Science, RIKEN, Japan Science 348, 1448 (2015) QSHE and topological insulators The quantum spin Hall effect means the presence
Konstantin Y. Bliokh, Daria Smirnova, Franco Nori Center for Emergent Matter Science, RIKEN, Japan Science 348, 1448 (2015) QSHE and topological insulators The quantum spin Hall effect means the presence
Laurens W. Molenkamp. Physikalisches Institut, EP3 Universität Würzburg
 Laurens W. Molenkamp Physikalisches Institut, EP3 Universität Würzburg Onsager Coefficients I electric current density J particle current density J Q heat flux, heat current density µ chemical potential
Laurens W. Molenkamp Physikalisches Institut, EP3 Universität Würzburg Onsager Coefficients I electric current density J particle current density J Q heat flux, heat current density µ chemical potential
Spin Superfluidity and Graphene in a Strong Magnetic Field
 Spin Superfluidity and Graphene in a Strong Magnetic Field by B. I. Halperin Nano-QT 2016 Kyiv October 11, 2016 Based on work with So Takei (CUNY), Yaroslav Tserkovnyak (UCLA), and Amir Yacoby (Harvard)
Spin Superfluidity and Graphene in a Strong Magnetic Field by B. I. Halperin Nano-QT 2016 Kyiv October 11, 2016 Based on work with So Takei (CUNY), Yaroslav Tserkovnyak (UCLA), and Amir Yacoby (Harvard)
Chiral Majorana fermion from quantum anomalous Hall plateau transition
 Chiral Majorana fermion from quantum anomalous Hall plateau transition Phys. Rev. B, 2015 王靖复旦大学物理系 wjingphys@fudan.edu.cn Science, 2017 1 Acknowledgements Stanford Biao Lian Quan Zhou Xiao-Liang Qi Shou-Cheng
Chiral Majorana fermion from quantum anomalous Hall plateau transition Phys. Rev. B, 2015 王靖复旦大学物理系 wjingphys@fudan.edu.cn Science, 2017 1 Acknowledgements Stanford Biao Lian Quan Zhou Xiao-Liang Qi Shou-Cheng
Graphene and Carbon Nanotubes
 Graphene and Carbon Nanotubes 1 atom thick films of graphite atomic chicken wire Novoselov et al - Science 306, 666 (004) 100μm Geim s group at Manchester Novoselov et al - Nature 438, 197 (005) Kim-Stormer
Graphene and Carbon Nanotubes 1 atom thick films of graphite atomic chicken wire Novoselov et al - Science 306, 666 (004) 100μm Geim s group at Manchester Novoselov et al - Nature 438, 197 (005) Kim-Stormer
Andreev transport in 2D topological insulators
 Andreev transport in 2D topological insulators Jérôme Cayssol Bordeaux University Visiting researcher UC Berkeley (2010-2012) Villard de Lans Workshop 09/07/2011 1 General idea - Topological insulators
Andreev transport in 2D topological insulators Jérôme Cayssol Bordeaux University Visiting researcher UC Berkeley (2010-2012) Villard de Lans Workshop 09/07/2011 1 General idea - Topological insulators
Topological Physics in Band Insulators. Gene Mele DRL 2N17a
 Topological Physics in Band Insulators Gene Mele DRL 2N17a Electronic States of Matter Benjamin Franklin (University of Pennsylvania) That the Electrical Fire freely removes from Place to Place in and
Topological Physics in Band Insulators Gene Mele DRL 2N17a Electronic States of Matter Benjamin Franklin (University of Pennsylvania) That the Electrical Fire freely removes from Place to Place in and
Topological states of matter in correlated electron systems
 Seminar @ Tsinghua, Dec.5/2012 Topological states of matter in correlated electron systems Qiang-Hua Wang National Lab of Solid State Microstructures, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093, China Collaborators:Dunghai
Seminar @ Tsinghua, Dec.5/2012 Topological states of matter in correlated electron systems Qiang-Hua Wang National Lab of Solid State Microstructures, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093, China Collaborators:Dunghai
Recent developments in topological materials
 Recent developments in topological materials NHMFL Winter School January 6, 2014 Joel Moore University of California, Berkeley, and Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Berkeley students: Andrew Essin,
Recent developments in topological materials NHMFL Winter School January 6, 2014 Joel Moore University of California, Berkeley, and Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Berkeley students: Andrew Essin,
HIGHER INVARIANTS: TOPOLOGICAL INSULATORS
 HIGHER INVARIANTS: TOPOLOGICAL INSULATORS Sponsoring This material is based upon work supported by the National Science Foundation Grant No. DMS-1160962 Jean BELLISSARD Georgia Institute of Technology,
HIGHER INVARIANTS: TOPOLOGICAL INSULATORS Sponsoring This material is based upon work supported by the National Science Foundation Grant No. DMS-1160962 Jean BELLISSARD Georgia Institute of Technology,
Energy Spectrum and Broken spin-surface locking in Topological Insulator quantum dots
 Energy Spectrum and Broken spin-surface locking in Topological Insulator quantum dots A. Kundu 1 1 Heinrich-Heine Universität Düsseldorf, Germany The Capri Spring School on Transport in Nanostructures
Energy Spectrum and Broken spin-surface locking in Topological Insulator quantum dots A. Kundu 1 1 Heinrich-Heine Universität Düsseldorf, Germany The Capri Spring School on Transport in Nanostructures
Building Frac-onal Topological Insulators. Collaborators: Michael Levin Maciej Kosh- Janusz Ady Stern
 Building Frac-onal Topological Insulators Collaborators: Michael Levin Maciej Kosh- Janusz Ady Stern The program Background: Topological insulators Frac-onaliza-on Exactly solvable Hamiltonians for frac-onal
Building Frac-onal Topological Insulators Collaborators: Michael Levin Maciej Kosh- Janusz Ady Stern The program Background: Topological insulators Frac-onaliza-on Exactly solvable Hamiltonians for frac-onal
3D Weyl metallic states realized in the Bi 1-x Sb x alloy and BiTeI. Heon-Jung Kim Department of Physics, Daegu University, Korea
 3D Weyl metallic states realized in the Bi 1-x Sb x alloy and BiTeI Heon-Jung Kim Department of Physics, Daegu University, Korea Content 3D Dirac metals Search for 3D generalization of graphene Bi 1-x
3D Weyl metallic states realized in the Bi 1-x Sb x alloy and BiTeI Heon-Jung Kim Department of Physics, Daegu University, Korea Content 3D Dirac metals Search for 3D generalization of graphene Bi 1-x
Topological Physics in Band Insulators IV
 Topological Physics in Band Insulators IV Gene Mele University of Pennsylvania Wannier representation and band projectors Modern view: Gapped electronic states are equivalent Kohn (1964): insulator is
Topological Physics in Band Insulators IV Gene Mele University of Pennsylvania Wannier representation and band projectors Modern view: Gapped electronic states are equivalent Kohn (1964): insulator is
v. Tε n k =ε n k T r T = r, T v T = r, I v I = I r I = v. Iε n k =ε n k Berry curvature: Symmetry Consideration n k = n k
 Berry curvature: Symmetry Consideration Time reversal (i.e. motion reversal) 1 1 T r T = r, T v T = v. Tε n k =ε n k n k = n k Inversion Symmetry: 1 1 I r I = r, I v I = v. Iε n k =ε n k n k = n k θ
Berry curvature: Symmetry Consideration Time reversal (i.e. motion reversal) 1 1 T r T = r, T v T = v. Tε n k =ε n k n k = n k Inversion Symmetry: 1 1 I r I = r, I v I = v. Iε n k =ε n k n k = n k θ
Kouki Nakata. University of Basel. KN, S. K. Kim (UCLA), J. Klinovaja, D. Loss (2017) arxiv:
 Magnon Transport Both in Ferromagnetic and Antiferromagnetic Insulating Magnets Kouki Nakata University of Basel KN, S. K. Kim (UCLA), J. Klinovaja, D. Loss (2017) arxiv:1707.07427 See also review article
Magnon Transport Both in Ferromagnetic and Antiferromagnetic Insulating Magnets Kouki Nakata University of Basel KN, S. K. Kim (UCLA), J. Klinovaja, D. Loss (2017) arxiv:1707.07427 See also review article
Topological Defects inside a Topological Band Insulator
 Topological Defects inside a Topological Band Insulator Ashvin Vishwanath UC Berkeley Refs: Ran, Zhang A.V., Nature Physics 5, 289 (2009). Hosur, Ryu, AV arxiv: 0908.2691 Part 1: Outline A toy model of
Topological Defects inside a Topological Band Insulator Ashvin Vishwanath UC Berkeley Refs: Ran, Zhang A.V., Nature Physics 5, 289 (2009). Hosur, Ryu, AV arxiv: 0908.2691 Part 1: Outline A toy model of
Three Most Important Topics (MIT) Today
 Three Most Important Topics (MIT) Today Electrons in periodic potential Energy gap nearly free electron Bloch Theorem Energy gap tight binding Chapter 1 1 Electrons in Periodic Potential We now know the
Three Most Important Topics (MIT) Today Electrons in periodic potential Energy gap nearly free electron Bloch Theorem Energy gap tight binding Chapter 1 1 Electrons in Periodic Potential We now know the
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 20 Aug 2013
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 20 Aug 2013 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 20 Aug 2013](/thumbs/74/69948385.jpg) The resistance of D Topological insulator in the absence of the quantized transport arxiv:8.56v [cond-mat.mes-hall] Aug G.M.Gusev, Z.D.Kvon,, E.B Olshanetsky, A.D.Levin, Y. Krupko, J.C. Portal,,5 N.N.Mikhailov,
The resistance of D Topological insulator in the absence of the quantized transport arxiv:8.56v [cond-mat.mes-hall] Aug G.M.Gusev, Z.D.Kvon,, E.B Olshanetsky, A.D.Levin, Y. Krupko, J.C. Portal,,5 N.N.Mikhailov,
Exploring topological states with cold atoms and photons
 Exploring topological states with cold atoms and photons Theory: Takuya Kitagawa, Dima Abanin, Erez Berg, Mark Rudner, Liang Fu, Takashi Oka, Immanuel Bloch, Eugene Demler Experiments: I. Bloch s group
Exploring topological states with cold atoms and photons Theory: Takuya Kitagawa, Dima Abanin, Erez Berg, Mark Rudner, Liang Fu, Takashi Oka, Immanuel Bloch, Eugene Demler Experiments: I. Bloch s group
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 17 Jan 2013
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 17 Jan 2013 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 17 Jan 2013](/thumbs/92/108463391.jpg) Electrically Tunable Topological State in [111] Perovskite Materials with Antiferromagnetic Exchange Field Qi-Feng Liang, 1,2 Long-Hua Wu, 1 and Xiao Hu 1 1 International Center for Materials Nanoarchitectornics
Electrically Tunable Topological State in [111] Perovskite Materials with Antiferromagnetic Exchange Field Qi-Feng Liang, 1,2 Long-Hua Wu, 1 and Xiao Hu 1 1 International Center for Materials Nanoarchitectornics
Abelian and non-abelian gauge fields in the Brillouin zone for insulators and metals
 Abelian and non-abelian gauge fields in the Brillouin zone for insulators and metals Vienna, August 19, 2014 Joel Moore University of California, Berkeley, and Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Outline
Abelian and non-abelian gauge fields in the Brillouin zone for insulators and metals Vienna, August 19, 2014 Joel Moore University of California, Berkeley, and Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Outline
Tutorial: Berry phase and Berry curvature in solids
 Tutorial: Berry phase and Berry curvature in solids Justin Song Division of Physics, Nanyang Technological University (Singapore) & Institute of High Performance Computing (Singapore) Funding: (Singapore)
Tutorial: Berry phase and Berry curvature in solids Justin Song Division of Physics, Nanyang Technological University (Singapore) & Institute of High Performance Computing (Singapore) Funding: (Singapore)
Emergent topological phenomena in antiferromagnets with noncoplanar spins
 Emergent topological phenomena in antiferromagnets with noncoplanar spins - Surface quantum Hall effect - Dimensional crossover Bohm-Jung Yang (RIKEN, Center for Emergent Matter Science (CEMS), Japan)
Emergent topological phenomena in antiferromagnets with noncoplanar spins - Surface quantum Hall effect - Dimensional crossover Bohm-Jung Yang (RIKEN, Center for Emergent Matter Science (CEMS), Japan)
Floquet Topological Insulators and Majorana Modes
 Floquet Topological Insulators and Majorana Modes Manisha Thakurathi Journal Club Centre for High Energy Physics IISc Bangalore January 17, 2013 References Floquet Topological Insulators by J. Cayssol
Floquet Topological Insulators and Majorana Modes Manisha Thakurathi Journal Club Centre for High Energy Physics IISc Bangalore January 17, 2013 References Floquet Topological Insulators by J. Cayssol
Spin-orbit effects in graphene and graphene-like materials. Józef Barnaś
 Spin-orbit effects in graphene and graphene-like materials Józef Barnaś Faculty of Physics, Adam Mickiewicz University, Poznań & Institute of Molecular Physics PAN, Poznań In collaboration with: A. Dyrdał,
Spin-orbit effects in graphene and graphene-like materials Józef Barnaś Faculty of Physics, Adam Mickiewicz University, Poznań & Institute of Molecular Physics PAN, Poznań In collaboration with: A. Dyrdał,
Observation of topological surface state quantum Hall effect in an intrinsic three-dimensional topological insulator
 Observation of topological surface state quantum Hall effect in an intrinsic three-dimensional topological insulator Authors: Yang Xu 1,2, Ireneusz Miotkowski 1, Chang Liu 3,4, Jifa Tian 1,2, Hyoungdo
Observation of topological surface state quantum Hall effect in an intrinsic three-dimensional topological insulator Authors: Yang Xu 1,2, Ireneusz Miotkowski 1, Chang Liu 3,4, Jifa Tian 1,2, Hyoungdo
STM spectra of graphene
 STM spectra of graphene K. Sengupta Theoretical Physics Division, IACS, Kolkata. Collaborators G. Baskaran, I.M.Sc Chennai, K. Saha, IACS Kolkata I. Paul, Grenoble France H. Manoharan, Stanford USA Refs:
STM spectra of graphene K. Sengupta Theoretical Physics Division, IACS, Kolkata. Collaborators G. Baskaran, I.M.Sc Chennai, K. Saha, IACS Kolkata I. Paul, Grenoble France H. Manoharan, Stanford USA Refs:
Weyl semi-metal: a New Topological State in Condensed Matter
 Weyl semi-metal: a New Topological State in Condensed Matter Sergey Savrasov Department of Physics, University of California, Davis Xiangang Wan Nanjing University Ari Turner and Ashvin Vishwanath UC Berkeley
Weyl semi-metal: a New Topological State in Condensed Matter Sergey Savrasov Department of Physics, University of California, Davis Xiangang Wan Nanjing University Ari Turner and Ashvin Vishwanath UC Berkeley
Splitting of a Cooper pair by a pair of Majorana bound states
 Chapter 7 Splitting of a Cooper pair by a pair of Majorana bound states 7.1 Introduction Majorana bound states are coherent superpositions of electron and hole excitations of zero energy, trapped in the
Chapter 7 Splitting of a Cooper pair by a pair of Majorana bound states 7.1 Introduction Majorana bound states are coherent superpositions of electron and hole excitations of zero energy, trapped in the
LCI -birthplace of liquid crystal display. May, protests. Fashion school is in top-3 in USA. Clinical Psychology program is Top-5 in USA
 LCI -birthplace of liquid crystal display May, 4 1970 protests Fashion school is in top-3 in USA Clinical Psychology program is Top-5 in USA Topological insulators driven by electron spin Maxim Dzero Kent
LCI -birthplace of liquid crystal display May, 4 1970 protests Fashion school is in top-3 in USA Clinical Psychology program is Top-5 in USA Topological insulators driven by electron spin Maxim Dzero Kent
Topological Insulators in 3D and Bosonization
 Topological Insulators in 3D and Bosonization Andrea Cappelli, INFN Florence (w. E. Randellini, J. Sisti) Outline Topological states of matter: bulk and edge Fermions and bosons on the (1+1)-dimensional
Topological Insulators in 3D and Bosonization Andrea Cappelli, INFN Florence (w. E. Randellini, J. Sisti) Outline Topological states of matter: bulk and edge Fermions and bosons on the (1+1)-dimensional
Electrical Control of the Kondo Effect at the Edge of a Quantum Spin Hall System
 Correlations and coherence in quantum systems Évora, Portugal, October 11 2012 Electrical Control of the Kondo Effect at the Edge of a Quantum Spin Hall System Erik Eriksson (University of Gothenburg)
Correlations and coherence in quantum systems Évora, Portugal, October 11 2012 Electrical Control of the Kondo Effect at the Edge of a Quantum Spin Hall System Erik Eriksson (University of Gothenburg)
