Electrical Control of the Kondo Effect at the Edge of a Quantum Spin Hall System
|
|
|
- Noreen Floyd
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Correlations and coherence in quantum systems Évora, Portugal, October Electrical Control of the Kondo Effect at the Edge of a Quantum Spin Hall System Erik Eriksson (University of Gothenburg) Anders Ström (University of Gothenburg) Girish Sharma (École Polytechnique) Henrik Johannesson (University of Gothenburg) supported by the Swedish Research Council
2 Outline Quantum spin Hall effect... some basics At the edge: A new kind of electron liquid Adding a magnetic impurity and a Rashba spin-orbit interaction Electrical control of the Kondo effect! Summary and outlook
3 Quantum spin Hall effect... some basics
4 Quantum spin Hall effect
5 Integer Quantum Hall effect B skipping currents quantization chiral edge states B. I. Halperin, PRB 25, 2185 (1982) no channel for backscattering ballistic transport along the edge, accounts for the quantization of the Hall conductance M. Büttiker, PRB 38, 9375 (1988)
6 Can a system be stable against local perturbations without breaking time-reversal invariance?
7 Consider a Gedanken experiment... B. A. Bernevig and S.-C. Zhang, PRL 96, (2006) > uniformly charged cylinder with electric field E = E(x, y, 0) spin-orbit interaction (E k) σ = Eσ z (k y x k x y) > B = A cf. with the IQHE in a symmetric gauge A = B 2 (y, x, 0) > Lorentz force A k eb(k y x k x y)
8 Quantum spin Hall (QSH) system single Kramers pair Two copies of a IQH system, bulk insulator with helical edge states > > First proposed by Kane and Mele for graphene (2005) too weak spin-orbit interaction, doesn t quite work... Bernevig et al. proposal for HgTe quantum wells (2006) Experimental observation by König et al. (2007)
9 Bernevig et al. proposal for HgTe quantum wells (2006) Experimental observation by König et al. (2007) from M. König et al., Science 318, 766 (2007)
10 Are the helical edge states stable against local perturbations? Yes! As long as the perturbations are time-reversal invariant! Look at the band structure of an HgTe quantum well... strong spin-orbit interactions in atomic p-orbitals create an inverted band gap (p-band on top of s-band) supports a single Kramers pair of helical edge states inside the inverted gap Kramers degeneracy at k=0 protects the stability of the edge states ballistic transport B. A. Bernevig et al., PRL 95, (2005) G = 2e2 h 4-terminal measurement, equilibration in contacts
11 At the edge: A new kind of electron liquid # of Kramers pair in a nontrivial (trivial) helical liquid 2D topological insulator (a.k.a. quantum spin Hall system) NK = 1 mod 2 = 0 mod 2 ν =0, 1 is a Z2 topological invariant and can be calculated from the band structure of the bulk ( bulk-edge correspondence ) L. Fu and C. L. Kane, PRB 76, (2007)
12 At the edge: A new kind of electron liquid # of Kramers pair in a nontrivial (trivial) helical liquid NK = 1 mod 2 = 0 mod 2 ν =0, 1 is a Z2 topological invariant and can be calculated from the band structure of the bulk ( bulk-edge correspondence ) 2D topological insulator (a.k.a. quantum spin Hall system) L. Fu and C. L. Kane, PRB 76, (2007) What if time-reversal symmetry is broken...?
13 ... for example, by the presence of a magnetic impurity? case study: Mn 2+ large and positive single-ion anisotropy (S z ) 2 from M. König et al., Science 318, 766 (2007) S =5/2 S eff =1/2 low T anisotropic spin exchange with the edge electrons R. Zitko et al., PRB 78, (2008) H K = Ψ (0) J (σ + S eff + σ S + eff )+J zσ z Seff z Ψ(0), Ψ T = ψ, ψ
14 Adding a magnetic impurity... The Kondo interaction is time-reversal invariant! Could it still cause a spontaneous breaking of time reversal invariance and collapse the QSH state?
15 Adding a magnetic impurity... Recall the Kondo effect One-loop RG equations: P. W. Anderson, J. Phys. C 3, 2436 (1970) J D = νj J z +... J z D = νj strong-coupling physics for T<<T K T K = D 0 exp( const./j 0 ) J 0 max(j,j z ) D=D0 formation of impurity-electron singlet ( Kondo screening )
16 Adding a magnetic impurity... T=0 insulator! Pauli principle: punctured 1D lattice
17 Adding a magnetic impurity... Does this really happen for the helical liquid? To find out, first add e-e interactions... important in 1D! bulk k F k F k + local (at impurity site) + + ( ) from Kondo 0 if U(1) spin symmetry is broken T. L. Schmidt et al., PRL 108, (2012)
18 Adding a magnetic impurity... Adding the kinetic energy and bosonizing... H = (v/2) dx ( x ϕ) 2 +( x ϑ) 2 + A κ cos( 4πKϕ)+ B κ sin( 4πKϕ)+ C K x ϑ Luttinger liquid parameter functions of Kondo couplings + + g U 2(πκ) 2 cos( 16πKϕ) g ie 2π 2 K :( 2 xϑ) cos( 4πKϕ) :...perturbative RG and linear response J. Maciejko et al., PRL 102, (2009)
19 Adding a magnetic impurity... no correction to the edge conductance at T = 0! G =2e 2 /h weak e-e interaction strong e-e interaction from J. Maciejko et al., PRL 102, (2009)
20 Adding a magnetic impurity... Due to its topological nature, the QSH state follows the new shape of the edge. Weak coupling QSH states are robust against local breaking of time-reversal symmetry! J. Maciejko et al., PRL 102, (2009)
21 But... one important thing is missing from the analysis!
22 Rashba spin-orbit interaction! z 2DEG d semiconductor heterostructure d z Spatial asymmetry of band edges mimics an E-field in the z-direction H R = α(k x σ y k y σ x ) Yu. A. Bychkov and E. I. Rashba, J. Phys. C 17, 6039 (1984)
23 Rashba spin-orbit interaction! z d x semiconductor heterostructure d z H R = α k x σ y doesn t conserve spin x
24 reversal invariance electron transport then becomes balwhich sets the scale below which the electrons screen the listic, provided that the electron-electron (e-e) interaction impurity can be controlled by varying the strength is sufficiently well-screened so that higher-order scatterof the Rashba interaction. Surprisingly, for a strongly?? ing processes do not come into play. anisotropic Kondo exchange, a non-collinear spin inter action mediated by the Rashba coupling becomes rel The picture gets an added twist when including effects breaks the locking of spin to momentum. However, stillcompetes with the evant (in the sense there of RG)isand from... magnetic impurities, contributed by dopant ions or Kondo screening. This challenges the expectation that electronsatrapped potential inhomogeneities. an edge, singlebykramers pair on thesince QSH and this is all that matters! the Kondo effect is stable against time-reversal invari edge electron can backscatter from an impurity via spin L. Kane and E.?J. Mele, PRL 95, (2005) ant C. perturbations. Moreover, we show that the im exchange, time-reversal invariance no longer protects the purity contribution to the dc conductance at tempera helical states from mixing. In addition, correlated twotures T > TK can be switched on and off by adjusting electron? and inelastic single-electron processes?? must kinetic term Rashba 1 coupling. With the Rashba coupling being now also be accounted for. As a result, at high temper- the Rashba tunable by a gate voltage, this suggests a new inroad to atures T electron scattering off the impurity leads to a z y? H = vf of dx Ψ (x) [ iσat low Ψ(x) + α control dx Ψcharge (x) [ iσ x ]atψ(x) transport the edge of a QSH device. ln(t ) correction the conductance x ] frequencies Model. To model the ω, which, however, vanishes? in the dc limit ω 0. At edge electrons, we introduce T 2 2 two-spinors Ψ = ψ, ψ, where ψ (ψ ) annihi low T, for weak e-e interactions, the quantized vedge vf + αthe α = conlates a right-moving (left-moving) electron with ductance G0 = e2 /h is restored as T 0 with power 1 spin-up x iσ(spin-down) θ/2 laws distinctive of a helical edge liquid. For strong Ψx inter=e Ψ along the growth direction of the quantum well. Neglecting e-e interactions, the edge Hamiltonian actions the edge liquid freezes into an insulator at T = 0, 2 + α2 cos θ = v /v v = v F α α F can then be written as with thermally induced transport via tunneling of frac tionalized charge excitations through the impurity?. 1 in σ H = vf dx Ψ (x) [ iσ z x ] Ψ(x) + A more complete description of edge H transport ay R = α k x H =must vα include dx Ψ iσ z ofx a sin Ψ QSH system also(x) the presence Rashba θ(x) = α/vα cos θ = F /vα z v z spin-orbit interaction. This interaction, which can be +α dx Ψ (x) [ iσ y x ] Ψ(x) + (1) tuned by an external gate voltage, is a built-in feature T? x Ψ = ψ, ψ of a quantum well. In fact, HgTe quantum wells ex +Ψ (0) [Jx σ x SH += Jyv σ y S y + dx Jz σ z Ψ S z ] Ψ(0), T K (x) [ θ Ψ = ψ, ψ sin θ = α/vα F hibit some of the largest known Rashba couplings of any semiconductor heterostructures?the. As Rashba-rotated a consequence, spinor with vf the Fermi velocity parameterizing the linear ki isaassumed Kramers spin is no longer conserved, contrary to defines what second term encodes the Rashba inter pairnetic energy. still The? 2 2 z 2(.dx T K λ/2) action strength 2 2( K+λ/2) 1 the 2 term 2 in the minimal model of However, of α, with being 1 iσ z =y )v2= Ψ (x) Ψ (x) αt v x Ψ = ψ, ψ γ0 a QSH (JxH +system J, γ (J J ) T, γ0e third JN T 2K 1, γ 0Ean anti JN 2 2 H dx Ψ (x) iσ Ψ (x) xx α 0 y C = (v/2) dxtime-reversal ( x ϕ) + in( x ϑ)ferromagnetic Kondo interaction between electrons (withc since the Rashba H interaction preserves variance, Kramers theorem guarantees that the edge Pauli matrices σ i, i = x, y, z) and a spin-1/2 magnetic im A B C z + cos( 4πKϕ)+ sin( 4πKϕ)+ ϑ H = v Idx=ΨG (x) V iσ δix Ψ (x) Adding the Rashba interaction...
25 Adding the Rashba interaction... e-e interaction is invariant under Ψ Ψ Kondo interaction H K = Ψ (0) J (σ + S eff + σ S + eff )+J zσ z S z eff Ψ(0), Ψ =e iσx θ/2 Ψ S =e isx θ/2 Se isx θ/2 H K = Ψ (0)[J x σ x S x + J yσ y S y + J zσ z S z + J NC (σ y S z + σ z S y )]Ψ (0) XYZ Kondo Non-Collinear term depend on the Rashba coupling controllable by a gate voltage α...bosonization and perturbative RG E. Eriksson et al., PRB 86, (R) (2012)
26 Electrical control of the Kondo temperature via the Rashba angle θ ~ gate voltage easy-plane Kondo J x = J y = 20 mev, J z = 10 mev easy-axis Kondo J x = J y =5meV, J z = 50 mev J NC Region where dominates the RG flow obstruction of Kondo screening! challenges the Meir-Wingreen conjecture that the Kondo effect is blind to time-reversal invariant perturbations Y. Meir and N.S. Wingreen, PRB 50, 4947 (1994)
27 Low-temperature transport, T T K (away from the dome ) weak e-e interaction K>1/4 T =0 G = 2e2 h
28 Low-temperature transport, T T K (away from the dome ) weak e-e interaction G = 2e2 h δg 1/4 <K<2/3 K>2/3 (T/T K ) 8K 2 (T/T K ) 2K+2 signature of Rashba!
29 Low-temperature transport, T T K (away from the dome ) weak e-e interaction G = 2e2 h δg 1/4 <K<2/3 K>2/3 (T/T K ) 8K 2 (T/T K ) 2K+2 signature of Rashba! strong e-e interaction T =0 G =0 K<1/4
30 Low-temperature transport, T T K (away from the dome ) weak e-e interaction G = 2e2 h δg 1/4 <K<2/3 K>2/3 (T/T K ) 8K 2 (T/T K ) 2K+2 signature of Rashba! strong e-e interaction K<1/4 G (T/T K ) 2(1/4K 1) blind to Rashba from instanton processes J. Maciejko et al., PRL 102, (2009)
31 High-temperature transport, T T K I = G 0 V δi J,z ω T
32 High-temperature transport, T T K I = G 0 V δi J,z ω T conductance correction in dc limit: γ 0 (J x + J y) 2 T 2( K λ/2) 2 1, γ 0 (J x J y) 2 T 2( K+λ/2) 2 1, γ E 0 J 2 NCT 2K 1, γ E 0 J 2 NCT
33 Summary and outlook E. Eriksson et al., PRB 86, (R) (2012) Magnetic impurity in a helical edge liquid: Rashba coupling allows electrical control of Kondo temperature and IV-characteristics blocking of Kondo screening!? Rashba-induced impurity correction accessible in experiment? Interesting open problems: Two-loop RG, thermal transport, effects from Dresselhaus spin-orbit interactions, Kondo lattice in a helical liquid, higher-spin impurities... and more!
5 Topological insulator with time-reversal symmetry
 Phys62.nb 63 5 Topological insulator with time-reversal symmetry It is impossible to have quantum Hall effect without breaking the time-reversal symmetry. xy xy. If we want xy to be invariant under, xy
Phys62.nb 63 5 Topological insulator with time-reversal symmetry It is impossible to have quantum Hall effect without breaking the time-reversal symmetry. xy xy. If we want xy to be invariant under, xy
What is a topological insulator? Ming-Che Chang Dept of Physics, NTNU
 What is a topological insulator? Ming-Che Chang Dept of Physics, NTNU A mini course on topology extrinsic curvature K vs intrinsic (Gaussian) curvature G K 0 G 0 G>0 G=0 K 0 G=0 G
What is a topological insulator? Ming-Che Chang Dept of Physics, NTNU A mini course on topology extrinsic curvature K vs intrinsic (Gaussian) curvature G K 0 G 0 G>0 G=0 K 0 G=0 G
Topological Kondo Insulator SmB 6. Tetsuya Takimoto
 Topological Kondo Insulator SmB 6 J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 80 123720, (2011). Tetsuya Takimoto Department of Physics, Hanyang University Collaborator: Ki-Hoon Lee (POSTECH) Content 1. Introduction of SmB 6 in-gap
Topological Kondo Insulator SmB 6 J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 80 123720, (2011). Tetsuya Takimoto Department of Physics, Hanyang University Collaborator: Ki-Hoon Lee (POSTECH) Content 1. Introduction of SmB 6 in-gap
Notes on Topological Insulators and Quantum Spin Hall Effect. Jouko Nieminen Tampere University of Technology.
 Notes on Topological Insulators and Quantum Spin Hall Effect Jouko Nieminen Tampere University of Technology. Not so much discussed concept in this session: topology. In math, topology discards small details
Notes on Topological Insulators and Quantum Spin Hall Effect Jouko Nieminen Tampere University of Technology. Not so much discussed concept in this session: topology. In math, topology discards small details
Topological insulators
 http://www.physik.uni-regensburg.de/forschung/fabian Topological insulators Jaroslav Fabian Institute for Theoretical Physics University of Regensburg Stara Lesna, 21.8.212 DFG SFB 689 what are topological
http://www.physik.uni-regensburg.de/forschung/fabian Topological insulators Jaroslav Fabian Institute for Theoretical Physics University of Regensburg Stara Lesna, 21.8.212 DFG SFB 689 what are topological
Spin orbit interaction in graphene monolayers & carbon nanotubes
 Spin orbit interaction in graphene monolayers & carbon nanotubes Reinhold Egger Institut für Theoretische Physik, Düsseldorf Alessandro De Martino Andreas Schulz, Artur Hütten MPI Dresden, 25.10.2011 Overview
Spin orbit interaction in graphene monolayers & carbon nanotubes Reinhold Egger Institut für Theoretische Physik, Düsseldorf Alessandro De Martino Andreas Schulz, Artur Hütten MPI Dresden, 25.10.2011 Overview
Topological insulator with time-reversal symmetry
 Phys620.nb 101 7 Topological insulator with time-reversal symmetry Q: Can we get a topological insulator that preserves the time-reversal symmetry? A: Yes, with the help of the spin degree of freedom.
Phys620.nb 101 7 Topological insulator with time-reversal symmetry Q: Can we get a topological insulator that preserves the time-reversal symmetry? A: Yes, with the help of the spin degree of freedom.
Spin Hall and quantum spin Hall effects. Shuichi Murakami Department of Physics, Tokyo Institute of Technology PRESTO, JST
 YKIS2007 (Kyoto) Nov.16, 2007 Spin Hall and quantum spin Hall effects Shuichi Murakami Department of Physics, Tokyo Institute of Technology PRESTO, JST Introduction Spin Hall effect spin Hall effect in
YKIS2007 (Kyoto) Nov.16, 2007 Spin Hall and quantum spin Hall effects Shuichi Murakami Department of Physics, Tokyo Institute of Technology PRESTO, JST Introduction Spin Hall effect spin Hall effect in
The Quantum Spin Hall Effect
 The Quantum Spin Hall Effect Shou-Cheng Zhang Stanford University with Andrei Bernevig, Taylor Hughes Science, 314,1757 2006 Molenamp et al, Science, 318, 766 2007 XL Qi, T. Hughes, SCZ preprint The quantum
The Quantum Spin Hall Effect Shou-Cheng Zhang Stanford University with Andrei Bernevig, Taylor Hughes Science, 314,1757 2006 Molenamp et al, Science, 318, 766 2007 XL Qi, T. Hughes, SCZ preprint The quantum
Universal transport at the edge: Disorder, interactions, and topological protection
 Universal transport at the edge: Disorder, interactions, and topological protection Matthew S. Foster, Rice University March 31 st, 2016 Universal transport coefficients at the edges of 2D topological
Universal transport at the edge: Disorder, interactions, and topological protection Matthew S. Foster, Rice University March 31 st, 2016 Universal transport coefficients at the edges of 2D topological
Topological insulator (TI)
 Topological insulator (TI) Haldane model: QHE without Landau level Quantized spin Hall effect: 2D topological insulators: Kane-Mele model for graphene HgTe quantum well InAs/GaSb quantum well 3D topological
Topological insulator (TI) Haldane model: QHE without Landau level Quantized spin Hall effect: 2D topological insulators: Kane-Mele model for graphene HgTe quantum well InAs/GaSb quantum well 3D topological
Symmetries in Quantum Transport : From Random Matrix Theory to Topological Insulators. Philippe Jacquod. U of Arizona
 Symmetries in Quantum Transport : From Random Matrix Theory to Topological Insulators Philippe Jacquod U of Arizona UA Phys colloquium - feb 1, 2013 Continuous symmetries and conservation laws Noether
Symmetries in Quantum Transport : From Random Matrix Theory to Topological Insulators Philippe Jacquod U of Arizona UA Phys colloquium - feb 1, 2013 Continuous symmetries and conservation laws Noether
Hartmut Buhmann. Physikalisches Institut, EP3 Universität Würzburg Germany
 Hartmut Buhmann Physikalisches Institut, EP3 Universität Würzburg Germany Part I and II Insulators and Topological Insulators HgTe crystal structure Part III quantum wells Two-Dimensional TI Quantum Spin
Hartmut Buhmann Physikalisches Institut, EP3 Universität Würzburg Germany Part I and II Insulators and Topological Insulators HgTe crystal structure Part III quantum wells Two-Dimensional TI Quantum Spin
Topological Insulator Surface States and Electrical Transport. Alexander Pearce Intro to Topological Insulators: Week 11 February 2, / 21
 Topological Insulator Surface States and Electrical Transport Alexander Pearce Intro to Topological Insulators: Week 11 February 2, 2017 1 / 21 This notes are predominately based on: J.K. Asbóth, L. Oroszlány
Topological Insulator Surface States and Electrical Transport Alexander Pearce Intro to Topological Insulators: Week 11 February 2, 2017 1 / 21 This notes are predominately based on: J.K. Asbóth, L. Oroszlány
Topological Insulators
 Topological Insulators Aira Furusai (Condensed Matter Theory Lab.) = topological insulators (3d and 2d) Outline Introduction: band theory Example of topological insulators: integer quantum Hall effect
Topological Insulators Aira Furusai (Condensed Matter Theory Lab.) = topological insulators (3d and 2d) Outline Introduction: band theory Example of topological insulators: integer quantum Hall effect
Introductory lecture on topological insulators. Reza Asgari
 Introductory lecture on topological insulators Reza Asgari Workshop on graphene and topological insulators, IPM. 19-20 Oct. 2011 Outlines -Introduction New phases of materials, Insulators -Theory quantum
Introductory lecture on topological insulators Reza Asgari Workshop on graphene and topological insulators, IPM. 19-20 Oct. 2011 Outlines -Introduction New phases of materials, Insulators -Theory quantum
Topological Physics in Band Insulators II
 Topological Physics in Band Insulators II Gene Mele University of Pennsylvania Topological Insulators in Two and Three Dimensions The canonical list of electric forms of matter is actually incomplete Conductor
Topological Physics in Band Insulators II Gene Mele University of Pennsylvania Topological Insulators in Two and Three Dimensions The canonical list of electric forms of matter is actually incomplete Conductor
Topological Defects inside a Topological Band Insulator
 Topological Defects inside a Topological Band Insulator Ashvin Vishwanath UC Berkeley Refs: Ran, Zhang A.V., Nature Physics 5, 289 (2009). Hosur, Ryu, AV arxiv: 0908.2691 Part 1: Outline A toy model of
Topological Defects inside a Topological Band Insulator Ashvin Vishwanath UC Berkeley Refs: Ran, Zhang A.V., Nature Physics 5, 289 (2009). Hosur, Ryu, AV arxiv: 0908.2691 Part 1: Outline A toy model of
LCI -birthplace of liquid crystal display. May, protests. Fashion school is in top-3 in USA. Clinical Psychology program is Top-5 in USA
 LCI -birthplace of liquid crystal display May, 4 1970 protests Fashion school is in top-3 in USA Clinical Psychology program is Top-5 in USA Topological insulators driven by electron spin Maxim Dzero Kent
LCI -birthplace of liquid crystal display May, 4 1970 protests Fashion school is in top-3 in USA Clinical Psychology program is Top-5 in USA Topological insulators driven by electron spin Maxim Dzero Kent
From graphene to Z2 topological insulator
 From graphene to Z2 topological insulator single Dirac topological AL mass U U valley WL ordinary mass or ripples WL U WL AL AL U AL WL Rashba Ken-Ichiro Imura Condensed-Matter Theory / Tohoku Univ. Dirac
From graphene to Z2 topological insulator single Dirac topological AL mass U U valley WL ordinary mass or ripples WL U WL AL AL U AL WL Rashba Ken-Ichiro Imura Condensed-Matter Theory / Tohoku Univ. Dirac
Konstantin Y. Bliokh, Daria Smirnova, Franco Nori. Center for Emergent Matter Science, RIKEN, Japan. Science 348, 1448 (2015)
 Konstantin Y. Bliokh, Daria Smirnova, Franco Nori Center for Emergent Matter Science, RIKEN, Japan Science 348, 1448 (2015) QSHE and topological insulators The quantum spin Hall effect means the presence
Konstantin Y. Bliokh, Daria Smirnova, Franco Nori Center for Emergent Matter Science, RIKEN, Japan Science 348, 1448 (2015) QSHE and topological insulators The quantum spin Hall effect means the presence
Topological insulators
 Oddelek za fiziko Seminar 1 b 1. letnik, II. stopnja Topological insulators Author: Žiga Kos Supervisor: prof. dr. Dragan Mihailović Ljubljana, June 24, 2013 Abstract In the seminar, the basic ideas behind
Oddelek za fiziko Seminar 1 b 1. letnik, II. stopnja Topological insulators Author: Žiga Kos Supervisor: prof. dr. Dragan Mihailović Ljubljana, June 24, 2013 Abstract In the seminar, the basic ideas behind
First-Principles Calculation of Topological Invariants (Wannier Functions Approach) Alexey A. Soluyanov
 First-Principles Calculation of Topological Invariants (Wannier Functions Approach) Alexey A. Soluyanov ES'12, WFU, June 8, 212 The present work was done in collaboration with David Vanderbilt Outline:
First-Principles Calculation of Topological Invariants (Wannier Functions Approach) Alexey A. Soluyanov ES'12, WFU, June 8, 212 The present work was done in collaboration with David Vanderbilt Outline:
Field Theory Description of Topological States of Matter. Andrea Cappelli INFN, Florence (w. E. Randellini, J. Sisti)
 Field Theory Description of Topological States of Matter Andrea Cappelli INFN, Florence (w. E. Randellini, J. Sisti) Topological States of Matter System with bulk gap but non-trivial at energies below
Field Theory Description of Topological States of Matter Andrea Cappelli INFN, Florence (w. E. Randellini, J. Sisti) Topological States of Matter System with bulk gap but non-trivial at energies below
Topological Insulators in 3D and Bosonization
 Topological Insulators in 3D and Bosonization Andrea Cappelli, INFN Florence (w. E. Randellini, J. Sisti) Outline Topological states of matter: bulk and edge Fermions and bosons on the (1+1)-dimensional
Topological Insulators in 3D and Bosonization Andrea Cappelli, INFN Florence (w. E. Randellini, J. Sisti) Outline Topological states of matter: bulk and edge Fermions and bosons on the (1+1)-dimensional
Spins and spin-orbit coupling in semiconductors, metals, and nanostructures
 B. Halperin Spin lecture 1 Spins and spin-orbit coupling in semiconductors, metals, and nanostructures Behavior of non-equilibrium spin populations. Spin relaxation and spin transport. How does one produce
B. Halperin Spin lecture 1 Spins and spin-orbit coupling in semiconductors, metals, and nanostructures Behavior of non-equilibrium spin populations. Spin relaxation and spin transport. How does one produce
Vortex States in a Non-Abelian Magnetic Field
 Vortex States in a Non-Abelian Magnetic Field Predrag Nikolić George Mason University Institute for Quantum Matter @ Johns Hopkins University SESAPS November 10, 2016 Acknowledgments Collin Broholm IQM
Vortex States in a Non-Abelian Magnetic Field Predrag Nikolić George Mason University Institute for Quantum Matter @ Johns Hopkins University SESAPS November 10, 2016 Acknowledgments Collin Broholm IQM
Hartmut Buhmann. Physikalisches Institut, EP3 Universität Würzburg Germany
 Hartmut Buhmann Physikalisches Institut, EP3 Universität Würzburg Germany Outline Insulators and Topological Insulators HgTe quantum well structures Two-Dimensional TI Quantum Spin Hall Effect experimental
Hartmut Buhmann Physikalisches Institut, EP3 Universität Würzburg Germany Outline Insulators and Topological Insulators HgTe quantum well structures Two-Dimensional TI Quantum Spin Hall Effect experimental
Topological Insulators and Ferromagnets: appearance of flat surface bands
 Topological Insulators and Ferromagnets: appearance of flat surface bands Thomas Dahm University of Bielefeld T. Paananen and T. Dahm, PRB 87, 195447 (2013) T. Paananen et al, New J. Phys. 16, 033019 (2014)
Topological Insulators and Ferromagnets: appearance of flat surface bands Thomas Dahm University of Bielefeld T. Paananen and T. Dahm, PRB 87, 195447 (2013) T. Paananen et al, New J. Phys. 16, 033019 (2014)
STM spectra of graphene
 STM spectra of graphene K. Sengupta Theoretical Physics Division, IACS, Kolkata. Collaborators G. Baskaran, I.M.Sc Chennai, K. Saha, IACS Kolkata I. Paul, Grenoble France H. Manoharan, Stanford USA Refs:
STM spectra of graphene K. Sengupta Theoretical Physics Division, IACS, Kolkata. Collaborators G. Baskaran, I.M.Sc Chennai, K. Saha, IACS Kolkata I. Paul, Grenoble France H. Manoharan, Stanford USA Refs:
2D Materials with Strong Spin-orbit Coupling: Topological and Electronic Transport Properties
 2D Materials with Strong Spin-orbit Coupling: Topological and Electronic Transport Properties Artem Pulkin California Institute of Technology (Caltech), Pasadena, CA 91125, US Institute of Physics, Ecole
2D Materials with Strong Spin-orbit Coupling: Topological and Electronic Transport Properties Artem Pulkin California Institute of Technology (Caltech), Pasadena, CA 91125, US Institute of Physics, Ecole
Floquet Topological Insulators and Majorana Modes
 Floquet Topological Insulators and Majorana Modes Manisha Thakurathi Journal Club Centre for High Energy Physics IISc Bangalore January 17, 2013 References Floquet Topological Insulators by J. Cayssol
Floquet Topological Insulators and Majorana Modes Manisha Thakurathi Journal Club Centre for High Energy Physics IISc Bangalore January 17, 2013 References Floquet Topological Insulators by J. Cayssol
Basics of topological insulator
 011/11/18 @ NTU Basics of topological insulator Ming-Che Chang Dept of Physics, NTNU A brief history of insulators Band insulator (Wilson, Bloch) Mott insulator Anderson insulator Quantum Hall insulator
011/11/18 @ NTU Basics of topological insulator Ming-Che Chang Dept of Physics, NTNU A brief history of insulators Band insulator (Wilson, Bloch) Mott insulator Anderson insulator Quantum Hall insulator
Effects of spin-orbit coupling on the BKT transition and the vortexantivortex structure in 2D Fermi Gases
 Effects of spin-orbit coupling on the BKT transition and the vortexantivortex structure in D Fermi Gases Carlos A. R. Sa de Melo Georgia Institute of Technology QMath13 Mathematical Results in Quantum
Effects of spin-orbit coupling on the BKT transition and the vortexantivortex structure in D Fermi Gases Carlos A. R. Sa de Melo Georgia Institute of Technology QMath13 Mathematical Results in Quantum
Electron spins in nonmagnetic semiconductors
 Electron spins in nonmagnetic semiconductors Yuichiro K. Kato Institute of Engineering Innovation, The University of Tokyo Physics of non-interacting spins Optical spin injection and detection Spin manipulation
Electron spins in nonmagnetic semiconductors Yuichiro K. Kato Institute of Engineering Innovation, The University of Tokyo Physics of non-interacting spins Optical spin injection and detection Spin manipulation
3.15. Some symmetry properties of the Berry curvature and the Chern number.
 50 Phys620.nb z M 3 at the K point z M 3 3 t ' sin 3 t ' sin (3.36) (3.362) Therefore, as long as M 3 3 t ' sin, the system is an topological insulator ( z flips sign). If M 3 3 t ' sin, z is always positive
50 Phys620.nb z M 3 at the K point z M 3 3 t ' sin 3 t ' sin (3.36) (3.362) Therefore, as long as M 3 3 t ' sin, the system is an topological insulator ( z flips sign). If M 3 3 t ' sin, z is always positive
InAs/GaSb A New 2D Topological Insulator
 InAs/GaSb A New 2D Topological Insulator 1. Old Material for New Physics 2. Quantized Edge Modes 3. Adreev Reflection 4. Summary Rui-Rui Du Rice University Superconductor Hybrids Villard de Lans, France
InAs/GaSb A New 2D Topological Insulator 1. Old Material for New Physics 2. Quantized Edge Modes 3. Adreev Reflection 4. Summary Rui-Rui Du Rice University Superconductor Hybrids Villard de Lans, France
Physics of Semiconductors
 Physics of Semiconductors 13 th 2016.7.11 Shingo Katsumoto Department of Physics and Institute for Solid State Physics University of Tokyo Outline today Laughlin s justification Spintronics Two current
Physics of Semiconductors 13 th 2016.7.11 Shingo Katsumoto Department of Physics and Institute for Solid State Physics University of Tokyo Outline today Laughlin s justification Spintronics Two current
Dirac-Fermion-Induced Parity Mixing in Superconducting Topological Insulators. Nagoya University Masatoshi Sato
 Dirac-Fermion-Induced Parity Mixing in Superconducting Topological Insulators Nagoya University Masatoshi Sato In collaboration with Yukio Tanaka (Nagoya University) Keiji Yada (Nagoya University) Ai Yamakage
Dirac-Fermion-Induced Parity Mixing in Superconducting Topological Insulators Nagoya University Masatoshi Sato In collaboration with Yukio Tanaka (Nagoya University) Keiji Yada (Nagoya University) Ai Yamakage
Disordered topological insulators with time-reversal symmetry: Z 2 invariants
 Keio Topo. Science (2016/11/18) Disordered topological insulators with time-reversal symmetry: Z 2 invariants Hosho Katsura Department of Physics, UTokyo Collaborators: Yutaka Akagi (UTokyo) Tohru Koma
Keio Topo. Science (2016/11/18) Disordered topological insulators with time-reversal symmetry: Z 2 invariants Hosho Katsura Department of Physics, UTokyo Collaborators: Yutaka Akagi (UTokyo) Tohru Koma
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.other] 20 Apr 2010
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.other] 20 Apr 2010 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.other] 20 Apr 2010](/thumbs/93/114512366.jpg) Characterization of 3d topological insulators by 2d invariants Rahul Roy Rudolf Peierls Centre for Theoretical Physics, 1 Keble Road, Oxford, OX1 3NP, UK arxiv:1004.3507v1 [cond-mat.other] 20 Apr 2010
Characterization of 3d topological insulators by 2d invariants Rahul Roy Rudolf Peierls Centre for Theoretical Physics, 1 Keble Road, Oxford, OX1 3NP, UK arxiv:1004.3507v1 [cond-mat.other] 20 Apr 2010
Rashba vs Kohn-Luttinger: evolution of p-wave superconductivity in magnetized two-dimensional Fermi gas subject to spin-orbit interaction
 Rashba vs Kohn-Luttinger: evolution of p-wave superconductivity in magnetized two-dimensional Fermi gas subject to spin-orbit interaction Oleg Starykh, University of Utah with Dima Pesin, Ethan Lake, Caleb
Rashba vs Kohn-Luttinger: evolution of p-wave superconductivity in magnetized two-dimensional Fermi gas subject to spin-orbit interaction Oleg Starykh, University of Utah with Dima Pesin, Ethan Lake, Caleb
Introduction to topological insulators. Jennifer Cano
 Introduction to topological insulators Jennifer Cano Adapted from Charlie Kane s Windsor Lectures: http://www.physics.upenn.edu/~kane/ Review article: Hasan & Kane Rev. Mod. Phys. 2010 What is an insulator?
Introduction to topological insulators Jennifer Cano Adapted from Charlie Kane s Windsor Lectures: http://www.physics.upenn.edu/~kane/ Review article: Hasan & Kane Rev. Mod. Phys. 2010 What is an insulator?
Kondo effect in multi-level and multi-valley quantum dots. Mikio Eto Faculty of Science and Technology, Keio University, Japan
 Kondo effect in multi-level and multi-valley quantum dots Mikio Eto Faculty of Science and Technology, Keio University, Japan Outline 1. Introduction: next three slides for quantum dots 2. Kondo effect
Kondo effect in multi-level and multi-valley quantum dots Mikio Eto Faculty of Science and Technology, Keio University, Japan Outline 1. Introduction: next three slides for quantum dots 2. Kondo effect
Luttinger Liquid at the Edge of a Graphene Vacuum
 Luttinger Liquid at the Edge of a Graphene Vacuum H.A. Fertig, Indiana University Luis Brey, CSIC, Madrid I. Introduction: Graphene Edge States (Non-Interacting) II. III. Quantum Hall Ferromagnetism and
Luttinger Liquid at the Edge of a Graphene Vacuum H.A. Fertig, Indiana University Luis Brey, CSIC, Madrid I. Introduction: Graphene Edge States (Non-Interacting) II. III. Quantum Hall Ferromagnetism and
SIGNATURES OF SPIN-ORBIT DRIVEN ELECTRONIC TRANSPORT IN TRANSITION- METAL-OXIDE INTERFACES
 SIGNATURES OF SPIN-ORBIT DRIVEN ELECTRONIC TRANSPORT IN TRANSITION- METAL-OXIDE INTERFACES Nicandro Bovenzi Bad Honnef, 19-22 September 2016 LAO/STO heterostructure: conducting interface between two insulators
SIGNATURES OF SPIN-ORBIT DRIVEN ELECTRONIC TRANSPORT IN TRANSITION- METAL-OXIDE INTERFACES Nicandro Bovenzi Bad Honnef, 19-22 September 2016 LAO/STO heterostructure: conducting interface between two insulators
Topological Electromagnetic and Thermal Responses of Time-Reversal Invariant Superconductors and Chiral-Symmetric band insulators
 Topological Electromagnetic and Thermal Responses of Time-Reversal Invariant Superconductors and Chiral-Symmetric band insulators Satoshi Fujimoto Dept. Phys., Kyoto University Collaborator: Ken Shiozaki
Topological Electromagnetic and Thermal Responses of Time-Reversal Invariant Superconductors and Chiral-Symmetric band insulators Satoshi Fujimoto Dept. Phys., Kyoto University Collaborator: Ken Shiozaki
InAs/GaSb A New Quantum Spin Hall Insulator
 InAs/GaSb A New Quantum Spin Hall Insulator Rui-Rui Du Rice University 1. Old Material for New Physics 2. Quantized Edge Modes 3. Andreev Reflection 4. Summary KITP Workshop on Topological Insulator/Superconductor
InAs/GaSb A New Quantum Spin Hall Insulator Rui-Rui Du Rice University 1. Old Material for New Physics 2. Quantized Edge Modes 3. Andreev Reflection 4. Summary KITP Workshop on Topological Insulator/Superconductor
Building Frac-onal Topological Insulators. Collaborators: Michael Levin Maciej Kosh- Janusz Ady Stern
 Building Frac-onal Topological Insulators Collaborators: Michael Levin Maciej Kosh- Janusz Ady Stern The program Background: Topological insulators Frac-onaliza-on Exactly solvable Hamiltonians for frac-onal
Building Frac-onal Topological Insulators Collaborators: Michael Levin Maciej Kosh- Janusz Ady Stern The program Background: Topological insulators Frac-onaliza-on Exactly solvable Hamiltonians for frac-onal
Topological Insulators
 Topological Insulators A new state of matter with three dimensional topological electronic order L. Andrew Wray Lawrence Berkeley National Lab Princeton University Surface States (Topological Order in
Topological Insulators A new state of matter with three dimensional topological electronic order L. Andrew Wray Lawrence Berkeley National Lab Princeton University Surface States (Topological Order in
Topological insulator part I: Phenomena
 Phys60.nb 5 Topological insulator part I: Phenomena (Part II and Part III discusses how to understand a topological insluator based band-structure theory and gauge theory) (Part IV discusses more complicated
Phys60.nb 5 Topological insulator part I: Phenomena (Part II and Part III discusses how to understand a topological insluator based band-structure theory and gauge theory) (Part IV discusses more complicated
Electronic transport in topological insulators
 Electronic transport in topological insulators Reinhold Egger Institut für Theoretische Physik, Düsseldorf Alex Zazunov, Alfredo Levy Yeyati Trieste, November 011 To the memory of my dear friend Please
Electronic transport in topological insulators Reinhold Egger Institut für Theoretische Physik, Düsseldorf Alex Zazunov, Alfredo Levy Yeyati Trieste, November 011 To the memory of my dear friend Please
Quantum Hall effect. Quantization of Hall resistance is incredibly precise: good to 1 part in I believe. WHY?? G xy = N e2 h.
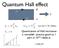 Quantum Hall effect V1 V2 R L I I x = N e2 h V y V x =0 G xy = N e2 h n.b. h/e 2 = 25 kohms Quantization of Hall resistance is incredibly precise: good to 1 part in 10 10 I believe. WHY?? Robustness Why
Quantum Hall effect V1 V2 R L I I x = N e2 h V y V x =0 G xy = N e2 h n.b. h/e 2 = 25 kohms Quantization of Hall resistance is incredibly precise: good to 1 part in 10 10 I believe. WHY?? Robustness Why
Dirac semimetal in three dimensions
 Dirac semimetal in three dimensions Steve M. Young, Saad Zaheer, Jeffrey C. Y. Teo, Charles L. Kane, Eugene J. Mele, and Andrew M. Rappe University of Pennsylvania 6/7/12 1 Dirac points in Graphene Without
Dirac semimetal in three dimensions Steve M. Young, Saad Zaheer, Jeffrey C. Y. Teo, Charles L. Kane, Eugene J. Mele, and Andrew M. Rappe University of Pennsylvania 6/7/12 1 Dirac points in Graphene Without
Topological insulator part II: Berry Phase and Topological index
 Phys60.nb 11 3 Topological insulator part II: Berry Phase and Topological index 3.1. Last chapter Topological insulator: an insulator in the bulk and a metal near the boundary (surface or edge) Quantum
Phys60.nb 11 3 Topological insulator part II: Berry Phase and Topological index 3.1. Last chapter Topological insulator: an insulator in the bulk and a metal near the boundary (surface or edge) Quantum
SPINTRONICS. Waltraud Buchenberg. Faculty of Physics Albert-Ludwigs-University Freiburg
 SPINTRONICS Waltraud Buchenberg Faculty of Physics Albert-Ludwigs-University Freiburg July 14, 2010 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 WHAT IS SPINTRONICS? 2 MAGNETO-RESISTANCE STONER MODEL ANISOTROPIC MAGNETO-RESISTANCE
SPINTRONICS Waltraud Buchenberg Faculty of Physics Albert-Ludwigs-University Freiburg July 14, 2010 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 WHAT IS SPINTRONICS? 2 MAGNETO-RESISTANCE STONER MODEL ANISOTROPIC MAGNETO-RESISTANCE
Local currents in a two-dimensional topological insulator
 Local currents in a two-dimensional topological insulator Xiaoqian Dang, J. D. Burton and Evgeny Y. Tsymbal Department of Physics and Astronomy Nebraska Center for Materials and Nanoscience University
Local currents in a two-dimensional topological insulator Xiaoqian Dang, J. D. Burton and Evgeny Y. Tsymbal Department of Physics and Astronomy Nebraska Center for Materials and Nanoscience University
Effective Field Theories of Topological Insulators
 Effective Field Theories of Topological Insulators Eduardo Fradkin University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Workshop on Field Theoretic Computer Simulations for Particle Physics and Condensed Matter
Effective Field Theories of Topological Insulators Eduardo Fradkin University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Workshop on Field Theoretic Computer Simulations for Particle Physics and Condensed Matter
Defects in topologically ordered states. Xiao-Liang Qi Stanford University Mag Lab, Tallahassee, 01/09/2014
 Defects in topologically ordered states Xiao-Liang Qi Stanford University Mag Lab, Tallahassee, 01/09/2014 References Maissam Barkeshli & XLQ, PRX, 2, 031013 (2012) Maissam Barkeshli, Chaoming Jian, XLQ,
Defects in topologically ordered states Xiao-Liang Qi Stanford University Mag Lab, Tallahassee, 01/09/2014 References Maissam Barkeshli & XLQ, PRX, 2, 031013 (2012) Maissam Barkeshli, Chaoming Jian, XLQ,
Spin Superfluidity and Graphene in a Strong Magnetic Field
 Spin Superfluidity and Graphene in a Strong Magnetic Field by B. I. Halperin Nano-QT 2016 Kyiv October 11, 2016 Based on work with So Takei (CUNY), Yaroslav Tserkovnyak (UCLA), and Amir Yacoby (Harvard)
Spin Superfluidity and Graphene in a Strong Magnetic Field by B. I. Halperin Nano-QT 2016 Kyiv October 11, 2016 Based on work with So Takei (CUNY), Yaroslav Tserkovnyak (UCLA), and Amir Yacoby (Harvard)
Topological Defects in the Topological Insulator
 Topological Defects in the Topological Insulator Ashvin Vishwanath UC Berkeley arxiv:0810.5121 YING RAN Frank YI ZHANG Quantum Hall States Exotic Band Topology Topological band Insulators (quantum spin
Topological Defects in the Topological Insulator Ashvin Vishwanath UC Berkeley arxiv:0810.5121 YING RAN Frank YI ZHANG Quantum Hall States Exotic Band Topology Topological band Insulators (quantum spin
Spin-Orbit Interactions in Semiconductor Nanostructures
 Spin-Orbit Interactions in Semiconductor Nanostructures Branislav K. Nikolić Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Delaware, U.S.A. http://www.physics.udel.edu/~bnikolic Spin-Orbit Hamiltonians
Spin-Orbit Interactions in Semiconductor Nanostructures Branislav K. Nikolić Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Delaware, U.S.A. http://www.physics.udel.edu/~bnikolic Spin-Orbit Hamiltonians
Topological insulators and the quantum anomalous Hall state. David Vanderbilt Rutgers University
 Topological insulators and the quantum anomalous Hall state David Vanderbilt Rutgers University Outline Berry curvature and topology 2D quantum anomalous Hall (QAH) insulator TR-invariant insulators (Z
Topological insulators and the quantum anomalous Hall state David Vanderbilt Rutgers University Outline Berry curvature and topology 2D quantum anomalous Hall (QAH) insulator TR-invariant insulators (Z
TOPOLOGICAL BANDS IN GRAPHENE SUPERLATTICES
 TOPOLOGICAL BANDS IN GRAPHENE SUPERLATTICES 1) Berry curvature in superlattice bands 2) Energy scales for Moire superlattices 3) Spin-Hall effect in graphene Leonid Levitov (MIT) @ ISSP U Tokyo MIT Manchester
TOPOLOGICAL BANDS IN GRAPHENE SUPERLATTICES 1) Berry curvature in superlattice bands 2) Energy scales for Moire superlattices 3) Spin-Hall effect in graphene Leonid Levitov (MIT) @ ISSP U Tokyo MIT Manchester
Classification of Symmetry Protected Topological Phases in Interacting Systems
 Classification of Symmetry Protected Topological Phases in Interacting Systems Zhengcheng Gu (PI) Collaborators: Prof. Xiao-Gang ang Wen (PI/ PI/MIT) Prof. M. Levin (U. of Chicago) Dr. Xie Chen(UC Berkeley)
Classification of Symmetry Protected Topological Phases in Interacting Systems Zhengcheng Gu (PI) Collaborators: Prof. Xiao-Gang ang Wen (PI/ PI/MIT) Prof. M. Levin (U. of Chicago) Dr. Xie Chen(UC Berkeley)
/21. Tsuneya Yoshida. Collaborators: Robert Peters, Satoshi Fujimoto, and N. Kawakami 2013/6/07 (EQPCM) 1. Kyoto Univ.
 2013/6/07 (EQPCM) 1 /21 Tsuneya Yoshida Kyoto Univ. Collaborators: Robert Peters, Satoshi Fujimoto, and N. Kawakami T.Y., Satoshi Fujimoto, and Norio Kawakami Phys. Rev. B 85, 125113 (2012) Outline 2 /21
2013/6/07 (EQPCM) 1 /21 Tsuneya Yoshida Kyoto Univ. Collaborators: Robert Peters, Satoshi Fujimoto, and N. Kawakami T.Y., Satoshi Fujimoto, and Norio Kawakami Phys. Rev. B 85, 125113 (2012) Outline 2 /21
Transport through interacting Majorana devices. Reinhold Egger Institut für Theoretische Physik
 Transport through interacting Maorana devices Reinhold Egger Institut für Theoretische Physik Overview Coulomb charging effects on quantum transport through Maorana nanowires: Two-terminal device: Maorana
Transport through interacting Maorana devices Reinhold Egger Institut für Theoretische Physik Overview Coulomb charging effects on quantum transport through Maorana nanowires: Two-terminal device: Maorana
Lecture notes on topological insulators
 Lecture notes on topological insulators Ming-Che Chang Department of Physics, National Taiwan Normal University, Taipei, Taiwan (Dated: November 1, 18) Contents I. D Topological insulator 1 A. General
Lecture notes on topological insulators Ming-Che Chang Department of Physics, National Taiwan Normal University, Taipei, Taiwan (Dated: November 1, 18) Contents I. D Topological insulator 1 A. General
Proximity-induced magnetization dynamics, interaction effects, and phase transitions on a topological surface
 Proximity-induced magnetization dynamics, interaction effects, and phase transitions on a topological surface Ilya Eremin Theoretische Physik III, Ruhr-Uni Bochum Work done in collaboration with: F. Nogueira
Proximity-induced magnetization dynamics, interaction effects, and phase transitions on a topological surface Ilya Eremin Theoretische Physik III, Ruhr-Uni Bochum Work done in collaboration with: F. Nogueira
A Short Introduction to Topological Superconductors
 A Short Introduction to Topological Superconductors --- A Glimpse of Topological Phases of Matter Jyong-Hao Chen Condensed Matter Theory, PSI & Institute for Theoretical Physics, ETHZ Dec. 09, 2015 @ Superconductivity
A Short Introduction to Topological Superconductors --- A Glimpse of Topological Phases of Matter Jyong-Hao Chen Condensed Matter Theory, PSI & Institute for Theoretical Physics, ETHZ Dec. 09, 2015 @ Superconductivity
Coulomb Drag in Graphene
 Graphene 2017 Coulomb Drag in Graphene -Toward Exciton Condensation Philip Kim Department of Physics, Harvard University Coulomb Drag Drag Resistance: R D = V 2 / I 1 Onsager Reciprocity V 2 (B)/ I 1 =
Graphene 2017 Coulomb Drag in Graphene -Toward Exciton Condensation Philip Kim Department of Physics, Harvard University Coulomb Drag Drag Resistance: R D = V 2 / I 1 Onsager Reciprocity V 2 (B)/ I 1 =
POEM: Physics of Emergent Materials
 POEM: Physics of Emergent Materials Nandini Trivedi L1: Spin Orbit Coupling L2: Topology and Topological Insulators Reference: Bernevig Topological Insulators and Topological Superconductors Tutorials:
POEM: Physics of Emergent Materials Nandini Trivedi L1: Spin Orbit Coupling L2: Topology and Topological Insulators Reference: Bernevig Topological Insulators and Topological Superconductors Tutorials:
Surface Majorana Fermions in Topological Superconductors. ISSP, Univ. of Tokyo. Nagoya University Masatoshi Sato
 Surface Majorana Fermions in Topological Superconductors ISSP, Univ. of Tokyo Nagoya University Masatoshi Sato Kyoto Tokyo Nagoya In collaboration with Satoshi Fujimoto (Kyoto University) Yoshiro Takahashi
Surface Majorana Fermions in Topological Superconductors ISSP, Univ. of Tokyo Nagoya University Masatoshi Sato Kyoto Tokyo Nagoya In collaboration with Satoshi Fujimoto (Kyoto University) Yoshiro Takahashi
Impact of disorder and topology in two dimensional systems at low carrier densities
 Impact of disorder and topology in two dimensional systems at low carrier densities A Thesis Submitted For the Degree of Doctor of Philosophy in the Faculty of Science by Mohammed Ali Aamir Department
Impact of disorder and topology in two dimensional systems at low carrier densities A Thesis Submitted For the Degree of Doctor of Philosophy in the Faculty of Science by Mohammed Ali Aamir Department
v. Tε n k =ε n k T r T = r, T v T = r, I v I = I r I = v. Iε n k =ε n k Berry curvature: Symmetry Consideration n k = n k
 Berry curvature: Symmetry Consideration Time reversal (i.e. motion reversal) 1 1 T r T = r, T v T = v. Tε n k =ε n k n k = n k Inversion Symmetry: 1 1 I r I = r, I v I = v. Iε n k =ε n k n k = n k θ
Berry curvature: Symmetry Consideration Time reversal (i.e. motion reversal) 1 1 T r T = r, T v T = v. Tε n k =ε n k n k = n k Inversion Symmetry: 1 1 I r I = r, I v I = v. Iε n k =ε n k n k = n k θ
Energy Spectrum and Broken spin-surface locking in Topological Insulator quantum dots
 Energy Spectrum and Broken spin-surface locking in Topological Insulator quantum dots A. Kundu 1 1 Heinrich-Heine Universität Düsseldorf, Germany The Capri Spring School on Transport in Nanostructures
Energy Spectrum and Broken spin-surface locking in Topological Insulator quantum dots A. Kundu 1 1 Heinrich-Heine Universität Düsseldorf, Germany The Capri Spring School on Transport in Nanostructures
Berry s phase in Hall Effects and Topological Insulators
 Lecture 6 Berry s phase in Hall Effects and Topological Insulators Given the analogs between Berry s phase and vector potentials, it is not surprising that Berry s phase can be important in the Hall effect.
Lecture 6 Berry s phase in Hall Effects and Topological Insulators Given the analogs between Berry s phase and vector potentials, it is not surprising that Berry s phase can be important in the Hall effect.
Detecting and using Majorana fermions in superconductors
 Detecting and using Majorana fermions in superconductors Anton Akhmerov with Carlo Beenakker, Jan Dahlhaus, Fabian Hassler, and Michael Wimmer New J. Phys. 13, 053016 (2011) and arxiv:1105.0315 Superconductor
Detecting and using Majorana fermions in superconductors Anton Akhmerov with Carlo Beenakker, Jan Dahlhaus, Fabian Hassler, and Michael Wimmer New J. Phys. 13, 053016 (2011) and arxiv:1105.0315 Superconductor
Studying Topological Insulators. Roni Ilan UC Berkeley
 Studying Topological Insulators via time reversal symmetry breaking and proximity effect Roni Ilan UC Berkeley Joel Moore, Jens Bardarson, Jerome Cayssol, Heung-Sun Sim Topological phases Insulating phases
Studying Topological Insulators via time reversal symmetry breaking and proximity effect Roni Ilan UC Berkeley Joel Moore, Jens Bardarson, Jerome Cayssol, Heung-Sun Sim Topological phases Insulating phases
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 13 Aug 2008
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 13 Aug 2008 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 13 Aug 2008](/thumbs/92/110141994.jpg) Corner Junction as a Probe of Helical Edge States Chang-Yu Hou, Eun-Ah Kim,3, and Claudio Chamon Physics Department, Boston University, Boston, MA 05, USA Department of Physics, Stanford University, Stanford,
Corner Junction as a Probe of Helical Edge States Chang-Yu Hou, Eun-Ah Kim,3, and Claudio Chamon Physics Department, Boston University, Boston, MA 05, USA Department of Physics, Stanford University, Stanford,
Anderson localization, topology, and interaction
 Anderson localization, topology, and interaction Pavel Ostrovsky in collaboration with I. V. Gornyi, E. J. König, A. D. Mirlin, and I. V. Protopopov PRL 105, 036803 (2010), PRB 85, 195130 (2012) Cambridge,
Anderson localization, topology, and interaction Pavel Ostrovsky in collaboration with I. V. Gornyi, E. J. König, A. D. Mirlin, and I. V. Protopopov PRL 105, 036803 (2010), PRB 85, 195130 (2012) Cambridge,
3.14. The model of Haldane on a honeycomb lattice
 4 Phys60.n..7. Marginal case: 4 t Dirac points at k=(,). Not an insulator. No topological index...8. case IV: 4 t All the four special points has z 0. We just use u I for the whole BZ. No singularity.
4 Phys60.n..7. Marginal case: 4 t Dirac points at k=(,). Not an insulator. No topological index...8. case IV: 4 t All the four special points has z 0. We just use u I for the whole BZ. No singularity.
SPIN-LIQUIDS ON THE KAGOME LATTICE: CHIRAL TOPOLOGICAL, AND GAPLESS NON-FERMI-LIQUID PHASE
 SPIN-LIQUIDS ON THE KAGOME LATTICE: CHIRAL TOPOLOGICAL, AND GAPLESS NON-FERMI-LIQUID PHASE ANDREAS W.W. LUDWIG (UC-Santa Barbara) work done in collaboration with: Bela Bauer (Microsoft Station-Q, Santa
SPIN-LIQUIDS ON THE KAGOME LATTICE: CHIRAL TOPOLOGICAL, AND GAPLESS NON-FERMI-LIQUID PHASE ANDREAS W.W. LUDWIG (UC-Santa Barbara) work done in collaboration with: Bela Bauer (Microsoft Station-Q, Santa
ARPES experiments on 3D topological insulators. Inna Vishik Physics 250 (Special topics: spectroscopies of quantum materials) UC Davis, Fall 2016
 ARPES experiments on 3D topological insulators Inna Vishik Physics 250 (Special topics: spectroscopies of quantum materials) UC Davis, Fall 2016 Outline Using ARPES to demonstrate that certain materials
ARPES experiments on 3D topological insulators Inna Vishik Physics 250 (Special topics: spectroscopies of quantum materials) UC Davis, Fall 2016 Outline Using ARPES to demonstrate that certain materials
Valence Bonds in Random Quantum Magnets
 Valence Bonds in Random Quantum Magnets theory and application to YbMgGaO 4 Yukawa Institute, Kyoto, November 2017 Itamar Kimchi I.K., Adam Nahum, T. Senthil, arxiv:1710.06860 Valence Bonds in Random Quantum
Valence Bonds in Random Quantum Magnets theory and application to YbMgGaO 4 Yukawa Institute, Kyoto, November 2017 Itamar Kimchi I.K., Adam Nahum, T. Senthil, arxiv:1710.06860 Valence Bonds in Random Quantum
Protection of the surface states of a topological insulator: Berry phase perspective
 Protection of the surface states of a topological insulator: Berry phase perspective Ken-Ichiro Imura Hiroshima University collaborators: Yositake Takane Tomi Ohtsuki Koji Kobayashi Igor Herbut Takahiro
Protection of the surface states of a topological insulator: Berry phase perspective Ken-Ichiro Imura Hiroshima University collaborators: Yositake Takane Tomi Ohtsuki Koji Kobayashi Igor Herbut Takahiro
Quantum Hall Effect in Graphene p-n Junctions
 Quantum Hall Effect in Graphene p-n Junctions Dima Abanin (MIT) Collaboration: Leonid Levitov, Patrick Lee, Harvard and Columbia groups UIUC January 14, 2008 Electron transport in graphene monolayer New
Quantum Hall Effect in Graphene p-n Junctions Dima Abanin (MIT) Collaboration: Leonid Levitov, Patrick Lee, Harvard and Columbia groups UIUC January 14, 2008 Electron transport in graphene monolayer New
Anomalous spin suscep.bility and suppressed exchange energy of 2D holes
 Anomalous spin suscep.bility and suppressed exchange energy of 2D holes School of Chemical and Physical Sciences & MacDiarmid Ins7tute for Advanced Materials and Nanotechnology Victoria University of Wellington
Anomalous spin suscep.bility and suppressed exchange energy of 2D holes School of Chemical and Physical Sciences & MacDiarmid Ins7tute for Advanced Materials and Nanotechnology Victoria University of Wellington
Structure and Topology of Band Structures in the 1651 Magnetic Space Groups
 Structure and Topology of Band Structures in the 1651 Magnetic Space Groups Haruki Watanabe University of Tokyo [Noninteracting] Sci Adv (2016) PRL (2016) Nat Commun (2017) (New) arxiv:1707.01903 [Interacting]
Structure and Topology of Band Structures in the 1651 Magnetic Space Groups Haruki Watanabe University of Tokyo [Noninteracting] Sci Adv (2016) PRL (2016) Nat Commun (2017) (New) arxiv:1707.01903 [Interacting]
3D Weyl metallic states realized in the Bi 1-x Sb x alloy and BiTeI. Heon-Jung Kim Department of Physics, Daegu University, Korea
 3D Weyl metallic states realized in the Bi 1-x Sb x alloy and BiTeI Heon-Jung Kim Department of Physics, Daegu University, Korea Content 3D Dirac metals Search for 3D generalization of graphene Bi 1-x
3D Weyl metallic states realized in the Bi 1-x Sb x alloy and BiTeI Heon-Jung Kim Department of Physics, Daegu University, Korea Content 3D Dirac metals Search for 3D generalization of graphene Bi 1-x
Dirac fermions in condensed matters
 Dirac fermions in condensed matters Bohm Jung Yang Department of Physics and Astronomy, Seoul National University Outline 1. Dirac fermions in relativistic wave equations 2. How do Dirac fermions appear
Dirac fermions in condensed matters Bohm Jung Yang Department of Physics and Astronomy, Seoul National University Outline 1. Dirac fermions in relativistic wave equations 2. How do Dirac fermions appear
Edge Transport in Quantum Hall Systems
 Lectures on Mesoscopic Physics and Quantum Transport, June 15, 018 Edge Transport in Quantum Hall Systems Xin Wan Zhejiang University xinwan@zju.edu.cn Outline Theory of edge states in IQHE Edge excitations
Lectures on Mesoscopic Physics and Quantum Transport, June 15, 018 Edge Transport in Quantum Hall Systems Xin Wan Zhejiang University xinwan@zju.edu.cn Outline Theory of edge states in IQHE Edge excitations
Symmetric Surfaces of Topological Superconductor
 Symmetric Surfaces of Topological Superconductor Sharmistha Sahoo Zhao Zhang Jeffrey Teo Outline Introduction Brief description of time reversal symmetric topological superconductor. Coupled wire model
Symmetric Surfaces of Topological Superconductor Sharmistha Sahoo Zhao Zhang Jeffrey Teo Outline Introduction Brief description of time reversal symmetric topological superconductor. Coupled wire model
Part III: Impurities in Luttinger liquids
 Functional RG for interacting fermions... Part III: Impurities in Luttinger liquids 1. Luttinger liquids 2. Impurity effects 3. Microscopic model 4. Flow equations 5. Results S. Andergassen, T. Enss (Stuttgart)
Functional RG for interacting fermions... Part III: Impurities in Luttinger liquids 1. Luttinger liquids 2. Impurity effects 3. Microscopic model 4. Flow equations 5. Results S. Andergassen, T. Enss (Stuttgart)
Integer quantum Hall effect for bosons: A physical realization
 Integer quantum Hall effect for bosons: A physical realization T. Senthil (MIT) and Michael Levin (UMCP). (arxiv:1206.1604) Thanks: Xie Chen, Zhengchen Liu, Zhengcheng Gu, Xiao-gang Wen, and Ashvin Vishwanath.
Integer quantum Hall effect for bosons: A physical realization T. Senthil (MIT) and Michael Levin (UMCP). (arxiv:1206.1604) Thanks: Xie Chen, Zhengchen Liu, Zhengcheng Gu, Xiao-gang Wen, and Ashvin Vishwanath.
Ideas on non-fermi liquid metals and quantum criticality. T. Senthil (MIT).
 Ideas on non-fermi liquid metals and quantum criticality T. Senthil (MIT). Plan Lecture 1: General discussion of heavy fermi liquids and their magnetism Review of some experiments Concrete `Kondo breakdown
Ideas on non-fermi liquid metals and quantum criticality T. Senthil (MIT). Plan Lecture 1: General discussion of heavy fermi liquids and their magnetism Review of some experiments Concrete `Kondo breakdown
Magnets, 1D quantum system, and quantum Phase transitions
 134 Phys620.nb 10 Magnets, 1D quantum system, and quantum Phase transitions In 1D, fermions can be mapped into bosons, and vice versa. 10.1. magnetization and frustrated magnets (in any dimensions) Consider
134 Phys620.nb 10 Magnets, 1D quantum system, and quantum Phase transitions In 1D, fermions can be mapped into bosons, and vice versa. 10.1. magnetization and frustrated magnets (in any dimensions) Consider
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 6 May 2010
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 6 May 2010 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 6 May 2010](/thumbs/81/83686509.jpg) MIT-CTP/4147 Correlated Topological Insulators and the Fractional Magnetoelectric Effect B. Swingle, M. Barkeshli, J. McGreevy, and T. Senthil Department of Physics, Massachusetts Institute of Technology,
MIT-CTP/4147 Correlated Topological Insulators and the Fractional Magnetoelectric Effect B. Swingle, M. Barkeshli, J. McGreevy, and T. Senthil Department of Physics, Massachusetts Institute of Technology,
Quantum Confinement in Graphene
 Quantum Confinement in Graphene from quasi-localization to chaotic billards MMM dominikus kölbl 13.10.08 1 / 27 Outline some facts about graphene quasibound states in graphene numerical calculation of
Quantum Confinement in Graphene from quasi-localization to chaotic billards MMM dominikus kölbl 13.10.08 1 / 27 Outline some facts about graphene quasibound states in graphene numerical calculation of
Topological insulators. Pavel Buividovich (Regensburg)
 Topological insulators Pavel Buividovich (Regensburg) Hall effect Classical treatment Dissipative motion for point-like particles (Drude theory) Steady motion Classical Hall effect Cyclotron frequency
Topological insulators Pavel Buividovich (Regensburg) Hall effect Classical treatment Dissipative motion for point-like particles (Drude theory) Steady motion Classical Hall effect Cyclotron frequency
